(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
|
|
|
- Imogene Reynolds
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1 Ullberg et al. US A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR CREATING TOMOSYNTHESIS AND PROJECTION IMAGES Inventors: Christer Ullberg, Sollentuna (SE): Tom Francke, Sollentuna (SE) Correspondence Address: HARNESS, DICKEY & PIERCE, P.L.C. P.O. BOX8910 RESTON, VA Assignee: May 22, 2006 XCounter AB Appl. No.: 11/447,901 Filed: Jun. 7, 2006 Foreign Application Priority Data (SE)... O6O Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl. H05G L/60 ( ) A6IB 6/00 ( ) GOIN 23/00 ( ) G2III/2 ( ) (52) U.S. Cl /21 (57) ABSTRACT An apparatus for creating tomosynthesis and projection images of an object from tomosynthesis image data obtained in a single measurement comprising an X-ray apparatus provided for obtaining the tomosynthesis image data of the object in a single measurement, a device provided for creating a three-dimensional tomosynthesis image of the object from the tomosynthesis image data, and a device provided for creating a two-dimensional projection image of the object from the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image by means of projecting the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image on a plane.
2 Patent Application Publication Sheet 1 of 3 US 2007/ A1
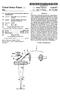
3 Patent Application Publication Sheet 2 of 3 US 2007/ A N 34 b bn "if ILA 1-1 \\ NON
4 Patent Application Publication Sheet 3 of 3 US 2007/ A1
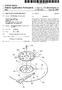
5 APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR CREATING TOMOSYNTHESIS AND PROJECTION IMAGES PRIORITY STATEMENT This application claims priority under 35 U.S.C. S 119 to Swedish Patent Application No , filed on May 22, 2006, in the Swedish Patent and Registration Office, the entire contents of which are incorporated herein by reference. FIELD OF THE INVENTION 0002 The invention relates generally to an apparatus and a method for creating tomosynthesis and projection images of an object. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION AND RELATED ART An X-ray medical diagnostic method such as mam mography or general body imaging is a low-dose procedure that creates one or more images of a part of a patient Such as a breast or any other organ thereof, which is to be examined, e.g. for detection of early stages of cancer The mammography diagnostic procedure generally includes obtaining two projection images of each of the patient s breasts, one from above and one from the side. A physician or radiologist then reviews the images of the breast, i.e., mammograms, to identify any breast cancer There is, however, a trend today towards different kinds of three-dimensional imaging of the object in order to provide more information of the object that is being exam ined. Tomosynthesis imaging, in which image data is acquired at different angles, is one of these three-dimen sional imaging techniques. By e.g. shifting and adding the images, it is possible to reconstruct planes in the object being imaged that is parallel to each other to thereby form a three-dimensional image of the object One example of a detector apparatus for creating such image data is described in U.S. Pat. No. 6,940,942. The detector apparatus comprises a radiation Source emitting radiation centered around an axis of symmetry; a radiation detector comprising a stack of line detectors, each being directed towards the divergent radiation source to allow a ray bundle of the radiation that propagates in a respective one of a plurality of different angles to enter the line detector; an object area arranged in the radiation path between the divergent radiation Source and the radiation detector for housing the object; and a device for moving the radiation source and the radiation detector relative the object essentially linearly in a direction essentially orthogonal to the axis of symmetry, while each of the stack of line detectors is adapted to record a plurality of line images of radiation as transmitted through the object in a respective one of the plurality of different angles However, sometimes the physician or radiologist needs to compare the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image with a more familiar two-dimensional projection image of the object. In other circumstances the physician or radiologist may want to study the more familiar two-dimen sional projection image only, e.g. to save time in the examination of the images. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION A main object of the invention is therefore to provide an apparatus and a method, respectively, for creating tomosynthesis and projection images of an object from tomosynthesis image data obtained in a single measurement In this respect there is a particular object to provide Such an apparatus and Such a method, which are uncompli cated and can produce high-quality three-dimensional tomo synthesis images and high-quality two-dimensional images Such as two-dimensional projection images with high spatial resolution, signal-to-noise ratio, dynamic range, and image contrast, while the imaging object is exposed to a minimum radiation dose A yet further object of the invention is to provide Such an apparatus and Such a method, which are reliable, accurate, and inexpensive These objects, among others, are attained by appa ratuses and methods as claimed in the appended claims An apparatus for creating tomosynthesis and pro jection images of an object from tomosynthesis image data obtained in a single measurement comprises an X-ray appa ratus provided for obtaining the tomosynthesis image data of the object in a single measurement, a device provided for creating a three-dimensional tomosynthesis image of the object from the tomosynthesis image data, and a device provided for creating a two-dimensional projection image of the object from the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image by means of projecting the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image on a plane The device provided for creating a two-dimen sional projection image is preferably arranged for projecting the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image on a plane by means of Summing, for each of the pixels of the two dimensional projection image, pixel values of pixels along a respective straight line in the three-dimensional tomosyn thesis image, wherein the straight lines converge in a single point Yet preferably, the X-ray apparatus comprises an X-ray source that emits radiation photons, and the single point is located at a distance from the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image, which is identical to the distance that the X-ray source is located from the object during the single measurement Further, the apparatus may comprise a device pro vided for displaying the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image and the two-dimensional projection image The present invention thus provides for the creation of three-dimensional tomosynthesis and two-dimensional projection images of an object from tomosynthesis image data obtained in a single measurement. The two-dimensional projection image is formed from the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image and is of high quality. A physician or radiologist may study a single one of the two images and if needed he/she may compare the studied image with the other one of the images without having to call back the patient (in medical applications) or to perform another measurement According to a further aspect of the invention three-dimensional tomosynthesis and two-dimensional attenuation images of the object are created, wherein the tomosynthesis image data of the object is collected in a
6 single measurement, a three-dimensional tomosynthesis image of the object is created from the tomosynthesis image data, wherein the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image comprises a plurality of stacked two-dimensional images, and a two-dimensional attenuation image of the object is created from the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image by means of selecting a single one, or adding multiple ones, but maybe not all, of the plurality of stacked two-dimensional images It shall be understood that during the collection of the tomosynthesis image data of the object image data may be collected that is sufficient to directly form a two-dimen sional attenuation image where each of the image pixels are formed from a single detector element measurement. How ever, in order to not expose the object to high radiation doses the measurement is performed at low radiation flux and/or with short detection times, which generally means that Such formed two-dimensional attenuation image would be too noisy to be used The present invention is applicable to all kind of X-ray medical applications including mammography and general body examinations. Further, the invention may find use in other technical fields such as material testing and baggage checking Further characteristics of the invention and advan tages thereof, will be evident from the detailed description of preferred embodiments of the present invention given hereinafter and the accompanying FIGS. 1-4, which are given by way of illustration only and thus, are not limitative of the present invention. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS 0021 FIG. 1 illustrates schematically, in a block diagram, an apparatus for creating tomosynthesis and projection images of an object according to an embodiment of the present invention FIG. 2 illustrates how the creation of a two-dimen sional projection image of an object is performed by the apparatus of FIG FIG. 3 illustrates schematically, in a top view, an example of an X-ray apparatus for use in the apparatus of FIG FIGS. 4a-c illustrate each schematically, in a top view, a particular X-ray bundle as it traverses the object during scanning by the X-ray apparatus of FIG. 3. DESCRIPTION OF PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS The apparatus of FIG. 1 comprises an X-ray appa ratus 11 for obtaining tomosynthesis image data of an object 13, a reconstruction device 15 for creating a three-dimen sional tomosynthesis image of the object 13 from the tomosynthesis image data, a projection image construction device 17 for creating a two-dimensional projection image of the object 13 from the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image, and a display device 19 for displaying the three dimensional tomosynthesis image and the two-dimensional projection image The X-ray apparatus comprises generally an X-ray source 21 and an X-ray detector 23 as being illustrated in FIG. 2 and is provided for obtaining the tomosynthesis image data in a single measurement, in which image data is acquired at different angles. Details of how the measurement may be performed will be given further below in this description The reconstruction device 15 for creating a three dimensional tomosynthesis image of the object 13 from the tomosynthesis image data may e.g. be any device known in the art. The reconstruction may be based on e.g. shift-and add, filtered back projection, Fourier, or iterative methods for calculating the attenuation in the object 13 in three dimensions. Typically, the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image is obtained in the shape as a stack of parallel two dimensional images 25 as being illustrated in FIG. 2. The tomosynthesis image could also be in the shape of a three dimensional model of the object segmented into three dimensional Sub Volumes, so called voxels'. The voxels are preferably, but necessarily placed in parallel layers parallel to the lines The projection image construction device 17 is arranged for creating the two-dimensional projection image of the object 13 by means of projecting the three-dimen sional tomosynthesis image on a first plane. Hereby, a high-quality two-dimensional projection image with high spatial resolution, signal-to-noise ratio, dynamic range, and image contrast is obtained Preferably, the two-dimensional projection image is formed by means of Summing, for each of the pixels of the two-dimensional projection image 27, pixel values of pixels along a respective straight line 29 in the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image 25 as shown in FIG. 2. The converge in a single point, which is located at a distance from the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image 25, which is iden tical to the distance that the X-ray source 21 is located from the object 13 during the single measurement. This is sche matically indicated in FIG The geometry that is reconstructed is cone-shaped with an almost point-shaped X-ray source 21 at the top, from which a cone-shaped X-ray bundle of radiation is originat ing. The X-ray bundle traverses the object 13 and strikes the X-ray detector 23. The straight lines 29 thus coincide with the propagation path of radiation photons of the cone-shaped X-ray bundle If the tomosynthesis image is in the form of a reconstructed three dimensional model of the object, the Summation could alternatively be done in any direction through the three dimensional model. For instance, the Summation could be done in along parallel lines direction through the three dimensional model, e.g. perpendicular to the planes Further, the invention does not exclude that the two dimensional projection image is calculated in the same way as a three dimensional model of the object is calculated, but where the three dimensional model only consists of a single layer of voxels. The attenuation of X-rays in each voxel is then a representation of the two dimensional projection image Thus, according to a further embodiment of the invention three-dimensional tomosynthesis and two-dimen sional attenuation images of the object 13 are created, wherein the tomosynthesis image data of the object is collected in a single measurement, a three-dimensional tomosynthesis image 25 of the object is created from the tomosynthesis image data, wherein the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image 25 comprises a plurality of stacked two-dimensional images (in some sense all three-dimen
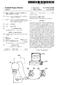
7 sional images can be seen as a stack of two-dimensional images), and a two-dimensional attenuation image of the object is created from the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image by means of selecting a single one of the plurality of stacked two-dimensional images Alternatively, multiple ones, but maybe not all, of the plurality of stacked two-dimensional images are added to create the two-dimensional attenuation image of the object The reconstruction device 15 and the projection image construction device 17 may be integrated as Software program modules in a common apparatus such as a micro computer. The microcomputer and/or the display device 19 may further be integrated into the X-ray apparatus 11 or may be separate devices The microcomputer is advantageously provided for displaying the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image and the two-dimensional projection image simultaneously side by side on the display device 19 so that the physician or radiologist will be able to compare the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image with the more familiar two-dimen sional projection image More advantageously though, the microcomputer comprises input means, e.g. a keyboard, a pointing device, or voice command receiving means for receiving user selec tions, and the display device 19 is provided for displaying the two-dimensional projection image in response to a first user selection through the input means and for displaying the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image in response to a second Subsequent user selection through the input means. Hereby, the physician or radiologist is able to study the more familiar two-dimensional projection image firstly, and then if something Suspicious is found, the physician or radiologist may select to display the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image without having to perform a second measurement. The microcomputer may have means for displaying the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image in various manners and layouts and means for displaying several three-dimen sional tomosynthesis images from different angles one after the other or several at the same time Further, the projection image construction device 17 may be arranged for creating a second two-dimensional projection image of the object 13 from the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image 25 by means of projecting the three dimensional tomosynthesis image on a second plane, wherein the first and second planes are non-parallel. Hereby, a second two-dimensional projection image of the object 13 at another view angle is obtained. Such second two-dimen sional projection image may be of importance to the phy sician or radiologist, not at least in mammography applica tions If the X-ray apparatus 11 is provided for obtaining the tomosynthesis image data at angles defining an angular range of at least 90, the first and second planes may be Substantially perpendicular to each another. In case of mam mography two two-dimensional projection images may be taken of each of the patient s breast one two-dimensional projection image from above and one two-dimensional projection image from the side It shall be appreciated that in case the three dimensional tomosynthesis image is formed by a three dimensional set of pixels or picture elements, each in the shape of e.g. a cube or cuboid, and each representing the X-ray attenuation in a corresponding Voxel of the object 13, each of the Summations of pixel values of pixels along a respective straight line in the three-dimensional tomosyn thesis image may be weighted depending on how the straight line passes or cuts through the pixels. For example, if the straight line passes or cuts through a pixel in the middle thereof the pixel value of that pixel should be given high weight in the Summation, whereas if the Straight line passes or cuts through a corner portion of a pixel the pixel value of that pixel should be given low weight in the Summation Generally, if the pixels in the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image are cubic or cuboidic, the weight of the pixel value of each cubic or cuboidic pixel along each straight line may depend on the length of the straight line that is within the cubic or cuboidic pixel With reference now to FIGS. 3 and 4 an example of an X-ray apparatus for use in the apparatus of FIG. 1 will briefly be described The X-ray apparatus comprises a divergent X-ray source 31, which produces X-rays 32 centered around an axis of symmetry 33, a collimator 34, a radiation detector 36, and a device 37, which rigidly connects the X-ray source 31, the collimator 34, and the radiation detector 36 to each other and which moves the X-ray source 31, the collimator 34, and the radiation detector 36 linearly in direction 38 essentially orthogonal to the axis of symmetry 33 to Scan scan an object 35, which is to be examined. 