Aliasing. Can t draw smooth lines on discrete raster device get staircased lines ( jaggies ):
|
|
|
- Buck Conley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (Anti)Aliasing and Image Manipulation for (y = 0; y < Size; y++) { for (x = 0; x < Size; x++) { Image[x][y] = * sin((sqr(x Size) + SQR(y Size)) / 3.0); } } // Size = Size / ;
2 Aliasing Can t draw smooth lines on discrete raster device get staircased lines ( jaggies ): Images with too fine details create artifacts (Moire patterns) Why? How to solve? Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion
3 Antialiasing Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 3
4 Antialiasing Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 4
5 Sampling D raster image = discrete sampling of continuous image (signal) Consider D signal sampling Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 5
6 Sampling D raster image = discrete sampling of continuous image (signal) Consider D signal sampling Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 6
7 Sampling D raster image = discrete sampling of continuous image (signal) Consider D signal sampling Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 7
8 Sampling D raster image = discrete sampling of continuous image (signal) Consider D signal sampling Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 8
9 Sampling Theory in a Nutshell Terminology Cycle a repeated sequence over infinite signal Frequency number of cycles in a unit length Example sine wave Cycle = π Frequency = / π Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 9
10 Sampling Theory Theorem: Any periodic signal can be represented as (infinite) sum of sine waves, at different frequencies Can represent signal using coefficients of the sine waves - alternative basis used by Fourier Analysis Fourier Transform- Tool to transform to/from sine basis, to/from the frequency domain Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 0
11 Example A square wave is represented by infinite sum sin(3t) sin(5t) SqrWave( t) = sin( t) First few components: Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion
12 Shannon Sampling Theorem Shannon Theorem: Any signal that is band-limited to frequency f max and sampled at equally spaced intervals smaller than t s = /(f max ) can be fully reconstructed The minimal sampling frequency of t s = /(f max ) is called the Nyquist frequency of the signal That this condition is necessary can be trivially shown: Question: What is the result of this sampling? Aliasing! Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion
13 More Aliasing Examples Sampling high frequency wave below Nyquist frequency yields results that look like a low frequency wave The appearance of high frequencies as low frequencies, due to sampling, is called Aliasing: Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 3
14 Even More Aliasing Examples Consider two sine waves: -sin(3t) and sin(5t): -sin(3t) = sin(5t) is satisfied for t = π n / 4 Sampling sin(5t) at t i = π i / 4 looks like sampling sin(3t) Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 4
15 Aliasing Aliasing the appearance of high frequencies as low frequencies To avoid Sample at a higher frequency - only if band-limited to begin with A-priori remove high frequencies Low pass filtering before sampling For images the discrete image is a sampling set of a continuous image (band limits?) Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 5
16 The Fourier Transform Takes us from the spatial domain to the frequency domain: F( t) = f ( x) e itx dx The inverse Fourier transform equals f ( t) = F( x) π e itx dx We will see some examples shortly Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 6
17 Convolution The convolution, denoted by *, is defined as: ( f * g)( x) = f ( t) g( x t) dt Question Question: What is the intuition behind the convolution operation? Theorem: Convolution in the spatial domain is the same as a multiplication in the frequency domain and vice-versa Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 7
18 The Fourier Transform (cont d) Question: What is the Fourier transform of a hat? Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 8
19 Convolution Consider an f max band-limited signal. Sampling is the same as multiplying the signal with equally spaced impulse functions δ(x): By the theorem, this operation is equivalent to a convolution in the frequency domain: Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 9
20 Convolution (cont d) During the reconstruction process, we apply a low pass filter that removes all frequencies above f max This ideal filter is a box filter in the frequency domain: Samples that are less dense in the spatial domain will become more dense in the frequency domain Question: What will happen if we sample below the Nyquist limit Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 0
21 We will get aliasing: Convolution (cont d) The different convolved elements, in the frequency domain, overlap. We have high frequencies intermixed with low frequencies and they are inseparable. The only way to prevent aliasing is pre-filtering Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion
22 Back to Computer Graphics Question: how all this sampling theory relates to computer graphics? When a discrete image I d (x,y) is created, we are effectively generating a sample set of a (possibly imaginary) continuous image I c (x,y) Extending sampling theory to two dimensions: I c (x,y) should be band-limited for it to be reconstructable Sampling should be above the Nyquist limit for I c (x,y) to be reconstructable The box filter in the frequency domain is the ideal low-pass filter (what is it in the spatial domain?) Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion
23 Back to Computer Graphics (cont d) Question: is I c (x,y) band-limited? Question: can we pre-filter I c (x,y)? One can reduce aliasing by super-sampling Question: can we post-filter the data using convolution with a sinc filter in the spatial domain? sin ( ) x + y x + y Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 3
24 Sinc/Truncated sinc Box ) sin( y x y x + + and, y x Common Filters Aliasing Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 4 Triangle (Hat) Guassian otherwise 0, + + otherwise 0,, y x y x y x e + π
25 Common Filters (cont d) All filters are normalized so they sum to one. Why? Due to obvious reasons we cannot apply the infinite filters and must compromise on the truncated versions Note the sinc filter can assume negative values which is a potential for minor problems. Why? The difference between different filters are quite minor and most filters of size 4 4 offers similar improvements Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 5
26 Filter results Unfiltered Box Gaussian Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 6
27 Supersampling Example None 3x3 5x5 Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 7
28 A Word on Temporal Aliasing So far we dealt with Spatial Aliasing In animation, aliasing could also occur between one frame and the next This aliasing is known as Temporal Aliasing Recall that in a movie each frame represents a finite time range of /5 or /30 of a second. Hence, it would serve better to accumulate the influence of moving objects over this time Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 8
29 The technique of Motion Blur accumulates the affect of each object over the time step of the frame The result will look like the image on the right Playing animation with motion blur is more natural to the eye Motion Blur Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 9
