Soil Trace Element Model (Single Layer) Documentation
|
|
|
- Clemence Allison
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Soil Trace Element Model (Single Layer) Documentation Written by Weiping Chen, Edited by Xuan Wu Model Structure The model was used to evaluate the long-term behavior of trace elements (TE) in cropland soils and to evaluate the effects of soil characteristics, plant uptake factors, and input sources on trace element accumulation in receiving soils. The model frame is based on mass balance. The change in total metal content (T) in the root zone is balanced with the input (I) at the soil surface, the output caused by leaching from the root zone, and by uptake removal in harvested products. In the model, dynamic uptake and leaching related to trace element soil solution concentration were adopted; two important chemical processes, adsorption-desorption and precipitation-dissolution, were considered as well, which affect the soil solution concentration dynamically. In addition, part of the plant uptake will be reintroduced into the soil through biomass return in organic form and the mineralization of the TE in organic phase will in turn contribute to the change in the soil solution. An illustration of the model structure follows. External Inputs (I) Plant Uptake (U) Mineral Phase (M) Solution Phase (C) Adsorbed Phase (Ad) Labile Phase (Q) Organic Phase (O) ROOT ZONE Leached
2 The change in the mobile trace element concentration in soil (Q, µmol/l soil) with time in a completely mixed soil layer is described by the continuity equation: Q F M O = + + U + I [Eq. 1] z In the model, the trace elements in mobile phase Q (µmol/l soil) are represented by those in solution and those adsorbed by the soil (exchangeable and surface adsorbed part), which is in instantaneous equilibrium with soil solution concentration. Thus, Q = Ad + θ C = K d C + θ C [Eq. 2] where K d is the linear adsorption constant (L soil solution/l soil), θ is the volumetric water content of the soil (L/L), and C is the trace element concentration in the soil solution (µm). M represents another important chemical process: precipitation-dissolution, which also affects the soil solution concentration. The trace element solubility is controlled by the mineral phase and the kinetics is described by: M = k f (K d + θ)c kb M [Eq. 3] where k f and k b (hr -1 ) are the forward and backward precipitation/dissolution rate constants, respectively. In the model, the first order mineralization process of organic matter was used: O kim O = [Eq. 4] where k im is the mineralization rate constant (hr -1 ) and O is the organic matter content (µmol/l soil). The term L represents the downward transport flux (leaching), which is described by: L = K bf θ f C [Eq. 5] where K bf is the percolation rate (cm hr -1 ) at the field water content θ f.
3 The term U represents the plant uptake process that is described by: U R J = [Eq. 6] d where R is root density (cm root cm -2 soil) in the soil layer of depth d (cm), and J (µmol cm -1 root hr -1 ) is the flux of trace element uptake by the roots described by the Michaelis-Menten kinetics equation: J J C = max [Eq. 7] K + m C where J max is the maximum J and K m is the root permeability coefficient (µm). The term I represents the input flux of the addition of trace elements to the soil. It comprises the trace element that is found in P fertilizers, irrigation water, atmospheric deposition, and other sources. The model integrates all of these processes and equations to evaluate the long-term behavior of TE in cropland soils.
4 Model Application For running the model, the user needs to enter the data for simulation or open an existing input file. There are 7 separate sections for entering different types of information, which will be described below. General Information. Here, the user specifies the simulation type to be conducted standard, sensitivity, or uncertainty analysis. The standard analysis will perform one simulation according to the data entered, the sensitivity analysis allows the user to conduct multiple simulations by varying the value of one model parameter, and the uncertainty analysis allows the user to conduct Monte Carlo simulations according to the probability distributions of the uncertain parameters. Then, the user enters the trace element to be evaluated. This entry globally sets the element name to be displayed in all of the data summary and output files. Finally, the user selects the number of simulations to be run when uncertainty analysis is selected. This option is only available when running the uncertainty analysis. The computation time is directly dependent on the number of simulations to be conducted. The user may go to the File menu on top left corner of the screen and selects Open Input File (Ctrl+O). When this menu option is selected, an Open File dialog box appears to let the user choose from previously saved input files. This model ships with some default files. The data entry boxes will be loaded with data from the file. When all the boxes are filled, the user may proceed by clicking on the Run button at the bottom right corner of the window. The user may manually change a value in a data entry box should it need modification. To reset the data entry boxes to a clean state, the user may selected New Input (Ctrl+N) from the File menu. The data entry boxes will be cleared and ready for entering the new data. The user may also save his/her own inputs by selected Save (Ctrl+S) or Save File As (F12) from the File menu. Selecting Save after modifying an opened file will overwrite that file. Simulation Period. The time parameters for the simulation are provided in this section. The beginning time usually is 0 and the ending time is dependent on the number of years to be simulated. Specifying 0 for beginning time and 10 for ending time should give the same result as specifying 1990 for beginning time and 2000 for ending time. The Computation Time Step specifies the time resolution of the simulation; the user enters the number of hours that each simulation time step spans. It may be set at 10 or larger. Smaller time steps may provide more accurate computation but will take longer for the simulation to finish and will require more memory. The Output Summary Time Step determines the temporal separation of each entry in the output data table.
5 Initial TE Pools. In this section, the user needs to enter the initial values for the trace element pools of the soils. TE denotes the trace element under consideration. Each entry box is selfexplanatory (see Model Structure for more details). They include: concentrations in soil solution, mineral phase, organic phase, and total TE content in the soil. Input Information. In this section, the user enters information on trace element inputs. The Continuous Input mode will uniformly distribute the specified input rate over each computation time step. The Point Source Input mode allows the user to enter specific days on which to add trace element to the soil. To edit the Point Source Input, click the data entry box and a table will appear for entering the inputs in tabulated form. The model can accept continuous inputs (i.e. atmospheric fallout) and point source inputs (i.e. fertilizer applications and irrigation) simultaneously. Soil Properties. In this section, information on the properties of the soil is provided. Profile Depth refers to the depth of soil being considered in the simulation. Usually, it is the depth of the root zone. Other parameters to be entered (Bulk Density, Percolation Rate, and Volumetric Water Content) are self-explanatory and correspond to the same parameters defined in the mathematical forms of the model (see Model Structure). For standard simulation and sensitivity analysis only the mean values are needed. For uncertainty analysis, the variance and probability distribution of the parameters also need to be specified. Plant Uptake Information. In this section, the parameters that define the plant uptake of trace elements are specified. They include the Root Permeability Coefficient (K m ), Maximum Influx (V max ), and Root Density (R). They correspond to the parameters in the mass balance model described in Model Structure. Among them, the Maximum Influx and Root Density are uncertain parameters and their variance and probability distribution should be specified for uncertainty analysis. In addition, the fraction of the harvested biomass that is reincorporated should also be specified. It is assumed that comparable amounts of the trace elements absorbed by plants in the previous half year will reenter the soil in the organic form. Constants. In this section, reaction constants that define the transformation of trace elements among different pools are entered. They are the TE Adsorption Constant (K d ), Mineralization Rate (K im ), and the forward and backward Precipitation/Dissolution Rate (k f and k b ). (See equations 2, 3, and 4.)
