Midterm Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 11
|
|
|
- Ruth Dalton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Midterm Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 11 Student Name: Class Account Username: Instructions: Read them carefully! The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must turn your exam in when time is announced or risk not having it accepted. Make sure you fill in your name and class account above, and that you sign below. Anonymous tests will not be graded. Write legibly. If the person grading the test cannot read something, s/he will simply assume that you meant the illegible portion as a note to yourself and they will ignore it. If you lose points because part of your answer could not be read, you will not be given the opportunity to explain what it says. Be clear and concise. The answers to most questions should be short. If you find yourself writing an excessively long response, you may want to think more carefully about the question. Long rambling answers generally get fewer points that short ones do because there are more opportunities to mark something wrong. You may use one page of notes while taking the exam. You may not ask questions of other students, look at another student s exam, use a textbook, use a phone or calculator, or seek any other form of assistance. In summary: do not cheat. Persons caught cheating will be subject to disciplinary action. Do not ask questions during the exam. Most questions are unnecessary and they disturb other students. Figuring out what the exam question is asking is part of the test. If you think you have to make some unusual assumption to answer a problem, note what that assumption is on the test. I have read these instructions, I understand them, and I will follow them. Your Signature: Date: Student ID: Total Points: You Scored: _ + _
2 Midterm Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 2 of Please fill in each of the blanks with an appropriate answer. 2 points each blank, 64 Total True or False: Modern computer displays can display a greater dynamic range than the human can view. True or False: Mach banding is is an algorithm for displaying smooth image gradients in rendered images. Fill in the three missing colors in order by wavelength: Red, orange,, green,, indigo,. True or False: The light coming from most light sources consist of just a narrow range of wavelengths in the visible spectrum. The sensitivity curve for the rods in the human eye peeks between the and cones. The letters AABB in the term AABB Tree stand for :. True or False: If light could be negative then any color humans can see could be reproduced using any two distinctly colored light sources. is the main phenomenon that causes the rainbow-like color patterns observed when a thin layer of oil floats on the surface of still water. Finding the intersection of a ray with a/an requires solving a quadratic equation. The BRDF is a function describes how much coming in from one incoming direction goes out in another outgoing direction. True of False: Caustics may be generated by either reflection or refraction of light.
3 Midterm Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 3 of 11 A can be thought of as the limit case for a perspective camera as the center of projection moves further away from objects in the scene. True or False: Rotation is a linear transformation. True or False: Bump mapping changes the shape of an object. True of False: Image morphing techniques often use a warping method to align corresponding features in the images. True of False: Pasteurized coordinates are needed to allow perspective to be expressed as matrix multiplication. Of the various methods discussed in class for representing rotations, the method of uses points in a 3-dimensional sphere embedded in a 4-dimensional space. Most realtime rendering methods use a surface removal. for hidden True or False: Anti-aliasing methods can be used to accelerate ray intersection tests for complex scenes. Visible light roughly corresponds to wavelengths between and nanometers. True or False: Area light sources can be approximated using a handful of point-lights, but banding artifacts may be produced in penumbra regions. Rotation matrices have determinant of. The breaks a matrix C into C = ( U S Transpose(V) ) where U and V are orthonormal and S is diagonal.
4 Midterm Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 4 of 11 True or False: A BSP tree can be used to quickly sort polygons in front-to-back order. True or False: Systems like OpenGL typically convert everything to spheres before rendering. The S in HSV color space stands for. True or False: The term black-body radiation refers to electromagnetic energy outside the visible spectrum.. True or False: Lambertian materials lack strong specular highlights.. 2. You have two pieces of perfectly opaque plastic. They look the same color when held sideby-side in your dorm room. When you take them outside into the sunlight, they look to be different colors. Provide the most plausible explanation. 6 points 3. You have a sphere centered at [2,3,4] with radius 5, and a ray from [0,0,0] in the direction [ 1, 1, 1]. Write the implicit equation for the sphere, the parametric equation for the ray, and compute the coordinates of the intersection point[s]. Be neat and clear! 9 points Sphere equation: Ray equation: Intersection[s] at =
5 Midterm Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 5 of Write out a 3x3 transformation matrix that will perform a +90 rotation degrees about the axis [ 1, 0, 0]. 3 points 5. Place an through the matrices that could not be valid camera matrices. 3 points Draw the single convex hull that encloses all four shapes shown: 6 point 7. Draw the single axis-aligned bounding box that encloses all four shapes shown: 6 points
6 Midterm Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 6 of This diagram shows a triangle with vertices labeled a, b, and c. Five locations have been indicated with circles. The list of numbers to the right contains triples of numbers representing the barycentric coordinates of these circles. Draw a line connecting each triple with the correct circle. 10 points C [1,0,0] A [0,0,1] [1/3,1/3,1/3] [1/2,1/2,0] [-1,1.5,1.5] 9. Write down plausible RGB values for the following materials: 16 points Glossy Metallic Blue Kd = Ks = Glossy Plastic Yellow Kd = Ks = Flat Yellow Kd = Ks = Glossy Plastic Black Kd = Ks = B 10. Given a rotation encoded as a axis-angle (a.k.a. exponential map), in general how is the rotation changed when the representation is doubled? 4 points
7 Midterm Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 7 of If shading a point at the origin with normal [1,0,0] and Kd=[0.25, 0.00,0.20], where the light is located at [4,3,0] with intensity [10, 10, 0] and the eye located at [27,91,17], compute the RGB value of the diffuse lighting term. 12 points 12. Circle the 3D homogenized matrix that effectively does nothing. 4 points / One of the diagrams below shows a cube under orthographic projection, the other under perspective projection. Label which is which. 4 points 14. In what direction will the +Z axis point after a -90 degree rotation about the +Y axis? 2 points
8 Midterm Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 8 of The following line segments will be inserted into a BSP Tree in the order indicated. As discussed in class, the lines themselves will be used to define the split planes. The numbers are on the positive side of each line. The negative-side children should be on the left of your tree and the positive-side on the right. Diagram the resulting tree below. If needed, show where line segments need to be split by marking on the above figure. Also, indicate the names of the split parts by writing labels on the figure above. (For example, if there were a segment 11 and it was to be split, you would draw a mark showing where it would be split and label the resulting pieces 11a and 11b.) 12 points List the back-to-front traversal order that would result for the location indicated by the viewer icon (the star). 9 points
9 Midterm Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 9 of Imagine that you have a RGB monitor where the wires have been swapped so that the red, green, and blue outputs from the computer have been respectively attached to the green, red, and blue inputs on the monitor. When one attempts to display the following colors, what colors will actually appear on the screen? 8 points Cyan Magenta Yellow Red Green Blue Black White 17. Write out a series of 4x4 matrices that would scale an object by 2x along the X axis and by 3x along the Y and Z axes, with the point [0,3,4] staying fixed in space. 10 points
10 Midterm Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 10 of On the figure below write the appropriate letter in each of the blanks to label the diagram properly. Some of the letters are just there to confuse you. 16 points Near n Far f Top t Y Up View Bottom b Center -Z Distance to image plane i A Distance to image plane I Center of attention B Zoom factor J Focal distance C View up vector K Right clipping plane distance D Projection singularity distance L View plane normal E Top clipping plane distance M Bottom clipping plane distance F View direction N Far clipping plane distance G Near clipping plane distance O Aperture limit point H Look-at direction P Center of projection
11 Midterm Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 11 of 11 EXTRA CREDIT +10 points Given a plane and a sphere: Plane:! Sphere:! ˆn x + f =0 c x r =0 Write out a simple mathematical expression that will give the point on the sphere which is furthest away from the plane. (You may not include conditional statements.) When is this point not unique? When the point is not unique, what will your expression produce? Your answers must be neat and clear. No points will be awarded for imprecise answers. Your answers should be in the form a simple mathematical expressions that you have drawn a box around. Do not attempt this question until you have completed the rest of the exam! There will be no partial credit for this question. Use the below space and back of the page to work out your answers, and do not clutter up the above space with anything other than your final answers.
