Geometric Acoustics in High-Speed Boundary Layers
|
|
|
- Winifred Goodman
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Accepted for presentation at the 9th International Symposium on Shock Waves. Madison, WI. July -9,. Paper #8 Geometric Acoustics in High-Speed Boundary Layers N. J. Parziale, J. E. Shepherd, and H. G. Hornung Introduction A key mechanism responsible for the instability of high-speed boundary layers are the high-frequency modes discovered by Mack []. These modes are primarily acoustic in nature, are always present if the edge Mach number is sufficiently large, and are the dominant instability mechanism when the wall temperature is sufficiently low compared to the recovery temperature. The propagation of acoustic waves within the boundary layer is profoundly influenced by the velocity and sound speed gradients created by the action of viscosity and heat conduction within the layer. These gradients form a waveguide that may trap acoustic waves and provide a mechanism for the formation of large amplitude disturbances. This suggests that geometrical acoustic analysis of these waveguides can provide insights into the potential for boundary layer acoustic instability. In this work, we outline the basics of geometric acoustics, apply the ray-tracing technique to example problems, and then high-speed boundary layers. The refractive behavior of different high-speed boundary layer profiles is compared. Our approach follows the classical ray-tracing approach [, ] to geometrical acoustics in which the propagation of a wavefront is calculated by computing the paths (rays) along which a point on the wavefront moves. From a physical point of view, geometrical acoustics is a high-frequency approximation that is valid when: ) the wavelengths are small compared to the geometrical features in the flow, in this case the height of the boundary layer; ) the amplitude and front curvature do not vary too rapidly along the wavefront; ) cusps or folds (caustics) do not form in the wavefront. In high-speed boundary layer profiles, the most amplified acoustic wavelength is known to be approximately boundary layer thicknesses [] and caustics are known to form [] so we acknowledge from the outset that our GALCIT, California Insitute of Technology E California Blvd; MC 5 5, Pasadena, CA 95, United States of America
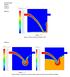
2 N. J. Parziale, J. E. Shepherd, H. G. Hornung results may be limited in quantitative applicability and will be more qualitative in nature. The rate of change of the position of a point x p on the wave-front can be written as, dx pi = n i c+v i = v ray,i () dt where v i is the local velocity, n i is the unit normal to the wave-front τ i (Fig. ). The speed of the wave-front normal to itself (c+ n i v i ) is in general different than the magnitude of the ray velocity n i c+v i. The evolution of the unit normal n i is n i c+v i = v ray,i x i n i c v i τ i at t+ t τ i at t Fig. Vector addition to find the velocity of the rays. cumbersome to compute directly so we use the formulation by Pierce [] in terms of the wave-slowness vector (s i = τ i ) components. where, ds i dt dx i dt = Ω c = c s i Ω + v i, dc dx i j= Ω = v i s i, s i = n i c+n i v i. s j dv j dx i, (a) (b) (a) (b) Example Problems Solutions to two example problems are presented here to provide basic insight into geometric acoustics as well as test our numerical methods. The first test problem is an adaptation from the work of Goodman and Duykers [5]. Analytic solutions for ray paths are found for a parabolic sound speed profile of the form c=c + α y, with /c =(/c )( y /L ), and L= c /α. In the example presented here, c = m/s, α = c /, and a rigid boundary at y= is imposed. The solution
3 Geometric Acoustics in High-Speed Boundary Layers for a ray path with initial angle of inclination to the horizontal θ, is y/l=sinθ sin(x/(lcosθ )). () This solution (solid line) and results from numerically integrating Eqs. (circular markers) are shown to agree favorably in Fig.. In this scenario, s x is a constant, per Eq. b. To calculate the point at which acoustic rays are refracted back to the surface, it is recognized that the ray direction is parallel to the unit normal, n, when horizontal [], and from Eq b, s x = cosθ c + cosθ v x = c h + v xh, (5) where the subscript indicates where local value at ray origin, and the subscript h indicates local value where the ray is horizontal. Using this observation, the wall normal distance where the ray is refracted back to the surface can be obtained algebraically. The predicted height (dashed line) shows favorable agreement with the analytic and numerical results in Fig.. Note the acoustic rays are refracted towards a sound speed minimum, consistent with the vertical component of Eq. b. y/l c/c x/(πlcos(θ )).5 Fig. A slight modification to the problem posed by Goodman and Duykers [5], with the analytical solution (solid line), numerical integration (circular markers), and predicted turning height (dashed line) showing good agreement. Initial angle of inclination of acoustic ray to the surface: θ =,6. The sound speed profile is plotted on the left. The second test problem is ray tracing through the Sound Fixing and Ranging (SOFAR) channel as previously computed by Munk [6], who assumed that the sound speed in the ocean, c, varies as c = c(y) = c (+ε(η(y)+e η(y) )), due to temperature and density gradients, where c =.9 km/s, ε =.7, η = η(y)=(z z )/(z /), and z =. km. Numerical integration of Eqs. with this sound speed profile gives reasonable visual agreement with Munk s results, although precise quantitative comparison is not possible. Acoustic rays are observed to be refracted to a sound speed minimum, which is consistent with Eq. b.
4 N. J. Parziale, J. E. Shepherd, H. G. Hornung Distance (km) c (km/s) Distance (km) 5 Fig. Replication of the case done by Munk [6], tracing acoustic rays through the SOFAR channel. The distance marks depth from the ocean surface, and the initial angle of the ray to the horizontal is denoted by a number overlaid on the line. High-speed Boundary Layers Geometrical acoustic implications for a selection of high-speed boundary layer profiles are presented in this section. Boundary layer profiles are computed using the similarity solution for a laminar, compressible, perfect-gas flow on a flat plate [7]. It was noted in the previous section that acoustic rays tend to be refracted towards sound speed minima. The mean flow of the boundary layer modifies this and the rays are refracted toward u + c minima, consistent with the vertical component of Eq. b. Three different profiles are presented in Figs. (a), (b), and (c) to illustrate the range of u + c profiles that are possible y/δ.6 y/δ.6 y/δ u/u E, c/c W, u+c u E+c E (a) u/u E, c/c W, u+c u E+c E (b).5.5 u/u E, c/c W, u+c u E+c E (c) Fig. a: Boundary layer profile for M E =, γ = 7/5, T W = T ad. b: Boundary layer profile for M E = 6, γ = 7/5, T W = T ad. c: Boundary layer profile for M E = 6, γ = 7/5, T W = T ad /. Each velocity profile (u/u E ) is normalized by the edge value (dash-dot). Each sound speed profile c/c W is normalized by the value at the wall (dashed). Each combined profile (u+c)/(u E + c E ) is normalized by the edge values (solid). Using Eq. 5 and assuming that the flow is locally parallel, the maximum angle that is refracted back to the surface can be found. We postulate that the larger this angle, the more unstable the boundary layer due to the larger amount of acous-
5 Geometric Acoustics in High-Speed Boundary Layers 5 tic energy trapped within the layer. The maximum angle of inclination is computed for rays originating at the surface of the plate for a range of Mach numbers (M E =.5 8) with an adiabatic wall and three different ratios of specific heats in Fig. 5(a). The maximum angle increases with increasing Mach number, reaching a constant value for M E 5. Wall temperature ratio (T W /T ad, where T ad is the adiabatic wall temperature) is another important parameter in determining the maximum initial angle of inclination for rays originating at the surface of the plate (Fig. 5(b)); at M E = 6, colder walls are observed to trap more acoustic rays. In Fig. 5(c), the wall normal distance of the origin of the acoustic ray is varied for an adiabatic plate with M E = 6. Fewer rays are trapped as the ray origin is translated from the surface. The results in Figs. 5(a), 5(b), and 5(c) do not change with Re x because the flow field is assumed to be locally parallel and the boundary layer profiles are self-similar. The non-parallel nature of the flow field can be included by interpolating the velocity and sound speed profiles calculated from the similarity solution for a certain range of Re x and solving Eqs.. In Fig. 6, ray traces originating from the surface of an adiabatic flat plate with M E = and γ = 7/5 with an initial angle of inclination of θ = 56,57,58 are observed to bracket the value predicted in Fig. 5(a). The edge Mach number is increased to 6 for the rays in Fig. 7 and ray traces with an initial angle of inclination of θ = 67,68,69 bracket the maximum value predicted in Fig. 5(a). Changing the boundary condition at the wall to T W = T ad / should increase the maximum initial angle of inclination per Fig. 5(b). This is reflected in the rays with an initial angle of θ = 8,8,8. Inclination to plate: θ γ = 6/5 γ = 7/5 γ = 5/ Edge Mach Number: M E (a) Inclination to plate: θ γ = 6/5 5 γ = 7/5 5 γ = 5/ Wall Temperature Ratio: T W/T ad (b) Inclination to plate: θ γ=5/ γ=7/5 γ=6/ Distance from wall: y/δ (c) Fig. 5 a: Largest angle of inclination to the plate of acoustic ray that is refracted back to the surface, M E =.5 8, γ = 6/5,7/5,5/, T W = T ad. b: Largest angle of inclination to the plate of acoustic ray that is refracted back to the surface, M E = 6, γ = 6/5,7/5,5/, T W = KT ad, where K is varied between and 5. c: Largest angle of inclination to the plate of acoustic ray that is refracted back to the surface at different wall normal origins, M E = 6, γ = 6/5,7/5,5/, T W = T ad.
