Rigid Body Transformations
|
|
|
- Erica Greene
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 F1/10 th Racing Rigid Body Transformations (Or How Different sensors see the same world) By, Paritosh Kelkar
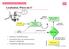
2 Mapping the surroundings Specify destination and generate path to goal The colored cells represent a potential that is used to plan paths Rviz is used to specify different goals to the robot
3 Why should you watch these lectures Following the wall here blindly is going to be really hard You will need a very complicated Route definition file
4 Why should you watch these lectures Simultaneous Localization and Planning Planning
5 Lets begin
6 Scope of the Lecture PART 1 The concept of frames and transforms (different views of the same world) Why is this important to us The Homogenous Transformation Matrix PART 2 How ROS deals with these frames, conventions in ROS
7 Frames of Reference
8 Part 1
9 Transformations and Frames: Heads up 1. w.r.t = with respect to 2. Map frame where are you w.r.t the map co-oridnates from origin
10 Transformations and Frames: Heads up The Sensor frame how does the world look w.r.t the sensor Does this tell you anything about where obstacles are in the map? Does this tell you anything about where we are in the map? We must link frames together Transformations
11 Transformations and Frames The frame of reference in which the measurement is taken Z Δz X Distance measurements returned by LIDAR
12 Transformations and Frames The frame of reference in which the measurement is taken Δz X Z Y The scan Values from the LIDAR will not tell us how far away are the obstacles. We must take care of the offsets Δx
13 Transformations and Frames Δz X Z Y Note: Axes X,Y,Z of Frames of Reference are orthogonal(90 o ) to each other. X,Y,Z represent the axes along the 3 dimensions.
14 Transformations and Frames Car frame X Z Y Y Map frame Y laser frame Between frames there will exist transformations that convert measurements from one frame to another Important Point: Note what the transformation means w.r.t frames
15 Transformations and Frames Between frames there will exist transformations that convert measurements from one frame to another Z Y laser frame Y There should exist a relationship Between these frames Car frame X Y Y Map frame Y Transform from car to laser Y Transform from map to car
16 A world without frames and transformations
17 The actual motion of the car
18 Rigid Body Transforms: An Aside What s with it being Rigid? The distance between any two given points of a rigid body remains constant in time regardless of external forces exerted on it. Play-Doh: Obviously not a rigid body
19 Rigid Body Transforms Y A Z A X A
20 Rigid Body Transforms Y A Z A X A
21 Rigid Body Transforms θ Y A Z A X A
22 Rigid Body Transforms θ Y A A d B Z A X A
23 Rigid Body Transforms B p θ Y A A d B Z A X A
24 Rigid Body Transforms B p A p θ Y A A d B Z A X A
25 Rigid Body Transforms What we need is Point p with respect to Frame A, given its pose in Frame B B p A p θ Y A A d B Z A X A
26 Rigid Body Transforms Special type of matrices called Rotation matrices X B = R 11 X A + R 21 Y A + R 31 Z A Y A Y B = R 12 X A + R 22 Y A + R 32 Z A Z B = R 13 X A + R 23 Y A + R 33 Z A Z A X A θ
27 Rigid Body Transforms Special type of matrices called Rotation matrices X B = R 11 X A + R 21 Y A + R 31 Z A Y B = R 12 X A + R 22 Y A + R 32 Z A Z B = R 13 X A + R 23 Y A + R 33 Z A Y A Z A A R B = R 11 R 12 R 13 R 21 R 22 R 23 R 31 R 32 R 33 Takes points in frame B and represents their orientation in frame A θ X A
28 Rigid Body Transforms: Rotation Matrices X B = R 11 X A + R 21 Y A + R 31 Z A (0,5,0) A p =? Y B = R 12 X A + R 22 Y A + R 32 Z A Y A B p Sine component Z B = R 13 X A + R 23 Y A + R 33 Z A Z A θ Cosine component XA X B = cos(θ) X A +sin(θ) Y A +0 Z A R 11 R 21 R 31
29 Rigid Body Transforms: Rotation Matrices A R B = Cos(θ) R 12 R 13 Sin(θ) R 22 R 23 0 R 32 R 33 X A Y A Z A A C S 0 RB S C X B Y B Z B ) C θ = Cos(θ ) S θ = Sin(θ
30 We have the Rotation Matrix, so now what? p R p A A B B R = For example θ We now have the point P as referenced in frame A Τ = π 6 Known Known A p = (-2.5,4.3,0) (-2.5,4.3,0) Y A A p Z A X A
31 Important point to remember The rotation matrix will take care of perspectives of orientation, what about displacement? Y A Y A Z A Z A X A X A Origins of both the frames are at the same location A d B
32 Rigid Body Transforms: And We are back to the Future A A B A B p R p d B Y B Y A Z B X B Z A X A
33 Rigid Body Transforms What we need is Point p with respect to Frame A, given its pose in Frame B p H p B p A A B B p A p θ Y A Z A X A A d B A H = Homogenous transformations that transforms B measurements in Frame B to those in Frame A A C S 0 RB S C R d A A A B B H B 0 1
34 Part 2
35 Map frame Map Frame
36 Map frame: Importance Position with respect to map MAP FRAME
37 Map Frame: Properties Used as a long term reference Dependence on localization engine (Adaptive Monte Carlo Localization AMCL used in our system more about this in later lectures) Localization engine - responsible for providing pose w.r.t map Frame Authority
38 Map Frame: ROS The tf package tracks multiple 3D coordinate frames - maintains a tree structure b/w frames access relationship b/w any 2 frames at any point of time ROS REP(ROS Enhancement Proposals) 105 describes the various frames involved Normal hierarchy world_frame Has no parent A tf tree is a structure that maintains relations between the linked frames. Note: Tf = transformer class map Child of world frame
39 Odom Frame
40 Odom frame: Calculation Frame in which odometry is measured Odometry is used by some robots, whether they be legged or wheeled, to estimate (not determine) their position relative to a starting location -Wikipedia Source: eg: Wheel encoders. Count wheel ticks
41 Odom Frame: Calculation Difference in count of ticks of wheels orientation Integrating the commanded velocities/accelarations Integrating values from IMU
42 Odom Frame: Uncertainty Initial Position Error can accumulate leading to a drift in values Incorrect diameter used? Slippage? Dead Reckoning Notice how the uncertainty increases
43 Odom Frame: Properties Continuous actual data from actuators/motors Evolves in a smooth manner, without discrete jumps Short term ; accurate local reference
44 Odom Frame: ROS General ROS frame hierarchy world_frame map Note that if the frame is connected in the tf tree, we can obtain a representation of that frame with any other frame in the tree odom Tf tree
45 Base_link and fixed frames attached to the robot
46 Base link: What is it Attached to the robot itself base_footprint; base_link; base_stabilized
47 Base link: Properties Odom -> base link transform provided by Odometry source Map -> base_link transform provided by localization component
48 Fixed Frames: Source Where do we get the relationships between the fixed frame on the car Frame for various hardware components(sensors) Robot description provides the transformations Urdf file Look up the tutorial related to this lecture
49 Base_link Frame: ROS General ROS frame hierarchy world_frame map odom base_link Tf tree
50 ROS.W.T.F Its actually a tool just very cleverly named Host of tf debugging tools provided by ROS Look at tutorial for further details $ rosrun tf view_frames $ rosrun tf view_monitor $ roswtf
51 In Conclusion Rigid Body Transformations the concept and the importance in robotic systems We now know how to correlate measurements from different sensors The upcoming lecture SLAM Simultaneous Localization and Mapping
52 Why do you have to remember all of this stuff Again, you are developing the platform in this framework Don t you want to know how you could get maps of your surroundings? what we just covered are building blocks of the upcoming topics
53 Upcoming Lectures We will go into detail about the packages that we use for mapping and localizing
54 Map frame: Properties Discontinuity Y Z Map frame (0,0,0) X
55 Map frame: Properties New sensor reading gives us new information Discontinuity Y Z Map frame (0,0,0) X Jump in position, i.e, not continuous (2,0,0)
