Simultaneous Localization
|
|
|
- Griselda Cobb
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) RSS Technical Lecture 16 April 9, 2012 Prof. Teller Text: Siegwart and Nourbakhsh S. 5.8 Navigation Overview Where am I? Where am I going? Localization Assumed perfect map, but imperfect sensing How can I get there from here? Planning Assumed perfect map, sensing, and actuation Exploration(Mapping and Localization) Mapping SLAM (Today) 1
2 SLAM Problem Statement Inputs: No external coordinate reference Time sequence of proprioceptive and exteroceptive measurements* made as robot moves through an initially unknown environment Outputs: A map* of the environment A robot pose estimate associated with each measurement, in the coordinate system in which the map is defined *Not yet fully defined SLAM Problem -- Incremental State/Output: Map of env t observed so far Robot pose estimate w.r.t. map Action/Input: Move to a new position/orientation Acquire additional observation(s) Update State: Re-estimate the robot s pose Revise the map appropriately 2
3 SLAM Aspects What is a measurement? What is a map? How are map, pose coupled? How should robot move? What is hard about SLAM? But first: some intuition Illustration of SLAM without Landmarks With only dead reckoning, vehicle pose uncertainty grows without bound 3
4 Illustration of SLAM with Landmarks Process continues as the vehicle moves through the environment Why is SLAM Hard? Grand challenge -level robotics problem Autonomous, persistent, collaborative robots mapping multi-scale, generic environments Map-making = learning Difficult even for humans Even skilled humans make mapping mistakes Scaling issues Space: Large extent (combinatorial growth) Time: Persistent autonomous operation Chicken and Egg nature of problem If robot had a map, localization would be easier If robot could localize, mapping would be easier But robot has neither; starts from blank slate Must also execute an exploration strategy Uncertainty at every level of problem 4
5 Uncertainty in Robotic Mapping Uncertainty: Continuous Discrete Scale: Local Sensor noise Data association Global Navigation drift Loop closing MIT Killian Court Path Laser Sonar Odometry (two hours, 15 minutes; 2.2 km) 5
6 Common range-and-bearing sensors Polaroid sonar ring 12 range returns, one per 30 degrees, at ~4 Hz (+ servoed rotation) Robot SICK laser scanner 180 range returns, one per degree, at 5-75 Hz Robot Other possibilities: Stereo/monocular vision; Robot itself (stall, bump sensing) Tracking & long-baseline monocular vision Bosse Track points, edges, texture patches from frame to frame; triangulate to recover local 3D structure. Also called SFM, Structure From camera Motion, or object motion in the image Chou 6
7 Loop Closing Gutman, Konolige What is a map? Collection of features with some relationship to one another What is a feature? Occupancy grid cell Line segment Surface patch What is a feature relationship? Uncertainty Rigid-body transform (metrical mapping) Topological path (chain of co-visibility) Hybrid representation (geom. + topo.) 7
8 Atlas hybrid maps (Bosse et al.) E A B D C Features: point, line, patch clouds Geometry: rigid frames, submaps Topology: map adjacencies Hybrid: uncertain map-to-map transformations What is pose w.r.t. a map? Pose estimate that is (maximally) consistent with the estimated features observed from vicinity Consistency can be evaluated locally, semi-locally, or globally Note tension between estimation precision and solution consistency 8
9 Example SLAM with laser scanning Observations Local mapping Iterated closest point Loop closing Scan matching Deferred validation Search strategies Observations 9
10 Observations Scan Matching Robot scans, moves, scans again Short-term odometry/imu error causes misregistration of scans Scan matching is the process of bringing scan data into alignment Ground truth (unknown) Scan from pose 1 Scan from pose 2 10
11 Iterated Closest Point For each point in scan 1 Find closest point in scan Iterated Closest Point Find the transformation that best aligns the matching sets of points
12 Iterated Closest Point Repeat until convergence 2 2 Can ICP across scans, across a scan and a (sub)map, or even across submaps! Limitations / failure modes Computational cost (two scans of size n) Naively, O(n 2 ) plus cost of alignment step False minima If ICP starts far from true alignment If scans exhibit repeated local structure Bias Anisotropic point sampling Differing sensor fields of view (occlusion) Lots of research on improved ICP methods (see, e.g., Rusinkiewicz) 12
13 Loop Closing ICP solves small-scale, short-duration SLAM fairly well But now, consider: Large scale High uncertainty Gutman, Konolige Loop Closing Naive ICP ruled out: Too CPU-intensive Assume we have a pose uncertainty bound This limits portion of existing map that must be searched Still have to face the problem of matching two partial scans that are far from aligned Gutman, Konolige 13
14 Scan Matching Strategies Exhaustive search Discretize robot poses Find implied alignments Assign score to each Choose highest score Pros, Cons? Randomized search Choose minimal suff- icient match, at random Align and score Choose highest score RANSAC (1981) Pros, Cons? Gutman, Konolige Loop Closing Ambiguity Consider SLAM state after ABC XY Large open-loop navigation uncertainty Y matches both A & B What to do? 14
15 Loop Closing Choices Choose neither match Pros, cons? Choose one match Pros, cons? Choose both matches Pros, cons? Deferred Loop Validation Continue SLAM until Z matches C Examine graph for ~identity cycle 15
16 Some SLAM results See rvsn.csail.mit.edu group page Summary SLAM is a hard robotics problem: Requires sensor fusion over large areas Scaling issues arise quickly with real data Key issue is managing uncertainty Low-level to high-level Continuous and discrete Saw several SLAM strategies Local and global alignment Randomization Deferred validation SLAM is only part of the solution for most applications (need naming, semantics) 16
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM)
 Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) RSS Lecture 16 April 8, 2013 Prof. Teller Text: Siegwart and Nourbakhsh S. 5.8 SLAM Problem Statement Inputs: No external coordinate reference Time series of
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) RSS Lecture 16 April 8, 2013 Prof. Teller Text: Siegwart and Nourbakhsh S. 5.8 SLAM Problem Statement Inputs: No external coordinate reference Time series of
COS Lecture 13 Autonomous Robot Navigation
 COS 495 - Lecture 13 Autonomous Robot Navigation Instructor: Chris Clark Semester: Fall 2011 1 Figures courtesy of Siegwart & Nourbakhsh Control Structure Prior Knowledge Operator Commands Localization
COS 495 - Lecture 13 Autonomous Robot Navigation Instructor: Chris Clark Semester: Fall 2011 1 Figures courtesy of Siegwart & Nourbakhsh Control Structure Prior Knowledge Operator Commands Localization
Localization and Map Building
 Localization and Map Building Noise and aliasing; odometric position estimation To localize or not to localize Belief representation Map representation Probabilistic map-based localization Other examples
Localization and Map Building Noise and aliasing; odometric position estimation To localize or not to localize Belief representation Map representation Probabilistic map-based localization Other examples
Localization, Where am I?