6 6 N. J. Parziale, J. E. Shepherd, H. G. Hornung y (mm) 8 6 δ x (mm) Fig. 6 Ray traces for M E =, γ = 7/5, T W = T ad, with θ = 56,57,58 at Re x = 5. y (mm) 6 5 δ x (mm) Fig. 7 Ray traces for M E = 6, γ = 7/5, T W = T ad, with θ = 67,68,69 at Re x = 5. y (mm).5 δ x (mm) Fig. 8 Ray traces for M E = 6, γ = 7/5, T W = T ad /, with θ = 8,8,8 at Re x = 5. Conclusion Ray-tracing in high-speed boundary layers has been used to explore the potential for acoustic energy trapping as function of edge Mach number, wall temperature ratio, and thermodynamic parameters. We proposed a figure of merit for acoustic energy trapping as the critical angle of inclination for rays originating in the boundary that are trapped, i.e., these rays always stay within the boundary layer. Using this concept, we find that an increasing amount of acoustic energy is trapped with increasing edge Mach number (M E ), and decreasing wall temperature ratio (T W /T ad ). These trends agree qualitatively with the results of high-speed boundary layer stability calculation by Mack []. References. Mack, L. M., Boundary-layer Linear Stability Theory, AGARD Rep 79, Special Course on Stability Transitional Laminar Flows 98.. Pierce, A. D., Acoustics: An Introduction to its Physical Principles and Applications, Acoustical Society of America, Second ed., Thompson, P. A., Compressible-Fluid Dynamics, McGraw-Hill, 97.. G. A. Kriegsmann and E. L. Reiss, Acoustic Propagation in Wall Shear Flows and the Formation of Caustics, Journal of The Acoustical Society Of America. 5. Goodman, R. R. and Duykers, L. R. B., Calculations of Convergent Zones in a Sound Channel, The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, Vol., No. 7, 96, pp Munk, W. H., Sound Channel in an Exponentially Stratified Ocean, with Application to SO- FAR, Journal of The Acoustical Society Of America, Vol. 55, No., 97, pp White, F., Viscous Fluid Flow, McGraw-Hill, rd ed., 6.
Numerical and theoretical analysis of shock waves interaction and reflection
 Fluid Structure Interaction and Moving Boundary Problems IV 299 Numerical and theoretical analysis of shock waves interaction and reflection K. Alhussan Space Research Institute, King Abdulaziz City for
Fluid Structure Interaction and Moving Boundary Problems IV 299 Numerical and theoretical analysis of shock waves interaction and reflection K. Alhussan Space Research Institute, King Abdulaziz City for
MODELING OF THREE-DIMENSIONAL PROPAGATION ON A COASTAL WEDGE WITH A SEDIMENT SUPPORTING SHEAR
 MODELING OF THREE-DIMENSIONAL PROPAGATION ON A COASTAL WEDGE WITH A SEDIMENT SUPPORTING SHEAR Piotr Borejko Vienna University of Technology, Karlsplatz 13/E26/3, 14 Vienna, Austria Fax: + 43 1 588 1 21
MODELING OF THREE-DIMENSIONAL PROPAGATION ON A COASTAL WEDGE WITH A SEDIMENT SUPPORTING SHEAR Piotr Borejko Vienna University of Technology, Karlsplatz 13/E26/3, 14 Vienna, Austria Fax: + 43 1 588 1 21
Oblique Shock Reflection From Wall
 Reflected Waves Already examined what happens when normal shock hits a boundary if incident shock hits solid wall, get reflected (normal) shock - required to satisfy velocity (bc) boundary condition (v=0)
Reflected Waves Already examined what happens when normal shock hits a boundary if incident shock hits solid wall, get reflected (normal) shock - required to satisfy velocity (bc) boundary condition (v=0)
Lab #5 Ocean Acoustic Environment
 Lab #5 Ocean Acoustic Environment 2.S998 Unmanned Marine Vehicle Autonomy, Sensing and Communications Contents 1 The ocean acoustic environment 3 1.1 Ocean Acoustic Waveguide................................
Lab #5 Ocean Acoustic Environment 2.S998 Unmanned Marine Vehicle Autonomy, Sensing and Communications Contents 1 The ocean acoustic environment 3 1.1 Ocean Acoustic Waveguide................................
