Analysing Spatial Data in R: Vizualising Spatial Data
|
|
|
- Clarence Washington
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Analysing Spatial Data in R: Vizualising Spatial Data Roger Bivand Department of Economics Norwegian School of Economics and Business Administration Bergen, Norway 31 August 2007
2 Vizualising Spatial Data Displaying spatial data is one of the chief reasons for providing ways of handling it in a statistical environment Of course, there will be differences between analytical and presentation graphics here as well the main point is to get a usable display quickly, and move to presentation quality cartography later In general, maintaining aspect is vital, and that can be done in both base and lattice graphics in R (note that both sp and maps display methods for spatial data with geographical coordinates stretch the y-axis) We ll look at the basic methods for displaying spatial data in sp; other packages have their own methods, but the next unit will show ways of moving data from them to sp classes
3 Just spatial objects There are base graphics plot methods for the key Spatial* classes, including the Spatial class, which just sets up the axes In base graphics, additional plots can be added by overplotting as usual, and the locator() and identify() functions work as expected In general, most par() options will also work, as will the full range of graphics devices (although some copying operations may disturb aspect) First we will display the positional data of the objects discussed in the first unit
4 Plotting a SpatialPoints object While plotting the SpatialPoints object would have called the plot method for Spatial objects internally to set up the axes, we start by doing it separately: > plot(as(meuse1, "Spatial"), + axes = TRUE) > plot(meuse1, add = TRUE) > plot(meuse1[meuse1$ffreq == + 1, ], col = "green", add = TRUE) Then we plot the points with the default plotting character, and subset, overplotting points in flood frequency class 1 in green, using the [ method
5 Plotting a SpatialPolygons object In plotting the SpatialPolygons object, we use the ylim= argument to restrict the display area to match the soil sample points. > plot(rivers, axes = TRUE, col = "azure1", + ylim = c(329400, )) > box() If the axes= argument is FALSE or omitted, no axes are shown the default is the opposite from standard base graphics plot methods
6 Plotting a SpatialPixels object Both SpatialPixels and SpatialGrid objects are plotted like SpatialPoints objects, with plotting characters > plot(rivers, axes = TRUE, col = "azure1", + ylim = c(329400, )) > box() > plot(meuseg1, add = TRUE, col = "grey60", + cex = 0.15) While points, lines, and polygons are often plotted without attributes, this is rarely the case for gridded objects
7 Including attributes To include attribute values means making choices about how to represent their values graphically, known in some GIS as symbology It involves choices of symbol shape, colour and size, and of which objects to differentiate When the data are categorical, the choices are given, unless there are so many different categories that reclassification is needed for clear display Once we ve looked at some examples, we ll go on to see how class intervals may be chosen for continuous data
8 Flood frequencies at soil sample sites annual every 2 5 years > 5 years We will usually need to get the category levels and match them to colours (or plotting characters) by hand > meuse1$ffreq1 <- as.numeric(meuse1$ffreq) > plot(meuse1, col = meuse1$ffreq1, + pch = 19) > labs <- c("annual", "every 2-5 years", + "> 5 years") > cols <- 1:nlevels(meuse1$ffreq) > legend("topleft", legend = labs, + col = cols, pch = 19, bty = "n") It is also typical that the legend() involves more code than everything else together, but very often the same vectors are used repeatedly and can be assigned just once
9 Coloured contour lines Here again, the values are represented as a categorical variable, and so do not require classification > volcano_sl$level1 <- as.numeric(volcano_sl$level) > pal <- terrain.colors(nlevels(volcano_sl$level)) > plot(volcano_sl, bg = "grey70", + col = pal[volcano_sl$level1], + lwd = 3) Using class membership for colour palette look-up is a very typical idiom, so that the col= argument is in fact a vector of colour values
10 Displaying gridded data annual every 2 5 years > 5 years Since we also have 40m grid flood frequencies, we can try to display them here we use the image() method, which first fills in the NAs, the makes a matrix of the chosen variable > meuseg1$ffreq1 <- as.numeric(meuseg1$ffreq) > image(meuseg1, "ffreq1", col = cols) > legend("topleft", legend = labs, + fill = cols, bty = "n") Some of the arguments here are like those we ll meet soon for lattice graphics
11 Class intervals Class intervals can be chosen in many ways, and some have been collected for convenience in the classint package The first problem is to assign class boundaries to values in a single dimension, for which many classification techniques may be used, including pretty, quantile, natural breaks among others, or even simple fixed values From there, the intervals can be used to generate colours from a colour palette, using the very nice colorramppalette() function Because there are potentially many alternative class memberships even for a given number of classes (by default from nclass.sturges), choosing a communicative set matters
12 Class intervals We will try just two styles, quantiles and Fisher-Jenks natural breaks for five classes, among the many available. They yield quite different impressions, as we will see: > library(classint) > library(rcolorbrewer) > pal <- brewer.pal(3, "Blues") > q5 <- classintervals(meuse1$zinc, n = 5, style = "quantile") > q5 style: quantile one of 14,891,626 possible partitions of this variable into 5 classes under over > fj5 <- classintervals(meuse1$zinc, n = 5, style = "fisher") > fj5 style: fisher one of 14,891,626 possible partitions of this variable into 5 classes under over > plot(q5, pal = pal) > plot(fj5, pal = pal)
13 Class interval plots Quantile Fisher Jenks natural breaks
14 Two versions of zinc ppm Quantile under over Fisher Jenks natural breaks under over
15 Lattice graphics Lattice graphics will only come into their own later on, when we want to plot several variables with the same scale together for comparison The workhorse method is spplot, which can be used as an interface to the underlying xyplot or levelplot methods, or others as suitable; overplotting must be done in the single call to spplot see gallery It is often worthwhile to load the lattice package so as to have direct access to its facilities Please remember that lattice graphics are displayed on the current graphics device by default only in interactive sessions in loops or functions, they must be explicitly print ed
