IMPROVING THE ACCURACY OF DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELS
|
|
|
- Vernon Martin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 STUDIA UNIV. BABEŞ BOLYAI, INFORMATICA, Volume XLV, Number 1, 2000 IMPROVING THE ACCURACY OF DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELS GABRIELA DROJ Abstract. The change from paper maps to GIS, in various kinds of geographical data analysis and applications, has made it easy to use the same spatial data for different applications and also for combining several layers into quite complex spatial models, including the three-dimensional reference space (surface), known as Digital Terrain Model (DTM). The objectives of this study are: (1) to compare the different algorithms involved in producing a DTM, (2) to establish the factors which affect the accuracy of the DTM and (3) to improve the quality of the generated DTM. 1. Introduction The change from paper maps to digital data, in various kinds of geographical data analysis and applications, has made easy to use the same spatial data for different applications and also for combining several layers into quite complex spatial models. Using GIS technology, contemporary maps have taken radical new forms of display beyond the usual 2D planimetric paper map. Today, it is expected to be able to drape spatial information on a 3D view of the terrain. The 3D view of the terrain is called Digital Terrain Model (DTM) or Digital Elevation Model (DEM) [2]. The digital terrain models are frequently used to take important decisions like to answer hydrological questions concerning flooding. In order to judge these decisions the quality of DTM must be known. The quality of DTM is, unfortunately, rarely checked. While the development of GIS advances, DTM research has so far been neglected. The objectives of this study are: (1) to compare the different algorithms involved in producing a DTM, (2) to establish the factors which affect the accuracy of the DTM and (3) to improve the quality of the generated DTM. Received by the editors: Mathematics Subject Classification. 65D05, 65D07,68U CR Categories and Descriptors. I.3.5 [Computational Geometry and Object Modeling]: Subtopic Curve, surface, solid, and object representations I.3.7 [Three- Dimensional Graphics and Realism]: Subtopic Visible line/surface algorithms. 1
2 2 GABRIELA DROJ 2. Digital Terrain Modeling A digital terrain model (DTM) is a digital representation of ground surface, topography or terrain. It is also known as digital elevation model (DEM). DTM can be represented as a raster (a grid of squares), as contour lines or as a triangular irregular network (TIN) [3, 4, 9]. Two methods are frequently used to obtaining digital terrain model: cartographic digitizing, or automatic measurements [6]. The cartographic digitizing method is widely used because topographic maps are usually available. The input data form the basis for the computation of the DTM, consisting of points. The computation itself consists in spatial interpolation algorithms. Automatic measurement techniques like photogrammetry and airborne laser scanning, output bulk points, with a high density. The DTM is realized in the post processing phase usually by creating the TIN or by interpolation Interpolation. The current research and industrial projects in GIS require higher standards for the accuracy of spatial data. The data in geographical informational systems (GIS) are usually collected as points, where a point is considered a triplet (x,y,z), where x and y are the coordinates of the point and z is the specific information. This specific information can be for example: the altitude level in the point (x, y), the quantity of precipitations, the level of pollution, type of soil, socio-economic parameters etc.. The mapping and spatial analysis often requires converting this type of field measurements into continuous space. Interpolation is one of the frequently used methods to transform field data, especially the point samples into a continuous form such as grid or raster data formats. There are several interpolation methods frequently used in GIS. The following eight widely used methods are compared and studied in this paper. These methods are Inverse distance weighted (IDW), Spline Biquadratic interpolation, Spline Bicubic interpolation, B-spline interpolation, Nearest neighbors - Voronoi diagrams, Delaunay Triangulation, Quadratic Shepard interpolation, Kriging interpolation [1, 5, 7] Quality of surface. Measurement of errors for the results is often impossible because the true value for every geographic feature or phenomenon represented in this geographic data set is rarely determinable. Therefore the uncertainty, instead of error, should be used to describe the quality of an interpolation result. Quantifying uncertainty in these cases requires comparison of the known data with the created surface [10]. To analyze the pattern of deviation between two sets of elevation data, conventional ways are to yield statistical expressions of the accuracy, such as the root mean square error, standard deviation, mean, variance, coefficient of
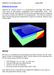
3 IMPROVING THE ACCURACY OF DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELS 3 variation. In fact, all statistical measures that are effective for describing a frequency distribution, including central tendency and dispersion measures, may be used, as long as various assumptions for specific methods are satisfied [6, 10]. For the evaluation of DTM the most widely used measure, usually the only one, is the well known Root Mean Square Error (RMSE). Actually, it measures the dispersion of the frequency distribution of deviations between the original elevation data and the DTM data, mathematically expressed as: RMSE = 1 n (z d,i z r,i ) 2 n where: Z d,i is the ith elevation value measured on the DTM surface; Z r,i is the corresponding original elevation; n is the number of elevation points checked. It s important to mention that for an accurate evaluation, is necessary to evaluate the surface by using an independent set of data. In this case the RMSE mirrors the quality of the surface but for a correct evaluation we recommend to analyze at least one more statistical index like standard deviation or Median absolute deviation. i=1 3. Experiments with real-world data DTMs are the most popular results of interpolation. In the following, we will test different methods and algorithms for creation of DTM in order to compare the different algorithms involved in producing a DTM, to establish the factors which affect the accuracy of the DTM, and to determine how to improve the quality of the generated DTM. To test and compare the methods with real data we have selected an area from north hills of Oradea municipality. Figure 1. The Oradea 3D Model
4 4 GABRIELA DROJ For the first DTM we used photogrammetric measurement of spot elevations from orthorectified airborne image of the area. This is the fastest way of obtaining the digital elevation model. In the case of collecting data with close-range photogrammetry or airborne laser scan the result consists in a high density of points with three coordinates (x,y,z). By computing the TIN model of these points we obtain fast a DTM. The TIN of the area was generated using ARCGIS Desktop 9.1. In the figure 1 we represented the 3D model created. This model will consider the reference for testing and evaluating the most popular interpolation algorithms used for DTM creation. These methods are Inverse distance weighted (IDW), Spline Biquadratic interpolation, Spline Bicubic interpolation, B-spline interpolation, Nearest neighbors - Voronoi diagrams, Delaunay Triangulation, Quadratic Shepard interpolation and Kriging interpolation. The comparisons of these algorithms were made by analyzing their results. The evaluation of the created surfaces was made by direct observation: with visual comparisons of the models using the spot image as reference and by using statistical parameters. The first step was to create a regular grid with the step of 500 m, for a total of 30 points. On this set of points we tested the algorithms specified before. In Figure2 we represented the results of these algorithms. In the second experiment, we have created a regular grid with the step of 250 m, for a total of 121 points. On this sets of points we tested the algorithms specified before. In Figure 3 we represented the results of these algorithms. The visual comparisons show a high similarity with the reference for the Delaunay Triangulation and Shepard interpolation in both test cases. In order to evaluate the surfaces generated by using statistical methods it is necessary to test the quality of the surfaces with an independent set of data, which were not considered in the interpolation. In the following we will evaluate the surfaces generated by using a random set of points for which was determined the real value of the altitude. For this independent random set we have determined the following statistical parameters: variation, median absolute deviation, standard deviation and the root mean square error. The determined values are presented in the table below: 4. Results of test cases The results obtained in the both cases show that the most accurate surfaces are generated, for the first case (grid of 500 m), by Kriging, Shepard and B-spline algorithms and for the second case (grid of 250m) by Delauney triangulation followed by Shepard and Kriging.
5 IMPROVING THE ACCURACY OF DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELS 5 Figure 2. DTM model generated with 30 known points If we evaluate all the statistical data we notice that the Delauney triangulation represents the optimal method. Similar results can be obtained by Kriging and Shepard interpolation. Even these methods are sometimes more efficient than the Delauney triangulation. Nevertheless, the Delauney algorithm is recommended because it needs less computing time and it is not changing the original values of the points. The b-spline algorithm gives also a good result but in this case the computing time is much higher and it is smoothing the surface, fact which is making this method inadequate for surfaces with a high altitude difference.
