THE DEPTH-BUFFER VISIBLE SURFACE ALGORITHM
|
|
|
- Eleanore Clark
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 On-Line Computer Graphics Notes THE DEPTH-BUFFER VISIBLE SURFACE ALGORITHM Kenneth I. Joy Visualization and Graphics Research Group Department of Computer Science University of California, Davis To accurately represent a complex model, it is imperative that those surfaces normally invisible from a certain point, be also invisible in the computer generated image. This problem normally called the visiblesurface problem (determining the surfaces that are visible), or the hidden-surface problem (determining those that are invisible), and has been the fundamental research problem in computer graphics over the past 20 years. The effects of this algorithm are easily seen, even in relatively simple pictures. If we consider the following illustration, we can obtain much more information about the relative positions of the objects by using the right hand figure, rather than using the left hand one. Of all algorithms for visible surface determination, the depth-buffer is perhaps the simplest, and is the most widely used. For each pixel on the display, we keep a record of the depth of the object in the scene that is closest to the viewer, plus a record of the intensity that should be displayed to show the object. When a new polygon is to be processed, a z-value and intensity value are calculated for each pixel that lies within the boundary of the polygon. If the z-value at a pixel indicates that the polygon is closer to the viewer than the z-value in the z-buffer, the z-value and the intensity values recorded in the buffers are replaced by the polygon s values. After processing all polygons, the resulting intensity buffer can be displayed
2 The z-buffer algorithm works in device space and it can be easily implemented as a modification of the scan-conversion algorithms that have been discussed in previous sections. The z-buffer, from which this algorithm derives its name, is an n n array for which the (i, j)th element corresponds to the (i, j)th pixel. This array holds the image-space z value of the currently visible object at the pixel. There is also another n n array whose elements correspond to the color that is to be assigned to the pixel. We illustrate the operation of the z-buffer algorithm by considering a two-dimensional example, with an eight-pixel-wide screen and polygons represented as lines. The steps to perform the algorithm are nearly identical in three dimensions. Initially, since we have rendered no polygons yet, we set all elements of the z-buffer array to (actually, some suitably large negative number). We also initialize the color array to black (or suitable a background color). Taking each polygon, scan convert the polygon and, within the scan-conversion algorithm, perform the following steps 2
3 For each pixel that intersects the polygon, if the image-space z value associated with this pixel is greater than the corresponding value in the z buffer, then calculate the color associated with the pixel, insert this color into the corresponding entry in the color array, and insert the pixel s z value into the corresponding element in the z buffer. If the z value associated with this pixel is not greater than the corresponding value in the z buffer, then no action is taken. As an example, inserting one line into our two-dimensional z-buffer, we log the depth value at the center of each pixel, and obtain! "!# $ % & ' Inserting a second line in the same way, we note that the z-buffer has been accruately updated to indicate the line that is visible at each pixel 3
4 "! #"$ We can give a simple pseudocode implementation of the z-buffer algorithm as follows: Z-Buffer Algorithm Given List of polygons {P 1, P 2,..., P n An array z-buffer[x,y] initialized to An array Intensity[x,y] begin for each polygon P in the polygon list do { for each pixel (x,y) that intersects P do { calculate z-depth of P at (x,y) if z-depth < z-buffer[x,y] then { Intensity[x,y] = intensity of P at (x,y) z-buffer[x,y] = z-depth Display Intensity array 4
5 end Since any polygon can be divided into a set of trapezoids, it is sufficient to consider the z-buffer algorithm on trapezoids. We can directly modify the rasterization algorithm given in the rasterization notes to create the z-buffer algorithm above. We utilize the same update and initialize procedures as in the rasterization algorithm. All contents copyright (c) 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999 Computer Science Department, University of California, Davis All rights reserved. 5
RASTERIZING POLYGONS IN IMAGE SPACE
 On-Line Computer Graphics Notes RASTERIZING POLYGONS IN IMAGE SPACE Kenneth I. Joy Visualization and Graphics Research Group Department of Computer Science University of California, Davis A fundamental
On-Line Computer Graphics Notes RASTERIZING POLYGONS IN IMAGE SPACE Kenneth I. Joy Visualization and Graphics Research Group Department of Computer Science University of California, Davis A fundamental
8. Hidden Surface Elimination
 8. Hidden Surface Elimination Identification and Removal of parts of picture that are not visible from a chosen viewing position. 1 8. Hidden Surface Elimination Basic idea: Overwriting Paint things in
8. Hidden Surface Elimination Identification and Removal of parts of picture that are not visible from a chosen viewing position. 1 8. Hidden Surface Elimination Basic idea: Overwriting Paint things in
Rendering. Converting a 3D scene to a 2D image. Camera. Light. Rendering. View Plane
 Rendering Pipeline Rendering Converting a 3D scene to a 2D image Rendering Light Camera 3D Model View Plane Rendering Converting a 3D scene to a 2D image Basic rendering tasks: Modeling: creating the world
Rendering Pipeline Rendering Converting a 3D scene to a 2D image Rendering Light Camera 3D Model View Plane Rendering Converting a 3D scene to a 2D image Basic rendering tasks: Modeling: creating the world
9. Visible-Surface Detection Methods
 9. Visible-Surface Detection Methods More information about Modelling and Perspective Viewing: Before going to visible surface detection, we first review and discuss the followings: 1. Modelling Transformation:
9. Visible-Surface Detection Methods More information about Modelling and Perspective Viewing: Before going to visible surface detection, we first review and discuss the followings: 1. Modelling Transformation:
Hidden Surface Removal
 Outline Introduction Hidden Surface Removal Hidden Surface Removal Simone Gasparini gasparini@elet.polimi.it Back face culling Depth sort Z-buffer Introduction Graphics pipeline Introduction Modeling Geom
