CATIA V5 FEA Tutorials Release 14
|
|
|
- Rafe Hamilton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CATIA V5 FEA Tutorials Release 14 Nader G. Zamani University of Windsor SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation
2 CATIA V5 FEA Tutorials 2-1 Chapter 2 Analysis of a Bent Rod with Solid Elements
3 2-2 CATIA V5 FEA Tutorials Introduction In this tutorial, a solid FEA model of a bent rod experiencing a combined load is created. significance of the von Mises stress in design equation is discussed. 1 Problem Statement No planes of symmetry exist and therefore simplifications cannot be made. Finally, the The bent rod, shown to the right, is clamped at one end and subjected to a load of 2000 lb as displayed. The steel rod has a Young modulus of 30E+6 psi and Poisson ratio 0.3. The nominal dimensions of the rod are also displayed below. Although this problem is more efficiently handled with beam elements, we propose to use solid elements. There are two main types of solid elements available in CATIA V5, linear and parabolic. Both are referred to as tetrahedron elements and shown below. Clamped end Clamped end loaded end Tetrahedron Elements Tetrahedron Elements 5 in 1 in 8 in linear Cross sectional Radius is 1 in parabolic accurate results. Another important feature of parabolic elements is that they can fit The linear tetrahedron elements are faster computationally but less accurate. On the other hand, the parabolic elements require more computational resources but lead to more curved surfaces better. In general, the analysis of bulky objects requires the use of solid elements. Hexahedral elements are also available on a limited basis in recent releases of CATIA. These elements will be discussed in a later chapter. 2 Creation of the Part in Mechanical Design Solutions Enter the Part Design workbench which can be achieved by different means depending on your CATIA customization. For example, from the standard windows. From the box shown on the right, select Part. This moves you to the part design workbench and creates a part with the default name Part.1. toolbar, select File > New
4 Analysis of a Bent Rod with Solid Elements 2-3 In order to change the default name, move the curser to Part.1 in the tree, right click and select Properties from the menu list. From the Properties box, select the Product tab and in Part Number type wrench. This will be the new part name throughout the chapter. The tree on the top left corner of the screen should look as displayed below. From the tree, select the xy plane and enter the Sketcher bent rod by using Profile. In the Sketcher, draw a circle, and dimension it. In order to change the dimension, double click on the dimension on the screen and in the resulting box enter radius 1. Your simple sketch and the Constraint Definition box used to enter the correct radius are shown below. Leave the Sketcher. From the tree, select the yz plane and enter the Sketcher. Draw the spine of the and dimension it to meet the geometric specs. In the Sketcher, the spine should match the figure shown next. Upon leaving the Sketcher, the screen and the tree should resemble the following figures.
5 2-4 CATIA V5 FEA Tutorials You will now use the ribbing operation to extrude the circle along the spine (path). Upon selecting the rib icon, the Rib Definition box opens. For Profile select the circle (Sketch.1) and the Center Curve select (Sketch.2) as indicated. The result is the final part shown below. The next step is to apply material properties on the part created. opens the material database box shown below. Use the Apply icon from the bottom row of toolbars. The use of this icon
6 Analysis of a Bent Rod with Solid Elements 2-5 Choose the Metal tab on the top, select Steel. Use your cursor to pick the part on the screen at which time the OK, and Apply can be selected. Close the box. The material property is now reflected in the tree. In order to inspect the values of the material properties assigned, double click on Steel in the tree. It may take a minute before the database is searched. You will notice that the Properties box shown below opens. Choose the Analysis tab from this box, and the values will be displayed. Note that these values can be edited. Since your Young modulus and Poisson ratio are different from what is shown, in appropriate boxes, type Young modulus = 3E+7 and Poisson ratio =.3. Press OK.
7 2-6 CATIA V5 FEA Tutorials If the part is still gray, one can change the rendering style. From the View toolbar, select the View mode toolbar. Next choose the Shading with The part now appears shaded as shown on the right. 3 Entering the Analysis Solutions From the standard windows tool bar, select There is a second workbench known as the Advanced Meshing Tools which will be discussed later. Start > Analysis & Simulation > Generative Structural Analysis The New Analysis Case box pops up. The default choice is Static Analysis which is precisely what we intend to use. Therefore, close the box by clicking on OK. Note that the tree structure gets considerably longer. The bottom branches of the tree are presently unfilled, and as we proceed in this workbench, assign loads and restraints, the branches gradually get filled. Another point that cannot be missed is the appearance of an icon close to the part that reflects a representative size and sag. This is displayed in the next figure.
8 Analysis of a Bent Rod with Solid Elements 2-7 Representative sag Representative sag Representative size The concept of element size is self-explanatory. A smaller element size leads to more accurate results at the expense of a larger computation time. The sag terminology is unique to CATIA. In FEA, the geometry of a part is approximated with the elements. The surface of the part and the FEA approximation of a part do not coincide. The sag parameter controls the deviation between the two. Therefore, a smaller sag value could lead to better results. There is a relationship between these parameters that one does not have to be concerned with at this point. The physical sizes of the representative size and sag on the screen, which also limit the coarseness of the mesh can be changed by the user. There are two ways to change these parameters: The first method is to double click on the representative icons on the screen which forces the OCTREE Tetrahedron Mesh box to open as shown to the right. Change the default values to match the numbers in the box. Notice that the type of the elements used (linear/parabolic) is also set in this box. Select OK. The second method of reaching this box is through the tree. By double clicking on the branch labeled OCTREE Tetrahedron Mesh shown below, the same box opens allowing the user to modify the values. In order to view the generated mesh, you can point the curser to the branch Nodes and Elements, right click and select Mesh Visualization. This step may be slightly different in some UNIX machines. Upon performing this operation a Warning box appears which can be ignored by selecting OK. For the mesh parameters used, the following mesh is displayed on the screen.
9 2-8 CATIA V5 FEA Tutorials The representative size and sag icons can be removed from the display by simply pointing to them click and select Hide. This is the standard process for hiding any entity in CATIA V5. Before proceeding with the rest of the model, a few more points regarding the mesh size are discussed. As indicated earlier, a smaller mesh could result in a more accurate solution; however, this cannot be done indiscriminately. The elements must be small in the regions of high stress gradient such as stress concentrations. These are areas where the geometry changes rapidly such as bends, fillets, and keyways. Uniformly reducing the element size for the whole part is a poor strategy. CONGRATULATIONS! You now have a mesh with the correct material properties. Regularly save your work. Applying Restraints: CATIA s FEA module is geometrically based. This means that the boundary conditions cannot be applied to nodes and elements. The boundary conditions can only be applied at the part level. As soon as you enter the Generative Structural Analysis workbench, the part is automatically hidden. Therefore, before boundary conditions are applied, the part must be brought to the unhide mode. This can be carried out by pointing the curser to the top of the tree, the Links Manager.1 branch, right click, select Show. At this point, the part and the mesh are superimposed as shown to the right and you have access to the part. If, the presence of the mesh is annoying, you can always hide it. Point the cursor to Nodes and Elements, right click, Hide. Instead of hiding the mesh as indicated above, one can point the cursor to the Mesh.1 item in the tree, right click, and select Activate/Deactivate. The result is that the mesh is hidden and the part is displayed. The steps are graphically in the next figure.
