INCREASING CLASSIFICATION QUALITY BY USING FUZZY LOGIC
|
|
|
- Edward Holland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 JOURNAL OF APPLIED ENGINEERING SCIENCES VOL. 1(14), issue 4_2011 ISSN ISSN-L (Print) / e-issn: INCREASING CLASSIFICATION QUALITY BY USING FUZZY LOGIC DROJ Gabriela, University of Oradea, g_abyg@yahoo.com A B S T R A C T Developed initially for the storage of the graphical information mainly maps into digital format, in the last decades geographical information systems have become one of the main supporting instruments for the decision making in the various fields. This development led to the necessity of reducing processing time by using more advanced applied mathematical and computer science knowledge. One of these mathematical theories, which give the possibility of enhancing spatial data management with the modelling of uncertainty, is fuzzy logic. This paper will present possibilities for increasing the quality of image classification by using fuzzy logic. Received: September 2011 Accepted: September 2011 Revised: October 2011 Available online: November 2011 Keywords: GIS, image classification, fuzzy logic INTRODUCTION Developed initially for the storage of the graphical information mainly maps into digital format, in the last decades geographical information systems have become one of the main supporting instrument for the decision making in the various fields. Geographical informational systems are used for decision support tool in fields like urban planning, investment planning, economic development, resource management, impact studies and in critical systems. The evolution of GIS led to the necessity of faster and better results, requirement fulfilled with the increase usage of advanced and applied mathematical and computer science knowledge like spatial databases or complex algorithms from computational geometry, artificial intelligence and fuzzy logic. This paper will present possibilities for increasing the quality of image classification by using fuzzy set theory. MATERIALS AND METHODS The fuzzy set theory gives the possibility to use computers in representing and processing uncertain data or incomplete rules, and information described in a common language and for which no certainty degree can be determine. In fuzzy logic geospatial data or layers are evaluated based on qualitative information and not for quantitative ones. In this way the fuzzy logic theory gives the possibility of enhancing spatial data management with the modelling of uncertainty. Fuzzy logic was implemented successfully in various GIS processes [2] like: Data collection analysis and processing remote sensing data for classification algorithms and object recognition [1]; Spatial analysis - processing qualitative data, in order to defining relationships between uncertain geospatial objects; Complex operations based on genetic algorithms or artificial intelligence; like object recognition from airborne images [2]. In many cases fuzzy concepts are more suitable for modeling information like land cover or land use, because there is no exact threshold between different categories of similar information like
2 INCREASING CLASSIFICATION QUALITY BY USING FUZZY LOGIC DROJ G., pp vegetation. In order to define boundaries between such areas, clear polygon boundaries are difficult to be determined. In such cases a widely used procedure is to allocate all grid cells to classes based on fuzzy membership than 0/1 membership. Membership functions are mathematical function which defines the degree of an element s membership in a fuzzy set. The sigmoidal ( s - shaped ) membership function is perhaps the most commonly used function in fuzzy set theory it is produced by a combination of linear and cos 2 () functions [3]. J-shaped functions, which are rather like the sigmoidal membership function but with the rounded top sliced off flat over some distance [3]. Linear functions, which are like the J-shaped function but with linear sides, like the slope of a pitched roof, and are thus simple to calculate and have a fixed and well-defined extent, and User-defined functions, which are self-explanatory. In most applications membership functions are symmetric, although monotonic increasing or decreasing options are provided in Idrisi [3]. Fig. 1. Sigmoidal Membership Functions Fig. 2. J-shaped Membership Functions Fig. 3. Linear Membership Functions Fuzzy set membership is used in order to obtain the standardization of criteria. Exactly which function should be used will depend on the understanding of the relationship between the criterion and the decision set, and on the availability of information to infer fuzzy membership. In most cases, either the sigmoidal of linear functions will be sufficient. Image classification represents the processing technique, through which the data represented in the image (pixels) is grouped in a certain number of classes. The classification methods are divided in two big categories: supervised clusterization and unsupervised clusterization. Supervised clusterization is the process of classification assisted by the user. In the process of supervised classification we can distinguish three stages: learning, assigning and testing. The training stage consists in collection of references, information and data about the image which should be classified, which will be used for defining a vectorial file, for each cluster being defined a layer within the file. The result of the learning stage is represented by the signature type files which are characterizing the information which should be classified.
3 JOURNAL OF APPLIED ENGINEERING SCIENCES VOL. 1(14), issue 4_2011 ISSN ISSN-L (Print) / e-issn: In the second stage: of assigning, the pixels from the image are allocated in the basis of static results in accordance with the signatures files. The final stage is testing of the results by comparing the classified image with the previous data. The pixels which were classified in different clusters are stored in the error matrix and later being analyzed by the user. The fuzzy logic can be used in the creation of the signatures files and also in the process of the classification itself, but is not necessary to be used in both stages [1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]. The signatures files based on this training site can be created using unsupervised classification methods (like ISODATA), classical methods (like Maximum Likehood or Minim Distance) or by computing a fuzzy matrix filled with the values indicated by the membership grade of each training site [3]. The membership degree is computed by using fuzzy membership functions like: sigmoidal, linear or j-shaped presented before. The evaluation on the training can be done using statistical methods: minimum, maximum, mean, and standard deviation for each band independent and covariance matrix for all the three bands [2]. The most relevant signature file evaluation is creating an error matrix as a matrix of percentages based on pixel counts that allows us to see how many pixels in each training sample were assigned to each class [3, 8]. The second step of the supervised classification can also be processed with traditional methods (Minimum distance, Mahalanobis distance, Maximum Likehood so on) or by using fuzzy membership functions or genetic algorithm [2]. This stage cannot be evaluated alone, it can be evaluated just the final result of the supervised classification [8]. In order to optimize the accuracy of the results we consider that is appropriate to use fuzzy logic in both stages of supervised classification. In the next chapter we are testing these hypotheses [2]. Independently of the classification method used, in order to increase the quality of the results we propose usage of the fuzzy convolution operation. Fuzzy convolution allow to create a single classification band by calculating the total weighted inverse distance of all the classes first and assigning the center pixel the class with the largest total inverse distance summed over the entire set of fuzzy classification bands [9]. This has the effect of creating a context-based classification to reduce the noise of the classification [3, 4, 9]. Classes with a very small distance value remain unchanged while classes with higher distance values may change to a neighboring value if there are a sufficient number of neighboring pixels with class values and small corresponding distance values [3, 4]. RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS Input data. For the procedures of image classification was used an orthorectified airborne image from the upper hills of Oradea municipality. This image contains three channels recorded in three bands: the first band for green, the second for red and the third for blue. In the figure 4, we present this image [2]. Standardization criteria In order to analyses the standardization criteria for the build area the minimum distortion of the border of it was studied the possibility of using different membership functions, which function should be used depend relationship between the criteria of classification [8].
4 INCREASING CLASSIFICATION QUALITY BY USING FUZZY LOGIC DROJ G., pp Fig. 4. Input image In the first experiment we used a sigmoidal monotonic decreasing membership function. The result is represented in the image presented in Figure 5a). The test was repeated for linear monotonic decreasing membership function but the result was identical. In the second case we used a j-shaped monotonic increasing membership function. The result is represented in the image presented in Figure 5b). a b Fig. 5. Membership function Supervised classification. Training is the first stage of a supervised classification. In this step the user must define training areas for each class interactively on the displayed image. The areas may be specified both on polygon and on pixel basis. The three classes of information defined are: green areas, houses and streets. The signature files were created using a fuzzy membership function based on the j-shaped membership function presented before, in this case the accuracy of the signature files are acceptable, over 90 % (table below) [2]. Fig. 6. Training sites of signature files( fragment)
5 JOURNAL OF APPLIED ENGINEERING SCIENCES VOL. 1(14), issue 4_2011 ISSN ISSN-L (Print) / e-issn: Table 1. Evaluation of signature files Data streets houses green areas streets houses green areas The classification of the input images, with the signature files defined before, was done by using a classifying method which combined the Maximum Likehood method with a fuzzy membership function (linear). The output images are represented in the figure 7, each image represent a cluster in the following order houses, green areas, streets [2, 8]. Fig. 7. Supervised classification Classification results can be optimized through fuzzy convolution. The scope of this procedure is to combine the previously created bands in one band by interpolation. The interpolation method used is the weight inverse distance. Applying the fuzzy convolution on the results, obtained after the second case of supervised classification, we obtained the image below [2]. Fig. 8. Fuzzy convolution CONCLUSIONS The mathematical set theory used in GIS software enforce an artificial precision sometimes on vague information about the real world, fuzzy logic propose a new way to handle the uncertainty of the real world. Fuzzy procedures could increase the quality of raster image classification and object recognition.