Midterm Exam! CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics! page 1 of 13!
 Midterm Exam! CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics! page 1 of 13! Student Name:!! Class Account Username:! Instructions: Read them carefully!! The exam begins at 1:10pm and ends at 2:30pm. You must
Midterm Exam! CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics! page 1 of 13! Student Name:!! Class Account Username:! Instructions: Read them carefully!! The exam begins at 1:10pm and ends at 2:30pm. You must
Midterm Exam! CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics! page 1 of 14!
 Midterm Exam! CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics! page 1 of 14! Student Name:!! Class Account Username:! Instructions: Read them carefully!! The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must
Midterm Exam! CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics! page 1 of 14! Student Name:!! Class Account Username:! Instructions: Read them carefully!! The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must
The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must turn your exam in when time is announced or risk not having it accepted.
 CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 10 Student Name: Class Account Username: Instructions: Read them carefully! The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must turn your exam in when
CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 10 Student Name: Class Account Username: Instructions: Read them carefully! The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must turn your exam in when
The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must turn your exam in when time is announced or risk not having it accepted.
 CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 12 Student Name: Student ID: Instructions: Read them carefully! The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must turn your exam in when time is
CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 12 Student Name: Student ID: Instructions: Read them carefully! The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must turn your exam in when time is
The exam begins at 5:10pm and ends at 8:00pm. You must turn your exam in when time is announced or risk not having it accepted.
 CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 11 Student Name: Student ID: Instructions: Read them carefully! The exam begins at 5:10pm and ends at 8:00pm. You must turn your exam in when time is
CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 11 Student Name: Student ID: Instructions: Read them carefully! The exam begins at 5:10pm and ends at 8:00pm. You must turn your exam in when time is
Final Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics! page 1 of 12!
 Final Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics! page 1 of 12! Student Name:! Class Account Username: Instructions: Read them carefully!! The exam begins at 8:10pm and ends at 10:00pm. You must turn
Final Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics! page 1 of 12! Student Name:! Class Account Username: Instructions: Read them carefully!! The exam begins at 8:10pm and ends at 10:00pm. You must turn
Final Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 14 Fall 2016 Prof. James O Brien
 Final Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 14 Student Name: Student ID: Instructions: Read them carefully The exam begins at 3:10pm and ends at 6:00pm. You must turn your exam in when
Final Exam CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 14 Student Name: Student ID: Instructions: Read them carefully The exam begins at 3:10pm and ends at 6:00pm. You must turn your exam in when
Make sure you fill in your name and the above information, and that you sign below. Anonymous tests will not be graded.
 CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics! page 1 of 14 Student Name: Class Account Username: Instructions: Read them carefully! You must turn your exam in when time is an- The exam begins at 7:10pm and
CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics! page 1 of 14 Student Name: Class Account Username: Instructions: Read them carefully! You must turn your exam in when time is an- The exam begins at 7:10pm and
Topics and things to know about them:
 Practice Final CMSC 427 Distributed Tuesday, December 11, 2007 Review Session, Monday, December 17, 5:00pm, 4424 AV Williams Final: 10:30 AM Wednesday, December 19, 2007 General Guidelines: The final will
Practice Final CMSC 427 Distributed Tuesday, December 11, 2007 Review Session, Monday, December 17, 5:00pm, 4424 AV Williams Final: 10:30 AM Wednesday, December 19, 2007 General Guidelines: The final will
CS 130 Exam I. Fall 2015
 S 3 Exam I Fall 25 Name Student ID Signature You may not ask any questions during the test. If you believe that there is something wrong with a question, write down what you think the question is trying
S 3 Exam I Fall 25 Name Student ID Signature You may not ask any questions during the test. If you believe that there is something wrong with a question, write down what you think the question is trying
CS 130 Final. Fall 2015
 CS 130 Final Fall 2015 Name Student ID Signature You may not ask any questions during the test. If you believe that there is something wrong with a question, write down what you think the question is trying
CS 130 Final Fall 2015 Name Student ID Signature You may not ask any questions during the test. If you believe that there is something wrong with a question, write down what you think the question is trying
CS 130 Exam I. Fall 2015
 CS 130 Exam I Fall 2015 Name Student ID Signature You may not ask any questions during the test. If you believe that there is something wrong with a question, write down what you think the question is
CS 130 Exam I Fall 2015 Name Student ID Signature You may not ask any questions during the test. If you believe that there is something wrong with a question, write down what you think the question is
U.C. Berkeley, EECS, Computer Science TAKE HOME EXAM. Your Class Computer Account: DO NOT OPEN THIS INSIDE SODA HALL -- WAIT UNTIL YOU ARE ALONE!