6 6 GABRIELA DROJ Figure 3. DTM model generated with 121 known points Many studies have examined the DTMs generated by interpolation but the earlier studies compare fewer methods, usually by testing a strong algorithm with a fast one or by testing one algorithm with two or three different point density. Some examples of studies are: a comparison between IDW and Voronoi [4], IDW vs. Kriging [11], and between IDW, Kriging, Thiessen polygons and TIN [8] and IDW, minimum curvature, modified Shepard and TIN [10]. Except the study made by Weng, all of them are using only one set of input data. Our results regarding the accuracy of surfaces created by interpolation are similar with the earlier studies. By testing a higher number of methods and in
7 Methods IMPROVING THE ACCURACY OF DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELS 7 Variation 250 Variation 500 Median absolute deviation 250 Median absolute deviation 500 Standard deviation 250 Standard deviation 500 RMSE 250 RMSE 500 IDW Biquadratic Bi-cubic B-spline Voronoi Delaunay Shepard Kriging Table 1. The statistics for all the created surfaces,based on a set of random control points two different cases we demonstrated that DTM accuracy can vary to a certain degree with different interpolation algorithms and interpolation parameters. 5. Conclusion In this paper we compared the most popular algorithms involved in producing a DTM, in order to establish the main factors which affect the accuracy of the DTM and to improve the quality of the generated DTM. The performance of eight methods, in two different cases, was evaluated in this paper, based on the accuracy of the generated surface. The first conclusion which is pointed up by the values presented in table 1 and by the analysis of the visual results, in the both cases, shows that input data form the basis for the computation of the DTM. The density of the known points is a more important factor in increasing DTM quality than the algorithm used in surface creation. A second conclusion is that there is no optimal algorithm for any situation, the results given by different computational method are influenced by more factors like: the conformation of the field, the density of the initial points, the quality of the known values and nevertheless by algorithm used. The last conclusion is that, we can improve the quality of the DTM by using the Delauney algorithm and a high density of known points. Regarding the way of computing for Delaunay triangulation, it is necessary to have at least 3 points for each hill or valley.
8 8 GABRIELA DROJ References [1] M. R. Asim, M. Ghulam, K. Brodlie, Constrained Visualization of 2D Positive Data using Modified Quadratic Shepard Method, WSCG 2004, Plzen, Czech Republic. [2] J. K. Berry and Associates The GIS Primer - An Introduction to Geographic Information Systems, May [3] L. De Floriani, E. Puppo, P. Magillo Application of Computational Geometry to Geographic Informational Systems, Handbook of Computational Geometry, 1999 Elsevier Science, pp [4] Chongjiang Du An Interpolation Method for Grid-Based Terrain Modeling, The Computer Journal,vol.39, nr. 10, 1996 [5] ESRI. Environmental Science Research Institute Arc/Info 8.0.1, ESRI, Inc [6] W. Karel, N. Pfeifer, C. Briese DTM Quality Assessment, ISPRS Technical Commission II Symposium, 2006 XXXVI/2, pp [7] R. T. Trambitas Analiza numerica. Note de curs, tradu/narom.html, 2003 [8] P. Siska, I. Hung Assessment of Kriging Accuracy in the GIS Environment, Annual ESRI International User Conference, San Diego, CA, [9] M. van Kreveld Algorithms for Triangulated Terrains, Conference on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Informatics, [10] Qihao Weng, Quantifying Uncertainty of Digital Elevation Model, December [11] Y. Ziary, H. Safari, To Compare Two Interpolation Methods: IDW, KRIGING for Providing Properties (Area) Surface Interpolation Map Land Price, FIG Working Week, 2007 Oradea address: gaby@oradea.ro
Surface Analysis with 3D Analyst
 2013 Esri International User Conference July 8 12, 2013 San Diego, California Technical Workshop Surface Analysis with 3D Analyst Khalid H. Duri Esri UC2013. Technical Workshop. Why use 3D GIS? Because
2013 Esri International User Conference July 8 12, 2013 San Diego, California Technical Workshop Surface Analysis with 3D Analyst Khalid H. Duri Esri UC2013. Technical Workshop. Why use 3D GIS? Because
DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELS
 DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELS 1 Digital Terrain Models Dr. Mohsen Mostafa Hassan Badawy Remote Sensing Center GENERAL: A Digital Terrain Models (DTM) is defined as the digital representation of the spatial distribution
DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELS 1 Digital Terrain Models Dr. Mohsen Mostafa Hassan Badawy Remote Sensing Center GENERAL: A Digital Terrain Models (DTM) is defined as the digital representation of the spatial distribution
Surface Creation & Analysis with 3D Analyst
 Esri International User Conference July 23 27 San Diego Convention Center Surface Creation & Analysis with 3D Analyst Khalid Duri Surface Basics Defining the surface Representation of any continuous measurement
Esri International User Conference July 23 27 San Diego Convention Center Surface Creation & Analysis with 3D Analyst Khalid Duri Surface Basics Defining the surface Representation of any continuous measurement
Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS
 HOUSEKEEPING Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Quizzes Lab 8? WEEK EIGHT Lecture INTERPOLATION & SPATIAL ESTIMATION Joe Wheaton READING FOR TODAY WHAT CAN WE COLLECT AT POINTS?
HOUSEKEEPING Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Quizzes Lab 8? WEEK EIGHT Lecture INTERPOLATION & SPATIAL ESTIMATION Joe Wheaton READING FOR TODAY WHAT CAN WE COLLECT AT POINTS?
Statistical surfaces and interpolation. This is lecture ten
 Statistical surfaces and interpolation This is lecture ten Data models for representation of surfaces So far have considered field and object data models (represented by raster and vector data structures).
Statistical surfaces and interpolation This is lecture ten Data models for representation of surfaces So far have considered field and object data models (represented by raster and vector data structures).
What can we represent as a Surface?