30 Image Manipulation Image operations Scaling Rotation Composition Scientific American, Feb 994 Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 30
31 Image Scaling & Rotation Consider Linear Transformation L of image I: ImageLinTrans( I, L) clear I to background color For x from 0 to XMax(I) For y from 0 to YMax(I) I( L( x, y)) = I( x, y); What is wrong with this algorithm? Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 3
32 Correct Image Scaling & Rotation Guarantee coverage iterate over target ImageLinTrans( I, L) clear For For I to background color x from 0 to I( x, y) = XMax(I) y from 0 to YMax(I) I( L ( x, y)); What can be wrong with this algorithm? Any reason to limit L to a linear transformations? Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 3
33 Image Transformations Each pixel in the target image is computed from a single source pixel prone to Aliasing Solution in filtering A pixel in target image is some affine combination of several source pixels Coefficients based on area coverage Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 33
34 Rotation By Shear Convenient for images as it involved only intra-row or intra-column operations Rotation can be performed by two shears can be lossy for large angles x cosθ = y sinθ Image size might be reduced in intermediate stage Rotation by three shears is lossless up to integer precision. cosθ sinθ 0 sinθ 0 = θ θ sinθ cosθ tan 0 tan Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 34 sinθ x cosθ y
35 Image Composition + = Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 35
36 Basic Method Composition ImageOverC ompose(, I clear I to background color For x from 0 to XMax(I) For y from 0 to YMax(I) if I ( x, y) = background I ( x, y) = I else I ( x, y) = I I ) ( x, y); ( x, y); color Will work until portion of foreground has background color Unfortunately we are facing more problems Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 36
37 Composition (cont d) Question: This is the result of applying the basic algorithm to teapot-over-whitebackground. What is going on? Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 37
38 Composition (cont d) The reason for this behavior could be found in the filtering (anti-aliasing) conducted during the rendering process On the boundary there exist pixels that are only partially covered by the teapot Rendered with black background, these boundary pixels are darker Yet, as dark as they are, they are not black and hence they are being copied verbatim Question: Any remedy? Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 38
39 Composition (cont d) A background pixel has zero coverage while a pixel totally contained in the teapot s projection will have a coverage of one. This coverage information is also known as the Alpha channel that accompanies the RGB Question: How can we compute the Alpha channel? Question: How can we use the Alpha channel to resolve this boundary problem? Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 39
40 Composition (cont d) T Teapot, S - Sand Over: Tα T + S( -α T ) Out: S( -α T ) In: Sα T Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 40
41 Composition (cont d) Scientific American, Feb 994 Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 4
42 Special Effects Chroma Key Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 4
43 Special Effects Chroma Key II Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 43
44 Special Effects No Blue Background Aliasing - Center for Graphics and Geometric Computing, Technion 44
Theoretically Perfect Sensor
 Sampling 1/60 Sampling The ray tracer samples the geometry, only gathering information from the parts of the world that interact with a finite number of rays In contrast, a scanline renderer can push all
Sampling 1/60 Sampling The ray tracer samples the geometry, only gathering information from the parts of the world that interact with a finite number of rays In contrast, a scanline renderer can push all
Theoretically Perfect Sensor
 Sampling 1/67 Sampling The ray tracer samples the geometry, only gathering information from the parts of the world that interact with a finite number of rays In contrast, a scanline renderer can push all
Sampling 1/67 Sampling The ray tracer samples the geometry, only gathering information from the parts of the world that interact with a finite number of rays In contrast, a scanline renderer can push all
Aliasing and Antialiasing. ITCS 4120/ Aliasing and Antialiasing
 Aliasing and Antialiasing ITCS 4120/5120 1 Aliasing and Antialiasing What is Aliasing? Errors and Artifacts arising during rendering, due to the conversion from a continuously defined illumination field
Aliasing and Antialiasing ITCS 4120/5120 1 Aliasing and Antialiasing What is Aliasing? Errors and Artifacts arising during rendering, due to the conversion from a continuously defined illumination field
The main goal of Computer Graphics is to generate 2D images 2D images are continuous 2D functions (or signals)
 Motivation The main goal of Computer Graphics is to generate 2D images 2D images are continuous 2D functions (or signals) monochrome f(x,y) or color r(x,y), g(x,y), b(x,y) These functions are represented
Motivation The main goal of Computer Graphics is to generate 2D images 2D images are continuous 2D functions (or signals) monochrome f(x,y) or color r(x,y), g(x,y), b(x,y) These functions are represented
Motivation. The main goal of Computer Graphics is to generate 2D images. 2D images are continuous 2D functions (or signals)
 Motivation The main goal of Computer Graphics is to generate 2D images 2D images are continuous 2D functions (or signals) monochrome f(x,y) or color r(x,y), g(x,y), b(x,y) These functions are represented
Motivation The main goal of Computer Graphics is to generate 2D images 2D images are continuous 2D functions (or signals) monochrome f(x,y) or color r(x,y), g(x,y), b(x,y) These functions are represented
To Do. Advanced Computer Graphics. Sampling and Reconstruction. Outline. Sign up for Piazza
 Advanced Computer Graphics CSE 63 [Spring 207], Lecture 3 Ravi Ramamoorthi http://www.cs.ucsd.edu/~ravir Sign up for Piazza To Do Assignment, Due Apr 28. Anyone need help finding partners? Any issues with
Advanced Computer Graphics CSE 63 [Spring 207], Lecture 3 Ravi Ramamoorthi http://www.cs.ucsd.edu/~ravir Sign up for Piazza To Do Assignment, Due Apr 28. Anyone need help finding partners? Any issues with
Advanced Computer Graphics. Aliasing. Matthias Teschner. Computer Science Department University of Freiburg
 Advanced Computer Graphics Aliasing Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline motivation Fourier analysis filtering sampling reconstruction / aliasing antialiasing University
Advanced Computer Graphics Aliasing Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline motivation Fourier analysis filtering sampling reconstruction / aliasing antialiasing University
Image Filtering, Warping and Sampling
 Image Filtering, Warping and Sampling Connelly Barnes CS 4810 University of Virginia Acknowledgement: slides by Jason Lawrence, Misha Kazhdan, Allison Klein, Tom Funkhouser, Adam Finkelstein and David
Image Filtering, Warping and Sampling Connelly Barnes CS 4810 University of Virginia Acknowledgement: slides by Jason Lawrence, Misha Kazhdan, Allison Klein, Tom Funkhouser, Adam Finkelstein and David
Sampling and Reconstruction
 Page 1 Sampling and Reconstruction The sampling and reconstruction process Real world: continuous Digital world: discrete Basic signal processing Fourier transforms The convolution theorem The sampling
