CS 4731: Computer Graphics Lecture 16: Phong Illumination and Shading. Emmanuel Agu
|
|
|
- Derrick Goodman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CS 4731: Computer Graphics Lecture 16: Phong Illumination and Shading Emmanuel Agu
2 Recall: Setting Light Property Define colors and position a light GLfloat light_ambient[] = {0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0}; GLfloat light_diffuse[] = {1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0}; GLfloat light_specular[] = {1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0}; GLfloat light_position[] = {0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0}; gllightfv(gl_light0, GL_AMBIENT, light_ambient); gllightfv(gl_light0, GL_DIFFUSE, light_diffuse); gllightfv(gl_light0, GL_SPECULAR, light_specular); gllightfv(gl_light0, GL_POSITION, light_position); Position colors What if I set Position to (0,0,1,0)?
3 Recall: Setting Material Example Define ambient/diffuse/specular reflection and shininess GLfloat mat_amb_diff[] = {1.0, 0.5, 0.8, 1.0}; GLfloat mat_specular[] = {1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0}; refl. coeff. GLfloat shininess[] = {5.0}; (range: dull 0 very shiny 128) glmaterialfv(gl_front_and_back, GL_AMBIENT_AND_DIFFUSE, mat_amb_diff); glmaterialfv(gl_front, GL_SPECULAR, mat_speacular); glmaterialfv(gl_front, GL_SHININESS, shininess);
4 Recall: Calculating Color at Vertices Illumination from a light: Illum = ambient + diffuse + specular = Ka x I + Kd x I x (cos θ) + Ks x I x cos(φ) If there are N lights Total illumination for a point P = Σ (Illum) Sometimes light or surfaces are colored Treat R,G and B components separately i.e. can specify different RGB values for either light or material To: n Illum_r = Kar x Ir + Kdr x Ir x (cos θ) + Ksr x Ir x cos(φ) n Illum_g = Kag x Ig + Kdg x Ig x (cos θ) + Ksg x Ig x cos(φ) n Illum_b = Kab x Ib + Kdb x Ib x (cos θ) + Ksb x Ib x cos(φ) n
5 Recall: Calculating Color at Vertices Illum = ambient + diffuse + specular n = Ka x I + Kd x I x (cos θ) + Ks x I x cos(φ) (cos θ) and cos(φ) are calculated as dot products of Light vector L, Normal N, and Mirror direction vector R L θ N V φ R p To give Illum = Ka x I + Kd x I x (N.L) + Ks x I x (R.V) n
6 Surface Normals Correct normals are essential for correct lighting Associate a normal to each vertex glbegin( ) glnormal3f(x,y,z) glvertex3f(x,y,z) glend() The normals you provide need to have a unit length You can use glenable(gl_normalize) to have OpenGL normalize all the normals
7 Lighting revisit Light calculation so far is at vertices Pixel may not fall right on vertex Shading: calculates color to set interior pixel to Where are lighting/shading performed in the pipeline? v1, m1 modeling and viewing per vertex lighting projection v2, m2 v3, m3 Rasterization texturing shading viewport mapping interpolate vertex colors clipping Display
8 Example Shading Function (Pg. 432 of Hill) for(int y = y bott ; y < y top ; y++) { } find x left and x right for(int x = x left ; x < x right ; x++) { find the color c for this pixel put c into the pixel at (x, y) } ytop color4 y4 color3 Scans pixels, row by row, calculating color for each pixel ys ybott xleft color1 color2 xright
9 Polygon shading model Flat shading - compute lighting once and assign the color to the whole (mesh) polygon
10 Flat shading Only use one vertex normaland material property to compute the color for the polygon Benefit: fast to compute Used when: Polygon is small enough Light source is far away (why?) Eye is very far away (why?) OpenGL command: glshademodel(gl_flat)
11 Mach Band Effect Flat shading suffers from mach band effect Mach band effect human eyes accentuate the discontinuity at the boundary perceived intensity Side view of a polygonal surface
12 Smooth shading Fix the mach band effect remove edge discontinuity Compute lighting for more points on each face Flat shading Smooth shading
13 Smooth shading Two popular methods: Gouraud shading (used by OpenGL) Phong shading (better specular highlight, not in OpenGL)
14 Gouraud Shading The smooth shading algorithm used in OpenGL glshademodel(gl_smooth) Lighting is calculated for each of the polygon vertices Colors are interpolated for interior pixels
15 Gouraud Shading Per-vertex lighting calculation Normal is needed for each vertex Per-vertex normal can be computed by averaging the adjust face normals n1 n n2 n3 n4 n = (n1 + n2 + n3 + n4) / 4.0
16 Gouraud Shading Compute vertex illumination (color) before the projection transformation Shade interior pixels: color interpolation (normals are not needed) C1 Ca = lerp(c1, C2) Cb = lerp(c1, C3) for all scanlines C2 C3 Lerp(Ca, Cb) * lerp: linear interpolation
17 Gouraud Shading Linear interpolation v1 a x b v2 x = b / (a+b) * v1 + a/(a+b) * v2 Interpolate triangle color: use y distance to interpolate the two end points in the scanline, and use x distance to interpolate interior pixel colors
18 Gouraud Shading Function (Pg. 433 of Hill) for(int y = y bott ; y < y top ; y++) // for each scan line { find x left and x right } find color left and color right color inc = (color right color left )/ (x right x left ) for(int x = x left, c = color left ; x < x right ; x++, c+ = color inc ) { put c into the pixel at (x, y) }
19 Gouraud Shading Problem Lighting in the polygon interior can be inaccurate
20 Phong Shading Instead of interpolation, we calculate lighting for each pixel inside the polygon (per pixel lighting) Need normals for all the pixels not provided by user Phong shading algorithm interpolates the normals and compute lighting during rasterization (need to map the normal back to world or eye space though)
21 Phong Shading Normal interpolation n1 na = lerp(n1, n2) nb = lerp(n1, n3) n2 lerp(na, nb) Slow not supported by OpenGL and most graphics hardware n3
22 References Hill, chapter 8
Illumination Model. The governing principles for computing the. Apply the lighting model at a set of points across the entire surface.