0044) The radiation detector 36 comprises a stack of line detectors 36a, each being directed towards the divergent radiation source 31 to allow a respective ray bundle b,..., b,.... by of the radiation 32 that propagates in a respective one of a plurality of different angles C...., C,.. Cy with respect to the front Surface of the radiation detector 36 to enter the respective line detector 36a The collimator 34 may be a thin foil of e.g. tungsten with narrow radiation transparent slits etched away, the number of which corresponds to the number of line detectors 36a of the radiation detector 36. The slits are aligned with the line detectors 36a so that X-rays passing through the slits of the collimator 34 will reach the detector units 36a, i.e. as the respective ray bundles b,..., b,.... by. The collimator 34, which is optional, prevents radiation, which is not directed directly towards the line detectors 36a, from impinging on the object 35, thereby reducing the radiation dose to the object 35. This is advan tageous in all applications where the object 35 is a human or an animal, or parts thereof During scanning the device 37 moves the radiation source 31, the collimator 34, and the radiation detector 36 relative to the object 35 in a linear manner parallel with the front of the radiation detector as being indicated by arrow 38, while each of the line detectors 36a records a plurality of line images of radiation as transmitted through the object 35 in a respective one of the different angles C...., C,.... C.N The scanning may alternatively be performed by rotating the radiation source 31, the collimator 34, and the radiation detector 36 relative to the object 35. It shall also be appreciated that a similar scanning is obtained by holding the radiation source 31, the collimator 34, and the radiation detector 36 still and instead moving the object 35 to be examined The scanning of the object 35 is performed a length, which is Sufficiently large so that each one of the line detectors 36a can be scanned across the entire object of
8 interest to obtain, for each of the line detectors 6a, a two-dimensional image of radiation as transmitted through the object 35 in a respective one of the different angles C.,.... C..... C.N In FIGS. 4a-c three different X-ray bundles b, b. and by are schematically illustrated as they traverse the examination object 35 during scanning by the X-ray appa ratus of FIG. 3. Reference numeral 39 indicates a plane parallel with the scanning direction 38 and with the front of the radiation detector As can be seen in FIGS. 4a-c each line detector/ X-ray bundle pair produces a complete two-dimensional image at a distinct one of the different angles. FIG. 4a illustrates the formation of a two-dimensional image of radiation transmitted through the object at an angle C, FIG. 4b illustrates the formation of a two-dimensional image of radiation transmitted through the same object, but at an angle C, and FIG. 4c illustrates the formation of a similar two-dimensional image, but at an angle C A preferred line detector for use in the X-ray apparatus of FIGS. 3 and 4 is a gaseous-based parallel plate detector, preferably provided with an electron avalanche amplifier. Such a gaseous-based parallel plate detector is an ionization detector, wherein electrons freed as a result of ionization by ionizing radiation are accelerated in a direction essentially perpendicular to the direction of the radiation For further details regarding such kind of gaseous based line detectors for use in the present invention, refer ence is made to the following U.S. Patents by Tom Francke et al. and assigned to XCounter AB of Sweden, which patents are hereby incorporated by reference: U.S. Pat. Nos. 6,546,070; 6,522,722: 6,518,578; 6,118,125; 6,373,065; 6,337,482; 6,385,282; 6,414,317; 6,476,397; and 6,477, It shall, nevertheless, be realized that any other line detector may be used in the X-ray apparatus of FIGS. 3 and 4. Such line detectors include scintillator-based arrays, CCD arrays, TFT- and CMOS-based detectors, liquid detectors, and solid-state detectors such as one-dimensional PIN-diode arrays with edge-on, near edge-on or perpendicular inci dence of X-rays Still further, other X-ray apparatuses such as e.g. one including a two-dimensional flat panel detector for detection may be used in the apparatus of FIG. 1 and thus in the present invention. Such X-ray apparatus is rotated or tilted so that a number of two-dimensional projection images (e.g ) of the object are taken at different angles. What is claimed is: 1. An apparatus for creating tomosynthesis and projection images of an object from tomosynthesis image data obtained in a single measurement comprising: an X-ray apparatus provided for obtaining the tomosyn thesis image data of the object in a single measurement; a device provided for creating a three-dimensional tomo synthesis image of the object from the tomosynthesis image data; and a device provided for creating a two-dimensional projec tion image of the object from the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image by means of projecting the three dimensional tomosynthesis image on a first plane. 2. The apparatus of claim 1 wherein the device provided for creating a two-dimensional projection image is arranged for projecting the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image on a first plane by means of Summing, for each of the pixels of the two-dimensional projection image, pixel values of pixels along a respective straight line in the three-dimen sional tomosynthesis image, wherein the straight lines con verge in a single point. 3. The apparatus of claim 2 wherein the X-ray apparatus comprises an X-ray Source that emits radiation photons; and the single point is located at a distance from the three dimensional tomosynthesis image, which is identical to the distance that the X-ray source is located from the object during the single measurement. 4. The apparatus of claim 1 wherein the apparatus com prises a device provided for displaying the three-dimen sional tomosynthesis image and the two-dimensional pro jection image. 5. The apparatus of claim 4 wherein the device provided for displaying the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image and the two-dimensional projection image is arranged for displaying the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image and the two-dimensional projection image simultaneously side by side. 6. The apparatus of claim 4 wherein said apparatus comprises input means; and the device provided for displaying the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image and the two-dimensional projec tion image is arranged for displaying the two-dimen sional projection image in response to a first user Selection via the input means and for displaying the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image in response to a second, preferably Subsequent, user selection via the input means. 7. The apparatus of claim 1 wherein the device provided for creating a two-dimensional projection image of the object is arranged for creating a second two-dimensional projection image of the object from the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image by means of projecting the three dimensional tomosynthesis image on a second plane, wherein the first and second planes are non-parallel. 8. The apparatus of claim 7 wherein the X-ray apparatus is provided for obtaining the tomo synthesis image data at angles defining an angular range of at least 90, and the first and second planes are substantially perpendicular to each another. 9. The apparatus of claim 1 wherein the X-ray apparatus comprises: a divergent radiation Source emitting radiation centered around an axis of symmetry; a radiation detector comprising a stack of line detectors, each being directed towards the divergent radiation source to allow a ray bundle of the radiation that propagates in a respective one of a plurality of different angles to enter the line detector; an object area arranged in the radiation path between the divergent radiation source and the radiation detector for housing the object; and a device for moving the divergent radiation source and the radiation detector relative the object essentially linearly in a direction essentially orthogonal to the axis of symmetry, while each of the line detectors is adapted to record a plurality of line images of radiation as trans mitted through the object in a respective one of the plurality of different angles, wherein the device for moving is adapted to move the divergent radiation source and the radiation detector relative the