Page 1 Sampling and Reconstruction The sampling and reconstruction process Real world: continuous Digital world: discrete Basic signal processing Fourier transforms The convolution theorem The sampling
CS354 Computer Graphics Sampling and Aliasing
 Slide Credit: http://www.siggraph.org/education/materials/hypergraph/aliasing/alias0.htm CS354 Computer Graphics Sampling and Aliasing Qixing Huang February 12th 2018 Sampling and Aliasing Display is discrete
Slide Credit: http://www.siggraph.org/education/materials/hypergraph/aliasing/alias0.htm CS354 Computer Graphics Sampling and Aliasing Qixing Huang February 12th 2018 Sampling and Aliasing Display is discrete
Lecture 6 Basic Signal Processing
 Lecture 6 Basic Signal Processing Copyright c1996, 1997 by Pat Hanrahan Motivation Many aspects of computer graphics and computer imagery differ from aspects of conventional graphics and imagery because
Lecture 6 Basic Signal Processing Copyright c1996, 1997 by Pat Hanrahan Motivation Many aspects of computer graphics and computer imagery differ from aspects of conventional graphics and imagery because
Computer Graphics. Sampling Theory & Anti-Aliasing. Philipp Slusallek
 Computer Graphics Sampling Theory & Anti-Aliasing Philipp Slusallek Dirac Comb (1) Constant & δ-function flash Comb/Shah function 2 Dirac Comb (2) Constant & δ-function Duality f(x) = K F(ω) = K (ω) And
Computer Graphics Sampling Theory & Anti-Aliasing Philipp Slusallek Dirac Comb (1) Constant & δ-function flash Comb/Shah function 2 Dirac Comb (2) Constant & δ-function Duality f(x) = K F(ω) = K (ω) And
Drawing a Triangle (and an introduction to sampling)
 Lecture 4: Drawing a Triangle (and an introduction to sampling) Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Spring 2017 Assignment 1 is out! https://15462-s17.github.io/asst1_drawsvg/ Let s draw some triangles
Lecture 4: Drawing a Triangle (and an introduction to sampling) Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Spring 2017 Assignment 1 is out! https://15462-s17.github.io/asst1_drawsvg/ Let s draw some triangles
Computer Vision and Graphics (ee2031) Digital Image Processing I
 Computer Vision and Graphics (ee203) Digital Image Processing I Dr John Collomosse J.Collomosse@surrey.ac.uk Centre for Vision, Speech and Signal Processing University of Surrey Learning Outcomes After
Computer Vision and Graphics (ee203) Digital Image Processing I Dr John Collomosse J.Collomosse@surrey.ac.uk Centre for Vision, Speech and Signal Processing University of Surrey Learning Outcomes After
Image Sampling and Quantisation
 Image Sampling and Quantisation Introduction to Signal and Image Processing Prof. Dr. Philippe Cattin MIAC, University of Basel 1 of 46 22.02.2016 09:17 Contents Contents 1 Motivation 2 Sampling Introduction
Image Sampling and Quantisation Introduction to Signal and Image Processing Prof. Dr. Philippe Cattin MIAC, University of Basel 1 of 46 22.02.2016 09:17 Contents Contents 1 Motivation 2 Sampling Introduction
Lecture 5: Frequency Domain Transformations
 #1 Lecture 5: Frequency Domain Transformations Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu From Last Lecture Spatial Domain Transformation Point Processing for Enhancement Area/Mask Processing Transformations Image
#1 Lecture 5: Frequency Domain Transformations Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu From Last Lecture Spatial Domain Transformation Point Processing for Enhancement Area/Mask Processing Transformations Image
Image Processing. Overview. Trade spatial resolution for intensity resolution Reduce visual artifacts due to quantization. Sampling and Reconstruction
 Image Processing Overview Image Representation What is an image? Halftoning and Dithering Trade spatial resolution for intensity resolution Reduce visual artifacts due to quantization Sampling and Reconstruction
Image Processing Overview Image Representation What is an image? Halftoning and Dithering Trade spatial resolution for intensity resolution Reduce visual artifacts due to quantization Sampling and Reconstruction
Image Sampling & Quantisation
 Image Sampling & Quantisation Biomedical Image Analysis Prof. Dr. Philippe Cattin MIAC, University of Basel Contents 1 Motivation 2 Sampling Introduction and Motivation Sampling Example Quantisation Example
Image Sampling & Quantisation Biomedical Image Analysis Prof. Dr. Philippe Cattin MIAC, University of Basel Contents 1 Motivation 2 Sampling Introduction and Motivation Sampling Example Quantisation Example
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps
 Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps Last Time? Monte-Carlo Integration Importance Sampling Ray Tracing vs. Path Tracing source hemisphere Sampling sensitive to choice of samples less sensitive to choice of samples
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps Last Time? Monte-Carlo Integration Importance Sampling Ray Tracing vs. Path Tracing source hemisphere Sampling sensitive to choice of samples less sensitive to choice of samples
Computer Graphics Geometry and Transform
 ! Computer Graphics 2014! 5. Geometry and Transform Hongxin Zhang State Key Lab of CAD&CG, Zhejiang University 2014-10-11! Today outline Triangle rasterization Basic vector algebra ~ geometry! Antialiasing
! Computer Graphics 2014! 5. Geometry and Transform Hongxin Zhang State Key Lab of CAD&CG, Zhejiang University 2014-10-11! Today outline Triangle rasterization Basic vector algebra ~ geometry! Antialiasing
28 SAMPLING. ALIASING AND ANTI-ALIASING
 28 SAMPLING. ALIASING AND ANTI-ALIASING Textbook: 16 UGRAD.CS.UBC.CA/~CS314 Alla Sheffer, 2016 ALIASING & ANTI-ALIASING Adobe, inc., https://helpx.adobe.com/photoshop/key concepts/aliasing anti aliasing.html
28 SAMPLING. ALIASING AND ANTI-ALIASING Textbook: 16 UGRAD.CS.UBC.CA/~CS314 Alla Sheffer, 2016 ALIASING & ANTI-ALIASING Adobe, inc., https://helpx.adobe.com/photoshop/key concepts/aliasing anti aliasing.html
Fourier analysis and sampling theory
 Reading Required: Shirley, Ch. 9 Recommended: Fourier analysis and sampling theory Ron Bracewell, The Fourier Transform and Its Applications, McGraw-Hill. Don P. Mitchell and Arun N. Netravali, Reconstruction
Reading Required: Shirley, Ch. 9 Recommended: Fourier analysis and sampling theory Ron Bracewell, The Fourier Transform and Its Applications, McGraw-Hill. Don P. Mitchell and Arun N. Netravali, Reconstruction
Aliasing And Anti-Aliasing Sampling and Reconstruction
 Aliasing And Anti-Aliasing Sampling and Reconstruction An Introduction Computer Overview Intro - Aliasing Problem definition, Examples Ad-hoc Solutions Sampling theory Fourier transform Convolution Reconstruction
Aliasing And Anti-Aliasing Sampling and Reconstruction An Introduction Computer Overview Intro - Aliasing Problem definition, Examples Ad-hoc Solutions Sampling theory Fourier transform Convolution Reconstruction
Drawing a Triangle (and an Intro to Sampling)
 Lecture 4: Drawing a Triangle (and an Intro to Sampling) Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Spring 2018 HW 0.5 Due, HW 1 Out Today! GOAL: Implement a basic rasterizer - (Topic of today s lecture) - We
Lecture 4: Drawing a Triangle (and an Intro to Sampling) Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Spring 2018 HW 0.5 Due, HW 1 Out Today! GOAL: Implement a basic rasterizer - (Topic of today s lecture) - We
Outline. Sampling and Reconstruction. Sampling and Reconstruction. Foundations of Computer Graphics (Fall 2012)
 Foundations of Computer Graphics (Fall 2012) CS 184, Lectures 19: Sampling and Reconstruction http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs184 Outline Basic ideas of sampling, reconstruction, aliasing Signal processing
