The Number Plane THE NUMBER PLANE PASSPORT.
|
|
|
- Abraham Charles
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE NUMBER PLANE PASSPORT
2
3 Fill in the mind-map below with what you already know about number planes. A start has been made for you! Uses a coordinate system developed by the French Mathematician René Descartes and its full name is: The Cartesian Number Plane Number Plane Give this a go! Q A company charges $ to host a party. It also charges extra for each guest. The extra charge amounts to $ for every guests. Use a graph to find how much it would cost for a party with guests. Cost ($) Number of guests Work through the book for a great way to solve this P Learning H SERIES TOPIC
4 How does it work? Grid plane Grid planes have a vertical axis and a horizontal axis. They can be used to help us find places on maps such as street directories. The horizontal axis reference is always written first. Use this map and key to answer the questions below: Vertical axis Key Park Football field Building Lake Road A B C D E F G H Horizontal axis (i) Write the grid reference for the two buildings on the map. Building is in grid B A B C D E F G H Building is in grid G (ii) Which grid is completely covered by the lake? A B C D E F G H grid E H SERIES TOPIC P Learning
5 How does it work? Here is another example. Use this map and key to answer the questions below: Vertical axis North Ave Pi St Main Road Li le Lane Happy St A B C D E F G H Horizontal axis (i) Name the road that connects to Main Road at B. North Ave Pi St Main Road North Ave connects to Main Road at B Happy p St Li le Lane A B C D E F G H (ii) Which road changes direction at E? North Ave Pi St Main Road Li le Lane Happy St A B C D E F G H Happy St changes direction at E P Learning H SERIES TOPIC
6 How does it work? Your Turn Grid plane Use this map and key to answer the questions below: A A B B C C D E F G H D E F G H I I J J K L M Key State forest Dam Creek Building Road Walking track Bridge a At which grid reference does the walking track join the road? b Which grid reference is completely filled with dam water? c What is the grid reference where the creek joins with the dam? d What three features are located at grid reference C? e What is the grid reference where the creek enters the State forest? f Write down the four grid references that contain a building. g If you were moving towards the road on the walking track and had just exited the State forest, which grid are you in? H SERIES TOPIC P Learning
7 Oval Road Down St How does it work? Your Turn Grid plane GRID PLANE * GRID PLANE * GRID PLANE * Use this map and key to answer the questions below: 9 8 Ver cal Road Kink St Pi St Car Park Road Dog Leg Lane Eff St Park Circuit P.O. Horizontal Way West Bend Car Park Key Park Sports Oval Pond Ambulance Station P.O. Post Office Change Rooms Police Station.../.../... A B C D E F G H I J K L M a Where does Pi St join with Vertical Road? b Where are the change rooms located? c Where does Dog Leg Lane come to an end? d Write down the locations of the Police and Ambulance Stations. e Locate the pond in the smaller park. f A new Fire Station is going to be built on the corner of Car Park Road and Oval Road, across the road from the park. What will be the grid reference for the new Fire Station? g Write down the directions (using grid references only) you would give a driver entering the map from Eff St if they were driving to the Post Office on Horizontal Way. P Learning H SERIES TOPIC
8 How does it work? Axes and coordinates Number planes have two number lines as their axes. Vertical axis (usually labelled ) Horizontal axis (usually labelled ) Coordinates help us locate points and are always written in curved brackets separated by a comma (, ). Write down the coordinates of the points A, B and C shown on the number plane below: B A C 8 A 8 The coordinates of point A = (, ) x-value first Horizontal first y-value second Vertical second B 8 The coordinates of point B = (, ) x-value first Horizontal first y-value second Vertical second C 8 The coordinates of point C = (, ) x-value first Horizontal first y-value second Vertical second H SERIES TOPIC P Learning
9 How does it work? It is good practice to write the coordinates next to the points when plotting. Plot the points given by the coordinates below on the same number plane: D (, ) E (, ) F (, ) G (8, ) H (, ) Plotting points is done by placing a small dot where the x and y coordinate values cross each other. Remember: The horizontal value is always the first number G (8, ) E (, ) D (, ) H (, ) F (, ) 8 Coordinates can also be called ordered pairs because the order we write the numbers in is important. Ordered pairs can also have decimal values. Plot the points I, J and K on the number plane below: I (,.) J (., ) K (.,.) I (,.) K (.,.) J (., ) 8 P Learning H SERIES TOPIC
10 How does it work? Your Turn Axes and coordinates Write each letter plotted on the number plane with the matching coordinates below: N C 9 8! T F T I A A S 8 9 *(x, y) AXES AND COORDINATES * AXES AND COORDINATES.../.../... (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (9, ) (, ) (,.) (9., ) (8, 8) Plot and label these points on the number plane below: A (, ) B (, ) C (., ) D (, ) E (9, 8) F (,.) G (, ) H (8, ) H SERIES TOPIC P Learning
11 Where does it work? Plotting tables of values Tables of values give us coordinates to plot on a number plane and show the graph of the rule given. Graph the table below that was completed using the rule: y = x+ x 8 y 9 The x and y values are paired into coordinates to plot. x 8 y 9 (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, 9) (8, ) (8, ) 9 (, 9) 8 (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) 8 9 The plotted points for the rule above lie on a straight line. When this happens, the rule is called a linear relationship. P Learning H SERIES TOPIC 9
12 Where does it work? Here is another example using different variables. Use the rule b = a + to complete the table of values below: a b 9 a = a = a = a = a = a = b = # + b = # + b = # + b = # + b = # + b = # + = = = = = 9 = After a table of values is completed, we usually plot all the points. Plot the completed table of values on the number plane below: a b 9 (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, 9) (, ) b-axis 9 8 (, ) (, 9) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) 8 9 a-axis H SERIES TOPIC P Learning
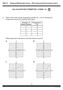
13 Where does it work? Your Turn Plotting tables of values Plot each of the completed table of values below: a y = x+ b b = -a x y a b b-axis 8 8 a-axis c m = n d y = x ' n m x y.. m-axis 8 n-axis 8 P Learning H SERIES TOPIC
14 * PLOTTING TABLES OF VALUES * PLOTTING TABLES OF VALUES Where does it work? Your Turn Plotting tables of values (i) Use the rules to complete the table of values. (ii) Plot the table of values..../.../... a y = x+ x y b q 8 = - p p q 8 q-axis 8 p-axis c n = m - d c = d + m 8 d 8 n c n-axis c-axis 8 m-axis 8 d-axis H SERIES TOPIC P Learning
15 Where does it work? Dependent and independent variables The y-value in the table of values is the answer (or output) after x-values are put into the rule. y x = + x Input Independent variable Its value is given, so is independent of y y 8 Output Dependent variable Its value depends on the value of x Dependent variable (vertical axis) y x Independent variable (horizontal axis) Remember: We can use different variables such as a, b, m, n, p, q etc Identify the dependent and independent variables in the rules below: (i) y x = + y x = + Axis labelling y Output ` Dependent variable Input Independent variable x (ii) b- = a b- = a Axis labelling a Input ` Independent variable Output Dependent variable b (iii) n = m n = m Axis labelling n Output ` Dependent variable Input Independent variable m Did you notice a pattern? In these cases, the dependent variable is the one by itself on one side of the equal sign. When a variable is by itself in a rule, it is called the subject of the rule. P Learning H SERIES TOPIC
16 DEPENDENT AND INDEPENDENT VARIABLES * Where does it work? Your Turn Dependent and independent variables (i) For the rules given below, circle the independent variables. a y = x+ b - b = a c m = n'.../.../... (ii) Circle the correct answer to the statement: Independent variable values are placed onto the horizontal axis. True False (i) For the rules given below, circle the dependent variables. a y - = x b a = b+ c m = n (ii) Circle the correct answer to the statement: Dependent variables are not affected by the values of the independent variables. True False Label each of these axes with the correct variable for the given rule if they were to be graphed. a y = x- b m+ = n c a = b d y = x + e + p = q f x+ = y H SERIES TOPIC P Learning
17 Where does it work? Fees and charges Fees charged by companies are often graphed on number planes to help you quickly read how much it would cost you for different situations. The cost is usually dependent on how far you travel, how long you use the service etc. Therefore cost is always put on the vertical axis. A bus company charges per kilometre travelled. One passenger is charged $ for travelling km. (i) Graph the bus company charges on the number plane below. Bus charges (,) is called the Origin Cost ($) Kilometres (km) Step Plot the charge for the passenger travelling km Step Draw a line from (,) through the plotted point (ii) Use the graph to find how much it would cost a passenger to travel 8km. Cost ($) Step Draw a horizontal line to the vertical axis to read the cost 8 9 Bus charges 9 8 Kilometres (km) Step Draw a vertical line from 8km up to the graphed line From the graph, the cost for travelling 8km is $. P Learning H SERIES TOPIC
