Prof. Fanny Ficuciello Robotics for Bioengineering Visual Servoing
|
|
|
- Chad Butler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Visual servoing vision allows a robotic system to obtain geometrical and qualitative information on the surrounding environment high level control motion planning (look-and-move visual grasping) low level control measures used in the control loop visual servoing control is based on feedback of visual measurements position-based visual servoing image-based visual servoing hybrid visual servoing image processing is aimed at extracting numerical information referred to as image feature parameters pose estimation methods are based on the measurement of a certain number of points or correspondences numerical pose estimation methods are based on the integration of the linear mapping between the camera velocity in the operational space and the time derivative of the feature parameters in the image plane camera calibration is based on the measurement of a certain number of correspondences
2 Configuration of the visual system multi-camera systems information about its depth by evaluating its distance with respect to the visual system 3D vision or stereo vision mono-camera systems two images of the same object from two different poses if only a single image is available, the depth can be estimated on the basis of geometrical characteristics of the object known in advance. This cheaper and easier to calibrate lower accuracy eye-to-hand fixed location advantage is that the camera field of view does not change during the execution of the task, implying that the accuracy of such measurements is constant the manipulator occludes, in part or in whole, the view of the objects eye-in-hand mobile configuration the camera is placed on the manipulator high variability in the accuracy of measurements the accuracy becomes almost constant and is usually higher than that achievable with eye-tohand cameras hybrid configuration consisting of one or more cameras in eye-to-hand configuration, and one or more cameras in eye-in-hand configuration ensures a good accuracy throughout the workspace, while avoiding the problems of occlusions
3 Image processing visual information is very rich and varied complex and computational expensive transformations before it can be used for controlling a robotic system extraction of numerical information from the image image feature parameters two basic operations segmentation a representation suitable for the identification of measurable features of the image interpretation measurement of the feature parameters of the image the source information is contained in a two dimensional memory array representing the spatial sample of the image image function I(X,Y) is a vector function whose components represent the values of one or more physical quantities related to the pixel in a sampled and quantized form light intensity in the wavelengths of red, green and blue or in shades of gray (number of gray levels depends on resolution 256 gray levels)
4 Perspective transformation
5 Gray-level histogram provides the frequency of occurrence of each gray level in the image the gray levels are quantized from 0 to 255 the value h(p) of the histogram at a particular gray level p [0, 255] is the number of image pixels with gray level p if this value is divided by the total number of pixels, the histogram is termed normalized histogram
6 Image segmentation consists of a grouping process, by which the image is divided into a certain number of groups, referred to as segments (component of each group similar with respect to one or more characteristics) distinct objects of the environment or homogeneous object parts finding connected regions of the image grouping sets of pixels sharing common features into two-dimensional connected areas high memory usage low computational load detection of boundaries identifying the pixels corresponding to object contours and isolating them from the rest of the image the boundary of an object, once extracted, can be used to define the position and shape of the object itself complementary
7 Region-based segmentation obtaining connected regions by continuous merging of initially small groups of adjacent pixels into larger ones if the pixels belonging to these regions satisfy a common property, termed uniformity predicate (verifying gray level) binary segmentation or image binarization by comparing the gray level of each pixel with a threshold l the peaks of the histogram are termed modes (for the dark objects the closest minimum to the left) in the presence of multiple objects, a further elaboration is required to separate the connected regions corresponding to the single objects the gray-scale histogram is noisy and the modes are difficult to identify various techniques have been developed to increase the robustness of binary segmentation appropriate filtering of the image before binarization algorithms for automatic selection of the threshold
8 Boundary-based segmentation boundary-based segmentation techniques usually obtain a boundary by grouping many single local edges corresponding to local discontinuities of image gray level local edges are sets of pixels where the light intensity changes abruptly the algorithms for boundary detection derive an intermediate image based on local edges from the original gray-scale image construct short-curve segments by edge linking obtain the boundaries by joining these curve segments through geometric primitives often known in advance edge detection is essentially a filtering process whereas boundary detection is a higher level task usually requiring more sophisticated software edge detection can be performed by grouping the pixels where the magnitude of the gradient is greater than a threshold in case of simple and well-defined shapes, boundary detection becomes straightforward and segmentation reduces to the sole edge detection several edge detection techniques exist, most of them require the calculation of the gradient or of the Laplacian of function I(XI, YI )
9 image interpretation is the process of calculating the image feature parameters from the segments, represented in terms of boundaries or in terms of regions characterize the position, orientation and shape of the two-dimensional object Moment of a region Image interpretation area of the region, total number of pixels coordinates of the centroid central moments second order central moments inertia moments inertia tensor relative to the center of mass (eigenvalues define the principal moments of inertia, eigenvectors define the principal axes of inertia)
10 Pose estimation visual servoing is based on the mapping between the feature parameters of an object measured in the image plane of the camera and the operational space variables defining the relative pose of the object with respect to the camera often it is sufficient to derive a differential mapping in terms of velocity (easier to solve linear, numerical integration algoritms) (k 1) vector s, termed feature vector (normalized pixel coordinates) the problem to solve is of computing the elements of from the measurements of object feature parameters in the camera image plane consider n points on the object and the corresponding position vectors with respect to the object frame projections of points on the image plane defines the feature vector
11 Pose estimation the homogeneous coordinates of the points of the object with respect to the camera frame can be expressed as the homogeneous coordinates of the projections of these points on the image plane are given by n correspondences are available for n points of the object, whose coordinates are known both in the object frame and in the image plane these correspondences define a system of equations to be solved for the unknown elements of matrix if the object is in motion with respect to the camera, the feature vector s is time-varying the interaction matrix defines the linear mapping between the absolute velocity of the camera and the corresponding image plane velocity (object is fixed with respect to the base frame)
12 The visual servoing problem visual measurements are used to compute the end-effector pose with respect to an object observed by the camera on the basis of visual measurements elaborated in real time the goal is to reach and keep a (constant or time-varying) desired pose with respect to the observed object the direct measurements provided by the visual system are concerned with feature parameters in the image plane the robotic task is defined in the operational space position-based visual servoing termed visual servoing in the operational space image-based visual servoing termed visual servoing in the image space
13 Position-based visual servoing conceptually similar to the operational space control but feedback is based on the real-time estimation of the pose of the observed object with respect to the camera using visual measurements the estimation can be performed analytically iterative numerical algorithms advantage possibility of acting directly on operational space variables drawback due to the absence of direct control of the image features, the object may exit from the camera field of view during the transient or as a consequence of planning errors the feedback loop is open due to lack of visual measurements and instability may occur
