6. Make use of glviewport() to display two sine curves on the same screen, one on the
|
|
|
- Vivien Walters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Duc Nguyen CSE-420: Computer Graphics 10/17/18 1. Modify lines.cpp to display lines in the following patterns: a. a long dash and a dot, (.. ) b. two close dots followed by a distant dot ( ) 2. Modify the program by adding a filled green polygon with 6 sides and a filled yellow polygon with 9 sides. 3. Repeat the above step with two different polygon modes. 4. Draw one polygon with vertices ordered in anti-clockwise direction and another in clockwise direction. Enable culling to see its effects. 5. Suppose you use the Bresenham line algorithm to draw a line from (20, 30) to (250, 100). If the current point drawn is (33, 34), what will be the next two points drawn? Show your steps. 6. Make use of glviewport() to display two sine curves on the same screen, one on the
2 upper left region of the screen and one on the lower right. Report: Drawing objects in 3D space requires a lot of mathematical skills and interaction in order to render a simple image on a computer screen. Tools like OpenGL were not made to solve these problems with brute force, but rather were highly optimized and tweaked superfluously in order to efficiently render pixels in milliseconds. These involve simple lines, stippled lines, polygons, and even 3D polygons that contain a front and back face that can be flipped clockwise or counter-clockwise. The methods that were developed to make them required little processing power and memory, but also had to use a lot of thought to solve line by line. By finishing and completing this lab, I believe I have earned full credit, including an extra twenty points for completing problems 5 and 6. Mastering these concepts were not an easy endeavor
3 Problems 1-4 #include <GL/glut.h> #include <math.h> #define drawoneline(x1,y1,x2,y2) glbegin(gl_lines); glvertex2f ((x1),(y1)); glvertex2f ((x2),(y2)); // prototype function void draw_poly(int Starting x, int Starting Y, int sides, int radius, float rotationangle) void draw_poly(int, int, int, int, float); void draw_poly(int x0, int y0, int n, int radius, float rotangle) glbegin(gl_polygon); double angle = rotangle * / 180; //initial angle double angleinc = 2 * / n; // angle increment for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) //repeat n times angle += angleinc; glvertex2i((int)(radius * cos(angle) + x0), (int) (radius * sin(angle) + y0)); // Text Function void text(char* string) char* p; for (p = string; *p; p++) glutbitmapcharacter(glut_bitmap_helvetica_10, *p); void init(void) glclearcolor(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0); glshademodel(gl_flat);
4 void display(void) // Starting (x,y) points for shapes int x0, y0; // XY Axis and formatting lines glclear(gl_color_buffer_bit); glrasterpos2i(-490, -480); //text("(-500, -500)"); glrasterpos2i(390, 470); //text("(500, 500)"); glrasterpos2i(0, 5); //text("(0, 0)"); glbegin(gl_lines); // x axis glvertex2f(-500, 0); glvertex2f(500, 0); // y axis glvertex2f(0, -500); glvertex2f(0, 500); glvertex2f(-500, 450); glvertex2f(500, 450); glvertex2f(-500, -50); glvertex2f(500, -50); glvertex2f(0, -250); glvertex2f(500, -250); // Problem 1: glrasterpos2i(-490, 460); //text("1: Stipple Lines"); glenable(gl_line_stipple); // 1st row: a long dash and a dot, (.
5 . ) glcolor3f(1.0, 0.0, 0.0); glrasterpos2i(-490, 350); //text("row1: gllinestipple(1, 0xF99F)"); gllinestipple(1, 0xF99F); drawoneline(-490.0, 300.0, 0.0, 300); // drawoneline(-490.0x, 300.0y is starting point of Stipple line // 0.0x, 300y) is the ending point of Stipple line; // 2nd row: Two close dots followed by a distant dot ( ) glcolor3f(0.0, 0.0, 1.0); glrasterpos2i(-490, 250); //text("row2: Factor 1: gllinestipple(1, 0x252525);"); gllinestipple(1, 0x252525); drawoneline(-490.0, 200.0, 0, 200.0); // 3rd row: Two close dots followed by a distant dot ( ) glcolor3f(0.0, 0.0, 1.0); glrasterpos2i(-490, 150); //text("row3: Factor 5: gllinestipple(5, 0x252525);"); gllinestipple(5, 0x252525); drawoneline(-490.0, 100, 0, 100); gldisable(gl_line_stipple); //Problem 2: glrasterpos2i(10, 460); //text("2: Green Hexagon & Yellow Nonagon"); //Hexagon: Green glfrontface(gl_cw); glpolygonmode(gl_front, GL_FILL); glcolor3f(0.0, 1.0, 0.0); glbegin(gl_polygon); x0 = 250;
6 y0 = 440; glvertex2i(x0, y0); glvertex2i(x , y0-50); glvertex2i(x , y0-150); glvertex2i(x0, y0-200); glvertex2i(x0-100, y0-150); glvertex2i(x0-100, y0-50); // 9 Sided Poly: Yellow. glpolygonmode(gl_front, GL_FILL); glcolor3f(1.0, 1.0, 0.0); draw_poly(250, 120, 9, 110, 40); // Problem 3 glrasterpos2i(-490, -35); //text("3: 3 Different Polygon Modes"); glrasterpos2i(-490, -80); //text("1: glpolygonmode(gl_front, GL_POINT);"); glrasterpos2i(-490, -120); //text("2: glpolygonmode(gl_front, GL_LINE);"); glrasterpos2i(-490, -160); //text("3: glpolygonmode(gl_front, GL_FILL);"); // 8 Points/Vertices of a Polygon glpolygonmode(gl_front, GL_POINT); glpointsize(8); draw_poly(-250, -320, 8, 120, 45); // 8 Sided Poly: No Fill
7 glpolygonmode(gl_front, GL_LINE); glcolor3f(0.0, 1.0, 1.0); draw_poly(-250, -320, 8, 80, 45); // 8 Sided Poly: Fill: Red glpolygonmode(gl_front, GL_FILL); glcolor3f(1.0, 0.0, 0.0); draw_poly(-250, -320, 8, 40, 45); //Problem 4: glrasterpos2i(10, -35); //text("4: Polygons: CCW and CW with culling."); glrasterpos2i(10, -80); //text("red Diamond: glfrontface(gl_ccw)"); glpolygonmode(gl_front, GL_LINE); draw_poly(250, -175, 8, 50, 45); // Counter-Clockwise glpolygonmode(gl_front, GL_FILL); glcolor3f(1.0, 0.0, 0.0); draw_poly(250, -175, 4, 50, 90); glrasterpos2i(10, -280); //text("red Diamond: glfrontface(gl_cw)");
8 glpolygonmode(gl_front, GL_LINE); draw_poly(250, -375, 8, 50, 45); // Clockwise glfrontface(gl_cw); glpolygonmode(gl_front, GL_FILL); glcolor3f(1.0, 0.0, 0.0); draw_poly(250, -375, 4, 50, 90); glflush(); void reshape(int w, int h) glviewport(0, 0, (GLsizei)w, (GLsizei)h); glmatrixmode(gl_projection); glloadidentity(); // gluortho2d(-500, (GLdouble)w, 500, (GLdouble)h); // Doesn't work with this. gluortho2d(-500, 500, -500, 500); // gluortho2d(left, RIGHT, BOTTOM, TOP); // gluortho2d(-500x to 500x, -500y to 500y); int main(int argc, char** argv) glutinit(&argc, argv); glutinitdisplaymode(glut_single GLUT_RGB); glutinitwindowsize(500, 500); glutinitwindowposition(50, 50); glutcreatewindow("cse-420: Lab4"); init(); glutdisplayfunc(display); glutreshapefunc(reshape); glutmainloop(); return 0;
