Waves-Refraction. 5. A change in the speed of a wave as it enters a new medium produces a change in 1. frequency 2. period 3. wavelength 4.
|
|
|
- Gabriel Hudson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1. In which way does blue light change as it travels from diamond into crown glass? 1. Its frequency decreases. 2. Its frequency increases. 3. Its speed decreases. 4. Its speed increases. Base your answers to questions 2 through 4 on the information and diagram below. 5. A change in the speed of a wave as it enters a new medium produces a change in 1. frequency 2. period 3. wavelength 4. phase 6. The diagram below represents a ray of monochromatic light (f= Hz) passing from medium X (n=1.46) into fused quartz (n=1.46). A monochromatic light ray (f= Hz) traveling in air is incident on the surface of a rectangular block of Lucite (n=1.50). Which path will the ray follow in the quartz? 1. A 2. B 3. C 4. D 2. Measure the angle of incidence for the light ray to the nearest degree. 7. A straight glass rod appears to bend when placed in a beaker of water, as shown in the diagram below. 3. Calculate the angle of refraction of the light ray when it enters the Lucite block. {Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units.] 4. What is the angle of refraction of the light ray as it emerges from the Lucite block back into the air? Page 182 WAV.C2 What is the best explanation for this phenomenon? 1. The water is warmer than the air. 2. Light travels faster in water than in air. 3. Light is reflected at the air-water interface. 4. Light is refracted as it crosses the air-water interface. APlusPhysics:
2 Base your answers to questions 8 through 10 on the information and diagram below. A ray of monochromatic light having a frequency of hertz is incident on an interface of air and corn oil (n=1.47) at an angle of 35 as shown. The ray is transmitted through parallel layers of corn oil and glycerol (n=1.47) and is then reflected from the surface of a plane mirror, located below and parallel to the glycerol layer. The ray then emerges from the corn oil back into the air at point P. 8. Calculate the angle of refraction of the light ray as it enters the corn oil from air. [Show all work, including the equation and the substitution with units. 9. Explain why the ray does not bend at the corn oil-glycerol interface. 10. On the diagram, use a protractor and straightedge to construct the refracted ray representing the light emerging at point P into air. 11. Which diagram best represents the behavior of a ray of monochromatic light in air incident on a block of crown glass (n=1.52)? APlusPhysics: WAV.C2 Page 183
3 Base your answers to questions 12 through 14 on the information below. A ray of monochromatic light (f= Hz) passes through air and a rectangular transparent block, as shown in the diagram below. 12. Using a protractor, determine the angle of incidence of the light ray as it enters the transparent block from air. 13. Calculate the absolute index of refraction for the medium of the transparent block. [Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units.] 14. Calculate the speed of the light ray in the transparent block. [Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units.] 15. A wave generator having a constant frequency produces parallel wave fronts in a tank of water of two different depths. The diagram below represents the wave fronts in the deep water. As the wave travels from the deep water into the shallow water, the speed of the waves decreases. On the diagram at right, use a straightedge to draw at least three lines to represent the wave fronts, with appropriate spacing, in the shallow water. Page 184 WAV.C2 APlusPhysics:
4 16. A laser beam is directed at the surface of a smooth, calm pond as represented in the diagram below. Which organisms could be illuminated by the laser light? 1. the bird and the fish 2. the bird and the seaweed 3. the crab and the seaweed 4. the crab and the fish Base your answers to questions 17 through 19 on the information and diagram below. A ray of light (f= Hz) is incident on the boundary between air and an unknown material X at an angle of incidence of 55, as shown. The absolute index of refraction of material X is Determine the speed of this ray of light in material X. 18. Calculate the angle of refraction of the ray of light in material X. 19. On the diagram above, use a straightedge and protractor to draw the refracted ray of light in material X. APlusPhysics: WAV.C2 Page 185
5 20. A ray of monochromatic light (f= Hz) passes from water through flint glass (n=1.66) and into medium X, as shown below. Base your answers to questions 24 through 26 on the information and diagram below. A ray of light passes from air into a block of transparent material X as shown in the diagram below. The absolute index of refraction of medium X is 1. less than greater than 1.33 and less than greater than 1.52 and less than equal to A beam of light travels through medium X with a speed of meters per second. Calculate the absolute index of refraction of medium X. [Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units.] 22. What happens to the speed and frequency of a light ray when it passes from air into water? 1. The speed decreases and the frequency increases. 2. The speed decreases and the frequency remains the same. 3. The speed increases and the frequency increases. 4. The speed increases and the frequency remains the same. 23. A ray of monochromatic light (f= Hz) in air is incident at an angle of 30 on a boundary with corn oil (n=1.47). What is the angle of refraction, to the nearest degree, for this light ray in the corn oil? Measure the angles of incidence and refraction to the nearest degree for this light ray at the air into material X boundary. θ i = θ r = 25. Calculate the absolute index of refraction of material X. [Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units.] 26. The refracted light ray is reflected from the material X air boundary at point P. Using a protractor and straightedge, on the diagram in your answer booklet, draw the reflected ray from point P. 27. If the speed of a wave doubles as it passes from shallow water into deeper water, its wavelength will be 1. unchanged 2. doubled 3. halved 4. quadrupled Page 186 WAV.C2 APlusPhysics:
6 Base your answers to questions 28 and 29 on the information and diagram below. A ray of monochromatic light (f= Hz) passes from air into Lucite at an angle of incidence of Calculate the angle of refraction in the Lucite. [Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units.] 29. Using a protractor and straightedge, on the diagram draw the refracted ray in the Lucite. 30. Which ray diagram best represents the phenomenon of refraction? 31. The diagram at right represents straight wave fronts passing from deep water into shallow water, with a change in speed and direction. Which phenomenon is illustrated in the diagram? 1. reflection 2. refraction 3. diffraction 4. interference APlusPhysics: WAV.C2 Page 187