Lab 6 - Ocean Acoustic Environment
 Lab 6 - Ocean Acoustic Environment 2.680 Unmanned Marine Vehicle Autonomy, Sensing and Communications Feb 26th 2019 Henrik Schmidt, henrik@mit.edu Michael Benjamin, mikerb@mit.edu Department of Mechanical
Lab 6 - Ocean Acoustic Environment 2.680 Unmanned Marine Vehicle Autonomy, Sensing and Communications Feb 26th 2019 Henrik Schmidt, henrik@mit.edu Michael Benjamin, mikerb@mit.edu Department of Mechanical
Characteristic Aspects of SPH Solutions
 Characteristic Aspects of SPH Solutions for Free Surface Problems: Source and Possible Treatment of High Frequency Numerical Oscillations of Local Loads. A. Colagrossi*, D. Le Touzé & G.Colicchio* *INSEAN
Characteristic Aspects of SPH Solutions for Free Surface Problems: Source and Possible Treatment of High Frequency Numerical Oscillations of Local Loads. A. Colagrossi*, D. Le Touzé & G.Colicchio* *INSEAN
LES Analysis on Shock-Vortex Ring Interaction
 LES Analysis on Shock-Vortex Ring Interaction Yong Yang Jie Tang Chaoqun Liu Technical Report 2015-08 http://www.uta.edu/math/preprint/ LES Analysis on Shock-Vortex Ring Interaction Yong Yang 1, Jie Tang
LES Analysis on Shock-Vortex Ring Interaction Yong Yang Jie Tang Chaoqun Liu Technical Report 2015-08 http://www.uta.edu/math/preprint/ LES Analysis on Shock-Vortex Ring Interaction Yong Yang 1, Jie Tang
Example 13 - Shock Tube
 Example 13 - Shock Tube Summary This famous experiment is interesting for observing the shock-wave propagation. Moreover, this case uses the representation of perfect gas and compares the different formulations:
Example 13 - Shock Tube Summary This famous experiment is interesting for observing the shock-wave propagation. Moreover, this case uses the representation of perfect gas and compares the different formulations:
Faculty of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia (UTHM), Parit Raja, Batu Pahat, Johor, Malaysia
 Applied Mechanics and Materials Vol. 393 (2013) pp 305-310 (2013) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.393.305 The Implementation of Cell-Centred Finite Volume Method
Applied Mechanics and Materials Vol. 393 (2013) pp 305-310 (2013) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.393.305 The Implementation of Cell-Centred Finite Volume Method
A COUPLED FINITE VOLUME SOLVER FOR THE SOLUTION OF LAMINAR TURBULENT INCOMPRESSIBLE AND COMPRESSIBLE FLOWS
 A COUPLED FINITE VOLUME SOLVER FOR THE SOLUTION OF LAMINAR TURBULENT INCOMPRESSIBLE AND COMPRESSIBLE FLOWS L. Mangani Maschinentechnik CC Fluidmechanik und Hydromaschinen Hochschule Luzern Technik& Architektur
A COUPLED FINITE VOLUME SOLVER FOR THE SOLUTION OF LAMINAR TURBULENT INCOMPRESSIBLE AND COMPRESSIBLE FLOWS L. Mangani Maschinentechnik CC Fluidmechanik und Hydromaschinen Hochschule Luzern Technik& Architektur
Driven Cavity Example
 BMAppendixI.qxd 11/14/12 6:55 PM Page I-1 I CFD Driven Cavity Example I.1 Problem One of the classic benchmarks in CFD is the driven cavity problem. Consider steady, incompressible, viscous flow in a square
BMAppendixI.qxd 11/14/12 6:55 PM Page I-1 I CFD Driven Cavity Example I.1 Problem One of the classic benchmarks in CFD is the driven cavity problem. Consider steady, incompressible, viscous flow in a square
An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2010
 An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2010 John E. Matsson, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation Chapter 2 Flat Plate Boundary Layer Objectives Creating
An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2010 John E. Matsson, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation Chapter 2 Flat Plate Boundary Layer Objectives Creating
Reflection and Refraction. Chapter 29
 Reflection and Refraction Chapter 29 Reflection When a wave reaches a boundary between two media, some or all of the wave bounces back into the first medium. Reflection The angle of incidence is equal
Reflection and Refraction Chapter 29 Reflection When a wave reaches a boundary between two media, some or all of the wave bounces back into the first medium. Reflection The angle of incidence is equal
Verification and Validation for Seismic Wave Propagation Problems
 Chapter 26 Verification and Validation for Seismic Wave Propagation Problems (1989-2-24-25-28-29-21-211-217-) (In collaboration with Dr. Nima Tafazzoli, Dr. Federico Pisanò, Mr. Kohei Watanabe and Mr.
Chapter 26 Verification and Validation for Seismic Wave Propagation Problems (1989-2-24-25-28-29-21-211-217-) (In collaboration with Dr. Nima Tafazzoli, Dr. Federico Pisanò, Mr. Kohei Watanabe and Mr.
Application of Finite Volume Method for Structural Analysis
 Application of Finite Volume Method for Structural Analysis Saeed-Reza Sabbagh-Yazdi and Milad Bayatlou Associate Professor, Civil Engineering Department of KNToosi University of Technology, PostGraduate
Application of Finite Volume Method for Structural Analysis Saeed-Reza Sabbagh-Yazdi and Milad Bayatlou Associate Professor, Civil Engineering Department of KNToosi University of Technology, PostGraduate
Modeling Supersonic Jet Screech Noise Using Direct Computational Aeroacoustics (CAA) 14.5 Release
 Modeling Supersonic Jet Screech Noise Using Direct Computational Aeroacoustics (CAA) 14.5 Release 2011 ANSYS, Inc. November 7, 2012 1 Workshop Advanced ANSYS FLUENT Acoustics Introduction This tutorial
Modeling Supersonic Jet Screech Noise Using Direct Computational Aeroacoustics (CAA) 14.5 Release 2011 ANSYS, Inc. November 7, 2012 1 Workshop Advanced ANSYS FLUENT Acoustics Introduction This tutorial
COMPUTATIONALLY EFFICIENT RAY TRACING ALGORITHM FOR SIMULATION OF TRANSDUCER FIELDS IN ANISOTROPIC MATERIALS
 Proceedings of the National Seminar & Exhibition on Non-Destructive Evaluation NDE 2011, December 8-10, 2011 COMPUTATIONALLY EFFICIENT RAY TRACING ALGORITHM FOR SIMULATION OF TRANSDUCER FIELDS IN ANISOTROPIC
Proceedings of the National Seminar & Exhibition on Non-Destructive Evaluation NDE 2011, December 8-10, 2011 COMPUTATIONALLY EFFICIENT RAY TRACING ALGORITHM FOR SIMULATION OF TRANSDUCER FIELDS IN ANISOTROPIC
Non-Newtonian Transitional Flow in an Eccentric Annulus
 Tutorial 8. Non-Newtonian Transitional Flow in an Eccentric Annulus Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate the setup and solution of a 3D, turbulent flow of a non-newtonian fluid. Turbulent
Tutorial 8. Non-Newtonian Transitional Flow in an Eccentric Annulus Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate the setup and solution of a 3D, turbulent flow of a non-newtonian fluid. Turbulent
Technical Report TR
 Technical Report TR-2015-09 Boundary condition enforcing methods for smoothed particle hydrodynamics Arman Pazouki 1, Baofang Song 2, Dan Negrut 1 1 University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, 53706-1572,
Technical Report TR-2015-09 Boundary condition enforcing methods for smoothed particle hydrodynamics Arman Pazouki 1, Baofang Song 2, Dan Negrut 1 1 University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, 53706-1572,
Validation of aspects of BeamTool
 Vol.19 No.05 (May 2014) - The e-journal of Nondestructive Testing - ISSN 1435-4934 www.ndt.net/?id=15673 Validation of aspects of BeamTool E. GINZEL 1, M. MATHESON 2, P. CYR 2, B. BROWN 2 1 Materials Research
Vol.19 No.05 (May 2014) - The e-journal of Nondestructive Testing - ISSN 1435-4934 www.ndt.net/?id=15673 Validation of aspects of BeamTool E. GINZEL 1, M. MATHESON 2, P. CYR 2, B. BROWN 2 1 Materials Research
Numerical Analysis of Shock Tube Problem by using TVD and ACM Schemes
 Numerical Analysis of Shock Tube Problem by using TVD and Schemes Dr. Mukkarum Husain, Dr. M. Nauman Qureshi, Syed Zaid Hasany IST Karachi, Email: mrmukkarum@yahoo.com Abstract Computational Fluid Dynamics
Numerical Analysis of Shock Tube Problem by using TVD and Schemes Dr. Mukkarum Husain, Dr. M. Nauman Qureshi, Syed Zaid Hasany IST Karachi, Email: mrmukkarum@yahoo.com Abstract Computational Fluid Dynamics
New Conjugate-Heat Transfer Solvers in the Compressible CESE Solver in LS-DYNA
 New Conjugate-Heat Transfer Solvers in the Compressible CESE Solver in LS-DYNA Grant O. Cook, Jr. and Zeng-Chan Zhang Livermore Software Technology Corp., Livermore, CA 94551 Abstract Standard coupling