6 Results When data entry is completed, Click the Run button at the lower right corner of the screen. The simulation begins and a small screen will appear to track the progress of the computation. It generally takes only a few seconds for a standard simulation to complete. The time required for the sensitivity and uncertainty analysis is dependent on the number of simulations to be run. When the simulation completes, a window will appear with the results. The outputs are organized into tabs. The Simulation Parameters tab summarizes the input data used in the simulation. The user can go to the file menu on top left corner of the output screen and select Save Output (Ctrl+S) to save all the results, including simulation parameters, data tables, and graphs. The Mass Balance tab shows the mass balance of trace element over the simulation period, including the fluxes balance (input, leaching, and uptake removal) and the pools balance (mobile phase, mineral phase, and organic phase). Theoretically, the change in total soil trace element content based on these two types of mass balance should be equal. The user can check it. If the changes are not equal, it means the model computation was not good. The user will have to adjust the time step. If the user wants to check the mass balance at any other period, it can be obtained by setting the Beginning Time and Ending Time in the output interface and clicking the Recompute button. The Simulation Results tab show the temporal change of all the components of the trace element mass balance over the simulation period. It is further divided into tabs, one for output data table, and the rest for plots of individual output parameters. The Data Table tab tabulates the entire set of output data. A legend explaining the abbreviations in each data column is located at the bottom of the screen. Click on Copy Selection at the bottom right corner of the window to copy the data onto the clipboard, from where the user can paste the data into a word processing or spreadsheet program. The tabulated data in the Simulation Parameters and Mass Balance may be exported in the same manner.
7 Contact Weiping Chen may be reached at Xuan Wu may be reached at If you encounter any bugs, please contact Weiping or Xuan as soon as possible.
Appendix 3 Description on Excel files accompanying WaNuLCAS model
 Appendix 3 Description on Excel files accompanying WaNuLCAS model The WaNuLCAS model is accompanied by 2 excel file; Wanulcas.xls and TreeParameterization.xls. Wanulcas.xls contains input parameters and
Appendix 3 Description on Excel files accompanying WaNuLCAS model The WaNuLCAS model is accompanied by 2 excel file; Wanulcas.xls and TreeParameterization.xls. Wanulcas.xls contains input parameters and
Tutorial: Modeling Liquid Reactions in CIJR Using the Eulerian PDF transport (DQMOM-IEM) Model
 Tutorial: Modeling Liquid Reactions in CIJR Using the Eulerian PDF transport (DQMOM-IEM) Model Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to demonstrate setup and solution procedure of liquid chemical
Tutorial: Modeling Liquid Reactions in CIJR Using the Eulerian PDF transport (DQMOM-IEM) Model Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to demonstrate setup and solution procedure of liquid chemical
MT3DMS Advanced Transport MT3DMS dispersion, sorption, and dual domain options
 v. 10.1 GMS 10.1 Tutorial MT3DMS dispersion, sorption, and dual domain options Objectives Learn about the dispersion, sorption, and dual domain options in MT3DMS Prerequisite Tutorials MT2DMS Grid Approach
v. 10.1 GMS 10.1 Tutorial MT3DMS dispersion, sorption, and dual domain options Objectives Learn about the dispersion, sorption, and dual domain options in MT3DMS Prerequisite Tutorials MT2DMS Grid Approach
PHT3D Transport and Mineral Reactions
 v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial PHT3D Geochemical Reactions Objectives Learn about transport and mineral reactions in PHT3D. Prerequisite Tutorials MT3DMS Grid Approach Required Components Grid Module MODFLOW
v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial PHT3D Geochemical Reactions Objectives Learn about transport and mineral reactions in PHT3D. Prerequisite Tutorials MT3DMS Grid Approach Required Components Grid Module MODFLOW
TOUGHREACT Example: Aqueous Transport with Adsorption and Decay
 403 Poyntz Avenue, Suite B Manhattan, KS 66502 USA +1.785.770.8511 www.thunderheadeng.com TOUGHREACT Example: Aqueous Transport with Adsorption and Decay PetraSim 2016.1 Table of Contents Overview...1
403 Poyntz Avenue, Suite B Manhattan, KS 66502 USA +1.785.770.8511 www.thunderheadeng.com TOUGHREACT Example: Aqueous Transport with Adsorption and Decay PetraSim 2016.1 Table of Contents Overview...1
Towards a robust model of planetary thermal profiles
 Towards a robust model of planetary thermal profiles RT Equation: General Solution: RT Equation: General Solution: Extinction coefficient Emission coefficient How would you express the Source function
Towards a robust model of planetary thermal profiles RT Equation: General Solution: RT Equation: General Solution: Extinction coefficient Emission coefficient How would you express the Source function
v MT3DMS Conceptual Model Approach GMS 10.3 Tutorial Using MT3DMS with a conceptual model
 v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial Using MT3DMS with a conceptual model Objectives Learn how to use a conceptual model when using MT3DMS. Perform two transport simulations, analyzing the long-term potential for
v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial Using MT3DMS with a conceptual model Objectives Learn how to use a conceptual model when using MT3DMS. Perform two transport simulations, analyzing the long-term potential for
EXERCISE 3: CALCULATION OF RADON TRANSPORT IN THE ATMOSPHERE FROM URANIUM TAILING SITE AND RESULTING INHALATION DOSES TO REFERENCE INDIVIDUALS
 EXERCISE 3: CALCULATION OF RADON TRANSPORT IN THE ATMOSPHERE FROM URANIUM TAILING SITE AND RESULTING INHALATION DOSES TO REFERENCE INDIVIDUALS 1. General description of problem In this exercise we use
EXERCISE 3: CALCULATION OF RADON TRANSPORT IN THE ATMOSPHERE FROM URANIUM TAILING SITE AND RESULTING INHALATION DOSES TO REFERENCE INDIVIDUALS 1. General description of problem In this exercise we use
RT3D Instantaneous Aerobic Degradation
 GMS TUTORIALS RT3D Instantaneous Aerobic Degradation This tutorial illustrates the steps involved in performing a reactive transport simulation using the RT3D model. Several types of contaminant reactions
GMS TUTORIALS RT3D Instantaneous Aerobic Degradation This tutorial illustrates the steps involved in performing a reactive transport simulation using the RT3D model. Several types of contaminant reactions
Objectives Construct an MT3DMS model using the grid approach, and learn how to simulate heat transport using MT3DMS.
