9.4. Perform Rotations. Draw a rotation. STEP 1 Draw a segment from A to P. STEP 2 Draw a ray to form a 1208 angle with } PA.
|
|
|
- Stephen Riley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 erform otations efore You rotated figures about the origin. Now You will rotate figures about a point. Wh? So ou can classif transformations, as in Es Ke Vocabular center of rotation angle of rotation rotation, p. 272 DIETION O OTTION ecall from Lesson 4.8 that a rotation is a transformation in which a figure is turned about a fied point called the center of rotation. as drawn from the center of rotation to a point and its image form the angle of rotation. rotation about a point through an angle of 8 maps ever point Q in the plane to a point Q9 so that one of the following properties is true: If Q is not the center of rotation, then Q 5 Q9 and m QQ9 5 8, or If Q is the center of rotation, then the image of Q is Q. 408 counterclockwise rotation is shown at the right. otations can be clockwise or counterclockwise. In this chapter, all rotations are counterclockwise ngle of rotation enter of rotation clockwise E X M L E Draw a rotation Draw a 208 rotation of n about. counterclockwise Solution STE Draw a segment from to. STE 2 Draw a ra to form a 208 angle with } STE 3 Draw 9 so that 9 5. STE 4 epeat Steps 3 for each verte. Draw n hapter 9 roperties of Transformations
2 USE OTTIONS You can rotate a figure more than However, the effect is the same as rotating the figure b the angle minus OTTIONS OUT THE OIGIN You can rotate a figure more than 808. The diagram shows rotations of point 308, 2208, and 308 about the origin. rotation of 3608 returns a figure to its original coordinates. There are coordinate rules that can be used to find the coordinates of a point after rotations of 908, 808, or 2708 about the origin KEY ONET or Your Notebook oordinate ules for otations about the Origin When a point (a, b) is rotated counterclockwise about the origin, the following are true:. or a rotation of 908, (a, b) (2b, a). 2. or a rotation of 808, (a, b) (2a, 2b). 3. or a rotation of 2708, (a, b) (b, 2a). (2b, a) (2a, 2b) (a, b) (b, 2a) E X M L E 2 otate a figure using the coordinate rules Graph quadrilateral STU with vertices (3, ), S(5, ), T(5, 23), and U(2, 2). Then rotate the quadrilateral 2708 about the origin. NOTHE WY or an alternative method for solving the problem in Eample 2, turn to page 606 for the roblem Solving Workshop. Solution Graph STU. Use the coordinate rule for a 2708 rotation to find the images of the vertices. (a, b) (b, 2a) (3, ) 9(, 23) S(5, ) S9(, 25) T(5, 23) T9(23, 25) U(2, 2) U9(2, 22) Graph the image 9S9T9U9. at classzone.com S U9 U 9 T T9 S9 GUIDED TIE for Eamples and 2. Trace nde and. Then draw a 508 rotation of nde about. E 2. Graph njkl with vertices J(3, 0), K(4, 3), and L(6, 0). otate the triangle 908 about the origin. D 9.4 erform otations 599
3 USING MTIES You can find certain images of a polgon rotated about the origin using matri multiplication. Write the rotation matri to the left of the polgon matri, then multipl. KEY ONET or Your Notebook otation Matrices (ounterclockwise) 908 rotation 0 2 0G 808 rotation G ED VOULY Notice that a 3608 rotation returns the figure to its original position. Multipling b the matri that represents this rotation gives ou the polgon matri ou started with, which is wh it is also called the identit matri rotation 0 2 0G 3608 rotation 0 0 G E X M L E 3 Use matrices to rotate a figure Trapezoid EGH has vertices E(23, 2), (23, 4), G(, 4), and H(2, 2). ind the image matri for a 808 rotation of EGH about the origin. Graph EGH and its image. VOID EOS ecause matri multiplication is not commutative, ou should alwas write the rotation matri first, then the polgon matri. Solution STE Write the polgon matri: E G H G STE 2 Multipl b the matri for a 808 rotation G E G H G 5 E9 9 G9 H G otation olgon Image matri matri matri STE 3 Graph the preimage EGH. Graph the image E99G9H9. E H9 G9 G H E9 9 GUIDED TIE for Eample 3 Use the quadrilateral EGH in Eample 3. ind the image matri after the rotation about the origin. Graph the image hapter 9 roperties of Transformations
4 THEOEM THEOEM 9.3 otation Theorem rotation is an isometr. roof: Es , p. 604 or Your Notebook n > n 999 SES O THEOEM 9.3 To prove the otation Theorem, ou need to show that a rotation preserves the length of a segment. onsider a segment } Q rotated about point to produce } Q99. There are three cases to prove: ase, Q, and are noncollinear. ase 2, Q, and are collinear. ase 3 and are the same point. E X M L E 4 Standardized Test ractice The quadrilateral is rotated about. What is the value of? 8 } D Solution Theorem 9.3, the rotation is an isometr, so corresponding side lengths are equal. Then 2 5 6, so 5 3. Now set up an equation to solve for (3) Substitute 3 for. 5 2 Solve for. orresponding lengths in an isometr are equal. c The correct answer is.d GUIDED TIE for Eample 4 6. ind the value of r in the rotation of the triangle D 5 2s 4r 2 3 3r s erform otations 60
5 9.4 EXEISES SKILL TIE HOMEWOK KEY 5 WOKED-OUT SOLUTIONS on p. WS for Es. 3, 5, and 29 5 STNDDIZED TEST TIE Es. 2, 20, 2, 23, 24, and 37. VOULY What is a center of rotation? 2. WITING ompare the coordinate rules and the rotation matrices for a rotation of 908. EXMLE on p. 598 for Es. 3 IDENTIYING TNSOMTIONS Identif the tpe of transformation, translation, reflection, or rotation, in the photo. Eplain our reasoning NGLE O OTTION Match the diagram with the angle of rotation at classzone.com OTTING IGUE Trace the polgon and point on paper. Then draw a rotation of the polgon the given number of degrees about G J T S EXMLE 2 on p. 599 for Es. 2 4 USING OODINTE ULES otate the figure the given number of degrees about the origin. List the coordinates of the vertices of the image J K S 2 M L T 602 hapter 9 roperties of Transformations
