FiberMesh. Due: 4/12/10, 11:59 PM
|
|
|
- Thomasina Cummings
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CS224: Interactive Computer Graphics FiberMesh Due: 4/12/10, 11:59 PM Least Squares Solver 5 Mesh triangulation 10 Optimization Problem 1: Curve Dragging 25 Optimization Problem 2: Surface Optimization 35 Adding New Control Curves 15 UI Quality 10 Extra Credit +25 Total 100 This assignment is new / experimental, and its worth towards your final grade has yet to be determined.
2 1 Introduction In this assignment, you will be implementing FiberMesh: Andrew Nealen, et. al, FiberMesh: Designing Freeform Surfaces with 3D Curves takeo/papers/fibermesh.pdf You should already be familiar with the paper from the FiberMesh HW, and the following papers may also provide useful references: Sorkine, O Differential Coordinates for Interactive Mesh Editing. - sorkine/projectpages/editing/ Andrew Nealen s Ph.D. Thesis: - andrew.pdf This assignment will be difficult and time consuming; it is recommended that you start early. 2 Requirements This project can roughly be broken down into three parts: surface creation / optimization, curve deformation, and adding additional control curves. The first two are fairly independent, and you can therefore implement them in either order you d like. As a note, the TAs implemented curve deformation before surface optimization because the optimization problem itself is simpler. 2.1 Surface Creation and Optimization This is where you get to put the Mesh in FiberMesh.. The skeleton we give you comes with bare-bones example code for responding to mouse events and recording and drawing user-drawn curves. After the user finishes drawing a curve, you must: Resample the curve regularly (your meshes will look awful if you don t). Compute a bunch of interior points and use Delaunay triangulation to create a mesh. (see MeshUtils::triangulate in the FiberMesh support code which will perform Delaunay triangulation for you) Remember that you ll need to duplicate triangles, being careful not to duplicate boundary vertices, so that our inflated mesh will not be flat. Project the curve / mesh into world-space. 2
3 Inflate / optimize the mesh by repeatedly applying the 3 optimization problems listed in the Surface Optimization section of the paper (equations 6, 8, and 10). We recommend starting off without using the iterative solution and just trying to get your mesh to inflate just a little bit after one iteration (which will probably take awhile in and of itself), and only then, moving on to the iterative solution which will actually converge to a stable solution (hopefully). Pay particularly close attention to exactly what s supposed to change in terms of constraints in the first iteration versus all of the subsequent iterations. Keep in mind that things Gouraud surface normals won t make much sense for the boundary vertices during the first iteration. 2.2 Curve Deformation Once a curve exists, you must make sure it deforms smoothly when the user grabs and drags it. This means solving the optimization problem discussed in the Curve Deformation section of the paper. NOTE: you are not required to implement the rotation part of curve deformation. Dealing with rotations when deforming a control curve is extra credit. To be explicit, we expect you to solve the following optimization problem: min{ L(v) i δ i 2 + v i v i 2 } (1) i V i V \ROI Note that this is the same as equation 1 in the FiberMesh paper without the rotations. There are no strict requirements on how your curve drawing/deformation interface has to work, but here s a reasonable approach. When the user clicks down, if not near any existing curve vertices, begin drawing a new curve. Otherwise, when the user clicks down on or near an existing curve vertex, enter curve deformation mode. Select the nearest vertex to the user s click as the handle vertex that the user moves directly. On each mouse drag, move the handle vertex and reoptimize the curve. You ll also want to reoptimize the attached surface once you ve implemented the surface optimization portion of FiberMesh. End when the mouse button is lifted. Note: during dragging, you may want to optimize the attached surface cheaply by not iterating as much as you would normally, and then only update the surface completely by iterating a lot once the mouse is done dragging. 3
4 You can perform mesh creation and surface optimization immediately after a curve is drawn, or you can assign controls to each phase; e.g. press one key to generate the mesh, and another to perform the surface optimization. For debugging, it may be helpful to have a control to perform one iteration of the optimization problem. That way, you can step through the optimization and watch your mesh inflate. Again, you don t have to follow this scheme exactly, as long as you do something reasonable and explain it in your README. 2.3 Additional Control Curves Once you have surface optimization and curve deformation working, it s time to allow the user to draw new control curves onto the surface of a pre-existing mesh. This is harder than it sounds. Taking additional curves into account during future surface optimizations isn t that bad, but defining which mesh vertices should be bound to your newly drawn curve, assuming that it was drawn entirely on the surface of a mesh, can get messy. There are multiple ways of binding a newly drawn curve to a mesh s underlying vertices; Nealen et al handle new control curves by subdividing triangles to create new triangles whose vertices match up with points in your curve (Nealen et al s demo implementation is available as a downloadable Java app online on Nealen s website). An alternative way to bind newly drawn curve vertices to mesh vertices is to connect adjacent curve vertices via their shortest path along the surface of the mesh, throwing out duplicate mesh vertices and along the way. It is up to you how you choose to implement the handling of additional control curves, but at the end of the day, the user should be able to draw a curve which resides completely on the surface of an existing mesh, and a new constraint curve should be bound to that surface in some sane fashion. Be sure to explain how you chose to handle additional control curves in your README. 3 Support Code Support code is located at: /course/cs224/asgn/fibermesh. A demo executable is available at: /course/cs224/demo/fibermesh. Use the CTRL+mouse buttons to rotate, pan, and zoom for left, middle, and right 4
5 mouse button respectively. You are by default in draw mode, and drawing a closed-ish curve should create a triangulated surface. Press the spacebar to inflate / optimize the surface. Press 2 to switch to drag mode to deform curves and press 1 to go back to draw mode. Keep in mind that this was a quickly hacked up UI for demonstration purposes only, and we d like to expect your UI to be a bit more intuitive. The support code uses a small subset of the Milton codebase, namely Vector, Point, and Mesh. We ve tried to provide you with as minimal support code as possible so you can concentrate your effort on implementing FiberMesh. As with every assignment in CS224, our support code is strictly for your convenience, and you are more than welcome to ignore it entirely if you wish. Here is a breakdown of the classes that we give you: F rontend is where all the magic happens. It responds to mouse and key events and handles OpenGL (and non-opengl) drawing. The sketon version of Frontend that we give you contains a bunch of places marked TODO, with specific explanations of what s expected or notes to be aware of. This will be the main entrypoint for all of the code you write in this project, though it is up to you how you design your FiberMesh engine (we recommend separating the deformation engine logic out into a separate class and leaving Frontend as Gui-oriented as possible). The skeleton Frontend we give you also contains basic, Maya-inspired camera interactions via CTRL+mouse buttons, similar in effect to the trackball rotate, pan, and zoom interactions in the Modeler assignment from CS123. LinearSolver is a wrapper around UMFPack for efficiently solving sparse linear systems of the standard form Ax=b, including a cache of the factorization of A=LU such that repeated invocations of solving Ax=b with the same A=LU can be performed in nearly linear time by back-substitution of LUx=b. Fun bit of trivia: UMFPack is the hardcore C library that Matlab invokes under the hood when you solve A\b. SparseM atrix provides basic functionality for a reasonably efficient, easyto-use sparse matrix class that should look and feel very similar to the CS123Matrix and Milton s Matrix<M, N, T> that you may already be familiar with. MeshUtils is a handy set of utility routines we ve provided that you ll definitely want to take a look at. MeshUtils contains thoroughly tested / efficient implementations of several key routines that you will likely need along the way, though it may not be completely obvious at first where each will be used. In particular, MeshUtils::getNeighbors (for finding connectivity information about a mesh), MeshUtils::triangulate, MeshUtils::isPointInPolygon, and MeshUtils::getWorldVertex will also come in very handy, and depending on how you implement drawing curves onto pre-existing surfaces, 5
6 MeshUtils::computeVertexShortestPaths may also come in handy. See the inline documentation in MeshUtils.h for more info. 4 Extra Credit Rotational constraints for curve deformation (see equation (2) in Fiber- Mesh) Any additional interaction techniques presented in the paper besides the fairly easy erasing technique (eg, extrusion, change-curve-type, creating holes in a mesh, etc.) 5 Handing In Besides the usual README stuff (compiling instructions, bugs, extra credit, usage, etc.), please identify where your code is for the following: Least Squares Solver Both Optimization Problems Any extra credit Run the following command from within your source directory to handin your code: /course/cs224/bin/cs224 handin fibermesh 6
CS 4620 Program 3: Pipeline
 CS 4620 Program 3: Pipeline out: Wednesday 14 October 2009 due: Friday 30 October 2009 1 Introduction In this assignment, you will implement several types of shading in a simple software graphics pipeline.
