Ray Tracer I: Ray Casting Due date: 12:00pm December 3, 2001
|
|
|
- Laurel Robertson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Computer graphics Assignment 5 1 Overview Ray Tracer I: Ray Casting Due date: 12:00pm December 3, 2001 In this assignment you will implement the camera and several primitive objects for a ray tracer. We will not do recursive ray tracing yet, just ray casting. The input language of the ray tracer will be a subset of the geometry file format of POV-Ray raytracer. 2 What your program should do Your program should read a file specified on the command line and create an image of the scene described in the file using ray casting. In addition to the name of the file, on the command line you should be able to specify the size of the output image. 3 File format description The input file format is a subset of the POV-Ray file format. When in doubt, consult the POV-Ray manual (the link is posted at the class Web page). Installing POV-Ray on your computer is strongly recommended. The file in POV-Ray format is a sequence of object descriptions. You should implement the following POV-Ray objects: box, sphere, cone, cylinder, quadric. Comments. Two slashes are used for single line comments in the file. Anything on a line after a double slash // is ignored by the ray tracer. For example: // This line is ignored sphere { <0,0,0>, 1 // a sphere of radius 1 centered at the origin Objects. The basic syntax of an object is a keyword describing its type, some floats, vectors or other parameters which further define its location and/or shape and some optional object modifiers such as pigments or transformations. In this assignment the only modifiers that we consider are transformations. Sphere. The syntax for a sphere is: sphere { <CENTER>, RADIUS where <CENTER> is a 3d point, and RADIUS is a real value specifying the radius. You can also add translations, rotations, and scaling to the sphere. For example, this is a sphere of radius 10 centered at 25 on the Y axis: sphere { <0,0,0>, 1.0 scale 10 translate <0,25,0> 1
2 Note that a 3D vector or point is specified using angular brackets, and the components are separated by commas. Transformations can be also applied to all other objects (see details on transformations below). Box. A simple box can be defined by listing two corners of the box like this: box { <CORNER1>, <CORNER2> Where <CORNER1> and <CORNER2> are vectors defining the x,y,z coordinates of opposite corners of the box. For example: box { <0, 0, 0>, <1, 1, 1> Note that all boxes are defined with their faces parallel to the coordinate axes. They may later be rotated to any orientation using a rotate parameter. Each element of <CORNER1>. should always be less than the corresponding element in <CORNER2> Cone. A finite length cone or a frustum (a cone with the point cut off) may be defined by cone { <POINT1>, RADIUS1, <POINT2>, RADIUS2 where <POINT1> and <POINT2> are the centers of the end caps of the cone and RADIUS1 and RADIUS2 are radii of the caps of the cone. For example, cone { <0,0,0>, 2, <0,3,0>, 0 is a cone 3 units tall pointing up the y axis. The base has a radius of 2. The other end has a radius of 0 which means it comes to a sharp point. If neither radius is zero then the results look like a tapered cylinder or a cone with the point cut off. The ends of a cone are closed by flat planes which are parallel to each other and perpendicular to the axis of the cone. Cylinder. A finite length cylinder with parallel end caps may be defined by cylinder { <POINT1>, <POINT2>, RADIUS where <POINT1> and <POINT2> are the centers of the end caps, and RADIUS is the cylinder radius. cylinder { <0,0,0>, <0,3,0>, 2 is a cylinder of height 3 with a radius of 2, and base centered at the origin in the XZ plane. The ends of a cylinder are closed by flat planes which are parallel to each other and perpendicular to the length of the cylinder. 2
3 Polygon. A polygon with N vertices is defined by: polygon { N,<VERTEX1>, <VERTEX2>,..., <VERTEXN> where <VERTEXi> is a vector defining the x,y,z coordinates of each corner of the triangle. Quadric. Quadric surfaces can produce shapes like ellipsoids, spheres, cones, cylinders, paraboloids (dish shapes), and hyperboloids (saddle or hourglass shapes). A quadric is defined in POV-Ray by: quadric { <A,B,C>, <D,E,F>, <G,H,I>, J where A through J are float expressions. This defines a surface of x,y,z points which satisfy the equation: Ax 2 + By 2 +Cz 2 + Dxy + Exz + Fyz + Gx + Hy + Iz + J = 0 Different values of A,B,C,...J will give different shapes. So, if you take any three dimensional point and use its x, y, and z coordinates in the above equation, the answer will be 0 if the point is on the surface of the object. The answer will be negative if the point is inside the object and positive if the point is outside the object. Here are some examples: x 2 + y 2 + z 2 1 = 0 defines a sphere; x 2 + y 2 1 = 0 defines an infinitely long cylinder along the Z axis; x 2 + y 2 z 2 = 0 defines an infinitely long cone along the Z axis. Camera. The camera definition describes a camera used for viewing the scene. If you do not specify a camera then a default camera is used. The camera is defined by the following parameters: location, look at, angle, up, right. The location is simply the X, Y, Z coordinates of the camera. The default location is 0,0,0. The lookat method of positioning the camera have been discussed at a previous lecture in the context of OpenGL. In addition to the location ( eye in the glulookat function call), we specify the the up vector and the look at point (the center argument of glulookat). When the look at point is specified, the up vector should be forced to be perpendicular to the viewing direction, that is, the component of up parallel to the viewing direction should be subtracted from it and it should be normalized to 1. By default, the look at point is 1 unit in Z direction from the location.the angle keyword followed by a float expression specifies the (horizontal) viewing angle in degrees. The right vector plays a limited role: we use the ratio of the length of this vector to the length of the up vector to determine the aspect ratio of the image. The default values are: up <0,1,0> right < ,0,0> The main use of the camera model in ray tracing is to compute pixel rays. For the simplified model that we use, formulas are included in the lecture notes. Warning: POV-Ray has a relatively complicated camera model with many interdependent parameters; we are using a small subset. You may end up confused if you try to sort out the complete model from the POV-Ray documentation, so I suggest using this description together with the lecture notes. Under many circumstances just two vectors in the camera statement are all you need: location and look at. For example: 3
4 camera { location <3,5,-10> look_at <0,2,1> The up vector. The keyword up is used to define a vector for the vertical direction. Before using the vector, subtract the component parallel to the viewing direction, if any. Also, normalize it to be of unit length. The default up vector points along the Y axis, unless it is the viewing direction. In the latter case, it points along the X axis. In addition to the standard parameters, a camera may have a transformation attached to it; the parser reads it, if there is one, but you are not required to implement it. Transformations. Three standard types of transformations can be applied in any order to any object: translate, rotate and scale. Any number of transformations can be applied in any order. The argument of rotate is a vector with three components, which are angles of rotation around x, y and z axes in degrees. Example rotate <0,45,0> // rotate around Y axis by degrees The scale is a nonuniform scale and its argument is a vector of three scale factors in x,y and z directions. The translate takes the translation vector as an argument. The parser reads all transformations and converts them to 4 by 4 matrices. It is possible to transform each object before rendering, and this is the most efficient approach. However, deriving the necessary transformations of the object parameters may be tricky. A simpler approach is to transform the ray to the coordiante system in which the object is defined. This means that each time we intersect a ray with an object that has a transformation attached to it, we need to apply the inverse of the transformation to the ray. Thus, it makes sense to store both the transformation matrix and its inverse together with the object. 4 What to turn in Create a test image from the file that is provided on the Web page. Also, create 3 images of a 1x1 square in the XY plane for the following camera parameters: camera { location <0.5,0.5,1> look_at <0.5,0.5,0> angle 90 camera { location <2,1,2> right <1.5,0,0> look_at <1,1,1> angle 90 camera { location <2,2,2> 4