7 Base your answers to questions 32 through 34 on the information and diagram below. A light ray with a frequency of hertz traveling in air is incident at an angle of 40 on an air-water interface as shown. At the interface, part of the ray is refracted as it enters the water and part of the ray is reflected from the interface. 36. The speed of light in a piece of plastic is meters per second. What is the absolute index of refraction of this plastic? A ray of monochromatic light is incident on an airsodium chloride (n=1.54) boundary as shown in the diagram below. At the boundary, part of the ray is reflected back into the air and part is refracted as it enters the sodium chloride. 32. Calculate the angle of refraction of the light ray as it enters the water. [Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units.] 33. On the diagram above, using a protractor and straightedge, draw the refracted ray. Label this ray Refracted ray. Compared to the ray s angle of refraction in the sodium chloride, the ray s angle of reflection in the air is 1. smaller 2. larger 3. the same 38. The diagram below shows a ray of light passing from air into glass at an angle of incidence of On the diagram above, using a protractor and straightedge, draw the reflected ray. Label this ray Reflected ray. 35. An electromagnetic wave of wavelength meter traveling through air is incident on an interface with corn oil (n=1.47). Calculate the wavelength of the EM wave in corn oil. Page 188 WAV.C2 Which statement best describes the speed and direction of the light ray as it passes into the glass? 1. Only speed changes. 2. Only direction changes. 3. Both speed and direction change. 4. Neither speed nor direction changes. APlusPhysics:
8 Base your answers to questions 39 through 42 on the diagram below, which represents a ray of monochromatic light ( Hz) in air incident on flint glass (n=1.66). 39. Determine the angle of incidence of the light ray in air. 40. Calculate the angle of refraction of the light ray in the flint glass. [Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units.] 41. Using a protractor and straightedge, draw the refracted ray on the diagram. 42. What happens to the light from the incident ray that is not refracted or absorbed? 43. The diagram below represents a wave. What is the speed of the wave if its frequency is 8.0 hertz? m/s m/s m/s m/s 44. What is the wavelength of a light ray with frequency hertz as it travels through Lucite (n=1.50)? m m m m 45. The speed of light (f= Hz) in a transparent material is 0.75 times its speed in air. The absolute index of refraction of the material is approximately APlusPhysics: WAV.C2 Page 189
9 46. A light ray traveling in air enters a second medium and its speed slows to meters per second. What is the absolute index of refraction of the second medium? Base your answers to questions 47 and 48 on the diagram below, which represents a light ray traveling from air to Lucite (n=1.50) to medium Y and back into air. 50. What is the speed of light (f= Hz) in flint glass? m/s m/s m/s m/s 51. What happens to the frequency and the speed of an electromagnetic wave as it passes from air into glass? 1. The frequency decreases and the speed increases. 2. The frequency increases and the speed decreases. 3. The frequency remains the same and the speed increases. 4. The frequency remains the same and the speed decreases. 52. When a light wave enters a new medium and is refracted, there must be a change in the light wave s 1. color 2. frequency 3. period 4. speed 47. The sine of angle θ x is Light travels slowest in 1. air, only 2. Lucite, only 3. medium Y, only 4. air, Lucite, and medium Y 49. Which quantity is equivalent to the product of the absolute index of refraction of water and the speed of light in water? 1. wavelength of light in a vacuum 2. frequency of light in water 3. sine of the angle of incidence 4. speed of light in a vacuum 53. As a sound wave passes from water, where the speed is meters per second, into air, the wave s speed 1. decreases and its frequency remains the same 2. increases and its frequency remains the same 3. remains the same and its frequency decreases 4. remains the same and its frequency increases 54. In a certain material, a beam of monochromatic light (f= Hz) has a speed of meters per second. The material could be 1. crown glass (n=1.52) 2. flint glass (n=1.66) 3. glycerol (n=1.47) 4. water (n=1.33) 55. A ray of monochromatic light with frequency Hz is transmitted through four different media: corn oil, ethyl alcohol, flint glass, and water. Rank the four media from the one through which the light travels at the slowest speed to the one through which light travels at the fastest speed. Page 190 WAV.C2 APlusPhysics:
10 Base your answers to questions 56 through 59 on the information below. A light ray (f= Hz) is refracted as it travels from water into flint glass. The path of the light ray in the flint glass is shown in the diagram. 56. Using a protractor, measure the angle of refraction of the light ray in the flint glass. 57. Calculate the angle of incidence for the light ray in water. [Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units.] 58. Using a protractor and straight edge, on the diagram draw the path of the incident light ray in the water. 59. Identify one physical event, other than transmission or refraction, that occurs as the light interacts with the water-flint glass boundary. 60. The wavelength of a wave doubles as it travels from medium A into medium B. Compared to the wave in medium A, the wave in medium B has 1. half the speed 2. twice the speed 3. half the frequency 4. twice the frequency 62. What is the speed of light (f= Hz) in ethyl alcohol? m/s m/s m/s m/s 61. A ray of light (f= Hz) travels through various substances. Which graph best represents the relationship between the absolute index of refraction of these substances and the corresponding speed of light in these substances? APlusPhysics: WAV.C2 Page 191
11 Base your answers to questions 63 through 66 on the information below. A light ray (f= Hz) traveling in water has an angle of incidence of 35 on a water-air interface. At the interface, part of the ray is reflected from the interface and part of the ray is refracted as it enters the air. 67. As a monochromatic light ray passes from air into water, two characteristics of the ray that will not change are 1. wavelength and period 2. frequency and period 3. wavelength and speed 4. frequency and speed 63. What is the angle of reflection of the light ray at the interface? 68. Which graph best represents the relationship between the absolute index of refraction and the speed of light (f= Hz) in various media? 64. On the diagram below, using a protractor and a straightedge, draw the reflected ray. 69. When a ray of light traveling in water reaches a boundary with air, part of the light ray is reflected and part is refracted. Which ray diagram best represents the paths of the reflected and refracted rays? 65. Calculate the angle of refraction of the light ray as it enters the air. [Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units.] 66. Identify one characteristic of this light ray that is the same in both the water and the air. Page 192 WAV.C2 APlusPhysics:
12 70. Which characteristic of a light wave must increase as the light wave passes from glass into air? 1. amplitude 2. frequency 3. period 4. wavelength 71. A ray of yellow light (f = Hz) travels at a speed of meters per second in 1. ethyl alcohol 2. water 3. Lucite 4. glycerol Base your answers to questions 72 and 73 on the information and diagram below. A ray of light (f= Hz) traveling through a block of an unknown material, passes at an angle of incidence of 30 into air, as shown in the diagram below. 72. Use a protractor to determine the angle of refraction of the light ray as it passes from the unknown material into air. 73. Calculate the index of refraction of the unknown material. [Show all work, including the equation and substitution with units.] APlusPhysics: WAV.C2 Page 193