9 object a length which is sufficient for scanning each of the line detectors across the entire object to obtain, for each of the line detectors, a two-dimensional image of radiation as transmitted through the object in a respec tive one of the plurality of different angles. 10. The apparatus of claim 9 wherein the divergent radiation source is an X-ray source; and the line detectors are each a gaseous-based ionization detector, wherein electrons freed as a result of ioniza tion by a respective ray bundle are accelerated in a direction essentially perpendicular to the direction of that ray bundle. 11. A method for creating tomosynthesis and projection images of an object from tomosynthesis image data obtained in a single measurement comprising the steps of collecting the tomosynthesis image data of the object in a single measurement; creating a three-dimensional tomosynthesis image of the object from the tomosynthesis image data; and creating a two-dimensional projection image of the object from the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image by means of projecting the three-dimensional tomosynthe sis image on a plane. 12. The method of claim 11 wherein the three-dimen sional tomosynthesis image is projected onto a plane by means of Summing, for each of the pixels of the two dimensional projection image, pixel values of pixels along a respective straight line in the three-dimensional tomosyn thesis image, wherein the straight lines converge in a single point. 13. An apparatus for creating three-dimensional tomosyn thesis and two-dimensional attenuation images of an object from tomosynthesis image data obtained in a single mea Surement comprising: an X-ray apparatus provided for obtaining the tomosyn thesis image data of the object in a single measurement; a device provided for creating a three-dimensional tomo synthesis image of the object from the tomosynthesis image data, wherein said three-dimensional tomosyn thesis image comprises a plurality of Stacked two dimensional images; and a device provided for creating a two-dimensional attenu ation image of the object from the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image by means of selecting a single one, or adding multiple ones, of said plurality of stacked two-dimensional images. 14. A method for creating three-dimensional tomosynthe sis and two-dimensional attenuation images of an object from tomosynthesis image data obtained in a single mea Surement comprising the steps: collecting the tomosynthesis image data of the object in a single measurement; creating a three-dimensional tomosynthesis image of the object from the tomosynthesis image data, wherein said three-dimensional tomosynthesis image comprises a plurality of Stacked two-dimensional images; and creating a two-dimensional attenuation image of the object from the three-dimensional tomosynthesis image by means of selecting a single one, or adding multiple ones, of said plurality of Stacked two-dimensional images.
IIIHIIIHIII IIHIII. United States Patent (19) Biber. 5,126,877 Jun. 30, lens, and two reflecting mirrors (4,6) which are located
 United States Patent (19) Biber 54). ILLUMINATIONSYSTEM FOR ASURGICAL MCROSCOPE 75 Inventor: Klaus Biber, Aalen, Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee: Carl-Zeiss-Stiftung, Heidenheim, Fed. Rep. of Germany
United States Patent (19) Biber 54). ILLUMINATIONSYSTEM FOR ASURGICAL MCROSCOPE 75 Inventor: Klaus Biber, Aalen, Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee: Carl-Zeiss-Stiftung, Heidenheim, Fed. Rep. of Germany
(FSN JSO (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 2005O146349A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0146349 A1 Lai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 7, 2005 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS FOR FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O146349A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0146349 A1 Lai et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 7, 2005 (54) TESTINGAPPARATUS FOR FLAT-PANEL DISPLAY (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,399,323 B1
 US0093.99323B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 26, 2016 (54) THREE-DIMENSIONAL PRINTING USPC... 425/470; 264/401, 497, 212, 308 STRUCTURE See application
US0093.99323B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 26, 2016 (54) THREE-DIMENSIONAL PRINTING USPC... 425/470; 264/401, 497, 212, 308 STRUCTURE See application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.0128245A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0128245 A1 Inagaki et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 27, 2010 (54) DISTANCE MEASUREMENT DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2010.0128245A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0128245 A1 Inagaki et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 27, 2010 (54) DISTANCE MEASUREMENT DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
(19) United States US 2004O231004A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0231004 A1 Seo (43) Pub. Date: (54) HTTP BASED VIDEO STREAMING APPARATUS AND METHOD IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION
= N (see. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1. (19) United States. BOSSelmann et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug.
 (19) United States US 2010O2O8247A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0208247 A1 BOSSelmann et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 19, 2010 (54) QUALITY ASSURANCE TESTING FOR ROTOR BLADES
(19) United States US 2010O2O8247A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0208247 A1 BOSSelmann et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 19, 2010 (54) QUALITY ASSURANCE TESTING FOR ROTOR BLADES
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160364902A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0364902 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH QUALITY EMBEDDED GRAPHICS (52) U.S. Cl. FOR REMOTE VISUALIZATION
US 20160364902A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0364902 A1 Hong et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH QUALITY EMBEDDED GRAPHICS (52) U.S. Cl. FOR REMOTE VISUALIZATION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,777 B2
 US008253777B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,777 B2 Lin (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2012 (54) PANORAMIC CAMERA WITH A PLURALITY 7,424,218 B2 * 9/2008 Baudisch et al.... 396,322 OF
US008253777B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,253,777 B2 Lin (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2012 (54) PANORAMIC CAMERA WITH A PLURALITY 7,424,218 B2 * 9/2008 Baudisch et al.... 396,322 OF
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2004
 (19) United States US 20040189577A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2004 (54) PIXEL CIRCUIT FOR LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 20040189577A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2004 (54) PIXEL CIRCUIT FOR LIQUID CRYSTAL (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
United States Patent (19) O Brien
 United States Patent (19) O Brien 54) HOLOGRAPHIC DIRECT MANIPULATION INTERFACE 76 Inventor: Wayne P. O'Brien, 507 N. Roosevelt Blvd., C 315, Falls Church, Va. 22044 21 Appl. No.: 09/001,101 22 Filed:
United States Patent (19) O Brien 54) HOLOGRAPHIC DIRECT MANIPULATION INTERFACE 76 Inventor: Wayne P. O'Brien, 507 N. Roosevelt Blvd., C 315, Falls Church, Va. 22044 21 Appl. No.: 09/001,101 22 Filed:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 US 20170069991A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0069991 A1 HOmb0 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2017 (54) ELECTRONIC APPARATUS H05K L/4 (2006.01) (71) Applicant:
US 20170069991A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0069991 A1 HOmb0 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 9, 2017 (54) ELECTRONIC APPARATUS H05K L/4 (2006.01) (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0255765A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0255765 A1 Carlson et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 20, 2011 (54) REDUCTION AND REMOVAL OF ARTIFACTS FROMA THREE-DIMIENSIONAL
(19) United States US 2011 0255765A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0255765 A1 Carlson et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 20, 2011 (54) REDUCTION AND REMOVAL OF ARTIFACTS FROMA THREE-DIMIENSIONAL
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2. Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003
 USOO6657548B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2 Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) SYSTEMSTATUS LIGHT INDICATOR 6,501,897 B1 * 12/2002 German et al.... 385/134 DEVICE EMBEDDED
USOO6657548B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,657,548 B2 Dai (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) SYSTEMSTATUS LIGHT INDICATOR 6,501,897 B1 * 12/2002 German et al.... 385/134 DEVICE EMBEDDED
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,640,289 B2
 USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
USOO7640289B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Chen (45) Date of Patent: *Dec. 29, 2009 (54) INTELLIGENT COMPUTER SWITCH 6,388,658 B1 5/2002 Ahern et al. 6,567,869 B2 5/2003 Shirley (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
