Lecture 9: inverting the imaging process calibration, recovery of world position, mosaicing
|
|
|
- Meghan Tucker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 9: inverting the imaging process calibration, recovery of world position, mosaicing Dr. Richard E. Turner November 7, 2013
2 House keeping examples sheet solutions will be put on the website today webpage:
3 Recap: perspective camera world pixel
4 Recap: perspective camera world pixel
5 Recap: perspective camera world pixel
6 Recap: perspective camera world pixel
7 Recap: perspective camera world pixel
8 Recap: perspective camera world pixel
9 Recap: perspective camera world pixel
10 Recap: perspective camera world pixel perspective camera projection matrix camera calibration matrix rigid body motion matrix
11 Recap: perspective camera world pixel 10 d.o.f. perspective camera projection matrix complex structure camera calibration matrix rigid body motion matrix
12 Recap: perspective camera world pixel projective camera projection matrix
13 Recap: perspective camera world pixel 11 d.o.f. projective camera projection matrix simple structure
14 Recap: perspective camera world pixel viewing a wlg can be set to 0
15 Recap: perspective camera world pixel viewing a wlg can be set to 0
16 Recap: perspective camera world pixel viewing a can be removed wlg can be set to 0
17 Recap: perspective camera world pixel viewing a nb: this is exact
18 Recap: perspective camera world pixel viewing a line wlg can be set to 0
19 Recap: perspective camera world pixel viewing a line wlg can be set to 0
20 Recap: perspective camera world pixel viewing a line can be removed wlg can be set to 0
21 Recap: perspective camera world pixel viewing a line
22 Outstanding problems how do we calibrate cameras from known world/ points? (3D,2D,1D) how do we recover world position from a calibrated camera? how do we do mosaicing? (how do we calibrate and recover world position from multiple s)
23 Problems with standard fitting methods parameter fitting methods strongly affected by outliers
24 Problems with standard fitting methods parameter fitting methods strongly affected by outliers X 2 X 1
25 Problems with standard fitting methods parameter fitting methods strongly affected by outliers linear regression solution X 2 X 1
26 Problems with standard fitting methods parameter fitting methods strongly affected by outliers linear regression solution desired solution X 2 X 1
27 RANSAC Algorithm computationally cheap way of approximating desired solution linear regression solution desired solution X 2 X 1
28 RANSAC Algorithm initialise count of number of points fit X 2 nbest = 0 while i<niterations S = selectrandsubset(x) = fitparams(s) ninliers = countinliers(x, ) if ninliers>nbest = nbest = ninliers endif endwhile X 1
29 RANSAC Algorithm begin loop X 2 nbest = 0 while i<niterations S = selectrandsubset(x) = fitparams(s) ninliers = countinliers(x, ) if ninliers>nbest = nbest = ninliers endif endwhile X 1
30 RANSAC Algorithm: RAndom SAmple pick a subset of K points randomly (here K=2) X 2 nbest = 0 while i<niterations S = selectrandsubset(x) = fitparams(s) ninliers = countinliers(x, ) if ninliers>nbest = nbest = ninliers endif endwhile X 1
31 RANSAC Algorithm fit parameters to subset S X 2 nbest = 0 while i<niterations S = selectrandsubset(x) = fitparams(s) ninliers = countinliers(x, ) if ninliers>nbest = nbest = ninliers endif endwhile X 1
32 RANSAC Algorithm count number of points which are inliers X 2 nbest = 0 while i<niterations S = selectrandsubset(x) = fitparams(s) ninliers = countinliers(x, ) if ninliers>nbest = nbest = ninliers endif endwhile X 1
33 RANSAC Algorithm count number of points which are inliers, here ninliers = 4 X 2 nbest = 0 while i<niterations S = selectrandsubset(x) = fitparams(s) ninliers = countinliers(x, ) if ninliers>nbest = nbest = ninliers endif endwhile X 1
34 RANSAC Algorithm: Consensus if number of inliers is larger than before, save parameters & ninliers X 2 nbest = 0 while i<niterations S = selectrandsubset(x) = fitparams(s) ninliers = countinliers(x, ) if ninliers>nbest = nbest = ninliers endif endwhile X 1
35 RANSAC Algorithm pick a subset of K points randomly (here K=2) X 2 nbest = 0 while i<niterations S = selectrandsubset(x) = fitparams(s) ninliers = countinliers(x, ) if ninliers>nbest = nbest = ninliers endif endwhile X 1
36 RANSAC Algorithm fit parameters X 2 nbest = 0 while i<niterations S = selectrandsubset(x) = fitparams(s) ninliers = countinliers(x, ) if ninliers>nbest = nbest = ninliers endif endwhile X 1
37 RANSAC Algorithm count number if inliers, here ninliers = 6 X 2 nbest = 0 while i<niterations S = selectrandsubset(x) = fitparams(s) ninliers = countinliers(x, ) if ninliers>nbest = nbest = ninliers endif endwhile X 1
38 RANSAC Algorithm if number of inliers larger than best, update parameters etc. X 2 nbest = 0 while i<niterations S = selectrandsubset(x) = fitparams(s) ninliers = countinliers(x, ) if ninliers>nbest = nbest = ninliers endif endwhile X 1
39 RANSAC Algorithm pick a subset of K points randomly (here K=2) X 2 nbest = 0 while i<niterations S = selectrandsubset(x) = fitparams(s) ninliers = countinliers(x, ) if ninliers>nbest = nbest = ninliers endif endwhile X 1
40 RANSAC Algorithm fit parameters X 2 nbest = 0 while i<niterations S = selectrandsubset(x) = fitparams(s) ninliers = countinliers(x, ) if ninliers>nbest = nbest = ninliers endif endwhile X 1
41 RANSAC Algorithm count inliers X 2 nbest = 0 while i<niterations S = selectrandsubset(x) = fitparams(s) ninliers = countinliers(x, ) if ninliers>nbest = nbest = ninliers endif endwhile X 1
42 RANSAC Algorithm no need to update as not an improvement X 2 nbest = 0 while i<niterations S = selectrandsubset(x) = fitparams(s) ninliers = countinliers(x, ) if ninliers>nbest = nbest = ninliers endif endwhile X 1
43 RANSAC Algorithm pick a subset of K points randomly (here K=2) X 2 nbest = 0 while i<niterations S = selectrandsubset(x) = fitparams(s) ninliers = countinliers(x, ) if ninliers>nbest = nbest = ninliers endif endwhile X 1
44 RANSAC Algorithm fit parameters X 2 nbest = 0 while i<niterations S = selectrandsubset(x) = fitparams(s) ninliers = countinliers(x, ) if ninliers>nbest = nbest = ninliers endif endwhile X 1
45 RANSAC Algorithm count number of inliers X 2 nbest = 0 while i<niterations S = selectrandsubset(x) = fitparams(s) ninliers = countinliers(x, ) if ninliers>nbest = nbest = ninliers endif endwhile X 1
46 RANSAC Algorithm update stored parameters X 2 nbest = 0 while i<niterations S = selectrandsubset(x) = fitparams(s) ninliers = countinliers(x, ) if ninliers>nbest = nbest = ninliers endif endwhile X 1