Foundations of Computer Graphics (Fall 2012) CS 184, Lectures 19: Sampling and Reconstruction http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs184 Outline Basic ideas of sampling, reconstruction, aliasing Signal processing
Outline. Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2012)
 Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2012) CS 184, Lectures 19: Sampling and Reconstruction http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs184 Basic ideas of sampling, reconstruction, aliasing Signal processing
Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2012) CS 184, Lectures 19: Sampling and Reconstruction http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs184 Basic ideas of sampling, reconstruction, aliasing Signal processing
Scaled representations
 Scaled representations Big bars (resp. spots, hands, etc.) and little bars are both interesting Stripes and hairs, say Inefficient to detect big bars with big filters And there is superfluous detail in
Scaled representations Big bars (resp. spots, hands, etc.) and little bars are both interesting Stripes and hairs, say Inefficient to detect big bars with big filters And there is superfluous detail in
The simplest and most obvious method to go from a continuous to a discrete image is by point sampling,
 Sampling our scenes are described with triangles giving a continuous 2d color field our images are digital/discrete made up of a grid of dots need to make a bridge between these two worlds else we will
Sampling our scenes are described with triangles giving a continuous 2d color field our images are digital/discrete made up of a grid of dots need to make a bridge between these two worlds else we will
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps
 Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps Last Time? Monte-Carlo Integration Importance Sampling Ray Tracing vs. Path Tracing source hemisphere What is a Pixel? Sampling & Reconstruction Filters in Computer Graphics
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps Last Time? Monte-Carlo Integration Importance Sampling Ray Tracing vs. Path Tracing source hemisphere What is a Pixel? Sampling & Reconstruction Filters in Computer Graphics
Computer Graphics. Texture Filtering & Sampling Theory. Hendrik Lensch. Computer Graphics WS07/08 Texturing
 Computer Graphics Texture Filtering & Sampling Theory Hendrik Lensch Overview Last time Texture Parameterization Procedural Shading Today Texturing Filtering 2D Texture Mapping Forward mapping Object surface
Computer Graphics Texture Filtering & Sampling Theory Hendrik Lensch Overview Last time Texture Parameterization Procedural Shading Today Texturing Filtering 2D Texture Mapping Forward mapping Object surface
Filtering theory: Battling Aliasing with Antialiasing. Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology
 Filtering theory: Battling Aliasing with Antialiasing Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology 1 What is aliasing? 2 Why care at all? l Quality!! l Example: Final fantasy The
Filtering theory: Battling Aliasing with Antialiasing Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology 1 What is aliasing? 2 Why care at all? l Quality!! l Example: Final fantasy The
To graph the point (r, θ), simply go out r units along the initial ray, then rotate through the angle θ. The point (1, 5π 6
 Polar Coordinates Any point in the plane can be described by the Cartesian coordinates (x, y), where x and y are measured along the corresponding axes. However, this is not the only way to represent points
Polar Coordinates Any point in the plane can be described by the Cartesian coordinates (x, y), where x and y are measured along the corresponding axes. However, this is not the only way to represent points
Image Processing, Warping, and Sampling
 Image Processing, Warping, and Sampling Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) HB Ch. 4.8 FvDFH Ch. 14.10 Outline Image Processing Image Warping Image Sampling Image Processing What about the case when the modification
Image Processing, Warping, and Sampling Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) HB Ch. 4.8 FvDFH Ch. 14.10 Outline Image Processing Image Warping Image Sampling Image Processing What about the case when the modification
Sampling: Application to 2D Transformations
 Sampling: Application to 2D Transformations University of the Philippines - Diliman August Diane Lingrand lingrand@polytech.unice.fr http://www.essi.fr/~lingrand Sampling Computer images are manipulated
Sampling: Application to 2D Transformations University of the Philippines - Diliman August Diane Lingrand lingrand@polytech.unice.fr http://www.essi.fr/~lingrand Sampling Computer images are manipulated
Sampling and Monte-Carlo Integration
 Sampling and Monte-Carlo Integration Sampling and Monte-Carlo Integration Last Time Pixels are samples Sampling theorem Convolution & multiplication Aliasing: spectrum replication Ideal filter And its
Sampling and Monte-Carlo Integration Sampling and Monte-Carlo Integration Last Time Pixels are samples Sampling theorem Convolution & multiplication Aliasing: spectrum replication Ideal filter And its
Basics. Sampling and Reconstruction. Sampling and Reconstruction. Outline. (Spatial) Aliasing. Advanced Computer Graphics (Fall 2010)
 Advanced Computer Graphics (Fall 2010) CS 283, Lecture 3: Sampling and Reconstruction Ravi Ramamoorthi http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs283/fa10 Some slides courtesy Thomas Funkhouser and Pat Hanrahan
Advanced Computer Graphics (Fall 2010) CS 283, Lecture 3: Sampling and Reconstruction Ravi Ramamoorthi http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs283/fa10 Some slides courtesy Thomas Funkhouser and Pat Hanrahan
An Intuitive Explanation of Fourier Theory
 An Intuitive Explanation of Fourier Theory Steven Lehar slehar@cns.bu.edu Fourier theory is pretty complicated mathematically. But there are some beautifully simple holistic concepts behind Fourier theory
An Intuitive Explanation of Fourier Theory Steven Lehar slehar@cns.bu.edu Fourier theory is pretty complicated mathematically. But there are some beautifully simple holistic concepts behind Fourier theory
Lecture 4: Spatial Domain Transformations
 # Lecture 4: Spatial Domain Transformations Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Reminder 2 nd Quiz on the manipulator Part is this Fri, April 7 205, :5 AM to :0 PM Open Book, Open Notes, Focus on the material
# Lecture 4: Spatial Domain Transformations Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Reminder 2 nd Quiz on the manipulator Part is this Fri, April 7 205, :5 AM to :0 PM Open Book, Open Notes, Focus on the material
Filtering theory: Battling Aliasing with Antialiasing. Tomas Akenine-Möller Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology
 Filtering theory: Battling Aliasing with Antialiasing Tomas Akenine-Möller Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology 1 What is aliasing? 2 Why care at all? l Quality!! l Example:
Filtering theory: Battling Aliasing with Antialiasing Tomas Akenine-Möller Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology 1 What is aliasing? 2 Why care at all? l Quality!! l Example:
Computational Aspects of MRI
 David Atkinson Philip Batchelor David Larkman Programme 09:30 11:00 Fourier, sampling, gridding, interpolation. Matrices and Linear Algebra 11:30 13:00 MRI Lunch (not provided) 14:00 15:30 SVD, eigenvalues.
David Atkinson Philip Batchelor David Larkman Programme 09:30 11:00 Fourier, sampling, gridding, interpolation. Matrices and Linear Algebra 11:30 13:00 MRI Lunch (not provided) 14:00 15:30 SVD, eigenvalues.