(19) United States US 20070135182A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0135182 A1 Hanif et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) CELL PHONE DEVICE (75) Inventors: Sadeque Mohammad Hanif, Tokyo
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0234591 A1 Sanger et al. US 2016O234591 A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 11, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (30) MCROPHONE MODULE WITH
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0234591 A1 Sanger et al. US 2016O234591 A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 11, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (30) MCROPHONE MODULE WITH
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2
 USOO6731259B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2 Yer et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT OF A LIQUID CRYSTAL 6,121.950 A * 9/2000 Zavracky et al.... 34.5/101
USOO6731259B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,731,259 B2 Yer et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT OF A LIQUID CRYSTAL 6,121.950 A * 9/2000 Zavracky et al.... 34.5/101
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Zhou et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 29, 2006
 US 2006O1394.94A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/01394.94 A1 Zhou et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 29, 2006 (54) METHOD OF TEMPORAL NOISE (52) U.S. Cl.... 348/607;
US 2006O1394.94A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/01394.94 A1 Zhou et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 29, 2006 (54) METHOD OF TEMPORAL NOISE (52) U.S. Cl.... 348/607;
ED 302C A t 302B (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0035764 A1 Michihata et al. US 2015 0035764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) DIGITIZER PEN
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0035764 A1 Michihata et al. US 2015 0035764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) DIGITIZER PEN
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 200800 13292A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0013292 A1 SlikkerVeer et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 17, 2008 (54) ROLLABLE ELECTRONIC PANEL DEVICE (86). PCT
US 200800 13292A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0013292 A1 SlikkerVeer et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 17, 2008 (54) ROLLABLE ELECTRONIC PANEL DEVICE (86). PCT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O260967A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0260967 A1 Guha et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 23, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR EFFICIENT FAULTTOLERANT
(19) United States US 2004O260967A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0260967 A1 Guha et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 23, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR EFFICIENT FAULTTOLERANT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0024764 A1 LOu et al. US 2013 OO24764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD FORTRANSFORMINGWEB
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0024764 A1 LOu et al. US 2013 OO24764A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) METHOD FORTRANSFORMINGWEB
58 Field of Search ,154.15s, a housing adapted to be affixed to the interior of the mailbox,
 USOO5975713A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,975,713 Brothers (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 1999 54 INTERIOR MAILBOX LIGHT 2,411,100 11/1946 MacDonald... 362/155 2,772,349 11/1956 Chamberlin......
USOO5975713A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,975,713 Brothers (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 1999 54 INTERIOR MAILBOX LIGHT 2,411,100 11/1946 MacDonald... 362/155 2,772,349 11/1956 Chamberlin......
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 2013 O142354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0142354 A1 KRIEGEL (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 6, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1. (51) Int. Cl. (52) U.S. Cl COMMUNICATIONS
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0036568 A1 HWANG US 2015.0036568A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONSTERMINAL
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Matsuda USOO6211649B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 3, 2001 (54) USB CABLE AND METHOD FOR CHARGING BATTERY OF EXTERNAL APPARATUS BY USING USB CABLE (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent Matsuda USOO6211649B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 3, 2001 (54) USB CABLE AND METHOD FOR CHARGING BATTERY OF EXTERNAL APPARATUS BY USING USB CABLE (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 201200O8852A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0008852 A1 NU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 12, 2012 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD OF ENHANCING Publication Classification
(19) United States US 201200O8852A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0008852 A1 NU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 12, 2012 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD OF ENHANCING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0031621 A1 Liu US 2014003 1621A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 30, 2014 (54) (76) (21) (22) (51) (52) CUTTINGAPPARATUS WITH IMAGE CAPTURE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0031621 A1 Liu US 2014003 1621A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 30, 2014 (54) (76) (21) (22) (51) (52) CUTTINGAPPARATUS WITH IMAGE CAPTURE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2008.0068375A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0068375 A1 Min et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 20, 2008 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR EARLY Z (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Margalit et al. USOO6554621B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2003 (54) CABLE APPARATUS (75) Inventors: Yanki Margalit, Ramat Gan (IL); Dany Margalit, Ramat Gan
(12) United States Patent Margalit et al. USOO6554621B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2003 (54) CABLE APPARATUS (75) Inventors: Yanki Margalit, Ramat Gan (IL); Dany Margalit, Ramat Gan
wo W /1997 * cited by examiner
 111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US006963980Bl (12) United States Patent Matts son (10) Patent No.: US 6,963,980 Bl (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 2005 (54) COMBINED HARDWARE
111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US006963980Bl (12) United States Patent Matts son (10) Patent No.: US 6,963,980 Bl (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 2005 (54) COMBINED HARDWARE
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007 140922B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,140,922 B2 Lulu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 28, 2006 (54) MULTI-OUTLET AC/DC ADAPTER (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Daniel V.
(12) United States Patent US007 140922B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,140,922 B2 Lulu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 28, 2006 (54) MULTI-OUTLET AC/DC ADAPTER (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Daniel V.
United States Patent (19) Soshi et al.
 United States Patent (19) Soshi et al. 54 CAMERA WITH IMPROVED POSITIONING OF VEBRATION DETECTING SENSORS THEREN 75 Inventors: Isao Soshi, Tokyo; Hidenori Miyamoto, Urayasu; Seijiro Noda, Yokohama, all
United States Patent (19) Soshi et al. 54 CAMERA WITH IMPROVED POSITIONING OF VEBRATION DETECTING SENSORS THEREN 75 Inventors: Isao Soshi, Tokyo; Hidenori Miyamoto, Urayasu; Seijiro Noda, Yokohama, all
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,655,370 B1. Beckwith (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003
 USOO665537OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,655,370 B1 Beckwith (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) FIRECRACKER LAUNCHING DEVICE 3,794,325 * 2/1974 Stender 4,995,371. A 2/1991 Kuizinas...
USOO665537OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,655,370 B1 Beckwith (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2003 (54) FIRECRACKER LAUNCHING DEVICE 3,794,325 * 2/1974 Stender 4,995,371. A 2/1991 Kuizinas...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 20100305853A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0305853 A1 Schulze et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 2, 2010 (54) 3-D MAP DISPLAY (52) U.S. Cl.... 701/212:345/419
(19) United States US 20100305853A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0305853 A1 Schulze et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 2, 2010 (54) 3-D MAP DISPLAY (52) U.S. Cl.... 701/212:345/419
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012
 US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
US 20120023517A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0023517 A1 Hsu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AN INTERNET PROTOCOL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. (19) United States. Frequency. Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan.