14 Image-space visual servoing the error is defined as the difference between the value of the image feature parameters in the desired configuration and the value of the parameters measured with the camera in the current pose advantage real-time estimate of the pose of the object with respect to the camera is not required it is possible to keep the object within the camera field of view during the motion disadvantage due to the nonlinearity of the mapping between the image feature parameters and the operational space variables, singular configurations may occur, which cause instability or saturation of the control action the end-effector trajectories cannot be easily predicted in advance and may produce collisions with obstacles or joint limits violation
15 Comparison camera calibration position-based visual servoing is more sensitive to camera calibration errors compared to image-based visual servoing for the first approach, the presence of uncertainties on calibration parameters, both intrinsic and extrinsic, produces errors on the estimate of operational space variables that may be seen as an external disturbance in the image-based visual servoing approach, the quantities used for the computation of the control action are directly defined in the image plane and measured in pixel units the desired value of the feature parameters is measured using the camera the uncertainty affecting calibration parameters can be seen as a disturbance acting on the forward path of the control loop, where disturbance rejection capability is high geometric model of the object for position-based visual servoing, the object geometry must be known if only one camera is used, because it is necessary for pose estimation, while it may be unknown when a stereo camera system is used image-based visual servoing does not require, in principle, knowledge of the object geometry, even for mono-camera systems for both approaches, the problem of regulation to a constant set-point is presented the object is assumed to be fixed with respect to the base frame single calibrated camera, mounted on the manipulator s end-effector the end-effector frame is chosen so as to coincide with the camera frame
16 Position-based visual servoing visual measurements are used to estimate in real time the homogeneous transformation matrix (relative pose of object with respect to camera frame) the object is fixed with respect to the base frame the position-based visual servoing problem can be formulated by imposing a desired value to the relative pose of the object frame with respect to the camera frame homogeneous transformation matrix expressing the position and orientation displacement of the camera frame in the current pose with respect to the desired pose the error does not depend on the object pose and represents the error between the desired pose and the current pose of the camera frame
17 PD control with gravity compensation the control has to be designed so that the operational space error tends to zero asymptotically by deriving the error considering that
18 PD control with gravity compensation
19 Resolved-velocity control the information deriving from visual measurements is computed at a frequency lower or equal to the camera frame rate one order of magnitude lower than the typical frequencies used for motion control of robot manipulators to preserve stability the control gains must be set to values much lower than those typically used for motion control the performance of the closed-loop system in terms of speed of convergence and disturbance rejection capability turns out to be poor solution: high-gain motion controller in the joint space or in the operational space neglecting the effects on the tracking errors deriving from manipulator dynamics and disturbances the controlled manipulator can be considered as an ideal positioning device in the case of joint space motion control, the following equality holds:
20 Resolved-velocity control visual servoing can be achieved by computing the trajectory visual measurements on the basis of so that the operational space tracking error goes asymptotically to zero the possibility of knowing in advance the trajectory of the camera is important because, during the motion, the object may exit from the camera field of view, making visual measurements unavailable
21 Image-based visual servoing the object is fixed with respect to the base frame image-based visual servoing can be formulated by stipulating that the vector of the object feature parameters has a desired constant value corresponding to the desired pose of the camera a desired pose exists so that the camera pose belongs to the dexterous workspace of the manipulator and the feature parameters can be chosen as the coordinates of n points of the object n 4 for coplanar points (and no triplets of collinear points) n 6 in case of noncoplanar points the interaction matrix Ls(s, zc) depends on variables zc with zc = [ zc,1... zc,n]t, zc,i being the third coordinate of the generic feature point of the object and s the control law must be designed to guarantee that the image space error tends asymptotically to zero
22 PD control with gravity compensation the object is fixed with respect to the base frame
23 Resolved-velocity control the concept of resolved-velocity control can easily be extended to the image space the convergence to zero of the image space error ensures the asymptotic convergence of to the desired pose
Table of Contents. Chapter 1. Modeling and Identification of Serial Robots... 1 Wisama KHALIL and Etienne DOMBRE
 Chapter 1. Modeling and Identification of Serial Robots.... 1 Wisama KHALIL and Etienne DOMBRE 1.1. Introduction... 1 1.2. Geometric modeling... 2 1.2.1. Geometric description... 2 1.2.2. Direct geometric
Chapter 1. Modeling and Identification of Serial Robots.... 1 Wisama KHALIL and Etienne DOMBRE 1.1. Introduction... 1 1.2. Geometric modeling... 2 1.2.1. Geometric description... 2 1.2.2. Direct geometric
Written exams of Robotics 2
 Written exams of Robotics 2 http://www.diag.uniroma1.it/~deluca/rob2_en.html All materials are in English, unless indicated (oldies are in Year Date (mm.dd) Number of exercises Topics 2018 07.11 4 Inertia
Written exams of Robotics 2 http://www.diag.uniroma1.it/~deluca/rob2_en.html All materials are in English, unless indicated (oldies are in Year Date (mm.dd) Number of exercises Topics 2018 07.11 4 Inertia
EXAM SOLUTIONS. Image Processing and Computer Vision Course 2D1421 Monday, 13 th of March 2006,
 School of Computer Science and Communication, KTH Danica Kragic EXAM SOLUTIONS Image Processing and Computer Vision Course 2D1421 Monday, 13 th of March 2006, 14.00 19.00 Grade table 0-25 U 26-35 3 36-45
School of Computer Science and Communication, KTH Danica Kragic EXAM SOLUTIONS Image Processing and Computer Vision Course 2D1421 Monday, 13 th of March 2006, 14.00 19.00 Grade table 0-25 U 26-35 3 36-45
Robotics 2 Visual servoing
 Robotics 2 Visual servoing Prof. Alessandro De Luca Visual servoing! objective use information acquired by vision sensors (cameras) for feedback control of the pose/motion of a robot (or of parts of it)
Robotics 2 Visual servoing Prof. Alessandro De Luca Visual servoing! objective use information acquired by vision sensors (cameras) for feedback control of the pose/motion of a robot (or of parts of it)
Robotics 2 Iterative Learning for Gravity Compensation
 Robotics 2 Iterative Learning for Gravity Compensation Prof. Alessandro De Luca Control goal! regulation of arbitrary equilibium configurations in the presence of gravity! without explicit knowledge of
Robotics 2 Iterative Learning for Gravity Compensation Prof. Alessandro De Luca Control goal! regulation of arbitrary equilibium configurations in the presence of gravity! without explicit knowledge of
CS4733 Class Notes, Computer Vision
 CS4733 Class Notes, Computer Vision Sources for online computer vision tutorials and demos - http://www.dai.ed.ac.uk/hipr and Computer Vision resources online - http://www.dai.ed.ac.uk/cvonline Vision
CS4733 Class Notes, Computer Vision Sources for online computer vision tutorials and demos - http://www.dai.ed.ac.uk/hipr and Computer Vision resources online - http://www.dai.ed.ac.uk/cvonline Vision
Region-based Segmentation
 Region-based Segmentation Image Segmentation Group similar components (such as, pixels in an image, image frames in a video) to obtain a compact representation. Applications: Finding tumors, veins, etc.
Region-based Segmentation Image Segmentation Group similar components (such as, pixels in an image, image frames in a video) to obtain a compact representation. Applications: Finding tumors, veins, etc.
Multiple View Geometry
 Multiple View Geometry CS 6320, Spring 2013 Guest Lecture Marcel Prastawa adapted from Pollefeys, Shah, and Zisserman Single view computer vision Projective actions of cameras Camera callibration Photometric
Multiple View Geometry CS 6320, Spring 2013 Guest Lecture Marcel Prastawa adapted from Pollefeys, Shah, and Zisserman Single view computer vision Projective actions of cameras Camera callibration Photometric
Parallel Robots. Mechanics and Control H AMID D. TAG HI RAD. CRC Press. Taylor & Francis Group. Taylor & Francis Croup, Boca Raton London NewYoric
 Parallel Robots Mechanics and Control H AMID D TAG HI RAD CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London NewYoric CRC Press Is an Imprint of the Taylor & Francis Croup, an informs business Contents
Parallel Robots Mechanics and Control H AMID D TAG HI RAD CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group Boca Raton London NewYoric CRC Press Is an Imprint of the Taylor & Francis Croup, an informs business Contents
What is Computer Vision?