New Conjugate-Heat Transfer Solvers in the Compressible CESE Solver in LS-DYNA Grant O. Cook, Jr. and Zeng-Chan Zhang Livermore Software Technology Corp., Livermore, CA 94551 Abstract Standard coupling
Modeling External Compressible Flow
 Tutorial 3. Modeling External Compressible Flow Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to compute the turbulent flow past a transonic airfoil at a nonzero angle of attack. You will use the Spalart-Allmaras
Tutorial 3. Modeling External Compressible Flow Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to compute the turbulent flow past a transonic airfoil at a nonzero angle of attack. You will use the Spalart-Allmaras
Let s review the four equations we now call Maxwell s equations. (Gauss s law for magnetism) (Faraday s law)
 Electromagnetic Waves Let s review the four equations we now call Maxwell s equations. E da= B d A= Q encl ε E B d l = ( ic + ε ) encl (Gauss s law) (Gauss s law for magnetism) dφ µ (Ampere s law) dt dφ
Electromagnetic Waves Let s review the four equations we now call Maxwell s equations. E da= B d A= Q encl ε E B d l = ( ic + ε ) encl (Gauss s law) (Gauss s law for magnetism) dφ µ (Ampere s law) dt dφ
Travel-Time Sensitivity Kernels in Long-Range Propagation
 Travel-Time Sensitivity Kernels in Long-Range Propagation Emmanuel Skarsoulis Foundation for Research and Technology Hellas Institute of Applied and Computational Mathematics P.O. Box 1385, GR-71110 Heraklion,
Travel-Time Sensitivity Kernels in Long-Range Propagation Emmanuel Skarsoulis Foundation for Research and Technology Hellas Institute of Applied and Computational Mathematics P.O. Box 1385, GR-71110 Heraklion,
Part Images Formed by Flat Mirrors. This Chapter. Phys. 281B Geometric Optics. Chapter 2 : Image Formation. Chapter 2: Image Formation
 Phys. 281B Geometric Optics This Chapter 3 Physics Department Yarmouk University 21163 Irbid Jordan 1- Images Formed by Flat Mirrors 2- Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors 3- Images Formed by Refraction
Phys. 281B Geometric Optics This Chapter 3 Physics Department Yarmouk University 21163 Irbid Jordan 1- Images Formed by Flat Mirrors 2- Images Formed by Spherical Mirrors 3- Images Formed by Refraction
Influence of mesh quality and density on numerical calculation of heat exchanger with undulation in herringbone pattern
 Influence of mesh quality and density on numerical calculation of heat exchanger with undulation in herringbone pattern Václav Dvořák, Jan Novosád Abstract Research of devices for heat recovery is currently
Influence of mesh quality and density on numerical calculation of heat exchanger with undulation in herringbone pattern Václav Dvořák, Jan Novosád Abstract Research of devices for heat recovery is currently
Use of CFD in Design and Development of R404A Reciprocating Compressor
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2006 Use of CFD in Design and Development of R404A Reciprocating Compressor Yogesh V. Birari
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2006 Use of CFD in Design and Development of R404A Reciprocating Compressor Yogesh V. Birari
Estimating Vertical Drag on Helicopter Fuselage during Hovering
 Estimating Vertical Drag on Helicopter Fuselage during Hovering A. A. Wahab * and M.Hafiz Ismail ** Aeronautical & Automotive Dept., Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310
Estimating Vertical Drag on Helicopter Fuselage during Hovering A. A. Wahab * and M.Hafiz Ismail ** Aeronautical & Automotive Dept., Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310
Reflection seismic Method - 2D
 Reflection seismic Method - 2D Acoustic Impedance Seismic events Wavelets Convolutional model Resolution Stacking and Signal/Noise Data orders Reading: Sheriff and Geldart, Chapters 6, 8 Acoustic Impedance
Reflection seismic Method - 2D Acoustic Impedance Seismic events Wavelets Convolutional model Resolution Stacking and Signal/Noise Data orders Reading: Sheriff and Geldart, Chapters 6, 8 Acoustic Impedance
ON INVESTIGATING THE C-TRANSITION CURVE FOR NOISE REDUCTION
 On Investigating The C-Transition Curve for Noise Reduction ON INVESTIGATING THE C-TRANSITION CURVE FOR NOISE REDUCTION Azma Putra 1*, Or Khai Hee 2, Saifudin Hafiz Yahaya 3 1,2 Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,
On Investigating The C-Transition Curve for Noise Reduction ON INVESTIGATING THE C-TRANSITION CURVE FOR NOISE REDUCTION Azma Putra 1*, Or Khai Hee 2, Saifudin Hafiz Yahaya 3 1,2 Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,
Fluent User Services Center
 Solver Settings 5-1 Using the Solver Setting Solver Parameters Convergence Definition Monitoring Stability Accelerating Convergence Accuracy Grid Independence Adaption Appendix: Background Finite Volume
Solver Settings 5-1 Using the Solver Setting Solver Parameters Convergence Definition Monitoring Stability Accelerating Convergence Accuracy Grid Independence Adaption Appendix: Background Finite Volume
SEG/New Orleans 2006 Annual Meeting
 Accuracy improvement for super-wide angle one-way waves by wavefront reconstruction Ru-Shan Wu* and Xiaofeng Jia, Modeling and Imaging Laboratory, IGPP, University of California, Santa Cruz Summary To
Accuracy improvement for super-wide angle one-way waves by wavefront reconstruction Ru-Shan Wu* and Xiaofeng Jia, Modeling and Imaging Laboratory, IGPP, University of California, Santa Cruz Summary To
We N Converted-phase Seismic Imaging - Amplitudebalancing Source-independent Imaging Conditions
 We N106 02 Converted-phase Seismic Imaging - Amplitudebalancing -independent Imaging Conditions A.H. Shabelansky* (Massachusetts Institute of Technology), A.E. Malcolm (Memorial University of Newfoundland)
We N106 02 Converted-phase Seismic Imaging - Amplitudebalancing -independent Imaging Conditions A.H. Shabelansky* (Massachusetts Institute of Technology), A.E. Malcolm (Memorial University of Newfoundland)
EXPLICIT AND IMPLICIT TVD AND ENO HIGH RESOLUTION ALGORITHMS APPLIED TO THE EULER AND NAVIER-STOKES EQUATIONS IN THREE-DIMENSIONS RESULTS
 EXPLICIT AND IMPLICIT TVD AND ENO HIGH RESOLUTION ALGORITHMS APPLIED TO THE EULER AND NAVIER-STOKES EQUATIONS IN THREE-DIMENSIONS RESULTS Edisson Sávio de Góes Maciel, edissonsavio@yahoo.com.br Mechanical
EXPLICIT AND IMPLICIT TVD AND ENO HIGH RESOLUTION ALGORITHMS APPLIED TO THE EULER AND NAVIER-STOKES EQUATIONS IN THREE-DIMENSIONS RESULTS Edisson Sávio de Góes Maciel, edissonsavio@yahoo.com.br Mechanical
Geometric Effects on the Amplification of First Mode Instability Waves
 Geometric Effects on the Amplification of First Mode Instability Waves A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Lindsay Christine Kirk IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT
Geometric Effects on the Amplification of First Mode Instability Waves A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Lindsay Christine Kirk IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT
SPH: Towards the simulation of wave-body interactions in extreme seas
 SPH: Towards the simulation of wave-body interactions in extreme seas Guillaume Oger, Mathieu Doring, Bertrand Alessandrini, and Pierre Ferrant Fluid Mechanics Laboratory (CNRS UMR6598) Ecole Centrale
SPH: Towards the simulation of wave-body interactions in extreme seas Guillaume Oger, Mathieu Doring, Bertrand Alessandrini, and Pierre Ferrant Fluid Mechanics Laboratory (CNRS UMR6598) Ecole Centrale
Design Optimization of a Subsonic Diffuser. for a Supersonic Aircraft
 Chapter 5 Design Optimization of a Subsonic Diffuser for a Supersonic Aircraft 5. Introduction The subsonic diffuser is part of the engine nacelle leading the subsonic flow from the intake to the turbo-fan
Chapter 5 Design Optimization of a Subsonic Diffuser for a Supersonic Aircraft 5. Introduction The subsonic diffuser is part of the engine nacelle leading the subsonic flow from the intake to the turbo-fan
Chapter 11 Application of High Speed Imaging in Particle Dynamics Study with Explosives
 Chapter 11 Application of High Speed Imaging in Particle Dynamics Study with Explosives Elena Jacobs and Vilem Petr Abstract High-speed imaging can provide invaluable information during any explosive testing.
Chapter 11 Application of High Speed Imaging in Particle Dynamics Study with Explosives Elena Jacobs and Vilem Petr Abstract High-speed imaging can provide invaluable information during any explosive testing.
