Edges and Binary Images
|
|
|
- Noreen Walsh
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CS 699: Intro to Computer Vision Edges and Binary Images Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh September 5, 205
2 Plan for today Edge detection Binary image analysis
3 Homework Due on 9/22, :59pm Review slides from 9/03 regarding how to do Part IV There are different ways to compute image gradients Office hours for 9/7 will be at am-2pm on 9/8
4 Edge detection Goal: map image from 2d array of pixels to a set of curves or line segments or contours. Why? Figure from J. Shotton et al., PAMI 2007 Main idea: look for strong gradients, post-process
5 Origin of Edges surface normal discontinuity depth discontinuity surface color discontinuity illumination discontinuity Edges are caused by a variety of factors Source: S. Seitz
6 What causes an edge? Reflectance change: appearance information, texture Depth discontinuity: object boundary Cast shadows Change in surface orientation: shape
7 Edges/gradients and invariance
8 Closeup of edges Source: D. Hoiem
9 Closeup of edges Source: D. Hoiem
10 Characterizing edges An edge is a place of rapid change in the image intensity function image intensity function (along horizontal scanline) first derivative edges correspond to extrema of derivative Source: L. Lazebnik
11 Intensity profile Intensity Gradient Source: D. Hoiem
12 With a little Gaussian noise Gradient Source: D. Hoiem
13 Effects of noise Consider a single row or column of the image Plotting intensity as a function of position gives a signal Where is the edge? Source: S. Seitz
14 Effects of noise Difference filters respond strongly to noise Image noise results in pixels that look very different from their neighbors Generally, the larger the noise the stronger the response What can we do about it? Source: D. Forsyth
15 Solution: smooth first f g f * g d dx ( f g) d dx To find edges, look for peaks in ( f g) Source: S. Seitz
16 Derivative theorem of convolution Differentiation is convolution, and convolution is associative: d d ( f g) f g dx dx This saves us one operation: f d dx g f d dx g Source: S. Seitz
17 Derivative of Gaussian filter * [ 0 -] = Is this filter separable? Source: D. Hoiem
18 Tradeoff between smoothing and localization pixel 3 pixels 7 pixels Smoothed derivative removes noise, but blurs edge. Also finds edges at different scales. Source: D. Forsyth
19 Designing an edge detector Criteria for a good edge detector: Good detection: find all real edges, ignoring noise or other artifacts Good localization detect edges as close as possible to the true edges return one point only for each true edge point Cues of edge detection Differences in color, intensity, or texture across the boundary Continuity and closure High-level knowledge Source: L. Fei-Fei
20 Gradients -> edges Primary edge detection steps:. Smoothing: suppress noise 2. Edge enhancement: filter for contrast 3. Edge localization Determine which local maxima from filter output are actually edges vs. noise Threshold, Thin
21 Thresholding Choose a threshold value t Set any pixels less than t to zero (off) Set any pixels greater than or equal to t to one (on)
22 Original image
23 Gradient magnitude image
24 Thresholding gradient with a lower threshold
25 Thresholding gradient with a higher threshold
26 Canny edge detector This is probably the most widely used edge detector in computer vision Theoretical model: step-edges corrupted by additive Gaussian noise Canny has shown that the first derivative of the Gaussian closely approximates the operator that optimizes the product of signal-to-noise ratio and localization J. Canny, A Computational Approach To Edge Detection, IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 8:679-74, 986. Source: L. Fei-Fei
27 Canny edge detector Filter image with derivative of Gaussian Find magnitude and orientation of gradient Non-maximum suppression: Thin wide ridges down to single pixel width Linking and thresholding (hysteresis): Define two thresholds: low and high Use the high threshold to start edge curves and the low threshold to continue them MATLAB: edge(image, canny ); >>help edge Source: D. Lowe, L. Fei-Fei
28 Example input image ( Lena )
29 Derivative of Gaussian filter x-direction y-direction Source: L. Lazebnik
30 Compute Gradients (DoG) X-Derivative of Gaussian Y-Derivative of Gaussian Gradient Magnitude Source: D. Hoiem
31 Get Orientation at Each Pixel Threshold at minimum level Get orientation theta = atan2(-gy, gx) Source: D. Hoiem
32 The Canny edge detector norm of the gradient
33 The Canny edge detector thresholding
34 The Canny edge detector How to turn these thick regions of the gradient into curves? thresholding
35 Non-maximum suppression Check if pixel is local maximum along gradient direction, select single max across width of the edge requires checking interpolated pixels p and r
36 Bilinear Interpolation
37 The Canny edge detector Problem: pixels along this edge didn t survive the thresholding thinning (non-maximum suppression)
38 Hysteresis thresholding Use a high threshold to start edge curves, and a low threshold to continue them. Source: S. Seitz
39 Hysteresis thresholding original image high threshold (strong edges) low threshold (weak edges) hysteresis threshold Source: L. Fei-Fei
40 Hysteresis thresholding original image high threshold (strong edges) low threshold (weak edges) hysteresis threshold Source: L. Fei-Fei
41 Recap: Canny edge detector Filter image with derivative of Gaussian Find magnitude and orientation of gradient Non-maximum suppression: Thin wide ridges down to single pixel width Linking and thresholding (hysteresis): Define two thresholds: low and high Use the high threshold to start edge curves and the low threshold to continue them MATLAB: edge(image, canny ); >>help edge Source: D. Lowe, L. Fei-Fei
42 Effect of (Gaussian kernel spread/size) original Canny with Canny with The choice of depends on desired behavior large detects large scale edges small detects fine features Source: S. Seitz
43 Low-level edges vs. perceived contours Background Texture Shadows
44 Low-level edges vs. perceived contours image human segmentation gradient magnitude Berkeley segmentation database: Source: L. Lazebnik
45 pb Boundary Detector Martin, Fowlkes, Malik 2004: Learning to Detection Natural Boundaries S/vision/grouping/papers/mfm-pami-boundary.pdf Figure from Fowlkes
46 Learn from humans which combination of features is most indicative of a good contour? [D. Martin et al. PAMI 2004] Human-marked segment boundaries
47 pb Boundary Detector Figure from Fowlkes
48 Brightness Color Texture Combined Human
49 Results Pb (0.88) Human (0.95) Source: D. Hoiem
50 Results Pb Global Pb (0.88) Pb Human Human (0.96) Source: D. Hoiem
51 Pb (0.63) Human (0.95) Source: D. Hoiem
52 Pb (0.35) Human (0.90) For more: /CS/vision/bsds/bench/html/08082-color.html
53 Plan for today Edge detection Binary image analysis
54 Binary images
55 Binary image analysis: basic steps Convert the image into binary form Thresholding Clean up the thresholded image Morphological operators Extract separate blobs Connected components Describe the blobs with region properties
56 Two pixel values Binary images Foreground and background Mark region(s) of interest
57 Thresholding Grayscale -> binary mask Useful if object of interest s intensity distribution is distinct from background Example simplebinary.html
58 Thresholding Given a grayscale image or an intermediate matrix threshold to create a binary output. Example: edge detection Gradient magnitude fg_pix = find(gradient_mag > t); Looking for pixels where gradient is strong.