47 RANSAC for mosaicing H = eye(3,3) homography, H = KRK 1, initialised to identity nbest = 0 for int i = 0; i < niterations; i++ do P4 = SelectRandomSubset(P) select subset of points (e.g. 4) Hi = ComputeHomography(P4) compute homography from subset ninliers = ComputeInliers(Hi) compute no. of consistent points if ninliers > nbest then H = Hi nbest = ninliers end if end for
CSE 527: Introduction to Computer Vision
 CSE 527: Introduction to Computer Vision Week 5 - Class 1: Matching, Stitching, Registration September 26th, 2017 ??? Recap Today Feature Matching Image Alignment Panoramas HW2! Feature Matches Feature
CSE 527: Introduction to Computer Vision Week 5 - Class 1: Matching, Stitching, Registration September 26th, 2017 ??? Recap Today Feature Matching Image Alignment Panoramas HW2! Feature Matches Feature
Automatic Panoramic Image Stitching. Dr. Matthew Brown, University of Bath
 Automatic Panoramic Image Stitching Dr. Matthew Brown, University of Bath Automatic 2D Stitching The old days: panoramic stitchers were limited to a 1-D sweep 2005: 2-D stitchers use object recognition
Automatic Panoramic Image Stitching Dr. Matthew Brown, University of Bath Automatic 2D Stitching The old days: panoramic stitchers were limited to a 1-D sweep 2005: 2-D stitchers use object recognition
Stereo and Epipolar geometry
 Previously Image Primitives (feature points, lines, contours) Today: Stereo and Epipolar geometry How to match primitives between two (multiple) views) Goals: 3D reconstruction, recognition Jana Kosecka
Previously Image Primitives (feature points, lines, contours) Today: Stereo and Epipolar geometry How to match primitives between two (multiple) views) Goals: 3D reconstruction, recognition Jana Kosecka
Homographies and RANSAC
 Homographies and RANSAC Computer vision 6.869 Bill Freeman and Antonio Torralba March 30, 2011 Homographies and RANSAC Homographies RANSAC Building panoramas Phototourism 2 Depth-based ambiguity of position
Homographies and RANSAC Computer vision 6.869 Bill Freeman and Antonio Torralba March 30, 2011 Homographies and RANSAC Homographies RANSAC Building panoramas Phototourism 2 Depth-based ambiguity of position
Dr. Ulas Bagci
 CAP5415-Computer Vision Lecture 17-Fundamental Matrix Dr. Ulas Bagci bagci@ucf.edu 1 Reminders PA#4 is due on 22 nd October (extended to next Monday) PA#5 is due on 5 th of November (no extension). Mini-project
CAP5415-Computer Vision Lecture 17-Fundamental Matrix Dr. Ulas Bagci bagci@ucf.edu 1 Reminders PA#4 is due on 22 nd October (extended to next Monday) PA#5 is due on 5 th of November (no extension). Mini-project
Image Stitching. Slides from Rick Szeliski, Steve Seitz, Derek Hoiem, Ira Kemelmacher, Ali Farhadi
 Image Stitching Slides from Rick Szeliski, Steve Seitz, Derek Hoiem, Ira Kemelmacher, Ali Farhadi Combine two or more overlapping images to make one larger image Add example Slide credit: Vaibhav Vaish
Image Stitching Slides from Rick Szeliski, Steve Seitz, Derek Hoiem, Ira Kemelmacher, Ali Farhadi Combine two or more overlapping images to make one larger image Add example Slide credit: Vaibhav Vaish
CSE 252B: Computer Vision II
 CSE 252B: Computer Vision II Lecturer: Serge Belongie Scribes: Jeremy Pollock and Neil Alldrin LECTURE 14 Robust Feature Matching 14.1. Introduction Last lecture we learned how to find interest points
CSE 252B: Computer Vision II Lecturer: Serge Belongie Scribes: Jeremy Pollock and Neil Alldrin LECTURE 14 Robust Feature Matching 14.1. Introduction Last lecture we learned how to find interest points
Perception IV: Place Recognition, Line Extraction
 Perception IV: Place Recognition, Line Extraction Davide Scaramuzza University of Zurich Margarita Chli, Paul Furgale, Marco Hutter, Roland Siegwart 1 Outline of Today s lecture Place recognition using
Perception IV: Place Recognition, Line Extraction Davide Scaramuzza University of Zurich Margarita Chli, Paul Furgale, Marco Hutter, Roland Siegwart 1 Outline of Today s lecture Place recognition using
3D Computer Vision. Structure from Motion. Prof. Didier Stricker
 3D Computer Vision Structure from Motion Prof. Didier Stricker Kaiserlautern University http://ags.cs.uni-kl.de/ DFKI Deutsches Forschungszentrum für Künstliche Intelligenz http://av.dfki.de 1 Structure
3D Computer Vision Structure from Motion Prof. Didier Stricker Kaiserlautern University http://ags.cs.uni-kl.de/ DFKI Deutsches Forschungszentrum für Künstliche Intelligenz http://av.dfki.de 1 Structure
Week 2: Two-View Geometry. Padua Summer 08 Frank Dellaert
 Week 2: Two-View Geometry Padua Summer 08 Frank Dellaert Mosaicking Outline 2D Transformation Hierarchy RANSAC Triangulation of 3D Points Cameras Triangulation via SVD Automatic Correspondence Essential
Week 2: Two-View Geometry Padua Summer 08 Frank Dellaert Mosaicking Outline 2D Transformation Hierarchy RANSAC Triangulation of 3D Points Cameras Triangulation via SVD Automatic Correspondence Essential
CS231A Midterm Review. Friday 5/6/2016
 CS231A Midterm Review Friday 5/6/2016 Outline General Logistics Camera Models Non-perspective cameras Calibration Single View Metrology Epipolar Geometry Structure from Motion Active Stereo and Volumetric
CS231A Midterm Review Friday 5/6/2016 Outline General Logistics Camera Models Non-perspective cameras Calibration Single View Metrology Epipolar Geometry Structure from Motion Active Stereo and Volumetric
Agenda. Rotations. Camera calibration. Homography. Ransac
 Agenda Rotations Camera calibration Homography Ransac Geometric Transformations y x Transformation Matrix # DoF Preserves Icon translation rigid (Euclidean) similarity affine projective h I t h R t h sr
Agenda Rotations Camera calibration Homography Ransac Geometric Transformations y x Transformation Matrix # DoF Preserves Icon translation rigid (Euclidean) similarity affine projective h I t h R t h sr
Automatic Image Alignment
 Automatic Image Alignment Mike Nese with a lot of slides stolen from Steve Seitz and Rick Szeliski 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2010 Live Homography DEMO Check out panoramio.com
Automatic Image Alignment Mike Nese with a lot of slides stolen from Steve Seitz and Rick Szeliski 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2010 Live Homography DEMO Check out panoramio.com
Epipolar Geometry CSE P576. Dr. Matthew Brown
 Epipolar Geometry CSE P576 Dr. Matthew Brown Epipolar Geometry Epipolar Lines, Plane Constraint Fundamental Matrix, Linear solution + RANSAC Applications: Structure from Motion, Stereo [ Szeliski 11] 2