 Illumination and Shading Illumination (Lighting) Model the interaction of light with surface points to determine their final color and brightness OpenGL computes illumination at vertices illumination Shading
Illumination and Shading Illumination (Lighting) Model the interaction of light with surface points to determine their final color and brightness OpenGL computes illumination at vertices illumination Shading
Illumination and Shading
 Illumination and Shading Illumination (Lighting) Model the interaction of light with surface points to determine their final color and brightness OpenGL computes illumination at vertices illumination Shading
Illumination and Shading Illumination (Lighting) Model the interaction of light with surface points to determine their final color and brightness OpenGL computes illumination at vertices illumination Shading
Illumination and Shading
 Illumination and Shading Illumination (Lighting)! Model the interaction of light with surface points to determine their final color and brightness! The illumination can be computed either at vertices or
Illumination and Shading Illumination (Lighting)! Model the interaction of light with surface points to determine their final color and brightness! The illumination can be computed either at vertices or
CS Computer Graphics: Illumination and Shading I
 CS 543 - Computer Graphics: Illumination and Shading I by Robert W. Lindeman gogo@wpi.edu (with help from Emmanuel Agu ;-) Illumination and Shading Problem: Model light/surface point interactions to determine
CS 543 - Computer Graphics: Illumination and Shading I by Robert W. Lindeman gogo@wpi.edu (with help from Emmanuel Agu ;-) Illumination and Shading Problem: Model light/surface point interactions to determine
CS Computer Graphics: Illumination and Shading I
 CS 543 - Computer Graphics: Illumination and Shading I by Robert W. Lindeman gogo@wpi.edu (with help from Emmanuel Agu ;-) Illumination and Shading Problem: Model light/surface point interactions to determine
CS 543 - Computer Graphics: Illumination and Shading I by Robert W. Lindeman gogo@wpi.edu (with help from Emmanuel Agu ;-) Illumination and Shading Problem: Model light/surface point interactions to determine
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 8a: Per-Vertex lighting, Shading and Per-Fragment lighting
 Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 8a: Per-Vertex lighting, Shading and Per-Fragment lighting Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Computation of Vectors To calculate
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 8a: Per-Vertex lighting, Shading and Per-Fragment lighting Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Computation of Vectors To calculate
Shading and Illumination
 Shading and Illumination OpenGL Shading Without Shading With Shading Physics Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function (BRDF) f r (ω i,ω ) = dl(ω ) L(ω i )cosθ i dω i = dl(ω ) L(ω i )( ω i n)dω
Shading and Illumination OpenGL Shading Without Shading With Shading Physics Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function (BRDF) f r (ω i,ω ) = dl(ω ) L(ω i )cosθ i dω i = dl(ω ) L(ω i )( ω i n)dω
Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 18: Lighting, Shading and Materials (Part 3)
 Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 18: Lighting, Shading and Materials (Part 3) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Recall: Flat Shading compute lighting once
Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 18: Lighting, Shading and Materials (Part 3) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Recall: Flat Shading compute lighting once
Illumination & Shading I
 CS 543: Computer Graphics Illumination & Shading I Robert W. Lindeman Associate Professor Interactive Media & Game Development Department of Computer Science Worcester Polytechnic Institute gogo@wpi.edu
CS 543: Computer Graphics Illumination & Shading I Robert W. Lindeman Associate Professor Interactive Media & Game Development Department of Computer Science Worcester Polytechnic Institute gogo@wpi.edu
5.2 Shading in OpenGL
 Fall 2017 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 5.2 Shading in OpenGL Hao Li http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 Outline Normal Vectors in OpenGL Polygonal Shading Light Sources in OpenGL Material Properties in OpenGL Example:
Fall 2017 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 5.2 Shading in OpenGL Hao Li http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 Outline Normal Vectors in OpenGL Polygonal Shading Light Sources in OpenGL Material Properties in OpenGL Example:
Shading in OpenGL. Outline. Defining and Maintaining Normals. Normalization. Enabling Lighting and Lights. Outline
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 10 Shading in OpenGL Normal Vectors in OpenGL Polygonal Shading Light Source in OpenGL Material Properties in OpenGL Approximating a Sphere [Angel Ch. 6.5-6.9] Jernej
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 10 Shading in OpenGL Normal Vectors in OpenGL Polygonal Shading Light Source in OpenGL Material Properties in OpenGL Approximating a Sphere [Angel Ch. 6.5-6.9] Jernej
Shading , Fall 2004 Nancy Pollard Mark Tomczak
 15-462, Fall 2004 Nancy Pollard Mark Tomczak Shading Shading Concepts Shading Equations Lambertian, Gouraud shading Phong Illumination Model Non-photorealistic rendering [Shirly, Ch. 8] Announcements Written
15-462, Fall 2004 Nancy Pollard Mark Tomczak Shading Shading Concepts Shading Equations Lambertian, Gouraud shading Phong Illumination Model Non-photorealistic rendering [Shirly, Ch. 8] Announcements Written
Methodology for Lecture. Importance of Lighting. Outline. Shading Models. Brief primer on Color. Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2010)
 Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2010) CS 184, Lecture 11: OpenGL 3 http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs184 Methodology for Lecture Lecture deals with lighting (teapot shaded as in HW1) Some Nate
Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2010) CS 184, Lecture 11: OpenGL 3 http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs184 Methodology for Lecture Lecture deals with lighting (teapot shaded as in HW1) Some Nate
Illumination Model. The governing principles for computing the. Apply the lighting model at a set of points across the entire surface.
 Illumination and Shading Illumination (ighting) Model the interaction of light with surface oints to determine their final color and brightness OenG comutes illumination at vertices illumination Shading
Illumination and Shading Illumination (ighting) Model the interaction of light with surface oints to determine their final color and brightness OenG comutes illumination at vertices illumination Shading
CS 148, Summer 2012 Introduction to Computer Graphics and Imaging
 http://www.ann.jussieu.fr/~frey/papers/scivi/cook%20r.l.,%20a%20reflectance%20model%20for%20computer%20graphics.pdf CS 148, Summer 2012 Introduction to Computer Graphics and Imaging f(~v 2 ) A 3 A 1 f(~v
http://www.ann.jussieu.fr/~frey/papers/scivi/cook%20r.l.,%20a%20reflectance%20model%20for%20computer%20graphics.pdf CS 148, Summer 2012 Introduction to Computer Graphics and Imaging f(~v 2 ) A 3 A 1 f(~v
Lecture 17: Shading in OpenGL. CITS3003 Graphics & Animation
 Lecture 17: Shading in OpenGL CITS3003 Graphics & Animation E. Angel and D. Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 6E Addison-Wesley 2012 Objectives Introduce the OpenGL shading methods - per vertex shading
Lecture 17: Shading in OpenGL CITS3003 Graphics & Animation E. Angel and D. Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 6E Addison-Wesley 2012 Objectives Introduce the OpenGL shading methods - per vertex shading
Reading. Shading. An abundance of photons. Introduction. Required: Angel , 6.5, Optional: Angel 6.4 OpenGL red book, chapter 5.
