Lesson 4: Angular measure and azimuths
|
|
|
- Claude Juniper Hancock
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PRO TIPS: Map Reading Lesson 4: Angular measure and azimuths References: FM 21-25; FM 21-26; Map Lesson 4 in map section. Study assignment: read FM Chapters 7 to 9, then go through this lesson and take the self-assessment quiz at the end. Finding directions Soldiers need to be able to specify directions not just "the way to the PX" or "South", but precise angular measures. With this information in hand, for example, we can find our precise coordinates on a map my triangulation, adjust artillery fire, or locate and report enemy activity visible from yout location. To do this, we require: a map; a protractor; a compass; and some special knowledge of how to use them. Why bother" Because most reenactor units will go into the field several times a year, and it helps to know where you are and how to get where you're going. AND as with map reading in general it's a basic soldier skill taught to recruits in basic training. No reenactor who expects to interpret soldier experience should ignore basic soldier skills. Degrees and angular measure For navigation and routine map work, we generally us the degree as our measure. A full circle comprises 360 degrees (and has since the days of Babylonian astronomy!). Most of us know that a quarter of a circle is 90 degrees, half a circle is 180 degrees, and so on. In this lesson we will build on that, and add some rules of thumb that will help you handle a compass. Note that gunnery uses a different angular measure: mils. A mil is 1/6400 of a circle. We do this because specifying a precise direction through a gun sight is hard if you're juggling degrees, minutes, and seconds. A mil is fine enough to allow us to use one simple statement of shift ("RIGHT THREE MILS, FIRE FOR EFFECT"). We will consider mils in other training topics. The azimuth A compass direction is called an azimuth. It's an odd word, and comes to us from Arabic. It expresses an angular direction from due north measures in degrees, from one defined point to another defined point. For exaple, a location due east from where you stand lies along an azimuth of 90º. (That's simple enough, but it gets messier, since there are really three definitions of "north": grid north, magnetic north, and true north. We'll be worrying mostly about the first two.)
2 Always remember: no matter which direction you are facing, north is always 0º. When you use the GPS in your car, you can generally set it so "up" is the direction you are taveling, or set it so "up" is north. Not so standing in the field with a compass. So, let's go stand in the field. Actually, on a hilltop. You are standing on the hill crest in the center of the map display (at the small compass symbol) manning an observation post (OP). You notice something moving north on a secondary road a bit over a kilometer away; it is a German tank (the red diamond is the military symbol for an enemy tank). You need to report its location, want to use a distance and an azimuth. You determine the azimuth from your position to be 120º at a range of about 1.55 km. First, how did you find the azimuth? There are two possible ways. First, we assume you have a map. If the target is at a known point and the target is at a known point, all you have to do is draw a line between them and fins the azimuth using your handy map protractor. Here are two examples of map protractors issued in WWII:
3 I prefer to use my own handy protractor, the kind I used for decades. It's transparent plastic and I can put it directly on the monitor screen to extract measurements. Note that it also has grid scales. The outer azimuth scale is in mils; the inner one in degrees. The back azimuth On occasion you may want to calculate a back azimuth, which is the opposite direction of an azimuth; in this example, it is the azimuth the German tank commander has calculated for a shot from his location to yours. Take a moment to move to your alternate OP position. How do you calcumate a back azimuth? Easy, and you don't even need a protractor. Just remember this rule: If the azimuth is less than 180, add 180 to get the back azimuth. If your azimuth is more than 180, subtract 180. In our example, your azimuth (no need to call it a "front azimuth") is 120º. That is less than 180, so add = 300º. So the German tank commander sighting you on his compass is reading 300.
4 Declination Now the bad news: there are really three "norths". True north is the exact direction to the geographic North Pole, the point at which all the longitude lines meet. This doesn't change; it's arbitrary. It is important on large maps. But you will be using a small-scale map, and because of the mechanics of the projection used to translate a piece of a sphere onto a flat piece of paper, it isn't quite the same as the vertical grid lines on your map. Grid north is a map convention based on the closest approximation of a polyconic projection to a small patch of the world. (If you're determined to be a map geek, check this out in FM Advanced Map and Aerial Photograph Reading in the resource library.) The vertical grid lines on your map are aligned to grid north. Magnetic north is north as read on the floating needle of your magnetic compass. The compass points to the magnrtic north pole, confluence of the top end of the lines of electromagnetic energy that surround the world and produced by sloshy rotation of molten ferromagnetic core materials in the center of the planet. But the magnetic north pole wanders around like a drunken monkey as time passes, and coincides with true north or grid north only by occasional accidents. The differences between these directions is called declination. Here is a declination diagram for a particular map: The half-arrow ponts to magnetic north, the y to grid north, and the star (representing Polaris) to true north. On a map, the angular declination will be marked in degrees. I say "for a particular map" because the declinations differ from place to place. There are places (which are found along "orthogonic lines" where grid and magnetic north are the same. Fort Benning Georgia lies close to an orthogonic line. So, how do we shift from one to another north? What's most important is grid to magnetic and back the GM angle. First, we will orient the map. Find a flat spot, preferably with a view of the surrounding terrain, and place the map oriented roughly north.
5 In WW II, maps were sometimes issued with pivot line printed; sometimes soldiers added them based on the declination diagram. In this case, the origin of the line, called a pivot point, is at the bottom edge of the mapped area, and the junction of the vertical grid line 64 and the edge of the map. Grid line 64 points to grid north; the dootted pivot line points 10º west of grid north (note the declination diagram inset, slowing a GM declination of 10º west at that location as of June Unfold the compass so that it can be laid directly along the pivot line. Then gently turn the entire map, without displacing the compass, so that the compass arrow points north. The map is now oriented to the ground it describes. Without consulting the map, we can add a GM correction factor for our compass azimuths using the "left add right subtract" (LARS) rule. First, find the map's GM angle by inspecting the declination diagram. On this map we see that it is 10º west (left) of grid north. If the azimuth you are converting to is left of the azimuth you are converting from, add the GM angle. If the line is to the right, subtract the GM angle.