 Page 1 of 7 U.C. Berkeley, EECS, Computer Science CS 184 - Spring 2011 COMPUTER GRAPHICS Prof. C. H. Séquin TAKE HOME EXAM Your Name: Your Class Computer Account: Your student ID #: DO NOT OPEN THIS INSIDE
Page 1 of 7 U.C. Berkeley, EECS, Computer Science CS 184 - Spring 2011 COMPUTER GRAPHICS Prof. C. H. Séquin TAKE HOME EXAM Your Name: Your Class Computer Account: Your student ID #: DO NOT OPEN THIS INSIDE
U.C. Berkeley, EECS, Computer Science TAKE HOME EXAM. Your Class Computer Account: Your student ID #:
 U.C. Berkeley, EECS, Computer Science CS 184 - Spring 2009 COMPUTER GRAPHICS Prof. C. H. Séquin TAKE HOME EXAM Your Name: Your Class Computer Account: Your student ID #: DO NOT OPEN THIS INSIDE SODA HALL
U.C. Berkeley, EECS, Computer Science CS 184 - Spring 2009 COMPUTER GRAPHICS Prof. C. H. Séquin TAKE HOME EXAM Your Name: Your Class Computer Account: Your student ID #: DO NOT OPEN THIS INSIDE SODA HALL
Raytracing CS148 AS3. Due :59pm PDT
 Raytracing CS148 AS3 Due 2010-07-25 11:59pm PDT We start our exploration of Rendering - the process of converting a high-level object-based description of scene into an image. We will do this by building
Raytracing CS148 AS3 Due 2010-07-25 11:59pm PDT We start our exploration of Rendering - the process of converting a high-level object-based description of scene into an image. We will do this by building
Interactive Real-Time Raycasting
 Interactive Real-Time Raycasting CS184 AS4 Due 2009-02-26 11:00pm We start our exploration of Rendering - the process of converting a high-level object-based description into a graphical image for display.
Interactive Real-Time Raycasting CS184 AS4 Due 2009-02-26 11:00pm We start our exploration of Rendering - the process of converting a high-level object-based description into a graphical image for display.
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #6: Lights. Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2016
 CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #6: Lights Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2016 Announcements Thursday in class: midterm #1 Closed book Material
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #6: Lights Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2016 Announcements Thursday in class: midterm #1 Closed book Material
Problem Set 4 Part 1 CMSC 427 Distributed: Thursday, November 1, 2007 Due: Tuesday, November 20, 2007
 Problem Set 4 Part 1 CMSC 427 Distributed: Thursday, November 1, 2007 Due: Tuesday, November 20, 2007 Programming For this assignment you will write a simple ray tracer. It will be written in C++ without
Problem Set 4 Part 1 CMSC 427 Distributed: Thursday, November 1, 2007 Due: Tuesday, November 20, 2007 Programming For this assignment you will write a simple ray tracer. It will be written in C++ without
Queen s University CISC 454 Final Exam. April 19, :00pm Duration: 3 hours. One two sided aid sheet allowed. Initial of Family Name:
 Page 1 of 11 Queen s University CISC 454 Final Exam April 19, 2005 2:00pm Duration: 3 hours One two sided aid sheet allowed. Initial of Family Name: Student Number: (Write this at the top of every page.)
Page 1 of 11 Queen s University CISC 454 Final Exam April 19, 2005 2:00pm Duration: 3 hours One two sided aid sheet allowed. Initial of Family Name: Student Number: (Write this at the top of every page.)
Institutionen för systemteknik
 Code: Day: Lokal: M7002E 19 March E1026 Institutionen för systemteknik Examination in: M7002E, Computer Graphics and Virtual Environments Number of sections: 7 Max. score: 100 (normally 60 is required
Code: Day: Lokal: M7002E 19 March E1026 Institutionen för systemteknik Examination in: M7002E, Computer Graphics and Virtual Environments Number of sections: 7 Max. score: 100 (normally 60 is required
TDA361/DIT220 Computer Graphics, January 15 th 2016
 TDA361/DIT220 Computer Graphics, January 15 th 2016 EXAM (Same exam for both CTH- and GU students) Friday January 15 th, 2016, 8.30 12.30 Examiner Ulf Assarsson, tel. 0701-738535 Permitted Technical Aids
TDA361/DIT220 Computer Graphics, January 15 th 2016 EXAM (Same exam for both CTH- and GU students) Friday January 15 th, 2016, 8.30 12.30 Examiner Ulf Assarsson, tel. 0701-738535 Permitted Technical Aids
Computer Science 426 Midterm 3/11/04, 1:30PM-2:50PM
 NAME: Login name: Computer Science 46 Midterm 3//4, :3PM-:5PM This test is 5 questions, of equal weight. Do all of your work on these pages (use the back for scratch space), giving the answer in the space
NAME: Login name: Computer Science 46 Midterm 3//4, :3PM-:5PM This test is 5 questions, of equal weight. Do all of your work on these pages (use the back for scratch space), giving the answer in the space
Illumination and Shading
 Illumination and Shading Light sources emit intensity: assigns intensity to each wavelength of light Humans perceive as a colour - navy blue, light green, etc. Exeriments show that there are distinct I
Illumination and Shading Light sources emit intensity: assigns intensity to each wavelength of light Humans perceive as a colour - navy blue, light green, etc. Exeriments show that there are distinct I
Spring 2012 Final. CS184 - Foundations of Computer Graphics. University of California at Berkeley
 Spring 2012 Final CS184 - Foundations of Computer Graphics University of California at Berkeley Write your name HERE: Write your login HERE: Closed book. You may not use any notes or printed/electronic
Spring 2012 Final CS184 - Foundations of Computer Graphics University of California at Berkeley Write your name HERE: Write your login HERE: Closed book. You may not use any notes or printed/electronic
CSE 167: Lecture #7: Color and Shading. Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2011
 CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #7: Color and Shading Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2011 Announcements Homework project #3 due this Friday,
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #7: Color and Shading Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2011 Announcements Homework project #3 due this Friday,
Computer Graphics I Lecture 11
 15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 11 Midterm Review Assignment 3 Movie Midterm Review Midterm Preview February 26, 2002 Frank Pfenning Carnegie Mellon University http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~fp/courses/graphics/
15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 11 Midterm Review Assignment 3 Movie Midterm Review Midterm Preview February 26, 2002 Frank Pfenning Carnegie Mellon University http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~fp/courses/graphics/