Lecture 2: 2D Fourier transforms and applications
 Lecture 2: 2D Fourier transforms and applications B14 Image Analysis Michaelmas 2017 Dr. M. Fallon Fourier transforms and spatial frequencies in 2D Definition and meaning The Convolution Theorem Applications
Lecture 2: 2D Fourier transforms and applications B14 Image Analysis Michaelmas 2017 Dr. M. Fallon Fourier transforms and spatial frequencies in 2D Definition and meaning The Convolution Theorem Applications
Noise Model. Important Noise Probability Density Functions (Cont.) Important Noise Probability Density Functions
 Others -- Noise Removal Techniques -- Edge Detection Techniques -- Geometric Operations -- Color Image Processing -- Color Spaces Xiaojun Qi Noise Model The principal sources of noise in digital images
Others -- Noise Removal Techniques -- Edge Detection Techniques -- Geometric Operations -- Color Image Processing -- Color Spaces Xiaojun Qi Noise Model The principal sources of noise in digital images
convolution shift invariant linear system Fourier Transform Aliasing and sampling scale representation edge detection corner detection
 COS 429: COMPUTER VISON Linear Filters and Edge Detection convolution shift invariant linear system Fourier Transform Aliasing and sampling scale representation edge detection corner detection Reading:
COS 429: COMPUTER VISON Linear Filters and Edge Detection convolution shift invariant linear system Fourier Transform Aliasing and sampling scale representation edge detection corner detection Reading:
To graph the point (r, θ), simply go out r units along the initial ray, then rotate through the angle θ. The point (1, 5π 6. ) is graphed below:
 Polar Coordinates Any point in the plane can be described by the Cartesian coordinates (x, y), where x and y are measured along the corresponding axes. However, this is not the only way to represent points
Polar Coordinates Any point in the plane can be described by the Cartesian coordinates (x, y), where x and y are measured along the corresponding axes. However, this is not the only way to represent points
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps
 Last Time? Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps 2D Texture Mapping Perspective Correct Interpolation Common Texture Coordinate Projections Bump Mapping Displacement Mapping Environment Mapping Texture Maps for
Last Time? Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps 2D Texture Mapping Perspective Correct Interpolation Common Texture Coordinate Projections Bump Mapping Displacement Mapping Environment Mapping Texture Maps for
Biomedical Image Analysis. Spatial Filtering
 Biomedical Image Analysis Contents: Spatial Filtering The mechanics of Spatial Filtering Smoothing and sharpening filters BMIA 15 V. Roth & P. Cattin 1 The Mechanics of Spatial Filtering Spatial filter:
Biomedical Image Analysis Contents: Spatial Filtering The mechanics of Spatial Filtering Smoothing and sharpening filters BMIA 15 V. Roth & P. Cattin 1 The Mechanics of Spatial Filtering Spatial filter:
Announcements. Image Matching! Source & Destination Images. Image Transformation 2/ 3/ 16. Compare a big image to a small image
 2/3/ Announcements PA is due in week Image atching! Leave time to learn OpenCV Think of & implement something creative CS 50 Lecture #5 February 3 rd, 20 2/ 3/ 2 Compare a big image to a small image So
2/3/ Announcements PA is due in week Image atching! Leave time to learn OpenCV Think of & implement something creative CS 50 Lecture #5 February 3 rd, 20 2/ 3/ 2 Compare a big image to a small image So
CS559: Computer Graphics. Lecture 12: Antialiasing & Visibility Li Zhang Spring 2008
 CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 12: Antialiasing & Visibility Li Zhang Spring 2008 Antialising Today Hidden Surface Removal Reading: Shirley ch 3.7 8 OpenGL ch 1 Last time A 2 (x 0 y 0 ) (x 1 y 1 ) P
CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 12: Antialiasing & Visibility Li Zhang Spring 2008 Antialising Today Hidden Surface Removal Reading: Shirley ch 3.7 8 OpenGL ch 1 Last time A 2 (x 0 y 0 ) (x 1 y 1 ) P
Texture. Outline. Image representations: spatial and frequency Fourier transform Frequency filtering Oriented pyramids Texture representation
 Texture Outline Image representations: spatial and frequency Fourier transform Frequency filtering Oriented pyramids Texture representation 1 Image Representation The standard basis for images is the set
Texture Outline Image representations: spatial and frequency Fourier transform Frequency filtering Oriented pyramids Texture representation 1 Image Representation The standard basis for images is the set
Computer Vision. Fourier Transform. 20 January Copyright by NHL Hogeschool and Van de Loosdrecht Machine Vision BV All rights reserved
 Van de Loosdrecht Machine Vision Computer Vision Fourier Transform 20 January 2017 Copyright 2001 2017 by NHL Hogeschool and Van de Loosdrecht Machine Vision BV All rights reserved j.van.de.loosdrecht@nhl.nl,
Van de Loosdrecht Machine Vision Computer Vision Fourier Transform 20 January 2017 Copyright 2001 2017 by NHL Hogeschool and Van de Loosdrecht Machine Vision BV All rights reserved j.van.de.loosdrecht@nhl.nl,
Optimised corrections for finite-difference modelling in two dimensions
 Optimized corrections for 2D FD modelling Optimised corrections for finite-difference modelling in two dimensions Peter M. Manning and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Finite-difference two-dimensional correction
Optimized corrections for 2D FD modelling Optimised corrections for finite-difference modelling in two dimensions Peter M. Manning and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Finite-difference two-dimensional correction
Reading. 2. Fourier analysis and sampling theory. Required: Watt, Section 14.1 Recommended:
 Reading Required: Watt, Section 14.1 Recommended: 2. Fourier analysis and sampling theory Ron Bracewell, The Fourier Transform and Its Applications, McGraw-Hill. Don P. Mitchell and Arun N. Netravali,
Reading Required: Watt, Section 14.1 Recommended: 2. Fourier analysis and sampling theory Ron Bracewell, The Fourier Transform and Its Applications, McGraw-Hill. Don P. Mitchell and Arun N. Netravali,
Dr Pavan Chakraborty IIIT-Allahabad
 GVC-43 Lecture - 5 Ref: Donald Hearn & M. Pauline Baker, Comuter Grahics Foley, van Dam, Feiner & Hughes, Comuter Grahics Princiles & Practice Dr Pavan Chakraborty IIIT-Allahabad Summary of line drawing
GVC-43 Lecture - 5 Ref: Donald Hearn & M. Pauline Baker, Comuter Grahics Foley, van Dam, Feiner & Hughes, Comuter Grahics Princiles & Practice Dr Pavan Chakraborty IIIT-Allahabad Summary of line drawing
Biomedical Image Analysis. Point, Edge and Line Detection
 Biomedical Image Analysis Point, Edge and Line Detection Contents: Point and line detection Advanced edge detection: Canny Local/regional edge processing Global processing: Hough transform BMIA 15 V. Roth
Biomedical Image Analysis Point, Edge and Line Detection Contents: Point and line detection Advanced edge detection: Canny Local/regional edge processing Global processing: Hough transform BMIA 15 V. Roth
CS 543: Computer Graphics. Rasterization
 CS 543: Computer Graphics Rasterization Robert W. Lindeman Associate Professor Interactive Media & Game Development Department of Computer Science Worcester Polytechnic Institute gogo@wpi.edu (with lots
