Influence of the edge subdivision on the convex domination number
|
|
|
- Derek Scott
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Influence of the edge subdivision on the convex domination number Magda Dettlaff, Magdalena Lemańska Faculty of Applied Physics and Mathematics, Gdansk University of Technology, Poland September 18-23, 2011, Szklarska Poreba
2 Basic definitions Domination number
3 Basic definitions Domination number A set D V is a dominating set of G if N G [D] = V.
4 Basic definitions Domination number A set D V is a dominating set of G if N G [D] = V. The domination number of G, denoted γ(g), is the minimum cardinality of a dominating set in G.
5 Basic definitions Domination number A set D V is a dominating set of G if N G [D] = V. The domination number of G, denoted γ(g), is the minimum cardinality of a dominating set in G. Geodesic path
6 Basic definitions Domination number A set D V is a dominating set of G if N G [D] = V. The domination number of G, denoted γ(g), is the minimum cardinality of a dominating set in G. Geodesic path The distance d G (u, v) between two vertices u and v in a connected graph G is the length of the shortest (u v) path in G.
7 Basic definitions Domination number A set D V is a dominating set of G if N G [D] = V. The domination number of G, denoted γ(g), is the minimum cardinality of a dominating set in G. Geodesic path The distance d G (u, v) between two vertices u and v in a connected graph G is the length of the shortest (u v) path in G. A (u v) path of length d G (u, v) is called (u v)-geodesic.
8 Convex domination number Definition
9 Convex domination number Definition A set X is convex in G if vertices from all (a b)-geodesics belong to X for every two vertices a, b X.
10 Convex domination number Definition A set X is convex in G if vertices from all (a b)-geodesics belong to X for every two vertices a, b X. A set X is a convex dominating set if it is convex and dominating.
11 Convex domination number Definition A set X is convex in G if vertices from all (a b)-geodesics belong to X for every two vertices a, b X. A set X is a convex dominating set if it is convex and dominating. The convex domination number γ con(g) of a graph G is the minimum cardinality of a convex dominating set.
12 Convex domination number Definition A set X is convex in G if vertices from all (a b)-geodesics belong to X for every two vertices a, b X. A set X is a convex dominating set if it is convex and dominating. The convex domination number γ con(g) of a graph G is the minimum cardinality of a convex dominating set. The convex domination number was first introduced by Jerzy Topp, (2002) and studied in [1], [3], [4].
13 Example Example Figure: Graph G.
14 Edge subdivision Edge subdivision
15 Edge subdivision Edge subdivision The subdivision of some edge e = uv in a graph G yields to a graph containing one new vertex w, and with an edge set replacing e by two new edges with endpoints uw and wv.
16 Edge subdivision Edge subdivision The subdivision of some edge e = uv in a graph G yields to a graph containing one new vertex w, and with an edge set replacing e by two new edges with endpoints uw and wv. We denote by G uv or G e graph obtained from a graph G by subdivision of an edge e = uv in G.
17 Theorem 1
18 Theorem 1 The difference between γ con(g) and γ con(g uv ) and between γ con(g uv ) and γ con(g) can be arbitrarily large.
19 Theorem 1 The difference between γ con(g) and γ con(g uv ) and between γ con(g uv ) and γ con(g) can be arbitrarily large. Firstly we show that γ con(g uv ) γ con(g) can be arbitrarily large. We show that for any positive integer k there exists a graph G such that γ con(g uv ) γ con(g) = k.
20 Theorem 1 The difference between γ con(g) and γ con(g uv ) and between γ con(g uv ) and γ con(g) can be arbitrarily large. Firstly we show that γ con(g uv ) γ con(g) can be arbitrarily large. We show that for any positive integer k there exists a graph G such that γ con(g uv ) γ con(g) = k. Secondly we show that the difference γ con(g) γ con(g uv ) can be arbitrarily large. We show that for any positive integer k there exists a graph G such that γ con(g) γ con(g uv ) = k.
21 First case Exemple u v u v Figure: Graphs G and G uv for k = 4.
22 Second case Example v 2 u v 1 w 1 w 2 v 3 w 3 z v 2 u v 1 w w 1 w 2 v 3 w 3 z Figure: Graphs G and G uw1 for k = 3.
23 Unicyclic graphs and trees
24 Unicyclic graphs and trees Observation 1 If G is an unicyclic graph with the unique cycle C and if D is a minimum convex dominating set of G, then at most two vertices of C does not belong to D.
25 Unicyclic graphs and trees Observation 1 If G is an unicyclic graph with the unique cycle C and if D is a minimum convex dominating set of G, then at most two vertices of C does not belong to D. Theorem 2 If G is an unicyclic graph with the unique cycle C, then γ con(g) γ con(g uv ) γ con(g) + 3.
26 Unicyclic graphs and trees Corollary 3 Let G be a unicyclic graph with the only cycle C and let D be a minimum convex dominating set of G. If e is not a cyclic edge, then γ con(g e) = γ con(g) + 1; If V (C) D, then for every edge e E(G) we obtain γ con(g e) = γ con(g) + 1; If there is v V (C) such that v D, then C = C 3 or C = C 4 or C = C 5 : If C = C 3 and V (C) D = 1, then for every edge e E(G) we obtain γ con(g e) = γ con(g) + 1. If V (C) D = 2, let us say x, y, z V (C) and x, y D, then γ con(g e) = γ con(g) + 1 for e = xy and γ con(g e) = γ con(g) for e = xz and e = yz; If C = C 4, then V (C) D = 2 and for every edge e E(G) we obtain γ con(g e) = γ con(g) + 1; If C = C 5, then V (C) D = 3 and for every edge e V (C) we obtain γ con(g e) = γ con(g) + 3.
27 The convex domination number increases after subdividing an edge by exactly one.
28 The convex domination number increases after subdividing an edge by exactly one. Proposition 4 If T is a tree of order at least three, then for every edge of T is γ con(t uv ) = γ con(t ) + 1.
29 The convex domination number increases after subdividing an edge by exactly one. Proposition 4 If T is a tree of order at least three, then for every edge of T is γ con(t uv ) = γ con(t ) + 1. Observation 2 Let G be a connected graph with δ(g) = 1 and let u be an end-vertex of G which is adjacent to v. Then γ con(g uv ) = γ con(g) + 1.
30 The convex domination number increases after subdividing an edge by exactly one. Proposition 4 If T is a tree of order at least three, then for every edge of T is γ con(t uv ) = γ con(t ) + 1. Observation 2 Let G be a connected graph with δ(g) = 1 and let u be an end-vertex of G which is adjacent to v. Then γ con(g uv ) = γ con(g) + 1. Observation 3 Let G be a connected graph with (G) = n(g) 1. Then γ con(g uv ) = γ con(g) + 1 for any edge uv E(G).
31 The convex domination number increases after subdividing an edge by exactly one. Proposition 4 If T is a tree of order at least three, then for every edge of T is γ con(t uv ) = γ con(t ) + 1. Observation 2 Let G be a connected graph with δ(g) = 1 and let u be an end-vertex of G which is adjacent to v. Then γ con(g uv ) = γ con(g) + 1. Observation 3 Let G be a connected graph with (G) = n(g) 1. Then γ con(g uv ) = γ con(g) + 1 for any edge uv E(G). Theorem 5 [1] If G is a connected graph with δ(g) 2 and g(g) 6, then γ con(g) = n(g).
