Solid Modelling. Graphics Systems / Computer Graphics and Interfaces COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING UNIVERSITY OF PORTO
|
|
|
- Cameron Wiggins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Solid Modelling Graphics Systems / Computer Graphics and Interfaces 1
2 Solid Modelling In 2D, one set 2D line segments or curves does not necessarily form a closed area. In 3D, a collection of surfaces does not necessarily involve a closed volume. Solid modeling: In some applications it is important to: distinguish between the interior and exterior surface of a 3D object; and evaluate properties of objects that depend on this distinction. Ex: Simulation of mechanisms, volume, center of mass, application of finite elements to determine response to factors such as stress and temperature, etc. Applications: CAD / CAM and photo-realistic imaging. 2
3 Characteristics of a solid model 1. Should cover a domain representation broad enough to incorporate all kinds of objects we want to model. 2. The representation must be unambiguous and unique: A given representation must correspond to a single solid; and each object must have only one possible representation. The only representation allows us to compare two objects to determine equality. 3. Precision / Correctness: accurate modeling allows to represent the object without approximations. Systems that only accept representation by line segments only approximate curved surfaces. 4. Impossibility of creating invalid objects, i.e. that do not correspond to a solid. 5. Closed representation: The representation must remain valid after the application of any valid operations. 6. Compact representation to optimize the use of memory. 3
4 Characteristics of a solid model Example of invalid objects as a solid. - The representation of a) does not clearly identify the faces of the cube, only indicates edges. - We can consider that a sequence of 4 segments form a face? But solid b) would be (wrong) considered as a solid. In general, the representations used do not have all the features presented. 4
5 Boolean operations The combination of Boolean operations allows to define new objects, independently of the representation used. Operations are: union, difference / subtraction intersection. a) Objects A and B b) The U B c) A B d) A - B e) B - A 5
6 Operating two objects... Consider the two objects, CUBE and CYLINDER. 6
7 Example: CUBE - CYLINDER Subtraction 7
8 Union Example: CUBE U CYLINDER 8
9 Example: CUBE CYLINDER Intersection 9
10 Example - Ask Lego performed with Boolean operations. The solids are used cube and cylinder. This type of modeling is mainly used for regular objects as exemplified. 9
11 Types of Representation 1. Representation by Instantiating Primitives 2. Representation by Extrusion 3. Boundary Representation (Representação pela Fronteira) 4. Representation by Spatial Decomposition 5. Constructive Solid Geometry Representation (CSG) 10
12 Representation by Instantiating Primitives The modeling system has, pre-defined, a set of useful 3D solid for the desired modeling. The user can control the shape of the object defining the parameters that characterize it. It does not include the combination of objects as Boolean operations. Used for complex parts. 11
13 Representation by Extrusion The displacement of an object according to a trajectory defines another object: Translation (Extrusion) Rotation Ex: The translation a 2D rectangle along its perpendicular to the plane creates a parallelepiped. A simple extension is to modify the dimensions of the 2D object along the path. 12
14 Representation by Extrusion Using this method without path constraints can result in inefficient modeling of the object. Ex: If the object intersects itself complicates the calculation of volume. Can not generate a valid solid if the motion is in the plane containing the 2D shape. In general, software tools convert objects created by extrusion into other representations of the same objects. Boolean operations with objects created by extrusion. 13
15 Representation by Extrusion - Example 14
16 Representation by Extrusion - Example 1. Defining a way to make scanning for translation. 15
17 Representation by Extrusion - Example 2. Defining the shape of the section of the final object. 16
18 Representation by Extrusion - Example Object obtained by translation. 17
19 Representation by Extrusion - Example Object obtained by translation, rotation around the axis shifting and scaling along the route. 18
20 Boundary Representation (B-rep) The solids are described by its boundary surface. Uses the description by vertices, edges and faces. The most common representation is the boundary by a closed polygonal mesh. Will be considered only the solids with boundary 2-manifolds : Ie the neighbors of any point of the boundary surfasse are in a disk (that is to say that each edge is shared by two faces) (a) and (b) are 2-manifold (c) is not 2-manifold 19
21 Boundary Representation (B-rep) Polyhedron Solid delimited by a set of polygons whose edges belong to two polygons (solids 2- manifolds). Euler Formula A simple polyhedron without holes, obeys Euler's formula: V - E + F = 2 V - Vertex E - Edges (edges) F - Faces 20
22 By Boundary Representation (B-rep) The Euler's formula is necessary but it is not sufficient to ensure that an object is a simple polyhedron / valid solid. Additional conditions: 1. Each edge connects 2 vertices and is shared by 2 faces 2. At least three edges are at the same vertex 21
23 By Boundary Representation (B-rep) Generalization of Euler's Formula for polyhedra with holes: V - E + F - H = 2 (C - G) V - Vertex E - Edges (edges) F - Faces H - number of holes in the faces G - Number of holes crossing the object C - number of parts of the object 21
24 Exercise 22
25 Representation by Spatial Decomposition A solid is decomposed into: In a number of more primitive solids than the original The primitive solids are adjacent and do not intersect Types of Representation for Spatial Decomposition Cell Decomposition Enumeration of Space Occupation Octrees Binary trees Space Partition 23
26 Representation by Spatial Decomposition Cell Decomposition In Cell Decomposition: There is a set of primitive, parameterized cells Can be Curves Differs from Instance Primitives, by admitting the composition of more complex objects from other already established Gluing operation It is a union of cells that do not intersect a) Primitive cells to transform b) c) are the same final object created with different combinations 24
27 Representation by Spatial Decomposition Space Occupation Enumeration The Space Occupation Enumeration is a particular case of Cell Decomposition: Solid formed by identical cells of equal size, placed in a regular grid. The cells are designated Voxels (Volume elements) by analogy with pixels It controls only the presence or absence of each cell in the grid The most common form for cells is the cube The object is encoded by a single list of occupied cells 25
28 Representation for Spatial Decomposition Octrees The Octree is similar to quadtree The octree is 3D and the division of space is made by octants Number of nodes of an octree It is proportional to the object surface because of the need to subdivide occurs on the surface. Enumeration of octree 26