CS 4620 Program 3: Pipeline out: Wednesday 14 October 2009 due: Friday 30 October 2009 1 Introduction In this assignment, you will implement several types of shading in a simple software graphics pipeline.
Art-based Rendering with Graftals
 : Interactive Computer Graphics Art-based Rendering with Graftals 1 Introduction Due: 3/13/10, 11:59 PM Between Ray in 123 and Photon Mapping that you just did, you ve now had a good deal of exposure to
: Interactive Computer Graphics Art-based Rendering with Graftals 1 Introduction Due: 3/13/10, 11:59 PM Between Ray in 123 and Photon Mapping that you just did, you ve now had a good deal of exposure to
CS 283: Assignment 1 Geometric Modeling and Mesh Simplification
 CS 283: Assignment 1 Geometric Modeling and Mesh Simplification Ravi Ramamoorthi 1 Introduction This assignment is about triangle meshes as a tool for geometric modeling. As the complexity of models becomes
CS 283: Assignment 1 Geometric Modeling and Mesh Simplification Ravi Ramamoorthi 1 Introduction This assignment is about triangle meshes as a tool for geometric modeling. As the complexity of models becomes
This is the opening view of blender.
 This is the opening view of blender. Note that interacting with Blender is a little different from other programs that you may be used to. For example, left clicking won t select objects on the scene,
This is the opening view of blender. Note that interacting with Blender is a little different from other programs that you may be used to. For example, left clicking won t select objects on the scene,
Shading and Texturing Due: Friday, Feb 17 at 6:00pm
 CMSC 23700 Winter 2012 Introduction to Computer Graphics Project 2 Feb 2 Shading and Texturing Due: Friday, Feb 17 at 6:00pm (v1.0 Feb 2: initial version) 1 Summary You can complete this project in pairs
CMSC 23700 Winter 2012 Introduction to Computer Graphics Project 2 Feb 2 Shading and Texturing Due: Friday, Feb 17 at 6:00pm (v1.0 Feb 2: initial version) 1 Summary You can complete this project in pairs
COS 116 The Computational Universe Laboratory 10: Computer Graphics
 COS 116 The Computational Universe Laboratory 10: Computer Graphics As mentioned in lecture, computer graphics has four major parts: imaging, rendering, modeling, and animation. In this lab you will learn
COS 116 The Computational Universe Laboratory 10: Computer Graphics As mentioned in lecture, computer graphics has four major parts: imaging, rendering, modeling, and animation. In this lab you will learn
the NXT-G programming environment
 2 the NXT-G programming environment This chapter takes a close look at the NXT-G programming environment and presents a few simple programs. The NXT-G programming environment is fairly complex, with lots
2 the NXT-G programming environment This chapter takes a close look at the NXT-G programming environment and presents a few simple programs. The NXT-G programming environment is fairly complex, with lots
Getting Started with Silo
 CHAPTER 1 Getting Started with Silo In this chapter, we discuss how to view, select, and manipulate models in Silo. If you are not familiar with Silo or polygon modeling, make sure to read the About Silo
CHAPTER 1 Getting Started with Silo In this chapter, we discuss how to view, select, and manipulate models in Silo. If you are not familiar with Silo or polygon modeling, make sure to read the About Silo
[175 points] The purpose of this assignment is to give you practice with shaders in OpenGL.