5 look_at <0,0,0> up <1,0,0> angle 90 5 Implementation Suggestions General organization. Your ray tracer will consist of two main parts: the rendering engine and a set of modules to manage the parameters of the camera, databases of shapes, light sources and materials. These suggestions are for C++ programming. However, similar style can be maintained in C code. It is convenient to represent each shape with a class derived from a base shape class, and use virtual methods for operations like intersecting the object with a ray. You will need to perform a lot of vector arithmetics. Unless you already have it, write a small library of standard vector functions (addition, multiplication by a constant, dot product, cross product etc.) using the code provided with the parser as the starting point. Parsing the geometry file. To simplify your task, a parser is provided. Currently, the parser simply prints out the parameters of the objects that are parsed. You need to add code to it to create the objects. The parser uses a standard approach: there is a function gettoken, that skips the comments and returns the next token in the input file. A token is either a reserved keyword, a floating point number, a comma, or one of the symbols {,, <, >. Numbers and identifiers have to be separated from each other by whitespace characters (space, tab, newline), but need not be separated from the comma or {,, <, >. The parser calls gettoken, determines the object type from the first token and calls the function that parses the object definition for each object. These functions, in turn, may call functions for parsing transform definitions, vectors etc. Only simple error processing is done: if there is a syntax error in the file, the parser prints a message and aborts. In general, each object type (sphere, cone, cylinder, polygon, quadric) should correspond to a class in your program. Any object may have a transformation attached; assemble all transformations for each object into a single matrix, and transform the ray into the object s coordinate system when computing intersections. For this, you need to multiply both the direction and the origin of the ray by the inverse of the transformation matrix. Create a data structure to describe rays. Initially, it should contain at least three fields: double[3] orig; // origin of the ray double[3] dir; // direction of the ray float[3] color; Note that we use doubles for all fields except color. In the geometric calculations, double precision is preferable, although the geometry itself can be described by floats. In lighting calculations single precision is sufficient. Feel free to use your 3D vector classes for the fields instead of double[3]. Implement the intersection algorithms for polygons and quadrics described in class. Boxes can be treated as collections of polygons. Dummy lighting. As we do not have any lighting yet, we should chose a way to define the color of the ray after we found the intersection point with an object. If the ray did not hit any object, use a background color (e.g. blue). Otherwise, choose a function of coordinates of the intersection point to paint the ray. The simplest choice would be simply Z-coordinate with appropriate scaling, so that the resulting value is 255 for the points closest to the camera and 0 for the most distant points, but you can be more creative, provided that 5
6 your choice allows to distinguish the shapes in the picture. Another simple approach is to assign a color to each shape. 6
Ray Tracer Due date: April 27, 2011
 Computer graphics Assignment 4 1 Overview Ray Tracer Due date: April 27, 2011 In this assignment you will implement the camera and several primitive objects for a ray tracer, and a basic ray tracing algorithm.
Computer graphics Assignment 4 1 Overview Ray Tracer Due date: April 27, 2011 In this assignment you will implement the camera and several primitive objects for a ray tracer, and a basic ray tracing algorithm.
Lecture 11. More Ray Casting/Tracing
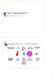
 Lecture 11 More Ray Casting/Tracing Basic Algorithm For each pixel { } Shoot a ray from camera to pixel for all objects in scene Compute intersection with ray Find object with closest intersection Display
Lecture 11 More Ray Casting/Tracing Basic Algorithm For each pixel { } Shoot a ray from camera to pixel for all objects in scene Compute intersection with ray Find object with closest intersection Display
Quadric Surfaces. Philippe B. Laval. Today KSU. Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Quadric Surfaces Today 1 / 24
 Quadric Surfaces Philippe B. Laval KSU Today Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Quadric Surfaces Today 1 / 24 Introduction A quadric surface is the graph of a second degree equation in three variables. The general
Quadric Surfaces Philippe B. Laval KSU Today Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Quadric Surfaces Today 1 / 24 Introduction A quadric surface is the graph of a second degree equation in three variables. The general
Quadric Surfaces. Philippe B. Laval. Spring 2012 KSU. Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Quadric Surfaces Spring /
 .... Quadric Surfaces Philippe B. Laval KSU Spring 2012 Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Quadric Surfaces Spring 2012 1 / 15 Introduction A quadric surface is the graph of a second degree equation in three variables.
.... Quadric Surfaces Philippe B. Laval KSU Spring 2012 Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Quadric Surfaces Spring 2012 1 / 15 Introduction A quadric surface is the graph of a second degree equation in three variables.
Ray casting. Ray casting/ray tracing
 Ray casting Ray casting/ray tracing Iterate over pixels, not objects Effects that are difficult with Z-buffer, are easy with ray tracing: shadows, reflections, transparency, procedural textures and objects
Ray casting Ray casting/ray tracing Iterate over pixels, not objects Effects that are difficult with Z-buffer, are easy with ray tracing: shadows, reflections, transparency, procedural textures and objects
Section 12.2: Quadric Surfaces
 Section 12.2: Quadric Surfaces Goals: 1. To recognize and write equations of quadric surfaces 2. To graph quadric surfaces by hand Definitions: 1. A quadric surface is the three-dimensional graph of an
Section 12.2: Quadric Surfaces Goals: 1. To recognize and write equations of quadric surfaces 2. To graph quadric surfaces by hand Definitions: 1. A quadric surface is the three-dimensional graph of an
Key Idea. It is not helpful to plot points to sketch a surface. Mainly we use traces and intercepts to sketch
 Section 12.7 Quadric surfaces 12.7 1 Learning outcomes After completing this section, you will inshaallah be able to 1. know what are quadric surfaces 2. how to sketch quadric surfaces 3. how to identify