29 Representation for Spatial Decomposition Binary Space Partitioning Trees (BSP) At each step, the space is divided by a plane of arbitrary position and orientation Each internal node of the tree is associated with a plane and two pointers (one to inside and the other to outside). If a sub-space is homogeneous (fully indoors or outdoors), cease to be divided. 27
30 (CSG - Constructive Solid Geometry) The object is obtained by combining simple primitives using Boolean operators. The object is stored as a tree, where the interior nodes are operators and leaves are simple primitives Nodes represent Boolean operations and geometric transformations. 28
31 Exercise 29
32 References 3D Modeling & Surfacing Bill Fleming Morgan Kaufmann, Academic Press, 1999 Introduction to Computer Graphics James Foley, A. van Dam, S. Feiner, J. Hughes, R. Phillips Addison-Wesley Publishing Company,
CSG obj. oper3. obj1 obj2 obj3. obj5. obj4
 Solid Modeling Solid: Boundary + Interior Volume occupied by geometry Solid representation schemes Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) Boundary representations (B-reps) Space-partition representations Operations
Solid Modeling Solid: Boundary + Interior Volume occupied by geometry Solid representation schemes Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) Boundary representations (B-reps) Space-partition representations Operations
Introduction to 2D and 3D Computer Graphics. Realistic Rendering. -- Solids Modeling --
 Introduction to 2D and 3D Computer Graphics Realistic Rendering -- Solids Modeling -- CS447/547 10-1 CS447/547 10-2 Solid objects can be defined......by sweeping an object along a trajectory through space...this
Introduction to 2D and 3D Computer Graphics Realistic Rendering -- Solids Modeling -- CS447/547 10-1 CS447/547 10-2 Solid objects can be defined......by sweeping an object along a trajectory through space...this
SOME 024: Computer Aided Design. E. Rozos
 SOME 024: Computer Aided Design E. Rozos Introduction to CAD theory part 2 Lesson structure Why Solid modelling Solid modelling methods Representation based Manufacturing based Solid modelling storage
SOME 024: Computer Aided Design E. Rozos Introduction to CAD theory part 2 Lesson structure Why Solid modelling Solid modelling methods Representation based Manufacturing based Solid modelling storage
Lecture 17: Solid Modeling.... a cubit on the one side, and a cubit on the other side Exodus 26:13
 Lecture 17: Solid Modeling... a cubit on the one side, and a cubit on the other side Exodus 26:13 Who is on the LORD's side? Exodus 32:26 1. Solid Representations A solid is a 3-dimensional shape with
Lecture 17: Solid Modeling... a cubit on the one side, and a cubit on the other side Exodus 26:13 Who is on the LORD's side? Exodus 32:26 1. Solid Representations A solid is a 3-dimensional shape with
Solid Modeling. Ron Goldman Department of Computer Science Rice University
 Solid Modeling Ron Goldman Department of Computer Science Rice University Solids Definition 1. A model which has a well defined inside and outside. 2. For each point, we can in principle determine whether
Solid Modeling Ron Goldman Department of Computer Science Rice University Solids Definition 1. A model which has a well defined inside and outside. 2. For each point, we can in principle determine whether
Geometric Modeling. Introduction
 Geometric Modeling Introduction Geometric modeling is as important to CAD as governing equilibrium equations to classical engineering fields as mechanics and thermal fluids. intelligent decision on the
Geometric Modeling Introduction Geometric modeling is as important to CAD as governing equilibrium equations to classical engineering fields as mechanics and thermal fluids. intelligent decision on the
9. Three Dimensional Object Representations
 9. Three Dimensional Object Representations Methods: Polygon and Quadric surfaces: For simple Euclidean objects Spline surfaces and construction: For curved surfaces Procedural methods: Eg. Fractals, Particle
9. Three Dimensional Object Representations Methods: Polygon and Quadric surfaces: For simple Euclidean objects Spline surfaces and construction: For curved surfaces Procedural methods: Eg. Fractals, Particle
3D Modeling: Solid Models
 CS 430/536 Computer Graphics I 3D Modeling: Solid Models Week 9, Lecture 18 David Breen, William Regli and Maxim Peysakhov Geometric and Intelligent Computing Laboratory Department of Computer Science
CS 430/536 Computer Graphics I 3D Modeling: Solid Models Week 9, Lecture 18 David Breen, William Regli and Maxim Peysakhov Geometric and Intelligent Computing Laboratory Department of Computer Science
3D Representation and Solid Modeling
 MCS 585/480 Computer Graphics I 3D Representation and Solid Modeling Week 8, Lecture 16 William Regli and Maxim Peysakhov Geometric and Intelligent Computing Laboratory Department of Computer Science Drexel
MCS 585/480 Computer Graphics I 3D Representation and Solid Modeling Week 8, Lecture 16 William Regli and Maxim Peysakhov Geometric and Intelligent Computing Laboratory Department of Computer Science Drexel
Chapter 12 Solid Modeling. Disadvantages of wireframe representations
 Chapter 12 Solid Modeling Wireframe, surface, solid modeling Solid modeling gives a complete and unambiguous definition of an object, describing not only the shape of the boundaries but also the object
Chapter 12 Solid Modeling Wireframe, surface, solid modeling Solid modeling gives a complete and unambiguous definition of an object, describing not only the shape of the boundaries but also the object
Geometric Modeling Mortenson Chapter 11. Complex Model Construction
 Geometric Modeling 91.580.201 Mortenson Chapter 11 Complex Model Construction Topics Topology of Models Connectivity and other intrinsic properties Graph-Based Models Emphasize topological structure Boolean
Geometric Modeling 91.580.201 Mortenson Chapter 11 Complex Model Construction Topics Topology of Models Connectivity and other intrinsic properties Graph-Based Models Emphasize topological structure Boolean
Lecture notes: Object modeling
 Lecture notes: Object modeling One of the classic problems in computer vision is to construct a model of an object from an image of the object. An object model has the following general principles: Compact
Lecture notes: Object modeling One of the classic problems in computer vision is to construct a model of an object from an image of the object. An object model has the following general principles: Compact
Introduction to Solid Modeling
 Introduction to Solid Modeling Hongxin Zhang and Jieqing Feng 2007-01-15 State Key Lab of CAD&CG Zhejiang University Contents Solid Representations: An Introduction Wireframe Models Boundary Representations
Introduction to Solid Modeling Hongxin Zhang and Jieqing Feng 2007-01-15 State Key Lab of CAD&CG Zhejiang University Contents Solid Representations: An Introduction Wireframe Models Boundary Representations
Solid Modeling Lecture Series. Prof. Gary Wang Department of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering The University of Manitoba
 Solid Modeling 25.353 Lecture Series Prof. Gary Wang Department of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering The University of Manitoba Information complete, unambiguous, accurate solid model Solid Modeling
Solid Modeling 25.353 Lecture Series Prof. Gary Wang Department of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering The University of Manitoba Information complete, unambiguous, accurate solid model Solid Modeling