6 Example: You shoot a magnetic azimuth to a landmark with a resulting value of 60º. The GM angle from your map is 10º left (west); therefore, add 10º to your magnetic azimuth line to find a grid angle of 70º. Finding your location on a map You have a map and a compass. Orient the map. Now look around and try to find two spots shown on the map that are visible a hilltop, rainroad bridge, whatever you can identify. Shoot compass azimuths to those two points. Convert them to back azimuths. From each known point, draw a line along the back azimuth for that point. (It helps if the reference points are not close together!) The lines will meet at your location. Since your location and the two reference points form a triangle, this is called "triangulation." (We're getting into the hard stuff now.) If you are standing along a road or some other identifiable line on the map, but you don't know exactly where, the process is simpler. Find a single reference point, find its back azimuth, and draw a line from thnat point to the point it crosses your road. Note: Be certain you are on the road you think you are on! Example: You know you are on a hillside, somewhere within the red oval. Peeking between the trees, you can see two road junctions recognizable from the map (blue circles). You shoot two azimuths and find the northern RJ at 67º by mthe compass (magnetic azimuth; the southern
7 RJ is at 115º. Because the GM declination is 10º west, we convert to grid: 77º and 125º. Because the GM declination is west (left) we apply the LARS rule to find the back azimuths; since both front azimuths are less than 180º, we ADD 180º ("left add, right subtract"), resulting in back azumuths (grid) of 257º and 305º. Using a pencil and the straight edge of your protractor (you will need a protractor for this), draw lines along the back azimuths. If you have (a) identified the right landmarks and (b) done your work properly, you are standing at the point where the lines intersect (red cross). Actually using the compass in the field, during daylight hours and at night, is fairly complicated and hard to teach without actually going to the field. More information is found in FM 21-25, and a look at FM Scouting, patrolling, and sniping can also help. The best strategy is to learn the theory hers, then find a compass and learn to do it in practice.
8 LESSON SUMMARY 1. Specifying and using angular measures (azimuths) with map and compass is critical to specifying places and things on the map. 2. Compass directions may be specified in degrees or mils; for most applications we will use degrees. 3. There are three "norths": true north, grid north, and magnetic north. You will have to be able to convert from grid to magnetic azimuths and back to reduce error. 4. Map reading requires skilled use of compass and protractor; precision is required, and "eyeball" will not be enough. 5. You will need to calculate back azimuths (the direction exactly opposite a given azimuth) for essential battlefield judgment. Take the self-test for this lesson, then go to Lesson 5. LESSON 5 will introduce you to the critical skills of terrain analysis how to look at a map and visualize the terrain and how it will influence battle: cover and concealment, observation and fields of fire, key terrain, obstacles, and avenues of maneuver.
FM CHAPTER 6 DIRECTION
 CHAPTER 6 DIRECTION Being in the right place at the prescribed time is necessary to successfully accomplish military missions. Direction plays an important role in a soldier's everyday life. It can be
CHAPTER 6 DIRECTION Being in the right place at the prescribed time is necessary to successfully accomplish military missions. Direction plays an important role in a soldier's everyday life. It can be
6-1. METHODS OF EXPRESSING DIRECTION
 CHAPTER 6 DIRECTION Being in the right place at the prescribed time is necessary to successfully accomplish military missions. Direction plays an important role in a soldier's everyday life. It can be
CHAPTER 6 DIRECTION Being in the right place at the prescribed time is necessary to successfully accomplish military missions. Direction plays an important role in a soldier's everyday life. It can be
Lesson 7 Determining Direction. Key Terms. azimuth back azimuth degree grid azimuth grid north magnetic azimuth magnetic north true north
 Lesson 7 Determining Direction U.S. ARMY Key Terms J R O T C azimuth back azimuth degree grid azimuth grid north magnetic azimuth magnetic north true north WHAT YOU WILL LEARN TO DO Calculate direction
Lesson 7 Determining Direction U.S. ARMY Key Terms J R O T C azimuth back azimuth degree grid azimuth grid north magnetic azimuth magnetic north true north WHAT YOU WILL LEARN TO DO Calculate direction
LESSON 6: DETERMINING DIRECTION
 LESSON 6: DETERMINING DIRECTION PURPOSE Directions play an important role in everyday life. People oftentimes express them as right, left, straight ahead, and so forth; but then the question arises, to
LESSON 6: DETERMINING DIRECTION PURPOSE Directions play an important role in everyday life. People oftentimes express them as right, left, straight ahead, and so forth; but then the question arises, to
Reconnaissance and Surveillance Leader s Course Map Reading self study worksheet (Tenino, Washington Map)
 Reconnaissance and Surveillance Leader s Course Map Reading self study worksheet (Tenino, Washington Map) General Knowledge 1. Name the five Basic Colors on a map and what they represent? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Reconnaissance and Surveillance Leader s Course Map Reading self study worksheet (Tenino, Washington Map) General Knowledge 1. Name the five Basic Colors on a map and what they represent? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
DIRECTION W140003XQ STUDENT HANDOUT
 UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS THE BASIC SCHOOL MARINE CORPS TRAINING COMMAND CAMP BARRETT, VIRGINIA 22134-5019 DIRECTION W140003XQ STUDENT HANDOUT Warrant Officer Basic Course Introduction Importance In This
UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS THE BASIC SCHOOL MARINE CORPS TRAINING COMMAND CAMP BARRETT, VIRGINIA 22134-5019 DIRECTION W140003XQ STUDENT HANDOUT Warrant Officer Basic Course Introduction Importance In This
LOCATION W140005XQ STUDENT HANDOUT
 UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS THE BASIC SCHOOL MARINE CORPS TRAINING COMMAND CAMP BARRETT, VIRGINIA 22134-5019 LOCATION W140005XQ STUDENT HANDOUT W14005XQ Introduction Importance In This Lesson The class
UNITED STATES MARINE CORPS THE BASIC SCHOOL MARINE CORPS TRAINING COMMAND CAMP BARRETT, VIRGINIA 22134-5019 LOCATION W140005XQ STUDENT HANDOUT W14005XQ Introduction Importance In This Lesson The class
TEST EXAM PART 2 INTERMEDIATE LAND NAVIGATION
 NAME DATE TEST EXAM PART 2 INTERMEDIATE LAND NAVIGATION 1. Knowing these four basic skills, it is impossible to be totally lost; what are they? a. Track Present Location / Determine Distance / Sense of
NAME DATE TEST EXAM PART 2 INTERMEDIATE LAND NAVIGATION 1. Knowing these four basic skills, it is impossible to be totally lost; what are they? a. Track Present Location / Determine Distance / Sense of
FIELD-EXPEDIENT SURVEY TECHNIQUES
 APPENDIX C FIELD-EXPEDIENT SURVEY TECHNIQUES Surveyed locations may be provided by the artillery survey personnel. Normally, a map spot location to six-digit or eight-digit grid coordinates is estimated
APPENDIX C FIELD-EXPEDIENT SURVEY TECHNIQUES Surveyed locations may be provided by the artillery survey personnel. Normally, a map spot location to six-digit or eight-digit grid coordinates is estimated
Physical Geography Lab Activity #08
 Physical Geography Lab Activity #08 Due date Name Using a compass COR Objective 4 8.1. Introduction The compass is undeniably a valuable tool in finding your way, but it is also useless if you don t know
Physical Geography Lab Activity #08 Due date Name Using a compass COR Objective 4 8.1. Introduction The compass is undeniably a valuable tool in finding your way, but it is also useless if you don t know
2.1 Motion in Two Dimensions A Scale Diagram Approach
 Figure The motion of these cyclists is two-dimensional in the plane of the road. carr LInK aval offi cers use gyroscopic compasses and satellite navigation to navigate Canada s naval fl eet. However, every
Figure The motion of these cyclists is two-dimensional in the plane of the road. carr LInK aval offi cers use gyroscopic compasses and satellite navigation to navigate Canada s naval fl eet. However, every
Modeling a Gear Standard Tools, Surface Tools Solid Tool View, Trackball, Show-Hide Snaps Window 1-1
 Modeling a Gear This tutorial describes how to create a toothed gear. It combines using wireframe, solid, and surface modeling together to create a part. The model was created in standard units. To begin,
Modeling a Gear This tutorial describes how to create a toothed gear. It combines using wireframe, solid, and surface modeling together to create a part. The model was created in standard units. To begin,
Grade 6 Math Circles October 16 & Non-Euclidean Geometry and the Globe
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles October 16 & 17 2018 Non-Euclidean Geometry and the Globe (Euclidean) Geometry Review:
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles October 16 & 17 2018 Non-Euclidean Geometry and the Globe (Euclidean) Geometry Review:
Grade 6 Math Circles October 16 & Non-Euclidean Geometry and the Globe
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles October 16 & 17 2018 Non-Euclidean Geometry and the Globe (Euclidean) Geometry Review:
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles October 16 & 17 2018 Non-Euclidean Geometry and the Globe (Euclidean) Geometry Review:
Applications. 40 Shapes and Designs. 1. Tell whether each diagram shows an angle formed by a wedge, two sides meeting at a common point, or a turn.
