Analysis of the effect of target scattering on the operational effectiveness of seeker
|
|
|
- Bryce Cameron
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2nd International Conference on Materials Science, Machinery and Energy Engineering (MSMEE 2017) Analysis of the effect of target scattering on the operational effectiveness of seeker Jun-chao Yuan1, a, Xiao-kuan Zhang1, Sheng-yuan WU1, Mao Liu1 1 School of Air Force Engineering University, Xi an , China a @163.com Abstract: The scattering characteristics of targets are important factors influencing the combat effectiveness of the seeker. First, RCS of complex target is calculated by combining PO and MEC based on surface elements. Then, by establishing missile-target intersection model, kill probability and the curve of RCS under different conditions are obtained by simulation. The results show that RCS of the target changes with the change of miss distance and miss azimuth. The changes have a direct impact on the operational effectiveness of the seeker. Severely, seeker will not start. Keywords: electromagnetic scattering, miss distance, miss azimuth 1. Introduction Seeker is an important part of the air defense missile weapon system. Combat effectiveness of seeker is the final index to reflect the terminal effectiveness of guided weapon system. In the period of missile-target intersection, the distance between the seeker and the target is very close. The distance determines that seeker operates near the scattering area of the target. Under different conditions, the target scattering characteristics are different [1] which will affect the operational effectiveness of seeker necessarily. Therefore, the research on the influence of the missile target scattering characteristics on the seeker's combat effectiveness has become a hot topic in Military Science. The scattering field of the target is obtained by combining PO and MEC based on surface element. Typical missile-target intersection model is established. The paper focuses on influences of the scattering characteristics of the target on the operational effectiveness of the seeker. 2. Calculation of complex target scattering Method of surface elements is an effective method to calculate the scattering of complex targets. The basic idea is to take each surface element in the target mesh model as a scattering point. The total scattering field of the target is considered as the complex vector superposition of the far field scattering field at each observation point. The method of physical optics (PO) is taken to calculate the specular scattering of surface element and the method of equivalent currents (MEC) is taken to calculate the edge diffraction. The total scattering field of target is obtained by superposition of two kinds of scattering fields. 2.1 Solutions of the incident field [2] The amplitude and polarization direction of the incident field of each target scattering unit are different, because the incident wave is an inhomogeneous spherical wave. In order to calculate the scattering, the incident field of each scattering unit should be determined at first. Antenna radiation intensity of far field E ( r,, ) is 60 I A E ( r,, ) er f (, )e jkr (1) r In Eq. (1), I A is aerial current, and er is unit position vector. Normalized antenna pattern function F (, ) is defined as f (, ) E1 (, ) F (, ) (2) f max Emax Copyright 2017, the Authors. Published by Atlantis Press. This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC license ( 544
2 In Eq. (2), E max is the intensity of electric field in the direction of maximum radiation. E1 (, ) is the intensity of electric field at the same distance in the direction of (, ). When the electric field intensity E 0 is in the direction of maximum radiation at the distance r0, the amplitude of the radiated electric field at any position E (r,, ) can be obtained by simultaneous Eq. (1) and Eq. (2). E ( r,, ) E0 r0 er F (, )e jk( r r0 ) r (3) E ( r,, ) in Eq. (3) is complex number which does not contain the polarization direction of electric field. In this paper, the electric field polarization mode is to take er as the propagation direction of electromagnetic wave in the spherical coordinate system. e and e are considered as two bases of orthogonal polarization. Then, arbitrary elliptical polarization p e can be expressed as pe e cos R e sin R e( j R ) (4) In Eq. (4), R is the intersection angle between p e and e. R is the phase angle which shows that e component of p e advances e component. The direction of the incident electric field can be obtained when coordinates of each scattering unit are known. The incident electric field E i of ith scattering unit with coordinates ( ri, i, i ) can be expressed as Ei E ( r,, ) pe (5) 2.2 Physical optics method Physical optics method replaces the scatterer with the equivalent current on the scatterer. The scattering field is obtained by the approximation and integration of surface. The basic starting point is Stratton - chu integral equation. Es jk e jkr s ( Ms 0 s J s ) 4 r s (6) exp[ jkr ( s i )]ds In Eq. (6), i and s are unit vectors of incident and scattering direction. r is the position of field point. r stands for the position vector of source point. s indicates the illuminated part of object. J s and M s stand for equivalent surface current and equivalent edge currents on s. For the conductor target, equation can be simplified as J s 2n H i ; Ms 0 (7) n stands for unit vector in the normal direction of the surface. H i stands for the incident magnetic field on the surface. 2.3 Equivalent electromagnetic flow method [3] Edge diffraction field of any wedge, the edge of which is C, can be expressed as follows. jke jkr Ed { 0 s [ s J ( r )] 4 r C (8) s M ( r )}e jks r dl In the above equation, J (r ' ) I e (r ' )t and M (r ' ) I m (r ' )t are equivalent edge current and equivalent marginal magnetic current separately. t is the tangential unit vector of C. r is the location of field point. r ' is position vector of edge element. 2.4 GRCS Generalized RCS considering receiving polarization is defined as follows [4]. 2 2 Es ( r ) er GRCS 4 r0 r (9) 2 Ei ( r0 ) 545
3 In Eq. (9), r0 is geometric center coordinates of scatter. r is the phase center of receiving antenna. er is the polarization of receiving antenna. 3. Operational effectiveness of Seeker The operation process of the seeker is that in the projectile encounter section, the warhead kill material can hit the target most likely through the timely initiation of the warhead. In other words, dynamic killing zone of warhead and antenna pattern of seeker try to overlap in order to maximize the hit of target and get the satisfied destruction effect. The operational effectiveness of the seeker is an indicator of the coordination between them. Fig. 1 gives a schematic diagram of the ideal operation of the seeker. Fig. 1 Ideal operation of the seeker 3.1 Conditional kill probability Conditional kill probability Pdf (, ) is defined under given conditions of miss distance and miss azimuth. xmax Pdf (, ) Pf (, ) Pd ( x, ) f f ( x, )dx (10) xmin Pf (, ) stands for the starting probability of seeker. Pd ( x, ) is the kill probability of target when the seeker is under the condition of ( x,, ) and warhead explores. f f ( x, ) is the density function of the relative trajectory of start point x. The paper assumes that the warhead of air defense missile uses fragmentation warhead, and simple rod kill model is chosen as the target vulnerability model. Specific definitions and calculation methods of the parameters can be found in [5]. Parameters in simulation are given. Although the conditional kill probability is a statistical index, it is determined for the start point x during one determined intersection process. Thus, the paper takes Pdf (, ) as a quantitative index to describe the operational effectiveness of seeker. 3.2 Start point of seeker The start point of the seeker is the position of the warhead when the target is sensed. In the process of missile-target rendezvous, the radiation of the antenna beam to the target can be regarded as the scanning process of the narrow beam to the target. Therefore, the illumination area of the target is changed, when the scattering characteristics of the target are changed, and the echo intensity is also changed [6]. It is assumed that when the echo intensity exceeds sensitivity of the seeker, the seeker starts absolutely. Then, the central position of the warhead is the starting point of the seeker. Sensitivity of the seeker is defined as S f 0 10 lg(pt / Pr min ) (11) In the above equation, Pt is transmitting power of the seeker. Prmin is minimum starting power of the seeker. Pt ( 4 )3 r 4 Pr Gt Gr 2 (12) 546