 v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 utorial Simulate heat transport using M3DMS Objectives Construct an M3DMS model using the grid approach, and learn how to simulate heat transport using M3DMS. Prerequisite utorials M3DMS
v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 utorial Simulate heat transport using M3DMS Objectives Construct an M3DMS model using the grid approach, and learn how to simulate heat transport using M3DMS. Prerequisite utorials M3DMS
Porous Reactor with Injection Needle
 Porous Reactor with Injection Needle Introduction This model treats the flow field and species distribution in an experimental reactor for studies of heterogeneous catalysis. The model exemplifies the
Porous Reactor with Injection Needle Introduction This model treats the flow field and species distribution in an experimental reactor for studies of heterogeneous catalysis. The model exemplifies the
ProMISE user manual. System requirements. Installation
 ProMISE user manual Probabilistic model for immiscible separations and extractions (ProMISE) developed by Joost de Folter, is freely available for non-commercial purposes (academic e-mail address required
ProMISE user manual Probabilistic model for immiscible separations and extractions (ProMISE) developed by Joost de Folter, is freely available for non-commercial purposes (academic e-mail address required
ProMISE 2 user manual
 ProMISE 2 user manual Probabilistic model for immiscible separations and extractions (ProMISE) developed by Joost de Folter, is freely available for non-commercial purposes. The model can be downloaded
ProMISE 2 user manual Probabilistic model for immiscible separations and extractions (ProMISE) developed by Joost de Folter, is freely available for non-commercial purposes. The model can be downloaded
Quick Feature Tour. Quick Feature Tour Overview
 Quick Feature Tour Quick Feature Tour Overview This chapter highlights some of the features available in the latest version of BioWin. These are demonstrated using the "An Example" configuration installed
Quick Feature Tour Quick Feature Tour Overview This chapter highlights some of the features available in the latest version of BioWin. These are demonstrated using the "An Example" configuration installed
Temporal Modeling and Missing Data Estimation for MODIS Vegetation data
 Temporal Modeling and Missing Data Estimation for MODIS Vegetation data Rie Honda 1 Introduction The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) is the primary instrument on board NASA s Earth
Temporal Modeling and Missing Data Estimation for MODIS Vegetation data Rie Honda 1 Introduction The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) is the primary instrument on board NASA s Earth
Homogenization and numerical Upscaling. Unsaturated flow and two-phase flow
 Homogenization and numerical Upscaling Unsaturated flow and two-phase flow Insa Neuweiler Institute of Hydromechanics, University of Stuttgart Outline Block 1: Introduction and Repetition Homogenization
Homogenization and numerical Upscaling Unsaturated flow and two-phase flow Insa Neuweiler Institute of Hydromechanics, University of Stuttgart Outline Block 1: Introduction and Repetition Homogenization
TerraStation II v7 Training
 WORKED EXAMPLE Loading and using Core Analysis Data Core Analysis Data is frequently not available at exact well increments. In order to retain the exact depth at which this data is sampled, it needs to
WORKED EXAMPLE Loading and using Core Analysis Data Core Analysis Data is frequently not available at exact well increments. In order to retain the exact depth at which this data is sampled, it needs to
Scientific Graphing in Excel 2007
 Scientific Graphing in Excel 2007 When you start Excel, you will see the screen below. Various parts of the display are labelled in red, with arrows, to define the terms used in the remainder of this overview.
Scientific Graphing in Excel 2007 When you start Excel, you will see the screen below. Various parts of the display are labelled in red, with arrows, to define the terms used in the remainder of this overview.
Spreadsheet and Graphing Exercise Biology 210 Introduction to Research
 1 Spreadsheet and Graphing Exercise Biology 210 Introduction to Research There are many good spreadsheet programs for analyzing data. In this class we will use MS Excel. Below are a series of examples
1 Spreadsheet and Graphing Exercise Biology 210 Introduction to Research There are many good spreadsheet programs for analyzing data. In this class we will use MS Excel. Below are a series of examples
IMPROVING THE NUMERICAL ACCURACY OF HYDROTHERMAL RESERVOIR SIMULATIONS USING THE CIP SCHEME WITH THIRD-ORDER ACCURACY
 PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Seventh Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 30 - February 1, 2012 SGP-TR-194 IMPROVING THE NUMERICAL ACCURACY OF HYDROTHERMAL
PROCEEDINGS, Thirty-Seventh Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering Stanford University, Stanford, California, January 30 - February 1, 2012 SGP-TR-194 IMPROVING THE NUMERICAL ACCURACY OF HYDROTHERMAL
Tutorial 2 Materials and Loading
 Tutorial 2 Materials and Loading Multiple material slope with weak layer Pore pressure defined by water table Uniformly distributed external load Circular slip surface search (Grid search) Introduction
Tutorial 2 Materials and Loading Multiple material slope with weak layer Pore pressure defined by water table Uniformly distributed external load Circular slip surface search (Grid search) Introduction
Installation. Overview. Quick start
 Installation The RSD2013 software is compiled to run on a Windows platform. It mainly consist out of two executables: RSD2013_GUI.exe and RSD2013.exe. The first executable is the graphical user interface
Installation The RSD2013 software is compiled to run on a Windows platform. It mainly consist out of two executables: RSD2013_GUI.exe and RSD2013.exe. The first executable is the graphical user interface
Settle 3D 3.0 is here! Become a Rocscience Beta Tester
 Settle 3D 3.0 is here! Become a Rocscience Beta Tester RocNews Winter 2014 Settle 3D 3.0 An Exciting New Upgrade! Settle 3D is a 3-dimensional program for the analysis of vertical consolidation and settlement
Settle 3D 3.0 is here! Become a Rocscience Beta Tester RocNews Winter 2014 Settle 3D 3.0 An Exciting New Upgrade! Settle 3D is a 3-dimensional program for the analysis of vertical consolidation and settlement
Application of MCNP Code in Shielding Design for Radioactive Sources
 Application of MCNP Code in Shielding Design for Radioactive Sources Ibrahim A. Alrammah Abstract This paper presents three tasks: Task 1 explores: the detected number of as a function of polythene moderator
Application of MCNP Code in Shielding Design for Radioactive Sources Ibrahim A. Alrammah Abstract This paper presents three tasks: Task 1 explores: the detected number of as a function of polythene moderator
Valley. Scheduling. Client User Manual _ Valmont Industries, Inc., Valley, NE USA. All rights reserved.