32 The convex domination number increases after subdividing an edge by exactly one. Proposition 4 If T is a tree of order at least three, then for every edge of T is γ con(t uv ) = γ con(t ) + 1. Observation 2 Let G be a connected graph with δ(g) = 1 and let u be an end-vertex of G which is adjacent to v. Then γ con(g uv ) = γ con(g) + 1. Observation 3 Let G be a connected graph with (G) = n(g) 1. Then γ con(g uv ) = γ con(g) + 1 for any edge uv E(G). Theorem 5 [1] If G is a connected graph with δ(g) 2 and g(g) 6, then γ con(g) = n(g). Corollary 6 If G is a connected graph with δ(g) 2 and g(g) 6, then γ con(g uv ) = γ con(g) + 1 for any edge uv E(G).
33 The convex domination number increases after subdividing an edge by exactly one.
34 The convex domination number increases after subdividing an edge by exactly one. Theorem 7 If G is a connected graph with g(g) 6, then γ con(g) = n(g) n 1 (G).
35 The convex domination number increases after subdividing an edge by exactly one. Theorem 7 If G is a connected graph with g(g) 6, then γ con(g) = n(g) n 1 (G). Corollary 8 If g(g) 6, then γ con(g uv ) = γ con(g) + 1 for any edge uv E(G).
36 Lemma
37 Lemma Lemma 9 For any integer number k 3 there exists a graph G such that for any edge e E(G) we have γ con(g e) = γ con(g) + k.
38 Lemma Lemma 9 For any integer number k 3 there exists a graph G such that for any edge e E(G) we have γ con(g e) = γ con(g) + k. Construction u 1 u 2 u 3 u 4 u k 3 u k 2 u k 1 v 1 v 2 v 3 v 4 v k 3 v k 2 v k 1 v k Figure: Graph H k
39 Construction
40 Construction Graph G k w 1 w 2 w 3
41 Summary
42 Summary We give the examples of graphs for which for any edge e is γ con(g e) = γ con(g) + k for k = 1 or k 3. The existence of graphs G for which for any edge e is γ con(g e) = γ con(g) + k where k < 1 or k = 0 or k = 2 remains as an open problem.
43 Summary We give the examples of graphs for which for any edge e is γ con(g e) = γ con(g) + k for k = 1 or k 3. The existence of graphs G for which for any edge e is γ con(g e) = γ con(g) + k where k < 1 or k = 0 or k = 2 remains as an open problem. γ con(g e) = γ con(g) 1 for any edge e G Figure: Graph G
44 References 1. J. Cyman, M. Lemanska, J. Raczek, Graphs with convex domination number close to their order, Disscusioness Mathematicae Graph Theory 26 (2006). 2. T.Haynes, S.Hedetniemi, P.Slater, Fundamentals of domination in graphs, Marcel Dekker, Inc. (1998). 3. M. Lemańska, Weakly convex and convex domination numbers, Opuscula Mathematica 24/2 (2004), J. Raczek, NP-completeness of weakly convex and convex dominating set decision problems, Opuscula Mathematica 24 (2004),
Influence of edge subdivision on the convex domination number
 AUSTRALASIAN JOURNAL OF COMBINATORICS Volume 53 (2012), Pages 19 30 Influence of edge subdivision on the convex domination number Magda Dettlaff Magdalena Lemańska Department of Technical Physics and Applied
AUSTRALASIAN JOURNAL OF COMBINATORICS Volume 53 (2012), Pages 19 30 Influence of edge subdivision on the convex domination number Magda Dettlaff Magdalena Lemańska Department of Technical Physics and Applied
GEODETIC DOMINATION IN GRAPHS
 GEODETIC DOMINATION IN GRAPHS H. Escuadro 1, R. Gera 2, A. Hansberg, N. Jafari Rad 4, and L. Volkmann 1 Department of Mathematics, Juniata College Huntingdon, PA 16652; escuadro@juniata.edu 2 Department
GEODETIC DOMINATION IN GRAPHS H. Escuadro 1, R. Gera 2, A. Hansberg, N. Jafari Rad 4, and L. Volkmann 1 Department of Mathematics, Juniata College Huntingdon, PA 16652; escuadro@juniata.edu 2 Department
Rainbow game domination subdivision number of a graph
 Rainbow game domination subdivision number of a graph J. Amjadi Department of Mathematics Azarbaijan Shahid Madani University Tabriz, I.R. Iran j-amjadi@azaruniv.edu Abstract The rainbow game domination
Rainbow game domination subdivision number of a graph J. Amjadi Department of Mathematics Azarbaijan Shahid Madani University Tabriz, I.R. Iran j-amjadi@azaruniv.edu Abstract The rainbow game domination
Outer-2-independent domination in graphs
 Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Math. Sci.) Vol. 126, No. 1, February 2016, pp. 11 20. c Indian Academy of Sciences Outer-2-independent domination in graphs MARCIN KRZYWKOWSKI 1,2,, DOOST ALI MOJDEH 3 and MARYEM
Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Math. Sci.) Vol. 126, No. 1, February 2016, pp. 11 20. c Indian Academy of Sciences Outer-2-independent domination in graphs MARCIN KRZYWKOWSKI 1,2,, DOOST ALI MOJDEH 3 and MARYEM
A note on isolate domination
 Electronic Journal of Graph Theory and Applications 4 (1) (016), 94 100 A note on isolate domination I. Sahul Hamid a, S. Balamurugan b, A. Navaneethakrishnan c a Department of Mathematics, The Madura
Electronic Journal of Graph Theory and Applications 4 (1) (016), 94 100 A note on isolate domination I. Sahul Hamid a, S. Balamurugan b, A. Navaneethakrishnan c a Department of Mathematics, The Madura
Roman Domination in Complementary Prism Graphs
 International J.Math. Combin. Vol.2(2012), 24-31 Roman Domination in Complementary Prism Graphs B.Chaluvaraju and V.Chaitra 1(Department of Mathematics, Bangalore University, Central College Campus, Bangalore
International J.Math. Combin. Vol.2(2012), 24-31 Roman Domination in Complementary Prism Graphs B.Chaluvaraju and V.Chaitra 1(Department of Mathematics, Bangalore University, Central College Campus, Bangalore
THE RAINBOW DOMINATION SUBDIVISION NUMBERS OF GRAPHS. N. Dehgardi, S. M. Sheikholeslami and L. Volkmann. 1. Introduction
 MATEMATIQKI VESNIK 67, 2 (2015), 102 114 June 2015 originalni nauqni rad research paper THE RAINBOW DOMINATION SUBDIVISION NUMBERS OF GRAPHS N. Dehgardi, S. M. Sheikholeslami and L. Volkmann Abstract.
MATEMATIQKI VESNIK 67, 2 (2015), 102 114 June 2015 originalni nauqni rad research paper THE RAINBOW DOMINATION SUBDIVISION NUMBERS OF GRAPHS N. Dehgardi, S. M. Sheikholeslami and L. Volkmann Abstract.
Chromatic Transversal Domatic Number of Graphs
 International Mathematical Forum, 5, 010, no. 13, 639-648 Chromatic Transversal Domatic Number of Graphs L. Benedict Michael Raj 1, S. K. Ayyaswamy and I. Sahul Hamid 3 1 Department of Mathematics, St.
International Mathematical Forum, 5, 010, no. 13, 639-648 Chromatic Transversal Domatic Number of Graphs L. Benedict Michael Raj 1, S. K. Ayyaswamy and I. Sahul Hamid 3 1 Department of Mathematics, St.