4 According to the distance formula of seeker, is equivalent scattering cross section of the target. is length of operating wave of the seeker. r is the distance between missile and target. Gt Gr are transmitting and receiving antenna gain respectively. The target GRCS achieved in section 2.4 is put into equation (12) and compared with the relative sensitivity of seeker S f 0. The position of start point of the seeker can be obtained under given conditions. 3.3 Missile-target intersection model The calculation of target scattering characteristics of the seeker is the problem of dynamic simulation about missile-target intersection. The target and the missile can be approximated as a uniform linear flight due to the short duration of operation of the seeker. Thus, the relative velocity coordinate system is choose to study the problem. In the relative velocity coordinate system, the direction of relative velocity Vcl is the positive direction of x axis. The Y axis is taken in the vertical plane and upward direction is positive. Z axis is set in the horizontal plane and has right spiral relationship with x axis and y axis. Miss distance is defined as distance between the hit point and the target in the missing plane. The missing plane is defined as the plane which is over the target and is perpendicular to the direction of missile-target relative velocity. The relationship is shown in fig.2. y missing plane z -x V cl missile Fig. 2 Relative velocity coordinate system 4. The results and analysis of simulation Fig. 3 describes the process of simulation of the seeker s operation. First, the relative parameters such as the relative position and relative velocity of missile-target are obtained by the model of missile-target intersection. Then, the GRCS of the target is obtained by vector synthesis, using the scattering field of each scattering unit achieved from PO+MEC calculation model of scattering. Scattering information of the target is used to judge the start. If the start condition is reached, the kill probability of the warhead under the position of the starting point is calculated. Otherwise, simulation at next time will be calculated. Fig. 3 Simulation process of seeker s operation In the simulation, relative velocity is Vcl 1000m / s. The sensitivity of the seeker is taken as S f 0 75dB [7]. Fig. 4 shows the conditional kill probability of warhead when missile approaches target from different rendezvous trajectory. 547
5 warhead condition of killing probability Pd Fig. 4 The change of seeker s operational effectiveness with the change of miss azimuth According to fig. 4, the reduction of the miss distance can effectively improve the conditional kill probability of warhead and the operational effectiveness of the seeker. The conditional kill probability of warhead Pd is close to 1 when the miss distance of trajectory is between 5m and 10m. It means that the seeker has ideal operational effectiveness. The Pd, when 10m, is a little smaller than that when 5m. Then reason is that when the distance between missile and target is far, the velocity of fragments is reduced by air resistance. Pd equals to 0 under some conditions, for example that the miss distance is 10m and the miss azimuth is 0, 90, 100 and 180. Another example is that the miss distance is 5m and the miss azimuth is 160. It is because that the seeker does not start. Three trajectories are selected to illustrate in table 1. The intersection parameters of different trajectories are also given in table 1. Fig. 5 shows the RCS curves of three intersection trajectories. The remaining time is flight time when the missile reaches the missing plane. When t 0, missile position corresponds to the miss point. Table 1 Parameters of different trajectories Parameters ρ θ Initial time t1 /ms Starting time t 2 /ms Starting point x/m Conditional kill probability of warhead Trajectory 1 5m,90o Trajectory 2 10m,80o Trajectory 3 10m,90o Not start None 0 Trajectory 548
6 Fig. 5 Comparison of RCS in different trajectories In trajectory 1, while t1 t 2 two time are different in trajectory 2. The reason is that the precondition of seeker s initiation is that the echo s power does not reach the seeker s sensitivity. According to fig. 5, when the GRCS of target is small during the period that the sensitivity of the seeker reaches the condition of start, the start of the seeker will be delayed(such as trajectory 2) or the seeker will not start(such as trajectory 3). Combining fig. 4, although the maximum value of GRCS of the target is much larger compared with other trajectories with the same miss distance under the condition that the miss distance is 10m and the miss azimuth is 90, the seeker cannot start. It can be seen that the maximum GRCS value is not the key factor that determines the start of the seeker. The influence of the GRCS of the whole missile rendezvous process on the launch of the seeker should be fully considered. Based on the analysis, in order to ensure that the seeker can start effectively to achieve high combat effectiveness, the target RCS should be taken as the design index and the scattering characteristics of the whole rendezvous process should be taken into account in the design of seeker s sensitivity. 5. Conclusion The paper analyzes impacts of scattering characteristics on the operational effectiveness of the seeker through simulation. According to the results, RCS of target has an important impact on the operational effectiveness of the seeker. Therefore, in order to ensure the reliable start of the rendezvous trajectory, it is necessary to consider the influence of the RCS and the optimization scheme of the combination of the missile and target rendezvous in the design of the seeker launching scheme. References [1] Wu Ling and Xia Yingqing, The Impact of Antenna Pattern on Targets Near-field Scattering Characteristics, Journal of HuaZhong Normal University, Natural Sciences, Vol. 48 (Nat.Sci, 2014) pp [2]Wang Xinwen, Li Yanping and Li Ping, Microwave Technology and Antenna, Electronic Industry Press (2011) [3]Zhao Weijiang, Gong Shuxi and Liu Qizhong, New Expressions for Fringe Current Components of Equivalent Edge Currents, Acta Electronica Sinica, Vol. 30 (2002)pp [4]Gao Hongwei, Gong Li and Sheng xinqing, Computation of Near-field Scattering by 3-D Complex Target, Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, Vol. 34 (2014)pp [5]Liu Tong, The Lethality Assessment Method of Air-Denfense Missile Warhead[D], Nanjing University of Science and Technology, [6]Nie Jiankun, Study on the Related Problems of the Near EM field of Missile-borne Antenna, Master's thesis, Xidian University (2012) [7]Zhao Qi, Chen Ning, Fei Yuanchun. Modeling and Realizing of Seeker Target Echo s Simulation[J], Joural of system simulation, 2008, 20(10):
Supplementary Figure 1 Optimum transmissive mask design for shaping an incident light to a desired
 Supplementary Figure 1 Optimum transmissive mask design for shaping an incident light to a desired tangential form. (a) The light from the sources and scatterers in the half space (1) passes through the
Supplementary Figure 1 Optimum transmissive mask design for shaping an incident light to a desired tangential form. (a) The light from the sources and scatterers in the half space (1) passes through the
WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE
 WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT Optical Metrology and NDT ME-593L, C 2018 Introduction: Wave Optics January 2018 Wave optics: coherence Temporal coherence Review interference
WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT Optical Metrology and NDT ME-593L, C 2018 Introduction: Wave Optics January 2018 Wave optics: coherence Temporal coherence Review interference
Numerical Simulation of RCS for A Spherical Convergent Flap Nozzle with A Non-rectangular Divergent Duct
 Numerical Simulation of RCS for A Spherical Convergent Flap Nozzle with A Non-rectangular Divergent Duct CUI Jinhui a, SHANG Shoutang a, YANG Qingzhen b, CHEN Lihai b a AVIC Shenyang Engine Design and
Numerical Simulation of RCS for A Spherical Convergent Flap Nozzle with A Non-rectangular Divergent Duct CUI Jinhui a, SHANG Shoutang a, YANG Qingzhen b, CHEN Lihai b a AVIC Shenyang Engine Design and
High-Frequency Method for Terahertz Radar Cross Section of Conductive Targets in Free Space
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 59, 193 04, 014 High-Frequency Method for Terahertz Radar Cross Section of Conductive Targets in Free Space Houqiang Hua, Yuesong Jiang *, and Yuntao He Abstract
Progress In Electromagnetics Research B, Vol. 59, 193 04, 014 High-Frequency Method for Terahertz Radar Cross Section of Conductive Targets in Free Space Houqiang Hua, Yuesong Jiang *, and Yuntao He Abstract
Location of air-borne SAR imagery without GCPs and error analysis
 International Conference on Remote Sensing, Environment and Transportation Engineering (RSETE 2013) Location of air-borne SAR imagery without GCPs and error analysis FAN Ning-jun, ZHAO Ling-jun, KUANG
International Conference on Remote Sensing, Environment and Transportation Engineering (RSETE 2013) Location of air-borne SAR imagery without GCPs and error analysis FAN Ning-jun, ZHAO Ling-jun, KUANG
Trajectory Planning for Reentry Maneuverable Ballistic Missiles
 International Conference on Manufacturing Science and Engineering (ICMSE 215) rajectory Planning for Reentry Maneuverable Ballistic Missiles XIE Yu1, a *, PAN Liang1,b and YUAN ianbao2,c 1 College of mechatronic
International Conference on Manufacturing Science and Engineering (ICMSE 215) rajectory Planning for Reentry Maneuverable Ballistic Missiles XIE Yu1, a *, PAN Liang1,b and YUAN ianbao2,c 1 College of mechatronic
result, it is very important to design a simulation system for dynamic laser scanning
 3rd International Conference on Multimedia Technology(ICMT 2013) Accurate and Fast Simulation of Laser Scanning Imaging Luyao Zhou 1 and Huimin Ma Abstract. In order to design a more accurate simulation
3rd International Conference on Multimedia Technology(ICMT 2013) Accurate and Fast Simulation of Laser Scanning Imaging Luyao Zhou 1 and Huimin Ma Abstract. In order to design a more accurate simulation
PATTERN SYNTHESIS FOR PLANAR ARRAY BASED ON ELEMENTS ROTATION
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 11, 55 64, 2009 PATTERN SYNTHESIS FOR PLANAR ARRAY BASED ON ELEMENTS ROTATION F. Zhang, F.-S. Zhang, C. Lin, G. Zhao, and Y.-C. Jiao National Key Laboratory
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 11, 55 64, 2009 PATTERN SYNTHESIS FOR PLANAR ARRAY BASED ON ELEMENTS ROTATION F. Zhang, F.-S. Zhang, C. Lin, G. Zhao, and Y.-C. Jiao National Key Laboratory
Basic Polarization Techniques and Devices 1998, 2003 Meadowlark Optics, Inc
 Basic Polarization Techniques and Devices 1998, 2003 Meadowlark Optics, Inc This application note briefly describes polarized light, retardation and a few of the tools used to manipulate the polarization
Basic Polarization Techniques and Devices 1998, 2003 Meadowlark Optics, Inc This application note briefly describes polarized light, retardation and a few of the tools used to manipulate the polarization
The Death of the Aerial Image
 Tutor50.doc: Version 5/9/05 T h e L i t h o g r a p h y E x p e r t (August 005) The Death of the Aerial Image Chris A. Mack, KLA-Tencor, FINLE Division, Austin, Texas The aerial image is, quite literally,
Tutor50.doc: Version 5/9/05 T h e L i t h o g r a p h y E x p e r t (August 005) The Death of the Aerial Image Chris A. Mack, KLA-Tencor, FINLE Division, Austin, Texas The aerial image is, quite literally,
Keywords: Quasi-static principle; Moving target group; Multilevel fast multipole; Electromagnetic scattering; RCS
 4th International Conference on Machinery, Materials and Information Technology Applications (ICMMITA 2016) Analysis of Electromagnetic Scattering Characteristics of Moving Target Group Based on Quasi-static
4th International Conference on Machinery, Materials and Information Technology Applications (ICMMITA 2016) Analysis of Electromagnetic Scattering Characteristics of Moving Target Group Based on Quasi-static
Lecture 17 (Polarization and Scattering) Physics Spring 2018 Douglas Fields
 Lecture 17 (Polarization and Scattering) Physics 262-01 Spring 2018 Douglas Fields Reading Quiz When unpolarized light passes through an ideal polarizer, the intensity of the transmitted light is: A) Unchanged
Lecture 17 (Polarization and Scattering) Physics 262-01 Spring 2018 Douglas Fields Reading Quiz When unpolarized light passes through an ideal polarizer, the intensity of the transmitted light is: A) Unchanged
Experiment 8 Wave Optics
 Physics 263 Experiment 8 Wave Optics In this laboratory, we will perform two experiments on wave optics. 1 Double Slit Interference In two-slit interference, light falls on an opaque screen with two closely
Physics 263 Experiment 8 Wave Optics In this laboratory, we will perform two experiments on wave optics. 1 Double Slit Interference In two-slit interference, light falls on an opaque screen with two closely
Maneuver Strategy in Beyond-Visual-Range Air Combat
 2011 International Conference on Information Communication and Management IPCSIT vol.16 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Maneuver Strategy in Beyond-Visual-Range Air Combat Liang Xiao, Jun Huang Beijing
2011 International Conference on Information Communication and Management IPCSIT vol.16 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Maneuver Strategy in Beyond-Visual-Range Air Combat Liang Xiao, Jun Huang Beijing
ITERATIVE HYBRID METHOD FOR ELECTROMAG- NETIC SCATTERING FROM A 3-D OBJECT ABOVE A 2-D RANDOM DIELECTRIC ROUGH SURFACE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 117, 435 448, 2011 ITERATIVE HYBRID METHOD FOR ELECTROMAG- NETIC SCATTERING FROM A 3-D OBJECT ABOVE A 2-D RANDOM DIELECTRIC ROUGH SURFACE W. Yang, Z. Q. Zhao
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 117, 435 448, 2011 ITERATIVE HYBRID METHOD FOR ELECTROMAG- NETIC SCATTERING FROM A 3-D OBJECT ABOVE A 2-D RANDOM DIELECTRIC ROUGH SURFACE W. Yang, Z. Q. Zhao
Performance Analysis on the Target Detection of Linear Camera of CCD Vertical Target Coordinate Measurement System
 Sensors & Transducers, Vol. 17, Issue 7, July 21, pp. 285-291 Sensors & Transducers 21 y IFSA Pulishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Performance Analysis on the Target Detection of Linear Camera
Sensors & Transducers, Vol. 17, Issue 7, July 21, pp. 285-291 Sensors & Transducers 21 y IFSA Pulishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Performance Analysis on the Target Detection of Linear Camera
Diffraction. Single-slit diffraction. Diffraction by a circular aperture. Chapter 38. In the forward direction, the intensity is maximal.
 Diffraction Chapter 38 Huygens construction may be used to find the wave observed on the downstream side of an aperture of any shape. Diffraction The interference pattern encodes the shape as a Fourier
Diffraction Chapter 38 Huygens construction may be used to find the wave observed on the downstream side of an aperture of any shape. Diffraction The interference pattern encodes the shape as a Fourier
Diffraction Calculation of Arbitrarily Curved Wedge Modeled with NURBS Surfaces
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 43, 63 70, 2015 Diffraction Calculation of Arbitrarily Curved Wedge Modeled with NURBS Surfaces Jun Yan 1,JunHu *, 1, Hua Peng Zhao 2, and Zai Ping Nie 1 Abstract
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 43, 63 70, 2015 Diffraction Calculation of Arbitrarily Curved Wedge Modeled with NURBS Surfaces Jun Yan 1,JunHu *, 1, Hua Peng Zhao 2, and Zai Ping Nie 1 Abstract
specular diffuse reflection.