10 Analysis of a Bent Rod with Solid Elements 2-9 In FEA, restraints refer to applying displacement boundary conditions which is achieved through the Restraint toolbar pick the bottom face of the rod. Be careful not to pick the circumference (edge) of the circle instead of the face. In this. In the present problem, you can assume that the base of the longer section is clamped. The Clamp condition means that the displacements in all three directions are zero. Select the Clamp icon case, only two restraint symbols will be shown attached to the circumference. Applying Loads: and In FEA, loads refer to forces. The Load toolbar is used for this purpose. Select the Distributed force icon should be applied in the negative x-direction., and with the curser pick the other face of the rod which is loaded. The Distributed force box shown below opens. A visual inspection of the global axis on your screen indicates that the force of magnitude 2000 lb
11 2-10 CATIA V5 FEA Tutorials Although in our problem the 2000 lb force is applied in the global direction x, it is possible to the force symbols will appear as shown below. apply forces in the local direction specified by the user. Upon selection of the appropriate face, If the circumference of the circle is accidentally picked, only two arrows attached to the circle will appear. Although in our present problem there may be small differences in the results, one should apply the loads and restraints as intended. The portion of the tree which reports the restraints and loads is shown below. To run the analysis, you need to use the Compute Launching the Solver: toolbar by selecting the Compute icon. This leads to the Compute box shown to the right. Leave the defaults as All which means everything is computed. Upon closing this box, after a brief pause, the second box shown below appears. This box provides information on the resources needed to complete the analysis. If the estimates are zero in the listing, then there is a problem in the previous step and should be looked into. If all the numbers are zero in the box, the
12 Analysis of a Bent Rod with Solid Elements 2-11 program may run but would not produce any useful results. The tree has been changed to reflect the location of the Results and Computations as shown below. The user can change these locations by double clicking on the branch. The box, shown on the right, will open and can be modified. Postprocessing: The main postprocessing toolbar is called Image shape you have to use the Deformation icon displayed below. The deformation image can be very deceiving because one could have the impression that the wrench actually displaces to that extent. Keep in mind that the displacements are scaled considerably so that one can observe the deformed shape. Although the scale factor is set automatically, one can change. To view the deformed. The resulting deformed shape is this value with the Deformation Scale Factor icon in the Analysis Tools toolbar. Clicking on the above icon leads to the box shown on the right where the desired scale factor can be typed. The deformed shape displayed corresponds to a scale factor of 120. The value in. is 120 times the actual maximum displacement.
13 2-12 CATIA V5 FEA Tutorials In order to see the displacement field, the Displacement icon in the Image toolbar should be used. The default display is in terms of displacement arrows as shown on the right. The color and the length of arrows represent the size of the displacement. The contour legend indicates a maximum displacement of.0353 in. The arrow plot is not particularly useful. In order to view the contour plot of the displacement field, position the cursor on the arrow field and double click. The Image Edition box shown below opens. Note that the default is to draw the contour on the deformed shape. If this is not desired, uncheck the box On deformed mesh. Next, select AVERAGE-ISO and press OK. The contour of the displacement field as shown is plotted. It is difficult to read the contour lines from the above figure. You can change the render style by using Shading with View Mode toolbar icon in the. Note that the elements are not showing in this plot. If you prefer that the elements are displayed at the same time, you need to go through the following step. Select the Custom View Mode icon from
14 Analysis of a Bent Rod with Solid Elements 2-13 the above tool bar. In the resulting pop up box, make sure that Edges and points checked. Ignoring the fillet radius of the bend, the beam bending solution of this problem can be obtained using Castigliano s theorem. This approximate value is.044 in which is in the same ball park as the FEA solution of.0392 in. The discrepancy is primarily due to the large bend radius. Clearly, the maximum displacement is below the point of the application of the load, in the negative x-direction. (Note: The color map has been changed otherwise everything looks black in the figure.) The next step in the postprocessing is to plot the contours of the von Mises stress using the von Mises Stress icon toolbar. The von Mises stress is displayed to the right. in the Image The maximum stress is at the support with a value of 2.06E+4 psi which is below the yield strength of most steels.
15 2-14 CATIA V5 FEA Tutorials Double clicking on the contour legend leads to the Color Map box displayed on the right. the user can describe the range of stresses to be plotted. The contour can be plotted as Smooth or Stepped. The number of color bands is also specified in this box. Finally, Occasionally, you may be interested in plotting the von Mises stress contour in either the load area or the support section. In order to achieve this, double click on the contour levels on the screen to open the image edition box. Next use the Selections tab as shown below. Here, you have the choice of selecting different areas. The contours on the display the von Mises stress at Distributed Force.1, and Calmp.1 sections. Unfortunately in the current release of CATIA this contour is rather useless. In a later chapter, you will be shown how to use the Group concept to generate a better contour plot as indicated below.
16 Analysis of a Bent Rod with Solid Elements 2-15 As the postprocessing proceeds and we generate different plots, they are recorded in the tree as shown. Each plot generated deactivates the previous one on the screen. By pointing to a desired plot in the tree and right clicking, you can activate the plot. Clearly any plot can be deleted from the tree in the usual way (right click, Delete). The location and magnitude of the extremum values of a contour (e.g. von Mises stress) can be identified in a plot. This is achieved by using the Image Extrema icon Image Analysis toolbar. Before the plot is generated, the Extrema Creation box pops up as shown to the right. If the default values are maintained, the global maximum and minimum are found and their location pin-pointed in a contour plot as displayed below. in the At this point we have generated two plots. The displacement and the von Mises stress contours which can be displayed individually. However, CATIA also allows you to show both plots side by side. First make sure that both images to be plotted are active in the tree. If not, point to the graph in the tree, right click, select Active. Click the Image Layout icon from the Image Analysis toolbar. The Images box, shown to the right, asks you to specify the direction along which the two plots are expected to be aligned.
17 2-16 CATIA V5 FEA Tutorials The outcome is side-by-side plots shown below. (Note: The color map has been changed otherwise everything looks black.) Before describing how the principal stresses are plotted, we like to elaborate on the significance of the von Mises stress plot. The state of stress is described by the six Cauchy stresses {, σ, σ, τ, τ τ } σ which x y z xy xz, vary from point to point. The von Mises stress is a combination of these according to the following expression: yz σ VM = 2 ) [( σ σ ) + ( σ σ ) + ( σ σ ) + 6( τ + τ + τ ] 1 2 x y x z y z xy xz yz For an obvious reason, this is also known as the effective stress. Note that by definition, the von Mises is always a positive number. In terms of principal stresses, σ VM can also be written as σ = [( σ σ ) + ( σ σ ) + ( σ σ ] VM ) For many ductile materials, the onset of yielding (permanent plastic deformation) takes σ σ =. place when σ = σ where σy is the yield strength of the material. For design purposes, VM Y a factor of safety N is introduced leading to the condition Therefore, a safe design is considered to be one where σ < N contour plot allows you to check the above condition. VM VM σ Y Y N. The von Mises stress
18 Analysis of a Bent Rod with Solid Elements 2-17 The Cutting Plane icon from the Analysis tools toolbar can be used to make a cut through the part at a desired location and inspect the stresses inside of the part. The Cut Plane box allows you to keep the plane or to remove it for display purposes. A typical cutting plane is shown below. The principal stresses are postprocessed next. The principal directions are three mutually perpendicular directions along which only normal stresses act. These normal stresses are known as the principal stresses. The figure to the right displays the principal directions x 1, x 2, and x 3, together with the σ 3 principal directions σ 1, σ 2, and σ 3. The standard convention in stress analysis is to label the stresses according to σ 1 σ2 σ3. The principal stresses are important for both theoretical reasons and practical ones. In experimental stress analysis, the positioning of strain gauges relies on the principal directions on the surface of a part. σ 2 σ 1 From the Image toolbar, select the Principal Stress icon. The result is the principal stress directions in the vector form as displayed to the right. Due to the large number of arrows, the interpretation of this plot is difficult. A zoomed view of the tip is also shown below.