THE CONNECTED COMPLEMENT DOMINATION IN GRAPHS V.MOHANASELVI 1. Assistant Professor of Mathematics, Nehru Memorial College, Puthanampatti,
 THE CONNECTED COMPLEMENT DOMINATION IN GRAPHS V.MOHANASELVI 1 Assistant Professor of Mathematics, Nehru Memorial College, Puthanampatti, Tiruchirappalli-621 00 S.DHIVYAKANNU 2 Assistant Professor of Mathematics,
THE CONNECTED COMPLEMENT DOMINATION IN GRAPHS V.MOHANASELVI 1 Assistant Professor of Mathematics, Nehru Memorial College, Puthanampatti, Tiruchirappalli-621 00 S.DHIVYAKANNU 2 Assistant Professor of Mathematics,
Bounds for the m-eternal Domination Number of a Graph
 Bounds for the m-eternal Domination Number of a Graph Michael A. Henning Department of Pure and Applied Mathematics University of Johannesburg South Africa mahenning@uj.ac.za Gary MacGillivray Department
Bounds for the m-eternal Domination Number of a Graph Michael A. Henning Department of Pure and Applied Mathematics University of Johannesburg South Africa mahenning@uj.ac.za Gary MacGillivray Department
Graph Theory S 1 I 2 I 1 S 2 I 1 I 2
 Graph Theory S I I S S I I S Graphs Definition A graph G is a pair consisting of a vertex set V (G), and an edge set E(G) ( ) V (G). x and y are the endpoints of edge e = {x, y}. They are called adjacent
Graph Theory S I I S S I I S Graphs Definition A graph G is a pair consisting of a vertex set V (G), and an edge set E(G) ( ) V (G). x and y are the endpoints of edge e = {x, y}. They are called adjacent
DOUBLE DOMINATION CRITICAL AND STABLE GRAPHS UPON VERTEX REMOVAL 1
 Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 32 (2012) 643 657 doi:10.7151/dmgt.1633 DOUBLE DOMINATION CRITICAL AND STABLE GRAPHS UPON VERTEX REMOVAL 1 Soufiane Khelifi Laboratory LMP2M, Bloc of laboratories
Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 32 (2012) 643 657 doi:10.7151/dmgt.1633 DOUBLE DOMINATION CRITICAL AND STABLE GRAPHS UPON VERTEX REMOVAL 1 Soufiane Khelifi Laboratory LMP2M, Bloc of laboratories
Jordan Curves. A curve is a subset of IR 2 of the form
 Jordan Curves A curve is a subset of IR 2 of the form α = {γ(x) : x [0, 1]}, where γ : [0, 1] IR 2 is a continuous mapping from the closed interval [0, 1] to the plane. γ(0) and γ(1) are called the endpoints
Jordan Curves A curve is a subset of IR 2 of the form α = {γ(x) : x [0, 1]}, where γ : [0, 1] IR 2 is a continuous mapping from the closed interval [0, 1] to the plane. γ(0) and γ(1) are called the endpoints
LOWER BOUNDS FOR THE DOMINATION NUMBER
 Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 0 (010 ) 475 487 LOWER BOUNDS FOR THE DOMINATION NUMBER Ermelinda Delaviña, Ryan Pepper and Bill Waller University of Houston Downtown Houston, TX, 7700, USA Abstract
Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 0 (010 ) 475 487 LOWER BOUNDS FOR THE DOMINATION NUMBER Ermelinda Delaviña, Ryan Pepper and Bill Waller University of Houston Downtown Houston, TX, 7700, USA Abstract
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 5, 2011, no. 49, Július Czap
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 5, 011, no. 49, 437-44 M i -Edge Colorings of Graphs Július Czap Department of Applied Mathematics and Business Informatics Faculty of Economics, Technical University
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 5, 011, no. 49, 437-44 M i -Edge Colorings of Graphs Július Czap Department of Applied Mathematics and Business Informatics Faculty of Economics, Technical University
Characterizing Graphs (3) Characterizing Graphs (1) Characterizing Graphs (2) Characterizing Graphs (4)
 S-72.2420/T-79.5203 Basic Concepts 1 S-72.2420/T-79.5203 Basic Concepts 3 Characterizing Graphs (1) Characterizing Graphs (3) Characterizing a class G by a condition P means proving the equivalence G G
S-72.2420/T-79.5203 Basic Concepts 1 S-72.2420/T-79.5203 Basic Concepts 3 Characterizing Graphs (1) Characterizing Graphs (3) Characterizing a class G by a condition P means proving the equivalence G G
Section 3.1: Nonseparable Graphs Cut vertex of a connected graph G: A vertex x G such that G x is not connected. Theorem 3.1, p. 57: Every connected
 Section 3.1: Nonseparable Graphs Cut vertex of a connected graph G: A vertex x G such that G x is not connected. Theorem 3.1, p. 57: Every connected graph G with at least 2 vertices contains at least 2
Section 3.1: Nonseparable Graphs Cut vertex of a connected graph G: A vertex x G such that G x is not connected. Theorem 3.1, p. 57: Every connected graph G with at least 2 vertices contains at least 2
Price of Connectivity for the vertex cover problem and the dominating set problem: conjectures and investigation of critical graphs
 Price of Connectivity for the vertex cover problem and the dominating set problem: conjectures and investigation of critical graphs Eglantine Camby Université Libre de Bruxelles, Brussels, Belgium GERAD
Price of Connectivity for the vertex cover problem and the dominating set problem: conjectures and investigation of critical graphs Eglantine Camby Université Libre de Bruxelles, Brussels, Belgium GERAD
TREES WITH UNIQUE MINIMUM DOMINATING SETS
 TREES WITH UNIQUE MINIMUM DOMINATING SETS Sharada B Department of Studies in Computer Science, University of Mysore, Manasagangothri, Mysore ABSTRACT A set D of vertices of a graph G is a dominating set
TREES WITH UNIQUE MINIMUM DOMINATING SETS Sharada B Department of Studies in Computer Science, University of Mysore, Manasagangothri, Mysore ABSTRACT A set D of vertices of a graph G is a dominating set
Bounds on the signed domination number of a graph.