Comparison of two P-S conversion-point mapping approaches for Vertical Transversely Isotropic (VTI) media
 Comparison of two P-S conversion-point mapping approaches for Vertical Transversely Isotropic (VTI) media Jianli Yang* and Don C. Lawton CREWES, University of Calgary, 5 UniversityDR.NW, Calgary, AB, TN
Comparison of two P-S conversion-point mapping approaches for Vertical Transversely Isotropic (VTI) media Jianli Yang* and Don C. Lawton CREWES, University of Calgary, 5 UniversityDR.NW, Calgary, AB, TN
Modeling & Simulation of Supersonic Flow Using McCormack s Technique
 Modeling & Simulation of Supersonic Flow Using McCormack s Technique M. Saif Ullah Khalid*, Afzaal M. Malik** Abstract In this work, two-dimensional inviscid supersonic flow around a wedge has been investigated
Modeling & Simulation of Supersonic Flow Using McCormack s Technique M. Saif Ullah Khalid*, Afzaal M. Malik** Abstract In this work, two-dimensional inviscid supersonic flow around a wedge has been investigated
Stream Function-Vorticity CFD Solver MAE 6263
 Stream Function-Vorticity CFD Solver MAE 66 Charles O Neill April, 00 Abstract A finite difference CFD solver was developed for transient, two-dimensional Cartesian viscous flows. Flow parameters are solved
Stream Function-Vorticity CFD Solver MAE 66 Charles O Neill April, 00 Abstract A finite difference CFD solver was developed for transient, two-dimensional Cartesian viscous flows. Flow parameters are solved
2D numerical simulation of ocean waves
 2D numerical simulation of ocean waves Qingjie. Du,*, Y.C. Dennis. Leung Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China * Corresponding author. Tel: +852 51743593,
2D numerical simulation of ocean waves Qingjie. Du,*, Y.C. Dennis. Leung Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China * Corresponding author. Tel: +852 51743593,
dp i = u ray c2 dt with t the travel time.
 Three dimensional two point ray tracing using paraxial rays in cartessian coordinates Ronit Strahilevitz*, Paradigm Geophysical; Dan Kosloff, Department of Geophysics, Tel Aviv University, Israel and Paradigm
Three dimensional two point ray tracing using paraxial rays in cartessian coordinates Ronit Strahilevitz*, Paradigm Geophysical; Dan Kosloff, Department of Geophysics, Tel Aviv University, Israel and Paradigm
The Interface Fresnel Zone revisited
 The Interface Fresnel Zone revisited Nathalie Favretto-Cristini, Paul Cristini and Eric de Bazelaire ABSTRACT We determine the part of reflectors which actually affects the reflected wavefield, which is
The Interface Fresnel Zone revisited Nathalie Favretto-Cristini, Paul Cristini and Eric de Bazelaire ABSTRACT We determine the part of reflectors which actually affects the reflected wavefield, which is
EVALUATING STAGE SOUND FIELD FOR ACOUSTIC DESIGN BASED ON BOUNDARY ELEMENT METHOD
 EVALUATING STAGE SOUND FIELD FOR ACOUSTIC DESIGN BASED ON BOUNDARY ELEMENT METHOD PACS REFERENCE: 43.55.Ka Ikeda, Masahiro; Kishinaga, Shinji; Kawakami, Fukushi YAMAHA Advanced System Development Center
EVALUATING STAGE SOUND FIELD FOR ACOUSTIC DESIGN BASED ON BOUNDARY ELEMENT METHOD PACS REFERENCE: 43.55.Ka Ikeda, Masahiro; Kishinaga, Shinji; Kawakami, Fukushi YAMAHA Advanced System Development Center
A new method for determination of a wave-ray trace based on tsunami isochrones
 Bull. Nov. Comp. Center, Math. Model. in Geoph., 13 (2010), 93 101 c 2010 NCC Publisher A new method for determination of a wave-ray trace based on tsunami isochrones An.G. Marchuk Abstract. A new method
Bull. Nov. Comp. Center, Math. Model. in Geoph., 13 (2010), 93 101 c 2010 NCC Publisher A new method for determination of a wave-ray trace based on tsunami isochrones An.G. Marchuk Abstract. A new method
Analysis Comparison between CFD and FEA of an Idealized Concept V- Hull Floor Configuration in Two Dimensions
 2010 NDIA GROUND VEHICLE SYSTEMS ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SYMPOSIUM MODELING & SIMULATION, TESTING AND VALIDATION (MSTV) MINI-SYMPOSIUM AUGUST 17-19 DEARBORN, MICHIGAN Analysis Comparison between CFD
2010 NDIA GROUND VEHICLE SYSTEMS ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SYMPOSIUM MODELING & SIMULATION, TESTING AND VALIDATION (MSTV) MINI-SYMPOSIUM AUGUST 17-19 DEARBORN, MICHIGAN Analysis Comparison between CFD
Related topics Interference, wavelength, refractive index, speed of light, phase, virtuallight source.
 Determination of the refractive index TEP Overview Related topics Interference, wavelength, refractive index, speed of light, phase, virtuallight source. Principle Light is brought to interference by two
Determination of the refractive index TEP Overview Related topics Interference, wavelength, refractive index, speed of light, phase, virtuallight source. Principle Light is brought to interference by two
A NOVEL APPROACH FOR OPTIMIZED DISPERSION IN OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION
 A NOVEL APPROACH FOR OPTIMIZED DISPERSION IN OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION M.V. Raghavendra 1 & P.L.H. Vara Prasad 2 Research Scholar Department of Instrument Technology 1, Professor & Chairman (BOS) Department
A NOVEL APPROACH FOR OPTIMIZED DISPERSION IN OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION M.V. Raghavendra 1 & P.L.H. Vara Prasad 2 Research Scholar Department of Instrument Technology 1, Professor & Chairman (BOS) Department
Simulation of Droplet Impingement on a Solid Surface by the Level Set Method
 Simulation of Droplet Impingement on a Solid Surface by the Level Set Method Junling Hu *1, Ruoxu Jia 1, Kai-tak Wan 2, Xingguo Xiong 3 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Bridgeport,
Simulation of Droplet Impingement on a Solid Surface by the Level Set Method Junling Hu *1, Ruoxu Jia 1, Kai-tak Wan 2, Xingguo Xiong 3 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Bridgeport,
Physics 272 Lecture 27 Interference (Ch ) Diffraction (Ch )
 Physics 272 Lecture 27 Interference (Ch 35.4-5) Diffraction (Ch 36.1-3) Thin Film Interference 1 2 n 0 =1 (air) t n 1 (thin film) n 2 Get two waves by reflection off of two different interfaces. Ray 2
Physics 272 Lecture 27 Interference (Ch 35.4-5) Diffraction (Ch 36.1-3) Thin Film Interference 1 2 n 0 =1 (air) t n 1 (thin film) n 2 Get two waves by reflection off of two different interfaces. Ray 2
Acknowledgements. Prof. Dan Negrut Prof. Darryl Thelen Prof. Michael Zinn. SBEL Colleagues: Hammad Mazar, Toby Heyn, Manoj Kumar
 Philipp Hahn Acknowledgements Prof. Dan Negrut Prof. Darryl Thelen Prof. Michael Zinn SBEL Colleagues: Hammad Mazar, Toby Heyn, Manoj Kumar 2 Outline Motivation Lumped Mass Model Model properties Simulation
Philipp Hahn Acknowledgements Prof. Dan Negrut Prof. Darryl Thelen Prof. Michael Zinn SBEL Colleagues: Hammad Mazar, Toby Heyn, Manoj Kumar 2 Outline Motivation Lumped Mass Model Model properties Simulation
Debojyoti Ghosh. Adviser: Dr. James Baeder Alfred Gessow Rotorcraft Center Department of Aerospace Engineering
 Debojyoti Ghosh Adviser: Dr. James Baeder Alfred Gessow Rotorcraft Center Department of Aerospace Engineering To study the Dynamic Stalling of rotor blade cross-sections Unsteady Aerodynamics: Time varying
Debojyoti Ghosh Adviser: Dr. James Baeder Alfred Gessow Rotorcraft Center Department of Aerospace Engineering To study the Dynamic Stalling of rotor blade cross-sections Unsteady Aerodynamics: Time varying
Figure 2: Water Into Kerosene, Volume Fraction (Left) And Total Density Of Mixture (Right)
 Jared Bottlinger MAE598 Project 3 11/16/17 Task 1 a) Figure 1: Volume Fraction Of Water At 0.4s Task 1 b) Figure 2: Water Into Kerosene, Volume Fraction (Left) And Total Density Of Mixture (Right) Task
Jared Bottlinger MAE598 Project 3 11/16/17 Task 1 a) Figure 1: Volume Fraction Of Water At 0.4s Task 1 b) Figure 2: Water Into Kerosene, Volume Fraction (Left) And Total Density Of Mixture (Right) Task