18 Where does it work? Companies often use a rule to determine how much they charge customers. This rule can be graphed by first completing a table of values. A professional party clown uses this rule to calculate how much he charges for parties:. C n = + C = the amount charged in dollars and n = the number of children (i) Complete the table of values and graph it on the number plane below: n 8 C 8 9 C-axis Clown charges 9 (, 9) 8 Amount charged ($) (8, ) (, ) (, ) n-axis 8 Number of children (, 8) Step Plot the points from the table of values Step Draw a straight line through the plotted points (ii) Use the graph to find how many children can attend the party for $. C-axis 9 Clown charges Step Draw a horizontal line from $ to the graphed line Amount charged ($) 8 Step Draw a vertical line to the horizontal axis to read the value 8 Number of children n-axis From the graph, children could attend the party for $. This example shows that you can start from either axis to read values from the graph. H SERIES TOPIC P Learning
19 * FEES AND CHARGES * FEES AND CHARGES Where does it work? Your Turn Fees and charges A recent survey on studying found that marks achieved increased by an average of marks from a previous test for every minutes of study. (i) Graph this relationship between study time and marks below: (psst: plot the extra marks after minutes study first) Increase in marks from studying.../.../... Extra marks 8 9 Minutes spent studying (ii) Use the graph to find how many more marks a student could get after studying for minutes. Expected extra marks achieved by studying for minutes = marks. A company charges $ to host a party. It also charges extra for each guest. The extra charge amounts to $ for every guests. (i) Graph this relationship between charges and guests below: (psst: plot the charge for guests and the extra charge for guests.) Graph showing cost of hosting party per guest Cost ($) Remember me? Number of guests (ii) Use the graph to find how much it would cost for a party with guests. A party with guests will cost: $ P Learning H SERIES TOPIC
20 Where does it work? Your Turn Fees and charges A cab company uses the following rule to determine the fares for passengers: F = $. # k+ F = The total fare in dollars and k = the number of kilometres travelled (i) Complete the table of values and graph it on the number plane below: F = $. # k+ k 8 F F-axis Cab fare per kilometre travelled 8 Fare ($) 8 9 Kilometres travelled k-axis (ii) Use the graph to find how far someone could travel by cab if they had $. A person with $ could travel: km Matthew is paid by his favourite rugby union club to encourage fan support at every home game according to the following rule: P = g+ P = The total paid and g = the number of home games (i) Complete the table of values and graph it on the number plane below: P = g+ g P P-axis Graph showing payment for Matthew 8 Pay ($) 8 Number of home games g-axis (ii) Use the graph to find how many games he must attend to earn $. Matthew must attend games to earn $. 8 H SERIES TOPIC P Learning
21 What else can you do? More axes and coordinates We can extend the number plane to include all integers by introducing negative numbers. x-values decrease y-values increase nd st - rd - - th x-values increase 8 y-values decrease Remember: (, ) is called The Origin. Usually labelled The axes of a Cartesian number plane splits the grid into four sections called quadrants. The quadrants are numbered as shown above. The coordinates in each quadrant have different combinations of positive and negative values. Coordinate combinations nd quadrant: negative, positive (-, +) st quadrant: positive, positive (+, +) rd quadrant: negative, negative (-, -) th quadrant: positive, negative (+, -) Points on the horizontal axis ( ) have a second coordinate value of eg: (, ). Points on the vertical axis ( ) have a first coordinate value of eg: (, ). H SERIES TOPIC 9
22 What else can you do? Write down the coordinates of the points A, B, C and D shown on the number plane below: B nd st A D C rd th nd quadrant: x negative, y positive x-value first y-value second Point B: (-, ) C - Point C: (-, -) - - x-value first y-value second - rd quadrant: x negative, y negative B D A st quadrant: x positive, y positive x-value first y-value second Point A: (, ) Point D: (, -) x-value first y-value second th quadrant: x positive, y negative H SERIES TOPIC P Learning
23 What else can you do? Remember, when plotting points the first number is always the x-value (or horizontal value). Plot and label these points on the same number plane: E (, ) F (-,.) G (-, ) H (., -) I (-, -) O (, ) E (, ) F (-,.) G (-, ) O (, ) I (-, -) H (., -) P Learning H SERIES TOPIC
24 What else can you do? Your Turn More axes and coordinates Put the letter for the coordinates below into the correct group where they would be found if plotted. There may be one or two that fit into more than one group. A (-, ) B (8, ) C (, ) D (-, ) E (, -) F (, -) G (-, -) H (, ) I (-, ) J (, ) K (-, ) L (-, -) M (, 9) N (, -) O (, ) P (-, -) Q (9, -8) R (, ) S (9, ) T (, -) U (, -8) V (-., -.) W (-.,.) X (, -.) Y (-8, ) Z (-.,.) nd quadrant rd quadrant st quadrant th quadrant Coordinates H SERIES TOPIC P Learning
25 What else can you do? Your Turn More axes and coordinates What does a Penrose Triangle look like? Follow the instructions below to find out! Plot and join the following sets of coordinates together with straight lines using a ruler. st Line: start (, -) (, ) (-, ) (, -) stop nd Line: start (-, ) (9, ) (, -) (, -) (, ) (-, ) (-, ) stop Colour in the shape formed by the second line. rd Line: start (, -) (-, -) (-, ) (-, ) (, -) stop Colour in the V shape formed by the third line a different colour. th Line: start (-, ) (, 9) (9, ) stop P Learning H SERIES TOPIC
26 What else can you do? Interesting applications Let s look at some applications of number planes requiring a little more thought. An electronic artist lights up displays of squares from a large grid of numbered LCD screens according to a rule. She must enter the coordinates into the lighting unit so the correct squares are lit up. (i) What coordinates must she enter for the grid below if the rule is: Any multiple of or a number with a in it? Blank screens 8 9 Screens lit according to rule ` The coordinates to be lit up are: (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (ii) If the rule is changed to Any multiple of, which coordinates will remain lit from the previous rule? (, ) (, ) (, ) (iii) What rule did the artist use if she entered the following coordinates? (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) ` Rule = Any multiple of 9 Identify the numbered LCD screens at the given coordinates H SERIES TOPIC P Learning
27 What else can you do? Distances between points on the number plane are measured in units. NORTH WEST EAST SOUTH Directions can be given as East (right), West (left), North (up) and South (down). The skate park Jill is going to is four units East and one unit North of the Post Office located at (-, -). Jill needs to post a letter for her mother before going to the skate park. Her house is five units North from the Post Office: (i) Plot the coordinates of her house, the skate park and Post Office below. Jill's home (-, ) Post Office (-, -) (, -) skate park (ii) Jill made a new friend at the skate park and gave the following directions to reach her house: I live four vertical and four horizontal units away from here. Explain why these directions are not enough information. From the skate park, there are four different coordinates that match. Jill s instructions: (-, ), (, ), (-, -) and (, -). Her new friend could go to the wrong place. (iii) What directions should Jill have given to be more accurate? From the skate park, I live four units West then four units North. P Learning H SERIES TOPIC
28 What else can you do? Your Turn Interesting applications The electronic artist in the example lights up the numbered LCD screens using the following rule: Any multiple of or a number with a in it. (i) Lightly colour in the LCD screens that suit this rule and write down their coordinates * AWESOME *.../.../... * AWESOME * (ii) The artist changes the rule to: Any number divisible by and including numbers with a in it. List the coordinates of the LCD screens that will be turned off from the previous rule. (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) Mark and Fabio are using portable radios in a bush-walking exercise. Mark's location is at the Look Out, four units West and three units North from the Base Camp located at (, ). Fabio s location is a Waterfall which is five units East and six units South from the Base Camp. (i) Plot the locations of the Look Out, Base Camp and Waterfall. (ii) Do these locations form a straight line? Yes No (iii) What directions should Fabio radio to Mark to guide him to the Waterfall? H SERIES TOPIC P Learning