 Perceptual Grouping in Computer Vision Gérard Medioni University of Southern California What is Computer Vision? Computer Vision Attempt to emulate Human Visual System Perceive visual stimuli with cameras
Perceptual Grouping in Computer Vision Gérard Medioni University of Southern California What is Computer Vision? Computer Vision Attempt to emulate Human Visual System Perceive visual stimuli with cameras
ROBOTICS 01PEEQW. Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino
 ROBOTICS 01PEEQW Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino Control Part 4 Other control strategies These slides are devoted to two advanced control approaches, namely Operational space control Interaction
ROBOTICS 01PEEQW Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino Control Part 4 Other control strategies These slides are devoted to two advanced control approaches, namely Operational space control Interaction
Moving Object Tracking in Video Using MATLAB
 Moving Object Tracking in Video Using MATLAB Bhavana C. Bendale, Prof. Anil R. Karwankar Abstract In this paper a method is described for tracking moving objects from a sequence of video frame. This method
Moving Object Tracking in Video Using MATLAB Bhavana C. Bendale, Prof. Anil R. Karwankar Abstract In this paper a method is described for tracking moving objects from a sequence of video frame. This method
Robot vision review. Martin Jagersand
 Robot vision review Martin Jagersand What is Computer Vision? Computer Graphics Three Related fields Image Processing: Changes 2D images into other 2D images Computer Graphics: Takes 3D models, renders
Robot vision review Martin Jagersand What is Computer Vision? Computer Graphics Three Related fields Image Processing: Changes 2D images into other 2D images Computer Graphics: Takes 3D models, renders
COS Lecture 10 Autonomous Robot Navigation
 COS 495 - Lecture 10 Autonomous Robot Navigation Instructor: Chris Clark Semester: Fall 2011 1 Figures courtesy of Siegwart & Nourbakhsh Control Structure Prior Knowledge Operator Commands Localization
COS 495 - Lecture 10 Autonomous Robot Navigation Instructor: Chris Clark Semester: Fall 2011 1 Figures courtesy of Siegwart & Nourbakhsh Control Structure Prior Knowledge Operator Commands Localization
Automatic Control Industrial robotics
 Automatic Control Industrial robotics Prof. Luca Bascetta (luca.bascetta@polimi.it) Politecnico di Milano Dipartimento di Elettronica, Informazione e Bioingegneria Prof. Luca Bascetta Industrial robots
Automatic Control Industrial robotics Prof. Luca Bascetta (luca.bascetta@polimi.it) Politecnico di Milano Dipartimento di Elettronica, Informazione e Bioingegneria Prof. Luca Bascetta Industrial robots
A comparison between Position Based and Image Based Visual Servoing on a 3 DOFs translating robot
 A comparison between Position Based and Image Based Visual Servoing on a 3 DOFs translating robot Giacomo Palmieri 1, Matteo Palpacelli 2, Massimiliano Battistelli 2 1 Università degli Studi e-campus,
A comparison between Position Based and Image Based Visual Servoing on a 3 DOFs translating robot Giacomo Palmieri 1, Matteo Palpacelli 2, Massimiliano Battistelli 2 1 Università degli Studi e-campus,
Dynamic Time Warping for Binocular Hand Tracking and Reconstruction
 Dynamic Time Warping for Binocular Hand Tracking and Reconstruction Javier Romero, Danica Kragic Ville Kyrki Antonis Argyros CAS-CVAP-CSC Dept. of Information Technology Institute of Computer Science KTH,
Dynamic Time Warping for Binocular Hand Tracking and Reconstruction Javier Romero, Danica Kragic Ville Kyrki Antonis Argyros CAS-CVAP-CSC Dept. of Information Technology Institute of Computer Science KTH,
Accurate 3D Face and Body Modeling from a Single Fixed Kinect
 Accurate 3D Face and Body Modeling from a Single Fixed Kinect Ruizhe Wang*, Matthias Hernandez*, Jongmoo Choi, Gérard Medioni Computer Vision Lab, IRIS University of Southern California Abstract In this
Accurate 3D Face and Body Modeling from a Single Fixed Kinect Ruizhe Wang*, Matthias Hernandez*, Jongmoo Choi, Gérard Medioni Computer Vision Lab, IRIS University of Southern California Abstract In this
calibrated coordinates Linear transformation pixel coordinates
 1 calibrated coordinates Linear transformation pixel coordinates 2 Calibration with a rig Uncalibrated epipolar geometry Ambiguities in image formation Stratified reconstruction Autocalibration with partial
1 calibrated coordinates Linear transformation pixel coordinates 2 Calibration with a rig Uncalibrated epipolar geometry Ambiguities in image formation Stratified reconstruction Autocalibration with partial
EE 701 ROBOT VISION. Segmentation
 EE 701 ROBOT VISION Regions and Image Segmentation Histogram-based Segmentation Automatic Thresholding K-means Clustering Spatial Coherence Merging and Splitting Graph Theoretic Segmentation Region Growing
EE 701 ROBOT VISION Regions and Image Segmentation Histogram-based Segmentation Automatic Thresholding K-means Clustering Spatial Coherence Merging and Splitting Graph Theoretic Segmentation Region Growing
Robot Vision Control of robot motion from video. M. Jagersand
 Robot Vision Control of robot motion from video M. Jagersand Vision-Based Control (Visual Servoing) Initial Image User Desired Image Vision-Based Control (Visual Servoing) : Current Image Features : Desired
Robot Vision Control of robot motion from video M. Jagersand Vision-Based Control (Visual Servoing) Initial Image User Desired Image Vision-Based Control (Visual Servoing) : Current Image Features : Desired
Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Kinematic Control
 Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Kinematic Control 151-0851-00 V lecture: CAB G11 Tuesday 10:15 12:00, every week exercise: HG E1.2 Wednesday 8:15 10:00, according to schedule (about every 2nd week) Marco Hutter,
Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Kinematic Control 151-0851-00 V lecture: CAB G11 Tuesday 10:15 12:00, every week exercise: HG E1.2 Wednesday 8:15 10:00, according to schedule (about every 2nd week) Marco Hutter,
Finite Element Method. Chapter 7. Practical considerations in FEM modeling
 Finite Element Method Chapter 7 Practical considerations in FEM modeling Finite Element Modeling General Consideration The following are some of the difficult tasks (or decisions) that face the engineer
Finite Element Method Chapter 7 Practical considerations in FEM modeling Finite Element Modeling General Consideration The following are some of the difficult tasks (or decisions) that face the engineer
Image processing and features
 Image processing and features Gabriele Bleser gabriele.bleser@dfki.de Thanks to Harald Wuest, Folker Wientapper and Marc Pollefeys Introduction Previous lectures: geometry Pose estimation Epipolar geometry
Image processing and features Gabriele Bleser gabriele.bleser@dfki.de Thanks to Harald Wuest, Folker Wientapper and Marc Pollefeys Introduction Previous lectures: geometry Pose estimation Epipolar geometry
Keeping features in the camera s field of view: a visual servoing strategy
 Keeping features in the camera s field of view: a visual servoing strategy G. Chesi, K. Hashimoto,D.Prattichizzo,A.Vicino Department of Information Engineering, University of Siena Via Roma 6, 3 Siena,
Keeping features in the camera s field of view: a visual servoing strategy G. Chesi, K. Hashimoto,D.Prattichizzo,A.Vicino Department of Information Engineering, University of Siena Via Roma 6, 3 Siena,