19 2-18 CATIA V5 FEA Tutorials You can improve on the display of principal stresses by selecting a specific stress component to be plotted. To do so, double click on the arrows on the screen which causes the Image Edition, shown to the right to open. Click on the More button to expand the window as shown below. Choose the Component C11. In CATIA, C11 represents σ 1, the largest principal stress. At this point the vector plot displays only the directions associated with σ 1 as shown in the plot below. An alternative to the vector plot of the principal stress is the contour plot of σ 1. This can be achieved through the Image Edition box, under the Visu tab. You should select AVERAGE-ISO instead of Symbol. The resulting contour plot is shown below.
20 Analysis of a Bent Rod with Solid Elements 2-19 Using the icon Basic Analysis Results results of the FEA model. The first page of this report is displayed below. in the Analysis Results toolbar an HTML based report can be generated which summarizes the features and Finally, animation of the model can be achieved through the Animate icon in the Analysis Tools toolbar generated. and AVI files can easily be
21 2-20 CATIA V5 FEA Tutorials Exercises for Chapter 2 Problem 1: Analysis of a Foot Pedal The foot pedal shown below is made of steel with Young modulus 30E+6 psi and Poisson ratio 0.3. The pedal is loaded with a normal force of 100 lb along the edge shown. The other end of the pedal is clamped. The geometrical dimensions are provided at the bottom of the page where all the dimensions are in inches.
22 Analysis of a Bent Rod with Solid Elements 2-21 Try running the model with the two different element size and sag with both the linear and parabolic type of elements. Record the results in terms of the maximum depending on the type of processor used. displacement and the maximum von Mises stress in a table and comment on the results. The run time of the parabolic elements with element size of 0.1 could be substantial Partial Answer: Size =.3, sag =.05 Element Type Linear Parabolic Maximum.0158 in in. Displacement Maximum von Mises Srtess 5.32E+3 psi 1.1E+4 psi Size =.1, sag =.05 Element Type Linear Parabolic Maximum.021 in in. Displacement Maximum von Mises Stress 9.43E+4 psi 1.6E+4 psi The above tables reveal an extremely important fact about finite element analysis. Making a single run and accepting the results at face value is a serious mistake. Note that for linear elements as the mesh is refined, there is a significant change in both displacement and von Mises stress. The user should not accept either value as being correct and must refine the mesh further. The refinement should reach a point at which the difference with the previous mesh is not deemed to be significant to user. This process is referred to as a mesh convergence study. Keep in mind that the refinement need not be uniform throughout the part. One should perform the refinement in the critical areas only. It is clear that parabolic elements are superior in accuracy to linear element. Furthermore, note that although the displacement seems to have stabilized, the von Mises is still unreliable. It is well known that the displacements in FEA are more accurate than stresses. The reason is, that the stresses are obtained by differentiating the displacement, a process which magnifies the error.
23 2-22 CATIA V5 FEA Tutorials Problem 2: Analysis of a Cylindrical Bar under Torsion The cylindrical bar shown below has a clamped end. The other end is subjected to a couple caused by opposite forces on magnitude 1000 lb separated by 1.5 in. This is equivalent to a torque of 1500 lb.in applied to the cylinder. The material is steel with Young modulus 30E+6 and Poisson ratio of 0.3. The diameter of the cylinder is 1 in. and the dimensions of the loaded end are shown below. Although not showing, the length of the padded cylinder is 5 in. and the length of the padded rectangle is 0.5 in. All sharp corners at the loaded end have surface fillet of radius 0.1 in.
24 Analysis of a Bent Rod with Solid Elements 2-23 Model the part with linear solid elements with size = 0.1 and sag = which results in the mesh shown in the previous page. Compare the hoop stress (The hoop stress is the largest principal stress C11 ) with the theoretical solution from strength of materials. Partial Answer: The strength of materials solution is based on = Tr J τ where T is the applied torque, r is the radius of the cylinder and J is the polar moment of inertia. In terms of the diameter, 4 D πd r =, and J =. The hoop stress C1 which numerically equals τ is calculated T. For the present problem, T = 1500 lb.in and D = 1in. Based on these from 3 πd circular fringe patterns are another qualitative check on the validity of the FEA results. parameters, a value of 7643 psi for the hoop stress is predicted. The FEA results can be assessed by plotting the contour of C1 at the clamped section. The resulting plot shown below agrees quite well with 7643 psi obtained earlier. The
25 2-24 CATIA V5 FEA Tutorials NOTES:
3DEXPERIENCE 2017x FINITE ELEMENT ESSENTIALS IN SDC USING SIMULIA/CATIA APPLICATIONS. Nader G. Zamani
 Nader G. Zamani FINITE ELEMENT ESSENTIALS IN 3DEXPERIENCE 2017x USING SIMULIA/CATIA APPLICATIONS SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)
Nader G. Zamani FINITE ELEMENT ESSENTIALS IN 3DEXPERIENCE 2017x USING SIMULIA/CATIA APPLICATIONS SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)
ABAQUS for CATIA V5 Tutorials
 ABAQUS for CATIA V5 Tutorials AFC V2.5 Nader G. Zamani University of Windsor Shuvra Das University of Detroit Mercy SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com ABAQUS for CATIA V5,
ABAQUS for CATIA V5 Tutorials AFC V2.5 Nader G. Zamani University of Windsor Shuvra Das University of Detroit Mercy SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com ABAQUS for CATIA V5,
FEA BENDING, TORSION, TENSION, and SHEAR TUTORIAL in CATIA
 1 FEA BENDING, TORSION, TENSION, and SHEAR TUTORIAL in CATIA This tutorial shows the basics of a solid bending, torsional, tension, and shear FEA (Finite Elemental Analysis) model in CATIA. Torsion - page
1 FEA BENDING, TORSION, TENSION, and SHEAR TUTORIAL in CATIA This tutorial shows the basics of a solid bending, torsional, tension, and shear FEA (Finite Elemental Analysis) model in CATIA. Torsion - page
SDC. Engineering Analysis with COSMOSWorks. Paul M. Kurowski Ph.D., P.Eng. SolidWorks 2003 / COSMOSWorks 2003
 Engineering Analysis with COSMOSWorks SolidWorks 2003 / COSMOSWorks 2003 Paul M. Kurowski Ph.D., P.Eng. SDC PUBLICATIONS Design Generator, Inc. Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com
Engineering Analysis with COSMOSWorks SolidWorks 2003 / COSMOSWorks 2003 Paul M. Kurowski Ph.D., P.Eng. SDC PUBLICATIONS Design Generator, Inc. Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com
Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE
 Getting Started with Abaqus: Interactive Edition Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you
Getting Started with Abaqus: Interactive Edition Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you
DMU Engineering Analysis Review
 DMU Engineering Analysis Review Overview Conventions What's New? Getting Started Entering DMU Engineering Analysis Review Workbench Generating an Image Visualizing Extrema Generating a Basic Analysis Report
DMU Engineering Analysis Review Overview Conventions What's New? Getting Started Entering DMU Engineering Analysis Review Workbench Generating an Image Visualizing Extrema Generating a Basic Analysis Report
2: Static analysis of a plate
 2: Static analysis of a plate Topics covered Project description Using SolidWorks Simulation interface Linear static analysis with solid elements Finding reaction forces Controlling discretization errors
2: Static analysis of a plate Topics covered Project description Using SolidWorks Simulation interface Linear static analysis with solid elements Finding reaction forces Controlling discretization errors
DMU Engineering Analysis Review
 Page 1 DMU Engineering Analysis Review Preface Using This Guide Where to Find More Information Conventions What's New? Getting Started Inserting a CATAnalysis Document Using DMU Space Analysis From CATAnalysis
Page 1 DMU Engineering Analysis Review Preface Using This Guide Where to Find More Information Conventions What's New? Getting Started Inserting a CATAnalysis Document Using DMU Space Analysis From CATAnalysis
Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE
 Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you through the Abaqus/CAE modeling process by visiting
Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you through the Abaqus/CAE modeling process by visiting
Lesson: Static Stress Analysis of a Connecting Rod Assembly
 Lesson: Static Stress Analysis of a Connecting Rod Assembly In this tutorial we determine the effects of a 2,000 pound tensile load acting on a connecting rod assembly (consisting of the rod and two pins).