Outline Introduction Hidden Surface Removal Hidden Surface Removal Simone Gasparini gasparini@elet.polimi.it Back face culling Depth sort Z-buffer Introduction Graphics pipeline Introduction Modeling Geom
Page 1. Area-Subdivision Algorithms z-buffer Algorithm List Priority Algorithms BSP (Binary Space Partitioning Tree) Scan-line Algorithms
 Visible Surface Determination Visibility Culling Area-Subdivision Algorithms z-buffer Algorithm List Priority Algorithms BSP (Binary Space Partitioning Tree) Scan-line Algorithms Divide-and-conquer strategy:
Visible Surface Determination Visibility Culling Area-Subdivision Algorithms z-buffer Algorithm List Priority Algorithms BSP (Binary Space Partitioning Tree) Scan-line Algorithms Divide-and-conquer strategy:
Pipeline Operations. CS 4620 Lecture 10
 Pipeline Operations CS 4620 Lecture 10 2008 Steve Marschner 1 Hidden surface elimination Goal is to figure out which color to make the pixels based on what s in front of what. Hidden surface elimination
Pipeline Operations CS 4620 Lecture 10 2008 Steve Marschner 1 Hidden surface elimination Goal is to figure out which color to make the pixels based on what s in front of what. Hidden surface elimination
Computer Graphics. Lecture 9 Hidden Surface Removal. Taku Komura
 Computer Graphics Lecture 9 Hidden Surface Removal Taku Komura 1 Why Hidden Surface Removal? A correct rendering requires correct visibility calculations When multiple opaque polygons cover the same screen
Computer Graphics Lecture 9 Hidden Surface Removal Taku Komura 1 Why Hidden Surface Removal? A correct rendering requires correct visibility calculations When multiple opaque polygons cover the same screen
Hidden surface removal. Computer Graphics
 Lecture Hidden Surface Removal and Rasterization Taku Komura Hidden surface removal Drawing polygonal faces on screen consumes CPU cycles Illumination We cannot see every surface in scene We don t want
Lecture Hidden Surface Removal and Rasterization Taku Komura Hidden surface removal Drawing polygonal faces on screen consumes CPU cycles Illumination We cannot see every surface in scene We don t want
Graphics and Games. Penny Rheingans University of Maryland Baltimore County
 Graphics and Games IS 101Y/CMSC 104Y First Year IT Penny Rheingans University of Maryland Baltimore County Announcements Quizzes Project Questions Other questions Questions about Reading Asst Games with
Graphics and Games IS 101Y/CMSC 104Y First Year IT Penny Rheingans University of Maryland Baltimore County Announcements Quizzes Project Questions Other questions Questions about Reading Asst Games with
Visible-Surface Detection Methods. Chapter? Intro. to Computer Graphics Spring 2008, Y. G. Shin
 Visible-Surface Detection Methods Chapter? Intro. to Computer Graphics Spring 2008, Y. G. Shin The Visibility Problem [Problem Statement] GIVEN: a set of 3-D surfaces, a projection from 3-D to 2-D screen,
Visible-Surface Detection Methods Chapter? Intro. to Computer Graphics Spring 2008, Y. G. Shin The Visibility Problem [Problem Statement] GIVEN: a set of 3-D surfaces, a projection from 3-D to 2-D screen,
Two basic types: image-precision and object-precision. Image-precision For each pixel, determine which object is visable Requires np operations
 walters@buffalo.edu CSE 480/580 Lecture 21 Slide 1 Visible-Surface Determination (Hidden Surface Removal) Computationaly expensive Two basic types: image-precision and object-precision For n objects and
walters@buffalo.edu CSE 480/580 Lecture 21 Slide 1 Visible-Surface Determination (Hidden Surface Removal) Computationaly expensive Two basic types: image-precision and object-precision For n objects and
Shadows. COMP 575/770 Spring 2013
 Shadows COMP 575/770 Spring 2013 Shadows in Ray Tracing Shadows are important for realism Basic idea: figure out whether a point on an object is illuminated by a light source Easy for ray tracers Just
Shadows COMP 575/770 Spring 2013 Shadows in Ray Tracing Shadows are important for realism Basic idea: figure out whether a point on an object is illuminated by a light source Easy for ray tracers Just
THE CAMERA TRANSFORM
 On-Line Computer Graphics Notes THE CAMERA TRANSFORM Kenneth I. Joy Visualization and Graphics Research Group Department of Computer Science University of California, Davis Overview To understanding the
On-Line Computer Graphics Notes THE CAMERA TRANSFORM Kenneth I. Joy Visualization and Graphics Research Group Department of Computer Science University of California, Davis Overview To understanding the
Computer Graphics. Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University The University of Tokyo
 Computer Graphics Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University The University of Tokyo Hidden-Surface Removal Back-Face Culling The Depth-Sort Algorithm Binary Space-Partitioning Trees The z-buffer Algorithm
Computer Graphics Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University The University of Tokyo Hidden-Surface Removal Back-Face Culling The Depth-Sort Algorithm Binary Space-Partitioning Trees The z-buffer Algorithm
Rasterization Overview
 Rendering Overview The process of generating an image given a virtual camera objects light sources Various techniques rasterization (topic of this course) raytracing (topic of the course Advanced Computer
Rendering Overview The process of generating an image given a virtual camera objects light sources Various techniques rasterization (topic of this course) raytracing (topic of the course Advanced Computer
8. Hidden Surface Elimination
 -04-8 Hidden Surface Elimination To eliminate edges and surfaces not visible to the viewer Two categories: Object space methods: Image space methods: deal with object definitions directly Order the surfaces
-04-8 Hidden Surface Elimination To eliminate edges and surfaces not visible to the viewer Two categories: Object space methods: Image space methods: deal with object definitions directly Order the surfaces
4.5 VISIBLE SURFACE DETECTION METHODES
 4.5 VISIBLE SURFACE DETECTION METHODES A major consideration in the generation of realistic graphics displays is identifying those parts of a scene that are visible from a chosen viewing position. There
4.5 VISIBLE SURFACE DETECTION METHODES A major consideration in the generation of realistic graphics displays is identifying those parts of a scene that are visible from a chosen viewing position. There
Werner Purgathofer
 Einführung in Visual Computing 186.822 Visible Surface Detection Werner Purgathofer Visibility in the Rendering Pipeline scene objects in object space object capture/creation ti modeling viewing projection
Einführung in Visual Computing 186.822 Visible Surface Detection Werner Purgathofer Visibility in the Rendering Pipeline scene objects in object space object capture/creation ti modeling viewing projection
Hidden-Surface Removal.