56 Map Frame: Properties
57 Map Frame: Why Discontinuity is a Problem What pose coordinates will the controller act on?
58 Transformations and Frames The frame of reference in which the measurement is taken Z Δz X Y Δx
59 Odom Frame: Uncertainty Initial placement of odom and map frames Final placement of odom and map frames after robot has moved some distance
F1/10 th Autonomous Racing. Localization. Nischal K N
 F1/10 th Autonomous Racing Localization Nischal K N System Overview Mapping Hector Mapping Localization Path Planning Control System Overview Mapping Hector Mapping Localization Adaptive Monte Carlo Localization
F1/10 th Autonomous Racing Localization Nischal K N System Overview Mapping Hector Mapping Localization Path Planning Control System Overview Mapping Hector Mapping Localization Adaptive Monte Carlo Localization
CS 309: Autonomous Intelligent Robotics FRI I. Lecture 18: Coordinate Frames TF2 Alvar. Instructor: Justin Hart
 CS 309: Autonomous Intelligent Robotics FRI I Lecture 18: Coordinate Frames TF2 Alvar Instructor: Justin Hart http://justinhart.net/teaching/2018_spring_cs309/ A couple of quick notes Homework 4 Due March
CS 309: Autonomous Intelligent Robotics FRI I Lecture 18: Coordinate Frames TF2 Alvar Instructor: Justin Hart http://justinhart.net/teaching/2018_spring_cs309/ A couple of quick notes Homework 4 Due March
Robot Programming with Lisp
 7. Coordinate Transformations, TF, ActionLib Institute for Artificial University of Bremen Outline Coordinate Transformations TF ActionLib 2 Outline Coordinate Transformations TF ActionLib 3 Poses in 3D
7. Coordinate Transformations, TF, ActionLib Institute for Artificial University of Bremen Outline Coordinate Transformations TF ActionLib 2 Outline Coordinate Transformations TF ActionLib 3 Poses in 3D
EECS 4330/7330 Introduction to Mechatronics and Robotic Vision, Fall Lab 5. Controlling Puma Using Leap Motion Device
 1 Lab 5 Controlling Puma Using Leap Motion Device Objective In this experiment, students will use Leap Motion device to achieve the following goals: - Get familiar with the Leap Motion device - Experience
1 Lab 5 Controlling Puma Using Leap Motion Device Objective In this experiment, students will use Leap Motion device to achieve the following goals: - Get familiar with the Leap Motion device - Experience
MTRX4700 Experimental Robotics
 MTRX 4700 : Experimental Robotics Lecture 2 Stefan B. Williams Slide 1 Course Outline Week Date Content Labs Due Dates 1 5 Mar Introduction, history & philosophy of robotics 2 12 Mar Robot kinematics &
MTRX 4700 : Experimental Robotics Lecture 2 Stefan B. Williams Slide 1 Course Outline Week Date Content Labs Due Dates 1 5 Mar Introduction, history & philosophy of robotics 2 12 Mar Robot kinematics &
Development of intelligent systems
 Development of intelligent systems (RInS) Transformations between coordinate frames Danijel Skočaj University of Ljubljana Faculty of Computer and Information Science Literature: Tadej Bajd (2006). Osnove
Development of intelligent systems (RInS) Transformations between coordinate frames Danijel Skočaj University of Ljubljana Faculty of Computer and Information Science Literature: Tadej Bajd (2006). Osnove
Exam in DD2426 Robotics and Autonomous Systems
 Exam in DD2426 Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecturer: Patric Jensfelt KTH, March 16, 2010, 9-12 No aids are allowed on the exam, i.e. no notes, no books, no calculators, etc. You need a minimum of 20
Exam in DD2426 Robotics and Autonomous Systems Lecturer: Patric Jensfelt KTH, March 16, 2010, 9-12 No aids are allowed on the exam, i.e. no notes, no books, no calculators, etc. You need a minimum of 20
Localization, Where am I?
 5.1 Localization, Where am I?? position Position Update (Estimation?) Encoder Prediction of Position (e.g. odometry) YES matched observations Map data base predicted position Matching Odometry, Dead Reckoning
5.1 Localization, Where am I?? position Position Update (Estimation?) Encoder Prediction of Position (e.g. odometry) YES matched observations Map data base predicted position Matching Odometry, Dead Reckoning
ROS navigation stack Costmaps Localization Sending goal commands (from rviz) (C)2016 Roi Yehoshua
 ROS navigation stack Costmaps Localization Sending goal commands (from rviz) Robot Navigation One of the most basic things that a robot can do is to move around the world. To do this effectively, the robot
ROS navigation stack Costmaps Localization Sending goal commands (from rviz) Robot Navigation One of the most basic things that a robot can do is to move around the world. To do this effectively, the robot
ROBOT NAVIGATION ROBOTICS
 ROBOT NAVIGATION ROBOTICS OUR IMPLEMENTATION /joy joy_cmd /cmd_joy / /velocity ROBOT joy_node /odom JOYPAD pose OUR IMPLEMENTATION /mode /joy joy_cmd /cmd_joy mux / /velocity /cmd_auto ROBOT joy_node planner
ROBOT NAVIGATION ROBOTICS OUR IMPLEMENTATION /joy joy_cmd /cmd_joy / /velocity ROBOT joy_node /odom JOYPAD pose OUR IMPLEMENTATION /mode /joy joy_cmd /cmd_joy mux / /velocity /cmd_auto ROBOT joy_node planner
RoboCup Rescue Summer School Navigation Tutorial
 RoboCup Rescue Summer School 2012 Institute for Software Technology, Graz University of Technology, Austria 1 Literature Choset, Lynch, Hutchinson, Kantor, Burgard, Kavraki and Thrun. Principle of Robot
RoboCup Rescue Summer School 2012 Institute for Software Technology, Graz University of Technology, Austria 1 Literature Choset, Lynch, Hutchinson, Kantor, Burgard, Kavraki and Thrun. Principle of Robot
Localization and Map Building
 Localization and Map Building Noise and aliasing; odometric position estimation To localize or not to localize Belief representation Map representation Probabilistic map-based localization Other examples
Localization and Map Building Noise and aliasing; odometric position estimation To localize or not to localize Belief representation Map representation Probabilistic map-based localization Other examples
Humanoid Robotics. Monte Carlo Localization. Maren Bennewitz
 Humanoid Robotics Monte Carlo Localization Maren Bennewitz 1 Basis Probability Rules (1) If x and y are independent: Bayes rule: Often written as: The denominator is a normalizing constant that ensures
Humanoid Robotics Monte Carlo Localization Maren Bennewitz 1 Basis Probability Rules (1) If x and y are independent: Bayes rule: Often written as: The denominator is a normalizing constant that ensures
Investigating Simultaneous Localization and Mapping for AGV systems