![[175 points] The purpose of this assignment is to give you practice with shaders in OpenGL. [175 points] The purpose of this assignment is to give you practice with shaders in OpenGL.](/thumbs/93/112144408.jpg) CPSC 441 Computer Graphics Assignment 5 due 11/20/18 (11:59 p.m.) [175 points] The purpose of this assignment is to give you practice with shaders in OpenGL. Part 1: First, download and get the code itself
CPSC 441 Computer Graphics Assignment 5 due 11/20/18 (11:59 p.m.) [175 points] The purpose of this assignment is to give you practice with shaders in OpenGL. Part 1: First, download and get the code itself
Project 1 Balanced binary
 CMSC262 DS/Alg Applied Blaheta Project 1 Balanced binary Due: 7 September 2017 You saw basic binary search trees in 162, and may remember that their weakness is that in the worst case they behave like
CMSC262 DS/Alg Applied Blaheta Project 1 Balanced binary Due: 7 September 2017 You saw basic binary search trees in 162, and may remember that their weakness is that in the worst case they behave like
1: Introduction to Object (1)
 1: Introduction to Object (1) 김동원 2003.01.20 Overview (1) The progress of abstraction Smalltalk Class & Object Interface The hidden implementation Reusing the implementation Inheritance: Reusing the interface
1: Introduction to Object (1) 김동원 2003.01.20 Overview (1) The progress of abstraction Smalltalk Class & Object Interface The hidden implementation Reusing the implementation Inheritance: Reusing the interface
BTRY/STSCI 6520, Fall 2012, Homework 3
 BTRY/STSCI 6520, Fall 2012, Homework 3 Due at 8:00am on October 24, 2012, by email (see submission instructions) 1 Introduction K-Means Clustering The K-means algorithm is the simplest and most widely
BTRY/STSCI 6520, Fall 2012, Homework 3 Due at 8:00am on October 24, 2012, by email (see submission instructions) 1 Introduction K-Means Clustering The K-means algorithm is the simplest and most widely
Basics of Computational Geometry
 Basics of Computational Geometry Nadeem Mohsin October 12, 2013 1 Contents This handout covers the basic concepts of computational geometry. Rather than exhaustively covering all the algorithms, it deals
Basics of Computational Geometry Nadeem Mohsin October 12, 2013 1 Contents This handout covers the basic concepts of computational geometry. Rather than exhaustively covering all the algorithms, it deals
3 Polygonal Modeling. Getting Started with Maya 103
 3 Polygonal Modeling In Maya, modeling refers to the process of creating virtual 3D surfaces for the characters and objects in the Maya scene. Surfaces play an important role in the overall Maya workflow
3 Polygonal Modeling In Maya, modeling refers to the process of creating virtual 3D surfaces for the characters and objects in the Maya scene. Surfaces play an important role in the overall Maya workflow
CS 465 Program 4: Modeller
 CS 465 Program 4: Modeller out: 30 October 2004 due: 16 November 2004 1 Introduction In this assignment you will work on a simple 3D modelling system that uses simple primitives and curved surfaces organized
CS 465 Program 4: Modeller out: 30 October 2004 due: 16 November 2004 1 Introduction In this assignment you will work on a simple 3D modelling system that uses simple primitives and curved surfaces organized
On the Web sun.com/aboutsun/comm_invest STAROFFICE 8 DRAW
 STAROFFICE 8 DRAW Graphics They say a picture is worth a thousand words. Pictures are often used along with our words for good reason. They help communicate our thoughts. They give extra information that
STAROFFICE 8 DRAW Graphics They say a picture is worth a thousand words. Pictures are often used along with our words for good reason. They help communicate our thoughts. They give extra information that
INVESTIGATE: PARAMETRIC AND CUSTOMIZABLE MODELS
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES General Confidence writing basic code with simple parameters Understanding measurement and dimensions 3D Design (Parametric Modeling) Modifying parameters Basic OpenSCAD code Translation
LEARNING OBJECTIVES General Confidence writing basic code with simple parameters Understanding measurement and dimensions 3D Design (Parametric Modeling) Modifying parameters Basic OpenSCAD code Translation
n! = 1 * 2 * 3 * 4 * * (n-1) * n
 The Beauty and Joy of Computing 1 Lab Exercise 9: Problem self-similarity and recursion Objectives By completing this lab exercise, you should learn to Recognize simple self-similar problems which are
The Beauty and Joy of Computing 1 Lab Exercise 9: Problem self-similarity and recursion Objectives By completing this lab exercise, you should learn to Recognize simple self-similar problems which are
2D rendering takes a photo of the 2D scene with a virtual camera that selects an axis aligned rectangle from the scene. The photograph is placed into
 2D rendering takes a photo of the 2D scene with a virtual camera that selects an axis aligned rectangle from the scene. The photograph is placed into the viewport of the current application window. A pixel
2D rendering takes a photo of the 2D scene with a virtual camera that selects an axis aligned rectangle from the scene. The photograph is placed into the viewport of the current application window. A pixel
CS 184: Assignment 4 Simple Raytracer
 CS 184: Assignment 4 Simple Raytracer Ravi Ramamoorthi 1 Introduction This assignment asks you to write a first simple raytracer. Raytracers can produce some of the most impressive renderings, with high
CS 184: Assignment 4 Simple Raytracer Ravi Ramamoorthi 1 Introduction This assignment asks you to write a first simple raytracer. Raytracers can produce some of the most impressive renderings, with high
15-498: Distributed Systems Project #1: Design and Implementation of a RMI Facility for Java
 15-498: Distributed Systems Project #1: Design and Implementation of a RMI Facility for Java Dates of Interest Assigned: During class, Friday, January 26, 2007 Due: 11:59PM, Friday, February 13, 2007 Credits
15-498: Distributed Systems Project #1: Design and Implementation of a RMI Facility for Java Dates of Interest Assigned: During class, Friday, January 26, 2007 Due: 11:59PM, Friday, February 13, 2007 Credits
VBA Foundations, Part 12
 As quickly as you can Snatch the Pebble from my hand, he had said as he extended his hand toward you. You reached for the pebble but you opened it only to find that it was indeed still empty. Looking down
As quickly as you can Snatch the Pebble from my hand, he had said as he extended his hand toward you. You reached for the pebble but you opened it only to find that it was indeed still empty. Looking down
CSE 163: Assignment 2 Geometric Modeling and Mesh Simplification
 CSE 163: Assignment 2 Geometric Modeling and Mesh Simplification Ravi Ramamoorthi 1 Introduction This assignment is about triangle meshes as a tool for geometric modeling. As the complexity of models becomes
CSE 163: Assignment 2 Geometric Modeling and Mesh Simplification Ravi Ramamoorthi 1 Introduction This assignment is about triangle meshes as a tool for geometric modeling. As the complexity of models becomes
SketchUp Tool Basics
 SketchUp Tool Basics Open SketchUp Click the Start Button Click All Programs Open SketchUp Scroll Down to the SketchUp 2013 folder Click on the folder to open. Click on SketchUp. Set Up SketchUp (look
SketchUp Tool Basics Open SketchUp Click the Start Button Click All Programs Open SketchUp Scroll Down to the SketchUp 2013 folder Click on the folder to open. Click on SketchUp. Set Up SketchUp (look