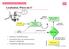 5.1 Localization, Where am I?? position Position Update (Estimation?) Encoder Prediction of Position (e.g. odometry) YES matched observations Map data base predicted position Matching Odometry, Dead Reckoning
5.1 Localization, Where am I?? position Position Update (Estimation?) Encoder Prediction of Position (e.g. odometry) YES matched observations Map data base predicted position Matching Odometry, Dead Reckoning
Robot Mapping. SLAM Front-Ends. Cyrill Stachniss. Partial image courtesy: Edwin Olson 1
 Robot Mapping SLAM Front-Ends Cyrill Stachniss Partial image courtesy: Edwin Olson 1 Graph-Based SLAM Constraints connect the nodes through odometry and observations Robot pose Constraint 2 Graph-Based
Robot Mapping SLAM Front-Ends Cyrill Stachniss Partial image courtesy: Edwin Olson 1 Graph-Based SLAM Constraints connect the nodes through odometry and observations Robot pose Constraint 2 Graph-Based
CSE 527: Introduction to Computer Vision
 CSE 527: Introduction to Computer Vision Week 10 Class 2: Visual Odometry November 2nd, 2017 Today Visual Odometry Intro Algorithm SLAM Visual Odometry Input Output Images, Video Camera trajectory, motion
CSE 527: Introduction to Computer Vision Week 10 Class 2: Visual Odometry November 2nd, 2017 Today Visual Odometry Intro Algorithm SLAM Visual Odometry Input Output Images, Video Camera trajectory, motion
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping
 Sebastian Lembcke SLAM 1 / 29 MIN Faculty Department of Informatics Simultaneous Localization and Mapping Visual Loop-Closure Detection University of Hamburg Faculty of Mathematics, Informatics and Natural
Sebastian Lembcke SLAM 1 / 29 MIN Faculty Department of Informatics Simultaneous Localization and Mapping Visual Loop-Closure Detection University of Hamburg Faculty of Mathematics, Informatics and Natural
Structured light 3D reconstruction
 Structured light 3D reconstruction Reconstruction pipeline and industrial applications rodola@dsi.unive.it 11/05/2010 3D Reconstruction 3D reconstruction is the process of capturing the shape and appearance
Structured light 3D reconstruction Reconstruction pipeline and industrial applications rodola@dsi.unive.it 11/05/2010 3D Reconstruction 3D reconstruction is the process of capturing the shape and appearance
Dense Tracking and Mapping for Autonomous Quadrocopters. Jürgen Sturm
 Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers Dense Tracking and Mapping for Autonomous Quadrocopters Jürgen Sturm Joint work with Frank Steinbrücker, Jakob Engel, Christian Kerl, Erik Bylow, and Daniel Cremers
Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers Dense Tracking and Mapping for Autonomous Quadrocopters Jürgen Sturm Joint work with Frank Steinbrücker, Jakob Engel, Christian Kerl, Erik Bylow, and Daniel Cremers
Roadmaps. Vertex Visibility Graph. Reduced visibility graph, i.e., not including segments that extend into obstacles on either side.
 Roadmaps Vertex Visibility Graph Full visibility graph Reduced visibility graph, i.e., not including segments that extend into obstacles on either side. (but keeping endpoints roads) what else might we
Roadmaps Vertex Visibility Graph Full visibility graph Reduced visibility graph, i.e., not including segments that extend into obstacles on either side. (but keeping endpoints roads) what else might we
Basics of Localization, Mapping and SLAM. Jari Saarinen Aalto University Department of Automation and systems Technology
 Basics of Localization, Mapping and SLAM Jari Saarinen Aalto University Department of Automation and systems Technology Content Introduction to Problem (s) Localization A few basic equations Dead Reckoning
Basics of Localization, Mapping and SLAM Jari Saarinen Aalto University Department of Automation and systems Technology Content Introduction to Problem (s) Localization A few basic equations Dead Reckoning
3D Point Cloud Processing
 3D Point Cloud Processing The image depicts how our robot Irma3D sees itself in a mirror. The laser looking into itself creates distortions as well as changes in intensity that give the robot a single
3D Point Cloud Processing The image depicts how our robot Irma3D sees itself in a mirror. The laser looking into itself creates distortions as well as changes in intensity that give the robot a single
Autonomous Mobile Robot Design
 Autonomous Mobile Robot Design Topic: EKF-based SLAM Dr. Kostas Alexis (CSE) These slides have partially relied on the course of C. Stachniss, Robot Mapping - WS 2013/14 Autonomous Robot Challenges Where
Autonomous Mobile Robot Design Topic: EKF-based SLAM Dr. Kostas Alexis (CSE) These slides have partially relied on the course of C. Stachniss, Robot Mapping - WS 2013/14 Autonomous Robot Challenges Where
Zürich. Roland Siegwart Margarita Chli Martin Rufli Davide Scaramuzza. ETH Master Course: L Autonomous Mobile Robots Summary
 Roland Siegwart Margarita Chli Martin Rufli Davide Scaramuzza ETH Master Course: 151-0854-00L Autonomous Mobile Robots Summary 2 Lecture Overview Mobile Robot Control Scheme knowledge, data base mission
Roland Siegwart Margarita Chli Martin Rufli Davide Scaramuzza ETH Master Course: 151-0854-00L Autonomous Mobile Robots Summary 2 Lecture Overview Mobile Robot Control Scheme knowledge, data base mission
IROS 05 Tutorial. MCL: Global Localization (Sonar) Monte-Carlo Localization. Particle Filters. Rao-Blackwellized Particle Filters and Loop Closing
 IROS 05 Tutorial SLAM - Getting it Working in Real World Applications Rao-Blackwellized Particle Filters and Loop Closing Cyrill Stachniss and Wolfram Burgard University of Freiburg, Dept. of Computer
IROS 05 Tutorial SLAM - Getting it Working in Real World Applications Rao-Blackwellized Particle Filters and Loop Closing Cyrill Stachniss and Wolfram Burgard University of Freiburg, Dept. of Computer
L17. OCCUPANCY MAPS. NA568 Mobile Robotics: Methods & Algorithms
 L17. OCCUPANCY MAPS NA568 Mobile Robotics: Methods & Algorithms Today s Topic Why Occupancy Maps? Bayes Binary Filters Log-odds Occupancy Maps Inverse sensor model Learning inverse sensor model ML map
L17. OCCUPANCY MAPS NA568 Mobile Robotics: Methods & Algorithms Today s Topic Why Occupancy Maps? Bayes Binary Filters Log-odds Occupancy Maps Inverse sensor model Learning inverse sensor model ML map
ECE276A: Sensing & Estimation in Robotics Lecture 11: Simultaneous Localization and Mapping using a Particle Filter
 ECE276A: Sensing & Estimation in Robotics Lecture 11: Simultaneous Localization and Mapping using a Particle Filter Lecturer: Nikolay Atanasov: natanasov@ucsd.edu Teaching Assistants: Siwei Guo: s9guo@eng.ucsd.edu
ECE276A: Sensing & Estimation in Robotics Lecture 11: Simultaneous Localization and Mapping using a Particle Filter Lecturer: Nikolay Atanasov: natanasov@ucsd.edu Teaching Assistants: Siwei Guo: s9guo@eng.ucsd.edu
Large-Scale. Point Cloud Processing Tutorial. Application: Mobile Mapping
 Large-Scale 3D Point Cloud Processing Tutorial 2013 Application: Mobile Mapping The image depicts how our robot Irma3D sees itself in a mirror. The laser looking into itself creates distortions as well
Large-Scale 3D Point Cloud Processing Tutorial 2013 Application: Mobile Mapping The image depicts how our robot Irma3D sees itself in a mirror. The laser looking into itself creates distortions as well
Planetary Rover Absolute Localization by Combining Visual Odometry with Orbital Image Measurements
 Planetary Rover Absolute Localization by Combining Visual Odometry with Orbital Image Measurements M. Lourakis and E. Hourdakis Institute of Computer Science Foundation for Research and Technology Hellas
Planetary Rover Absolute Localization by Combining Visual Odometry with Orbital Image Measurements M. Lourakis and E. Hourdakis Institute of Computer Science Foundation for Research and Technology Hellas
Colorado School of Mines. Computer Vision. Professor William Hoff Dept of Electrical Engineering &Computer Science.