 Lesson 8 Light and Optics The Nature of Light Properties of Light: Reflection Refraction Interference Diffraction Polarization Dispersion and Prisms Total Internal Reflection Huygens s Principle The Nature
Lesson 8 Light and Optics The Nature of Light Properties of Light: Reflection Refraction Interference Diffraction Polarization Dispersion and Prisms Total Internal Reflection Huygens s Principle The Nature
Chapter 2 Research on Conformal Phased Array Antenna Pattern Synthesis
 Chapter 2 Research on Conformal Phased Array Antenna Pattern Synthesis Guoqi Zeng, Siyin Li and Zhimian Wei Abstract Phased array antenna has many technical advantages: high power efficiency, shaped beam,
Chapter 2 Research on Conformal Phased Array Antenna Pattern Synthesis Guoqi Zeng, Siyin Li and Zhimian Wei Abstract Phased array antenna has many technical advantages: high power efficiency, shaped beam,
Numerical Simulation on the Radar Cross Section of Variable-Sweep Wing Aircraft
 doi: 1.528/jatm.v7i2.416 Numerical Simulation on the Radar Cross Section of Variable-Sweep Wing Aircraft Shichun Chen 1, Kuizhi Yue 1,2, Bing Hu 1, Rui Guo 1 ABSTRACT: The influence of variable-sweep wing
doi: 1.528/jatm.v7i2.416 Numerical Simulation on the Radar Cross Section of Variable-Sweep Wing Aircraft Shichun Chen 1, Kuizhi Yue 1,2, Bing Hu 1, Rui Guo 1 ABSTRACT: The influence of variable-sweep wing
ISAR IMAGING OF MULTIPLE TARGETS BASED ON PARTICLE SWARM OPTIMIZATION AND HOUGH TRANSFORM
 J. of Electromagn. Waves and Appl., Vol. 23, 1825 1834, 2009 ISAR IMAGING OF MULTIPLE TARGETS BASED ON PARTICLE SWARM OPTIMIZATION AND HOUGH TRANSFORM G.G.Choi,S.H.Park,andH.T.Kim Department of Electronic
J. of Electromagn. Waves and Appl., Vol. 23, 1825 1834, 2009 ISAR IMAGING OF MULTIPLE TARGETS BASED ON PARTICLE SWARM OPTIMIZATION AND HOUGH TRANSFORM G.G.Choi,S.H.Park,andH.T.Kim Department of Electronic
Ray Optics I. Last time, finished EM theory Looked at complex boundary problems TIR: Snell s law complex Metal mirrors: index complex
 Phys 531 Lecture 8 20 September 2005 Ray Optics I Last time, finished EM theory Looked at complex boundary problems TIR: Snell s law complex Metal mirrors: index complex Today shift gears, start applying
Phys 531 Lecture 8 20 September 2005 Ray Optics I Last time, finished EM theory Looked at complex boundary problems TIR: Snell s law complex Metal mirrors: index complex Today shift gears, start applying
axis, and wavelength tuning is achieved by translating the grating along a scan direction parallel to the x
 Exponential-Grating Monochromator Kenneth C. Johnson, October 0, 08 Abstract A monochromator optical design is described, which comprises a grazing-incidence reflection and two grazing-incidence mirrors,
Exponential-Grating Monochromator Kenneth C. Johnson, October 0, 08 Abstract A monochromator optical design is described, which comprises a grazing-incidence reflection and two grazing-incidence mirrors,
Design of Electromagnetic Test Sites
 Sensor and Simulation Notes Note 533 3 August 2008 Design of Electromagnetic Test Sites Carl E. Baum University of New Mexico Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Albuquerque New Mexico 87131
Sensor and Simulation Notes Note 533 3 August 2008 Design of Electromagnetic Test Sites Carl E. Baum University of New Mexico Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Albuquerque New Mexico 87131
The sources must be coherent. This means they emit waves with a constant phase with respect to each other.
 CH. 24 Wave Optics The sources must be coherent. This means they emit waves with a constant phase with respect to each other. The waves need to have identical wavelengths. Can t be coherent without this.
CH. 24 Wave Optics The sources must be coherent. This means they emit waves with a constant phase with respect to each other. The waves need to have identical wavelengths. Can t be coherent without this.
INTRODUCTION TO The Uniform Geometrical Theory of Diffraction
 INTRODUCTION TO The Uniform Geometrical Theory of Diffraction D.A. McNamara, C.W.I. Pistorius J.A.G. Malherbe University of Pretoria Artech House Boston London CONTENTS Preface xiii Chapter 1 The Nature
INTRODUCTION TO The Uniform Geometrical Theory of Diffraction D.A. McNamara, C.W.I. Pistorius J.A.G. Malherbe University of Pretoria Artech House Boston London CONTENTS Preface xiii Chapter 1 The Nature
Diffraction and Interference of Plane Light Waves
 1 Diffraction and Interference of Plane Light Waves Introduction In this experiment you will become familiar with diffraction patterns created when a beam of light scatters from objects placed in its path.
1 Diffraction and Interference of Plane Light Waves Introduction In this experiment you will become familiar with diffraction patterns created when a beam of light scatters from objects placed in its path.
Physical or wave optics
 Physical or wave optics In the last chapter, we have been studying geometric optics u light moves in straight lines u can summarize everything by indicating direction of light using a ray u light behaves
Physical or wave optics In the last chapter, we have been studying geometric optics u light moves in straight lines u can summarize everything by indicating direction of light using a ray u light behaves
MEASUREMENT OF THE WAVELENGTH WITH APPLICATION OF A DIFFRACTION GRATING AND A SPECTROMETER
 Warsaw University of Technology Faculty of Physics Physics Laboratory I P Irma Śledzińska 4 MEASUREMENT OF THE WAVELENGTH WITH APPLICATION OF A DIFFRACTION GRATING AND A SPECTROMETER 1. Fundamentals Electromagnetic
Warsaw University of Technology Faculty of Physics Physics Laboratory I P Irma Śledzińska 4 MEASUREMENT OF THE WAVELENGTH WITH APPLICATION OF A DIFFRACTION GRATING AND A SPECTROMETER 1. Fundamentals Electromagnetic
Micro-motion Recognition of Spatial Cone Target Based on ISAR Image Sequences
 doi: 1.528/jatm.v8i2.63 Micro-motion Recognition of Spatial Cone Target Based on ISAR Image Sequences Changyong Shu 1, Fengli Xue 1, Shengjun Zhang 2, Peiling Huang 1, Jinzu Ji 1 Abstract: The accurate
doi: 1.528/jatm.v8i2.63 Micro-motion Recognition of Spatial Cone Target Based on ISAR Image Sequences Changyong Shu 1, Fengli Xue 1, Shengjun Zhang 2, Peiling Huang 1, Jinzu Ji 1 Abstract: The accurate
Supplementary Figure 1: Schematic of the nanorod-scattered wave along the +z. direction.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Schematic of the nanorod-scattered wave along the +z direction. Supplementary Figure 2: The nanorod functions as a half-wave plate. The fast axis of the waveplate is parallel to
Supplementary Figure 1: Schematic of the nanorod-scattered wave along the +z direction. Supplementary Figure 2: The nanorod functions as a half-wave plate. The fast axis of the waveplate is parallel to
Chapter 38. Diffraction Patterns and Polarization
 Chapter 38 Diffraction Patterns and Polarization Diffraction Light of wavelength comparable to or larger than the width of a slit spreads out in all forward directions upon passing through the slit This
Chapter 38 Diffraction Patterns and Polarization Diffraction Light of wavelength comparable to or larger than the width of a slit spreads out in all forward directions upon passing through the slit This
An algorithm of lips secondary positioning and feature extraction based on YCbCr color space SHEN Xian-geng 1, WU Wei 2
 International Conference on Advances in Mechanical Engineering and Industrial Informatics (AMEII 015) An algorithm of lips secondary positioning and feature extraction based on YCbCr color space SHEN Xian-geng
International Conference on Advances in Mechanical Engineering and Industrial Informatics (AMEII 015) An algorithm of lips secondary positioning and feature extraction based on YCbCr color space SHEN Xian-geng
Visible-frequency dielectric metasurfaces for multi-wavelength achromatic and highly-dispersive holograms