6 INCREASING CLASSIFICATION QUALITY BY USING FUZZY LOGIC DROJ G., pp Fuzzy logic offers instruments for both type of classification. The unsupervised fuzzy based classification allows clustering of data, where no initial information is known, but the supervised classification is offering higher quality. The experiments revealed that by using fuzzy based algorithm in all stage of the supervised classification the quality of the result is increased [2]. We demonstrated through the experiments presented in this paper that fuzzy logic could be used to increase the quality of classification. These represent a follow up of previous experiments described in other works [2, 8] when we demonstrated that the Fuzzy set theory could be used as a very powerful tool in designing and implementing algorithms for geographical informational systems and also to support spatial decision-making process. REFERENCES 1. STEFANAKIS, E., SELLIS, T. (1999), Enhancing a Database Management System for GIS with Fuzzy Set Methodologies, Proceedings of the 19 th International Cartographic Conference, Ottawa, Canada, August DROJ, GABRIELA (2007), The Applicability Of Fuzzy Theory In Remote Sensing Image Classification, STUDIA University Babes-Bolyai, INFORMATICA, Volume LII, Number EASTMAN, R. (2001), Idrisi 32 Release 2, Guide to GIS and Image Processing, Volume I- II, Clark University, May. 4. BENZ, U., HOFMANN, P., WILLHAUCK, G., LINGENFELDER, I., HEYNEN, M. (2004), Multi-resolution, object-oriented fuzzy analysis of remote sensing data for GIS-ready information, Journal of Photogrammetry & Remote Sensing (ISI). 5. ERDAS (1999), Erdas Field Guide, Erdas 5 th ed., USA. 6. GUESGEN, H., HERTZBERG, J., LOBB, R., MANTLER, A. (2003), Buffering Fuzzy Maps in GIS, Spatial Cognition and Computation (ISI). 7. LIU, H., LI. J., CHAPMAN, M. A. (2003), Automated Road Extraction from Satellite Imagery Using Hybrid Genetic Algorithms and Cluster Analysis, Journal of Environmental Informatics 1 (2) (ISI). 8. DROJ, GABRIELA (2011), The Applicability of Fuzzy Theory In Spatial Data Analyses, Geoprevi. 9. ANASTASSIOU G.A. (2004), Fuzzy approximation by fuzzy convolution type operators, Computers & Mathematics with Applications Volume 48, Issue 9, November (ISI).
CHAPTER 5 OBJECT ORIENTED IMAGE ANALYSIS
 85 CHAPTER 5 OBJECT ORIENTED IMAGE ANALYSIS 5.1 GENERAL Urban feature mapping is one of the important component for the planning, managing and monitoring the rapid urbanized growth. The present conventional
85 CHAPTER 5 OBJECT ORIENTED IMAGE ANALYSIS 5.1 GENERAL Urban feature mapping is one of the important component for the planning, managing and monitoring the rapid urbanized growth. The present conventional
IMPROVING THE ACCURACY OF DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELS
 STUDIA UNIV. BABEŞ BOLYAI, INFORMATICA, Volume XLV, Number 1, 2000 IMPROVING THE ACCURACY OF DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELS GABRIELA DROJ Abstract. The change from paper maps to GIS, in various kinds of geographical
STUDIA UNIV. BABEŞ BOLYAI, INFORMATICA, Volume XLV, Number 1, 2000 IMPROVING THE ACCURACY OF DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELS GABRIELA DROJ Abstract. The change from paper maps to GIS, in various kinds of geographical
DIGITAL IMAGE ANALYSIS. Image Classification: Object-based Classification
 DIGITAL IMAGE ANALYSIS Image Classification: Object-based Classification Image classification Quantitative analysis used to automate the identification of features Spectral pattern recognition Unsupervised
DIGITAL IMAGE ANALYSIS Image Classification: Object-based Classification Image classification Quantitative analysis used to automate the identification of features Spectral pattern recognition Unsupervised
Object-oriented Classification of Urban Areas Using Lidar and Aerial Images
 Journal of the Korean Society of Surveying, Geodesy, Photogrammetry and Cartography Vol. 33, No. 3, 173-179, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.7848/ksgpc.2015.33.3.173 ISSN 1598-4850(Print) ISSN 2288-260X(Online)
Journal of the Korean Society of Surveying, Geodesy, Photogrammetry and Cartography Vol. 33, No. 3, 173-179, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.7848/ksgpc.2015.33.3.173 ISSN 1598-4850(Print) ISSN 2288-260X(Online)
Data: a collection of numbers or facts that require further processing before they are meaningful
 Digital Image Classification Data vs. Information Data: a collection of numbers or facts that require further processing before they are meaningful Information: Derived knowledge from raw data. Something
Digital Image Classification Data vs. Information Data: a collection of numbers or facts that require further processing before they are meaningful Information: Derived knowledge from raw data. Something
A Vector Agent-Based Unsupervised Image Classification for High Spatial Resolution Satellite Imagery
 A Vector Agent-Based Unsupervised Image Classification for High Spatial Resolution Satellite Imagery K. Borna 1, A. B. Moore 2, P. Sirguey 3 School of Surveying University of Otago PO Box 56, Dunedin,
A Vector Agent-Based Unsupervised Image Classification for High Spatial Resolution Satellite Imagery K. Borna 1, A. B. Moore 2, P. Sirguey 3 School of Surveying University of Otago PO Box 56, Dunedin,
Presented at the FIG Congress 2018, May 6-11, 2018 in Istanbul, Turkey
 Presented at the FIG Congress 2018, May 6-11, 2018 in Istanbul, Turkey Evangelos MALTEZOS, Charalabos IOANNIDIS, Anastasios DOULAMIS and Nikolaos DOULAMIS Laboratory of Photogrammetry, School of Rural
Presented at the FIG Congress 2018, May 6-11, 2018 in Istanbul, Turkey Evangelos MALTEZOS, Charalabos IOANNIDIS, Anastasios DOULAMIS and Nikolaos DOULAMIS Laboratory of Photogrammetry, School of Rural
IMAGINE Objective. The Future of Feature Extraction, Update & Change Mapping
 IMAGINE ive The Future of Feature Extraction, Update & Change Mapping IMAGINE ive provides object based multi-scale image classification and feature extraction capabilities to reliably build and maintain
IMAGINE ive The Future of Feature Extraction, Update & Change Mapping IMAGINE ive provides object based multi-scale image classification and feature extraction capabilities to reliably build and maintain
Hybrid Model with Super Resolution and Decision Boundary Feature Extraction and Rule based Classification of High Resolution Data
 Hybrid Model with Super Resolution and Decision Boundary Feature Extraction and Rule based Classification of High Resolution Data Navjeet Kaur M.Tech Research Scholar Sri Guru Granth Sahib World University
Hybrid Model with Super Resolution and Decision Boundary Feature Extraction and Rule based Classification of High Resolution Data Navjeet Kaur M.Tech Research Scholar Sri Guru Granth Sahib World University
BerkeleyImageSeg User s Guide
 BerkeleyImageSeg User s Guide 1. Introduction Welcome to BerkeleyImageSeg! This is designed to be a lightweight image segmentation application, easy to learn and easily automated for repetitive processing
BerkeleyImageSeg User s Guide 1. Introduction Welcome to BerkeleyImageSeg! This is designed to be a lightweight image segmentation application, easy to learn and easily automated for repetitive processing