Computer Graphics Prof. Sukhendu Das Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 24 Solid Modelling
 Computer Graphics Prof. Sukhendu Das Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 24 Solid Modelling Welcome to the lectures on computer graphics. We have
Computer Graphics Prof. Sukhendu Das Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 24 Solid Modelling Welcome to the lectures on computer graphics. We have
L1 - Introduction. Contents. Introduction of CAD/CAM system Components of CAD/CAM systems Basic concepts of graphics programming
 L1 - Introduction Contents Introduction of CAD/CAM system Components of CAD/CAM systems Basic concepts of graphics programming 1 Definitions Computer-Aided Design (CAD) The technology concerned with the
L1 - Introduction Contents Introduction of CAD/CAM system Components of CAD/CAM systems Basic concepts of graphics programming 1 Definitions Computer-Aided Design (CAD) The technology concerned with the
Geometric and Solid Modeling. Problems
 Geometric and Solid Modeling Problems Define a Solid Define Representation Schemes Devise Data Structures Construct Solids Page 1 Mathematical Models Points Curves Surfaces Solids A shape is a set of Points
Geometric and Solid Modeling Problems Define a Solid Define Representation Schemes Devise Data Structures Construct Solids Page 1 Mathematical Models Points Curves Surfaces Solids A shape is a set of Points
Implicit Surfaces & Solid Representations COS 426
 Implicit Surfaces & Solid Representations COS 426 3D Object Representations Desirable properties of an object representation Easy to acquire Accurate Concise Intuitive editing Efficient editing Efficient
Implicit Surfaces & Solid Representations COS 426 3D Object Representations Desirable properties of an object representation Easy to acquire Accurate Concise Intuitive editing Efficient editing Efficient
Spatial Data Structures
 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) [Angel 9.10] Outline Ray tracing review what rays matter? Ray tracing speedup faster
Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) [Angel 9.10] Outline Ray tracing review what rays matter? Ray tracing speedup faster
Solid Modeling. Thomas Funkhouser Princeton University C0S 426, Fall Represent solid interiors of objects
 Solid Modeling Thomas Funkhouser Princeton University C0S 426, Fall 2000 Solid Modeling Represent solid interiors of objects Surface may not be described explicitly Visible Human (National Library of Medicine)
Solid Modeling Thomas Funkhouser Princeton University C0S 426, Fall 2000 Solid Modeling Represent solid interiors of objects Surface may not be described explicitly Visible Human (National Library of Medicine)
Solids as point set. Solid models. Solid representation schemes (cont d) Solid representation schemes. Solid representation schemes (cont d)
 Solid models Solid models developed to address limitations of wireframe modeling. Attempt was to create systems which create only complete representations. Modelers would support direct creation of 3D
Solid models Solid models developed to address limitations of wireframe modeling. Attempt was to create systems which create only complete representations. Modelers would support direct creation of 3D
Physically-Based Modeling and Animation. University of Missouri at Columbia
 Overview of Geometric Modeling Overview 3D Shape Primitives: Points Vertices. Curves Lines, polylines, curves. Surfaces Triangle meshes, splines, subdivision surfaces, implicit surfaces, particles. Solids
Overview of Geometric Modeling Overview 3D Shape Primitives: Points Vertices. Curves Lines, polylines, curves. Surfaces Triangle meshes, splines, subdivision surfaces, implicit surfaces, particles. Solids
Introduction to Computer Graphics
 Introduction to Computer Graphics James D. Foley Georgia Institute of Technology Andries van Dam Brown University Steven K. Feiner Columbia University John F. Hughes Brown University Richard L. Phillips
Introduction to Computer Graphics James D. Foley Georgia Institute of Technology Andries van Dam Brown University Steven K. Feiner Columbia University John F. Hughes Brown University Richard L. Phillips
Ray Tracing Acceleration Data Structures
 Ray Tracing Acceleration Data Structures Sumair Ahmed October 29, 2009 Ray Tracing is very time-consuming because of the ray-object intersection calculations. With the brute force method, each ray has
Ray Tracing Acceleration Data Structures Sumair Ahmed October 29, 2009 Ray Tracing is very time-consuming because of the ray-object intersection calculations. With the brute force method, each ray has
Computer Aided Engineering Applications
 Computer Aided Engineering Applications 1A.Geometric Modeling 1.1 Geometric modelling methods 1.2 Data representation 1.3 Modeling functions 1.4 Structure of a CAD system Engi 6928 - Fall 2014 1.Geometric
Computer Aided Engineering Applications 1A.Geometric Modeling 1.1 Geometric modelling methods 1.2 Data representation 1.3 Modeling functions 1.4 Structure of a CAD system Engi 6928 - Fall 2014 1.Geometric
Development of Reverse Engineering System for Machine Engineering Using 3D Bit-map Data. Tatsuro Yashiki* and Tarou Takagi*
 Development of Reverse Engineering System for Machine Engineering Using 3D Bit-map Data Tatsuro Yashiki* and Tarou Takagi* *Power & Industrial Systems R&D Laboratory, Hitachi, Ltd. Abstract In this paper,
Development of Reverse Engineering System for Machine Engineering Using 3D Bit-map Data Tatsuro Yashiki* and Tarou Takagi* *Power & Industrial Systems R&D Laboratory, Hitachi, Ltd. Abstract In this paper,
13.472J/1.128J/2.158J/16.940J COMPUTATIONAL GEOMETRY
 13.472J/1.128J/2.158J/16.940J COMPUTATIONAL GEOMETRY Lecture 1 Nicholas M. Patrikalakis Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139-4307, USA Copyright 2003 c Massachusetts Institute of Technology
13.472J/1.128J/2.158J/16.940J COMPUTATIONAL GEOMETRY Lecture 1 Nicholas M. Patrikalakis Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139-4307, USA Copyright 2003 c Massachusetts Institute of Technology
MODELING AND HIERARCHY
 MODELING AND HIERARCHY Introduction Models are abstractions of the world both of the real world in which we live and of virtual worlds that we create with computers. We are all familiar with mathematical
MODELING AND HIERARCHY Introduction Models are abstractions of the world both of the real world in which we live and of virtual worlds that we create with computers. We are all familiar with mathematical
3/3/2014. Sharif University of Technology. Session # 5. Instructor. Class time. Course evaluation. Department of Industrial Engineering
 Advanced Manufacturing Laboratory Department of Industrial Engineering Sharif University of Technology Session # 5 Instructor Omid Fatahi Valilai, Ph.D. Industrial Engineering Department, Sharif University
Advanced Manufacturing Laboratory Department of Industrial Engineering Sharif University of Technology Session # 5 Instructor Omid Fatahi Valilai, Ph.D. Industrial Engineering Department, Sharif University
Spatial Data Structures
 15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 17 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) April 1, 2003 [Angel 9.10] Frank Pfenning Carnegie
15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 17 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) April 1, 2003 [Angel 9.10] Frank Pfenning Carnegie
Introduction to Solid Modeling Parametric Modeling. Mechanical Engineering Dept.