16 Bubble plots zinc Bubble plots are a convenient way of representing the attribute values by the size of a symbol > library(lattice) > bubble(meuse1, "zinc", maxsize = 2, + key.entries = 100 * 2^(0:4)) As with all lattice graphics objects, the function can return an object from which symbol sizes can be recovered
17 Level plots The use of lattice plotting methods yields easy legend generation, which is another attraction > bpal <- colorramppalette(pal)(41) > spplot(meuseg1, "dist", col.regions = bpal, + cuts = 40) Here we are showing the distances from the river of grid points in the study area; we can also pass in intervals chosen previously 0.0
18 More realism So far we have just used canned data and spatial objects rather than anything richer The vizualisation methods are also quite flexible both the base graphics and lattice graphics methods can be extensively customised It is also worth recalling the range of methods available for sp objects, in particular the overlay and spsample methods with a range of argument signatures These can permit further flexibility in display, in addition to their primary uses
Analysing Spatial Data in R: Representing Spatial Data
 Analysing Spatial Data in R: Representing Spatial Data Roger Bivand Department of Economics Norwegian School of Economics and Business Administration Bergen, Norway 31 August 2007 Object framework To begin
Analysing Spatial Data in R: Representing Spatial Data Roger Bivand Department of Economics Norwegian School of Economics and Business Administration Bergen, Norway 31 August 2007 Object framework To begin
Package Grid2Polygons
 Package Grid2Polygons February 15, 2013 Version 0.1-2 Date 2013-01-28 Title Convert Spatial Grids to Polygons Author Jason C. Fisher Maintainer Jason C. Fisher Depends R (>= 2.15.0),
Package Grid2Polygons February 15, 2013 Version 0.1-2 Date 2013-01-28 Title Convert Spatial Grids to Polygons Author Jason C. Fisher Maintainer Jason C. Fisher Depends R (>= 2.15.0),
Visualising Spatial Data UCL Geography R Spatial Workshop Tuesday 9 th November 2010 rspatialtips.org.uk
 Visualising Spatial Data UCL Geography R Spatial Workshop Tuesday 9 th November 2010 james.cheshire@ucl.ac.uk rspatialtips.org.uk The previous workshop served as an in depth introduction to R's spatial
Visualising Spatial Data UCL Geography R Spatial Workshop Tuesday 9 th November 2010 james.cheshire@ucl.ac.uk rspatialtips.org.uk The previous workshop served as an in depth introduction to R's spatial
Module 10. Data Visualization. Andrew Jaffe Instructor
 Module 10 Data Visualization Andrew Jaffe Instructor Basic Plots We covered some basic plots on Wednesday, but we are going to expand the ability to customize these basic graphics first. 2/37 But first...
Module 10 Data Visualization Andrew Jaffe Instructor Basic Plots We covered some basic plots on Wednesday, but we are going to expand the ability to customize these basic graphics first. 2/37 But first...
SISMID Spatial Statistics in Epidemiology and Public Health 2015 R Notes: Introduction
 SISMID Spatial Statistics in Epidemiology and Public Health 2015 R Notes: Introduction Jon Wakefield Departments of Statistics and Biostatistics, University of Washington 2015-07-19 R for Spatial Analysis
SISMID Spatial Statistics in Epidemiology and Public Health 2015 R Notes: Introduction Jon Wakefield Departments of Statistics and Biostatistics, University of Washington 2015-07-19 R for Spatial Analysis
Advanced Multivariate Continuous Displays and Diagnostics
 Advanced Multivariate Continuous Displays and Diagnostics 37 This activity explores advanced multivariate plotting. With the advanced diagnostic functions, output graphs are more readable and useful for
Advanced Multivariate Continuous Displays and Diagnostics 37 This activity explores advanced multivariate plotting. With the advanced diagnostic functions, output graphs are more readable and useful for
Package automap. May 30, 2011
 Package automap May 30, 2011 Version 1.0-10 Date 2010/30/05 Title Automatic interpolation package Author Paul Hiemstra Maintainer Paul Hiemstra Description
Package automap May 30, 2011 Version 1.0-10 Date 2010/30/05 Title Automatic interpolation package Author Paul Hiemstra Maintainer Paul Hiemstra Description
Data Visualization. Andrew Jaffe Instructor
 Module 9 Data Visualization Andrew Jaffe Instructor Basic Plots We covered some basic plots previously, but we are going to expand the ability to customize these basic graphics first. 2/45 Read in Data
Module 9 Data Visualization Andrew Jaffe Instructor Basic Plots We covered some basic plots previously, but we are going to expand the ability to customize these basic graphics first. 2/45 Read in Data
Lab 1 Introduction to R
 Lab 1 Introduction to R Date: August 23, 2011 Assignment and Report Due Date: August 30, 2011 Goal: The purpose of this lab is to get R running on your machines and to get you familiar with the basics
Lab 1 Introduction to R Date: August 23, 2011 Assignment and Report Due Date: August 30, 2011 Goal: The purpose of this lab is to get R running on your machines and to get you familiar with the basics
Applied Statistics : Practical 11
 Applied Statistics : Practical 11 This practical will introduce basic tools for geostatistics in R. You may need first to install and load a few packages. The packages sp and lattice contain useful function
Applied Statistics : Practical 11 This practical will introduce basic tools for geostatistics in R. You may need first to install and load a few packages. The packages sp and lattice contain useful function
plot(seq(0,10,1), seq(0,10,1), main = "the Title", xlim=c(1,20), ylim=c(1,20), col="darkblue");
 R for Biologists Day 3 Graphing and Making Maps with Your Data Graphing is a pretty convenient use for R, especially in Rstudio. plot() is the most generalized graphing function. If you give it all numeric
R for Biologists Day 3 Graphing and Making Maps with Your Data Graphing is a pretty convenient use for R, especially in Rstudio. plot() is the most generalized graphing function. If you give it all numeric
Key Terms. Symbology. Categorical attributes. Style. Layer file
 Key Terms Symbology Categorical attributes Style Layer file Review Questions POP-RANGE is a string field of the Cities feature class with the following entries: 0-9,999, 10,000-49,999, 50,000-99,000 This
Key Terms Symbology Categorical attributes Style Layer file Review Questions POP-RANGE is a string field of the Cities feature class with the following entries: 0-9,999, 10,000-49,999, 50,000-99,000 This
Raman Spectra of Chondrocytes in Cartilage: hyperspec s chondro data set
 Raman Spectra of Chondrocytes in Cartilage: hyperspec s chondro data set Claudia Beleites CENMAT and DI3, University of Trieste Spectroscopy Imaging, IPHT Jena e.v. February 13,
Raman Spectra of Chondrocytes in Cartilage: hyperspec s chondro data set Claudia Beleites CENMAT and DI3, University of Trieste Spectroscopy Imaging, IPHT Jena e.v. February 13,