29 What else can you do? Your Turn Interesting applications The coordinates (, ) and (, ) are two vertices of a square. Write down two different sets of coordinates that could be the other two vertices of this square First set: (, ) and (, ) Second set: (, ) and (, ) Vertices are the corner points Which of the following ticket locations are closest to the stage for the concert venue pictured here? Location : st quadrant, two units away from both axes. Location : (, -) Location : Four units along the horizontal axis between the st and th quadrants. Location : (-, ) Location : Three units along the horizontal axis and two units directly below the nd quadrant Location : The centre of the venue (, ). Closest Location: - - Stage P Learning H SERIES TOPIC
30 What else can you do? Your Turn Interesting applications Akido s intelligent touchpad has the five application icons on the front screen as shown in the diagram below. This touchpad uses coordinates to recognise where Akido has touched the screen so the correct application is started. If any of these 9 points on the application icon are pressed, the application will start: Application icon 9 8 Calculator Music Documents Shares Gymnas cs 8 a Write down all the coordinates that will open the Gymnastics application if a touch was detected there. (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) b Akido moves all his picture icons to new locations. He moves the Music application icon down five units and to the left two units. What are the new coordinates that will open his Music application? (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) 8 H SERIES TOPIC P Learning
31 What else can you do? Your Turn A bit of fun at the end.../.../... Coordy the Frog likes to sit on every lily pad in the pond at different times of the day. Coordy cannot adjust how far he jumps very well, so he always jumps the same distance. Starting from his current lily pad his first jump is to the closest Y. Write down the letter order and coordinates of the lily pads he jumps to during each day. O Y 9 A D R C 8 O O F F U Y F N A O R G 8 9 N H I - D - - O P - -8 P -9 Order and coordinates are: Hint:!rewsna ruoy kcehc ot sdrawkcab em daer (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) (, ) P Learning H SERIES TOPIC 9
32 Cheat Sheet Here is a summary of the things you need to remember for the number plane Grid plane Grid planes have a vertical axis (usually marked with numbers) and a horizontal axis (usually marked with letters). A letter paired with a number is used to locate a grid area on maps. Axes and coordinates Number planes have two number lines as their axes. The Origin (, ) nd Quadrant (negative, positive) Vertical axis () st Quadrant (positive, positive) rd Quadrant th Quadrant - (negative, negative) (positive, negative) Coordinates help us locate points and are always written in curved brackets with a comma in between. (horizontal value, vertical value) Horizontal axis () Horizontal value is always written first. E.g. (-, ) means move two units horizontally to the left, then three units vertically up from the origin. Dependent and independent variables y = x+ x y 9 (, ) (, ) Input Independent variable Its value is given, so is independent of y Output Dependent variable Its value depends on the value of x Graphing tables of values Coordinates can be formed by pairing dependent and independent variables from a table of values. Plotting these points on a number plane will graph the rule used to complete the table of values. When plotting graphs of fees for services, the cost is placed on the vertical axis. H SERIES TOPIC P Learning
33 Notes P Learning H SERIES TOPIC
34 Notes H SERIES TOPIC P Learning
35
36 AXES AND COORDINATES * AXES AND COORDINATES GRID PLANE * GRID PLANE * GRID PLANE * * FEES AND CHARGES * FEES AND CHARGES * PLOTTING TABLES OF VALUES * PLOTTING TABLES OF VALUES *(x, y).../.../....../.../....../.../....../.../....../.../... DEPENDENT AND INDEPENDENT VARIABLES *
Activity The Coordinate System and Descriptive Geometry
 Activity 1.5.1 The Coordinate System and Descriptive Geometry Introduction North, east, south, and west. Go down the street about six blocks, take a left, and then go north for about 2 miles; you will
Activity 1.5.1 The Coordinate System and Descriptive Geometry Introduction North, east, south, and west. Go down the street about six blocks, take a left, and then go north for about 2 miles; you will
1.1. Driving Around Euclid. Goals. Launch 1.1
 1.1 Driving Around Euclid Goals Review the coordinate system Explore distances on a coordinate grid In this problem, students review the concept of the coordinate grid and are introduced to the idea of
1.1 Driving Around Euclid Goals Review the coordinate system Explore distances on a coordinate grid In this problem, students review the concept of the coordinate grid and are introduced to the idea of
Coordinate Graphing Quadrants and Reading Ordered Pairs. TeacherTwins 2015
 Coordinate Graphing Quadrants and Reading Ordered Pairs TeacherTwins 2015 Warm Up Graph the integers on a number line. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. -5, - 2, 5, 2 0, -3, 7, -2-4, 1, -6, 8-1, 4, -7, 0 6, -8, 5, -4 Warm
Coordinate Graphing Quadrants and Reading Ordered Pairs TeacherTwins 2015 Warm Up Graph the integers on a number line. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. -5, - 2, 5, 2 0, -3, 7, -2-4, 1, -6, 8-1, 4, -7, 0 6, -8, 5, -4 Warm
Class IX Mathematics (Ex. 3.1) Questions
 Class IX Mathematics (Ex. 3.1) Questions 1. How will you describe the position of a table lamp on your study table to another person? 2. (Street Plan): A city has two main roads which cross each other
Class IX Mathematics (Ex. 3.1) Questions 1. How will you describe the position of a table lamp on your study table to another person? 2. (Street Plan): A city has two main roads which cross each other
6th Grade Graphing
 1 6th Grade Graphing 2015-12-02 www.njctl.org 2 Graphing 6th Grade Topics Cartesian Plane Click on the topic to go to that section Graphing Ordered Pairs Polygons in the Coordinate Plane Cartesian Plane
1 6th Grade Graphing 2015-12-02 www.njctl.org 2 Graphing 6th Grade Topics Cartesian Plane Click on the topic to go to that section Graphing Ordered Pairs Polygons in the Coordinate Plane Cartesian Plane
Exercise (3.1) Question 1: How will you describe the position of a table lamp on your study table to another person?
 Class IX - NCERT Maths Exercise (3.1) Question 1: How will you describe the position of a table lamp on your study table to another person? Solution 1: Let us consider the given below figure of a study
Class IX - NCERT Maths Exercise (3.1) Question 1: How will you describe the position of a table lamp on your study table to another person? Solution 1: Let us consider the given below figure of a study
UNIT 6. Coordinate Plane CCM6+ Name: Math Teacher:
 UNIT 6 2017 2018 Coordinate Plane CCM6+ Name: Math Teacher: Main Concept 1 P a g e Page(s) Descartes and the Fly / Unit 6 Vocabulary 2 Daily Warm-Ups 3 5 Graphing on the Coordinate Plane 6 11 Reflections
UNIT 6 2017 2018 Coordinate Plane CCM6+ Name: Math Teacher: Main Concept 1 P a g e Page(s) Descartes and the Fly / Unit 6 Vocabulary 2 Daily Warm-Ups 3 5 Graphing on the Coordinate Plane 6 11 Reflections
Integers and the Coordinate Plane
 Name Date Class 9A Dear Family, A Family Letter: Understanding Integers The student will begin the study of an important set of numbers called integers. Integers are the set of numbers that include all
Name Date Class 9A Dear Family, A Family Letter: Understanding Integers The student will begin the study of an important set of numbers called integers. Integers are the set of numbers that include all
Rational Numbers: Graphing: The Coordinate Plane
 Rational Numbers: Graphing: The Coordinate Plane A special kind of plane used in mathematics is the coordinate plane, sometimes called the Cartesian plane after its inventor, René Descartes. It is one
Rational Numbers: Graphing: The Coordinate Plane A special kind of plane used in mathematics is the coordinate plane, sometimes called the Cartesian plane after its inventor, René Descartes. It is one
Rational Numbers and the Coordinate Plane
 Rational Numbers and the Coordinate Plane LAUNCH (8 MIN) Before How can you use the numbers placed on the grid to figure out the scale that is used? Can you tell what the signs of the x- and y-coordinates
Rational Numbers and the Coordinate Plane LAUNCH (8 MIN) Before How can you use the numbers placed on the grid to figure out the scale that is used? Can you tell what the signs of the x- and y-coordinates
Higher tier unit 6a check in test. Calculator
 Higher tier unit 6a check in test Calculator Q1. The point A has coordinates (2, 3). The point B has coordinates (6, 8). M is the midpoint of the line AB. Find the coordinates of M. Q2. The points A, B
Higher tier unit 6a check in test Calculator Q1. The point A has coordinates (2, 3). The point B has coordinates (6, 8). M is the midpoint of the line AB. Find the coordinates of M. Q2. The points A, B
Math 7 Notes - Unit 4 Pattern & Functions
 Math 7 Notes - Unit 4 Pattern & Functions Syllabus Objective: (3.2) The student will create tables, charts, and graphs to extend a pattern in order to describe a linear rule, including integer values.