Computer Vision & Digital Image Processing. Image segmentation: thresholding
 Computer Vision & Digital Image Processing Image Segmentation: Thresholding Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 18-1 Image segmentation: thresholding Suppose an image f(y) is composed of several light objects on
Computer Vision & Digital Image Processing Image Segmentation: Thresholding Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 18-1 Image segmentation: thresholding Suppose an image f(y) is composed of several light objects on
Visual Recognition: Image Formation
 Visual Recognition: Image Formation Raquel Urtasun TTI Chicago Jan 5, 2012 Raquel Urtasun (TTI-C) Visual Recognition Jan 5, 2012 1 / 61 Today s lecture... Fundamentals of image formation You should know
Visual Recognition: Image Formation Raquel Urtasun TTI Chicago Jan 5, 2012 Raquel Urtasun (TTI-C) Visual Recognition Jan 5, 2012 1 / 61 Today s lecture... Fundamentals of image formation You should know
Image Processing Fundamentals. Nicolas Vazquez Principal Software Engineer National Instruments
 Image Processing Fundamentals Nicolas Vazquez Principal Software Engineer National Instruments Agenda Objectives and Motivations Enhancing Images Checking for Presence Locating Parts Measuring Features
Image Processing Fundamentals Nicolas Vazquez Principal Software Engineer National Instruments Agenda Objectives and Motivations Enhancing Images Checking for Presence Locating Parts Measuring Features
MCE/EEC 647/747: Robot Dynamics and Control. Lecture 1: Introduction
 MCE/EEC 647/747: Robot Dynamics and Control Lecture 1: Introduction Reading: SHV Chapter 1 Robotics and Automation Handbook, Chapter 1 Assigned readings from several articles. Cleveland State University
MCE/EEC 647/747: Robot Dynamics and Control Lecture 1: Introduction Reading: SHV Chapter 1 Robotics and Automation Handbook, Chapter 1 Assigned readings from several articles. Cleveland State University
Structured Light II. Thanks to Ronen Gvili, Szymon Rusinkiewicz and Maks Ovsjanikov
 Structured Light II Johannes Köhler Johannes.koehler@dfki.de Thanks to Ronen Gvili, Szymon Rusinkiewicz and Maks Ovsjanikov Introduction Previous lecture: Structured Light I Active Scanning Camera/emitter
Structured Light II Johannes Köhler Johannes.koehler@dfki.de Thanks to Ronen Gvili, Szymon Rusinkiewicz and Maks Ovsjanikov Introduction Previous lecture: Structured Light I Active Scanning Camera/emitter
Laser sensors. Transmitter. Receiver. Basilio Bona ROBOTICA 03CFIOR
 Mobile & Service Robotics Sensors for Robotics 3 Laser sensors Rays are transmitted and received coaxially The target is illuminated by collimated rays The receiver measures the time of flight (back and
Mobile & Service Robotics Sensors for Robotics 3 Laser sensors Rays are transmitted and received coaxially The target is illuminated by collimated rays The receiver measures the time of flight (back and
Hand-Eye Calibration from Image Derivatives
 Hand-Eye Calibration from Image Derivatives Abstract In this paper it is shown how to perform hand-eye calibration using only the normal flow field and knowledge about the motion of the hand. The proposed
Hand-Eye Calibration from Image Derivatives Abstract In this paper it is shown how to perform hand-eye calibration using only the normal flow field and knowledge about the motion of the hand. The proposed
Outline 7/2/201011/6/
 Outline Pattern recognition in computer vision Background on the development of SIFT SIFT algorithm and some of its variations Computational considerations (SURF) Potential improvement Summary 01 2 Pattern
Outline Pattern recognition in computer vision Background on the development of SIFT SIFT algorithm and some of its variations Computational considerations (SURF) Potential improvement Summary 01 2 Pattern
Complex Sensors: Cameras, Visual Sensing. The Robotics Primer (Ch. 9) ECE 497: Introduction to Mobile Robotics -Visual Sensors
 Complex Sensors: Cameras, Visual Sensing The Robotics Primer (Ch. 9) Bring your laptop and robot everyday DO NOT unplug the network cables from the desktop computers or the walls Tuesday s Quiz is on Visual
Complex Sensors: Cameras, Visual Sensing The Robotics Primer (Ch. 9) Bring your laptop and robot everyday DO NOT unplug the network cables from the desktop computers or the walls Tuesday s Quiz is on Visual
Experiments with Edge Detection using One-dimensional Surface Fitting
 Experiments with Edge Detection using One-dimensional Surface Fitting Gabor Terei, Jorge Luis Nunes e Silva Brito The Ohio State University, Department of Geodetic Science and Surveying 1958 Neil Avenue,
Experiments with Edge Detection using One-dimensional Surface Fitting Gabor Terei, Jorge Luis Nunes e Silva Brito The Ohio State University, Department of Geodetic Science and Surveying 1958 Neil Avenue,
Stereo CSE 576. Ali Farhadi. Several slides from Larry Zitnick and Steve Seitz
 Stereo CSE 576 Ali Farhadi Several slides from Larry Zitnick and Steve Seitz Why do we perceive depth? What do humans use as depth cues? Motion Convergence When watching an object close to us, our eyes
Stereo CSE 576 Ali Farhadi Several slides from Larry Zitnick and Steve Seitz Why do we perceive depth? What do humans use as depth cues? Motion Convergence When watching an object close to us, our eyes
Machine vision. Summary # 11: Stereo vision and epipolar geometry. u l = λx. v l = λy
 1 Machine vision Summary # 11: Stereo vision and epipolar geometry STEREO VISION The goal of stereo vision is to use two cameras to capture 3D scenes. There are two important problems in stereo vision:
1 Machine vision Summary # 11: Stereo vision and epipolar geometry STEREO VISION The goal of stereo vision is to use two cameras to capture 3D scenes. There are two important problems in stereo vision:
A NOUVELLE MOTION STATE-FEEDBACK CONTROL SCHEME FOR RIGID ROBOTIC MANIPULATORS
 A NOUVELLE MOTION STATE-FEEDBACK CONTROL SCHEME FOR RIGID ROBOTIC MANIPULATORS Ahmad Manasra, 135037@ppu.edu.ps Department of Mechanical Engineering, Palestine Polytechnic University, Hebron, Palestine
A NOUVELLE MOTION STATE-FEEDBACK CONTROL SCHEME FOR RIGID ROBOTIC MANIPULATORS Ahmad Manasra, 135037@ppu.edu.ps Department of Mechanical Engineering, Palestine Polytechnic University, Hebron, Palestine
10/25/2018. Robotics and automation. Dr. Ibrahim Al-Naimi. Chapter two. Introduction To Robot Manipulators
 Robotics and automation Dr. Ibrahim Al-Naimi Chapter two Introduction To Robot Manipulators 1 Robotic Industrial Manipulators A robot manipulator is an electronically controlled mechanism, consisting of
Robotics and automation Dr. Ibrahim Al-Naimi Chapter two Introduction To Robot Manipulators 1 Robotic Industrial Manipulators A robot manipulator is an electronically controlled mechanism, consisting of
Range Imaging Through Triangulation. Range Imaging Through Triangulation. Range Imaging Through Triangulation. Range Imaging Through Triangulation
 Obviously, this is a very slow process and not suitable for dynamic scenes. To speed things up, we can use a laser that projects a vertical line of light onto the scene. This laser rotates around its vertical
Obviously, this is a very slow process and not suitable for dynamic scenes. To speed things up, we can use a laser that projects a vertical line of light onto the scene. This laser rotates around its vertical
Camera calibration. Robotic vision. Ville Kyrki
 Camera calibration Robotic vision 19.1.2017 Where are we? Images, imaging Image enhancement Feature extraction and matching Image-based tracking Camera models and calibration Pose estimation Motion analysis