 Hidden-Surface emoval. Here we need to discover whether an object is visible or another one obscures it. here are two fundamental approaches to remove the hidden surfaces: ) he object-space approach )
Hidden-Surface emoval. Here we need to discover whether an object is visible or another one obscures it. here are two fundamental approaches to remove the hidden surfaces: ) he object-space approach )
Visible Surface Detection. (Chapt. 15 in FVD, Chapt. 13 in Hearn & Baker)
 Visible Surface Detection (Chapt. 15 in FVD, Chapt. 13 in Hearn & Baker) 1 Given a set of 3D objects and a viewing specifications, determine which lines or surfaces of the objects should be visible. A
Visible Surface Detection (Chapt. 15 in FVD, Chapt. 13 in Hearn & Baker) 1 Given a set of 3D objects and a viewing specifications, determine which lines or surfaces of the objects should be visible. A
3D graphics, raster and colors CS312 Fall 2010
 Computer Graphics 3D graphics, raster and colors CS312 Fall 2010 Shift in CG Application Markets 1989-2000 2000 1989 3D Graphics Object description 3D graphics model Visualization 2D projection that simulates
Computer Graphics 3D graphics, raster and colors CS312 Fall 2010 Shift in CG Application Markets 1989-2000 2000 1989 3D Graphics Object description 3D graphics model Visualization 2D projection that simulates
Visible Surface Detection Methods
 Visible urface Detection Methods Visible-urface Detection identifying visible parts of a scene (also hidden- elimination) type of algorithm depends on: complexity of scene type of objects available equipment
Visible urface Detection Methods Visible-urface Detection identifying visible parts of a scene (also hidden- elimination) type of algorithm depends on: complexity of scene type of objects available equipment
CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Fall 2007
 Visible Surface Detection CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Fall 2007 Visible Surface Detection Visible surface detection or hidden surface removal. Realistic scenes: closer objects occludes the
Visible Surface Detection CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Fall 2007 Visible Surface Detection Visible surface detection or hidden surface removal. Realistic scenes: closer objects occludes the
Surface Graphics. 200 polys 1,000 polys 15,000 polys. an empty foot. - a mesh of spline patches:
 Surface Graphics Objects are explicitely defined by a surface or boundary representation (explicit inside vs outside) This boundary representation can be given by: - a mesh of polygons: 200 polys 1,000
Surface Graphics Objects are explicitely defined by a surface or boundary representation (explicit inside vs outside) This boundary representation can be given by: - a mesh of polygons: 200 polys 1,000
Computer Graphics. Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University
 Computer Graphics Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Visible-Surface Determination Back-Face Culling The Depth-Sort Algorithm Binary Space-Partitioning Trees The z-buffer Algorithm Scan-Line Algorithm
Computer Graphics Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Visible-Surface Determination Back-Face Culling The Depth-Sort Algorithm Binary Space-Partitioning Trees The z-buffer Algorithm Scan-Line Algorithm
CSE 690: GPGPU. Lecture 2: Understanding the Fabric - Intro to Graphics. Klaus Mueller Stony Brook University Computer Science Department
 CSE 690: GPGPU Lecture 2: Understanding the Fabric - Intro to Graphics Klaus Mueller Stony Brook University Computer Science Department Klaus Mueller, Stony Brook 2005 1 Surface Graphics Objects are explicitely
CSE 690: GPGPU Lecture 2: Understanding the Fabric - Intro to Graphics Klaus Mueller Stony Brook University Computer Science Department Klaus Mueller, Stony Brook 2005 1 Surface Graphics Objects are explicitely
Drawing the Visible Objects
 Drawing the Visible Objects We want to generate the image that the eye would see, given the objects in our space How do we draw the correct object at each pixel, given that some objects may obscure others
Drawing the Visible Objects We want to generate the image that the eye would see, given the objects in our space How do we draw the correct object at each pixel, given that some objects may obscure others
From Vertices To Fragments-1
 From Vertices To Fragments-1 1 Objectives Clipping Line-segment clipping polygon clipping 2 Overview At end of the geometric pipeline, vertices have been assembled into primitives Must clip out primitives
From Vertices To Fragments-1 1 Objectives Clipping Line-segment clipping polygon clipping 2 Overview At end of the geometric pipeline, vertices have been assembled into primitives Must clip out primitives
COMP371 COMPUTER GRAPHICS
 COMP371 COMPUTER GRAPHICS LECTURE 14 RASTERIZATION 1 Lecture Overview Review of last class Line Scan conversion Polygon Scan conversion Antialiasing 2 Rasterization The raster display is a matrix of picture
COMP371 COMPUTER GRAPHICS LECTURE 14 RASTERIZATION 1 Lecture Overview Review of last class Line Scan conversion Polygon Scan conversion Antialiasing 2 Rasterization The raster display is a matrix of picture
COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Scan Converting Polygons and Lines
 COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Scan Converting Polygons and Lines Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction Scan conversion Scan-line algorithm Edge coherence
COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Scan Converting Polygons and Lines Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction Scan conversion Scan-line algorithm Edge coherence
Identifying those parts of a scene that are visible from a chosen viewing position, and only process (scan convert) those parts
 Visible Surface Detection Identifying those parts of a scene that are visible from a chosen viewing position, and only process (scan convert) those parts Two approaches: 1. Object space methods 2. Image
Visible Surface Detection Identifying those parts of a scene that are visible from a chosen viewing position, and only process (scan convert) those parts Two approaches: 1. Object space methods 2. Image
Computer Graphics. Chapter 1 (Related to Introduction to Computer Graphics Using Java 2D and 3D)
 Computer Graphics Chapter 1 (Related to Introduction to Computer Graphics Using Java 2D and 3D) Introduction Applications of Computer Graphics: 1) Display of Information 2) Design 3) Simulation 4) User
Computer Graphics Chapter 1 (Related to Introduction to Computer Graphics Using Java 2D and 3D) Introduction Applications of Computer Graphics: 1) Display of Information 2) Design 3) Simulation 4) User
Renderer Implementation: Basics and Clipping. Overview. Preliminaries. David Carr Virtual Environments, Fundamentals Spring 2005