Epipolar Geometry CSE P576 Dr. Matthew Brown Epipolar Geometry Epipolar Lines, Plane Constraint Fundamental Matrix, Linear solution + RANSAC Applications: Structure from Motion, Stereo [ Szeliski 11] 2
Homography estimation
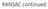 RANSAC continued Homography estimation x w? ~x img H~x w Homography estimation? x img ~x w = H 1 ~x img Homography estimation (0,0) (1,0) (6.4,2.8) (8.0,2.9) (5.6, 4.0) (7.8, 4.2) (0,1) (1,1) Ah =0s.tkhk
RANSAC continued Homography estimation x w? ~x img H~x w Homography estimation? x img ~x w = H 1 ~x img Homography estimation (0,0) (1,0) (6.4,2.8) (8.0,2.9) (5.6, 4.0) (7.8, 4.2) (0,1) (1,1) Ah =0s.tkhk
Model Fitting. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 11
 Model Fitting CSE 152 Lecture 11 Announcements Homework 3 is due May 9, 11:59 PM Reading: Chapter 10: Grouping and Model Fitting What to do with edges? Segment linked edge chains into curve features (e.g.,
Model Fitting CSE 152 Lecture 11 Announcements Homework 3 is due May 9, 11:59 PM Reading: Chapter 10: Grouping and Model Fitting What to do with edges? Segment linked edge chains into curve features (e.g.,
Agenda. Rotations. Camera models. Camera calibration. Homographies
 Agenda Rotations Camera models Camera calibration Homographies D Rotations R Y = Z r r r r r r r r r Y Z Think of as change of basis where ri = r(i,:) are orthonormal basis vectors r rotated coordinate
Agenda Rotations Camera models Camera calibration Homographies D Rotations R Y = Z r r r r r r r r r Y Z Think of as change of basis where ri = r(i,:) are orthonormal basis vectors r rotated coordinate
Srikumar Ramalingam. Review. 3D Reconstruction. Pose Estimation Revisited. School of Computing University of Utah
 School of Computing University of Utah Presentation Outline 1 2 3 Forward Projection (Reminder) u v 1 KR ( I t ) X m Y m Z m 1 Backward Projection (Reminder) Q K 1 q Presentation Outline 1 2 3 Sample Problem
School of Computing University of Utah Presentation Outline 1 2 3 Forward Projection (Reminder) u v 1 KR ( I t ) X m Y m Z m 1 Backward Projection (Reminder) Q K 1 q Presentation Outline 1 2 3 Sample Problem
Rectification. Dr. Gerhard Roth
 Rectification Dr. Gerhard Roth Problem Definition Given a pair of stereo images, the intrinsic parameters of each camera, and the extrinsic parameters of the system, R, and, compute the image transformation
Rectification Dr. Gerhard Roth Problem Definition Given a pair of stereo images, the intrinsic parameters of each camera, and the extrinsic parameters of the system, R, and, compute the image transformation
CS 395T Lecture 12: Feature Matching and Bundle Adjustment. Qixing Huang October 10 st 2018
 CS 395T Lecture 12: Feature Matching and Bundle Adjustment Qixing Huang October 10 st 2018 Lecture Overview Dense Feature Correspondences Bundle Adjustment in Structure-from-Motion Image Matching Algorithm
CS 395T Lecture 12: Feature Matching and Bundle Adjustment Qixing Huang October 10 st 2018 Lecture Overview Dense Feature Correspondences Bundle Adjustment in Structure-from-Motion Image Matching Algorithm
Structure from Motion. Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 10
 Structure from Motion CSE 152 Lecture 10 Announcements Homework 3 is due May 9, 11:59 PM Reading: Chapter 8: Structure from Motion Optional: Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision, 2nd edition, Hartley
Structure from Motion CSE 152 Lecture 10 Announcements Homework 3 is due May 9, 11:59 PM Reading: Chapter 8: Structure from Motion Optional: Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision, 2nd edition, Hartley
Srikumar Ramalingam. Review. 3D Reconstruction. Pose Estimation Revisited. School of Computing University of Utah
 School of Computing University of Utah Presentation Outline 1 2 3 Forward Projection (Reminder) u v 1 KR ( I t ) X m Y m Z m 1 Backward Projection (Reminder) Q K 1 q Q K 1 u v 1 What is pose estimation?
School of Computing University of Utah Presentation Outline 1 2 3 Forward Projection (Reminder) u v 1 KR ( I t ) X m Y m Z m 1 Backward Projection (Reminder) Q K 1 q Q K 1 u v 1 What is pose estimation?
Feature Matching and RANSAC
 Feature Matching and RANSAC Recognising Panoramas. [M. Brown and D. Lowe,ICCV 2003] [Brown, Szeliski, Winder, CVPR 2005] with a lot of slides stolen from Steve Seitz, Rick Szeliski, A. Efros Introduction
Feature Matching and RANSAC Recognising Panoramas. [M. Brown and D. Lowe,ICCV 2003] [Brown, Szeliski, Winder, CVPR 2005] with a lot of slides stolen from Steve Seitz, Rick Szeliski, A. Efros Introduction
Automatic Image Alignment
 Automatic Image Alignment with a lot of slides stolen from Steve Seitz and Rick Szeliski Mike Nese CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2018 Live Homography
Automatic Image Alignment with a lot of slides stolen from Steve Seitz and Rick Szeliski Mike Nese CS194: Image Manipulation & Computational Photography Alexei Efros, UC Berkeley, Fall 2018 Live Homography
Image correspondences and structure from motion
 Image correspondences and structure from motion http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2017, Lecture 20 Course announcements Homework 5 posted.
Image correspondences and structure from motion http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463 15-463, 15-663, 15-862 Computational Photography Fall 2017, Lecture 20 Course announcements Homework 5 posted.
Vision par ordinateur
 Epipolar geometry π Vision par ordinateur Underlying structure in set of matches for rigid scenes l T 1 l 2 C1 m1 l1 e1 M L2 L1 e2 Géométrie épipolaire Fundamental matrix (x rank 2 matrix) m2 C2 l2 Frédéric
Epipolar geometry π Vision par ordinateur Underlying structure in set of matches for rigid scenes l T 1 l 2 C1 m1 l1 e1 M L2 L1 e2 Géométrie épipolaire Fundamental matrix (x rank 2 matrix) m2 C2 l2 Frédéric
Automatic Image Alignment (feature-based)
 Automatic Image Alignment (feature-based) Mike Nese with a lot of slides stolen from Steve Seitz and Rick Szeliski 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2006 Today s lecture Feature
Automatic Image Alignment (feature-based) Mike Nese with a lot of slides stolen from Steve Seitz and Rick Szeliski 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2006 Today s lecture Feature
Multiple View Geometry. Frank Dellaert
 Multiple View Geometry Frank Dellaert Outline Intro Camera Review Stereo triangulation Geometry of 2 views Essential Matrix Fundamental Matrix Estimating E/F from point-matches Why Consider Multiple Views?