 Investigating Simultaneous Localization and Mapping for AGV systems With open-source modules available in ROS Master s thesis in Computer Systems and Networks ALBIN PÅLSSON MARKUS SMEDBERG Department of
Investigating Simultaneous Localization and Mapping for AGV systems With open-source modules available in ROS Master s thesis in Computer Systems and Networks ALBIN PÅLSSON MARKUS SMEDBERG Department of
CALCULATING TRANSFORMATIONS OF KINEMATIC CHAINS USING HOMOGENEOUS COORDINATES
 CALCULATING TRANSFORMATIONS OF KINEMATIC CHAINS USING HOMOGENEOUS COORDINATES YINGYING REN Abstract. In this paper, the applications of homogeneous coordinates are discussed to obtain an efficient model
CALCULATING TRANSFORMATIONS OF KINEMATIC CHAINS USING HOMOGENEOUS COORDINATES YINGYING REN Abstract. In this paper, the applications of homogeneous coordinates are discussed to obtain an efficient model
ME 597/747 Autonomous Mobile Robots. Mid Term Exam. Duration: 2 hour Total Marks: 100
 ME 597/747 Autonomous Mobile Robots Mid Term Exam Duration: 2 hour Total Marks: 100 Instructions: Read the exam carefully before starting. Equations are at the back, but they are NOT necessarily valid
ME 597/747 Autonomous Mobile Robots Mid Term Exam Duration: 2 hour Total Marks: 100 Instructions: Read the exam carefully before starting. Equations are at the back, but they are NOT necessarily valid
Coordinate Frames and Transforms
 Coordinate Frames and Transforms 1 Specifiying Position and Orientation We need to describe in a compact way the position of the robot. In 2 dimensions (planar mobile robot), there are 3 degrees of freedom
Coordinate Frames and Transforms 1 Specifiying Position and Orientation We need to describe in a compact way the position of the robot. In 2 dimensions (planar mobile robot), there are 3 degrees of freedom
LOAM: LiDAR Odometry and Mapping in Real Time
 LOAM: LiDAR Odometry and Mapping in Real Time Aayush Dwivedi (14006), Akshay Sharma (14062), Mandeep Singh (14363) Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur 1 Abstract This project deals with online simultaneous
LOAM: LiDAR Odometry and Mapping in Real Time Aayush Dwivedi (14006), Akshay Sharma (14062), Mandeep Singh (14363) Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur 1 Abstract This project deals with online simultaneous
EEE 187: Robotics Summary 2
 1 EEE 187: Robotics Summary 2 09/05/2017 Robotic system components A robotic system has three major components: Actuators: the muscles of the robot Sensors: provide information about the environment and
1 EEE 187: Robotics Summary 2 09/05/2017 Robotic system components A robotic system has three major components: Actuators: the muscles of the robot Sensors: provide information about the environment and
TF (transform) in ROS
 TF (transform) in ROS ECET 49900/58100 Credit: PhD comics and Willow Garage 1 ROS tf (transform) package Goal: Maintain relationship between multiple coordinate frames overtime. Transform points, or vectors
TF (transform) in ROS ECET 49900/58100 Credit: PhD comics and Willow Garage 1 ROS tf (transform) package Goal: Maintain relationship between multiple coordinate frames overtime. Transform points, or vectors
ROS-Industrial Basic Developer s Training Class. Southwest Research Institute
 ROS-Industrial Basic Developer s Training Class Southwest Research Institute 1 Session 3: Motion Control of Manipulators Southwest Research Institute 2 URDF: Unified Robot Description Format 3 URDF: Overview
ROS-Industrial Basic Developer s Training Class Southwest Research Institute 1 Session 3: Motion Control of Manipulators Southwest Research Institute 2 URDF: Unified Robot Description Format 3 URDF: Overview
Introduction to Mobile Robotics
 Introduction to Mobile Robotics Olivier Aycard Associate Professor University of Grenoble Laboratoire d Informatique de Grenoble http://membres-liglab.imag.fr/aycard 1/29 Some examples of mobile robots
Introduction to Mobile Robotics Olivier Aycard Associate Professor University of Grenoble Laboratoire d Informatique de Grenoble http://membres-liglab.imag.fr/aycard 1/29 Some examples of mobile robots
EE-565-Lab2. Dr. Ahmad Kamal Nasir
 EE-565-Lab2 Introduction to Simulation Environment Dr. Ahmad Kamal Nasir 29.01.2016 Dr. -Ing. Ahmad Kamal Nasir 1 Today s Objectives Introduction to Gazebo Building a robot model in Gazebo Populating robot
EE-565-Lab2 Introduction to Simulation Environment Dr. Ahmad Kamal Nasir 29.01.2016 Dr. -Ing. Ahmad Kamal Nasir 1 Today s Objectives Introduction to Gazebo Building a robot model in Gazebo Populating robot
ICRA 2016 Tutorial on SLAM. Graph-Based SLAM and Sparsity. Cyrill Stachniss
 ICRA 2016 Tutorial on SLAM Graph-Based SLAM and Sparsity Cyrill Stachniss 1 Graph-Based SLAM?? 2 Graph-Based SLAM?? SLAM = simultaneous localization and mapping 3 Graph-Based SLAM?? SLAM = simultaneous
ICRA 2016 Tutorial on SLAM Graph-Based SLAM and Sparsity Cyrill Stachniss 1 Graph-Based SLAM?? 2 Graph-Based SLAM?? SLAM = simultaneous localization and mapping 3 Graph-Based SLAM?? SLAM = simultaneous
Mobile Robotics. Mathematics, Models, and Methods. HI Cambridge. Alonzo Kelly. Carnegie Mellon University UNIVERSITY PRESS
 Mobile Robotics Mathematics, Models, and Methods Alonzo Kelly Carnegie Mellon University HI Cambridge UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface page xiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Applications of Mobile Robots 2 1.2
Mobile Robotics Mathematics, Models, and Methods Alonzo Kelly Carnegie Mellon University HI Cambridge UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface page xiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Applications of Mobile Robots 2 1.2
Practical Course WS12/13 Introduction to Monte Carlo Localization
 Practical Course WS12/13 Introduction to Monte Carlo Localization Cyrill Stachniss and Luciano Spinello 1 State Estimation Estimate the state of a system given observations and controls Goal: 2 Bayes Filter
Practical Course WS12/13 Introduction to Monte Carlo Localization Cyrill Stachniss and Luciano Spinello 1 State Estimation Estimate the state of a system given observations and controls Goal: 2 Bayes Filter
Least Squares and SLAM Pose-SLAM
 Least Squares and SLAM Pose-SLAM Giorgio Grisetti Part of the material of this course is taken from the Robotics 2 lectures given by G.Grisetti, W.Burgard, C.Stachniss, K.Arras, D. Tipaldi and M.Bennewitz
Least Squares and SLAM Pose-SLAM Giorgio Grisetti Part of the material of this course is taken from the Robotics 2 lectures given by G.Grisetti, W.Burgard, C.Stachniss, K.Arras, D. Tipaldi and M.Bennewitz