 Reading Required: Angel 6.1-6.3, 6.5, 6.7-6.8 Optional: Shading Angel 6.4 OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 1 2 Introduction An abundance of photons So far, we ve talked exclusively about geometry. Properly
Reading Required: Angel 6.1-6.3, 6.5, 6.7-6.8 Optional: Shading Angel 6.4 OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 1 2 Introduction An abundance of photons So far, we ve talked exclusively about geometry. Properly
CS Illumination and Shading. Slide 1
 CS 112 - Illumination and Shading Slide 1 Illumination/Lighting Interaction between light and surfaces Physics of optics and thermal radiation Very complex: Light bounces off several surface before reaching
CS 112 - Illumination and Shading Slide 1 Illumination/Lighting Interaction between light and surfaces Physics of optics and thermal radiation Very complex: Light bounces off several surface before reaching
Ligh%ng and Shading. Ligh%ng and Shading. q Is this a plate or a ball? q What color should I set for each pixel?
 Ligh%ng and Shading Ligh%ng and Shading Is this a plate or a ball? What color should I set for each pixel? 1 Physical Reality As light hits the surface: Part is absorbed Part is reflected Visible light
Ligh%ng and Shading Ligh%ng and Shading Is this a plate or a ball? What color should I set for each pixel? 1 Physical Reality As light hits the surface: Part is absorbed Part is reflected Visible light
Illumination and Shading
 CT4510: Computer Graphics Illumination and Shading BOCHANG MOON Photorealism The ultimate goal of rendering is to produce photo realistic images. i.e., rendered images should be indistinguishable from
CT4510: Computer Graphics Illumination and Shading BOCHANG MOON Photorealism The ultimate goal of rendering is to produce photo realistic images. i.e., rendered images should be indistinguishable from
OpenGL Lighting Computer Graphics Spring Frank Palermo
 OpenGL Lighting 15-462 Computer Graphics Spring 2009 Frank Palermo OpenGL is just a bunch of hacks. -Adrien Treuille What Adrien Means... What Adrien means is that OpenGL was designed to produce reasonable-looking
OpenGL Lighting 15-462 Computer Graphics Spring 2009 Frank Palermo OpenGL is just a bunch of hacks. -Adrien Treuille What Adrien Means... What Adrien means is that OpenGL was designed to produce reasonable-looking
Objectives Shading in OpenGL. Front and Back Faces. OpenGL shading. Introduce the OpenGL shading methods. Discuss polygonal shading
 Objectives Shading in OpenGL Introduce the OpenGL shading methods - per vertex shading vs per fragment shading - Where to carry out Discuss polygonal shading - Flat - Smooth - Gouraud CITS3003 Graphics
Objectives Shading in OpenGL Introduce the OpenGL shading methods - per vertex shading vs per fragment shading - Where to carry out Discuss polygonal shading - Flat - Smooth - Gouraud CITS3003 Graphics
Rendering. Illumination Model. Wireframe rendering simple, ambiguous Color filling flat without any 3D information
 llumination Model Wireframe rendering simple, ambiguous Color filling flat without any 3D information Requires modeling interaction of light with the object/surface to have a different color (shade in
llumination Model Wireframe rendering simple, ambiguous Color filling flat without any 3D information Requires modeling interaction of light with the object/surface to have a different color (shade in
Lighting. CSC 7443: Scientific Information Visualization
 Lighting Why Lighting? What light source is used and how the object response to the light makes difference Ocean looks bright bluish green in sunny day but dim gray green in cloudy day Lighting gives you
Lighting Why Lighting? What light source is used and how the object response to the light makes difference Ocean looks bright bluish green in sunny day but dim gray green in cloudy day Lighting gives you
Lighting/Shading III. Week 7, Wed Mar 3
 University of British Columbia CPSC 314 Computer Graphics Jan-Apr 2010 Tamara Munzner Lighting/Shading III Week 7, Wed Mar 3 http://www.ugrad.cs.ubc.ca/~cs314/vjan2010 reminders News don't need to tell
University of British Columbia CPSC 314 Computer Graphics Jan-Apr 2010 Tamara Munzner Lighting/Shading III Week 7, Wed Mar 3 http://www.ugrad.cs.ubc.ca/~cs314/vjan2010 reminders News don't need to tell
CS5620 Intro to Computer Graphics
 So Far wireframe hidden surfaces Next step 1 2 Light! Need to understand: How lighting works Types of lights Types of surfaces How shading works Shading algorithms What s Missing? Lighting vs. Shading
So Far wireframe hidden surfaces Next step 1 2 Light! Need to understand: How lighting works Types of lights Types of surfaces How shading works Shading algorithms What s Missing? Lighting vs. Shading
Reading. Shading. Introduction. An abundance of photons. Required: Angel , Optional: OpenGL red book, chapter 5.