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 26.1 The Reflection of Light 26.2 Forming Images With a Plane Mirror 26.3 Spherical Mirrors 26.4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 26.5 The Refraction of Light 26.6 Ray
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 26.1 The Reflection of Light 26.2 Forming Images With a Plane Mirror 26.3 Spherical Mirrors 26.4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 26.5 The Refraction of Light 26.6 Ray
2-D Tank Sloshing Using the Coupled Eulerian- LaGrangian (CEL) Capability of Abaqus/Explicit
 2-D Tank Sloshing Using the Coupled Eulerian- LaGrangian (CEL) Capability of Abaqus/Explicit Jeff D. Tippmann, Sharat C. Prasad 2, and Parthiv N. Shah ATA Engineering, Inc. San Diego, CA 923 2 Dassault
2-D Tank Sloshing Using the Coupled Eulerian- LaGrangian (CEL) Capability of Abaqus/Explicit Jeff D. Tippmann, Sharat C. Prasad 2, and Parthiv N. Shah ATA Engineering, Inc. San Diego, CA 923 2 Dassault
Guidelines for proper use of Plate elements
 Guidelines for proper use of Plate elements In structural analysis using finite element method, the analysis model is created by dividing the entire structure into finite elements. This procedure is known
Guidelines for proper use of Plate elements In structural analysis using finite element method, the analysis model is created by dividing the entire structure into finite elements. This procedure is known
CHAPTER 3. Elementary Fluid Dynamics
 CHAPTER 3. Elementary Fluid Dynamics - Understanding the physics of fluid in motion - Derivation of the Bernoulli equation from Newton s second law Basic Assumptions of fluid stream, unless a specific
CHAPTER 3. Elementary Fluid Dynamics - Understanding the physics of fluid in motion - Derivation of the Bernoulli equation from Newton s second law Basic Assumptions of fluid stream, unless a specific
CFD Post-Processing of Rampressor Rotor Compressor
 Gas Turbine Industrial Fellowship Program 2006 CFD Post-Processing of Rampressor Rotor Compressor Curtis Memory, Brigham Young niversity Ramgen Power Systems Mentor: Rob Steele I. Introduction Recent movements
Gas Turbine Industrial Fellowship Program 2006 CFD Post-Processing of Rampressor Rotor Compressor Curtis Memory, Brigham Young niversity Ramgen Power Systems Mentor: Rob Steele I. Introduction Recent movements
Computer Project 3. AA Computational Fluid Dyanmics University of Washington. Mishaal Aleem March 17, 2015
 Computer Project 3 AA 543 - Computational Fluid Dyanmics University of Washington Mishaal Aleem March 17, 2015 Contents Introduction........................................... 1 3.1 Grid Generator.......................................
Computer Project 3 AA 543 - Computational Fluid Dyanmics University of Washington Mishaal Aleem March 17, 2015 Contents Introduction........................................... 1 3.1 Grid Generator.......................................
Anisotropic 3D Amplitude Variation with Azimuth (AVAZ) Methods to Detect Fracture-Prone Zones in Tight Gas Resource Plays*
 Anisotropic 3D Amplitude Variation with Azimuth (AVAZ) Methods to Detect Fracture-Prone Zones in Tight Gas Resource Plays* Bill Goodway 1, John Varsek 1, and Christian Abaco 1 Search and Discovery Article
Anisotropic 3D Amplitude Variation with Azimuth (AVAZ) Methods to Detect Fracture-Prone Zones in Tight Gas Resource Plays* Bill Goodway 1, John Varsek 1, and Christian Abaco 1 Search and Discovery Article
PARALLEL DNS USING A COMPRESSIBLE TURBULENT CHANNEL FLOW BENCHMARK
 European Congress on Computational Methods in Applied Sciences and Engineering ECCOMAS Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference 2001 Swansea, Wales, UK, 4-7 September 2001 ECCOMAS PARALLEL DNS USING A COMPRESSIBLE
European Congress on Computational Methods in Applied Sciences and Engineering ECCOMAS Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference 2001 Swansea, Wales, UK, 4-7 September 2001 ECCOMAS PARALLEL DNS USING A COMPRESSIBLE
Room Acoustics. CMSC 828D / Spring 2006 Lecture 20
 Room Acoustics CMSC 828D / Spring 2006 Lecture 20 Lecture Plan Room acoustics basics Structure of room impulse response Characterization of room acoustics Modeling of reverberant response Basics All our
Room Acoustics CMSC 828D / Spring 2006 Lecture 20 Lecture Plan Room acoustics basics Structure of room impulse response Characterization of room acoustics Modeling of reverberant response Basics All our
Andrew Carter. Vortex shedding off a back facing step in laminar flow.
 Flow Visualization MCEN 5151, Spring 2011 Andrew Carter Team Project 2 4/6/11 Vortex shedding off a back facing step in laminar flow. Figure 1, Vortex shedding from a back facing step in a laminar fluid
Flow Visualization MCEN 5151, Spring 2011 Andrew Carter Team Project 2 4/6/11 Vortex shedding off a back facing step in laminar flow. Figure 1, Vortex shedding from a back facing step in a laminar fluid
3D angle decomposition for elastic reverse time migration Yuting Duan & Paul Sava, Center for Wave Phenomena, Colorado School of Mines
 3D angle decomposition for elastic reverse time migration Yuting Duan & Paul Sava, Center for Wave Phenomena, Colorado School of Mines SUMMARY We propose 3D angle decomposition methods from elastic reverse
3D angle decomposition for elastic reverse time migration Yuting Duan & Paul Sava, Center for Wave Phenomena, Colorado School of Mines SUMMARY We propose 3D angle decomposition methods from elastic reverse
This is an author-deposited version published in: Eprints ID: 4362
 This is an author-deposited version published in: http://oatao.univ-toulouse.fr/ Eprints ID: 4362 To cite this document: CHIKHAOUI Oussama, GRESSIER Jérémie, GRONDIN Gilles. Assessment of the Spectral
This is an author-deposited version published in: http://oatao.univ-toulouse.fr/ Eprints ID: 4362 To cite this document: CHIKHAOUI Oussama, GRESSIER Jérémie, GRONDIN Gilles. Assessment of the Spectral
Rocking Component of Earthquake Induced by Horizontal Motion in Irregular Form Foundation
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 121 Rocking Component of Earthquake Induced by Horizontal Motion in Irregular Form Foundation Tohru Jomen
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 121 Rocking Component of Earthquake Induced by Horizontal Motion in Irregular Form Foundation Tohru Jomen
Finite Element Modeling and Multiphysics Simulation of Air Coupled Ultrasonic with Time Domain Analysis
 More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=15194 Finite Element Modeling and Multiphysics Simulation of Air Coupled Ultrasonic with Time Domain Analysis Bikash Ghose 1, a, Krishnan Balasubramaniam
More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=15194 Finite Element Modeling and Multiphysics Simulation of Air Coupled Ultrasonic with Time Domain Analysis Bikash Ghose 1, a, Krishnan Balasubramaniam
Anisotropic 3D Amplitude Variation with Azimuth (AVAZ) Methods to Detect Fracture Prone Zones in Tight Gas Resource Plays
 Antropic 3D Amplitude Variation with Azimuth (AVAZ) Methods to Detect Fracture Prone Zones in Tight Gas Resource Plays Bill Goodway* EnCana Corp., Calgary, AB, Canada william.goodway@encana.com and John
Antropic 3D Amplitude Variation with Azimuth (AVAZ) Methods to Detect Fracture Prone Zones in Tight Gas Resource Plays Bill Goodway* EnCana Corp., Calgary, AB, Canada william.goodway@encana.com and John
ULTRASONIC WAVE PROPAGATION THROUGH NOZZLES AND PIPES WITH
 ULTRASONIC WAVE PROPAGATION THROUGH NOZZLES AND PIPES WITH CLADDINGS AROUND THEIR INNER WALLS INTRODUCTION A. Minachi and R. B. Thompson Center for NDE Iowa State University Ames, Iowa 5001 J The inner
ULTRASONIC WAVE PROPAGATION THROUGH NOZZLES AND PIPES WITH CLADDINGS AROUND THEIR INNER WALLS INTRODUCTION A. Minachi and R. B. Thompson Center for NDE Iowa State University Ames, Iowa 5001 J The inner
Physics 9 Friday, September 28, 2018
 Physics 9 Friday, September 28, 2018 Turn in HW#3. HW#4 will be due two weeks from today; I will hand out HW#4 Monday. I found a way to run both Odeon and CATT-Acoustic on MacOS without a virtual machine!