59 Thresholding Given a grayscale image or an intermediate matrix threshold to create a binary output. Example: background subtraction - = Looking for pixels that differ significantly from the empty background. fg_pix = find(diff > t);
60 Thresholding Given a grayscale image or an intermediate matrix threshold to create a binary output. Example: intensity-based detection Looking for dark pixels fg_pix = find(im < 65);
61 Thresholding Given a grayscale image or an intermediate matrix threshold to create a binary output. Example: color-based detection fg_pix = find(hue > t & hue < t2); Looking for pixels within a certain hue range.
62 A nice case: bimodal intensity histograms Ideal histogram, light object on dark background Actual observed histogram with noise Images:
63 Issues What to do with noisy binary outputs? Holes Extra small fragments How to demarcate multiple regions of interest? Count objects Compute further features per object
64 Morphological operators Change the shape of the foreground regions via intersection/union operations between a scanning structuring element and binary image. Useful to clean up result from thresholding Basic operators are: Dilation Erosion
65 Dilation Expands connected components Grow features Fill holes Before dilation After dilation
66 Erosion Erode connected components Shrink features Remove bridges, branches, noise Before erosion After erosion
67 Structuring elements Masks of varying shapes and sizes used to perform morphology, for example: Scan mask across foreground pixels to transform the binary image >> help strel
68 Dilation vs. Erosion At each position: Dilation: if current pixel is foreground, OR the structuring element with the input image.
69 Example for Dilation (D) Input image Structuring Element g( x) f ( x) SE Output Image Adapted from T. Moeslund
70 Example for Dilation Input image Structuring Element Output Image
71 Example for Dilation Input image Structuring Element Output Image 0
72 Example for Dilation Input image Structuring Element Output Image 0 0
73 Example for Dilation Input image Structuring Element Output Image 0
74 Example for Dilation Input image Structuring Element Output Image 0
75 Example for Dilation Input image Structuring Element Output Image 0
76 Example for Dilation Input image Structuring Element Output Image 0
77 Example for Dilation Input image Structuring Element Output Image 0 Note that the object gets bigger and holes are filled. >> help imdilate
78 2D example for dilation Source: Shapiro and Stockman
79 Dilation vs. Erosion At each position: Dilation: if current pixel is foreground, OR the structuring element with the input image. Erosion: if every pixel under the structuring element s nonzero entries is foreground, OR the current pixel with S.
80 Example for Erosion (D) Input image Structuring Element g( x) f _ ( x) OSE Output Image 0
81 Example for Erosion (D) Input image Structuring Element g( x) f _ ( x) OSE Output Image 0 0
82 Example for Erosion Input image Structuring Element Output Image 0 0 0
83 Example for Erosion Input image Structuring Element Output Image
84 Example for Erosion Input image Structuring Element Output Image
85 Example for Erosion Input image Structuring Element Output Image
86 Example for Erosion Input image Structuring Element Output Image
87 Example for Erosion Input image Structuring Element Output Image
88 Example for Erosion Input image Structuring Element Output Image
89 Example for Erosion Input image Structuring Element Output Image Note that the object gets smaller >> help imerode
90 2D example for erosion Source: Shapiro and Stockman
91 Erode, then dilate Opening Remove small objects, keep original shape Before opening After opening
92 Dilate, then erode Closing Fill holes, but keep original shape Before closing After closing Applet:
93 Summary Can use filters to process and describe local neighborhood Derivatives to locate gradients Convolution properties will influence efficiency Edge detection processes the image gradient to find curves Clean up thresholding outputs with binary image morphology operations Adapted from K. Grauman
94 Next time Computing image features: Detecting and describing keypoints
[ ] Review. Edges and Binary Images. Edge detection. Derivative of Gaussian filter. Image gradient. Tuesday, Sept 16
![[ ] Review. Edges and Binary Images. Edge detection. Derivative of Gaussian filter. Image gradient. Tuesday, Sept 16 [ ] Review. Edges and Binary Images. Edge detection. Derivative of Gaussian filter. Image gradient. Tuesday, Sept 16](/thumbs/89/98496315.jpg) Review Edges and Binary Images Tuesday, Sept 6 Thought question: how could we compute a temporal gradient from video data? What filter is likely to have produced this image output? original filtered output
Review Edges and Binary Images Tuesday, Sept 6 Thought question: how could we compute a temporal gradient from video data? What filter is likely to have produced this image output? original filtered output
Edges and Binary Image Analysis April 12 th, 2018
 4/2/208 Edges and Binary Image Analysis April 2 th, 208 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis Previously Filters allow local image neighborhood to influence our description and features Smoothing to reduce noise Derivatives
4/2/208 Edges and Binary Image Analysis April 2 th, 208 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis Previously Filters allow local image neighborhood to influence our description and features Smoothing to reduce noise Derivatives
Previously. Edge detection. Today. Thresholding. Gradients -> edges 2/1/2011. Edges and Binary Image Analysis
 2//20 Previously Edges and Binary Image Analysis Mon, Jan 3 Prof. Kristen Grauman UT-Austin Filters allow local image neighborhood to influence our description and features Smoothing to reduce noise Derivatives
2//20 Previously Edges and Binary Image Analysis Mon, Jan 3 Prof. Kristen Grauman UT-Austin Filters allow local image neighborhood to influence our description and features Smoothing to reduce noise Derivatives
Edge and Texture. CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University
 Edge and Texture CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University Filters for features Previously, thinking of filtering as a way to remove or reduce noise Now, consider how filters will allow us
Edge and Texture CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University Filters for features Previously, thinking of filtering as a way to remove or reduce noise Now, consider how filters will allow us
Edges and Binary Image Analysis. Thurs Jan 26 Kristen Grauman UT Austin. Today. Edge detection and matching
 /25/207 Edges and Binary Image Analysis Thurs Jan 26 Kristen Grauman UT Austin Today Edge detection and matching process the image gradient to find curves/contours comparing contours Binary image analysis
/25/207 Edges and Binary Image Analysis Thurs Jan 26 Kristen Grauman UT Austin Today Edge detection and matching process the image gradient to find curves/contours comparing contours Binary image analysis
Review of Filtering. Filtering in frequency domain
 Review of Filtering Filtering in frequency domain Can be faster than filtering in spatial domain (for large filters) Can help understand effect of filter Algorithm: 1. Convert image and filter to fft (fft2
Review of Filtering Filtering in frequency domain Can be faster than filtering in spatial domain (for large filters) Can help understand effect of filter Algorithm: 1. Convert image and filter to fft (fft2
Edge detection. Goal: Identify sudden. an image. Ideal: artist s line drawing. object-level knowledge)
 Edge detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, most semantic and shape information from the image can be encoded in the edges More compact than pixels Ideal: artist
Edge detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, most semantic and shape information from the image can be encoded in the edges More compact than pixels Ideal: artist
Edge Detection. Computer Vision Shiv Ram Dubey, IIIT Sri City