Homework #2. Hidden Surfaces, Projections, Shading and Texture, Ray Tracing, and Parametric Curves
 Computer Graphics Instructor: Brian Curless CSE 457 Spring 2013 Homework #2 Hidden Surfaces, Projections, Shading and Texture, Ray Tracing, and Parametric Curves Assigned: Sunday, May 12 th Due: Thursday,
Computer Graphics Instructor: Brian Curless CSE 457 Spring 2013 Homework #2 Hidden Surfaces, Projections, Shading and Texture, Ray Tracing, and Parametric Curves Assigned: Sunday, May 12 th Due: Thursday,
CS 325 Computer Graphics
 CS 325 Computer Graphics 04 / 02 / 2012 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Illumination modelling Ambient, Diffuse, Specular Reflection Surface Rendering / Shading models Flat
CS 325 Computer Graphics 04 / 02 / 2012 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Illumination modelling Ambient, Diffuse, Specular Reflection Surface Rendering / Shading models Flat
CPSC GLOBAL ILLUMINATION
 CPSC 314 21 GLOBAL ILLUMINATION Textbook: 20 UGRAD.CS.UBC.CA/~CS314 Mikhail Bessmeltsev ILLUMINATION MODELS/ALGORITHMS Local illumination - Fast Ignore real physics, approximate the look Interaction of
CPSC 314 21 GLOBAL ILLUMINATION Textbook: 20 UGRAD.CS.UBC.CA/~CS314 Mikhail Bessmeltsev ILLUMINATION MODELS/ALGORITHMS Local illumination - Fast Ignore real physics, approximate the look Interaction of
CS 464 Review. Review of Computer Graphics for Final Exam
 CS 464 Review Review of Computer Graphics for Final Exam Goal: Draw 3D Scenes on Display Device 3D Scene Abstract Model Framebuffer Matrix of Screen Pixels In Computer Graphics: If it looks right then
CS 464 Review Review of Computer Graphics for Final Exam Goal: Draw 3D Scenes on Display Device 3D Scene Abstract Model Framebuffer Matrix of Screen Pixels In Computer Graphics: If it looks right then
Homework #2. Shading, Projections, Texture Mapping, Ray Tracing, and Bezier Curves
 Computer Graphics Instructor: Brian Curless CSEP 557 Autumn 2016 Homework #2 Shading, Projections, Texture Mapping, Ray Tracing, and Bezier Curves Assigned: Wednesday, Nov 16 th Due: Wednesday, Nov 30
Computer Graphics Instructor: Brian Curless CSEP 557 Autumn 2016 Homework #2 Shading, Projections, Texture Mapping, Ray Tracing, and Bezier Curves Assigned: Wednesday, Nov 16 th Due: Wednesday, Nov 30
Lecture 1. Computer Graphics and Systems. Tuesday, January 15, 13
 Lecture 1 Computer Graphics and Systems What is Computer Graphics? Image Formation Sun Object Figure from Ed Angel,D.Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics, 6 th Ed., 2012 Addison Wesley Computer Graphics
Lecture 1 Computer Graphics and Systems What is Computer Graphics? Image Formation Sun Object Figure from Ed Angel,D.Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics, 6 th Ed., 2012 Addison Wesley Computer Graphics
light light light B E
 CS 324E Elements of Computer Graphics Fall 2002 Second Exam NAME: Please write your answers on THESE SHEETS. If you must turn in extra sheets, put your name on each one of them. You should not need substantial
CS 324E Elements of Computer Graphics Fall 2002 Second Exam NAME: Please write your answers on THESE SHEETS. If you must turn in extra sheets, put your name on each one of them. You should not need substantial
Introduction to 3D Concepts
 PART I Introduction to 3D Concepts Chapter 1 Scene... 3 Chapter 2 Rendering: OpenGL (OGL) and Adobe Ray Tracer (ART)...19 1 CHAPTER 1 Scene s0010 1.1. The 3D Scene p0010 A typical 3D scene has several
PART I Introduction to 3D Concepts Chapter 1 Scene... 3 Chapter 2 Rendering: OpenGL (OGL) and Adobe Ray Tracer (ART)...19 1 CHAPTER 1 Scene s0010 1.1. The 3D Scene p0010 A typical 3D scene has several
CS 4620 Midterm, March 21, 2017
 CS 460 Midterm, March 1, 017 This 90-minute exam has 4 questions worth a total of 100 points. Use the back of the pages if you need more space. Academic Integrity is expected of all students of Cornell
CS 460 Midterm, March 1, 017 This 90-minute exam has 4 questions worth a total of 100 points. Use the back of the pages if you need more space. Academic Integrity is expected of all students of Cornell
Today. Global illumination. Shading. Interactive applications. Rendering pipeline. Computergrafik. Shading Introduction Local shading models
 Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2009 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation of physics Global
Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2009 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation of physics Global
Midterm Exam Fundamentals of Computer Graphics (COMP 557) Thurs. Feb. 19, 2015 Professor Michael Langer
 Midterm Exam Fundamentals of Computer Graphics (COMP 557) Thurs. Feb. 19, 2015 Professor Michael Langer The exam consists of 10 questions. There are 2 points per question for a total of 20 points. You
Midterm Exam Fundamentals of Computer Graphics (COMP 557) Thurs. Feb. 19, 2015 Professor Michael Langer The exam consists of 10 questions. There are 2 points per question for a total of 20 points. You
CS5670: Computer Vision
 CS5670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Light & Perception Announcements Quiz on Tuesday Project 3 code due Monday, April 17, by 11:59pm artifact due Wednesday, April 19, by 11:59pm Can we determine shape
CS5670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Light & Perception Announcements Quiz on Tuesday Project 3 code due Monday, April 17, by 11:59pm artifact due Wednesday, April 19, by 11:59pm Can we determine shape
The University of Calgary
 The University of Calgary Department of Computer Science Final Examination, Questions ENEL/CPSC 555 Computer Graphics Time: 2 Hours Closed Book, calculators are permitted. The questions carry equal weight.
The University of Calgary Department of Computer Science Final Examination, Questions ENEL/CPSC 555 Computer Graphics Time: 2 Hours Closed Book, calculators are permitted. The questions carry equal weight.
Computer Graphics Ray Casting. Matthias Teschner
 Computer Graphics Ray Casting Matthias Teschner Outline Context Implicit surfaces Parametric surfaces Combined objects Triangles Axis-aligned boxes Iso-surfaces in grids Summary University of Freiburg
Computer Graphics Ray Casting Matthias Teschner Outline Context Implicit surfaces Parametric surfaces Combined objects Triangles Axis-aligned boxes Iso-surfaces in grids Summary University of Freiburg
What is it? How does it work? How do we use it?