Introduction to using R for Spatial Analysis
 Introduction to using R for Spatial Analysis Learning outcomes: Tools & techniques: Use R to read in spatial data (pg. 5) read.csv (pg. 4) Know how to Plot spatial data using R (pg. 6) readshapespatial()
Introduction to using R for Spatial Analysis Learning outcomes: Tools & techniques: Use R to read in spatial data (pg. 5) read.csv (pg. 4) Know how to Plot spatial data using R (pg. 6) readshapespatial()
Package r2d2. February 20, 2015
 Package r2d2 February 20, 2015 Version 1.0-0 Date 2014-03-31 Title Bivariate (Two-Dimensional) Confidence Region and Frequency Distribution Author Arni Magnusson [aut], Julian Burgos [aut, cre], Gregory
Package r2d2 February 20, 2015 Version 1.0-0 Date 2014-03-31 Title Bivariate (Two-Dimensional) Confidence Region and Frequency Distribution Author Arni Magnusson [aut], Julian Burgos [aut, cre], Gregory
Practical 11: Interpolating Point Data in R
 Practical 11: Interpolating Point Data in R This practical provides an introduction to some techniques which are useful for interpolating point data across space in R. Interpolation describes a means of
Practical 11: Interpolating Point Data in R This practical provides an introduction to some techniques which are useful for interpolating point data across space in R. Interpolation describes a means of
Introduction to Geospatial Analysis
 Introduction to Geospatial Analysis Introduction to Geospatial Analysis 1 Descriptive Statistics Descriptive statistics. 2 What and Why? Descriptive Statistics Quantitative description of data Why? Allow
Introduction to Geospatial Analysis Introduction to Geospatial Analysis 1 Descriptive Statistics Descriptive statistics. 2 What and Why? Descriptive Statistics Quantitative description of data Why? Allow
Logical operators: R provides an extensive list of logical operators. These include
 meat.r: Explanation of code Goals of code: Analyzing a subset of data Creating data frames with specified X values Calculating confidence and prediction intervals Lists and matrices Only printing a few
meat.r: Explanation of code Goals of code: Analyzing a subset of data Creating data frames with specified X values Calculating confidence and prediction intervals Lists and matrices Only printing a few
Using Spatial Data in a Desktop GIS; QGIS 2.8 Practical 2
 Using Spatial Data in a Desktop GIS; QGIS 2.8 Practical 2 Practical 2 Learning objectives: To work with a vector base map within a GIS and overlay point data. To practise using Ordnance Survey mapping
Using Spatial Data in a Desktop GIS; QGIS 2.8 Practical 2 Practical 2 Learning objectives: To work with a vector base map within a GIS and overlay point data. To practise using Ordnance Survey mapping
DSCI 325: Handout 18 Introduction to Graphics in R
 DSCI 325: Handout 18 Introduction to Graphics in R Spring 2016 This handout will provide an introduction to creating graphics in R. One big advantage that R has over SAS (and over several other statistical
DSCI 325: Handout 18 Introduction to Graphics in R Spring 2016 This handout will provide an introduction to creating graphics in R. One big advantage that R has over SAS (and over several other statistical
Announcements. Data Sources a list of data files and their sources, an example of what I am looking for:
 Data Announcements Data Sources a list of data files and their sources, an example of what I am looking for: Source Map of Bangor MEGIS NG911 road file for Bangor MEGIS Tax maps for Bangor City Hall, may
Data Announcements Data Sources a list of data files and their sources, an example of what I am looking for: Source Map of Bangor MEGIS NG911 road file for Bangor MEGIS Tax maps for Bangor City Hall, may
Geographic Information Systems. using QGIS
 Geographic Information Systems using QGIS 1 - INTRODUCTION Generalities A GIS (Geographic Information System) consists of: -Computer hardware -Computer software - Digital Data Generalities GIS softwares
Geographic Information Systems using QGIS 1 - INTRODUCTION Generalities A GIS (Geographic Information System) consists of: -Computer hardware -Computer software - Digital Data Generalities GIS softwares
Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS
 Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS WATS 4930/6920 WHERE WE RE GOING WATS 6915 welcome to tag along for any, all or none WEEK FIVE Lecture VECTOR ANALYSES Joe Wheaton HOUSEKEEPING
Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS WATS 4930/6920 WHERE WE RE GOING WATS 6915 welcome to tag along for any, all or none WEEK FIVE Lecture VECTOR ANALYSES Joe Wheaton HOUSEKEEPING
Plotting Complex Figures Using R. Simon Andrews v
 Plotting Complex Figures Using R Simon Andrews simon.andrews@babraham.ac.uk v2017-11 The R Painters Model Plot area Base plot Overlays Core Graph Types Local options to change a specific plot Global options
Plotting Complex Figures Using R Simon Andrews simon.andrews@babraham.ac.uk v2017-11 The R Painters Model Plot area Base plot Overlays Core Graph Types Local options to change a specific plot Global options
Exploratory Data Analysis - Part 2 September 8, 2005
 Exploratory Data Analysis - Part 2 September 8, 2005 Exploratory Data Analysis - Part 2 p. 1/20 Trellis Plots Trellis plots (S-Plus) and Lattice plots in R also create layouts for multiple plots. A trellis
Exploratory Data Analysis - Part 2 September 8, 2005 Exploratory Data Analysis - Part 2 p. 1/20 Trellis Plots Trellis plots (S-Plus) and Lattice plots in R also create layouts for multiple plots. A trellis
Tutorial 1 Exploring ArcGIS
 Tutorial 1 Exploring ArcGIS Before beginning this tutorial, you should make sure your GIS network folder is mapped on the computer you are using. Please refer to the How to map your GIS server folder as
Tutorial 1 Exploring ArcGIS Before beginning this tutorial, you should make sure your GIS network folder is mapped on the computer you are using. Please refer to the How to map your GIS server folder as
Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 ADVANCED GIS
 Slides by Wheaton et al. (2009-2014) are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 ADVANCED GIS VECTOR ANALYSES Joe Wheaton
Slides by Wheaton et al. (2009-2014) are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 ADVANCED GIS VECTOR ANALYSES Joe Wheaton
Map overlay and spatial aggregation in sp
 Map overlay and spatial aggregation in sp Edzer Pebesma Nov 2010 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Geometry overlays 2 3 Extraction, aggregation of attributes 5 3.1 Extracting attribute values.....................
Map overlay and spatial aggregation in sp Edzer Pebesma Nov 2010 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Geometry overlays 2 3 Extraction, aggregation of attributes 5 3.1 Extracting attribute values.....................