Section 12.7 Quadric surfaces 12.7 1 Learning outcomes After completing this section, you will inshaallah be able to 1. know what are quadric surfaces 2. how to sketch quadric surfaces 3. how to identify
Ray Tracing. CS334 Fall Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University
 Ray Tracing CS334 Fall 2013 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Ray Casting and Ray Tracing Ray Casting Arthur Appel, started around 1968 Ray Tracing Turner Whitted, started
Ray Tracing CS334 Fall 2013 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Ray Casting and Ray Tracing Ray Casting Arthur Appel, started around 1968 Ray Tracing Turner Whitted, started
COMP 175 COMPUTER GRAPHICS. Ray Casting. COMP 175: Computer Graphics April 26, Erik Anderson 09 Ray Casting
 Ray Casting COMP 175: Computer Graphics April 26, 2018 1/41 Admin } Assignment 4 posted } Picking new partners today for rest of the assignments } Demo in the works } Mac demo may require a new dylib I
Ray Casting COMP 175: Computer Graphics April 26, 2018 1/41 Admin } Assignment 4 posted } Picking new partners today for rest of the assignments } Demo in the works } Mac demo may require a new dylib I
Geometric Queries for Ray Tracing
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 16 Geometric Queries for Ray Tracing Ray-Surface Intersection Barycentric Coordinates [Angel Ch. 11] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California 1 Ray-Surface Intersections
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 16 Geometric Queries for Ray Tracing Ray-Surface Intersection Barycentric Coordinates [Angel Ch. 11] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California 1 Ray-Surface Intersections
Ray Tracing. Foley & Van Dam, Chapters 15 and 16
 Ray Tracing Foley & Van Dam, Chapters 15 and 16 Ray Tracing Visible Surface Ray Tracing (Ray Casting) Examples Efficiency Issues Computing Boolean Set Operations Recursive Ray Tracing Determine visibility
Ray Tracing Foley & Van Dam, Chapters 15 and 16 Ray Tracing Visible Surface Ray Tracing (Ray Casting) Examples Efficiency Issues Computing Boolean Set Operations Recursive Ray Tracing Determine visibility
Ray Tracing Foley & Van Dam, Chapters 15 and 16
 Foley & Van Dam, Chapters 15 and 16 (Ray Casting) Examples Efficiency Issues Computing Boolean Set Operations Recursive Determine visibility of a surface by tracing rays of light from the viewer s eye
Foley & Van Dam, Chapters 15 and 16 (Ray Casting) Examples Efficiency Issues Computing Boolean Set Operations Recursive Determine visibility of a surface by tracing rays of light from the viewer s eye
1999, Denis Zorin. Ray tracing
 Ray tracing Ray tracing shadow rays normal reflected ray pixel ray camera normal Ray casting/ray tracing Iterate over pixels, not objects. Effects that are difficult with Z-buffer, are easy with ray tracing:
Ray tracing Ray tracing shadow rays normal reflected ray pixel ray camera normal Ray casting/ray tracing Iterate over pixels, not objects. Effects that are difficult with Z-buffer, are easy with ray tracing:
12.6 Cylinders and Quadric Surfaces
 12 Vectors and the Geometry of Space 12.6 and Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. and We have already looked at two special types of surfaces:
12 Vectors and the Geometry of Space 12.6 and Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. and We have already looked at two special types of surfaces:
Lecture 3 Sections 2.2, 4.4. Mon, Aug 31, 2009
 Model s Lecture 3 Sections 2.2, 4.4 World s Eye s Clip s s s Window s Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Aug 31, 2009 Outline Model s World s Eye s Clip s s s Window s 1 2 3 Model s World s Eye s Clip s s s Window
Model s Lecture 3 Sections 2.2, 4.4 World s Eye s Clip s s s Window s Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Aug 31, 2009 Outline Model s World s Eye s Clip s s s Window s 1 2 3 Model s World s Eye s Clip s s s Window
Quadric Surfaces. Six basic types of quadric surfaces: ellipsoid. cone. elliptic paraboloid. hyperboloid of one sheet. hyperboloid of two sheets
 Quadric Surfaces Six basic types of quadric surfaces: ellipsoid cone elliptic paraboloid hyperboloid of one sheet hyperboloid of two sheets hyperbolic paraboloid (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) 1. For each surface,
Quadric Surfaces Six basic types of quadric surfaces: ellipsoid cone elliptic paraboloid hyperboloid of one sheet hyperboloid of two sheets hyperbolic paraboloid (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) 1. For each surface,
1.6 Quadric Surfaces Brief review of Conic Sections 74 CHAPTER 1. VECTORS AND THE GEOMETRY OF SPACE. Figure 1.18: Parabola y = 2x 2
 7 CHAPTER 1. VECTORS AND THE GEOMETRY OF SPACE Figure 1.18: Parabola y = x 1.6 Quadric Surfaces Figure 1.19: Parabola x = y 1.6.1 Brief review of Conic Sections You may need to review conic sections for
7 CHAPTER 1. VECTORS AND THE GEOMETRY OF SPACE Figure 1.18: Parabola y = x 1.6 Quadric Surfaces Figure 1.19: Parabola x = y 1.6.1 Brief review of Conic Sections You may need to review conic sections for
Topics and things to know about them:
 Practice Final CMSC 427 Distributed Tuesday, December 11, 2007 Review Session, Monday, December 17, 5:00pm, 4424 AV Williams Final: 10:30 AM Wednesday, December 19, 2007 General Guidelines: The final will
Practice Final CMSC 427 Distributed Tuesday, December 11, 2007 Review Session, Monday, December 17, 5:00pm, 4424 AV Williams Final: 10:30 AM Wednesday, December 19, 2007 General Guidelines: The final will
Ray tracing. Methods of Programming DV2. Introduction to ray tracing and XML. Forward ray tracing. The image plane. Backward ray tracing
 Methods of Programming DV2 Introduction to ray tracing and XML Ray tracing Suppose we have a description of a 3-dimensional world consisting of various objects spheres, triangles (flat), planes (flat,
Methods of Programming DV2 Introduction to ray tracing and XML Ray tracing Suppose we have a description of a 3-dimensional world consisting of various objects spheres, triangles (flat), planes (flat,
What you will learn today
 What you will learn today Conic Sections (in 2D coordinates) Cylinders (3D) Quadric Surfaces (3D) Vectors and the Geometry of Space 1/24 Parabolas ellipses Hyperbolas Shifted Conics Conic sections result
What you will learn today Conic Sections (in 2D coordinates) Cylinders (3D) Quadric Surfaces (3D) Vectors and the Geometry of Space 1/24 Parabolas ellipses Hyperbolas Shifted Conics Conic sections result
4 = 1 which is an ellipse of major axis 2 and minor axis 2. Try the plane z = y2
 12.6 Quadrics and Cylinder Surfaces: Example: What is y = x? More correctly what is {(x,y,z) R 3 : y = x}? It s a plane. What about y =? Its a cylinder surface. What about y z = Again a cylinder surface
12.6 Quadrics and Cylinder Surfaces: Example: What is y = x? More correctly what is {(x,y,z) R 3 : y = x}? It s a plane. What about y =? Its a cylinder surface. What about y z = Again a cylinder surface
Chapter 15: Functions of Several Variables
 Chapter 15: Functions of Several Variables Section 15.1 Elementary Examples a. Notation: Two Variables b. Example c. Notation: Three Variables d. Functions of Several Variables e. Examples from the Sciences
Chapter 15: Functions of Several Variables Section 15.1 Elementary Examples a. Notation: Two Variables b. Example c. Notation: Three Variables d. Functions of Several Variables e. Examples from the Sciences
Assignment 6: Ray Tracing
 Assignment 6: Ray Tracing Programming Lab Due: Monday, April 20 (midnight) 1 Introduction Throughout this semester you have written code that manipulated shapes and cameras to prepare a scene for rendering.
Assignment 6: Ray Tracing Programming Lab Due: Monday, April 20 (midnight) 1 Introduction Throughout this semester you have written code that manipulated shapes and cameras to prepare a scene for rendering.