 Geography 38/42:376 GIS II Topic 7: Surface Representation and Analysis (Chang: Chapters 13 & 15) DeMers: Chapter 10 What can we represent as a Surface? Surfaces can be used to represent: Continuously
Geography 38/42:376 GIS II Topic 7: Surface Representation and Analysis (Chang: Chapters 13 & 15) DeMers: Chapter 10 What can we represent as a Surface? Surfaces can be used to represent: Continuously
CPSC 695. Methods for interpolation and analysis of continuing surfaces in GIS Dr. M. Gavrilova
 CPSC 695 Methods for interpolation and analysis of continuing surfaces in GIS Dr. M. Gavrilova Overview Data sampling for continuous surfaces Interpolation methods Global interpolation Local interpolation
CPSC 695 Methods for interpolation and analysis of continuing surfaces in GIS Dr. M. Gavrilova Overview Data sampling for continuous surfaces Interpolation methods Global interpolation Local interpolation
INCREASING CLASSIFICATION QUALITY BY USING FUZZY LOGIC
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED ENGINEERING SCIENCES VOL. 1(14), issue 4_2011 ISSN 2247-3769 ISSN-L 2247-3769 (Print) / e-issn:2284-7197 INCREASING CLASSIFICATION QUALITY BY USING FUZZY LOGIC DROJ Gabriela, University
JOURNAL OF APPLIED ENGINEERING SCIENCES VOL. 1(14), issue 4_2011 ISSN 2247-3769 ISSN-L 2247-3769 (Print) / e-issn:2284-7197 INCREASING CLASSIFICATION QUALITY BY USING FUZZY LOGIC DROJ Gabriela, University
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 24: Spatial Analyst Continued
 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 24: Spatial Analyst Continued Spatial Analyst - Spatial Analyst is an ArcGIS extension designed to work with raster data - in lecture I went through a series of demonstrations
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 24: Spatial Analyst Continued Spatial Analyst - Spatial Analyst is an ArcGIS extension designed to work with raster data - in lecture I went through a series of demonstrations
Contents of Lecture. Surface (Terrain) Data Models. Terrain Surface Representation. Sampling in Surface Model DEM
 Lecture 13: Advanced Data Models: Terrain mapping and Analysis Contents of Lecture Surface Data Models DEM GRID Model TIN Model Visibility Analysis Geography 373 Spring, 2006 Changjoo Kim 11/29/2006 1
Lecture 13: Advanced Data Models: Terrain mapping and Analysis Contents of Lecture Surface Data Models DEM GRID Model TIN Model Visibility Analysis Geography 373 Spring, 2006 Changjoo Kim 11/29/2006 1
Geostatistics Predictions with Deterministic Procedures
 Instituto Superior de Estatística e Gestão de Informação Universidade Nova de Lisboa Master of Science in Geospatial Technologies Geostatistics Predictions with Deterministic Procedures Carlos Alberto
Instituto Superior de Estatística e Gestão de Informação Universidade Nova de Lisboa Master of Science in Geospatial Technologies Geostatistics Predictions with Deterministic Procedures Carlos Alberto
On the Selection of an Interpolation Method for Creating a Terrain Model (TM) from LIDAR Data
 On the Selection of an Interpolation Method for Creating a Terrain Model (TM) from LIDAR Data Tarig A. Ali Department of Technology and Geomatics East Tennessee State University P. O. Box 70552, Johnson
On the Selection of an Interpolation Method for Creating a Terrain Model (TM) from LIDAR Data Tarig A. Ali Department of Technology and Geomatics East Tennessee State University P. O. Box 70552, Johnson
Spatial Interpolation & Geostatistics
 (Z i Z j ) 2 / 2 Spatial Interpolation & Geostatistics Lag Lag Mean Distance between pairs of points 1 Tobler s Law All places are related, but nearby places are related more than distant places Corollary:
(Z i Z j ) 2 / 2 Spatial Interpolation & Geostatistics Lag Lag Mean Distance between pairs of points 1 Tobler s Law All places are related, but nearby places are related more than distant places Corollary:
Investigation of Sampling and Interpolation Techniques for DEMs Derived from Different Data Sources
 Investigation of Sampling and Interpolation Techniques for DEMs Derived from Different Data Sources FARRAG ALI FARRAG 1 and RAGAB KHALIL 2 1: Assistant professor at Civil Engineering Department, Faculty
Investigation of Sampling and Interpolation Techniques for DEMs Derived from Different Data Sources FARRAG ALI FARRAG 1 and RAGAB KHALIL 2 1: Assistant professor at Civil Engineering Department, Faculty
Lesson 5 overview. Concepts. Interpolators. Assessing accuracy Exercise 5
 Interpolation Tools Lesson 5 overview Concepts Sampling methods Creating continuous surfaces Interpolation Density surfaces in GIS Interpolators IDW, Spline,Trend, Kriging,Natural neighbors TopoToRaster
Interpolation Tools Lesson 5 overview Concepts Sampling methods Creating continuous surfaces Interpolation Density surfaces in GIS Interpolators IDW, Spline,Trend, Kriging,Natural neighbors TopoToRaster
Spatial Interpolation - Geostatistics 4/3/2018
 Spatial Interpolation - Geostatistics 4/3/201 (Z i Z j ) 2 / 2 Spatial Interpolation & Geostatistics Lag Distance between pairs of points Lag Mean Tobler s Law All places are related, but nearby places
Spatial Interpolation - Geostatistics 4/3/201 (Z i Z j ) 2 / 2 Spatial Interpolation & Geostatistics Lag Distance between pairs of points Lag Mean Tobler s Law All places are related, but nearby places
Spatial Analysis and Modeling (GIST 4302/5302) Guofeng Cao Department of Geosciences Texas Tech University
 Spatial Analysis and Modeling (GIST 4302/5302) Guofeng Cao Department of Geosciences Texas Tech University 1 Outline of This Week Last topic, we learned: Spatial autocorrelation of areal data Spatial regression
Spatial Analysis and Modeling (GIST 4302/5302) Guofeng Cao Department of Geosciences Texas Tech University 1 Outline of This Week Last topic, we learned: Spatial autocorrelation of areal data Spatial regression
Lab 12: Sampling and Interpolation
 Lab 12: Sampling and Interpolation What You ll Learn: -Systematic and random sampling -Majority filtering -Stratified sampling -A few basic interpolation methods Data for the exercise are in the L12 subdirectory.
Lab 12: Sampling and Interpolation What You ll Learn: -Systematic and random sampling -Majority filtering -Stratified sampling -A few basic interpolation methods Data for the exercise are in the L12 subdirectory.
Assimilation of Break line and LiDAR Data within ESRI s Terrain Data Structure (TDS) for creating a Multi-Resolution Terrain Model
 Assimilation of Break line and LiDAR Data within ESRI s Terrain Data Structure (TDS) for creating a Multi-Resolution Terrain Model Tarig A. Ali Department of Civil Engineering American University of Sharjah,
Assimilation of Break line and LiDAR Data within ESRI s Terrain Data Structure (TDS) for creating a Multi-Resolution Terrain Model Tarig A. Ali Department of Civil Engineering American University of Sharjah,
DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELLING. Endre Katona University of Szeged Department of Informatics
 DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELLING Endre Katona University of Szeged Department of Informatics katona@inf.u-szeged.hu The problem: data sources data structures algorithms DTM = Digital Terrain Model Terrain function:
DIGITAL TERRAIN MODELLING Endre Katona University of Szeged Department of Informatics katona@inf.u-szeged.hu The problem: data sources data structures algorithms DTM = Digital Terrain Model Terrain function:
Dijkstra's Algorithm
 Shortest Path Algorithm Dijkstra's Algorithm To find the shortest path from the origin node to the destination node No matrix calculation Floyd s Algorithm To find all the shortest paths from the nodes
Shortest Path Algorithm Dijkstra's Algorithm To find the shortest path from the origin node to the destination node No matrix calculation Floyd s Algorithm To find all the shortest paths from the nodes