6 EXMLE 3 on p. 600 for Es. 5 9 USING MTIES ind the image matri that represents the rotation of the polgon about the origin. Then graph the polgon and its image G; J K L G; Q S G; EO NLYSIS The endpoints of } are (2, ) and (2, 3). Describe and correct the error in setting up the matri multiplication for a 2708 rotation about the origin rotation of } 0 2 0G 2 2 3G 2708 rotation of } 2 2 3G 0 2 0G EXMLE 4 on p. 60 for Es MULTILE HOIE What is the value of in the rotation of the triangle about? } 3 D MULTILE HOIE Suppose quadrilateral QST is rotated 808 about the origin. In which quadrant is Q9? I II III D IV INDING TTEN The vertices of n are (2, 0), (3, 4), and (5, 2). Make a table to show the vertices of each image after a 908, 808, 2708, 3608, 4508, 5408, 6308, and 7208 rotation. What would be the coordinates of 9 after a rotation of 8908? Eplain. T S 23. MULTILE HOIE rectangle has vertices at (4, 0), (4, 2), (7, 0), and (7, 2). Which image has a verte at the origin? Translation right 4 units and down 2 units otation of 808 about the origin eflection in the line 5 4 D otation of 808 about the point (2, 0) 24. SHOT ESONSE otate the triangle in Eercise about the origin. Show that corresponding sides of the preimage and image are perpendicular. Eplain. 25. VISUL ESONING point in space has three coordinates (,, z). What is the image of point (3, 2, 0) rotated 808 about the origin in the z-plane? (See Eercise 30, page 585.) HLLENGE otate the line the given number of degrees (a) about the -intercept and (b) about the -intercept. Write the equation of each image ; ; } 2 5; erform otations 603
7 OLEM SOLVING NGLE O OTTION Use the photo to find the angle of rotation that maps onto 9. Eplain our reasoning EVOLVING DOO You enter a revolving door and rotate the door 808. What does this mean in the contet of the situation? Now, suppose ou enter a revolving door and rotate the door What does this mean in the contet of the situation? Eplain. 33. OVING THEOEM 9.3 op and complete the proof of ase. ase The segment is noncollinear with the center of rotation. GIVEN c rotation about maps Q to Q9 and to 9. OVE c Q 5 Q99 STTEMENTS. Q 5 Q9, 5 9, m QQ9 5 m 9 2. m QQ9 5 m Q9 m 9Q9 m 9 5 m Q m Q9 3. m Q9 m 9Q9 5 m Q m Q9 4. m Q 5 m Q99 5.? >? 6. } Q > } Q99 7. Q 5 Q99 ESONS. Definition of? 2.? 3.? ropert of Equalit 4.? ropert of Equalit 5. SS ongruence ostulate 6.? 7.? 9 9 OVING THEOEM 9.3 Write a proof for ase 2 and ase 3. (efer to the diagrams on page 60.) 34. ase 2 The segment is collinear with 35. ase 3 The center of rotation is one the center of rotation. endpoint of the segment. GIVEN c rotation about maps Q to GIVEN c rotation about maps Q Q9 and to 9. to Q9 and to 9., Q, and are collinear. and are the same point. OVE c Q 5 Q99 OVE c Q 5 Q WOKED-OUT SOLUTIONS on p. WS 5 STNDDIZED TEST TIE
8 36. MULTI-STE OLEM Use the graph of a. otate the line 908, 808, 2708, and 3608 about the origin. Describe the relationship between the equation of the preimage and each image. 2 b. Do ou think that the relationships ou described in part (a) are true for an line? Eplain our reasoning. 37. EXTENDED ESONSE Use the graph of the quadratic equation 5 2 at the right. a. otate the parabola b replacing with and with in the original equation, then graph this new equation. 3 b. What is the angle of rotation? c. re the image and the preimage both functions? Eplain. TWO OTTIONS The endpoints of } G are (, 2) and G(3, 4). Graph } 9G9 and } 99G99 after the given rotations. 38. otation: 908 about the origin 39. otation: 2708 about the origin otation: 808 about (0, 4) otation: 908 about (22, 0) 40. HLLENGE polar coordinate sstem locates a point in a plane b its distance from the origin O and b the measure of an angle with its verte at the origin. or eample, the point (2, 308) at the right is 2 units from the origin and m XO What are the polar coordinates of the image of point after a 908 rotation? 808 rotation? 2708 rotation? Eplain X EVIEW repare for Lesson 9.5 in Es MIXED EVIEW In the diagram, ] D is the perpendicular bisector of }. (p. 303) 4. What segment lengths are equal? 42. What is the value of? 43. ind D. (p. 433) D Use a sine or cosine ratio to find the value of each variable. ound decimals to the nearest tenth. (p. 473) 44. v w a b EXT TIE for Lesson 9.4, p. 92 ONLINE QUIZ at classzone.com 605
9 LESSON 9.4 Using LTENTIVE METHODS nother Wa to Solve Eample 2, page 599 MULTILE EESENTTIONS In Eample 2 on page 599, ou saw how to use a coordinate rule to rotate a figure. You can also use tracing paper and move a cop of the figure around the coordinate plane. O L E M Graph quadrilateral STU with vertices (3, ), S(5, ), T(5, 23), and U(2, 2). Then rotate the quadrilateral 2708 about the origin. M E T H O D Using Tracing aper You can use tracing paper to rotate a figure. STE Graph the original figure in the coordinate plane. STE 2 Trace the quadrilateral and the aes on tracing paper. STE 3 otate the tracing paper Then transfer the resulting image onto the graph paper. T I E. GH Graph quadrilateral D with vertices (2, 22), (5, 23), (4, 25), and D(2, 24). Then rotate the quadrilateral 808 about the origin using tracing paper. 2. GH Graph nst with vertices (0, 6), S(, 4), and T(22, 3). Then rotate the triangle 2708 about the origin using tracing paper. 3. SHOT ESONSE Eplain wh rotating a figure 908 clockwise is the same as rotating the figure 2708 counterclockwise. 4. SHOT ESONSE Eplain how ou could use tracing paper to do a reflection. 5. ESONING If ou rotate the point (3, 4) 908 about the origin, what happens to the -coordinate? What happens to the -coordinate? 6. GH Graph njkl with vertices J(4, 8), K(4, 6), and L(2, 6). Then rotate the triangle 908 about the point (2, 4) using tracing paper. 606 hapter 9 roperties of Transformations
9.7 Investigate Dilations
 Investigating g eometr ONSTUTION Use before Lesson 9.7 9.7 Investigate Dilations M T E I LS straightedge compass ruler Q U E S T I O N How do ou construct a dilation of a figure? ecall from Lesson 6.7
Investigating g eometr ONSTUTION Use before Lesson 9.7 9.7 Investigate Dilations M T E I LS straightedge compass ruler Q U E S T I O N How do ou construct a dilation of a figure? ecall from Lesson 6.7
Properties Transformations
 9 Properties of Transformations 9. Translate Figures and Use Vectors 9.2 Use Properties of Matrices 9.3 Perform Reflections 9.4 Perform Rotations 9.5 ppl ompositions of Transformations 9.6 Identif Smmetr
9 Properties of Transformations 9. Translate Figures and Use Vectors 9.2 Use Properties of Matrices 9.3 Perform Reflections 9.4 Perform Rotations 9.5 ppl ompositions of Transformations 9.6 Identif Smmetr
Rotations. Essential Question How can you rotate a figure in a coordinate plane?