 Applications. Tell whether each diagram shows an angle formed by a wedge, two sides meeting at a common point, or a turn. a. b. c. 2. Give the degree measure of each turn. a. One right-angle turn b. Four
Applications. Tell whether each diagram shows an angle formed by a wedge, two sides meeting at a common point, or a turn. a. b. c. 2. Give the degree measure of each turn. a. One right-angle turn b. Four
Name: Tutor s
 Name: Tutor s Email: Bring a couple, just in case! Necessary Equipment: Black Pen Pencil Rubber Pencil Sharpener Scientific Calculator Ruler Protractor (Pair of) Compasses 018 AQA Exam Dates Paper 1 4
Name: Tutor s Email: Bring a couple, just in case! Necessary Equipment: Black Pen Pencil Rubber Pencil Sharpener Scientific Calculator Ruler Protractor (Pair of) Compasses 018 AQA Exam Dates Paper 1 4
Distance in mm from nearest latitude line to location x 150 = seconds of latitude Distance in mm between latitude 2.5 tick marks (along the sides)
 LATITUDE FORMULA FOR 1:24000 SCALE WITH 2.5 TICK MARKS Distance in mm from nearest latitude line to location x 150 = seconds of latitude Distance in mm between latitude 2.5 tick marks (along the sides)
LATITUDE FORMULA FOR 1:24000 SCALE WITH 2.5 TICK MARKS Distance in mm from nearest latitude line to location x 150 = seconds of latitude Distance in mm between latitude 2.5 tick marks (along the sides)
Physics Experiment 13
 Fig. 13-1 Equipment This side of the mirror is gray. Place this side on the baseline. You can see your reflection on this side of the mirror. Fig. 13-2 Mirror Placement: The "Plexi-Ray Kit" contains a
Fig. 13-1 Equipment This side of the mirror is gray. Place this side on the baseline. You can see your reflection on this side of the mirror. Fig. 13-2 Mirror Placement: The "Plexi-Ray Kit" contains a
Distance in mm from nearest latitude line to location x 150 = seconds of latitude Distance in mm between latitude 2.5 tick marks (along the sides)
 LATITUDE FORMULA FOR 1:24000 SCALE WITH 2.5 TICK MARKS Distance in mm from nearest latitude line to location x 150 = seconds of latitude Distance in mm between latitude 2.5 tick marks (along the sides)
LATITUDE FORMULA FOR 1:24000 SCALE WITH 2.5 TICK MARKS Distance in mm from nearest latitude line to location x 150 = seconds of latitude Distance in mm between latitude 2.5 tick marks (along the sides)
(Equation 24.1: Index of refraction) We can make sense of what happens in Figure 24.1
 24-1 Refraction To understand what happens when light passes from one medium to another, we again use a model that involves rays and wave fronts, as we did with reflection. Let s begin by creating a short
24-1 Refraction To understand what happens when light passes from one medium to another, we again use a model that involves rays and wave fronts, as we did with reflection. Let s begin by creating a short
Module 4. Stereographic projection: concept and application. Lecture 4. Stereographic projection: concept and application
 Module 4 Stereographic projection: concept and application Lecture 4 Stereographic projection: concept and application 1 NPTEL Phase II : IIT Kharagpur : Prof. R. N. Ghosh, Dept of Metallurgical and Materials
Module 4 Stereographic projection: concept and application Lecture 4 Stereographic projection: concept and application 1 NPTEL Phase II : IIT Kharagpur : Prof. R. N. Ghosh, Dept of Metallurgical and Materials
How to print a Hypercube
 How to print a Hypercube Henry Segerman One of the things that mathematics is about, perhaps the thing that mathematics is about, is trying to make things easier to understand. John von Neumann once said
How to print a Hypercube Henry Segerman One of the things that mathematics is about, perhaps the thing that mathematics is about, is trying to make things easier to understand. John von Neumann once said
Rotator Genius Manual
 Rotator Genius Manual During the time of writing the firmware and app versions are 1.4.3 Table of Contents 1. Introduction and Overview...2 2. Powering Up!...2 2.1 Buttons and Controls...3 2.2 Network
Rotator Genius Manual During the time of writing the firmware and app versions are 1.4.3 Table of Contents 1. Introduction and Overview...2 2. Powering Up!...2 2.1 Buttons and Controls...3 2.2 Network
Surface Modeling Tutorial
 Surface Modeling Tutorial Complex Surfacing in SolidWorks By Matthew Perez By Matthew Perez Who is this tutorial for? This tutorial assumes that you have prior surfacing knowledge as well as a general
Surface Modeling Tutorial Complex Surfacing in SolidWorks By Matthew Perez By Matthew Perez Who is this tutorial for? This tutorial assumes that you have prior surfacing knowledge as well as a general
Section 1.4: Adding and Subtracting Linear and Perpendicular Vectors
 Section 1.4: Adding and Subtracting Linear and Perpendicular Vectors Motion in two dimensions must use vectors and vector diagrams. Vector Representation: tail head magnitude (size): given by the length
Section 1.4: Adding and Subtracting Linear and Perpendicular Vectors Motion in two dimensions must use vectors and vector diagrams. Vector Representation: tail head magnitude (size): given by the length
Surveying Prof. Bharat Lohani Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur. Lecture - 1 Module - 6 Triangulation and Trilateration
 Surveying Prof. Bharat Lohani Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture - 1 Module - 6 Triangulation and Trilateration (Refer Slide Time: 00:21) Welcome to this another lecture on basic surveying.