Functions of Several Variables
 . Functions of Two Variables Functions of Several Variables Rectangular Coordinate System in -Space The rectangular coordinate system in R is formed by mutually perpendicular axes. It is a right handed
. Functions of Two Variables Functions of Several Variables Rectangular Coordinate System in -Space The rectangular coordinate system in R is formed by mutually perpendicular axes. It is a right handed
The feature set you are required to implement in your ray tracer is as follows (by order from easy to hard):
 Ray Tracing exercise TAU, Computer Graphics, 0368.3014, semester B Go to the Updates and FAQ Page Overview The objective of this exercise is to implement a ray casting/tracing engine. Ray tracing is a
Ray Tracing exercise TAU, Computer Graphics, 0368.3014, semester B Go to the Updates and FAQ Page Overview The objective of this exercise is to implement a ray casting/tracing engine. Ray tracing is a
Lecture 8 Ray tracing Part 1: Basic concept Yong-Jin Liu.
 Fundamentals of Computer Graphics Lecture 8 Ray tracing Part 1: Basic concept Yong-Jin Liu liuyongjin@tsinghua.edu.cn Material by S.M.Lea (UNC) Goals To set up the mathematics and algorithms to perform
Fundamentals of Computer Graphics Lecture 8 Ray tracing Part 1: Basic concept Yong-Jin Liu liuyongjin@tsinghua.edu.cn Material by S.M.Lea (UNC) Goals To set up the mathematics and algorithms to perform
Assignment 2 Ray Tracing
 Assignment 2 Ray Tracing Overview The concept of ray tracing: a technique for generating an image by tracing the path of light through pixels in an image plane and simulating the effects of its encounters
Assignment 2 Ray Tracing Overview The concept of ray tracing: a technique for generating an image by tracing the path of light through pixels in an image plane and simulating the effects of its encounters
Computer Graphics Ray Casting. Matthias Teschner
 Computer Graphics Ray Casting Matthias Teschner Outline Context Implicit surfaces Parametric surfaces Combined objects Triangles Axis-aligned boxes Iso-surfaces in grids Summary University of Freiburg
Computer Graphics Ray Casting Matthias Teschner Outline Context Implicit surfaces Parametric surfaces Combined objects Triangles Axis-aligned boxes Iso-surfaces in grids Summary University of Freiburg
CSCI 4620/8626. Coordinate Reference Frames
 CSCI 4620/8626 Computer Graphics Graphics Output Primitives Last update: 2014-02-03 Coordinate Reference Frames To describe a picture, the world-coordinate reference frame (2D or 3D) must be selected.
CSCI 4620/8626 Computer Graphics Graphics Output Primitives Last update: 2014-02-03 Coordinate Reference Frames To describe a picture, the world-coordinate reference frame (2D or 3D) must be selected.
Solid Modeling. Ron Goldman Department of Computer Science Rice University
 Solid Modeling Ron Goldman Department of Computer Science Rice University Solids Definition 1. A model which has a well defined inside and outside. 2. For each point, we can in principle determine whether
Solid Modeling Ron Goldman Department of Computer Science Rice University Solids Definition 1. A model which has a well defined inside and outside. 2. For each point, we can in principle determine whether
Raycasting. Chapter Raycasting foundations. When you look at an object, like the ball in the picture to the left, what do
 Chapter 4 Raycasting 4. Raycasting foundations When you look at an, like the ball in the picture to the left, what do lamp you see? You do not actually see the ball itself. Instead, what you see is the
Chapter 4 Raycasting 4. Raycasting foundations When you look at an, like the ball in the picture to the left, what do lamp you see? You do not actually see the ball itself. Instead, what you see is the
3D Rendering and Ray Casting
 3D Rendering and Ray Casting Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) HB Ch. 13.7, 14.6 FvDFH 15.5, 15.10 Rendering Generate an image from geometric primitives Rendering Geometric Primitives (3D) Raster Image (2D)
3D Rendering and Ray Casting Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) HB Ch. 13.7, 14.6 FvDFH 15.5, 15.10 Rendering Generate an image from geometric primitives Rendering Geometric Primitives (3D) Raster Image (2D)
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 13b Ray Tracing (Part 1) Prof Emmanuel Agu. Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI)
 Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 13b Ray Tracing (Part 1) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Raytracing Global illumination-based rendering method Simulates
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 13b Ray Tracing (Part 1) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Raytracing Global illumination-based rendering method Simulates
Section 2.5. Functions and Surfaces
 Section 2.5. Functions and Surfaces ² Brief review for one variable functions and curves: A (one variable) function is rule that assigns to each member x in a subset D in R 1 a unique real number denoted
Section 2.5. Functions and Surfaces ² Brief review for one variable functions and curves: A (one variable) function is rule that assigns to each member x in a subset D in R 1 a unique real number denoted
3D Rendering and Ray Casting
 3D Rendering and Ray Casting Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) HB Ch. 13.7, 14.6 FvDFH 15.5, 15.10 Rendering Generate an image from geometric primitives Rendering Geometric Primitives (3D) Raster Image (2D)
3D Rendering and Ray Casting Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) HB Ch. 13.7, 14.6 FvDFH 15.5, 15.10 Rendering Generate an image from geometric primitives Rendering Geometric Primitives (3D) Raster Image (2D)
Ray Tracing I. Internet Raytracing Competition
 History Ray Tracing came from the Physics of lens making. The process was that of drawing lines or rays through a glass shape to determine it s lens properties. It is also related to early perspective
History Ray Tracing came from the Physics of lens making. The process was that of drawing lines or rays through a glass shape to determine it s lens properties. It is also related to early perspective
SFU CMPT 361 Computer Graphics Fall 2017 Assignment 2. Assignment due Thursday, October 19, 11:59pm
 SFU CMPT 361 Computer Graphics Fall 2017 Assignment 2 Assignment due Thursday, October 19, 11:59pm For this assignment, you are to interpret a 3D graphics specification language, along with doing some
SFU CMPT 361 Computer Graphics Fall 2017 Assignment 2 Assignment due Thursday, October 19, 11:59pm For this assignment, you are to interpret a 3D graphics specification language, along with doing some
Fog and Cloud Effects. Karl Smeltzer Alice Cao John Comstock
 Fog and Cloud Effects Karl Smeltzer Alice Cao John Comstock Goal Explore methods of rendering scenes containing fog or cloud-like effects through a variety of different techniques Atmospheric effects make
Fog and Cloud Effects Karl Smeltzer Alice Cao John Comstock Goal Explore methods of rendering scenes containing fog or cloud-like effects through a variety of different techniques Atmospheric effects make
8.1 Geometric Queries for Ray Tracing
 Fall 2017 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 8.1 Geometric Queries for Ray Tracing Hao Li http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 Outline Ray-Surface Intersections Special cases: sphere, polygon Barycentric coordinates 2 Outline