 (19) United States US 201200 14334A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0014334 A1 Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANAGING RESOURCES FOR P2P
(19) United States US 201200 14334A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0014334 A1 Oh et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 19, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MANAGING RESOURCES FOR P2P
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1
 (19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(19) United States US 2010.019 1896A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0191896 A1 Yang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 29, 2010 (54) SOLID STATE DRIVE CONTROLLER WITH FAST NVRAM BUFFER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050044179A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0044179 A1 Hunter (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 24, 2005 (54) AUTOMATIC ACCESS OF INTERNET CONTENT WITH A CAMERA-ENABLED
(19) United States US 20050044179A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0044179 A1 Hunter (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 24, 2005 (54) AUTOMATIC ACCESS OF INTERNET CONTENT WITH A CAMERA-ENABLED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006O181685A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Hasegawa (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 17, 2006 (54) PROJECTOR, METHOD OF CONTROLLING THE PROJECTOR, PROGRAM FOR CONTROLLING
(19) United States US 2006O181685A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Hasegawa (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 17, 2006 (54) PROJECTOR, METHOD OF CONTROLLING THE PROJECTOR, PROGRAM FOR CONTROLLING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(19) United States US 2011 0004845A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0004845 A1 Ciabarra (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 6, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR NOTIFYINGA USER OF AN EVENT OR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0019726A1 Park et al. US 2006OO19726A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) LOCKINGAPPARATUS OF SWING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0019726A1 Park et al. US 2006OO19726A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 26, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) LOCKINGAPPARATUS OF SWING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(19) United States US 2014025631 7A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0256317 A1 ZHAO et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (63) (30) METHOD, APPARATUS, AND SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O104164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0104164 A1 YASUDA (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 16, 2015 (54) CAMERA BODY (71) Applicant: PANASONIC CORPORATION, Osaka
(19) United States US 2015O104164A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0104164 A1 YASUDA (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 16, 2015 (54) CAMERA BODY (71) Applicant: PANASONIC CORPORATION, Osaka
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0186073 A1 Bryan et al. US 201701 86.073A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 29, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) SHOPPING CART DISPLAY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0186073 A1 Bryan et al. US 201701 86.073A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 29, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) SHOPPING CART DISPLAY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,611,682 B1
 USOO661 1682B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Pröjtz (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 2003 (54) MOBILE TELEPHONE APPARATUS AND 6,188.888 B1 * 2/2001 Bartle et al.... 455/417 METHOD FOR CALL DIVERT
USOO661 1682B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Pröjtz (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 2003 (54) MOBILE TELEPHONE APPARATUS AND 6,188.888 B1 * 2/2001 Bartle et al.... 455/417 METHOD FOR CALL DIVERT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.0156354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0156354 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 21, 2003 (54) DISK CLAMP OF HARD DISK DRIVE (75) Inventor: Do-Wan Kim,
(19) United States US 2003.0156354A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0156354 A1 Kim (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 21, 2003 (54) DISK CLAMP OF HARD DISK DRIVE (75) Inventor: Do-Wan Kim,
United States Patent (19) Jones et al.
 United States Patent (19) Jones et al. 11 Patent Number: () Date of Patent: 4,764,129 Aug. 16, 1988 54 ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR ASSEMBLIES (75) Inventors: Brian Jones; Graeme S. Allan, both of Solihull, England
United States Patent (19) Jones et al. 11 Patent Number: () Date of Patent: 4,764,129 Aug. 16, 1988 54 ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR ASSEMBLIES (75) Inventors: Brian Jones; Graeme S. Allan, both of Solihull, England
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Niwa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2008
 (19) United States US 20080000981A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0000981 A1 Niwa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2008 (54) BARCODE PRINT DATA CREATION (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 20080000981A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0000981 A1 Niwa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2008 (54) BARCODE PRINT DATA CREATION (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2
 USOO7561411 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,561.411 B2 Johnson, Jr. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 14, 2009 (54) UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER DISTRIBUTION 7,400,066 B2 * 7/2008 Tassitino et al....
USOO7561411 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,561.411 B2 Johnson, Jr. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 14, 2009 (54) UNINTERRUPTIBLE POWER DISTRIBUTION 7,400,066 B2 * 7/2008 Tassitino et al....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(19) United States US 20050281269A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0281269 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: (54) MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEM (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,280,033 B1
 USOO6280033B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Pedack (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2001 (54) INDIRECT OPHTHALMOSCOPE 5,629,747 * 5/1997 Miyake... 351/218 5,793,524 8/1998 Luloh...... 359/381
USOO6280033B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Pedack (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2001 (54) INDIRECT OPHTHALMOSCOPE 5,629,747 * 5/1997 Miyake... 351/218 5,793,524 8/1998 Luloh...... 359/381
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2
 US007.917832B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2 Hsieh et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 2011 (54) APPARATUS FOR IMPROVING DATA 6,725,321 B1 4/2004 Sinclair et al.... T11 103
US007.917832B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,917,832 B2 Hsieh et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 2011 (54) APPARATUS FOR IMPROVING DATA 6,725,321 B1 4/2004 Sinclair et al.... T11 103
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2. Peng (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007
 United States Patent US007194291B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,194.291 B2 Peng (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) PROTECTIVE MASK OF MOBILE PHONE 6,591,088 B1* 7/2003 Watanabe... 455/90.3 6,594,472
United States Patent US007194291B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,194.291 B2 Peng (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) PROTECTIVE MASK OF MOBILE PHONE 6,591,088 B1* 7/2003 Watanabe... 455/90.3 6,594,472
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,172,601 B1. Wada et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2001
 USOO61726O1B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Wada et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2001 (54) THREE-DIMENSIONAL SCOPE SYSTEM 5,646,614 * 7/1997 Abersfelder et al.... 340/932.2 WITH A SINGLE
USOO61726O1B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Wada et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 9, 2001 (54) THREE-DIMENSIONAL SCOPE SYSTEM 5,646,614 * 7/1997 Abersfelder et al.... 340/932.2 WITH A SINGLE
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO8836702B2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,836,702 B2 Yoon et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 (54) RAY TRACING CORE AND METHOD FOR (58) Field of Classification Search PROCESSING
(12) United States Patent USOO8836702B2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,836,702 B2 Yoon et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 (54) RAY TRACING CORE AND METHOD FOR (58) Field of Classification Search PROCESSING
US A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1 Meyer et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb.