9 Problem 5: Bresenham Line 1. Points (x 0, y 0 ) = (20, 30) (x 1, y 1 ) = (250, 100) 2. Calculate Δxx and Δxy Δxx = x 1 - x 0 = = 230 Δxy = y 1 - y 0 = = Calculate 2*Δxx and 2*Δxy. 2Δxx = 2 * 230 = 460 2Δxy = 2 * 70 = Deltas give P 0 P 0 = 2Δxy - Δxx 5. Use upper or lower formula if P < 0; P k < 0 (x k + 1, y k ) is next plot point P k + 1 = P k + 2Δxy P k > 0 (x k + 1, y k + 1) is next plot point P k + 1 = P k +2Δxy - 2Δxx 6. Calculate Slope m. m = Δxy/Δxx = 70/230 = Values m x0 x1 dx 2dx y0 y1 dy 2dy Plotting k P Upper or Lower Eq. Plug Numbers P x y 0 P 0 P 0 = 2dy - dx P 1 P 1 = P 0 + 2dy P 2 P 2 = P 1 + 2dy - 2dx P 3 P 3 = P 2 + 2dy P 4 P 4 = P 3 + 2dy
10 5 P 5 P 5 = P 4 + 2dy P 6 P 6 = P 5 + 2dy -2dx P 7 P 7 = P 6 + 2dy P 8 P 8 = P 7 + 2dy P 9 P 9 = P 8 + 2dy - 2dx P 10 P 10 = P 9 + 2dy P 11 P 11 = P dy P 12 P 12 = P dy P 13 P 13 = P dy P 14 P 14 = P dy - 2dx P 15 P 15 = P dy Result a. Next two points from (33, 34) is i. (34, 34) ii. (35, 34)
11 Problem 6: Viewport #include <GL/glut.h> #include <math.h> void init(void) glclearcolor(1, 1, 1, 0); glmatrixmode(gl_projection); glloadidentity(); // Draw Sine and Negative Sine Function void drawsin(); void drawsin() float x; //First Sine Curve glcolor3f(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f); glbegin(gl_line_strip); for (x = -2.0; x <= 2.0; x += 0.01) glvertex2f(x, sin(2 * 3.14*x)); //Second Sine Curve glbegin(gl_line_strip); glcolor3f(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f); for (x = -2.0; x <= 2.0; x += 0.01) glvertex2f(x, -sin(2 * 3.14*x)); //XY Axis Lines
12 glbegin(gl_lines); glvertex2f(-2, 0); glvertex2f(2, 0); glvertex2f(0, -2); glvertex2f(0, 2); void display(void) glclear(gl_color_buffer_bit); // 1st Viewport // Scale View to (-2, 2, -2, 2) cause sine -1 < y < 1 gluortho2d(-2, 2, -2, 2); glviewport(0, 250, 250, 250); // (0x, 250y,... is the point of the bottom-left corner of this 1st viewport. // Original window 500px wide by 500px high. glutinitwindowsize(500, 500); drawsin(); glloadidentity(); // Reset Identity //2nd Viewport gluortho2d(-2, 2, -2, 2); glviewport(250, 0, 250, 250); // (250x, 0y,... is the point of the bottom-left corner of this 2nd viewport. drawsin(); glloadidentity(); // Reset Back to original Size; glviewport(0, 0, 500, 500); // XY axis lines: Blue glcolor3f(0.0, 0.0, 1.0); glbegin(gl_lines); glvertex2f(-2, 0); glvertex2f(2, 0); glvertex2f(0, -2);
13 glvertex2f(0, 2); glflush(); int main(int argc, char** argv) glutinit(&argc, argv); glutinitwindowsize(500, 500); glutinitwindowposition(200, 20); glutcreatewindow("cse-420: Lab4, Viewports"); init(); glutdisplayfunc(display); glutmainloop(); return 0;
Duc Nguyen CSE 420 Computer Graphics 10/10/2018 Homework 1
 Duc Nguyen CSE 420 Computer Graphics 10/10/2018 Homework 1 1. The endpoints of a given line are (0, 0) and (18, 6). Compute the first 4 values of y manually using Bresenham's Line Algorithm as x steps
Duc Nguyen CSE 420 Computer Graphics 10/10/2018 Homework 1 1. The endpoints of a given line are (0, 0) and (18, 6). Compute the first 4 values of y manually using Bresenham's Line Algorithm as x steps
Andrew Yenalavitch Homework 1 CSE Fall 2014
 Andrew Yenalavitch Homework 1 CSE 420 - Fall 2014 1.) ( 20 points ) In the class, we have discussed how to draw a line given by y = m x + b using Besenham's algorithm with m 1. Extend the algorithm to
Andrew Yenalavitch Homework 1 CSE 420 - Fall 2014 1.) ( 20 points ) In the class, we have discussed how to draw a line given by y = m x + b using Besenham's algorithm with m 1. Extend the algorithm to
by modifying the glutinitwindowsize() function you can change the screen size to whatever you please.
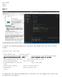 Zoe Veale Lab 2 Draw2 part 1: I edited the glutinitwindowsize() function tom change the size of my screen window. int main(int argc, char** argv) glutinit(&argc, argv); //initialize toolkit glutinitdisplaymode
Zoe Veale Lab 2 Draw2 part 1: I edited the glutinitwindowsize() function tom change the size of my screen window. int main(int argc, char** argv) glutinit(&argc, argv); //initialize toolkit glutinitdisplaymode
Lecture 3. Understanding of OPenGL programming
 Lecture 3 Understanding of OPenGL programming What is OpenGL GL: stands for Graphic Library Software interface for rendering purposes for 2D or 3D geometric data objects. Various Pieces gl: The basic libraries.
Lecture 3 Understanding of OPenGL programming What is OpenGL GL: stands for Graphic Library Software interface for rendering purposes for 2D or 3D geometric data objects. Various Pieces gl: The basic libraries.
Drawing Primitives. OpenGL basics
 CSC 706 Computer Graphics / Dr. N. Gueorguieva 1 OpenGL Libraries Drawing Primitives OpenGL basics OpenGL core library OpenGL32 on Windows GL on most unix/linux systems (libgl.a) OpenGL Utility Library
CSC 706 Computer Graphics / Dr. N. Gueorguieva 1 OpenGL Libraries Drawing Primitives OpenGL basics OpenGL core library OpenGL32 on Windows GL on most unix/linux systems (libgl.a) OpenGL Utility Library
COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB # 3
 COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB # 3 Chapter 2: COMPUTER GRAPHICS by F.S HILLs. Initial steps in drawing figures (polygon, rectangle etc) Objective: Basic understanding of simple code in OpenGL and initial steps
COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB # 3 Chapter 2: COMPUTER GRAPHICS by F.S HILLs. Initial steps in drawing figures (polygon, rectangle etc) Objective: Basic understanding of simple code in OpenGL and initial steps
Graphics Programming
 Graphics Programming 3 rd Week, 2011 OpenGL API (1) API (application programming interface) Interface between an application program and a graphics system Application Program OpenGL API Graphics Library
Graphics Programming 3 rd Week, 2011 OpenGL API (1) API (application programming interface) Interface between an application program and a graphics system Application Program OpenGL API Graphics Library
CS559: Computer Graphics. Lecture 12: OpenGL Li Zhang Spring 2008
 CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 12: OpenGL Li Zhang Spring 2008 Reading Redbook Ch 1 & 2 So far: 3D Geometry Pipeline Model Space (Object Space) Rotation Translation Resizing World Space M Rotation Translation
CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 12: OpenGL Li Zhang Spring 2008 Reading Redbook Ch 1 & 2 So far: 3D Geometry Pipeline Model Space (Object Space) Rotation Translation Resizing World Space M Rotation Translation
Assignment 1. Simple Graphics program using OpenGL
 Assignment 1 Simple Graphics program using OpenGL In this assignment we will use basic OpenGL functions to draw some basic graphical figures. Example: Consider following program to draw a point on screen.