 11.3 Rotations Essential Question How can ou rotate a figure in a coordinate plane? Rotating a Triangle in a oordinate lane ONSTRUTING VILE RGUMENTS To be proficient in math, ou need to use previousl established
11.3 Rotations Essential Question How can ou rotate a figure in a coordinate plane? Rotating a Triangle in a oordinate lane ONSTRUTING VILE RGUMENTS To be proficient in math, ou need to use previousl established
Properties of Transformations
 Lesson 9..9-2.G.O.5 9.2.9-2.N.VM.8 9.3.9-2.G.O.5 9.4.9-2.G.O.5 9.5.9-2.G.O.5 9.6.9-2.G.O.3 9.7.9-2.G.SRT. 9 roperties of Transformations 9. Translate igures and Use Vectors 9.2 Use roperties of Matrices
Lesson 9..9-2.G.O.5 9.2.9-2.N.VM.8 9.3.9-2.G.O.5 9.4.9-2.G.O.5 9.5.9-2.G.O.5 9.6.9-2.G.O.3 9.7.9-2.G.SRT. 9 roperties of Transformations 9. Translate igures and Use Vectors 9.2 Use roperties of Matrices
Transformations. Before
 9roperties G.7. TEXS G.5. G.0. G.9. G.5. G.9. G.. of Transformations 9. Translate Figures and Use Vectors 9. Use roperties of Matrices 9.3 erform Reflections 9.4 erform Rotations 9.5 ppl ompositions of
9roperties G.7. TEXS G.5. G.0. G.9. G.5. G.9. G.. of Transformations 9. Translate Figures and Use Vectors 9. Use roperties of Matrices 9.3 erform Reflections 9.4 erform Rotations 9.5 ppl ompositions of
7.3 Similar Right Triangles
 Investigating g Geometr IVIY Use before Lesson 7. 7. imilar ight riangles MEIL rectangular piece of paper ruler scissors colored pencils Q U E I O N How are geometric means related to the altitude of a
Investigating g Geometr IVIY Use before Lesson 7. 7. imilar ight riangles MEIL rectangular piece of paper ruler scissors colored pencils Q U E I O N How are geometric means related to the altitude of a
Translations. Essential Question How can you translate a figure in a coordinate plane? A B
 . Translations Essential Question How can ou translate a figure in a coordinate plane? Translating a Triangle in a oordinate Plane USING TOOLS STRTEGILLY To be proficient in math, ou need to use appropriate
. Translations Essential Question How can ou translate a figure in a coordinate plane? Translating a Triangle in a oordinate Plane USING TOOLS STRTEGILLY To be proficient in math, ou need to use appropriate
Rotate. A bicycle wheel can rotate clockwise or counterclockwise. ACTIVITY: Three Basic Ways to Move Things
 . Rotations object in a plane? What are the three basic was to move an Rotate A biccle wheel can rotate clockwise or counterclockwise. 0 0 0 9 9 9 8 8 8 7 6 7 6 7 6 ACTIVITY: Three Basic Was to Move Things
. Rotations object in a plane? What are the three basic was to move an Rotate A biccle wheel can rotate clockwise or counterclockwise. 0 0 0 9 9 9 8 8 8 7 6 7 6 7 6 ACTIVITY: Three Basic Was to Move Things
Performing Congruence and Similarity Transformations. C m
 9 ig Idea HPTER SUMMRY IG IES Performing ongruence and Similarit Transformations For Your Notebook Translation Translate a figure right or left, up or down. Reflection Reflect a figure in a line. 9 9 9
9 ig Idea HPTER SUMMRY IG IES Performing ongruence and Similarit Transformations For Your Notebook Translation Translate a figure right or left, up or down. Reflection Reflect a figure in a line. 9 9 9
ACTIVITY: Frieze Patterns and Reflections. a. Is the frieze pattern a reflection of itself when folded horizontally? Explain.
 . Reflections frieze pattern? How can ou use reflections to classif a Reflection When ou look at a mountain b a lake, ou can see the reflection, or mirror image, of the mountain in the lake. If ou fold
. Reflections frieze pattern? How can ou use reflections to classif a Reflection When ou look at a mountain b a lake, ou can see the reflection, or mirror image, of the mountain in the lake. If ou fold
9-1. Translations. Vocabulary. Review. Vocabulary Builder. Use Your Vocabulary
 9- Translations Vocabular Review. Underline the correct word to complete the sentence. If two triangles are congruent, corresponding angle measures are the same/ different and corresponding side lengths
9- Translations Vocabular Review. Underline the correct word to complete the sentence. If two triangles are congruent, corresponding angle measures are the same/ different and corresponding side lengths
Lesson 9.1 Properties of Transformations
 Lesson 9.1 roperties of Transformations Name eriod Date In Eercises 1 3, draw the image according to the rule and identif the tpe of transformation. 1. (, ) (, ) 2. (, ) ( 4, 6) 3. (, ) (4, ) 6 4 2 6 4
Lesson 9.1 roperties of Transformations Name eriod Date In Eercises 1 3, draw the image according to the rule and identif the tpe of transformation. 1. (, ) (, ) 2. (, ) ( 4, 6) 3. (, ) (4, ) 6 4 2 6 4
To identify congruence transformations To prove triangle congruence using isometries
 9-5 ongruence ransformations ommon ore tate tandards G-.B.7 Use the definition of congruence in terms of rigid motions to show that two triangles are congruent... lso G-.B.6, G-.B.8 M 1, M 3, M bjective
9-5 ongruence ransformations ommon ore tate tandards G-.B.7 Use the definition of congruence in terms of rigid motions to show that two triangles are congruent... lso G-.B.6, G-.B.8 M 1, M 3, M bjective
To identify congruence transformations To prove triangle congruence using isometries
 9-5 -0-1 ongruence ransformations ontent tandards G..7 Use the definition of congruence in terms of rigid motions to show that two triangles are congruent... lso G..6, G..8 bjective o identif congruence
9-5 -0-1 ongruence ransformations ontent tandards G..7 Use the definition of congruence in terms of rigid motions to show that two triangles are congruent... lso G..6, G..8 bjective o identif congruence
Graphing a Reflection Image
 9- Reflections oon ore State Standards G-O.. Given a geoetric figure and a rotation, reflection, or translation, draw the transfored figure.... lso G-O.., G-O.., G-O..6 MP 1, MP 3, MP Objective To find
9- Reflections oon ore State Standards G-O.. Given a geoetric figure and a rotation, reflection, or translation, draw the transfored figure.... lso G-O.., G-O.., G-O..6 MP 1, MP 3, MP Objective To find
To prove theorems using figures in the coordinate plane
 6-9 s Using Coordinate Geometr Content Standard G.GPE.4 Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraicall. bjective To prove theorems using figures in the coordinate plane Better draw a diagram!
6-9 s Using Coordinate Geometr Content Standard G.GPE.4 Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraicall. bjective To prove theorems using figures in the coordinate plane Better draw a diagram!
Name Date. In Exercises 1 and 2, find the scale factor of the dilation. Then tell whether the dilation is a reduction or an enlargement.
 Name ate. ractice In Eercises 1 and, find the scale factor of the dilation. Then tell whether the dilation is a reduction or an enlargement. 1.. 9 7 10 In Eercises 3, cop the diagram. Then use a compass
Name ate. ractice In Eercises 1 and, find the scale factor of the dilation. Then tell whether the dilation is a reduction or an enlargement. 1.. 9 7 10 In Eercises 3, cop the diagram. Then use a compass
Plot and connect the points in a coordinate plane to make a polygon. Name the polygon.
 . Start Thinking Find at least two objects in each of the following categories: circle, square, triangle, and rectangle (nonsquare). Use a table to compare each object of the same categor in the following
. Start Thinking Find at least two objects in each of the following categories: circle, square, triangle, and rectangle (nonsquare). Use a table to compare each object of the same categor in the following
5.7 Reflections and Symmetry
 Page of 9 5.7 Reflections and Setr oal Identif and use reflections and lines of setr. Ke Words iage p. 52 reflection line of setr reflection is a transforation that creates a irror iage. The original figure
Page of 9 5.7 Reflections and Setr oal Identif and use reflections and lines of setr. Ke Words iage p. 52 reflection line of setr reflection is a transforation that creates a irror iage. The original figure
5 and Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
 Ch 3: Parallel and Perpendicular Lines 3 1 Properties of Parallel Lines 3 Proving Lines Parallel 3 3 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines 3 Parallel Lines and the Triangle Angles Sum Theorem 3 5 The Polgon
Ch 3: Parallel and Perpendicular Lines 3 1 Properties of Parallel Lines 3 Proving Lines Parallel 3 3 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines 3 Parallel Lines and the Triangle Angles Sum Theorem 3 5 The Polgon
Lesson 7.1 Transformations and Symmetry
 Lesson 7.1 ransformations and Smmetr Name eriod Date In Eercises 1 3, perform each transformation. 1. eflect I across line.. otate AL 70 clockwise 3. ranslate ENA b about Q. the given vector. I L A N Q
Lesson 7.1 ransformations and Smmetr Name eriod Date In Eercises 1 3, perform each transformation. 1. eflect I across line.. otate AL 70 clockwise 3. ranslate ENA b about Q. the given vector. I L A N Q
What Should I Recall?