A DATA DRIVEN METHOD FOR FLAT ROOF BUILDING RECONSTRUCTION FROM LiDAR POINT CLOUDS
 A DATA DRIVEN METHOD FOR FLAT ROOF BUILDING RECONSTRUCTION FROM LiDAR POINT CLOUDS A. Mahphood, H. Arefi *, School of Surveying and Geospatial Engineering, College of Engineering, University of Tehran,
A DATA DRIVEN METHOD FOR FLAT ROOF BUILDING RECONSTRUCTION FROM LiDAR POINT CLOUDS A. Mahphood, H. Arefi *, School of Surveying and Geospatial Engineering, College of Engineering, University of Tehran,
Background. Advanced Remote Sensing. Background contd. Land is a scarce resource. Lecture-5
 Advanced Remote Sensing Lecture-5 Multi Criteria Evaluation contd. Background Multicriteria analysis appeared in the 1960s as a decisionmaking tool. It is used to make a comparative assessment of alternative
Advanced Remote Sensing Lecture-5 Multi Criteria Evaluation contd. Background Multicriteria analysis appeared in the 1960s as a decisionmaking tool. It is used to make a comparative assessment of alternative
APPLICATION OF SOFTMAX REGRESSION AND ITS VALIDATION FOR SPECTRAL-BASED LAND COVER MAPPING
 APPLICATION OF SOFTMAX REGRESSION AND ITS VALIDATION FOR SPECTRAL-BASED LAND COVER MAPPING J. Wolfe a, X. Jin a, T. Bahr b, N. Holzer b, * a Harris Corporation, Broomfield, Colorado, U.S.A. (jwolfe05,
APPLICATION OF SOFTMAX REGRESSION AND ITS VALIDATION FOR SPECTRAL-BASED LAND COVER MAPPING J. Wolfe a, X. Jin a, T. Bahr b, N. Holzer b, * a Harris Corporation, Broomfield, Colorado, U.S.A. (jwolfe05,
Automated Extraction of Buildings from Aerial LiDAR Point Cloud and Digital Imaging Datasets for 3D Cadastre - Preliminary Results
 Automated Extraction of Buildings from Aerial LiDAR Point Cloud and Digital Imaging Datasets for 3D Pankaj Kumar 1*, Alias Abdul Rahman 1 and Gurcan Buyuksalih 2 ¹Department of Geoinformation Universiti
Automated Extraction of Buildings from Aerial LiDAR Point Cloud and Digital Imaging Datasets for 3D Pankaj Kumar 1*, Alias Abdul Rahman 1 and Gurcan Buyuksalih 2 ¹Department of Geoinformation Universiti
RASTER ANALYSIS GIS Analysis Fall 2013
 RASTER ANALYSIS GIS Analysis Fall 2013 Raster Data The Basics Raster Data Format Matrix of cells (pixels) organized into rows and columns (grid); each cell contains a value representing information. What
RASTER ANALYSIS GIS Analysis Fall 2013 Raster Data The Basics Raster Data Format Matrix of cells (pixels) organized into rows and columns (grid); each cell contains a value representing information. What
FUZZY DIJKSTRA ALGORITHM FOR SHORTEST PATH PROBLEM IN GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS
 ENGLISH SEMINAR FUZZY DIJKSTRA ALGORITHM FOR SHORTEST PATH PROBLEM IN GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Presenter: Huy Nguyen Phuong Contents 1. Introduction to GIS 2. Shortest Path Problem in GIS 3. Dijkstra's
ENGLISH SEMINAR FUZZY DIJKSTRA ALGORITHM FOR SHORTEST PATH PROBLEM IN GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Presenter: Huy Nguyen Phuong Contents 1. Introduction to GIS 2. Shortest Path Problem in GIS 3. Dijkstra's
layers in a raster model
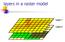 layers in a raster model Layer 1 Layer 2 layers in an vector-based model (1) Layer 2 Layer 1 layers in an vector-based model (2) raster versus vector data model Raster model Vector model Simple data structure
layers in a raster model Layer 1 Layer 2 layers in an vector-based model (1) Layer 2 Layer 1 layers in an vector-based model (2) raster versus vector data model Raster model Vector model Simple data structure
CO-REGISTERING AND NORMALIZING STEREO-BASED ELEVATION DATA TO SUPPORT BUILDING DETECTION IN VHR IMAGES
 CO-REGISTERING AND NORMALIZING STEREO-BASED ELEVATION DATA TO SUPPORT BUILDING DETECTION IN VHR IMAGES Alaeldin Suliman, Yun Zhang, Raid Al-Tahir Department of Geodesy and Geomatics Engineering, University
CO-REGISTERING AND NORMALIZING STEREO-BASED ELEVATION DATA TO SUPPORT BUILDING DETECTION IN VHR IMAGES Alaeldin Suliman, Yun Zhang, Raid Al-Tahir Department of Geodesy and Geomatics Engineering, University
Object-Based Classification & ecognition. Zutao Ouyang 11/17/2015
 Object-Based Classification & ecognition Zutao Ouyang 11/17/2015 What is Object-Based Classification The object based image analysis approach delineates segments of homogeneous image areas (i.e., objects)
Object-Based Classification & ecognition Zutao Ouyang 11/17/2015 What is Object-Based Classification The object based image analysis approach delineates segments of homogeneous image areas (i.e., objects)
A Technique for Optimal Selection of Segmentation Scale Parameters for Object-oriented Classification of Urban Scenes
 A Technique for Optimal Selection of Segmentation Scale Parameters for Object-oriented Classification of Urban Scenes Guy Blanchard Ikokou, Julian Smit Geomatics Division, University of Cape Town, Rondebosch,
A Technique for Optimal Selection of Segmentation Scale Parameters for Object-oriented Classification of Urban Scenes Guy Blanchard Ikokou, Julian Smit Geomatics Division, University of Cape Town, Rondebosch,
Digital Image Classification Geography 4354 Remote Sensing
 Digital Image Classification Geography 4354 Remote Sensing Lab 11 Dr. James Campbell December 10, 2001 Group #4 Mark Dougherty Paul Bartholomew Akisha Williams Dave Trible Seth McCoy Table of Contents:
Digital Image Classification Geography 4354 Remote Sensing Lab 11 Dr. James Campbell December 10, 2001 Group #4 Mark Dougherty Paul Bartholomew Akisha Williams Dave Trible Seth McCoy Table of Contents:
CHANGE DETECTION OF LINEAR MAN-MADE OBJECTS USING FEATURE EXTRACTION TECHNIQUE
 CHANGE DETECTION OF LINEAR MAN-MADE OBJECTS USING FEATURE EXTRACTION TECHNIQUE S. M. Phalke and I. Couloigner Department of Geomatics Engineering, University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta, Canada T2N 1N4
CHANGE DETECTION OF LINEAR MAN-MADE OBJECTS USING FEATURE EXTRACTION TECHNIQUE S. M. Phalke and I. Couloigner Department of Geomatics Engineering, University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta, Canada T2N 1N4
Cluster Validity Classification Approaches Based on Geometric Probability and Application in the Classification of Remotely Sensed Images
 Sensors & Transducers 04 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Cluster Validity ification Approaches Based on Geometric Probability and Application in the ification of Remotely Sensed
Sensors & Transducers 04 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Cluster Validity ification Approaches Based on Geometric Probability and Application in the ification of Remotely Sensed
Extraction of representative learning set from measured geospatial data
 Extraction of representative learning set from measured geospatial data Béla Paláncz 1, Lajos Völgyesi 2, Piroska Zaletnyik 2, Levente Kovács 3 1 Department of Photogrammetry and Geoinformatics, Faculty
Extraction of representative learning set from measured geospatial data Béla Paláncz 1, Lajos Völgyesi 2, Piroska Zaletnyik 2, Levente Kovács 3 1 Department of Photogrammetry and Geoinformatics, Faculty
RASTER ANALYSIS GIS Analysis Winter 2016
 RASTER ANALYSIS GIS Analysis Winter 2016 Raster Data The Basics Raster Data Format Matrix of cells (pixels) organized into rows and columns (grid); each cell contains a value representing information.