Math 7 Notes - Unit 4 Pattern & Functions Syllabus Objective: (3.2) The student will create tables, charts, and graphs to extend a pattern in order to describe a linear rule, including integer values.
X & Y COORDINATES. Teachers Guide
 Teachers Guide Background: One piece of information that is essential to us on a daily basis is our location. We may not realize how often we use this type of information, but a little reflection on your
Teachers Guide Background: One piece of information that is essential to us on a daily basis is our location. We may not realize how often we use this type of information, but a little reflection on your
February 13, notebook
 Module 12 Lesson 1: Graphing on the coordinate plane Lesson 2: Independent and dependent variables in tables and graphs Lesson 3: Writing equations from tables Lesson 4: Representing Algebraic relationships
Module 12 Lesson 1: Graphing on the coordinate plane Lesson 2: Independent and dependent variables in tables and graphs Lesson 3: Writing equations from tables Lesson 4: Representing Algebraic relationships
Page 1 CCM6+ Unit 10 Graphing UNIT 10 COORDINATE PLANE. CCM Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date:
 Page 1 CCM6+ Unit 10 Graphing UNIT 10 COORDINATE PLANE CCM6+ 2015-16 Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: Main Concept Page(s) Vocabulary 2 Coordinate Plane Introduction graph and 3-6 label Reflect
Page 1 CCM6+ Unit 10 Graphing UNIT 10 COORDINATE PLANE CCM6+ 2015-16 Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: Main Concept Page(s) Vocabulary 2 Coordinate Plane Introduction graph and 3-6 label Reflect
The Cartesian plane 15B
 Weblink attleship Game e A bishop can move diagonall an number of (unoccupied) squares at a time. omplete the following sentence: With its net move, the bishop at b could capture the........ (name the
Weblink attleship Game e A bishop can move diagonall an number of (unoccupied) squares at a time. omplete the following sentence: With its net move, the bishop at b could capture the........ (name the
Name Date Period. Unit 9: The Coordinate Plane Test Review
 Name Date Period Unit 9: The Coordinate Plane Test Review Complete this review to help you prepare for the upcoming test. The more effort you put in, the more you will get out of it. This is due the day
Name Date Period Unit 9: The Coordinate Plane Test Review Complete this review to help you prepare for the upcoming test. The more effort you put in, the more you will get out of it. This is due the day
Coordinates - Activity 1 Plotting whole number ordered pairs.
 Name: Class: p 3 Maths Helper Plus Resource Set 1. Copyright 2002 Bruce A. Vaughan, Teachers Choice Software Coordinates - Activity 1 Plotting whole number ordered pairs. 1) Start Maths Helper Plus and
Name: Class: p 3 Maths Helper Plus Resource Set 1. Copyright 2002 Bruce A. Vaughan, Teachers Choice Software Coordinates - Activity 1 Plotting whole number ordered pairs. 1) Start Maths Helper Plus and
Section 2 0: The Rectangular Coordinate System. The Coordinate System
 Section 2 : The Rectangular Coordinate System The rectangular coordinate system is based on two number lines. A horizontal line called the x axis and a vertical line called the y axis. Each axis has marks
Section 2 : The Rectangular Coordinate System The rectangular coordinate system is based on two number lines. A horizontal line called the x axis and a vertical line called the y axis. Each axis has marks
The Rectangular Coordinate Systems and Graphs
 OpenStax-CNX module: m51252 1 The Rectangular Coordinate Systems and Graphs OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 In this
OpenStax-CNX module: m51252 1 The Rectangular Coordinate Systems and Graphs OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 In this
Systems of Linear Equations and Graphs
 8.1 Systems of Linear Equations and Graphs Focus on explaining the meaning of the point of intersection of two linear equations solving systems of linear equations by creating graphs, with and without
8.1 Systems of Linear Equations and Graphs Focus on explaining the meaning of the point of intersection of two linear equations solving systems of linear equations by creating graphs, with and without
Unit 2A: Systems of Equations and Inequalities
 Unit A: Systems of Equations and Inequalities In this unit, you will learn how to do the following: Learning Target #1: Creating and Solving Systems of Equations Identify the solution to a system from
Unit A: Systems of Equations and Inequalities In this unit, you will learn how to do the following: Learning Target #1: Creating and Solving Systems of Equations Identify the solution to a system from
Chapter12. Coordinate geometry
 Chapter1 Coordinate geometr Contents: A The Cartesian plane B Plotting points from a table of values C Linear relationships D Plotting graphs of linear equations E Horizontal and vertical lines F Points
Chapter1 Coordinate geometr Contents: A The Cartesian plane B Plotting points from a table of values C Linear relationships D Plotting graphs of linear equations E Horizontal and vertical lines F Points
7/7/2016 Unit 4: Linear Relations Grade 9 Mathematics
 Rene Descartes, a mathematician who lived during the 17 th century, developed a system for graphing ordered pairs on a grid. This system is called the Cartesian Coordinate System. 1 In this system, ordered
Rene Descartes, a mathematician who lived during the 17 th century, developed a system for graphing ordered pairs on a grid. This system is called the Cartesian Coordinate System. 1 In this system, ordered
Unit 6: Formulas and Patterns
 Section 6.1: Connect the Dots? Section 6.2: Equations and Graphs Section 6.3: Graphing Equations by Plotting Points Section 6.4: Intercepts Section 6.5: Horizontal and Vertical Lines Section 6.6: Looking
Section 6.1: Connect the Dots? Section 6.2: Equations and Graphs Section 6.3: Graphing Equations by Plotting Points Section 6.4: Intercepts Section 6.5: Horizontal and Vertical Lines Section 6.6: Looking
Lesson 20: Solution Sets to Equations with Two Variables
 Student Outcomes Students recognize and identify solutions to two variable equations. They represent the solution set graphically. They create two variable equations to represent a situation. They understand
Student Outcomes Students recognize and identify solutions to two variable equations. They represent the solution set graphically. They create two variable equations to represent a situation. They understand
11.6 The Coordinate Plane
 11.6 The Coordinate Plane Introduction The Map Kevin and his pen pal Charlotte are both creating maps of their neighborhoods to show each other what it looks like where they live. Kevin has decided to
11.6 The Coordinate Plane Introduction The Map Kevin and his pen pal Charlotte are both creating maps of their neighborhoods to show each other what it looks like where they live. Kevin has decided to
Section 3.1 Graphing Using the Rectangular Coordinate System
 Objectives Section 3.1 Graphing Using the Rectangular Coordinate System n Construct a rectangular coordinate system n Plot ordered pairs and determine the coordinates of a point n Graph paired data n Read
Objectives Section 3.1 Graphing Using the Rectangular Coordinate System n Construct a rectangular coordinate system n Plot ordered pairs and determine the coordinates of a point n Graph paired data n Read
Name Period Date LINEAR FUNCTIONS STUDENT PACKET 2: MULTIPLE REPRESENTATIONS 2
 Name Period Date LINEAR FUNCTIONS STUDENT PACKET 2: MULTIPLE REPRESENTATIONS 2 LF2.1 LF2.2 LF2.3 Growing Shapes Use variables, parentheses, and exponents in expressions. Use formulas to find perimeter
Name Period Date LINEAR FUNCTIONS STUDENT PACKET 2: MULTIPLE REPRESENTATIONS 2 LF2.1 LF2.2 LF2.3 Growing Shapes Use variables, parentheses, and exponents in expressions. Use formulas to find perimeter
Objective: Construct a coordinate system on a plane.