 Supporting Materials Visible-frequency dielectric metasurfaces for multi-wavelength achromatic and highly-dispersive holograms Bo Wang,, Fengliang Dong,, Qi-Tong Li, Dong Yang, Chengwei Sun, Jianjun Chen,,
Supporting Materials Visible-frequency dielectric metasurfaces for multi-wavelength achromatic and highly-dispersive holograms Bo Wang,, Fengliang Dong,, Qi-Tong Li, Dong Yang, Chengwei Sun, Jianjun Chen,,
Chapter 36 Diffraction
 Chapter 36 Diffraction In Chapter 35, we saw how light beams passing through different slits can interfere with each other and how a beam after passing through a single slit flares diffracts in Young's
Chapter 36 Diffraction In Chapter 35, we saw how light beams passing through different slits can interfere with each other and how a beam after passing through a single slit flares diffracts in Young's
Chapter 36. Diffraction. Copyright 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 36 Diffraction Copyright 36-1 Single-Slit Diffraction Learning Objectives 36.01 Describe the diffraction of light waves by a narrow opening and an edge, and also describe the resulting interference
Chapter 36 Diffraction Copyright 36-1 Single-Slit Diffraction Learning Objectives 36.01 Describe the diffraction of light waves by a narrow opening and an edge, and also describe the resulting interference
normal angle of incidence increases special angle no light is reflected
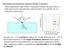 Reflection from transparent materials (Chapt. 33 last part) When unpolarized light strikes a transparent surface like glass there is both transmission and reflection, obeying Snell s law and the law of
Reflection from transparent materials (Chapt. 33 last part) When unpolarized light strikes a transparent surface like glass there is both transmission and reflection, obeying Snell s law and the law of
NEW BENCHMARK RADAR TARGETS FOR SCATTERING ANALYSIS AND ELECTROMAGNETIC SOFTWARE VALIDATION
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 88, 39 52, 2008 NEW BENCHMARK RADAR TARGETS FOR SCATTERING ANALYSIS AND ELECTROMAGNETIC SOFTWARE VALIDATION D. Escot-Bocanegra, D. Poyatos-Martinez R. Fernández-Recio,
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 88, 39 52, 2008 NEW BENCHMARK RADAR TARGETS FOR SCATTERING ANALYSIS AND ELECTROMAGNETIC SOFTWARE VALIDATION D. Escot-Bocanegra, D. Poyatos-Martinez R. Fernández-Recio,
Lecture 24 EM waves Geometrical optics
 Physics 2102 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 24 EM waves Geometrical optics EM spherical waves The intensity of a wave is power per unit area. If one has a source that emits isotropically (equally in all directions)
Physics 2102 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 24 EM waves Geometrical optics EM spherical waves The intensity of a wave is power per unit area. If one has a source that emits isotropically (equally in all directions)
SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT. Key Concepts. X-planation. Physical Sciences Grade In this session we:
 SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT Key Concepts In this session we: Explain what light is, where light comes from and why it is important Identify what happens when light strikes the surface of different objects
SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT Key Concepts In this session we: Explain what light is, where light comes from and why it is important Identify what happens when light strikes the surface of different objects
Diffraction and Interference
 Experiment #32 Diffraction and Interference Goals: Perform a quantitative investigation of two-slit interference Explore use of a photodiode to measure light intensity References 1. I. G. Main, Vibrations
Experiment #32 Diffraction and Interference Goals: Perform a quantitative investigation of two-slit interference Explore use of a photodiode to measure light intensity References 1. I. G. Main, Vibrations
PHY 171 Lecture 6 (January 18, 2012)
 PHY 171 Lecture 6 (January 18, 2012) Light Throughout most of the next 2 weeks, we will be concerned with the wave properties of light, and phenomena based on them (interference & diffraction). Light also
PHY 171 Lecture 6 (January 18, 2012) Light Throughout most of the next 2 weeks, we will be concerned with the wave properties of light, and phenomena based on them (interference & diffraction). Light also
Master-Slave Node Method of Processing Plane Node SU Zhi-Gang 1,a, WANG Fei 1,b, LI Qing-Hua 1,c,SHANG Wei-Fang 2,d, ZHANG Zi-Fu 1,e
 International Conference on Advances in Energy, Environment and Chemical Engineering (AEECE-2015) Master-Slave Node Method of Processing Plane Node SU Zhi-Gang 1,a, WANG Fei 1,b, LI Qing-Hua 1,c,SHANG
International Conference on Advances in Energy, Environment and Chemical Engineering (AEECE-2015) Master-Slave Node Method of Processing Plane Node SU Zhi-Gang 1,a, WANG Fei 1,b, LI Qing-Hua 1,c,SHANG
Deterministic Approach to Achieve Broadband Polarization-Independent Diffusive Scatterings Based on Metasurfaces
 Supporting Information for Deterministic Approach to Achieve Broadband Polarization-Independent Diffusive Scatterings Based on Metasurfaces He-Xiu Xu 1,,6 *, Shaojie Ma 1, Xiaohui Ling 1,6, Xiao-Kuan Zhang,
Supporting Information for Deterministic Approach to Achieve Broadband Polarization-Independent Diffusive Scatterings Based on Metasurfaces He-Xiu Xu 1,,6 *, Shaojie Ma 1, Xiaohui Ling 1,6, Xiao-Kuan Zhang,
Electromagnetic waves
 Electromagnetic waves Now we re back to thinking of light as specifically being an electromagnetic wave u u u oscillating electric and magnetic fields perpendicular to each other propagating through space
Electromagnetic waves Now we re back to thinking of light as specifically being an electromagnetic wave u u u oscillating electric and magnetic fields perpendicular to each other propagating through space
Wavefronts and Rays. When light or other electromagnetic waves interact with systems much larger than the wavelength, it s a good approximation to
 Chapter 33: Optics Wavefronts and Rays When light or other electromagnetic waves interact with systems much larger than the wavelength, it s a good approximation to Neglect the wave nature of light. Consider
Chapter 33: Optics Wavefronts and Rays When light or other electromagnetic waves interact with systems much larger than the wavelength, it s a good approximation to Neglect the wave nature of light. Consider
Physics Midterm I
 Phys121 - February 6, 2009 1 Physics 121 - Midterm I Last Name First Name Student Number Signature Tutorial T.A. (circle one): Ricky Chu Firuz Demir Maysam Emadi Alireza Jojjati Answer ALL 10 questions.
Phys121 - February 6, 2009 1 Physics 121 - Midterm I Last Name First Name Student Number Signature Tutorial T.A. (circle one): Ricky Chu Firuz Demir Maysam Emadi Alireza Jojjati Answer ALL 10 questions.
Modeling And Simulation Of Polar Coordinates Seeker Control System Based On Full-Map Plane
 International Conference on Software Engineering and Computer Science (ICSECS3) Modeling And Simulation Of Polar Coordinates Seeker Control System Based On Full-Map Plane Yufu Guo, Ping Zhang School of
International Conference on Software Engineering and Computer Science (ICSECS3) Modeling And Simulation Of Polar Coordinates Seeker Control System Based On Full-Map Plane Yufu Guo, Ping Zhang School of
Reflection, Refraction and Polarization of Light
 Reflection, Refraction and Polarization of Light Physics 246/Spring2012 In today's laboratory several properties of light, including the laws of reflection, refraction, total internal reflection and polarization,
Reflection, Refraction and Polarization of Light Physics 246/Spring2012 In today's laboratory several properties of light, including the laws of reflection, refraction, total internal reflection and polarization,
Fig The light rays that exit the prism enter longitudinally into an astronomical telescope adjusted for infinite distance.