Fall 2017 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 8.1 Geometric Queries for Ray Tracing Hao Li http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 Outline Ray-Surface Intersections Special cases: sphere, polygon Barycentric coordinates 2 Outline
Cylinders and Quadric Surfaces A cylinder is a three dimensional shape that is determined by
 Cylinders and Quadric Surfaces A cylinder is a three dimensional shape that is determined by a two dimensional (plane) curve C in three dimensional space a line L in a plane not parallel to the one in
Cylinders and Quadric Surfaces A cylinder is a three dimensional shape that is determined by a two dimensional (plane) curve C in three dimensional space a line L in a plane not parallel to the one in
Motivation. Sampling and Reconstruction of Visual Appearance. Effects needed for Realism. Ray Tracing. Outline
 Sampling and Reconstruction of Visual Appearance CSE 274 [Fall 2018], Special Lecture Ray Tracing Ravi Ramamoorthi http://www.cs.ucsd.edu/~ravir Motivation Ray Tracing is a core aspect of both offline
Sampling and Reconstruction of Visual Appearance CSE 274 [Fall 2018], Special Lecture Ray Tracing Ravi Ramamoorthi http://www.cs.ucsd.edu/~ravir Motivation Ray Tracing is a core aspect of both offline
Transformations in Ray Tracing. MIT EECS 6.837, Durand and Cutler
 Transformations in Ray Tracing Linear Algebra Review Session Tonight! 7:30 9 PM Last Time: Simple Transformations Classes of Transformations Representation homogeneous coordinates Composition not commutative
Transformations in Ray Tracing Linear Algebra Review Session Tonight! 7:30 9 PM Last Time: Simple Transformations Classes of Transformations Representation homogeneous coordinates Composition not commutative
CS Simple Raytracer for students new to Rendering
 CS 294-13 Simple Raytracer for students new to Rendering Ravi Ramamoorthi This assignment should be done only by those small number of students who have not yet written a raytracer. For those students
CS 294-13 Simple Raytracer for students new to Rendering Ravi Ramamoorthi This assignment should be done only by those small number of students who have not yet written a raytracer. For those students
CSE328 Fundamentals of Computer Graphics
 CSE328 Fundamentals of Computer Graphics Hong Qin State University of New York at Stony Brook (Stony Brook University) Stony Brook, New York 794--44 Tel: (63)632-845; Fax: (63)632-8334 qin@cs.sunysb.edu
CSE328 Fundamentals of Computer Graphics Hong Qin State University of New York at Stony Brook (Stony Brook University) Stony Brook, New York 794--44 Tel: (63)632-845; Fax: (63)632-8334 qin@cs.sunysb.edu
Ray Tracing I. History
 History Ray Tracing came from the Physics of lens making. The process was that of drawing lines or rays through a glass shape to determine it s lens properties. It is also related to early perspective
History Ray Tracing came from the Physics of lens making. The process was that of drawing lines or rays through a glass shape to determine it s lens properties. It is also related to early perspective
CSE528 Computer Graphics: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications
 CSE528 Computer Graphics: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications Hong Qin Stony Brook University (SUNY at Stony Brook) Stony Brook, New York 11794-2424 Tel: (631)632-845; Fax: (631)632-8334 qin@cs.stonybrook.edu
CSE528 Computer Graphics: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications Hong Qin Stony Brook University (SUNY at Stony Brook) Stony Brook, New York 11794-2424 Tel: (631)632-845; Fax: (631)632-8334 qin@cs.stonybrook.edu
CPSC GLOBAL ILLUMINATION
 CPSC 314 21 GLOBAL ILLUMINATION Textbook: 20 UGRAD.CS.UBC.CA/~CS314 Mikhail Bessmeltsev ILLUMINATION MODELS/ALGORITHMS Local illumination - Fast Ignore real physics, approximate the look Interaction of
CPSC 314 21 GLOBAL ILLUMINATION Textbook: 20 UGRAD.CS.UBC.CA/~CS314 Mikhail Bessmeltsev ILLUMINATION MODELS/ALGORITHMS Local illumination - Fast Ignore real physics, approximate the look Interaction of
Rectangular Coordinates in Space
 Rectangular Coordinates in Space Philippe B. Laval KSU Today Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Rectangular Coordinates in Space Today 1 / 11 Introduction We quickly review one and two-dimensional spaces and then
Rectangular Coordinates in Space Philippe B. Laval KSU Today Philippe B. Laval (KSU) Rectangular Coordinates in Space Today 1 / 11 Introduction We quickly review one and two-dimensional spaces and then
CS451Real-time Rendering Pipeline
 1 CS451Real-time Rendering Pipeline JYH-MING LIEN DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE GEORGE MASON UNIVERSITY Based on Tomas Akenine-Möller s lecture note You say that you render a 3D 2 scene, but what does
1 CS451Real-time Rendering Pipeline JYH-MING LIEN DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE GEORGE MASON UNIVERSITY Based on Tomas Akenine-Möller s lecture note You say that you render a 3D 2 scene, but what does
DH2323 DGI13. Lab 2 Raytracing
 DH2323 DGI13 Lab 2 Raytracing In this lab you will implement a Raytracer, which draws images of 3D scenes by tracing the light rays reaching the simulated camera. The lab is divided into several steps.
DH2323 DGI13 Lab 2 Raytracing In this lab you will implement a Raytracer, which draws images of 3D scenes by tracing the light rays reaching the simulated camera. The lab is divided into several steps.
Ray Tracing Basics I. Computer Graphics as Virtual Photography. camera (captures light) real scene. photo. Photographic print. Photography: processing
 Ray Tracing Basics I Computer Graphics as Virtual Photography Photography: real scene camera (captures light) photo processing Photographic print processing Computer Graphics: 3D models camera model (focuses
Ray Tracing Basics I Computer Graphics as Virtual Photography Photography: real scene camera (captures light) photo processing Photographic print processing Computer Graphics: 3D models camera model (focuses
Computer Graphics and Image Processing Ray Tracing I
 Computer Graphics and Image Processing Ray Tracing I Part 1 Lecture 9 1 Today s Outline Introduction to Ray Tracing Ray Casting Intersecting Rays with Primitives Intersecting Rays with Transformed Primitives
Computer Graphics and Image Processing Ray Tracing I Part 1 Lecture 9 1 Today s Outline Introduction to Ray Tracing Ray Casting Intersecting Rays with Primitives Intersecting Rays with Transformed Primitives
Lecture 17: Recursive Ray Tracing. Where is the way where light dwelleth? Job 38:19
 Lecture 17: Recursive Ray Tracing Where is the way where light dwelleth? Job 38:19 1. Raster Graphics Typical graphics terminals today are raster displays. A raster display renders a picture scan line
Lecture 17: Recursive Ray Tracing Where is the way where light dwelleth? Job 38:19 1. Raster Graphics Typical graphics terminals today are raster displays. A raster display renders a picture scan line
The University of Calgary
 The University of Calgary Department of Computer Science Final Examination, Questions ENEL/CPSC 555 Computer Graphics Time: 2 Hours Closed Book, calculators are permitted. The questions carry equal weight.
The University of Calgary Department of Computer Science Final Examination, Questions ENEL/CPSC 555 Computer Graphics Time: 2 Hours Closed Book, calculators are permitted. The questions carry equal weight.