CS283: Robotics Fall 2016: Sensors
 CS283: Robotics Fall 2016: Sensors Sören Schwertfeger / 师泽仁 ShanghaiTech University Robotics ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 23.09.2016 2 REVIEW TRANSFORMS Robotics ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 23.09.2016
CS283: Robotics Fall 2016: Sensors Sören Schwertfeger / 师泽仁 ShanghaiTech University Robotics ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 23.09.2016 2 REVIEW TRANSFORMS Robotics ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 23.09.2016
Localization, Mapping and Exploration with Multiple Robots. Dr. Daisy Tang
 Localization, Mapping and Exploration with Multiple Robots Dr. Daisy Tang Two Presentations A real-time algorithm for mobile robot mapping with applications to multi-robot and 3D mapping, by Thrun, Burgard
Localization, Mapping and Exploration with Multiple Robots Dr. Daisy Tang Two Presentations A real-time algorithm for mobile robot mapping with applications to multi-robot and 3D mapping, by Thrun, Burgard
Basics of Localization, Mapping and SLAM. Jari Saarinen Aalto University Department of Automation and systems Technology
 Basics of Localization, Mapping and SLAM Jari Saarinen Aalto University Department of Automation and systems Technology Content Introduction to Problem (s) Localization A few basic equations Dead Reckoning
Basics of Localization, Mapping and SLAM Jari Saarinen Aalto University Department of Automation and systems Technology Content Introduction to Problem (s) Localization A few basic equations Dead Reckoning
tf: On the PR2 ROS + PR2 Training Workshop
 tf: On the PR2 What is tf? A coordinate frame tracking system A standardized protocol for publishing transform data to a distributed system Helper classes and methods for: Publishing coordinate frame data
tf: On the PR2 What is tf? A coordinate frame tracking system A standardized protocol for publishing transform data to a distributed system Helper classes and methods for: Publishing coordinate frame data
Mapping and Navigation
 Mapping and Navigation Principles and Shortcuts January 15 th, 2009 Matt Walter, mwalter@mit.edu Slides courtesy of Edwin Olson Goals for this talk Why should I build a map? Three mapping algorithms Forgetful
Mapping and Navigation Principles and Shortcuts January 15 th, 2009 Matt Walter, mwalter@mit.edu Slides courtesy of Edwin Olson Goals for this talk Why should I build a map? Three mapping algorithms Forgetful
Individual Lab Report #6. Pratik Chatrath. Team A / Team Avengers. Teammates: Tushar Agrawal, Sean Bryan. January 28, 2016
 Individual Lab Report #6 Pratik Chatrath Team A / Team Avengers Teammates: Tushar Agrawal, Sean Bryan January 28, 2016 I. Individual Progress Overall in the last semester, I worked on developing obstacle
Individual Lab Report #6 Pratik Chatrath Team A / Team Avengers Teammates: Tushar Agrawal, Sean Bryan January 28, 2016 I. Individual Progress Overall in the last semester, I worked on developing obstacle
Nonlinear State Estimation for Robotics and Computer Vision Applications: An Overview
 Nonlinear State Estimation for Robotics and Computer Vision Applications: An Overview Arun Das 05/09/2017 Arun Das Waterloo Autonomous Vehicles Lab Introduction What s in a name? Arun Das Waterloo Autonomous
Nonlinear State Estimation for Robotics and Computer Vision Applications: An Overview Arun Das 05/09/2017 Arun Das Waterloo Autonomous Vehicles Lab Introduction What s in a name? Arun Das Waterloo Autonomous
Robotics. Lecture 5: Monte Carlo Localisation. See course website for up to date information.
 Robotics Lecture 5: Monte Carlo Localisation See course website http://www.doc.ic.ac.uk/~ajd/robotics/ for up to date information. Andrew Davison Department of Computing Imperial College London Review:
Robotics Lecture 5: Monte Carlo Localisation See course website http://www.doc.ic.ac.uk/~ajd/robotics/ for up to date information. Andrew Davison Department of Computing Imperial College London Review:
Teaching Assistant: Roi Yehoshua
 Teaching Assistant: Roi Yehoshua roiyeho@gmail.com Agenda ROS transformation system Writing a tf broadcaster Writing a tf listener What is tf? A robotic system typically has many coordinate frames that
Teaching Assistant: Roi Yehoshua roiyeho@gmail.com Agenda ROS transformation system Writing a tf broadcaster Writing a tf listener What is tf? A robotic system typically has many coordinate frames that
Robot Mapping. Least Squares Approach to SLAM. Cyrill Stachniss
 Robot Mapping Least Squares Approach to SLAM Cyrill Stachniss 1 Three Main SLAM Paradigms Kalman filter Particle filter Graphbased least squares approach to SLAM 2 Least Squares in General Approach for
Robot Mapping Least Squares Approach to SLAM Cyrill Stachniss 1 Three Main SLAM Paradigms Kalman filter Particle filter Graphbased least squares approach to SLAM 2 Least Squares in General Approach for
Graphbased. Kalman filter. Particle filter. Three Main SLAM Paradigms. Robot Mapping. Least Squares Approach to SLAM. Least Squares in General
 Robot Mapping Three Main SLAM Paradigms Least Squares Approach to SLAM Kalman filter Particle filter Graphbased Cyrill Stachniss least squares approach to SLAM 1 2 Least Squares in General! Approach for
Robot Mapping Three Main SLAM Paradigms Least Squares Approach to SLAM Kalman filter Particle filter Graphbased Cyrill Stachniss least squares approach to SLAM 1 2 Least Squares in General! Approach for
MTRX4700: Experimental Robotics
 Stefan B. Williams April, 2013 MTR4700: Experimental Robotics Assignment 3 Note: This assignment contributes 10% towards your final mark. This assignment is due on Friday, May 10 th during Week 9 before
Stefan B. Williams April, 2013 MTR4700: Experimental Robotics Assignment 3 Note: This assignment contributes 10% towards your final mark. This assignment is due on Friday, May 10 th during Week 9 before
Advanced Techniques for Mobile Robotics Graph-based SLAM using Least Squares. Wolfram Burgard, Cyrill Stachniss, Kai Arras, Maren Bennewitz
 Advanced Techniques for Mobile Robotics Graph-based SLAM using Least Squares Wolfram Burgard, Cyrill Stachniss, Kai Arras, Maren Bennewitz SLAM Constraints connect the poses of the robot while it is moving
Advanced Techniques for Mobile Robotics Graph-based SLAM using Least Squares Wolfram Burgard, Cyrill Stachniss, Kai Arras, Maren Bennewitz SLAM Constraints connect the poses of the robot while it is moving
COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Three-dimensional transformation geometry and perspective
 COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Three-dimensional transformation geometry and perspective Department of Computing and Information Systems The Lecture outline Introduction Rotation about artibrary axis
COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Three-dimensional transformation geometry and perspective Department of Computing and Information Systems The Lecture outline Introduction Rotation about artibrary axis
Humanoid Robotics. Least Squares. Maren Bennewitz
 Humanoid Robotics Least Squares Maren Bennewitz Goal of This Lecture Introduction into least squares Use it yourself for odometry calibration, later in the lecture: camera and whole-body self-calibration
Humanoid Robotics Least Squares Maren Bennewitz Goal of This Lecture Introduction into least squares Use it yourself for odometry calibration, later in the lecture: camera and whole-body self-calibration
Laser, Kinect, Gmapping, Localization, PathPlanning
 Soso s knowledge Laser, Kinect, Gmapping, Localization, PathPlanning Faculty of Information Technology, Brno University of Technology Bozetechova 2, 612 66 Brno name@fit.vutbr.cz 99.99.9999 Sensors Stereo
Soso s knowledge Laser, Kinect, Gmapping, Localization, PathPlanning Faculty of Information Technology, Brno University of Technology Bozetechova 2, 612 66 Brno name@fit.vutbr.cz 99.99.9999 Sensors Stereo
METR 4202: Advanced Control & Robotics
 Position & Orientation & State t home with Homogenous Transformations METR 4202: dvanced Control & Robotics Drs Surya Singh, Paul Pounds, and Hanna Kurniawati Lecture # 2 July 30, 2012 metr4202@itee.uq.edu.au
Position & Orientation & State t home with Homogenous Transformations METR 4202: dvanced Control & Robotics Drs Surya Singh, Paul Pounds, and Hanna Kurniawati Lecture # 2 July 30, 2012 metr4202@itee.uq.edu.au
MCE/EEC 647/747: Robot Dynamics and Control. Lecture 3: Forward and Inverse Kinematics
 MCE/EEC 647/747: Robot Dynamics and Control Lecture 3: Forward and Inverse Kinematics Denavit-Hartenberg Convention Reading: SHV Chapter 3 Mechanical Engineering Hanz Richter, PhD MCE503 p.1/12 Aims of
MCE/EEC 647/747: Robot Dynamics and Control Lecture 3: Forward and Inverse Kinematics Denavit-Hartenberg Convention Reading: SHV Chapter 3 Mechanical Engineering Hanz Richter, PhD MCE503 p.1/12 Aims of
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM)
 Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) RSS Lecture 16 April 8, 2013 Prof. Teller Text: Siegwart and Nourbakhsh S. 5.8 SLAM Problem Statement Inputs: No external coordinate reference Time series of
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) RSS Lecture 16 April 8, 2013 Prof. Teller Text: Siegwart and Nourbakhsh S. 5.8 SLAM Problem Statement Inputs: No external coordinate reference Time series of
The Kinematic Chain or Tree can be represented by a graph of links connected though joints between each Link and other links.
 Lab 3 URDF and Hydra Robot Models In this Lab we will learn how Unified Robot Description Format (URDF) describes robots and use it to design our own Robot. We will use the Ubuntu Linux editor gedit to
Lab 3 URDF and Hydra Robot Models In this Lab we will learn how Unified Robot Description Format (URDF) describes robots and use it to design our own Robot. We will use the Ubuntu Linux editor gedit to
Simultaneous local and global state estimation for robotic navigation
 Simultaneous local and global state estimation for robotic navigation The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As
Simultaneous local and global state estimation for robotic navigation The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As
Kinematics, Kinematics Chains CS 685
 Kinematics, Kinematics Chains CS 685 Previously Representation of rigid body motion Two different interpretations - as transformations between different coord. frames - as operators acting on a rigid body
Kinematics, Kinematics Chains CS 685 Previously Representation of rigid body motion Two different interpretations - as transformations between different coord. frames - as operators acting on a rigid body
Vision-based Mobile Robot Localization and Mapping using Scale-Invariant Features
 Vision-based Mobile Robot Localization and Mapping using Scale-Invariant Features Stephen Se, David Lowe, Jim Little Department of Computer Science University of British Columbia Presented by Adam Bickett
Vision-based Mobile Robot Localization and Mapping using Scale-Invariant Features Stephen Se, David Lowe, Jim Little Department of Computer Science University of British Columbia Presented by Adam Bickett
Programming for Robotics Introduction to ROS
 Programming for Robotics Introduction to ROS Course 3 Péter Fankhauser, Dominic Jud, Martin Wermelinger Prof. Dr. Marco Hutter Péter Fankhauser 24.02.2017 1 Course Structure Course 1 Course 2 Course 3
Programming for Robotics Introduction to ROS Course 3 Péter Fankhauser, Dominic Jud, Martin Wermelinger Prof. Dr. Marco Hutter Péter Fankhauser 24.02.2017 1 Course Structure Course 1 Course 2 Course 3
Lecture 14: Basic Multi-View Geometry
 Lecture 14: Basic Multi-View Geometry Stereo If I needed to find out how far point is away from me, I could use triangulation and two views scene point image plane optical center (Graphic from Khurram
Lecture 14: Basic Multi-View Geometry Stereo If I needed to find out how far point is away from me, I could use triangulation and two views scene point image plane optical center (Graphic from Khurram
Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates
 433-324 Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction Vectors and matrices Translation
433-324 Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction Vectors and matrices Translation
COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates
 COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction Vectors and matrices Translation
COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction Vectors and matrices Translation
Overview. EECS 124, UC Berkeley, Spring 2008 Lecture 23: Localization and Mapping. Statistical Models
 Introduction ti to Embedded dsystems EECS 124, UC Berkeley, Spring 2008 Lecture 23: Localization and Mapping Gabe Hoffmann Ph.D. Candidate, Aero/Astro Engineering Stanford University Statistical Models
Introduction ti to Embedded dsystems EECS 124, UC Berkeley, Spring 2008 Lecture 23: Localization and Mapping Gabe Hoffmann Ph.D. Candidate, Aero/Astro Engineering Stanford University Statistical Models