 What Should I Recall? Suppose I have to solve this problem: etermine the unknown measures of the angles and sides in. The given measures are rounded to the nearest whole number. I think of what I alread
What Should I Recall? Suppose I have to solve this problem: etermine the unknown measures of the angles and sides in. The given measures are rounded to the nearest whole number. I think of what I alread
4 Transformations 4.1 Translations 4.2 Reflections 4.3 Rotations 4.4 Congruence and Transformations 4.5 Dilations 4.6 Similarity and Transformations
 Transformations.1 Translations. Reflections.3 Rotations. ongruence and Transformations.5 ilations.6 Similarit and Transformations hapter Learning Target: Understand transformations. hapter Success riteria:
Transformations.1 Translations. Reflections.3 Rotations. ongruence and Transformations.5 ilations.6 Similarit and Transformations hapter Learning Target: Understand transformations. hapter Success riteria:
Name Date. Go to BigIdeasMath.com for an interactive tool to investigate this exploration. and those of A BC?
 ame Date.3 Rotations For use with Eploration.3 Essential Question How can ou rotate a figure in a coordinate plane? EXPLORTIO: Rotating a Triangle in a oordinate Plane Go to igideasath.com for an interactive
ame Date.3 Rotations For use with Eploration.3 Essential Question How can ou rotate a figure in a coordinate plane? EXPLORTIO: Rotating a Triangle in a oordinate Plane Go to igideasath.com for an interactive
9 3 Rotations 9 4 Symmetry
 h 9: Transformations 9 1 Translations 9 Reflections 9 3 Rotations 9 Smmetr 9 1 Translations: Focused Learning Target: I will be able to Identif Isometries. Find translation images of figures. Vocabular:
h 9: Transformations 9 1 Translations 9 Reflections 9 3 Rotations 9 Smmetr 9 1 Translations: Focused Learning Target: I will be able to Identif Isometries. Find translation images of figures. Vocabular:
Name Date. using the vector 1, 4. Graph ABC. and its image. + to find the image
 _.1 ractice 1. Name the vector and write its component form. K J. The vertices of, 3, 1,, and 0, 1. Translate using the vector 1,. Graph and its image. are ( ) ( ) ( ) 3. Find the component form of the
_.1 ractice 1. Name the vector and write its component form. K J. The vertices of, 3, 1,, and 0, 1. Translate using the vector 1,. Graph and its image. are ( ) ( ) ( ) 3. Find the component form of the
Graph and Write Equations of Hyperbolas
 TEKS 9.5 a.5, 2A.5.B, 2A.5.C Graph and Write Equations of Hperbolas Before You graphed and wrote equations of parabolas, circles, and ellipses. Now You will graph and write equations of hperbolas. Wh?
TEKS 9.5 a.5, 2A.5.B, 2A.5.C Graph and Write Equations of Hperbolas Before You graphed and wrote equations of parabolas, circles, and ellipses. Now You will graph and write equations of hperbolas. Wh?
Apply the Tangent Ratio. You used congruent or similar triangles for indirect measurement. You will use the tangent ratio for indirect measurement.
 7.5 pply the Tangent Ratio efore Now You used congruent or similar triangles for indirect measurement. You will use the tangent ratio for indirect measurement. Why? So you can find the height of a roller
7.5 pply the Tangent Ratio efore Now You used congruent or similar triangles for indirect measurement. You will use the tangent ratio for indirect measurement. Why? So you can find the height of a roller
3. (9x + 9) x 45 5x. 5. (7x + 6)
 5 hapter eview 5.1 ngles of riangles (pp. 231 238) ynamic Solutions available at igideasath.com lassify the triangle by its sides and by measuring its angles. he triangle does not have any congruent sides,
5 hapter eview 5.1 ngles of riangles (pp. 231 238) ynamic Solutions available at igideasath.com lassify the triangle by its sides and by measuring its angles. he triangle does not have any congruent sides,
Reteaching Inequalities in Two Triangles
 Name ate lass Inequalities in Two Triangles INV You have worked with segments and angles in triangles. Now ou will eplore inequalities with triangles. Hinge Theorem If two sides of one triangle are congruent
Name ate lass Inequalities in Two Triangles INV You have worked with segments and angles in triangles. Now ou will eplore inequalities with triangles. Hinge Theorem If two sides of one triangle are congruent
Chapter 9 Transformations
 Section 9-1: Reflections SOL: G.2 The student will use pictorial representations, including computer software, constructions, and coordinate methods, to solve problems involving smmetr and transformation.
Section 9-1: Reflections SOL: G.2 The student will use pictorial representations, including computer software, constructions, and coordinate methods, to solve problems involving smmetr and transformation.
Think About. Unit 5 Lesson 3. Investigation. This Situation. Name: a Where do you think the origin of a coordinate system was placed in creating this
 Think About This Situation Unit 5 Lesson 3 Investigation 1 Name: Eamine how the sequence of images changes from frame to frame. a Where do ou think the origin of a coordinate sstem was placed in creating
Think About This Situation Unit 5 Lesson 3 Investigation 1 Name: Eamine how the sequence of images changes from frame to frame. a Where do ou think the origin of a coordinate sstem was placed in creating
Isometries and Congruence
 Honors Geometr Section.1 Name: Date: Period: Isometries and Congruence transformation of a geometric figure is a change in its position, shape, or size.. The original figure is called the preimage. The
Honors Geometr Section.1 Name: Date: Period: Isometries and Congruence transformation of a geometric figure is a change in its position, shape, or size.. The original figure is called the preimage. The
8.G.1c. Trace triangle ABC onto a piece of paper. Cut out your traced triangle.
 ? LESSON 9.3 Properties of Rotations ESSENTIL QUESTION 8.G.1c Verif eperimentall the properties of rotations, reflections, and translations: Parallel lines are taken to parallel lines. lso 8.G.1a, 8.G.1b,
? LESSON 9.3 Properties of Rotations ESSENTIL QUESTION 8.G.1c Verif eperimentall the properties of rotations, reflections, and translations: Parallel lines are taken to parallel lines. lso 8.G.1a, 8.G.1b,
To understand dilation images of figures
 9- Dilations ommon ore State Standards G-ST.A.a A dilation takes a line not passing through the center of the dilation to a parallel line,... Also G-ST.A.b, G-O.A., G-ST.A. M, M, M, M 7 Objective To understand
9- Dilations ommon ore State Standards G-ST.A.a A dilation takes a line not passing through the center of the dilation to a parallel line,... Also G-ST.A.b, G-O.A., G-ST.A. M, M, M, M 7 Objective To understand
12.1. Angle Relationships. Identifying Complementary, Supplementary Angles. Goal: Classify special pairs of angles. Vocabulary. Complementary. angles.