1. Which diagram best represents the reflection of light from an irregular surface?
 waves 6-2-04 Name 02-JUN-04 1. Which diagram best represents the reflection of light from an irregular surface? 1. 1 3. 3 2. 2 4. 4 2. In a vacuum, a monochromatic beam of light as a frequency of 6.3 X
waves 6-2-04 Name 02-JUN-04 1. Which diagram best represents the reflection of light from an irregular surface? 1. 1 3. 3 2. 2 4. 4 2. In a vacuum, a monochromatic beam of light as a frequency of 6.3 X
Basic Waves, Sound & Light Waves, and the E & M Spectrum
 Basic Waves, Sound & Light Waves, and the E & M Spectrum 1. What are the amplitude and wavelength of the wave shown below? A) amplitude = 0.10 m, wavelength = 0.30 m B) amplitude = 0.10 m, wavelength =
Basic Waves, Sound & Light Waves, and the E & M Spectrum 1. What are the amplitude and wavelength of the wave shown below? A) amplitude = 0.10 m, wavelength = 0.30 m B) amplitude = 0.10 m, wavelength =
Midterm Review Exam. 1. The diagram below represents a transverse wave.
 Midterm Review Exam Name: 1. The diagram below represents a transverse wave. 4. The graph below represents the displacement of a particle in a medium over a period of time. The wavelength of the wave is
Midterm Review Exam Name: 1. The diagram below represents a transverse wave. 4. The graph below represents the displacement of a particle in a medium over a period of time. The wavelength of the wave is
Refraction of Light. c = m / s. n = c v. The index of refraction is never less than 1. Some common indices of refraction are listed below.
 Refraction of Light The speed of light in a vacuum is c = 3.00 10 8 m / s In air, the speed is only slightly less. In other transparent materials, such as glass and water, the speed is always less than
Refraction of Light The speed of light in a vacuum is c = 3.00 10 8 m / s In air, the speed is only slightly less. In other transparent materials, such as glass and water, the speed is always less than
Index of refraction n
 Refraction 1 Refraction Cause 2 Index of refraction n In texbook n values Diamond Flint Glass Crown Glass Fused quartz Ice Benzene Ethyl Alcohol Water Carbon Dioxide Air Others corn oil glycerol Lucite
Refraction 1 Refraction Cause 2 Index of refraction n In texbook n values Diamond Flint Glass Crown Glass Fused quartz Ice Benzene Ethyl Alcohol Water Carbon Dioxide Air Others corn oil glycerol Lucite
Plane mirror. Norrnal. Nome. Take Home - Reflection ondrefroction
 Take Home - Reflection ondrefroction Nome ') A ray of monochromatic light traveling in air is.incident on a plane minor at an angle of 30'o, as shown in the diagram below. Plane mirror The angle of reflection
Take Home - Reflection ondrefroction Nome ') A ray of monochromatic light traveling in air is.incident on a plane minor at an angle of 30'o, as shown in the diagram below. Plane mirror The angle of reflection
Unit 5.A Properties of Light Essential Fundamentals of Light 1. Electromagnetic radiation has oscillating magnetic and electric components.
 Unit 5.A Properties of Light Essential Fundamentals of Light 1. Electromagnetic radiation has oscillating magnetic and electric components. Early Booklet E.C.: + 1 Unit 5.A Hwk. Pts.: / 18 Unit 5.A Lab
Unit 5.A Properties of Light Essential Fundamentals of Light 1. Electromagnetic radiation has oscillating magnetic and electric components. Early Booklet E.C.: + 1 Unit 5.A Hwk. Pts.: / 18 Unit 5.A Lab
Geometrical optics: Refraction *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m40065 1 Geometrical optics: Refraction * Free High School Science Texts Project This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0
OpenStax-CNX module: m40065 1 Geometrical optics: Refraction * Free High School Science Texts Project This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0
Reflection & Refraction
 Name: Anwer Key Date: Regent Phyic Tet # 14 Review Reflection & Refraction 1. Ue GUESS method and indicate all vector direction.. Term to know: electromagnetic pectrum, diffue reflection, regular reflection,
Name: Anwer Key Date: Regent Phyic Tet # 14 Review Reflection & Refraction 1. Ue GUESS method and indicate all vector direction.. Term to know: electromagnetic pectrum, diffue reflection, regular reflection,
Physics 11 - Waves Extra Practice Questions
 Physics - Waves xtra Practice Questions. Wave motion in a medium transfers ) energy, only ) mass, only. both mass and energy. neither mass nor energy. single vibratory disturbance that moves from point
Physics - Waves xtra Practice Questions. Wave motion in a medium transfers ) energy, only ) mass, only. both mass and energy. neither mass nor energy. single vibratory disturbance that moves from point
SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT. Key Concepts. X-planation. Physical Sciences Grade In this session we:
 SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT Key Concepts In this session we: Explain what light is, where light comes from and why it is important Identify what happens when light strikes the surface of different objects
SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT Key Concepts In this session we: Explain what light is, where light comes from and why it is important Identify what happens when light strikes the surface of different objects
ACTIVITY A FIRST LOOK AT REFRACTION OBJECTIVE To observe optical refraction and theorize the mechanism for the observation.