 Valley Scheduling Client User Manual 09805_0 09 Valmont Industries, Inc., Valley, NE 6806 USA. All rights reserved. www.valleyirrigation.com Valley Scheduling This page was left blank intentionally Table
Valley Scheduling Client User Manual 09805_0 09 Valmont Industries, Inc., Valley, NE 6806 USA. All rights reserved. www.valleyirrigation.com Valley Scheduling This page was left blank intentionally Table
CVEN 5835 Cable Supported Structures 1
 CVEN 5835 Cable Supported Structures George.Hearn@colorado.edu 1 Cable Structures An app for force-displacement analysis is used to set up a model of a single strand carrying three point loads. We worked
CVEN 5835 Cable Supported Structures George.Hearn@colorado.edu 1 Cable Structures An app for force-displacement analysis is used to set up a model of a single strand carrying three point loads. We worked
Airport Tutorial - Contaminant Transport Modeling. Visual MODFLOW Flex. Integrated Conceptual & Numerical Groundwater Modeling
 Airport Tutorial - Contaminant Transport Modeling Visual MODFLOW Flex Integrated Conceptual & Numerical Groundwater Modeling Airport Tutorial: Numerical Modeling with Transport The following example is
Airport Tutorial - Contaminant Transport Modeling Visual MODFLOW Flex Integrated Conceptual & Numerical Groundwater Modeling Airport Tutorial: Numerical Modeling with Transport The following example is
Using the Discrete Ordinates Radiation Model
 Tutorial 6. Using the Discrete Ordinates Radiation Model Introduction This tutorial illustrates the set up and solution of flow and thermal modelling of a headlamp. The discrete ordinates (DO) radiation
Tutorial 6. Using the Discrete Ordinates Radiation Model Introduction This tutorial illustrates the set up and solution of flow and thermal modelling of a headlamp. The discrete ordinates (DO) radiation
Sheri Singerling v /12/2014
 PENEPMA Instructions (.geo files): *additional information for these procedures is available on the PFE forum: http://www.probesoftware.com/smf/index.php 1. Open the Standard.exe ( ) file with the following
PENEPMA Instructions (.geo files): *additional information for these procedures is available on the PFE forum: http://www.probesoftware.com/smf/index.php 1. Open the Standard.exe ( ) file with the following
NCAR SUMMER COLLOQUIUM: July 24-Aug.6, 2011 Boulder, Colorado, USA. General Large Area Crop Model (GLAM) TUTORIAL
 NCAR SUMMER COLLOQUIUM: July 24-Aug.6, 2011 Boulder, Colorado, USA General Large Area Crop Model (GLAM) TUTORIAL Gizaw Mengistu, Dept. of Physics, Addis Ababa University, Ethiopia This document provides
NCAR SUMMER COLLOQUIUM: July 24-Aug.6, 2011 Boulder, Colorado, USA General Large Area Crop Model (GLAM) TUTORIAL Gizaw Mengistu, Dept. of Physics, Addis Ababa University, Ethiopia This document provides
Stat 528 (Autumn 2008) Density Curves and the Normal Distribution. Measures of center and spread. Features of the normal distribution
 Stat 528 (Autumn 2008) Density Curves and the Normal Distribution Reading: Section 1.3 Density curves An example: GRE scores Measures of center and spread The normal distribution Features of the normal
Stat 528 (Autumn 2008) Density Curves and the Normal Distribution Reading: Section 1.3 Density curves An example: GRE scores Measures of center and spread The normal distribution Features of the normal
MODELING PARTICLE DEPOSITION IN VENTILATION DUCTS
 MODELING PARTICLE DEPOSITION IN VENTILATION DUCTS MR Sippola 1* and WW Nazaroff 1,2 1 Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of California, Berkeley, CA, USA 2 Indoor Environment Dept.,
MODELING PARTICLE DEPOSITION IN VENTILATION DUCTS MR Sippola 1* and WW Nazaroff 1,2 1 Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of California, Berkeley, CA, USA 2 Indoor Environment Dept.,
Tekla Structures Analysis Guide. Product version 21.0 March Tekla Corporation
 Tekla Structures Analysis Guide Product version 21.0 March 2015 2015 Tekla Corporation Contents 1 Getting started with analysis... 7 1.1 What is an analysis model... 7 Analysis model objects...9 1.2 About
Tekla Structures Analysis Guide Product version 21.0 March 2015 2015 Tekla Corporation Contents 1 Getting started with analysis... 7 1.1 What is an analysis model... 7 Analysis model objects...9 1.2 About
Step 1: Problem Type Specification. (1) Open COMSOL Multiphysics 4.1. (2) Under Select Space Dimension tab, select 2D Axisymmetric.
 Step 1: Problem Type Specification (1) Open COMSOL Multiphysics 4.1. (2) Under Select Space Dimension tab, select 2D Axisymmetric. (3) Click on blue arrow next to Select Space Dimension title. (4) Click
Step 1: Problem Type Specification (1) Open COMSOL Multiphysics 4.1. (2) Under Select Space Dimension tab, select 2D Axisymmetric. (3) Click on blue arrow next to Select Space Dimension title. (4) Click
Groundwater in Hydrologic Cycle
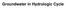 Groundwater in Hydrologic Cycle Types of Terrestrial Water Surface Water Soil Moisture Ground water Pores Full of Combination of Air and Water Unsaturated Zone / Zone of Aeration / Vadose (Soil Water)
Groundwater in Hydrologic Cycle Types of Terrestrial Water Surface Water Soil Moisture Ground water Pores Full of Combination of Air and Water Unsaturated Zone / Zone of Aeration / Vadose (Soil Water)
Modeling with Uncertainty Interval Computations Using Fuzzy Sets
 Modeling with Uncertainty Interval Computations Using Fuzzy Sets J. Honda, R. Tankelevich Department of Mathematical and Computer Sciences, Colorado School of Mines, Golden, CO, U.S.A. Abstract A new method
Modeling with Uncertainty Interval Computations Using Fuzzy Sets J. Honda, R. Tankelevich Department of Mathematical and Computer Sciences, Colorado School of Mines, Golden, CO, U.S.A. Abstract A new method
EXCEL SPREADSHEET TUTORIAL
 EXCEL SPREADSHEET TUTORIAL Note to all 200 level physics students: You will be expected to properly format data tables and graphs in all lab reports, as described in this tutorial. Therefore, you are responsible
EXCEL SPREADSHEET TUTORIAL Note to all 200 level physics students: You will be expected to properly format data tables and graphs in all lab reports, as described in this tutorial. Therefore, you are responsible
SPACSYS (v5.20) Installation and operation manual
 SPACSYS (v5.20) Installation and operation manual Developed by Dr. Lianhai Wu Sustainable Agriculture Systems Rothamsted Research North Wyke, Okehampton EX20 2SB, UK Email: Lianhai.Wu@rothamsted.ac.uk
SPACSYS (v5.20) Installation and operation manual Developed by Dr. Lianhai Wu Sustainable Agriculture Systems Rothamsted Research North Wyke, Okehampton EX20 2SB, UK Email: Lianhai.Wu@rothamsted.ac.uk
Tutorial: Airport Numerical Model with Transport
 Tutorial: Visual MODFLOW Flex 5.0 Integrated Conceptual & Numerical Groundwater Modeling Software 1 1 Visual MODFLOW Flex 5.0 The following example walks through creating a numerical model with groundwater
Tutorial: Visual MODFLOW Flex 5.0 Integrated Conceptual & Numerical Groundwater Modeling Software 1 1 Visual MODFLOW Flex 5.0 The following example walks through creating a numerical model with groundwater
ARTMO s Global Sensitivity Analysis (GSA) toolbox to quantify driving variables of leaf and canopy radiative transfer models
 [1] ARTMO s Sobol', I.M., Global GSA sensitivity toolbox indices for nonlinear mathematical models and their Monte Carlo estimates, Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, 55(1-3), 271-28, 21. 1/2 ARTMO
[1] ARTMO s Sobol', I.M., Global GSA sensitivity toolbox indices for nonlinear mathematical models and their Monte Carlo estimates, Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, 55(1-3), 271-28, 21. 1/2 ARTMO
WMS 8.4 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface (GISbased) Delineate a watershed and build a MODRAT model
 v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface (GISbased) Delineate a watershed and build a MODRAT model Objectives Delineate a watershed from a DEM and derive many of the MODRAT input parameters
v. 8.4 WMS 8.4 Tutorial Watershed Modeling MODRAT Interface (GISbased) Delineate a watershed and build a MODRAT model Objectives Delineate a watershed from a DEM and derive many of the MODRAT input parameters
Chemistry 30 Tips for Creating Graphs using Microsoft Excel
 Chemistry 30 Tips for Creating Graphs using Microsoft Excel Graphing is an important skill to learn in the science classroom. Students should be encouraged to use spreadsheet programs to create graphs.