An introduction to ggplot: An implementation of the grammar of graphics in R
 An introduction to ggplot: An implementation of the grammar of graphics in R Hadley Wickham 00-0-7 1 Introduction Currently, R has two major systems for plotting data, base graphics and lattice graphics
An introduction to ggplot: An implementation of the grammar of graphics in R Hadley Wickham 00-0-7 1 Introduction Currently, R has two major systems for plotting data, base graphics and lattice graphics
Examples of implementation of pre-processing method described in paper with R code snippets - Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI)
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Examples of implementation of pre-processing method described in paper with R code snippets - Electronic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Examples of implementation of pre-processing method described in paper with R code snippets - Electronic
GGR 375 QGIS Tutorial
 GGR 375 QGIS Tutorial With text taken from: Sherman, Gary E. Shuffling Quantum GIS into the Open Source GIS Stack. Free and Open Source Software for Geospatial (FOSS4G) Conference. 2007. Available online
GGR 375 QGIS Tutorial With text taken from: Sherman, Gary E. Shuffling Quantum GIS into the Open Source GIS Stack. Free and Open Source Software for Geospatial (FOSS4G) Conference. 2007. Available online
Package smoothr. April 4, 2018
 Type Package Title Smooth and Tidy Spatial Features Version 0.1.0 Package smoothr April 4, 2018 Tools for smoothing and tidying spatial features (i.e. lines and polygons) to make them more aesthetically
Type Package Title Smooth and Tidy Spatial Features Version 0.1.0 Package smoothr April 4, 2018 Tools for smoothing and tidying spatial features (i.e. lines and polygons) to make them more aesthetically
Package hextri. April 22, 2016
 Type Package Title Hexbin Plots with Triangles Version 0.6 Package hextri April 22, 2016 Author Thomas Lumley (Jie Fu Yu made a prototype) Maintainer Thomas Lumley Description
Type Package Title Hexbin Plots with Triangles Version 0.6 Package hextri April 22, 2016 Author Thomas Lumley (Jie Fu Yu made a prototype) Maintainer Thomas Lumley Description
In math, the rate of change is called the slope and is often described by the ratio rise
 Chapter 3 Equations of Lines Sec. Slope The idea of slope is used quite often in our lives, however outside of school, it goes by different names. People involved in home construction might talk about
Chapter 3 Equations of Lines Sec. Slope The idea of slope is used quite often in our lives, however outside of school, it goes by different names. People involved in home construction might talk about
Terms and definitions * keep definitions of processes and terms that may be useful for tests, assignments
 Lecture 1 Core of GIS Thematic layers Terms and definitions * keep definitions of processes and terms that may be useful for tests, assignments Lecture 2 What is GIS? Info: value added data Data to solve
Lecture 1 Core of GIS Thematic layers Terms and definitions * keep definitions of processes and terms that may be useful for tests, assignments Lecture 2 What is GIS? Info: value added data Data to solve
layers in a raster model
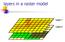 layers in a raster model Layer 1 Layer 2 layers in an vector-based model (1) Layer 2 Layer 1 layers in an vector-based model (2) raster versus vector data model Raster model Vector model Simple data structure
layers in a raster model Layer 1 Layer 2 layers in an vector-based model (1) Layer 2 Layer 1 layers in an vector-based model (2) raster versus vector data model Raster model Vector model Simple data structure
Using R as a GIS. Alan R. Pearse. 31 July 2017
 Using R as a GIS Alan R. Pearse 31 July 2017 Contact Email: ar.pearse@qut.edu.au Contents Data sources A note on syntax What is R? Why do GIS in R? Must-have R packages Overview of spatial data types in
Using R as a GIS Alan R. Pearse 31 July 2017 Contact Email: ar.pearse@qut.edu.au Contents Data sources A note on syntax What is R? Why do GIS in R? Must-have R packages Overview of spatial data types in
Types of Plotting Functions. Managing graphics devices. Further High-level Plotting Functions. The plot() Function
 3 / 23 5 / 23 Outline The R Statistical Environment R Graphics Peter Dalgaard Department of Biostatistics University of Copenhagen January 16, 29 1 / 23 2 / 23 Overview Standard R Graphics The standard
3 / 23 5 / 23 Outline The R Statistical Environment R Graphics Peter Dalgaard Department of Biostatistics University of Copenhagen January 16, 29 1 / 23 2 / 23 Overview Standard R Graphics The standard
Map overlay and spatial aggregation in sp
 Map overlay and spatial aggregation in sp Edzer Pebesma September 4, 2013 Abstract Numerical map overlay combines spatial features from one map layer with the attribute (numerical) properties of another.
Map overlay and spatial aggregation in sp Edzer Pebesma September 4, 2013 Abstract Numerical map overlay combines spatial features from one map layer with the attribute (numerical) properties of another.