CS 543: Computer Graphics Rasterization Robert W. Lindeman Associate Professor Interactive Media & Game Development Department of Computer Science Worcester Polytechnic Institute gogo@wpi.edu (with lots
Sampling, Resampling, and Warping. COS 426, Spring 2014 Tom Funkhouser
 Sampling, Resampling, and Warping COS 426, Spring 2014 Tom Funkhouser Image Processing Goal: read an image, process it, write the result input.jpg output.jpg imgpro input.jpg output.jpg histogram_equalization
Sampling, Resampling, and Warping COS 426, Spring 2014 Tom Funkhouser Image Processing Goal: read an image, process it, write the result input.jpg output.jpg imgpro input.jpg output.jpg histogram_equalization
Scan line algorithm. Jacobs University Visualization and Computer Graphics Lab : Graphics and Visualization 272
 Scan line algorithm The scan line algorithm is an alternative to the seed fill algorithm. It does not require scan conversion of the edges before filling the polygons It can be applied simultaneously to
Scan line algorithm The scan line algorithm is an alternative to the seed fill algorithm. It does not require scan conversion of the edges before filling the polygons It can be applied simultaneously to
Interactive Computer Graphics. Hearn & Baker, chapter D transforms Hearn & Baker, chapter 5. Aliasing and Anti-Aliasing
 Interactive Computer Graphics Aliasing and Anti-Aliasing Hearn & Baker, chapter 4-7 D transforms Hearn & Baker, chapter 5 Aliasing and Anti-Aliasing Problem: jaggies Also known as aliasing. It results
Interactive Computer Graphics Aliasing and Anti-Aliasing Hearn & Baker, chapter 4-7 D transforms Hearn & Baker, chapter 5 Aliasing and Anti-Aliasing Problem: jaggies Also known as aliasing. It results
Anti-aliasing and sampling
 Anti-aliasing and sampling 1996-2017 Josef Pelikán CGG MFF UK Praha pepca@cgg.mff.cuni.cz http://cgg.mff.cuni.cz/~pepca/ Sampling 2017 Josef Pelikán, http://cgg.mff.cuni.cz/~pepca 1 / 34 Spatial and temporal
Anti-aliasing and sampling 1996-2017 Josef Pelikán CGG MFF UK Praha pepca@cgg.mff.cuni.cz http://cgg.mff.cuni.cz/~pepca/ Sampling 2017 Josef Pelikán, http://cgg.mff.cuni.cz/~pepca 1 / 34 Spatial and temporal
Prof. Feng Liu. Fall /25/2018
 Prof. Feng Liu Fall 08 http://www.cs.pd.edu/~fliu/courses/cs7/ 0/5/08 Last time Clipping Toda Rasterization In-class Mid-term November Close-book eam Notes on page of A or Letter size paper Where We Stand
Prof. Feng Liu Fall 08 http://www.cs.pd.edu/~fliu/courses/cs7/ 0/5/08 Last time Clipping Toda Rasterization In-class Mid-term November Close-book eam Notes on page of A or Letter size paper Where We Stand
Section 10.1 Polar Coordinates
 Section 10.1 Polar Coordinates Up until now, we have always graphed using the rectangular coordinate system (also called the Cartesian coordinate system). In this section we will learn about another system,
Section 10.1 Polar Coordinates Up until now, we have always graphed using the rectangular coordinate system (also called the Cartesian coordinate system). In this section we will learn about another system,
3. Image formation, Fourier analysis and CTF theory. Paula da Fonseca
 3. Image formation, Fourier analysis and CTF theory Paula da Fonseca EM course 2017 - Agenda - Overview of: Introduction to Fourier analysis o o o o Sine waves Fourier transform (simple examples of 1D
3. Image formation, Fourier analysis and CTF theory Paula da Fonseca EM course 2017 - Agenda - Overview of: Introduction to Fourier analysis o o o o Sine waves Fourier transform (simple examples of 1D
Digital Image Processing. Lecture 6
 Digital Image Processing Lecture 6 (Enhancement in the Frequency domain) Bu-Ali Sina University Computer Engineering Dep. Fall 2016 Image Enhancement In The Frequency Domain Outline Jean Baptiste Joseph
Digital Image Processing Lecture 6 (Enhancement in the Frequency domain) Bu-Ali Sina University Computer Engineering Dep. Fall 2016 Image Enhancement In The Frequency Domain Outline Jean Baptiste Joseph
Differential Geometry: Circle Patterns (Part 1) [Discrete Conformal Mappinngs via Circle Patterns. Kharevych, Springborn and Schröder]
![Differential Geometry: Circle Patterns (Part 1) [Discrete Conformal Mappinngs via Circle Patterns. Kharevych, Springborn and Schröder] Differential Geometry: Circle Patterns (Part 1) [Discrete Conformal Mappinngs via Circle Patterns. Kharevych, Springborn and Schröder]](/thumbs/93/111713975.jpg) Differential Geometry: Circle Patterns (Part 1) [Discrete Conformal Mappinngs via Circle Patterns. Kharevych, Springborn and Schröder] Preliminaries Recall: Given a smooth function f:r R, the function
Differential Geometry: Circle Patterns (Part 1) [Discrete Conformal Mappinngs via Circle Patterns. Kharevych, Springborn and Schröder] Preliminaries Recall: Given a smooth function f:r R, the function
Lecture 7: Most Common Edge Detectors
 #1 Lecture 7: Most Common Edge Detectors Saad Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Edge Detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, most semantic and shape information from the
#1 Lecture 7: Most Common Edge Detectors Saad Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Edge Detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, most semantic and shape information from the
1 Affine and Projective Coordinate Notation
 CS348a: Computer Graphics Handout #9 Geometric Modeling Original Handout #9 Stanford University Tuesday, 3 November 992 Original Lecture #2: 6 October 992 Topics: Coordinates and Transformations Scribe:
CS348a: Computer Graphics Handout #9 Geometric Modeling Original Handout #9 Stanford University Tuesday, 3 November 992 Original Lecture #2: 6 October 992 Topics: Coordinates and Transformations Scribe:
Computer Graphics Geometry and Transform
 Computer Graphics 2012 5. Geometry and Transform Hongxin Zhang State Key Lab of CAD&CG, Zhejiang University 2012-09-26 上机实践 地址 :ftp://give.zju.edu.cn 用户 :cgzhang 密码 :cgzhang 请大家把上机作业结果和报告内容, 上传至 学号 _ 姓名
Computer Graphics 2012 5. Geometry and Transform Hongxin Zhang State Key Lab of CAD&CG, Zhejiang University 2012-09-26 上机实践 地址 :ftp://give.zju.edu.cn 用户 :cgzhang 密码 :cgzhang 请大家把上机作业结果和报告内容, 上传至 学号 _ 姓名
Math 26: Fall (part 1) The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine (Evaluating Cosine and Sine, and The Pythagorean Identity)
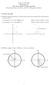 Math : Fall 0 0. (part ) The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine (Evaluating Cosine and Sine, and The Pthagorean Identit) Cosine and Sine Angle θ standard position, P denotes point where the terminal side of
Math : Fall 0 0. (part ) The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine (Evaluating Cosine and Sine, and The Pthagorean Identit) Cosine and Sine Angle θ standard position, P denotes point where the terminal side of
Lecture 6: Edge Detection
 #1 Lecture 6: Edge Detection Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Review From Last Lecture Options for Image Representation Introduced the concept of different representation or transformation Fourier Transform
#1 Lecture 6: Edge Detection Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Review From Last Lecture Options for Image Representation Introduced the concept of different representation or transformation Fourier Transform
Buffers, Textures, Compositing, and Blending. Overview. Buffers. David Carr Virtual Environments, Fundamentals Spring 2005 Based on Slides by E.