 Reading Required: Angel 6.1-6.5, 6.7-6.8 Optional: Shading OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 1 2 Introduction So far, we ve talked exclusively about geometry. What is the shape of an obect? How do I place it
Reading Required: Angel 6.1-6.5, 6.7-6.8 Optional: Shading OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 1 2 Introduction So far, we ve talked exclusively about geometry. What is the shape of an obect? How do I place it
Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 16: Lighting, Shading and Materials (Part 1)
 Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 16: Lighting, Shading and Materials (Part 1) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Why do we need Lighting & shading? Sphere
Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 16: Lighting, Shading and Materials (Part 1) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Why do we need Lighting & shading? Sphere
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 7b: Intro to lighting, Shading and Materials + Phong Lighting Model
 Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 7b: Intro to lighting, Shading and Materials + Phong Lighting Model Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Why do we need Lighting
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 7b: Intro to lighting, Shading and Materials + Phong Lighting Model Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Why do we need Lighting
CS Surface Rendering
 CS10101001 Surface Rendering Junqiao Zhao 赵君峤 Department of Computer Science and Technology College of Electronics and Information Engineering Tongji University Surface rendering How do we choose a color
CS10101001 Surface Rendering Junqiao Zhao 赵君峤 Department of Computer Science and Technology College of Electronics and Information Engineering Tongji University Surface rendering How do we choose a color
Shading Intro. Shading & Lighting. Light and Matter. Light and Matter
 Shading Intro Shading & Lighting Move from flat to 3-D models Orthographic view of sphere was uniformly color, thus, a flat circle A circular shape with many gradations or shades of color Courtesy of Vincent
Shading Intro Shading & Lighting Move from flat to 3-D models Orthographic view of sphere was uniformly color, thus, a flat circle A circular shape with many gradations or shades of color Courtesy of Vincent
Illumination & Shading: Part 1
 Illumination & Shading: Part 1 Light Sources Empirical Illumination Shading Local vs Global Illumination Lecture 10 Comp 236 Spring 2005 Computer Graphics Jargon: Illumination Models Illumination - the
Illumination & Shading: Part 1 Light Sources Empirical Illumination Shading Local vs Global Illumination Lecture 10 Comp 236 Spring 2005 Computer Graphics Jargon: Illumination Models Illumination - the
CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Fall
 Illumination Models and Surface-Rendering Methods CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Fall 2007 2008 Illumination Models and Surface Rendering Methods In order to achieve realism in computer generated
Illumination Models and Surface-Rendering Methods CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Fall 2007 2008 Illumination Models and Surface Rendering Methods In order to achieve realism in computer generated
Projections and Hardware Rendering. Brian Curless CSE 557 Fall 2014
 Projections and Hardware Rendering Brian Curless CSE 557 Fall 2014 1 Reading Required: Shirley, Ch. 7, Sec. 8.2, Ch. 18 Further reading: Foley, et al, Chapter 5.6 and Chapter 6 David F. Rogers and J. Alan
Projections and Hardware Rendering Brian Curless CSE 557 Fall 2014 1 Reading Required: Shirley, Ch. 7, Sec. 8.2, Ch. 18 Further reading: Foley, et al, Chapter 5.6 and Chapter 6 David F. Rogers and J. Alan
Computer Graphics. Illumination and Shading
 () Illumination and Shading Dr. Ayman Eldeib Lighting So given a 3-D triangle and a 3-D viewpoint, we can set the right pixels But what color should those pixels be? If we re attempting to create a realistic
() Illumination and Shading Dr. Ayman Eldeib Lighting So given a 3-D triangle and a 3-D viewpoint, we can set the right pixels But what color should those pixels be? If we re attempting to create a realistic
Illumination and Shading ECE 567
 Illumination and Shading ECE 567 Overview Lighting Models Ambient light Diffuse light Specular light Shading Models Flat shading Gouraud shading Phong shading OpenGL 2 Introduction To add realism to drawings
Illumination and Shading ECE 567 Overview Lighting Models Ambient light Diffuse light Specular light Shading Models Flat shading Gouraud shading Phong shading OpenGL 2 Introduction To add realism to drawings
Illumination and Reflection in OpenGL CS 460/560. Computer Graphics. Shadows. Photo-Realism: Ray Tracing. Binghamton University.
 Binghamton University EngiNet State University of New York EngiNet Thomas J. Watson School of Engineering and Applied Science WARNING All rights reserved. No Part of this video lecture series may be reproduced
Binghamton University EngiNet State University of New York EngiNet Thomas J. Watson School of Engineering and Applied Science WARNING All rights reserved. No Part of this video lecture series may be reproduced
Shading. CSE 457 Winter 2015
 Shading CSE 457 Winter 2015 Reading Required: Angel chapter 5. Optional: OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 2 Basic 3D graphics With affine matrices, we can now transform virtual 3D objects in their local coordinate
Shading CSE 457 Winter 2015 Reading Required: Angel chapter 5. Optional: OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 2 Basic 3D graphics With affine matrices, we can now transform virtual 3D objects in their local coordinate
INF3320 Computer Graphics and Discrete Geometry
 INF3320 Computer Graphics and Discrete Geometry Visual appearance Christopher Dyken and Martin Reimers 23.09.2009 Page 1 Visual appearance Real Time Rendering: Chapter 5 Light Sources and materials Shading
INF3320 Computer Graphics and Discrete Geometry Visual appearance Christopher Dyken and Martin Reimers 23.09.2009 Page 1 Visual appearance Real Time Rendering: Chapter 5 Light Sources and materials Shading
Shading. Brian Curless CSE 457 Spring 2015
 Shading Brian Curless CSE 457 Spring 2015 1 Reading Required: Angel chapter 5. Optional: OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 2 Basic 3D graphics With affine matrices, we can now transform virtual 3D objects in
Shading Brian Curless CSE 457 Spring 2015 1 Reading Required: Angel chapter 5. Optional: OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 2 Basic 3D graphics With affine matrices, we can now transform virtual 3D objects in
CSE 167: Lecture #8: Lighting. Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2011
 CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #8: Lighting Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2011 Announcements Homework project #4 due Friday, October 28 Introduction:
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #8: Lighting Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2011 Announcements Homework project #4 due Friday, October 28 Introduction:
Light Sources. Spotlight model
 lecture 12 Light Sources sunlight (parallel) Sunny day model : "point source at infinity" - lighting - materials: diffuse, specular, ambient spotlight - shading: Flat vs. Gouraud vs Phong light bulb ambient
lecture 12 Light Sources sunlight (parallel) Sunny day model : "point source at infinity" - lighting - materials: diffuse, specular, ambient spotlight - shading: Flat vs. Gouraud vs Phong light bulb ambient
How do we draw a picture?