 Bounds on the signed domination number of a graph. Ruth Haas and Thomas B. Wexler September 7, 00 Abstract Let G = (V, E) be a simple graph on vertex set V and define a function f : V {, }. The function
Bounds on the signed domination number of a graph. Ruth Haas and Thomas B. Wexler September 7, 00 Abstract Let G = (V, E) be a simple graph on vertex set V and define a function f : V {, }. The function
DOMINATION PARAMETERS OF A GRAPH AND ITS COMPLEMENT
 Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 38 (2018) 203 215 doi:10.7151/dmgt.2002 DOMINATION PARAMETERS OF A GRAPH AND ITS COMPLEMENT Wyatt J. Desormeaux 1, Teresa W. Haynes 1,2 and Michael A. Henning 1 1
Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 38 (2018) 203 215 doi:10.7151/dmgt.2002 DOMINATION PARAMETERS OF A GRAPH AND ITS COMPLEMENT Wyatt J. Desormeaux 1, Teresa W. Haynes 1,2 and Michael A. Henning 1 1
Planar graphs. Chapter 8
 Chapter 8 Planar graphs Definition 8.1. A graph is called planar if it can be drawn in the plane so that edges intersect only at vertices to which they are incident. Example 8.2. Different representations
Chapter 8 Planar graphs Definition 8.1. A graph is called planar if it can be drawn in the plane so that edges intersect only at vertices to which they are incident. Example 8.2. Different representations
The Dual Neighborhood Number of a Graph
 Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sciences, Vol. 5, 2010, no. 47, 2327-2334 The Dual Neighborhood Number of a Graph B. Chaluvaraju 1, V. Lokesha 2 and C. Nandeesh Kumar 1 1 Department of Mathematics Central College
Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sciences, Vol. 5, 2010, no. 47, 2327-2334 The Dual Neighborhood Number of a Graph B. Chaluvaraju 1, V. Lokesha 2 and C. Nandeesh Kumar 1 1 Department of Mathematics Central College
Eternal Domination: Criticality and Reachability
 Eternal Domination: Criticality and Reachability William F. Klostermeyer School of Computing University of North Florida Jacksonville, FL 32224-2669 wkloster@unf.edu Gary MacGillivray Department of Mathematics
Eternal Domination: Criticality and Reachability William F. Klostermeyer School of Computing University of North Florida Jacksonville, FL 32224-2669 wkloster@unf.edu Gary MacGillivray Department of Mathematics
ON MINIMAL GEODETIC DOMINATION IN GRAPHS
 Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 35 (2015) 403 418 doi:107151/dmgt1803 ON MINIMAL GEODETIC DOMINATION IN GRAPHS Hearty M Nuenay 1 and Ferdinand P Jamil 2 Department of Mathematics and Statistics
Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 35 (2015) 403 418 doi:107151/dmgt1803 ON MINIMAL GEODETIC DOMINATION IN GRAPHS Hearty M Nuenay 1 and Ferdinand P Jamil 2 Department of Mathematics and Statistics
Complementary nil vertex edge dominating sets
 Proyecciones Journal of Mathematics Vol. 34, N o 1, pp. 1-13, March 2015. Universidad Católica del Norte Antofagasta - Chile Complementary nil vertex edge dominating sets S. V. Siva Rama Raju Ibra College
Proyecciones Journal of Mathematics Vol. 34, N o 1, pp. 1-13, March 2015. Universidad Católica del Norte Antofagasta - Chile Complementary nil vertex edge dominating sets S. V. Siva Rama Raju Ibra College
Graffiti.pc on the 2-domination number of a graph
 Graffiti.pc on the -domination number of a graph Ermelinda DeLaViña, Craig E. Larson, Ryan Pepper and Bill Waller University of Houston-Downtown, Houston, Texas 7700 delavinae@uhd.edu, pepperr@uhd.edu,
Graffiti.pc on the -domination number of a graph Ermelinda DeLaViña, Craig E. Larson, Ryan Pepper and Bill Waller University of Houston-Downtown, Houston, Texas 7700 delavinae@uhd.edu, pepperr@uhd.edu,
Number Theory and Graph Theory
 1 Number Theory and Graph Theory Chapter 6 Basic concepts and definitions of graph theory By A. Satyanarayana Reddy Department of Mathematics Shiv Nadar University Uttar Pradesh, India E-mail: satya8118@gmail.com
1 Number Theory and Graph Theory Chapter 6 Basic concepts and definitions of graph theory By A. Satyanarayana Reddy Department of Mathematics Shiv Nadar University Uttar Pradesh, India E-mail: satya8118@gmail.com
(1,2) - Domination in Line Graphs of C n, P n and K 1,n
 American Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics 03, 3(3): 6-67 DOI: 0.593/j.ajcam.030303.0 (,) - Domination in Line Graphs of C n, P n and K,n N. Murugesan, Deepa. S. Nair * Post Graduate and
American Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics 03, 3(3): 6-67 DOI: 0.593/j.ajcam.030303.0 (,) - Domination in Line Graphs of C n, P n and K,n N. Murugesan, Deepa. S. Nair * Post Graduate and
Graph Theory Day Four
 Graph Theory Day Four February 8, 018 1 Connected Recall from last class, we discussed methods for proving a graph was connected. Our two methods were 1) Based on the definition, given any u, v V(G), there
Graph Theory Day Four February 8, 018 1 Connected Recall from last class, we discussed methods for proving a graph was connected. Our two methods were 1) Based on the definition, given any u, v V(G), there
129 (2004) MATHEMATICA BOHEMICA No. 4, , Liberec
 129 (2004) MATHEMATICA BOHEMICA No. 4, 393 398 SIGNED 2-DOMINATION IN CATERPILLARS, Liberec (Received December 19, 2003) Abstract. A caterpillar is a tree with the property that after deleting all its
129 (2004) MATHEMATICA BOHEMICA No. 4, 393 398 SIGNED 2-DOMINATION IN CATERPILLARS, Liberec (Received December 19, 2003) Abstract. A caterpillar is a tree with the property that after deleting all its
Bipartite Roots of Graphs
 Bipartite Roots of Graphs Lap Chi Lau Department of Computer Science University of Toronto Graph H is a root of graph G if there exists a positive integer k such that x and y are adjacent in G if and only
Bipartite Roots of Graphs Lap Chi Lau Department of Computer Science University of Toronto Graph H is a root of graph G if there exists a positive integer k such that x and y are adjacent in G if and only
Global Alliance Partition in Trees
 Global Alliance Partition in Trees Linda Eroh Department of Mathematics University of Wisconsin Oshkosh, Oshkosh, WI, 54901 eroh@uwoshedu and Ralucca Gera Department of Applied Mathematics Naval Postgraduate
Global Alliance Partition in Trees Linda Eroh Department of Mathematics University of Wisconsin Oshkosh, Oshkosh, WI, 54901 eroh@uwoshedu and Ralucca Gera Department of Applied Mathematics Naval Postgraduate
Complete Cototal Domination
 Chapter 5 Complete Cototal Domination Number of a Graph Published in Journal of Scientific Research Vol. () (2011), 547-555 (Bangladesh). 64 ABSTRACT Let G = (V,E) be a graph. A dominating set D V is said
Chapter 5 Complete Cototal Domination Number of a Graph Published in Journal of Scientific Research Vol. () (2011), 547-555 (Bangladesh). 64 ABSTRACT Let G = (V,E) be a graph. A dominating set D V is said
Lecture 4: Walks, Trails, Paths and Connectivity
 Lecture 4: Walks, Trails, Paths and Connectivity Rosa Orellana Math 38 April 6, 2015 Graph Decompositions Def: A decomposition of a graph is a list of subgraphs such that each edge appears in exactly one
Lecture 4: Walks, Trails, Paths and Connectivity Rosa Orellana Math 38 April 6, 2015 Graph Decompositions Def: A decomposition of a graph is a list of subgraphs such that each edge appears in exactly one
SANDRA SPIROFF AND CAMERON WICKHAM
 A ZERO DIVISOR GRAPH DETERMINED BY EQUIVALENCE CLASSES OF ZERO DIVISORS arxiv:0801.0086v2 [math.ac] 17 Aug 2009 SANDRA SPIROFF AND CAMERON WICKHAM Abstract. We study the zero divisor graph determined by
A ZERO DIVISOR GRAPH DETERMINED BY EQUIVALENCE CLASSES OF ZERO DIVISORS arxiv:0801.0086v2 [math.ac] 17 Aug 2009 SANDRA SPIROFF AND CAMERON WICKHAM Abstract. We study the zero divisor graph determined by
Jordan Curves. A curve is a subset of IR 2 of the form
 Jordan Curves A curve is a subset of IR 2 of the form α = {γ(x) : x [0,1]}, where γ : [0,1] IR 2 is a continuous mapping from the closed interval [0,1] to the plane. γ(0) and γ(1) are called the endpoints
Jordan Curves A curve is a subset of IR 2 of the form α = {γ(x) : x [0,1]}, where γ : [0,1] IR 2 is a continuous mapping from the closed interval [0,1] to the plane. γ(0) and γ(1) are called the endpoints
On t-restricted Optimal Rubbling of Graphs
 East Tennessee State University Digital Commons @ East Tennessee State University Electronic Theses and Dissertations 5-2017 On t-restricted Optimal Rubbling of Graphs Kyle Murphy East Tennessee State
East Tennessee State University Digital Commons @ East Tennessee State University Electronic Theses and Dissertations 5-2017 On t-restricted Optimal Rubbling of Graphs Kyle Murphy East Tennessee State
Star coloring planar graphs from small lists
 Star coloring planar graphs from small lists André Kündgen Craig Timmons June 4, 2008 Abstract A star coloring of a graph is a proper vertex-coloring such that no path on four vertices is 2-colored. We
Star coloring planar graphs from small lists André Kündgen Craig Timmons June 4, 2008 Abstract A star coloring of a graph is a proper vertex-coloring such that no path on four vertices is 2-colored. We
Dynamic Dominating Sets: the Eviction Model for Eternal Domination
 Dynamic Dominating Sets: the Eviction Model for Eternal Domination William F. Klostermeyer School of Computing University of North Florida Jacksonville, FL 32224-2669 wkloster@unf.edu Mary Lawrence School
Dynamic Dominating Sets: the Eviction Model for Eternal Domination William F. Klostermeyer School of Computing University of North Florida Jacksonville, FL 32224-2669 wkloster@unf.edu Mary Lawrence School
On global location-domination in graphs
 Also available at http://amc-journal.eu ISSN 1855-3966 (printed edn.), ISSN 1855-3974 (electronic edn.) ARS MATHEMATICA CONTEMPORANEA 8 (2015) 365 379 On global location-domination in graphs Carmen Hernando
Also available at http://amc-journal.eu ISSN 1855-3966 (printed edn.), ISSN 1855-3974 (electronic edn.) ARS MATHEMATICA CONTEMPORANEA 8 (2015) 365 379 On global location-domination in graphs Carmen Hernando
How many colors are needed to color a map?