 Lesson 2 Objective: Construct a coordinate system on a plane. Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (10 minutes) (7 minutes) (33
Lesson 2 Objective: Construct a coordinate system on a plane. Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (10 minutes) (7 minutes) (33
Coatbridge High School Mathematics Department. Homework Booklet. CfE Level 4
 Coatbridge High School Mathematics Department Homework Booklet CfE Level 4 MNU 4-01a: Having investigated the practical impact of inaccuracy and error, I can use my knowledge of tolerance when choosing
Coatbridge High School Mathematics Department Homework Booklet CfE Level 4 MNU 4-01a: Having investigated the practical impact of inaccuracy and error, I can use my knowledge of tolerance when choosing
Rational Numbers on the Coordinate Plane. 6.NS.C.6c
 Rational Numbers on the Coordinate Plane 6.NS.C.6c Copy all slides into your composition notebook. Lesson 14 Ordered Pairs Objective: I can use ordered pairs to locate points on the coordinate plane. Guiding
Rational Numbers on the Coordinate Plane 6.NS.C.6c Copy all slides into your composition notebook. Lesson 14 Ordered Pairs Objective: I can use ordered pairs to locate points on the coordinate plane. Guiding
What You ll See in This Chapter. Word Cloud. René Descartes. Introduction. Ian Parberry University of North Texas. Fletcher Dunn
 What You ll See in This Chapter Chapter 1: Cartesian Coordinate Systems Fletcher Dunn Valve Software Ian Parberry University of North Texas This chapter describes the basic concepts of 3D math. It is divided
What You ll See in This Chapter Chapter 1: Cartesian Coordinate Systems Fletcher Dunn Valve Software Ian Parberry University of North Texas This chapter describes the basic concepts of 3D math. It is divided
Linear Equations in Two Variables IMPORTANT TERMS, DEFINITIONS AND RESULTS ANIL TUTORIALS SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 Linear Equations in Two Variables IMPORTANT TERMS, DEFINITIONS AND RESULTS l An equation of the form ax + by + c = 0, where a, b, c are real numbers, is called a linear equation in x and y. For example,
Linear Equations in Two Variables IMPORTANT TERMS, DEFINITIONS AND RESULTS l An equation of the form ax + by + c = 0, where a, b, c are real numbers, is called a linear equation in x and y. For example,
LEVEL 6. Level 6. Page (iv)
 LEVEL 6 Number Page N9... Fractions, Decimals and Percentages... 69 N20... Improper Fractions and Mixed Numbers... 70 N2... Prime Numbers, HCF and LCM... 7 Calculating C22... Percentage of an Amount...
LEVEL 6 Number Page N9... Fractions, Decimals and Percentages... 69 N20... Improper Fractions and Mixed Numbers... 70 N2... Prime Numbers, HCF and LCM... 7 Calculating C22... Percentage of an Amount...
Identify and graph ordered pairs on a coordinate grid.
 Ordered Pairs Teacher Notes Objective Identif and graph ordered pairs on a coordinate grid. Use these worksheets if students have trouble graphing on the coordinate plane graphing proportional relationships
Ordered Pairs Teacher Notes Objective Identif and graph ordered pairs on a coordinate grid. Use these worksheets if students have trouble graphing on the coordinate plane graphing proportional relationships
Factor Quadratic Expressions
 Factor Quadratic Expressions BLM 6... BLM 6 Factor Quadratic Expressions Get Ready BLM 6... Graph Quadratic Relations of the Form y = a(x h) + k. Sketch each parabola. Label the vertex, the axis of symmetry,
Factor Quadratic Expressions BLM 6... BLM 6 Factor Quadratic Expressions Get Ready BLM 6... Graph Quadratic Relations of the Form y = a(x h) + k. Sketch each parabola. Label the vertex, the axis of symmetry,
LCA Maths Department
 Name: LCA Maths Department Unit 9 Foundation Check-in test 1 Calculator Q1. GH. Write down the coordinates of the points G and H, and the coordinates of the midpoint of Q2. On the grid, mark with a cross
Name: LCA Maths Department Unit 9 Foundation Check-in test 1 Calculator Q1. GH. Write down the coordinates of the points G and H, and the coordinates of the midpoint of Q2. On the grid, mark with a cross
PATTERNS AND ALGEBRA. He opened mathematics to many discoveries and exciting applications.
 PATTERNS AND ALGEBRA The famous French philosopher and mathematician René Descartes (596 65) made a great contribution to mathematics in 67 when he published a book linking algebra and geometr for the
PATTERNS AND ALGEBRA The famous French philosopher and mathematician René Descartes (596 65) made a great contribution to mathematics in 67 when he published a book linking algebra and geometr for the
Year 2 Spring Term Week 5 to 7 - Geometry: Properties of Shape
 1 Year 2 Spring Term Week 5 to 7 - Geometry: Properties of Shape Recognise 2-D and 3-D shapes Count sides on 2-D shapes Count vertices on 2-D shapes Draw 2-D shapes Lines of symmetry Sort 2-D shapes Make
1 Year 2 Spring Term Week 5 to 7 - Geometry: Properties of Shape Recognise 2-D and 3-D shapes Count sides on 2-D shapes Count vertices on 2-D shapes Draw 2-D shapes Lines of symmetry Sort 2-D shapes Make
Working with Transformations on the Coordinate Plane
 Working with Transformations on the Coordinate Plane Movies create the illusion of movement by showing us 24 images per second. When the human eye processes 24 images per second it is interpreted in our
Working with Transformations on the Coordinate Plane Movies create the illusion of movement by showing us 24 images per second. When the human eye processes 24 images per second it is interpreted in our
This unit will help you to describe and use graphs correctly.
 Get started 6 Graph skills This unit will help you to describe and use graphs correctly. An important part of physics is describing the patterns we see in our observations about the universe. Graphs help
Get started 6 Graph skills This unit will help you to describe and use graphs correctly. An important part of physics is describing the patterns we see in our observations about the universe. Graphs help
Section 3.1 Objective 1: Plot Points in the Rectangular Coordinate System Video Length 12:35
 Section 3.1 Video Guide The Rectangular Coordinate System and Equations in Two Variables Objectives: 1. Plot Points in the Rectangular Coordinate System 2. Determine If an Ordered Pair Satisfies an Equation
Section 3.1 Video Guide The Rectangular Coordinate System and Equations in Two Variables Objectives: 1. Plot Points in the Rectangular Coordinate System 2. Determine If an Ordered Pair Satisfies an Equation
3.1. 3x 4y = 12 3(0) 4y = 12. 3x 4y = 12 3x 4(0) = y = x 0 = 12. 4y = 12 y = 3. 3x = 12 x = 4. The Rectangular Coordinate System
 3. The Rectangular Coordinate System Interpret a line graph. Objectives Interpret a line graph. Plot ordered pairs. 3 Find ordered pairs that satisfy a given equation. 4 Graph lines. 5 Find x- and y-intercepts.
3. The Rectangular Coordinate System Interpret a line graph. Objectives Interpret a line graph. Plot ordered pairs. 3 Find ordered pairs that satisfy a given equation. 4 Graph lines. 5 Find x- and y-intercepts.