3 Problems You Need to Tackle when Developing Robot Software
 ROS : Robot Operating System RSS Technical Lecture 6 Monday, February 27 th, 2012 Michael Fleder MIT 6-3, MEng, PhD 1 3 Problems You Need to Tackle when Developing Robot Software (1) Sequential programming
ROS : Robot Operating System RSS Technical Lecture 6 Monday, February 27 th, 2012 Michael Fleder MIT 6-3, MEng, PhD 1 3 Problems You Need to Tackle when Developing Robot Software (1) Sequential programming
Robot Mapping. SLAM Front-Ends. Cyrill Stachniss. Partial image courtesy: Edwin Olson 1
 Robot Mapping SLAM Front-Ends Cyrill Stachniss Partial image courtesy: Edwin Olson 1 Graph-Based SLAM Constraints connect the nodes through odometry and observations Robot pose Constraint 2 Graph-Based
Robot Mapping SLAM Front-Ends Cyrill Stachniss Partial image courtesy: Edwin Olson 1 Graph-Based SLAM Constraints connect the nodes through odometry and observations Robot pose Constraint 2 Graph-Based
ECE276A: Sensing & Estimation in Robotics Lecture 11: Simultaneous Localization and Mapping using a Particle Filter
 ECE276A: Sensing & Estimation in Robotics Lecture 11: Simultaneous Localization and Mapping using a Particle Filter Lecturer: Nikolay Atanasov: natanasov@ucsd.edu Teaching Assistants: Siwei Guo: s9guo@eng.ucsd.edu
ECE276A: Sensing & Estimation in Robotics Lecture 11: Simultaneous Localization and Mapping using a Particle Filter Lecturer: Nikolay Atanasov: natanasov@ucsd.edu Teaching Assistants: Siwei Guo: s9guo@eng.ucsd.edu
Data Association for SLAM
 CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ME/CS 132a, Winter 2011 Lab #2 Due: Mar 10th, 2011 Part I Data Association for SLAM 1 Introduction For this part, you will experiment with a simulation of an EKF SLAM
CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ME/CS 132a, Winter 2011 Lab #2 Due: Mar 10th, 2011 Part I Data Association for SLAM 1 Introduction For this part, you will experiment with a simulation of an EKF SLAM
Autonomous Navigation for Flying Robots
 Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers Autonomous Navigation for Flying Robots Lecture 3.1: 3D Geometry Jürgen Sturm Technische Universität München Points in 3D 3D point Augmented vector Homogeneous
Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers Autonomous Navigation for Flying Robots Lecture 3.1: 3D Geometry Jürgen Sturm Technische Universität München Points in 3D 3D point Augmented vector Homogeneous
ROS tf System February, Janyl Jumadinova
 ROS tf System 13-15 February, 2017 Janyl Jumadinova What is tf? A robotic system typically has many coordinate frames that change over time, such as a world frame, base frame, gripper frame, head frame,
ROS tf System 13-15 February, 2017 Janyl Jumadinova What is tf? A robotic system typically has many coordinate frames that change over time, such as a world frame, base frame, gripper frame, head frame,
5. Tests and results Scan Matching Optimization Parameters Influence
 126 5. Tests and results This chapter presents results obtained using the proposed method on simulated and real data. First, it is analyzed the scan matching optimization; after that, the Scan Matching
126 5. Tests and results This chapter presents results obtained using the proposed method on simulated and real data. First, it is analyzed the scan matching optimization; after that, the Scan Matching
Simultaneous Localization
 Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) RSS Technical Lecture 16 April 9, 2012 Prof. Teller Text: Siegwart and Nourbakhsh S. 5.8 Navigation Overview Where am I? Where am I going? Localization Assumed
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) RSS Technical Lecture 16 April 9, 2012 Prof. Teller Text: Siegwart and Nourbakhsh S. 5.8 Navigation Overview Where am I? Where am I going? Localization Assumed
CSE 490R P1 - Localization using Particle Filters Due date: Sun, Jan 28-11:59 PM
 CSE 490R P1 - Localization using Particle Filters Due date: Sun, Jan 28-11:59 PM 1 Introduction In this assignment you will implement a particle filter to localize your car within a known map. This will
CSE 490R P1 - Localization using Particle Filters Due date: Sun, Jan 28-11:59 PM 1 Introduction In this assignment you will implement a particle filter to localize your car within a known map. This will
Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Kinematics 3
 Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Kinematics 3 151-0851-00 V lecture: CAB G11 Tuesday 10:15 12:00, every week exercise: HG E1.2 Wednesday 8:15 10:00, according to schedule (about every 2nd week) office hour: LEE
Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Kinematics 3 151-0851-00 V lecture: CAB G11 Tuesday 10:15 12:00, every week exercise: HG E1.2 Wednesday 8:15 10:00, according to schedule (about every 2nd week) office hour: LEE
Preface...vii. Printed vs PDF Versions of the Book...ix. 1. Scope of this Volume Installing the ros-by-example Code...3
 Contents Preface...vii Printed vs PDF Versions of the Book...ix 1. Scope of this Volume...1 2. Installing the ros-by-example Code...3 3. Task Execution using ROS...7 3.1 A Fake Battery Simulator...8 3.2
Contents Preface...vii Printed vs PDF Versions of the Book...ix 1. Scope of this Volume...1 2. Installing the ros-by-example Code...3 3. Task Execution using ROS...7 3.1 A Fake Battery Simulator...8 3.2
Using the ikart mobile platform
 Using the mobile platform Marco Randazzo Sestri Levante, July 23th, 2012 General description A holonomic mobile base for icub: Omnidirectional movement (six omnidirectional wheels) Integrates an high-performance
Using the mobile platform Marco Randazzo Sestri Levante, July 23th, 2012 General description A holonomic mobile base for icub: Omnidirectional movement (six omnidirectional wheels) Integrates an high-performance
DD2429 Computational Photography :00-19:00
 . Examination: DD2429 Computational Photography 202-0-8 4:00-9:00 Each problem gives max 5 points. In order to pass you need about 0-5 points. You are allowed to use the lecture notes and standard list
. Examination: DD2429 Computational Photography 202-0-8 4:00-9:00 Each problem gives max 5 points. In order to pass you need about 0-5 points. You are allowed to use the lecture notes and standard list
+ i a y )( cosφ + isinφ) ( ) + i( a x. cosφ a y. = a x
 Rotation Matrices and Rotated Coordinate Systems Robert Bernecky April, 2018 Rotated Coordinate Systems is a confusing topic, and there is no one standard or approach 1. The following provides a simplified