 INSTITUTIONEN FÖR SYSTEMTEKNIK LULEÅ TEKNISKA UNIVERSITET Buffers, Textures, Compositing, and Blending David Carr Virtual Environments, Fundamentals Spring 2005 Based on Slides by E. Angel Compositing,
INSTITUTIONEN FÖR SYSTEMTEKNIK LULEÅ TEKNISKA UNIVERSITET Buffers, Textures, Compositing, and Blending David Carr Virtual Environments, Fundamentals Spring 2005 Based on Slides by E. Angel Compositing,
Computer Vision I. Announcements. Fourier Tansform. Efficient Implementation. Edge and Corner Detection. CSE252A Lecture 13.
 Announcements Edge and Corner Detection HW3 assigned CSE252A Lecture 13 Efficient Implementation Both, the Box filter and the Gaussian filter are separable: First convolve each row of input image I with
Announcements Edge and Corner Detection HW3 assigned CSE252A Lecture 13 Efficient Implementation Both, the Box filter and the Gaussian filter are separable: First convolve each row of input image I with
Sampling and Reconstruction
 Sampling and Reconstruction Sampling and Reconstruction Sampling and Spatial Resolution Spatial Aliasing Problem: Spatial aliasing is insufficient sampling of data along the space axis, which occurs because
Sampling and Reconstruction Sampling and Reconstruction Sampling and Spatial Resolution Spatial Aliasing Problem: Spatial aliasing is insufficient sampling of data along the space axis, which occurs because
Unit 2: Trigonometry. This lesson is not covered in your workbook. It is a review of trigonometry topics from previous courses.
 Unit 2: Trigonometry This lesson is not covered in your workbook. It is a review of trigonometry topics from previous courses. Pythagorean Theorem Recall that, for any right angled triangle, the square
Unit 2: Trigonometry This lesson is not covered in your workbook. It is a review of trigonometry topics from previous courses. Pythagorean Theorem Recall that, for any right angled triangle, the square
Homework #1. Displays, Image Processing, Affine Transformations, Hierarchical modeling, Projections
 Computer Graphics Instructor: rian Curless CSEP 557 Winter 213 Homework #1 Displays, Image Processing, Affine Transformations, Hierarchical modeling, Projections Assigned: Tuesday, January 22 nd Due: Tuesday,
Computer Graphics Instructor: rian Curless CSEP 557 Winter 213 Homework #1 Displays, Image Processing, Affine Transformations, Hierarchical modeling, Projections Assigned: Tuesday, January 22 nd Due: Tuesday,
8/5/2012. Introduction. Transparency. Anti-Aliasing. Applications. Conclusions. Introduction
 Introduction Transparency effects and applications Anti-Aliasing impact in the final image Why combine Transparency with Anti-Aliasing? Marilena Maule João Comba Rafael Torchelsen Rui Bastos UFRGS UFRGS
Introduction Transparency effects and applications Anti-Aliasing impact in the final image Why combine Transparency with Anti-Aliasing? Marilena Maule João Comba Rafael Torchelsen Rui Bastos UFRGS UFRGS
Computer Vision 2. SS 18 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Professur für Bildverarbeitung. Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier
 Computer Vision 2 SS 18 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Professur für Bildverarbeitung Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier 1. IMAGE PROCESSING Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Content of this Chapter Non-linear
Computer Vision 2 SS 18 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Professur für Bildverarbeitung Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier 1. IMAGE PROCESSING Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Content of this Chapter Non-linear
Computer Graphics. Attributes of Graphics Primitives. Somsak Walairacht, Computer Engineering, KMITL 1
 Computer Graphics Chapter 4 Attributes of Graphics Primitives Somsak Walairacht, Computer Engineering, KMITL 1 Outline OpenGL State Variables Point Attributes t Line Attributes Fill-Area Attributes Scan-Line
Computer Graphics Chapter 4 Attributes of Graphics Primitives Somsak Walairacht, Computer Engineering, KMITL 1 Outline OpenGL State Variables Point Attributes t Line Attributes Fill-Area Attributes Scan-Line
Fourier transforms and convolution
 Fourier transforms and convolution (without the agonizing pain) CS/CME/BioE/Biophys/BMI 279 Oct. 26, 2017 Ron Dror 1 Why do we care? Fourier transforms Outline Writing functions as sums of sinusoids The
Fourier transforms and convolution (without the agonizing pain) CS/CME/BioE/Biophys/BMI 279 Oct. 26, 2017 Ron Dror 1 Why do we care? Fourier transforms Outline Writing functions as sums of sinusoids The
Edge detection. Gradient-based edge operators
 Edge detection Gradient-based edge operators Prewitt Sobel Roberts Laplacian zero-crossings Canny edge detector Hough transform for detection of straight lines Circle Hough Transform Digital Image Processing:
Edge detection Gradient-based edge operators Prewitt Sobel Roberts Laplacian zero-crossings Canny edge detector Hough transform for detection of straight lines Circle Hough Transform Digital Image Processing:
Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates
 433-324 Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction Vectors and matrices Translation
433-324 Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction Vectors and matrices Translation
Homework #1. Displays, Image Processing, Affine Transformations, Hierarchical Modeling
 Computer Graphics Instructor: Brian Curless CSE 457 Spring 217 Homework #1 Displays, Image Processing, Affine Transformations, Hierarchical Modeling Assigned: Friday, April 7 th Due: Thursday, April 2
Computer Graphics Instructor: Brian Curless CSE 457 Spring 217 Homework #1 Displays, Image Processing, Affine Transformations, Hierarchical Modeling Assigned: Friday, April 7 th Due: Thursday, April 2
Transformations. Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico
 Transformations Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico Angel: Interactive Computer Graphics 4E Addison-Wesley 25 1 Objectives
Transformations Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico Angel: Interactive Computer Graphics 4E Addison-Wesley 25 1 Objectives
Homework #1. Displays, Alpha Compositing, Image Processing, Affine Transformations, Hierarchical Modeling
 Computer Graphics Instructor: Brian Curless CSE 457 Spring 2014 Homework #1 Displays, Alpha Compositing, Image Processing, Affine Transformations, Hierarchical Modeling Assigned: Saturday, April th Due:
Computer Graphics Instructor: Brian Curless CSE 457 Spring 2014 Homework #1 Displays, Alpha Compositing, Image Processing, Affine Transformations, Hierarchical Modeling Assigned: Saturday, April th Due:
COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates
 COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction Vectors and matrices Translation
COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction Vectors and matrices Translation
Matrix Transformations. Affine Transformations
 Matri ransformations Basic Graphics ransforms ranslation Scaling Rotation Reflection Shear All Can be Epressed As Linear Functions of the Original Coordinates : A + B + C D + E + F ' A ' D 1 B E C F 1
Matri ransformations Basic Graphics ransforms ranslation Scaling Rotation Reflection Shear All Can be Epressed As Linear Functions of the Original Coordinates : A + B + C D + E + F ' A ' D 1 B E C F 1