Page 1 CCM6 Unit 10 Graphing UNIT 10 COORDINATE PLANE. CCM Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date:
 Page 1 CCM6 Unit 10 Graphing UNIT 10 COORDINATE PLANE CCM6 2016-17 Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: Main Concept Page(s) Vocabulary 2 Coordinate Plane Introduction graph and label 3-6 Reflect across
Page 1 CCM6 Unit 10 Graphing UNIT 10 COORDINATE PLANE CCM6 2016-17 Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: Main Concept Page(s) Vocabulary 2 Coordinate Plane Introduction graph and label 3-6 Reflect across
Name: Unit 3 Beaumont Middle School 8th Grade, Introduction to Algebra
 Unit 3 Beaumont Middle School 8th Grade, 2016-2017 Introduction to Algebra Name: I can identify a function, the domain and range. I can identify a linear relationship from a situation, table, graph and
Unit 3 Beaumont Middle School 8th Grade, 2016-2017 Introduction to Algebra Name: I can identify a function, the domain and range. I can identify a linear relationship from a situation, table, graph and
Lesson 18: There is Only One Line Passing Through a Given Point with a Given
 Lesson 18: There is Only One Line Passing Through a Given Point with a Given Student Outcomes Students graph equations in the form of using information about slope and intercept. Students know that if
Lesson 18: There is Only One Line Passing Through a Given Point with a Given Student Outcomes Students graph equations in the form of using information about slope and intercept. Students know that if
Overview for Families
 unit: Graphing Equations Mathematical strand: Algebra The following pages will help you to understand the mathematics that your child is currently studying as well as the type of problems (s)he will solve
unit: Graphing Equations Mathematical strand: Algebra The following pages will help you to understand the mathematics that your child is currently studying as well as the type of problems (s)he will solve
h b LEVEL 4 GEOMETRY
 h b LEVEL 4 GEOMETRY To the Student This resource covers topics from the British Columbia Ministry of Education s Literacy Foundations Math Level 4. You may find this resource useful if you re a Literacy
h b LEVEL 4 GEOMETRY To the Student This resource covers topics from the British Columbia Ministry of Education s Literacy Foundations Math Level 4. You may find this resource useful if you re a Literacy
5.2 Functions as Graphs
 5.. Functions as Graphs www.ck1.org 5. Functions as Graphs Learning Objectives Graph a function from a rule or table. Write a function rule from a graph. Analyze the graph of a real world situation. Determine
5.. Functions as Graphs www.ck1.org 5. Functions as Graphs Learning Objectives Graph a function from a rule or table. Write a function rule from a graph. Analyze the graph of a real world situation. Determine
Polygons in the Coordinate Plane
 Polygons in the Coordinate Plane LAUNCH (8 MIN) Before How can you find the perimeter of the sandbox that the park worker made? During How will you determine whether the park worker s plan for the sandbox
Polygons in the Coordinate Plane LAUNCH (8 MIN) Before How can you find the perimeter of the sandbox that the park worker made? During How will you determine whether the park worker s plan for the sandbox
Algebra 1 Interactive Chalkboard Copyright by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Send all inquiries to:
 Algebra 1 Interactive Chalkboard Copyright by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Send all inquiries to: GLENCOE DIVISION Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 8787 Orion Place Columbus, Ohio 43240 Lesson 4-1 The Coordinate
Algebra 1 Interactive Chalkboard Copyright by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Send all inquiries to: GLENCOE DIVISION Glencoe/McGraw-Hill 8787 Orion Place Columbus, Ohio 43240 Lesson 4-1 The Coordinate
DRAFT CHAPTER. Surface Area GET READY. xxx. Math Link. 5.1 Warm Up xxx. 5.1 Views of Three-Dimensional Objects xxx. 5.
 CHAPTER 5 Surface Area GET READY Math Link xxx xxx 5.1 Warm Up xxx 5.1 Views of Three-Dimensional Objects xxx 5.2 Warm Up xxx 5.2 Nets of Three-Dimensional Objects xxx 5.3 Warm Up xxx 5.3 Surface Area
CHAPTER 5 Surface Area GET READY Math Link xxx xxx 5.1 Warm Up xxx 5.1 Views of Three-Dimensional Objects xxx 5.2 Warm Up xxx 5.2 Nets of Three-Dimensional Objects xxx 5.3 Warm Up xxx 5.3 Surface Area
Vector Addition and Subtraction: Analytical Methods
 Connexions module: m42128 1 Vector Addition and Subtraction: Analytical Methods OpenStax College This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
Connexions module: m42128 1 Vector Addition and Subtraction: Analytical Methods OpenStax College This work is produced by The Connexions Project and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
Math 3 Coordinate Geometry part 1 Unit November 3, 2016
 Reviewing the basics The number line A number line is a visual representation of all real numbers. Each of the images below are examples of number lines. The top left one includes only positive whole numbers,
Reviewing the basics The number line A number line is a visual representation of all real numbers. Each of the images below are examples of number lines. The top left one includes only positive whole numbers,
Revision of Level I. In this lesson you will: Revise the topics learnt in the previous level.
 A m In this lesson you will: Revise the topics learnt in the previous level. Lesson1 Revision of Level I Moz walks in and sees that Jyoti is wiping the monitor with a soft duster while Tejas is wiping
A m In this lesson you will: Revise the topics learnt in the previous level. Lesson1 Revision of Level I Moz walks in and sees that Jyoti is wiping the monitor with a soft duster while Tejas is wiping
Grade Common Core Math
 th 5 Grade Common Core Math Printable Review Problems Standards Included:.-Use a pair of perpendicular number lines, called axes, to define a coordinate system, with the intersection of the lines (the
th 5 Grade Common Core Math Printable Review Problems Standards Included:.-Use a pair of perpendicular number lines, called axes, to define a coordinate system, with the intersection of the lines (the
Section 4.4: Parabolas
 Objective: Graph parabolas using the vertex, x-intercepts, and y-intercept. Just as the graph of a linear equation y mx b can be drawn, the graph of a quadratic equation y ax bx c can be drawn. The graph
Objective: Graph parabolas using the vertex, x-intercepts, and y-intercept. Just as the graph of a linear equation y mx b can be drawn, the graph of a quadratic equation y ax bx c can be drawn. The graph
Downloaded from CHAPTER 3 PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATION IN TWO VARIABLE KEY POINTS
 Downloaded from CHAPTER 3 PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATION IN TWO VARIABLE KEY POINTS 1. The most general form of a pair of linear equations is : a 1 x + b 1 y + c 1 = 0 a x + b y + c = 0 Where a 1, a, b 1, b,
Downloaded from CHAPTER 3 PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATION IN TWO VARIABLE KEY POINTS 1. The most general form of a pair of linear equations is : a 1 x + b 1 y + c 1 = 0 a x + b y + c = 0 Where a 1, a, b 1, b,
Decimals should be spoken digit by digit eg 0.34 is Zero (or nought) point three four (NOT thirty four).
 Numeracy Essentials Section 1 Number Skills Reading and writing numbers All numbers should be written correctly. Most pupils are able to read, write and say numbers up to a thousand, but often have difficulty
Numeracy Essentials Section 1 Number Skills Reading and writing numbers All numbers should be written correctly. Most pupils are able to read, write and say numbers up to a thousand, but often have difficulty
Bellwork. Find the absolute value for each point
 Bellwork Find the absolute value for each point a 4 b 0 2 c 6 1) a = 2) b = 3) c = 1 How many of you have ever been to a concert or a sports event where you had a ticket. Let's talk about what was on the
Bellwork Find the absolute value for each point a 4 b 0 2 c 6 1) a = 2) b = 3) c = 1 How many of you have ever been to a concert or a sports event where you had a ticket. Let's talk about what was on the
Name: Std: 6. Q.1 Fill in the blanks (Select the correct option) (6 Marks)
 Name: Std: 6 Div: Q.1 Fill in the blanks (Select the correct option) (6 Marks) (Search engine, Venn diagram, Google Chrome, Devices, Identify the goal, Internet) 1) The is a combined collection of interconnected
Name: Std: 6 Div: Q.1 Fill in the blanks (Select the correct option) (6 Marks) (Search engine, Venn diagram, Google Chrome, Devices, Identify the goal, Internet) 1) The is a combined collection of interconnected
L13-Mon-3-Oct-2016-Sec-1-1-Dist-Midpt-HW Graph-HW12-Moodle-Q11, page 1 L13-Mon-3-Oct-2016-Sec-1-1-Dist-Midpt-HW Graph-HW12-Moodle-Q11
 L13-Mon-3-Oct-016-Sec-1-1-Dist-Midpt-HW11-1--Graph-HW1-Moodle-Q11, page 1 L13-Mon-3-Oct-016-Sec-1-1-Dist-Midpt-HW11-1--Graph-HW1-Moodle-Q11 1.1 Rectangular Coordinate System: Suppose we know the sum of
L13-Mon-3-Oct-016-Sec-1-1-Dist-Midpt-HW11-1--Graph-HW1-Moodle-Q11, page 1 L13-Mon-3-Oct-016-Sec-1-1-Dist-Midpt-HW11-1--Graph-HW1-Moodle-Q11 1.1 Rectangular Coordinate System: Suppose we know the sum of
Mathematics 504 CST. Mid-Year Examination January Question/Answer Booklet. Student's Name FOR TEACHER USE ONLY. Part A /24.