Technology Assignment: Scatter Plots
 The goal of this assignment is to create a scatter plot of a set of data. You could do this with any two columns of data, but for demonstration purposes we ll work with the data in the table below. You
The goal of this assignment is to create a scatter plot of a set of data. You could do this with any two columns of data, but for demonstration purposes we ll work with the data in the table below. You
QGIS LAB SERIES GST 102: Spatial Analysis Lab 2: Introduction to Geospatial Analysis
 QGIS LAB SERIES GST 102: Spatial Analysis Lab 2: Introduction to Geospatial Analysis Objective Understand Attribute Table Joins and Data Classification Document Version: 2014-06-16 (Beta) Contents Introduction...2
QGIS LAB SERIES GST 102: Spatial Analysis Lab 2: Introduction to Geospatial Analysis Objective Understand Attribute Table Joins and Data Classification Document Version: 2014-06-16 (Beta) Contents Introduction...2
This document will cover some of the key features available only in SMS Advanced, including:
 Key Differences between SMS Basic and SMS Advanced SMS Advanced includes all of the same functionality as the SMS Basic Software as well as adding numerous tools that provide management solutions for multiple
Key Differences between SMS Basic and SMS Advanced SMS Advanced includes all of the same functionality as the SMS Basic Software as well as adding numerous tools that provide management solutions for multiple
Applied Calculus. Lab 1: An Introduction to R
 1 Math 131/135/194, Fall 2004 Applied Calculus Profs. Kaplan & Flath Macalester College Lab 1: An Introduction to R Goal of this lab To begin to see how to use R. What is R? R is a computer package for
1 Math 131/135/194, Fall 2004 Applied Calculus Profs. Kaplan & Flath Macalester College Lab 1: An Introduction to R Goal of this lab To begin to see how to use R. What is R? R is a computer package for
Package sciplot. February 15, 2013
 Package sciplot February 15, 2013 Version 1.1-0 Title Scientific Graphing Functions for Factorial Designs Author Manuel Morales , with code developed by the R Development Core Team
Package sciplot February 15, 2013 Version 1.1-0 Title Scientific Graphing Functions for Factorial Designs Author Manuel Morales , with code developed by the R Development Core Team
Package desplot. R topics documented: April 3, 2018
 Package desplot April 3, 2018 Title Plotting Field Plans for Agricultural Experiments Version 1.4 Date 2018-04-02 Type Package Description A function for plotting maps of agricultural field experiments
Package desplot April 3, 2018 Title Plotting Field Plans for Agricultural Experiments Version 1.4 Date 2018-04-02 Type Package Description A function for plotting maps of agricultural field experiments
Package arphit. March 28, 2019
 Type Package Title RBA-style R Plots Version 0.3.1 Author Angus Moore Package arphit March 28, 2019 Maintainer Angus Moore Easily create RBA-style graphs
Type Package Title RBA-style R Plots Version 0.3.1 Author Angus Moore Package arphit March 28, 2019 Maintainer Angus Moore Easily create RBA-style graphs
SAS Visual Analytics 8.2: Getting Started with Reports
 SAS Visual Analytics 8.2: Getting Started with Reports Introduction Reporting The SAS Visual Analytics tools give you everything you need to produce and distribute clear and compelling reports. SAS Visual
SAS Visual Analytics 8.2: Getting Started with Reports Introduction Reporting The SAS Visual Analytics tools give you everything you need to produce and distribute clear and compelling reports. SAS Visual
2. Getting started with MLwiN
 2. Getting started with MLwiN Introduction This chapter aims to provide you with some practice with MLwiN commands before you begin to fit multilevel models. It is may be helpful if you have already read
2. Getting started with MLwiN Introduction This chapter aims to provide you with some practice with MLwiN commands before you begin to fit multilevel models. It is may be helpful if you have already read
Package beanplot. R topics documented: February 19, Type Package
 Type Package Package beanplot February 19, 2015 Title Visualization via Beanplots (like Boxplot/Stripchart/Violin Plot) Version 1.2 Date 2014-09-15 Author Peter Kampstra Maintainer Peter Kampstra
Type Package Package beanplot February 19, 2015 Title Visualization via Beanplots (like Boxplot/Stripchart/Violin Plot) Version 1.2 Date 2014-09-15 Author Peter Kampstra Maintainer Peter Kampstra
Roger D. Peng, Associate Professor of Biostatistics Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health
 The Lattice Plotting System in R Roger D. Peng, Associate Professor of Biostatistics Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health The Lattice Plotting System The lattice plotting system is implemented
The Lattice Plotting System in R Roger D. Peng, Associate Professor of Biostatistics Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health The Lattice Plotting System The lattice plotting system is implemented
A quick Matlab tutorial
 A quick Matlab tutorial Michael Robinson 1 Introduction In this course, we will be using MATLAB for computer-based matrix computations. MATLAB is a programming language/environment that provides easy access
A quick Matlab tutorial Michael Robinson 1 Introduction In this course, we will be using MATLAB for computer-based matrix computations. MATLAB is a programming language/environment that provides easy access
AN INTRODUCTION TO LATTICE GRAPHICS IN R
 AN INTRODUCTION TO LATTICE GRAPHICS IN R William G. Jacoby Michigan State University ICPSR Summer Program July 27-28, 2016 I. Introductory Thoughts about Lattice Graphics A. The lattice package 1. Created
AN INTRODUCTION TO LATTICE GRAPHICS IN R William G. Jacoby Michigan State University ICPSR Summer Program July 27-28, 2016 I. Introductory Thoughts about Lattice Graphics A. The lattice package 1. Created
rworldmap vignette Andy South October 5, 2012
 rworldmap vignette Andy South October 5, 2012 rworldmap is a package for visualising global data, concentrating on data referenced by country codes or gridded at half degree resolution. Funded by : Contents
rworldmap vignette Andy South October 5, 2012 rworldmap is a package for visualising global data, concentrating on data referenced by country codes or gridded at half degree resolution. Funded by : Contents
Charts in Excel 2003
 Charts in Excel 2003 Contents Introduction Charts in Excel 2003...1 Part 1: Generating a Basic Chart...1 Part 2: Adding Another Data Series...3 Part 3: Other Handy Options...5 Introduction Charts in Excel
Charts in Excel 2003 Contents Introduction Charts in Excel 2003...1 Part 1: Generating a Basic Chart...1 Part 2: Adding Another Data Series...3 Part 3: Other Handy Options...5 Introduction Charts in Excel
Geography 222 Quantitative Color for GIS Mike Pesses, Antelope Valley College
 Geography 222 Quantitative Color for GIS Mike Pesses, Antelope Valley College Introduction Building off of the previous color theory work, a cartographer must also understand how to tell a story with data
Geography 222 Quantitative Color for GIS Mike Pesses, Antelope Valley College Introduction Building off of the previous color theory work, a cartographer must also understand how to tell a story with data
ArcGIS Online (AGOL) Quick Start Guide Fall 2018
 ArcGIS Online (AGOL) Quick Start Guide Fall 2018 ArcGIS Online (AGOL) is a web mapping tool available to UC Merced faculty, students and staff. The Spatial Analysis and Research Center (SpARC) provides
ArcGIS Online (AGOL) Quick Start Guide Fall 2018 ArcGIS Online (AGOL) is a web mapping tool available to UC Merced faculty, students and staff. The Spatial Analysis and Research Center (SpARC) provides
1 Layering, and Alternatives to Layering
 Lattice With Layers layer() and as.layer() (from latticeextra) 1 J H Maindonald http://www.maths.anu.edu.au/~johnm Centre for Mathematics and Its Applications Australian National University. Contents 1
Lattice With Layers layer() and as.layer() (from latticeextra) 1 J H Maindonald http://www.maths.anu.edu.au/~johnm Centre for Mathematics and Its Applications Australian National University. Contents 1
Package ClustGeo. R topics documented: July 14, Type Package
 Type Package Package ClustGeo July 14, 2017 Title Hierarchical Clustering with Spatial Constraints Version 2.0 Author Marie Chavent [aut, cre], Vanessa Kuentz [aut], Amaury Labenne [aut], Jerome Saracco
Type Package Package ClustGeo July 14, 2017 Title Hierarchical Clustering with Spatial Constraints Version 2.0 Author Marie Chavent [aut, cre], Vanessa Kuentz [aut], Amaury Labenne [aut], Jerome Saracco
Basic Queries Exercise - Haiti
 Basic Queries Exercise - Haiti Written by Barbara Parmenter, revised by Carolyn Talmadge on September 18, 2016 SETTING UP... 1 WHERE ARE THE HOSPITALS THAT ARE STILL OPERATING? (SELECT BY ATTRIBUTE )...