 Professor William Hoff Dept of Electrical Engineering &Computer Science http://inside.mines.edu/~whoff/ 1 Bundle Adjustment 2 Example Application A vehicle needs to map its environment that it is moving
Professor William Hoff Dept of Electrical Engineering &Computer Science http://inside.mines.edu/~whoff/ 1 Bundle Adjustment 2 Example Application A vehicle needs to map its environment that it is moving
Spring Localization II. Roland Siegwart, Margarita Chli, Martin Rufli. ASL Autonomous Systems Lab. Autonomous Mobile Robots
 Spring 2016 Localization II Localization I 25.04.2016 1 knowledge, data base mission commands Localization Map Building environment model local map position global map Cognition Path Planning path Perception
Spring 2016 Localization II Localization I 25.04.2016 1 knowledge, data base mission commands Localization Map Building environment model local map position global map Cognition Path Planning path Perception
UAV Autonomous Navigation in a GPS-limited Urban Environment
 UAV Autonomous Navigation in a GPS-limited Urban Environment Yoko Watanabe DCSD/CDIN JSO-Aerial Robotics 2014/10/02-03 Introduction 2 Global objective Development of a UAV onboard system to maintain flight
UAV Autonomous Navigation in a GPS-limited Urban Environment Yoko Watanabe DCSD/CDIN JSO-Aerial Robotics 2014/10/02-03 Introduction 2 Global objective Development of a UAV onboard system to maintain flight
Today MAPS AND MAPPING. Features. process of creating maps. More likely features are things that can be extracted from images:
 MAPS AND MAPPING Features In the first class we said that navigation begins with what the robot can see. There are several forms this might take, but it will depend on: What sensors the robot has What
MAPS AND MAPPING Features In the first class we said that navigation begins with what the robot can see. There are several forms this might take, but it will depend on: What sensors the robot has What
Robotics. Lecture 7: Simultaneous Localisation and Mapping (SLAM)
 Robotics Lecture 7: Simultaneous Localisation and Mapping (SLAM) See course website http://www.doc.ic.ac.uk/~ajd/robotics/ for up to date information. Andrew Davison Department of Computing Imperial College
Robotics Lecture 7: Simultaneous Localisation and Mapping (SLAM) See course website http://www.doc.ic.ac.uk/~ajd/robotics/ for up to date information. Andrew Davison Department of Computing Imperial College
MULTI-MODAL MAPPING. Robotics Day, 31 Mar Frank Mascarich, Shehryar Khattak, Tung Dang
 MULTI-MODAL MAPPING Robotics Day, 31 Mar 2017 Frank Mascarich, Shehryar Khattak, Tung Dang Application-Specific Sensors Cameras TOF Cameras PERCEPTION LiDAR IMU Localization Mapping Autonomy Robotic Perception
MULTI-MODAL MAPPING Robotics Day, 31 Mar 2017 Frank Mascarich, Shehryar Khattak, Tung Dang Application-Specific Sensors Cameras TOF Cameras PERCEPTION LiDAR IMU Localization Mapping Autonomy Robotic Perception
3D Computer Vision. Structured Light II. Prof. Didier Stricker. Kaiserlautern University.
 3D Computer Vision Structured Light II Prof. Didier Stricker Kaiserlautern University http://ags.cs.uni-kl.de/ DFKI Deutsches Forschungszentrum für Künstliche Intelligenz http://av.dfki.de 1 Introduction
3D Computer Vision Structured Light II Prof. Didier Stricker Kaiserlautern University http://ags.cs.uni-kl.de/ DFKI Deutsches Forschungszentrum für Künstliche Intelligenz http://av.dfki.de 1 Introduction
Structured Light II. Thanks to Ronen Gvili, Szymon Rusinkiewicz and Maks Ovsjanikov
 Structured Light II Johannes Köhler Johannes.koehler@dfki.de Thanks to Ronen Gvili, Szymon Rusinkiewicz and Maks Ovsjanikov Introduction Previous lecture: Structured Light I Active Scanning Camera/emitter
Structured Light II Johannes Köhler Johannes.koehler@dfki.de Thanks to Ronen Gvili, Szymon Rusinkiewicz and Maks Ovsjanikov Introduction Previous lecture: Structured Light I Active Scanning Camera/emitter
SLAM: Robotic Simultaneous Location and Mapping
 SLAM: Robotic Simultaneous Location and Mapping William Regli Department of Computer Science (and Departments of ECE and MEM) Drexel University Acknowledgments to Sebastian Thrun & others SLAM Lecture
SLAM: Robotic Simultaneous Location and Mapping William Regli Department of Computer Science (and Departments of ECE and MEM) Drexel University Acknowledgments to Sebastian Thrun & others SLAM Lecture
EE565:Mobile Robotics Lecture 3
 EE565:Mobile Robotics Lecture 3 Welcome Dr. Ahmad Kamal Nasir Today s Objectives Motion Models Velocity based model (Dead-Reckoning) Odometry based model (Wheel Encoders) Sensor Models Beam model of range
EE565:Mobile Robotics Lecture 3 Welcome Dr. Ahmad Kamal Nasir Today s Objectives Motion Models Velocity based model (Dead-Reckoning) Odometry based model (Wheel Encoders) Sensor Models Beam model of range
Advanced Robotics Path Planning & Navigation
 Advanced Robotics Path Planning & Navigation 1 Agenda Motivation Basic Definitions Configuration Space Global Planning Local Planning Obstacle Avoidance ROS Navigation Stack 2 Literature Choset, Lynch,
Advanced Robotics Path Planning & Navigation 1 Agenda Motivation Basic Definitions Configuration Space Global Planning Local Planning Obstacle Avoidance ROS Navigation Stack 2 Literature Choset, Lynch,
Proceedings of the 2016 Winter Simulation Conference T. M. K. Roeder, P. I. Frazier, R. Szechtman, E. Zhou, T. Huschka, and S. E. Chick, eds.