 Introduction to Solid Modeling Parametric Modeling 1 Why draw 3D Models? 3D models are easier to interpret. Simulation under real-life conditions. Less expensive than building a physical model. 3D models
Introduction to Solid Modeling Parametric Modeling 1 Why draw 3D Models? 3D models are easier to interpret. Simulation under real-life conditions. Less expensive than building a physical model. 3D models
Second degree equations - quadratics. nonparametric: x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = r 2
 walters@buffalo.edu CSE 480/580 Lecture 20 Slide 1 Three Dimensional Representations Quadric Surfaces Superquadrics Sweep Representations Constructive Solid Geometry Octrees Quadric Surfaces Second degree
walters@buffalo.edu CSE 480/580 Lecture 20 Slide 1 Three Dimensional Representations Quadric Surfaces Superquadrics Sweep Representations Constructive Solid Geometry Octrees Quadric Surfaces Second degree
Spatial Data Structures
 15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 17 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) March 28, 2002 [Angel 8.9] Frank Pfenning Carnegie
15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 17 Spatial Data Structures Hierarchical Bounding Volumes Regular Grids Octrees BSP Trees Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) March 28, 2002 [Angel 8.9] Frank Pfenning Carnegie
Cell Decomposition for Building Model Generation at Different Scales
 Cell Decomposition for Building Model Generation at Different Scales Norbert Haala, Susanne Becker, Martin Kada Institute for Photogrammetry Universität Stuttgart Germany forename.lastname@ifp.uni-stuttgart.de
Cell Decomposition for Building Model Generation at Different Scales Norbert Haala, Susanne Becker, Martin Kada Institute for Photogrammetry Universität Stuttgart Germany forename.lastname@ifp.uni-stuttgart.de
Modeling 3D Objects: Part 2
 Modeling 3D Objects: Part 2 Patches, NURBS, Solids Modeling, Spatial Subdivisioning, and Implicit Functions 3D Computer Graphics by Alan Watt Third Edition, Pearson Education Limited, 2000 General Modeling
Modeling 3D Objects: Part 2 Patches, NURBS, Solids Modeling, Spatial Subdivisioning, and Implicit Functions 3D Computer Graphics by Alan Watt Third Edition, Pearson Education Limited, 2000 General Modeling
3D Object Representation. Michael Kazhdan ( /657)
 3D Object Representation Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) 3D Objects How can this object be represented in a computer? 3D Objects This one? H&B Figure 10.46 3D Objects This one? H&B Figure 9.9 3D Objects
3D Object Representation Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) 3D Objects How can this object be represented in a computer? 3D Objects This one? H&B Figure 10.46 3D Objects This one? H&B Figure 9.9 3D Objects
Overview of 3D Object Representations
 Overview of 3D Object Representations Thomas Funkhouser Princeton University C0S 597D, Fall 2003 3D Object Representations What makes a good 3D object representation? Stanford and Hearn & Baker 1 3D Object
Overview of 3D Object Representations Thomas Funkhouser Princeton University C0S 597D, Fall 2003 3D Object Representations What makes a good 3D object representation? Stanford and Hearn & Baker 1 3D Object
2/12/2015. Sharif University of Technology. Session # 4. Instructor. Class time. Course evaluation. Department of Industrial Engineering
 Advanced Manufacturing Laboratory Department of Industrial Engineering Sharif University of Technology Session # 4 Instructor Omid Fatahi Valilai, Ph.D. Industrial Engineering Department, Sharif University
Advanced Manufacturing Laboratory Department of Industrial Engineering Sharif University of Technology Session # 4 Instructor Omid Fatahi Valilai, Ph.D. Industrial Engineering Department, Sharif University
Advanced 3D-Data Structures
 Advanced 3D-Data Structures Eduard Gröller, Martin Haidacher Institute of Computer Graphics and Algorithms Vienna University of Technology Motivation For different data sources and applications different
Advanced 3D-Data Structures Eduard Gröller, Martin Haidacher Institute of Computer Graphics and Algorithms Vienna University of Technology Motivation For different data sources and applications different
Ray Tracing III. Wen-Chieh (Steve) Lin National Chiao-Tung University
 Ray Tracing III Wen-Chieh (Steve) Lin National Chiao-Tung University Shirley, Fundamentals of Computer Graphics, Chap 10 Doug James CG slides, I-Chen Lin s CG slides Ray-tracing Review For each pixel,
Ray Tracing III Wen-Chieh (Steve) Lin National Chiao-Tung University Shirley, Fundamentals of Computer Graphics, Chap 10 Doug James CG slides, I-Chen Lin s CG slides Ray-tracing Review For each pixel,
We have set up our axioms to deal with the geometry of space but have not yet developed these ideas much. Let s redress that imbalance.
 Solid geometry We have set up our axioms to deal with the geometry of space but have not yet developed these ideas much. Let s redress that imbalance. First, note that everything we have proven for the
Solid geometry We have set up our axioms to deal with the geometry of space but have not yet developed these ideas much. Let s redress that imbalance. First, note that everything we have proven for the
Computer Graphics. Instructor: Oren Kapah. Office Hours: T.B.A.
 Computer Graphics Instructor: Oren Kapah (orenkapahbiu@gmail.com) Office Hours: T.B.A. The CG-IDC slides for this course were created by Toky & Hagit Hel-Or 1 CG-IDC 2 Exercise and Homework The exercise
Computer Graphics Instructor: Oren Kapah (orenkapahbiu@gmail.com) Office Hours: T.B.A. The CG-IDC slides for this course were created by Toky & Hagit Hel-Or 1 CG-IDC 2 Exercise and Homework The exercise
Geometric Representations. Stelian Coros
 Geometric Representations Stelian Coros Geometric Representations Languages for describing shape Boundary representations Polygonal meshes Subdivision surfaces Implicit surfaces Volumetric models Parametric