Shading Techniques Denbigh Starkey
 Shading Techniques Denbigh Starkey 1. Summary of shading techniques 2 2. Lambert (flat) shading 3 3. Smooth shading and vertex normals 4 4. Gouraud shading 6 5. Phong shading 8 6. Why do Gouraud and Phong
Shading Techniques Denbigh Starkey 1. Summary of shading techniques 2 2. Lambert (flat) shading 3 3. Smooth shading and vertex normals 4 4. Gouraud shading 6 5. Phong shading 8 6. Why do Gouraud and Phong
May 7: The source code for your project, including instructions for compilation and running, are due today. This portion is worth 80% of your score:
 CS 294-74 Mesh Generation and Geometry Processing in Graphics, Engineering, and Modeling Second Project: Mesh Generator, Surface Reconstructor, or Mesh Processing Program 40% of final grade Implement a
CS 294-74 Mesh Generation and Geometry Processing in Graphics, Engineering, and Modeling Second Project: Mesh Generator, Surface Reconstructor, or Mesh Processing Program 40% of final grade Implement a
COS 116 The Computational Universe Laboratory 10: Computer Graphics
 COS 116 The Computational Universe Laboratory 10: Computer Graphics As mentioned in lecture, computer graphics has four major parts: imaging, rendering, modeling, and animation. In this lab you will learn
COS 116 The Computational Universe Laboratory 10: Computer Graphics As mentioned in lecture, computer graphics has four major parts: imaging, rendering, modeling, and animation. In this lab you will learn
FLUENT Secondary flow in a teacup Author: John M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 26 January 2016
 FLUENT Secondary flow in a teacup Author: John M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 26 January 2016 Note: These instructions are based on an older version of FLUENT, and some of the instructions
FLUENT Secondary flow in a teacup Author: John M. Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revision: 26 January 2016 Note: These instructions are based on an older version of FLUENT, and some of the instructions
CS 051 Homework Laboratory #2
 CS 051 Homework Laboratory #2 Dirty Laundry Objective: To gain experience using conditionals. The Scenario. One thing many students have to figure out for the first time when they come to college is how
CS 051 Homework Laboratory #2 Dirty Laundry Objective: To gain experience using conditionals. The Scenario. One thing many students have to figure out for the first time when they come to college is how
Blackfin Online Learning & Development
 Presentation Title: Multimedia Starter Kit Presenter Name: George Stephan Chapter 1: Introduction Sub-chapter 1a: Overview Chapter 2: Blackfin Starter Kits Sub-chapter 2a: What is a Starter Kit? Sub-chapter
Presentation Title: Multimedia Starter Kit Presenter Name: George Stephan Chapter 1: Introduction Sub-chapter 1a: Overview Chapter 2: Blackfin Starter Kits Sub-chapter 2a: What is a Starter Kit? Sub-chapter
CS193P: HelloPoly Walkthrough
 CS193P: HelloPoly Walkthrough Overview The goal of this walkthrough is to give you a fairly step by step path through building a simple Cocoa Touch application. You are encouraged to follow the walkthrough,
CS193P: HelloPoly Walkthrough Overview The goal of this walkthrough is to give you a fairly step by step path through building a simple Cocoa Touch application. You are encouraged to follow the walkthrough,
Reliable programming
 Reliable programming How to write programs that work Think about reliability during design and implementation Test systematically When things break, fix them correctly Make sure everything stays fixed
Reliable programming How to write programs that work Think about reliability during design and implementation Test systematically When things break, fix them correctly Make sure everything stays fixed
CS 553 Compiler Construction Fall 2006 Project #4 Garbage Collection Due November 27, 2005
 CS 553 Compiler Construction Fall 2006 Project #4 Garbage Collection Due November 27, 2005 In this assignment you will implement garbage collection for the MiniJava compiler. The project includes the two
CS 553 Compiler Construction Fall 2006 Project #4 Garbage Collection Due November 27, 2005 In this assignment you will implement garbage collection for the MiniJava compiler. The project includes the two
Interactive Geometry Editor Beth Werbaneth
 Interactive Geometry Editor Beth Werbaneth Introduction 3D modeling software allows artists to realize their visions in a digital format. By manipulating points, edges, surfaces, users can create representations
Interactive Geometry Editor Beth Werbaneth Introduction 3D modeling software allows artists to realize their visions in a digital format. By manipulating points, edges, surfaces, users can create representations
Bonus Ch. 1. Subdivisional Modeling. Understanding Sub-Ds
 Bonus Ch. 1 Subdivisional Modeling Throughout this book, you ve used the modo toolset to create various objects. Some objects included the use of subdivisional surfaces, and some did not. But I ve yet
Bonus Ch. 1 Subdivisional Modeling Throughout this book, you ve used the modo toolset to create various objects. Some objects included the use of subdivisional surfaces, and some did not. But I ve yet
CS 4349 Lecture October 18th, 2017
 CS 4349 Lecture October 18th, 2017 Main topics for #lecture include #minimum_spanning_trees. Prelude Homework 6 due today. Homework 7 due Wednesday, October 25th. Homework 7 has one normal homework problem.
CS 4349 Lecture October 18th, 2017 Main topics for #lecture include #minimum_spanning_trees. Prelude Homework 6 due today. Homework 7 due Wednesday, October 25th. Homework 7 has one normal homework problem.
insight3d quick tutorial
 insight3d quick tutorial What can it do? insight3d lets you create 3D models from photographs. You give it a series of photos of a real scene (e.g., of a building), it automatically matches them and then
insight3d quick tutorial What can it do? insight3d lets you create 3D models from photographs. You give it a series of photos of a real scene (e.g., of a building), it automatically matches them and then
CS195H Homework 5. Due:March 12th, 2015
 CS195H Homework 5 Due:March 12th, 2015 As usual, please work in pairs. Math Stuff For us, a surface is a finite collection of triangles (or other polygons, but let s stick with triangles for now) with
CS195H Homework 5 Due:March 12th, 2015 As usual, please work in pairs. Math Stuff For us, a surface is a finite collection of triangles (or other polygons, but let s stick with triangles for now) with
CS 4349 Lecture August 21st, 2017
 CS 4349 Lecture August 21st, 2017 Main topics for #lecture include #administrivia, #algorithms, #asymptotic_notation. Welcome and Administrivia Hi, I m Kyle! Welcome to CS 4349. This a class about algorithms.
CS 4349 Lecture August 21st, 2017 Main topics for #lecture include #administrivia, #algorithms, #asymptotic_notation. Welcome and Administrivia Hi, I m Kyle! Welcome to CS 4349. This a class about algorithms.
BACK TO MATH LET S START EASY.
 BACK TO MATH LET S START EASY. Of all rectangles of the same perimeter, which one has the largest area? (Yes, you have all solved this problem before, in Calc I. Apologies if this insults your intelligence.
BACK TO MATH LET S START EASY. Of all rectangles of the same perimeter, which one has the largest area? (Yes, you have all solved this problem before, in Calc I. Apologies if this insults your intelligence.