Physics 9 Friday, September 28, 2018 Turn in HW#3. HW#4 will be due two weeks from today; I will hand out HW#4 Monday. I found a way to run both Odeon and CATT-Acoustic on MacOS without a virtual machine!
INFLUENCE OF CURVATURE ILLUMINATION WAVEFRONT IN QUANTITATIVE SHEAROGRAPHY NDT MEASUREMENT
 1 th A-PCNDT 6 Asia-Pacific Conference on NDT, 5 th 1 th Nov 6, Auckland, New Zealand INFLUENCE OF CURVATURE ILLUMINATION WAVEFRONT IN QUANTITATIVE SHEAROGRAPHY NDT MEASUREMENT Wan Saffiey Wan Abdullah
1 th A-PCNDT 6 Asia-Pacific Conference on NDT, 5 th 1 th Nov 6, Auckland, New Zealand INFLUENCE OF CURVATURE ILLUMINATION WAVEFRONT IN QUANTITATIVE SHEAROGRAPHY NDT MEASUREMENT Wan Saffiey Wan Abdullah
SEG/San Antonio 2007 Annual Meeting
 Imaging steep salt flanks by super-wide angle one-way method Xiaofeng Jia* and Ru-Shan Wu, Modeling and Imaging Laboratory, IGPP, University of California, Santa Cruz Summary The super-wide angle one-way
Imaging steep salt flanks by super-wide angle one-way method Xiaofeng Jia* and Ru-Shan Wu, Modeling and Imaging Laboratory, IGPP, University of California, Santa Cruz Summary The super-wide angle one-way
Coupling of surface roughness to the performance of computer-generated holograms
 Coupling of surface roughness to the performance of computer-generated holograms Ping Zhou* and Jim Burge College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 85721, USA *Corresponding author:
Coupling of surface roughness to the performance of computer-generated holograms Ping Zhou* and Jim Burge College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 85721, USA *Corresponding author:
Best Practices: Electronics Cooling. Ruben Bons - CD-adapco
 Best Practices: Electronics Cooling Ruben Bons - CD-adapco Best Practices Outline Geometry Mesh Materials Conditions Solution Results Design exploration / Optimization Best Practices Outline Geometry Solids
Best Practices: Electronics Cooling Ruben Bons - CD-adapco Best Practices Outline Geometry Mesh Materials Conditions Solution Results Design exploration / Optimization Best Practices Outline Geometry Solids
A more general model for the analysis of the rock slope stability
 Sādhanā Vol. 33, Part 4, August 2008, pp. 433 441. Printed in India A more general model for the analysis of the rock slope stability MEHDI ZAMANI Department of Technology and Engineering, Yasouj University,
Sādhanā Vol. 33, Part 4, August 2008, pp. 433 441. Printed in India A more general model for the analysis of the rock slope stability MEHDI ZAMANI Department of Technology and Engineering, Yasouj University,
Computational Ocean Acoustics
 Computational Ocean Acoustics Ray Tracing Wavenumber Integration Normal Modes Parabolic Equation Wavenumber Integration Range-independent Integral Transform solution Exact depth-dependent solution Global
Computational Ocean Acoustics Ray Tracing Wavenumber Integration Normal Modes Parabolic Equation Wavenumber Integration Range-independent Integral Transform solution Exact depth-dependent solution Global
3D Modeling of Urban Areas for Built Environment CFD Applications
 3D Modeling of Urban Areas for Built Environment CFD Applications using C A.W.M. (Jos) van Schijndel Eindhoven University of Technology P.O. Box 513; 5600 MB Eindhoven; Netherlands, A.W.M.v.Schijndel@tue.nl
3D Modeling of Urban Areas for Built Environment CFD Applications using C A.W.M. (Jos) van Schijndel Eindhoven University of Technology P.O. Box 513; 5600 MB Eindhoven; Netherlands, A.W.M.v.Schijndel@tue.nl
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE
 REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB No. 0704-088 The public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB No. 0704-088 The public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average hour per response, including the time for reviewing instructions,
GG450 4/5/2010. Today s material comes from p and in the text book. Please read and understand all of this material!