Chemistry 30 Tips for Creating Graphs using Microsoft Excel Graphing is an important skill to learn in the science classroom. Students should be encouraged to use spreadsheet programs to create graphs.
Solve Non-Linear Parabolic Partial Differential Equation by Spline Collocation Method
 Solve Non-Linear Parabolic Partial Differential Equation by Spline Collocation Method P.B. Choksi 1 and A.K. Pathak 2 1 Research Scholar, Rai University,Ahemdabad. Email:pinalchoksey@gmail.com 2 H.O.D.
Solve Non-Linear Parabolic Partial Differential Equation by Spline Collocation Method P.B. Choksi 1 and A.K. Pathak 2 1 Research Scholar, Rai University,Ahemdabad. Email:pinalchoksey@gmail.com 2 H.O.D.
Microsoft Word for Report-Writing (2016 Version)
 Microsoft Word for Report-Writing (2016 Version) Microsoft Word is a versatile, widely-used tool for producing presentation-quality documents. Most students are well-acquainted with the program for generating
Microsoft Word for Report-Writing (2016 Version) Microsoft Word is a versatile, widely-used tool for producing presentation-quality documents. Most students are well-acquainted with the program for generating
Solved with COMSOL Multiphysics 4.2
 Laminar Static Mixer Introduction In static mixers, also called motionless or in-line mixers, a fluid is pumped through a pipe containing stationary blades. This mixing technique is particularly well suited
Laminar Static Mixer Introduction In static mixers, also called motionless or in-line mixers, a fluid is pumped through a pipe containing stationary blades. This mixing technique is particularly well suited
KINETICS CALCS AND GRAPHS INSTRUCTIONS
 KINETICS CALCS AND GRAPHS INSTRUCTIONS 1. Open a new Excel or Google Sheets document. I will be using Google Sheets for this tutorial, but Excel is nearly the same. 2. Enter headings across the top as
KINETICS CALCS AND GRAPHS INSTRUCTIONS 1. Open a new Excel or Google Sheets document. I will be using Google Sheets for this tutorial, but Excel is nearly the same. 2. Enter headings across the top as
This document will cover some of the key features available only in SMS Advanced, including:
 Key Differences between SMS Basic and SMS Advanced SMS Advanced includes all of the same functionality as the SMS Basic Software as well as adding numerous tools that provide management solutions for multiple
Key Differences between SMS Basic and SMS Advanced SMS Advanced includes all of the same functionality as the SMS Basic Software as well as adding numerous tools that provide management solutions for multiple
8 Modeling Fractured Rock
 8 Modeling Fractured Rock Groundwater flow and chemical transport models can help to characterize and remediate fractured rock sites at all scales. It is critical that any modeling be performed by modelers
8 Modeling Fractured Rock Groundwater flow and chemical transport models can help to characterize and remediate fractured rock sites at all scales. It is critical that any modeling be performed by modelers
Unsteady-State Diffusion in a Slab by Robert P. Hesketh 3 October 2006
 Unsteady-State Diffusion in a Slab by Robert P. Hesketh 3 October 2006 Unsteady-State Diffusion in a Slab This simple example is based on Cutlip and Shacham Problem 7.13: Unsteady-State Mass Transfer in
Unsteady-State Diffusion in a Slab by Robert P. Hesketh 3 October 2006 Unsteady-State Diffusion in a Slab This simple example is based on Cutlip and Shacham Problem 7.13: Unsteady-State Mass Transfer in
KCS Motion. Video Motion Analysis Software
 Video Motion Analysis Software Software and supporting material is property of G. Mason, Seattle University, 2007 Overview Overview KCS Motion tracks moving objects in a video clip and analyzes their position,
Video Motion Analysis Software Software and supporting material is property of G. Mason, Seattle University, 2007 Overview Overview KCS Motion tracks moving objects in a video clip and analyzes their position,
2. Using the Hybrid-Maize Model
 2. Using the Hybrid-Maize Model 2.1. Installation System requirements: Free disk space: depending on weather data included. Full installation amounts to about 18.5 MB, including 6.8 MB of weather data
2. Using the Hybrid-Maize Model 2.1. Installation System requirements: Free disk space: depending on weather data included. Full installation amounts to about 18.5 MB, including 6.8 MB of weather data
Rendering Equation & Monte Carlo Path Tracing I
 Rendering Equation & Monte Carlo Path Tracing I CS295, Spring 2017 Shuang Zhao Computer Science Department University of California, Irvine CS295, Spring 2017 Shuang Zhao 1 Announcements Homework 1 due
Rendering Equation & Monte Carlo Path Tracing I CS295, Spring 2017 Shuang Zhao Computer Science Department University of California, Irvine CS295, Spring 2017 Shuang Zhao 1 Announcements Homework 1 due
Chapter 16. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents BANK FAILURE CALCULATIONS IN HEC-6T...16-1 Introduction...16-1 Approach...16-2 Conceptual Model...16-3 Theoretical Development...16-4 Two Foot Test...16-6 Mass Conservation...16-6 Command
Table of Contents BANK FAILURE CALCULATIONS IN HEC-6T...16-1 Introduction...16-1 Approach...16-2 Conceptual Model...16-3 Theoretical Development...16-4 Two Foot Test...16-6 Mass Conservation...16-6 Command
Chemical Equilibrium CHAPTER 15. Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter, 6 th edition By Jesperson, Brady, & Hyslop
 Chemical Equilibrium CHAPTER 15 Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter, 6 th edition By Jesperson, Brady, & Hyslop CHAPTER 15 Chemical Equilibrium Learning Objectives: q Reversible Reactions and Equilibrium
Chemical Equilibrium CHAPTER 15 Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter, 6 th edition By Jesperson, Brady, & Hyslop CHAPTER 15 Chemical Equilibrium Learning Objectives: q Reversible Reactions and Equilibrium
Free Convection in a Water Glass
 Solved with COMSOL Multiphysics 4.1. Free Convection in a Water Glass Introduction This model treats free convection in a glass of water. Free convection is a phenomenon that is often disregarded in chemical
Solved with COMSOL Multiphysics 4.1. Free Convection in a Water Glass Introduction This model treats free convection in a glass of water. Free convection is a phenomenon that is often disregarded in chemical
An Example Eddy Currents
 An Example Eddy Currents Introduction To help you understand how to create models using the AC/DC Module, this section walks through an example in great detail. You can apply these techniques to all the
An Example Eddy Currents Introduction To help you understand how to create models using the AC/DC Module, this section walks through an example in great detail. You can apply these techniques to all the
Development of the Compliant Mooring Line Model for FLOW-3D
 Flow Science Report 08-15 Development of the Compliant Mooring Line Model for FLOW-3D Gengsheng Wei Flow Science, Inc. October 2015 1. Introduction Mooring systems are common in offshore structures, ship
Flow Science Report 08-15 Development of the Compliant Mooring Line Model for FLOW-3D Gengsheng Wei Flow Science, Inc. October 2015 1. Introduction Mooring systems are common in offshore structures, ship
Investigation of mixing chamber for experimental FGD reactor
 Investigation of mixing chamber for experimental FGD reactor Jan Novosád 1,a, Petra Danová 1 and Tomáš Vít 1 1 Department of Power Engineering Equipment, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Technical University