Basic Queries Exercise - Haiti Written by Barbara Parmenter, revised by Carolyn Talmadge on September 18, 2016 SETTING UP... 1 WHERE ARE THE HOSPITALS THAT ARE STILL OPERATING? (SELECT BY ATTRIBUTE )...
2013 edition (version 1.1)
 2013 edition (version 1.1) Contents 1 Introduction... 3 2 Signing in to your Office 365 account... 3 2.1 Acceptable Use Policy and Terms of Use... 4 3 Setting your profile and options... 4 3.1 Settings:
2013 edition (version 1.1) Contents 1 Introduction... 3 2 Signing in to your Office 365 account... 3 2.1 Acceptable Use Policy and Terms of Use... 4 3 Setting your profile and options... 4 3.1 Settings:
Lab 1: Introduction to ArcGIS
 Lab 1: Introduction to ArcGIS Objectives In this lab you will: 1) Learn the basics of the software package we will be using for the remainder of the semester, and 2) Discover the role that climate and
Lab 1: Introduction to ArcGIS Objectives In this lab you will: 1) Learn the basics of the software package we will be using for the remainder of the semester, and 2) Discover the role that climate and
Raman Spectra of Chondrocytes in Cartilage: hyperspec s chondro data set
 Raman Spectra of Chondrocytes in Cartilage: hyperspec s chondro data set Claudia Beleites DIA Raman Spectroscopy Group, University of Trieste/Italy (2 28) Spectroscopy Imaging,
Raman Spectra of Chondrocytes in Cartilage: hyperspec s chondro data set Claudia Beleites DIA Raman Spectroscopy Group, University of Trieste/Italy (2 28) Spectroscopy Imaging,
Lecture-14 Lookup Functions
 Lecture-14 Lookup Functions How do I write a formula to compute tax rates based on income? Given a product ID, how can I look up the product s price? Suppose that a product s price changes over time. I
Lecture-14 Lookup Functions How do I write a formula to compute tax rates based on income? Given a product ID, how can I look up the product s price? Suppose that a product s price changes over time. I
GIS LAB 8. Raster Data Applications Watershed Delineation
 GIS LAB 8 Raster Data Applications Watershed Delineation This lab will require you to further your familiarity with raster data structures and the Spatial Analyst. The data for this lab are drawn from
GIS LAB 8 Raster Data Applications Watershed Delineation This lab will require you to further your familiarity with raster data structures and the Spatial Analyst. The data for this lab are drawn from
From Getting Started with the Graph Template Language in SAS. Full book available for purchase here.
 From Getting Started with the Graph Template Language in SAS. Full book available for purchase here. Contents About This Book... xi About The Author... xv Acknowledgments...xvii Chapter 1: Introduction
From Getting Started with the Graph Template Language in SAS. Full book available for purchase here. Contents About This Book... xi About The Author... xv Acknowledgments...xvii Chapter 1: Introduction
Practical guidance on mapping and visualisation of crime and social data in QGIS
 Practical guidance on mapping and visualisation of crime and social data in QGIS Lesson 4: Mapping of aggregated crime data in QGIS This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Practical guidance on mapping and visualisation of crime and social data in QGIS Lesson 4: Mapping of aggregated crime data in QGIS This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Profiles - Objectives
 Profiles - Objectives What is an InRoads Profile? Creating new Profiles Sources of Profiling paths Display of surfaces & offsets on profiles Available Profiling Controls Displaying Surface Features on
Profiles - Objectives What is an InRoads Profile? Creating new Profiles Sources of Profiling paths Display of surfaces & offsets on profiles Available Profiling Controls Displaying Surface Features on
Mixed models in R using the lme4 package Part 2: Lattice graphics
 Mixed models in R using the lme4 package Part 2: Lattice graphics Douglas Bates University of Wisconsin - Madison and R Development Core Team University of Lausanne July 1,
Mixed models in R using the lme4 package Part 2: Lattice graphics Douglas Bates University of Wisconsin - Madison and R Development Core Team University of Lausanne July 1,
Mapping Great Circles Tutorial
 Mapping Great Circles Tutorial Charles DiMaggio February 21, 2012 I came across what may very well be one of my all time favorite uses of R graphics. It was by Paul Butler, and presents a visualization
Mapping Great Circles Tutorial Charles DiMaggio February 21, 2012 I came across what may very well be one of my all time favorite uses of R graphics. It was by Paul Butler, and presents a visualization
Intro to R Graphics Center for Social Science Computation and Research, 2010 Stephanie Lee, Dept of Sociology, University of Washington
 Intro to R Graphics Center for Social Science Computation and Research, 2010 Stephanie Lee, Dept of Sociology, University of Washington Class Outline - The R Environment and Graphics Engine - Basic Graphs
Intro to R Graphics Center for Social Science Computation and Research, 2010 Stephanie Lee, Dept of Sociology, University of Washington Class Outline - The R Environment and Graphics Engine - Basic Graphs
Package fso. February 19, 2015
 Version 2.0-1 Date 2013-02-26 Title Fuzzy Set Ordination Package fso February 19, 2015 Author David W. Roberts Maintainer David W. Roberts Description Fuzzy
Version 2.0-1 Date 2013-02-26 Title Fuzzy Set Ordination Package fso February 19, 2015 Author David W. Roberts Maintainer David W. Roberts Description Fuzzy
Spatial Data Models. Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities
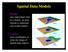 Spatial Data Models Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities Vector uses coordinates to store the shape of spatial data objects David Tenenbaum GEOG 7
Spatial Data Models Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities Vector uses coordinates to store the shape of spatial data objects David Tenenbaum GEOG 7
Performance Evaluation
 Chapter 4 Performance Evaluation For testing and comparing the effectiveness of retrieval and classification methods, ways of evaluating the performance are required. This chapter discusses several of
Chapter 4 Performance Evaluation For testing and comparing the effectiveness of retrieval and classification methods, ways of evaluating the performance are required. This chapter discusses several of
Spatial data and QGIS
 Spatial data and QGIS Xue Jingbo IT Center 2017.08.07 A GIS consists of: Spatial Data. Computer Hardware. Computer Software. Longitude Latitude Disease Date 26.870436-31.909519 Mumps 13/12/2008 26.868682-31.909259
Spatial data and QGIS Xue Jingbo IT Center 2017.08.07 A GIS consists of: Spatial Data. Computer Hardware. Computer Software. Longitude Latitude Disease Date 26.870436-31.909519 Mumps 13/12/2008 26.868682-31.909259
Intro to GIS (requirements: basic Windows computer skills and a flash drive)
 Introduction to GIS Intro to GIS (requirements: basic Windows computer skills and a flash drive) Part 1. What is GIS. 1. System: hardware (computers, devices), software (proprietary or free), people. 2.