Assignment 1 Simple Graphics program using OpenGL In this assignment we will use basic OpenGL functions to draw some basic graphical figures. Example: Consider following program to draw a point on screen.
Announcements OpenGL. Computer Graphics. Autumn 2009 CS4815
 Computer Graphics Autumn 2009 Outline 1 Labs 2 Labs Outline 1 Labs 2 Labs Labs Week02 lab Marking 8 10 labs in total each lab worth 2 3% of overall grade marked on attendance and completion of lab completed
Computer Graphics Autumn 2009 Outline 1 Labs 2 Labs Outline 1 Labs 2 Labs Labs Week02 lab Marking 8 10 labs in total each lab worth 2 3% of overall grade marked on attendance and completion of lab completed
Programming with OpenGL Part 2: Complete Programs Computer Graphics I, Fall
 Programming with OpenGL Part 2: Complete Programs 91.427 Computer Graphics I, Fall 2008 1 1 Objectives Refine first program Alter default values Introduce standard program structure Simple viewing 2-D
Programming with OpenGL Part 2: Complete Programs 91.427 Computer Graphics I, Fall 2008 1 1 Objectives Refine first program Alter default values Introduce standard program structure Simple viewing 2-D
Source code: #include <iostream>
 Andrew Yenalavitch Homework 4 CSE 520 - Winter 2015 1. ( 10 points ) Write a program that finds the knot vector ( u 0,..., u n-1 ) of a B-spline. It asks for 'number of control points' and 'degree of spline'
Andrew Yenalavitch Homework 4 CSE 520 - Winter 2015 1. ( 10 points ) Write a program that finds the knot vector ( u 0,..., u n-1 ) of a B-spline. It asks for 'number of control points' and 'degree of spline'
Lectures OpenGL Introduction
 Lectures OpenGL Introduction By Tom Duff Pixar Animation Studios Emeryville, California and George Ledin Jr Sonoma State University Rohnert Park, California 2004, Tom Duff and George Ledin Jr 1 What is
Lectures OpenGL Introduction By Tom Duff Pixar Animation Studios Emeryville, California and George Ledin Jr Sonoma State University Rohnert Park, California 2004, Tom Duff and George Ledin Jr 1 What is
Computer Graphics. Making Pictures. Computer Graphics CSC470 1
 Computer Graphics Making Pictures Computer Graphics CSC470 1 Getting Started Making Pictures Graphics display: Entire screen (a); windows system (b); [both have usual screen coordinates, with y-axis y
Computer Graphics Making Pictures Computer Graphics CSC470 1 Getting Started Making Pictures Graphics display: Entire screen (a); windows system (b); [both have usual screen coordinates, with y-axis y
Graphics Programming. August 31, Programming of the Sierpinski gasket. Programming with OpenGL and C/C++
 Computer Graphics Graphics Programming August 31, 2005 Contents Our Goal in This Chapter Programming of the Sierpinski gasket How To? Programming with OpenGL and C/C++ OpenGL API (Application Programmer
Computer Graphics Graphics Programming August 31, 2005 Contents Our Goal in This Chapter Programming of the Sierpinski gasket How To? Programming with OpenGL and C/C++ OpenGL API (Application Programmer
Bob s Concise Introduction to Doxygen
 Bob s Concise Introduction to Doxygen by Robert S Laramee Visual and Interactive Computing Group Department of Computer Science Swansea University Swansea, Wales, UK 1 Comment Standard February 14, 2011
Bob s Concise Introduction to Doxygen by Robert S Laramee Visual and Interactive Computing Group Department of Computer Science Swansea University Swansea, Wales, UK 1 Comment Standard February 14, 2011
Announcements OpenGL. Computer Graphics. Spring CS4815
 Computer Graphics Spring 2017-2018 Outline 1 2 Tutes and Labs Tute02, vector review (see matrix) Week02 lab Lab Marking 10 labs in total each lab worth 3% of overall grade marked on attendance and completion
Computer Graphics Spring 2017-2018 Outline 1 2 Tutes and Labs Tute02, vector review (see matrix) Week02 lab Lab Marking 10 labs in total each lab worth 3% of overall grade marked on attendance and completion
Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2
 Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 A more complex example recursive refinement Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 A more complex example recursive refinement Can OpenGL draw continuous
Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 A more complex example recursive refinement Introduction to OpenGL: Part 2 A more complex example recursive refinement Can OpenGL draw continuous
Basic Graphics Programming
 15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 2 Basic Graphics Programming Graphics Pipeline OpenGL API Primitives: Lines, Polygons Attributes: Color Example January 17, 2002 [Angel Ch. 2] Frank Pfenning Carnegie
15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 2 Basic Graphics Programming Graphics Pipeline OpenGL API Primitives: Lines, Polygons Attributes: Color Example January 17, 2002 [Angel Ch. 2] Frank Pfenning Carnegie
PART-I: Lab for MCS-051 (Advanced Internet Technologies)
 PART-I: Lab for MCS-051 (Advanced Internet Technologies) Q.1. Write a Program using Servlet and JDBC for developing online application for students attendance management for MCA V semester students of
PART-I: Lab for MCS-051 (Advanced Internet Technologies) Q.1. Write a Program using Servlet and JDBC for developing online application for students attendance management for MCA V semester students of
CS559: Computer Graphics. Lecture 12: OpenGL Transformation Li Zhang Spring 2008
 CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 2: OpenGL Transformation Li Zhang Spring 28 Today Transformation in OpenGL Reading Chapter 3 Last time Primitive Details glpolygonmode(glenum face, GLenum mode); face:
CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 2: OpenGL Transformation Li Zhang Spring 28 Today Transformation in OpenGL Reading Chapter 3 Last time Primitive Details glpolygonmode(glenum face, GLenum mode); face:
To Do. Computer Graphics (Fall 2008) Course Outline. Course Outline. Methodology for Lecture. Demo: Surreal (HW 3)
 Computer Graphics (Fall 2008) COMS 4160, Lecture 9: OpenGL 1 http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~cs4160 To Do Start thinking (now) about HW 3. Milestones are due soon. Course Course 3D Graphics Pipeline 3D Graphics
Computer Graphics (Fall 2008) COMS 4160, Lecture 9: OpenGL 1 http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~cs4160 To Do Start thinking (now) about HW 3. Milestones are due soon. Course Course 3D Graphics Pipeline 3D Graphics
Using OpenGL with CUDA
 Using OpenGL with CUDA Installing OpenGL and GLUT; compiling with nvcc Basics of OpenGL and GLUT in C Interoperability between OpenGL and CUDA OpenGL = Open Graphic Library creation of 3D graphic primitives