Outline. Introduction Surface of Revolution Hierarchical Modeling Blinn-Phong Shader Custom Shader(s)
 Modeler Help Outline Introduction Surface of Revolution Hierarchical Modeling Blinn-Phong Shader Custom Shader(s) Objects in the Scene Controls of the object selected in the Scene. Currently the Scene
Modeler Help Outline Introduction Surface of Revolution Hierarchical Modeling Blinn-Phong Shader Custom Shader(s) Objects in the Scene Controls of the object selected in the Scene. Currently the Scene
Advanced Computer Graphics
 G22.2274 001, Fall 2010 Advanced Computer Graphics Project details and tools 1 Projects Details of each project are on the website under Projects Please review all the projects and come see me if you would
G22.2274 001, Fall 2010 Advanced Computer Graphics Project details and tools 1 Projects Details of each project are on the website under Projects Please review all the projects and come see me if you would
Hello! ios Development
 SAMPLE CHAPTER Hello! ios Development by Lou Franco Eitan Mendelowitz Chapter 1 Copyright 2013 Manning Publications Brief contents PART 1 HELLO! IPHONE 1 1 Hello! iphone 3 2 Thinking like an iphone developer
SAMPLE CHAPTER Hello! ios Development by Lou Franco Eitan Mendelowitz Chapter 1 Copyright 2013 Manning Publications Brief contents PART 1 HELLO! IPHONE 1 1 Hello! iphone 3 2 Thinking like an iphone developer
Table of Laplace Transforms
 Table of Laplace Transforms 1 1 2 3 4, p > -1 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 Heaviside Function 27 28. Dirac Delta Function 29 30. 31 32. 1 33 34. 35 36. 37 Laplace Transforms
Table of Laplace Transforms 1 1 2 3 4, p > -1 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 Heaviside Function 27 28. Dirac Delta Function 29 30. 31 32. 1 33 34. 35 36. 37 Laplace Transforms
Rasterization. COMP 575/770 Spring 2013
 Rasterization COMP 575/770 Spring 2013 The Rasterization Pipeline you are here APPLICATION COMMAND STREAM 3D transformations; shading VERTEX PROCESSING TRANSFORMED GEOMETRY conversion of primitives to
Rasterization COMP 575/770 Spring 2013 The Rasterization Pipeline you are here APPLICATION COMMAND STREAM 3D transformations; shading VERTEX PROCESSING TRANSFORMED GEOMETRY conversion of primitives to
CS2 Algorithms and Data Structures Note 10. Depth-First Search and Topological Sorting
 CS2 Algorithms and Data Structures Note 10 Depth-First Search and Topological Sorting In this lecture, we will analyse the running time of DFS and discuss a few applications. 10.1 A recursive implementation
CS2 Algorithms and Data Structures Note 10 Depth-First Search and Topological Sorting In this lecture, we will analyse the running time of DFS and discuss a few applications. 10.1 A recursive implementation
Porsche 91 1GT D m o d e ling tutorial - by Nim
 orsche 911GT 3D modeling tutorial - by Nimish In this tutorial you will learn to model a car using Spline modeling method. This method is not very much famous as it requires considerable amount of skill
orsche 911GT 3D modeling tutorial - by Nimish In this tutorial you will learn to model a car using Spline modeling method. This method is not very much famous as it requires considerable amount of skill
Dice in Google SketchUp
 A die (the singular of dice) looks so simple. But if you want the holes placed exactly and consistently, you need to create some extra geometry to use as guides. Plus, using components for the holes is
A die (the singular of dice) looks so simple. But if you want the holes placed exactly and consistently, you need to create some extra geometry to use as guides. Plus, using components for the holes is
CS1114 Assignment 5, Part 1
 CS4 Assignment 5, Part out: Friday, March 27, 2009. due: Friday, April 3, 2009, 5PM. This assignment covers three topics in two parts: interpolation and image transformations (Part ), and feature-based
CS4 Assignment 5, Part out: Friday, March 27, 2009. due: Friday, April 3, 2009, 5PM. This assignment covers three topics in two parts: interpolation and image transformations (Part ), and feature-based
Programming Project 4: COOL Code Generation
 CS 331 Compilers Fall 2017 Programming Project 4: COOL Code Generation Prof. Szajda Due Tuesday, December 5, 11:59:59 pm NOTE: There will be no extensions whatsoever given for this project! So, begin it
CS 331 Compilers Fall 2017 Programming Project 4: COOL Code Generation Prof. Szajda Due Tuesday, December 5, 11:59:59 pm NOTE: There will be no extensions whatsoever given for this project! So, begin it
CS 106 Winter 2016 Craig S. Kaplan. Module 07 Recursion and fractals Topics. Recursion as an extension of hierarchical modelling Simple fractals
 CS 106 Winter 2016 Craig S. Kaplan Module 07 Recursion and fractals Topics Recursion as an extension of hierarchical modelling Simple fractals Readings Learning Processing, Section 13.11 Nature of Code,
CS 106 Winter 2016 Craig S. Kaplan Module 07 Recursion and fractals Topics Recursion as an extension of hierarchical modelling Simple fractals Readings Learning Processing, Section 13.11 Nature of Code,
Lab 2 Building on Linux
 Lab 2 Building on Linux Assignment Details Assigned: January 28 th, 2013. Due: January 30 th, 2013 at midnight. Background This assignment should introduce the basic development tools on Linux. This assumes
Lab 2 Building on Linux Assignment Details Assigned: January 28 th, 2013. Due: January 30 th, 2013 at midnight. Background This assignment should introduce the basic development tools on Linux. This assumes
6.837 Computer Graphics Fall 2012 Programming Assignment 0: OpenGL Mesh Viewer
 6.837 Computer Graphics Fall 2012 Programming Assignment 0: OpenGL Mesh Viewer 1 Getting Started Let s start off by looking at main.cpp. It contains a fully functional application that displays a teapot.
6.837 Computer Graphics Fall 2012 Programming Assignment 0: OpenGL Mesh Viewer 1 Getting Started Let s start off by looking at main.cpp. It contains a fully functional application that displays a teapot.