Lesson: Static Stress Analysis of a Connecting Rod Assembly In this tutorial we determine the effects of a 2,000 pound tensile load acting on a connecting rod assembly (consisting of the rod and two pins).
Similar Pulley Wheel Description J.E. Akin, Rice University
 Similar Pulley Wheel Description J.E. Akin, Rice University The SolidWorks simulation tutorial on the analysis of an assembly suggested noting another type of boundary condition that is not illustrated
Similar Pulley Wheel Description J.E. Akin, Rice University The SolidWorks simulation tutorial on the analysis of an assembly suggested noting another type of boundary condition that is not illustrated
ME 442. Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1
 ME 442 Overview Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1 The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the new user to the MSC/MARC/MENTAT finite element program. It should take about one hour to complete. The MARC/MENTAT
ME 442 Overview Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1 The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the new user to the MSC/MARC/MENTAT finite element program. It should take about one hour to complete. The MARC/MENTAT
Generative Part Structural Analysis Fundamentals
 CATIA V5 Training Foils Generative Part Structural Analysis Fundamentals Version 5 Release 19 September 2008 EDU_CAT_EN_GPF_FI_V5R19 About this course Objectives of the course Upon completion of this course
CATIA V5 Training Foils Generative Part Structural Analysis Fundamentals Version 5 Release 19 September 2008 EDU_CAT_EN_GPF_FI_V5R19 About this course Objectives of the course Upon completion of this course
Static Stress Analysis
 Static Stress Analysis Determine stresses and displacements in a connecting rod assembly. Lesson: Static Stress Analysis of a Connecting Rod Assembly In this tutorial we determine the effects of a 2,000-pound
Static Stress Analysis Determine stresses and displacements in a connecting rod assembly. Lesson: Static Stress Analysis of a Connecting Rod Assembly In this tutorial we determine the effects of a 2,000-pound
Engineering Analysis with SolidWorks Simulation 2012
 Engineering Analysis with SolidWorks Simulation 2012 Paul M. Kurowski SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Visit the following websites
Engineering Analysis with SolidWorks Simulation 2012 Paul M. Kurowski SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Visit the following websites
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Structural Analysis of a Plate with Hole
 ANSYS AIM Tutorial Structural Analysis of a Plate with Hole Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Analytical vs. Numerical Approaches
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Structural Analysis of a Plate with Hole Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Analytical vs. Numerical Approaches
Visit the following websites to learn more about this book:
 Visit the following websites to learn more about this book: 6 Introduction to Finite Element Simulation Historically, finite element modeling tools were only capable of solving the simplest engineering
Visit the following websites to learn more about this book: 6 Introduction to Finite Element Simulation Historically, finite element modeling tools were only capable of solving the simplest engineering
Engineering Analysis with
 Engineering Analysis with SolidWorks Simulation 2013 Paul M. Kurowski SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Visit the following websites
Engineering Analysis with SolidWorks Simulation 2013 Paul M. Kurowski SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Visit the following websites
Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 4 Plate With a Hole
 Problem Specification Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 4 Plate With a Hole Consider the classic example of a circular hole in a rectangular plate of constant thickness. The plate
Problem Specification Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 4 Plate With a Hole Consider the classic example of a circular hole in a rectangular plate of constant thickness. The plate
TUTORIAL 7: Stress Concentrations and Elastic-Plastic (Yielding) Material Behavior Initial Project Space Setup Static Structural ANSYS ZX Plane
 TUTORIAL 7: Stress Concentrations and Elastic-Plastic (Yielding) Material Behavior In this tutorial you will learn how to recognize and deal with a common modeling issues involving stress concentrations
TUTORIAL 7: Stress Concentrations and Elastic-Plastic (Yielding) Material Behavior In this tutorial you will learn how to recognize and deal with a common modeling issues involving stress concentrations
Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial
 Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial Tutorials> Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial Static Analysis of a Corner Bracket Problem Specification Problem Description Build Geometry Define Materials Generate Mesh Apply
Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial Tutorials> Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial Static Analysis of a Corner Bracket Problem Specification Problem Description Build Geometry Define Materials Generate Mesh Apply
file://c:\documents and Settings\sala\Configuración local\temp\~hha54f.htm
 Página 1 de 26 Tutorials Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial 2.1. Static Analysis of a Corner Bracket 2.1.1. Problem Specification Applicable ANSYS Products: Level of Difficulty: Interactive Time Required:
Página 1 de 26 Tutorials Chapter 2. Structural Tutorial 2.1. Static Analysis of a Corner Bracket 2.1.1. Problem Specification Applicable ANSYS Products: Level of Difficulty: Interactive Time Required:
FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY
 1 FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY In this chapter a first application of PLAXIS 3D is considered, namely the settlement of a foundation in clay. This is the first step in becoming familiar with the
1 FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY In this chapter a first application of PLAXIS 3D is considered, namely the settlement of a foundation in clay. This is the first step in becoming familiar with the
SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND
 1 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND In this chapter a first application is considered, namely the settlement of a circular foundation footing on sand. This is the first step in becoming familiar
1 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND In this chapter a first application is considered, namely the settlement of a circular foundation footing on sand. This is the first step in becoming familiar
TUTORIAL 2. OBJECTIVE: Use SolidWorks/COSMOS to model and analyze a cattle gate bracket that is subjected to a force of 100,000 lbs.
 TUTORIAL 2 OBJECTIVE: Use SolidWorks/COSMOS to model and analyze a cattle gate bracket that is subjected to a force of 100,000 lbs. GETTING STARTED: 1. Open the SolidWorks program. 2. Open a new part file.
TUTORIAL 2 OBJECTIVE: Use SolidWorks/COSMOS to model and analyze a cattle gate bracket that is subjected to a force of 100,000 lbs. GETTING STARTED: 1. Open the SolidWorks program. 2. Open a new part file.