Using OpenGL with CUDA Installing OpenGL and GLUT; compiling with nvcc Basics of OpenGL and GLUT in C Interoperability between OpenGL and CUDA OpenGL = Open Graphic Library creation of 3D graphic primitives
C++ is Fun Part 13 at Turbine/Warner Bros.! Russell Hanson
 C++ is Fun Part 13 at Turbine/Warner Bros.! Russell Hanson Syllabus 1) First program and introduction to data types and control structures with applications for games learning how to use the programming
C++ is Fun Part 13 at Turbine/Warner Bros.! Russell Hanson Syllabus 1) First program and introduction to data types and control structures with applications for games learning how to use the programming
Programming with OpenGL Part 3: Three Dimensions
 Programming with OpenGL Part 3: Three Dimensions Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico Objectives Develop a more sophisticated
Programming with OpenGL Part 3: Three Dimensions Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico Objectives Develop a more sophisticated
 OpenGL for dummies hello.c #include int main(int argc, char** argv) { glutinit(&argc, argv); glutinitdisplaymode (GLUT_SINGLE GLUT_RGB); glutinitwindowsize (250, 250); glutinitwindowposition
OpenGL for dummies hello.c #include int main(int argc, char** argv) { glutinit(&argc, argv); glutinitdisplaymode (GLUT_SINGLE GLUT_RGB); glutinitwindowsize (250, 250); glutinitwindowposition
Drawing and Coordinate Systems
 Drawing and Coordinate Systems Coordinate Systems World Coordinate system World window Screen Coordinate system Viewport Window to viewport mapping Screen Coordinate System Glut OpenGL (0,0) 0) Screen
Drawing and Coordinate Systems Coordinate Systems World Coordinate system World window Screen Coordinate system Viewport Window to viewport mapping Screen Coordinate System Glut OpenGL (0,0) 0) Screen
Drawing and Coordinate Systems
 Drawing and Coordinate Systems Coordinate Systems Screen Coordinate system World Coordinate system World window Viewport Window to viewport mapping Screen Coordinate System Glut OpenGL (0,0) Screen Coordinate
Drawing and Coordinate Systems Coordinate Systems Screen Coordinate system World Coordinate system World window Viewport Window to viewport mapping Screen Coordinate System Glut OpenGL (0,0) Screen Coordinate
Teacher Assistant : Tamir Grossinger Reception hours: by - Building 37 / office -102 Assignments: 4 programing using
 Teacher Assistant : Tamir Grossinger email: tamirgr@gmail.com Reception hours: by email - Building 37 / office -102 Assignments: 4 programing using C++ 1 theoretical You can find everything you need in
Teacher Assistant : Tamir Grossinger email: tamirgr@gmail.com Reception hours: by email - Building 37 / office -102 Assignments: 4 programing using C++ 1 theoretical You can find everything you need in
UNIT 7 LIGHTING AND SHADING. 1. Explain phong lighting model. Indicate the advantages and disadvantages. (Jun2012) 10M
 UNIT 7 LIGHTING AND SHADING 1. Explain phong lighting model. Indicate the advantages and disadvantages. (Jun2012) 10M Ans: Phong developed a simple model that can be computed rapidly It considers three
UNIT 7 LIGHTING AND SHADING 1. Explain phong lighting model. Indicate the advantages and disadvantages. (Jun2012) 10M Ans: Phong developed a simple model that can be computed rapidly It considers three
CSE4030 Introduction to Computer Graphics
 CSE4030 Introduction to Computer Graphics Dongguk University Jeong-Mo Hong Week 2 The first step on a journey to the virtual world An introduction to computer graphics and interactive techniques How to
CSE4030 Introduction to Computer Graphics Dongguk University Jeong-Mo Hong Week 2 The first step on a journey to the virtual world An introduction to computer graphics and interactive techniques How to
Programming using OpenGL: A first Introduction
 Programming using OpenGL: A first Introduction CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Machiraju/Zhang/Möller 1 Today Overview GL, GLU, GLUT, and GLUI First example OpenGL functions and
Programming using OpenGL: A first Introduction CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Machiraju/Zhang/Möller 1 Today Overview GL, GLU, GLUT, and GLUI First example OpenGL functions and
GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT, GL_PROJECTION, GL_MODELVIEW
 OpenGL Syntax Functions have prefix gl and initial capital letters for each word glclearcolor(), glenable(), glpushmatrix() glu for GLU functions glulookat(), gluperspective() constants begin with GL_,
OpenGL Syntax Functions have prefix gl and initial capital letters for each word glclearcolor(), glenable(), glpushmatrix() glu for GLU functions glulookat(), gluperspective() constants begin with GL_,
FAKULTI TEKNOLOGI MAKLUMAT DAN KOMUNIKASI BITM INTERACTIVE COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB SESSION 4. C++ - OpenGL
 FAKULTI TEKNOLOGI MAKLUMAT DAN KOMUNIKASI BITM 3213 - INTERACTIVE COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB SESSION 4 C++ - OpenGL Part 1- C++ - Texture Mapping 1. Download texture file and put it into your current folder
FAKULTI TEKNOLOGI MAKLUMAT DAN KOMUNIKASI BITM 3213 - INTERACTIVE COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB SESSION 4 C++ - OpenGL Part 1- C++ - Texture Mapping 1. Download texture file and put it into your current folder
Computer Graphics: Line Drawing Algorithms
 Computer Graphics: Line Drawing Algorithms 1 Graphics hardware The problem scan conversion Considerations Line equations Scan converting algorithms A very simple solution The DDA algorithm, Bresenham algorithm
Computer Graphics: Line Drawing Algorithms 1 Graphics hardware The problem scan conversion Considerations Line equations Scan converting algorithms A very simple solution The DDA algorithm, Bresenham algorithm
Basic Graphics Programming
 CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 2 Basic Graphics Programming January 11, 2012 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~jbarbic/cs480-s12/ Graphics Pipeline OpenGL API
CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 2 Basic Graphics Programming January 11, 2012 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~jbarbic/cs480-s12/ Graphics Pipeline OpenGL API
Display Lists in OpenGL
 Display Lists in OpenGL Display lists are a mechanism for improving performance of interactive OpenGL applications. A display list is a group of OpenGL commands that have been stored for later execution.
Display Lists in OpenGL Display lists are a mechanism for improving performance of interactive OpenGL applications. A display list is a group of OpenGL commands that have been stored for later execution.