Rotation Matrices and Rotated Coordinate Systems Robert Bernecky April, 2018 Rotated Coordinate Systems is a confusing topic, and there is no one standard or approach 1. The following provides a simplified
θ x Week Date Lecture (M: 2:05p-3:50, 50-N202) 1 23-Jul Introduction + Representing Position & Orientation & State 2 30-Jul
 θ x 2018 School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering at the University of Queensland Lecture Schedule Week Date Lecture (M: 2:05p-3:50, 50-N202) 1 23-Jul Introduction + Representing Position
θ x 2018 School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering at the University of Queensland Lecture Schedule Week Date Lecture (M: 2:05p-3:50, 50-N202) 1 23-Jul Introduction + Representing Position
CS283: Robotics Fall 2016: Software
 CS283: Robotics Fall 2016: Software Sören Schwertfeger / 师泽仁 ShanghaiTech University Mobile Robotics ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 18.09.2016 2 Review Definition Robot: A machine capable of performing
CS283: Robotics Fall 2016: Software Sören Schwertfeger / 师泽仁 ShanghaiTech University Mobile Robotics ShanghaiTech University - SIST - 18.09.2016 2 Review Definition Robot: A machine capable of performing
ME5286 Robotics Spring 2014 Quiz 1 Solution. Total Points: 30
 Page 1 of 7 ME5286 Robotics Spring 2014 Quiz 1 Solution Total Points: 30 (Note images from original quiz are not included to save paper/ space. Please see the original quiz for additional information and
Page 1 of 7 ME5286 Robotics Spring 2014 Quiz 1 Solution Total Points: 30 (Note images from original quiz are not included to save paper/ space. Please see the original quiz for additional information and
2D/3D Geometric Transformations and Scene Graphs
 2D/3D Geometric Transformations and Scene Graphs Week 4 Acknowledgement: The course slides are adapted from the slides prepared by Steve Marschner of Cornell University 1 A little quick math background
2D/3D Geometric Transformations and Scene Graphs Week 4 Acknowledgement: The course slides are adapted from the slides prepared by Steve Marschner of Cornell University 1 A little quick math background
RIGID IMAGE REGISTRATION
 RIGID IMAGE REGISTRATION Duygu Tosun-Turgut, Ph.D. Center for Imaging of Neurodegenerative Diseases Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging duygu.tosun@ucsf.edu What is registration? Image registration
RIGID IMAGE REGISTRATION Duygu Tosun-Turgut, Ph.D. Center for Imaging of Neurodegenerative Diseases Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging duygu.tosun@ucsf.edu What is registration? Image registration
ME 597: AUTONOMOUS MOBILE ROBOTICS SECTION 2 COORDINATE TRANSFORMS. Prof. Steven Waslander
 ME 597: AUTONOMOUS MOILE ROOTICS SECTION 2 COORDINATE TRANSFORMS Prof. Steven Waslander OUTLINE Coordinate Frames and Transforms Rotation Matrices Euler Angles Quaternions Homogeneous Transforms 2 COORDINATE
ME 597: AUTONOMOUS MOILE ROOTICS SECTION 2 COORDINATE TRANSFORMS Prof. Steven Waslander OUTLINE Coordinate Frames and Transforms Rotation Matrices Euler Angles Quaternions Homogeneous Transforms 2 COORDINATE
Hello, welcome to the video lecture series on Digital Image Processing. So in today's lecture
 Digital Image Processing Prof. P. K. Biswas Department of Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Module 02 Lecture Number 10 Basic Transform (Refer
Digital Image Processing Prof. P. K. Biswas Department of Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Module 02 Lecture Number 10 Basic Transform (Refer
Robot Mapping. Graph-Based SLAM with Landmarks. Cyrill Stachniss
 Robot Mapping Graph-Based SLAM with Landmarks Cyrill Stachniss 1 Graph-Based SLAM (Chap. 15) Use a graph to represent the problem Every node in the graph corresponds to a pose of the robot during mapping
Robot Mapping Graph-Based SLAM with Landmarks Cyrill Stachniss 1 Graph-Based SLAM (Chap. 15) Use a graph to represent the problem Every node in the graph corresponds to a pose of the robot during mapping
Introduction to Mobile Robotics
 Introduction to Mobile Robotics Olivier Aycard Associate Professor University of Grenoble Laboratoire d Informatique de Grenoble http://membres-liglab.imag.fr/aycard olivier. 1/22 What is a robot? Robot
Introduction to Mobile Robotics Olivier Aycard Associate Professor University of Grenoble Laboratoire d Informatique de Grenoble http://membres-liglab.imag.fr/aycard olivier. 1/22 What is a robot? Robot
Visual Recognition: Image Formation
 Visual Recognition: Image Formation Raquel Urtasun TTI Chicago Jan 5, 2012 Raquel Urtasun (TTI-C) Visual Recognition Jan 5, 2012 1 / 61 Today s lecture... Fundamentals of image formation You should know
Visual Recognition: Image Formation Raquel Urtasun TTI Chicago Jan 5, 2012 Raquel Urtasun (TTI-C) Visual Recognition Jan 5, 2012 1 / 61 Today s lecture... Fundamentals of image formation You should know
INDOOR AND OUTDOOR LOCALIZATION OF A MOBILE ROBOT FUSING SENSOR DATA. A Thesis Presented. Md Maruf Ibne Hasan
 INDOOR AND OUTDOOR LOCALIZATION OF A MOBILE ROBOT FUSING SENSOR DATA A Thesis Presented By Md Maruf Ibne Hasan to The Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering in partial fulfillment of the requirements
INDOOR AND OUTDOOR LOCALIZATION OF A MOBILE ROBOT FUSING SENSOR DATA A Thesis Presented By Md Maruf Ibne Hasan to The Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering in partial fulfillment of the requirements
Introducing MoveIt! First, start the Baxter simulator in Gazebo:
 Introducing MoveIt! One of the challenging aspects of robotics is defining a path for the motion of a robot's arms to grasp an object, especially when obstacles may obstruct the most obvious path of motion.
Introducing MoveIt! One of the challenging aspects of robotics is defining a path for the motion of a robot's arms to grasp an object, especially when obstacles may obstruct the most obvious path of motion.
CS 445 / 645 Introduction to Computer Graphics. Lecture 21 Representing Rotations
 CS 445 / 645 Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture 21 Representing Rotations Parameterizing Rotations Straightforward in 2D A scalar, θ, represents rotation in plane More complicated in 3D Three scalars
CS 445 / 645 Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture 21 Representing Rotations Parameterizing Rotations Straightforward in 2D A scalar, θ, represents rotation in plane More complicated in 3D Three scalars
Mobile Robots: An Introduction.