 Romanian Master of Physics 07 Problem I Reflection and refraction of light A. An interesting prism The main section of a glass prism, situated in air n '.00, has the form of a rhomb with. A thin yellow
Romanian Master of Physics 07 Problem I Reflection and refraction of light A. An interesting prism The main section of a glass prism, situated in air n '.00, has the form of a rhomb with. A thin yellow
Application and design of virtual reality technology in wellbore oil production process of pumping unit system
 International Forum on Mechanical, Control and utomation (IFMC 016) pplication and design of virtual reality technology in wellbore oil production process of pumping unit system Tingting Liu 1,a, Jiaheng
International Forum on Mechanical, Control and utomation (IFMC 016) pplication and design of virtual reality technology in wellbore oil production process of pumping unit system Tingting Liu 1,a, Jiaheng
RCS Numerical Simulation of Stealth Modified Three-Surface Aircraft
 Paper Int l J. of Aeronautical & Space Sci. 17(1), 11 18 (216) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.5139/ijass.216.17.1.11 RCS Numerical Simulation of Stealth Modified Three-Surface Aircraft Cheng Liangliang* School
Paper Int l J. of Aeronautical & Space Sci. 17(1), 11 18 (216) DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.5139/ijass.216.17.1.11 RCS Numerical Simulation of Stealth Modified Three-Surface Aircraft Cheng Liangliang* School
Diffraction and Interference of Plane Light Waves
 PHY 92 Diffraction and Interference of Plane Light Waves Diffraction and Interference of Plane Light Waves Introduction In this experiment you will become familiar with diffraction patterns created when
PHY 92 Diffraction and Interference of Plane Light Waves Diffraction and Interference of Plane Light Waves Introduction In this experiment you will become familiar with diffraction patterns created when
Chapter 33 The Nature and Propagation of Light by C.-R. Hu
 Chapter 33 The Nature and Propagation of Light by C.-R. Hu Light is a transverse wave of the electromagnetic field. In 1873, James C. Maxwell predicted it from the Maxwell equations. The speed of all electromagnetic
Chapter 33 The Nature and Propagation of Light by C.-R. Hu Light is a transverse wave of the electromagnetic field. In 1873, James C. Maxwell predicted it from the Maxwell equations. The speed of all electromagnetic
f. (5.3.1) So, the higher frequency means the lower wavelength. Visible part of light spectrum covers the range of wavelengths from
 Lecture 5-3 Interference and Diffraction of EM Waves During our previous lectures we have been talking about electromagnetic (EM) waves. As we know, harmonic waves of any type represent periodic process
Lecture 5-3 Interference and Diffraction of EM Waves During our previous lectures we have been talking about electromagnetic (EM) waves. As we know, harmonic waves of any type represent periodic process
Since a projectile moves in 2-dimensions, it therefore has 2 components just like a resultant vector: Horizontal Vertical
 Since a projectile moves in 2-dimensions, it therefore has 2 components just like a resultant vector: Horizontal Vertical With no gravity the projectile would follow the straight-line path (dashed line).
Since a projectile moves in 2-dimensions, it therefore has 2 components just like a resultant vector: Horizontal Vertical With no gravity the projectile would follow the straight-line path (dashed line).
Unit 5.C Physical Optics Essential Fundamentals of Physical Optics
 Unit 5.C Physical Optics Essential Fundamentals of Physical Optics Early Booklet E.C.: + 1 Unit 5.C Hwk. Pts.: / 25 Unit 5.C Lab Pts.: / 20 Late, Incomplete, No Work, No Units Fees? Y / N 1. Light reflects
Unit 5.C Physical Optics Essential Fundamentals of Physical Optics Early Booklet E.C.: + 1 Unit 5.C Hwk. Pts.: / 25 Unit 5.C Lab Pts.: / 20 Late, Incomplete, No Work, No Units Fees? Y / N 1. Light reflects
Study on Tool Interference Checking for Complex Surface Machining
 2017 International Conference on Mechanical Engineering and Control Automation (ICMECA 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-449-3 Study on Tool Interference Checking for Complex Surface Machining Li LI 1,3,a, Li-Jin
2017 International Conference on Mechanical Engineering and Control Automation (ICMECA 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-449-3 Study on Tool Interference Checking for Complex Surface Machining Li LI 1,3,a, Li-Jin
INTRODUCTION REFLECTION AND REFRACTION AT BOUNDARIES. Introduction. Reflection and refraction at boundaries. Reflection at a single surface
 Chapter 8 GEOMETRICAL OPTICS Introduction Reflection and refraction at boundaries. Reflection at a single surface Refraction at a single boundary Dispersion Summary INTRODUCTION It has been shown that
Chapter 8 GEOMETRICAL OPTICS Introduction Reflection and refraction at boundaries. Reflection at a single surface Refraction at a single boundary Dispersion Summary INTRODUCTION It has been shown that
An Analysis of Interference as a Source for Diffraction
 J. Electromagnetic Analysis & Applications, 00,, 60-606 doi:0.436/jemaa.00.0079 Published Online October 00 (http://.scirp.org/journal/jemaa) 60 An Analysis of Interference as a Source for Diffraction
J. Electromagnetic Analysis & Applications, 00,, 60-606 doi:0.436/jemaa.00.0079 Published Online October 00 (http://.scirp.org/journal/jemaa) 60 An Analysis of Interference as a Source for Diffraction
ELECTROMAGNETIC diffraction by perfectly conducting
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 47, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 1999 1697 Oblique Scattering by a Pair of Conducting Half Planes: TM Case Jong-Won Yu and Noh-Hoon Myung Abstract An exact series
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ANTENNAS AND PROPAGATION, VOL. 47, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 1999 1697 Oblique Scattering by a Pair of Conducting Half Planes: TM Case Jong-Won Yu and Noh-Hoon Myung Abstract An exact series
Design of wideband graded-index antireflection coatings at oblique light incidence
 Design of wideband graded-index antireflection coatings at oblique light incidence Zhang Jun-Chao( ) a)b), Fang Ming( ) a), Jin Yun-Xia( ) a), and He Hong-Bo( ) a) a) Key Laboratory of Material Science
Design of wideband graded-index antireflection coatings at oblique light incidence Zhang Jun-Chao( ) a)b), Fang Ming( ) a), Jin Yun-Xia( ) a), and He Hong-Bo( ) a) a) Key Laboratory of Material Science
Measurement of period difference in grating pair based on analysis of grating phase shift
 Measurement of period difference in grating pair based on analysis of grating phase shift Chao Guo, Lijiang Zeng State Key Laboratory of Precision Measurement Technology and Instruments Department of Precision
Measurement of period difference in grating pair based on analysis of grating phase shift Chao Guo, Lijiang Zeng State Key Laboratory of Precision Measurement Technology and Instruments Department of Precision
Dispersion Polarization
 Dispersion Polarization Phys Phys 2435: 22: Chap. 33, 31, Pg 1 Dispersion New Topic Phys 2435: Chap. 33, Pg 2 The Visible Spectrum Remember that white light contains all the colors of the s p e c t r u
Dispersion Polarization Phys Phys 2435: 22: Chap. 33, 31, Pg 1 Dispersion New Topic Phys 2435: Chap. 33, Pg 2 The Visible Spectrum Remember that white light contains all the colors of the s p e c t r u
A MATLAB PHYSICAL OPTICS RCS PREDICTION CODE
 A MATLAB PHYSICAL OPTICS RCS PREDICTION CODE Elmo E. Garrido, Jr. and David C. Jenn Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943 SUMMARY POFACETS is an implementation of the physical optics approximation
A MATLAB PHYSICAL OPTICS RCS PREDICTION CODE Elmo E. Garrido, Jr. and David C. Jenn Naval Postgraduate School Monterey, CA 93943 SUMMARY POFACETS is an implementation of the physical optics approximation