 . Angle Relationships Goal: Classif special pairs of angles. Vocabular Complementar angles: Supplementar angles: Vertical angles: Eample Identifing Complementar, Supplementar Angles In quadrilateral PQRS,
. Angle Relationships Goal: Classif special pairs of angles. Vocabular Complementar angles: Supplementar angles: Vertical angles: Eample Identifing Complementar, Supplementar Angles In quadrilateral PQRS,
Objectives To identify isometries To find translation images of figures
 -8 9-1 Translations ontent tandards G.O. epresent transformations in the plane... describe transformations as functions that take points in the plane as inputs and give other points as outputs... Also
-8 9-1 Translations ontent tandards G.O. epresent transformations in the plane... describe transformations as functions that take points in the plane as inputs and give other points as outputs... Also
23.1 Perpendicular Bisectors of Triangles
 Name lass Date 3.1 Perpendicular isectors of Triangles Essential Question: How can ou use perpendicular bisectors to find the point that is equidistant from all the vertices of a triangle? Resource Locker
Name lass Date 3.1 Perpendicular isectors of Triangles Essential Question: How can ou use perpendicular bisectors to find the point that is equidistant from all the vertices of a triangle? Resource Locker
Three-Dimensional Coordinates
 CHAPTER Three-Dimensional Coordinates Three-dimensional movies superimpose two slightl different images, letting viewers with polaried eeglasses perceive depth (the third dimension) on a two-dimensional
CHAPTER Three-Dimensional Coordinates Three-dimensional movies superimpose two slightl different images, letting viewers with polaried eeglasses perceive depth (the third dimension) on a two-dimensional
Properties of Rotations 8.10.A. Sketch the image of the rotation. Label the images of points A, B, and C as A, B, and C.
 ? LESSON 1.3 ESSENTIL QUESTION Properties of Rotations How do ou describe the properties of orientation and congruence of rotations? Two-dimensional shapes 8.10. Generalize the properties of orientation
? LESSON 1.3 ESSENTIL QUESTION Properties of Rotations How do ou describe the properties of orientation and congruence of rotations? Two-dimensional shapes 8.10. Generalize the properties of orientation
13.2. General Angles and Radian Measure. What you should learn
 Page 1 of 1. General Angles and Radian Measure What ou should learn GOAL 1 Measure angles in standard position using degree measure and radian measure. GOAL Calculate arc lengths and areas of sectors,
Page 1 of 1. General Angles and Radian Measure What ou should learn GOAL 1 Measure angles in standard position using degree measure and radian measure. GOAL Calculate arc lengths and areas of sectors,
(0, 2) y = x 1 2. y = x (2, 2) y = 2x + 2
 .5 Equations of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines COMMON CORE Learning Standards HSG-GPE.B.5 HSG-GPE.B. Essential Question How can ou write an equation of a line that is parallel or perpendicular to a given
.5 Equations of Parallel and Perpendicular Lines COMMON CORE Learning Standards HSG-GPE.B.5 HSG-GPE.B. Essential Question How can ou write an equation of a line that is parallel or perpendicular to a given
Translations, Reflections, and Rotations
 Translations, Reflections, and Rotations The Marching Cougars Lesson 9-1 Transformations Learning Targets: Perform transformations on and off the coordinate plane. Identif characteristics of transformations
Translations, Reflections, and Rotations The Marching Cougars Lesson 9-1 Transformations Learning Targets: Perform transformations on and off the coordinate plane. Identif characteristics of transformations
Geometry. Chapter 4 Resource Masters
 Geometr hapter 4 esource asters N I 4 eading to Learn athematics Vocabular uilder his is an alphabetical list of the ke vocabular terms ou will learn in hapter 4. s ou stud the chapter, complete each term
Geometr hapter 4 esource asters N I 4 eading to Learn athematics Vocabular uilder his is an alphabetical list of the ke vocabular terms ou will learn in hapter 4. s ou stud the chapter, complete each term
Transformation Packet
 Name Transformation Packet UE: TEST: 1 . Transformation Vocabular Transformation Related Terms Sketch Reflection (flip across a line) Line of reflection Pre-image and image Rigid Rotation (turn about a
Name Transformation Packet UE: TEST: 1 . Transformation Vocabular Transformation Related Terms Sketch Reflection (flip across a line) Line of reflection Pre-image and image Rigid Rotation (turn about a
Ready to Go On? Skills Intervention 1-1 Understanding Points, Lines, and Planes
 1 Read to Go On? Skills Intervention 1-1 Understanding Points, Lines, and Planes Find these vocabular words in Lesson 1-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular point line plane collinear coplanar segment
1 Read to Go On? Skills Intervention 1-1 Understanding Points, Lines, and Planes Find these vocabular words in Lesson 1-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular point line plane collinear coplanar segment
Geometry Review. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Geometr Review Multiple hoice Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Tell whether the ordered pair (5, 3) is a solution of the sstem. a. es b. no 2. Solve Express
Geometr Review Multiple hoice Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Tell whether the ordered pair (5, 3) is a solution of the sstem. a. es b. no 2. Solve Express
Name Class Date. Congruence and Transformations Going Deeper
 Name lass ate 4-1 ongruence and Transformations Going eeper ssential question: How can ou use transformations to determine whether figures are congruent? Two figures are congruent if the have the same
Name lass ate 4-1 ongruence and Transformations Going eeper ssential question: How can ou use transformations to determine whether figures are congruent? Two figures are congruent if the have the same
9 LESSON 9.1. Transformations and Congruence. Properties of Translations ESSENTIAL QUESTION
 Transformations and ongruence? MULE 9 LESSN 9.1 ESSENTIL QUESTIN Properties of Translations How can ou use transformations and congruence to solve realworld problems? 8.G.1, 8.G.3 LESSN 9. Properties of
Transformations and ongruence? MULE 9 LESSN 9.1 ESSENTIL QUESTIN Properties of Translations How can ou use transformations and congruence to solve realworld problems? 8.G.1, 8.G.3 LESSN 9. Properties of
The windows of this building are made up of repeating panes of glass. How many different shapes are in each window?
 MESUEMENT N GEOMETY 7 7 ongruent figures 7 Triangle constructions 7 ongruent triangles 7 uadrilaterals WHT O YOU KNOW? 1 List what ou know aout congruence and transformations. reate a concept map to show
MESUEMENT N GEOMETY 7 7 ongruent figures 7 Triangle constructions 7 ongruent triangles 7 uadrilaterals WHT O YOU KNOW? 1 List what ou know aout congruence and transformations. reate a concept map to show
Properties of Rotations 8.10.A. Sketch the image of the rotation. Label the images of points A, B, and C as A, B, and C.
 ? LESSN 1.3 ESSENTIL QUESTIN Properties of Rotations How do ou describe the properties of orientation and congruence of rotations? Two-dimensional shapes 8.10. Generalize the properties of orientation
? LESSN 1.3 ESSENTIL QUESTIN Properties of Rotations How do ou describe the properties of orientation and congruence of rotations? Two-dimensional shapes 8.10. Generalize the properties of orientation
How can you enlarge or reduce a figure in the coordinate plane? Dilate. ACTIVITY: Comparing Triangles in a Coordinate Plane.