Study Guide and Review
 State whether each sentence is or false. If false, replace the underlined term to make a sentence. 1. Euclidean geometry deals with a system of points, great circles (lines), and spheres (planes). false,
State whether each sentence is or false. If false, replace the underlined term to make a sentence. 1. Euclidean geometry deals with a system of points, great circles (lines), and spheres (planes). false,
6.837 Introduction to Computer Graphics Final Exam Tuesday, December 20, :05-12pm Two hand-written sheet of notes (4 pages) allowed 1 SSD [ /17]
![6.837 Introduction to Computer Graphics Final Exam Tuesday, December 20, :05-12pm Two hand-written sheet of notes (4 pages) allowed 1 SSD [ /17] 6.837 Introduction to Computer Graphics Final Exam Tuesday, December 20, :05-12pm Two hand-written sheet of notes (4 pages) allowed 1 SSD [ /17]](/thumbs/87/95541269.jpg) 6.837 Introduction to Computer Graphics Final Exam Tuesday, December 20, 2011 9:05-12pm Two hand-written sheet of notes (4 pages) allowed NAME: 1 / 17 2 / 12 3 / 35 4 / 8 5 / 18 Total / 90 1 SSD [ /17]
6.837 Introduction to Computer Graphics Final Exam Tuesday, December 20, 2011 9:05-12pm Two hand-written sheet of notes (4 pages) allowed NAME: 1 / 17 2 / 12 3 / 35 4 / 8 5 / 18 Total / 90 1 SSD [ /17]
Movie: Geri s Game. Announcements. Ray Casting 2. Programming 2 Recap. Programming 3 Info Test data for part 1 (Lines) is available
 Now Playing: Movie: Geri s Game Pixar, 1997 Academny Award Winner, Best Short Film Quicksand Under Carpet New Radiant Storm King from Leftover Blues: 1991-003 Released 004 Ray Casting Rick Skarbez, Instructor
Now Playing: Movie: Geri s Game Pixar, 1997 Academny Award Winner, Best Short Film Quicksand Under Carpet New Radiant Storm King from Leftover Blues: 1991-003 Released 004 Ray Casting Rick Skarbez, Instructor
Shading, Advanced Rendering. Week 7, Wed Feb 28
 University of British Columbia CPSC 314 Computer Graphics Jan-Apr 2007 Tamara Munzner Shading, Advanced Rendering Week 7, Wed Feb 28 http://www.ugrad.cs.ubc.ca/~cs314/vjan2007 Reading for Today and Tomorrow
University of British Columbia CPSC 314 Computer Graphics Jan-Apr 2007 Tamara Munzner Shading, Advanced Rendering Week 7, Wed Feb 28 http://www.ugrad.cs.ubc.ca/~cs314/vjan2007 Reading for Today and Tomorrow
MAT175 Overview and Sample Problems
 MAT175 Overview and Sample Problems The course begins with a quick review/overview of one-variable integration including the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, u-substitutions, integration by parts, and
MAT175 Overview and Sample Problems The course begins with a quick review/overview of one-variable integration including the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, u-substitutions, integration by parts, and
Quadric surface. Ellipsoid
 Quadric surface Quadric surfaces are the graphs of any equation that can be put into the general form 11 = a x + a y + a 33z + a1xy + a13xz + a 3yz + a10x + a 0y + a 30z + a 00 where a ij R,i, j = 0,1,,
Quadric surface Quadric surfaces are the graphs of any equation that can be put into the general form 11 = a x + a y + a 33z + a1xy + a13xz + a 3yz + a10x + a 0y + a 30z + a 00 where a ij R,i, j = 0,1,,
Adaptive Point Cloud Rendering
 1 Adaptive Point Cloud Rendering Project Plan Final Group: May13-11 Christopher Jeffers Eric Jensen Joel Rausch Client: Siemens PLM Software Client Contact: Michael Carter Adviser: Simanta Mitra 4/29/13
1 Adaptive Point Cloud Rendering Project Plan Final Group: May13-11 Christopher Jeffers Eric Jensen Joel Rausch Client: Siemens PLM Software Client Contact: Michael Carter Adviser: Simanta Mitra 4/29/13
CS 465 Program 5: Ray II
 CS 465 Program 5: Ray II out: Friday 2 November 2007 due: Saturday 1 December 2007 Sunday 2 December 2007 midnight 1 Introduction In the first ray tracing assignment you built a simple ray tracer that
CS 465 Program 5: Ray II out: Friday 2 November 2007 due: Saturday 1 December 2007 Sunday 2 December 2007 midnight 1 Introduction In the first ray tracing assignment you built a simple ray tracer that
Course Number: Course Title: Geometry
 Course Number: 1206310 Course Title: Geometry RELATED GLOSSARY TERM DEFINITIONS (89) Altitude The perpendicular distance from the top of a geometric figure to its opposite side. Angle Two rays or two line
Course Number: 1206310 Course Title: Geometry RELATED GLOSSARY TERM DEFINITIONS (89) Altitude The perpendicular distance from the top of a geometric figure to its opposite side. Angle Two rays or two line
TNM079 Modeling & Animation Lecture 6 (Implicit surfaces)
 TNM079 Modeling & Animation Lecture 6 (Implicit surfaces) Mark Eric Dieckmann, Media and Information Technology, ITN Linköpings universitet Campus Norrköping SE-60174 Norrköping May 4, 2016 Content of
TNM079 Modeling & Animation Lecture 6 (Implicit surfaces) Mark Eric Dieckmann, Media and Information Technology, ITN Linköpings universitet Campus Norrköping SE-60174 Norrköping May 4, 2016 Content of
2D rendering takes a photo of the 2D scene with a virtual camera that selects an axis aligned rectangle from the scene. The photograph is placed into
 2D rendering takes a photo of the 2D scene with a virtual camera that selects an axis aligned rectangle from the scene. The photograph is placed into the viewport of the current application window. A pixel
2D rendering takes a photo of the 2D scene with a virtual camera that selects an axis aligned rectangle from the scene. The photograph is placed into the viewport of the current application window. A pixel
Ray Tracing. CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 15. Ray Casting Shadow Rays Reflection and Transmission [Ch ]
![Ray Tracing. CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 15. Ray Casting Shadow Rays Reflection and Transmission [Ch ] Ray Tracing. CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 15. Ray Casting Shadow Rays Reflection and Transmission [Ch ]](/thumbs/78/78594982.jpg) CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 15 Ray Tracing Ray Casting Shadow Rays Reflection and Transmission [Ch. 13.2-13.3] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California 1 Local Illumination Object illuminations
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 15 Ray Tracing Ray Casting Shadow Rays Reflection and Transmission [Ch. 13.2-13.3] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California 1 Local Illumination Object illuminations
CS 184: Assignment 4 Simple Raytracer
 CS 184: Assignment 4 Simple Raytracer Ravi Ramamoorthi 1 Introduction This assignment asks you to write a first simple raytracer. Raytracers can produce some of the most impressive renderings, with high
CS 184: Assignment 4 Simple Raytracer Ravi Ramamoorthi 1 Introduction This assignment asks you to write a first simple raytracer. Raytracers can produce some of the most impressive renderings, with high
Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems
 Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester 2009-10 Lecture 17 Notes These notes correspond to Section 10.1 in the text. Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems Over the course of the next several lectures, we will
Jim Lambers MAT 169 Fall Semester 2009-10 Lecture 17 Notes These notes correspond to Section 10.1 in the text. Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems Over the course of the next several lectures, we will
CSC418 / CSCD18 / CSC2504
 5 5.1 Surface Representations As with 2D objects, we can represent 3D objects in parametric and implicit forms. (There are also explicit forms for 3D surfaces sometimes called height fields but we will
5 5.1 Surface Representations As with 2D objects, we can represent 3D objects in parametric and implicit forms. (There are also explicit forms for 3D surfaces sometimes called height fields but we will
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Intersecting Simple Surfaces. Dr. Scott Schaefer
 Intersecting Simple Surfaces Dr. Scott Schaefer 1 Types of Surfaces Infinite Planes Polygons Convex Ray Shooting Winding Number Spheres Cylinders 2/66 Infinite Planes Defined by a unit normal n and a point
Intersecting Simple Surfaces Dr. Scott Schaefer 1 Types of Surfaces Infinite Planes Polygons Convex Ray Shooting Winding Number Spheres Cylinders 2/66 Infinite Planes Defined by a unit normal n and a point
A triangle that has three acute angles Example:
 1. acute angle : An angle that measures less than a right angle (90 ). 2. acute triangle : A triangle that has three acute angles 3. angle : A figure formed by two rays that meet at a common endpoint 4.