To Do. Advanced Computer Graphics. Discrete Convolution. Outline. Outline. Implementing Discrete Convolution
 Advanced Computer Graphics CSE 163 [Spring 2018], Lecture 4 Ravi Ramamoorthi http://www.cs.ucsd.edu/~ravir To Do Assignment 1, Due Apr 27. Please START EARLY This lecture completes all the material you
Advanced Computer Graphics CSE 163 [Spring 2018], Lecture 4 Ravi Ramamoorthi http://www.cs.ucsd.edu/~ravir To Do Assignment 1, Due Apr 27. Please START EARLY This lecture completes all the material you
COMP371 COMPUTER GRAPHICS
 COMP371 COMPUTER GRAPHICS LECTURE 14 RASTERIZATION 1 Lecture Overview Review of last class Line Scan conversion Polygon Scan conversion Antialiasing 2 Rasterization The raster display is a matrix of picture
COMP371 COMPUTER GRAPHICS LECTURE 14 RASTERIZATION 1 Lecture Overview Review of last class Line Scan conversion Polygon Scan conversion Antialiasing 2 Rasterization The raster display is a matrix of picture
CS1114 Assignment 5, Part 1
 CS4 Assignment 5, Part out: Friday, March 27, 2009. due: Friday, April 3, 2009, 5PM. This assignment covers three topics in two parts: interpolation and image transformations (Part ), and feature-based
CS4 Assignment 5, Part out: Friday, March 27, 2009. due: Friday, April 3, 2009, 5PM. This assignment covers three topics in two parts: interpolation and image transformations (Part ), and feature-based
Image Metamorphosis By Affine Transformations
 Image Metamorphosis B Affine Transformations Tim Mers and Peter Spiegel December 16, 2005 Abstract Among the man was to manipulate an image is a technique known as morphing. Image morphing is a special
Image Metamorphosis B Affine Transformations Tim Mers and Peter Spiegel December 16, 2005 Abstract Among the man was to manipulate an image is a technique known as morphing. Image morphing is a special
Rasterization. Rasterization (scan conversion) Digital Differential Analyzer (DDA) Rasterizing a line. Digital Differential Analyzer (DDA)
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 14 Rasterization Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Scan Conversion Antialiasing [Angel Ch. 6] Rasterization (scan conversion) Final step in pipeline: rasterization
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 14 Rasterization Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Scan Conversion Antialiasing [Angel Ch. 6] Rasterization (scan conversion) Final step in pipeline: rasterization
Honors Precalculus: Solving equations and inequalities graphically and algebraically. Page 1
 Solving equations and inequalities graphically and algebraically 1. Plot points on the Cartesian coordinate plane. P.1 2. Represent data graphically using scatter plots, bar graphs, & line graphs. P.1
Solving equations and inequalities graphically and algebraically 1. Plot points on the Cartesian coordinate plane. P.1 2. Represent data graphically using scatter plots, bar graphs, & line graphs. P.1
Digital Image Processing. Prof. P. K. Biswas. Department of Electronic & Electrical Communication Engineering
 Digital Image Processing Prof. P. K. Biswas Department of Electronic & Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 21 Image Enhancement Frequency Domain Processing
Digital Image Processing Prof. P. K. Biswas Department of Electronic & Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 21 Image Enhancement Frequency Domain Processing
Image Warping: A Review. Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York
 Image Warping: A Review Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives In this lecture we review digital image warping: - Geometric transformations - Forward inverse
Image Warping: A Review Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives In this lecture we review digital image warping: - Geometric transformations - Forward inverse
Announcements. Written Assignment 2 out (due March 8) Computer Graphics
 Announcements Written Assignment 2 out (due March 8) 1 Advanced Ray Tracing (Recursive) Ray Tracing Antialiasing Motion Blur Distribution Ray Tracing Ray Tracing and Radiosity Assumptions Simple shading
Announcements Written Assignment 2 out (due March 8) 1 Advanced Ray Tracing (Recursive) Ray Tracing Antialiasing Motion Blur Distribution Ray Tracing Ray Tracing and Radiosity Assumptions Simple shading
Discrete Techniques. 11 th Week, Define a buffer by its spatial resolution (n m) and its depth (or precision) k, the number of
 Discrete Techniques 11 th Week, 2010 Buffer Define a buffer by its spatial resolution (n m) and its depth (or precision) k, the number of bits/pixel Pixel OpenGL Frame Buffer OpenGL Buffers Color buffers
Discrete Techniques 11 th Week, 2010 Buffer Define a buffer by its spatial resolution (n m) and its depth (or precision) k, the number of bits/pixel Pixel OpenGL Frame Buffer OpenGL Buffers Color buffers
Digital Signal Processing Lecture Notes 22 November 2010
 Digital Signal Processing Lecture otes 22 ovember 2 Topics: Discrete Cosine Transform FFT Linear and Circular Convolution Rate Conversion Includes review of Fourier transforms, properties of Fourier transforms,
Digital Signal Processing Lecture otes 22 ovember 2 Topics: Discrete Cosine Transform FFT Linear and Circular Convolution Rate Conversion Includes review of Fourier transforms, properties of Fourier transforms,
Digital Image Processing. Image Enhancement in the Frequency Domain
 Digital Image Processing Image Enhancement in the Frequency Domain Topics Frequency Domain Enhancements Fourier Transform Convolution High Pass Filtering in Frequency Domain Low Pass Filtering in Frequency
Digital Image Processing Image Enhancement in the Frequency Domain Topics Frequency Domain Enhancements Fourier Transform Convolution High Pass Filtering in Frequency Domain Low Pass Filtering in Frequency
2D rendering takes a photo of the 2D scene with a virtual camera that selects an axis aligned rectangle from the scene. The photograph is placed into
 2D rendering takes a photo of the 2D scene with a virtual camera that selects an axis aligned rectangle from the scene. The photograph is placed into the viewport of the current application window. A pixel
2D rendering takes a photo of the 2D scene with a virtual camera that selects an axis aligned rectangle from the scene. The photograph is placed into the viewport of the current application window. A pixel
Image Acquisition + Histograms
 Image Processing - Lesson 1 Image Acquisition + Histograms Image Characteristics Image Acquisition Image Digitization Sampling Quantization Histograms Histogram Equalization What is an Image? An image
Image Processing - Lesson 1 Image Acquisition + Histograms Image Characteristics Image Acquisition Image Digitization Sampling Quantization Histograms Histogram Equalization What is an Image? An image
Cecil Jones Academy Mathematics Fundamentals
 Year 10 Fundamentals Core Knowledge Unit 1 Unit 2 Estimate with powers and roots Calculate with powers and roots Explore the impact of rounding Investigate similar triangles Explore trigonometry in right-angled
Year 10 Fundamentals Core Knowledge Unit 1 Unit 2 Estimate with powers and roots Calculate with powers and roots Explore the impact of rounding Investigate similar triangles Explore trigonometry in right-angled