Surveying Prof. Bharat Lohani Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture - 1 Module - 6 Triangulation and Trilateration (Refer Slide Time: 00:21) Welcome to this another lecture on basic surveying.
COORDINATE TRANSFORMATION. Lecture 6
 COORDINATE TRANSFORMATION Lecture 6 SGU 1053 SURVEY COMPUTATION 1 Introduction Geomatic professional are mostly confronted in their work with transformations from one two/three-dimensional coordinate system
COORDINATE TRANSFORMATION Lecture 6 SGU 1053 SURVEY COMPUTATION 1 Introduction Geomatic professional are mostly confronted in their work with transformations from one two/three-dimensional coordinate system
Homework Set 3 Due Thursday, 07/14
 Homework Set 3 Due Thursday, 07/14 Problem 1 A room contains two parallel wall mirrors, on opposite walls 5 meters apart. The mirrors are 8 meters long. Suppose that one person stands in a doorway, in
Homework Set 3 Due Thursday, 07/14 Problem 1 A room contains two parallel wall mirrors, on opposite walls 5 meters apart. The mirrors are 8 meters long. Suppose that one person stands in a doorway, in
ILLUSTRATOR. Introduction to Adobe Illustrator. You will;
 ILLUSTRATOR You will; 1. Learn Basic Navigation. 2. Learn about Paths. 3. Learn about the Line Tools. 4. Learn about the Shape Tools. 5. Learn about Strokes and Fills. 6. Learn about Transformations. 7.
ILLUSTRATOR You will; 1. Learn Basic Navigation. 2. Learn about Paths. 3. Learn about the Line Tools. 4. Learn about the Shape Tools. 5. Learn about Strokes and Fills. 6. Learn about Transformations. 7.
Stereographic Projections
 C6H3 PART IIA and PART IIB C6H3 MATERIALS SCIENCE AND METALLURGY Course C6: Crystallography Stereographic Projections Representation of directions and plane orientations In studying crystallographic and
C6H3 PART IIA and PART IIB C6H3 MATERIALS SCIENCE AND METALLURGY Course C6: Crystallography Stereographic Projections Representation of directions and plane orientations In studying crystallographic and
GSN SunShot Procedures Using Internet Solar Position Calculator
 GSN SunShot Procedures Using Internet Solar Position Calculator Purpose: Determine astronomical (true) north for instrument orientation by observing the Sun s azimuth using a Theodolite and Sun Position
GSN SunShot Procedures Using Internet Solar Position Calculator Purpose: Determine astronomical (true) north for instrument orientation by observing the Sun s azimuth using a Theodolite and Sun Position
Referred Deflection. NOTE: Use 2800 and 0700 to avoid any sight blocks caused by the cannon. Figure Preparation of the plotting board.
 Chapter 12 Referred Deflection 12-5. The aiming circle operator gives the referred deflection to the FDC after the section is laid. The referred deflection can be any 100-mil deflection from 0 to 6300,
Chapter 12 Referred Deflection 12-5. The aiming circle operator gives the referred deflection to the FDC after the section is laid. The referred deflection can be any 100-mil deflection from 0 to 6300,
Teach Yourself Microsoft PowerPoint Topic 4: Slide Master, Comments and Save Options
 Teach Yourself Microsoft PowerPoint Topic 4: Slide Master, Comments and Save Options http://www.gerrykruyer.com This week you will work with slide masters, add comments, find out how to save your presentations
Teach Yourself Microsoft PowerPoint Topic 4: Slide Master, Comments and Save Options http://www.gerrykruyer.com This week you will work with slide masters, add comments, find out how to save your presentations
PLC Papers. Created For:
 PLC Papers Created For: 3D shapes 2 Grade 4 Objective: Identify the properties of 3-D shapes Question 1. The diagram shows four 3-D solid shapes. (a) What is the name of shape B.. (1) (b) Write down the
PLC Papers Created For: 3D shapes 2 Grade 4 Objective: Identify the properties of 3-D shapes Question 1. The diagram shows four 3-D solid shapes. (a) What is the name of shape B.. (1) (b) Write down the
place value Thousands Hundreds Tens Units
 Number add total altogether sum plus + take away subtract minus the difference multiply times lots of groups of product divide share equally remainder (rem.) digit two digit numbers three digit numbers
Number add total altogether sum plus + take away subtract minus the difference multiply times lots of groups of product divide share equally remainder (rem.) digit two digit numbers three digit numbers
Chapter 5. Transforming Shapes
 Chapter 5 Transforming Shapes It is difficult to walk through daily life without being able to see geometric transformations in your surroundings. Notice how the leaves of plants, for example, are almost
Chapter 5 Transforming Shapes It is difficult to walk through daily life without being able to see geometric transformations in your surroundings. Notice how the leaves of plants, for example, are almost
Translations, Reflections, and Rotations
 Translations, Reflections, and Rotations This photo shows a classic optical illusion called the Necker Cube. It's an example of an impossible object. Optical illusions are often helpful to scientists who
Translations, Reflections, and Rotations This photo shows a classic optical illusion called the Necker Cube. It's an example of an impossible object. Optical illusions are often helpful to scientists who
Navigational Aids 1 st Semester/2007/TF 7:30 PM -9:00 PM
 Glossary of Navigation Terms accelerometer. A device that senses inertial reaction to measure linear or angular acceleration. In its simplest form, it consists of a case-mounted spring and mass arrangement
Glossary of Navigation Terms accelerometer. A device that senses inertial reaction to measure linear or angular acceleration. In its simplest form, it consists of a case-mounted spring and mass arrangement
(Refer Slide Time: 00:02:00)
 Computer Graphics Prof. Sukhendu Das Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 18 Polyfill - Scan Conversion of a Polygon Today we will discuss the concepts
Computer Graphics Prof. Sukhendu Das Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 18 Polyfill - Scan Conversion of a Polygon Today we will discuss the concepts
Surveying Prof. Bharat Lohani Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur
 Surveying Prof. Bharat Lohani Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module - 6 Lecture - 2 Triangulation and Trilateration Welcome to this another lecture on basic surveying.