Multiple View Geometry Frank Dellaert Outline Intro Camera Review Stereo triangulation Geometry of 2 views Essential Matrix Fundamental Matrix Estimating E/F from point-matches Why Consider Multiple Views?
Image stitching. Announcements. Outline. Image stitching
 Announcements Image stitching Project #1 was due yesterday. Project #2 handout will be available on the web later tomorrow. I will set up a webpage for artifact voting soon. Digital Visual Effects, Spring
Announcements Image stitching Project #1 was due yesterday. Project #2 handout will be available on the web later tomorrow. I will set up a webpage for artifact voting soon. Digital Visual Effects, Spring
Computer Vision I. Announcements. Random Dot Stereograms. Stereo III. CSE252A Lecture 16
 Announcements Stereo III CSE252A Lecture 16 HW1 being returned HW3 assigned and due date extended until 11/27/12 No office hours today No class on Thursday 12/6 Extra class on Tuesday 12/4 at 6:30PM in
Announcements Stereo III CSE252A Lecture 16 HW1 being returned HW3 assigned and due date extended until 11/27/12 No office hours today No class on Thursday 12/6 Extra class on Tuesday 12/4 at 6:30PM in
CS664 Lecture #19: Layers, RANSAC, panoramas, epipolar geometry
 CS664 Lecture #19: Layers, RANSAC, panoramas, epipolar geometry Some material taken from: David Lowe, UBC Jiri Matas, CMP Prague http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~matas/papers/presentations/matas_beyondransac_cvprac05.ppt
CS664 Lecture #19: Layers, RANSAC, panoramas, epipolar geometry Some material taken from: David Lowe, UBC Jiri Matas, CMP Prague http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~matas/papers/presentations/matas_beyondransac_cvprac05.ppt
Feature Based Registration - Image Alignment
 Feature Based Registration - Image Alignment Image Registration Image registration is the process of estimating an optimal transformation between two or more images. Many slides from Alexei Efros http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463/2007_fall/463.html
Feature Based Registration - Image Alignment Image Registration Image registration is the process of estimating an optimal transformation between two or more images. Many slides from Alexei Efros http://graphics.cs.cmu.edu/courses/15-463/2007_fall/463.html
Multiview Stereo COSC450. Lecture 8
 Multiview Stereo COSC450 Lecture 8 Stereo Vision So Far Stereo and epipolar geometry Fundamental matrix captures geometry 8-point algorithm Essential matrix with calibrated cameras 5-point algorithm Intersect
Multiview Stereo COSC450 Lecture 8 Stereo Vision So Far Stereo and epipolar geometry Fundamental matrix captures geometry 8-point algorithm Essential matrix with calibrated cameras 5-point algorithm Intersect
Observations. Basic iteration Line estimated from 2 inliers
 Line estimated from 2 inliers 3 Observations We need (in this case!) a minimum of 2 points to determine a line Given such a line l, we can determine how well any other point y fits the line l For example:
Line estimated from 2 inliers 3 Observations We need (in this case!) a minimum of 2 points to determine a line Given such a line l, we can determine how well any other point y fits the line l For example:
An Evaluation of the Performance of RANSAC Algorithms for Stereo Camera Calibration
 Tina Memo No. 2000-009 Presented at BMVC 2000 An Evaluation of the Performance of RANSAC Algorithms for Stereo Camera Calibration A. J. Lacey, N. Pinitkarn and N. A. Thacker Last updated 21 / 02 / 2002
Tina Memo No. 2000-009 Presented at BMVC 2000 An Evaluation of the Performance of RANSAC Algorithms for Stereo Camera Calibration A. J. Lacey, N. Pinitkarn and N. A. Thacker Last updated 21 / 02 / 2002
Hough Transform and RANSAC
 CS4501: Introduction to Computer Vision Hough Transform and RANSAC Various slides from previous courses by: D.A. Forsyth (Berkeley / UIUC), I. Kokkinos (Ecole Centrale / UCL). S. Lazebnik (UNC / UIUC),
CS4501: Introduction to Computer Vision Hough Transform and RANSAC Various slides from previous courses by: D.A. Forsyth (Berkeley / UIUC), I. Kokkinos (Ecole Centrale / UCL). S. Lazebnik (UNC / UIUC),
Image stitching. Digital Visual Effects Yung-Yu Chuang. with slides by Richard Szeliski, Steve Seitz, Matthew Brown and Vaclav Hlavac
 Image stitching Digital Visual Effects Yung-Yu Chuang with slides by Richard Szeliski, Steve Seitz, Matthew Brown and Vaclav Hlavac Image stitching Stitching = alignment + blending geometrical registration
Image stitching Digital Visual Effects Yung-Yu Chuang with slides by Richard Szeliski, Steve Seitz, Matthew Brown and Vaclav Hlavac Image stitching Stitching = alignment + blending geometrical registration
Combining Appearance and Topology for Wide
 Combining Appearance and Topology for Wide Baseline Matching Dennis Tell and Stefan Carlsson Presented by: Josh Wills Image Point Correspondences Critical foundation for many vision applications 3-D reconstruction,
Combining Appearance and Topology for Wide Baseline Matching Dennis Tell and Stefan Carlsson Presented by: Josh Wills Image Point Correspondences Critical foundation for many vision applications 3-D reconstruction,
Step-by-Step Model Buidling
 Step-by-Step Model Buidling Review Feature selection Feature selection Feature correspondence Camera Calibration Euclidean Reconstruction Landing Augmented Reality Vision Based Control Sparse Structure
Step-by-Step Model Buidling Review Feature selection Feature selection Feature correspondence Camera Calibration Euclidean Reconstruction Landing Augmented Reality Vision Based Control Sparse Structure
Structure from motion
 Structure from motion Structure from motion Given a set of corresponding points in two or more images, compute the camera parameters and the 3D point coordinates?? R 1,t 1 R 2,t R 2 3,t 3 Camera 1 Camera
Structure from motion Structure from motion Given a set of corresponding points in two or more images, compute the camera parameters and the 3D point coordinates?? R 1,t 1 R 2,t R 2 3,t 3 Camera 1 Camera
Computer Vision, Assignment 4 Model Fitting
 Centre for Mathematical Sciences, February 2013 Due 2013-02-26 Computer Vision, Assignment 4 Model Fitting 1 Instructions In this assignment you will study model fitting. In particular you will use random
Centre for Mathematical Sciences, February 2013 Due 2013-02-26 Computer Vision, Assignment 4 Model Fitting 1 Instructions In this assignment you will study model fitting. In particular you will use random
Image warping and stitching
 Image warping and stitching Thurs Oct 15 Last time Feature-based alignment 2D transformations Affine fit RANSAC 1 Robust feature-based alignment Extract features Compute putative matches Loop: Hypothesize
Image warping and stitching Thurs Oct 15 Last time Feature-based alignment 2D transformations Affine fit RANSAC 1 Robust feature-based alignment Extract features Compute putative matches Loop: Hypothesize