 INSTITUTIONEN FÖR SYSTEMTEKNIK LULEÅ TEKNISKA UNIVERSITET Renderer Implementation: Basics and Clipping David Carr Virtual Environments, Fundamentals Spring 2005 Feb-28-05 SMM009, Basics and Clipping 1
INSTITUTIONEN FÖR SYSTEMTEKNIK LULEÅ TEKNISKA UNIVERSITET Renderer Implementation: Basics and Clipping David Carr Virtual Environments, Fundamentals Spring 2005 Feb-28-05 SMM009, Basics and Clipping 1
Hermite Curves. Hermite curves. Interpolation versus approximation Hermite curve interpolates the control points Piecewise cubic polynomials
 Hermite Curves Hermite curves Interpolation versus approximation Hermite curve interpolates the control points Piecewise cubic polynomials Focus on one segment T1 P0 Q(t) T0 Control points of Bezier curve
Hermite Curves Hermite curves Interpolation versus approximation Hermite curve interpolates the control points Piecewise cubic polynomials Focus on one segment T1 P0 Q(t) T0 Control points of Bezier curve
CS 498 VR. Lecture 18-4/4/18. go.illinois.edu/vrlect18
 CS 498 VR Lecture 18-4/4/18 go.illinois.edu/vrlect18 Review and Supplement for last lecture 1. What is aliasing? What is Screen Door Effect? 2. How image-order rendering works? 3. If there are several
CS 498 VR Lecture 18-4/4/18 go.illinois.edu/vrlect18 Review and Supplement for last lecture 1. What is aliasing? What is Screen Door Effect? 2. How image-order rendering works? 3. If there are several
On-Line Computer Graphics Notes CLIPPING
 On-Line Computer Graphics Notes CLIPPING Kenneth I. Joy Visualization and Graphics Research Group Department of Computer Science University of California, Davis 1 Overview The primary use of clipping in
On-Line Computer Graphics Notes CLIPPING Kenneth I. Joy Visualization and Graphics Research Group Department of Computer Science University of California, Davis 1 Overview The primary use of clipping in
9. Illumination and Shading
 9. Illumination and Shading Approaches for visual realism: - Remove hidden surfaces - Shade visible surfaces and reproduce shadows - Reproduce surface properties Texture Degree of transparency Roughness,
9. Illumination and Shading Approaches for visual realism: - Remove hidden surfaces - Shade visible surfaces and reproduce shadows - Reproduce surface properties Texture Degree of transparency Roughness,
Graphics for VEs. Ruth Aylett
 Graphics for VEs Ruth Aylett Overview VE Software Graphics for VEs The graphics pipeline Projections Lighting Shading Runtime VR systems Two major parts: initialisation and update loop. Initialisation
Graphics for VEs Ruth Aylett Overview VE Software Graphics for VEs The graphics pipeline Projections Lighting Shading Runtime VR systems Two major parts: initialisation and update loop. Initialisation
CS Computer Graphics: Hidden Surface Removal
 CS 543 - Computer Graphics: Hidden Surface Removal by Robert W. Lindeman gogo@wpi.edu (with help from Emmanuel Agu ;-) Hidden Surface Removal Drawing polygonal faces on screen consumes CPU cycles We cannot
CS 543 - Computer Graphics: Hidden Surface Removal by Robert W. Lindeman gogo@wpi.edu (with help from Emmanuel Agu ;-) Hidden Surface Removal Drawing polygonal faces on screen consumes CPU cycles We cannot
Overview. Pipeline implementation I. Overview. Required Tasks. Preliminaries Clipping. Hidden Surface removal
 Overview Pipeline implementation I Preliminaries Clipping Line clipping Hidden Surface removal Overview At end of the geometric pipeline, vertices have been assembled into primitives Must clip out primitives
Overview Pipeline implementation I Preliminaries Clipping Line clipping Hidden Surface removal Overview At end of the geometric pipeline, vertices have been assembled into primitives Must clip out primitives
CSE 167: Lecture #5: Rasterization. Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2012
 CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #5: Rasterization Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2012 Announcements Homework project #2 due this Friday, October
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #5: Rasterization Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2012 Announcements Homework project #2 due this Friday, October
Computing Visibility. Backface Culling for General Visibility. One More Trick with Planes. BSP Trees Ray Casting Depth Buffering Quiz
 Computing Visibility BSP Trees Ray Casting Depth Buffering Quiz Power of Plane Equations We ve gotten a lot of mileage out of one simple equation. Basis for D outcode-clipping Basis for plane-at-a-time
Computing Visibility BSP Trees Ray Casting Depth Buffering Quiz Power of Plane Equations We ve gotten a lot of mileage out of one simple equation. Basis for D outcode-clipping Basis for plane-at-a-time
Advanced Shading I: Shadow Rasterization Techniques
 Advanced Shading I: Shadow Rasterization Techniques Shadow Terminology umbra: light totally blocked penumbra: light partially blocked occluder: object blocking light Shadow Terminology umbra: light totally
Advanced Shading I: Shadow Rasterization Techniques Shadow Terminology umbra: light totally blocked penumbra: light partially blocked occluder: object blocking light Shadow Terminology umbra: light totally
Computer Graphics II
 Computer Graphics II Autumn 2017-2018 Outline Visible Surface Determination Methods (contd.) 1 Visible Surface Determination Methods (contd.) Outline Visible Surface Determination Methods (contd.) 1 Visible
Computer Graphics II Autumn 2017-2018 Outline Visible Surface Determination Methods (contd.) 1 Visible Surface Determination Methods (contd.) Outline Visible Surface Determination Methods (contd.) 1 Visible
CS4620/5620: Lecture 14 Pipeline
 CS4620/5620: Lecture 14 Pipeline 1 Rasterizing triangles Summary 1! evaluation of linear functions on pixel grid 2! functions defined by parameter values at vertices 3! using extra parameters to determine
CS4620/5620: Lecture 14 Pipeline 1 Rasterizing triangles Summary 1! evaluation of linear functions on pixel grid 2! functions defined by parameter values at vertices 3! using extra parameters to determine
Faster Scan Conversion Using the TMS320C80
 Disclaimer: This document was part of the First European DSP Education and Research Conference. It may have been written by someone whose native language is not English. TI assumes no liability for the
Disclaimer: This document was part of the First European DSP Education and Research Conference. It may have been written by someone whose native language is not English. TI assumes no liability for the
Computer Graphics: 8-Hidden Surface Removal
 Computer Graphics: 8-Hidden Surface Removal Prof. Dr. Charles A. Wüthrich, Fakultät Medien, Medieninformatik Bauhaus-Universität Weimar caw AT medien.uni-weimar.de Depth information Depth information is