Investigation of mixing chamber for experimental FGD reactor Jan Novosád 1,a, Petra Danová 1 and Tomáš Vít 1 1 Department of Power Engineering Equipment, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Technical University
APPENDIX B STEP-BY-STEP APPLICATIONS OF THE FEMWATER-LHS
 APPENDIX B STEP-BY-STEP APPLICATIONS OF THE FEMWATER-LHS Steady Two-Dimensional Drainage Problem 1. Double-click on the Argus ONE icon to open Argus ONE. 2. From the PIEs menu found along the top of the
APPENDIX B STEP-BY-STEP APPLICATIONS OF THE FEMWATER-LHS Steady Two-Dimensional Drainage Problem 1. Double-click on the Argus ONE icon to open Argus ONE. 2. From the PIEs menu found along the top of the
GoldSim 12.1 Summary. Summary of New Features and Changes. June 2018
 GoldSim 12.1 Summary Summary of New Features and Changes June 2018 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Documentation of New Features... 3 Installation Instructions for this Version... 3 Significant New
GoldSim 12.1 Summary Summary of New Features and Changes June 2018 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Documentation of New Features... 3 Installation Instructions for this Version... 3 Significant New
Quantifying the Dynamic Ocean Surface Using Underwater Radiometric Measurement
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Quantifying the Dynamic Ocean Surface Using Underwater Radiometric Measurement Lian Shen Department of Mechanical Engineering
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Quantifying the Dynamic Ocean Surface Using Underwater Radiometric Measurement Lian Shen Department of Mechanical Engineering
ELECTRON DOSE KERNELS TO ACCOUNT FOR SECONDARY PARTICLE TRANSPORT IN DETERMINISTIC SIMULATIONS
 Computational Medical Physics Working Group Workshop II, Sep 30 Oct 3, 2007 University of Florida (UF), Gainesville, Florida USA on CD-ROM, American Nuclear Society, LaGrange Park, IL (2007) ELECTRON DOSE
Computational Medical Physics Working Group Workshop II, Sep 30 Oct 3, 2007 University of Florida (UF), Gainesville, Florida USA on CD-ROM, American Nuclear Society, LaGrange Park, IL (2007) ELECTRON DOSE
Error Analysis, Statistics and Graphing
 Error Analysis, Statistics and Graphing This semester, most of labs we require us to calculate a numerical answer based on the data we obtain. A hard question to answer in most cases is how good is your
Error Analysis, Statistics and Graphing This semester, most of labs we require us to calculate a numerical answer based on the data we obtain. A hard question to answer in most cases is how good is your
Spread Map Tab - Soil Zones
 Spread Map Tab - Soil Zones The Spread Map page provides functions for creating spread maps. To activate the options, select the Spread Map tab. 1. The Rx Export tab will display immediately. Select the
Spread Map Tab - Soil Zones The Spread Map page provides functions for creating spread maps. To activate the options, select the Spread Map tab. 1. The Rx Export tab will display immediately. Select the
Physics 101, Lab 1: LINEAR KINEMATICS PREDICTION SHEET
 Physics 101, Lab 1: LINEAR KINEMATICS PREDICTION SHEET After reading through the Introduction, Purpose and Principles sections of the lab manual (and skimming through the procedures), answer the following
Physics 101, Lab 1: LINEAR KINEMATICS PREDICTION SHEET After reading through the Introduction, Purpose and Principles sections of the lab manual (and skimming through the procedures), answer the following
MODFLOW UZF Package The MODFLOW Unsaturated-Zone Flow (UZF) Package Interface in GMS
 v. 10.2 GMS 10.2 Tutorial The MODFLOW Unsaturated-Zone Flow (UZF) Package Interface in GMS Objectives This tutorial explains how to use the MODFLOW Unsaturated-Zone Flow (UZF) package and compares it to
v. 10.2 GMS 10.2 Tutorial The MODFLOW Unsaturated-Zone Flow (UZF) Package Interface in GMS Objectives This tutorial explains how to use the MODFLOW Unsaturated-Zone Flow (UZF) package and compares it to
Lab Practical - Limit Equilibrium Analysis of Engineered Slopes
 Lab Practical - Limit Equilibrium Analysis of Engineered Slopes Part 1: Planar Analysis A Deterministic Analysis This exercise will demonstrate the basics of a deterministic limit equilibrium planar analysis
Lab Practical - Limit Equilibrium Analysis of Engineered Slopes Part 1: Planar Analysis A Deterministic Analysis This exercise will demonstrate the basics of a deterministic limit equilibrium planar analysis
IDS 101 Introduction to Spreadsheets
 IDS 101 Introduction to Spreadsheets A spreadsheet will be a valuable tool in our analysis of the climate data we will examine this year. The specific goals of this module are to help you learn: how to
IDS 101 Introduction to Spreadsheets A spreadsheet will be a valuable tool in our analysis of the climate data we will examine this year. The specific goals of this module are to help you learn: how to
Watershed Modeling Using Online Spatial Data to Create an HEC-HMS Model
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Using Online Spatial Data to Create an HEC-HMS Model Learn how to setup an HEC-HMS model using WMS online spatial data Objectives This tutorial shows how to
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Using Online Spatial Data to Create an HEC-HMS Model Learn how to setup an HEC-HMS model using WMS online spatial data Objectives This tutorial shows how to
lecture 8 Groundwater Modelling -1
 The Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering Department Water Resources Msc. Groundwater Hydrology- ENGC 6301 lecture 8 Groundwater Modelling -1 Instructor: Dr. Yunes Mogheir
The Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering Department Water Resources Msc. Groundwater Hydrology- ENGC 6301 lecture 8 Groundwater Modelling -1 Instructor: Dr. Yunes Mogheir
Topaze NL (RTA) Tutorial #1
 Topaze NL (RTA) Tutorial #1 1. Introduction This tutorial provides a description of the options of RTA in KAPPA Workstation G5 through the analysis of a gas producer well example. We recommend that you
Topaze NL (RTA) Tutorial #1 1. Introduction This tutorial provides a description of the options of RTA in KAPPA Workstation G5 through the analysis of a gas producer well example. We recommend that you
Computational analysis of hydrodynamics and light distribution in algal photo-bioreactors
 Computational analysis of hydrodynamics and light distribution in algal photo-bioreactors Varun Loomba 1,2, Eric von Lieres 2, Gregor Huber 1 1 Forschungszentrum Jülich, Institute of Bio- and Geosciences,
Computational analysis of hydrodynamics and light distribution in algal photo-bioreactors Varun Loomba 1,2, Eric von Lieres 2, Gregor Huber 1 1 Forschungszentrum Jülich, Institute of Bio- and Geosciences,
Monte Carlo simulation of photon and electron transport
 First Barcelona Techno Week Course on semiconductor detectors ICCUB, 11-15th July 2016 Monte Carlo simulation of photon and electron transport Francesc Salvat Monte Carlo 1 Simulations performed with the
First Barcelona Techno Week Course on semiconductor detectors ICCUB, 11-15th July 2016 Monte Carlo simulation of photon and electron transport Francesc Salvat Monte Carlo 1 Simulations performed with the
Methodology for spatial homogenization in Serpent 2