 GG450 April 6, 2010 Seismic Reflection I Today s material comes from p. 32-33 and 81-116 in the text book. Please read and understand all of this material! Back to seismic waves Last week we talked about
GG450 April 6, 2010 Seismic Reflection I Today s material comes from p. 32-33 and 81-116 in the text book. Please read and understand all of this material! Back to seismic waves Last week we talked about
Fall 2010 RED barcode here Physics 123 section 2 Exam 3
 Fall 2010 RED barcode here Physics 123 section 2 Exam 3 Colton 2-3669 Please write your CID here No time limit. One 3 5 note card (handwritten, both sides). No books. Student calculators OK. Constants
Fall 2010 RED barcode here Physics 123 section 2 Exam 3 Colton 2-3669 Please write your CID here No time limit. One 3 5 note card (handwritten, both sides). No books. Student calculators OK. Constants
SYNTHETIC SCHLIEREN. Stuart B Dalziel, Graham O Hughes & Bruce R Sutherland. Keywords: schlieren, internal waves, image processing
 8TH INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON FLOW VISUALIZATION (998) SYNTHETIC SCHLIEREN Keywords: schlieren, internal waves, image processing Abstract This paper outlines novel techniques for producing qualitative
8TH INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON FLOW VISUALIZATION (998) SYNTHETIC SCHLIEREN Keywords: schlieren, internal waves, image processing Abstract This paper outlines novel techniques for producing qualitative
CHAPTER 4 RAY COMPUTATION. 4.1 Normal Computation
 CHAPTER 4 RAY COMPUTATION Ray computation is the second stage of the ray tracing procedure and is composed of two steps. First, the normal to the current wavefront is computed. Then the intersection of
CHAPTER 4 RAY COMPUTATION Ray computation is the second stage of the ray tracing procedure and is composed of two steps. First, the normal to the current wavefront is computed. Then the intersection of
SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2014
 An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2014 John E. Matsson, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites
An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2014 John E. Matsson, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites
Visualization of Shocked Mixing Zones Using Differential Interferometry and X-Rays
 Originally published in Proceedings of the Fifth International Workshop on Compressible Turbulent Mixing, ed. R. Young, J. Glimm & B. Boston. ISBN 9810229100, World Scientific (1996). Reproduced with the
Originally published in Proceedings of the Fifth International Workshop on Compressible Turbulent Mixing, ed. R. Young, J. Glimm & B. Boston. ISBN 9810229100, World Scientific (1996). Reproduced with the
Recent Progress of NPLS Technique and Its Applications. in Measuring Supersonic Flows
 Abstract APCOM & ISCM 11-14 th December, 2013, Singapore Recent Progress of NPLS Technique and Its Applications in Measuring Supersonic Flows YI Shi-he, *CHEN Zhi, HE Lin, ZHAO Yu-xin, TIAN Li-feng, WU
Abstract APCOM & ISCM 11-14 th December, 2013, Singapore Recent Progress of NPLS Technique and Its Applications in Measuring Supersonic Flows YI Shi-he, *CHEN Zhi, HE Lin, ZHAO Yu-xin, TIAN Li-feng, WU
/D D C (?> 00 SACLANT ASW RESEARCH CENTER NATO UNCLASSIFIED. Cfia'^Tr WRIS W NATO UNC'JLSSIFIED A HOT* OH CONVERGENT ZONES
 I-: (?> Tsohaleal Raport No. 7 00 o 00 SACLANT ASW RESEARCH CENTER A HOT* OH CONVERGENT ZONES 1 r* m A* o R. R. GOODMAN L.R.B. DUYKIRS r ) i 2 Fabruary 1M2 /D D C Cfia'^Tr WRIS W OPBRATBO BV SIRII VIAL*
I-: (?> Tsohaleal Raport No. 7 00 o 00 SACLANT ASW RESEARCH CENTER A HOT* OH CONVERGENT ZONES 1 r* m A* o R. R. GOODMAN L.R.B. DUYKIRS r ) i 2 Fabruary 1M2 /D D C Cfia'^Tr WRIS W OPBRATBO BV SIRII VIAL*
Comparison of two P-S conversion-point mapping approaches for Vertical Transversely Isotropic (VTI) media
 Raytracing in VTI media Comparison of two P-S conversion-point mapping approaches for Vertical Transversely Isotropic (VTI) media Jianli Yang and Don C. Lawton ABSTRACT Determination of the conversion
Raytracing in VTI media Comparison of two P-S conversion-point mapping approaches for Vertical Transversely Isotropic (VTI) media Jianli Yang and Don C. Lawton ABSTRACT Determination of the conversion
Shock Tube Richtmyer-Meshkov Experiments: Inverse Chevron and Half Height
 Shock Tube Richtmyer-Meshkov Experiments: Inverse Chevron and Half Height Presented by: David Holder D A Holder, C J Barton and D L Youngs British Crown Copyright 24/MOD Published with the permission of
Shock Tube Richtmyer-Meshkov Experiments: Inverse Chevron and Half Height Presented by: David Holder D A Holder, C J Barton and D L Youngs British Crown Copyright 24/MOD Published with the permission of
 A Contact Angle Model for the Parallel Free Surface Lattice Boltzmann Method in walberla Stefan Donath (stefan.donath@informatik.uni-erlangen.de) Computer Science 10 (System Simulation) University of Erlangen-Nuremberg
A Contact Angle Model for the Parallel Free Surface Lattice Boltzmann Method in walberla Stefan Donath (stefan.donath@informatik.uni-erlangen.de) Computer Science 10 (System Simulation) University of Erlangen-Nuremberg
CHAPTER 3 WAVEFRONT RECONSTRUCTION METHODS. 3.1 Spatial Correlation Method
 CHAPTER 3 WAVEFRONT RECONSTRUCTION METHODS Pierce [9] defines a wavefront as any moving surface along which a waveform feature is being simultaneously received. The first step in performing ray tracing
CHAPTER 3 WAVEFRONT RECONSTRUCTION METHODS Pierce [9] defines a wavefront as any moving surface along which a waveform feature is being simultaneously received. The first step in performing ray tracing
LS-DYNA 980 : Recent Developments, Application Areas and Validation Process of the Incompressible fluid solver (ICFD) in LS-DYNA.
 12 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference FSI/ALE(1) LS-DYNA 980 : Recent Developments, Application Areas and Validation Process of the Incompressible fluid solver (ICFD) in LS-DYNA Part 1 Facundo Del
12 th International LS-DYNA Users Conference FSI/ALE(1) LS-DYNA 980 : Recent Developments, Application Areas and Validation Process of the Incompressible fluid solver (ICFD) in LS-DYNA Part 1 Facundo Del
Multipath Clamp-On Acoustic Flow Meter. Ing. Jürgen Skripalle HydroVision GmbH, Germany
 Dr.-Ing Ing. Jürgen Skripalle HydroVision GmbH, Germany Content Motivation Project Kopswerk II / Austria Signal Coupling Path Angle / Wall Thickness Optical 3D-System / Determination of Positions Discharge
Dr.-Ing Ing. Jürgen Skripalle HydroVision GmbH, Germany Content Motivation Project Kopswerk II / Austria Signal Coupling Path Angle / Wall Thickness Optical 3D-System / Determination of Positions Discharge
Comparison of Classic and Finned Piston Reciprocating Linear Air Compressor Using COMSOL Multiphysics
 Comparison of Classic and Finned Piston Reciprocating Linear Air Compressor Using COMSOL Multiphysics M. Heidari*, P. Barrade, and A. Rufer LEI, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland
Comparison of Classic and Finned Piston Reciprocating Linear Air Compressor Using COMSOL Multiphysics M. Heidari*, P. Barrade, and A. Rufer LEI, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland
Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Workshop 04 Fluid Flow Around the NACA0012 Airfoil
 Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Workshop 04 Fluid Flow Around the NACA0012 Airfoil Dimitrios Sofialidis Technical Manager, SimTec Ltd. Mechanical Engineer, PhD PRACE Autumn School 2013 -
Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Workshop 04 Fluid Flow Around the NACA0012 Airfoil Dimitrios Sofialidis Technical Manager, SimTec Ltd. Mechanical Engineer, PhD PRACE Autumn School 2013 -
Investigation of the behaviour of single span reinforced concrete historic bridges by using the finite element method
 Structural Studies, Repairs and Maintenance of Heritage Architecture XI 279 Investigation of the behaviour of single span reinforced concrete historic bridges by using the finite element method S. B. Yuksel
Structural Studies, Repairs and Maintenance of Heritage Architecture XI 279 Investigation of the behaviour of single span reinforced concrete historic bridges by using the finite element method S. B. Yuksel
Multiphase flow metrology in oil and gas production: Case study of multiphase flow in horizontal tube
 Multiphase flow metrology in oil and gas production: Case study of multiphase flow in horizontal tube Deliverable 5.1.2 of Work Package WP5 (Creating Impact) Authors: Stanislav Knotek Czech Metrology Institute
Multiphase flow metrology in oil and gas production: Case study of multiphase flow in horizontal tube Deliverable 5.1.2 of Work Package WP5 (Creating Impact) Authors: Stanislav Knotek Czech Metrology Institute
Numerical Simulations of Granular Materials Flow around Obstacles: The role of the interstitial gas
 Numerical Simulations of Granular Materials Flow around Obstacles: The role of the interstitial gas Avi Levy, Dept. Mech. Eng., Ben Gurion University, Beer Sheva, Israel. Mohamed Sayed, CHC, National Research
Numerical Simulations of Granular Materials Flow around Obstacles: The role of the interstitial gas Avi Levy, Dept. Mech. Eng., Ben Gurion University, Beer Sheva, Israel. Mohamed Sayed, CHC, National Research
Aberrations in Holography
 Aberrations in Holography D Padiyar, J Padiyar 1070 Commerce St suite A, San Marcos, CA 92078 dinesh@triple-take.com joy@triple-take.com Abstract. The Seidel aberrations are described as they apply to
Aberrations in Holography D Padiyar, J Padiyar 1070 Commerce St suite A, San Marcos, CA 92078 dinesh@triple-take.com joy@triple-take.com Abstract. The Seidel aberrations are described as they apply to