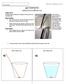 Name (printed) ACTIVITY A FIRST LOOK AT REFRACTION OBJECTIVE To observe optical refraction and theorize the mechanism for the observation. PROCEDURE 1. Start with no water in the cup and orient your line
Name (printed) ACTIVITY A FIRST LOOK AT REFRACTION OBJECTIVE To observe optical refraction and theorize the mechanism for the observation. PROCEDURE 1. Start with no water in the cup and orient your line
AP Practice Test ch 22
 AP Practice Test ch 22 Multiple Choice 1. Tripling the wavelength of the radiation from a monochromatic source will change the energy content of the individually radiated photons by what factor? a. 0.33
AP Practice Test ch 22 Multiple Choice 1. Tripling the wavelength of the radiation from a monochromatic source will change the energy content of the individually radiated photons by what factor? a. 0.33
AP* Optics Free Response Questions
 AP* Optics Free Response Questions 1978 Q5 MIRRORS An object 6 centimeters high is placed 30 centimeters from a concave mirror of focal length 10 centimeters as shown above. (a) On the diagram above, locate
AP* Optics Free Response Questions 1978 Q5 MIRRORS An object 6 centimeters high is placed 30 centimeters from a concave mirror of focal length 10 centimeters as shown above. (a) On the diagram above, locate
NAME:... REFRACTION. Page 1
 NAME:... REFRACTION 1. A ray of red light enters a semi-circular glass block normal to the curved surface. Which diagram correctly shows the partial reflection and refraction of the ray? www.kcpe-kcse.com
NAME:... REFRACTION 1. A ray of red light enters a semi-circular glass block normal to the curved surface. Which diagram correctly shows the partial reflection and refraction of the ray? www.kcpe-kcse.com
EM Spectrum, Reflection & Refraction Test
 EM Spectrum, Reflection & Refraction Test Name: 1. For each of the diagrams below, an object is shown in position before a concave mirror. The shiny side is on the left, facing the object. For each case,
EM Spectrum, Reflection & Refraction Test Name: 1. For each of the diagrams below, an object is shown in position before a concave mirror. The shiny side is on the left, facing the object. For each case,
AP Physics Problems -- Waves and Light
 AP Physics Problems -- Waves and Light 1. 1975-4 (Physical Optics) a. Light of a single wavelength is incident on a single slit of width w. (w is a few wavelengths.) Sketch a graph of the intensity as
AP Physics Problems -- Waves and Light 1. 1975-4 (Physical Optics) a. Light of a single wavelength is incident on a single slit of width w. (w is a few wavelengths.) Sketch a graph of the intensity as
Option G 1: Refraction
 Name: Date: Option G 1: Refraction 1. The table below relates to the electromagnetic spectrum. Complete the table by stating the name of the region of the spectrum and the name of a possible source of
Name: Date: Option G 1: Refraction 1. The table below relates to the electromagnetic spectrum. Complete the table by stating the name of the region of the spectrum and the name of a possible source of
specular diffuse reflection.
 Lesson 8 Light and Optics The Nature of Light Properties of Light: Reflection Refraction Interference Diffraction Polarization Dispersion and Prisms Total Internal Reflection Huygens s Principle The Nature
Lesson 8 Light and Optics The Nature of Light Properties of Light: Reflection Refraction Interference Diffraction Polarization Dispersion and Prisms Total Internal Reflection Huygens s Principle The Nature
CfE Higher Physics. Particles and Waves
 Wallace Hall Academy CfE Higher Physics Particles and Waves Exam Questions Part 2 P&W: Exam Questions Part 2 Version 2013 Contents Section 5: Interference and Diffraction 1 Section 6: Refraction of Light
Wallace Hall Academy CfE Higher Physics Particles and Waves Exam Questions Part 2 P&W: Exam Questions Part 2 Version 2013 Contents Section 5: Interference and Diffraction 1 Section 6: Refraction of Light
Light. Form of Electromagnetic Energy Only part of Electromagnetic Spectrum that we can really see
 Light Form of Electromagnetic Energy Only part of Electromagnetic Spectrum that we can really see Facts About Light The speed of light, c, is constant in a vacuum. Light can be: REFLECTED ABSORBED REFRACTED
Light Form of Electromagnetic Energy Only part of Electromagnetic Spectrum that we can really see Facts About Light The speed of light, c, is constant in a vacuum. Light can be: REFLECTED ABSORBED REFRACTED
Particles and Waves Final Revision Exam Questions Part 2
 Particles and Waves Final Revision Exam Questions Part 2 This illustration shows the dual nature of light, which acts like both particles and waves. In a new experiment reported in November 2012, researchers
Particles and Waves Final Revision Exam Questions Part 2 This illustration shows the dual nature of light, which acts like both particles and waves. In a new experiment reported in November 2012, researchers
Reflection & refraction
 2015 EdExcel A Level Physics 2015 EdExcel A Level Physics Topic Topic 5 5 Reflection & refraction Reflection revision Reflection is the bouncing of light rays off a surface Reflection from a mirror: Normal
2015 EdExcel A Level Physics 2015 EdExcel A Level Physics Topic Topic 5 5 Reflection & refraction Reflection revision Reflection is the bouncing of light rays off a surface Reflection from a mirror: Normal
Purpose: To determine the index of refraction of glass, plastic and water.