AUTOMATIC EXTRACTION OF TERRAIN SKELETON LINES FROM DIGITAL ELEVATION MODELS
 AUTOMATIC EXTRACTION OF TERRAIN SKELETON LINES FROM DIGITAL ELEVATION MODELS F. Gülgen, T. Gökgöz Yildiz Technical University, Department of Geodetic and Photogrammetric Engineering, 34349 Besiktas Istanbul,
AUTOMATIC EXTRACTION OF TERRAIN SKELETON LINES FROM DIGITAL ELEVATION MODELS F. Gülgen, T. Gökgöz Yildiz Technical University, Department of Geodetic and Photogrammetric Engineering, 34349 Besiktas Istanbul,
POSITIONING A PIXEL IN A COORDINATE SYSTEM
 GEOREFERENCING AND GEOCODING EARTH OBSERVATION IMAGES GABRIEL PARODI STUDY MATERIAL: PRINCIPLES OF REMOTE SENSING AN INTRODUCTORY TEXTBOOK CHAPTER 6 POSITIONING A PIXEL IN A COORDINATE SYSTEM The essential
GEOREFERENCING AND GEOCODING EARTH OBSERVATION IMAGES GABRIEL PARODI STUDY MATERIAL: PRINCIPLES OF REMOTE SENSING AN INTRODUCTORY TEXTBOOK CHAPTER 6 POSITIONING A PIXEL IN A COORDINATE SYSTEM The essential
Creating Surfaces. Steve Kopp Steve Lynch
 Steve Kopp Steve Lynch Overview Learn the types of surfaces and the data structures used to store them Emphasis on surface interpolation Learn the interpolation workflow Understand how interpolators work
Steve Kopp Steve Lynch Overview Learn the types of surfaces and the data structures used to store them Emphasis on surface interpolation Learn the interpolation workflow Understand how interpolators work
Spatial Analysis (Vector) II
 Spatial Analysis (Vector) II GEOG 300, Lecture 9 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 A Spatial Network is a set of geographic locations interconnected in a system by a number of routes is a system of linear features
Spatial Analysis (Vector) II GEOG 300, Lecture 9 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 A Spatial Network is a set of geographic locations interconnected in a system by a number of routes is a system of linear features
Spatial Interpolation & Geostatistics
 (Z i Z j ) 2 / 2 Spatial Interpolation & Geostatistics Lag Lag Mean Distance between pairs of points 11/3/2016 GEO327G/386G, UT Austin 1 Tobler s Law All places are related, but nearby places are related
(Z i Z j ) 2 / 2 Spatial Interpolation & Geostatistics Lag Lag Mean Distance between pairs of points 11/3/2016 GEO327G/386G, UT Austin 1 Tobler s Law All places are related, but nearby places are related
Surface Analysis. Data for Surface Analysis. What are Surfaces 4/22/2010
 Surface Analysis Cornell University Data for Surface Analysis Vector Triangulated Irregular Networks (TIN) a surface layer where space is partitioned into a set of non-overlapping triangles Attribute and
Surface Analysis Cornell University Data for Surface Analysis Vector Triangulated Irregular Networks (TIN) a surface layer where space is partitioned into a set of non-overlapping triangles Attribute and
FOUR ADVANCES IN HANDLING UNCERTAINTIES IN SPATIAL DATA AND ANALYSIS
 FOUR ADVANCES IN HANDLING UNCERTAINTIES IN SPATIAL DATA AND ANALYSIS Wenzhong Shi Advanced Research Centre for Spatial Information Technology Department of Land Surveying and Geo-Informatics The Hong Kong
FOUR ADVANCES IN HANDLING UNCERTAINTIES IN SPATIAL DATA AND ANALYSIS Wenzhong Shi Advanced Research Centre for Spatial Information Technology Department of Land Surveying and Geo-Informatics The Hong Kong
L7 Raster Algorithms
 L7 Raster Algorithms NGEN6(TEK23) Algorithms in Geographical Information Systems by: Abdulghani Hasan, updated Nov 216 by Per-Ola Olsson Background Store and analyze the geographic information: Raster
L7 Raster Algorithms NGEN6(TEK23) Algorithms in Geographical Information Systems by: Abdulghani Hasan, updated Nov 216 by Per-Ola Olsson Background Store and analyze the geographic information: Raster
Estimating the Accuracy of Digital Elevation Model Produced by Surfer Package
 International Journal of Computer Science and Telecommunications [Volume 4, Issue 11, November 213] 2 ISSN 247-3338 Estimating the Accuracy of Digital Elevation Model Produced by Surfer Package Dr. Nagi
International Journal of Computer Science and Telecommunications [Volume 4, Issue 11, November 213] 2 ISSN 247-3338 Estimating the Accuracy of Digital Elevation Model Produced by Surfer Package Dr. Nagi
GIS Tools - Geometry. A GIS stores data as different layers of information Different feature types are stored in individual files.
 A Definition of GIS GIS is a system of hardware, software, and procedures designed to support the capture, management, manipulation, analysis, modeling and display of spatially referenced data for solving
A Definition of GIS GIS is a system of hardware, software, and procedures designed to support the capture, management, manipulation, analysis, modeling and display of spatially referenced data for solving
A METHOD TO PREDICT ACCURACY OF LEAST SQUARES SURFACE MATCHING FOR AIRBORNE LASER SCANNING DATA SETS
 A METHOD TO PREDICT ACCURACY OF LEAST SQUARES SURFACE MATCHING FOR AIRBORNE LASER SCANNING DATA SETS Robert Pâquet School of Engineering, University of Newcastle Callaghan, NSW 238, Australia (rpaquet@mail.newcastle.edu.au)
A METHOD TO PREDICT ACCURACY OF LEAST SQUARES SURFACE MATCHING FOR AIRBORNE LASER SCANNING DATA SETS Robert Pâquet School of Engineering, University of Newcastle Callaghan, NSW 238, Australia (rpaquet@mail.newcastle.edu.au)
Lecture 9. Raster Data Analysis. Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University
 Lecture 9 Raster Data Analysis Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Raster Data Model The GIS raster data model represents datasets in which square
Lecture 9 Raster Data Analysis Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Raster Data Model The GIS raster data model represents datasets in which square
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 13. TERRAIN MAPPING AND ANALYSIS 13.1 Data for Terrain Mapping and Analysis 13.1.1 DEM 13.1.2 TIN Box 13.1 Terrain Data Format 13.2 Terrain Mapping 13.2.1 Contouring 13.2.2 Vertical Profiling 13.2.3
Chapter 13. TERRAIN MAPPING AND ANALYSIS 13.1 Data for Terrain Mapping and Analysis 13.1.1 DEM 13.1.2 TIN Box 13.1 Terrain Data Format 13.2 Terrain Mapping 13.2.1 Contouring 13.2.2 Vertical Profiling 13.2.3
Esri International User Conference. San Diego, California. Technical Workshops. July Creating Surfaces. Steve Kopp and Steve Lynch
 Esri International User Conference San Diego, California Technical Workshops July 2011 Creating Surfaces Steve Kopp and Steve Lynch Overview Learn the types of surfaces and the data structures used to
Esri International User Conference San Diego, California Technical Workshops July 2011 Creating Surfaces Steve Kopp and Steve Lynch Overview Learn the types of surfaces and the data structures used to
Lecture 4: Digital Elevation Models
 Lecture 4: Digital Elevation Models GEOG413/613 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 Digital Terrain Modeling Terms: DEM, DTM, DTEM, DSM, DHM not synonyms. The concepts they illustrate are different Digital Terrain Modeling
Lecture 4: Digital Elevation Models GEOG413/613 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 Digital Terrain Modeling Terms: DEM, DTM, DTEM, DSM, DHM not synonyms. The concepts they illustrate are different Digital Terrain Modeling
Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL. Lecture-7 Chapters 13 and 14
 Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL Lecture-7 Chapters 13 and 14 Data for Terrain Mapping and Analysis DEM (digital elevation model) and TIN (triangulated irregular network) are two
Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL Lecture-7 Chapters 13 and 14 Data for Terrain Mapping and Analysis DEM (digital elevation model) and TIN (triangulated irregular network) are two
COMPARISON OF TWO METHODS FOR DERIVING SKELETON LINES OF TERRAIN