 Mobile Robots: An Introduction Amirkabir University of Technology Computer Engineering & Information Technology Department http://ce.aut.ac.ir/~shiry/lecture/robotics-2004/robotics04.html Introduction
Mobile Robots: An Introduction Amirkabir University of Technology Computer Engineering & Information Technology Department http://ce.aut.ac.ir/~shiry/lecture/robotics-2004/robotics04.html Introduction
Computer Graphics 7: Viewing in 3-D
 Computer Graphics 7: Viewing in 3-D In today s lecture we are going to have a look at: Transformations in 3-D How do transformations in 3-D work? Contents 3-D homogeneous coordinates and matrix based transformations
Computer Graphics 7: Viewing in 3-D In today s lecture we are going to have a look at: Transformations in 3-D How do transformations in 3-D work? Contents 3-D homogeneous coordinates and matrix based transformations
COMP3431 Robot Software Architectures
 COMP3431 Robot Software Architectures Week 2 ROS Continued David Rajaratnam Click to edit Present s Name ROS Continued What we're doing today: Recap from last week Example of turtlebot setup Frames of
COMP3431 Robot Software Architectures Week 2 ROS Continued David Rajaratnam Click to edit Present s Name ROS Continued What we're doing today: Recap from last week Example of turtlebot setup Frames of
Lecture 18: Voronoi Graphs and Distinctive States. Problem with Metrical Maps
 Lecture 18: Voronoi Graphs and Distinctive States CS 344R/393R: Robotics Benjamin Kuipers Problem with Metrical Maps Metrical maps are nice, but they don t scale. Storage requirements go up with the square
Lecture 18: Voronoi Graphs and Distinctive States CS 344R/393R: Robotics Benjamin Kuipers Problem with Metrical Maps Metrical maps are nice, but they don t scale. Storage requirements go up with the square
Today. Parity. General Polygons? Non-Zero Winding Rule. Winding Numbers. CS559 Lecture 11 Polygons, Transformations
 CS559 Lecture Polygons, Transformations These are course notes (not used as slides) Written by Mike Gleicher, Oct. 005 With some slides adapted from the notes of Stephen Chenney Final version (after class)
CS559 Lecture Polygons, Transformations These are course notes (not used as slides) Written by Mike Gleicher, Oct. 005 With some slides adapted from the notes of Stephen Chenney Final version (after class)
Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Multi-body Kinematics
 Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Multi-body Kinematics 151-0851-00 V lecture: CAB G11 Tuesday 10:15 12:00, every week exercise: HG E1.2 Wednesday 8:15 10:00, according to schedule (about every 2nd week) Marco
Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Multi-body Kinematics 151-0851-00 V lecture: CAB G11 Tuesday 10:15 12:00, every week exercise: HG E1.2 Wednesday 8:15 10:00, according to schedule (about every 2nd week) Marco
Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Kinematics 3
 Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Kinematics 3 151-0851-00 V lecture: CAB G11 Tuesday 10:15 12:00, every week exercise: HG E1.2 Wednesday 8:15 10:00, according to schedule (about every 2nd week) Marco Hutter,
Lecture «Robot Dynamics»: Kinematics 3 151-0851-00 V lecture: CAB G11 Tuesday 10:15 12:00, every week exercise: HG E1.2 Wednesday 8:15 10:00, according to schedule (about every 2nd week) Marco Hutter,
W4. Perception & Situation Awareness & Decision making
 W4. Perception & Situation Awareness & Decision making Robot Perception for Dynamic environments: Outline & DP-Grids concept Dynamic Probabilistic Grids Bayesian Occupancy Filter concept Dynamic Probabilistic
W4. Perception & Situation Awareness & Decision making Robot Perception for Dynamic environments: Outline & DP-Grids concept Dynamic Probabilistic Grids Bayesian Occupancy Filter concept Dynamic Probabilistic
CSE 490R P3 - Model Learning and MPPI Due date: Sunday, Feb 28-11:59 PM
 CSE 490R P3 - Model Learning and MPPI Due date: Sunday, Feb 28-11:59 PM 1 Introduction In this homework, we revisit the concept of local control for robot navigation, as well as integrate our local controller
CSE 490R P3 - Model Learning and MPPI Due date: Sunday, Feb 28-11:59 PM 1 Introduction In this homework, we revisit the concept of local control for robot navigation, as well as integrate our local controller
CSE 527: Introduction to Computer Vision
 CSE 527: Introduction to Computer Vision Week 10 Class 2: Visual Odometry November 2nd, 2017 Today Visual Odometry Intro Algorithm SLAM Visual Odometry Input Output Images, Video Camera trajectory, motion
CSE 527: Introduction to Computer Vision Week 10 Class 2: Visual Odometry November 2nd, 2017 Today Visual Odometry Intro Algorithm SLAM Visual Odometry Input Output Images, Video Camera trajectory, motion
Forward kinematics and Denavit Hartenburg convention
 Forward kinematics and Denavit Hartenburg convention Prof. Enver Tatlicioglu Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Izmir Institute of Technology Chapter 5 Dr. Tatlicioglu (EEE@IYTE) EE463
Forward kinematics and Denavit Hartenburg convention Prof. Enver Tatlicioglu Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Izmir Institute of Technology Chapter 5 Dr. Tatlicioglu (EEE@IYTE) EE463
GEOMETRIC TRANSFORMATIONS AND VIEWING
 GEOMETRIC TRANSFORMATIONS AND VIEWING 2D and 3D 1/44 2D TRANSFORMATIONS HOMOGENIZED Transformation Scaling Rotation Translation Matrix s x s y cosθ sinθ sinθ cosθ 1 dx 1 dy These 3 transformations are
GEOMETRIC TRANSFORMATIONS AND VIEWING 2D and 3D 1/44 2D TRANSFORMATIONS HOMOGENIZED Transformation Scaling Rotation Translation Matrix s x s y cosθ sinθ sinθ cosθ 1 dx 1 dy These 3 transformations are
Vector Calculus: Understanding the Cross Product
 University of Babylon College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Dept. Subject : Mathematics III Class : 2 nd year - first semester Date: / 10 / 2016 2016 \ 2017 Vector Calculus: Understanding the Cross
University of Babylon College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Dept. Subject : Mathematics III Class : 2 nd year - first semester Date: / 10 / 2016 2016 \ 2017 Vector Calculus: Understanding the Cross
Robotics (Kinematics) Winter 1393 Bonab University
 Robotics () Winter 1393 Bonab University : most basic study of how mechanical systems behave Introduction Need to understand the mechanical behavior for: Design Control Both: Manipulators, Mobile Robots
Robotics () Winter 1393 Bonab University : most basic study of how mechanical systems behave Introduction Need to understand the mechanical behavior for: Design Control Both: Manipulators, Mobile Robots
Teaching Assistant: Roi Yehoshua
 Teaching Assistant: Roi Yehoshua roiyeho@gmail.com Agenda ROS navigation stack Navigation planners Costmaps Running ROS navigation with Stage and rviz Sending goal commands ROS Navigation Stack http://wiki.ros.org/navigation
Teaching Assistant: Roi Yehoshua roiyeho@gmail.com Agenda ROS navigation stack Navigation planners Costmaps Running ROS navigation with Stage and rviz Sending goal commands ROS Navigation Stack http://wiki.ros.org/navigation
IntroductionToRobotics-Lecture02
 IntroductionToRobotics-Lecture02 Instructor (Oussama Khatib):Okay. Let's get started. So as always, the lecture starts with a video segment, and today's video segment comes from 1991, and from the group
IntroductionToRobotics-Lecture02 Instructor (Oussama Khatib):Okay. Let's get started. So as always, the lecture starts with a video segment, and today's video segment comes from 1991, and from the group
Introduction to Robotics
 Introduction to Robotics Ph.D. Antonio Marin-Hernandez Artificial Intelligence Department Universidad Veracruzana Sebastian Camacho # 5 Xalapa, Veracruz Robotics Action and Perception LAAS-CNRS 7, av du
Introduction to Robotics Ph.D. Antonio Marin-Hernandez Artificial Intelligence Department Universidad Veracruzana Sebastian Camacho # 5 Xalapa, Veracruz Robotics Action and Perception LAAS-CNRS 7, av du
Spring 2010: Lecture 9. Ashutosh Saxena. Ashutosh Saxena
 CS 4758/6758: Robot Learning Spring 2010: Lecture 9 Why planning and control? Video Typical Architecture Planning 0.1 Hz Control 50 Hz Does it apply to all robots and all scenarios? Previous Lecture: Potential
CS 4758/6758: Robot Learning Spring 2010: Lecture 9 Why planning and control? Video Typical Architecture Planning 0.1 Hz Control 50 Hz Does it apply to all robots and all scenarios? Previous Lecture: Potential