RASTER ANALYSIS GIS Analysis Winter 2016 Raster Data The Basics Raster Data Format Matrix of cells (pixels) organized into rows and columns (grid); each cell contains a value representing information.
Change Detection in Remotely Sensed Images Based on Image Fusion and Fuzzy Clustering
 International Journal of Electronics Engineering Research. ISSN 0975-6450 Volume 9, Number 1 (2017) pp. 141-150 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Change Detection in Remotely Sensed
International Journal of Electronics Engineering Research. ISSN 0975-6450 Volume 9, Number 1 (2017) pp. 141-150 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Change Detection in Remotely Sensed
Aerial photography: Principles. Visual interpretation of aerial imagery
 Aerial photography: Principles Visual interpretation of aerial imagery Overview Introduction Benefits of aerial imagery Image interpretation Elements Tasks Strategies Keys Accuracy assessment Benefits
Aerial photography: Principles Visual interpretation of aerial imagery Overview Introduction Benefits of aerial imagery Image interpretation Elements Tasks Strategies Keys Accuracy assessment Benefits
Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis. GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University
 Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University 1 Spatial Data It can be most simply defined as information that describes the distribution
Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University 1 Spatial Data It can be most simply defined as information that describes the distribution
Limit of the Paper should not be more than 3000 Words = 7/8 Pages) Abstract: About the Author:
 SEMI-AUTOMATIC EXTRACTION OF TOPOGRAPHICAL DATABASE FROM HIGH RESOLUTION MULTISPECTRAL REMOTE SENSING DATA KASTURI ROY 1, ALTE SAKET RAOSAHEB 2 1 Student, Symbiosis Institute of Geoinformatics 2 Student,
SEMI-AUTOMATIC EXTRACTION OF TOPOGRAPHICAL DATABASE FROM HIGH RESOLUTION MULTISPECTRAL REMOTE SENSING DATA KASTURI ROY 1, ALTE SAKET RAOSAHEB 2 1 Student, Symbiosis Institute of Geoinformatics 2 Student,
DIGITAL SURFACE MODELS OF CITY AREAS BY VERY HIGH RESOLUTION SPACE IMAGERY
 DIGITAL SURFACE MODELS OF CITY AREAS BY VERY HIGH RESOLUTION SPACE IMAGERY Jacobsen, K. University of Hannover, Institute of Photogrammetry and Geoinformation, Nienburger Str.1, D30167 Hannover phone +49
DIGITAL SURFACE MODELS OF CITY AREAS BY VERY HIGH RESOLUTION SPACE IMAGERY Jacobsen, K. University of Hannover, Institute of Photogrammetry and Geoinformation, Nienburger Str.1, D30167 Hannover phone +49
Automatic urbanity cluster detection in street vector databases with a raster-based algorithm
 Automatic urbanity cluster detection in street vector databases with a raster-based algorithm Volker Walter, Steffen Volz University of Stuttgart Institute for Photogrammetry Geschwister-Scholl-Str. 24D
Automatic urbanity cluster detection in street vector databases with a raster-based algorithm Volker Walter, Steffen Volz University of Stuttgart Institute for Photogrammetry Geschwister-Scholl-Str. 24D
COMBINING HIGH SPATIAL RESOLUTION OPTICAL AND LIDAR DATA FOR OBJECT-BASED IMAGE CLASSIFICATION
 COMBINING HIGH SPATIAL RESOLUTION OPTICAL AND LIDAR DATA FOR OBJECT-BASED IMAGE CLASSIFICATION Ruonan Li 1, Tianyi Zhang 1, Ruozheng Geng 1, Leiguang Wang 2, * 1 School of Forestry, Southwest Forestry
COMBINING HIGH SPATIAL RESOLUTION OPTICAL AND LIDAR DATA FOR OBJECT-BASED IMAGE CLASSIFICATION Ruonan Li 1, Tianyi Zhang 1, Ruozheng Geng 1, Leiguang Wang 2, * 1 School of Forestry, Southwest Forestry
Figure 1: Workflow of object-based classification
 Technical Specifications Object Analyst Object Analyst is an add-on package for Geomatica that provides tools for segmentation, classification, and feature extraction. Object Analyst includes an all-in-one
Technical Specifications Object Analyst Object Analyst is an add-on package for Geomatica that provides tools for segmentation, classification, and feature extraction. Object Analyst includes an all-in-one
FOUR ADVANCES IN HANDLING UNCERTAINTIES IN SPATIAL DATA AND ANALYSIS
 FOUR ADVANCES IN HANDLING UNCERTAINTIES IN SPATIAL DATA AND ANALYSIS Wenzhong Shi Advanced Research Centre for Spatial Information Technology Department of Land Surveying and Geo-Informatics The Hong Kong
FOUR ADVANCES IN HANDLING UNCERTAINTIES IN SPATIAL DATA AND ANALYSIS Wenzhong Shi Advanced Research Centre for Spatial Information Technology Department of Land Surveying and Geo-Informatics The Hong Kong
Fuzzy Segmentation. Chapter Introduction. 4.2 Unsupervised Clustering.
 Chapter 4 Fuzzy Segmentation 4. Introduction. The segmentation of objects whose color-composition is not common represents a difficult task, due to the illumination and the appropriate threshold selection
Chapter 4 Fuzzy Segmentation 4. Introduction. The segmentation of objects whose color-composition is not common represents a difficult task, due to the illumination and the appropriate threshold selection
CHAPTER 5 FUZZY LOGIC CONTROL
 64 CHAPTER 5 FUZZY LOGIC CONTROL 5.1 Introduction Fuzzy logic is a soft computing tool for embedding structured human knowledge into workable algorithms. The idea of fuzzy logic was introduced by Dr. Lofti
64 CHAPTER 5 FUZZY LOGIC CONTROL 5.1 Introduction Fuzzy logic is a soft computing tool for embedding structured human knowledge into workable algorithms. The idea of fuzzy logic was introduced by Dr. Lofti
An Approach To Classify The Object From The Satellite Image Using Image Analysis Tool
 IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 4 September 2014 ISSN(online) : 2349-6010 An Approach To Classify The Object From The Satellite Image Using Image
IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 4 September 2014 ISSN(online) : 2349-6010 An Approach To Classify The Object From The Satellite Image Using Image
A CONSISTENCY MAINTENANCE OF SHARED BOUNDARY AFTER POLYGON GENERALIZATION
 CO-182 A CONSISTENCY MAINTENANCE OF SHARED BOUNDARY AFTER POLYGON GENERALIZATION AI T.(1), ZHANG W.(2) (1) Wuhan University, WUHAN CITY, CHINA ; (2) Zhongnan University of Economics and Law, WUHAN CITY,
CO-182 A CONSISTENCY MAINTENANCE OF SHARED BOUNDARY AFTER POLYGON GENERALIZATION AI T.(1), ZHANG W.(2) (1) Wuhan University, WUHAN CITY, CHINA ; (2) Zhongnan University of Economics and Law, WUHAN CITY,
A TRAINED SEGMENTATION TECHNIQUE FOR OPTIMIZATION OF OBJECT- ORIENTED CLASSIFICATION
 A TRAINED SEGMENTATION TECHNIQUE FOR OPTIMIZATION OF OBJECT- ORIENTED CLASSIFICATION Yun Zhang a and Travis Maxwell b a Department of Geodesy and Geomatics Engineering, University of New Brunswick, Fredericton,
A TRAINED SEGMENTATION TECHNIQUE FOR OPTIMIZATION OF OBJECT- ORIENTED CLASSIFICATION Yun Zhang a and Travis Maxwell b a Department of Geodesy and Geomatics Engineering, University of New Brunswick, Fredericton,
Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images
 Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images Airborne TerrestriaL Applications Sensor (ATLAS) Nine flight paths were recorded over the city of Providence. 1 True color ATLAS image (bands 4, 2, 1 in
Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images Airborne TerrestriaL Applications Sensor (ATLAS) Nine flight paths were recorded over the city of Providence. 1 True color ATLAS image (bands 4, 2, 1 in
CHAPTER 6 HYBRID AI BASED IMAGE CLASSIFICATION TECHNIQUES
 CHAPTER 6 HYBRID AI BASED IMAGE CLASSIFICATION TECHNIQUES 6.1 INTRODUCTION The exploration of applications of ANN for image classification has yielded satisfactory results. But, the scope for improving
CHAPTER 6 HYBRID AI BASED IMAGE CLASSIFICATION TECHNIQUES 6.1 INTRODUCTION The exploration of applications of ANN for image classification has yielded satisfactory results. But, the scope for improving
Recognition of Changes in SAR Images Based on Gauss-Log Ratio and MRFFCM
 Recognition of Changes in SAR Images Based on Gauss-Log Ratio and MRFFCM Jismy Alphonse M.Tech Scholar Computer Science and Engineering Department College of Engineering Munnar, Kerala, India Biju V. G.