 563-504 Mathematics 504 CST Mid-Year Examination January 2011 Question/Answer Booklet Student's Name Group Date FOR TEACHER USE ONLY Part A /24 Part B /16 Part C /60 Total /100 Question/Answer Booklet
563-504 Mathematics 504 CST Mid-Year Examination January 2011 Question/Answer Booklet Student's Name Group Date FOR TEACHER USE ONLY Part A /24 Part B /16 Part C /60 Total /100 Question/Answer Booklet
BETWEEN PAPERS PRACTICE (F&H)
 BETWEEN PAPERS PRACTICE (F&H) Summer 2018 QUESTIONS Not A best Guess paper. Neither is it a prediction... only the examiners know what is going to come up! Fact! You also need to REMEMBER that just because
BETWEEN PAPERS PRACTICE (F&H) Summer 2018 QUESTIONS Not A best Guess paper. Neither is it a prediction... only the examiners know what is going to come up! Fact! You also need to REMEMBER that just because
Chapter 1 Section 3. Page 22. A graph is a visual display of information or data. There are three types of graphs.
 Chapter 1 Section 3 Page 22 A graph is a visual display of information or data. There are three types of graphs. Graphs are pictures that help us understand amounts. These amounts are called data. There
Chapter 1 Section 3 Page 22 A graph is a visual display of information or data. There are three types of graphs. Graphs are pictures that help us understand amounts. These amounts are called data. There
Eureka Math. Grade, Module 6. Student File_B. Contains Sprint and Fluency, Exit Ticket, and Assessment Materials
 A Story of Units Eureka Math Grade, Module 6 Student File_B Contains Sprint and Fluency, Exit Ticket, and Assessment Materials Published by the non-profit Great Minds. Copyright 05 Great Minds. No part
A Story of Units Eureka Math Grade, Module 6 Student File_B Contains Sprint and Fluency, Exit Ticket, and Assessment Materials Published by the non-profit Great Minds. Copyright 05 Great Minds. No part
MAT 003 Brian Killough s Instructor Notes Saint Leo University
 MAT 003 Brian Killough s Instructor Notes Saint Leo University Success in online courses requires self-motivation and discipline. It is anticipated that students will read the textbook and complete sample
MAT 003 Brian Killough s Instructor Notes Saint Leo University Success in online courses requires self-motivation and discipline. It is anticipated that students will read the textbook and complete sample
In this lesson, you will: Use the Pythagorean Theorem to derive the Distance Formula. Apply the Distance Formula on the coordinate plane.
 A Let s Trip Move! to the Moon Using Translating Tables and to Represent Equivalent Constructing Ratios Line Segments..2 LEARNING GOALS KEY TERMS KEY TERM CONSTRUCTIONS In this lesson, you will: Pythagorean
A Let s Trip Move! to the Moon Using Translating Tables and to Represent Equivalent Constructing Ratios Line Segments..2 LEARNING GOALS KEY TERMS KEY TERM CONSTRUCTIONS In this lesson, you will: Pythagorean
Distance in Coordinate Geometry
 Page 1 of 6 L E S S O N 9.5 We talk too much; we should talk less and draw more. Distance in Coordinate Geometry Viki is standing on the corner of Seventh Street and 8th Avenue, and her brother Scott is
Page 1 of 6 L E S S O N 9.5 We talk too much; we should talk less and draw more. Distance in Coordinate Geometry Viki is standing on the corner of Seventh Street and 8th Avenue, and her brother Scott is
AP Calculus. Extreme Values: Graphically. Slide 1 / 163 Slide 2 / 163. Slide 4 / 163. Slide 3 / 163. Slide 5 / 163. Slide 6 / 163
 Slide 1 / 163 Slide 2 / 163 AP Calculus Analyzing Functions Using Derivatives 2015-11-04 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 163 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Slide 4 / 163 Extreme Values
Slide 1 / 163 Slide 2 / 163 AP Calculus Analyzing Functions Using Derivatives 2015-11-04 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 163 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Slide 4 / 163 Extreme Values
Week 8 Problems. #2 Points possible: 1. Total attempts: 2 Enter your answer rounded to two decimal places.
 Week 8 Problems Name: Neal Nelson Show Scored View # Points possible:. Total attempts: A pilot is flying over a straight highway. He determines the angles of depression to two mileposts,.6 mi apart, to
Week 8 Problems Name: Neal Nelson Show Scored View # Points possible:. Total attempts: A pilot is flying over a straight highway. He determines the angles of depression to two mileposts,.6 mi apart, to
2.1 Solutions to Exercises
 Last edited 9/6/17.1 Solutions to Exercises 1. P(t) = 1700t + 45,000. D(t) = t + 10 5. Timmy will have the amount A(n) given by the linear equation A(n) = 40 n. 7. From the equation, we see that the slope
Last edited 9/6/17.1 Solutions to Exercises 1. P(t) = 1700t + 45,000. D(t) = t + 10 5. Timmy will have the amount A(n) given by the linear equation A(n) = 40 n. 7. From the equation, we see that the slope
Angle, symmetry and transformation
 Terms Illustrations Definition Acute angle An angle greater than 0 and less than 90. Alternate angles Where two straight lines are cut by a third, as in the diagrams, the angles d and f (also c and e)
Terms Illustrations Definition Acute angle An angle greater than 0 and less than 90. Alternate angles Where two straight lines are cut by a third, as in the diagrams, the angles d and f (also c and e)
Math 7 Notes - Unit 4 Pattern & Functions
 Math 7 Notes - Unit 4 Pattern & Functions Syllabus Objective: (.) The student will create tables, charts, and graphs to etend a pattern in order to describe a linear rule, including integer values. Syllabus
Math 7 Notes - Unit 4 Pattern & Functions Syllabus Objective: (.) The student will create tables, charts, and graphs to etend a pattern in order to describe a linear rule, including integer values. Syllabus
Processing, representing and interpreting data
 Processing, representing and interpreting data 21 CHAPTER 2.1 A head CHAPTER 17 21.1 polygons A diagram can be drawn from grouped discrete data. A diagram looks the same as a bar chart except that the
Processing, representing and interpreting data 21 CHAPTER 2.1 A head CHAPTER 17 21.1 polygons A diagram can be drawn from grouped discrete data. A diagram looks the same as a bar chart except that the
PBL, Projects, and Activities downloaded from NextLesson are provided on an online platform.
 PBL, Projects, and Activities downloaded from NextLesson are provided on an online platform. driving question *example lesson teacher guide, answer keys, links, and rubrics share with students customize
PBL, Projects, and Activities downloaded from NextLesson are provided on an online platform. driving question *example lesson teacher guide, answer keys, links, and rubrics share with students customize
STAAR Mixed Practice HW
 Show all work and label units of measurement. 1. The equation y = x + 7 represents a linear relationship that is non-proportional. What change could you make to the equation to make it proportional? Name:
Show all work and label units of measurement. 1. The equation y = x + 7 represents a linear relationship that is non-proportional. What change could you make to the equation to make it proportional? Name:
GCSE Mathematics Practice Tests: Set 6
 GCSE Mathematics Practice Tests: Set 6 Paper 2H (Calculator) Time: 1 hour 30 minutes You should have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, pair of compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser,
GCSE Mathematics Practice Tests: Set 6 Paper 2H (Calculator) Time: 1 hour 30 minutes You should have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, protractor, pair of compasses, pen, HB pencil, eraser,
Multiply using the grid method.