Surveying Prof. Bharat Lohani Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module - 6 Lecture - 2 Triangulation and Trilateration Welcome to this another lecture on basic surveying.
On the Web sun.com/aboutsun/comm_invest STAROFFICE 8 DRAW
 STAROFFICE 8 DRAW Graphics They say a picture is worth a thousand words. Pictures are often used along with our words for good reason. They help communicate our thoughts. They give extra information that
STAROFFICE 8 DRAW Graphics They say a picture is worth a thousand words. Pictures are often used along with our words for good reason. They help communicate our thoughts. They give extra information that
Operation: a) Compass calibration mode 1.When battery is replaced,the device will enter into calibration mode.the LCD will display CAL, indicating the
 MULTIFUNCTIONS DIGITAL COMPASS USER MANUAL General description: Your digital compass is using the last electromagnetic sensing technology. It is also a combination of watch, stop-watch, and thermometer.
MULTIFUNCTIONS DIGITAL COMPASS USER MANUAL General description: Your digital compass is using the last electromagnetic sensing technology. It is also a combination of watch, stop-watch, and thermometer.
A stratum is a pair of surfaces. When defining a stratum, you are prompted to select Surface1 and Surface2.
 That CAD Girl J ennifer dib ona Website: www.thatcadgirl.com Email: thatcadgirl@aol.com Phone: (919) 417-8351 Fax: (919) 573-0351 Volume Calculations Initial Setup You must be attached to the correct Land
That CAD Girl J ennifer dib ona Website: www.thatcadgirl.com Email: thatcadgirl@aol.com Phone: (919) 417-8351 Fax: (919) 573-0351 Volume Calculations Initial Setup You must be attached to the correct Land
Connect the Dots NEW! Reveal a picture through your skill at working on a coordinate plane.
 NEW! Connect the Dots Reveal a picture through your skill at working on a coordinate plane. Typically in a connect-the-dots puzzle, the dots are already given, but not in the National Math Club s version!
NEW! Connect the Dots Reveal a picture through your skill at working on a coordinate plane. Typically in a connect-the-dots puzzle, the dots are already given, but not in the National Math Club s version!
Orion StarShoot P1 Polar Alignment Camera
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Orion StarShoot P1 Polar Alignment Camera #6236 Providing Exceptional Consumer Optical Products Since 1975 OrionTelescopes.com Customer Support (800) 447-1001 E-mail: support@telescope.com
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Orion StarShoot P1 Polar Alignment Camera #6236 Providing Exceptional Consumer Optical Products Since 1975 OrionTelescopes.com Customer Support (800) 447-1001 E-mail: support@telescope.com
FINDING THE INDEX OF REFRACTION - WebAssign
 Name: Book: Period: Due Date: Lab Partners: FINDING THE INDEX OF REFRACTION - WebAssign Purpose: The theme in this lab is the interaction between light and matter. Matter and light seem very different
Name: Book: Period: Due Date: Lab Partners: FINDING THE INDEX OF REFRACTION - WebAssign Purpose: The theme in this lab is the interaction between light and matter. Matter and light seem very different
Using Google Earth. Middlebury College Library and Information Services
 Using Google Earth Middlebury College Introduction: While Google Earth can be a fun tool for simply looking at the surface of the earth, there are many other more sophisticated features to explore. Google
Using Google Earth Middlebury College Introduction: While Google Earth can be a fun tool for simply looking at the surface of the earth, there are many other more sophisticated features to explore. Google
Mapping Distance and Density
 Mapping Distance and Density Distance functions allow you to determine the nearest location of something or the least-cost path to a particular destination. Density functions, on the other hand, allow
Mapping Distance and Density Distance functions allow you to determine the nearest location of something or the least-cost path to a particular destination. Density functions, on the other hand, allow
Geometry Summer Packet
 Geometry Summer Packet Level 3 Geometry Teachers OVERVIEW This packet is a representation of the type of work and thinking that will be used by High School Geometry students at Columbia High School. The
Geometry Summer Packet Level 3 Geometry Teachers OVERVIEW This packet is a representation of the type of work and thinking that will be used by High School Geometry students at Columbia High School. The
Section 10.1 Polar Coordinates
 Section 10.1 Polar Coordinates Up until now, we have always graphed using the rectangular coordinate system (also called the Cartesian coordinate system). In this section we will learn about another system,
Section 10.1 Polar Coordinates Up until now, we have always graphed using the rectangular coordinate system (also called the Cartesian coordinate system). In this section we will learn about another system,
MatterHackers. How to make a 3D model using Google Earth. Written By: Ryan Lutz. How to make a 3D model using Google Earth data
 MatterHackers How to make a 3D model using Google Earth data Written By: Ryan Lutz 2017 matterhackers.dozuki.com Page 1 of 20 INTRODUCTION EDIT 7/25/17: Sadly, Sketchup has changed the map service they
MatterHackers How to make a 3D model using Google Earth data Written By: Ryan Lutz 2017 matterhackers.dozuki.com Page 1 of 20 INTRODUCTION EDIT 7/25/17: Sadly, Sketchup has changed the map service they
(Refer Slide Time: 1:40)
 Computer Architecture Prof. Anshul Kumar Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 3 Instruction Set Architecture - 1 Today I will start discussion
Computer Architecture Prof. Anshul Kumar Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 3 Instruction Set Architecture - 1 Today I will start discussion
Rutherford Atomic Model: Hidden Obstacles Student Advanced Version
 Rutherford Atomic Model: Hidden Obstacles Student Advanced Version This lab demonstrates the techniques that scientists used over a century ago to determine the basic structure of the atom. By rolling
Rutherford Atomic Model: Hidden Obstacles Student Advanced Version This lab demonstrates the techniques that scientists used over a century ago to determine the basic structure of the atom. By rolling
Reflection and Image Formation by Mirrors
 Purpose Theory a. To study the reflection of light Reflection and Image Formation by Mirrors b. To study the formation and characteristics of images formed by different types of mirrors. When light (wave)
Purpose Theory a. To study the reflection of light Reflection and Image Formation by Mirrors b. To study the formation and characteristics of images formed by different types of mirrors. When light (wave)
Mapping the Yerkes Grounds Christopher Thom, Zosia A. C. Krusberg & Robert B. Friedman
 Mapping the Yerkes Grounds Christopher Thom, Zosia A. C. Krusberg & Robert B. Friedman Introduction You don't need to read this introduction to know the importance of maps. Maps are ubiquitous (everywhere),