 Edge Detection Computer Vision Shiv Ram Dubey, IIIT Sri City Previous two classes: Image Filtering Spatial domain Smoothing, sharpening, measuring texture * = FFT FFT Inverse FFT = Frequency domain Denoising,
Edge Detection Computer Vision Shiv Ram Dubey, IIIT Sri City Previous two classes: Image Filtering Spatial domain Smoothing, sharpening, measuring texture * = FFT FFT Inverse FFT = Frequency domain Denoising,
Edge Detection. CSC320: Introduction to Visual Computing Michael Guerzhoy. René Magritte, Decalcomania. Many slides from Derek Hoiem, Robert Collins
 Edge Detection René Magritte, Decalcomania Many slides from Derek Hoiem, Robert Collins CSC320: Introduction to Visual Computing Michael Guerzhoy Discontinuities in Intensity Source: Robert Collins Origin
Edge Detection René Magritte, Decalcomania Many slides from Derek Hoiem, Robert Collins CSC320: Introduction to Visual Computing Michael Guerzhoy Discontinuities in Intensity Source: Robert Collins Origin
Edge Detection CSC 767
 Edge Detection CSC 767 Edge detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Most semantic and shape information from the image can be encoded in the edges More compact than pixels
Edge Detection CSC 767 Edge detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Most semantic and shape information from the image can be encoded in the edges More compact than pixels
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING
 The image part with relationship ID rid2 was not found in the file. DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING Lecture 6 Wavelets (cont), Lines and edges Tammy Riklin Raviv Electrical and Computer Engineering Ben-Gurion
The image part with relationship ID rid2 was not found in the file. DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING Lecture 6 Wavelets (cont), Lines and edges Tammy Riklin Raviv Electrical and Computer Engineering Ben-Gurion
Edge detection. Winter in Kraków photographed by Marcin Ryczek
 Edge detection Winter in Kraków photographed by Marcin Ryczek Edge detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, most semantic and shape information from the image
Edge detection Winter in Kraków photographed by Marcin Ryczek Edge detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, most semantic and shape information from the image
Edge detection. Winter in Kraków photographed by Marcin Ryczek
 Edge detection Winter in Kraków photographed by Marcin Ryczek Edge detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, edges carry most of the semantic and shape information
Edge detection Winter in Kraków photographed by Marcin Ryczek Edge detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, edges carry most of the semantic and shape information
Edge and corner detection
 Edge and corner detection Prof. Stricker Doz. G. Bleser Computer Vision: Object and People Tracking Goals Where is the information in an image? How is an object characterized? How can I find measurements
Edge and corner detection Prof. Stricker Doz. G. Bleser Computer Vision: Object and People Tracking Goals Where is the information in an image? How is an object characterized? How can I find measurements
Edge Detection. CSE 576 Ali Farhadi. Many slides from Steve Seitz and Larry Zitnick
 Edge Detection CSE 576 Ali Farhadi Many slides from Steve Seitz and Larry Zitnick Edge Attneave's Cat (1954) Origin of edges surface normal discontinuity depth discontinuity surface color discontinuity
Edge Detection CSE 576 Ali Farhadi Many slides from Steve Seitz and Larry Zitnick Edge Attneave's Cat (1954) Origin of edges surface normal discontinuity depth discontinuity surface color discontinuity
Solution: filter the image, then subsample F 1 F 2. subsample blur subsample. blur
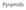 Pyramids Gaussian pre-filtering Solution: filter the image, then subsample blur F 0 subsample blur subsample * F 0 H F 1 F 1 * H F 2 { Gaussian pyramid blur F 0 subsample blur subsample * F 0 H F 1 F 1
Pyramids Gaussian pre-filtering Solution: filter the image, then subsample blur F 0 subsample blur subsample * F 0 H F 1 F 1 * H F 2 { Gaussian pyramid blur F 0 subsample blur subsample * F 0 H F 1 F 1
CS 4495 Computer Vision. Linear Filtering 2: Templates, Edges. Aaron Bobick. School of Interactive Computing. Templates/Edges
 CS 4495 Computer Vision Linear Filtering 2: Templates, Edges Aaron Bobick School of Interactive Computing Last time: Convolution Convolution: Flip the filter in both dimensions (right to left, bottom to
CS 4495 Computer Vision Linear Filtering 2: Templates, Edges Aaron Bobick School of Interactive Computing Last time: Convolution Convolution: Flip the filter in both dimensions (right to left, bottom to
CS 2770: Computer Vision. Edges and Segments. Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh February 21, 2017
 CS 2770: Computer Vision Edges and Segments Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh February 21, 2017 Edges vs Segments Figure adapted from J. Hays Edges vs Segments Edges More low-level Don t
CS 2770: Computer Vision Edges and Segments Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh February 21, 2017 Edges vs Segments Figure adapted from J. Hays Edges vs Segments Edges More low-level Don t
CS5670: Computer Vision
 CS5670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 2: Edge detection From Sandlot Science Announcements Project 1 (Hybrid Images) is now on the course webpage (see Projects link) Due Wednesday, Feb 15, by 11:59pm
CS5670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 2: Edge detection From Sandlot Science Announcements Project 1 (Hybrid Images) is now on the course webpage (see Projects link) Due Wednesday, Feb 15, by 11:59pm
Prof. Feng Liu. Winter /15/2019
 Prof. Feng Liu Winter 2019 http://www.cs.pdx.edu/~fliu/courses/cs410/ 01/15/2019 Last Time Filter 2 Today More on Filter Feature Detection 3 Filter Re-cap noisy image naïve denoising Gaussian blur better
Prof. Feng Liu Winter 2019 http://www.cs.pdx.edu/~fliu/courses/cs410/ 01/15/2019 Last Time Filter 2 Today More on Filter Feature Detection 3 Filter Re-cap noisy image naïve denoising Gaussian blur better
Does everyone have an override code?
 Does everyone have an override code? Project 1 due Friday 9pm Review of Filtering Filtering in frequency domain Can be faster than filtering in spatial domain (for large filters) Can help understand effect
Does everyone have an override code? Project 1 due Friday 9pm Review of Filtering Filtering in frequency domain Can be faster than filtering in spatial domain (for large filters) Can help understand effect
What is an edge? Paint. Depth discontinuity. Material change. Texture boundary
 EDGES AND TEXTURES The slides are from several sources through James Hays (Brown); Srinivasa Narasimhan (CMU); Silvio Savarese (U. of Michigan); Bill Freeman and Antonio Torralba (MIT), including their
EDGES AND TEXTURES The slides are from several sources through James Hays (Brown); Srinivasa Narasimhan (CMU); Silvio Savarese (U. of Michigan); Bill Freeman and Antonio Torralba (MIT), including their
Image gradients and edges
 Image gradients and edges Thurs Sept 3 Prof. Kristen Grauman UT-Austin Last time Various models for image noise Linear filters and convolution useful for Image smoothing, remov ing noise Box filter Gaussian
Image gradients and edges Thurs Sept 3 Prof. Kristen Grauman UT-Austin Last time Various models for image noise Linear filters and convolution useful for Image smoothing, remov ing noise Box filter Gaussian
Lecture 7: Most Common Edge Detectors
 #1 Lecture 7: Most Common Edge Detectors Saad Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Edge Detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, most semantic and shape information from the
#1 Lecture 7: Most Common Edge Detectors Saad Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Edge Detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, most semantic and shape information from the
Image Analysis. Edge Detection
 Image Analysis Edge Detection Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: Computer Vision course by Kristen Grauman, University of Texas at Austin (http://www.cs.utexas.edu/~grauman/courses/spring2011/index.html).