Recognition of Changes in SAR Images Based on Gauss-Log Ratio and MRFFCM Jismy Alphonse M.Tech Scholar Computer Science and Engineering Department College of Engineering Munnar, Kerala, India Biju V. G.
Cover Page. Abstract ID Paper Title. Automated extraction of linear features from vehicle-borne laser data
 Cover Page Abstract ID 8181 Paper Title Automated extraction of linear features from vehicle-borne laser data Contact Author Email Dinesh Manandhar (author1) dinesh@skl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp Phone +81-3-5452-6417
Cover Page Abstract ID 8181 Paper Title Automated extraction of linear features from vehicle-borne laser data Contact Author Email Dinesh Manandhar (author1) dinesh@skl.iis.u-tokyo.ac.jp Phone +81-3-5452-6417
Raster Classification with ArcGIS Desktop. Rebecca Richman Andy Shoemaker
 Raster Classification with ArcGIS Desktop Rebecca Richman Andy Shoemaker Raster Classification What is it? - Classifying imagery into different land use/ land cover classes based on the pixel values of
Raster Classification with ArcGIS Desktop Rebecca Richman Andy Shoemaker Raster Classification What is it? - Classifying imagery into different land use/ land cover classes based on the pixel values of
COLOR BASED REMOTE SENSING IMAGE SEGMENTATION USING FUZZY C-MEANS AND IMPROVED SOBEL EDGE DETECTION ALGORITHM
 COLOR BASED REMOTE SENSING IMAGE SEGMENTATION USING FUZZY C-MEANS AND IMPROVED SOBEL EDGE DETECTION ALGORITHM Ms. B.SasiPrabha, Mrs.R.uma, MCA,M.Phil,M.Ed, Research scholar, Asst. professor, Department
COLOR BASED REMOTE SENSING IMAGE SEGMENTATION USING FUZZY C-MEANS AND IMPROVED SOBEL EDGE DETECTION ALGORITHM Ms. B.SasiPrabha, Mrs.R.uma, MCA,M.Phil,M.Ed, Research scholar, Asst. professor, Department
City-Modeling. Detecting and Reconstructing Buildings from Aerial Images and LIDAR Data
 City-Modeling Detecting and Reconstructing Buildings from Aerial Images and LIDAR Data Department of Photogrammetrie Institute for Geodesy and Geoinformation Bonn 300000 inhabitants At river Rhine University
City-Modeling Detecting and Reconstructing Buildings from Aerial Images and LIDAR Data Department of Photogrammetrie Institute for Geodesy and Geoinformation Bonn 300000 inhabitants At river Rhine University
Introducing ArcScan for ArcGIS
 Introducing ArcScan for ArcGIS An ESRI White Paper August 2003 ESRI 380 New York St., Redlands, CA 92373-8100, USA TEL 909-793-2853 FAX 909-793-5953 E-MAIL info@esri.com WEB www.esri.com Copyright 2003
Introducing ArcScan for ArcGIS An ESRI White Paper August 2003 ESRI 380 New York St., Redlands, CA 92373-8100, USA TEL 909-793-2853 FAX 909-793-5953 E-MAIL info@esri.com WEB www.esri.com Copyright 2003
GIS Data Models. 4/9/ GIS Data Models
 GIS Data Models 1 Conceptual models of the real world The real world can be described using two conceptually different models: 1. As discrete objects, possible to represent as points, lines or polygons.
GIS Data Models 1 Conceptual models of the real world The real world can be described using two conceptually different models: 1. As discrete objects, possible to represent as points, lines or polygons.
Generalized Fuzzy Clustering Model with Fuzzy C-Means
 Generalized Fuzzy Clustering Model with Fuzzy C-Means Hong Jiang 1 1 Computer Science and Engineering, University of South Carolina, Columbia, SC 29208, US jiangh@cse.sc.edu http://www.cse.sc.edu/~jiangh/
Generalized Fuzzy Clustering Model with Fuzzy C-Means Hong Jiang 1 1 Computer Science and Engineering, University of South Carolina, Columbia, SC 29208, US jiangh@cse.sc.edu http://www.cse.sc.edu/~jiangh/
OBJECT IDENTIFICATION AND FEATURE EXTRACTION TECHNIQUES OF A SATELLITE DATA: A REVIEW
 OBJECT IDENTIFICATION AND FEATURE EXTRACTION TECHNIQUES OF A SATELLITE DATA: A REVIEW Navjeet 1, Simarjeet Kaur 2 1 Department of Computer Engineering Sri Guru Granth Sahib World University Fatehgarh Sahib,
OBJECT IDENTIFICATION AND FEATURE EXTRACTION TECHNIQUES OF A SATELLITE DATA: A REVIEW Navjeet 1, Simarjeet Kaur 2 1 Department of Computer Engineering Sri Guru Granth Sahib World University Fatehgarh Sahib,
Biometrics Technology: Image Processing & Pattern Recognition (by Dr. Dickson Tong)
 Biometrics Technology: Image Processing & Pattern Recognition (by Dr. Dickson Tong) References: [1] http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/hipr2/index.htm [2] http://www.cs.wisc.edu/~dyer/cs540/notes/vision.html
Biometrics Technology: Image Processing & Pattern Recognition (by Dr. Dickson Tong) References: [1] http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/hipr2/index.htm [2] http://www.cs.wisc.edu/~dyer/cs540/notes/vision.html
Detection of Rooftop Regions in Rural Areas Using Support Vector Machine
 549 Detection of Rooftop Regions in Rural Areas Using Support Vector Machine Liya Joseph 1, Laya Devadas 2 1 (M Tech Scholar, Department of Computer Science, College of Engineering Munnar, Kerala) 2 (Associate
549 Detection of Rooftop Regions in Rural Areas Using Support Vector Machine Liya Joseph 1, Laya Devadas 2 1 (M Tech Scholar, Department of Computer Science, College of Engineering Munnar, Kerala) 2 (Associate
Similarity Measures of Pentagonal Fuzzy Numbers
 Volume 119 No. 9 2018, 165-175 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Similarity Measures of Pentagonal Fuzzy Numbers T. Pathinathan 1 and
Volume 119 No. 9 2018, 165-175 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Similarity Measures of Pentagonal Fuzzy Numbers T. Pathinathan 1 and
Introduction to digital image classification
 Introduction to digital image classification Dr. Norman Kerle, Wan Bakx MSc a.o. INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR GEO-INFORMATION SCIENCE AND EARTH OBSERVATION Purpose of lecture Main lecture topics Review
Introduction to digital image classification Dr. Norman Kerle, Wan Bakx MSc a.o. INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR GEO-INFORMATION SCIENCE AND EARTH OBSERVATION Purpose of lecture Main lecture topics Review
UPDATING OBJECT FOR GIS DATABASE INFORMATION USING HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGES: A CASE STUDY ZONGULDAK
 UPDATING OBJECT FOR GIS DATABASE INFORMATION USING HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGES: A CASE STUDY ZONGULDAK M. Alkan 1, *, D. Arca 1, Ç. Bayik 1, A.M. Marangoz 1 1 Zonguldak Karaelmas University, Engineering