Mapping the Yerkes Grounds Christopher Thom, Zosia A. C. Krusberg & Robert B. Friedman Introduction You don't need to read this introduction to know the importance of maps. Maps are ubiquitous (everywhere),
Pre-release User Guide. Version 2.0 August 2015
 Pre-release User Guide Version 2.0 August 2015 Copyright 2015 EagleView Technologies. Copyright 2015 Pictometry International Corp. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored
Pre-release User Guide Version 2.0 August 2015 Copyright 2015 EagleView Technologies. Copyright 2015 Pictometry International Corp. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored
Angle, symmetry and transformation
 Terms Illustrations Definition Acute angle An angle greater than 0 and less than 90. Alternate angles Where two straight lines are cut by a third, as in the diagrams, the angles d and f (also c and e)
Terms Illustrations Definition Acute angle An angle greater than 0 and less than 90. Alternate angles Where two straight lines are cut by a third, as in the diagrams, the angles d and f (also c and e)
About the S-PolKa Web Cameras
 About the S-PolKa Web Cameras General Four Netcam XL cameras have been set up at S-PolKa, pointed in the four cardinal directions. For manufacturer technical details and support, see http://www.stardottech.com
About the S-PolKa Web Cameras General Four Netcam XL cameras have been set up at S-PolKa, pointed in the four cardinal directions. For manufacturer technical details and support, see http://www.stardottech.com
Understand and Apply Theorems About Circles
 Teaching Circles in High School Geometry According to the Common Core Standards For 9 th and 10 th grade using Basic Geometry by Ray Jurgensen and Richard G. brown V. Martinez January 27, 2014 Understand
Teaching Circles in High School Geometry According to the Common Core Standards For 9 th and 10 th grade using Basic Geometry by Ray Jurgensen and Richard G. brown V. Martinez January 27, 2014 Understand
User Manual Alpine Navigation
 User Manual Alpine Navigation Navigation software for the Alpine INE-W960/INE-W960S/INE-NAV-60 US English January 2015, ver. 1.0 Thank you for choosing the Alpine unit as your navigator. Start using your
User Manual Alpine Navigation Navigation software for the Alpine INE-W960/INE-W960S/INE-NAV-60 US English January 2015, ver. 1.0 Thank you for choosing the Alpine unit as your navigator. Start using your
Measurement of Direction: Bearing vs. Azimuth
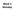 Week 5 Monday Measurement of Direction: Bearing vs. Azimuth Bearing Is an angle of 90 o or less Measured from either North or South in easterly & westerly directions. North 22 o West, South 89 o West,
Week 5 Monday Measurement of Direction: Bearing vs. Azimuth Bearing Is an angle of 90 o or less Measured from either North or South in easterly & westerly directions. North 22 o West, South 89 o West,
Navigation coordinate systems
 Lecture 3 Navigation coordinate systems Topic items: 1. Basic Coordinate Systems. 2. Plane Cartesian Coordinate Systems. 3. Polar Coordinate Systems. 4. Earth-Based Locational Reference Systems. 5. Reference
Lecture 3 Navigation coordinate systems Topic items: 1. Basic Coordinate Systems. 2. Plane Cartesian Coordinate Systems. 3. Polar Coordinate Systems. 4. Earth-Based Locational Reference Systems. 5. Reference
Year 6 Summer Term Week 1 to 2 Geometry: Properties of Shapes
 Measure with a protractor Introduce angles Calculate angles Vertically opposite angles Angles in a triangle Angles in a triangle special cases Angles in a triangle missing angles Angles in special quadrilaterals
Measure with a protractor Introduce angles Calculate angles Vertically opposite angles Angles in a triangle Angles in a triangle special cases Angles in a triangle missing angles Angles in special quadrilaterals
In this lesson, you ll learn how to:
 LESSON 5: ADVANCED DRAWING TECHNIQUES OBJECTIVES In this lesson, you ll learn how to: apply gradient fills modify graphics by smoothing, straightening, and optimizing understand the difference between
LESSON 5: ADVANCED DRAWING TECHNIQUES OBJECTIVES In this lesson, you ll learn how to: apply gradient fills modify graphics by smoothing, straightening, and optimizing understand the difference between
Earthwork 3D for Dummies Doing a digitized dirt takeoff calculation the swift and easy way
 Introduction Earthwork 3D for Dummies Doing a digitized dirt takeoff calculation the swift and easy way Getting to know you Earthwork has inherited its layout from its ancestors, Sitework 98 and Edge.
Introduction Earthwork 3D for Dummies Doing a digitized dirt takeoff calculation the swift and easy way Getting to know you Earthwork has inherited its layout from its ancestors, Sitework 98 and Edge.
Grade Common Core Math
 th 5 Grade Common Core Math Printable Review Problems Standards Included:.-Use a pair of perpendicular number lines, called axes, to define a coordinate system, with the intersection of the lines (the
th 5 Grade Common Core Math Printable Review Problems Standards Included:.-Use a pair of perpendicular number lines, called axes, to define a coordinate system, with the intersection of the lines (the
Mathematics Success Grade 8
 T616 Mathematics Success Grade 8 [OBJECTIVE] The student will explore angle relationships within triangles. [PREREQUISITE SKILLS] angles, congruency, supplementary angles, adjacent angles [MATERIALS] Student
T616 Mathematics Success Grade 8 [OBJECTIVE] The student will explore angle relationships within triangles. [PREREQUISITE SKILLS] angles, congruency, supplementary angles, adjacent angles [MATERIALS] Student
PREPARATION OF FIRE CONTROL EQUIPMENT
 CHAPTER 12 PREPARATION OF FIRE CONTROL EQUIPMENT Three types of firing charts can be constructed on the M16/M19 plotting board: the observed firing chart, the modified-observed firing chart, and the surveyed
CHAPTER 12 PREPARATION OF FIRE CONTROL EQUIPMENT Three types of firing charts can be constructed on the M16/M19 plotting board: the observed firing chart, the modified-observed firing chart, and the surveyed
Trigonometry made somewhat easier
 Trigonometry made somewhat easier To understand trigonometry, it is most useful to first understand two properties of triangles: the Pythagorean theorem and the relationships between similar triangles
Trigonometry made somewhat easier To understand trigonometry, it is most useful to first understand two properties of triangles: the Pythagorean theorem and the relationships between similar triangles
HOW TO USE THE INSTANCING LAB IN BRYCE 7.1 PRO/ A complete tutorial
 http://www.daz3d.com/forums/viewthread/3381/ Rashad Carter, Posted: 03 July 2012 01:43 PM HOW TO USE THE INSTANCING LAB IN BRYCE 7.1 PRO/ A complete tutorial The Instancing Lab in Bryce 7.1 Pro is a mysterious
http://www.daz3d.com/forums/viewthread/3381/ Rashad Carter, Posted: 03 July 2012 01:43 PM HOW TO USE THE INSTANCING LAB IN BRYCE 7.1 PRO/ A complete tutorial The Instancing Lab in Bryce 7.1 Pro is a mysterious
The Nautical Almanac's Concise Sight Reduction Tables
 The Nautical Almanac's Concise Sight Reduction Tables W. Robert Bernecky February, 2015 This document describes the mathematics used to derive the Nautical Almanac's Concise Sight Reduction Tables (NACSR).