Image Analysis Edge Detection Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: Computer Vision course by Kristen Grauman, University of Texas at Austin (http://www.cs.utexas.edu/~grauman/courses/spring2011/index.html).
Edge Detection. EE/CSE 576 Linda Shapiro
 Edge Detection EE/CSE 576 Linda Shapiro Edge Attneave's Cat (1954) 2 Origin of edges surface normal discontinuity depth discontinuity surface color discontinuity illumination discontinuity Edges are caused
Edge Detection EE/CSE 576 Linda Shapiro Edge Attneave's Cat (1954) 2 Origin of edges surface normal discontinuity depth discontinuity surface color discontinuity illumination discontinuity Edges are caused
CS4670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely
 CS4670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 2: Edge detection From Sandlot Science Announcements Project 1 released, due Friday, September 7 1 Edge detection Convert a 2D image into a set of curves Extracts
CS4670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 2: Edge detection From Sandlot Science Announcements Project 1 released, due Friday, September 7 1 Edge detection Convert a 2D image into a set of curves Extracts
Image gradients and edges April 11 th, 2017
 4//27 Image gradients and edges April th, 27 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis PS due this Friday Announcements Questions? 2 Last time Image formation Linear filters and convolution useful for Image smoothing, removing
4//27 Image gradients and edges April th, 27 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis PS due this Friday Announcements Questions? 2 Last time Image formation Linear filters and convolution useful for Image smoothing, removing
Image gradients and edges April 10 th, 2018
 Image gradients and edges April th, 28 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis PS due this Friday Announcements Questions? 2 Last time Image formation Linear filters and convolution useful for Image smoothing, removing
Image gradients and edges April th, 28 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis PS due this Friday Announcements Questions? 2 Last time Image formation Linear filters and convolution useful for Image smoothing, removing
Image Analysis. Edge Detection
 Image Analysis Edge Detection Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: Computer Vision course by Kristen Grauman, University of Texas at Austin (http://www.cs.utexas.edu/~grauman/courses/spring2011/index.html).
Image Analysis Edge Detection Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: Computer Vision course by Kristen Grauman, University of Texas at Austin (http://www.cs.utexas.edu/~grauman/courses/spring2011/index.html).
Edge Detection. Today s reading. Cipolla & Gee on edge detection (available online) From Sandlot Science
 Edge Detection From Sandlot Science Today s reading Cipolla & Gee on edge detection (available online) Project 1a assigned last Friday due this Friday Last time: Cross-correlation Let be the image, be
Edge Detection From Sandlot Science Today s reading Cipolla & Gee on edge detection (available online) Project 1a assigned last Friday due this Friday Last time: Cross-correlation Let be the image, be
Image gradients and edges
 Image gradients and edges April 7 th, 2015 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis Announcements PS0 due this Friday Questions? 2 Last time Image formation Linear filters and convolution useful for Image smoothing, removing
Image gradients and edges April 7 th, 2015 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis Announcements PS0 due this Friday Questions? 2 Last time Image formation Linear filters and convolution useful for Image smoothing, removing
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393
 Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 21 Nov 16 th, 2017 Pranav Mantini Ack: Shah. M Image Processing Geometric Transformation Point Operations Filtering (spatial, Frequency) Input Restoration/
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 21 Nov 16 th, 2017 Pranav Mantini Ack: Shah. M Image Processing Geometric Transformation Point Operations Filtering (spatial, Frequency) Input Restoration/
Filtering in frequency domain
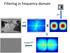 Filtering in frequency domain FFT FFT = Inverse FFT Filtering in frequency domain Can be faster than filtering in spatial domain (for large filters) Can help understand effect of filter Algorithm: 1. Convert
Filtering in frequency domain FFT FFT = Inverse FFT Filtering in frequency domain Can be faster than filtering in spatial domain (for large filters) Can help understand effect of filter Algorithm: 1. Convert
Low-level Vision Processing Algorithms Speaker: Ito, Dang Supporter: Ishii, Toyama and Y. Murakami
 Low-level Vision Processing Algorithms Speaker: Ito, Dang Supporter: Ishii, Toyama and Y. Murakami Adaptive Systems Lab The University of Aizu Overview Introduction What is Vision Processing? Basic Knowledge
Low-level Vision Processing Algorithms Speaker: Ito, Dang Supporter: Ishii, Toyama and Y. Murakami Adaptive Systems Lab The University of Aizu Overview Introduction What is Vision Processing? Basic Knowledge
2%34 #5 +,,% ! # %& ()% #% +,,%. & /%0%)( 1 ! # %& % %()# +(& ,.+/ +&0%//#/ &
 ! # %& ()% #% +,,%. & /%0%)( 1 2%34 #5 +,,%! # %& % %()# +(&,.+/ +&0%//#/ & & Many slides in this lecture are due to other authors; they are credited on the bottom right Topics of This Lecture Problem
! # %& ()% #% +,,%. & /%0%)( 1 2%34 #5 +,,%! # %& % %()# +(&,.+/ +&0%//#/ & & Many slides in this lecture are due to other authors; they are credited on the bottom right Topics of This Lecture Problem
Edge Detection. Announcements. Edge detection. Origin of Edges. Mailing list: you should have received messages
 Announcements Mailing list: csep576@cs.washington.edu you should have received messages Project 1 out today (due in two weeks) Carpools Edge Detection From Sandlot Science Today s reading Forsyth, chapters
Announcements Mailing list: csep576@cs.washington.edu you should have received messages Project 1 out today (due in two weeks) Carpools Edge Detection From Sandlot Science Today s reading Forsyth, chapters
convolution shift invariant linear system Fourier Transform Aliasing and sampling scale representation edge detection corner detection
 COS 429: COMPUTER VISON Linear Filters and Edge Detection convolution shift invariant linear system Fourier Transform Aliasing and sampling scale representation edge detection corner detection Reading:
COS 429: COMPUTER VISON Linear Filters and Edge Detection convolution shift invariant linear system Fourier Transform Aliasing and sampling scale representation edge detection corner detection Reading:
Lecture 4: Finding lines: from detection to model fitting
 Lecture 4: Finding lines: from detection to model fitting Professor Fei Fei Li Stanford Vision Lab 1 What we will learn today Edge detection Canny edge detector Line fitting Hough Transform RANSAC (Problem
Lecture 4: Finding lines: from detection to model fitting Professor Fei Fei Li Stanford Vision Lab 1 What we will learn today Edge detection Canny edge detector Line fitting Hough Transform RANSAC (Problem
CS334: Digital Imaging and Multimedia Edges and Contours. Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University
 CS334: Digital Imaging and Multimedia Edges and Contours Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines What makes an edge? Gradient-based edge detection Edge Operators From Edges
CS334: Digital Imaging and Multimedia Edges and Contours Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines What makes an edge? Gradient-based edge detection Edge Operators From Edges
Straight Lines and Hough
 09/30/11 Straight Lines and Hough Computer Vision CS 143, Brown James Hays Many slides from Derek Hoiem, Lana Lazebnik, Steve Seitz, David Forsyth, David Lowe, Fei-Fei Li Project 1 A few project highlights
09/30/11 Straight Lines and Hough Computer Vision CS 143, Brown James Hays Many slides from Derek Hoiem, Lana Lazebnik, Steve Seitz, David Forsyth, David Lowe, Fei-Fei Li Project 1 A few project highlights
Anno accademico 2006/2007. Davide Migliore
 Robotica Anno accademico 6/7 Davide Migliore migliore@elet.polimi.it Today What is a feature? Some useful information The world of features: Detectors Edges detection Corners/Points detection Descriptors?!?!?