Generative Part Structural Analysis Expert
 CATIA V5 Training Foils Generative Part Structural Analysis Expert Version 5 Release 19 September 2008 EDU_CAT_EN_GPE_FI_V5R19 About this course Objectives of the course Upon completion of this course
CATIA V5 Training Foils Generative Part Structural Analysis Expert Version 5 Release 19 September 2008 EDU_CAT_EN_GPE_FI_V5R19 About this course Objectives of the course Upon completion of this course
ES 230 Strengths Intro to Finite Element Modeling & Analysis Homework Assignment 5
 ES 230 Strengths Intro to Finite Element Modeling & Analysis Homework Assignment 5 The GREAT Combined Load Problem Moving on to Principal Stresses and von Mises Failure Criteria Open up your ANSYS model
ES 230 Strengths Intro to Finite Element Modeling & Analysis Homework Assignment 5 The GREAT Combined Load Problem Moving on to Principal Stresses and von Mises Failure Criteria Open up your ANSYS model
Analysis Steps 1. Start Abaqus and choose to create a new model database
 Source: Online tutorials for ABAQUS Problem Description The two dimensional bridge structure, which consists of steel T sections (b=0.25, h=0.25, I=0.125, t f =t w =0.05), is simply supported at its lower
Source: Online tutorials for ABAQUS Problem Description The two dimensional bridge structure, which consists of steel T sections (b=0.25, h=0.25, I=0.125, t f =t w =0.05), is simply supported at its lower
Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam
 Problem Specification Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam Consider the beam in the figure below. It is clamped on the left side and has a point force of 8kN acting
Problem Specification Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam Consider the beam in the figure below. It is clamped on the left side and has a point force of 8kN acting
Pro MECHANICA STRUCTURE WILDFIRE 4. ELEMENTS AND APPLICATIONS Part I. Yves Gagnon, M.A.Sc. Finite Element Analyst & Structural Consultant SDC
 Pro MECHANICA STRUCTURE WILDFIRE 4 ELEMENTS AND APPLICATIONS Part I Yves Gagnon, M.A.Sc. Finite Element Analyst & Structural Consultant SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com
Pro MECHANICA STRUCTURE WILDFIRE 4 ELEMENTS AND APPLICATIONS Part I Yves Gagnon, M.A.Sc. Finite Element Analyst & Structural Consultant SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com
Advanced Meshing Tools
 Page 1 Advanced Meshing Tools Preface Using This Guide More Information Conventions What's New? Getting Started Entering the Advanced Meshing Tools Workbench Defining the Surface Mesh Parameters Setting
Page 1 Advanced Meshing Tools Preface Using This Guide More Information Conventions What's New? Getting Started Entering the Advanced Meshing Tools Workbench Defining the Surface Mesh Parameters Setting
Exercise Guide. Published: August MecSoft Corpotation
 VisualCAD Exercise Guide Published: August 2018 MecSoft Corpotation Copyright 1998-2018 VisualCAD 2018 Exercise Guide by Mecsoft Corporation User Notes: Contents 2 Table of Contents About this Guide 4
VisualCAD Exercise Guide Published: August 2018 MecSoft Corpotation Copyright 1998-2018 VisualCAD 2018 Exercise Guide by Mecsoft Corporation User Notes: Contents 2 Table of Contents About this Guide 4
Structural Analysis of an Aluminum Spiral Staircase. EMCH 407 Final Project Presented by: Marcos Lopez and Dillan Nguyen
 Structural Analysis of an Aluminum Spiral Staircase EMCH 407 Final Project Presented by: Marcos Lopez and Dillan Nguyen Abstract An old aluminum spiral staircase at Marcos home has been feeling really
Structural Analysis of an Aluminum Spiral Staircase EMCH 407 Final Project Presented by: Marcos Lopez and Dillan Nguyen Abstract An old aluminum spiral staircase at Marcos home has been feeling really
Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam
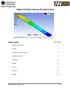 Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Workbench Analysis System 4 Engineering Data 5 Geometry 6 Model 11 Setup 13 Solution 14 Results
Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Workbench Analysis System 4 Engineering Data 5 Geometry 6 Model 11 Setup 13 Solution 14 Results
Quarter Symmetry Tank Stress (Draft 4 Oct 24 06)
 Quarter Symmetry Tank Stress (Draft 4 Oct 24 06) Introduction You need to carry out the stress analysis of an outdoor water tank. Since it has quarter symmetry you start by building only one-fourth of
Quarter Symmetry Tank Stress (Draft 4 Oct 24 06) Introduction You need to carry out the stress analysis of an outdoor water tank. Since it has quarter symmetry you start by building only one-fourth of
Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10
 Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10 This document contains an Abaqus tutorial for performing a buckling analysis using the finite element program
Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10 This document contains an Abaqus tutorial for performing a buckling analysis using the finite element program
Exercise 2: Bike Frame Analysis
 Exercise 2: Bike Frame Analysis This exercise will analyze a new, innovative mountain bike frame design under structural loads. The objective is to determine the maximum stresses in the frame due to the
Exercise 2: Bike Frame Analysis This exercise will analyze a new, innovative mountain bike frame design under structural loads. The objective is to determine the maximum stresses in the frame due to the
Exercise 2: Bike Frame Analysis
 Exercise 2: Bike Frame Analysis This exercise will analyze a new, innovative mountain bike frame design under structural loads. The objective is to determine the maximum stresses in the frame due to the
Exercise 2: Bike Frame Analysis This exercise will analyze a new, innovative mountain bike frame design under structural loads. The objective is to determine the maximum stresses in the frame due to the
Aufgabe 1: Dreipunktbiegung mit ANSYS Workbench
 Aufgabe 1: Dreipunktbiegung mit ANSYS Workbench Contents Beam under 3-Pt Bending [Balken unter 3-Pkt-Biegung]... 2 Taking advantage of symmetries... 3 Starting and Configuring ANSYS Workbench... 4 A. Pre-Processing:
Aufgabe 1: Dreipunktbiegung mit ANSYS Workbench Contents Beam under 3-Pt Bending [Balken unter 3-Pkt-Biegung]... 2 Taking advantage of symmetries... 3 Starting and Configuring ANSYS Workbench... 4 A. Pre-Processing:
Parametric Modeling with UGS NX 4
 Parametric Modeling with UGS NX 4 Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com 2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling
Parametric Modeling with UGS NX 4 Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com 2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS
 Problem Description: FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Dimitri Soteropoulos Programs Utilized: Abaqus/CAE 6.11-2 This tutorial explains how to build
Problem Description: FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Dimitri Soteropoulos Programs Utilized: Abaqus/CAE 6.11-2 This tutorial explains how to build
Introduction To Finite Element Analysis
 Creating a Part In this part of the tutorial we will introduce you to some basic modelling concepts. If you are already familiar with modelling in Pro Engineer you will find this section very easy. Before
Creating a Part In this part of the tutorial we will introduce you to some basic modelling concepts. If you are already familiar with modelling in Pro Engineer you will find this section very easy. Before
CATIA V5 Parametric Surface Modeling
 CATIA V5 Parametric Surface Modeling Version 5 Release 16 A- 1 Toolbars in A B A. Wireframe: Create 3D curves / lines/ points/ plane B. Surfaces: Create surfaces C. Operations: Join surfaces, Split & Trim
CATIA V5 Parametric Surface Modeling Version 5 Release 16 A- 1 Toolbars in A B A. Wireframe: Create 3D curves / lines/ points/ plane B. Surfaces: Create surfaces C. Operations: Join surfaces, Split & Trim
Exercise 2: Mesh Resolution, Element Shapes, Basis Functions & Convergence Analyses
 Exercise 2: Mesh Resolution, Element Shapes, Basis Functions & Convergence Analyses Goals In this exercise, we will explore the strengths and weaknesses of different element types (tetrahedrons vs. hexahedrons,
Exercise 2: Mesh Resolution, Element Shapes, Basis Functions & Convergence Analyses Goals In this exercise, we will explore the strengths and weaknesses of different element types (tetrahedrons vs. hexahedrons,
Abaqus/CAE Axisymmetric Tutorial (Version 2016)
 Abaqus/CAE Axisymmetric Tutorial (Version 2016) Problem Description A round bar with tapered diameter has a total load of 1000 N applied to its top face. The bottom of the bar is completely fixed. Determine
Abaqus/CAE Axisymmetric Tutorial (Version 2016) Problem Description A round bar with tapered diameter has a total load of 1000 N applied to its top face. The bottom of the bar is completely fixed. Determine
Parametric Modeling. With. Autodesk Inventor. Randy H. Shih. Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS
 Parametric Modeling With Autodesk Inventor R10 Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com 2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric
Parametric Modeling With Autodesk Inventor R10 Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com 2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric
Tutorial 1: Welded Frame - Problem Description
 Tutorial 1: Welded Frame - Problem Description Introduction In this first tutorial, we will analyse a simple frame: firstly as a welded frame, and secondly as a pin jointed truss. In each case, we will
Tutorial 1: Welded Frame - Problem Description Introduction In this first tutorial, we will analyse a simple frame: firstly as a welded frame, and secondly as a pin jointed truss. In each case, we will
The part to be analyzed is the bracket from the tutorial of Chapter 3.