Camera calibration Robotic vision 19.1.2017 Where are we? Images, imaging Image enhancement Feature extraction and matching Image-based tracking Camera models and calibration Pose estimation Motion analysis
Visual Tracking of Unknown Moving Object by Adaptive Binocular Visual Servoing
 Visual Tracking of Unknown Moving Object by Adaptive Binocular Visual Servoing Minoru Asada, Takamaro Tanaka, and Koh Hosoda Adaptive Machine Systems Graduate School of Engineering Osaka University, Suita,
Visual Tracking of Unknown Moving Object by Adaptive Binocular Visual Servoing Minoru Asada, Takamaro Tanaka, and Koh Hosoda Adaptive Machine Systems Graduate School of Engineering Osaka University, Suita,
Dense 3D Reconstruction. Christiano Gava
 Dense 3D Reconstruction Christiano Gava christiano.gava@dfki.de Outline Previous lecture: structure and motion II Structure and motion loop Triangulation Today: dense 3D reconstruction The matching problem
Dense 3D Reconstruction Christiano Gava christiano.gava@dfki.de Outline Previous lecture: structure and motion II Structure and motion loop Triangulation Today: dense 3D reconstruction The matching problem
Depth. Common Classification Tasks. Example: AlexNet. Another Example: Inception. Another Example: Inception. Depth
 Common Classification Tasks Recognition of individual objects/faces Analyze object-specific features (e.g., key points) Train with images from different viewing angles Recognition of object classes Analyze
Common Classification Tasks Recognition of individual objects/faces Analyze object-specific features (e.g., key points) Train with images from different viewing angles Recognition of object classes Analyze
Inverse Kinematics. Given a desired position (p) & orientation (R) of the end-effector
 Inverse Kinematics Given a desired position (p) & orientation (R) of the end-effector q ( q, q, q ) 1 2 n Find the joint variables which can bring the robot the desired configuration z y x 1 The Inverse
Inverse Kinematics Given a desired position (p) & orientation (R) of the end-effector q ( q, q, q ) 1 2 n Find the joint variables which can bring the robot the desired configuration z y x 1 The Inverse
3D Geometry and Camera Calibration
 3D Geometry and Camera Calibration 3D Coordinate Systems Right-handed vs. left-handed x x y z z y 2D Coordinate Systems 3D Geometry Basics y axis up vs. y axis down Origin at center vs. corner Will often
3D Geometry and Camera Calibration 3D Coordinate Systems Right-handed vs. left-handed x x y z z y 2D Coordinate Systems 3D Geometry Basics y axis up vs. y axis down Origin at center vs. corner Will often
MAPI Computer Vision. Multiple View Geometry
 MAPI Computer Vision Multiple View Geometry Geometry o Multiple Views 2- and 3- view geometry p p Kpˆ [ K R t]p Geometry o Multiple Views 2- and 3- view geometry Epipolar Geometry The epipolar geometry
MAPI Computer Vision Multiple View Geometry Geometry o Multiple Views 2- and 3- view geometry p p Kpˆ [ K R t]p Geometry o Multiple Views 2- and 3- view geometry Epipolar Geometry The epipolar geometry
Computer and Machine Vision
 Computer and Machine Vision Lecture Week 4 Part-2 February 5, 2014 Sam Siewert Outline of Week 4 Practical Methods for Dealing with Camera Streams, Frame by Frame and De-coding/Re-encoding for Analysis
Computer and Machine Vision Lecture Week 4 Part-2 February 5, 2014 Sam Siewert Outline of Week 4 Practical Methods for Dealing with Camera Streams, Frame by Frame and De-coding/Re-encoding for Analysis
3D Computer Vision. Structured Light II. Prof. Didier Stricker. Kaiserlautern University.
 3D Computer Vision Structured Light II Prof. Didier Stricker Kaiserlautern University http://ags.cs.uni-kl.de/ DFKI Deutsches Forschungszentrum für Künstliche Intelligenz http://av.dfki.de 1 Introduction
3D Computer Vision Structured Light II Prof. Didier Stricker Kaiserlautern University http://ags.cs.uni-kl.de/ DFKI Deutsches Forschungszentrum für Künstliche Intelligenz http://av.dfki.de 1 Introduction
Feature Detectors and Descriptors: Corners, Lines, etc.
 Feature Detectors and Descriptors: Corners, Lines, etc. Edges vs. Corners Edges = maxima in intensity gradient Edges vs. Corners Corners = lots of variation in direction of gradient in a small neighborhood
Feature Detectors and Descriptors: Corners, Lines, etc. Edges vs. Corners Edges = maxima in intensity gradient Edges vs. Corners Corners = lots of variation in direction of gradient in a small neighborhood
Structured light 3D reconstruction
 Structured light 3D reconstruction Reconstruction pipeline and industrial applications rodola@dsi.unive.it 11/05/2010 3D Reconstruction 3D reconstruction is the process of capturing the shape and appearance
Structured light 3D reconstruction Reconstruction pipeline and industrial applications rodola@dsi.unive.it 11/05/2010 3D Reconstruction 3D reconstruction is the process of capturing the shape and appearance
Physiological Motion Compensation in Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery Part I
 Physiological Motion Compensation in Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery Part I Tobias Ortmaier Laboratoire de Robotique de Paris 18, route du Panorama - BP 61 92265 Fontenay-aux-Roses Cedex France Tobias.Ortmaier@alumni.tum.de
Physiological Motion Compensation in Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery Part I Tobias Ortmaier Laboratoire de Robotique de Paris 18, route du Panorama - BP 61 92265 Fontenay-aux-Roses Cedex France Tobias.Ortmaier@alumni.tum.de
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393
 Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 21 Nov 16 th, 2017 Pranav Mantini Ack: Shah. M Image Processing Geometric Transformation Point Operations Filtering (spatial, Frequency) Input Restoration/
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 21 Nov 16 th, 2017 Pranav Mantini Ack: Shah. M Image Processing Geometric Transformation Point Operations Filtering (spatial, Frequency) Input Restoration/
HOUGH TRANSFORM CS 6350 C V
 HOUGH TRANSFORM CS 6350 C V HOUGH TRANSFORM The problem: Given a set of points in 2-D, find if a sub-set of these points, fall on a LINE. Hough Transform One powerful global method for detecting edges
HOUGH TRANSFORM CS 6350 C V HOUGH TRANSFORM The problem: Given a set of points in 2-D, find if a sub-set of these points, fall on a LINE. Hough Transform One powerful global method for detecting edges
Gaze interaction (2): models and technologies
 Gaze interaction (2): models and technologies Corso di Interazione uomo-macchina II Prof. Giuseppe Boccignone Dipartimento di Scienze dell Informazione Università di Milano boccignone@dsi.unimi.it http://homes.dsi.unimi.it/~boccignone/l
Gaze interaction (2): models and technologies Corso di Interazione uomo-macchina II Prof. Giuseppe Boccignone Dipartimento di Scienze dell Informazione Università di Milano boccignone@dsi.unimi.it http://homes.dsi.unimi.it/~boccignone/l
Geometric camera models and calibration
 Geometric camera models and calibration http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2018, Lecture 13 Course announcements Homework 3 is out. - Due October
Geometric camera models and calibration http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2018, Lecture 13 Course announcements Homework 3 is out. - Due October
Perception. Autonomous Mobile Robots. Sensors Vision Uncertainties, Line extraction from laser scans. Autonomous Systems Lab. Zürich.