 LAB 9 REFRACTION-THE BENDING OF LIGHT Purpose: To determine the index of refraction of glass, plastic and water. Materials: Common pins, glass block, plastic block, small semi-circular water container,
LAB 9 REFRACTION-THE BENDING OF LIGHT Purpose: To determine the index of refraction of glass, plastic and water. Materials: Common pins, glass block, plastic block, small semi-circular water container,
Name Section Date. Experiment Reflection and Refraction
 Name Section Date Introduction: Experiment Reflection and Refraction The travel of light is often represented in geometric optics by a light ray, a line that is drawn to represent the straight-line movement
Name Section Date Introduction: Experiment Reflection and Refraction The travel of light is often represented in geometric optics by a light ray, a line that is drawn to represent the straight-line movement
Light. Electromagnetic wave with wave-like nature Refraction Interference Diffraction
 Light Electromagnetic wave with wave-like nature Refraction Interference Diffraction Light Electromagnetic wave with wave-like nature Refraction Interference Diffraction Photons with particle-like nature
Light Electromagnetic wave with wave-like nature Refraction Interference Diffraction Light Electromagnetic wave with wave-like nature Refraction Interference Diffraction Photons with particle-like nature
speed of light in vacuum = speed of light in the material
 Chapter 5 Let Us Entertain You Snell s law states that as light enters a substance such as acrylic (high index of refraction) from air (low index of refraction), the light bends toward the normal. When
Chapter 5 Let Us Entertain You Snell s law states that as light enters a substance such as acrylic (high index of refraction) from air (low index of refraction), the light bends toward the normal. When
Wavefronts and Rays. When light or other electromagnetic waves interact with systems much larger than the wavelength, it s a good approximation to
 Chapter 33: Optics Wavefronts and Rays When light or other electromagnetic waves interact with systems much larger than the wavelength, it s a good approximation to Neglect the wave nature of light. Consider
Chapter 33: Optics Wavefronts and Rays When light or other electromagnetic waves interact with systems much larger than the wavelength, it s a good approximation to Neglect the wave nature of light. Consider
Physics 122 Spring 2013 Test 1
 Name: Instructions: Physics 122 Spring 2013 Test 1 All answers should be decimal numbers (not functions or fractions) using scientific notation to three significant figures. SI units must be included on
Name: Instructions: Physics 122 Spring 2013 Test 1 All answers should be decimal numbers (not functions or fractions) using scientific notation to three significant figures. SI units must be included on
index of refraction-light speed
 AP Physics Study Guide Chapters 22, 23, 24 Reflection, Refraction and Interference Name Write each of the equations specified below, include units for all quantities. Law of Reflection Lens-Mirror Equation
AP Physics Study Guide Chapters 22, 23, 24 Reflection, Refraction and Interference Name Write each of the equations specified below, include units for all quantities. Law of Reflection Lens-Mirror Equation
16/05/2016. Book page 110 and 112 Syllabus 3.18, Snell s Law. cgrahamphysics.com 2016
 16/05/2016 Snell s Law cgrahamphysics.com 2016 Book page 110 and 112 Syllabus 3.18, 3.19 Match the words to the objects absorbs transmits emits diffracts disperses refracts reflects Fibre optics Totally
16/05/2016 Snell s Law cgrahamphysics.com 2016 Book page 110 and 112 Syllabus 3.18, 3.19 Match the words to the objects absorbs transmits emits diffracts disperses refracts reflects Fibre optics Totally
Textbook Reference: Glencoe Physics: Chapters 16-18
 Honors Physics-121B Geometric Optics Introduction: A great deal of evidence suggests that light travels in straight lines. A source of light like the sun casts distinct shadows. We can hear sound from
Honors Physics-121B Geometric Optics Introduction: A great deal of evidence suggests that light travels in straight lines. A source of light like the sun casts distinct shadows. We can hear sound from
Physics 11. Unit 8 Geometric Optics Part 1
 Physics 11 Unit 8 Geometric Optics Part 1 1.Review of waves In the previous section, we have investigated the nature and behaviors of waves in general. We know that all waves possess the following characteristics:
Physics 11 Unit 8 Geometric Optics Part 1 1.Review of waves In the previous section, we have investigated the nature and behaviors of waves in general. We know that all waves possess the following characteristics:
Light and Electromagnetic Waves. Honors Physics
 Light and Electromagnetic Waves Honors Physics Electromagnetic Waves EM waves are a result of accelerated charges and disturbances in electric and magnetic fields (Radio wave example here) As electrons
Light and Electromagnetic Waves Honors Physics Electromagnetic Waves EM waves are a result of accelerated charges and disturbances in electric and magnetic fields (Radio wave example here) As electrons
Class X Chapter 04 Refraction of Light at Plane Surface Physics
 EXERCISE - 4 (A) Question 1: What do you understand by refraction of light? Solution 1: The change in the direction of the path of light, when it passes from one transparent medium to another transparent
EXERCISE - 4 (A) Question 1: What do you understand by refraction of light? Solution 1: The change in the direction of the path of light, when it passes from one transparent medium to another transparent
Reflection and Refraction of Light
 PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics II Reflection and Refraction of Light 1 Objectives Investigate for reflection of rays from a plane surface, the dependence of the angle of reflection on the angle of incidence.
PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics II Reflection and Refraction of Light 1 Objectives Investigate for reflection of rays from a plane surface, the dependence of the angle of reflection on the angle of incidence.