11/1/13. Basic Graphics Programming. Teaching Assistant. What is OpenGL. Course Producer. Where is OpenGL used. Graphics library (API)
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 2 Basic Graphics Programming Teaching Assistant Yijing Li Office hours TBA Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Graphics Pipeline OpenGL API Primitives: Lines,
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 2 Basic Graphics Programming Teaching Assistant Yijing Li Office hours TBA Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Graphics Pipeline OpenGL API Primitives: Lines,
3D computer graphics: geometric modeling of objects in the computer and rendering them
 SE313: Computer Graphics and Visual Programming Computer Graphics Notes Gazihan Alankus, Spring 2012 Computer Graphics 3D computer graphics: geometric modeling of objects in the computer and rendering
SE313: Computer Graphics and Visual Programming Computer Graphics Notes Gazihan Alankus, Spring 2012 Computer Graphics 3D computer graphics: geometric modeling of objects in the computer and rendering
Computer Graphics Introduction to OpenGL
 Computer Graphics 2015 3. Introduction to OpenGL Hongxin Zhang State Key Lab of CAD&CG, Zhejiang University 2015-09-28 2. 2D Graphics Algorithms (cont.) Rasterization Computer Graphics @ ZJU Hongxin Zhang,
Computer Graphics 2015 3. Introduction to OpenGL Hongxin Zhang State Key Lab of CAD&CG, Zhejiang University 2015-09-28 2. 2D Graphics Algorithms (cont.) Rasterization Computer Graphics @ ZJU Hongxin Zhang,
CS 4731 Lecture 3: Introduction to OpenGL and GLUT: Part II. Emmanuel Agu
 CS 4731 Lecture 3: Introduction to OpenGL and GLUT: Part II Emmanuel Agu Recall: OpenGL Skeleton void main(int argc, char** argv){ // First initialize toolkit, set display mode and create window glutinit(&argc,
CS 4731 Lecture 3: Introduction to OpenGL and GLUT: Part II Emmanuel Agu Recall: OpenGL Skeleton void main(int argc, char** argv){ // First initialize toolkit, set display mode and create window glutinit(&argc,
Computer Graphics Anatomy of GUI. Computer Graphics CSC470 1
 Computer Graphics Anatomy of GUI 1 Anatomy of GLUT keyboard mouse OpenGL Application if (key == f key == F ) { glutfullscreen(); } else if(key == w key == W ) { glutreshapewindow(640,480); } display reshape
Computer Graphics Anatomy of GUI 1 Anatomy of GLUT keyboard mouse OpenGL Application if (key == f key == F ) { glutfullscreen(); } else if(key == w key == W ) { glutreshapewindow(640,480); } display reshape
COS340A Assignment 1 I Pillemer Student# March 25 th 2007 p1/15
 COS340A Assignment 1 I Pillemer Student# 3257 495 9 March 25 th 2007 p1/15 Assignment 1 I Pillemer Student#: 3257 495 9 COS340A Date submitted: March 25, 2007 Question 1... p2 3 Question 2... p4 Question
COS340A Assignment 1 I Pillemer Student# 3257 495 9 March 25 th 2007 p1/15 Assignment 1 I Pillemer Student#: 3257 495 9 COS340A Date submitted: March 25, 2007 Question 1... p2 3 Question 2... p4 Question
CS380: Computer Graphics Basic OpenGL Structure. Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL:
 CS380: Computer Graphics Basic OpenGL Structure Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL: http://sglab.kaist.ac.kr/~sungeui/cg Class Objectives Understand the basic OpenGL program structure and how OpenGL supports
CS380: Computer Graphics Basic OpenGL Structure Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL: http://sglab.kaist.ac.kr/~sungeui/cg Class Objectives Understand the basic OpenGL program structure and how OpenGL supports
CS621 Lab 1 Name: Ihab Zbib
 CS621 Lab 1 Name: Ihab Zbib 1) The program draw.cpp draws two rectangles and two triangles. The program compiles and executes successfully. What follows are the snap shots of the output. Illustration 1:
CS621 Lab 1 Name: Ihab Zbib 1) The program draw.cpp draws two rectangles and two triangles. The program compiles and executes successfully. What follows are the snap shots of the output. Illustration 1:
Chapter 13 Selection and Feedback
 OpenGL Programming Guide (Addison-Wesley Publishing Company) Chapter 13 Selection and Feedback Chapter Objectives After reading this chapter, you ll be able to do the following: Create applications that
OpenGL Programming Guide (Addison-Wesley Publishing Company) Chapter 13 Selection and Feedback Chapter Objectives After reading this chapter, you ll be able to do the following: Create applications that
OpenGL JOGL. OpenGL & JOGL. Shaoting Zhang, or Tony. September 12, 2007
 September 12, 2007 1 Program 2 HW: Graphing in I m Program Cross-language (C, C++, C#, Java, Python, Delphi) Cross-platform (Linux, Windows, Unix, PS3) Low-level (provides only rendering func.) State machine
September 12, 2007 1 Program 2 HW: Graphing in I m Program Cross-language (C, C++, C#, Java, Python, Delphi) Cross-platform (Linux, Windows, Unix, PS3) Low-level (provides only rendering func.) State machine
Precept 2 Aleksey Boyko February 18, 2011
 Precept 2 Aleksey Boyko February 18, 2011 Getting started Initialization Drawing Transformations Cameras Animation Input Keyboard Mouse Joystick? Textures Lights Programmable pipeline elements (shaders)
Precept 2 Aleksey Boyko February 18, 2011 Getting started Initialization Drawing Transformations Cameras Animation Input Keyboard Mouse Joystick? Textures Lights Programmable pipeline elements (shaders)
Chapter 7 Display Lists
 OpenGL Programming Guide (Addison-Wesley Publishing Company) Chapter 7 Display Lists Chapter Objectives After reading this chapter, you ll be able to do the following: Understand how display lists can
OpenGL Programming Guide (Addison-Wesley Publishing Company) Chapter 7 Display Lists Chapter Objectives After reading this chapter, you ll be able to do the following: Understand how display lists can
Fourier Series. Given a periodic function, x(t), (-T <t <T): + b n sin n t T. a n cos n t T. 2 a 0 + Z T. a n = 1 T. x(t) cos n t T. b n = 1 T.
 x(t) = 1 1X 2 a 0 + Fourier Series Given a periodic function, x(t), (-T
x(t) = 1 1X 2 a 0 + Fourier Series Given a periodic function, x(t), (-T
CMSC 425: Lecture 4 More about OpenGL and GLUT Tuesday, Feb 5, 2013
 CMSC 425: Lecture 4 More about OpenGL and GLUT Tuesday, Feb 5, 2013 Reading: See any standard reference on OpenGL or GLUT. Basic Drawing: In the previous lecture, we showed how to create a window in GLUT,
CMSC 425: Lecture 4 More about OpenGL and GLUT Tuesday, Feb 5, 2013 Reading: See any standard reference on OpenGL or GLUT. Basic Drawing: In the previous lecture, we showed how to create a window in GLUT,
CS 4204 Computer Graphics
 CS 4204 Computer Graphics OpenGL Basics Yong Cao Virginia Tech References: 2001 Siggraph, An Interactive Introduction to OpenGL Programming, Dave Shreiner,Ed Angel, Vicki Shreiner Official Presentation
CS 4204 Computer Graphics OpenGL Basics Yong Cao Virginia Tech References: 2001 Siggraph, An Interactive Introduction to OpenGL Programming, Dave Shreiner,Ed Angel, Vicki Shreiner Official Presentation
Books, OpenGL, GLUT, GLUI, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, and G3D
 Books, OpenGL, GLUT, GLUI, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, and G3D CS334 Spring 2012 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Computer Graphics Pipeline Geometric Primitives
Books, OpenGL, GLUT, GLUI, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, and G3D CS334 Spring 2012 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Computer Graphics Pipeline Geometric Primitives