Robotica Anno accademico 6/7 Davide Migliore migliore@elet.polimi.it Today What is a feature? Some useful information The world of features: Detectors Edges detection Corners/Points detection Descriptors?!?!?
Edge Detection (with a sidelight introduction to linear, associative operators). Images
 Images (we will, eventually, come back to imaging geometry. But, now that we know how images come from the world, we will examine operations on images). Edge Detection (with a sidelight introduction to
Images (we will, eventually, come back to imaging geometry. But, now that we know how images come from the world, we will examine operations on images). Edge Detection (with a sidelight introduction to
Lecture 6: Edge Detection
 #1 Lecture 6: Edge Detection Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Review From Last Lecture Options for Image Representation Introduced the concept of different representation or transformation Fourier Transform
#1 Lecture 6: Edge Detection Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Review From Last Lecture Options for Image Representation Introduced the concept of different representation or transformation Fourier Transform
CS534: Introduction to Computer Vision Edges and Contours. Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University
 CS534: Introduction to Computer Vision Edges and Contours Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines What makes an edge? Gradient-based edge detection Edge Operators Laplacian
CS534: Introduction to Computer Vision Edges and Contours Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines What makes an edge? Gradient-based edge detection Edge Operators Laplacian
Topic 4 Image Segmentation
 Topic 4 Image Segmentation What is Segmentation? Why? Segmentation important contributing factor to the success of an automated image analysis process What is Image Analysis: Processing images to derive
Topic 4 Image Segmentation What is Segmentation? Why? Segmentation important contributing factor to the success of an automated image analysis process What is Image Analysis: Processing images to derive
Announcements. Edge Detection. An Isotropic Gaussian. Filters are templates. Assignment 2 on tracking due this Friday Midterm: Tuesday, May 3.
 Announcements Edge Detection Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 9 Assignment 2 on tracking due this Friday Midterm: Tuesday, May 3. Reading from textbook An Isotropic Gaussian The picture
Announcements Edge Detection Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 9 Assignment 2 on tracking due this Friday Midterm: Tuesday, May 3. Reading from textbook An Isotropic Gaussian The picture
Edge Detection Lecture 03 Computer Vision
 Edge Detection Lecture 3 Computer Vision Suggested readings Chapter 5 Linda G. Shapiro and George Stockman, Computer Vision, Upper Saddle River, NJ, Prentice Hall,. Chapter David A. Forsyth and Jean Ponce,
Edge Detection Lecture 3 Computer Vision Suggested readings Chapter 5 Linda G. Shapiro and George Stockman, Computer Vision, Upper Saddle River, NJ, Prentice Hall,. Chapter David A. Forsyth and Jean Ponce,
Local Image preprocessing (cont d)
 Local Image preprocessing (cont d) 1 Outline - Edge detectors - Corner detectors - Reading: textbook 5.3.1-5.3.5 and 5.3.10 2 What are edges? Edges correspond to relevant features in the image. An edge
Local Image preprocessing (cont d) 1 Outline - Edge detectors - Corner detectors - Reading: textbook 5.3.1-5.3.5 and 5.3.10 2 What are edges? Edges correspond to relevant features in the image. An edge
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems
 EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 WRI C225 Lecture 04 130131 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Histogram Equalization Image Filtering Linear
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 WRI C225 Lecture 04 130131 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Histogram Equalization Image Filtering Linear
Texture Representation + Image Pyramids
 CS 1674: Intro to Computer Vision Texture Representation + Image Pyramids Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh September 14, 2016 Reminders/Announcements HW2P due tonight, 11:59pm HW3W, HW3P
CS 1674: Intro to Computer Vision Texture Representation + Image Pyramids Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh September 14, 2016 Reminders/Announcements HW2P due tonight, 11:59pm HW3W, HW3P
Computer Vision I. Announcement. Corners. Edges. Numerical Derivatives f(x) Edge and Corner Detection. CSE252A Lecture 11
 Announcement Edge and Corner Detection Slides are posted HW due Friday CSE5A Lecture 11 Edges Corners Edge is Where Change Occurs: 1-D Change is measured by derivative in 1D Numerical Derivatives f(x)
Announcement Edge and Corner Detection Slides are posted HW due Friday CSE5A Lecture 11 Edges Corners Edge is Where Change Occurs: 1-D Change is measured by derivative in 1D Numerical Derivatives f(x)
Comparison between Various Edge Detection Methods on Satellite Image
 Comparison between Various Edge Detection Methods on Satellite Image H.S. Bhadauria 1, Annapurna Singh 2, Anuj Kumar 3 Govind Ballabh Pant Engineering College ( Pauri garhwal),computer Science and Engineering
Comparison between Various Edge Detection Methods on Satellite Image H.S. Bhadauria 1, Annapurna Singh 2, Anuj Kumar 3 Govind Ballabh Pant Engineering College ( Pauri garhwal),computer Science and Engineering
Ulrik Söderström 16 Feb Image Processing. Segmentation
 Ulrik Söderström ulrik.soderstrom@tfe.umu.se 16 Feb 2011 Image Processing Segmentation What is Image Segmentation? To be able to extract information from an image it is common to subdivide it into background
Ulrik Söderström ulrik.soderstrom@tfe.umu.se 16 Feb 2011 Image Processing Segmentation What is Image Segmentation? To be able to extract information from an image it is common to subdivide it into background
Boundaries and Sketches
 Boundaries and Sketches Szeliski 4.2 Computer Vision James Hays Many slides from Michael Maire, Jitendra Malek Today s lecture Segmentation vs Boundary Detection Why boundaries / Grouping? Recap: Canny
Boundaries and Sketches Szeliski 4.2 Computer Vision James Hays Many slides from Michael Maire, Jitendra Malek Today s lecture Segmentation vs Boundary Detection Why boundaries / Grouping? Recap: Canny
Image Processing
 Image Processing 159.731 Canny Edge Detection Report Syed Irfanullah, Azeezullah 00297844 Danh Anh Huynh 02136047 1 Canny Edge Detection INTRODUCTION Edges Edges characterize boundaries and are therefore
Image Processing 159.731 Canny Edge Detection Report Syed Irfanullah, Azeezullah 00297844 Danh Anh Huynh 02136047 1 Canny Edge Detection INTRODUCTION Edges Edges characterize boundaries and are therefore
Computer Vision I. Announcements. Fourier Tansform. Efficient Implementation. Edge and Corner Detection. CSE252A Lecture 13.