 Introduction to Solid Modeling Using SolidWorks 2007 COSMOSWorks Tutorial Page 1 In this tutorial, we will use the COSMOSWorks finite element analysis (FEA) program to analyze the response of a component
Introduction to Solid Modeling Using SolidWorks 2007 COSMOSWorks Tutorial Page 1 In this tutorial, we will use the COSMOSWorks finite element analysis (FEA) program to analyze the response of a component
Exercise 1: 3-Pt Bending using ANSYS Workbench
 Exercise 1: 3-Pt Bending using ANSYS Workbench Contents Starting and Configuring ANSYS Workbench... 2 1. Starting Windows on the MAC... 2 2. Login into Windows... 2 3. Start ANSYS Workbench... 2 4. Configuring
Exercise 1: 3-Pt Bending using ANSYS Workbench Contents Starting and Configuring ANSYS Workbench... 2 1. Starting Windows on the MAC... 2 2. Login into Windows... 2 3. Start ANSYS Workbench... 2 4. Configuring
CHAPTER 8 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS
 If you have any questions about this tutorial, feel free to contact Wenjin Tao (w.tao@mst.edu). CHAPTER 8 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is a practical application of the Finite
If you have any questions about this tutorial, feel free to contact Wenjin Tao (w.tao@mst.edu). CHAPTER 8 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is a practical application of the Finite
ME Week 12 Piston Mechanical Event Simulation
 Introduction to Mechanical Event Simulation The purpose of this introduction to Mechanical Event Simulation (MES) project is to explorer the dynamic simulation environment of Autodesk Simulation. This
Introduction to Mechanical Event Simulation The purpose of this introduction to Mechanical Event Simulation (MES) project is to explorer the dynamic simulation environment of Autodesk Simulation. This
Module 1.3W Distributed Loading of a 1D Cantilever Beam
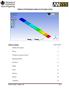 Module 1.3W Distributed Loading of a 1D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Workbench Analysis System 4 Engineering Data 5 Geometry 6 Model 11 Setup 13 Solution
Module 1.3W Distributed Loading of a 1D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Workbench Analysis System 4 Engineering Data 5 Geometry 6 Model 11 Setup 13 Solution
Finite Element Analysis Using NEi Nastran
 Appendix B Finite Element Analysis Using NEi Nastran B.1 INTRODUCTION NEi Nastran is engineering analysis and simulation software developed by Noran Engineering, Inc. NEi Nastran is a general purpose finite
Appendix B Finite Element Analysis Using NEi Nastran B.1 INTRODUCTION NEi Nastran is engineering analysis and simulation software developed by Noran Engineering, Inc. NEi Nastran is a general purpose finite
ANSYS Workbench Guide
 ANSYS Workbench Guide Introduction This document serves as a step-by-step guide for conducting a Finite Element Analysis (FEA) using ANSYS Workbench. It will cover the use of the simulation package through
ANSYS Workbench Guide Introduction This document serves as a step-by-step guide for conducting a Finite Element Analysis (FEA) using ANSYS Workbench. It will cover the use of the simulation package through
Multi-Step Analysis of a Cantilever Beam
 LESSON 4 Multi-Step Analysis of a Cantilever Beam LEGEND 75000. 50000. 25000. 0. -25000. -50000. -75000. 0. 3.50 7.00 10.5 14.0 17.5 21.0 Objectives: Demonstrate multi-step analysis set up in MSC/Advanced_FEA.
LESSON 4 Multi-Step Analysis of a Cantilever Beam LEGEND 75000. 50000. 25000. 0. -25000. -50000. -75000. 0. 3.50 7.00 10.5 14.0 17.5 21.0 Objectives: Demonstrate multi-step analysis set up in MSC/Advanced_FEA.
CATIA V5 Analysis. CATIA V5 Training Foils. CATIA V5 Analysis. Copyright DASSAULT SYSTEMES 1. Student Notes:
 CATIA V5 Training Foils CATIA V5 Analysis Version 5 Release 19 January 2009 EDU_CAT_EN_V5A_FF_V5R19 1 Lesson 1: Introduction to Finite Element Analysis About this Course Introduction CATIA is a robust
CATIA V5 Training Foils CATIA V5 Analysis Version 5 Release 19 January 2009 EDU_CAT_EN_V5A_FF_V5R19 1 Lesson 1: Introduction to Finite Element Analysis About this Course Introduction CATIA is a robust
Linear and Nonlinear Analysis of a Cantilever Beam
 LESSON 1 Linear and Nonlinear Analysis of a Cantilever Beam P L Objectives: Create a beam database to be used for the specified subsequent exercises. Compare small vs. large displacement analysis. Linear
LESSON 1 Linear and Nonlinear Analysis of a Cantilever Beam P L Objectives: Create a beam database to be used for the specified subsequent exercises. Compare small vs. large displacement analysis. Linear
CHAPTER 4. Numerical Models. descriptions of the boundary conditions, element types, validation, and the force
 CHAPTER 4 Numerical Models This chapter presents the development of numerical models for sandwich beams/plates subjected to four-point bending and the hydromat test system. Detailed descriptions of the
CHAPTER 4 Numerical Models This chapter presents the development of numerical models for sandwich beams/plates subjected to four-point bending and the hydromat test system. Detailed descriptions of the
Module 1.7: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.7: Point Loading of a D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 6 Element Type 6 Material Properties 7 Meshing 8 Loads 9 Solution 15 General
Module 1.7: Point Loading of a D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description Theory Geometry 4 Preprocessor 6 Element Type 6 Material Properties 7 Meshing 8 Loads 9 Solution 15 General
ANSYS. Geometry. Material Properties. E=2.8E7 psi v=0.3. ansys.fem.ir Written By:Mehdi Heydarzadeh Page 1
 Attention: This tutorial is outdated, you will be redirected automatically to the new site. If you are not redirected, click this link to the confluence site. Problem Specification Geometry Material Properties
Attention: This tutorial is outdated, you will be redirected automatically to the new site. If you are not redirected, click this link to the confluence site. Problem Specification Geometry Material Properties
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Stepped Shaft in Axial Tension
 ANSYS AIM Tutorial Stepped Shaft in Axial Tension Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Contents: Problem Specification 3 Learning Goals 4 Pre-Analysis & Start Up 5 Calculation
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Stepped Shaft in Axial Tension Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Contents: Problem Specification 3 Learning Goals 4 Pre-Analysis & Start Up 5 Calculation
16 SW Simulation design resources
 16 SW Simulation design resources 16.1 Introduction This is simply a restatement of the SW Simulation online design scenarios tutorial with a little more visual detail supplied on the various menu picks
16 SW Simulation design resources 16.1 Introduction This is simply a restatement of the SW Simulation online design scenarios tutorial with a little more visual detail supplied on the various menu picks
Learning Module 8 Shape Optimization
 Learning Module 8 Shape Optimization What is a Learning Module? Title Page Guide A Learning Module (LM) is a structured, concise, and self-sufficient learning resource. An LM provides the learner with
Learning Module 8 Shape Optimization What is a Learning Module? Title Page Guide A Learning Module (LM) is a structured, concise, and self-sufficient learning resource. An LM provides the learner with
Exercise 1. 3-Point Bending Using the Static Structural Module of. Ansys Workbench 14.0
 Exercise 1 3-Point Bending Using the Static Structural Module of Contents Ansys Workbench 14.0 Learn how to...1 Given...2 Questions...2 Taking advantage of symmetries...2 A. Getting started...3 A.1 Choose
Exercise 1 3-Point Bending Using the Static Structural Module of Contents Ansys Workbench 14.0 Learn how to...1 Given...2 Questions...2 Taking advantage of symmetries...2 A. Getting started...3 A.1 Choose
Introduction: RS 3 Tutorial 1 Quick Start
 Introduction: RS 3 Tutorial 1 Quick Start Welcome to RS 3. This tutorial introduces some basic features of RS 3. The model analyzes the effect of tank loading on an existing sloped underground tunnel.