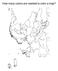 How many colors are needed to color a map? Is 4 always enough? Two relevant concepts How many colors do we need to color a map so neighboring countries get different colors? Simplifying assumption (not
How many colors are needed to color a map? Is 4 always enough? Two relevant concepts How many colors do we need to color a map so neighboring countries get different colors? Simplifying assumption (not
DOMINATION GAME: EXTREMAL FAMILIES FOR THE 3/5-CONJECTURE FOR FORESTS
 Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 37 (2017) 369 381 doi:10.7151/dmgt.1931 DOMINATION GAME: EXTREMAL FAMILIES FOR THE 3/5-CONJECTURE FOR FORESTS Michael A. Henning 1 Department of Pure and Applied
Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 37 (2017) 369 381 doi:10.7151/dmgt.1931 DOMINATION GAME: EXTREMAL FAMILIES FOR THE 3/5-CONJECTURE FOR FORESTS Michael A. Henning 1 Department of Pure and Applied
Domination in Jahangir Graph J 2,m
 Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sciences, Vol., 007, no. 4, 119-1199 Domination in Jahangir Graph J,m D. A. Mojdeh and A. N. Ghameshlou Department of Mathematics University of Mazandaran P.O. Box 47416-1467, Babolsar,
Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sciences, Vol., 007, no. 4, 119-1199 Domination in Jahangir Graph J,m D. A. Mojdeh and A. N. Ghameshlou Department of Mathematics University of Mazandaran P.O. Box 47416-1467, Babolsar,
Dominating sequences in graphs
 Dominating sequences in graphs Boštjan Brešar a,b Tanja Gologranc b Martin Milanič c,b Douglas F. Rall d Romeo Rizzi e July 18, 2014 a Faculty of Natural Sciences and Mathematics, University of Maribor,
Dominating sequences in graphs Boštjan Brešar a,b Tanja Gologranc b Martin Milanič c,b Douglas F. Rall d Romeo Rizzi e July 18, 2014 a Faculty of Natural Sciences and Mathematics, University of Maribor,
POINT-SET DOMATIC NUMBERS OF GRAPHS
 124 (1999) MATHEMATICA BOHEMICA No. 1, 77 82 POINT-SET DOMATIC NUMBERS OF GRAPHS Bohdan Zelinka, Liberec (Received September 10, 1997) Abstract. A subset D of the vertex set V (G) of a graph G is called
124 (1999) MATHEMATICA BOHEMICA No. 1, 77 82 POINT-SET DOMATIC NUMBERS OF GRAPHS Bohdan Zelinka, Liberec (Received September 10, 1997) Abstract. A subset D of the vertex set V (G) of a graph G is called
{ 1} Definitions. 10. Extremal graph theory. Problem definition Paths and cycles Complete subgraphs
 Problem definition Paths and cycles Complete subgraphs 10. Extremal graph theory 10.1. Definitions Let us examine the following forbidden subgraph problems: At most how many edges are in a graph of order
Problem definition Paths and cycles Complete subgraphs 10. Extremal graph theory 10.1. Definitions Let us examine the following forbidden subgraph problems: At most how many edges are in a graph of order
NP-Completeness. Algorithms
 NP-Completeness Algorithms The NP-Completeness Theory Objective: Identify a class of problems that are hard to solve. Exponential time is hard. Polynomial time is easy. Why: Do not try to find efficient
NP-Completeness Algorithms The NP-Completeness Theory Objective: Identify a class of problems that are hard to solve. Exponential time is hard. Polynomial time is easy. Why: Do not try to find efficient
Connected Liar s Domination in Graphs: Complexity and Algorithm 1
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 12, 2018, no. 10, 489-494 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ams.2018.8344 Connected Liar s Domination in Graphs: Complexity and Algorithm 1 Chengye
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 12, 2018, no. 10, 489-494 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/ams.2018.8344 Connected Liar s Domination in Graphs: Complexity and Algorithm 1 Chengye
Subdivisions of Graphs: A Generalization of Paths and Cycles
 Subdivisions of Graphs: A Generalization of Paths and Cycles Ch. Sobhan Babu and Ajit A. Diwan Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400076,
Subdivisions of Graphs: A Generalization of Paths and Cycles Ch. Sobhan Babu and Ajit A. Diwan Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400076,
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 4 Apr 2011
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 4 Apr 2011 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 4 Apr 2011](/thumbs/94/118782109.jpg) arxiv:1104.0510v1 [math.co] 4 Apr 2011 Minimal non-extensible precolorings and implicit-relations José Antonio Martín H. Abstract. In this paper I study a variant of the general vertex coloring problem
arxiv:1104.0510v1 [math.co] 4 Apr 2011 Minimal non-extensible precolorings and implicit-relations José Antonio Martín H. Abstract. In this paper I study a variant of the general vertex coloring problem
Two Characterizations of Hypercubes
 Two Characterizations of Hypercubes Juhani Nieminen, Matti Peltola and Pasi Ruotsalainen Department of Mathematics, University of Oulu University of Oulu, Faculty of Technology, Mathematics Division, P.O.
Two Characterizations of Hypercubes Juhani Nieminen, Matti Peltola and Pasi Ruotsalainen Department of Mathematics, University of Oulu University of Oulu, Faculty of Technology, Mathematics Division, P.O.
A ZERO DIVISOR GRAPH DETERMINED BY EQUIVALENCE CLASSES OF ZERO DIVISORS. Introduction
 A ZERO DIVISOR GRAPH DETERMINED BY EQUIVALENCE CLASSES OF ZERO DIVISORS SANDRA SPIROFF AND CAMERON WICKHAM Abstract. We study the zero divisor graph determined by equivalence classes of zero divisors of
A ZERO DIVISOR GRAPH DETERMINED BY EQUIVALENCE CLASSES OF ZERO DIVISORS SANDRA SPIROFF AND CAMERON WICKHAM Abstract. We study the zero divisor graph determined by equivalence classes of zero divisors of
Vertex Minimal and Common Minimal Equitable Dominating Graphs
 Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sciences, Vol. 7, 2012, no. 10, 499-505 Vertex Minimal and Common Minimal Equitable Dominating Graphs G. Deepak a, N. D. Soner b and Anwar Alwardi b a Department of Mathematics The
Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sciences, Vol. 7, 2012, no. 10, 499-505 Vertex Minimal and Common Minimal Equitable Dominating Graphs G. Deepak a, N. D. Soner b and Anwar Alwardi b a Department of Mathematics The
Graphs & Algorithms: Advanced Topics Planar Separators
 Graphs & Algorithms: Advanced Topics Planar Separators Johannes Lengler, Uli Wagner ETH Zürich Separators Definition Let G = (V, E) be a graph on n vertices, f : N 0 R a function, α (0, 1) a parameter.