 Announcements Edge and Corner Detection HW3 assigned CSE252A Lecture 13 Efficient Implementation Both, the Box filter and the Gaussian filter are separable: First convolve each row of input image I with
Announcements Edge and Corner Detection HW3 assigned CSE252A Lecture 13 Efficient Implementation Both, the Box filter and the Gaussian filter are separable: First convolve each row of input image I with
Image Processing. Bilkent University. CS554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu
 Image Processing CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University Today Image Formation Point and Blob Processing Binary Image Processing Readings: Gonzalez & Woods, Ch. 3 Slides are adapted from
Image Processing CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University Today Image Formation Point and Blob Processing Binary Image Processing Readings: Gonzalez & Woods, Ch. 3 Slides are adapted from
EE 584 MACHINE VISION
 EE 584 MACHINE VISION Binary Images Analysis Geometrical & Topological Properties Connectedness Binary Algorithms Morphology Binary Images Binary (two-valued; black/white) images gives better efficiency
EE 584 MACHINE VISION Binary Images Analysis Geometrical & Topological Properties Connectedness Binary Algorithms Morphology Binary Images Binary (two-valued; black/white) images gives better efficiency
Edge detection. Convert a 2D image into a set of curves. Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels
 Edge Detection Edge detection Convert a 2D image into a set of curves Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels Origin of Edges surface normal discontinuity depth discontinuity surface
Edge Detection Edge detection Convert a 2D image into a set of curves Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels Origin of Edges surface normal discontinuity depth discontinuity surface
Binary Image Processing. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 5
 Binary Image Processing CSE 152 Lecture 5 Announcements Homework 2 is due Apr 25, 11:59 PM Reading: Szeliski, Chapter 3 Image processing, Section 3.3 More neighborhood operators Binary System Summary 1.
Binary Image Processing CSE 152 Lecture 5 Announcements Homework 2 is due Apr 25, 11:59 PM Reading: Szeliski, Chapter 3 Image processing, Section 3.3 More neighborhood operators Binary System Summary 1.
Multimedia Computing: Algorithms, Systems, and Applications: Edge Detection
 Multimedia Computing: Algorithms, Systems, and Applications: Edge Detection By Dr. Yu Cao Department of Computer Science The University of Massachusetts Lowell Lowell, MA 01854, USA Part of the slides
Multimedia Computing: Algorithms, Systems, and Applications: Edge Detection By Dr. Yu Cao Department of Computer Science The University of Massachusetts Lowell Lowell, MA 01854, USA Part of the slides
Detection of Edges Using Mathematical Morphological Operators
 OPEN TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION PROCESSING Volume 1, Number 1, MAY 2014 OPEN TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION PROCESSING Detection of Edges Using Mathematical Morphological Operators Suman Rani*, Deepti Bansal,
OPEN TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION PROCESSING Volume 1, Number 1, MAY 2014 OPEN TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION PROCESSING Detection of Edges Using Mathematical Morphological Operators Suman Rani*, Deepti Bansal,
Digital Image Processing. Image Enhancement - Filtering
 Digital Image Processing Image Enhancement - Filtering Derivative Derivative is defined as a rate of change. Discrete Derivative Finite Distance Example Derivatives in 2-dimension Derivatives of Images
Digital Image Processing Image Enhancement - Filtering Derivative Derivative is defined as a rate of change. Discrete Derivative Finite Distance Example Derivatives in 2-dimension Derivatives of Images
Edge Detection. CS664 Computer Vision. 3. Edges. Several Causes of Edges. Detecting Edges. Finite Differences. The Gradient
 Edge Detection CS664 Computer Vision. Edges Convert a gray or color image into set of curves Represented as binary image Capture properties of shapes Dan Huttenlocher Several Causes of Edges Sudden changes
Edge Detection CS664 Computer Vision. Edges Convert a gray or color image into set of curves Represented as binary image Capture properties of shapes Dan Huttenlocher Several Causes of Edges Sudden changes
Practical Image and Video Processing Using MATLAB
 Practical Image and Video Processing Using MATLAB Chapter 14 Edge detection What will we learn? What is edge detection and why is it so important to computer vision? What are the main edge detection techniques
Practical Image and Video Processing Using MATLAB Chapter 14 Edge detection What will we learn? What is edge detection and why is it so important to computer vision? What are the main edge detection techniques
Edge detection. Stefano Ferrari. Università degli Studi di Milano Elaborazione delle immagini (Image processing I)
 Edge detection Stefano Ferrari Università degli Studi di Milano stefano.ferrari@unimi.it Elaborazione delle immagini (Image processing I) academic year 2011 2012 Image segmentation Several image processing
Edge detection Stefano Ferrari Università degli Studi di Milano stefano.ferrari@unimi.it Elaborazione delle immagini (Image processing I) academic year 2011 2012 Image segmentation Several image processing
Bias-Variance Trade-off (cont d) + Image Representations
 CS 275: Machine Learning Bias-Variance Trade-off (cont d) + Image Representations Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh January 2, 26 Announcement Homework now due Feb. Generalization Training
CS 275: Machine Learning Bias-Variance Trade-off (cont d) + Image Representations Prof. Adriana Kovashka University of Pittsburgh January 2, 26 Announcement Homework now due Feb. Generalization Training
Filtering Images. Contents
 Image Processing and Data Visualization with MATLAB Filtering Images Hansrudi Noser June 8-9, 010 UZH, Multimedia and Robotics Summer School Noise Smoothing Filters Sigmoid Filters Gradient Filters Contents
Image Processing and Data Visualization with MATLAB Filtering Images Hansrudi Noser June 8-9, 010 UZH, Multimedia and Robotics Summer School Noise Smoothing Filters Sigmoid Filters Gradient Filters Contents
What Are Edges? Lecture 5: Gradients and Edge Detection. Boundaries of objects. Boundaries of Lighting. Types of Edges (1D Profiles)
 What Are Edges? Simple answer: discontinuities in intensity. Lecture 5: Gradients and Edge Detection Reading: T&V Section 4.1 and 4. Boundaries of objects Boundaries of Material Properties D.Jacobs, U.Maryland
What Are Edges? Simple answer: discontinuities in intensity. Lecture 5: Gradients and Edge Detection Reading: T&V Section 4.1 and 4. Boundaries of objects Boundaries of Material Properties D.Jacobs, U.Maryland
Biomedical Image Analysis. Point, Edge and Line Detection
 Biomedical Image Analysis Point, Edge and Line Detection Contents: Point and line detection Advanced edge detection: Canny Local/regional edge processing Global processing: Hough transform BMIA 15 V. Roth
Biomedical Image Analysis Point, Edge and Line Detection Contents: Point and line detection Advanced edge detection: Canny Local/regional edge processing Global processing: Hough transform BMIA 15 V. Roth