 Multiply using the grid method. Learning Objective Read and plot coordinates in all quadrants DEFINITION Grid A pattern of horizontal and vertical lines, usually forming squares. DEFINITION Coordinate
Multiply using the grid method. Learning Objective Read and plot coordinates in all quadrants DEFINITION Grid A pattern of horizontal and vertical lines, usually forming squares. DEFINITION Coordinate
SPH3U1 Lesson 09 Kinematics
 VECTORS IN TWO-DIMENSIONS LEARNING GOALS Students will Draw vector scale diagrams to visualize and analyze the nature of motion in a plane. Analyze motion by using scale diagrams to add vectors. Solve
VECTORS IN TWO-DIMENSIONS LEARNING GOALS Students will Draw vector scale diagrams to visualize and analyze the nature of motion in a plane. Analyze motion by using scale diagrams to add vectors. Solve
GAP CLOSING. Integers. Intermediate / Senior Facilitator s Guide
 GAP CLOSING Integers Intermediate / Senior Facilitator s Guide Topic 3 Integers Diagnostic...5 Administer the diagnostic...5 Using diagnostic results to personalize interventions solutions...5 Using Intervention
GAP CLOSING Integers Intermediate / Senior Facilitator s Guide Topic 3 Integers Diagnostic...5 Administer the diagnostic...5 Using diagnostic results to personalize interventions solutions...5 Using Intervention
Math 2 Coordinate Geometry Part 1 Slope & Transformations
 Math 2 Coordinate Geometry Part 1 Slope & Transformations 1 MATH 1 REVIEW: THE NUMBER LINE A number line is a visual representation of all real numbers. Each of the images below are examples of number
Math 2 Coordinate Geometry Part 1 Slope & Transformations 1 MATH 1 REVIEW: THE NUMBER LINE A number line is a visual representation of all real numbers. Each of the images below are examples of number
Topic. Section 4.1 (3, 4)
 Topic.. California Standards: 6.0: Students graph a linear equation and compute the x- and y-intercepts (e.g., graph x + 6y = ). They are also able to sketch the region defined by linear inequality (e.g.,
Topic.. California Standards: 6.0: Students graph a linear equation and compute the x- and y-intercepts (e.g., graph x + 6y = ). They are also able to sketch the region defined by linear inequality (e.g.,
MATHEMATICS (SYLLABUS D) 4024/02
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level MATHEMATICS (SYLLABUS D) 4024/02 Paper 2 Additional Materials: Answer Booklet/Paper Electronic calculator Geometrical
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level MATHEMATICS (SYLLABUS D) 4024/02 Paper 2 Additional Materials: Answer Booklet/Paper Electronic calculator Geometrical
LET S PLOT POINTS. Time Frame Several classes. This concept must be reinforced repeatedly over many sessions.
 LET S PLOT POINTS Outcome (lesson objective) Students will understand and be able to correctly solve problems using coordinate geometry to describe spatial relationships. They will specify locations using
LET S PLOT POINTS Outcome (lesson objective) Students will understand and be able to correctly solve problems using coordinate geometry to describe spatial relationships. They will specify locations using
Example 1: Give the coordinates of the points on the graph.
 Ordered Pairs Often, to get an idea of the behavior of an equation, we will make a picture that represents the solutions to the equation. A graph gives us that picture. The rectangular coordinate plane,
Ordered Pairs Often, to get an idea of the behavior of an equation, we will make a picture that represents the solutions to the equation. A graph gives us that picture. The rectangular coordinate plane,
Grade 9 Assessment of Mathematics, Academic Booklet 1
 Grade 9 Assessment of Mathematics, 22 23 Academic Booklet 1 1. Which distance-time graph below best illustrates a car that gradually increases its speed? 2. In the figure, B = 45 and BC is produced to
Grade 9 Assessment of Mathematics, 22 23 Academic Booklet 1 1. Which distance-time graph below best illustrates a car that gradually increases its speed? 2. In the figure, B = 45 and BC is produced to
Unit 0: Extending Algebra 1 Concepts
 1 What is a Function? Unit 0: Extending Algebra 1 Concepts Definition: ---Function Notation--- Example: f(x) = x 2 1 Mapping Diagram Use the Vertical Line Test Interval Notation A convenient and compact
1 What is a Function? Unit 0: Extending Algebra 1 Concepts Definition: ---Function Notation--- Example: f(x) = x 2 1 Mapping Diagram Use the Vertical Line Test Interval Notation A convenient and compact
Shape & Space Part C: Transformations
 Name: Homeroom: Shape & Space Part C: Transformations Student Learning Expectations Outcomes: I can describe and analyze position and motion of objects and shapes by Checking for Understanding identifying
Name: Homeroom: Shape & Space Part C: Transformations Student Learning Expectations Outcomes: I can describe and analyze position and motion of objects and shapes by Checking for Understanding identifying
1 When Calvin woke up the temperature outside was. He checked the
 CALCULATOR NOT PERMITTED ITEMS 1 8 202639 1 When Calvin woke up the temperature outside was. He checked the temperature hourly and made the table below. Which graph shows the data in the table plotted
CALCULATOR NOT PERMITTED ITEMS 1 8 202639 1 When Calvin woke up the temperature outside was. He checked the temperature hourly and made the table below. Which graph shows the data in the table plotted
Mathematics. Unit 5: Transformations in the Coordinate Plane
 CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition Mathematics CCGPS Coordinate Algebra Unit 5: Transformations in the Coordinate Plane These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute
CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition Mathematics CCGPS Coordinate Algebra Unit 5: Transformations in the Coordinate Plane These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute
Targeting Maths. Middle Primary. Space. Over 90 BLMs. Graded activities that target all Maths topics
 Middle Primary Space Copying for Educational Purposes The purchasing educational institution and its staff have the right to make copies of the whole or part of this book, beyond their rights under the
Middle Primary Space Copying for Educational Purposes The purchasing educational institution and its staff have the right to make copies of the whole or part of this book, beyond their rights under the
Mathematics. Accelerated GSE Algebra I/Geometry A Unit 7: Transformations in the Coordinate Plane
 Georgia Standards of Excellence Frameworks Mathematics Accelerated GSE Algebra I/Geometry A Unit 7: Transformations in the Coordinate Plane These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only.
Georgia Standards of Excellence Frameworks Mathematics Accelerated GSE Algebra I/Geometry A Unit 7: Transformations in the Coordinate Plane These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only.
Maths PoS: Year 7 HT1. Students will colour code as they work through the scheme of work. Students will learn about Number and Shape
 Maths PoS: Year 7 HT1 Students will learn about Number and Shape Number: Use positive and negative numbers in context and position them on a number line. Recall quickly multiplication facts up to 10 10
Maths PoS: Year 7 HT1 Students will learn about Number and Shape Number: Use positive and negative numbers in context and position them on a number line. Recall quickly multiplication facts up to 10 10
WHOLE NUMBERS AND DECIMALS
 WHOLE NUMBERS AND DECIMALS 2 IN THIS CHAPTER YOU WILL: WHAT S IN CHAPTER 2? 2 01 Mental addition 2 02 Mental subtraction 2 03 Rounding decimals and money 2 04 Adding and subtracting decimals 2 05 Mental
WHOLE NUMBERS AND DECIMALS 2 IN THIS CHAPTER YOU WILL: WHAT S IN CHAPTER 2? 2 01 Mental addition 2 02 Mental subtraction 2 03 Rounding decimals and money 2 04 Adding and subtracting decimals 2 05 Mental
Did you ever think that a four hundred year-old spider may be why we study linear relationships today?
 Show Me: Determine if a Function is Linear M8221 Did you ever think that a four hundred year-old spider may be why we study linear relationships today? Supposedly, while lying in bed Rene Descartes noticed
Show Me: Determine if a Function is Linear M8221 Did you ever think that a four hundred year-old spider may be why we study linear relationships today? Supposedly, while lying in bed Rene Descartes noticed
Written test, 25 problems / 90 minutes
 Sponsored by: UGA Math Department and UGA Math Club Written test, 5 problems / 90 minutes October 1, 017 Instructions 1. At the top of the left of side 1 of your scan-tron answer sheet, fill in your last
Sponsored by: UGA Math Department and UGA Math Club Written test, 5 problems / 90 minutes October 1, 017 Instructions 1. At the top of the left of side 1 of your scan-tron answer sheet, fill in your last
4. TANGENTS AND NORMALS
 4. TANGENTS AND NORMALS 4. Equation of the Tangent at a Point Recall that the slope of a curve at a point is the slope of the tangent at that point. The slope of the tangent is the value of the derivative
4. TANGENTS AND NORMALS 4. Equation of the Tangent at a Point Recall that the slope of a curve at a point is the slope of the tangent at that point. The slope of the tangent is the value of the derivative
Curriculum Maps for Progress in Understanding Mathematics Assessment Termly content for Year 6
 Term-by-term mathematics assessment across primary school Curriculum Maps for Progress in Understanding Mathematics Assessment Termly content for Year 6 The PUMA tests provide thorough coverage of the
Term-by-term mathematics assessment across primary school Curriculum Maps for Progress in Understanding Mathematics Assessment Termly content for Year 6 The PUMA tests provide thorough coverage of the