CHAP: REFRACTION OF LIGHT AT PLANE SURFACES
 CHAP: REFRACTION OF LIGHT AT PLANE SURFACES Ex : 4A Q: 1 The change in the direction of the path of light, when it passes from one transparent medium to another transparent medium, is called refraction
CHAP: REFRACTION OF LIGHT AT PLANE SURFACES Ex : 4A Q: 1 The change in the direction of the path of light, when it passes from one transparent medium to another transparent medium, is called refraction
Physics 1C. Lecture 25B. "There are two ways of spreading light: to be the candle or the mirror that reflects it." --Edith Wharton
 Physics 1C Lecture 25B "There are two ways of spreading light: to be the candle or the mirror that reflects it." --Edith Wharton Refraction of Light When light passes from one medium to another, it is
Physics 1C Lecture 25B "There are two ways of spreading light: to be the candle or the mirror that reflects it." --Edith Wharton Refraction of Light When light passes from one medium to another, it is
Chapter 18 Ray Optics
 Chapter 18 Ray Optics Chapter Goal: To understand and apply the ray model of light. Slide 18-1 Chapter 18 Preview Looking Ahead Text p. 565 Slide 18-2 Wavefronts and Rays When visible light or other electromagnetic
Chapter 18 Ray Optics Chapter Goal: To understand and apply the ray model of light. Slide 18-1 Chapter 18 Preview Looking Ahead Text p. 565 Slide 18-2 Wavefronts and Rays When visible light or other electromagnetic
Exam Review: Geometric Optics 1. Know the meaning of the following terms and be able to apply or recognize them:
 Exam Review: Geometric Optics 1. Know the meaning of the following terms and be able to apply or recognize them: physics transparent convex mirror real image optics translucent refraction virtual image
Exam Review: Geometric Optics 1. Know the meaning of the following terms and be able to apply or recognize them: physics transparent convex mirror real image optics translucent refraction virtual image
Unit 5.C Physical Optics Essential Fundamentals of Physical Optics
 Unit 5.C Physical Optics Essential Fundamentals of Physical Optics Early Booklet E.C.: + 1 Unit 5.C Hwk. Pts.: / 25 Unit 5.C Lab Pts.: / 20 Late, Incomplete, No Work, No Units Fees? Y / N 1. Light reflects
Unit 5.C Physical Optics Essential Fundamentals of Physical Optics Early Booklet E.C.: + 1 Unit 5.C Hwk. Pts.: / 25 Unit 5.C Lab Pts.: / 20 Late, Incomplete, No Work, No Units Fees? Y / N 1. Light reflects
Lecture Wave Optics. Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org
 Lecture 1202 Wave Optics Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org Total Internal Reflection A phenomenon called total internal reflectioncan occur when light is directed from a medium having a given index
Lecture 1202 Wave Optics Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org Total Internal Reflection A phenomenon called total internal reflectioncan occur when light is directed from a medium having a given index
Willis High School Physics Workbook Unit 7 Waves and Optics
 Willis High School Physics Workbook Unit 7 Waves and Optics This workbook belongs to Period Waves and Optics Pacing Guide DAY DATE TEXTBOOK PREREADING CLASSWORK HOMEWORK ASSESSMENT M 2/25 T 2/26 W 2/27
Willis High School Physics Workbook Unit 7 Waves and Optics This workbook belongs to Period Waves and Optics Pacing Guide DAY DATE TEXTBOOK PREREADING CLASSWORK HOMEWORK ASSESSMENT M 2/25 T 2/26 W 2/27
Light and refractive index
 17 Fig. 7.1 shows a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass block at point X. W P X air glass Q R S Fig. 7.1 The ray of light is refracted at X. On Fig. 7.1, (a) draw the normal at X, [1] (b) draw
17 Fig. 7.1 shows a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass block at point X. W P X air glass Q R S Fig. 7.1 The ray of light is refracted at X. On Fig. 7.1, (a) draw the normal at X, [1] (b) draw
Which row could be correct for the colours seen at X, at Y and at Z?
 1 The ray diagram shows the image of an formed by a converging lens. converging lens image 50 cm What is the focal length of the lens? 40 cm 72 cm 40 cm 50 cm 72 cm 90 cm 2 The diagram shows the dispersion
1 The ray diagram shows the image of an formed by a converging lens. converging lens image 50 cm What is the focal length of the lens? 40 cm 72 cm 40 cm 50 cm 72 cm 90 cm 2 The diagram shows the dispersion
FLAP P6.2 Rays and geometrical optics COPYRIGHT 1998 THE OPEN UNIVERSITY S570 V1.1
 F1 The ray approximation in optics assumes that light travels from one point to another along a narrow path called a ray that may be represented by a directed line (i.e. a line with an arrow on it). In
F1 The ray approximation in optics assumes that light travels from one point to another along a narrow path called a ray that may be represented by a directed line (i.e. a line with an arrow on it). In
Refraction: Snell's Law. October 26, 2010
 Refraction: Snell's Law October 26, 2010 When light passes from one medium into another, part of the incident light is reflected at the boundary The remainder passes into the new medium. Unless it is perpendicular,
Refraction: Snell's Law October 26, 2010 When light passes from one medium into another, part of the incident light is reflected at the boundary The remainder passes into the new medium. Unless it is perpendicular,
3. For an incoming ray of light vacuum wavelength 589 nm, fill in the unknown values in the following table.
 Homework Set 15A: Mirrors and Lenses 1. Find the angle of refraction for a ray of light that enters a bucket of water from air at an angle of 25 degrees to the normal. 2. A ray of light of vacuum wavelength
Homework Set 15A: Mirrors and Lenses 1. Find the angle of refraction for a ray of light that enters a bucket of water from air at an angle of 25 degrees to the normal. 2. A ray of light of vacuum wavelength
Optics: Reflection and Refraction (approx. completion time: 2.5 h) (3/28/11)
 Optics: Reflection and Refraction (approx. completion time: 2.5 h) (3/28/11) Introduction In this lab you will investigate the reflection and refraction of light. Reflection of light from a surface is
Optics: Reflection and Refraction (approx. completion time: 2.5 h) (3/28/11) Introduction In this lab you will investigate the reflection and refraction of light. Reflection of light from a surface is
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Practice Test Light Equations Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which colour of light has the shortest wavelength? a. red c. green b. blue
Practice Test Light Equations Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which colour of light has the shortest wavelength? a. red c. green b. blue
Regents Physics Lab #30R. Due Date. Refraction of Light
 Name Date Regents Physics Lab #0R Period Mrs. Nadworny Research Problem Materials Refraction of Light Due Date When a ray of light passes obliquely (at an angle) from air to glass, it is refracted. The
Name Date Regents Physics Lab #0R Period Mrs. Nadworny Research Problem Materials Refraction of Light Due Date When a ray of light passes obliquely (at an angle) from air to glass, it is refracted. The
Refraction of Light. Research Problem. Materials. Procedure. Due Date. Glass Block Protractor Ruler PENCIL 4 Pins Cardboard