Geometric Representations Stelian Coros Geometric Representations Languages for describing shape Boundary representations Polygonal meshes Subdivision surfaces Implicit surfaces Volumetric models Parametric
CAR-TR-990 CS-TR-4526 UMIACS September 2003
 CAR-TR-990 CS-TR-4526 UMIACS 2003-94 September 2003 Object-based and Image-based Object Representations Hanan Samet Computer Science Department Center for Automation Research Institute for Advanced Computer
CAR-TR-990 CS-TR-4526 UMIACS 2003-94 September 2003 Object-based and Image-based Object Representations Hanan Samet Computer Science Department Center for Automation Research Institute for Advanced Computer
Grade VIII. Mathematics Geometry Notes. #GrowWithGreen
 Grade VIII Mathematics Geometry Notes #GrowWithGreen Polygons can be classified according to their number of sides (or vertices). The sum of all the interior angles of an n -sided polygon is given by,
Grade VIII Mathematics Geometry Notes #GrowWithGreen Polygons can be classified according to their number of sides (or vertices). The sum of all the interior angles of an n -sided polygon is given by,
Chapter 4-3D Modeling
 Chapter 4-3D Modeling Polygon Meshes Geometric Primitives Interpolation Curves Levels Of Detail (LOD) Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) Extrusion & Rotation Volume- and Point-based Graphics 1 The 3D rendering
Chapter 4-3D Modeling Polygon Meshes Geometric Primitives Interpolation Curves Levels Of Detail (LOD) Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG) Extrusion & Rotation Volume- and Point-based Graphics 1 The 3D rendering
Surface and Solid Geometry. 3D Polygons
 Surface and Solid Geometry D olygons Once we know our plane equation: Ax + By + Cz + D = 0, we still need to manage the truncation which leads to the polygon itself Functionally, we will need to do this
Surface and Solid Geometry D olygons Once we know our plane equation: Ax + By + Cz + D = 0, we still need to manage the truncation which leads to the polygon itself Functionally, we will need to do this
SOLID MODELLING. PARAMETRICALLY WE CAN DEFINE SOLID AS- X=x(u,v,w) Y=y(u,v,w) Z=z(u,v,w) Tricubic solid- u,v,w Є [0,1]
![SOLID MODELLING. PARAMETRICALLY WE CAN DEFINE SOLID AS- X=x(u,v,w) Y=y(u,v,w) Z=z(u,v,w) Tricubic solid- u,v,w Є [0,1] SOLID MODELLING. PARAMETRICALLY WE CAN DEFINE SOLID AS- X=x(u,v,w) Y=y(u,v,w) Z=z(u,v,w) Tricubic solid- u,v,w Є [0,1]](/thumbs/80/80530647.jpg) SOLID MODELLING PARAMETRICALLY WE CAN DEFINE SOLID AS- X=x(u,v,w) Y=y(u,v,w) Z=z(u,v,w) u w v Tricubic solid- 3 3 3 P(u,v,w) = Σ Σ Σ a ijk u i v j w k I=0 j=o k=0 u,v,w Є [0,1] GRAPH BASED MODELS OR B-Rep
SOLID MODELLING PARAMETRICALLY WE CAN DEFINE SOLID AS- X=x(u,v,w) Y=y(u,v,w) Z=z(u,v,w) u w v Tricubic solid- 3 3 3 P(u,v,w) = Σ Σ Σ a ijk u i v j w k I=0 j=o k=0 u,v,w Є [0,1] GRAPH BASED MODELS OR B-Rep
Mathematics Curriculum
 6 G R A D E Mathematics Curriculum GRADE 6 5 Table of Contents 1... 1 Topic A: Area of Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons (6.G.A.1)... 11 Lesson 1: The Area of Parallelograms Through Rectangle Facts...
6 G R A D E Mathematics Curriculum GRADE 6 5 Table of Contents 1... 1 Topic A: Area of Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons (6.G.A.1)... 11 Lesson 1: The Area of Parallelograms Through Rectangle Facts...
Collision Detection. These slides are mainly from Ming Lin s course notes at UNC Chapel Hill
 Collision Detection These slides are mainly from Ming Lin s course notes at UNC Chapel Hill http://www.cs.unc.edu/~lin/comp259-s06/ Computer Animation ILE5030 Computer Animation and Special Effects 2 Haptic
Collision Detection These slides are mainly from Ming Lin s course notes at UNC Chapel Hill http://www.cs.unc.edu/~lin/comp259-s06/ Computer Animation ILE5030 Computer Animation and Special Effects 2 Haptic
Week 7 Convex Hulls in 3D
 1 Week 7 Convex Hulls in 3D 2 Polyhedra A polyhedron is the natural generalization of a 2D polygon to 3D 3 Closed Polyhedral Surface A closed polyhedral surface is a finite set of interior disjoint polygons
1 Week 7 Convex Hulls in 3D 2 Polyhedra A polyhedron is the natural generalization of a 2D polygon to 3D 3 Closed Polyhedral Surface A closed polyhedral surface is a finite set of interior disjoint polygons
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK M.E: CAD/CAM I SEMESTER ED5151 COMPUTER APPLICATIONS IN DESIGN Regulation 2017 Academic
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK M.E: CAD/CAM I SEMESTER ED5151 COMPUTER APPLICATIONS IN DESIGN Regulation 2017 Academic
GEOMETRIC TOOLS FOR COMPUTER GRAPHICS
 GEOMETRIC TOOLS FOR COMPUTER GRAPHICS PHILIP J. SCHNEIDER DAVID H. EBERLY MORGAN KAUFMANN PUBLISHERS A N I M P R I N T O F E L S E V I E R S C I E N C E A M S T E R D A M B O S T O N L O N D O N N E W
GEOMETRIC TOOLS FOR COMPUTER GRAPHICS PHILIP J. SCHNEIDER DAVID H. EBERLY MORGAN KAUFMANN PUBLISHERS A N I M P R I N T O F E L S E V I E R S C I E N C E A M S T E R D A M B O S T O N L O N D O N N E W
Ray Tracing: Intersection
 Computer Graphics as Virtual Photography Ray Tracing: Intersection Photography: real scene camera (captures light) photo processing Photographic print processing Computer Graphics: 3D models camera tone
Computer Graphics as Virtual Photography Ray Tracing: Intersection Photography: real scene camera (captures light) photo processing Photographic print processing Computer Graphics: 3D models camera tone
Design Intent of Geometric Models
 School of Computer Science Cardiff University Design Intent of Geometric Models Frank C. Langbein GR/M78267 GR/S69085/01 NUF-NAL 00638/G Auckland University 15th September 2004; Version 1.1 Design Intent
School of Computer Science Cardiff University Design Intent of Geometric Models Frank C. Langbein GR/M78267 GR/S69085/01 NUF-NAL 00638/G Auckland University 15th September 2004; Version 1.1 Design Intent
Solid Modeling. Michael Kazhdan ( /657) HB , FvDFH 12.1, 12.2, 12.6, 12.7 Marching Cubes, Lorensen et al.