Image Warping. Many slides from Alyosha Efros + Steve Seitz. Photo by Sean Carroll
 Image Warping Man slides from Alosha Efros + Steve Seitz Photo b Sean Carroll Morphing Blend from one object to other with a series of local transformations Image Transformations image filtering: change
Image Warping Man slides from Alosha Efros + Steve Seitz Photo b Sean Carroll Morphing Blend from one object to other with a series of local transformations Image Transformations image filtering: change
calibrated coordinates Linear transformation pixel coordinates
 1 calibrated coordinates Linear transformation pixel coordinates 2 Calibration with a rig Uncalibrated epipolar geometry Ambiguities in image formation Stratified reconstruction Autocalibration with partial
1 calibrated coordinates Linear transformation pixel coordinates 2 Calibration with a rig Uncalibrated epipolar geometry Ambiguities in image formation Stratified reconstruction Autocalibration with partial
Structure from motion
 Structure from motion Structure from motion Given a set of corresponding points in two or more images, compute the camera parameters and the 3D point coordinates?? R 1,t 1 R 2,t 2 R 3,t 3 Camera 1 Camera
Structure from motion Structure from motion Given a set of corresponding points in two or more images, compute the camera parameters and the 3D point coordinates?? R 1,t 1 R 2,t 2 R 3,t 3 Camera 1 Camera
Leow Wee Kheng CS4243 Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Robust Methods. CS4243 Robust Methods 1
 Leow Wee Kheng CS4243 Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Robust Methods CS4243 Robust Methods 1 Consider this data set Fitting a line to blue points give blue line. Outliers cause fitting error (red
Leow Wee Kheng CS4243 Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Robust Methods CS4243 Robust Methods 1 Consider this data set Fitting a line to blue points give blue line. Outliers cause fitting error (red
Mosaics. Today s Readings
 Mosaics VR Seattle: http://www.vrseattle.com/ Full screen panoramas (cubic): http://www.panoramas.dk/ Mars: http://www.panoramas.dk/fullscreen3/f2_mars97.html Today s Readings Szeliski and Shum paper (sections
Mosaics VR Seattle: http://www.vrseattle.com/ Full screen panoramas (cubic): http://www.panoramas.dk/ Mars: http://www.panoramas.dk/fullscreen3/f2_mars97.html Today s Readings Szeliski and Shum paper (sections
3D Modeling using multiple images Exam January 2008
 3D Modeling using multiple images Exam January 2008 All documents are allowed. Answers should be justified. The different sections below are independant. 1 3D Reconstruction A Robust Approche Consider
3D Modeling using multiple images Exam January 2008 All documents are allowed. Answers should be justified. The different sections below are independant. 1 3D Reconstruction A Robust Approche Consider
A New Representation for Video Inspection. Fabio Viola
 A New Representation for Video Inspection Fabio Viola Outline Brief introduction to the topic and definition of long term goal. Description of the proposed research project. Identification of a short term
A New Representation for Video Inspection Fabio Viola Outline Brief introduction to the topic and definition of long term goal. Description of the proposed research project. Identification of a short term
Visual Odometry. Features, Tracking, Essential Matrix, and RANSAC. Stephan Weiss Computer Vision Group NASA-JPL / CalTech
 Visual Odometry Features, Tracking, Essential Matrix, and RANSAC Stephan Weiss Computer Vision Group NASA-JPL / CalTech Stephan.Weiss@ieee.org (c) 2013. Government sponsorship acknowledged. Outline The
Visual Odometry Features, Tracking, Essential Matrix, and RANSAC Stephan Weiss Computer Vision Group NASA-JPL / CalTech Stephan.Weiss@ieee.org (c) 2013. Government sponsorship acknowledged. Outline The
Index. 3D reconstruction, point algorithm, point algorithm, point algorithm, point algorithm, 253
 Index 3D reconstruction, 123 5+1-point algorithm, 274 5-point algorithm, 260 7-point algorithm, 255 8-point algorithm, 253 affine point, 43 affine transformation, 55 affine transformation group, 55 affine
Index 3D reconstruction, 123 5+1-point algorithm, 274 5-point algorithm, 260 7-point algorithm, 255 8-point algorithm, 253 affine point, 43 affine transformation, 55 affine transformation group, 55 affine
Parameter estimation. Christiano Gava Gabriele Bleser
 Parameter estimation Christiano Gava Christiano.Gava@dfki.de Gabriele Bleser gabriele.bleser@dfki.de Introduction Previous lectures: P-matrix 2D projective transformations Estimation (direct linear transform)
Parameter estimation Christiano Gava Christiano.Gava@dfki.de Gabriele Bleser gabriele.bleser@dfki.de Introduction Previous lectures: P-matrix 2D projective transformations Estimation (direct linear transform)
CS 231A Computer Vision (Winter 2018) Problem Set 3
 CS 231A Computer Vision (Winter 2018) Problem Set 3 Due: Feb 28, 2018 (11:59pm) 1 Space Carving (25 points) Dense 3D reconstruction is a difficult problem, as tackling it from the Structure from Motion
CS 231A Computer Vision (Winter 2018) Problem Set 3 Due: Feb 28, 2018 (11:59pm) 1 Space Carving (25 points) Dense 3D reconstruction is a difficult problem, as tackling it from the Structure from Motion
Perception. Autonomous Mobile Robots. Sensors Vision Uncertainties, Line extraction from laser scans. Autonomous Systems Lab. Zürich.
 Autonomous Mobile Robots Localization "Position" Global Map Cognition Environment Model Local Map Path Perception Real World Environment Motion Control Perception Sensors Vision Uncertainties, Line extraction
Autonomous Mobile Robots Localization "Position" Global Map Cognition Environment Model Local Map Path Perception Real World Environment Motion Control Perception Sensors Vision Uncertainties, Line extraction
Index. 3D reconstruction, point algorithm, point algorithm, point algorithm, point algorithm, 263
 Index 3D reconstruction, 125 5+1-point algorithm, 284 5-point algorithm, 270 7-point algorithm, 265 8-point algorithm, 263 affine point, 45 affine transformation, 57 affine transformation group, 57 affine
Index 3D reconstruction, 125 5+1-point algorithm, 284 5-point algorithm, 270 7-point algorithm, 265 8-point algorithm, 263 affine point, 45 affine transformation, 57 affine transformation group, 57 affine
PS3 Review Session. Kuan Fang CS231A 02/16/2018
 PS3 Review Session Kuan Fang CS231A 02/16/2018 Overview Space carving Single Object Recognition via SIFT Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG) Space Carving Objective: Implement the process of space carving.
PS3 Review Session Kuan Fang CS231A 02/16/2018 Overview Space carving Single Object Recognition via SIFT Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG) Space Carving Objective: Implement the process of space carving.