UPDATING OBJECT FOR GIS DATABASE INFORMATION USING HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGES: A CASE STUDY ZONGULDAK M. Alkan 1, *, D. Arca 1, Ç. Bayik 1, A.M. Marangoz 1 1 Zonguldak Karaelmas University, Engineering
Lab 9. Julia Janicki. Introduction
 Lab 9 Julia Janicki Introduction My goal for this project is to map a general land cover in the area of Alexandria in Egypt using supervised classification, specifically the Maximum Likelihood and Support
Lab 9 Julia Janicki Introduction My goal for this project is to map a general land cover in the area of Alexandria in Egypt using supervised classification, specifically the Maximum Likelihood and Support
3D Visualization and Spatial Data Mining for Analysis of LULC Images
 3D Visualization and Spatial Data Mining for Analysis of LULC Images Kodge B. G. Department of Computer Science, Swami Vivekanand Mahavidyalaya, Udgir, Latur, India kodgebg@hotmail.com Abstract: The present
3D Visualization and Spatial Data Mining for Analysis of LULC Images Kodge B. G. Department of Computer Science, Swami Vivekanand Mahavidyalaya, Udgir, Latur, India kodgebg@hotmail.com Abstract: The present
Topic 5: Raster and Vector Data Models
 Geography 38/42:286 GIS 1 Topic 5: Raster and Vector Data Models Chapters 3 & 4: Chang (Chapter 4: DeMers) 1 The Nature of Geographic Data Most features or phenomena occur as either: discrete entities
Geography 38/42:286 GIS 1 Topic 5: Raster and Vector Data Models Chapters 3 & 4: Chang (Chapter 4: DeMers) 1 The Nature of Geographic Data Most features or phenomena occur as either: discrete entities
GOVERNMENT GAZETTE REPUBLIC OF NAMIBIA
 GOVERNMENT GAZETTE OF THE REPUBLIC OF NAMIBIA N$7.20 WINDHOEK - 7 October 2016 No. 6145 CONTENTS Page GENERAL NOTICE No. 406 Namibia Statistics Agency: Data quality standard for the purchase, capture,
GOVERNMENT GAZETTE OF THE REPUBLIC OF NAMIBIA N$7.20 WINDHOEK - 7 October 2016 No. 6145 CONTENTS Page GENERAL NOTICE No. 406 Namibia Statistics Agency: Data quality standard for the purchase, capture,
Intensity Augmented ICP for Registration of Laser Scanner Point Clouds
 Intensity Augmented ICP for Registration of Laser Scanner Point Clouds Bharat Lohani* and Sandeep Sashidharan *Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Kanpur Email: blohani@iitk.ac.in. Abstract While using
Intensity Augmented ICP for Registration of Laser Scanner Point Clouds Bharat Lohani* and Sandeep Sashidharan *Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Kanpur Email: blohani@iitk.ac.in. Abstract While using
Image Classification. RS Image Classification. Present by: Dr.Weerakaset Suanpaga
 Image Classification Present by: Dr.Weerakaset Suanpaga D.Eng(RS&GIS) 6.1 Concept of Classification Objectives of Classification Advantages of Multi-Spectral data for Classification Variation of Multi-Spectra
Image Classification Present by: Dr.Weerakaset Suanpaga D.Eng(RS&GIS) 6.1 Concept of Classification Objectives of Classification Advantages of Multi-Spectral data for Classification Variation of Multi-Spectra
INTELLIGENT OBJECT BASED SMOOTHING: AN ALGORITHM FOR REMOVING NOISES IN THE CLASSIFIED SATELLITE IMAGE
 ISSN 2321 8355 IJARSGG (2013) Vol.1, No.1, 32-41 Research Article International Journal of Advancement in Remote Sensing, GIS and Geography INTELLIGENT OBJECT BASED SMOOTHING: AN ALGORITHM FOR REMOVING
ISSN 2321 8355 IJARSGG (2013) Vol.1, No.1, 32-41 Research Article International Journal of Advancement in Remote Sensing, GIS and Geography INTELLIGENT OBJECT BASED SMOOTHING: AN ALGORITHM FOR REMOVING
GEOBIA for ArcGIS (presentation) Jacek Urbanski
 GEOBIA for ArcGIS (presentation) Jacek Urbanski INTEGRATION OF GEOBIA WITH GIS FOR SEMI-AUTOMATIC LAND COVER MAPPING FROM LANDSAT 8 IMAGERY Presented at 5th GEOBIA conference 21 24 May in Thessaloniki.
GEOBIA for ArcGIS (presentation) Jacek Urbanski INTEGRATION OF GEOBIA WITH GIS FOR SEMI-AUTOMATIC LAND COVER MAPPING FROM LANDSAT 8 IMAGERY Presented at 5th GEOBIA conference 21 24 May in Thessaloniki.
What s New in Imagery in ArcGIS. Presented by: Christopher Patterson Date: October 18, 2017
 What s New in Imagery in ArcGIS Presented by: Christopher Patterson Date: October 18, 2017 Imagery in ArcGIS Advancing 2010 Stretch, Extract Bands Clip, Mask Reproject, Orthorectify, Pan Sharpen Vegetation
What s New in Imagery in ArcGIS Presented by: Christopher Patterson Date: October 18, 2017 Imagery in ArcGIS Advancing 2010 Stretch, Extract Bands Clip, Mask Reproject, Orthorectify, Pan Sharpen Vegetation
Automatically Extracting Manmade Objects from Pan-Sharpened High-Resolution Satellite Imagery Using a Fuzzy Segmentation Method
 Automatically Extracting Manmade Obects from Pan-Sharpened High-Resolution Satellite Imagery Using a Fuzzy Segmentation Method Yu Li, Jonathan Li and Michael A. Chapman Geomatics Engineering Program, Department
Automatically Extracting Manmade Obects from Pan-Sharpened High-Resolution Satellite Imagery Using a Fuzzy Segmentation Method Yu Li, Jonathan Li and Michael A. Chapman Geomatics Engineering Program, Department
Using Structural Features to Detect Buildings in Panchromatic Satellite Images
 Using Structural Features to Detect Buildings in Panchromatic Satellite Images Beril Sırmaçek German Aerospace Center (DLR) Remote Sensing Technology Institute Weßling, 82234, Germany E-mail: Beril.Sirmacek@dlr.de
Using Structural Features to Detect Buildings in Panchromatic Satellite Images Beril Sırmaçek German Aerospace Center (DLR) Remote Sensing Technology Institute Weßling, 82234, Germany E-mail: Beril.Sirmacek@dlr.de
SATELLITE IMAGE CLASSIFICATION USING WAVELET TRANSFORM
 International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering & Technology (IJECET) ISSN 0976 6464(Print), ISSN 0976 6472(Online) Volume 1, Number 1, Sep - Oct (2010), pp. 117-124 IAEME, http://www.iaeme.com/ijecet.html
International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering & Technology (IJECET) ISSN 0976 6464(Print), ISSN 0976 6472(Online) Volume 1, Number 1, Sep - Oct (2010), pp. 117-124 IAEME, http://www.iaeme.com/ijecet.html
THE USE OF ANISOTROPIC HEIGHT TEXTURE MEASURES FOR THE SEGMENTATION OF AIRBORNE LASER SCANNER DATA