 Solid Modeling Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) HB 10.15 10.17, 10.22 FvDFH 12.1, 12.2, 12.6, 12.7 Marching Cubes, Lorensen et al. 1987 Announcement OpenGL review session: When: Today @ 9:00 PM Where: Malone
Solid Modeling Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) HB 10.15 10.17, 10.22 FvDFH 12.1, 12.2, 12.6, 12.7 Marching Cubes, Lorensen et al. 1987 Announcement OpenGL review session: When: Today @ 9:00 PM Where: Malone
From curves to surfaces. Parametric surfaces and solid modeling. Extrusions. Surfaces of revolution. So far have discussed spline curves in 2D
 From curves to surfaces Parametric surfaces and solid modeling CS 465 Lecture 12 2007 Doug James & Steve Marschner 1 So far have discussed spline curves in 2D it turns out that this already provides of
From curves to surfaces Parametric surfaces and solid modeling CS 465 Lecture 12 2007 Doug James & Steve Marschner 1 So far have discussed spline curves in 2D it turns out that this already provides of
Geometric Modeling Systems
 Geometric Modeling Systems Wireframe Modeling use lines/curves and points for 2D or 3D largely replaced by surface and solid models Surface Modeling wireframe information plus surface definitions supports
Geometric Modeling Systems Wireframe Modeling use lines/curves and points for 2D or 3D largely replaced by surface and solid models Surface Modeling wireframe information plus surface definitions supports
Computer Aided Design. Solid models and B-REP
 Solid models and B-REP 1 Classical modelling problem : the intersection 3 independent representations of the intersection : - a 3D NURBS curve (giving points in the global XYZ coordinate system) - a 2D
Solid models and B-REP 1 Classical modelling problem : the intersection 3 independent representations of the intersection : - a 3D NURBS curve (giving points in the global XYZ coordinate system) - a 2D
CELL DECOMPOSITION FOR THE GENERATION OF BUILDING MODELS AT MULTIPLE SCALES
 CELL DECOMPOSITION FOR THE GENERATION OF BUILDING MODELS AT MULTIPLE SCALES Norbert Haala, Susanne Becker, Martin Kada Institute for Photogrammetry, Universitaet Stuttgart Geschwister-Scholl-Str. 24D,
CELL DECOMPOSITION FOR THE GENERATION OF BUILDING MODELS AT MULTIPLE SCALES Norbert Haala, Susanne Becker, Martin Kada Institute for Photogrammetry, Universitaet Stuttgart Geschwister-Scholl-Str. 24D,
A Method to Generate Exact Contour Files for Solid Freeform Fabrication
 A Method to Generate Exact Contour Files for Solid Freeform Fabrication Sashidhar Guduri, Graduate Research Assistant Richard H. Crawford, Assistant Professor Joseph J. Beaman, Professor Dept. of Mechanical
A Method to Generate Exact Contour Files for Solid Freeform Fabrication Sashidhar Guduri, Graduate Research Assistant Richard H. Crawford, Assistant Professor Joseph J. Beaman, Professor Dept. of Mechanical
Digital Image Processing Fundamentals
 Ioannis Pitas Digital Image Processing Fundamentals Chapter 7 Shape Description Answers to the Chapter Questions Thessaloniki 1998 Chapter 7: Shape description 7.1 Introduction 1. Why is invariance to
Ioannis Pitas Digital Image Processing Fundamentals Chapter 7 Shape Description Answers to the Chapter Questions Thessaloniki 1998 Chapter 7: Shape description 7.1 Introduction 1. Why is invariance to
Geometric Modeling Topics
 Geometric Modeling Topics George Allen, george.allen@siemens.com Outline General background Convergent modeling Multi-material objects Giga-face lattices Page 2 Boundary Representation (b-rep) Topology
Geometric Modeling Topics George Allen, george.allen@siemens.com Outline General background Convergent modeling Multi-material objects Giga-face lattices Page 2 Boundary Representation (b-rep) Topology
CS 352: Computer Graphics. Hierarchical Graphics, Modeling, And Animation
 CS 352: Computer Graphics Hierarchical Graphics, Modeling, And Animation Chapter 9-2 Overview Modeling Animation Data structures for interactive graphics CSG-tree BSP-tree Quadtrees and Octrees Visibility
CS 352: Computer Graphics Hierarchical Graphics, Modeling, And Animation Chapter 9-2 Overview Modeling Animation Data structures for interactive graphics CSG-tree BSP-tree Quadtrees and Octrees Visibility
Simulation in Computer Graphics Space Subdivision. Matthias Teschner
 Simulation in Computer Graphics Space Subdivision Matthias Teschner Outline Introduction Uniform grid Octree and k-d tree BSP tree University of Freiburg Computer Science Department 2 Model Partitioning
Simulation in Computer Graphics Space Subdivision Matthias Teschner Outline Introduction Uniform grid Octree and k-d tree BSP tree University of Freiburg Computer Science Department 2 Model Partitioning
Engineering Drawing II
 Instructional Unit Basic Shading and Rendering -Basic Shading -Students will be able -Demonstrate the ability Class Discussions 3.1.12.B, -Basic Rendering to shade a 3D model to apply shading to a 3D 3.2.12.C,
Instructional Unit Basic Shading and Rendering -Basic Shading -Students will be able -Demonstrate the ability Class Discussions 3.1.12.B, -Basic Rendering to shade a 3D model to apply shading to a 3D 3.2.12.C,
layers in a raster model
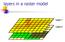 layers in a raster model Layer 1 Layer 2 layers in an vector-based model (1) Layer 2 Layer 1 layers in an vector-based model (2) raster versus vector data model Raster model Vector model Simple data structure
layers in a raster model Layer 1 Layer 2 layers in an vector-based model (1) Layer 2 Layer 1 layers in an vector-based model (2) raster versus vector data model Raster model Vector model Simple data structure
13.472J/1.128J/2.158J/16.940J COMPUTATIONAL GEOMETRY
 13.472J/1.128J/2.158J/16.940J COMPUTATIONAL GEOMETRY Lecture 23 Dr. W. Cho Prof. N. M. Patrikalakis Copyright c 2003 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Contents 23 F.E. and B.E. Meshing Algorithms 2
13.472J/1.128J/2.158J/16.940J COMPUTATIONAL GEOMETRY Lecture 23 Dr. W. Cho Prof. N. M. Patrikalakis Copyright c 2003 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Contents 23 F.E. and B.E. Meshing Algorithms 2
Computer Aided Design (CAD)
 CAD/CAM Dr. Ibrahim Al-Naimi Chapter two Computer Aided Design (CAD) The information-processing cycle in a typical manufacturing firm. PRODUCT DESIGN AND CAD Product design is a critical function in the
CAD/CAM Dr. Ibrahim Al-Naimi Chapter two Computer Aided Design (CAD) The information-processing cycle in a typical manufacturing firm. PRODUCT DESIGN AND CAD Product design is a critical function in the
Lesson 2 Constructive Solid Geometry Concept. Parametric Modeling with I-DEAS 2-1
 Lesson 2 Constructive Solid Geometry Concept Parametric Modeling with I-DEAS 2-1 2-2 Parametric Modeling with I-DEAS Introduction In the 1980s, one of the main advancements in Solid Modeling was the development
Lesson 2 Constructive Solid Geometry Concept Parametric Modeling with I-DEAS 2-1 2-2 Parametric Modeling with I-DEAS Introduction In the 1980s, one of the main advancements in Solid Modeling was the development
Example: The following is an example of a polyhedron. Fill the blanks with the appropriate answer. Vertices:
 11.1: Space Figures and Cross Sections Polyhedron: solid that is bounded by polygons Faces: polygons that enclose a polyhedron Edge: line segment that faces meet and form Vertex: point or corner where
11.1: Space Figures and Cross Sections Polyhedron: solid that is bounded by polygons Faces: polygons that enclose a polyhedron Edge: line segment that faces meet and form Vertex: point or corner where
Invariant Measures of Convex Sets. Eitan Grinspun, Columbia University Peter Schröder, Caltech
 Invariant Measures of Convex Sets Eitan Grinspun, Columbia University Peter Schröder, Caltech What will we measure? Subject to be measured, S an object living in n-dim space convex, compact subset of R
Invariant Measures of Convex Sets Eitan Grinspun, Columbia University Peter Schröder, Caltech What will we measure? Subject to be measured, S an object living in n-dim space convex, compact subset of R
Constructive Solid Geometry and Procedural Modeling. Stelian Coros
 Constructive Solid Geometry and Procedural Modeling Stelian Coros Somewhat unrelated Schedule for presentations February 3 5 10 12 17 19 24 26 March 3 5 10 12 17 19 24 26 30 April 2 7 9 14 16 21 23 28
Constructive Solid Geometry and Procedural Modeling Stelian Coros Somewhat unrelated Schedule for presentations February 3 5 10 12 17 19 24 26 March 3 5 10 12 17 19 24 26 30 April 2 7 9 14 16 21 23 28
Geometric Modeling. Creating 3D solid geometry in a computer! Partial History of Geometric Modeling
 Geometric Modeling Creating 3D solid geometry in a computer! Partial History of Geometric Modeling 1963 Wireframe Computer Graphics Invented (Ivan Sutherland, MIT) 2 1 Partial History 1964 DAC-1, General
Geometric Modeling Creating 3D solid geometry in a computer! Partial History of Geometric Modeling 1963 Wireframe Computer Graphics Invented (Ivan Sutherland, MIT) 2 1 Partial History 1964 DAC-1, General
Collision Detection based on Spatial Partitioning
 Simulation in Computer Graphics Collision Detection based on Spatial Partitioning Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline introduction uniform grid Octree and k-d tree
Simulation in Computer Graphics Collision Detection based on Spatial Partitioning Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline introduction uniform grid Octree and k-d tree
Invariant Measures. The Smooth Approach
 Invariant Measures Mathieu Desbrun & Peter Schröder 1 The Smooth Approach On this show lots of derivatives tedious expressions in coordinates For what? only to discover that there are invariant measures
Invariant Measures Mathieu Desbrun & Peter Schröder 1 The Smooth Approach On this show lots of derivatives tedious expressions in coordinates For what? only to discover that there are invariant measures
Data Representation in Visualisation
 Data Representation in Visualisation Visualisation Lecture 4 Taku Komura Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics Taku Komura Data Representation 1 Data Representation We have
Data Representation in Visualisation Visualisation Lecture 4 Taku Komura Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics Taku Komura Data Representation 1 Data Representation We have
The goal is the definition of points with numbers and primitives with equations or functions. The definition of points with numbers requires a
 The goal is the definition of points with numbers and primitives with equations or functions. The definition of points with numbers requires a coordinate system and then the measuring of the point with
The goal is the definition of points with numbers and primitives with equations or functions. The definition of points with numbers requires a coordinate system and then the measuring of the point with
UPEM Master 2 Informatique SIS. Digital Geometry. Topic 2: Digital topology: object boundaries and curves/surfaces. Yukiko Kenmochi.
 UPEM Master 2 Informatique SIS Digital Geometry Topic 2: Digital topology: object boundaries and curves/surfaces Yukiko Kenmochi October 5, 2016 Digital Geometry : Topic 2 1/34 Opening Representations
UPEM Master 2 Informatique SIS Digital Geometry Topic 2: Digital topology: object boundaries and curves/surfaces Yukiko Kenmochi October 5, 2016 Digital Geometry : Topic 2 1/34 Opening Representations
6 Mathematics Curriculum
 New York State Common Core 6 Mathematics Curriculum GRADE GRADE 6 MODULE 5 Table of Contents 1 Area, Surface Area, and Volume Problems... 3 Topic A: Area of Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons (6.G.A.1)...
New York State Common Core 6 Mathematics Curriculum GRADE GRADE 6 MODULE 5 Table of Contents 1 Area, Surface Area, and Volume Problems... 3 Topic A: Area of Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons (6.G.A.1)...
Autodesk Conceptual Design Curriculum 2011 Student Workbook Unit 2: Parametric Exploration Lesson 1: Parametric Modeling
 Autodesk Conceptual Design Curriculum 2011 Student Workbook Unit 2: Parametric Exploration Lesson 1: Parametric Modeling Overview: Parametric Modeling In this lesson, you learn the basic principles of
Autodesk Conceptual Design Curriculum 2011 Student Workbook Unit 2: Parametric Exploration Lesson 1: Parametric Modeling Overview: Parametric Modeling In this lesson, you learn the basic principles of
Hierarchical Solid Boolean Modeling
 Hierarchical Solid Boolean Modeling Bernie Freidin, 1999-2000 Division III Final Project Chair: Lee Specter Member: Ken Hoffman Abstract Here I present a data structure suitable for representing and constructing
Hierarchical Solid Boolean Modeling Bernie Freidin, 1999-2000 Division III Final Project Chair: Lee Specter Member: Ken Hoffman Abstract Here I present a data structure suitable for representing and constructing
Collision and Proximity Queries
 Collision and Proximity Queries Dinesh Manocha (based on slides from Ming Lin) COMP790-058 Fall 2013 Geometric Proximity Queries l Given two object, how would you check: If they intersect with each other
Collision and Proximity Queries Dinesh Manocha (based on slides from Ming Lin) COMP790-058 Fall 2013 Geometric Proximity Queries l Given two object, how would you check: If they intersect with each other
Subdivision Surfaces. Course Syllabus. Course Syllabus. Modeling. Equivalence of Representations. 3D Object Representations
 Subdivision Surfaces Adam Finkelstein Princeton University COS 426, Spring 2003 Course Syllabus I. Image processing II. Rendering III. Modeling IV. Animation Image Processing (Rusty Coleman, CS426, Fall99)
Subdivision Surfaces Adam Finkelstein Princeton University COS 426, Spring 2003 Course Syllabus I. Image processing II. Rendering III. Modeling IV. Animation Image Processing (Rusty Coleman, CS426, Fall99)
Topological Issues in Hexahedral Meshing
 Topological Issues in Hexahedral Meshing David Eppstein Univ. of California, Irvine Dept. of Information and Computer Science Outline I. What is meshing? Problem statement Types of mesh Quality issues
Topological Issues in Hexahedral Meshing David Eppstein Univ. of California, Irvine Dept. of Information and Computer Science Outline I. What is meshing? Problem statement Types of mesh Quality issues
CS3621 Midterm Solution (Fall 2005) 150 points