Image warping and stitching
 Image warping and stitching May 4 th, 2017 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis Last time Interactive segmentation Feature-based alignment 2D transformations Affine fit RANSAC 2 Alignment problem In alignment, we will
Image warping and stitching May 4 th, 2017 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis Last time Interactive segmentation Feature-based alignment 2D transformations Affine fit RANSAC 2 Alignment problem In alignment, we will
Vision Review: Image Formation. Course web page:
 Vision Review: Image Formation Course web page: www.cis.udel.edu/~cer/arv September 10, 2002 Announcements Lecture on Thursday will be about Matlab; next Tuesday will be Image Processing The dates some
Vision Review: Image Formation Course web page: www.cis.udel.edu/~cer/arv September 10, 2002 Announcements Lecture on Thursday will be about Matlab; next Tuesday will be Image Processing The dates some
Two-View Geometry (Course 23, Lecture D)
 Two-View Geometry (Course 23, Lecture D) Jana Kosecka Department of Computer Science George Mason University http://www.cs.gmu.edu/~kosecka General Formulation Given two views of the scene recover the
Two-View Geometry (Course 23, Lecture D) Jana Kosecka Department of Computer Science George Mason University http://www.cs.gmu.edu/~kosecka General Formulation Given two views of the scene recover the
Drawing in 3D (viewing, projection, and the rest of the pipeline)
 Drawing in 3D (viewing, projection, and the rest of the pipeline) CS559 Spring 2016 Lecture 6 February 11, 2016 The first 4 Key Ideas 1. Work in convenient coordinate systems. Use transformations to get
Drawing in 3D (viewing, projection, and the rest of the pipeline) CS559 Spring 2016 Lecture 6 February 11, 2016 The first 4 Key Ideas 1. Work in convenient coordinate systems. Use transformations to get
Image warping and stitching
 Image warping and stitching May 5 th, 2015 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis PS2 due next Friday Announcements 2 Last time Interactive segmentation Feature-based alignment 2D transformations Affine fit RANSAC 3 Alignment
Image warping and stitching May 5 th, 2015 Yong Jae Lee UC Davis PS2 due next Friday Announcements 2 Last time Interactive segmentation Feature-based alignment 2D transformations Affine fit RANSAC 3 Alignment
CS664 Lecture #16: Image registration, robust statistics, motion
 CS664 Lecture #16: Image registration, robust statistics, motion Some material taken from: Alyosha Efros, CMU http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~efros Xenios Papademetris http://noodle.med.yale.edu/~papad/various/papademetris_image_registration.p
CS664 Lecture #16: Image registration, robust statistics, motion Some material taken from: Alyosha Efros, CMU http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~efros Xenios Papademetris http://noodle.med.yale.edu/~papad/various/papademetris_image_registration.p
Drawing in 3D (viewing, projection, and the rest of the pipeline)
 Drawing in 3D (viewing, projection, and the rest of the pipeline) CS559 Fall 2016 Lecture 6/7 September 26-28 2016 The first 4 Key Ideas 1. Work in convenient coordinate systems. Use transformations to
Drawing in 3D (viewing, projection, and the rest of the pipeline) CS559 Fall 2016 Lecture 6/7 September 26-28 2016 The first 4 Key Ideas 1. Work in convenient coordinate systems. Use transformations to
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems
 EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 10 130221 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Canny Edge Detector Hough Transform Feature-Based
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 10 130221 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Canny Edge Detector Hough Transform Feature-Based
Uncertainties: Representation and Propagation & Line Extraction from Range data
 41 Uncertainties: Representation and Propagation & Line Extraction from Range data 42 Uncertainty Representation Section 4.1.3 of the book Sensing in the real world is always uncertain How can uncertainty
41 Uncertainties: Representation and Propagation & Line Extraction from Range data 42 Uncertainty Representation Section 4.1.3 of the book Sensing in the real world is always uncertain How can uncertainty
Instance-level recognition II.
 Reconnaissance d objets et vision artificielle 2010 Instance-level recognition II. Josef Sivic http://www.di.ens.fr/~josef INRIA, WILLOW, ENS/INRIA/CNRS UMR 8548 Laboratoire d Informatique, Ecole Normale
Reconnaissance d objets et vision artificielle 2010 Instance-level recognition II. Josef Sivic http://www.di.ens.fr/~josef INRIA, WILLOW, ENS/INRIA/CNRS UMR 8548 Laboratoire d Informatique, Ecole Normale
3D Reconstruction from Two Views
 3D Reconstruction from Two Views Huy Bui UIUC huybui1@illinois.edu Yiyi Huang UIUC huang85@illinois.edu Abstract In this project, we study a method to reconstruct a 3D scene from two views. First, we extract
3D Reconstruction from Two Views Huy Bui UIUC huybui1@illinois.edu Yiyi Huang UIUC huang85@illinois.edu Abstract In this project, we study a method to reconstruct a 3D scene from two views. First, we extract
UNIK 4690 Maskinsyn Introduction
 UNIK 4690 Maskinsyn Introduction 18.01.2018 Trym Vegard Haavardsholm (trym.haavardsholm@its.uio.no) Idar Dyrdal (idar.dyrdal@its.uio.no) Thomas Opsahl (thomasoo@its.uio.no) Ragnar Smestad (ragnar.smestad@ffi.no)
UNIK 4690 Maskinsyn Introduction 18.01.2018 Trym Vegard Haavardsholm (trym.haavardsholm@its.uio.no) Idar Dyrdal (idar.dyrdal@its.uio.no) Thomas Opsahl (thomasoo@its.uio.no) Ragnar Smestad (ragnar.smestad@ffi.no)
Computer Vision CSCI-GA Assignment 1.
 Computer Vision CSCI-GA.2272-001 Assignment 1. September 22, 2017 Introduction This assignment explores various methods for aligning images and feature extraction. There are four parts to the assignment:
Computer Vision CSCI-GA.2272-001 Assignment 1. September 22, 2017 Introduction This assignment explores various methods for aligning images and feature extraction. There are four parts to the assignment:
Miniature faking. In close-up photo, the depth of field is limited.