 Name SI Physics Period Date Lab #0(90 pts) Mrs. Nadworny Due Date Research Problem Materials Refraction of Light When a ray of light passes obliquely (at an angle) from air to glass, it is refracted. The
Name SI Physics Period Date Lab #0(90 pts) Mrs. Nadworny Due Date Research Problem Materials Refraction of Light When a ray of light passes obliquely (at an angle) from air to glass, it is refracted. The
Refraction of Light. This bending of the ray is called refraction
 Refraction & Lenses Refraction of Light When a ray of light traveling through a transparent medium encounters a boundary leading into another transparent medium, part of the ray is reflected and part of
Refraction & Lenses Refraction of Light When a ray of light traveling through a transparent medium encounters a boundary leading into another transparent medium, part of the ray is reflected and part of
Chapter 24. Geometric optics. Assignment No. 11, due April 27th before class: Problems 24.4, 24.11, 24.13, 24.15, 24.24
 Chapter 24 Geometric optics Assignment No. 11, due April 27th before class: Problems 24.4, 24.11, 24.13, 24.15, 24.24 A Brief History of Light 1000 AD It was proposed that light consisted of tiny particles
Chapter 24 Geometric optics Assignment No. 11, due April 27th before class: Problems 24.4, 24.11, 24.13, 24.15, 24.24 A Brief History of Light 1000 AD It was proposed that light consisted of tiny particles
Ray Optics. Lecture 23. Chapter 23. Physics II. Course website:
 Lecture 23 Chapter 23 Physics II Ray Optics Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Let s finish talking about a diffraction grating Diffraction Grating Let s improve (more
Lecture 23 Chapter 23 Physics II Ray Optics Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Let s finish talking about a diffraction grating Diffraction Grating Let s improve (more
3/10/2019. Models of Light. Waves and wave fronts. Wave fronts and rays
 Models of Light The wave model: Under many circumstances, light exhibits the same behavior as material waves. The study of light as a wave is called wave optics. The ray model: The properties of prisms,
Models of Light The wave model: Under many circumstances, light exhibits the same behavior as material waves. The study of light as a wave is called wave optics. The ray model: The properties of prisms,
Episode 317: Reflection and refraction of waves
 Episode 317: Reflection and refraction of waves This episode starts from the phenomenon of refraction and moves on to Snell s law. Summary Demonstration + discussion: Reflection and refraction with ripple
Episode 317: Reflection and refraction of waves This episode starts from the phenomenon of refraction and moves on to Snell s law. Summary Demonstration + discussion: Reflection and refraction with ripple
PSC20 - Properties of Waves 3
 PSC20 - Properties of Waves 3 The speed of light is in a vacuum. it travels 299 972 458 m/s. (rounded to m/s). Speed of light is given the symbol comes from the word meaning. How far do you think light
PSC20 - Properties of Waves 3 The speed of light is in a vacuum. it travels 299 972 458 m/s. (rounded to m/s). Speed of light is given the symbol comes from the word meaning. How far do you think light
Lecture 7 Notes: 07 / 11. Reflection and refraction
 Lecture 7 Notes: 07 / 11 Reflection and refraction When an electromagnetic wave, such as light, encounters the surface of a medium, some of it is reflected off the surface, while some crosses the boundary
Lecture 7 Notes: 07 / 11 Reflection and refraction When an electromagnetic wave, such as light, encounters the surface of a medium, some of it is reflected off the surface, while some crosses the boundary
New topic: Diffraction only one slit, but wide. From Last time. Huygen s principle. Overlapping diffraction patterns. Diffraction from other objects
 New topic: Diffraction only one slit, but wide From Last time Two-source interference: Interference-like pattern from a single slit. For a slit: a θ central width ~ 2 Diffraction grating Week3HW on Mastering
New topic: Diffraction only one slit, but wide From Last time Two-source interference: Interference-like pattern from a single slit. For a slit: a θ central width ~ 2 Diffraction grating Week3HW on Mastering
Past Paper Questions Waves
 Past Paper Questions Waves Name 1. Explain the differences between an undamped progressive transverse wave and a stationary transverse wave, in terms of amplitude, (ii) phase and (iii) energy transfer.
Past Paper Questions Waves Name 1. Explain the differences between an undamped progressive transverse wave and a stationary transverse wave, in terms of amplitude, (ii) phase and (iii) energy transfer.
Ray Optics. Lecture 23. Chapter 34. Physics II. Course website:
 Lecture 23 Chapter 34 Physics II Ray Optics Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 34: Section 34.1-3 Ray Optics Ray Optics Wave
Lecture 23 Chapter 34 Physics II Ray Optics Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 34: Section 34.1-3 Ray Optics Ray Optics Wave
Physics 10. Lecture 28A. "If Dracula can t see his reflection in the mirror, how come his hair is always so neatly combed?
 Physics 10 Lecture 28A "If Dracula can t see his reflection in the mirror, how come his hair is always so neatly combed?" --Steven Wright The Nature of Light From now on we will have to treat light as
Physics 10 Lecture 28A "If Dracula can t see his reflection in the mirror, how come his hair is always so neatly combed?" --Steven Wright The Nature of Light From now on we will have to treat light as
What is it? How does it work? How do we use it?
 What is it? How does it work? How do we use it? Dual Nature http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dfpeprq7ogc o Electromagnetic Waves display wave behavior o Created by oscillating electric and magnetic fields
What is it? How does it work? How do we use it? Dual Nature http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dfpeprq7ogc o Electromagnetic Waves display wave behavior o Created by oscillating electric and magnetic fields
Prac%ce Quiz 6. These are Q s from old quizzes. I do not guarantee that the Q s on this year s quiz will be the same, or even similar.
 Prac%ce Quiz 6 These are Q s from old quizzes. I do not guarantee that the Q s on this year s quiz will be the same, or even similar. B You see an airplane straight overhead at an altitude of 5.2km. Sound
Prac%ce Quiz 6 These are Q s from old quizzes. I do not guarantee that the Q s on this year s quiz will be the same, or even similar. B You see an airplane straight overhead at an altitude of 5.2km. Sound
On Fig. 7.1, draw a ray diagram to show the formation of this image.
 1- A small object is placed 30 cm from the centre of a convex lens of focal length 60 cm An enlarged image is observed from the other side of the lens (a) On Fig 71, draw a ray diagram to show the formation
1- A small object is placed 30 cm from the centre of a convex lens of focal length 60 cm An enlarged image is observed from the other side of the lens (a) On Fig 71, draw a ray diagram to show the formation
Figure 1 shows a right-angled glass prism in contact with a transparent substance on one of the faces. One of the other angles of the prism is θ.