 . Dilations How can ou enlarge or reduce a figure in the coordinate plane? Dilate When ou have our ees checked, the optometrist sometimes dilates one or both of the pupils of our ees. ACTIVITY: Comparing
. Dilations How can ou enlarge or reduce a figure in the coordinate plane? Dilate When ou have our ees checked, the optometrist sometimes dilates one or both of the pupils of our ees. ACTIVITY: Comparing
14-1. Translations. Vocabulary. Lesson
 Chapter 1 Lesson 1-1 Translations Vocabular slide, translation preimage translation image congruent figures Adding fied numbers to each of the coordinates of a figure has the effect of sliding or translating
Chapter 1 Lesson 1-1 Translations Vocabular slide, translation preimage translation image congruent figures Adding fied numbers to each of the coordinates of a figure has the effect of sliding or translating
14 Loci and Transformations
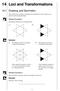 MEP Pupil Tet 1 1 Loci and Transformations 1.1 rawing and Smmetr This section revises the ideas of smmetr first introduced in Unit and gives ou practice in drawing simple shapes. Worked Eample 1 escribe
MEP Pupil Tet 1 1 Loci and Transformations 1.1 rawing and Smmetr This section revises the ideas of smmetr first introduced in Unit and gives ou practice in drawing simple shapes. Worked Eample 1 escribe
Fair Game Review. Chapter 11. Name Date. Reflect the point in (a) the x-axis and (b) the y-axis. 2. ( 2, 4) 1. ( 1, 1 ) 3. ( 3, 3) 4.
 Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review Reflect the point in (a) the -ais and (b) the -ais.. (, ). (, ). (, ). (, ) 5. (, ) 6. (, ) Copright Big Ideas Learning, LLC Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review (continued)
Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review Reflect the point in (a) the -ais and (b) the -ais.. (, ). (, ). (, ). (, ) 5. (, ) 6. (, ) Copright Big Ideas Learning, LLC Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review (continued)
Essential Question What conjectures can you make about a figure reflected in two lines?
 OO O earning tandard -O..5 -O..6. OTUTI VI UT To be proficient in ath, ou need to ae conjectures and justif our conclusions. ongruence and Transforations ssential uestion What conjectures can ou ae about
OO O earning tandard -O..5 -O..6. OTUTI VI UT To be proficient in ath, ou need to ae conjectures and justif our conclusions. ongruence and Transforations ssential uestion What conjectures can ou ae about
9-4. Compositions of Isometries R R R
 GEM1_SE_S_09L04.indd 570 6/3 9-4 -0-13 opositions of Isoetries ontent Standards G..5... Specif a sequence of transforation that will carr a given figure onto another. G..6 Use geoetric descriptions of
GEM1_SE_S_09L04.indd 570 6/3 9-4 -0-13 opositions of Isoetries ontent Standards G..5... Specif a sequence of transforation that will carr a given figure onto another. G..6 Use geoetric descriptions of
Translating Triangles in the Coordinate Plane
 hapter Summar Ke Terms transformation congruent line segments (71) () image congruent (71) angles () translation corresponding (71) sides () rotation corresponding (73) angles () SSS ongruence Theorem
hapter Summar Ke Terms transformation congruent line segments (71) () image congruent (71) angles () translation corresponding (71) sides () rotation corresponding (73) angles () SSS ongruence Theorem
The Coordinate Plane. Have you ever used a street directory? CHAPTER. Points on the Coordinate Plane. Length of Line Segments
 HPTER 9 The oordinate Plane 9. 9. 9. Points on the oordinate Plane Length of Line Segments Real-World Problems: Graphing Have ou ever used a street director? street director is useful for locating a street
HPTER 9 The oordinate Plane 9. 9. 9. Points on the oordinate Plane Length of Line Segments Real-World Problems: Graphing Have ou ever used a street director? street director is useful for locating a street
Name Date. Congruence and Transformations For use with Exploration 4.4
 Nae Date. Congruence and Transforations For use with Eploration. Essential Question What conjectures can ou ae about a figure reflected in two lines? 1 EXLORTION: Reflections in arallel Lines Go to igideasmath.co
Nae Date. Congruence and Transforations For use with Eploration. Essential Question What conjectures can ou ae about a figure reflected in two lines? 1 EXLORTION: Reflections in arallel Lines Go to igideasmath.co
STRAND I: Geometry and Trigonometry. UNIT 37 Further Transformations: Student Text Contents. Section Reflections. 37.
 MEP Jamaica: STRN I UNIT 7 Further Transformations: Student Tet ontents STRN I: Geometr and Trigonometr Unit 7 Further Transformations Student Tet ontents Section 7. Reflections 7. Rotations 7. Translations
MEP Jamaica: STRN I UNIT 7 Further Transformations: Student Tet ontents STRN I: Geometr and Trigonometr Unit 7 Further Transformations Student Tet ontents Section 7. Reflections 7. Rotations 7. Translations
H Geo Final Review Packet Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 H Geo Final Review Packet Multiple Choice Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which angle measures approximatel 7?.. In the figure below, what is the name of
H Geo Final Review Packet Multiple Choice Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which angle measures approximatel 7?.. In the figure below, what is the name of
Transformations. which the book introduces in this chapter. If you shift the graph of y 1 x to the left 2 units and up 3 units, the
 CHAPTER 8 Transformations Content Summar In Chapter 8, students continue their work with functions, especiall nonlinear functions, through further stud of function graphs. In particular, the consider three
CHAPTER 8 Transformations Content Summar In Chapter 8, students continue their work with functions, especiall nonlinear functions, through further stud of function graphs. In particular, the consider three
Reteaching Masters. To jump to a location in this book. 1. Click a bookmark on the left. To print a part of the book. 1. Click the Print button.
 Reteaching Masters To jump to a location in this book 1. lick a bookmark on the left. To print a part of the book 1. lick the rint button. 2. When the rint window opens, tpe in a range of pages to print.
Reteaching Masters To jump to a location in this book 1. lick a bookmark on the left. To print a part of the book 1. lick the rint button. 2. When the rint window opens, tpe in a range of pages to print.
Reteaching Golden Ratio
 Name Date Class Golden Ratio INV 11 You have investigated fractals. Now ou will investigate the golden ratio. The Golden Ratio in Line Segments The golden ratio is the irrational number 1 5. c On the line
Name Date Class Golden Ratio INV 11 You have investigated fractals. Now ou will investigate the golden ratio. The Golden Ratio in Line Segments The golden ratio is the irrational number 1 5. c On the line
5.8 Start Thinking. 5.8 Warm Up. 5.8 Cumulative Review Warm Up
 5.8 Start Thinking Use dnamic geometr software to create an ABC in a coordinate plane such that the center of the triangle is the origin. Use the software to manipulate the triangle so it has whole-number
5.8 Start Thinking Use dnamic geometr software to create an ABC in a coordinate plane such that the center of the triangle is the origin. Use the software to manipulate the triangle so it has whole-number
CHAPTER 7. Think & Discuss (p. 393) m Z m Z m Z 90 QR 2 RP 2 PQ 2 QR QR QR AB QR 7.
 HPTER 7 Think & Discuss (p. 393). The image in bo is flipped to get the image in bo. The image in bo is turned to get the image in bo D.. Sample answer: If ou look at the picture as a whole, the right
HPTER 7 Think & Discuss (p. 393). The image in bo is flipped to get the image in bo. The image in bo is turned to get the image in bo D.. Sample answer: If ou look at the picture as a whole, the right
5.4 Intersecting Medians
 Investigating g Geometry TIVITY Use before Lesson 5.4 5.4 Intersecting Medians M T I LS cardboard straightedge scissors metric ruler Q U S T I O N What is the relationship between segments formed by the
Investigating g Geometry TIVITY Use before Lesson 5.4 5.4 Intersecting Medians M T I LS cardboard straightedge scissors metric ruler Q U S T I O N What is the relationship between segments formed by the
Name: Period 2/3/2012 2/16/2012 PreAP
 Name: Period 2/3/2012 2/16/2012 PreP UNIT 11: TRNSFORMTIONS I can define, identify and illustrate the following terms: Symmetry Line of Symmetry Rotational Symmetry Translation Symmetry Isometry Pre-Image
Name: Period 2/3/2012 2/16/2012 PreP UNIT 11: TRNSFORMTIONS I can define, identify and illustrate the following terms: Symmetry Line of Symmetry Rotational Symmetry Translation Symmetry Isometry Pre-Image
Lesson 2.1 Exercises, pages 90 96
 Lesson.1 Eercises, pages 9 96 A. a) Complete the table of values. 1 1 1 1 1. 1 b) For each function in part a, sketch its graph then state its domain and range. For : the domain is ; and the range is.