 THE USE OF ANISOTROPIC HEIGHT TEXTURE MEASURES FOR THE SEGMENTATION OF AIRBORNE LASER SCANNER DATA Sander Oude Elberink* and Hans-Gerd Maas** *Faculty of Civil Engineering and Geosciences Department of
THE USE OF ANISOTROPIC HEIGHT TEXTURE MEASURES FOR THE SEGMENTATION OF AIRBORNE LASER SCANNER DATA Sander Oude Elberink* and Hans-Gerd Maas** *Faculty of Civil Engineering and Geosciences Department of
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 2, 2011
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 2, 2011 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 076 480 Image fusion techniques for accurate
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMATICS AND GEOSCIENCES Volume 2, No 2, 2011 Copyright 2010 All rights reserved Integrated Publishing services Research article ISSN 076 480 Image fusion techniques for accurate
Automatic Segmentation of Semantic Classes in Raster Map Images
 Automatic Segmentation of Semantic Classes in Raster Map Images Thomas C. Henderson, Trevor Linton, Sergey Potupchik and Andrei Ostanin School of Computing, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT 84112
Automatic Segmentation of Semantic Classes in Raster Map Images Thomas C. Henderson, Trevor Linton, Sergey Potupchik and Andrei Ostanin School of Computing, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT 84112
Image Classification Using Wavelet Coefficients in Low-pass Bands
 Proceedings of International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Orlando, Florida, USA, August -7, 007 Image Classification Using Wavelet Coefficients in Low-pass Bands Weibao Zou, Member, IEEE, and Yan
Proceedings of International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Orlando, Florida, USA, August -7, 007 Image Classification Using Wavelet Coefficients in Low-pass Bands Weibao Zou, Member, IEEE, and Yan
A FUZZY LOGIC APPROACH TO SUPERVISED SEGMENTATION FOR OBJECT- ORIENTED CLASSIFICATION INTRODUCTION
 A FUZZY LOGIC APPROACH TO SUPERVISED SEGMENTATION FOR OBJECT- ORIENTED CLASSIFICATION Yun Zhang, PhD Department of Geodesy and Geomatics Engineering University of New Brunswick P.O. Box 4400, Fredericton,
A FUZZY LOGIC APPROACH TO SUPERVISED SEGMENTATION FOR OBJECT- ORIENTED CLASSIFICATION Yun Zhang, PhD Department of Geodesy and Geomatics Engineering University of New Brunswick P.O. Box 4400, Fredericton,
Lab #4 Introduction to Image Processing II and Map Accuracy Assessment
 FOR 324 Natural Resources Information Systems Lab #4 Introduction to Image Processing II and Map Accuracy Assessment (Adapted from the Idrisi Tutorial, Introduction Image Processing Exercises, Exercise
FOR 324 Natural Resources Information Systems Lab #4 Introduction to Image Processing II and Map Accuracy Assessment (Adapted from the Idrisi Tutorial, Introduction Image Processing Exercises, Exercise
translatingnatureintoknowledge Dr Vanessa Lucieer
 Advancing quantitative techniques for the generation of acoustic variables to characterise seabed habitats. International workshop on seabed mapping methods and technology, Trondheim 17 th and 18 th October
Advancing quantitative techniques for the generation of acoustic variables to characterise seabed habitats. International workshop on seabed mapping methods and technology, Trondheim 17 th and 18 th October
Remote Sensed Image Classification based on Spatial and Spectral Features using SVM
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Remote Sensed Image Classification based on Spatial and Spectral Features using SVM Mary Jasmine. E PG Scholar Department of Computer Science and Engineering, University College
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Remote Sensed Image Classification based on Spatial and Spectral Features using SVM Mary Jasmine. E PG Scholar Department of Computer Science and Engineering, University College
CHAPTER-1 INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER-1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Fuzzy concept, digital image processing and application in medicine With the advancement of digital computers, it has become easy to store large amount of data and carry out
CHAPTER-1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Fuzzy concept, digital image processing and application in medicine With the advancement of digital computers, it has become easy to store large amount of data and carry out
BUILDINGS CHANGE DETECTION BASED ON SHAPE MATCHING FOR MULTI-RESOLUTION REMOTE SENSING IMAGERY
 BUILDINGS CHANGE DETECTION BASED ON SHAPE MATCHING FOR MULTI-RESOLUTION REMOTE SENSING IMAGERY Medbouh Abdessetar, Yanfei Zhong* State Key Laboratory of Information Engineering in Surveying, Mapping and
BUILDINGS CHANGE DETECTION BASED ON SHAPE MATCHING FOR MULTI-RESOLUTION REMOTE SENSING IMAGERY Medbouh Abdessetar, Yanfei Zhong* State Key Laboratory of Information Engineering in Surveying, Mapping and
Structural Analysis of Aerial Photographs (HB47 Computer Vision: Assignment)
 Structural Analysis of Aerial Photographs (HB47 Computer Vision: Assignment) Xiaodong Lu, Jin Yu, Yajie Li Master in Artificial Intelligence May 2004 Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Edge-Preserving
Structural Analysis of Aerial Photographs (HB47 Computer Vision: Assignment) Xiaodong Lu, Jin Yu, Yajie Li Master in Artificial Intelligence May 2004 Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Edge-Preserving
A NEW CLASSIFICATION METHOD FOR HIGH SPATIAL RESOLUTION REMOTE SENSING IMAGE BASED ON MAPPING MECHANISM
 Proceedings of the 4th GEOBIA, May 7-9, 2012 - Rio de Janeiro - Brazil. p.186 A NEW CLASSIFICATION METHOD FOR HIGH SPATIAL RESOLUTION REMOTE SENSING IMAGE BASED ON MAPPING MECHANISM Guizhou Wang a,b,c,1,
Proceedings of the 4th GEOBIA, May 7-9, 2012 - Rio de Janeiro - Brazil. p.186 A NEW CLASSIFICATION METHOD FOR HIGH SPATIAL RESOLUTION REMOTE SENSING IMAGE BASED ON MAPPING MECHANISM Guizhou Wang a,b,c,1,
Prof. Jose L. Flores, MS, PS Dept. of Civil Engineering & Surveying
 Prof. Jose L. Flores, MS, PS Dept. of Civil Engineering & Surveying Problem One of the challenges for any Geographic Information System (GIS) application is to keep the spatial data up to date and accurate.
Prof. Jose L. Flores, MS, PS Dept. of Civil Engineering & Surveying Problem One of the challenges for any Geographic Information System (GIS) application is to keep the spatial data up to date and accurate.