CS 370 The Pseudocode Programming Process D R. M I C H A E L J. R E A L E F A L L
 CS 370 The Pseudocode Programming Process D R. M I C H A E L J. R E A L E F A L L 2 0 1 5 Introduction At this point, you are ready to beginning programming at a lower level How do you actually write your
CS 370 The Pseudocode Programming Process D R. M I C H A E L J. R E A L E F A L L 2 0 1 5 Introduction At this point, you are ready to beginning programming at a lower level How do you actually write your
Java/RealJ Troubleshooting Guide
 Java/RealJ Troubleshooting Guide by Bob Clark / Sharon Curtis / Simon Jones, September 2000 Some of these tips you will come across during your practical sessions, however we felt it would be helpful to
Java/RealJ Troubleshooting Guide by Bob Clark / Sharon Curtis / Simon Jones, September 2000 Some of these tips you will come across during your practical sessions, however we felt it would be helpful to
WINDOWS 8 CHEAT SHEET
 WINDOWS 8 CHEAT SHEET FIVE BIG CHANGES IN WINDOWS 8 Windows 8 looks and behaves much differently from previous versions of Windows. Remember these five big changes, and you ll be well prepared for Windows
WINDOWS 8 CHEAT SHEET FIVE BIG CHANGES IN WINDOWS 8 Windows 8 looks and behaves much differently from previous versions of Windows. Remember these five big changes, and you ll be well prepared for Windows
CS 548: COMPUTER GRAPHICS PORTRAIT OF AN OPENGL PROGRAM SPRING 2015 DR. MICHAEL J. REALE
 CS 548: COMPUTER GRAPHICS PORTRAIT OF AN OPENGL PROGRAM SPRING 2015 DR. MICHAEL J. REALE INTRODUCTION We re going to talk a little bit about the structure and logic of a basic, interactive OpenGL/GLUT
CS 548: COMPUTER GRAPHICS PORTRAIT OF AN OPENGL PROGRAM SPRING 2015 DR. MICHAEL J. REALE INTRODUCTION We re going to talk a little bit about the structure and logic of a basic, interactive OpenGL/GLUT
Smoother Graphics Taking Control of Painting the Screen
 It is very likely that by now you ve tried something that made your game run rather slow. Perhaps you tried to use an image with a transparent background, or had a gazillion objects moving on the window
It is very likely that by now you ve tried something that made your game run rather slow. Perhaps you tried to use an image with a transparent background, or had a gazillion objects moving on the window
Geometric Features for Non-photorealistiic Rendering
 CS348a: Computer Graphics Handout # 6 Geometric Modeling and Processing Stanford University Monday, 27 February 2017 Homework #4: Due Date: Mesh simplification and expressive rendering [95 points] Wednesday,
CS348a: Computer Graphics Handout # 6 Geometric Modeling and Processing Stanford University Monday, 27 February 2017 Homework #4: Due Date: Mesh simplification and expressive rendering [95 points] Wednesday,
Homework #2. Shading, Projections, Texture Mapping, Ray Tracing, and Bezier Curves
 Computer Graphics Instructor: Brian Curless CSEP 557 Autumn 2016 Homework #2 Shading, Projections, Texture Mapping, Ray Tracing, and Bezier Curves Assigned: Wednesday, Nov 16 th Due: Wednesday, Nov 30
Computer Graphics Instructor: Brian Curless CSEP 557 Autumn 2016 Homework #2 Shading, Projections, Texture Mapping, Ray Tracing, and Bezier Curves Assigned: Wednesday, Nov 16 th Due: Wednesday, Nov 30
Area and Perimeter EXPERIMENT. How are the area and perimeter of a rectangle related? You probably know the formulas by heart:
 Area and Perimeter How are the area and perimeter of a rectangle related? You probably know the formulas by heart: Area Length Width Perimeter (Length Width) But if you look at data for many different
Area and Perimeter How are the area and perimeter of a rectangle related? You probably know the formulas by heart: Area Length Width Perimeter (Length Width) But if you look at data for many different
Due: Fri, Sept 15 th, 5:00 p.m. Parallel and Sequential Data Structures and Algorithms (Fall 17)
 Lab 2 - SkylineLab Due: Fri, Sept 15 th, 2017 @ 5:00 p.m. Parallel and Sequential Data Structures and Algorithms 15-210 (Fall 17) 1 Introduction This assignment is designed to give you more practice with
Lab 2 - SkylineLab Due: Fri, Sept 15 th, 2017 @ 5:00 p.m. Parallel and Sequential Data Structures and Algorithms 15-210 (Fall 17) 1 Introduction This assignment is designed to give you more practice with
Scanning Real World Objects without Worries 3D Reconstruction
 Scanning Real World Objects without Worries 3D Reconstruction 1. Overview Feng Li 308262 Kuan Tian 308263 This document is written for the 3D reconstruction part in the course Scanning real world objects
Scanning Real World Objects without Worries 3D Reconstruction 1. Overview Feng Li 308262 Kuan Tian 308263 This document is written for the 3D reconstruction part in the course Scanning real world objects
Using Flash Animation Basics
 Using Flash Contents Using Flash... 1 Animation Basics... 1 Exercise 1. Creating a Symbol... 2 Exercise 2. Working with Layers... 4 Exercise 3. Using the Timeline... 6 Exercise 4. Previewing an animation...
Using Flash Contents Using Flash... 1 Animation Basics... 1 Exercise 1. Creating a Symbol... 2 Exercise 2. Working with Layers... 4 Exercise 3. Using the Timeline... 6 Exercise 4. Previewing an animation...
Minecraft Due: Mar. 1, 2015
 CS1972 Topics in 3D Game Engine Development Barbara Meier Minecraft Due: Mar. 1, 2015 Introduction In this assignment you will build your own version of one of the most popular indie games ever: Minecraft.
CS1972 Topics in 3D Game Engine Development Barbara Meier Minecraft Due: Mar. 1, 2015 Introduction In this assignment you will build your own version of one of the most popular indie games ever: Minecraft.
To build shapes from scratch, use the tools are the far right of the top tool bar. These
 3D GAME STUDIO TUTORIAL EXERCISE #5 USE MED TO SKIN AND ANIMATE A CUBE REVISED 11/21/06 This tutorial covers basic model skinning and animation in MED the 3DGS model editor. This exercise was prepared
3D GAME STUDIO TUTORIAL EXERCISE #5 USE MED TO SKIN AND ANIMATE A CUBE REVISED 11/21/06 This tutorial covers basic model skinning and animation in MED the 3DGS model editor. This exercise was prepared
CS 184: Assignment 2 Scene Viewer
 CS 184: Assignment 2 Scene Viewer Ravi Ramamoorthi 1 Goals and Motivation This is a more substantial assignment than homework 1, including more transformations, shading, and a viewer for a scene specified
CS 184: Assignment 2 Scene Viewer Ravi Ramamoorthi 1 Goals and Motivation This is a more substantial assignment than homework 1, including more transformations, shading, and a viewer for a scene specified
1. CONVEX POLYGONS. Definition. A shape D in the plane is convex if every line drawn between two points in D is entirely inside D.