Graphs & Algorithms: Advanced Topics Planar Separators Johannes Lengler, Uli Wagner ETH Zürich Separators Definition Let G = (V, E) be a graph on n vertices, f : N 0 R a function, α (0, 1) a parameter.
Eccentric domination in splitting graph of some graphs
 Advances in Theoretical and Applied Mathematics ISSN 0973-4554 Volume 11, Number 2 (2016), pp. 179-188 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Eccentric domination in splitting graph of
Advances in Theoretical and Applied Mathematics ISSN 0973-4554 Volume 11, Number 2 (2016), pp. 179-188 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Eccentric domination in splitting graph of
Definition For vertices u, v V (G), the distance from u to v, denoted d(u, v), in G is the length of a shortest u, v-path. 1
 Graph fundamentals Bipartite graph characterization Lemma. If a graph contains an odd closed walk, then it contains an odd cycle. Proof strategy: Consider a shortest closed odd walk W. If W is not a cycle,
Graph fundamentals Bipartite graph characterization Lemma. If a graph contains an odd closed walk, then it contains an odd cycle. Proof strategy: Consider a shortest closed odd walk W. If W is not a cycle,
Triple Connected Domination Number of a Graph
 International J.Math. Combin. Vol.3(2012), 93-104 Triple Connected Domination Number of a Graph G.Mahadevan, Selvam Avadayappan, J.Paulraj Joseph and T.Subramanian Department of Mathematics Anna University:
International J.Math. Combin. Vol.3(2012), 93-104 Triple Connected Domination Number of a Graph G.Mahadevan, Selvam Avadayappan, J.Paulraj Joseph and T.Subramanian Department of Mathematics Anna University:
On the Geodetic Number of Line Graph
 Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sciences, Vol. 7, 01, no. 46, 89-95 On the Geodetic Number of Line Graph Venkanagouda M. Goudar Sri Gouthama Research Center [Affiliated to Kuvempu University] Department of Mathematics,
Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sciences, Vol. 7, 01, no. 46, 89-95 On the Geodetic Number of Line Graph Venkanagouda M. Goudar Sri Gouthama Research Center [Affiliated to Kuvempu University] Department of Mathematics,
Geodesic Convexity and Cartesian Products in Graphs
 Geodesic Convexity and Cartesian Products in Graphs Tao Jiang Ignacio Pelayo Dan Pritikin September 23, 2004 Abstract In this work we investigate the behavior of various geodesic convexity parameters with
Geodesic Convexity and Cartesian Products in Graphs Tao Jiang Ignacio Pelayo Dan Pritikin September 23, 2004 Abstract In this work we investigate the behavior of various geodesic convexity parameters with
CS 311 Discrete Math for Computer Science Dr. William C. Bulko. Graphs
 CS 311 Discrete Math for Computer Science Dr. William C. Bulko Graphs 2014 Definitions Definition: A graph G = (V,E) consists of a nonempty set V of vertices (or nodes) and a set E of edges. Each edge
CS 311 Discrete Math for Computer Science Dr. William C. Bulko Graphs 2014 Definitions Definition: A graph G = (V,E) consists of a nonempty set V of vertices (or nodes) and a set E of edges. Each edge
Planar Graph Characterization - Using γ - Stable Graphs
 Planar Graph Characterization - Using γ - Stable Graphs M. YAMUNA VIT University Vellore, Tamilnadu INDIA myamuna@vit.ac.in K. KARTHIKA VIT University Vellore, Tamilnadu INDIA karthika.k@vit.ac.in Abstract:
Planar Graph Characterization - Using γ - Stable Graphs M. YAMUNA VIT University Vellore, Tamilnadu INDIA myamuna@vit.ac.in K. KARTHIKA VIT University Vellore, Tamilnadu INDIA karthika.k@vit.ac.in Abstract:
Subdivided graphs have linear Ramsey numbers
 Subdivided graphs have linear Ramsey numbers Noga Alon Bellcore, Morristown, NJ 07960, USA and Department of Mathematics Raymond and Beverly Sackler Faculty of Exact Sciences Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv,
Subdivided graphs have linear Ramsey numbers Noga Alon Bellcore, Morristown, NJ 07960, USA and Department of Mathematics Raymond and Beverly Sackler Faculty of Exact Sciences Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv,
Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes 5: Planar graphs and coloring
 Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes 5: Planar graphs and coloring David Glickenstein October 10, 2014 1 Planar graphs The Three Houses and Three Utilities Problem: Given three houses and three utilities, can
Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes 5: Planar graphs and coloring David Glickenstein October 10, 2014 1 Planar graphs The Three Houses and Three Utilities Problem: Given three houses and three utilities, can
Chapter-0: Introduction. Chapter 0 INTRODUCTION
 Chapter 0 INTRODUCTION 1 Graph Theory is a branch of Mathematics which has become quite rich and interesting for several reasons. In last three decades hundreds of research article have been published
Chapter 0 INTRODUCTION 1 Graph Theory is a branch of Mathematics which has become quite rich and interesting for several reasons. In last three decades hundreds of research article have been published
Double Domination Edge Critical Graphs.
 East Tennessee State University Digital Commons @ East Tennessee State University Electronic Theses and Dissertations 5-2006 Double Domination Edge Critical Graphs. Derrick Wayne Thacker East Tennessee
East Tennessee State University Digital Commons @ East Tennessee State University Electronic Theses and Dissertations 5-2006 Double Domination Edge Critical Graphs. Derrick Wayne Thacker East Tennessee
Root Cover Pebbling on Graphs
 University of Dayton ecommons Honors Theses University Honors Program Spring 4-2015 Root Cover Pebbling on Graphs Claire A. Sonneborn Follow this and additional works at: https://ecommons.udayton.edu/uhp_theses
University of Dayton ecommons Honors Theses University Honors Program Spring 4-2015 Root Cover Pebbling on Graphs Claire A. Sonneborn Follow this and additional works at: https://ecommons.udayton.edu/uhp_theses
Domination Game. Sandi Klavžar. Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia
 Sandi Klavžar Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia Faculty of Natural Sciences and Mathematics, University of Maribor, Slovenia Institute of Mathematics, Physics and Mechanics,
Sandi Klavžar Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia Faculty of Natural Sciences and Mathematics, University of Maribor, Slovenia Institute of Mathematics, Physics and Mechanics,
Collapsible biclaw-free graphs
 Collapsible biclaw-free graphs Hong-Jian Lai, Xiangjuan Yao February 24, 2006 Abstract A graph is called biclaw-free if it has no biclaw as an induced subgraph. In this note, we prove that if G is a connected
Collapsible biclaw-free graphs Hong-Jian Lai, Xiangjuan Yao February 24, 2006 Abstract A graph is called biclaw-free if it has no biclaw as an induced subgraph. In this note, we prove that if G is a connected
DO NOT RE-DISTRIBUTE THIS SOLUTION FILE
 Professor Kindred Math 104, Graph Theory Homework 2 Solutions February 7, 2013 Introduction to Graph Theory, West Section 1.2: 26, 38, 42 Section 1.3: 14, 18 Section 2.1: 26, 29, 30 DO NOT RE-DISTRIBUTE
Professor Kindred Math 104, Graph Theory Homework 2 Solutions February 7, 2013 Introduction to Graph Theory, West Section 1.2: 26, 38, 42 Section 1.3: 14, 18 Section 2.1: 26, 29, 30 DO NOT RE-DISTRIBUTE
On Locating Domination Number of. Boolean Graph BG 2 (G)
 International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 12, 2017, no. 20, 973-982 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/imf.2017.7977 On Locating Domination Number of Boolean Graph BG 2 (G) M. Bhanumathi
International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 12, 2017, no. 20, 973-982 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/10.12988/imf.2017.7977 On Locating Domination Number of Boolean Graph BG 2 (G) M. Bhanumathi
Some Upper Bounds for Signed Star Domination Number of Graphs. S. Akbari, A. Norouzi-Fard, A. Rezaei, R. Rotabi, S. Sabour.