 CS362 Midterm Solution Fall 25. Geometric Transformation CS362 Midterm Solution (Fall 25) 5 points (a) [5 points] Find the 2D transformation matrix for the reflection about the y-axis transformation (i.e.,
CS362 Midterm Solution Fall 25. Geometric Transformation CS362 Midterm Solution (Fall 25) 5 points (a) [5 points] Find the 2D transformation matrix for the reflection about the y-axis transformation (i.e.,
Computer Graphics 1. Chapter 2 (May 19th, 2011, 2-4pm): 3D Modeling. LMU München Medieninformatik Andreas Butz Computergraphik 1 SS2011
 Computer Graphics 1 Chapter 2 (May 19th, 2011, 2-4pm): 3D Modeling 1 The 3D rendering pipeline (our version for this class) 3D models in model coordinates 3D models in world coordinates 2D Polygons in
Computer Graphics 1 Chapter 2 (May 19th, 2011, 2-4pm): 3D Modeling 1 The 3D rendering pipeline (our version for this class) 3D models in model coordinates 3D models in world coordinates 2D Polygons in
An Efficient Visual Hull Computation Algorithm
 An Efficient Visual Hull Computation Algorithm Wojciech Matusik Chris Buehler Leonard McMillan Laboratory for Computer Science Massachusetts institute of Technology (wojciech, cbuehler, mcmillan)@graphics.lcs.mit.edu
An Efficient Visual Hull Computation Algorithm Wojciech Matusik Chris Buehler Leonard McMillan Laboratory for Computer Science Massachusetts institute of Technology (wojciech, cbuehler, mcmillan)@graphics.lcs.mit.edu
Lecture 25 of 41. Spatial Sorting: Binary Space Partitioning Quadtrees & Octrees
 Spatial Sorting: Binary Space Partitioning Quadtrees & Octrees William H. Hsu Department of Computing and Information Sciences, KSU KSOL course pages: http://bit.ly/hgvxlh / http://bit.ly/evizre Public
Spatial Sorting: Binary Space Partitioning Quadtrees & Octrees William H. Hsu Department of Computing and Information Sciences, KSU KSOL course pages: http://bit.ly/hgvxlh / http://bit.ly/evizre Public
Multidimensional Data and Modelling
 Multidimensional Data and Modelling 1 Problems of multidimensional data structures l multidimensional (md-data or spatial) data and their implementation of operations between objects (spatial data practically
Multidimensional Data and Modelling 1 Problems of multidimensional data structures l multidimensional (md-data or spatial) data and their implementation of operations between objects (spatial data practically
Geometric Modeling in Graphics
 Geometric Modeling in Graphics Part 10: Surface reconstruction Martin Samuelčík www.sccg.sk/~samuelcik samuelcik@sccg.sk Curve, surface reconstruction Finding compact connected orientable 2-manifold surface
Geometric Modeling in Graphics Part 10: Surface reconstruction Martin Samuelčík www.sccg.sk/~samuelcik samuelcik@sccg.sk Curve, surface reconstruction Finding compact connected orientable 2-manifold surface
Flavor of Computational Geometry. Convex Hull in 2D. Shireen Y. Elhabian Aly A. Farag University of Louisville
 Flavor of Computational Geometry Convex Hull in 2D Shireen Y. Elhabian Aly A. Farag University of Louisville February 2010 Agenda Introduction Definitions of Convexity and Convex Hulls Naïve Algorithms
Flavor of Computational Geometry Convex Hull in 2D Shireen Y. Elhabian Aly A. Farag University of Louisville February 2010 Agenda Introduction Definitions of Convexity and Convex Hulls Naïve Algorithms
Computer Graphics. Modelling in 2D. 2D primitives. Lines and Polylines. OpenGL polygon primitives. Special polygons
 Computer Graphics Modelling in D Lecture School of EECS Queen Mar, Universit of London D primitives Digital line algorithms Digital circle algorithms Polgon filling CG - p.hao@qmul.ac.uk D primitives Line
Computer Graphics Modelling in D Lecture School of EECS Queen Mar, Universit of London D primitives Digital line algorithms Digital circle algorithms Polgon filling CG - p.hao@qmul.ac.uk D primitives Line
Triple Integrals in Rectangular Coordinates
 Triple Integrals in Rectangular Coordinates P. Sam Johnson April 10, 2017 P. Sam Johnson (NIT Karnataka) Triple Integrals in Rectangular Coordinates April 10, 2017 1 / 28 Overview We use triple integrals
Triple Integrals in Rectangular Coordinates P. Sam Johnson April 10, 2017 P. Sam Johnson (NIT Karnataka) Triple Integrals in Rectangular Coordinates April 10, 2017 1 / 28 Overview We use triple integrals
Lecture 4b. Surface. Lecture 3 1
 Lecture 4b Surface Lecture 3 1 Surface More complete and less ambiguous representation than its wireframe representation Can be considered as extension to wireframe representation In finite element, surface
Lecture 4b Surface Lecture 3 1 Surface More complete and less ambiguous representation than its wireframe representation Can be considered as extension to wireframe representation In finite element, surface
SHAPE SEGMENTATION FOR SHAPE DESCRIPTION
 SHAPE SEGMENTATION FOR SHAPE DESCRIPTION Olga Symonova GraphiTech Salita dei Molini 2, Villazzano (TN), Italy olga.symonova@graphitech.it Raffaele De Amicis GraphiTech Salita dei Molini 2, Villazzano (TN),
SHAPE SEGMENTATION FOR SHAPE DESCRIPTION Olga Symonova GraphiTech Salita dei Molini 2, Villazzano (TN), Italy olga.symonova@graphitech.it Raffaele De Amicis GraphiTech Salita dei Molini 2, Villazzano (TN),
Computer Aided Engineering Design Prof. Anupam Saxena Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur.
 (Refer Slide Time: 00:28) Computer Aided Engineering Design Prof. Anupam Saxena Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture - 6 Hello, this is lecture number 6 of
(Refer Slide Time: 00:28) Computer Aided Engineering Design Prof. Anupam Saxena Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture - 6 Hello, this is lecture number 6 of
Ray Tracing Foley & Van Dam, Chapters 15 and 16
 Foley & Van Dam, Chapters 15 and 16 (Ray Casting) Examples Efficiency Issues Computing Boolean Set Operations Recursive Determine visibility of a surface by tracing rays of light from the viewer s eye
Foley & Van Dam, Chapters 15 and 16 (Ray Casting) Examples Efficiency Issues Computing Boolean Set Operations Recursive Determine visibility of a surface by tracing rays of light from the viewer s eye
Ray Tracing. Foley & Van Dam, Chapters 15 and 16
 Ray Tracing Foley & Van Dam, Chapters 15 and 16 Ray Tracing Visible Surface Ray Tracing (Ray Casting) Examples Efficiency Issues Computing Boolean Set Operations Recursive Ray Tracing Determine visibility
Ray Tracing Foley & Van Dam, Chapters 15 and 16 Ray Tracing Visible Surface Ray Tracing (Ray Casting) Examples Efficiency Issues Computing Boolean Set Operations Recursive Ray Tracing Determine visibility
Topology and Boundary Representation. The ACIS boundary representation (B-rep) of a model is a hierarchical decomposition of the model s topology:
 Chapter 6. Model Topology Topology refers to the spatial relationships between the various entities in a model. Topology describes how geometric entities are connected (connectivity). On its own, topology
Chapter 6. Model Topology Topology refers to the spatial relationships between the various entities in a model. Topology describes how geometric entities are connected (connectivity). On its own, topology