 1. CONVEX POLYGONS Definition. A shape D in the plane is convex if every line drawn between two points in D is entirely inside D. Convex 6 gon Another convex 6 gon Not convex Question. Why is the third
1. CONVEX POLYGONS Definition. A shape D in the plane is convex if every line drawn between two points in D is entirely inside D. Convex 6 gon Another convex 6 gon Not convex Question. Why is the third
Kuratowski Notes , Fall 2005, Prof. Peter Shor Revised Fall 2007
 Kuratowski Notes 8.30, Fall 005, Prof. Peter Shor Revised Fall 007 Unfortunately, the OCW notes on Kuratowski s theorem seem to have several things substantially wrong with the proof, and the notes from
Kuratowski Notes 8.30, Fall 005, Prof. Peter Shor Revised Fall 007 Unfortunately, the OCW notes on Kuratowski s theorem seem to have several things substantially wrong with the proof, and the notes from
Implementing Continuations
 Implementing Continuations sk and dbtucker 2002-10-18 1 Changing Representations Now that we ve seen how continuations work, let s study how to implement them in an interpreter. For this lecture onward,
Implementing Continuations sk and dbtucker 2002-10-18 1 Changing Representations Now that we ve seen how continuations work, let s study how to implement them in an interpreter. For this lecture onward,
There will be duplication of information as we detail GoZ for Modeler here, but also in the Layout manual
 GoZ Interchange GoZ Setting Up GoZ for LightWave LightWave support of GoZ by ZBrush GoZ for Modeler GoZ for Layout Example: Using ZBrush to Edit Morph Maps Example: Converting ZBrush Fibermeshes to FiberFX
GoZ Interchange GoZ Setting Up GoZ for LightWave LightWave support of GoZ by ZBrush GoZ for Modeler GoZ for Layout Example: Using ZBrush to Edit Morph Maps Example: Converting ZBrush Fibermeshes to FiberFX
6.00 Introduction to Computer Science and Programming Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.00 Introduction to Computer Science and Programming Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.00 Introduction to Computer Science and Programming Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
CS195H Homework 1 Grid homotopies and free groups. Due: February 5, 2015, before class
 CS195H Homework 1 Grid homotopies and free groups This second homework is almost all about grid homotopies and grid curves, but with a little math in the middle. This homework, last year, took people about
CS195H Homework 1 Grid homotopies and free groups This second homework is almost all about grid homotopies and grid curves, but with a little math in the middle. This homework, last year, took people about
Let s Make a Front Panel using FrontCAD
 Let s Make a Front Panel using FrontCAD By Jim Patchell FrontCad is meant to be a simple, easy to use CAD program for creating front panel designs and artwork. It is a free, open source program, with the
Let s Make a Front Panel using FrontCAD By Jim Patchell FrontCad is meant to be a simple, easy to use CAD program for creating front panel designs and artwork. It is a free, open source program, with the
Programming Assignment III
 Programming Assignment III First Due Date: (Grammar) See online schedule (submission dated midnight). Second Due Date: (Complete) See online schedule (submission dated midnight). Purpose: This project
Programming Assignment III First Due Date: (Grammar) See online schedule (submission dated midnight). Second Due Date: (Complete) See online schedule (submission dated midnight). Purpose: This project
CS 248 Assignment 2 Polygon Scan Conversion. CS248 Presented by Michael Green Stanford University October 20, 2004
 CS 248 Assignment 2 Polygon Scan Conversion CS248 Presented by Michael Green Stanford University October 20, 2004 Announcements First thing: read README.animgui.. It should tell you everything you need
CS 248 Assignment 2 Polygon Scan Conversion CS248 Presented by Michael Green Stanford University October 20, 2004 Announcements First thing: read README.animgui.. It should tell you everything you need
Homework # 7 DUE: 11:59pm November 15, 2002 NO EXTENSIONS WILL BE GIVEN
 Homework #6 CS 450 - Operating Systems October 21, 2002 Homework # 7 DUE: 11:59pm November 15, 2002 NO EXTENSIONS WILL BE GIVEN 1. Overview In this assignment you will implement that FILES module of OSP.
Homework #6 CS 450 - Operating Systems October 21, 2002 Homework # 7 DUE: 11:59pm November 15, 2002 NO EXTENSIONS WILL BE GIVEN 1. Overview In this assignment you will implement that FILES module of OSP.
Chapter 1. Getting Started
 Chapter 1. Hey, Logy, whatcha doing? What s it look like I m doing. I m cleaning the windows so we can get started on our new adventure. Can t you leave the housekeeping until later. We ve got Logo work
Chapter 1. Hey, Logy, whatcha doing? What s it look like I m doing. I m cleaning the windows so we can get started on our new adventure. Can t you leave the housekeeping until later. We ve got Logo work
Quick Tips to Using I-DEAS. Learn about:
 Learn about: Quick Tips to Using I-DEAS I-DEAS Tutorials: Fundamental Skills windows mouse buttons applications and tasks menus icons part modeling viewing selecting data management using the online tutorials
Learn about: Quick Tips to Using I-DEAS I-DEAS Tutorials: Fundamental Skills windows mouse buttons applications and tasks menus icons part modeling viewing selecting data management using the online tutorials
Could you make the XNA functions yourself?
 1 Could you make the XNA functions yourself? For the second and especially the third assignment, you need to globally understand what s going on inside the graphics hardware. You will write shaders, which
1 Could you make the XNA functions yourself? For the second and especially the third assignment, you need to globally understand what s going on inside the graphics hardware. You will write shaders, which
Character Modeling COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL
 38 Character Modeling p a r t _ 1 COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 39 Character Modeling Character Modeling 40 1Subdivision & Polygon Modeling Many of Maya's features have seen great improvements in recent updates
38 Character Modeling p a r t _ 1 COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 39 Character Modeling Character Modeling 40 1Subdivision & Polygon Modeling Many of Maya's features have seen great improvements in recent updates
Jerry Cain Handout #5 CS 106AJ September 30, Using JSKarel
 Jerry Cain Handout #5 CS 106AJ September 30, 2017 Using JSKarel This handout describes how to download and run the JavaScript version of Karel that we ll be using for our first assignment. 1. Getting started
Jerry Cain Handout #5 CS 106AJ September 30, 2017 Using JSKarel This handout describes how to download and run the JavaScript version of Karel that we ll be using for our first assignment. 1. Getting started
CS 248 Assignment 2 Polygon Scan Converter. CS248 Presented by Abe Davis Stanford University October 17, 2008
 CS 248 Assignment 2 Polygon Scan Converter CS248 Presented by Abe Davis Stanford University October 17, 2008 Announcements First thing: read README.animgui. It should tell you everything you need to know
CS 248 Assignment 2 Polygon Scan Converter CS248 Presented by Abe Davis Stanford University October 17, 2008 Announcements First thing: read README.animgui. It should tell you everything you need to know
Geometric Modeling and Processing
 Geometric Modeling and Processing Tutorial of 3DIM&PVT 2011 (Hangzhou, China) May 16, 2011 6. Mesh Simplification Problems High resolution meshes becoming increasingly available 3D active scanners Computer
Geometric Modeling and Processing Tutorial of 3DIM&PVT 2011 (Hangzhou, China) May 16, 2011 6. Mesh Simplification Problems High resolution meshes becoming increasingly available 3D active scanners Computer
Getting started with simulating data in R: some helpful functions and how to use them Ariel Muldoon August 28, 2018
 Getting started with simulating data in R: some helpful functions and how to use them Ariel Muldoon August 28, 2018 Contents Overview 2 Generating random numbers 2 rnorm() to generate random numbers from
Getting started with simulating data in R: some helpful functions and how to use them Ariel Muldoon August 28, 2018 Contents Overview 2 Generating random numbers 2 rnorm() to generate random numbers from
Project 5: Computer Architecture
 Project 5: Computer Architecture CS 220 Start: Oct. 7; Due: Oct. 15 at 11:55 pm Background In previous projects we ve built the computer s basic processing and storage devices (ALU and RAM, respectively).