Lesson.1 Eercises, pages 9 96 A. a) Complete the table of values. 1 1 1 1 1. 1 b) For each function in part a, sketch its graph then state its domain and range. For : the domain is ; and the range is.
The Graph Scale-Change Theorem
 Lesson 3-5 Lesson 3-5 The Graph Scale-Change Theorem Vocabular horizontal and vertical scale change, scale factor size change BIG IDEA The graph of a function can be scaled horizontall, verticall, or in
Lesson 3-5 Lesson 3-5 The Graph Scale-Change Theorem Vocabular horizontal and vertical scale change, scale factor size change BIG IDEA The graph of a function can be scaled horizontall, verticall, or in
11.5 Inscribed Angles and
 age 1 of 6 11.5 Inscribed ngles and olygons Goal Use properties of inscribed angles. ey Words inscribed angle intercepted arc inscribed circumscribed n inscribed angle is an angle whose vertex is on a
age 1 of 6 11.5 Inscribed ngles and olygons Goal Use properties of inscribed angles. ey Words inscribed angle intercepted arc inscribed circumscribed n inscribed angle is an angle whose vertex is on a
2.4 Coordinate Proof Using Distance with Quadrilaterals
 Name Class Date.4 Coordinate Proof Using Distance with Quadrilaterals Essential Question: How can ou use slope and the distance formula in coordinate proofs? Resource Locker Eplore Positioning a Quadrilateral
Name Class Date.4 Coordinate Proof Using Distance with Quadrilaterals Essential Question: How can ou use slope and the distance formula in coordinate proofs? Resource Locker Eplore Positioning a Quadrilateral
Up, Down, and All Around Transformations of Lines
 Up, Down, and All Around Transformations of Lines WARM UP Identif whether the equation represents a proportional or non-proportional relationship. Then state whether the graph of the line will increase
Up, Down, and All Around Transformations of Lines WARM UP Identif whether the equation represents a proportional or non-proportional relationship. Then state whether the graph of the line will increase
Evaluate and Graph Polynomial Functions
 5.2 Evaluate and Graph Polnomial Functions Before You evaluated and graphed linear and quadratic functions. Now You will evaluate and graph other polnomial functions. Wh? So ou can model skateboarding
5.2 Evaluate and Graph Polnomial Functions Before You evaluated and graphed linear and quadratic functions. Now You will evaluate and graph other polnomial functions. Wh? So ou can model skateboarding
Name Class Date. Essential question: How do you find the tangent, sine, and cosine ratios for acute angles in a right triangle?
 Name lass Date 8-2 Trigonometric Ratios Going Deeper Essential question: How do you find the tangent, sine, and cosine ratios for acute angles in a right triangle? In this chapter, you will be working
Name lass Date 8-2 Trigonometric Ratios Going Deeper Essential question: How do you find the tangent, sine, and cosine ratios for acute angles in a right triangle? In this chapter, you will be working
Objectives To use the AA Postulate and the SAS and SSS Theorems To use similarity to find indirect measurements
 7-3 roving riangles imilar ontent tandards G..5 Use... similarity criteria for triangles to solve problems and to prove relationships in geometric figures. G.G.5 rove the slope criteria for parallel and
7-3 roving riangles imilar ontent tandards G..5 Use... similarity criteria for triangles to solve problems and to prove relationships in geometric figures. G.G.5 rove the slope criteria for parallel and
9. Tina wants to estimate the heights of two. a) Tina s shadow is 2.4 m and the first tree s. b) Tina s shadow is 0.
 b) J 1 15 G F 9. Tina wants to estimate the heights of two trees. For each tree, she stands so that one end of her shadow coincides with one end of the shadow of the tree. Tina s friend measures the lengths
b) J 1 15 G F 9. Tina wants to estimate the heights of two trees. For each tree, she stands so that one end of her shadow coincides with one end of the shadow of the tree. Tina s friend measures the lengths
ACTIVITY: Graphing a Linear Equation. 2 x x + 1?
 . Graphing Linear Equations How can ou draw its graph? How can ou recognize a linear equation? ACTIVITY: Graphing a Linear Equation Work with a partner. a. Use the equation = + to complete the table. (Choose
. Graphing Linear Equations How can ou draw its graph? How can ou recognize a linear equation? ACTIVITY: Graphing a Linear Equation Work with a partner. a. Use the equation = + to complete the table. (Choose
Find Rational Zeros. has integer coefficients, then every rational zero of f has the following form: x 1 a 0. } 5 factor of constant term a 0
 .6 Find Rational Zeros TEKS A.8.B; P..D, P..A, P..B Before You found the zeros of a polnomial function given one zero. Now You will find all real zeros of a polnomial function. Wh? So ou can model manufacturing
.6 Find Rational Zeros TEKS A.8.B; P..D, P..A, P..B Before You found the zeros of a polnomial function given one zero. Now You will find all real zeros of a polnomial function. Wh? So ou can model manufacturing
To draw and identify rotation images of figures
 9-3 -11 otations ontent Standards G..4 evelop definitions of rotations... in terms of angles, circles, perpendicular lines, parallel lines, and line segments. lso G.., G..6 bjective o draw and identify
9-3 -11 otations ontent Standards G..4 evelop definitions of rotations... in terms of angles, circles, perpendicular lines, parallel lines, and line segments. lso G.., G..6 bjective o draw and identify
Name Class Date. Investigating a Ratio in a Right Triangle
 Name lass Date Trigonometric Ratios Going Deeper Essential question: How do you find the tangent, sine, and cosine ratios for acute angles in a right triangle? In this chapter, you will be working etensively
Name lass Date Trigonometric Ratios Going Deeper Essential question: How do you find the tangent, sine, and cosine ratios for acute angles in a right triangle? In this chapter, you will be working etensively
You can use theorems about the interior and exterior angles of convex polygons to solve problems.
 8 Big Idea CATER SUMMARY BI IDEAS Using Angle Relationships in olygons You can use theorems about the interior and exterior angles of convex polygons to solve problems. or Your Notebook olygon Interior
8 Big Idea CATER SUMMARY BI IDEAS Using Angle Relationships in olygons You can use theorems about the interior and exterior angles of convex polygons to solve problems. or Your Notebook olygon Interior
Method 1: Use Pencil and Paper 1. Draw the triangle with vertices A(2, 5), B(1, 2), and C(6, 2). Use the. that it is isosceles.
 3. Verif Properties of Triangles Since triangular frames are strong and simple to make, the are widel used to strengthen buildings and other structures. This section applies analtic geometr to verif the
3. Verif Properties of Triangles Since triangular frames are strong and simple to make, the are widel used to strengthen buildings and other structures. This section applies analtic geometr to verif the
similar See margin. Yes; Sample answer: a preimage and its image after a dilation are ~. Enlargement; the dilation has and scale factor } 3 7 }.