 What is it? How does it work? How do we use it? Dual Nature http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dfpeprq7ogc o Electromagnetic Waves display wave behavior o Created by oscillating electric and magnetic fields
What is it? How does it work? How do we use it? Dual Nature http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dfpeprq7ogc o Electromagnetic Waves display wave behavior o Created by oscillating electric and magnetic fields
Introduction to Visualization and Computer Graphics
 Introduction to Visualization and Computer Graphics DH2320, Fall 2015 Prof. Dr. Tino Weinkauf Introduction to Visualization and Computer Graphics Visibility Shading 3D Rendering Geometric Model Color Perspective
Introduction to Visualization and Computer Graphics DH2320, Fall 2015 Prof. Dr. Tino Weinkauf Introduction to Visualization and Computer Graphics Visibility Shading 3D Rendering Geometric Model Color Perspective
6.837 Introduction to Computer Graphics Final Exam Tuesday, December 20, :05-12pm Two hand-written sheet of notes (4 pages) allowed 1 SSD [ /17]
![6.837 Introduction to Computer Graphics Final Exam Tuesday, December 20, :05-12pm Two hand-written sheet of notes (4 pages) allowed 1 SSD [ /17] 6.837 Introduction to Computer Graphics Final Exam Tuesday, December 20, :05-12pm Two hand-written sheet of notes (4 pages) allowed 1 SSD [ /17]](/thumbs/87/95541269.jpg) 6.837 Introduction to Computer Graphics Final Exam Tuesday, December 20, 2011 9:05-12pm Two hand-written sheet of notes (4 pages) allowed NAME: 1 / 17 2 / 12 3 / 35 4 / 8 5 / 18 Total / 90 1 SSD [ /17]
6.837 Introduction to Computer Graphics Final Exam Tuesday, December 20, 2011 9:05-12pm Two hand-written sheet of notes (4 pages) allowed NAME: 1 / 17 2 / 12 3 / 35 4 / 8 5 / 18 Total / 90 1 SSD [ /17]
SNC 2PI Optics Unit Review /95 Name:
 SNC 2PI Optics Unit Review /95 Name: Part 1: True or False Indicate in the space provided if the statement is true (T) or false(f) [15] 1. Light is a form of energy 2. Shadows are proof that light travels
SNC 2PI Optics Unit Review /95 Name: Part 1: True or False Indicate in the space provided if the statement is true (T) or false(f) [15] 1. Light is a form of energy 2. Shadows are proof that light travels
Orthogonal Projection Matrices. Angel and Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 7E Addison-Wesley 2015
 Orthogonal Projection Matrices 1 Objectives Derive the projection matrices used for standard orthogonal projections Introduce oblique projections Introduce projection normalization 2 Normalization Rather
Orthogonal Projection Matrices 1 Objectives Derive the projection matrices used for standard orthogonal projections Introduce oblique projections Introduce projection normalization 2 Normalization Rather
CS 4620 Midterm 1. Tuesday 22 October minutes
 CS 4620 Midterm 1 Tuesday 22 October 2013 90 minutes Problem 1: Transformations (20 pts) Consider the affine transformation on R 3 defined in homogeneous coordinates by the matrix: 1 M = 1 0 0 2 0 1 0
CS 4620 Midterm 1 Tuesday 22 October 2013 90 minutes Problem 1: Transformations (20 pts) Consider the affine transformation on R 3 defined in homogeneous coordinates by the matrix: 1 M = 1 0 0 2 0 1 0
CS 4620 Program 3: Pipeline
 CS 4620 Program 3: Pipeline out: Wednesday 14 October 2009 due: Friday 30 October 2009 1 Introduction In this assignment, you will implement several types of shading in a simple software graphics pipeline.
CS 4620 Program 3: Pipeline out: Wednesday 14 October 2009 due: Friday 30 October 2009 1 Introduction In this assignment, you will implement several types of shading in a simple software graphics pipeline.
Lighting. Figure 10.1
 We have learned to build three-dimensional graphical models and to display them. However, if you render one of our models, you might be disappointed to see images that look flat and thus fail to show the
We have learned to build three-dimensional graphical models and to display them. However, if you render one of our models, you might be disappointed to see images that look flat and thus fail to show the
CMSC427 Shading Intro. Credit: slides from Dr. Zwicker
 CMSC427 Shading Intro Credit: slides from Dr. Zwicker 2 Today Shading Introduction Radiometry & BRDFs Local shading models Light sources Shading strategies Shading Compute interaction of light with surfaces
CMSC427 Shading Intro Credit: slides from Dr. Zwicker 2 Today Shading Introduction Radiometry & BRDFs Local shading models Light sources Shading strategies Shading Compute interaction of light with surfaces
Ray Tracer Due date: April 27, 2011
 Computer graphics Assignment 4 1 Overview Ray Tracer Due date: April 27, 2011 In this assignment you will implement the camera and several primitive objects for a ray tracer, and a basic ray tracing algorithm.
Computer graphics Assignment 4 1 Overview Ray Tracer Due date: April 27, 2011 In this assignment you will implement the camera and several primitive objects for a ray tracer, and a basic ray tracing algorithm.
Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction Units of Chapter 32 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formation by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Mirrors Index of Refraction Refraction:
Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction Units of Chapter 32 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formation by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Mirrors Index of Refraction Refraction:
Deferred Rendering Due: Wednesday November 15 at 10pm
 CMSC 23700 Autumn 2017 Introduction to Computer Graphics Project 4 November 2, 2017 Deferred Rendering Due: Wednesday November 15 at 10pm 1 Summary This assignment uses the same application architecture
CMSC 23700 Autumn 2017 Introduction to Computer Graphics Project 4 November 2, 2017 Deferred Rendering Due: Wednesday November 15 at 10pm 1 Summary This assignment uses the same application architecture
Lecture 15: Shading-I. CITS3003 Graphics & Animation
 Lecture 15: Shading-I CITS3003 Graphics & Animation E. Angel and D. Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 6E Addison-Wesley 2012 Objectives Learn that with appropriate shading so objects appear as threedimensional
Lecture 15: Shading-I CITS3003 Graphics & Animation E. Angel and D. Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 6E Addison-Wesley 2012 Objectives Learn that with appropriate shading so objects appear as threedimensional
CHAPTER 1 Graphics Systems and Models 3
 ?????? 1 CHAPTER 1 Graphics Systems and Models 3 1.1 Applications of Computer Graphics 4 1.1.1 Display of Information............. 4 1.1.2 Design.................... 5 1.1.3 Simulation and Animation...........
?????? 1 CHAPTER 1 Graphics Systems and Models 3 1.1 Applications of Computer Graphics 4 1.1.1 Display of Information............. 4 1.1.2 Design.................... 5 1.1.3 Simulation and Animation...........