The Nautical Almanac's Concise Sight Reduction Tables W. Robert Bernecky February, 2015 This document describes the mathematics used to derive the Nautical Almanac's Concise Sight Reduction Tables (NACSR).
Math 4: Advanced Algebra Ms. Sheppard-Brick B Quiz Review Sections and
 3B Quiz Review Sections 2.8 2.10 and 3.1 3.6 Key Facts To add vectors, place the tail of one vector (the side without the arrow) at the head of the other vector (the side with the arrow). Draw the vector
3B Quiz Review Sections 2.8 2.10 and 3.1 3.6 Key Facts To add vectors, place the tail of one vector (the side without the arrow) at the head of the other vector (the side with the arrow). Draw the vector
Reteach. Chapter 14. Grade 4
 Reteach Chapter 14 Grade 4 Lesson 1 Reteach Draw Points, Lines, and Rays A point is an exact location that is represented by a dot. Example: point R R A line goes on forever in both directions. Example:
Reteach Chapter 14 Grade 4 Lesson 1 Reteach Draw Points, Lines, and Rays A point is an exact location that is represented by a dot. Example: point R R A line goes on forever in both directions. Example:
An object in 3D space
 An object in 3D space An object's viewpoint Every Alice object has a viewpoint. The viewpoint of an object is determined by: The position of the object in 3D space. The orientation of the object relative
An object in 3D space An object's viewpoint Every Alice object has a viewpoint. The viewpoint of an object is determined by: The position of the object in 3D space. The orientation of the object relative
This was written by a designer of inertial guidance machines, & is correct. **********************************************************************
 EXPLANATORY NOTES ON THE SIMPLE INERTIAL NAVIGATION MACHINE How does the missile know where it is at all times? It knows this because it knows where it isn't. By subtracting where it is from where it isn't
EXPLANATORY NOTES ON THE SIMPLE INERTIAL NAVIGATION MACHINE How does the missile know where it is at all times? It knows this because it knows where it isn't. By subtracting where it is from where it isn't
Understanding Geospatial Data Models
 Understanding Geospatial Data Models 1 A geospatial data model is a formal means of representing spatially referenced information. It is a simplified view of physical entities and a conceptualization of
Understanding Geospatial Data Models 1 A geospatial data model is a formal means of representing spatially referenced information. It is a simplified view of physical entities and a conceptualization of
Polar Coordinates. 2, π and ( )
 Polar Coordinates Up to this point we ve dealt exclusively with the Cartesian (or Rectangular, or x-y) coordinate system. However, as we will see, this is not always the easiest coordinate system to work
Polar Coordinates Up to this point we ve dealt exclusively with the Cartesian (or Rectangular, or x-y) coordinate system. However, as we will see, this is not always the easiest coordinate system to work
Activity 1.1.1: Using Google Earth to View the World
 Learning Objectives Upon completion of this activity, you will be able to: Explain the purpose of Google Earth. Explain the different versions of Google Earth. Explain the hardware and software requirements
Learning Objectives Upon completion of this activity, you will be able to: Explain the purpose of Google Earth. Explain the different versions of Google Earth. Explain the hardware and software requirements
CS251 Spring 2014 Lecture 7
 CS251 Spring 2014 Lecture 7 Stephanie R Taylor Feb 19, 2014 1 Moving on to 3D Today, we move on to 3D coordinates. But first, let s recap of what we did in 2D: 1. We represented a data point in 2D data
CS251 Spring 2014 Lecture 7 Stephanie R Taylor Feb 19, 2014 1 Moving on to 3D Today, we move on to 3D coordinates. But first, let s recap of what we did in 2D: 1. We represented a data point in 2D data
SARG GPS User s Guide
 SARG Guide Surrey Amphibian and Reptile Group Steve Langham December 2012 Version 1.0 1. Introduction 1.1. A Global Positioning System (GPS) hand-held device (or unit/receiver) is an immensely useful navigation
SARG Guide Surrey Amphibian and Reptile Group Steve Langham December 2012 Version 1.0 1. Introduction 1.1. A Global Positioning System (GPS) hand-held device (or unit/receiver) is an immensely useful navigation
Local Magnetic Distortion Effects on 3-Axis Compassing
 PNI White Paper Local Magnetic Distortion Effects on 3-Axis Compassing SUMMARY Digital 3-axis compasses from three different manufacturers were tested for heading error when a battery (having magnetic
PNI White Paper Local Magnetic Distortion Effects on 3-Axis Compassing SUMMARY Digital 3-axis compasses from three different manufacturers were tested for heading error when a battery (having magnetic
Owner's manual NX604. Navigation
 Owner's manual NX604 Navigation Thank you for choosing the Clarion NX604 as your navigator. Start using Clarion NX604 right away. This document is the detailed description of the navigation software. You
Owner's manual NX604 Navigation Thank you for choosing the Clarion NX604 as your navigator. Start using Clarion NX604 right away. This document is the detailed description of the navigation software. You
Module 7 Defining Coordinate Systems
 Module 7 Defining Coordinate Systems Introduction Objectives Outline of Topics Covered The use of coordinate systems is very important in managing 3D spatial data including point clouds. In this module
Module 7 Defining Coordinate Systems Introduction Objectives Outline of Topics Covered The use of coordinate systems is very important in managing 3D spatial data including point clouds. In this module
Full Search Map Tab. This map is the result of selecting the Map tab within Full Search.