 US 20040021975A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0021975 A1 Meyer et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR UTILIZING VARIABLE TRACKS
US 20040021975A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0021975 A1 Meyer et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR UTILIZING VARIABLE TRACKS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(19) United States US 2003.0109252A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0109252 A1 Prentice et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 12, 2003 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD OF CODEC EMPLOYMENT INA CELLULAR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2012O100868A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0100868 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2012 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150332058A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0332058 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2015 (54) METHOD FORENCRYPTING A 3D MODEL FILE AND SYSTEM
(19) United States US 20150332058A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0332058 A1 Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2015 (54) METHOD FORENCRYPTING A 3D MODEL FILE AND SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
US 20160261583A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0261583 A1 ZHANG (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 8, 2016 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR USER Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
(19) United States US 20110149932A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0149932 A1 KM et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ZIGBEE GATEWAY AND MESSAGE Publication Classification IDENTIFICATION
Medina (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, (54) FOOT CONTROLLED COMPUTER MOUSE 2004/ A1* 11/2004 Koda et al , 183
 (12) United States Patent US007576729B2 (10) Patent No.: Medina (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 2009 (54) FOOT CONTROLLED COMPUTER MOUSE 2004/022.7741 A1* 11/2004 Koda et al.... 345, 183 WITH FINGER CLICKERS
(12) United States Patent US007576729B2 (10) Patent No.: Medina (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 2009 (54) FOOT CONTROLLED COMPUTER MOUSE 2004/022.7741 A1* 11/2004 Koda et al.... 345, 183 WITH FINGER CLICKERS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016
 US 20160085322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0085322 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) WIRELESS MOUSE, MOUSE PAD AND Publication Classification
US 20160085322A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0085322 A1 PARK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2016 (54) WIRELESS MOUSE, MOUSE PAD AND Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Beck et al. USOO6842611B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2005 (54) RECEIVED DATA PROCESSING METHOD IN COMMUNICATION DEVICE FOR SUPPORTING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
(12) United States Patent Beck et al. USOO6842611B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 11, 2005 (54) RECEIVED DATA PROCESSING METHOD IN COMMUNICATION DEVICE FOR SUPPORTING WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 20090037782A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0037782 A1 Hughes (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2009 (54) DETECTION OF ADDRESS DECODER Publication Classification
US 20090037782A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0037782 A1 Hughes (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 5, 2009 (54) DETECTION OF ADDRESS DECODER Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O125217A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0125217 A1 MaZOr (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2005 (54) SERVER-BASED SPELL CHECK ENGINE (52) U.S. Cl.... 704/1
(19) United States US 2005O125217A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0125217 A1 MaZOr (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 9, 2005 (54) SERVER-BASED SPELL CHECK ENGINE (52) U.S. Cl.... 704/1
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
US 2011 O270691A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0270691 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 3, 2011 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR PROVIDING Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,181,053 B2
 US007 181053B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,181,053 B2 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 20, 2007 (54) USB DRIVE MASS STORAGE DEVICE WITH 6,886,104 B1 * 4/2005 McClurg et al....
US007 181053B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,181,053 B2 Wang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 20, 2007 (54) USB DRIVE MASS STORAGE DEVICE WITH 6,886,104 B1 * 4/2005 McClurg et al....
(12) United States Patent
 US00795391 OB2 (12) United States Patent Kakish (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 31, 2011 (54) ALL-IN-ONE PERSONAL COMPUTER WITH EXTERNAL VIDEO INPUT (75) Inventor: Musa Ibrahim Kakish, Anaheim,
US00795391 OB2 (12) United States Patent Kakish (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 31, 2011 (54) ALL-IN-ONE PERSONAL COMPUTER WITH EXTERNAL VIDEO INPUT (75) Inventor: Musa Ibrahim Kakish, Anaheim,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO7366822B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,366,822 B2 KWalk et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2008 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE (56) References Cited CAPABLE OF READING AND WRITING
(12) United States Patent USOO7366822B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,366,822 B2 KWalk et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 29, 2008 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORY DEVICE (56) References Cited CAPABLE OF READING AND WRITING
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9442667B2 (12) United States Patent Drosch (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.442,667 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) (60) (30) (51) (52) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR
USOO9442667B2 (12) United States Patent Drosch (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.442,667 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) (60) (30) (51) (52) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR
&23 SS. United States Patent (19) Fryrear. 11) 4,041,624 45) Aug. 16, 1977
 United States Patent (19) Fryrear 54 INTEGRAL RIPPERS FOR HYDRAULIC EXCAVATOR BUCKET 75) Inventors: Max Dennis Fryrear, Joliet, Ill. 73) Assignee: Caterpillar Tractor Co., Peoria, Ill. 21 Appl. No.: 461,608
United States Patent (19) Fryrear 54 INTEGRAL RIPPERS FOR HYDRAULIC EXCAVATOR BUCKET 75) Inventors: Max Dennis Fryrear, Joliet, Ill. 73) Assignee: Caterpillar Tractor Co., Peoria, Ill. 21 Appl. No.: 461,608
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0036860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003.6860 A1 Addy (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 14, 2008 (54) PTZ PRESETS CONTROL ANALYTIUCS CONFIGURATION (76) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2008.0036860A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003.6860 A1 Addy (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 14, 2008 (54) PTZ PRESETS CONTROL ANALYTIUCS CONFIGURATION (76) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Bani-Hashemi (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 13, 2006
 US 2006O152704A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0152704 A1 Bani-Hashemi (43) Pub. Date: (54) REMOTE CENTERRANGE FINDER (52) U.S. Cl.... 356/3.1: 356/623:
US 2006O152704A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0152704 A1 Bani-Hashemi (43) Pub. Date: (54) REMOTE CENTERRANGE FINDER (52) U.S. Cl.... 356/3.1: 356/623:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 20110242707A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0242707 A1 YOON et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 6, 2011 (54) HARD DISK DRIVE Publication Classification (51) Int.