Computer Graphics. OpenGL
 Computer Graphics OpenGL What is OpenGL? OpenGL (Open Graphics Library) is a library for computer graphics It consists of several procedures and functions that allow a programmer to specify the objects
Computer Graphics OpenGL What is OpenGL? OpenGL (Open Graphics Library) is a library for computer graphics It consists of several procedures and functions that allow a programmer to specify the objects
BOUNCING BALL IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR
 COMPUTER GRAPHICS LECTURE 07 BOUNCING BALL IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR WWW.IMRANIHSAN.COM /* * GL07BouncingBall.cpp: A ball bouncing inside the window */ #include // for MS Windows #include
COMPUTER GRAPHICS LECTURE 07 BOUNCING BALL IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR WWW.IMRANIHSAN.COM /* * GL07BouncingBall.cpp: A ball bouncing inside the window */ #include // for MS Windows #include
Introduction to Computer Graphics with OpenGL/GLUT
 Introduction to Computer Graphics with OpenGL/GLUT What is OpenGL? A software interface to graphics hardware Graphics rendering API (Low Level) High-quality color images composed of geometric and image
Introduction to Computer Graphics with OpenGL/GLUT What is OpenGL? A software interface to graphics hardware Graphics rendering API (Low Level) High-quality color images composed of geometric and image
C OMPUTER G RAPHICS Thursday
 C OMPUTER G RAPHICS 2017.04.27 Thursday Professor s original PPT http://calab.hanyang.ac.kr/ Courses Computer Graphics practice3.pdf TA s current PPT not uploaded yet GRAPHICS PIPELINE What is Graphics
C OMPUTER G RAPHICS 2017.04.27 Thursday Professor s original PPT http://calab.hanyang.ac.kr/ Courses Computer Graphics practice3.pdf TA s current PPT not uploaded yet GRAPHICS PIPELINE What is Graphics
Windows and Viewports. Windows and Viewports. Windows and Viewports. Windows and Viewports. CSC 706 Computer Graphics
 CSC 706 Computer Graphics World World Window, Screen Window and Viewport Setting Window and Viewport automatically Tiling Previously we looked at an OpenGL window where x and y were plotted as positive
CSC 706 Computer Graphics World World Window, Screen Window and Viewport Setting Window and Viewport automatically Tiling Previously we looked at an OpenGL window where x and y were plotted as positive
1/12/11. Basic Graphics Programming. What is OpenGL. OpenGL is cross-platform. How does OpenGL work. How does OpenGL work (continued) The result
 CSCI 480 Computer raphics Lecture 2 asic raphics Programming What is OpenL A low- level graphics API for 2D and 3D interac
CSCI 480 Computer raphics Lecture 2 asic raphics Programming What is OpenL A low- level graphics API for 2D and 3D interac
Lecture 2 CISC440/640 Spring Department of Computer and Information Science
 Lecture 2 CISC440/640 Spring 2015 Department of Computer and Information Science Today s Topic The secrets of Glut-tony 2 So let s do some graphics! For the next week or so this is your world: -1 1-1 1
Lecture 2 CISC440/640 Spring 2015 Department of Computer and Information Science Today s Topic The secrets of Glut-tony 2 So let s do some graphics! For the next week or so this is your world: -1 1-1 1
Programming with OpenGL Part 1: Background
 Programming with OpenGL Part 1: Background Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico 1 Objectives Development of the OpenGL API
Programming with OpenGL Part 1: Background Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico 1 Objectives Development of the OpenGL API
OpenGL Introduction Computer Graphics and Visualization
 Fall 2009 2 OpenGL OpenGL System Interaction Portable Consistent visual display regardless of hardware, OS and windowing system Callable from Ada, C, C++, Fortran, Python, Perl and Java Runs on all major
Fall 2009 2 OpenGL OpenGL System Interaction Portable Consistent visual display regardless of hardware, OS and windowing system Callable from Ada, C, C++, Fortran, Python, Perl and Java Runs on all major
2. OpenGL -I. 2.1 What is OpenGL? Things OpenGL can do: -23-
 2.1 What is OpenGL? -23-2. OpenGL -I - Device-independent, application program interface (API) to graphics hardware - 3D-oriented - Event-driven Things OpenGL can do: - wireframe models - depth-cuing effect
2.1 What is OpenGL? -23-2. OpenGL -I - Device-independent, application program interface (API) to graphics hardware - 3D-oriented - Event-driven Things OpenGL can do: - wireframe models - depth-cuing effect
Books, OpenGL, GLUT, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, G3D, and Qt
 Books, OpenGL, GLUT, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, G3D, and Qt CS334 Fall 2015 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Books (and by now means complete ) Interactive Computer
Books, OpenGL, GLUT, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, G3D, and Qt CS334 Fall 2015 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Books (and by now means complete ) Interactive Computer
Graphics Programming. 1. The Sierpinski Gasket. Chapter 2. Introduction:
 Graphics Programming Chapter 2 Introduction: - Our approach is programming oriented. - Therefore, we are going to introduce you to a simple but informative problem: the Sierpinski Gasket - The functionality
Graphics Programming Chapter 2 Introduction: - Our approach is programming oriented. - Therefore, we are going to introduce you to a simple but informative problem: the Sierpinski Gasket - The functionality
Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL)
 Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL) Thilo Kielmann Fall 2008 Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam kielmann@cs.vu.nl http://www.cs.vu.nl/ graphics/ Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL, Input and Interaction), ((57))
Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL) Thilo Kielmann Fall 2008 Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam kielmann@cs.vu.nl http://www.cs.vu.nl/ graphics/ Computer Graphics (Basic OpenGL, Input and Interaction), ((57))
Erik Anchondo cse 520 lab 4
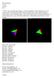 Erik Anchondo 2-6-19 cse 520 lab 4 1. Wrote a glsl program that displays a colored tetrahedron. The tetrahedron starts to rotate on the x axis when the mouse button is clicked once. If the mouse button
Erik Anchondo 2-6-19 cse 520 lab 4 1. Wrote a glsl program that displays a colored tetrahedron. The tetrahedron starts to rotate on the x axis when the mouse button is clicked once. If the mouse button
Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring Programming with OpenGL Part 2: First Program
 Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2017 Programming with OpenGL Part 2: First Program Objectives Refine the first program Introduce a standard program structure - Initialization Program Structure Most
Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2017 Programming with OpenGL Part 2: First Program Objectives Refine the first program Introduce a standard program structure - Initialization Program Structure Most
void drawdot(glint x, GLint y) { glbegin(gl_points); glvertex2i(x,y); glend();
 CSC 706 Computer Graphics Primitives, Stippling, Fitting In OpenGL Primitives Examples: GL_POINTS GL_LINES GL_LINE_STRIP GL_POLYGON GL_LINE_LOOP GL_ TRIANGLES GL_QUAD_STRIP GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP GL_TRIANGLE_FAN