 Proceedings of the 2016 Winter Simulation Conference T. M. K. Roeder, P. I. Frazier, R. Szechtman, E. Zhou, T. Huschka, and S. E. Chick, eds. SIMULATION RESULTS FOR LOCALIZATION AND MAPPING ALGORITHMS
Proceedings of the 2016 Winter Simulation Conference T. M. K. Roeder, P. I. Frazier, R. Szechtman, E. Zhou, T. Huschka, and S. E. Chick, eds. SIMULATION RESULTS FOR LOCALIZATION AND MAPPING ALGORITHMS
Dealing with Scale. Stephan Weiss Computer Vision Group NASA-JPL / CalTech
 Dealing with Scale Stephan Weiss Computer Vision Group NASA-JPL / CalTech Stephan.Weiss@ieee.org (c) 2013. Government sponsorship acknowledged. Outline Why care about size? The IMU as scale provider: The
Dealing with Scale Stephan Weiss Computer Vision Group NASA-JPL / CalTech Stephan.Weiss@ieee.org (c) 2013. Government sponsorship acknowledged. Outline Why care about size? The IMU as scale provider: The
Davide Scaramuzza. University of Zurich
 Davide Scaramuzza University of Zurich Robotics and Perception Group http://rpg.ifi.uzh.ch/ Scaramuzza, D., Fraundorfer, F., Visual Odometry: Part I - The First 30 Years and Fundamentals, IEEE Robotics
Davide Scaramuzza University of Zurich Robotics and Perception Group http://rpg.ifi.uzh.ch/ Scaramuzza, D., Fraundorfer, F., Visual Odometry: Part I - The First 30 Years and Fundamentals, IEEE Robotics
Lecture 10 Dense 3D Reconstruction
 Institute of Informatics Institute of Neuroinformatics Lecture 10 Dense 3D Reconstruction Davide Scaramuzza 1 REMODE: Probabilistic, Monocular Dense Reconstruction in Real Time M. Pizzoli, C. Forster,
Institute of Informatics Institute of Neuroinformatics Lecture 10 Dense 3D Reconstruction Davide Scaramuzza 1 REMODE: Probabilistic, Monocular Dense Reconstruction in Real Time M. Pizzoli, C. Forster,
Spring Localization II. Roland Siegwart, Margarita Chli, Juan Nieto, Nick Lawrance. ASL Autonomous Systems Lab. Autonomous Mobile Robots
 Spring 2018 Localization II Localization I 16.04.2018 1 knowledge, data base mission commands Localization Map Building environment model local map position global map Cognition Path Planning path Perception
Spring 2018 Localization II Localization I 16.04.2018 1 knowledge, data base mission commands Localization Map Building environment model local map position global map Cognition Path Planning path Perception
Humanoid Robotics. Least Squares. Maren Bennewitz
 Humanoid Robotics Least Squares Maren Bennewitz Goal of This Lecture Introduction into least squares Use it yourself for odometry calibration, later in the lecture: camera and whole-body self-calibration
Humanoid Robotics Least Squares Maren Bennewitz Goal of This Lecture Introduction into least squares Use it yourself for odometry calibration, later in the lecture: camera and whole-body self-calibration
Miniature faking. In close-up photo, the depth of field is limited.
 Miniature faking In close-up photo, the depth of field is limited. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:jodhpur_tilt_shift.jpg Miniature faking Miniature faking http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:oregon_state_beavers_tilt-shift_miniature_greg_keene.jpg
Miniature faking In close-up photo, the depth of field is limited. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:jodhpur_tilt_shift.jpg Miniature faking Miniature faking http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:oregon_state_beavers_tilt-shift_miniature_greg_keene.jpg
Localization and Map Building
 Localization and Map Building Noise and aliasing; odometric position estimation To localize or not to localize Belief representation Map representation Probabilistic map-based localization Other examples
Localization and Map Building Noise and aliasing; odometric position estimation To localize or not to localize Belief representation Map representation Probabilistic map-based localization Other examples
3D Computer Vision. Depth Cameras. Prof. Didier Stricker. Oliver Wasenmüller
 3D Computer Vision Depth Cameras Prof. Didier Stricker Oliver Wasenmüller Kaiserlautern University http://ags.cs.uni-kl.de/ DFKI Deutsches Forschungszentrum für Künstliche Intelligenz http://av.dfki.de
3D Computer Vision Depth Cameras Prof. Didier Stricker Oliver Wasenmüller Kaiserlautern University http://ags.cs.uni-kl.de/ DFKI Deutsches Forschungszentrum für Künstliche Intelligenz http://av.dfki.de
Lecture 10 Multi-view Stereo (3D Dense Reconstruction) Davide Scaramuzza
 Lecture 10 Multi-view Stereo (3D Dense Reconstruction) Davide Scaramuzza REMODE: Probabilistic, Monocular Dense Reconstruction in Real Time, ICRA 14, by Pizzoli, Forster, Scaramuzza [M. Pizzoli, C. Forster,
Lecture 10 Multi-view Stereo (3D Dense Reconstruction) Davide Scaramuzza REMODE: Probabilistic, Monocular Dense Reconstruction in Real Time, ICRA 14, by Pizzoli, Forster, Scaramuzza [M. Pizzoli, C. Forster,
Introduction to Mobile Robotics
 Introduction to Mobile Robotics Olivier Aycard Associate Professor University of Grenoble Laboratoire d Informatique de Grenoble http://membres-liglab.imag.fr/aycard 1/29 Some examples of mobile robots
Introduction to Mobile Robotics Olivier Aycard Associate Professor University of Grenoble Laboratoire d Informatique de Grenoble http://membres-liglab.imag.fr/aycard 1/29 Some examples of mobile robots
Introduction to Mobile Robotics. SLAM: Simultaneous Localization and Mapping
 Introduction to Mobile Robotics SLAM: Simultaneous Localization and Mapping The SLAM Problem SLAM is the process by which a robot builds a map of the environment and, at the same time, uses this map to
Introduction to Mobile Robotics SLAM: Simultaneous Localization and Mapping The SLAM Problem SLAM is the process by which a robot builds a map of the environment and, at the same time, uses this map to
Real-time Obstacle Avoidance and Mapping for AUVs Operating in Complex Environments
 Real-time Obstacle Avoidance and Mapping for AUVs Operating in Complex Environments Jacques C. Leedekerken, John J. Leonard, Michael C. Bosse, and Arjuna Balasuriya Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Real-time Obstacle Avoidance and Mapping for AUVs Operating in Complex Environments Jacques C. Leedekerken, John J. Leonard, Michael C. Bosse, and Arjuna Balasuriya Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Autonomous Navigation for Flying Robots
 Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers Autonomous Navigation for Flying Robots Lecture 7.1: 2D Motion Estimation in Images Jürgen Sturm Technische Universität München 3D to 2D Perspective Projections
Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers Autonomous Navigation for Flying Robots Lecture 7.1: 2D Motion Estimation in Images Jürgen Sturm Technische Universität München 3D to 2D Perspective Projections
Introduction to Information Science and Technology (IST) Part IV: Intelligent Machines and Robotics Planning
 Introduction to Information Science and Technology (IST) Part IV: Intelligent Machines and Robotics Planning Sören Schwertfeger / 师泽仁 ShanghaiTech University ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 10.05.2017
Introduction to Information Science and Technology (IST) Part IV: Intelligent Machines and Robotics Planning Sören Schwertfeger / 师泽仁 ShanghaiTech University ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 10.05.2017
7630 Autonomous Robotics Probabilities for Robotics
 7630 Autonomous Robotics Probabilities for Robotics Basics of probability theory The Bayes-Filter Introduction to localization problems Monte-Carlo-Localization Based on material from R. Triebel, R. Kästner