 Full Search Map Tab This map is the result of selecting the Map tab within Full Search. This map can be used when defining your parameters starting from a Full Search. Once you have entered your desired
Full Search Map Tab This map is the result of selecting the Map tab within Full Search. This map can be used when defining your parameters starting from a Full Search. Once you have entered your desired
Optics: Reflection and Refraction (approx. completion time: 2.5 h) (3/28/11)
 Optics: Reflection and Refraction (approx. completion time: 2.5 h) (3/28/11) Introduction In this lab you will investigate the reflection and refraction of light. Reflection of light from a surface is
Optics: Reflection and Refraction (approx. completion time: 2.5 h) (3/28/11) Introduction In this lab you will investigate the reflection and refraction of light. Reflection of light from a surface is
AWM 11 UNIT 4 TRIGONOMETRY OF RIGHT TRIANGLES
 AWM 11 UNIT 4 TRIGONOMETRY OF RIGHT TRIANGLES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagorean Theorem Exploring Pythagorean Theorem 3 More Pythagorean Theorem Using
AWM 11 UNIT 4 TRIGONOMETRY OF RIGHT TRIANGLES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagorean Theorem Exploring Pythagorean Theorem 3 More Pythagorean Theorem Using
Ready to Go On? Skills Intervention Building Blocks of Geometry
 8-1 Ready to Go On? Skills Intervention Building Blocks of Geometry A point is an exact location. A line is a straight path that extends without end in opposite directions. A plane is a flat surface that
8-1 Ready to Go On? Skills Intervention Building Blocks of Geometry A point is an exact location. A line is a straight path that extends without end in opposite directions. A plane is a flat surface that
2.1 The Tangent Ratio
 2.1 The Tangent Ratio C 2.1 Concept: 14, 15 PreAP FPCM 10 (Ms. Carignan) Outcome FP10.4 Trigonometry Chapter 2 Page 1 PreAP FPCM 10 (Ms. Carignan) Outcome FP10.4 Trigonometry Chapter 2 Page 2 Online Video
2.1 The Tangent Ratio C 2.1 Concept: 14, 15 PreAP FPCM 10 (Ms. Carignan) Outcome FP10.4 Trigonometry Chapter 2 Page 1 PreAP FPCM 10 (Ms. Carignan) Outcome FP10.4 Trigonometry Chapter 2 Page 2 Online Video
Note: Photoshop tutorial is spread over two pages. Click on 2 (top or bottom) to go to the second page.
 Introduction During the course of this Photoshop tutorial we're going through 9 major steps to create a glass ball. The main goal of this tutorial is that you get an idea how to approach this. It's not
Introduction During the course of this Photoshop tutorial we're going through 9 major steps to create a glass ball. The main goal of this tutorial is that you get an idea how to approach this. It's not
Lab 21.1 The Tangent Galvanometer
 Name School Date Lab 21.1 The Tangent Galvanometer Purpose To investigate the magnetic field at the center of a current-carrying loop of wire. To verify the right-hand rule for the field inside a current
Name School Date Lab 21.1 The Tangent Galvanometer Purpose To investigate the magnetic field at the center of a current-carrying loop of wire. To verify the right-hand rule for the field inside a current
5th Grade Mathematics Essential Standards
 Standard 1 Number Sense (10-20% of ISTEP/Acuity) Students compute with whole numbers*, decimals, and fractions and understand the relationship among decimals, fractions, and percents. They understand the
Standard 1 Number Sense (10-20% of ISTEP/Acuity) Students compute with whole numbers*, decimals, and fractions and understand the relationship among decimals, fractions, and percents. They understand the
GPS/GIS Activities Summary
 GPS/GIS Activities Summary Group activities Outdoor activities Use of GPS receivers Use of computers Calculations Relevant to robotics Relevant to agriculture 1. Information technologies in agriculture
GPS/GIS Activities Summary Group activities Outdoor activities Use of GPS receivers Use of computers Calculations Relevant to robotics Relevant to agriculture 1. Information technologies in agriculture
Pictometry for ArcGIS Desktop Local Guide For ArcGIS Desktop Version 10.3
 for ArcGIS Desktop Local Guide For ArcGIS Desktop Version 10.3 June 2015 Copyright 2010-2015 International Corp. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval
for ArcGIS Desktop Local Guide For ArcGIS Desktop Version 10.3 June 2015 Copyright 2010-2015 International Corp. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval
Owner s manual NZ503
 Owner s manual NZ503 US English Thank you for choosing the Clarion NZ503 as your navigator. Start using Clarion NZ503 right away. This document is the detailed description of the navigation software. You
Owner s manual NZ503 US English Thank you for choosing the Clarion NZ503 as your navigator. Start using Clarion NZ503 right away. This document is the detailed description of the navigation software. You
Using Syracuse Community Geography s MapSyracuse
 Using Syracuse Community Geography s MapSyracuse MapSyracuse allows the user to create custom maps with the data provided by Syracuse Community Geography. Starting with the basic template provided, you
Using Syracuse Community Geography s MapSyracuse MapSyracuse allows the user to create custom maps with the data provided by Syracuse Community Geography. Starting with the basic template provided, you
TM XX-XXXX-XXX-XX & X MISSION PLANNING PROCEDURES
 THIS WORK PACKAGE COVERS: Laptop Setup and Startup Loading Map Data LCMR Radar Software Startup Adding a Mission View to Favorites Creating a Mission Saving a Mission Opening an Existing Mission Mission
THIS WORK PACKAGE COVERS: Laptop Setup and Startup Loading Map Data LCMR Radar Software Startup Adding a Mission View to Favorites Creating a Mission Saving a Mission Opening an Existing Mission Mission
Robotics. Lecture 5: Monte Carlo Localisation. See course website for up to date information.
 Robotics Lecture 5: Monte Carlo Localisation See course website http://www.doc.ic.ac.uk/~ajd/robotics/ for up to date information. Andrew Davison Department of Computing Imperial College London Review:
Robotics Lecture 5: Monte Carlo Localisation See course website http://www.doc.ic.ac.uk/~ajd/robotics/ for up to date information. Andrew Davison Department of Computing Imperial College London Review:
Year. Small Steps Guidance and Examples. Block 1 Properties of Shapes. Released March 2018
 Released March 2018 The sequence of small steps has been produced by White Rose Maths. White Rose Maths gives permission to schools and teachers to use the small steps in their own teaching in their own
Released March 2018 The sequence of small steps has been produced by White Rose Maths. White Rose Maths gives permission to schools and teachers to use the small steps in their own teaching in their own
Vector Addition and Subtraction: Analytical Methods
 Connexions module: m42128 1 Vector Addition and Subtraction: Analytical Methods OpenStax College This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
Connexions module: m42128 1 Vector Addition and Subtraction: Analytical Methods OpenStax College This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
CCGPS UNIT 2 Semester 1 ANALYTIC GEOMETRY Page 1 of 15. Right Triangle Geometry Name:
 GPS UNIT 2 Semester 1 ANALYTI GEOMETRY Page 1 of 15 Right Triangle Geometry Name: Date: Define trigonometric ratios and solve problems involving right triangles. M9-12.G.SRT.6 Understand that by similarity,
GPS UNIT 2 Semester 1 ANALYTI GEOMETRY Page 1 of 15 Right Triangle Geometry Name: Date: Define trigonometric ratios and solve problems involving right triangles. M9-12.G.SRT.6 Understand that by similarity,