CSC 706 Computer Graphics Primitives, Stippling, Fitting In OpenGL Primitives Examples: GL_POINTS GL_LINES GL_LINE_STRIP GL_POLYGON GL_LINE_LOOP GL_ TRIANGLES GL_QUAD_STRIP GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP GL_TRIANGLE_FAN
CS418 OpenGL & GLUT Programming Tutorial (I) Presented by : Wei-Wen Feng 1/30/2008
 CS418 OpenGL & GLUT Programming Tutorial (I) Presented by : Wei-Wen Feng 1/30/2008 2008/2/3 Slide 2 I Am Your TA Name : Wei-Wen Wen Feng 4th Year Graduate Student in Graphics I will be Holding discussion/tutorial
CS418 OpenGL & GLUT Programming Tutorial (I) Presented by : Wei-Wen Feng 1/30/2008 2008/2/3 Slide 2 I Am Your TA Name : Wei-Wen Wen Feng 4th Year Graduate Student in Graphics I will be Holding discussion/tutorial
Cameras (and eye) Ideal Pinhole. Real Pinhole. Real + lens. Depth of field
 Cameras (and eye) Ideal Pinhole Real Pinhole Real + lens Depth of field 1 Z-buffer How do we draw objects? Polygon Based Fast Raytracing Ray/Object intersections Slow Copyright Pixar 2 Raytracing for each
Cameras (and eye) Ideal Pinhole Real Pinhole Real + lens Depth of field 1 Z-buffer How do we draw objects? Polygon Based Fast Raytracing Ray/Object intersections Slow Copyright Pixar 2 Raytracing for each
Lecture 3 Advanced Computer Graphics (CS & SE )
 Lecture 3 Advanced Computer Graphics (CS & SE 233.420) Programming with OpenGL Program Structure Primitives Attributes and States Programming in three dimensions Inputs and Interaction Working with Callbacks
Lecture 3 Advanced Computer Graphics (CS & SE 233.420) Programming with OpenGL Program Structure Primitives Attributes and States Programming in three dimensions Inputs and Interaction Working with Callbacks
Philip Calderon CSE 520 Lab 3 Color Shader
 Philip Calderon CSE 520 Lab 3 Color Shader Summary: The purpose of lab 4 is to produce a pyramid tetrahedron that we are able to rotate it when clicked. Part 1: Color Tetrahedron Part 2: Rotation to show
Philip Calderon CSE 520 Lab 3 Color Shader Summary: The purpose of lab 4 is to produce a pyramid tetrahedron that we are able to rotate it when clicked. Part 1: Color Tetrahedron Part 2: Rotation to show
Modeling Transform. Chapter 4 Geometric Transformations. Overview. Instancing. Specify transformation for objects 李同益
 Modeling Transform Chapter 4 Geometric Transformations 李同益 Specify transformation for objects Allow definitions of objects in own coordinate systems Allow use of object definition multiple times in a scene
Modeling Transform Chapter 4 Geometric Transformations 李同益 Specify transformation for objects Allow definitions of objects in own coordinate systems Allow use of object definition multiple times in a scene
Computer Graphics Primitive Attributes
 Computer Graphics 2015 4. Primitive Attributes Hongxin Zhang State Key Lab of CAD&CG, Zhejiang University 2015-10-12 Previous lessons - Rasterization - line - circle /ellipse? => homework - OpenGL and
Computer Graphics 2015 4. Primitive Attributes Hongxin Zhang State Key Lab of CAD&CG, Zhejiang University 2015-10-12 Previous lessons - Rasterization - line - circle /ellipse? => homework - OpenGL and
OpenGL/GLUT Intro. Week 1, Fri Jan 12
 University of British Columbia CPSC 314 Computer Graphics Jan-Apr 2007 Tamara Munzner OpenGL/GLUT Intro Week 1, Fri Jan 12 http://www.ugrad.cs.ubc.ca/~cs314/vjan2007 News Labs start next week Reminder:
University of British Columbia CPSC 314 Computer Graphics Jan-Apr 2007 Tamara Munzner OpenGL/GLUT Intro Week 1, Fri Jan 12 http://www.ugrad.cs.ubc.ca/~cs314/vjan2007 News Labs start next week Reminder:
Computer Graphics (4731) Lecture 4: 2D Graphics Systems (Drawing Polylines, tiling, & Aspect Ratio)
 Computer Graphics (4731) Lecture 4: 2D Graphics Systems (Drawing Polylines, tiling, & Aspect Ratio) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Screen Coordinate System
Computer Graphics (4731) Lecture 4: 2D Graphics Systems (Drawing Polylines, tiling, & Aspect Ratio) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Screen Coordinate System
Lectures Display List
 Lectures Display List By Tom Duff Pixar Animation Studios Emeryville, California and George Ledin Jr Sonoma State University Rohnert Park, California 2004, Tom Duff and George Ledin Jr 1 What is it? What
Lectures Display List By Tom Duff Pixar Animation Studios Emeryville, California and George Ledin Jr Sonoma State University Rohnert Park, California 2004, Tom Duff and George Ledin Jr 1 What is it? What
Announcement. Homework 1 has been posted in dropbox and course website. Due: 1:15 pm, Monday, September 12
 Announcement Homework 1 has been posted in dropbox and course website Due: 1:15 pm, Monday, September 12 Today s Agenda Primitives Programming with OpenGL OpenGL Primitives Polylines GL_POINTS GL_LINES
Announcement Homework 1 has been posted in dropbox and course website Due: 1:15 pm, Monday, September 12 Today s Agenda Primitives Programming with OpenGL OpenGL Primitives Polylines GL_POINTS GL_LINES
Abel J. P. Gomes LAB. 1. INTRODUCTION TO OpenGL
 Visual Computing and Multimedia Abel J. P. Gomes 1. Getting Started 2. Installing Graphics Libraries: OpenGL and GLUT 3. Setting up an IDE to run graphics programs in OpenGL/GLUT 4. A First OpenGL/GLUT
Visual Computing and Multimedia Abel J. P. Gomes 1. Getting Started 2. Installing Graphics Libraries: OpenGL and GLUT 3. Setting up an IDE to run graphics programs in OpenGL/GLUT 4. A First OpenGL/GLUT
2a. The triangles scale increases (expands) when the 'e' key is pressed and decreases (contracts) when the 'c' key is pressed.
 Erik Anchondo 1-29-19 cse 520 lab 3 1. Wrote a shader program to display three colored triangles, with one of each triangle being red, green, and blue. The colors change which triangle they are applied
Erik Anchondo 1-29-19 cse 520 lab 3 1. Wrote a shader program to display three colored triangles, with one of each triangle being red, green, and blue. The colors change which triangle they are applied
Ulf Assarsson Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology
 Ulf Assarsson Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology 1. I am located in room 4115 in EDIT-huset 2. Email: 3. Phone: 031-772 1775 (office) 4. Course assistant: Tomas Akenine-Mőller
Ulf Assarsson Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology 1. I am located in room 4115 in EDIT-huset 2. Email: 3. Phone: 031-772 1775 (office) 4. Course assistant: Tomas Akenine-Mőller
1.2 Basic Graphics Programming
 Fall 2018 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 1.2 Basic Graphics Programming Hao Li http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 Last time Last Time Story Computer Graphics Image Last Time 3D Printing 3D Capture Animation Modeling
Fall 2018 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 1.2 Basic Graphics Programming Hao Li http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 Last time Last Time Story Computer Graphics Image Last Time 3D Printing 3D Capture Animation Modeling
CS 543 Lecture 1 (Part 3) Prof Emmanuel Agu. Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI)
 Computer Graphics CS 543 Lecture 1 (Part 3) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Recall: OpenGL Skeleton void main(int argc, char** argv){ // First initialize
Computer Graphics CS 543 Lecture 1 (Part 3) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Recall: OpenGL Skeleton void main(int argc, char** argv){ // First initialize