7630 Autonomous Robotics Probabilities for Robotics Basics of probability theory The Bayes-Filter Introduction to localization problems Monte-Carlo-Localization Based on material from R. Triebel, R. Kästner
DEALING WITH SENSOR ERRORS IN SCAN MATCHING FOR SIMULTANEOUS LOCALIZATION AND MAPPING
 Inženýrská MECHANIKA, roč. 15, 2008, č. 5, s. 337 344 337 DEALING WITH SENSOR ERRORS IN SCAN MATCHING FOR SIMULTANEOUS LOCALIZATION AND MAPPING Jiří Krejsa, Stanislav Věchet* The paper presents Potential-Based
Inženýrská MECHANIKA, roč. 15, 2008, č. 5, s. 337 344 337 DEALING WITH SENSOR ERRORS IN SCAN MATCHING FOR SIMULTANEOUS LOCALIZATION AND MAPPING Jiří Krejsa, Stanislav Věchet* The paper presents Potential-Based
The Internet of Things: Roadmap to a Connected World. IoT and Localization
 IoT and Localization Daniela Rus Andrew (1956) and Erna Viterbi Prof., EECS Director, CSAIL Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) Massachusetts Institute of Technology 4x 4x
IoT and Localization Daniela Rus Andrew (1956) and Erna Viterbi Prof., EECS Director, CSAIL Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) Massachusetts Institute of Technology 4x 4x
Probabilistic Robotics
 Probabilistic Robotics Bayes Filter Implementations Discrete filters, Particle filters Piecewise Constant Representation of belief 2 Discrete Bayes Filter Algorithm 1. Algorithm Discrete_Bayes_filter(
Probabilistic Robotics Bayes Filter Implementations Discrete filters, Particle filters Piecewise Constant Representation of belief 2 Discrete Bayes Filter Algorithm 1. Algorithm Discrete_Bayes_filter(
W4. Perception & Situation Awareness & Decision making
 W4. Perception & Situation Awareness & Decision making Robot Perception for Dynamic environments: Outline & DP-Grids concept Dynamic Probabilistic Grids Bayesian Occupancy Filter concept Dynamic Probabilistic
W4. Perception & Situation Awareness & Decision making Robot Perception for Dynamic environments: Outline & DP-Grids concept Dynamic Probabilistic Grids Bayesian Occupancy Filter concept Dynamic Probabilistic
SLAM with SIFT (aka Mobile Robot Localization and Mapping with Uncertainty using Scale-Invariant Visual Landmarks ) Se, Lowe, and Little
 SLAM with SIFT (aka Mobile Robot Localization and Mapping with Uncertainty using Scale-Invariant Visual Landmarks ) Se, Lowe, and Little + Presented by Matt Loper CS296-3: Robot Learning and Autonomy Brown
SLAM with SIFT (aka Mobile Robot Localization and Mapping with Uncertainty using Scale-Invariant Visual Landmarks ) Se, Lowe, and Little + Presented by Matt Loper CS296-3: Robot Learning and Autonomy Brown
F1/10 th Autonomous Racing. Localization. Nischal K N
 F1/10 th Autonomous Racing Localization Nischal K N System Overview Mapping Hector Mapping Localization Path Planning Control System Overview Mapping Hector Mapping Localization Adaptive Monte Carlo Localization
F1/10 th Autonomous Racing Localization Nischal K N System Overview Mapping Hector Mapping Localization Path Planning Control System Overview Mapping Hector Mapping Localization Adaptive Monte Carlo Localization
Robot Motion Planning
 Robot Motion Planning James Bruce Computer Science Department Carnegie Mellon University April 7, 2004 Agent Planning An agent is a situated entity which can choose and execute actions within in an environment.
Robot Motion Planning James Bruce Computer Science Department Carnegie Mellon University April 7, 2004 Agent Planning An agent is a situated entity which can choose and execute actions within in an environment.
Semantic Mapping and Reasoning Approach for Mobile Robotics
 Semantic Mapping and Reasoning Approach for Mobile Robotics Caner GUNEY, Serdar Bora SAYIN, Murat KENDİR, Turkey Key words: Semantic mapping, 3D mapping, probabilistic, robotic surveying, mine surveying
Semantic Mapping and Reasoning Approach for Mobile Robotics Caner GUNEY, Serdar Bora SAYIN, Murat KENDİR, Turkey Key words: Semantic mapping, 3D mapping, probabilistic, robotic surveying, mine surveying
Data Association for SLAM
 CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ME/CS 132a, Winter 2011 Lab #2 Due: Mar 10th, 2011 Part I Data Association for SLAM 1 Introduction For this part, you will experiment with a simulation of an EKF SLAM
CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ME/CS 132a, Winter 2011 Lab #2 Due: Mar 10th, 2011 Part I Data Association for SLAM 1 Introduction For this part, you will experiment with a simulation of an EKF SLAM
Monte Carlo Localization using Dynamically Expanding Occupancy Grids. Karan M. Gupta
 1 Monte Carlo Localization using Dynamically Expanding Occupancy Grids Karan M. Gupta Agenda Introduction Occupancy Grids Sonar Sensor Model Dynamically Expanding Occupancy Grids Monte Carlo Localization
1 Monte Carlo Localization using Dynamically Expanding Occupancy Grids Karan M. Gupta Agenda Introduction Occupancy Grids Sonar Sensor Model Dynamically Expanding Occupancy Grids Monte Carlo Localization
Robotics. Haslum COMP3620/6320
 Robotics P@trik Haslum COMP3620/6320 Introduction Robotics Industrial Automation * Repetitive manipulation tasks (assembly, etc). * Well-known, controlled environment. * High-power, high-precision, very
Robotics P@trik Haslum COMP3620/6320 Introduction Robotics Industrial Automation * Repetitive manipulation tasks (assembly, etc). * Well-known, controlled environment. * High-power, high-precision, very
Sensor Modalities. Sensor modality: Different modalities:
 Sensor Modalities Sensor modality: Sensors which measure same form of energy and process it in similar ways Modality refers to the raw input used by the sensors Different modalities: Sound Pressure Temperature
Sensor Modalities Sensor modality: Sensors which measure same form of energy and process it in similar ways Modality refers to the raw input used by the sensors Different modalities: Sound Pressure Temperature
AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS. LOCALIZATION, MAPPING & SIMULTANEOUS LOCALIZATION AND MAPPING Part V Mapping & Occupancy Grid Mapping
 AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS LOCALIZATION, MAPPING & SIMULTANEOUS LOCALIZATION AND MAPPING Part V Mapping & Occupancy Grid Mapping Maria Isabel Ribeiro Pedro Lima with revisions introduced by Rodrigo Ventura Instituto
AUTONOMOUS SYSTEMS LOCALIZATION, MAPPING & SIMULTANEOUS LOCALIZATION AND MAPPING Part V Mapping & Occupancy Grid Mapping Maria Isabel Ribeiro Pedro Lima with revisions introduced by Rodrigo Ventura Instituto
SLAM in Large-scale Cyclic Environments using the Atlas Framework
 SLAM in Large-scale Cyclic Environments using the Atlas Framework Michael Bosse Paul Newman John Leonard Seth Teller Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Massachusetts Institute of Technology
SLAM in Large-scale Cyclic Environments using the Atlas Framework Michael Bosse Paul Newman John Leonard Seth Teller Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Application questions. Theoretical questions
 The oral exam will last 30 minutes and will consist of one application question followed by two theoretical questions. Please find below a non exhaustive list of possible application questions. The list
The oral exam will last 30 minutes and will consist of one application question followed by two theoretical questions. Please find below a non exhaustive list of possible application questions. The list
Mobile Robots: An Introduction.