1. acute angle : An angle that measures less than a right angle (90 ). 2. acute triangle : A triangle that has three acute angles 3. angle : A figure formed by two rays that meet at a common endpoint 4.
2D/3D Geometric Transformations and Scene Graphs
 2D/3D Geometric Transformations and Scene Graphs Week 4 Acknowledgement: The course slides are adapted from the slides prepared by Steve Marschner of Cornell University 1 A little quick math background
2D/3D Geometric Transformations and Scene Graphs Week 4 Acknowledgement: The course slides are adapted from the slides prepared by Steve Marschner of Cornell University 1 A little quick math background
The radius for a regular polygon is the same as the radius of the circumscribed circle.
 Perimeter and Area The perimeter and area of geometric shapes are basic properties that we need to know. The more complex a shape is, the more complex the process can be in finding its perimeter and area.
Perimeter and Area The perimeter and area of geometric shapes are basic properties that we need to know. The more complex a shape is, the more complex the process can be in finding its perimeter and area.
Vectors and the Geometry of Space
 Vectors and the Geometry of Space In Figure 11.43, consider the line L through the point P(x 1, y 1, z 1 ) and parallel to the vector. The vector v is a direction vector for the line L, and a, b, and c
Vectors and the Geometry of Space In Figure 11.43, consider the line L through the point P(x 1, y 1, z 1 ) and parallel to the vector. The vector v is a direction vector for the line L, and a, b, and c
Movie: For The Birds. Announcements. Ray Tracing 1. Programming 2 Recap. Programming 3 Info Test data for part 1 (Lines) is available
 Now Playing: Movie: For The Birds Pixar, 2000 Liar Built To Spill from You In Reverse Released April 11, 2006 Ray Tracing 1 Rick Skarbez, Instructor COMP 575 November 1, 2007 Announcements Programming
Now Playing: Movie: For The Birds Pixar, 2000 Liar Built To Spill from You In Reverse Released April 11, 2006 Ray Tracing 1 Rick Skarbez, Instructor COMP 575 November 1, 2007 Announcements Programming
Questions??? Announcements Assignment 3 due today
 Announcements Assignment 3 due today Questions??? Remember that you have late days (if you haven t used them yet ) Problem set 3 out at the end of the day Movie for Assignment 2 at the end of class 1 Ray
Announcements Assignment 3 due today Questions??? Remember that you have late days (if you haven t used them yet ) Problem set 3 out at the end of the day Movie for Assignment 2 at the end of class 1 Ray
Midterm Exam Fundamentals of Computer Graphics (COMP 557) Thurs. Feb. 19, 2015 Professor Michael Langer
 Midterm Exam Fundamentals of Computer Graphics (COMP 557) Thurs. Feb. 19, 2015 Professor Michael Langer The exam consists of 10 questions. There are 2 points per question for a total of 20 points. You
Midterm Exam Fundamentals of Computer Graphics (COMP 557) Thurs. Feb. 19, 2015 Professor Michael Langer The exam consists of 10 questions. There are 2 points per question for a total of 20 points. You
Problem Set 4 Part 1 CMSC 427 Distributed: Thursday, November 1, 2007 Due: Tuesday, November 20, 2007
 Problem Set 4 Part 1 CMSC 427 Distributed: Thursday, November 1, 2007 Due: Tuesday, November 20, 2007 Programming For this assignment you will write a simple ray tracer. It will be written in C++ without
Problem Set 4 Part 1 CMSC 427 Distributed: Thursday, November 1, 2007 Due: Tuesday, November 20, 2007 Programming For this assignment you will write a simple ray tracer. It will be written in C++ without
Conic Sections: Parabolas
 Conic Sections: Parabolas Why are the graphs of parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas called 'conic sections'? Because if you pass a plane through a double cone, the intersection of the plane and the cone
Conic Sections: Parabolas Why are the graphs of parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas called 'conic sections'? Because if you pass a plane through a double cone, the intersection of the plane and the cone
For this assignment, you are to expand your renderer from assignment 2 with perspective, a polygon clipper, ambient lighting, and obj file reading.
 SFU CMPT 361 Computer Graphics Fall 2017 Assignment 3 Assignment due Thursday November 9, by 11:59 pm. For this assignment, you are to expand your renderer from assignment 2 with perspective, a polygon
SFU CMPT 361 Computer Graphics Fall 2017 Assignment 3 Assignment due Thursday November 9, by 11:59 pm. For this assignment, you are to expand your renderer from assignment 2 with perspective, a polygon
Module 4A: Creating the 3D Model of Right and Oblique Pyramids
 Inventor (5) Module 4A: 4A- 1 Module 4A: Creating the 3D Model of Right and Oblique Pyramids In Module 4A, we will learn how to create 3D solid models of right-axis and oblique-axis pyramid (regular or
Inventor (5) Module 4A: 4A- 1 Module 4A: Creating the 3D Model of Right and Oblique Pyramids In Module 4A, we will learn how to create 3D solid models of right-axis and oblique-axis pyramid (regular or
Ray Tracing Part 1. CSC418/2504 Introduction to Computer Graphics. TA: Muhammed Anwar & Kevin Gibson
 Ray Tracing Part 1 CSC418/2504 Introduction to Computer Graphics TA: Muhammed Anwar & Kevin Gibson Email: manwar@cs.toronto.edu Overview Introduction / Motivation Rasterization vs Ray Tracing Basic Pseudocode
Ray Tracing Part 1 CSC418/2504 Introduction to Computer Graphics TA: Muhammed Anwar & Kevin Gibson Email: manwar@cs.toronto.edu Overview Introduction / Motivation Rasterization vs Ray Tracing Basic Pseudocode
CS354 Computer Graphics Ray Tracing. Qixing Huang Januray 24th 2017
 CS354 Computer Graphics Ray Tracing Qixing Huang Januray 24th 2017 Graphics Pipeline Elements of rendering Object Light Material Camera Geometric optics Modern theories of light treat it as both a wave
CS354 Computer Graphics Ray Tracing Qixing Huang Januray 24th 2017 Graphics Pipeline Elements of rendering Object Light Material Camera Geometric optics Modern theories of light treat it as both a wave
CMSC427 Transformations II: Viewing. Credit: some slides from Dr. Zwicker
 CMSC427 Transformations II: Viewing Credit: some slides from Dr. Zwicker What next? GIVEN THE TOOLS OF The standard rigid and affine transformations Their representation with matrices and homogeneous coordinates
CMSC427 Transformations II: Viewing Credit: some slides from Dr. Zwicker What next? GIVEN THE TOOLS OF The standard rigid and affine transformations Their representation with matrices and homogeneous coordinates
Number/Computation. addend Any number being added. digit Any one of the ten symbols: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9
 14 Number/Computation addend Any number being added algorithm A step-by-step method for computing array A picture that shows a number of items arranged in rows and columns to form a rectangle associative
14 Number/Computation addend Any number being added algorithm A step-by-step method for computing array A picture that shows a number of items arranged in rows and columns to form a rectangle associative
CS 4620 Midterm, March 21, 2017
 CS 460 Midterm, March 1, 017 This 90-minute exam has 4 questions worth a total of 100 points. Use the back of the pages if you need more space. Academic Integrity is expected of all students of Cornell
CS 460 Midterm, March 1, 017 This 90-minute exam has 4 questions worth a total of 100 points. Use the back of the pages if you need more space. Academic Integrity is expected of all students of Cornell
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #6: Lights. Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2014
 CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #6: Lights Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2014 Announcements Project 2 due Friday, Oct. 24 th Midterm Exam
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #6: Lights Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2014 Announcements Project 2 due Friday, Oct. 24 th Midterm Exam
CHAPTER 1 Graphics Systems and Models 3
 ?????? 1 CHAPTER 1 Graphics Systems and Models 3 1.1 Applications of Computer Graphics 4 1.1.1 Display of Information............. 4 1.1.2 Design.................... 5 1.1.3 Simulation and Animation...........