US 20110242707A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0242707 A1 YOON et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 6, 2011 (54) HARD DISK DRIVE Publication Classification (51) Int.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317029 A1 TASAK et al. US 20080317029A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) UNICAST/MULTICAST SYSTEM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006
 US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
US 20060090088A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0090088 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2006 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,760,924 B2. Ruth et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2010
 USOO7760924B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Ruth et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2010 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR GENERATING (51) Int. Cl. A 2D IMAGE FROMA TOMOSYNTHESIS G06K 9/00 (2006.01)
USOO7760924B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Ruth et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2010 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR GENERATING (51) Int. Cl. A 2D IMAGE FROMA TOMOSYNTHESIS G06K 9/00 (2006.01)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003.0113108A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0113108A1 Bittner (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 19, 2003 (54) LED REFLECTOR DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl.... 396/296 (76) Inventor:
US 2003.0113108A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0113108A1 Bittner (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 19, 2003 (54) LED REFLECTOR DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl.... 396/296 (76) Inventor:
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,074,411 Lai et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2000
 USOO6074411A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,074,411 Lai et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2000 54 MULTIPLE DIODE LASER APPARATUS AND 4,232,678 11/1980 Skovajsa. METHOD FOR LASER ACUPUNCTURE
USOO6074411A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,074,411 Lai et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 13, 2000 54 MULTIPLE DIODE LASER APPARATUS AND 4,232,678 11/1980 Skovajsa. METHOD FOR LASER ACUPUNCTURE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O226973A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0226973 A1 Kao (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 18, 2004 (54) ONE-HAND-HOLDING AID FORTABLET (52) U.S. Cl.... 224/218;
(19) United States US 2004O226973A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0226973 A1 Kao (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 18, 2004 (54) ONE-HAND-HOLDING AID FORTABLET (52) U.S. Cl.... 224/218;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O128237A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0128237 A1 SZEREMETA (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016 (54) SERVER WITH STORAGE DRIVE COOLING (52) U.S. Cl. SYSTEM
US 2016O128237A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0128237 A1 SZEREMETA (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016 (54) SERVER WITH STORAGE DRIVE COOLING (52) U.S. Cl. SYSTEM
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,198,206 B2
 US009 1982O6B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 9,198,206 B2 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 24, 2015 (54) AUTOMATIC CONNECTION METHOD AND (56) References Cited APPARATUS BETWEEN AN AUTOMOBILE
US009 1982O6B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 9,198,206 B2 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 24, 2015 (54) AUTOMATIC CONNECTION METHOD AND (56) References Cited APPARATUS BETWEEN AN AUTOMOBILE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1. Williams (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, (54) E-CARD Publication Classification
 (19) United States US 2011 0010283A1 () Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0010283 A1 Williams (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2011 (54) E-CARD Publication Classification (76) Inventor: Eddie
(19) United States US 2011 0010283A1 () Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0010283 A1 Williams (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 13, 2011 (54) E-CARD Publication Classification (76) Inventor: Eddie
(JAY VO 120 STA 1. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States PROCESSOR 160 SCHEDULER 170
 (19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2005O141495A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0141495 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2005 (54) FILLING THE SPACE-TIME CHANNELS IN SDMA (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080215829A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0215829 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2008 (54) OPTICAL DISC RECORDER AND BUFFER Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20080215829A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0215829 A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2008 (54) OPTICAL DISC RECORDER AND BUFFER Publication Classification
$26) 6, 2. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States Chien (43) Pub. Date: Jun.
 (19) United States US 2013 0147960A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0147960 A1 Chien (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013 (54) PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKSYSTEM, PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKVIDEO
(19) United States US 2013 0147960A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0147960 A1 Chien (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 13, 2013 (54) PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKSYSTEM, PLUG AND PLAYNETWORKVIDEO
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent 2 Number: LOe: 5,616,900 Seewoster (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 1, 1997
 IIII US005616900A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent 2 Number: LOe: 5,616,900 Seewoster (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 1, 1997 54 ATM KEYPAD OPERATING DEVICE 4,234,932 11/1980 Gorgens... 364/900 4,453,074
IIII US005616900A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent 2 Number: LOe: 5,616,900 Seewoster (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 1, 1997 54 ATM KEYPAD OPERATING DEVICE 4,234,932 11/1980 Gorgens... 364/900 4,453,074
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US008982274B2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,982.274 B2 Kang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 17, 2015 (54) CAMERA MODULE INCLUDING 2011/0063741 A1 3/2011 Park et al.... 359,823 2011/0091193
(12) United States Patent US008982274B2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,982.274 B2 Kang et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 17, 2015 (54) CAMERA MODULE INCLUDING 2011/0063741 A1 3/2011 Park et al.... 359,823 2011/0091193
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O1981 75A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0198175 A1 Badawi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) METHOD, SYSTEM, AND APPARATUS HIGH (22) Filed:
US 2006O1981 75A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0198175 A1 Badawi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 7, 2006 (54) METHOD, SYSTEM, AND APPARATUS HIGH (22) Filed:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 200700 10333A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0010333 A1 Chiu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 11, 2007 (54) COMPUTER GAME DEVELOPMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (75)
(19) United States US 200700 10333A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0010333 A1 Chiu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 11, 2007 (54) COMPUTER GAME DEVELOPMENT SYSTEMAND METHOD (75)
IIII 42 Y. United States Patent 19 RO et al. 46 G 40 N& 75) Inventors: Jong-Wong Ro; Yeong-Ju Kim, both
 United States Patent 19 RO et al. 54 OPTICAL COUPLING DEVICE WITH BALL LENS AND METHOD FOR MANUFACTURING THE SAME 75) Inventors: Jong-Wong Ro; Yeong-Ju Kim, both of Gumi, Keon-Joon Ahn, Daegukwangyeok,
United States Patent 19 RO et al. 54 OPTICAL COUPLING DEVICE WITH BALL LENS AND METHOD FOR MANUFACTURING THE SAME 75) Inventors: Jong-Wong Ro; Yeong-Ju Kim, both of Gumi, Keon-Joon Ahn, Daegukwangyeok,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Xiao US006663420B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADAPTER FOR EXCHANGING DATA AND TRANSMITTING POWER BETWEEN PC AND PORTABLE DEVICE (75) Inventor: Hui
(12) United States Patent Xiao US006663420B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADAPTER FOR EXCHANGING DATA AND TRANSMITTING POWER BETWEEN PC AND PORTABLE DEVICE (75) Inventor: Hui
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 2006O146786A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0146786 A1 Lian et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 6, 2006 (54) IMPLEMENTATION OF THE INTELLIGENT NETWORK IN THE
(19) United States US 2006O146786A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0146786 A1 Lian et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 6, 2006 (54) IMPLEMENTATION OF THE INTELLIGENT NETWORK IN THE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 2007 O123021A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0123021 A1 Su et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 31, 2007 (54) CIRCUIT UNDER PAD STRUCTURE AND (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2007 O123021A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0123021 A1 Su et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 31, 2007 (54) CIRCUIT UNDER PAD STRUCTURE AND (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO731.9457B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,319.457 B2 Lin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 15, 2008 (54) METHOD OF SCROLLING WINDOW (56) References Cited SCREEN BY MEANS OF CONTROLLING
(12) United States Patent USOO731.9457B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,319.457 B2 Lin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 15, 2008 (54) METHOD OF SCROLLING WINDOW (56) References Cited SCREEN BY MEANS OF CONTROLLING
STATEMENT REGARDING FEDERALLY SPONSORED RESEARCH OR THE NAMES OF THE PARTIES TO A JOINT RESEARCH AGREEMENT.
 TITLE OF INVENTION. A distance measuring device using a method of spanning separately targeted endpoints. This application claims the benefit of U.S. Provisional Application No. 61/477,511, filed April
TITLE OF INVENTION. A distance measuring device using a method of spanning separately targeted endpoints. This application claims the benefit of U.S. Provisional Application No. 61/477,511, filed April
e-a) (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1 (19) United States CAPSUE CAPSULE 2 6 Q A) A) ()
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0252365A1 Lin US 20090252365A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 8, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MCROPHONES
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0252365A1 Lin US 20090252365A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 8, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MCROPHONES
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
(19) United States US 2013 00277.43A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0027743 A1 ENAMI (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 31, 2013 (54) APPLICATION DELIVERING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 358/1.15