 COMPARISON OF TWO METHODS FOR DERIVING SKELETON LINES OF TERRAIN T. Gökgöz, F. Gülgen Yildiz Technical University, Dept. of Geodesy and Photogrammetry Engineering, 34349 Besiktas Istanbul, Turkey (gokgoz,
COMPARISON OF TWO METHODS FOR DERIVING SKELETON LINES OF TERRAIN T. Gökgöz, F. Gülgen Yildiz Technical University, Dept. of Geodesy and Photogrammetry Engineering, 34349 Besiktas Istanbul, Turkey (gokgoz,
Session / Séance 23-D Computing and Visualizing Morphologically Sound DEMs in a Raster Environment
 Session / Séance 23-D Computing and Visualizing Morphologically Sound DEMs in a Raster Environment Juha Oksanen and Olli Jaakkola Finnish Geodetic Institute, Cartography and Geoinformatics Geodeetinrinne
Session / Séance 23-D Computing and Visualizing Morphologically Sound DEMs in a Raster Environment Juha Oksanen and Olli Jaakkola Finnish Geodetic Institute, Cartography and Geoinformatics Geodeetinrinne
Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images
 Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images Airborne TerrestriaL Applications Sensor (ATLAS) Nine flight paths were recorded over the city of Providence. 1 True color ATLAS image (bands 4, 2, 1 in
Geometric Rectification of Remote Sensing Images Airborne TerrestriaL Applications Sensor (ATLAS) Nine flight paths were recorded over the city of Providence. 1 True color ATLAS image (bands 4, 2, 1 in
UPDATING ELEVATION DATA BASES
 UPDATING ELEVATION DATA BASES u MERGING OLD AND NEW DATA Poul Frederiksen Associate Professor Institute of Surveying and Photogrammetry Technical University of Denmark DK 2800 Lyngby, Denmark ISPRS Commission
UPDATING ELEVATION DATA BASES u MERGING OLD AND NEW DATA Poul Frederiksen Associate Professor Institute of Surveying and Photogrammetry Technical University of Denmark DK 2800 Lyngby, Denmark ISPRS Commission
Training i Course Remote Sensing Basic Theory & Image Processing Methods September 2011
 Training i Course Remote Sensing Basic Theory & Image Processing Methods 19 23 September 2011 Geometric Operations Michiel Damen (September 2011) damen@itc.nl ITC FACULTY OF GEO-INFORMATION SCIENCE AND
Training i Course Remote Sensing Basic Theory & Image Processing Methods 19 23 September 2011 Geometric Operations Michiel Damen (September 2011) damen@itc.nl ITC FACULTY OF GEO-INFORMATION SCIENCE AND
Aalborg Universitet. Published in: Accuracy Publication date: Document Version Early version, also known as pre-print
 Aalborg Universitet A method for checking the planimetric accuracy of Digital Elevation Models derived by Airborne Laser Scanning Høhle, Joachim; Øster Pedersen, Christian Published in: Accuracy 2010 Publication
Aalborg Universitet A method for checking the planimetric accuracy of Digital Elevation Models derived by Airborne Laser Scanning Høhle, Joachim; Øster Pedersen, Christian Published in: Accuracy 2010 Publication
Geostatistics 2D GMS 7.0 TUTORIALS. 1 Introduction. 1.1 Contents
 GMS 7.0 TUTORIALS 1 Introduction Two-dimensional geostatistics (interpolation) can be performed in GMS using the 2D Scatter Point module. The module is used to interpolate from sets of 2D scatter points
GMS 7.0 TUTORIALS 1 Introduction Two-dimensional geostatistics (interpolation) can be performed in GMS using the 2D Scatter Point module. The module is used to interpolate from sets of 2D scatter points
Literature review for 3D Design Terrain Models for Construction Plans and GPS Control of Highway Construction Equipment
 Literature review for 3D Design Terrain Models for Construction Plans and GPS Control of Highway Construction Equipment Cassie Hintz Construction and Materials Support Center Department of Civil and Environmental
Literature review for 3D Design Terrain Models for Construction Plans and GPS Control of Highway Construction Equipment Cassie Hintz Construction and Materials Support Center Department of Civil and Environmental
Neighbourhood Operations Specific Theory
 Neighbourhood Operations Specific Theory Neighbourhood operations are a method of analysing data in a GIS environment. They are especially important when a situation requires the analysis of relationships
Neighbourhood Operations Specific Theory Neighbourhood operations are a method of analysing data in a GIS environment. They are especially important when a situation requires the analysis of relationships
Geol 588. GIS for Geoscientists II. Zonal functions. Feb 22, Zonal statistics. Interpolation. Zonal statistics Sp. Analyst Tools - Zonal.
 Zonal functions Geol 588 GIS for Geoscientists II Feb 22, 2011 Zonal statistics Interpolation Zonal statistics Sp. Analyst Tools - Zonal Choose correct attribute for zones (usually: must be unique ID for
Zonal functions Geol 588 GIS for Geoscientists II Feb 22, 2011 Zonal statistics Interpolation Zonal statistics Sp. Analyst Tools - Zonal Choose correct attribute for zones (usually: must be unique ID for
SOME stereo image-matching methods require a user-selected
 IEEE GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING LETTERS, VOL. 3, NO. 2, APRIL 2006 207 Seed Point Selection Method for Triangle Constrained Image Matching Propagation Qing Zhu, Bo Wu, and Zhi-Xiang Xu Abstract In order
IEEE GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING LETTERS, VOL. 3, NO. 2, APRIL 2006 207 Seed Point Selection Method for Triangle Constrained Image Matching Propagation Qing Zhu, Bo Wu, and Zhi-Xiang Xu Abstract In order
Introduction to 3D Analysis. Jinwu Ma Jie Chang Khalid Duri
 Introduction to 3D Analysis Jinwu Ma Jie Chang Khalid Duri Area & Volume 3D Analyst Features Detect Change Determine Cut/Fill Calculate Surface Area & Volume Data Management Data Creation Data Conversion
Introduction to 3D Analysis Jinwu Ma Jie Chang Khalid Duri Area & Volume 3D Analyst Features Detect Change Determine Cut/Fill Calculate Surface Area & Volume Data Management Data Creation Data Conversion
Geographic Surfaces. David Tenenbaum EEOS 383 UMass Boston
 Geographic Surfaces Up to this point, we have talked about spatial data models that operate in two dimensions How about the rd dimension? Surface the continuous variation in space of a third dimension
Geographic Surfaces Up to this point, we have talked about spatial data models that operate in two dimensions How about the rd dimension? Surface the continuous variation in space of a third dimension
Crea%ng DEMs From LiDAR Point Cloud Data
 Crea%ng DEMs From LiDAR Point Cloud Data C. Crosby (ccrosby@sdsc.edu) San Diego Supercomputer Center / OpenTopography.org Ramon Arrowsmith SESE, ASU 2011 SCEC LiDAR Short Course Digital ElevaEon Models
Crea%ng DEMs From LiDAR Point Cloud Data C. Crosby (ccrosby@sdsc.edu) San Diego Supercomputer Center / OpenTopography.org Ramon Arrowsmith SESE, ASU 2011 SCEC LiDAR Short Course Digital ElevaEon Models
Crea%ng DEMs From LiDAR Point Cloud Data
 Crea%ng DEMs From LiDAR Point Cloud Data C. Crosby (ccrosby@sdsc.edu) San Diego Supercomputer Center / OpenTopography.org Ramon Arrowsmith SESE, ASU 2009 SCEC LiDAR Short Course Digital ElevaEon Models
Crea%ng DEMs From LiDAR Point Cloud Data C. Crosby (ccrosby@sdsc.edu) San Diego Supercomputer Center / OpenTopography.org Ramon Arrowsmith SESE, ASU 2009 SCEC LiDAR Short Course Digital ElevaEon Models
N.J.P.L.S. An Introduction to LiDAR Concepts and Applications
 N.J.P.L.S. An Introduction to LiDAR Concepts and Applications Presentation Outline LIDAR Data Capture Advantages of Lidar Technology Basics Intensity and Multiple Returns Lidar Accuracy Airborne Laser
N.J.P.L.S. An Introduction to LiDAR Concepts and Applications Presentation Outline LIDAR Data Capture Advantages of Lidar Technology Basics Intensity and Multiple Returns Lidar Accuracy Airborne Laser
EMIGMA V9.x Premium Series April 8, 2015