?????? 1 CHAPTER 1 Graphics Systems and Models 3 1.1 Applications of Computer Graphics 4 1.1.1 Display of Information............. 4 1.1.2 Design.................... 5 1.1.3 Simulation and Animation...........
Raytracing CS148 AS3. Due :59pm PDT
 Raytracing CS148 AS3 Due 2010-07-25 11:59pm PDT We start our exploration of Rendering - the process of converting a high-level object-based description of scene into an image. We will do this by building
Raytracing CS148 AS3 Due 2010-07-25 11:59pm PDT We start our exploration of Rendering - the process of converting a high-level object-based description of scene into an image. We will do this by building
ü 12.1 Vectors Students should read Sections of Rogawski's Calculus [1] for a detailed discussion of the material presented in this section.
![ü 12.1 Vectors Students should read Sections of Rogawski's Calculus [1] for a detailed discussion of the material presented in this section. ü 12.1 Vectors Students should read Sections of Rogawski's Calculus [1] for a detailed discussion of the material presented in this section.](/thumbs/75/71742148.jpg) Chapter 12 Vector Geometry Useful Tip: If you are reading the electronic version of this publication formatted as a Mathematica Notebook, then it is possible to view 3-D plots generated by Mathematica
Chapter 12 Vector Geometry Useful Tip: If you are reading the electronic version of this publication formatted as a Mathematica Notebook, then it is possible to view 3-D plots generated by Mathematica
Computer Science 426 Midterm 3/11/04, 1:30PM-2:50PM
 NAME: Login name: Computer Science 46 Midterm 3//4, :3PM-:5PM This test is 5 questions, of equal weight. Do all of your work on these pages (use the back for scratch space), giving the answer in the space
NAME: Login name: Computer Science 46 Midterm 3//4, :3PM-:5PM This test is 5 questions, of equal weight. Do all of your work on these pages (use the back for scratch space), giving the answer in the space
CS 563 Advanced Topics in Computer Graphics Lecture 2: Bare-Bones Raytracer. by Emmanuel Agu
 CS 563 Advanced Topics in Computer Graphics Lecture 2: Bare-Bones Raytracer by Emmanuel Agu Ray Casting (Appel, 1968) direct illumination Recursive ray tracing (Whitted, 1980) Pseudocode for Ray Tracer
CS 563 Advanced Topics in Computer Graphics Lecture 2: Bare-Bones Raytracer by Emmanuel Agu Ray Casting (Appel, 1968) direct illumination Recursive ray tracing (Whitted, 1980) Pseudocode for Ray Tracer
Lighting. To do. Course Outline. This Lecture. Continue to work on ray programming assignment Start thinking about final project
 To do Continue to work on ray programming assignment Start thinking about final project Lighting Course Outline 3D Graphics Pipeline Modeling (Creating 3D Geometry) Mesh; modeling; sampling; Interaction
To do Continue to work on ray programming assignment Start thinking about final project Lighting Course Outline 3D Graphics Pipeline Modeling (Creating 3D Geometry) Mesh; modeling; sampling; Interaction
Grade 9 Math Terminology
 Unit 1 Basic Skills Review BEDMAS a way of remembering order of operations: Brackets, Exponents, Division, Multiplication, Addition, Subtraction Collect like terms gather all like terms and simplify as
Unit 1 Basic Skills Review BEDMAS a way of remembering order of operations: Brackets, Exponents, Division, Multiplication, Addition, Subtraction Collect like terms gather all like terms and simplify as
Basic Elements. Geometry is the study of the relationships among objects in an n-dimensional space
 Basic Elements Geometry is the study of the relationships among objects in an n-dimensional space In computer graphics, we are interested in objects that exist in three dimensions We want a minimum set
Basic Elements Geometry is the study of the relationships among objects in an n-dimensional space In computer graphics, we are interested in objects that exist in three dimensions We want a minimum set
Revision Problems for Examination 2 in Algebra 1
 Centre for Mathematical Sciences Mathematics, Faculty of Science Revision Problems for Examination in Algebra. Let l be the line that passes through the point (5, 4, 4) and is at right angles to the plane
Centre for Mathematical Sciences Mathematics, Faculty of Science Revision Problems for Examination in Algebra. Let l be the line that passes through the point (5, 4, 4) and is at right angles to the plane
Programming projects. Assignment 1: Basic ray tracer. Assignment 1: Basic ray tracer. Assignment 1: Basic ray tracer. Assignment 1: Basic ray tracer
 Programming projects Rendering Algorithms Spring 2010 Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Description of assignments on class webpage Use programming language and environment of your choice We recommend
Programming projects Rendering Algorithms Spring 2010 Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Description of assignments on class webpage Use programming language and environment of your choice We recommend
CS 4204 Computer Graphics
 CS 4204 Computer Graphics Introduction to Ray Tracing Yong Cao Virginia Tech Reference: Ed Angle, Interactive Computer Graphics, University of New Mexico, class notes Raytracing (Picture from Povray.org)
CS 4204 Computer Graphics Introduction to Ray Tracing Yong Cao Virginia Tech Reference: Ed Angle, Interactive Computer Graphics, University of New Mexico, class notes Raytracing (Picture from Povray.org)
L15 POV-Ray - Part 1
 Geophysical Computing L15-1 L15 POV-Ray - Part 1 1. What is POV-Ray? POV-Ray stands for the Persistance of Vision Raytracer. POV-Ray belongs to a class of programs called ray tracers. For you seismologists
Geophysical Computing L15-1 L15 POV-Ray - Part 1 1. What is POV-Ray? POV-Ray stands for the Persistance of Vision Raytracer. POV-Ray belongs to a class of programs called ray tracers. For you seismologists