 Autonomous Mobile Robots Localization "Position" Global Map Cognition Environment Model Local Map Path Perception Real World Environment Motion Control Perception Sensors Vision Uncertainties, Line extraction
Autonomous Mobile Robots Localization "Position" Global Map Cognition Environment Model Local Map Path Perception Real World Environment Motion Control Perception Sensors Vision Uncertainties, Line extraction
Requirements for region detection
 Region detectors Requirements for region detection For region detection invariance transformations that should be considered are illumination changes, translation, rotation, scale and full affine transform
Region detectors Requirements for region detection For region detection invariance transformations that should be considered are illumination changes, translation, rotation, scale and full affine transform
Binary Image Processing. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 5
 Binary Image Processing CSE 152 Lecture 5 Announcements Homework 2 is due Apr 25, 11:59 PM Reading: Szeliski, Chapter 3 Image processing, Section 3.3 More neighborhood operators Binary System Summary 1.
Binary Image Processing CSE 152 Lecture 5 Announcements Homework 2 is due Apr 25, 11:59 PM Reading: Szeliski, Chapter 3 Image processing, Section 3.3 More neighborhood operators Binary System Summary 1.
Local qualitative shape from stereo. without detailed correspondence. Extended Abstract. Shimon Edelman. Internet:
 Local qualitative shape from stereo without detailed correspondence Extended Abstract Shimon Edelman Center for Biological Information Processing MIT E25-201, Cambridge MA 02139 Internet: edelman@ai.mit.edu
Local qualitative shape from stereo without detailed correspondence Extended Abstract Shimon Edelman Center for Biological Information Processing MIT E25-201, Cambridge MA 02139 Internet: edelman@ai.mit.edu
Colour Segmentation-based Computation of Dense Optical Flow with Application to Video Object Segmentation
 ÖGAI Journal 24/1 11 Colour Segmentation-based Computation of Dense Optical Flow with Application to Video Object Segmentation Michael Bleyer, Margrit Gelautz, Christoph Rhemann Vienna University of Technology
ÖGAI Journal 24/1 11 Colour Segmentation-based Computation of Dense Optical Flow with Application to Video Object Segmentation Michael Bleyer, Margrit Gelautz, Christoph Rhemann Vienna University of Technology
Matching. Compare region of image to region of image. Today, simplest kind of matching. Intensities similar.
 Matching Compare region of image to region of image. We talked about this for stereo. Important for motion. Epipolar constraint unknown. But motion small. Recognition Find object in image. Recognize object.
Matching Compare region of image to region of image. We talked about this for stereo. Important for motion. Epipolar constraint unknown. But motion small. Recognition Find object in image. Recognize object.
Towards the completion of assignment 1
 Towards the completion of assignment 1 What to do for calibration What to do for point matching What to do for tracking What to do for GUI COMPSCI 773 Feature Point Detection Why study feature point detection?
Towards the completion of assignment 1 What to do for calibration What to do for point matching What to do for tracking What to do for GUI COMPSCI 773 Feature Point Detection Why study feature point detection?
Centre for Digital Image Measurement and Analysis, School of Engineering, City University, Northampton Square, London, ECIV OHB
 HIGH ACCURACY 3-D MEASUREMENT USING MULTIPLE CAMERA VIEWS T.A. Clarke, T.J. Ellis, & S. Robson. High accuracy measurement of industrially produced objects is becoming increasingly important. The techniques
HIGH ACCURACY 3-D MEASUREMENT USING MULTIPLE CAMERA VIEWS T.A. Clarke, T.J. Ellis, & S. Robson. High accuracy measurement of industrially produced objects is becoming increasingly important. The techniques
Robots are built to accomplish complex and difficult tasks that require highly non-linear motions.
 Path and Trajectory specification Robots are built to accomplish complex and difficult tasks that require highly non-linear motions. Specifying the desired motion to achieve a specified goal is often a
Path and Trajectory specification Robots are built to accomplish complex and difficult tasks that require highly non-linear motions. Specifying the desired motion to achieve a specified goal is often a
3D Sensing. 3D Shape from X. Perspective Geometry. Camera Model. Camera Calibration. General Stereo Triangulation.
 3D Sensing 3D Shape from X Perspective Geometry Camera Model Camera Calibration General Stereo Triangulation 3D Reconstruction 3D Shape from X shading silhouette texture stereo light striping motion mainly
3D Sensing 3D Shape from X Perspective Geometry Camera Model Camera Calibration General Stereo Triangulation 3D Reconstruction 3D Shape from X shading silhouette texture stereo light striping motion mainly
Vision Review: Image Formation. Course web page:
 Vision Review: Image Formation Course web page: www.cis.udel.edu/~cer/arv September 10, 2002 Announcements Lecture on Thursday will be about Matlab; next Tuesday will be Image Processing The dates some
Vision Review: Image Formation Course web page: www.cis.udel.edu/~cer/arv September 10, 2002 Announcements Lecture on Thursday will be about Matlab; next Tuesday will be Image Processing The dates some
Prof. Fanny Ficuciello Robotics for Bioengineering Trajectory planning
 Trajectory planning to generate the reference inputs to the motion control system which ensures that the manipulator executes the planned trajectories path and trajectory joint space trajectories operational
Trajectory planning to generate the reference inputs to the motion control system which ensures that the manipulator executes the planned trajectories path and trajectory joint space trajectories operational
ELEC Dr Reji Mathew Electrical Engineering UNSW
 ELEC 4622 Dr Reji Mathew Electrical Engineering UNSW Review of Motion Modelling and Estimation Introduction to Motion Modelling & Estimation Forward Motion Backward Motion Block Motion Estimation Motion
ELEC 4622 Dr Reji Mathew Electrical Engineering UNSW Review of Motion Modelling and Estimation Introduction to Motion Modelling & Estimation Forward Motion Backward Motion Block Motion Estimation Motion
Perception and Action using Multilinear Forms
 Perception and Action using Multilinear Forms Anders Heyden, Gunnar Sparr, Kalle Åström Dept of Mathematics, Lund University Box 118, S-221 00 Lund, Sweden email: {heyden,gunnar,kalle}@maths.lth.se Abstract
Perception and Action using Multilinear Forms Anders Heyden, Gunnar Sparr, Kalle Åström Dept of Mathematics, Lund University Box 118, S-221 00 Lund, Sweden email: {heyden,gunnar,kalle}@maths.lth.se Abstract
Miniature faking. In close-up photo, the depth of field is limited.