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(3): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical esearch, 015, 7(3):175-179 esearch Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPC5 Thread image processing technology research based on
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical esearch, 015, 7(3):175-179 esearch Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPC5 Thread image processing technology research based on
Hole repair algorithm in hybrid sensor networks
 Advances in Engineering Research (AER), volume 116 International Conference on Communication and Electronic Information Engineering (CEIE 2016) Hole repair algorithm in hybrid sensor networks Jian Liu1,
Advances in Engineering Research (AER), volume 116 International Conference on Communication and Electronic Information Engineering (CEIE 2016) Hole repair algorithm in hybrid sensor networks Jian Liu1,
Chapter 24. Wave Optics
 Chapter 24 Wave Optics Diffraction Huygen s principle requires that the waves spread out after they pass through slits This spreading out of light from its initial line of travel is called diffraction
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Diffraction Huygen s principle requires that the waves spread out after they pass through slits This spreading out of light from its initial line of travel is called diffraction
Local Multilevel Fast Multipole Algorithm for 3D Electromagnetic Scattering
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2005, Hangzhou, China, August 22-26 745 Local Multilevel Fast Multipole Algorithm for 3D Electromagnetic Scattering Jun Hu, Zaiping Nie, Lin Lei, and Jun
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2005, Hangzhou, China, August 22-26 745 Local Multilevel Fast Multipole Algorithm for 3D Electromagnetic Scattering Jun Hu, Zaiping Nie, Lin Lei, and Jun
PH 222-3A Fall Diffraction Lectures Chapter 36 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition)
 PH 222-3A Fall 2012 Diffraction Lectures 28-29 Chapter 36 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 36 Diffraction In Chapter 35, we saw how light beams passing through
PH 222-3A Fall 2012 Diffraction Lectures 28-29 Chapter 36 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 36 Diffraction In Chapter 35, we saw how light beams passing through
ULTRASONIC WAVE PROPAGATION THROUGH NOZZLES AND PIPES WITH
 ULTRASONIC WAVE PROPAGATION THROUGH NOZZLES AND PIPES WITH CLADDINGS AROUND THEIR INNER WALLS INTRODUCTION A. Minachi and R. B. Thompson Center for NDE Iowa State University Ames, Iowa 5001 J The inner
ULTRASONIC WAVE PROPAGATION THROUGH NOZZLES AND PIPES WITH CLADDINGS AROUND THEIR INNER WALLS INTRODUCTION A. Minachi and R. B. Thompson Center for NDE Iowa State University Ames, Iowa 5001 J The inner
Optics II. Reflection and Mirrors
 Optics II Reflection and Mirrors Geometric Optics Using a Ray Approximation Light travels in a straight-line path in a homogeneous medium until it encounters a boundary between two different media The
Optics II Reflection and Mirrors Geometric Optics Using a Ray Approximation Light travels in a straight-line path in a homogeneous medium until it encounters a boundary between two different media The
A Graphical User Interface (GUI) for Two-Dimensional Electromagnetic Scattering Problems
 A Graphical User Interface (GUI) for Two-Dimensional Electromagnetic Scattering Problems Veysel Demir vdemir@olemiss.edu Mohamed Al Sharkawy malshark@olemiss.edu Atef Z. Elsherbeni atef@olemiss.edu Abstract
A Graphical User Interface (GUI) for Two-Dimensional Electromagnetic Scattering Problems Veysel Demir vdemir@olemiss.edu Mohamed Al Sharkawy malshark@olemiss.edu Atef Z. Elsherbeni atef@olemiss.edu Abstract
Update on the Gravitational-Wave Observatory project? Wikipedia OPL length questions: We ll go over this in lecture. Through the optics section, many
 More Interference Update on the Gravitational-Wave Observatory project? Wikipedia OPL length questions: We ll go over this in lecture. Through the optics section, many of the equations we use don't use
More Interference Update on the Gravitational-Wave Observatory project? Wikipedia OPL length questions: We ll go over this in lecture. Through the optics section, many of the equations we use don't use
Available online at ScienceDirect. Energy Procedia 69 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 69 (2015 ) 1885 1894 International Conference on Concentrating Solar Power and Chemical Energy Systems, SolarPACES 2014 Heliostat
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 69 (2015 ) 1885 1894 International Conference on Concentrating Solar Power and Chemical Energy Systems, SolarPACES 2014 Heliostat
ConcepTest PowerPoints
 ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 24 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
ConcepTest PowerPoints Chapter 24 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
13. Brewster angle measurement
 13. Brewster angle measurement Brewster angle measurement Objective: 1. Verification of Malus law 2. Measurement of reflection coefficient of a glass plate for p- and s- polarizations 3. Determination
13. Brewster angle measurement Brewster angle measurement Objective: 1. Verification of Malus law 2. Measurement of reflection coefficient of a glass plate for p- and s- polarizations 3. Determination
Modal Analysis of Three Dimensional Numerical Control Laser Cutting Machine Based on Finite Element Method Yun-Xin CHEN*
 Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2016) Modal Analysis of Three Dimensional Numerical Control Laser Cutting Machine Based on Finite Element
Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2016) Modal Analysis of Three Dimensional Numerical Control Laser Cutting Machine Based on Finite Element
Comparison Between Scattering Coefficients Determined By Specimen Rotation And By Directivity Correlation
 Comparison Between Scattering Coefficients Determined By Specimen Rotation And By Directivity Correlation Tetsuya Sakuma, Yoshiyuki Kosaka Institute of Environmental Studies, University of Tokyo 7-3-1
Comparison Between Scattering Coefficients Determined By Specimen Rotation And By Directivity Correlation Tetsuya Sakuma, Yoshiyuki Kosaka Institute of Environmental Studies, University of Tokyo 7-3-1
Contents 10. Graphs of Trigonometric Functions
 Contents 10. Graphs of Trigonometric Functions 2 10.2 Sine and Cosine Curves: Horizontal and Vertical Displacement...... 2 Example 10.15............................... 2 10.3 Composite Sine and Cosine
Contents 10. Graphs of Trigonometric Functions 2 10.2 Sine and Cosine Curves: Horizontal and Vertical Displacement...... 2 Example 10.15............................... 2 10.3 Composite Sine and Cosine
AUTOMATIC TARGET RECOGNITION IN HIGH RESOLUTION SAR IMAGE BASED ON BACKSCATTERING MODEL
 AUTOMATIC TARGET RECOGNITION IN HIGH RESOLUTION SAR IMAGE BASED ON BACKSCATTERING MODEL Wang Chao (1), Zhang Hong (2), Zhang Bo (1), Wen Xiaoyang (1), Wu Fan (1), Zhang Changyao (3) (1) National Key Laboratory
AUTOMATIC TARGET RECOGNITION IN HIGH RESOLUTION SAR IMAGE BASED ON BACKSCATTERING MODEL Wang Chao (1), Zhang Hong (2), Zhang Bo (1), Wen Xiaoyang (1), Wu Fan (1), Zhang Changyao (3) (1) National Key Laboratory
Chapter 2: Wave Optics
 Chapter : Wave Optics P-1. We can write a plane wave with the z axis taken in the direction of the wave vector k as u(,) r t Acos tkzarg( A) As c /, T 1/ and k / we can rewrite the plane wave as t z u(,)
Chapter : Wave Optics P-1. We can write a plane wave with the z axis taken in the direction of the wave vector k as u(,) r t Acos tkzarg( A) As c /, T 1/ and k / we can rewrite the plane wave as t z u(,)
P. H. Xie, K. S. Chen, and Z. S. He School of Electronic Engineering University of Electronic Science and Technology of China Chengdu , China