 1 How do we draw a picture? Define geometry. Now what? We can draw the edges of the faces. Wireframe. We can only draw the edges of faces that are visible. We can fill in the faces. Giving each object
1 How do we draw a picture? Define geometry. Now what? We can draw the edges of the faces. Wireframe. We can only draw the edges of faces that are visible. We can fill in the faces. Giving each object
Light Transport Baoquan Chen 2017
 Light Transport 1 Physics of Light and Color It s all electromagnetic (EM) radiation Different colors correspond to radiation of different wavelengths Intensity of each wavelength specified by amplitude
Light Transport 1 Physics of Light and Color It s all electromagnetic (EM) radiation Different colors correspond to radiation of different wavelengths Intensity of each wavelength specified by amplitude
Pipeline Operations. CS 4620 Lecture 10
 Pipeline Operations CS 4620 Lecture 10 2008 Steve Marschner 1 Hidden surface elimination Goal is to figure out which color to make the pixels based on what s in front of what. Hidden surface elimination
Pipeline Operations CS 4620 Lecture 10 2008 Steve Marschner 1 Hidden surface elimination Goal is to figure out which color to make the pixels based on what s in front of what. Hidden surface elimination
Illumination Models & Shading
 Illumination Models & Shading Lighting vs. Shading Lighting Interaction between materials and light sources Physics Shading Determining the color of a pixel Computer Graphics ZBuffer(Scene) PutColor(x,y,Col(P));
Illumination Models & Shading Lighting vs. Shading Lighting Interaction between materials and light sources Physics Shading Determining the color of a pixel Computer Graphics ZBuffer(Scene) PutColor(x,y,Col(P));
CPSC 314 LIGHTING AND SHADING
 CPSC 314 LIGHTING AND SHADING UGRAD.CS.UBC.CA/~CS314 slide credits: Mikhail Bessmeltsev et al 1 THE RENDERING PIPELINE Vertices and attributes Vertex Shader Modelview transform Per-vertex attributes Vertex
CPSC 314 LIGHTING AND SHADING UGRAD.CS.UBC.CA/~CS314 slide credits: Mikhail Bessmeltsev et al 1 THE RENDERING PIPELINE Vertices and attributes Vertex Shader Modelview transform Per-vertex attributes Vertex
University of British Columbia CPSC 314 Computer Graphics Sep-Dec Tamara Munzner (guest lecturing) Lighting/Shading
 University of British Columbia CPSC 314 Computer Graphics Sep-Dec 2010 Tamara Munzner (guest lecturing) Lighting/Shading Lighting 2 Rendering Pipeline Geometry Database Model/View Transform. Lighting Perspective
University of British Columbia CPSC 314 Computer Graphics Sep-Dec 2010 Tamara Munzner (guest lecturing) Lighting/Shading Lighting 2 Rendering Pipeline Geometry Database Model/View Transform. Lighting Perspective
Phong Lighting & Materials. Some slides modified from: David Kabala Others from: Andries Van Damm, Brown Univ.
 Phong Lighting & Materials Some slides modified from: David Kabala Others from: Andries Van Damm, Brown Univ. Lighting and Shading Lighting, or illumination, is the process of computing the intensity and
Phong Lighting & Materials Some slides modified from: David Kabala Others from: Andries Van Damm, Brown Univ. Lighting and Shading Lighting, or illumination, is the process of computing the intensity and
Today s class. Simple shadows Shading Lighting in OpenGL. Informationsteknologi. Wednesday, November 21, 2007 Computer Graphics - Class 10 1
 Today s class Simple shadows Shading Lighting in OpenGL Wednesday, November 21, 27 Computer Graphics - Class 1 1 Simple shadows Simple shadows can be gotten by using projection matrices Consider a light
Today s class Simple shadows Shading Lighting in OpenGL Wednesday, November 21, 27 Computer Graphics - Class 1 1 Simple shadows Simple shadows can be gotten by using projection matrices Consider a light
Illumination and Shading
 Illumination and Shading Illumination and Shading z Illumination Models y Ambient y Diffuse y Attenuation y Specular Reflection z Interpolated Shading Models y Flat, Gouraud, Phong y Problems CS4451: Fall
Illumination and Shading Illumination and Shading z Illumination Models y Ambient y Diffuse y Attenuation y Specular Reflection z Interpolated Shading Models y Flat, Gouraud, Phong y Problems CS4451: Fall
UNIT 7 LIGHTING AND SHADING. 1. Explain phong lighting model. Indicate the advantages and disadvantages. (Jun2012) 10M
 UNIT 7 LIGHTING AND SHADING 1. Explain phong lighting model. Indicate the advantages and disadvantages. (Jun2012) 10M Ans: Phong developed a simple model that can be computed rapidly It considers three
UNIT 7 LIGHTING AND SHADING 1. Explain phong lighting model. Indicate the advantages and disadvantages. (Jun2012) 10M Ans: Phong developed a simple model that can be computed rapidly It considers three
Illumination and Shading
 Illumination and Shading Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring 2007 Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 2/14/07 1 From last time Texture mapping overview notation wrapping Perspective-correct interpolation Texture
Illumination and Shading Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring 2007 Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 2/14/07 1 From last time Texture mapping overview notation wrapping Perspective-correct interpolation Texture
CPSC / Illumination and Shading
 CPSC 599.64 / 601.64 Rendering Pipeline usually in one step modelling of geometry transformation into world coordinate system placement of cameras and light sources transformation into camera coordinate
CPSC 599.64 / 601.64 Rendering Pipeline usually in one step modelling of geometry transformation into world coordinate system placement of cameras and light sources transformation into camera coordinate
Lighting/Shading II. Week 7, Mon Mar 1
 University of British Columbia CPSC 314 Computer Graphics Jan-Apr 2010 Tamara Munzner Lighting/Shading II Week 7, Mon Mar 1 http://www.ugrad.cs.ubc.ca/~cs314/vjan2010 News Homework 3 out today Homework
University of British Columbia CPSC 314 Computer Graphics Jan-Apr 2010 Tamara Munzner Lighting/Shading II Week 7, Mon Mar 1 http://www.ugrad.cs.ubc.ca/~cs314/vjan2010 News Homework 3 out today Homework
OpenGl Pipeline. triangles, lines, points, images. Per-vertex ops. Primitive assembly. Texturing. Rasterization. Per-fragment ops.
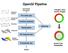 OpenGl Pipeline Individual Vertices Transformed Vertices Commands Processor Per-vertex ops Primitive assembly triangles, lines, points, images Primitives Fragments Rasterization Texturing Per-fragment
OpenGl Pipeline Individual Vertices Transformed Vertices Commands Processor Per-vertex ops Primitive assembly triangles, lines, points, images Primitives Fragments Rasterization Texturing Per-fragment
LIGHTING AND SHADING
 DH2323 DGI15 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER GRAPHICS AND INTERACTION LIGHTING AND SHADING Christopher Peters HPCViz, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden chpeters@kth.se http://kth.academia.edu/christopheredwardpeters
DH2323 DGI15 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER GRAPHICS AND INTERACTION LIGHTING AND SHADING Christopher Peters HPCViz, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden chpeters@kth.se http://kth.academia.edu/christopheredwardpeters
Ambient reflection. Jacobs University Visualization and Computer Graphics Lab : Graphics and Visualization 407
 Ambient reflection Phong reflection is a local illumination model. It only considers the reflection of light that directly comes from the light source. It does not compute secondary reflection of light
Ambient reflection Phong reflection is a local illumination model. It only considers the reflection of light that directly comes from the light source. It does not compute secondary reflection of light
Overview. Shading. Shading. Why we need shading. Shading Light-material interactions Phong model Shading polygons Shading in OpenGL
 Overview Shading Shading Light-material interactions Phong model Shading polygons Shading in OpenGL Why we need shading Suppose we build a model of a sphere using many polygons and color it with glcolor.