Introduction to GIS Intro to GIS (requirements: basic Windows computer skills and a flash drive) Part 1. What is GIS. 1. System: hardware (computers, devices), software (proprietary or free), people. 2.
ArcView QuickStart Guide. Contents. The ArcView Screen. Elements of an ArcView Project. Creating an ArcView Project. Adding Themes to Views
 ArcView QuickStart Guide Page 1 ArcView QuickStart Guide Contents The ArcView Screen Elements of an ArcView Project Creating an ArcView Project Adding Themes to Views Zoom and Pan Tools Querying Themes
ArcView QuickStart Guide Page 1 ArcView QuickStart Guide Contents The ArcView Screen Elements of an ArcView Project Creating an ArcView Project Adding Themes to Views Zoom and Pan Tools Querying Themes
Lab #4 Introduction to Image Processing II and Map Accuracy Assessment
 FOR 324 Natural Resources Information Systems Lab #4 Introduction to Image Processing II and Map Accuracy Assessment (Adapted from the Idrisi Tutorial, Introduction Image Processing Exercises, Exercise
FOR 324 Natural Resources Information Systems Lab #4 Introduction to Image Processing II and Map Accuracy Assessment (Adapted from the Idrisi Tutorial, Introduction Image Processing Exercises, Exercise
Stat 579: Objects in R Vectors
 Stat 579: Objects in R Vectors Ranjan Maitra 2220 Snedecor Hall Department of Statistics Iowa State University. Phone: 515-294-7757 maitra@iastate.edu, 1/23 Logical Vectors I R allows manipulation of logical
Stat 579: Objects in R Vectors Ranjan Maitra 2220 Snedecor Hall Department of Statistics Iowa State University. Phone: 515-294-7757 maitra@iastate.edu, 1/23 Logical Vectors I R allows manipulation of logical
Package EnQuireR. R topics documented: February 19, Type Package Title A package dedicated to questionnaires Version 0.
 Type Package Title A package dedicated to questionnaires Version 0.10 Date 2009-06-10 Package EnQuireR February 19, 2015 Author Fournier Gwenaelle, Cadoret Marine, Fournier Olivier, Le Poder Francois,
Type Package Title A package dedicated to questionnaires Version 0.10 Date 2009-06-10 Package EnQuireR February 19, 2015 Author Fournier Gwenaelle, Cadoret Marine, Fournier Olivier, Le Poder Francois,
_Tutorials. Arcmap. Linking additional files outside from Geodata
 _Tutorials Arcmap Linking additional files outside from Geodata 2017 Sourcing the Data (Option 1): Extracting Data from Auckland Council GIS P1 First you want to get onto the Auckland Council GIS website
_Tutorials Arcmap Linking additional files outside from Geodata 2017 Sourcing the Data (Option 1): Extracting Data from Auckland Council GIS P1 First you want to get onto the Auckland Council GIS website
An Introduction to R Graphics
 An Introduction to R Graphics PnP Group Seminar 25 th April 2012 Why use R for graphics? Fast data exploration Easy automation and reproducibility Create publication quality figures Customisation of almost
An Introduction to R Graphics PnP Group Seminar 25 th April 2012 Why use R for graphics? Fast data exploration Easy automation and reproducibility Create publication quality figures Customisation of almost
Leading provider of interactive statistics visualization software for the web
 Leading provider of interactive statistics visualization software for the web Explore, gain insight, create Stories with Snapshots and Publish Select statistics indicator data explore, inquire, animate
Leading provider of interactive statistics visualization software for the web Explore, gain insight, create Stories with Snapshots and Publish Select statistics indicator data explore, inquire, animate
Complete Display Control in Autodesk Architectural Desktop
 11/30/2005-10:00 am - 11:30 am Room:N. Hemispheres (Salon D) (Dolphin) Walt Disney World Swan and Dolphin Resort Orlando, Florida Complete Display Control in Autodesk Architectural Desktop Matt Dillon
11/30/2005-10:00 am - 11:30 am Room:N. Hemispheres (Salon D) (Dolphin) Walt Disney World Swan and Dolphin Resort Orlando, Florida Complete Display Control in Autodesk Architectural Desktop Matt Dillon
Introduction to using R for Spatial Analysis Nick Bearman
 Introduction to using R for Spatial Analysis Nick Bearman Learning Outcomes: R Functions & Libraries: Use R to read in CSV data (pg. 4) read.csv() (pg. 4) Use R to read in spatial data (pg. 5) readshapespatial()
Introduction to using R for Spatial Analysis Nick Bearman Learning Outcomes: R Functions & Libraries: Use R to read in CSV data (pg. 4) read.csv() (pg. 4) Use R to read in spatial data (pg. 5) readshapespatial()
Package osrm. November 13, 2017
 Package osrm November 13, 2017 Type Package Title Interface Between R and the OpenStreetMap-Based Routing Service OSRM Version 3.1.0 Date 2017-11-13 An interface between R and the OSRM API. OSRM is a routing
Package osrm November 13, 2017 Type Package Title Interface Between R and the OpenStreetMap-Based Routing Service OSRM Version 3.1.0 Date 2017-11-13 An interface between R and the OSRM API. OSRM is a routing
Geography 281 Map Making with GIS Project Three: Viewing Data Spatially
 Geography 281 Map Making with GIS Project Three: Viewing Data Spatially This activity introduces three of the most common thematic maps: Choropleth maps Dot density maps Graduated symbol maps You will
Geography 281 Map Making with GIS Project Three: Viewing Data Spatially This activity introduces three of the most common thematic maps: Choropleth maps Dot density maps Graduated symbol maps You will
Nearest Neighbor Predictors
 Nearest Neighbor Predictors September 2, 2018 Perhaps the simplest machine learning prediction method, from a conceptual point of view, and perhaps also the most unusual, is the nearest-neighbor method,
Nearest Neighbor Predictors September 2, 2018 Perhaps the simplest machine learning prediction method, from a conceptual point of view, and perhaps also the most unusual, is the nearest-neighbor method,
AN INTRODUCTION TO GRID ANALYSIS: HOTSPOT DETECTION