 EMIGMA V9.x Premium Series April 8, 2015 EMIGMA for Gravity EMIGMA for Gravity license is a comprehensive package that offers a wide array of processing, visualization and interpretation tools. The package
EMIGMA V9.x Premium Series April 8, 2015 EMIGMA for Gravity EMIGMA for Gravity license is a comprehensive package that offers a wide array of processing, visualization and interpretation tools. The package
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Geo-Environment. Close-Range Photogrammetry For Landslide Monitoring
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Geo-Environment Journal homepage:http://ijceg.ump.edu.my ISSN:21802742 Close-Range Photogrammetry For Landslide Monitoring Munirah Bt Radin Mohd Mokhtar,
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Geo-Environment Journal homepage:http://ijceg.ump.edu.my ISSN:21802742 Close-Range Photogrammetry For Landslide Monitoring Munirah Bt Radin Mohd Mokhtar,
Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis. GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University
 Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University 1 Spatial Data It can be most simply defined as information that describes the distribution
Lecture 6: GIS Spatial Analysis GE 118: INTRODUCTION TO GIS Engr. Meriam M. Santillan Caraga State University 1 Spatial Data It can be most simply defined as information that describes the distribution
DATA MODELS IN GIS. Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi
 DATA MODELS IN GIS Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi -110012 1. Introduction GIS depicts the real world through models involving geometry, attributes, relations, and data quality. Here the realization
DATA MODELS IN GIS Prachi Misra Sahoo I.A.S.R.I., New Delhi -110012 1. Introduction GIS depicts the real world through models involving geometry, attributes, relations, and data quality. Here the realization
3D Terrain Modelling of the Amyntaio Ptolemais Basin
 2nd International Workshop in Geoenvironment and 1 3D Terrain Modelling of the Amyntaio Ptolemais Basin G. Argyris, I. Kapageridis and A. Triantafyllou Department of Geotechnology and Environmental Engineering,
2nd International Workshop in Geoenvironment and 1 3D Terrain Modelling of the Amyntaio Ptolemais Basin G. Argyris, I. Kapageridis and A. Triantafyllou Department of Geotechnology and Environmental Engineering,
WAVELET AND SCALE-SPACE THEORY IN SEGMENTATION OF AIRBORNE LASER SCANNER DATA
 WAVELET AND SCALE-SPACE THEORY IN SEGMENTATION OF AIRBORNE LASER SCANNER DATA T.Thuy VU, Mitsuharu TOKUNAGA Space Technology Applications and Research Asian Institute of Technology P.O. Box 4 Klong Luang,
WAVELET AND SCALE-SPACE THEORY IN SEGMENTATION OF AIRBORNE LASER SCANNER DATA T.Thuy VU, Mitsuharu TOKUNAGA Space Technology Applications and Research Asian Institute of Technology P.O. Box 4 Klong Luang,
Implementation of Flight Simulator using 3-Dimensional Terrain Modeling
 Implementation of Flight Simulator using 3-Dimensional Terrain Modeling 1 1, First Author School of Computer Engineering, Hanshin University, Osan City, S. Korea, stryoo@hs.ac.kr Abstract During the last
Implementation of Flight Simulator using 3-Dimensional Terrain Modeling 1 1, First Author School of Computer Engineering, Hanshin University, Osan City, S. Korea, stryoo@hs.ac.kr Abstract During the last
Report: Comparison of Methods to Produce Digital Terrain Models
 Report: Comparison of Methods to Produce Digital Terrain Models Evan J Fedorko West Virginia GIS Technical Center 27 April 2005 Introduction This report compares Digital Terrain Models (DTM) created through
Report: Comparison of Methods to Produce Digital Terrain Models Evan J Fedorko West Virginia GIS Technical Center 27 April 2005 Introduction This report compares Digital Terrain Models (DTM) created through
[Youn *, 5(11): November 2018] ISSN DOI /zenodo Impact Factor
![[Youn *, 5(11): November 2018] ISSN DOI /zenodo Impact Factor [Youn *, 5(11): November 2018] ISSN DOI /zenodo Impact Factor](/thumbs/91/105079225.jpg) GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND RESEARCHES AUTOMATIC EXTRACTING DEM FROM DSM WITH CONSECUTIVE MORPHOLOGICAL FILTERING Junhee Youn *1 & Tae-Hoon Kim 2 *1,2 Korea Institute of Civil Engineering
GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND RESEARCHES AUTOMATIC EXTRACTING DEM FROM DSM WITH CONSECUTIVE MORPHOLOGICAL FILTERING Junhee Youn *1 & Tae-Hoon Kim 2 *1,2 Korea Institute of Civil Engineering
A QUALITY ASSESSMENT OF AIRBORNE LASER SCANNER DATA
 A QUALITY ASSESSMENT OF AIRBORNE LASER SCANNER DATA E. Ahokas, H. Kaartinen, J. Hyyppä Finnish Geodetic Institute, Geodeetinrinne 2, 243 Masala, Finland Eero.Ahokas@fgi.fi KEYWORDS: LIDAR, accuracy, quality,
A QUALITY ASSESSMENT OF AIRBORNE LASER SCANNER DATA E. Ahokas, H. Kaartinen, J. Hyyppä Finnish Geodetic Institute, Geodeetinrinne 2, 243 Masala, Finland Eero.Ahokas@fgi.fi KEYWORDS: LIDAR, accuracy, quality,
Lab 12: Sampling and Interpolation
 Lab 12: Sampling and Interpolation What You ll Learn: -Systematic and random sampling -Majority filtering -Stratified sampling -A few basic interpolation methods Videos that show how to copy/paste data
Lab 12: Sampling and Interpolation What You ll Learn: -Systematic and random sampling -Majority filtering -Stratified sampling -A few basic interpolation methods Videos that show how to copy/paste data
GIS Visualization, 3D Visualization and Animation. Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University
 GIS Visualization, 3D Visualization and Animation Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Definitions 3D Visualization: Presenting or observing spatial,
GIS Visualization, 3D Visualization and Animation Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Definitions 3D Visualization: Presenting or observing spatial,
Automatic DTM Extraction from Dense Raw LIDAR Data in Urban Areas
 Automatic DTM Extraction from Dense Raw LIDAR Data in Urban Areas Nizar ABO AKEL, Ofer ZILBERSTEIN and Yerach DOYTSHER, Israel Key words: LIDAR, DSM, urban areas, DTM extraction. SUMMARY Although LIDAR
Automatic DTM Extraction from Dense Raw LIDAR Data in Urban Areas Nizar ABO AKEL, Ofer ZILBERSTEIN and Yerach DOYTSHER, Israel Key words: LIDAR, DSM, urban areas, DTM extraction. SUMMARY Although LIDAR
A Method to Create a Single Photon LiDAR based Hydro-flattened DEM
 A Method to Create a Single Photon LiDAR based Hydro-flattened DEM Sagar Deshpande 1 and Alper Yilmaz 2 1 Surveying Engineering, Ferris State University 2 Department of Civil, Environmental, and Geodetic
A Method to Create a Single Photon LiDAR based Hydro-flattened DEM Sagar Deshpande 1 and Alper Yilmaz 2 1 Surveying Engineering, Ferris State University 2 Department of Civil, Environmental, and Geodetic
REFINEMENT OF FILTERED LIDAR DATA USING LOCAL SURFACE PROPERTIES INTRODUCTION
 REFINEMENT OF FILTERED LIDAR DATA USING LOCAL SURFACE PROPERTIES Suyoung Seo, Senior Research Associate Charles G. O Hara, Associate Research Professor GeoResources Institute Mississippi State University
REFINEMENT OF FILTERED LIDAR DATA USING LOCAL SURFACE PROPERTIES Suyoung Seo, Senior Research Associate Charles G. O Hara, Associate Research Professor GeoResources Institute Mississippi State University
Surface Modeling with GIS
 Surface Modeling with GIS By Abdul Mohsen Al Maskeen ID # 889360 For CRP 514: Introduction to GIS Course Instructor: Dr. Baqer Al-Ramadan Date: December 29, 2004 1 Outline Page # Outline -------------------------------------------------------------
Surface Modeling with GIS By Abdul Mohsen Al Maskeen ID # 889360 For CRP 514: Introduction to GIS Course Instructor: Dr. Baqer Al-Ramadan Date: December 29, 2004 1 Outline Page # Outline -------------------------------------------------------------
REGISTRATION OF AIRBORNE LASER DATA TO SURFACES GENERATED BY PHOTOGRAMMETRIC MEANS. Y. Postolov, A. Krupnik, K. McIntosh