Overview Shading Shading Light-material interactions Phong model Shading polygons Shading in OpenGL Why we need shading Suppose we build a model of a sphere using many polygons and color it with glcolor.
w Foley, Section16.1 Reading
 Shading w Foley, Section16.1 Reading Introduction So far, we ve talked exclusively about geometry. w What is the shape of an object? w How do I place it in a virtual 3D space? w How do I know which pixels
Shading w Foley, Section16.1 Reading Introduction So far, we ve talked exclusively about geometry. w What is the shape of an object? w How do I place it in a virtual 3D space? w How do I know which pixels
Reflection and Shading
 Reflection and Shading R. J. Renka Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of North Texas 10/19/2015 Light Sources Realistic rendering requires that we model the interaction between light
Reflection and Shading R. J. Renka Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of North Texas 10/19/2015 Light Sources Realistic rendering requires that we model the interaction between light
Visualisatie BMT. Rendering. Arjan Kok
 Visualisatie BMT Rendering Arjan Kok a.j.f.kok@tue.nl 1 Lecture overview Color Rendering Illumination 2 Visualization pipeline Raw Data Data Enrichment/Enhancement Derived Data Visualization Mapping Abstract
Visualisatie BMT Rendering Arjan Kok a.j.f.kok@tue.nl 1 Lecture overview Color Rendering Illumination 2 Visualization pipeline Raw Data Data Enrichment/Enhancement Derived Data Visualization Mapping Abstract
Computer Graphics. Shading. Based on slides by Dianna Xu, Bryn Mawr College
 Computer Graphics Shading Based on slides by Dianna Xu, Bryn Mawr College Image Synthesis and Shading Perception of 3D Objects Displays almost always 2 dimensional. Depth cues needed to restore the third
Computer Graphics Shading Based on slides by Dianna Xu, Bryn Mawr College Image Synthesis and Shading Perception of 3D Objects Displays almost always 2 dimensional. Depth cues needed to restore the third
Computer Graphics. Illumination and Shading
 Rendering Pipeline modelling of geometry transformation into world coordinates placement of cameras and light sources transformation into camera coordinates backface culling projection clipping w.r.t.
Rendering Pipeline modelling of geometry transformation into world coordinates placement of cameras and light sources transformation into camera coordinates backface culling projection clipping w.r.t.
Three-Dimensional Graphics V. Guoying Zhao 1 / 55
 Computer Graphics Three-Dimensional Graphics V Guoying Zhao 1 / 55 Shading Guoying Zhao 2 / 55 Objectives Learn to shade objects so their images appear three-dimensional Introduce the types of light-material
Computer Graphics Three-Dimensional Graphics V Guoying Zhao 1 / 55 Shading Guoying Zhao 2 / 55 Objectives Learn to shade objects so their images appear three-dimensional Introduce the types of light-material
Shading. Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller. Machiraju/Zhang/Möller/Fuhrmann
 Shading Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Machiraju/Zhang/Möller/Fuhrmann Reading Chapter 5.5 - Angel Chapter 6.3 - Hughes, van Dam, et al Machiraju/Zhang/Möller/Fuhrmann 2 Shading Illumination
Shading Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Machiraju/Zhang/Möller/Fuhrmann Reading Chapter 5.5 - Angel Chapter 6.3 - Hughes, van Dam, et al Machiraju/Zhang/Möller/Fuhrmann 2 Shading Illumination
Why we need shading?
 Why we need shading? Suppose we build a model of a sphere using many polygons and color it with glcolor. We get something like But we want Light-material interactions cause each point to have a different
Why we need shading? Suppose we build a model of a sphere using many polygons and color it with glcolor. We get something like But we want Light-material interactions cause each point to have a different
Pipeline Operations. CS 4620 Lecture Steve Marschner. Cornell CS4620 Spring 2018 Lecture 11
 Pipeline Operations CS 4620 Lecture 11 1 Pipeline you are here APPLICATION COMMAND STREAM 3D transformations; shading VERTEX PROCESSING TRANSFORMED GEOMETRY conversion of primitives to pixels RASTERIZATION
Pipeline Operations CS 4620 Lecture 11 1 Pipeline you are here APPLICATION COMMAND STREAM 3D transformations; shading VERTEX PROCESSING TRANSFORMED GEOMETRY conversion of primitives to pixels RASTERIZATION
ECS 175 COMPUTER GRAPHICS. Ken Joy.! Winter 2014
 ECS 175 COMPUTER GRAPHICS Ken Joy Winter 2014 Shading To be able to model shading, we simplify Uniform Media no scattering of light Opaque Objects No Interreflection Point Light Sources RGB Color (eliminating
ECS 175 COMPUTER GRAPHICS Ken Joy Winter 2014 Shading To be able to model shading, we simplify Uniform Media no scattering of light Opaque Objects No Interreflection Point Light Sources RGB Color (eliminating
CS 325 Computer Graphics
 CS 325 Computer Graphics 04 / 02 / 2012 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Illumination modelling Ambient, Diffuse, Specular Reflection Surface Rendering / Shading models Flat
CS 325 Computer Graphics 04 / 02 / 2012 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Illumination modelling Ambient, Diffuse, Specular Reflection Surface Rendering / Shading models Flat
Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 )
 CS380: Computer Graphics Illumination and Shading Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL: http://sglab.kaist.ac.kr/~sungeui/cg/ Course Objectives (Ch. 10) Know how to consider lights during rendering models
CS380: Computer Graphics Illumination and Shading Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL: http://sglab.kaist.ac.kr/~sungeui/cg/ Course Objectives (Ch. 10) Know how to consider lights during rendering models
9. Illumination and Shading
 9. Illumination and Shading Approaches for visual realism: - Remove hidden surfaces - Shade visible surfaces and reproduce shadows - Reproduce surface properties Texture Degree of transparency Roughness,
9. Illumination and Shading Approaches for visual realism: - Remove hidden surfaces - Shade visible surfaces and reproduce shadows - Reproduce surface properties Texture Degree of transparency Roughness,
Introduction to Computer Graphics. Farhana Bandukwala, PhD Lecture 14: Light Interacting with Surfaces
 Introduction to Computer Graphics Farhana Bandukwala, PhD Lecture 14: Light Interacting with Surfaces Outline Computational tools Reflection models Polygon shading Computation tools Surface normals Vector
Introduction to Computer Graphics Farhana Bandukwala, PhD Lecture 14: Light Interacting with Surfaces Outline Computational tools Reflection models Polygon shading Computation tools Surface normals Vector
Illumination Models and Surface-Rendering Methods. Chapter 10
 Illumination Models and Surface-Rendering Methods Chapter 10 Illumination and Surface- Rendering Given scene specifications object positions, optical properties of the surface, viewer position, viewing