 Miniature faking In close-up photo, the depth of field is limited. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:jodhpur_tilt_shift.jpg Miniature faking Miniature faking http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:oregon_state_beavers_tilt-shift_miniature_greg_keene.jpg
Miniature faking In close-up photo, the depth of field is limited. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:jodhpur_tilt_shift.jpg Miniature faking Miniature faking http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:oregon_state_beavers_tilt-shift_miniature_greg_keene.jpg
Task analysis based on observing hands and objects by vision
 Task analysis based on observing hands and objects by vision Yoshihiro SATO Keni Bernardin Hiroshi KIMURA Katsushi IKEUCHI Univ. of Electro-Communications Univ. of Karlsruhe Univ. of Tokyo Abstract In
Task analysis based on observing hands and objects by vision Yoshihiro SATO Keni Bernardin Hiroshi KIMURA Katsushi IKEUCHI Univ. of Electro-Communications Univ. of Karlsruhe Univ. of Tokyo Abstract In
Robot mechanics and kinematics
 University of Pisa Master of Science in Computer Science Course of Robotics (ROB) A.Y. 2016/17 cecilia.laschi@santannapisa.it http://didawiki.cli.di.unipi.it/doku.php/magistraleinformatica/rob/start Robot
University of Pisa Master of Science in Computer Science Course of Robotics (ROB) A.Y. 2016/17 cecilia.laschi@santannapisa.it http://didawiki.cli.di.unipi.it/doku.php/magistraleinformatica/rob/start Robot
Lecture 16: Computer Vision
 CS4442/9542b: Artificial Intelligence II Prof. Olga Veksler Lecture 16: Computer Vision Motion Slides are from Steve Seitz (UW), David Jacobs (UMD) Outline Motion Estimation Motion Field Optical Flow Field
CS4442/9542b: Artificial Intelligence II Prof. Olga Veksler Lecture 16: Computer Vision Motion Slides are from Steve Seitz (UW), David Jacobs (UMD) Outline Motion Estimation Motion Field Optical Flow Field
Lecture 16: Computer Vision
 CS442/542b: Artificial ntelligence Prof. Olga Veksler Lecture 16: Computer Vision Motion Slides are from Steve Seitz (UW), David Jacobs (UMD) Outline Motion Estimation Motion Field Optical Flow Field Methods
CS442/542b: Artificial ntelligence Prof. Olga Veksler Lecture 16: Computer Vision Motion Slides are from Steve Seitz (UW), David Jacobs (UMD) Outline Motion Estimation Motion Field Optical Flow Field Methods
SUMMARY: DISTINCTIVE IMAGE FEATURES FROM SCALE- INVARIANT KEYPOINTS
 SUMMARY: DISTINCTIVE IMAGE FEATURES FROM SCALE- INVARIANT KEYPOINTS Cognitive Robotics Original: David G. Lowe, 004 Summary: Coen van Leeuwen, s1460919 Abstract: This article presents a method to extract
SUMMARY: DISTINCTIVE IMAGE FEATURES FROM SCALE- INVARIANT KEYPOINTS Cognitive Robotics Original: David G. Lowe, 004 Summary: Coen van Leeuwen, s1460919 Abstract: This article presents a method to extract
Cecilia Laschi The BioRobotics Institute Scuola Superiore Sant Anna, Pisa
 University of Pisa Master of Science in Computer Science Course of Robotics (ROB) A.Y. 2016/17 cecilia.laschi@santannapisa.it http://didawiki.cli.di.unipi.it/doku.php/magistraleinformatica/rob/start Robot
University of Pisa Master of Science in Computer Science Course of Robotics (ROB) A.Y. 2016/17 cecilia.laschi@santannapisa.it http://didawiki.cli.di.unipi.it/doku.php/magistraleinformatica/rob/start Robot
Structure from Motion. Prof. Marco Marcon
 Structure from Motion Prof. Marco Marcon Summing-up 2 Stereo is the most powerful clue for determining the structure of a scene Another important clue is the relative motion between the scene and (mono)
Structure from Motion Prof. Marco Marcon Summing-up 2 Stereo is the most powerful clue for determining the structure of a scene Another important clue is the relative motion between the scene and (mono)
CHAPTER 5 MOTION DETECTION AND ANALYSIS
 CHAPTER 5 MOTION DETECTION AND ANALYSIS 5.1. Introduction: Motion processing is gaining an intense attention from the researchers with the progress in motion studies and processing competence. A series
CHAPTER 5 MOTION DETECTION AND ANALYSIS 5.1. Introduction: Motion processing is gaining an intense attention from the researchers with the progress in motion studies and processing competence. A series
Stereo Image Rectification for Simple Panoramic Image Generation
 Stereo Image Rectification for Simple Panoramic Image Generation Yun-Suk Kang and Yo-Sung Ho Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) 261 Cheomdan-gwagiro, Buk-gu, Gwangju 500-712 Korea Email:{yunsuk,
Stereo Image Rectification for Simple Panoramic Image Generation Yun-Suk Kang and Yo-Sung Ho Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) 261 Cheomdan-gwagiro, Buk-gu, Gwangju 500-712 Korea Email:{yunsuk,
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems
 EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 14 130307 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Stereo Dense Motion Estimation Translational
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 14 130307 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Stereo Dense Motion Estimation Translational
SIFT: SCALE INVARIANT FEATURE TRANSFORM SURF: SPEEDED UP ROBUST FEATURES BASHAR ALSADIK EOS DEPT. TOPMAP M13 3D GEOINFORMATION FROM IMAGES 2014
 SIFT: SCALE INVARIANT FEATURE TRANSFORM SURF: SPEEDED UP ROBUST FEATURES BASHAR ALSADIK EOS DEPT. TOPMAP M13 3D GEOINFORMATION FROM IMAGES 2014 SIFT SIFT: Scale Invariant Feature Transform; transform image
SIFT: SCALE INVARIANT FEATURE TRANSFORM SURF: SPEEDED UP ROBUST FEATURES BASHAR ALSADIK EOS DEPT. TOPMAP M13 3D GEOINFORMATION FROM IMAGES 2014 SIFT SIFT: Scale Invariant Feature Transform; transform image
Jane Li. Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute
 Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute (3 pts) Compare the testing methods for testing path segment and finding first
Jane Li Assistant Professor Mechanical Engineering Department, Robotic Engineering Program Worcester Polytechnic Institute (3 pts) Compare the testing methods for testing path segment and finding first
Operation of machine vision system
 ROBOT VISION Introduction The process of extracting, characterizing and interpreting information from images. Potential application in many industrial operation. Selection from a bin or conveyer, parts
ROBOT VISION Introduction The process of extracting, characterizing and interpreting information from images. Potential application in many industrial operation. Selection from a bin or conveyer, parts
2 1/2 D visual servoing with respect to planar. contours having complex and unknown shapes
 2 /2 D visual servoing with respect to planar contours having complex and unknown shapes E. Malis, G. Chesi and R. Cipolla Abstract In this paper we present a complete system for segmenting, matching,
2 /2 D visual servoing with respect to planar contours having complex and unknown shapes E. Malis, G. Chesi and R. Cipolla Abstract In this paper we present a complete system for segmenting, matching,
Surface Registration. Gianpaolo Palma
 Surface Registration Gianpaolo Palma The problem 3D scanning generates multiple range images Each contain 3D points for different parts of the model in the local coordinates of the scanner Find a rigid