 Miniature faking In close-up photo, the depth of field is limited. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:jodhpur_tilt_shift.jpg Miniature faking Miniature faking http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:oregon_state_beavers_tilt-shift_miniature_greg_keene.jpg
Miniature faking In close-up photo, the depth of field is limited. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:jodhpur_tilt_shift.jpg Miniature faking Miniature faking http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/file:oregon_state_beavers_tilt-shift_miniature_greg_keene.jpg
Lecture 3.3 Robust estimation with RANSAC. Thomas Opsahl
 Lecture 3.3 Robust estimation with RANSAC Thomas Opsahl Motivation If two perspective cameras captures an image of a planar scene, their images are related by a homography HH 2 Motivation If two perspective
Lecture 3.3 Robust estimation with RANSAC Thomas Opsahl Motivation If two perspective cameras captures an image of a planar scene, their images are related by a homography HH 2 Motivation If two perspective
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems
 EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 12 130228 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Panoramas, Mosaics, Stitching Two View Geometry
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 FDH 204 Lecture 12 130228 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Panoramas, Mosaics, Stitching Two View Geometry
C280, Computer Vision
 C280, Computer Vision Prof. Trevor Darrell trevor@eecs.berkeley.edu Lecture 11: Structure from Motion Roadmap Previous: Image formation, filtering, local features, (Texture) Tues: Feature-based Alignment
C280, Computer Vision Prof. Trevor Darrell trevor@eecs.berkeley.edu Lecture 11: Structure from Motion Roadmap Previous: Image formation, filtering, local features, (Texture) Tues: Feature-based Alignment
CIS 580, Machine Perception, Spring 2015 Homework 1 Due: :59AM
 CIS 580, Machine Perception, Spring 2015 Homework 1 Due: 2015.02.09. 11:59AM Instructions. Submit your answers in PDF form to Canvas. This is an individual assignment. 1 Camera Model, Focal Length and
CIS 580, Machine Perception, Spring 2015 Homework 1 Due: 2015.02.09. 11:59AM Instructions. Submit your answers in PDF form to Canvas. This is an individual assignment. 1 Camera Model, Focal Length and
Today s lecture. Image Alignment and Stitching. Readings. Motion models
 Today s lecture Image Alignment and Stitching Computer Vision CSE576, Spring 2005 Richard Szeliski Image alignment and stitching motion models cylindrical and spherical warping point-based alignment global
Today s lecture Image Alignment and Stitching Computer Vision CSE576, Spring 2005 Richard Szeliski Image alignment and stitching motion models cylindrical and spherical warping point-based alignment global
Fitting (LMedS, RANSAC)
 Fitting (LMedS, RANSAC) Thursday, 23/03/2017 Antonis Argyros e-mail: argyros@csd.uoc.gr LMedS and RANSAC What if we have very many outliers? 2 1 Least Median of Squares ri : Residuals Least Squares n 2
Fitting (LMedS, RANSAC) Thursday, 23/03/2017 Antonis Argyros e-mail: argyros@csd.uoc.gr LMedS and RANSAC What if we have very many outliers? 2 1 Least Median of Squares ri : Residuals Least Squares n 2
Epipolar Geometry Based On Line Similarity
 2016 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR) Cancún Center, Cancún, México, December 4-8, 2016 Epipolar Geometry Based On Line Similarity Gil Ben-Artzi Tavi Halperin Michael Werman
2016 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR) Cancún Center, Cancún, México, December 4-8, 2016 Epipolar Geometry Based On Line Similarity Gil Ben-Artzi Tavi Halperin Michael Werman
Instance-level recognition
 Instance-level recognition 1) Local invariant features 2) Matching and recognition with local features 3) Efficient visual search 4) Very large scale indexing Matching of descriptors Matching and 3D reconstruction
Instance-level recognition 1) Local invariant features 2) Matching and recognition with local features 3) Efficient visual search 4) Very large scale indexing Matching of descriptors Matching and 3D reconstruction
Introduction to Computer Vision
 Introduction to Computer Vision Michael J. Black Nov 2009 Perspective projection and affine motion Goals Today Perspective projection 3D motion Wed Projects Friday Regularization and robust statistics
Introduction to Computer Vision Michael J. Black Nov 2009 Perspective projection and affine motion Goals Today Perspective projection 3D motion Wed Projects Friday Regularization and robust statistics
Computational Optical Imaging - Optique Numerique. -- Multiple View Geometry and Stereo --
 Computational Optical Imaging - Optique Numerique -- Multiple View Geometry and Stereo -- Winter 2013 Ivo Ihrke with slides by Thorsten Thormaehlen Feature Detection and Matching Wide-Baseline-Matching
Computational Optical Imaging - Optique Numerique -- Multiple View Geometry and Stereo -- Winter 2013 Ivo Ihrke with slides by Thorsten Thormaehlen Feature Detection and Matching Wide-Baseline-Matching
3D Reconstruction of a Hopkins Landmark
 3D Reconstruction of a Hopkins Landmark Ayushi Sinha (461), Hau Sze (461), Diane Duros (361) Abstract - This paper outlines a method for 3D reconstruction from two images. Our procedure is based on known
3D Reconstruction of a Hopkins Landmark Ayushi Sinha (461), Hau Sze (461), Diane Duros (361) Abstract - This paper outlines a method for 3D reconstruction from two images. Our procedure is based on known
arxiv: v4 [cs.cv] 8 Jan 2017
![arxiv: v4 [cs.cv] 8 Jan 2017 arxiv: v4 [cs.cv] 8 Jan 2017](/thumbs/89/97563198.jpg) Epipolar Geometry Based On Line Similarity Gil Ben-Artzi Tavi Halperin Michael Werman Shmuel Peleg School of Computer Science and Engineering The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel arxiv:1604.04848v4
Epipolar Geometry Based On Line Similarity Gil Ben-Artzi Tavi Halperin Michael Werman Shmuel Peleg School of Computer Science and Engineering The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel arxiv:1604.04848v4
Detecting and recognizing centerlines as parabolic sections of the steerable filter response
 Detecting and recognizing centerlines as parabolic sections of the steerable filter response Petar Palašek, Petra Bosilj, Siniša Šegvić Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computing Unska 3, 10000 Zagreb
Detecting and recognizing centerlines as parabolic sections of the steerable filter response Petar Palašek, Petra Bosilj, Siniša Šegvić Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computing Unska 3, 10000 Zagreb
AUTOMATIC RECTIFICATION OF LONG IMAGE SEQUENCES. Kenji Okuma, James J. Little, David G. Lowe
 AUTOMATIC RECTIFICATION OF LONG IMAGE SEQUENCES Kenji Okuma, James J. Little, David G. Lowe The Laboratory of Computational Intelligence The University of British Columbia Vancouver, British Columbia,
AUTOMATIC RECTIFICATION OF LONG IMAGE SEQUENCES Kenji Okuma, James J. Little, David G. Lowe The Laboratory of Computational Intelligence The University of British Columbia Vancouver, British Columbia,
Model Fitting, RANSAC. Jana Kosecka
 Model Fitting, RANSAC Jana Kosecka Fitting: Overview If we know which points belong to the line, how do we find the optimal line parameters? Least squares What if there are outliers? Robust fitting, RANSAC