Project 5: Computer Architecture CS 220 Start: Oct. 7; Due: Oct. 15 at 11:55 pm Background In previous projects we ve built the computer s basic processing and storage devices (ALU and RAM, respectively).
A Comparison of Unified Parallel C, Titanium and Co-Array Fortran. The purpose of this paper is to compare Unified Parallel C, Titanium and Co-
 Shaun Lindsay CS425 A Comparison of Unified Parallel C, Titanium and Co-Array Fortran The purpose of this paper is to compare Unified Parallel C, Titanium and Co- Array Fortran s methods of parallelism
Shaun Lindsay CS425 A Comparison of Unified Parallel C, Titanium and Co-Array Fortran The purpose of this paper is to compare Unified Parallel C, Titanium and Co- Array Fortran s methods of parallelism
05: A Gentle Introduction to Virtools
 05: A Gentle Introduction to Virtools Download the archive for this lab Virtools is the part of this course that everyone seems to really hate. This year, we're going to do our best to go over it in several
05: A Gentle Introduction to Virtools Download the archive for this lab Virtools is the part of this course that everyone seems to really hate. This year, we're going to do our best to go over it in several
Installing and Using Trackside Cameras Revised November 2008
 Installing and Using Trackside Cameras Revised November 2008 Trackside cameras are a useful and creative way to add visual interest to your route. Rather than just look out the windshield of the locomotive
Installing and Using Trackside Cameras Revised November 2008 Trackside cameras are a useful and creative way to add visual interest to your route. Rather than just look out the windshield of the locomotive
COMPUTING CONSTRAINED DELAUNAY
 COMPUTING CONSTRAINED DELAUNAY TRIANGULATIONS IN THE PLANE By Samuel Peterson, University of Minnesota Undergraduate The Goal The Problem The Algorithms The Implementation Applications Acknowledgments
COMPUTING CONSTRAINED DELAUNAY TRIANGULATIONS IN THE PLANE By Samuel Peterson, University of Minnesota Undergraduate The Goal The Problem The Algorithms The Implementation Applications Acknowledgments
Lab 1 Implementing a Simon Says Game
 ECE2049 Embedded Computing in Engineering Design Lab 1 Implementing a Simon Says Game In the late 1970s and early 1980s, one of the first and most popular electronic games was Simon by Milton Bradley.
ECE2049 Embedded Computing in Engineering Design Lab 1 Implementing a Simon Says Game In the late 1970s and early 1980s, one of the first and most popular electronic games was Simon by Milton Bradley.
This lesson introduces Blender, covering the tools and concepts necessary to set up a minimal scene in virtual 3D space.
 3D Modeling with Blender: 01. Blender Basics Overview This lesson introduces Blender, covering the tools and concepts necessary to set up a minimal scene in virtual 3D space. Concepts Covered Blender s
3D Modeling with Blender: 01. Blender Basics Overview This lesson introduces Blender, covering the tools and concepts necessary to set up a minimal scene in virtual 3D space. Concepts Covered Blender s
A Guide to Autodesk Maya 2015
 A Guide to Autodesk Maya 2015 Written by Mitchell Youngerman Table of Contents Layout of Toolbars...pg 1 Creating Objects...pg 2 Selecting & Deselecting Objects...pg 3 Changing Perspective... pg 4 Transforming
A Guide to Autodesk Maya 2015 Written by Mitchell Youngerman Table of Contents Layout of Toolbars...pg 1 Creating Objects...pg 2 Selecting & Deselecting Objects...pg 3 Changing Perspective... pg 4 Transforming
Photoshop / Editing paths
 Photoshop / Editing paths Path segments, components, and points Select a path Adjust path segments Add or delete anchor points Convert between smooth points and corner points Adjust path components Path
Photoshop / Editing paths Path segments, components, and points Select a path Adjust path segments Add or delete anchor points Convert between smooth points and corner points Adjust path components Path
Chapter01.fm Page 1 Monday, August 23, :52 PM. Part I of Change. The Mechanics. of Change
 Chapter01.fm Page 1 Monday, August 23, 2004 1:52 PM Part I The Mechanics of Change The Mechanics of Change Chapter01.fm Page 2 Monday, August 23, 2004 1:52 PM Chapter01.fm Page 3 Monday, August 23, 2004
Chapter01.fm Page 1 Monday, August 23, 2004 1:52 PM Part I The Mechanics of Change The Mechanics of Change Chapter01.fm Page 2 Monday, August 23, 2004 1:52 PM Chapter01.fm Page 3 Monday, August 23, 2004
Full Screen Layout. Main Menu Property-specific Options. Object Tools ( t ) Outliner. Object Properties ( n ) Properties Buttons
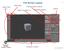 Object Tools ( t ) Full Screen Layout Main Menu Property-specific Options Object Properties ( n ) Properties Buttons Outliner 1 Animation Controls The Create and Add Menus 2 The Coordinate and Viewing
Object Tools ( t ) Full Screen Layout Main Menu Property-specific Options Object Properties ( n ) Properties Buttons Outliner 1 Animation Controls The Create and Add Menus 2 The Coordinate and Viewing
In this lesson, you ll learn how to:
 LESSON 5: ADVANCED DRAWING TECHNIQUES OBJECTIVES In this lesson, you ll learn how to: apply gradient fills modify graphics by smoothing, straightening, and optimizing understand the difference between
LESSON 5: ADVANCED DRAWING TECHNIQUES OBJECTIVES In this lesson, you ll learn how to: apply gradient fills modify graphics by smoothing, straightening, and optimizing understand the difference between
CS Simple Raytracer for students new to Rendering
 CS 294-13 Simple Raytracer for students new to Rendering Ravi Ramamoorthi This assignment should be done only by those small number of students who have not yet written a raytracer. For those students
CS 294-13 Simple Raytracer for students new to Rendering Ravi Ramamoorthi This assignment should be done only by those small number of students who have not yet written a raytracer. For those students
CS2110 Assignment 3 Inheritance and Trees, Summer 2008
 CS2110 Assignment 3 Inheritance and Trees, Summer 2008 Due Sunday July 13, 2008, 6:00PM 0 Introduction 0.1 Goals This assignment will help you get comfortable with basic tree operations and algorithms.
CS2110 Assignment 3 Inheritance and Trees, Summer 2008 Due Sunday July 13, 2008, 6:00PM 0 Introduction 0.1 Goals This assignment will help you get comfortable with basic tree operations and algorithms.
Agenda. Introduction Curve implementation. Particle System. - Requirements -What are all those vectors? -Where should I put things?
 Agenda Introduction Curve implementation - Requirements -What are all those vectors? -Where should I put things? Particle System - Requirements -What should I implement? - Suggestions - Cool forces Agenda
Agenda Introduction Curve implementation - Requirements -What are all those vectors? -Where should I put things? Particle System - Requirements -What should I implement? - Suggestions - Cool forces Agenda