 AN INTRODUCTION TO GRID ANALYSIS: HOTSPOT DETECTION etraining Introduction Use the Grid Analysis commands of GeoMedia to extract hotspot locations from a feature class containing a collection of incident
AN INTRODUCTION TO GRID ANALYSIS: HOTSPOT DETECTION etraining Introduction Use the Grid Analysis commands of GeoMedia to extract hotspot locations from a feature class containing a collection of incident
lab_03 September 20, 2016
 lab_03 September 20, 2016 1 Data mapping In this session, we will build on all we have learnt so far about loading and manipulating (spatial) data and apply it to one of the most commonly used forms of
lab_03 September 20, 2016 1 Data mapping In this session, we will build on all we have learnt so far about loading and manipulating (spatial) data and apply it to one of the most commonly used forms of
Data Classification 1
 Data Classification 1 Data Classification The idea of classification is to group together items that are alike The objective of classification is to group data in such a manner that not only are the observations
Data Classification 1 Data Classification The idea of classification is to group together items that are alike The objective of classification is to group data in such a manner that not only are the observations
An Introduction to R 2.2 Statistical graphics
 An Introduction to R 2.2 Statistical graphics Dan Navarro (daniel.navarro@adelaide.edu.au) School of Psychology, University of Adelaide ua.edu.au/ccs/people/dan DSTO R Workshop, 29-Apr-2015 Scatter plots
An Introduction to R 2.2 Statistical graphics Dan Navarro (daniel.navarro@adelaide.edu.au) School of Psychology, University of Adelaide ua.edu.au/ccs/people/dan DSTO R Workshop, 29-Apr-2015 Scatter plots
R Workshop Module 3: Plotting Data Katherine Thompson Department of Statistics, University of Kentucky
 R Workshop Module 3: Plotting Data Katherine Thompson (katherine.thompson@uky.edu Department of Statistics, University of Kentucky October 15, 2013 Reading in Data Start by reading the dataset practicedata.txt
R Workshop Module 3: Plotting Data Katherine Thompson (katherine.thompson@uky.edu Department of Statistics, University of Kentucky October 15, 2013 Reading in Data Start by reading the dataset practicedata.txt
ggplot2 basics Hadley Wickham Assistant Professor / Dobelman Family Junior Chair Department of Statistics / Rice University September 2011
 ggplot2 basics Hadley Wickham Assistant Professor / Dobelman Family Junior Chair Department of Statistics / Rice University September 2011 1. Diving in: scatterplots & aesthetics 2. Facetting 3. Geoms
ggplot2 basics Hadley Wickham Assistant Professor / Dobelman Family Junior Chair Department of Statistics / Rice University September 2011 1. Diving in: scatterplots & aesthetics 2. Facetting 3. Geoms
Package spark. July 21, 2017
 Title 'Sparklines' in the 'R' Terminal Version 2.0.0 Author Gábor Csárdi Package spark July 21, 2017 Maintainer Gábor Csárdi A 'sparkline' is a line chart, without axes and labels.
Title 'Sparklines' in the 'R' Terminal Version 2.0.0 Author Gábor Csárdi Package spark July 21, 2017 Maintainer Gábor Csárdi A 'sparkline' is a line chart, without axes and labels.
Lecturer 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models
 Lecturer 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Models of Spatial Information 2.3 Three-Step Database Design 2.4 Extending ER with Spatial Concepts 2.5 Summary Learning Objectives Learning
Lecturer 2: Spatial Concepts and Data Models 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Models of Spatial Information 2.3 Three-Step Database Design 2.4 Extending ER with Spatial Concepts 2.5 Summary Learning Objectives Learning
Package mixphm. July 23, 2015
 Type Package Title Mixtures of Proportional Hazard Models Version 0.7-2 Date 2015-07-23 Package mixphm July 23, 2015 Fits multiple variable mixtures of various parametric proportional hazard models using
Type Package Title Mixtures of Proportional Hazard Models Version 0.7-2 Date 2015-07-23 Package mixphm July 23, 2015 Fits multiple variable mixtures of various parametric proportional hazard models using
Chapter 5 An Introduction to Basic Plotting Tools
 Chapter 5 An Introduction to Basic Plotting Tools We have demonstrated the use of R tools for importing data, manipulating data, extracting subsets of data, and making simple calculations, such as mean,
Chapter 5 An Introduction to Basic Plotting Tools We have demonstrated the use of R tools for importing data, manipulating data, extracting subsets of data, and making simple calculations, such as mean,
MAPLOGIC CORPORATION. GIS Software Solutions. Getting Started. With MapLogic Layout Manager
 MAPLOGIC CORPORATION GIS Software Solutions Getting Started With MapLogic Layout Manager Getting Started with MapLogic Layout Manager 2011 MapLogic Corporation All Rights Reserved 330 West Canton Ave.,
MAPLOGIC CORPORATION GIS Software Solutions Getting Started With MapLogic Layout Manager Getting Started with MapLogic Layout Manager 2011 MapLogic Corporation All Rights Reserved 330 West Canton Ave.,
Graphics - Part III: Basic Graphics Continued
 Graphics - Part III: Basic Graphics Continued Statistics 135 Autumn 2005 Copyright c 2005 by Mark E. Irwin Highway MPG 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 y^i e i = y i y^i 2000 2500 3000 3500 4000 Car Weight Copyright
Graphics - Part III: Basic Graphics Continued Statistics 135 Autumn 2005 Copyright c 2005 by Mark E. Irwin Highway MPG 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 y^i e i = y i y^i 2000 2500 3000 3500 4000 Car Weight Copyright
Representing the Real World
 Representing the Real World The theory of representing the real world in a GIS using digital data The nature of digital data and binary notation The discrete object view of the world Entities, data objects,
Representing the Real World The theory of representing the real world in a GIS using digital data The nature of digital data and binary notation The discrete object view of the world Entities, data objects,