Illumination Models and Surface-Rendering Methods Chapter 10 Illumination and Surface- Rendering Given scene specifications object positions, optical properties of the surface, viewer position, viewing
Pipeline Operations. CS 4620 Lecture 14
 Pipeline Operations CS 4620 Lecture 14 2014 Steve Marschner 1 Pipeline you are here APPLICATION COMMAND STREAM 3D transformations; shading VERTEX PROCESSING TRANSFORMED GEOMETRY conversion of primitives
Pipeline Operations CS 4620 Lecture 14 2014 Steve Marschner 1 Pipeline you are here APPLICATION COMMAND STREAM 3D transformations; shading VERTEX PROCESSING TRANSFORMED GEOMETRY conversion of primitives
Lecture 4 Advanced Computer Graphics (CS & SE )
 Lecture 4 Advanced Computer Graphics (CS & SE 233.420) Topics Covered Animation Matrices Viewing Lighting Animating Interactive Programs Consider planet.c Want to animate rotating the Earth around the
Lecture 4 Advanced Computer Graphics (CS & SE 233.420) Topics Covered Animation Matrices Viewing Lighting Animating Interactive Programs Consider planet.c Want to animate rotating the Earth around the
Painter s HSR Algorithm
 Painter s HSR Algorithm Render polygons farthest to nearest Similar to painter layers oil paint Viewer sees B behind A Render B then A Depth Sort Requires sorting polygons (based on depth) O(n log n) complexity
Painter s HSR Algorithm Render polygons farthest to nearest Similar to painter layers oil paint Viewer sees B behind A Render B then A Depth Sort Requires sorting polygons (based on depth) O(n log n) complexity
CS 130 Final. Fall 2015
 CS 130 Final Fall 2015 Name Student ID Signature You may not ask any questions during the test. If you believe that there is something wrong with a question, write down what you think the question is trying
CS 130 Final Fall 2015 Name Student ID Signature You may not ask any questions during the test. If you believe that there is something wrong with a question, write down what you think the question is trying
Illumination & Shading
 Illumination & Shading Light Sources Empirical Illumination Shading Lecture 15 CISC440/640 Spring 2015 Illumination Models Computer Graphics Jargon: Illumination - the transport luminous flux from light
Illumination & Shading Light Sources Empirical Illumination Shading Lecture 15 CISC440/640 Spring 2015 Illumination Models Computer Graphics Jargon: Illumination - the transport luminous flux from light
Given: scene specification (object positions, optical properties p of the surface, viewer position, viewing direction, )
 Illumination and Shading Illumination and Shading Given: scene specification (object positions, optical properties p of the surface, viewer position, viewing direction, ) Find: intensity for each pixel
Illumination and Shading Illumination and Shading Given: scene specification (object positions, optical properties p of the surface, viewer position, viewing direction, ) Find: intensity for each pixel
Lighting and Shading II. Angel and Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 7E Addison-Wesley 2015
 Lighting and Shading II 1 Objectives Continue discussion of shading Introduce modified Phong model Consider computation of required vectors 2 Ambient Light Ambient light is the result of multiple interactions
Lighting and Shading II 1 Objectives Continue discussion of shading Introduce modified Phong model Consider computation of required vectors 2 Ambient Light Ambient light is the result of multiple interactions
Surface Rendering Methods
 Surface Rendering Methods 6 th Week, 2008 Sun-Jeong Kim Polygon Rendering Methods Determining the surface intensity at every projected pixel position using an illumination model Light-material interactions
Surface Rendering Methods 6 th Week, 2008 Sun-Jeong Kim Polygon Rendering Methods Determining the surface intensity at every projected pixel position using an illumination model Light-material interactions
Virtual Reality for Human Computer Interaction
 Virtual Reality for Human Computer Interaction Appearance: Lighting Representation of Light and Color Representation of Light and Color Do we need to represent all I! to represent a color C(I)? Representation
Virtual Reality for Human Computer Interaction Appearance: Lighting Representation of Light and Color Representation of Light and Color Do we need to represent all I! to represent a color C(I)? Representation
Illumination and Shading with GLSL/WebGL
 Illumination and Shading with GLSL/WebGL Illumination with Shaders! Remember the local illumination model (Phong illumination) Illumination = ambient + diffuse + specular = Ka x Ia + Kd x Id x (N.L) +
Illumination and Shading with GLSL/WebGL Illumination with Shaders! Remember the local illumination model (Phong illumination) Illumination = ambient + diffuse + specular = Ka x Ia + Kd x Id x (N.L) +
Shading Algorithms. Ron Goldman Department of Computer Science Rice University
 Shading Algorithms Ron Goldman Department of Computer Science Rice University Illumination and Shading Standard Assumptions Curved surfaces are approximated by planar polygons. All light sources are point
Shading Algorithms Ron Goldman Department of Computer Science Rice University Illumination and Shading Standard Assumptions Curved surfaces are approximated by planar polygons. All light sources are point
Local Illumination physics. Law of reflection and Snell s law of refraction
 Local Illumination physics Law of reflection and Snell s law of refraction What are we trying to model? Surface Proof of Lambert s cosine law n db da Computing R All vectors unit length!! The effect
Local Illumination physics Law of reflection and Snell s law of refraction What are we trying to model? Surface Proof of Lambert s cosine law n db da Computing R All vectors unit length!! The effect
Objectives. Introduce the OpenGL shading Methods 1) Light and material functions on MV.js 2) per vertex vs per fragment shading 3) Where to carry out
 Objectives Introduce the OpenGL shading Methods 1) Light and material functions on MV.js 2) per vertex vs per fragment shading 3) Where to carry out 1 Steps in OpenGL shading Enable shading and select
Objectives Introduce the OpenGL shading Methods 1) Light and material functions on MV.js 2) per vertex vs per fragment shading 3) Where to carry out 1 Steps in OpenGL shading Enable shading and select
TSBK 07! Computer Graphics! Ingemar Ragnemalm, ISY
 1(84) Information Coding / Computer Graphics, ISY, LiTH TSBK 07 Computer Graphics Ingemar Ragnemalm, ISY 1(84) Lecture 5 3D graphics part 3 Illumination Illumination applied: Shading Surface detail: Mappings
1(84) Information Coding / Computer Graphics, ISY, LiTH TSBK 07 Computer Graphics Ingemar Ragnemalm, ISY 1(84) Lecture 5 3D graphics part 3 Illumination Illumination applied: Shading Surface detail: Mappings
Mach band effect. The Mach band effect increases the visual unpleasant representation of curved surface using flat shading.