EN1610 Image Understanding Lab # 3: Edges
 EN1610 Image Understanding Lab # 3: Edges The goal of this fourth lab is to ˆ Understanding what are edges, and different ways to detect them ˆ Understand different types of edge detectors - intensity,
EN1610 Image Understanding Lab # 3: Edges The goal of this fourth lab is to ˆ Understanding what are edges, and different ways to detect them ˆ Understand different types of edge detectors - intensity,
Image Analysis Lecture Segmentation. Idar Dyrdal
 Image Analysis Lecture 9.1 - Segmentation Idar Dyrdal Segmentation Image segmentation is the process of partitioning a digital image into multiple parts The goal is to divide the image into meaningful
Image Analysis Lecture 9.1 - Segmentation Idar Dyrdal Segmentation Image segmentation is the process of partitioning a digital image into multiple parts The goal is to divide the image into meaningful
Edges, interpolation, templates. Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD (with thanks to David Forsyth)
 Edges, interpolation, templates Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD (with thanks to David Forsyth) Gradients and edges edges are points of large gradient magnitude edge detection strategy 1. determine
Edges, interpolation, templates Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD (with thanks to David Forsyth) Gradients and edges edges are points of large gradient magnitude edge detection strategy 1. determine
Other Linear Filters CS 211A
 Other Linear Filters CS 211A Slides from Cornelia Fermüller and Marc Pollefeys Edge detection Convert a 2D image into a set of curves Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels Origin
Other Linear Filters CS 211A Slides from Cornelia Fermüller and Marc Pollefeys Edge detection Convert a 2D image into a set of curves Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels Origin
Robust Zero Watermarking for Still and Similar Images Using a Learning Based Contour Detection
 Robust Zero Watermarking for Still and Similar Images Using a Learning Based Contour Detection Shahryar Ehsaee and Mansour Jamzad (&) Department of Computer Engineering, Sharif University of Technology,
Robust Zero Watermarking for Still and Similar Images Using a Learning Based Contour Detection Shahryar Ehsaee and Mansour Jamzad (&) Department of Computer Engineering, Sharif University of Technology,
Perception. Autonomous Mobile Robots. Sensors Vision Uncertainties, Line extraction from laser scans. Autonomous Systems Lab. Zürich.
 Autonomous Mobile Robots Localization "Position" Global Map Cognition Environment Model Local Map Path Perception Real World Environment Motion Control Perception Sensors Vision Uncertainties, Line extraction
Autonomous Mobile Robots Localization "Position" Global Map Cognition Environment Model Local Map Path Perception Real World Environment Motion Control Perception Sensors Vision Uncertainties, Line extraction
Morphological Image Processing
 Morphological Image Processing Ranga Rodrigo October 9, 29 Outline Contents Preliminaries 2 Dilation and Erosion 3 2. Dilation.............................................. 3 2.2 Erosion..............................................
Morphological Image Processing Ranga Rodrigo October 9, 29 Outline Contents Preliminaries 2 Dilation and Erosion 3 2. Dilation.............................................. 3 2.2 Erosion..............................................
Keywords: Thresholding, Morphological operations, Image filtering, Adaptive histogram equalization, Ceramic tile.
 Volume 3, Issue 7, July 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Blobs and Cracks
Volume 3, Issue 7, July 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Blobs and Cracks
SIFT: SCALE INVARIANT FEATURE TRANSFORM SURF: SPEEDED UP ROBUST FEATURES BASHAR ALSADIK EOS DEPT. TOPMAP M13 3D GEOINFORMATION FROM IMAGES 2014
 SIFT: SCALE INVARIANT FEATURE TRANSFORM SURF: SPEEDED UP ROBUST FEATURES BASHAR ALSADIK EOS DEPT. TOPMAP M13 3D GEOINFORMATION FROM IMAGES 2014 SIFT SIFT: Scale Invariant Feature Transform; transform image
SIFT: SCALE INVARIANT FEATURE TRANSFORM SURF: SPEEDED UP ROBUST FEATURES BASHAR ALSADIK EOS DEPT. TOPMAP M13 3D GEOINFORMATION FROM IMAGES 2014 SIFT SIFT: Scale Invariant Feature Transform; transform image
Neighborhood operations
 Neighborhood operations Generate an output pixel on the basis of the pixel and its neighbors Often involve the convolution of an image with a filter kernel or mask g ( i, j) = f h = f ( i m, j n) h( m,
Neighborhood operations Generate an output pixel on the basis of the pixel and its neighbors Often involve the convolution of an image with a filter kernel or mask g ( i, j) = f h = f ( i m, j n) h( m,
Filtering and Edge Detection. Computer Vision I. CSE252A Lecture 10. Announcement
 Filtering and Edge Detection CSE252A Lecture 10 Announcement HW1graded, will be released later today HW2 assigned, due Wed. Nov. 7 1 Image formation: Color Channel k " $ $ # $ I r I g I b % " ' $ ' = (
Filtering and Edge Detection CSE252A Lecture 10 Announcement HW1graded, will be released later today HW2 assigned, due Wed. Nov. 7 1 Image formation: Color Channel k " $ $ # $ I r I g I b % " ' $ ' = (
Feature Matching and Robust Fitting
 Feature Matching and Robust Fitting Computer Vision CS 143, Brown Read Szeliski 4.1 James Hays Acknowledgment: Many slides from Derek Hoiem and Grauman&Leibe 2008 AAAI Tutorial Project 2 questions? This
Feature Matching and Robust Fitting Computer Vision CS 143, Brown Read Szeliski 4.1 James Hays Acknowledgment: Many slides from Derek Hoiem and Grauman&Leibe 2008 AAAI Tutorial Project 2 questions? This
An Algorithm for Blurred Thermal image edge enhancement for security by image processing technique
 An Algorithm for Blurred Thermal image edge enhancement for security by image processing technique Vinay Negi 1, Dr.K.P.Mishra 2 1 ECE (PhD Research scholar), Monad University, India, Hapur 2 ECE, KIET,
An Algorithm for Blurred Thermal image edge enhancement for security by image processing technique Vinay Negi 1, Dr.K.P.Mishra 2 1 ECE (PhD Research scholar), Monad University, India, Hapur 2 ECE, KIET,
Introduction to Medical Imaging (5XSA0)
 1 Introduction to Medical Imaging (5XSA0) Visual feature extraction Color and texture analysis Sveta Zinger ( s.zinger@tue.nl ) Introduction (1) Features What are features? Feature a piece of information
1 Introduction to Medical Imaging (5XSA0) Visual feature extraction Color and texture analysis Sveta Zinger ( s.zinger@tue.nl ) Introduction (1) Features What are features? Feature a piece of information
C E N T E R A T H O U S T O N S C H O O L of H E A L T H I N F O R M A T I O N S C I E N C E S. Image Operations II
 T H E U N I V E R S I T Y of T E X A S H E A L T H S C I E N C E C E N T E R A T H O U S T O N S C H O O L of H E A L T H I N F O R M A T I O N S C I E N C E S Image Operations II For students of HI 5323
T H E U N I V E R S I T Y of T E X A S H E A L T H S C I E N C E C E N T E R A T H O U S T O N S C H O O L of H E A L T H I N F O R M A T I O N S C I E N C E S Image Operations II For students of HI 5323
Filtering Applications & Edge Detection. GV12/3072 Image Processing.