 REGISTRATION OF AIRBORNE LASER DATA TO SURFACES GENERATED BY PHOTOGRAMMETRIC MEANS Y. Postolov, A. Krupnik, K. McIntosh Department of Civil Engineering, Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa,
REGISTRATION OF AIRBORNE LASER DATA TO SURFACES GENERATED BY PHOTOGRAMMETRIC MEANS Y. Postolov, A. Krupnik, K. McIntosh Department of Civil Engineering, Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa,
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 25: 3D Analyst
 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 25: 3D Analyst 3D Analyst - 3D Analyst is an ArcGIS extension designed to work with TIN data (triangulated irregular network) - many of the tools in 3D Analyst also
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Lecture 25: 3D Analyst 3D Analyst - 3D Analyst is an ArcGIS extension designed to work with TIN data (triangulated irregular network) - many of the tools in 3D Analyst also
An Introduction to Dynamic Simulation Modeling
 Esri International User Conference San Diego, CA Technical Workshops ****************** An Introduction to Dynamic Simulation Modeling Kevin M. Johnston Shitij Mehta Outline Model types - Descriptive versus
Esri International User Conference San Diego, CA Technical Workshops ****************** An Introduction to Dynamic Simulation Modeling Kevin M. Johnston Shitij Mehta Outline Model types - Descriptive versus
Class #2. Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures
 Class #2 Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures Role of a Data Model Levels of Data Model Abstraction GIS as Digital
Class #2 Data Models: maps as models of reality, geographical and attribute measurement & vector and raster (and other) data structures Role of a Data Model Levels of Data Model Abstraction GIS as Digital
Terrestrial Laser Scanning: Applications in Civil Engineering Pauline Miller
 Terrestrial Laser Scanning: Applications in Civil Engineering Pauline Miller School of Civil Engineering & Geosciences Newcastle University Overview Laser scanning overview Research applications geometric
Terrestrial Laser Scanning: Applications in Civil Engineering Pauline Miller School of Civil Engineering & Geosciences Newcastle University Overview Laser scanning overview Research applications geometric
Ground and Non-Ground Filtering for Airborne LIDAR Data
 Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2016, Volume 5, Issue 1, pp. 1500-1506 ISSN 2320-0243, Crossref: 10.23953/cloud.ijarsg.41 Research Article Open Access Ground
Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS 2016, Volume 5, Issue 1, pp. 1500-1506 ISSN 2320-0243, Crossref: 10.23953/cloud.ijarsg.41 Research Article Open Access Ground
University of West Hungary, Faculty of Geoinformatics. Béla Márkus. Spatial Analysis 5. module SAN5. 3D analysis
 University of West Hungary, Faculty of Geoinformatics Béla Márkus Spatial Analysis 5. module SAN5 3D analysis SZÉKESFEHÉRVÁR 2010 The right to this intellectual property is protected by the 1999/LXXVI
University of West Hungary, Faculty of Geoinformatics Béla Márkus Spatial Analysis 5. module SAN5 3D analysis SZÉKESFEHÉRVÁR 2010 The right to this intellectual property is protected by the 1999/LXXVI
Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2)
 GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2) Today: Digital Elevation Models (DEMs), Topographic functions (surface analysis): slope, aspect hillshade, viewshed,
GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 21 - Chapter 8 (Raster Analysis, part2) Today: Digital Elevation Models (DEMs), Topographic functions (surface analysis): slope, aspect hillshade, viewshed,
THE IMPORTANCE OF UNDERSTANDING ERROR IN LIDAR DIGITAL ELEVATION MODELS
 THE IMPORTANCE OF UNDERSTANDING ERROR IN LIDAR DIGITAL ELEVATION MODELS b Smith, S.L a, Holland, D.A a, Longley, P.A b a Research & Innovation, Ordnance Survey, Romsey Road, Southampton, SO16 4GU e-mail
THE IMPORTANCE OF UNDERSTANDING ERROR IN LIDAR DIGITAL ELEVATION MODELS b Smith, S.L a, Holland, D.A a, Longley, P.A b a Research & Innovation, Ordnance Survey, Romsey Road, Southampton, SO16 4GU e-mail
MODELLING FOREST CANOPY USING AIRBORNE LIDAR DATA
 MODELLING FOREST CANOPY USING AIRBORNE LIDAR DATA Jihn-Fa JAN (Taiwan) Associate Professor, Department of Land Economics National Chengchi University 64, Sec. 2, Chih-Nan Road, Taipei 116, Taiwan Telephone:
MODELLING FOREST CANOPY USING AIRBORNE LIDAR DATA Jihn-Fa JAN (Taiwan) Associate Professor, Department of Land Economics National Chengchi University 64, Sec. 2, Chih-Nan Road, Taipei 116, Taiwan Telephone:
Follow-Up on the Nueces River Groundwater Problem Uvalde Co. TX
 Follow-Up on the Nueces River Groundwater Problem Uvalde Co. TX Analysis by Ryan Kraft 12/4/2014 1 Problem Formulation A reduction in discharge was detected at a gauging station along a portion of the
Follow-Up on the Nueces River Groundwater Problem Uvalde Co. TX Analysis by Ryan Kraft 12/4/2014 1 Problem Formulation A reduction in discharge was detected at a gauging station along a portion of the
Terrain Reconstruction from Contour Lines
 Terrain Reconstruction from Contour Lines JAN VANEK 1, BRUNO JEZEK 1, EVA MILKOVA 2 1 Faculty of Military Health Sciences, University of Defence 2 Faculty of Science, University of Hradec Kralove 500 01
Terrain Reconstruction from Contour Lines JAN VANEK 1, BRUNO JEZEK 1, EVA MILKOVA 2 1 Faculty of Military Health Sciences, University of Defence 2 Faculty of Science, University of Hradec Kralove 500 01
Assessing the performance of commercial Agisoft PhotoScan software to deliver reliable data for accurate 3D modelling
 Assessing the performance of commercial Agisoft PhotoScan software to deliver reliable data for accurate 3D modelling Ahmed Jebur 1,*, Fanar Abed 2 and Mamoun Mohammed 1 1 Engineering Technical College,
Assessing the performance of commercial Agisoft PhotoScan software to deliver reliable data for accurate 3D modelling Ahmed Jebur 1,*, Fanar Abed 2 and Mamoun Mohammed 1 1 Engineering Technical College,
17/07/2013 RASTER DATA STRUCTURE GIS LECTURE 4 GIS DATA MODELS AND STRUCTURES RASTER DATA MODEL& STRUCTURE TIN- TRIANGULAR IRREGULAR NETWORK
 RASTER DATA STRUCTURE GIS LECTURE 4 GIS DATA MODELS AND STRUCTURES Space is subdivided into regular grids of square grid cells or other forms of polygonal meshes known as picture elements (pixels) the
RASTER DATA STRUCTURE GIS LECTURE 4 GIS DATA MODELS AND STRUCTURES Space is subdivided into regular grids of square grid cells or other forms of polygonal meshes known as picture elements (pixels) the
BASE FLOOD ELEVATION DETERMINATION MODULE
 BASE FLOOD ELEVATION DETERMINATION MODULE FEDERAL EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT AGENCY PREPARED BY: NOLTE ASSOCIATES, INC. June, 2003 ABSTRACT The FEMA Base Flood Elevation Determination Module is a Visual Basic
BASE FLOOD ELEVATION DETERMINATION MODULE FEDERAL EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT AGENCY PREPARED BY: NOLTE ASSOCIATES, INC. June, 2003 ABSTRACT The FEMA Base Flood Elevation Determination Module is a Visual Basic
Representing Geography
 Data models and axioms Chapters 3 and 7 Representing Geography Road map Representing the real world Conceptual models: objects vs fields Implementation models: vector vs raster Vector topological model
Data models and axioms Chapters 3 and 7 Representing Geography Road map Representing the real world Conceptual models: objects vs fields Implementation models: vector vs raster Vector topological model
Experiments on Generation of 3D Virtual Geographic Environment Based on Laser Scanning Technique
 Experiments on Generation of 3D Virtual Geographic Environment Based on Laser Scanning Technique Jie Du 1, Fumio Yamazaki 2 Xiaoyong Chen 3 Apisit Eiumnoh 4, Michiro Kusanagi 3, R.P. Shrestha 4 1 School