Surface Registration Gianpaolo Palma The problem 3D scanning generates multiple range images Each contain 3D points for different parts of the model in the local coordinates of the scanner Find a rigid
High-Fidelity Augmented Reality Interactions Hrvoje Benko Researcher, MSR Redmond
 High-Fidelity Augmented Reality Interactions Hrvoje Benko Researcher, MSR Redmond New generation of interfaces Instead of interacting through indirect input devices (mice and keyboard), the user is interacting
High-Fidelity Augmented Reality Interactions Hrvoje Benko Researcher, MSR Redmond New generation of interfaces Instead of interacting through indirect input devices (mice and keyboard), the user is interacting
On-line and Off-line 3D Reconstruction for Crisis Management Applications
 On-line and Off-line 3D Reconstruction for Crisis Management Applications Geert De Cubber Royal Military Academy, Department of Mechanical Engineering (MSTA) Av. de la Renaissance 30, 1000 Brussels geert.de.cubber@rma.ac.be
On-line and Off-line 3D Reconstruction for Crisis Management Applications Geert De Cubber Royal Military Academy, Department of Mechanical Engineering (MSTA) Av. de la Renaissance 30, 1000 Brussels geert.de.cubber@rma.ac.be
Dense 3D Reconstruction. Christiano Gava
 Dense 3D Reconstruction Christiano Gava christiano.gava@dfki.de Outline Previous lecture: structure and motion II Structure and motion loop Triangulation Wide baseline matching (SIFT) Today: dense 3D reconstruction
Dense 3D Reconstruction Christiano Gava christiano.gava@dfki.de Outline Previous lecture: structure and motion II Structure and motion loop Triangulation Wide baseline matching (SIFT) Today: dense 3D reconstruction
Image Segmentation. Selim Aksoy. Bilkent University
 Image Segmentation Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr Examples of grouping in vision [http://poseidon.csd.auth.gr/lab_research/latest/imgs/s peakdepvidindex_img2.jpg]
Image Segmentation Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr Examples of grouping in vision [http://poseidon.csd.auth.gr/lab_research/latest/imgs/s peakdepvidindex_img2.jpg]
Image Segmentation. Selim Aksoy. Bilkent University
 Image Segmentation Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr Examples of grouping in vision [http://poseidon.csd.auth.gr/lab_research/latest/imgs/s peakdepvidindex_img2.jpg]
Image Segmentation Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr Examples of grouping in vision [http://poseidon.csd.auth.gr/lab_research/latest/imgs/s peakdepvidindex_img2.jpg]
Basilio Bona DAUIN Politecnico di Torino
 ROBOTICA 03CFIOR DAUIN Politecnico di Torino Mobile & Service Robotics Sensors for Robotics 3 Laser sensors Rays are transmitted and received coaxially The target is illuminated by collimated rays The
ROBOTICA 03CFIOR DAUIN Politecnico di Torino Mobile & Service Robotics Sensors for Robotics 3 Laser sensors Rays are transmitted and received coaxially The target is illuminated by collimated rays The
Learning and Inferring Depth from Monocular Images. Jiyan Pan April 1, 2009
 Learning and Inferring Depth from Monocular Images Jiyan Pan April 1, 2009 Traditional ways of inferring depth Binocular disparity Structure from motion Defocus Given a single monocular image, how to infer
Learning and Inferring Depth from Monocular Images Jiyan Pan April 1, 2009 Traditional ways of inferring depth Binocular disparity Structure from motion Defocus Given a single monocular image, how to infer
Unit 3 Multiple View Geometry
 Unit 3 Multiple View Geometry Relations between images of a scene Recovering the cameras Recovering the scene structure http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/hzbook/hzbook1.html 3D structure from images Recover
Unit 3 Multiple View Geometry Relations between images of a scene Recovering the cameras Recovering the scene structure http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/hzbook/hzbook1.html 3D structure from images Recover
1724. Mobile manipulators collision-free trajectory planning with regard to end-effector vibrations elimination
 1724. Mobile manipulators collision-free trajectory planning with regard to end-effector vibrations elimination Iwona Pajak 1, Grzegorz Pajak 2 University of Zielona Gora, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,
1724. Mobile manipulators collision-free trajectory planning with regard to end-effector vibrations elimination Iwona Pajak 1, Grzegorz Pajak 2 University of Zielona Gora, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,
Editorial Manager(tm) for International Journal of. Title: A Minimalist Approach to 3D Visually-Guided Grasping for Service Robots
 Computer Vision Editorial Manager(tm) for International Journal of Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: Title: A Minimalist Approach to 3D Visually-Guided Grasping for Service Robots Article Type: Special
Computer Vision Editorial Manager(tm) for International Journal of Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: Title: A Minimalist Approach to 3D Visually-Guided Grasping for Service Robots Article Type: Special
Range Sensors (time of flight) (1)
 Range Sensors (time of flight) (1) Large range distance measurement -> called range sensors Range information: key element for localization and environment modeling Ultrasonic sensors, infra-red sensors
Range Sensors (time of flight) (1) Large range distance measurement -> called range sensors Range information: key element for localization and environment modeling Ultrasonic sensors, infra-red sensors
Computer vision: models, learning and inference. Chapter 13 Image preprocessing and feature extraction
 Computer vision: models, learning and inference Chapter 13 Image preprocessing and feature extraction Preprocessing The goal of pre-processing is to try to reduce unwanted variation in image due to lighting,
Computer vision: models, learning and inference Chapter 13 Image preprocessing and feature extraction Preprocessing The goal of pre-processing is to try to reduce unwanted variation in image due to lighting,
1 Trajectories. Class Notes, Trajectory Planning, COMS4733. Figure 1: Robot control system.
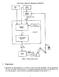 Class Notes, Trajectory Planning, COMS4733 Figure 1: Robot control system. 1 Trajectories Trajectories are characterized by a path which is a space curve of the end effector. We can parameterize this curve
Class Notes, Trajectory Planning, COMS4733 Figure 1: Robot control system. 1 Trajectories Trajectories are characterized by a path which is a space curve of the end effector. We can parameterize this curve
Computational Foundations of Cognitive Science
 Computational Foundations of Cognitive Science Lecture 16: Models of Object Recognition Frank Keller School of Informatics University of Edinburgh keller@inf.ed.ac.uk February 23, 2010 Frank Keller Computational
Computational Foundations of Cognitive Science Lecture 16: Models of Object Recognition Frank Keller School of Informatics University of Edinburgh keller@inf.ed.ac.uk February 23, 2010 Frank Keller Computational