CS559 Computer Graphics Fall 2015
 CS559 Computer Graphics Fall 2015 Practice Midterm Exam Time: 2 hrs 1. [XX Y Y % = ZZ%] MULTIPLE CHOICE SECTION. Circle or underline the correct answer (or answers). You do not need to provide a justification
CS559 Computer Graphics Fall 2015 Practice Midterm Exam Time: 2 hrs 1. [XX Y Y % = ZZ%] MULTIPLE CHOICE SECTION. Circle or underline the correct answer (or answers). You do not need to provide a justification
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 13b Ray Tracing (Part 1) Prof Emmanuel Agu. Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI)
 Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 13b Ray Tracing (Part 1) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Raytracing Global illumination-based rendering method Simulates
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 13b Ray Tracing (Part 1) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Raytracing Global illumination-based rendering method Simulates
Topic 12: Texture Mapping. Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates Bump mapping, mip-mapping & env mapping
 Topic 12: Texture Mapping Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates Bump mapping, mip-mapping & env mapping Texture sources: Photographs Texture sources: Procedural Texture sources: Solid textures
Topic 12: Texture Mapping Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates Bump mapping, mip-mapping & env mapping Texture sources: Photographs Texture sources: Procedural Texture sources: Solid textures
Homework #2 and #3 Due Friday, October 12 th and Friday, October 19 th
 Homework #2 and #3 Due Friday, October 12 th and Friday, October 19 th 1. a. Show that the following sequences commute: i. A rotation and a uniform scaling ii. Two rotations about the same axis iii. Two
Homework #2 and #3 Due Friday, October 12 th and Friday, October 19 th 1. a. Show that the following sequences commute: i. A rotation and a uniform scaling ii. Two rotations about the same axis iii. Two
Graphics for VEs. Ruth Aylett
 Graphics for VEs Ruth Aylett Overview VE Software Graphics for VEs The graphics pipeline Projections Lighting Shading VR software Two main types of software used: off-line authoring or modelling packages
Graphics for VEs Ruth Aylett Overview VE Software Graphics for VEs The graphics pipeline Projections Lighting Shading VR software Two main types of software used: off-line authoring or modelling packages
Today. Global illumination. Shading. Interactive applications. Rendering pipeline. Computergrafik. Shading Introduction Local shading models
 Computergrafik Thomas Buchberger, Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2008 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation
Computergrafik Thomas Buchberger, Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2008 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation
Graphics Hardware and Display Devices
 Graphics Hardware and Display Devices CSE328 Lectures Graphics/Visualization Hardware Many graphics/visualization algorithms can be implemented efficiently and inexpensively in hardware Facilitates interactive
Graphics Hardware and Display Devices CSE328 Lectures Graphics/Visualization Hardware Many graphics/visualization algorithms can be implemented efficiently and inexpensively in hardware Facilitates interactive
For each question, indicate whether the statement is true or false by circling T or F, respectively.
 True/False For each question, indicate whether the statement is true or false by circling T or F, respectively. 1. (T/F) Rasterization occurs before vertex transformation in the graphics pipeline. 2. (T/F)
True/False For each question, indicate whether the statement is true or false by circling T or F, respectively. 1. (T/F) Rasterization occurs before vertex transformation in the graphics pipeline. 2. (T/F)
Topic 11: Texture Mapping 11/13/2017. Texture sources: Solid textures. Texture sources: Synthesized
 Topic 11: Texture Mapping Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates Bump mapping, mip mapping & env mapping Texture sources: Photographs Texture sources: Procedural Texture sources: Solid textures
Topic 11: Texture Mapping Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates Bump mapping, mip mapping & env mapping Texture sources: Photographs Texture sources: Procedural Texture sources: Solid textures
CS6670: Computer Vision
 CS6670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 21: Light, reflectance and photometric stereo Announcements Final projects Midterm reports due November 24 (next Tuesday) by 11:59pm (upload to CMS) State the
CS6670: Computer Vision Noah Snavely Lecture 21: Light, reflectance and photometric stereo Announcements Final projects Midterm reports due November 24 (next Tuesday) by 11:59pm (upload to CMS) State the
Lecture 3 Sections 2.2, 4.4. Mon, Aug 31, 2009
 Model s Lecture 3 Sections 2.2, 4.4 World s Eye s Clip s s s Window s Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Aug 31, 2009 Outline Model s World s Eye s Clip s s s Window s 1 2 3 Model s World s Eye s Clip s s s Window
Model s Lecture 3 Sections 2.2, 4.4 World s Eye s Clip s s s Window s Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Aug 31, 2009 Outline Model s World s Eye s Clip s s s Window s 1 2 3 Model s World s Eye s Clip s s s Window
COS 116 The Computational Universe Laboratory 10: Computer Graphics
 COS 116 The Computational Universe Laboratory 10: Computer Graphics As mentioned in lecture, computer graphics has four major parts: imaging, rendering, modeling, and animation. In this lab you will learn
COS 116 The Computational Universe Laboratory 10: Computer Graphics As mentioned in lecture, computer graphics has four major parts: imaging, rendering, modeling, and animation. In this lab you will learn
file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/Jason%20Raftery/My%20Doc...e%20184%20-%20Spring%201998%20-%20Sequin%20-%20Midterm%202.htm
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA Dept. EECS/CS Div. CS 184 - Spring 1998 FOUNDATIONS OF COMPUTER GRAPHICS Prof. C.H.Sequin TAKE HOME QUIZ #2 Your Name: Your Class Computer Account: cs184- INSTRUCTIONS ( Read carefully!)
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA Dept. EECS/CS Div. CS 184 - Spring 1998 FOUNDATIONS OF COMPUTER GRAPHICS Prof. C.H.Sequin TAKE HOME QUIZ #2 Your Name: Your Class Computer Account: cs184- INSTRUCTIONS ( Read carefully!)
Shading. Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2017
 Shading Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2017 1 Reading Optional: Angel and Shreiner: chapter 5. Marschner and Shirley: chapter 10, chapter 17. Further reading: OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 2 Basic 3D graphics
Shading Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2017 1 Reading Optional: Angel and Shreiner: chapter 5. Marschner and Shirley: chapter 10, chapter 17. Further reading: OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 2 Basic 3D graphics
Topic 11: Texture Mapping 10/21/2015. Photographs. Solid textures. Procedural
 Topic 11: Texture Mapping Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates Bump mapping, mip mapping & env mapping Topic 11: Photographs Texture Mapping Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates
Topic 11: Texture Mapping Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates Bump mapping, mip mapping & env mapping Topic 11: Photographs Texture Mapping Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #6: Colors. Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2013
 CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #6: Colors Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2013 Announcements Homework project #3 due this Friday, October 18
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #6: Colors Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2013 Announcements Homework project #3 due this Friday, October 18
Color and Shading. Color. Shapiro and Stockman, Chapter 6. Color and Machine Vision. Color and Perception
 Color and Shading Color Shapiro and Stockman, Chapter 6 Color is an important factor for for human perception for object and material identification, even time of day. Color perception depends upon both
Color and Shading Color Shapiro and Stockman, Chapter 6 Color is an important factor for for human perception for object and material identification, even time of day. Color perception depends upon both
Pipeline Operations. CS 4620 Lecture Steve Marschner. Cornell CS4620 Spring 2018 Lecture 11
 Pipeline Operations CS 4620 Lecture 11 1 Pipeline you are here APPLICATION COMMAND STREAM 3D transformations; shading VERTEX PROCESSING TRANSFORMED GEOMETRY conversion of primitives to pixels RASTERIZATION
Pipeline Operations CS 4620 Lecture 11 1 Pipeline you are here APPLICATION COMMAND STREAM 3D transformations; shading VERTEX PROCESSING TRANSFORMED GEOMETRY conversion of primitives to pixels RASTERIZATION