Computer Graphics: 8-Hidden Surface Removal Prof. Dr. Charles A. Wüthrich, Fakultät Medien, Medieninformatik Bauhaus-Universität Weimar caw AT medien.uni-weimar.de Depth information Depth information is
Lecture 17: Recursive Ray Tracing. Where is the way where light dwelleth? Job 38:19
 Lecture 17: Recursive Ray Tracing Where is the way where light dwelleth? Job 38:19 1. Raster Graphics Typical graphics terminals today are raster displays. A raster display renders a picture scan line
Lecture 17: Recursive Ray Tracing Where is the way where light dwelleth? Job 38:19 1. Raster Graphics Typical graphics terminals today are raster displays. A raster display renders a picture scan line
CS184 : Foundations of Computer Graphics Professor David Forsyth Final Examination
 CS184 : Foundations of Computer Graphics Professor David Forsyth Final Examination (Total: 100 marks) Figure 1: A perspective view of a polyhedron on an infinite plane. Cameras and Perspective Rendering
CS184 : Foundations of Computer Graphics Professor David Forsyth Final Examination (Total: 100 marks) Figure 1: A perspective view of a polyhedron on an infinite plane. Cameras and Perspective Rendering
Real-Time Shadows. André Offringa Timo Laman
 Real-Time Shadows André Offringa Timo Laman Real-Time rendering Radiosity/Raytracing not feasible in real-time applications Scene rendered using projection & scan conversion of polygons Advantage: significant
Real-Time Shadows André Offringa Timo Laman Real-Time rendering Radiosity/Raytracing not feasible in real-time applications Scene rendered using projection & scan conversion of polygons Advantage: significant
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #5: Rasterization. Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2015
 CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #5: Rasterization Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2015 Announcements Project 2 due tomorrow at 2pm Grading window
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #5: Rasterization Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2015 Announcements Project 2 due tomorrow at 2pm Grading window
Graphics and Interaction Rendering pipeline & object modelling
 433-324 Graphics and Interaction Rendering pipeline & object modelling Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction to Modelling Polygonal geometry The rendering
433-324 Graphics and Interaction Rendering pipeline & object modelling Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction to Modelling Polygonal geometry The rendering
CS488. Visible-Surface Determination. Luc RENAMBOT
 CS488 Visible-Surface Determination Luc RENAMBOT 1 Visible-Surface Determination So far in the class we have dealt mostly with simple wireframe drawings of the models The main reason for this is so that
CS488 Visible-Surface Determination Luc RENAMBOT 1 Visible-Surface Determination So far in the class we have dealt mostly with simple wireframe drawings of the models The main reason for this is so that
VISIBILITY & CULLING. Don t draw what you can t see. Thomas Larsson, Afshin Ameri DVA338, Spring 2018, MDH
 VISIBILITY & CULLING Don t draw what you can t see. Thomas Larsson, Afshin Ameri DVA338, Spring 2018, MDH Visibility Visibility Given a set of 3D objects, which surfaces are visible from a specific point
VISIBILITY & CULLING Don t draw what you can t see. Thomas Larsson, Afshin Ameri DVA338, Spring 2018, MDH Visibility Visibility Given a set of 3D objects, which surfaces are visible from a specific point
Computer Science 426 Midterm 3/11/04, 1:30PM-2:50PM
 NAME: Login name: Computer Science 46 Midterm 3//4, :3PM-:5PM This test is 5 questions, of equal weight. Do all of your work on these pages (use the back for scratch space), giving the answer in the space
NAME: Login name: Computer Science 46 Midterm 3//4, :3PM-:5PM This test is 5 questions, of equal weight. Do all of your work on these pages (use the back for scratch space), giving the answer in the space
Chapter 5. Projections and Rendering
 Chapter 5 Projections and Rendering Topics: Perspective Projections The rendering pipeline In order to view manipulate and view a graphics object we must find ways of storing it a computer-compatible way.
Chapter 5 Projections and Rendering Topics: Perspective Projections The rendering pipeline In order to view manipulate and view a graphics object we must find ways of storing it a computer-compatible way.
CS184 : Foundations of Computer Graphics Professor David Forsyth Final Examination (Total: 100 marks)
 CS184 : Foundations of Computer Graphics Professor David Forsyth Final Examination (Total: 100 marks) Cameras and Perspective Figure 1: A perspective view of a polyhedron on an infinite plane. Rendering
CS184 : Foundations of Computer Graphics Professor David Forsyth Final Examination (Total: 100 marks) Cameras and Perspective Figure 1: A perspective view of a polyhedron on an infinite plane. Rendering
Graphics for VEs. Ruth Aylett
 Graphics for VEs Ruth Aylett Overview VE Software Graphics for VEs The graphics pipeline Projections Lighting Shading VR software Two main types of software used: off-line authoring or modelling packages
Graphics for VEs Ruth Aylett Overview VE Software Graphics for VEs The graphics pipeline Projections Lighting Shading VR software Two main types of software used: off-line authoring or modelling packages
THE VIEWING TRANSFORMATION
 ECS 178 Course Notes THE VIEWING TRANSFORMATION Kenneth I. Joy Institute for Data Analysis and Visualization Department of Computer Science University of California, Davis Overview One of the most important
ECS 178 Course Notes THE VIEWING TRANSFORMATION Kenneth I. Joy Institute for Data Analysis and Visualization Department of Computer Science University of California, Davis Overview One of the most important
Computer Graphics. Shadows
 Computer Graphics Lecture 10 Shadows Taku Komura Today Shadows Overview Projective shadows Shadow texture Shadow volume Shadow map Soft shadows Why Shadows? Shadows tell us about the relative locations
Computer Graphics Lecture 10 Shadows Taku Komura Today Shadows Overview Projective shadows Shadow texture Shadow volume Shadow map Soft shadows Why Shadows? Shadows tell us about the relative locations
CS 112 The Rendering Pipeline. Slide 1
 CS 112 The Rendering Pipeline Slide 1 Rendering Pipeline n Input 3D Object/Scene Representation n Output An image of the input object/scene n Stages (for POLYGON pipeline) n Model view Transformation n
CS 112 The Rendering Pipeline Slide 1 Rendering Pipeline n Input 3D Object/Scene Representation n Output An image of the input object/scene n Stages (for POLYGON pipeline) n Model view Transformation n
Rendering. Basic Math Review. Rasterizing Lines and Polygons Hidden Surface Remove Multi-pass Rendering with Accumulation Buffers.