 Methodology for spatial homogenization in erpent 2 Jaakko Leppänen Memo 204/05/26 Background patial homogenization has been one of the main motivations for developing erpent since the beginning of the
Methodology for spatial homogenization in erpent 2 Jaakko Leppänen Memo 204/05/26 Background patial homogenization has been one of the main motivations for developing erpent since the beginning of the
SEAWAT Tutorial - Elder Model
 SEAWAT Tutorial - Elder Model Introduction Saltwater intrusion is a common occurrence along coastlines throughout the world. Saltwater is denser than freshwater, and consequently will tend to migrate inland
SEAWAT Tutorial - Elder Model Introduction Saltwater intrusion is a common occurrence along coastlines throughout the world. Saltwater is denser than freshwater, and consequently will tend to migrate inland
Preliminary Lab Exercise Part 1 Calibration of Eppendorf Pipette
 Preliminary Lab Exercise Part 1 Calibration of Eppendorf Pipette Pipettes allow transfer of accurately known volume of solution from one container to another. Volumetric or transfer pipettes deliver a
Preliminary Lab Exercise Part 1 Calibration of Eppendorf Pipette Pipettes allow transfer of accurately known volume of solution from one container to another. Volumetric or transfer pipettes deliver a
FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY
 1 FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY In this chapter a first application of PLAXIS 3D is considered, namely the settlement of a foundation in clay. This is the first step in becoming familiar with the
1 FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY In this chapter a first application of PLAXIS 3D is considered, namely the settlement of a foundation in clay. This is the first step in becoming familiar with the
v Prerequisite Tutorials Required Components Time
 v. 10.0 GMS 10.0 Tutorial MODFLOW Stochastic Modeling, Parameter Randomization Run MODFLOW in Stochastic (Monte Carlo) Mode by Randomly Varying Parameters Objectives Learn how to develop a stochastic (Monte
v. 10.0 GMS 10.0 Tutorial MODFLOW Stochastic Modeling, Parameter Randomization Run MODFLOW in Stochastic (Monte Carlo) Mode by Randomly Varying Parameters Objectives Learn how to develop a stochastic (Monte
Rubis (NUM) Tutorial #1
 Rubis (NUM) Tutorial #1 1. Introduction This example is an introduction to the basic features of Rubis. The exercise is by no means intended to reproduce a realistic scenario. It is assumed that the user
Rubis (NUM) Tutorial #1 1. Introduction This example is an introduction to the basic features of Rubis. The exercise is by no means intended to reproduce a realistic scenario. It is assumed that the user
Design and Analysis of Experiments Prof. Jhareswar Maiti Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Design and Analysis of Experiments Prof. Jhareswar Maiti Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 59 Fractional Factorial Design using MINITAB
Design and Analysis of Experiments Prof. Jhareswar Maiti Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 59 Fractional Factorial Design using MINITAB
UNDERSTANDING FROTH BEHAVIOUR WITH CFD
 UNDERSTANDING FROTH BEHAVIOUR WITH CFD Jan Cilliers Rio Tinto Professor of Mineral Processing Royal School of Mines Imperial College London Outline Froths and Foams Modelling of Flotation Froths 3 Case
UNDERSTANDING FROTH BEHAVIOUR WITH CFD Jan Cilliers Rio Tinto Professor of Mineral Processing Royal School of Mines Imperial College London Outline Froths and Foams Modelling of Flotation Froths 3 Case
v MODFLOW Stochastic Modeling, Parameter Randomization GMS 10.3 Tutorial
 v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial MODFLOW Stochastic Modeling, Parameter Randomization Run MODFLOW in Stochastic (Monte Carlo) Mode by Randomly Varying Parameters Objectives Learn how to develop a stochastic (Monte
v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial MODFLOW Stochastic Modeling, Parameter Randomization Run MODFLOW in Stochastic (Monte Carlo) Mode by Randomly Varying Parameters Objectives Learn how to develop a stochastic (Monte
DANGER indicates that death or severe personal injury will result if proper precautions are not taken.
 Publisher 1 Introduction 2 COMOS Process Operating Manual Overview of various workflows 3 Creating a project structure 4 Creating pure components 5 Editing a block flow diagram 6 Preparing the simulation
Publisher 1 Introduction 2 COMOS Process Operating Manual Overview of various workflows 3 Creating a project structure 4 Creating pure components 5 Editing a block flow diagram 6 Preparing the simulation
This tutorial walks you through the process of using CC BATCH to simulate a batch distillation column.
 CC-BATCH Tutorial This tutorial walks you through the process of using CC BATCH to simulate a batch distillation column. Description of the Problem The simulation you will create is a five step batch distillation
CC-BATCH Tutorial This tutorial walks you through the process of using CC BATCH to simulate a batch distillation column. Description of the Problem The simulation you will create is a five step batch distillation
RAMES. FRAMES 1.X T u t o r i a l. tutorial BEGINNING OF TUTORIAL. Click to begin
 RAMES tutorial BEGINNING OF TUTORIAL FRAMES 1.X T u t o r i a l Click to begin TABLE OF CONTENTS Tutorial overview FAMILIARIZES USERS WITH TUTORIAL FEATURES Tutorial introduction INTRODUCES THE STORY IN
RAMES tutorial BEGINNING OF TUTORIAL FRAMES 1.X T u t o r i a l Click to begin TABLE OF CONTENTS Tutorial overview FAMILIARIZES USERS WITH TUTORIAL FEATURES Tutorial introduction INTRODUCES THE STORY IN
GAMES Webinar: Rendering Tutorial 2. Monte Carlo Methods. Shuang Zhao
 GAMES Webinar: Rendering Tutorial 2 Monte Carlo Methods Shuang Zhao Assistant Professor Computer Science Department University of California, Irvine GAMES Webinar Shuang Zhao 1 Outline 1. Monte Carlo integration
GAMES Webinar: Rendering Tutorial 2 Monte Carlo Methods Shuang Zhao Assistant Professor Computer Science Department University of California, Irvine GAMES Webinar Shuang Zhao 1 Outline 1. Monte Carlo integration
NEW FEATURES IN CHEMCAD VERSION 6: VERSION RELEASE NOTES. CHEMCAD New Features and Enhancements. CHEMCAD Maintenance
 NEW FEATURES IN CHEMCAD VERSION 6: Uses a single mode for flowsheet drawing, specification, calculation, and PFD creation Creates single-file simulations that are easy to work with and share Easy cloning
NEW FEATURES IN CHEMCAD VERSION 6: Uses a single mode for flowsheet drawing, specification, calculation, and PFD creation Creates single-file simulations that are easy to work with and share Easy cloning
v Water Distribution System Modeling Working with WMS Tutorials Building a Hydraulic Model Using Shapefiles Prerequisite Tutorials None
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Water Distribution System Modeling Working with EPANET Building a Hydraulic Model Using Shapefiles Objectives Open shapefiles containing the geometry and attributes of EPANET
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Water Distribution System Modeling Working with EPANET Building a Hydraulic Model Using Shapefiles Objectives Open shapefiles containing the geometry and attributes of EPANET
MoDisc User s Manual. Ranjan Srivastava
 MoDisc User s Manual Ranjan Srivastava Last modified - March 1, 2006 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Model Discrimination Theory 3 3 MoDisc Usage 5 3.1 Software Installation...............................