4. A bulb has a luminous flux of 2400 lm. What is the luminous intensity of the bulb?
 1. Match the physical quantities (first column) with the units (second column). 4. A bulb has a luminous flux of 2400 lm. What is the luminous intensity of the bulb? (π=3.) Luminous flux A. candela Radiant
1. Match the physical quantities (first column) with the units (second column). 4. A bulb has a luminous flux of 2400 lm. What is the luminous intensity of the bulb? (π=3.) Luminous flux A. candela Radiant
Rendering: Reality. Eye acts as pinhole camera. Photons from light hit objects
 Basic Ray Tracing Rendering: Reality Eye acts as pinhole camera Photons from light hit objects Rendering: Reality Eye acts as pinhole camera Photons from light hit objects Rendering: Reality Eye acts as
Basic Ray Tracing Rendering: Reality Eye acts as pinhole camera Photons from light hit objects Rendering: Reality Eye acts as pinhole camera Photons from light hit objects Rendering: Reality Eye acts as
S U N G - E U I YO O N, K A I S T R E N D E R I N G F R E E LY A VA I L A B L E O N T H E I N T E R N E T
 S U N G - E U I YO O N, K A I S T R E N D E R I N G F R E E LY A VA I L A B L E O N T H E I N T E R N E T Copyright 2018 Sung-eui Yoon, KAIST freely available on the internet http://sglab.kaist.ac.kr/~sungeui/render
S U N G - E U I YO O N, K A I S T R E N D E R I N G F R E E LY A VA I L A B L E O N T H E I N T E R N E T Copyright 2018 Sung-eui Yoon, KAIST freely available on the internet http://sglab.kaist.ac.kr/~sungeui/render
OpenGl Pipeline. triangles, lines, points, images. Per-vertex ops. Primitive assembly. Texturing. Rasterization. Per-fragment ops.
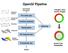 OpenGl Pipeline Individual Vertices Transformed Vertices Commands Processor Per-vertex ops Primitive assembly triangles, lines, points, images Primitives Fragments Rasterization Texturing Per-fragment
OpenGl Pipeline Individual Vertices Transformed Vertices Commands Processor Per-vertex ops Primitive assembly triangles, lines, points, images Primitives Fragments Rasterization Texturing Per-fragment
Unit 3: Optics Chapter 4
 Unit 3: Optics Chapter 4 History of Light https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j1yiapztlos History of Light Early philosophers (Pythagoras) believed light was made up of tiny particles Later scientist found
Unit 3: Optics Chapter 4 History of Light https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j1yiapztlos History of Light Early philosophers (Pythagoras) believed light was made up of tiny particles Later scientist found
CS 563 Advanced Topics in Computer Graphics Camera Models. by Kevin Kardian
 CS 563 Advanced Topics in Computer Graphics Camera Models by Kevin Kardian Introduction Pinhole camera is insufficient Everything in perfect focus Less realistic Different camera models are possible Create
CS 563 Advanced Topics in Computer Graphics Camera Models by Kevin Kardian Introduction Pinhole camera is insufficient Everything in perfect focus Less realistic Different camera models are possible Create
Announcements. Lighting. Camera s sensor. HW1 has been posted See links on web page for readings on color. Intro Computer Vision.
 Announcements HW1 has been posted See links on web page for readings on color. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 6 Deviations from the lens model Deviations from this ideal are aberrations
Announcements HW1 has been posted See links on web page for readings on color. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 6 Deviations from the lens model Deviations from this ideal are aberrations
Spatial Data Structures
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 17 Spatial Data Structures Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees [Angel Ch. 8] 1 Ray Tracing Acceleration
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 17 Spatial Data Structures Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees [Angel Ch. 8] 1 Ray Tracing Acceleration
EXAMINATIONS 2016 TRIMESTER 2
 EXAMINATIONS 2016 TRIMESTER 2 CGRA 151 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER GRAPHICS Time Allowed: TWO HOURS CLOSED BOOK Permitted materials: Silent non-programmable calculators or silent programmable calculators
EXAMINATIONS 2016 TRIMESTER 2 CGRA 151 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER GRAPHICS Time Allowed: TWO HOURS CLOSED BOOK Permitted materials: Silent non-programmable calculators or silent programmable calculators
CS580: Ray Tracing. Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL:
 CS580: Ray Tracing Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL: http://sglab.kaist.ac.kr/~sungeui/gcg/ Recursive Ray Casting Gained popularity in when Turner Whitted (1980) recognized that recursive ray casting could
CS580: Ray Tracing Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL: http://sglab.kaist.ac.kr/~sungeui/gcg/ Recursive Ray Casting Gained popularity in when Turner Whitted (1980) recognized that recursive ray casting could
All forms of EM waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum = 3.00 x 10 8 m/s This speed is constant in air as well
 Pre AP Physics Light & Optics Chapters 14-16 Light is an electromagnetic wave Electromagnetic waves: Oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to the direction the wave moves Difference
Pre AP Physics Light & Optics Chapters 14-16 Light is an electromagnetic wave Electromagnetic waves: Oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to the direction the wave moves Difference
Chapter 12 Notes: Optics
 Chapter 12 Notes: Optics How can the paths traveled by light rays be rearranged in order to form images? In this chapter we will consider just one form of electromagnetic wave: visible light. We will be
Chapter 12 Notes: Optics How can the paths traveled by light rays be rearranged in order to form images? In this chapter we will consider just one form of electromagnetic wave: visible light. We will be
Open GL Framework For A Computer Graphics Course
 Open GL Framework For A Computer Graphics Course Programmer: Daniel Odle Sponsor / Advisor: Dr. Morse University of Evansville 4-26-03 Table of Contents Introduction 3 Statement of Problem 3 Design Approach
Open GL Framework For A Computer Graphics Course Programmer: Daniel Odle Sponsor / Advisor: Dr. Morse University of Evansville 4-26-03 Table of Contents Introduction 3 Statement of Problem 3 Design Approach
CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Fall 2007
 Visible Surface Detection CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Fall 2007 Visible Surface Detection Visible surface detection or hidden surface removal. Realistic scenes: closer objects occludes the