 Mach band effect The Mach band effect increases the visual unpleasant representation of curved surface using flat shading. A B 320322: Graphics and Visualization 456 Mach band effect The Mach band effect
Mach band effect The Mach band effect increases the visual unpleasant representation of curved surface using flat shading. A B 320322: Graphics and Visualization 456 Mach band effect The Mach band effect
CS770/870 Spring 2017 Color and Shading
 Preview CS770/870 Spring 2017 Color and Shading Related material Cunningham: Ch 5 Hill and Kelley: Ch. 8 Angel 5e: 6.1-6.8 Angel 6e: 5.1-5.5 Making the scene more realistic Color models representing the
Preview CS770/870 Spring 2017 Color and Shading Related material Cunningham: Ch 5 Hill and Kelley: Ch. 8 Angel 5e: 6.1-6.8 Angel 6e: 5.1-5.5 Making the scene more realistic Color models representing the
Objectives. Introduce Phong model Introduce modified Phong model Consider computation of required vectors Discuss polygonal shading.
 Shading II 1 Objectives Introduce Phong model Introduce modified Phong model Consider computation of required vectors Discuss polygonal shading Flat Smooth Gouraud 2 Phong Lighting Model A simple model
Shading II 1 Objectives Introduce Phong model Introduce modified Phong model Consider computation of required vectors Discuss polygonal shading Flat Smooth Gouraud 2 Phong Lighting Model A simple model
Chapter 7 - Light, Materials, Appearance
 Chapter 7 - Light, Materials, Appearance Types of light in nature and in CG Shadows Using lights in CG Illumination models Textures and maps Procedural surface descriptions Literature: E. Angel/D. Shreiner,
Chapter 7 - Light, Materials, Appearance Types of light in nature and in CG Shadows Using lights in CG Illumination models Textures and maps Procedural surface descriptions Literature: E. Angel/D. Shreiner,
7: Rendering (1) COMP Computer Graphics and Image Processing. Local illumination model. Global illumination model. Direct Direct.
 COMP27112 Computer Graphics and Image Processing 7: Rendering (1) Toby.Howard@manchester.ac.uk Local and global illumination Direct Direct Direct Direct Indirect Local illumination model Global illumination
COMP27112 Computer Graphics and Image Processing 7: Rendering (1) Toby.Howard@manchester.ac.uk Local and global illumination Direct Direct Direct Direct Indirect Local illumination model Global illumination
Shading/Texturing. Dr. Scott Schaefer
 Shading/Texturing Dr. Scott Schaefer Problem / Problem / Problem 4/ Problem / Problem / Shading Algorithms Flat Shading Gouraud Shading Phong Shading / Flat Shading Apply same color across entire polygon
Shading/Texturing Dr. Scott Schaefer Problem / Problem / Problem 4/ Problem / Problem / Shading Algorithms Flat Shading Gouraud Shading Phong Shading / Flat Shading Apply same color across entire polygon
 Fundamentals of Computer Graphics Lecture 7 Visual realism Part 1: Lighting and rendering Yong-Jin Liu liuyongjin@tsinghua.edu.cn Material by S.M.Lea (UNC) Visual Realism Requirements Light Sources Materials
Fundamentals of Computer Graphics Lecture 7 Visual realism Part 1: Lighting and rendering Yong-Jin Liu liuyongjin@tsinghua.edu.cn Material by S.M.Lea (UNC) Visual Realism Requirements Light Sources Materials
Lets assume each object has a defined colour. Hence our illumination model is looks unrealistic.
 Shading Models There are two main types of rendering that we cover, polygon rendering ray tracing Polygon rendering is used to apply illumination models to polygons, whereas ray tracing applies to arbitrary
Shading Models There are two main types of rendering that we cover, polygon rendering ray tracing Polygon rendering is used to apply illumination models to polygons, whereas ray tracing applies to arbitrary
Recollection. Models Pixels. Model transformation Viewport transformation Clipping Rasterization Texturing + Lights & shadows
 Recollection Models Pixels Model transformation Viewport transformation Clipping Rasterization Texturing + Lights & shadows Can be computed in different stages 1 So far we came to Geometry model 3 Surface
Recollection Models Pixels Model transformation Viewport transformation Clipping Rasterization Texturing + Lights & shadows Can be computed in different stages 1 So far we came to Geometry model 3 Surface
Outline. Other Graphics Technology. OpenGL Background and History. Platform Specifics. The Drawing Process
 Outline 433-380 Graphics and Computation Introduction to OpenGL OpenGL Background and History Other Graphics Technology Drawing Viewing and Transformation Lighting GLUT Resources Some images in these slides
Outline 433-380 Graphics and Computation Introduction to OpenGL OpenGL Background and History Other Graphics Technology Drawing Viewing and Transformation Lighting GLUT Resources Some images in these slides
Graphics and Computation Introduction to OpenGL
 433-380 Graphics and Computation Introduction to OpenGL Some images in these slides are taken from The OpenGL Programming Manual, which is copyright Addison Wesley and the OpenGL Architecture Review Board.
433-380 Graphics and Computation Introduction to OpenGL Some images in these slides are taken from The OpenGL Programming Manual, which is copyright Addison Wesley and the OpenGL Architecture Review Board.
Illumination and Shading
 llumination and Shading llumination and Shading Given: scene specification (object positions, optical properties of the surface, viewer position, viewing direction, ) Find: intensity for each pixel viewer
llumination and Shading llumination and Shading Given: scene specification (object positions, optical properties of the surface, viewer position, viewing direction, ) Find: intensity for each pixel viewer