Introduction: RS 3 Tutorial 1 Quick Start Welcome to RS 3. This tutorial introduces some basic features of RS 3. The model analyzes the effect of tank loading on an existing sloped underground tunnel.
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS
 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Michael Schraiber, Dimitri Soteropoulos Programs Utilized: HyperMesh Desktop v12.0, OptiStruct, HyperView This tutorial
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Michael Schraiber, Dimitri Soteropoulos Programs Utilized: HyperMesh Desktop v12.0, OptiStruct, HyperView This tutorial
Lesson 6: Assembly Structural Analysis
 Lesson 6: Assembly Structural Analysis In this lesson you will learn different approaches to analyze the assembly using assembly analysis connection properties between assembly components. In addition
Lesson 6: Assembly Structural Analysis In this lesson you will learn different approaches to analyze the assembly using assembly analysis connection properties between assembly components. In addition
Lesson 5: Mesh Refinement
 Lesson 5: Mesh Refinement In this lesson, you will learn how to improve accuracy of solution using mesh refinement techniques. Lesson content: Case Study: Drill Press Table Mesh Refinement Design Intent
Lesson 5: Mesh Refinement In this lesson, you will learn how to improve accuracy of solution using mesh refinement techniques. Lesson content: Case Study: Drill Press Table Mesh Refinement Design Intent
In-plane principal stress output in DIANA
 analys: linear static. class: large. constr: suppor. elemen: hx24l solid tp18l. load: edge elemen force node. materi: elasti isotro. option: direct. result: cauchy displa princi stress total. In-plane
analys: linear static. class: large. constr: suppor. elemen: hx24l solid tp18l. load: edge elemen force node. materi: elasti isotro. option: direct. result: cauchy displa princi stress total. In-plane
A pipe bend is subjected to a concentrated force as shown: y All dimensions in inches. Material is stainless steel.
 Problem description A pipe bend is subjected to a concentrated force as shown: y 15 12 P 9 Displacement gauge Cross-section: 0.432 18 x 6.625 All dimensions in inches. Material is stainless steel. E =
Problem description A pipe bend is subjected to a concentrated force as shown: y 15 12 P 9 Displacement gauge Cross-section: 0.432 18 x 6.625 All dimensions in inches. Material is stainless steel. E =
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS
 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Michael Schraiber, Dimitri Soteropoulos, Sanjay Nainani Programs Utilized: HyperMesh Desktop v2017.2, OptiStruct,
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Michael Schraiber, Dimitri Soteropoulos, Sanjay Nainani Programs Utilized: HyperMesh Desktop v2017.2, OptiStruct,
Revised Sheet Metal Simulation, J.E. Akin, Rice University
 Revised Sheet Metal Simulation, J.E. Akin, Rice University A SolidWorks simulation tutorial is just intended to illustrate where to find various icons that you would need in a real engineering analysis.
Revised Sheet Metal Simulation, J.E. Akin, Rice University A SolidWorks simulation tutorial is just intended to illustrate where to find various icons that you would need in a real engineering analysis.
Introduction to MSC.Patran
 Exercise 1 Introduction to MSC.Patran Objectives: Create geometry for a Beam. Add Loads and Boundary Conditions. Review analysis results. MSC.Patran 301 Exercise Workbook - Release 9.0 1-1 1-2 MSC.Patran
Exercise 1 Introduction to MSC.Patran Objectives: Create geometry for a Beam. Add Loads and Boundary Conditions. Review analysis results. MSC.Patran 301 Exercise Workbook - Release 9.0 1-1 1-2 MSC.Patran
FEMAP Tutorial 2. Figure 1: Bar with defined dimensions
 FEMAP Tutorial 2 Consider a cantilevered beam with a vertical force applied to the right end. We will utilize the same geometry as the previous tutorial that considered an axial loading. Thus, this tutorial
FEMAP Tutorial 2 Consider a cantilevered beam with a vertical force applied to the right end. We will utilize the same geometry as the previous tutorial that considered an axial loading. Thus, this tutorial
ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IIA FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IIA LOCATION: DPO EXPERIMENT 3D7 FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Those who have performed the 3C7 experiment should bring the write-up along to this laboratory Objectives Show that the accuracy
ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IIA LOCATION: DPO EXPERIMENT 3D7 FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Those who have performed the 3C7 experiment should bring the write-up along to this laboratory Objectives Show that the accuracy
Problem description. It is desired to analyze the cracked body shown using a 3D finite element mesh: Top view. 50 radius. Material properties:
 Problem description It is desired to analyze the cracked body shown using a 3D finite element mesh: Top view 30 50 radius 30 Material properties: 5 2 E = 2.07 10 N/mm = 0.29 All dimensions in mm Crack
Problem description It is desired to analyze the cracked body shown using a 3D finite element mesh: Top view 30 50 radius 30 Material properties: 5 2 E = 2.07 10 N/mm = 0.29 All dimensions in mm Crack
Module 1: Basics of Solids Modeling with SolidWorks
 Module 1: Basics of Solids Modeling with SolidWorks Introduction SolidWorks is the state of the art in computer-aided design (CAD). SolidWorks represents an object in a virtual environment just as it exists
Module 1: Basics of Solids Modeling with SolidWorks Introduction SolidWorks is the state of the art in computer-aided design (CAD). SolidWorks represents an object in a virtual environment just as it exists
Module 4A: Creating the 3D Model of Right and Oblique Pyramids
 Inventor (5) Module 4A: 4A- 1 Module 4A: Creating the 3D Model of Right and Oblique Pyramids In Module 4A, we will learn how to create 3D solid models of right-axis and oblique-axis pyramid (regular or
Inventor (5) Module 4A: 4A- 1 Module 4A: Creating the 3D Model of Right and Oblique Pyramids In Module 4A, we will learn how to create 3D solid models of right-axis and oblique-axis pyramid (regular or
Getting Started. These tasks should take about 20 minutes to complete. Getting Started
 Getting Started Getting Started This tutorial will guide you step-by-step through your first ELFINI and Generative Part Structural Analysis session, allowing you to get acquainted with the product. You
Getting Started Getting Started This tutorial will guide you step-by-step through your first ELFINI and Generative Part Structural Analysis session, allowing you to get acquainted with the product. You
SolidWorks. An Overview of SolidWorks and Its Associated Analysis Programs
 An Overview of SolidWorks and Its Associated Analysis Programs prepared by Prof. D. Xue University of Calgary SolidWorks - a solid modeling CAD tool. COSMOSWorks - a design analysis system fully integrated
An Overview of SolidWorks and Its Associated Analysis Programs prepared by Prof. D. Xue University of Calgary SolidWorks - a solid modeling CAD tool. COSMOSWorks - a design analysis system fully integrated
Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.12) Vibrations Tutorial
 Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.12) Vibrations Tutorial Problem Description The two dimensional bridge structure, which consists of steel T sections, is simply supported at its lower corners. Determine the first 10
Abaqus/CAE (ver. 6.12) Vibrations Tutorial Problem Description The two dimensional bridge structure, which consists of steel T sections, is simply supported at its lower corners. Determine the first 10
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING. Part-1
 COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING Course no. 7962 Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Part-1 Modeling & Simulation System A system exists and operates in time and space.