Outline of Presentation. Introduction to Overwatch Geospatial Software Feature Analyst and LIDAR Analyst Software
 Outline of Presentation Automated Feature Extraction from Terrestrial and Airborne LIDAR Presented By: Stuart Blundell Overwatch Geospatial - VLS Ops Co-Author: David W. Opitz Overwatch Geospatial - VLS
Outline of Presentation Automated Feature Extraction from Terrestrial and Airborne LIDAR Presented By: Stuart Blundell Overwatch Geospatial - VLS Ops Co-Author: David W. Opitz Overwatch Geospatial - VLS
EVALUATION OF THE THEMATIC INFORMATION CONTENT OF THE ASTER-VNIR IMAGERY IN URBAN AREAS BY CLASSIFICATION TECHNIQUES
 EVALUATION OF THE THEMATIC INFORMATION CONTENT OF THE ASTER-VNIR IMAGERY IN URBAN AREAS BY CLASSIFICATION TECHNIQUES T. G. Panagou a *, G. Ch. Miliaresis a a TEI, Dpt. of Topography, 3 P.Drakou Str., Thiva,
EVALUATION OF THE THEMATIC INFORMATION CONTENT OF THE ASTER-VNIR IMAGERY IN URBAN AREAS BY CLASSIFICATION TECHNIQUES T. G. Panagou a *, G. Ch. Miliaresis a a TEI, Dpt. of Topography, 3 P.Drakou Str., Thiva,
Density Based Clustering using Modified PSO based Neighbor Selection
 Density Based Clustering using Modified PSO based Neighbor Selection K. Nafees Ahmed Research Scholar, Dept of Computer Science Jamal Mohamed College (Autonomous), Tiruchirappalli, India nafeesjmc@gmail.com
Density Based Clustering using Modified PSO based Neighbor Selection K. Nafees Ahmed Research Scholar, Dept of Computer Science Jamal Mohamed College (Autonomous), Tiruchirappalli, India nafeesjmc@gmail.com
Classification with Diffuse or Incomplete Information
 Classification with Diffuse or Incomplete Information AMAURY CABALLERO, KANG YEN Florida International University Abstract. In many different fields like finance, business, pattern recognition, communication
Classification with Diffuse or Incomplete Information AMAURY CABALLERO, KANG YEN Florida International University Abstract. In many different fields like finance, business, pattern recognition, communication
Image Segmentation Techniques
 A Study On Image Segmentation Techniques Palwinder Singh 1, Amarbir Singh 2 1,2 Department of Computer Science, GNDU Amritsar Abstract Image segmentation is very important step of image analysis which
A Study On Image Segmentation Techniques Palwinder Singh 1, Amarbir Singh 2 1,2 Department of Computer Science, GNDU Amritsar Abstract Image segmentation is very important step of image analysis which
Analytical model A structure and process for analyzing a dataset. For example, a decision tree is a model for the classification of a dataset.
 Glossary of data mining terms: Accuracy Accuracy is an important factor in assessing the success of data mining. When applied to data, accuracy refers to the rate of correct values in the data. When applied
Glossary of data mining terms: Accuracy Accuracy is an important factor in assessing the success of data mining. When applied to data, accuracy refers to the rate of correct values in the data. When applied
Classify Multi-Spectral Data Classify Geologic Terrains on Venus Apply Multi-Variate Statistics
 Classify Multi-Spectral Data Classify Geologic Terrains on Venus Apply Multi-Variate Statistics Operations What Do I Need? Classify Merge Combine Cross Scan Score Warp Respace Cover Subscene Rotate Translators
Classify Multi-Spectral Data Classify Geologic Terrains on Venus Apply Multi-Variate Statistics Operations What Do I Need? Classify Merge Combine Cross Scan Score Warp Respace Cover Subscene Rotate Translators
Image matching for historical maps comparison
 C. Balletti, F. Guerra Image matching for historical maps comparison Keywords: automatic maps comparison, image matching Summary In cartographic heritage we suddenly find maps of the same mapmaker and
C. Balletti, F. Guerra Image matching for historical maps comparison Keywords: automatic maps comparison, image matching Summary In cartographic heritage we suddenly find maps of the same mapmaker and
Aardobservatie en Data-analyse Image processing
 Aardobservatie en Data-analyse Image processing 1 Image processing: Processing of digital images aiming at: - image correction (geometry, dropped lines, etc) - image calibration: DN into radiance or into
Aardobservatie en Data-analyse Image processing 1 Image processing: Processing of digital images aiming at: - image correction (geometry, dropped lines, etc) - image calibration: DN into radiance or into
Measuring landscape pattern
 Measuring landscape pattern Why would we want to measure landscape patterns? Identify change over time Compare landscapes Compare alternative landscape scenarios Explain processes Steps in Application
Measuring landscape pattern Why would we want to measure landscape patterns? Identify change over time Compare landscapes Compare alternative landscape scenarios Explain processes Steps in Application
Accuracy, Support, and Interoperability. Michael F. Goodchild University of California Santa Barbara
 Accuracy, Support, and Interoperability Michael F. Goodchild University of California Santa Barbara The traditional view Every object has a true position and set of attributes with enough time and resources
Accuracy, Support, and Interoperability Michael F. Goodchild University of California Santa Barbara The traditional view Every object has a true position and set of attributes with enough time and resources
Color Space Projection, Feature Fusion and Concurrent Neural Modules for Biometric Image Recognition
 Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int. Conf. on COMPUTATIONAL INTELLIGENCE, MAN-MACHINE SYSTEMS AND CYBERNETICS, Venice, Italy, November 20-22, 2006 286 Color Space Projection, Fusion and Concurrent Neural
Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int. Conf. on COMPUTATIONAL INTELLIGENCE, MAN-MACHINE SYSTEMS AND CYBERNETICS, Venice, Italy, November 20-22, 2006 286 Color Space Projection, Fusion and Concurrent Neural
A Soft Computing-Based Method for the Identification of Best Practices, with Application in the Petroleum Industry
 CIMSA 2005 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence for Measurement Systems and Applications Giardini Naxos, Italy, 20-22 July 2005 A Soft Computing-Based Method for the Identification
CIMSA 2005 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence for Measurement Systems and Applications Giardini Naxos, Italy, 20-22 July 2005 A Soft Computing-Based Method for the Identification
Cost Minimization Fuzzy Assignment Problem applying Linguistic Variables
 Inter national Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics Volume 113 No. 6 2017, 404 412 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Cost Minimization
Inter national Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics Volume 113 No. 6 2017, 404 412 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Cost Minimization
Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models
 Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models GIS Data Models Raster Versus Vector in GIS Analysis Fundamental element used to represent spatial features: Raster: pixel or grid cell. Vector: x,y coordinate
Review of Cartographic Data Types and Data Models GIS Data Models Raster Versus Vector in GIS Analysis Fundamental element used to represent spatial features: Raster: pixel or grid cell. Vector: x,y coordinate
Geodatabase over Taita Hills, Kenya
 Geodatabase over Taita Hills, Kenya Anna Broberg & Antero Keskinen Abstract This article introduces the basics of geographical information systems (GIS) and explains how the Taita Hills project can benefit
Geodatabase over Taita Hills, Kenya Anna Broberg & Antero Keskinen Abstract This article introduces the basics of geographical information systems (GIS) and explains how the Taita Hills project can benefit
Contribution to Multicriterial Classification of Spatial Data
 Magyar Kutatók 8. Nemzetközi Szimpóziuma 8 th International Symposium of Hungarian Researchers on Computational Intelligence and Informatics Contribution to Multicriterial Classification of Spatial Data
Magyar Kutatók 8. Nemzetközi Szimpóziuma 8 th International Symposium of Hungarian Researchers on Computational Intelligence and Informatics Contribution to Multicriterial Classification of Spatial Data
Available Online through
 Available Online through www.ijptonline.com ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Research Article ANALYSIS OF CT LIVER IMAGES FOR TUMOUR DIAGNOSIS BASED ON CLUSTERING TECHNIQUE AND TEXTURE FEATURES M.Krithika
Available Online through www.ijptonline.com ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Research Article ANALYSIS OF CT LIVER IMAGES FOR TUMOUR DIAGNOSIS BASED ON CLUSTERING TECHNIQUE AND TEXTURE FEATURES M.Krithika
A Voxel-Based Skewness and Kurtosis Balancing Algorithm for Updating Road Networks from Airborne Lidar Data
 A Voxel-Based Skewness and Kurtosis Balancing Algorithm for Updating Road Networks from Airborne Lidar Data Li Liu & Samsung Lim School of Civil & Environmental Engineering University of New South Wales
A Voxel-Based Skewness and Kurtosis Balancing Algorithm for Updating Road Networks from Airborne Lidar Data Li Liu & Samsung Lim School of Civil & Environmental Engineering University of New South Wales
FOOTPRINTS EXTRACTION
 Building Footprints Extraction of Dense Residential Areas from LiDAR data KyoHyouk Kim and Jie Shan Purdue University School of Civil Engineering 550 Stadium Mall Drive West Lafayette, IN 47907, USA {kim458,
Building Footprints Extraction of Dense Residential Areas from LiDAR data KyoHyouk Kim and Jie Shan Purdue University School of Civil Engineering 550 Stadium Mall Drive West Lafayette, IN 47907, USA {kim458,