Experiments on Generation of 3D Virtual Geographic Environment Based on Laser Scanning Technique Jie Du 1, Fumio Yamazaki 2 Xiaoyong Chen 3 Apisit Eiumnoh 4, Michiro Kusanagi 3, R.P. Shrestha 4 1 School
University of Technology Building & Construction Department / Remote Sensing & GIS lecture
 5. Corrections 5.1 Introduction 5.2 Radiometric Correction 5.3 Geometric corrections 5.3.1 Systematic distortions 5.3.2 Nonsystematic distortions 5.4 Image Rectification 5.5 Ground Control Points (GCPs)
5. Corrections 5.1 Introduction 5.2 Radiometric Correction 5.3 Geometric corrections 5.3.1 Systematic distortions 5.3.2 Nonsystematic distortions 5.4 Image Rectification 5.5 Ground Control Points (GCPs)
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Spatial Analyst [10] Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri. [10] Spring 2018 GIS Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri Spatial Analyst
![Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Spatial Analyst [10] Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri. [10] Spring 2018 GIS Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri Spatial Analyst Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Spatial Analyst [10] Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri. [10] Spring 2018 GIS Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri Spatial Analyst](/thumbs/80/81171101.jpg) Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Spatial Analyst [10] Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri 1 Preface POINTS, LINES, and POLYGONS are good at representing geographic objects with distinct shapes They are less good
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Spatial Analyst [10] Dr. Mohammad N. Almasri 1 Preface POINTS, LINES, and POLYGONS are good at representing geographic objects with distinct shapes They are less good
Variable Resolution Spatial Interpolation Using the Simple Recursive Point Voronoi Diagram B. Boots 1 and R.D. Feick 2
 Variable Resolution Spatial Interpolation Using the Simple Recursive Point Voronoi Diagram B. Boots 1 and R.D. Feick 2 1 Department of Geography and Environmental Studies, Wilfrid Laurier University, Waterloo,
Variable Resolution Spatial Interpolation Using the Simple Recursive Point Voronoi Diagram B. Boots 1 and R.D. Feick 2 1 Department of Geography and Environmental Studies, Wilfrid Laurier University, Waterloo,
Chapter 1. Introduction
 Introduction 1 Chapter 1. Introduction We live in a three-dimensional world. Inevitably, any application that analyzes or visualizes this world relies on three-dimensional data. Inherent characteristics
Introduction 1 Chapter 1. Introduction We live in a three-dimensional world. Inevitably, any application that analyzes or visualizes this world relies on three-dimensional data. Inherent characteristics
Maps as Numbers: Data Models
 Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices E Reality S E S arcs S E Conceptual Models nodes E Logical Models S Start node E End node S Physical Models 1 The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can
Maps as Numbers: Data Models vertices E Reality S E S arcs S E Conceptual Models nodes E Logical Models S Start node E End node S Physical Models 1 The Task An accurate, registered, digital map that can
Accuracy, Support, and Interoperability. Michael F. Goodchild University of California Santa Barbara
 Accuracy, Support, and Interoperability Michael F. Goodchild University of California Santa Barbara The traditional view Every object has a true position and set of attributes with enough time and resources
Accuracy, Support, and Interoperability Michael F. Goodchild University of California Santa Barbara The traditional view Every object has a true position and set of attributes with enough time and resources
Getting Started with Spatial Analyst. Steve Kopp Elizabeth Graham
 Getting Started with Spatial Analyst Steve Kopp Elizabeth Graham Spatial Analyst Overview Over 100 geoprocessing tools plus raster functions Raster and vector analysis Construct workflows with ModelBuilder,
Getting Started with Spatial Analyst Steve Kopp Elizabeth Graham Spatial Analyst Overview Over 100 geoprocessing tools plus raster functions Raster and vector analysis Construct workflows with ModelBuilder,
THE TOOLS OF AUTOMATED GENERALIZATION AND BUILDING GENERALIZATION IN AN ArcGIS ENVIRONMENT
 Vol. XIX, 2011, No. 1, 1 7, DOI: 10.2478/v10189-011-0001-4 V. DROPPOVÁ THE TOOLS OF AUTOMATED GENERALIZATION AND BUILDING GENERALIZATION IN AN ArcGIS ENVIRONMENT Veronika Droppová email: veronika.droppova@gmail.com
Vol. XIX, 2011, No. 1, 1 7, DOI: 10.2478/v10189-011-0001-4 V. DROPPOVÁ THE TOOLS OF AUTOMATED GENERALIZATION AND BUILDING GENERALIZATION IN AN ArcGIS ENVIRONMENT Veronika Droppová email: veronika.droppova@gmail.com
Esri International User Conference. July San Diego Convention Center. Lidar Solutions. Clayton Crawford
 Esri International User Conference July 23 27 San Diego Convention Center Lidar Solutions Clayton Crawford Outline Data structures, tools, and workflows Assessing lidar point coverage and sample density
Esri International User Conference July 23 27 San Diego Convention Center Lidar Solutions Clayton Crawford Outline Data structures, tools, and workflows Assessing lidar point coverage and sample density
Spatial Interpolation of Airborne Laser Scanning Data with Variable Data Density
 Spatial Interpolation of Airborne Laser Scanning Data with Variable Data Density Jaroslav Hofierka *, Michal Gallay*, Ján Kaňuk * * Institute of Geography, Faculty of Science, Pavol Jozef Safarik University,
Spatial Interpolation of Airborne Laser Scanning Data with Variable Data Density Jaroslav Hofierka *, Michal Gallay*, Ján Kaňuk * * Institute of Geography, Faculty of Science, Pavol Jozef Safarik University,
WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Floodplain Delineation Learn how to us the WMS floodplain delineation tools
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Floodplain Delineation Learn how to us the WMS floodplain delineation tools Objectives Experiment with the various floodplain delineation options
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Floodplain Delineation Learn how to us the WMS floodplain delineation tools Objectives Experiment with the various floodplain delineation options
Roadway Design using GeoTools
 Roadway Design using GeoTools Introduction GeoTools is a general-purpose productivity tool for users of all types of geographic data. In the Civil Tools section, there are many tools for Civil engineering
Roadway Design using GeoTools Introduction GeoTools is a general-purpose productivity tool for users of all types of geographic data. In the Civil Tools section, there are many tools for Civil engineering
Getting Started with Spatial Analyst. Steve Kopp Elizabeth Graham
 Getting Started with Spatial Analyst Steve Kopp Elizabeth Graham Workshop Overview Fundamentals of using Spatial Analyst What analysis capabilities exist and where to find them How to build a simple site
Getting Started with Spatial Analyst Steve Kopp Elizabeth Graham Workshop Overview Fundamentals of using Spatial Analyst What analysis capabilities exist and where to find them How to build a simple site
Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment
 Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment Aligning Raster and Vector Data to the Real World Rotation Differential Scaling Distortion Skew Translation 1 The Problem How are geographically unregistered data, either
Georeferencing & Spatial Adjustment Aligning Raster and Vector Data to the Real World Rotation Differential Scaling Distortion Skew Translation 1 The Problem How are geographically unregistered data, either