 Some Upper Bounds for Signed Star Domination Number of Graphs S. Akbari, A. Norouzi-Fard, A. Rezaei, R. Rotabi, S. Sabour Abstract Let G be a graph with the vertex set V (G) and edge set E(G). A function
Some Upper Bounds for Signed Star Domination Number of Graphs S. Akbari, A. Norouzi-Fard, A. Rezaei, R. Rotabi, S. Sabour Abstract Let G be a graph with the vertex set V (G) and edge set E(G). A function
PAijpam.eu TOTAL CO-INDEPENDENT DOMINATION OF JUMP GRAPH
 International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics Volume 110 No. 1 2016, 43-48 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu doi: 10.12732/ijpam.v110i1.4
International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics Volume 110 No. 1 2016, 43-48 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu doi: 10.12732/ijpam.v110i1.4
Dominating Sets in Triangulations on Surfaces
 Dominating Sets in Triangulations on Surfaces Hong Liu Department of Mathematics University of Illinois This is a joint work with Michael Pelsmajer May 14, 2011 Introduction A dominating set D V of a graph
Dominating Sets in Triangulations on Surfaces Hong Liu Department of Mathematics University of Illinois This is a joint work with Michael Pelsmajer May 14, 2011 Introduction A dominating set D V of a graph
Discrete Mathematics I So Practice Sheet Solutions 1
 Discrete Mathematics I So 2016 Tibor Szabó Shagnik Das Practice Sheet Solutions 1 Provided below are possible solutions to the questions from the practice sheet issued towards the end of the course. Exercise
Discrete Mathematics I So 2016 Tibor Szabó Shagnik Das Practice Sheet Solutions 1 Provided below are possible solutions to the questions from the practice sheet issued towards the end of the course. Exercise
Weak Dynamic Coloring of Planar Graphs
 Weak Dynamic Coloring of Planar Graphs Caroline Accurso 1,5, Vitaliy Chernyshov 2,5, Leaha Hand 3,5, Sogol Jahanbekam 2,4,5, and Paul Wenger 2 Abstract The k-weak-dynamic number of a graph G is the smallest
Weak Dynamic Coloring of Planar Graphs Caroline Accurso 1,5, Vitaliy Chernyshov 2,5, Leaha Hand 3,5, Sogol Jahanbekam 2,4,5, and Paul Wenger 2 Abstract The k-weak-dynamic number of a graph G is the smallest
Domination Number of Jump Graph
 International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 8, 013, no. 16, 753-758 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com Domination Number of Jump Graph Y. B. Maralabhavi Department of Mathematics Bangalore University Bangalore-560001,
International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 8, 013, no. 16, 753-758 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com Domination Number of Jump Graph Y. B. Maralabhavi Department of Mathematics Bangalore University Bangalore-560001,
FUZZY DOUBLE DOMINATION NUMBER AND CHROMATIC NUMBER OF A FUZZY GRAPH
 International Journal of Information Technology and Knowledge Management July-December 2011 Volume 4 No 2 pp 495-499 FUZZY DOUBLE DOMINATION NUMBER AND CHROMATIC NUMBER OF A FUZZY GRAPH G MAHADEVAN 1 V
International Journal of Information Technology and Knowledge Management July-December 2011 Volume 4 No 2 pp 495-499 FUZZY DOUBLE DOMINATION NUMBER AND CHROMATIC NUMBER OF A FUZZY GRAPH G MAHADEVAN 1 V
Complementary Acyclic Weak Domination Preserving Sets
 International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 30-9364, ISSN (Print): 30-9356 ijresorg Volume 4 Issue 7 ǁ July 016 ǁ PP 44-48 Complementary Acyclic Weak Domination
International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 30-9364, ISSN (Print): 30-9356 ijresorg Volume 4 Issue 7 ǁ July 016 ǁ PP 44-48 Complementary Acyclic Weak Domination
A framework for faults in detectors within network monitoring systems
 A framework for faults in detectors within network monitoring systems University of Alabama in Huntsville Mathematical Sciences Department and Computer Science Department Huntsville, AL 35899, U.S.A slaterp@math.uah.edu;
A framework for faults in detectors within network monitoring systems University of Alabama in Huntsville Mathematical Sciences Department and Computer Science Department Huntsville, AL 35899, U.S.A slaterp@math.uah.edu;
ON VERTEX b-critical TREES. Mostafa Blidia, Noureddine Ikhlef Eschouf, and Frédéric Maffray
 Opuscula Math. 33, no. 1 (2013), 19 28 http://dx.doi.org/10.7494/opmath.2013.33.1.19 Opuscula Mathematica ON VERTEX b-critical TREES Mostafa Blidia, Noureddine Ikhlef Eschouf, and Frédéric Maffray Communicated
Opuscula Math. 33, no. 1 (2013), 19 28 http://dx.doi.org/10.7494/opmath.2013.33.1.19 Opuscula Mathematica ON VERTEX b-critical TREES Mostafa Blidia, Noureddine Ikhlef Eschouf, and Frédéric Maffray Communicated
Problem Set 3. MATH 776, Fall 2009, Mohr. November 30, 2009
 Problem Set 3 MATH 776, Fall 009, Mohr November 30, 009 1 Problem Proposition 1.1. Adding a new edge to a maximal planar graph of order at least 6 always produces both a T K 5 and a T K 3,3 subgraph. Proof.
Problem Set 3 MATH 776, Fall 009, Mohr November 30, 009 1 Problem Proposition 1.1. Adding a new edge to a maximal planar graph of order at least 6 always produces both a T K 5 and a T K 3,3 subgraph. Proof.