 Mobile Robots: An Introduction Amirkabir University of Technology Computer Engineering & Information Technology Department http://ce.aut.ac.ir/~shiry/lecture/robotics-2004/robotics04.html Introduction
Mobile Robots: An Introduction Amirkabir University of Technology Computer Engineering & Information Technology Department http://ce.aut.ac.ir/~shiry/lecture/robotics-2004/robotics04.html Introduction
Multiple View Geometry
 Multiple View Geometry CS 6320, Spring 2013 Guest Lecture Marcel Prastawa adapted from Pollefeys, Shah, and Zisserman Single view computer vision Projective actions of cameras Camera callibration Photometric
Multiple View Geometry CS 6320, Spring 2013 Guest Lecture Marcel Prastawa adapted from Pollefeys, Shah, and Zisserman Single view computer vision Projective actions of cameras Camera callibration Photometric
Scan Matching. Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley EECS. Many slides adapted from Thrun, Burgard and Fox, Probabilistic Robotics
 Scan Matching Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley EECS Many slides adapted from Thrun, Burgard and Fox, Probabilistic Robotics Scan Matching Overview Problem statement: Given a scan and a map, or a scan and a scan,
Scan Matching Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley EECS Many slides adapted from Thrun, Burgard and Fox, Probabilistic Robotics Scan Matching Overview Problem statement: Given a scan and a map, or a scan and a scan,
Scanning and Printing Objects in 3D Jürgen Sturm
 Scanning and Printing Objects in 3D Jürgen Sturm Metaio (formerly Technical University of Munich) My Research Areas Visual navigation for mobile robots RoboCup Kinematic Learning Articulated Objects Quadrocopters
Scanning and Printing Objects in 3D Jürgen Sturm Metaio (formerly Technical University of Munich) My Research Areas Visual navigation for mobile robots RoboCup Kinematic Learning Articulated Objects Quadrocopters
Building Reliable 2D Maps from 3D Features
 Building Reliable 2D Maps from 3D Features Dipl. Technoinform. Jens Wettach, Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Karsten Berns TU Kaiserslautern; Robotics Research Lab 1, Geb. 48; Gottlieb-Daimler- Str.1; 67663 Kaiserslautern;
Building Reliable 2D Maps from 3D Features Dipl. Technoinform. Jens Wettach, Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Karsten Berns TU Kaiserslautern; Robotics Research Lab 1, Geb. 48; Gottlieb-Daimler- Str.1; 67663 Kaiserslautern;
Nonlinear State Estimation for Robotics and Computer Vision Applications: An Overview
 Nonlinear State Estimation for Robotics and Computer Vision Applications: An Overview Arun Das 05/09/2017 Arun Das Waterloo Autonomous Vehicles Lab Introduction What s in a name? Arun Das Waterloo Autonomous
Nonlinear State Estimation for Robotics and Computer Vision Applications: An Overview Arun Das 05/09/2017 Arun Das Waterloo Autonomous Vehicles Lab Introduction What s in a name? Arun Das Waterloo Autonomous
Robot Localization based on Geo-referenced Images and G raphic Methods
 Robot Localization based on Geo-referenced Images and G raphic Methods Sid Ahmed Berrabah Mechanical Department, Royal Military School, Belgium, sidahmed.berrabah@rma.ac.be Janusz Bedkowski, Łukasz Lubasiński,
Robot Localization based on Geo-referenced Images and G raphic Methods Sid Ahmed Berrabah Mechanical Department, Royal Military School, Belgium, sidahmed.berrabah@rma.ac.be Janusz Bedkowski, Łukasz Lubasiński,
Project Updates Short lecture Volumetric Modeling +2 papers
 Volumetric Modeling Schedule (tentative) Feb 20 Feb 27 Mar 5 Introduction Lecture: Geometry, Camera Model, Calibration Lecture: Features, Tracking/Matching Mar 12 Mar 19 Mar 26 Apr 2 Apr 9 Apr 16 Apr 23
Volumetric Modeling Schedule (tentative) Feb 20 Feb 27 Mar 5 Introduction Lecture: Geometry, Camera Model, Calibration Lecture: Features, Tracking/Matching Mar 12 Mar 19 Mar 26 Apr 2 Apr 9 Apr 16 Apr 23
(W: 12:05-1:50, 50-N202)
 2016 School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering at the University of Queensland Schedule of Events Week Date Lecture (W: 12:05-1:50, 50-N202) 1 27-Jul Introduction 2 Representing Position
2016 School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering at the University of Queensland Schedule of Events Week Date Lecture (W: 12:05-1:50, 50-N202) 1 27-Jul Introduction 2 Representing Position
L16. Scan Matching and Image Formation
 EECS568 Mobile Robotics: Methods and Principles Prof. Edwin Olson L16. Scan Matching and Image Formation Scan Matching Before After 2 Scan Matching Before After 2 Map matching has to be fast 14 robots
EECS568 Mobile Robotics: Methods and Principles Prof. Edwin Olson L16. Scan Matching and Image Formation Scan Matching Before After 2 Scan Matching Before After 2 Map matching has to be fast 14 robots
Mobile Robotics. Mathematics, Models, and Methods. HI Cambridge. Alonzo Kelly. Carnegie Mellon University UNIVERSITY PRESS
 Mobile Robotics Mathematics, Models, and Methods Alonzo Kelly Carnegie Mellon University HI Cambridge UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface page xiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Applications of Mobile Robots 2 1.2
Mobile Robotics Mathematics, Models, and Methods Alonzo Kelly Carnegie Mellon University HI Cambridge UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface page xiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Applications of Mobile Robots 2 1.2
Probabilistic Robotics. FastSLAM
 Probabilistic Robotics FastSLAM The SLAM Problem SLAM stands for simultaneous localization and mapping The task of building a map while estimating the pose of the robot relative to this map Why is SLAM