 Rendering Rasterizing Lines and Polygons Hidden Surface Remove Multi-pass Rendering with Accumulation Buffers Basic Math Review Slope-Intercept Formula For Lines Given a third point on the line: P = (X,Y)
Rendering Rasterizing Lines and Polygons Hidden Surface Remove Multi-pass Rendering with Accumulation Buffers Basic Math Review Slope-Intercept Formula For Lines Given a third point on the line: P = (X,Y)
More Visible Surface Detection. CS116B Chris Pollett Mar. 16, 2005.
 More Visible Surface Detection CS116B Chris Pollett Mar. 16, 2005. Outline The A-Buffer Method The Scan-Line Method The Depth Sorting Method BSP Trees, Area Subdivision, and Octrees Wire-frame Visibility
More Visible Surface Detection CS116B Chris Pollett Mar. 16, 2005. Outline The A-Buffer Method The Scan-Line Method The Depth Sorting Method BSP Trees, Area Subdivision, and Octrees Wire-frame Visibility
3D Rasterization II COS 426
 3D Rasterization II COS 426 3D Rendering Pipeline (for direct illumination) 3D Primitives Modeling Transformation Lighting Viewing Transformation Projection Transformation Clipping Viewport Transformation
3D Rasterization II COS 426 3D Rendering Pipeline (for direct illumination) 3D Primitives Modeling Transformation Lighting Viewing Transformation Projection Transformation Clipping Viewport Transformation
Scan Conversion. Drawing Lines Drawing Circles
 Scan Conversion Drawing Lines Drawing Circles 1 How to Draw This? 2 Start From Simple How to draw a line: y(x) = mx + b? 3 Scan Conversion, a.k.a. Rasterization Ideal Picture Raster Representation Scan
Scan Conversion Drawing Lines Drawing Circles 1 How to Draw This? 2 Start From Simple How to draw a line: y(x) = mx + b? 3 Scan Conversion, a.k.a. Rasterization Ideal Picture Raster Representation Scan
Clipping. Angel and Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 7E Addison-Wesley 2015
 Clipping 1 Objectives Clipping lines First of implementation algorithms Clipping polygons (next lecture) Focus on pipeline plus a few classic algorithms 2 Clipping 2D against clipping window 3D against
Clipping 1 Objectives Clipping lines First of implementation algorithms Clipping polygons (next lecture) Focus on pipeline plus a few classic algorithms 2 Clipping 2D against clipping window 3D against
3D Rendering Pipeline (for direct illumination)
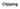 Clipping 3D Rendering Pipeline (for direct illumination) 3D Primitives 3D Modeling Coordinates Modeling Transformation Lighting 3D Camera Coordinates Projection Transformation Clipping 2D Screen Coordinates
Clipping 3D Rendering Pipeline (for direct illumination) 3D Primitives 3D Modeling Coordinates Modeling Transformation Lighting 3D Camera Coordinates Projection Transformation Clipping 2D Screen Coordinates
From Vertices to Fragments: Rasterization. Reading Assignment: Chapter 7. Special memory where pixel colors are stored.
 From Vertices to Fragments: Rasterization Reading Assignment: Chapter 7 Frame Buffer Special memory where pixel colors are stored. System Bus CPU Main Memory Graphics Card -- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
From Vertices to Fragments: Rasterization Reading Assignment: Chapter 7 Frame Buffer Special memory where pixel colors are stored. System Bus CPU Main Memory Graphics Card -- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
CS559: Computer Graphics. Lecture 12: Antialiasing & Visibility Li Zhang Spring 2008
 CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 12: Antialiasing & Visibility Li Zhang Spring 2008 Antialising Today Hidden Surface Removal Reading: Shirley ch 3.7 8 OpenGL ch 1 Last time A 2 (x 0 y 0 ) (x 1 y 1 ) P
CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 12: Antialiasing & Visibility Li Zhang Spring 2008 Antialising Today Hidden Surface Removal Reading: Shirley ch 3.7 8 OpenGL ch 1 Last time A 2 (x 0 y 0 ) (x 1 y 1 ) P
CS452/552; EE465/505. Clipping & Scan Conversion
 CS452/552; EE465/505 Clipping & Scan Conversion 3-31 15 Outline! From Geometry to Pixels: Overview Clipping (continued) Scan conversion Read: Angel, Chapter 8, 8.1-8.9 Project#1 due: this week Lab4 due:
CS452/552; EE465/505 Clipping & Scan Conversion 3-31 15 Outline! From Geometry to Pixels: Overview Clipping (continued) Scan conversion Read: Angel, Chapter 8, 8.1-8.9 Project#1 due: this week Lab4 due:
Hidden Line and Surface
 Copyright@00, YZU Optimal Design Laboratory. All rights resered. Last updated: Yeh-Liang Hsu (00--). Note: This is the course material for ME550 Geometric modeling and computer graphics, Yuan Ze Uniersity.
Copyright@00, YZU Optimal Design Laboratory. All rights resered. Last updated: Yeh-Liang Hsu (00--). Note: This is the course material for ME550 Geometric modeling and computer graphics, Yuan Ze Uniersity.
Computer Graphics. Lecture 9 Environment mapping, Mirroring
 Computer Graphics Lecture 9 Environment mapping, Mirroring Today Environment Mapping Introduction Cubic mapping Sphere mapping refractive mapping Mirroring Introduction reflection first stencil buffer
Computer Graphics Lecture 9 Environment mapping, Mirroring Today Environment Mapping Introduction Cubic mapping Sphere mapping refractive mapping Mirroring Introduction reflection first stencil buffer
Surface and Solid Geometry. 3D Polygons
 Surface and Solid Geometry D olygons Once we know our plane equation: Ax + By + Cz + D = 0, we still need to manage the truncation which leads to the polygon itself Functionally, we will need to do this
Surface and Solid Geometry D olygons Once we know our plane equation: Ax + By + Cz + D = 0, we still need to manage the truncation which leads to the polygon itself Functionally, we will need to do this
Lecture 8 Ray tracing Part 1: Basic concept Yong-Jin Liu.