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol 9, 47 56, 29 SYNTHESIS OF SPARSE CYLINDRICAL ARRAYS USING SIMULATED ANNEALING ALGORITHM P H Xie, K S Chen, and Z S He School of Electronic Engineering
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol 9, 47 56, 29 SYNTHESIS OF SPARSE CYLINDRICAL ARRAYS USING SIMULATED ANNEALING ALGORITHM P H Xie, K S Chen, and Z S He School of Electronic Engineering
Comparison of 3-D Fracture Analysis Methods Based on ANSYS Workbench
 International Conference on Material Science, Energy and Environmental Engineering (MSEEE 2017) Comparison of 3-D Fracture Analysis Methods Based on ANSYS Workbench Dejun Liua, Fang Xieb and Ningbo Gaoc
International Conference on Material Science, Energy and Environmental Engineering (MSEEE 2017) Comparison of 3-D Fracture Analysis Methods Based on ANSYS Workbench Dejun Liua, Fang Xieb and Ningbo Gaoc
Chapter 8: Physical Optics
 Chapter 8: Physical Optics Whether light is a particle or a wave had puzzled physicists for centuries. In this chapter, we only analyze light as a wave using basic optical concepts such as interference
Chapter 8: Physical Optics Whether light is a particle or a wave had puzzled physicists for centuries. In this chapter, we only analyze light as a wave using basic optical concepts such as interference
IMPLEMENTATION OF ANALYTICAL (MATLAB) AND NUMERICAL (HFSS) SOLUTIONS ADVANCED ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY SOHAIB SAADAT AFRIDI HAMMAD BUTT ZUNNURAIN AHMAD
 STUDY OF SCATTERING & RESULTANT RADIATION PATTERN: INFINITE LINE CURRENT SOURCE POSITIONED HORIZONTALLY OVER A PERFECTLY CONDUCTING INFINITE GROUND PLANE IMPLEMENTATION OF ANALYTICAL (MATLAB) AND NUMERICAL
STUDY OF SCATTERING & RESULTANT RADIATION PATTERN: INFINITE LINE CURRENT SOURCE POSITIONED HORIZONTALLY OVER A PERFECTLY CONDUCTING INFINITE GROUND PLANE IMPLEMENTATION OF ANALYTICAL (MATLAB) AND NUMERICAL
BACKSCATTERING OF ELECTRICALLY LARGE PERFECT CONDUCTING TARGETS MODELED BY NURBS SURFACES IN HALF-SPACE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 77, 215 224, 27 BACKSCATTERING OF ELECTRICALLY LARGE PERFECT CONDUCTING TARGETS MODELED BY NURBS SURFACES IN HALF-SPACE X. J. Chen and X. W. Shi National Key
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 77, 215 224, 27 BACKSCATTERING OF ELECTRICALLY LARGE PERFECT CONDUCTING TARGETS MODELED BY NURBS SURFACES IN HALF-SPACE X. J. Chen and X. W. Shi National Key
Chapter 36. Diffraction. Dr. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 36 Diffraction Dr. Armen Kocharian Diffraction Light of wavelength comparable to or larger than the width of a slit spreads out in all forward directions upon passing through the slit This phenomena
Chapter 36 Diffraction Dr. Armen Kocharian Diffraction Light of wavelength comparable to or larger than the width of a slit spreads out in all forward directions upon passing through the slit This phenomena
The Design of Electronic Color Screen Based on Proteus Visual Designer Ting-Yu HOU 1,a, Hao LIU 2,b,*
 2016 Joint International Conference on Service Science, Management and Engineering (SSME 2016) and International Conference on Information Science and Technology (IST 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-379-3 The
2016 Joint International Conference on Service Science, Management and Engineering (SSME 2016) and International Conference on Information Science and Technology (IST 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-379-3 The
1. Particle Scattering. Cogito ergo sum, i.e. Je pense, donc je suis. - René Descartes
 1. Particle Scattering Cogito ergo sum, i.e. Je pense, donc je suis. - René Descartes Generally gas and particles do not scatter isotropically. The phase function, scattering efficiency, and single scattering
1. Particle Scattering Cogito ergo sum, i.e. Je pense, donc je suis. - René Descartes Generally gas and particles do not scatter isotropically. The phase function, scattering efficiency, and single scattering
A Precision Grinding Technique for Radome Inner Surfaces. Z.Y. Jia, T. Ji, D.M. Guo and G.H. Bian
 Key Engineering Materials Online: 2004-02-15 ISSN: 1662-9795, Vols. 257-258, pp 177-182 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/kem.257-258.177 2004 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland A Precision Grinding Technique
Key Engineering Materials Online: 2004-02-15 ISSN: 1662-9795, Vols. 257-258, pp 177-182 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/kem.257-258.177 2004 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland A Precision Grinding Technique
Lab2: Single Photon Interference
 Lab2: Single Photon Interference Xiaoshu Chen* Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Rochester, NY, 14623 ABSTRACT The wave-particle duality of light was verified by multi and single photon
Lab2: Single Photon Interference Xiaoshu Chen* Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Rochester, NY, 14623 ABSTRACT The wave-particle duality of light was verified by multi and single photon
3 - SYNTHETIC APERTURE RADAR (SAR) SUMMARY David Sandwell, SIO 239, January, 2008
 1 3 - SYNTHETIC APERTURE RADAR (SAR) SUMMARY David Sandwell, SIO 239, January, 2008 Fraunhoffer diffraction To understand why a synthetic aperture in needed for microwave remote sensing from orbital altitude
1 3 - SYNTHETIC APERTURE RADAR (SAR) SUMMARY David Sandwell, SIO 239, January, 2008 Fraunhoffer diffraction To understand why a synthetic aperture in needed for microwave remote sensing from orbital altitude
Dielectric Optical-Controllable Magnifying Lens. by Nonlinear Negative Refraction
 Dielectric Optical-Controllable Magnifying Lens by Nonlinear Negative Refraction Jianjun Cao 1, Ce Shang 2, Yuanlin Zheng 1,Yaming Feng, Xianfeng Chen 1,3, Xiaogan Liang 4 and Wenjie Wan 1,2,3* 1 Key Laboratory
Dielectric Optical-Controllable Magnifying Lens by Nonlinear Negative Refraction Jianjun Cao 1, Ce Shang 2, Yuanlin Zheng 1,Yaming Feng, Xianfeng Chen 1,3, Xiaogan Liang 4 and Wenjie Wan 1,2,3* 1 Key Laboratory
Chapter 24. Wave Optics
 Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Effectiveness Evaluation of Air and Missile Defense System Based on Parametric Diagrams
 5th International Conference on Computer Sciences and Automation Engineering (ICCSAE 205) Effectiveness Evaluation of Air and Missile Defense System Based on Parametric Diagrams Lu Fa, a, Sun Wenhu, b
5th International Conference on Computer Sciences and Automation Engineering (ICCSAE 205) Effectiveness Evaluation of Air and Missile Defense System Based on Parametric Diagrams Lu Fa, a, Sun Wenhu, b
Chapter 33 cont. The Nature of Light and Propagation of Light (lecture 2) Dr. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 33 cont The Nature of Light and Propagation of Light (lecture 2) Dr. Armen Kocharian Polarization of Light Waves The direction of polarization of each individual wave is defined to be the direction
Chapter 33 cont The Nature of Light and Propagation of Light (lecture 2) Dr. Armen Kocharian Polarization of Light Waves The direction of polarization of each individual wave is defined to be the direction
Office Hours. Scattering and Polarization
 Office Hours Office hours are posted on the website. Molly: Tuesdays 2-4pm Dr. Keister: Wednesdays 10am-12 Prof. Goldman: Wednesdays 2-3:30pm All office hours are in the help room downstairs If none of
Office Hours Office hours are posted on the website. Molly: Tuesdays 2-4pm Dr. Keister: Wednesdays 10am-12 Prof. Goldman: Wednesdays 2-3:30pm All office hours are in the help room downstairs If none of
29. Diffraction of waves
 9. Diffraction of waves Light bends! Diffraction assumptions The Kirchhoff diffraction integral Fresnel Diffraction diffraction from a slit Diffraction Light does not always travel in a straight line.
9. Diffraction of waves Light bends! Diffraction assumptions The Kirchhoff diffraction integral Fresnel Diffraction diffraction from a slit Diffraction Light does not always travel in a straight line.