Probabilistic Robotics FastSLAM The SLAM Problem SLAM stands for simultaneous localization and mapping The task of building a map while estimating the pose of the robot relative to this map Why is SLAM
Visual SLAM. An Overview. L. Freda. ALCOR Lab DIAG University of Rome La Sapienza. May 3, 2016
 An Overview L. Freda ALCOR Lab DIAG University of Rome La Sapienza May 3, 2016 L. Freda (University of Rome La Sapienza ) Visual SLAM May 3, 2016 1 / 39 Outline 1 Introduction What is SLAM Motivations
An Overview L. Freda ALCOR Lab DIAG University of Rome La Sapienza May 3, 2016 L. Freda (University of Rome La Sapienza ) Visual SLAM May 3, 2016 1 / 39 Outline 1 Introduction What is SLAM Motivations
Probabilistic Robotics
 Probabilistic Robotics Probabilistic Motion and Sensor Models Some slides adopted from: Wolfram Burgard, Cyrill Stachniss, Maren Bennewitz, Kai Arras and Probabilistic Robotics Book SA-1 Sensors for Mobile
Probabilistic Robotics Probabilistic Motion and Sensor Models Some slides adopted from: Wolfram Burgard, Cyrill Stachniss, Maren Bennewitz, Kai Arras and Probabilistic Robotics Book SA-1 Sensors for Mobile
Autonomous robot motion path planning using shortest path planning algorithms
 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) e-issn: 2250-3021, p-issn: 2278-8719 Vol. 3, Issue 1 (Jan. 2013), V1 PP 65-69 Autonomous robot motion path planning using shortest path planning algorithms T. Ravi
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) e-issn: 2250-3021, p-issn: 2278-8719 Vol. 3, Issue 1 (Jan. 2013), V1 PP 65-69 Autonomous robot motion path planning using shortest path planning algorithms T. Ravi
Vision-based Mobile Robot Localization and Mapping using Scale-Invariant Features
 Vision-based Mobile Robot Localization and Mapping using Scale-Invariant Features Stephen Se, David Lowe, Jim Little Department of Computer Science University of British Columbia Presented by Adam Bickett
Vision-based Mobile Robot Localization and Mapping using Scale-Invariant Features Stephen Se, David Lowe, Jim Little Department of Computer Science University of British Columbia Presented by Adam Bickett
Calibration of a rotating multi-beam Lidar
 The 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems October 18-22, 2010, Taipei, Taiwan Calibration of a rotating multi-beam Lidar Naveed Muhammad 1,2 and Simon Lacroix 1,2 Abstract
The 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems October 18-22, 2010, Taipei, Taiwan Calibration of a rotating multi-beam Lidar Naveed Muhammad 1,2 and Simon Lacroix 1,2 Abstract
Introduction to Mobile Robotics SLAM Grid-based FastSLAM. Wolfram Burgard, Cyrill Stachniss, Maren Bennewitz, Diego Tipaldi, Luciano Spinello
 Introduction to Mobile Robotics SLAM Grid-based FastSLAM Wolfram Burgard, Cyrill Stachniss, Maren Bennewitz, Diego Tipaldi, Luciano Spinello 1 The SLAM Problem SLAM stands for simultaneous localization
Introduction to Mobile Robotics SLAM Grid-based FastSLAM Wolfram Burgard, Cyrill Stachniss, Maren Bennewitz, Diego Tipaldi, Luciano Spinello 1 The SLAM Problem SLAM stands for simultaneous localization
Topological Mapping. Discrete Bayes Filter
 Topological Mapping Discrete Bayes Filter Vision Based Localization Given a image(s) acquired by moving camera determine the robot s location and pose? Towards localization without odometry What can be
Topological Mapping Discrete Bayes Filter Vision Based Localization Given a image(s) acquired by moving camera determine the robot s location and pose? Towards localization without odometry What can be
Geometric Reconstruction Dense reconstruction of scene geometry
 Lecture 5. Dense Reconstruction and Tracking with Real-Time Applications Part 2: Geometric Reconstruction Dr Richard Newcombe and Dr Steven Lovegrove Slide content developed from: [Newcombe, Dense Visual
Lecture 5. Dense Reconstruction and Tracking with Real-Time Applications Part 2: Geometric Reconstruction Dr Richard Newcombe and Dr Steven Lovegrove Slide content developed from: [Newcombe, Dense Visual
Human Body Recognition and Tracking: How the Kinect Works. Kinect RGB-D Camera. What the Kinect Does. How Kinect Works: Overview
 Human Body Recognition and Tracking: How the Kinect Works Kinect RGB-D Camera Microsoft Kinect (Nov. 2010) Color video camera + laser-projected IR dot pattern + IR camera $120 (April 2012) Kinect 1.5 due
Human Body Recognition and Tracking: How the Kinect Works Kinect RGB-D Camera Microsoft Kinect (Nov. 2010) Color video camera + laser-projected IR dot pattern + IR camera $120 (April 2012) Kinect 1.5 due
ICRA 2016 Tutorial on SLAM. Graph-Based SLAM and Sparsity. Cyrill Stachniss
 ICRA 2016 Tutorial on SLAM Graph-Based SLAM and Sparsity Cyrill Stachniss 1 Graph-Based SLAM?? 2 Graph-Based SLAM?? SLAM = simultaneous localization and mapping 3 Graph-Based SLAM?? SLAM = simultaneous
ICRA 2016 Tutorial on SLAM Graph-Based SLAM and Sparsity Cyrill Stachniss 1 Graph-Based SLAM?? 2 Graph-Based SLAM?? SLAM = simultaneous localization and mapping 3 Graph-Based SLAM?? SLAM = simultaneous
Mini Survey Paper (Robotic Mapping) Ryan Hamor CPRE 583 September 2011
 Mini Survey Paper (Robotic Mapping) Ryan Hamor CPRE 583 September 2011 Introduction The goal of this survey paper is to examine the field of robotic mapping and the use of FPGAs in various implementations.
Mini Survey Paper (Robotic Mapping) Ryan Hamor CPRE 583 September 2011 Introduction The goal of this survey paper is to examine the field of robotic mapping and the use of FPGAs in various implementations.