 Fundamentals of Computer Graphics Lecture 8 Ray tracing Part 1: Basic concept Yong-Jin Liu liuyongjin@tsinghua.edu.cn Material by S.M.Lea (UNC) Goals To set up the mathematics and algorithms to perform
Fundamentals of Computer Graphics Lecture 8 Ray tracing Part 1: Basic concept Yong-Jin Liu liuyongjin@tsinghua.edu.cn Material by S.M.Lea (UNC) Goals To set up the mathematics and algorithms to perform
Visualisatie BMT. Rendering. Arjan Kok
 Visualisatie BMT Rendering Arjan Kok a.j.f.kok@tue.nl 1 Lecture overview Color Rendering Illumination 2 Visualization pipeline Raw Data Data Enrichment/Enhancement Derived Data Visualization Mapping Abstract
Visualisatie BMT Rendering Arjan Kok a.j.f.kok@tue.nl 1 Lecture overview Color Rendering Illumination 2 Visualization pipeline Raw Data Data Enrichment/Enhancement Derived Data Visualization Mapping Abstract
521493S Computer Graphics Exercise 1 (Chapters 1-3)
 521493S Computer Graphics Exercise 1 (Chapters 1-3) 1. Consider the clipping of a line segment defined by the latter s two endpoints (x 1, y 1 ) and (x 2, y 2 ) in two dimensions against a rectangular
521493S Computer Graphics Exercise 1 (Chapters 1-3) 1. Consider the clipping of a line segment defined by the latter s two endpoints (x 1, y 1 ) and (x 2, y 2 ) in two dimensions against a rectangular
Course Title: Computer Graphics Course no: CSC209
 Course Title: Computer Graphics Course no: CSC209 Nature of the Course: Theory + Lab Semester: III Full Marks: 60+20+20 Pass Marks: 24 +8+8 Credit Hrs: 3 Course Description: The course coversconcepts of
Course Title: Computer Graphics Course no: CSC209 Nature of the Course: Theory + Lab Semester: III Full Marks: 60+20+20 Pass Marks: 24 +8+8 Credit Hrs: 3 Course Description: The course coversconcepts of
Introduction to Computer Graphics with WebGL
 Introduction to Computer Graphics with WebGL Ed Angel Professor Emeritus of Computer Science Founding Director, Arts, Research, Technology and Science Laboratory University of New Mexico Models and Architectures
Introduction to Computer Graphics with WebGL Ed Angel Professor Emeritus of Computer Science Founding Director, Arts, Research, Technology and Science Laboratory University of New Mexico Models and Architectures
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Graphics & Visualization Chapter 1 Introduction Graphics & Visualization: Principles & Algorithms Brief History Milestones in the history of computer graphics: 2 Brief History (2) CPU Vs GPU 3 Applications
Graphics & Visualization Chapter 1 Introduction Graphics & Visualization: Principles & Algorithms Brief History Milestones in the history of computer graphics: 2 Brief History (2) CPU Vs GPU 3 Applications
CS 4731: Computer Graphics Lecture 21: Raster Graphics: Drawing Lines. Emmanuel Agu
 CS 4731: Computer Graphics Lecture 21: Raster Graphics: Drawing Lines Emmanuel Agu 2D Graphics Pipeline Clipping Object World Coordinates Applying world window Object subset window to viewport mapping
CS 4731: Computer Graphics Lecture 21: Raster Graphics: Drawing Lines Emmanuel Agu 2D Graphics Pipeline Clipping Object World Coordinates Applying world window Object subset window to viewport mapping
Image Precision Silhouette Edges
 Image Precision Silhouette Edges by Ramesh Raskar and Michael Cohen Presented at I3D 1999 Presented by Melanie Coggan Outline Motivation Previous Work Method Results Conclusions Outline Motivation Previous
Image Precision Silhouette Edges by Ramesh Raskar and Michael Cohen Presented at I3D 1999 Presented by Melanie Coggan Outline Motivation Previous Work Method Results Conclusions Outline Motivation Previous
The Traditional Graphics Pipeline
 Last Time? The Traditional Graphics Pipeline Participating Media Measuring BRDFs 3D Digitizing & Scattering BSSRDFs Monte Carlo Simulation Dipole Approximation Today Ray Casting / Tracing Advantages? Ray
Last Time? The Traditional Graphics Pipeline Participating Media Measuring BRDFs 3D Digitizing & Scattering BSSRDFs Monte Carlo Simulation Dipole Approximation Today Ray Casting / Tracing Advantages? Ray
Visibility: Z Buffering
 University of British Columbia CPSC 414 Computer Graphics Visibility: Z Buffering Week 1, Mon 3 Nov 23 Tamara Munzner 1 Poll how far are people on project 2? preferences for Plan A: status quo P2 stays
University of British Columbia CPSC 414 Computer Graphics Visibility: Z Buffering Week 1, Mon 3 Nov 23 Tamara Munzner 1 Poll how far are people on project 2? preferences for Plan A: status quo P2 stays
Models and Architectures. Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico
 Models and Architectures Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico 1 Objectives Learn the basic design of a graphics system Introduce
Models and Architectures Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico 1 Objectives Learn the basic design of a graphics system Introduce
Hidden Surfaces II. Week 9, Mon Mar 15
 University of British Columbia CPSC 314 Computer Graphics Jan-Apr 2010 Tamara Munzner Hidden Surfaces II Week 9, Mon Mar 15 http://www.ugrad.cs.ubc.ca/~cs314/vjan2010 ews yes, I'm granting the request
University of British Columbia CPSC 314 Computer Graphics Jan-Apr 2010 Tamara Munzner Hidden Surfaces II Week 9, Mon Mar 15 http://www.ugrad.cs.ubc.ca/~cs314/vjan2010 ews yes, I'm granting the request
CSE528 Computer Graphics: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications
 CSE528 Computer Graphics: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications Hong Qin State University of New York at Stony Brook (Stony Brook University) Stony Brook, New York 11794--4400 Tel: (631)632-8450; Fax: (631)632-8334
CSE528 Computer Graphics: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications Hong Qin State University of New York at Stony Brook (Stony Brook University) Stony Brook, New York 11794--4400 Tel: (631)632-8450; Fax: (631)632-8334
Models and Architectures
 Models and Architectures Objectives Learn the basic design of a graphics system Introduce graphics pipeline architecture Examine software components for an interactive graphics system 1 Image Formation