Visible Surface Detection CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Fall 2007 Visible Surface Detection Visible surface detection or hidden surface removal. Realistic scenes: closer objects occludes the
1 (5 max) 2 (10 max) 3 (20 max) 4 (30 max) 5 (10 max) 6 (15 extra max) total (75 max + 15 extra)
 Mierm Exam CS223b Stanford CS223b Computer Vision, Winter 2004 Feb. 18, 2004 Full Name: Email: This exam has 7 pages. Make sure your exam is not missing any sheets, and write your name on every page. The
Mierm Exam CS223b Stanford CS223b Computer Vision, Winter 2004 Feb. 18, 2004 Full Name: Email: This exam has 7 pages. Make sure your exam is not missing any sheets, and write your name on every page. The
Spatial Data Structures
 CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 7 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids BSP Trees [Ch. 0.] March 8, 0 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~jbarbic/cs480-s/
CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 7 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids BSP Trees [Ch. 0.] March 8, 0 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California http://www-bcf.usc.edu/~jbarbic/cs480-s/
CMSC427 Advanced shading getting global illumination by local methods. Credit: slides Prof. Zwicker
 CMSC427 Advanced shading getting global illumination by local methods Credit: slides Prof. Zwicker Topics Shadows Environment maps Reflection mapping Irradiance environment maps Ambient occlusion Reflection
CMSC427 Advanced shading getting global illumination by local methods Credit: slides Prof. Zwicker Topics Shadows Environment maps Reflection mapping Irradiance environment maps Ambient occlusion Reflection
CS 465 Program 4: Modeller
 CS 465 Program 4: Modeller out: 30 October 2004 due: 16 November 2004 1 Introduction In this assignment you will work on a simple 3D modelling system that uses simple primitives and curved surfaces organized
CS 465 Program 4: Modeller out: 30 October 2004 due: 16 November 2004 1 Introduction In this assignment you will work on a simple 3D modelling system that uses simple primitives and curved surfaces organized
Chapter 5. Projections and Rendering
 Chapter 5 Projections and Rendering Topics: Perspective Projections The rendering pipeline In order to view manipulate and view a graphics object we must find ways of storing it a computer-compatible way.
Chapter 5 Projections and Rendering Topics: Perspective Projections The rendering pipeline In order to view manipulate and view a graphics object we must find ways of storing it a computer-compatible way.
COMP environment mapping Mar. 12, r = 2n(n v) v
 Rendering mirror surfaces The next texture mapping method assumes we have a mirror surface, or at least a reflectance function that contains a mirror component. Examples might be a car window or hood,
Rendering mirror surfaces The next texture mapping method assumes we have a mirror surface, or at least a reflectance function that contains a mirror component. Examples might be a car window or hood,
LIGHT Measuring Angles
 1. Using a protractor LIGHT Measuring Angles This angle is 33 Put vertex (corner) of angle where lines cross One arm of angle goes through middle of 0 This angle is 45 Measure these angles: 66 Light an
1. Using a protractor LIGHT Measuring Angles This angle is 33 Put vertex (corner) of angle where lines cross One arm of angle goes through middle of 0 This angle is 45 Measure these angles: 66 Light an
Chapter 11 Global Illumination. Part 1 Ray Tracing. Reading: Angel s Interactive Computer Graphics (6 th ed.) Sections 11.1, 11.2, 11.
 Chapter 11 Global Illumination Part 1 Ray Tracing Reading: Angel s Interactive Computer Graphics (6 th ed.) Sections 11.1, 11.2, 11.3 CG(U), Chap.11 Part 1:Ray Tracing 1 Can pipeline graphics renders images
Chapter 11 Global Illumination Part 1 Ray Tracing Reading: Angel s Interactive Computer Graphics (6 th ed.) Sections 11.1, 11.2, 11.3 CG(U), Chap.11 Part 1:Ray Tracing 1 Can pipeline graphics renders images
Ray Tracing. CS334 Fall Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University
 Ray Tracing CS334 Fall 2013 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Ray Casting and Ray Tracing Ray Casting Arthur Appel, started around 1968 Ray Tracing Turner Whitted, started
Ray Tracing CS334 Fall 2013 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Ray Casting and Ray Tracing Ray Casting Arthur Appel, started around 1968 Ray Tracing Turner Whitted, started
Tutorial 4: Texture Mapping Techniques
 Tutorial 4: Texture Mapping Techniques Completion time 40 minutes In the previous tutorial we learned how to create materials, and how to assign texture maps to those materials. In this tutorial we will
Tutorial 4: Texture Mapping Techniques Completion time 40 minutes In the previous tutorial we learned how to create materials, and how to assign texture maps to those materials. In this tutorial we will
LIGHT. Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses
 LIGHT Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses Light = Electromagnetic Wave Requires No Medium to Travel Oscillating Electric and Magnetic Field Travel at the speed of light
LIGHT Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses Light = Electromagnetic Wave Requires No Medium to Travel Oscillating Electric and Magnetic Field Travel at the speed of light
CS184 : Foundations of Computer Graphics Professor David Forsyth Final Examination (Total: 100 marks)
 CS184 : Foundations of Computer Graphics Professor David Forsyth Final Examination (Total: 100 marks) Cameras and Perspective Figure 1: A perspective view of a polyhedron on an infinite plane. Rendering
CS184 : Foundations of Computer Graphics Professor David Forsyth Final Examination (Total: 100 marks) Cameras and Perspective Figure 1: A perspective view of a polyhedron on an infinite plane. Rendering
CS 559 Computer Graphics Midterm Exam March 22, :30-3:45 pm
 CS 559 Computer Graphics Midterm Exam March 22, 2010 2:30-3:45 pm This exam is closed book and closed notes. Please write your name and CS login on every page! (we may unstaple the exams for grading) Please
CS 559 Computer Graphics Midterm Exam March 22, 2010 2:30-3:45 pm This exam is closed book and closed notes. Please write your name and CS login on every page! (we may unstaple the exams for grading) Please
Shadows in the graphics pipeline
 Shadows in the graphics pipeline Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 19 February There are a number of visual cues that help let the viewer know about the 3D relationships between objects
Shadows in the graphics pipeline Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 19 February There are a number of visual cues that help let the viewer know about the 3D relationships between objects