MoDisc User s Manual Ranjan Srivastava Last modified - March 1, 2006 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Model Discrimination Theory 3 3 MoDisc Usage 5 3.1 Software Installation...............................
403 Poyntz Avenue, Suite B Manhattan, KS PetraSim Example Manual
 403 Poyntz Avenue, Suite B Manhattan, KS 66502-6081 1.785.770.8511 www.thunderheadeng.com PetraSim Example Manual July 2007 TMVOC Example Guide Table of Contents 1.... 1 Description... 1 Specify the Simulator
403 Poyntz Avenue, Suite B Manhattan, KS 66502-6081 1.785.770.8511 www.thunderheadeng.com PetraSim Example Manual July 2007 TMVOC Example Guide Table of Contents 1.... 1 Description... 1 Specify the Simulator
Using Periodic Boundary Conditions
 1 of 6 2004 11 08 15:20 Use periodic boundary conditions, periodic edge conditions, and periodic point conditions to define a constraint that makes two quantities equal on two different (but usually equally
1 of 6 2004 11 08 15:20 Use periodic boundary conditions, periodic edge conditions, and periodic point conditions to define a constraint that makes two quantities equal on two different (but usually equally
5 Chemicals Tutorial. Before proceeding, you should have read Chapter 1 - Introduction which precedes the Tutorials in this manual.
 Chemicals Tutorial 5-1 5 Chemicals Tutorial The complete case for this tutorial has been pre-built and is located in the file TUTOR3.HSC in your HYSYS\SAMPLES directory. In this Tutorial, a flowsheet for
Chemicals Tutorial 5-1 5 Chemicals Tutorial The complete case for this tutorial has been pre-built and is located in the file TUTOR3.HSC in your HYSYS\SAMPLES directory. In this Tutorial, a flowsheet for
EXPERIMENT #5 Physical Properties and Measurement: Density
 OBJECTIVES: EXPERIMENT #5 Physical Properties and Measurement: Density Determine the density of a liquid, a regular solid, and/or an irregular solid Determine the volume of the regular solid by calculation
OBJECTIVES: EXPERIMENT #5 Physical Properties and Measurement: Density Determine the density of a liquid, a regular solid, and/or an irregular solid Determine the volume of the regular solid by calculation
RT3D Sequential Anaerobic Degradation: PCE TCE DCE VC
 GMS 7.0 TUTORIALS RT3D Sequential Anaerobic Degradation: PCE TCE DCE VC This tutorial illustrates the steps involved in modeling sequential anaerobic degradation of PCE using the RT3D model. Since the
GMS 7.0 TUTORIALS RT3D Sequential Anaerobic Degradation: PCE TCE DCE VC This tutorial illustrates the steps involved in modeling sequential anaerobic degradation of PCE using the RT3D model. Since the
SEAWAT 4 Tutorial - Example Problem
 SEAWAT 4 Tutorial - Example Problem Introduction About SEAWAT-4 SEAWAT-4 is the latest release of SEAWAT computer program for simulation of threedimensional, variable-density, transient ground-water flow
SEAWAT 4 Tutorial - Example Problem Introduction About SEAWAT-4 SEAWAT-4 is the latest release of SEAWAT computer program for simulation of threedimensional, variable-density, transient ground-water flow
Sensitivity and Model Calibration for Nitrate Transport Modeling in Eggleston Heights and Julington Creek Neighborhoods, Jacksonville
 Sensitivity and Model Calibration for Nitrate Transport Modeling in Eggleston Heights and Julington Creek Neighborhoods, Jacksonville Liying Wang, Ming Ye, Fernando Rios, Raoul Fernandes Florida State
Sensitivity and Model Calibration for Nitrate Transport Modeling in Eggleston Heights and Julington Creek Neighborhoods, Jacksonville Liying Wang, Ming Ye, Fernando Rios, Raoul Fernandes Florida State
ECHO REACTION Standard Version Version 3.30 (For use with the WIC ECHO Controller Hardware) USER S MANUAL
 ECHO REACTION Standard Version Version 3.30 (For use with the WIC ECHO Controller Hardware) USER S MANUAL 1 of 33 Description Table of Contents Page Updates & New Features... 4 Key Concepts... 5 Terms
ECHO REACTION Standard Version Version 3.30 (For use with the WIC ECHO Controller Hardware) USER S MANUAL 1 of 33 Description Table of Contents Page Updates & New Features... 4 Key Concepts... 5 Terms
High School Science Acid and Base Concentrations (ph and poh) Lesson Objective: Subobjective 1: Subobjective 2: Subobjective 3: Subobjective 4:
 High School Science Acid and Base Concentrations (ph and poh) Lesson Objective: The student will determine acid and base concentrations. Subobjective 1: The student will use the ph scale to characterize
High School Science Acid and Base Concentrations (ph and poh) Lesson Objective: The student will determine acid and base concentrations. Subobjective 1: The student will use the ph scale to characterize
Supplementary Information: Heat generation and light scattering of green fluorescent protein-like pigments in coral tissue
 1 2 3 Supplementary Information: Heat generation and light scattering of green fluorescent protein-like pigments in coral tissue 4 5 6 Running title: Coral heating and FPs 7 8 Niclas H. Lyndby a, Michael
1 2 3 Supplementary Information: Heat generation and light scattering of green fluorescent protein-like pigments in coral tissue 4 5 6 Running title: Coral heating and FPs 7 8 Niclas H. Lyndby a, Michael
UTCHEM GMS TUTORIALS. 1.1 Outline
 GMS TUTORIALS is a highly sophisticated, multi-phase flow and multi-constituent, reactive transport model capable of performing a wide variety of groundwater simulations. was developed at the Center for
GMS TUTORIALS is a highly sophisticated, multi-phase flow and multi-constituent, reactive transport model capable of performing a wide variety of groundwater simulations. was developed at the Center for