Model Fitting, RANSAC Jana Kosecka Fitting: Overview If we know which points belong to the line, how do we find the optimal line parameters? Least squares What if there are outliers? Robust fitting, RANSAC
Announcements. Recognition (Part 3) Model-Based Vision. A Rough Recognition Spectrum. Pose consistency. Recognition by Hypothesize and Test
 Announcements (Part 3) CSE 152 Lecture 16 Homework 3 is due today, 11:59 PM Homework 4 will be assigned today Due Sat, Jun 4, 11:59 PM Reading: Chapter 15: Learning to Classify Chapter 16: Classifying
Announcements (Part 3) CSE 152 Lecture 16 Homework 3 is due today, 11:59 PM Homework 4 will be assigned today Due Sat, Jun 4, 11:59 PM Reading: Chapter 15: Learning to Classify Chapter 16: Classifying
A Summary of Projective Geometry
 A Summary of Projective Geometry Copyright 22 Acuity Technologies Inc. In the last years a unified approach to creating D models from multiple images has been developed by Beardsley[],Hartley[4,5,9],Torr[,6]
A Summary of Projective Geometry Copyright 22 Acuity Technologies Inc. In the last years a unified approach to creating D models from multiple images has been developed by Beardsley[],Hartley[4,5,9],Torr[,6]
Computational Optical Imaging - Optique Numerique. -- Single and Multiple View Geometry, Stereo matching --
 Computational Optical Imaging - Optique Numerique -- Single and Multiple View Geometry, Stereo matching -- Autumn 2015 Ivo Ihrke with slides by Thorsten Thormaehlen Reminder: Feature Detection and Matching
Computational Optical Imaging - Optique Numerique -- Single and Multiple View Geometry, Stereo matching -- Autumn 2015 Ivo Ihrke with slides by Thorsten Thormaehlen Reminder: Feature Detection and Matching
Structure from Motion. Lecture-15
 Structure from Motion Lecture-15 Shape From X Recovery of 3D (shape) from one or two (2D images). Shape From X Stereo Motion Shading Photometric Stereo Texture Contours Silhouettes Defocus Applications
Structure from Motion Lecture-15 Shape From X Recovery of 3D (shape) from one or two (2D images). Shape From X Stereo Motion Shading Photometric Stereo Texture Contours Silhouettes Defocus Applications
Lecture 9: Epipolar Geometry
 Lecture 9: Epipolar Geometry Professor Fei Fei Li Stanford Vision Lab 1 What we will learn today? Why is stereo useful? Epipolar constraints Essential and fundamental matrix Estimating F (Problem Set 2
Lecture 9: Epipolar Geometry Professor Fei Fei Li Stanford Vision Lab 1 What we will learn today? Why is stereo useful? Epipolar constraints Essential and fundamental matrix Estimating F (Problem Set 2
Feature-based methods for image matching
 Feature-based methods for image matching Bag of Visual Words approach Feature descriptors SIFT descriptor SURF descriptor Geometric consistency check Vocabulary tree Digital Image Processing: Bernd Girod,
Feature-based methods for image matching Bag of Visual Words approach Feature descriptors SIFT descriptor SURF descriptor Geometric consistency check Vocabulary tree Digital Image Processing: Bernd Girod,
Multiple View Geometry in computer vision
 Multiple View Geometry in computer vision Chapter 8: More Single View Geometry Olaf Booij Intelligent Systems Lab Amsterdam University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands HZClub 29-02-2008 Overview clubje Part
Multiple View Geometry in computer vision Chapter 8: More Single View Geometry Olaf Booij Intelligent Systems Lab Amsterdam University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands HZClub 29-02-2008 Overview clubje Part
Last lecture. Passive Stereo Spacetime Stereo
 Last lecture Passive Stereo Spacetime Stereo Today Structure from Motion: Given pixel correspondences, how to compute 3D structure and camera motion? Slides stolen from Prof Yungyu Chuang Epipolar geometry
Last lecture Passive Stereo Spacetime Stereo Today Structure from Motion: Given pixel correspondences, how to compute 3D structure and camera motion? Slides stolen from Prof Yungyu Chuang Epipolar geometry
Image Warping and Mosacing
 Image Warping and Mosacing 15-463: Rendering and Image Processing Alexei Efros with a lot of slides stolen from Steve Seitz and Rick Szeliski Today Mosacs Image Warping Homographies Programming Assignment
Image Warping and Mosacing 15-463: Rendering and Image Processing Alexei Efros with a lot of slides stolen from Steve Seitz and Rick Szeliski Today Mosacs Image Warping Homographies Programming Assignment
Midterm Examination CS 534: Computational Photography
 Midterm Examination CS 534: Computational Photography November 3, 2016 NAME: Problem Score Max Score 1 6 2 8 3 9 4 12 5 4 6 13 7 7 8 6 9 9 10 6 11 14 12 6 Total 100 1 of 8 1. [6] (a) [3] What camera setting(s)
Midterm Examination CS 534: Computational Photography November 3, 2016 NAME: Problem Score Max Score 1 6 2 8 3 9 4 12 5 4 6 13 7 7 8 6 9 9 10 6 11 14 12 6 Total 100 1 of 8 1. [6] (a) [3] What camera setting(s)
Lecture 9 & 10: Stereo Vision
 Lecture 9 & 10: Stereo Vision Professor Fei- Fei Li Stanford Vision Lab 1 What we will learn today? IntroducEon to stereo vision Epipolar geometry: a gentle intro Parallel images Image receficaeon Solving
Lecture 9 & 10: Stereo Vision Professor Fei- Fei Li Stanford Vision Lab 1 What we will learn today? IntroducEon to stereo vision Epipolar geometry: a gentle intro Parallel images Image receficaeon Solving
Planar homographies. Can we reconstruct another view from one image? vgg/projects/singleview/
 Planar homographies Goal: Introducing 2D Homographies Motivation: What is the relation between a plane in the world and a perspective image of it? Can we reconstruct another view from one image? Readings:
Planar homographies Goal: Introducing 2D Homographies Motivation: What is the relation between a plane in the world and a perspective image of it? Can we reconstruct another view from one image? Readings:
Lecture 6 Stereo Systems Multi-view geometry
 Lecture 6 Stereo Systems Multi-view geometry Professor Silvio Savarese Computational Vision and Geometry Lab Silvio Savarese Lecture 6-5-Feb-4 Lecture 6 Stereo Systems Multi-view geometry Stereo systems
Lecture 6 Stereo Systems Multi-view geometry Professor Silvio Savarese Computational Vision and Geometry Lab Silvio Savarese Lecture 6-5-Feb-4 Lecture 6 Stereo Systems Multi-view geometry Stereo systems
The University of Missouri - Columbia Electrical & Computer Engineering Department EE4330 Robotic Control and Intelligence
 The University of Missouri - Columbia Final Exam 1) Clear your desk top of all handwritten papers and personal notes. You may keep only your textbook, a cheat sheet, the test paper, a calculator and a
The University of Missouri - Columbia Final Exam 1) Clear your desk top of all handwritten papers and personal notes. You may keep only your textbook, a cheat sheet, the test paper, a calculator and a
Automatic Image Alignment (direct) with a lot of slides stolen from Steve Seitz and Rick Szeliski
 Automatic Image Alignment (direct) with a lot of slides stolen from Steve Seitz and Rick Szeliski 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2005 Today Go over Midterm Go over Project #3
Automatic Image Alignment (direct) with a lot of slides stolen from Steve Seitz and Rick Szeliski 15-463: Computational Photography Alexei Efros, CMU, Fall 2005 Today Go over Midterm Go over Project #3