 Filtering Applications & Edge Detection GV12/3072 1 Outline Sampling & Reconstruction Revisited Anti-Aliasing Edges Edge detection Simple edge detector Canny edge detector Performance analysis Hough Transform
Filtering Applications & Edge Detection GV12/3072 1 Outline Sampling & Reconstruction Revisited Anti-Aliasing Edges Edge detection Simple edge detector Canny edge detector Performance analysis Hough Transform
Biometrics Technology: Image Processing & Pattern Recognition (by Dr. Dickson Tong)
 Biometrics Technology: Image Processing & Pattern Recognition (by Dr. Dickson Tong) References: [1] http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/hipr2/index.htm [2] http://www.cs.wisc.edu/~dyer/cs540/notes/vision.html
Biometrics Technology: Image Processing & Pattern Recognition (by Dr. Dickson Tong) References: [1] http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/hipr2/index.htm [2] http://www.cs.wisc.edu/~dyer/cs540/notes/vision.html
Motion illusion, rotating snakes
 Motion illusion, rotating snakes Local features: main components 1) Detection: Find a set of distinctive key points. 2) Description: Extract feature descriptor around each interest point as vector. x 1
Motion illusion, rotating snakes Local features: main components 1) Detection: Find a set of distinctive key points. 2) Description: Extract feature descriptor around each interest point as vector. x 1
CS 4495 Computer Vision A. Bobick. CS 4495 Computer Vision. Features 2 SIFT descriptor. Aaron Bobick School of Interactive Computing
 CS 4495 Computer Vision Features 2 SIFT descriptor Aaron Bobick School of Interactive Computing Administrivia PS 3: Out due Oct 6 th. Features recap: Goal is to find corresponding locations in two images.
CS 4495 Computer Vision Features 2 SIFT descriptor Aaron Bobick School of Interactive Computing Administrivia PS 3: Out due Oct 6 th. Features recap: Goal is to find corresponding locations in two images.
Concepts in. Edge Detection
 Concepts in Edge Detection Dr. Sukhendu Das Deptt. of Computer Science and Engg., Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Chennai 600036, India. http://www.cs.iitm.ernet.in/~sdas Email: sdas@iitm.ac.in
Concepts in Edge Detection Dr. Sukhendu Das Deptt. of Computer Science and Engg., Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Chennai 600036, India. http://www.cs.iitm.ernet.in/~sdas Email: sdas@iitm.ac.in
Feature descriptors. Alain Pagani Prof. Didier Stricker. Computer Vision: Object and People Tracking
 Feature descriptors Alain Pagani Prof. Didier Stricker Computer Vision: Object and People Tracking 1 Overview Previous lectures: Feature extraction Today: Gradiant/edge Points (Kanade-Tomasi + Harris)
Feature descriptors Alain Pagani Prof. Didier Stricker Computer Vision: Object and People Tracking 1 Overview Previous lectures: Feature extraction Today: Gradiant/edge Points (Kanade-Tomasi + Harris)
Announcements. Edges. Last Lecture. Gradients: Numerical Derivatives f(x) Edge Detection, Lines. Intro Computer Vision. CSE 152 Lecture 10
 Announcements Assignment 2 due Tuesday, May 4. Edge Detection, Lines Midterm: Thursday, May 6. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 10 Edges Last Lecture 1. Object boundaries 2. Surface normal
Announcements Assignment 2 due Tuesday, May 4. Edge Detection, Lines Midterm: Thursday, May 6. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 10 Edges Last Lecture 1. Object boundaries 2. Surface normal
CS443: Digital Imaging and Multimedia Binary Image Analysis. Spring 2008 Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University
 CS443: Digital Imaging and Multimedia Binary Image Analysis Spring 2008 Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines A Simple Machine Vision System Image segmentation by thresholding
CS443: Digital Imaging and Multimedia Binary Image Analysis Spring 2008 Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines A Simple Machine Vision System Image segmentation by thresholding
Local Image Features
 Local Image Features Computer Vision CS 143, Brown Read Szeliski 4.1 James Hays Acknowledgment: Many slides from Derek Hoiem and Grauman&Leibe 2008 AAAI Tutorial This section: correspondence and alignment
Local Image Features Computer Vision CS 143, Brown Read Szeliski 4.1 James Hays Acknowledgment: Many slides from Derek Hoiem and Grauman&Leibe 2008 AAAI Tutorial This section: correspondence and alignment
From Pixels to Blobs
 From Pixels to Blobs 15-463: Rendering and Image Processing Alexei Efros Today Blobs Need for blobs Extracting blobs Image Segmentation Working with binary images Mathematical Morphology Blob properties
From Pixels to Blobs 15-463: Rendering and Image Processing Alexei Efros Today Blobs Need for blobs Extracting blobs Image Segmentation Working with binary images Mathematical Morphology Blob properties
COMPUTER AND ROBOT VISION
 VOLUME COMPUTER AND ROBOT VISION Robert M. Haralick University of Washington Linda G. Shapiro University of Washington A^ ADDISON-WESLEY PUBLISHING COMPANY Reading, Massachusetts Menlo Park, California
VOLUME COMPUTER AND ROBOT VISION Robert M. Haralick University of Washington Linda G. Shapiro University of Washington A^ ADDISON-WESLEY PUBLISHING COMPANY Reading, Massachusetts Menlo Park, California
ME/CS 132: Introduction to Vision-based Robot Navigation! Low-level Image Processing" Larry Matthies"
 ME/CS 132: Introduction to Vision-based Robot Navigation! Low-level Image Processing" Larry Matthies" lhm@jpl.nasa.gov, 818-354-3722" Announcements" First homework grading is done! Second homework is due
ME/CS 132: Introduction to Vision-based Robot Navigation! Low-level Image Processing" Larry Matthies" lhm@jpl.nasa.gov, 818-354-3722" Announcements" First homework grading is done! Second homework is due
CAP 5415 Computer Vision Fall 2012
 CAP 5415 Computer Vision Fall 01 Dr. Mubarak Shah Univ. of Central Florida Office 47-F HEC Lecture-5 SIFT: David Lowe, UBC SIFT - Key Point Extraction Stands for scale invariant feature transform Patented
CAP 5415 Computer Vision Fall 01 Dr. Mubarak Shah Univ. of Central Florida Office 47-F HEC Lecture-5 SIFT: David Lowe, UBC SIFT - Key Point Extraction Stands for scale invariant feature transform Patented
ECG782: Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing
 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu ECG782: Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing Spring 2014 TTh 14:30-15:45 CBC C313 Lecture 03 Image Processing Basics 13/01/28 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg782/
Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu ECG782: Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing Spring 2014 TTh 14:30-15:45 CBC C313 Lecture 03 Image Processing Basics 13/01/28 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg782/