COMPUTER AIDED ENGINEERING Course no. 7962 Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Finite Element Modelling and Simulation Part-1 Modeling & Simulation System A system exists and operates in time and space.
3 AXIS STANDARD CAD. BobCAD-CAM Version 28 Training Workbook 3 Axis Standard CAD
 3 AXIS STANDARD CAD This tutorial explains how to create the CAD model for the Mill 3 Axis Standard demonstration file. The design process includes using the Shape Library and other wireframe functions
3 AXIS STANDARD CAD This tutorial explains how to create the CAD model for the Mill 3 Axis Standard demonstration file. The design process includes using the Shape Library and other wireframe functions
Lesson 1 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals
 1-1 Lesson 1 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Parametric Models. Understand the Basic Parametric Modeling Process. Create and Profile Rough Sketches. Understand the "Shape before size" approach.
1-1 Lesson 1 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Parametric Models. Understand the Basic Parametric Modeling Process. Create and Profile Rough Sketches. Understand the "Shape before size" approach.
Tutorial Second Level
 AutoCAD 2018 Tutorial Second Level 3D Modeling Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites to learn
AutoCAD 2018 Tutorial Second Level 3D Modeling Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites to learn
Installation Guide. Beginners guide to structural analysis
 Installation Guide To install Abaqus, students at the School of Civil Engineering, Sohngaardsholmsvej 57, should log on to \\studserver, whereas the staff at the Department of Civil Engineering should
Installation Guide To install Abaqus, students at the School of Civil Engineering, Sohngaardsholmsvej 57, should log on to \\studserver, whereas the staff at the Department of Civil Engineering should
Nerf Blaster Redesign
 Nerf Blaster Redesign ME4041 Computer Graphics and CAD April 0, 010 Submitted By: Michael Schulman Greg Mann Table of Contents Introduction. Objectives Modeling. 4 External Components 4 Internal Components.
Nerf Blaster Redesign ME4041 Computer Graphics and CAD April 0, 010 Submitted By: Michael Schulman Greg Mann Table of Contents Introduction. Objectives Modeling. 4 External Components 4 Internal Components.
NEW WAVE OF CAD SYSTEMS AND ITS APPLICATION IN DESIGN
 Vol 4 No 3 NEW WAVE OF CAD SYSTEMS AND ITS APPLICATION IN DESIGN Ass Lecturer Mahmoud A Hassan Al-Qadisiyah University College of Engineering hasaaneng@yahoocom ABSTRACT This paper provides some lighting
Vol 4 No 3 NEW WAVE OF CAD SYSTEMS AND ITS APPLICATION IN DESIGN Ass Lecturer Mahmoud A Hassan Al-Qadisiyah University College of Engineering hasaaneng@yahoocom ABSTRACT This paper provides some lighting
Optimizing the Utility Scale Solar Megahelion Drive End-Cap (Imperial Units)
 Autodesk Inventor Tutorial Exercise Optimizing the Utility Scale Solar Megahelion Drive End-Cap www.autodesk.com/sustainabilityworkshop Contents OPTIMIZING THE USS SOLAR TRACKING END CAP... 3 OBJECTIVE...
Autodesk Inventor Tutorial Exercise Optimizing the Utility Scale Solar Megahelion Drive End-Cap www.autodesk.com/sustainabilityworkshop Contents OPTIMIZING THE USS SOLAR TRACKING END CAP... 3 OBJECTIVE...
ES 230 Strengths Intro to Finite Element Modeling & Analysis Homework Assignment 2
 ES 230 Strengths Intro to Finite Element Modeling & Analysis Homework Assignment 2 In this homework assignment you will use your rapidly developing ANSYS skill set to model and analyze three different
ES 230 Strengths Intro to Finite Element Modeling & Analysis Homework Assignment 2 In this homework assignment you will use your rapidly developing ANSYS skill set to model and analyze three different
Spur Gears Static Stress Analysis with Linear Material Models
 Exercise A Spur Gears Static Stress Analysis with Linear Material Models Beam and Brick Elements Objective: Geometry: Determine the stress distribution in the spur gears when a moment of 93.75 in-lb is
Exercise A Spur Gears Static Stress Analysis with Linear Material Models Beam and Brick Elements Objective: Geometry: Determine the stress distribution in the spur gears when a moment of 93.75 in-lb is
NX Tutorial - Centroids and Area Moments of Inertia ENAE 324 Aerospace Structures Spring 2015
 NX will automatically calculate area and mass information about any beam cross section you can think of. This tutorial will show you how to display a section s centroid, principal axes, 2 nd moments of
NX will automatically calculate area and mass information about any beam cross section you can think of. This tutorial will show you how to display a section s centroid, principal axes, 2 nd moments of
Autodesk Inventor - Basics Tutorial Exercise 1
 Autodesk Inventor - Basics Tutorial Exercise 1 Launch Inventor Professional 2015 1. Start a New part. Depending on how Inventor was installed, using this icon may get you an Inch or Metric file. To be
Autodesk Inventor - Basics Tutorial Exercise 1 Launch Inventor Professional 2015 1. Start a New part. Depending on how Inventor was installed, using this icon may get you an Inch or Metric file. To be
3. Preprocessing of ABAQUS/CAE
 3.1 Create new model database 3. Preprocessing of ABAQUS/CAE A finite element analysis in ABAQUS/CAE starts from create new model database in the toolbar. Then save it with a name user defined. To build
3.1 Create new model database 3. Preprocessing of ABAQUS/CAE A finite element analysis in ABAQUS/CAE starts from create new model database in the toolbar. Then save it with a name user defined. To build
Analysis of Machine Elements Using SolidWorks Simulation 2013
 Analysis of Machine Elements Using SolidWorks Simulation 2013 John R. Steffen, Ph.D., P.E. SDC P U B L I C AT I O N S Schroff Development Corporation Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com
Analysis of Machine Elements Using SolidWorks Simulation 2013 John R. Steffen, Ph.D., P.E. SDC P U B L I C AT I O N S Schroff Development Corporation Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com
CATIA Electrical Space Reservation TABLE OF CONTENTS
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...1 Manual Format...2 Electrical Reservations...3 Equipment Reservations...5 Pathway Reservations...31 Advanced Reservations...49 Reservation Analysis...67 Clash...69 Sectioning...73
TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...1 Manual Format...2 Electrical Reservations...3 Equipment Reservations...5 Pathway Reservations...31 Advanced Reservations...49 Reservation Analysis...67 Clash...69 Sectioning...73
An Introduction to Autodesk Inventor 2010 and AutoCAD Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS. Schroff Development Corporation
 An Introduction to Autodesk Inventor 2010 and AutoCAD 2010 Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com 2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Extruded
An Introduction to Autodesk Inventor 2010 and AutoCAD 2010 Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com 2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Extruded
A Comprehensive Introduction to SolidWorks 2011
 A Comprehensive Introduction to SolidWorks 2011 Godfrey Onwubolu, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation Chapter 2 Geometric Construction Tools Objectives: When
A Comprehensive Introduction to SolidWorks 2011 Godfrey Onwubolu, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation Chapter 2 Geometric Construction Tools Objectives: When
Finite Element Analysis Using Creo Simulate 4.0
 Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Using Creo Simulate 4.0 Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following
Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Using Creo Simulate 4.0 Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following
Parametric Modeling. with. Autodesk Inventor Randy H. Shih. Oregon Institute of Technology SDC
 Parametric Modeling with Autodesk Inventor 2009 Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. 2-1 Chapter
Parametric Modeling with Autodesk Inventor 2009 Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. 2-1 Chapter