ME 597/747 Autonomous Mobile Robots. Mid Term Exam. Duration: 2 hour Total Marks: 100
 ME 597/747 Autonomous Mobile Robots Mid Term Exam Duration: 2 hour Total Marks: 100 Instructions: Read the exam carefully before starting. Equations are at the back, but they are NOT necessarily valid
ME 597/747 Autonomous Mobile Robots Mid Term Exam Duration: 2 hour Total Marks: 100 Instructions: Read the exam carefully before starting. Equations are at the back, but they are NOT necessarily valid
Visual Navigation for Flying Robots Exploration, Multi-Robot Coordination and Coverage
 Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers Visual Navigation for Flying Robots Exploration, Multi-Robot Coordination and Coverage Dr. Jürgen Sturm Agenda for Today Exploration with a single robot Coordinated
Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers Visual Navigation for Flying Robots Exploration, Multi-Robot Coordination and Coverage Dr. Jürgen Sturm Agenda for Today Exploration with a single robot Coordinated
Visually Augmented POMDP for Indoor Robot Navigation
 Visually Augmented POMDP for Indoor obot Navigation LÓPEZ M.E., BAEA., BEGASA L.M., ESCUDEO M.S. Electronics Department University of Alcalá Campus Universitario. 28871 Alcalá de Henares (Madrid) SPAIN
Visually Augmented POMDP for Indoor obot Navigation LÓPEZ M.E., BAEA., BEGASA L.M., ESCUDEO M.S. Electronics Department University of Alcalá Campus Universitario. 28871 Alcalá de Henares (Madrid) SPAIN
Autonomous Navigation in Complex Indoor and Outdoor Environments with Micro Aerial Vehicles
 Autonomous Navigation in Complex Indoor and Outdoor Environments with Micro Aerial Vehicles Shaojie Shen Dept. of Electrical and Systems Engineering & GRASP Lab, University of Pennsylvania Committee: Daniel
Autonomous Navigation in Complex Indoor and Outdoor Environments with Micro Aerial Vehicles Shaojie Shen Dept. of Electrical and Systems Engineering & GRASP Lab, University of Pennsylvania Committee: Daniel
First scan matching algorithms. Alberto Quattrini Li University of South Carolina
 First scan matching algorithms Alberto Quattrini Li 2015-10-22 University of South Carolina Robot mapping through scan-matching Framework for consistent registration of multiple frames of measurements
First scan matching algorithms Alberto Quattrini Li 2015-10-22 University of South Carolina Robot mapping through scan-matching Framework for consistent registration of multiple frames of measurements
Improving Vision-based Topological Localization by Combining Local and Global Image Features
 Improving Vision-based Topological Localization by Combining Local and Global Image Features Shuai Yang and Han Wang Nanyang Technological University, Singapore Introduction Self-localization is crucial
Improving Vision-based Topological Localization by Combining Local and Global Image Features Shuai Yang and Han Wang Nanyang Technological University, Singapore Introduction Self-localization is crucial
Image Augmented Laser Scan Matching for Indoor Localization
 Image Augmented Laser Scan Matching for Indoor Localization Nikhil Naikal Avideh Zakhor John Kua Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley Technical Report No. UCB/EECS-2009-35
Image Augmented Laser Scan Matching for Indoor Localization Nikhil Naikal Avideh Zakhor John Kua Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley Technical Report No. UCB/EECS-2009-35
Multiview Stereo COSC450. Lecture 8
 Multiview Stereo COSC450 Lecture 8 Stereo Vision So Far Stereo and epipolar geometry Fundamental matrix captures geometry 8-point algorithm Essential matrix with calibrated cameras 5-point algorithm Intersect
Multiview Stereo COSC450 Lecture 8 Stereo Vision So Far Stereo and epipolar geometry Fundamental matrix captures geometry 8-point algorithm Essential matrix with calibrated cameras 5-point algorithm Intersect
3D Photography: Active Ranging, Structured Light, ICP
 3D Photography: Active Ranging, Structured Light, ICP Kalin Kolev, Marc Pollefeys Spring 2013 http://cvg.ethz.ch/teaching/2013spring/3dphoto/ Schedule (tentative) Feb 18 Feb 25 Mar 4 Mar 11 Mar 18 Mar
3D Photography: Active Ranging, Structured Light, ICP Kalin Kolev, Marc Pollefeys Spring 2013 http://cvg.ethz.ch/teaching/2013spring/3dphoto/ Schedule (tentative) Feb 18 Feb 25 Mar 4 Mar 11 Mar 18 Mar
3D Laserscanner App for Indoor Measurements
 3D Laserscanner App for Indoor Measurements V&R Vision & Robotics GmbH Prof. Dr.-Ing. Dietrich Paulus, Dipl.-Inform. Johannes Pellenz info@vision-robotics.de 20. April 2011 vr 3D Laserscanner App for Indoor
3D Laserscanner App for Indoor Measurements V&R Vision & Robotics GmbH Prof. Dr.-Ing. Dietrich Paulus, Dipl.-Inform. Johannes Pellenz info@vision-robotics.de 20. April 2011 vr 3D Laserscanner App for Indoor
Robot Mapping. TORO Gradient Descent for SLAM. Cyrill Stachniss
 Robot Mapping TORO Gradient Descent for SLAM Cyrill Stachniss 1 Stochastic Gradient Descent Minimize the error individually for each constraint (decomposition of the problem into sub-problems) Solve one
Robot Mapping TORO Gradient Descent for SLAM Cyrill Stachniss 1 Stochastic Gradient Descent Minimize the error individually for each constraint (decomposition of the problem into sub-problems) Solve one
Structured Light II. Thanks to Ronen Gvili, Szymon Rusinkiewicz and Maks Ovsjanikov
 Structured Light II Johannes Köhler Johannes.koehler@dfki.de Thanks to Ronen Gvili, Szymon Rusinkiewicz and Maks Ovsjanikov Introduction Previous lecture: Structured Light I Active Scanning Camera/emitter
Structured Light II Johannes Köhler Johannes.koehler@dfki.de Thanks to Ronen Gvili, Szymon Rusinkiewicz and Maks Ovsjanikov Introduction Previous lecture: Structured Light I Active Scanning Camera/emitter
An Iterative Graph Optimization Approach for 2D SLAM. He Zhang, Guoliang Liu, and Zifeng Hou Lenovo Institution of Research and Development
 An Iterative Graph Optimization Approach for 2D SLAM He Zhang, Guoliang Liu, and Zifeng Hou Lenovo Institution of Research and Development Self Introduction English name: David, Graduate student in UCAS
An Iterative Graph Optimization Approach for 2D SLAM He Zhang, Guoliang Liu, and Zifeng Hou Lenovo Institution of Research and Development Self Introduction English name: David, Graduate student in UCAS
A scalable hybrid multi-robot SLAM method for highly detailed maps Pfingsthorn, M.; Slamet, B.; Visser, A.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) A scalable hybrid multi-robot SLAM method for highly detailed maps Pfingsthorn, M.; Slamet, B.; Visser, A. Published in: Lecture Notes in Computer Science DOI: 10.1007/978-3-540-68847-1_48
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) A scalable hybrid multi-robot SLAM method for highly detailed maps Pfingsthorn, M.; Slamet, B.; Visser, A. Published in: Lecture Notes in Computer Science DOI: 10.1007/978-3-540-68847-1_48
Structure from Motion. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 10
 Structure from Motion CSE 152 Lecture 10 Announcements Homework 3 is due May 9, 11:59 PM Reading: Chapter 8: Structure from Motion Optional: Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision, 2nd edition, Hartley
Structure from Motion CSE 152 Lecture 10 Announcements Homework 3 is due May 9, 11:59 PM Reading: Chapter 8: Structure from Motion Optional: Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision, 2nd edition, Hartley
EE631 Cooperating Autonomous Mobile Robots
 EE631 Cooperating Autonomous Mobile Robots Lecture: Multi-Robot Motion Planning Prof. Yi Guo ECE Department Plan Introduction Premises and Problem Statement A Multi-Robot Motion Planning Algorithm Implementation
EE631 Cooperating Autonomous Mobile Robots Lecture: Multi-Robot Motion Planning Prof. Yi Guo ECE Department Plan Introduction Premises and Problem Statement A Multi-Robot Motion Planning Algorithm Implementation