1. Write a shader program that animates the morphing of Figure 'A' to Figure 'B' and back.
 Karl Zachary Maier CSE 520 Homework 1 1. Write a shader program that animates the morphing of Figure 'A' to Figure 'B' and back. /* morph.cpp */ #include #include #include
Karl Zachary Maier CSE 520 Homework 1 1. Write a shader program that animates the morphing of Figure 'A' to Figure 'B' and back. /* morph.cpp */ #include #include #include
Introduction to MS Visual C/C++
 3/4/2002 Burkhard Wünsche Introduction to C/C++ Page 1 of 9 0. Introduction: Introduction to MS Visual C/C++ This tutorial gives a simple introduction to MS Visual C/C++ with an emphasis on OpenGL graphics
3/4/2002 Burkhard Wünsche Introduction to C/C++ Page 1 of 9 0. Introduction: Introduction to MS Visual C/C++ This tutorial gives a simple introduction to MS Visual C/C++ with an emphasis on OpenGL graphics
Computer Graphics Course 2005
 Computer Graphics Course 2005 Introduction to GLUT, GLU and OpenGL Administrative Stuff Teaching Assistant: Rony Goldenthal Reception Hour: Wed. 18:00 19:00 Room 31 (Ross 1) Questions: E-mail: cg@cs Newsgroups:
Computer Graphics Course 2005 Introduction to GLUT, GLU and OpenGL Administrative Stuff Teaching Assistant: Rony Goldenthal Reception Hour: Wed. 18:00 19:00 Room 31 (Ross 1) Questions: E-mail: cg@cs Newsgroups:
Computer Graphics, Chapt 08
 Computer Graphics, Chapt 08 Creating an Image Components, parts of a scene to be displayed Trees, terrain Furniture, walls Store fronts and street scenes Atoms and molecules Stars and galaxies Describe
Computer Graphics, Chapt 08 Creating an Image Components, parts of a scene to be displayed Trees, terrain Furniture, walls Store fronts and street scenes Atoms and molecules Stars and galaxies Describe
20 GLuint objects; 36 Scale += 0.1; 37 break; 38 case GLUT_KEY_DOWN:
 1 1. 1 #include 2 #include 3 Program 1 (OpenGL Sample016) 4 // 5 static int MouseX = 0; // X 6 static int MouseY = 0; // Y 7 static float SpinX = 0; // X 8 static float SpinY = 0;
1 1. 1 #include 2 #include 3 Program 1 (OpenGL Sample016) 4 // 5 static int MouseX = 0; // X 6 static int MouseY = 0; // Y 7 static float SpinX = 0; // X 8 static float SpinY = 0;
2 Transformations and Homogeneous Coordinates
 Brief solutions to Exam in Computer Graphics Time and place: 08:00 3:00 Tuesday March 7, 2009, Gimogatan 4, sal Grades TD388: 3: 20pts; 4: 26pts; 5: 34pts. Glossary API Application Programmer s Interface.
Brief solutions to Exam in Computer Graphics Time and place: 08:00 3:00 Tuesday March 7, 2009, Gimogatan 4, sal Grades TD388: 3: 20pts; 4: 26pts; 5: 34pts. Glossary API Application Programmer s Interface.
// double buffering and RGB glutinitdisplaymode(glut_double GLUT_RGBA); // your own initializations
 #include int main(int argc, char** argv) { glutinit(&argc, argv); Typical OpenGL/GLUT Main Program // GLUT, GLU, and OpenGL defs // program arguments // initialize glut and gl // double buffering
#include int main(int argc, char** argv) { glutinit(&argc, argv); Typical OpenGL/GLUT Main Program // GLUT, GLU, and OpenGL defs // program arguments // initialize glut and gl // double buffering
QUESTION 1 [10] 2 COS340-A October/November 2009
![QUESTION 1 [10] 2 COS340-A October/November 2009 QUESTION 1 [10] 2 COS340-A October/November 2009](/thumbs/91/107455423.jpg) 2 COS340-A QUESTION 1 [10] a) OpenGL uses z-buffering for hidden surface removal. Explain how the z-buffer algorithm works and give one advantage of using this method. (5) Answer: OpenGL uses a hidden-surface
2 COS340-A QUESTION 1 [10] a) OpenGL uses z-buffering for hidden surface removal. Explain how the z-buffer algorithm works and give one advantage of using this method. (5) Answer: OpenGL uses a hidden-surface
Introduction to OpenGL
 CS100433 Introduction to OpenGL Junqiao Zhao 赵君峤 Department of Computer Science and Technology College of Electronics and Information Engineering Tongji University Before OpenGL Let s think what is need
CS100433 Introduction to OpenGL Junqiao Zhao 赵君峤 Department of Computer Science and Technology College of Electronics and Information Engineering Tongji University Before OpenGL Let s think what is need
Introduction to OpenGL Week 1
 CS 432/680 INTERACTIVE COMPUTER GRAPHICS Introduction to OpenGL Week 1 David Breen Department of Computer Science Drexel University Based on material from Ed Angel, University of New Mexico Objectives
CS 432/680 INTERACTIVE COMPUTER GRAPHICS Introduction to OpenGL Week 1 David Breen Department of Computer Science Drexel University Based on material from Ed Angel, University of New Mexico Objectives
Objectives. Image Formation Revisited. Physical Approaches. The Programmer s Interface. Practical Approach. Introduction to OpenGL Week 1
 CS 432/680 INTERACTIVE COMPUTER GRAPHICS Introduction to OpenGL Week 1 David Breen Department of Computer Science Drexel University Objectives Learn the basic design of a graphics system Introduce graphics
CS 432/680 INTERACTIVE COMPUTER GRAPHICS Introduction to OpenGL Week 1 David Breen Department of Computer Science Drexel University Objectives Learn the basic design of a graphics system Introduce graphics
(21) OpenGL GUI. OpenGL GUI 1 UNIX MAGAZINE UNIX. SGI (Silicon Graphics Inc.) Windows PC GUI. UNIX Windows GUI. Java. 1 prefposition() X X
 (21) OpenGL GUI UNIX Windows Macintosh UNIX Windows PC SGI (Silicon Graphics Inc.) Windows PC GUI UNIX Windows GUI Java OpenGL OpenGL SGI 3 / GL GUI OpenGL GL OpenGL SGI 3 GL SGI 3 / 3 1 GL /* GL sample
(21) OpenGL GUI UNIX Windows Macintosh UNIX Windows PC SGI (Silicon Graphics Inc.) Windows PC GUI UNIX Windows GUI Java OpenGL OpenGL SGI 3 / GL GUI OpenGL GL OpenGL SGI 3 GL SGI 3 / 3 1 GL /* GL sample
Computer Graphics 1 Computer Graphics 1
 Projects: an example Developed by Nate Robbins Shapes Tutorial What is OpenGL? Graphics rendering API high-quality color images composed of geometric and image primitives window system independent operating
Projects: an example Developed by Nate Robbins Shapes Tutorial What is OpenGL? Graphics rendering API high-quality color images composed of geometric and image primitives window system independent operating
Lattice Gas Cellular Automaton Model for Fluid Flow
 Lattice Gas Cellular Automaton Model for Fluid Flow lgca.cpp // Lattice Gas Cellular Automaton Model for Fluid Flow 1 #include 3 #include 4 #include 5 using namespace std;
Lattice Gas Cellular Automaton Model for Fluid Flow lgca.cpp // Lattice Gas Cellular Automaton Model for Fluid Flow 1 #include 3 #include 4 #include 5 using namespace std;
Interaction. CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 3
 CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 3 Interaction January 18, 2012 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Client/Server Model Callbacks Double Buffering Hidden Surface Removal Simple Transformations
CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 3 Interaction January 18, 2012 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Client/Server Model Callbacks Double Buffering Hidden Surface Removal Simple Transformations
Hierarchical Modeling: Tree of Transformations, Display Lists and Functions, Matrix and Attribute Stacks,
 Hierarchical Modeling: Tree of Transformations, Display Lists and Functions, Matrix and Attribute Stacks, Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 1 Modeling complex objects/motion Decompose object hierarchically
Hierarchical Modeling: Tree of Transformations, Display Lists and Functions, Matrix and Attribute Stacks, Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 1 Modeling complex objects/motion Decompose object hierarchically