1 Matchings in Graphs
 Matchings in Graphs J J 2 J 3 J 4 J 5 J J J 6 8 7 C C 2 C 3 C 4 C 5 C C 7 C 8 6 J J 2 J 3 J 4 J 5 J J J 6 8 7 C C 2 C 3 C 4 C 5 C C 7 C 8 6 Definition Two edges are called independent if they are not adjacent
Matchings in Graphs J J 2 J 3 J 4 J 5 J J J 6 8 7 C C 2 C 3 C 4 C 5 C C 7 C 8 6 J J 2 J 3 J 4 J 5 J J J 6 8 7 C C 2 C 3 C 4 C 5 C C 7 C 8 6 Definition Two edges are called independent if they are not adjacent
A Survey of the Algorithmic Properties of Simplicial, Upper Bound and Middle Graphs
 Journal of Graph Algorithms and Applications http://jgaa.info/ vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 159 190 (2006) A Survey of the Algorithmic Properties of Simplicial, Upper Bound and Middle Graphs Grant A. Cheston Tjoen
Journal of Graph Algorithms and Applications http://jgaa.info/ vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 159 190 (2006) A Survey of the Algorithmic Properties of Simplicial, Upper Bound and Middle Graphs Grant A. Cheston Tjoen
On the structure of 1-planar graphs
 Institute of Mathematics, P.J. Šafárik University, Košice, Slovakia 20.11.2008 Planar graphs Within the graph theory, one of oldest areas of research is the study of planar and plane graphs (the beginnings
Institute of Mathematics, P.J. Šafárik University, Košice, Slovakia 20.11.2008 Planar graphs Within the graph theory, one of oldest areas of research is the study of planar and plane graphs (the beginnings
Maximal Monochromatic Geodesics in an Antipodal Coloring of Hypercube
 Maximal Monochromatic Geodesics in an Antipodal Coloring of Hypercube Kavish Gandhi April 4, 2015 Abstract A geodesic in the hypercube is the shortest possible path between two vertices. Leader and Long
Maximal Monochromatic Geodesics in an Antipodal Coloring of Hypercube Kavish Gandhi April 4, 2015 Abstract A geodesic in the hypercube is the shortest possible path between two vertices. Leader and Long
Dominated colorings of graphs
 Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Dominated colorings of graphs Houcine Boumediene Merouane Mohammed Haddad Mustapha Chellali Hamamache Kheddouci Received: date / Accepted: date Abstract
Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Dominated colorings of graphs Houcine Boumediene Merouane Mohammed Haddad Mustapha Chellali Hamamache Kheddouci Received: date / Accepted: date Abstract
ON LOCAL STRUCTURE OF 1-PLANAR GRAPHS OF MINIMUM DEGREE 5 AND GIRTH 4
 Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 9 (009 ) 385 00 ON LOCAL STRUCTURE OF -PLANAR GRAPHS OF MINIMUM DEGREE 5 AND GIRTH Dávid Hudák and Tomáš Madaras Institute of Mathematics, Faculty of Sciences University
Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 9 (009 ) 385 00 ON LOCAL STRUCTURE OF -PLANAR GRAPHS OF MINIMUM DEGREE 5 AND GIRTH Dávid Hudák and Tomáš Madaras Institute of Mathematics, Faculty of Sciences University
Domination game on uniform hypergraphs
 Domination game on uniform hypergraphs Csilla Bujtás a Balázs Patkós b Zsolt Tuza a,b Máté Vizer b October 3, 2017 arxiv:1710.00298v1 [math.co] 1 Oct 2017 a Faculty of Information Technology, University
Domination game on uniform hypergraphs Csilla Bujtás a Balázs Patkós b Zsolt Tuza a,b Máté Vizer b October 3, 2017 arxiv:1710.00298v1 [math.co] 1 Oct 2017 a Faculty of Information Technology, University
A generalization of zero divisor graphs associated to commutative rings
 Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Math. Sci.) (2018) 128:9 https://doi.org/10.1007/s12044-018-0389-0 A generalization of zero divisor graphs associated to commutative rings M. AFKHAMI 1, A. ERFANIAN 2,, K. KHASHYARMANESH
Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Math. Sci.) (2018) 128:9 https://doi.org/10.1007/s12044-018-0389-0 A generalization of zero divisor graphs associated to commutative rings M. AFKHAMI 1, A. ERFANIAN 2,, K. KHASHYARMANESH
GRAPHS WITH 1-FACTORS
 proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 42, Number 1, January 1974 GRAPHS WITH 1-FACTORS DAVID P. SUMNER Abstract. In this paper it is shown that if G is a connected graph of order 2n (n>
proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 42, Number 1, January 1974 GRAPHS WITH 1-FACTORS DAVID P. SUMNER Abstract. In this paper it is shown that if G is a connected graph of order 2n (n>
Star Forests, Dominating Sets and Ramsey-type Problems
 Star Forests, Dominating Sets and Ramsey-type Problems Sheila Ferneyhough a, Ruth Haas b,denis Hanson c,1 and Gary MacGillivray a,1 a Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Victoria, P.O.
Star Forests, Dominating Sets and Ramsey-type Problems Sheila Ferneyhough a, Ruth Haas b,denis Hanson c,1 and Gary MacGillivray a,1 a Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Victoria, P.O.
1 Elementary number theory
 Math 215 - Introduction to Advanced Mathematics Spring 2019 1 Elementary number theory We assume the existence of the natural numbers and the integers N = {1, 2, 3,...} Z = {..., 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3,...},
Math 215 - Introduction to Advanced Mathematics Spring 2019 1 Elementary number theory We assume the existence of the natural numbers and the integers N = {1, 2, 3,...} Z = {..., 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3,...},
Hardness of Subgraph and Supergraph Problems in c-tournaments
 Hardness of Subgraph and Supergraph Problems in c-tournaments Kanthi K Sarpatwar 1 and N.S. Narayanaswamy 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, IIT madras, Chennai 600036, India kanthik@gmail.com,swamy@cse.iitm.ac.in
Hardness of Subgraph and Supergraph Problems in c-tournaments Kanthi K Sarpatwar 1 and N.S. Narayanaswamy 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering, IIT madras, Chennai 600036, India kanthik@gmail.com,swamy@cse.iitm.ac.in
Characterization of Super Strongly Perfect Graphs in Chordal and Strongly Chordal Graphs
 ISSN 0975-3303 Mapana J Sci, 11, 4(2012), 121-131 https://doi.org/10.12725/mjs.23.10 Characterization of Super Strongly Perfect Graphs in Chordal and Strongly Chordal Graphs R Mary Jeya Jothi * and A Amutha
ISSN 0975-3303 Mapana J Sci, 11, 4(2012), 121-131 https://doi.org/10.12725/mjs.23.10 Characterization of Super Strongly Perfect Graphs in Chordal and Strongly Chordal Graphs R Mary Jeya Jothi * and A Amutha
DETOUR DOMINATION NUMBER OF A GRAPH
 DETOUR DOMINATION NUMBER OF A GRAPH A.NELLAI MURUGAN 1 A.ESAKKIMUTHU 2 AND G.MAHADEVAN Abstract In [], the author introduced the detour number of a graph. In this paper, we introduce the new concepts of
DETOUR DOMINATION NUMBER OF A GRAPH A.NELLAI MURUGAN 1 A.ESAKKIMUTHU 2 AND G.MAHADEVAN Abstract In [], the author introduced the detour number of a graph. In this paper, we introduce the new concepts of
A Characterization of Connected (1,2)- Domination Graphs of Tournaments
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Mathematics, Statistics and Computer Science Faculty Research and Publications Mathematics, Statistics and Computer Science, Department of 1-1-2011 A Characterization
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Mathematics, Statistics and Computer Science Faculty Research and Publications Mathematics, Statistics and Computer Science, Department of 1-1-2011 A Characterization
Algorithm and Complexity of Disjointed Connected Dominating Set Problem on Trees
 Algorithm and Complexity of Disjointed Connected Dominating Set Problem on Trees Wei Wang joint with Zishen Yang, Xianliang Liu School of Mathematics and Statistics, Xi an Jiaotong University Dec 20, 2016
Algorithm and Complexity of Disjointed Connected Dominating Set Problem on Trees Wei Wang joint with Zishen Yang, Xianliang Liu School of Mathematics and Statistics, Xi an Jiaotong University Dec 20, 2016
Connectivity of the zero-divisor graph for finite rings
 Connectivity of the zero-divisor graph for finite rings Reza Akhtar and Lucas Lee Abstract The vertex-connectivity and edge-connectivity of the zero-divisor graph associated to a finite commutative ring
Connectivity of the zero-divisor graph for finite rings Reza Akhtar and Lucas Lee Abstract The vertex-connectivity and edge-connectivity of the zero-divisor graph associated to a finite commutative ring
Domination, Independence and Other Numbers Associated With the Intersection Graph of a Set of Half-planes
 Domination, Independence and Other Numbers Associated With the Intersection Graph of a Set of Half-planes Leonor Aquino-Ruivivar Mathematics Department, De La Salle University Leonorruivivar@dlsueduph
Domination, Independence and Other Numbers Associated With the Intersection Graph of a Set of Half-planes Leonor Aquino-Ruivivar Mathematics Department, De La Salle University Leonorruivivar@dlsueduph