Models and Architectures Objectives Learn the basic design of a graphics system Introduce graphics pipeline architecture Examine software components for an interactive graphics system 1 Image Formation
Triangle Rasterization
 Triangle Rasterization Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring 2007 Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 2/07/07 1 From last time Lines and planes Culling View frustum culling Back-face culling Occlusion culling
Triangle Rasterization Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring 2007 Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 2/07/07 1 From last time Lines and planes Culling View frustum culling Back-face culling Occlusion culling
Robust Stencil Shadow Volumes. CEDEC 2001 Tokyo, Japan
 Robust Stencil Shadow Volumes CEDEC 2001 Tokyo, Japan Mark J. Kilgard Graphics Software Engineer NVIDIA Corporation 2 Games Begin to Embrace Robust Shadows 3 John Carmack s new Doom engine leads the way
Robust Stencil Shadow Volumes CEDEC 2001 Tokyo, Japan Mark J. Kilgard Graphics Software Engineer NVIDIA Corporation 2 Games Begin to Embrace Robust Shadows 3 John Carmack s new Doom engine leads the way
General Hidden Surface Removal Algorithms. Binghamton University. EngiNet. Thomas J. Watson. School of Engineering and Applied Science CS 460/560
 Binghamton University EngiNet State University of New York EngiNet Thomas J. Watson School of Engineering and Applied Science WARNING All rights reserved. No Part of this video lecture series may be reproduced
Binghamton University EngiNet State University of New York EngiNet Thomas J. Watson School of Engineering and Applied Science WARNING All rights reserved. No Part of this video lecture series may be reproduced
From 3D World to 2D Screen. Hendrik Speleers
 Hendrik Speleers Overview Synthetic camera Rendering pipeline World window versus viewport Clipping Cohen-Sutherland algorithm Rasterizing Bresenham algorithm Three different actors in a scene Objects:
Hendrik Speleers Overview Synthetic camera Rendering pipeline World window versus viewport Clipping Cohen-Sutherland algorithm Rasterizing Bresenham algorithm Three different actors in a scene Objects:
FROM VERTICES TO FRAGMENTS. Lecture 5 Comp3080 Computer Graphics HKBU
 FROM VERTICES TO FRAGMENTS Lecture 5 Comp3080 Computer Graphics HKBU OBJECTIVES Introduce basic implementation strategies Clipping Scan conversion OCTOBER 9, 2011 2 OVERVIEW At end of the geometric pipeline,
FROM VERTICES TO FRAGMENTS Lecture 5 Comp3080 Computer Graphics HKBU OBJECTIVES Introduce basic implementation strategies Clipping Scan conversion OCTOBER 9, 2011 2 OVERVIEW At end of the geometric pipeline,
Previously... contour or image rendering in 2D
 Volume Rendering Visualisation Lecture 10 Taku Komura Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics Volume Rendering 1 Previously... contour or image rendering in 2D 2D Contour line
Volume Rendering Visualisation Lecture 10 Taku Komura Institute for Perception, Action & Behaviour School of Informatics Volume Rendering 1 Previously... contour or image rendering in 2D 2D Contour line
Rasteriza2on and Clipping
 Overview Scan conversion Computer Graphics Rasterizaon and Clipping Polygon filling Clipping in D Aleksandra Pizurica Raster Display PIEL (picture element) RASTER (a rectangular array of points or dots)
Overview Scan conversion Computer Graphics Rasterizaon and Clipping Polygon filling Clipping in D Aleksandra Pizurica Raster Display PIEL (picture element) RASTER (a rectangular array of points or dots)
Graphics Systems and Models
 Graphics Systems and Models 2 nd Week, 2007 Sun-Jeong Kim Five major elements Input device Processor Memory Frame buffer Output device Graphics System A Graphics System 2 Input Devices Most graphics systems
Graphics Systems and Models 2 nd Week, 2007 Sun-Jeong Kim Five major elements Input device Processor Memory Frame buffer Output device Graphics System A Graphics System 2 Input Devices Most graphics systems
From Ver(ces to Fragments: Rasteriza(on
 From Ver(ces to Fragments: Rasteriza(on From Ver(ces to Fragments 3D vertices vertex shader rasterizer fragment shader final pixels 2D screen fragments l determine fragments to be covered l interpolate
From Ver(ces to Fragments: Rasteriza(on From Ver(ces to Fragments 3D vertices vertex shader rasterizer fragment shader final pixels 2D screen fragments l determine fragments to be covered l interpolate
The Graphics Pipeline. Interactive Computer Graphics. The Graphics Pipeline. The Graphics Pipeline. The Graphics Pipeline: Clipping
 Interactive Computer Graphics The Graphics Pipeline: The Graphics Pipeline Input: - geometric model - illumination model - camera model - viewport Some slides adopted from F. Durand and B. Cutler, MIT
Interactive Computer Graphics The Graphics Pipeline: The Graphics Pipeline Input: - geometric model - illumination model - camera model - viewport Some slides adopted from F. Durand and B. Cutler, MIT
CSE328 Fundamentals of Computer Graphics: Concepts, Theory, Algorithms, and Applications
 CSE328 Fundamentals of Computer Graphics: Concepts, Theory, Algorithms, and Applications Hong Qin Stony Brook University (SUNY at Stony Brook) Stony Brook, New York 11794-4400 Tel: (631)632-8450; Fax:
CSE328 Fundamentals of Computer Graphics: Concepts, Theory, Algorithms, and Applications Hong Qin Stony Brook University (SUNY at Stony Brook) Stony Brook, New York 11794-4400 Tel: (631)632-8450; Fax:
Output Primitives Lecture: 3. Lecture 3. Output Primitives. Assuming we have a raster display, a picture is completely specified by:
 Lecture 3 Output Primitives Assuming we have a raster display, a picture is completely specified by: - A set of intensities for the pixel positions in the display. - A set of complex objects, such as trees
Lecture 3 Output Primitives Assuming we have a raster display, a picture is completely specified by: - A set of intensities for the pixel positions in the display. - A set of complex objects, such as trees