 UI TI Vocabular heck oncept heck. he found rather than. kill heck 3. nlargement; the scale factor is greater than. (lso, it is apparent that the image is larger than the preimage.) TI N ITION. In a dilation
UI TI Vocabular heck oncept heck. he found rather than. kill heck 3. nlargement; the scale factor is greater than. (lso, it is apparent that the image is larger than the preimage.) TI N ITION. In a dilation
Appendix C: Review of Graphs, Equations, and Inequalities
 Appendi C: Review of Graphs, Equations, and Inequalities C. What ou should learn Just as ou can represent real numbers b points on a real number line, ou can represent ordered pairs of real numbers b points
Appendi C: Review of Graphs, Equations, and Inequalities C. What ou should learn Just as ou can represent real numbers b points on a real number line, ou can represent ordered pairs of real numbers b points
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines. What are the slope and y-intercept of each equation?
 6 6-6 What You ll Learn To determine whether lines are parallel To determine whether lines are And Wh To use parallel and lines to plan a bike path, as in Eample Parallel Lines Parallel and Perpendicular
6 6-6 What You ll Learn To determine whether lines are parallel To determine whether lines are And Wh To use parallel and lines to plan a bike path, as in Eample Parallel Lines Parallel and Perpendicular
17.1 Translations. Exploring Translations. Explore
 Name lass Date 17.1 Translations Essential Question: How do ou draw the image of a figure under a translation? Eplore Eploring Translations translation slides all points of a figure the same distance in
Name lass Date 17.1 Translations Essential Question: How do ou draw the image of a figure under a translation? Eplore Eploring Translations translation slides all points of a figure the same distance in
Today s class. Geometric objects and transformations. Informationsteknologi. Wednesday, November 7, 2007 Computer Graphics - Class 5 1
 Toda s class Geometric objects and transformations Wednesda, November 7, 27 Computer Graphics - Class 5 Vector operations Review of vector operations needed for working in computer graphics adding two
Toda s class Geometric objects and transformations Wednesda, November 7, 27 Computer Graphics - Class 5 Vector operations Review of vector operations needed for working in computer graphics adding two
Inclination of a Line
 0_00.qd 78 /8/05 Chapter 0 8:5 AM Page 78 Topics in Analtic Geometr 0. Lines What ou should learn Find the inclination of a line. Find the angle between two lines. Find the distance between a point and
0_00.qd 78 /8/05 Chapter 0 8:5 AM Page 78 Topics in Analtic Geometr 0. Lines What ou should learn Find the inclination of a line. Find the angle between two lines. Find the distance between a point and
1. A(-2, 2), B(4, -2) 3 EXAMPLE. Graph the line y = Move up 3 units. Quick Check See left.
 -. Plan Objectives To graph lines given their equations To write equations of lines Eamples Graphing Lines in Slope- Intercept Form Graphing Lines Using Intercepts Transforming to Slope- Intercept Form
-. Plan Objectives To graph lines given their equations To write equations of lines Eamples Graphing Lines in Slope- Intercept Form Graphing Lines Using Intercepts Transforming to Slope- Intercept Form
5.2 ASA Triangle Congruence
 Name lass ate 5.2 S Triangle ongruence ssential question: What does the S Triangle ongruence Theorem tell you about triangles? xplore 1 rawing Triangles Given Two ngles and a Side You have seen that two
Name lass ate 5.2 S Triangle ongruence ssential question: What does the S Triangle ongruence Theorem tell you about triangles? xplore 1 rawing Triangles Given Two ngles and a Side You have seen that two
Given ABC with A(-1, 1), B(2, 4), and C(4, 1). Translate ABC left 4 units and up 1 unit. a) Vertex matrix: b) Algebraic (arrow) rule:
 Unit 7 Transformations 7 Rigid Motion in a Plane Transformation: The operation that maps, or moves, a preimage onto an image. Three basic transformations are reflection, rotation, and translation. Translation
Unit 7 Transformations 7 Rigid Motion in a Plane Transformation: The operation that maps, or moves, a preimage onto an image. Three basic transformations are reflection, rotation, and translation. Translation
Topic 5: Reflections in the Coordinate Plane
 Topic 5: Reflections in the oordinate Plane for use after Shapes and Designs (Investigation ) A reflection is a transformation that flips an image over a line called the line of reflection. If ou hold
Topic 5: Reflections in the oordinate Plane for use after Shapes and Designs (Investigation ) A reflection is a transformation that flips an image over a line called the line of reflection. If ou hold
3.1 Sequences of Transformations
 Name lass Date 3.1 Sequences of Transformations Essential Question: What happens when ou appl more than one transformation to a figure? Eplore ombining Rotations or Reflections transformation is a function
Name lass Date 3.1 Sequences of Transformations Essential Question: What happens when ou appl more than one transformation to a figure? Eplore ombining Rotations or Reflections transformation is a function
9.5 Double Reflections
 Investigating g Geoetry CTIVITY 9.5 Double Reflections M T ER I LS graphing calculator or coputer Use before Lesson 9.5 classzone.co Keystroes Q U E S T I O N What happens when you reflect a figure in
Investigating g Geoetry CTIVITY 9.5 Double Reflections M T ER I LS graphing calculator or coputer Use before Lesson 9.5 classzone.co Keystroes Q U E S T I O N What happens when you reflect a figure in
7 or 1.17 as your ratio of the lengths when
 .5. What id You Learn? ore Vocabular directed line segment, p. 50 ore oncepts Section.5 Side-Side-Side (SSS) Similarit heorem, p. 9 Side-ngle-Side (SS) Similarit heorem, p. 9 Section. riangle Proportionalit
.5. What id You Learn? ore Vocabular directed line segment, p. 50 ore oncepts Section.5 Side-Side-Side (SSS) Similarit heorem, p. 9 Side-ngle-Side (SS) Similarit heorem, p. 9 Section. riangle Proportionalit
1 Points and Distances
 Ale Zorn 1 Points and Distances 1. Draw a number line, and plot and label these numbers: 0, 1, 6, 2 2. Plot the following points: (A) (3,1) (B) (2,5) (C) (-1,1) (D) (2,-4) (E) (-3,-3) (F) (0,4) (G) (-2,0)
Ale Zorn 1 Points and Distances 1. Draw a number line, and plot and label these numbers: 0, 1, 6, 2 2. Plot the following points: (A) (3,1) (B) (2,5) (C) (-1,1) (D) (2,-4) (E) (-3,-3) (F) (0,4) (G) (-2,0)
Half Turns and Quarter Turns Rotations of Figures on the Coordinate Plane
 Half Turns and Quarter Turns Rotations of Figures on the Coordinate Plane 5 WARM UP 1. Redraw each given figure as described. a. so that it is turned 10 clockwise Before: After: s D b. so that it is turned
Half Turns and Quarter Turns Rotations of Figures on the Coordinate Plane 5 WARM UP 1. Redraw each given figure as described. a. so that it is turned 10 clockwise Before: After: s D b. so that it is turned
ACTIVITY 9. Learning Targets: 112 SpringBoard Mathematics Geometry, Unit 2 Transformations, Triangles, and Quadrilaterals. Reflection.
 Learning Targets: Perform reflections on and off the coordinate plane. Identif reflectional smmetr in plane figures. SUGGESTED LERNING STRTEGIES: Visualization, Create Representations, Predict and Confirm,
Learning Targets: Perform reflections on and off the coordinate plane. Identif reflectional smmetr in plane figures. SUGGESTED LERNING STRTEGIES: Visualization, Create Representations, Predict and Confirm,