 Q1.(a) Tick ( ) the appropriate boxes in the table to indicate how the wavelength, frequency and speed of light are affected when a ray of light travels from air into glass. Wavelength Frequency Speed
Q1.(a) Tick ( ) the appropriate boxes in the table to indicate how the wavelength, frequency and speed of light are affected when a ray of light travels from air into glass. Wavelength Frequency Speed
(Equation 24.1: Index of refraction) We can make sense of what happens in Figure 24.1
 24-1 Refraction To understand what happens when light passes from one medium to another, we again use a model that involves rays and wave fronts, as we did with reflection. Let s begin by creating a short
24-1 Refraction To understand what happens when light passes from one medium to another, we again use a model that involves rays and wave fronts, as we did with reflection. Let s begin by creating a short
Chapter 35. The Nature of Light and the Laws of Geometric Optics
 Chapter 35 The Nature of Light and the Laws of Geometric Optics Introduction to Light Light is basic to almost all life on Earth. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation. Light represents energy transfer
Chapter 35 The Nature of Light and the Laws of Geometric Optics Introduction to Light Light is basic to almost all life on Earth. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation. Light represents energy transfer
Physics 202, Lecture 23
 Physics 202, Lecture 23 Today s Topics Lights and Laws of Geometric Optics Nature of Light Reflection and Refraction Law of Reflection Law of Refraction Index of Reflection, Snell s Law Total Internal
Physics 202, Lecture 23 Today s Topics Lights and Laws of Geometric Optics Nature of Light Reflection and Refraction Law of Reflection Law of Refraction Index of Reflection, Snell s Law Total Internal
Phys 102 Lecture 17 Introduction to ray optics
 Phys 102 Lecture 17 Introduction to ray optics 1 Physics 102 lectures on light Light as a wave Lecture 15 EM waves Lecture 16 Polarization Lecture 22 & 23 Interference & diffraction Light as a ray Lecture
Phys 102 Lecture 17 Introduction to ray optics 1 Physics 102 lectures on light Light as a wave Lecture 15 EM waves Lecture 16 Polarization Lecture 22 & 23 Interference & diffraction Light as a ray Lecture
Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction Units of Chapter 32 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formation by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Mirrors Index of Refraction Refraction:
Chapter 32 Light: Reflection and Refraction Units of Chapter 32 The Ray Model of Light Reflection; Image Formation by a Plane Mirror Formation of Images by Spherical Mirrors Index of Refraction Refraction:
Optics: Laser Light Show Student Advanced Version
 Optics: Laser Light Show Student Advanced Version In this lab, you will explore the behavior of light. You will observe reflection and refraction of a laser beam in jello, and use a diffraction pattern
Optics: Laser Light Show Student Advanced Version In this lab, you will explore the behavior of light. You will observe reflection and refraction of a laser beam in jello, and use a diffraction pattern
Experiment 6. Snell s Law. Use Snell s Law to determine the index of refraction of Lucite.
 Experiment 6 Snell s Law 6.1 Objectives Use Snell s Law to determine the index of refraction of Lucite. Observe total internal reflection and calculate the critical angle. Explain the basis of how optical
Experiment 6 Snell s Law 6.1 Objectives Use Snell s Law to determine the index of refraction of Lucite. Observe total internal reflection and calculate the critical angle. Explain the basis of how optical
Conceptual Physics Fundamentals
 Conceptual Physics Fundamentals Chapter 14: PROPERTIES OF LIGHT This lecture will help you understand: Reflection Refraction Dispersion Total Internal Reflection Lenses Polarization Properties of Light
Conceptual Physics Fundamentals Chapter 14: PROPERTIES OF LIGHT This lecture will help you understand: Reflection Refraction Dispersion Total Internal Reflection Lenses Polarization Properties of Light
Investigation 21A: Refraction of light
 Investigation 21A: Refraction of light Essential question: How does light refract at a boundary? What is the index of refraction of water? Refraction may change the direction of light rays passing from
Investigation 21A: Refraction of light Essential question: How does light refract at a boundary? What is the index of refraction of water? Refraction may change the direction of light rays passing from
Introduction: The Nature of Light
 O1 Introduction: The Nature of Light Introduction Optical elements and systems Basic properties O1.1 Overview Generally Geometrical Optics is considered a less abstract subject than Waves or Physical Optics
O1 Introduction: The Nature of Light Introduction Optical elements and systems Basic properties O1.1 Overview Generally Geometrical Optics is considered a less abstract subject than Waves or Physical Optics
Physics 1C. Lecture 22A. "There are two ways of spreading light: to be the candle or the mirror that reflects it." --Edith Wharton
 Physics 1C Lecture 22A "There are two ways of spreading light: to be the candle or the mirror that reflects it." --Edith Wharton The Nature of Light An interesting question developed as to the nature of
Physics 1C Lecture 22A "There are two ways of spreading light: to be the candle or the mirror that reflects it." --Edith Wharton The Nature of Light An interesting question developed as to the nature of
Physics 132: Lecture Fundamentals of Physics II Agenda for Today
 Physics 132: Lecture Fundamentals of Physics II Agenda for Today Reflection of light Law of reflection Refraction of light Snell s law Dispersion PHY132 Lecture 17, Pg1 Electromagnetic waves A changing
Physics 132: Lecture Fundamentals of Physics II Agenda for Today Reflection of light Law of reflection Refraction of light Snell s law Dispersion PHY132 Lecture 17, Pg1 Electromagnetic waves A changing
Speed of Light in Glass
 Name Date Regents Physics Lab #R Period Mrs. Nadworny Research Problem Materials Speed of Light in Glass Due Date When a ray of light passes obliquely (at an angle) from air to glass, it is refracted.
Name Date Regents Physics Lab #R Period Mrs. Nadworny Research Problem Materials Speed of Light in Glass Due Date When a ray of light passes obliquely (at an angle) from air to glass, it is refracted.
REFRACTION OF LIGHT INDEX NUMBER. Explain this observation (3 marks) 1 Pyramid Assignments / All subjects, All topics available
 NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE REFRACTION OF LIGHT 1. 1995 Q18 P1 Light travels through glass of refractive index 1.5 with a speed v. Calculate the value of v (speed of light in air = 3.0 x 10 8 m/s) (3
NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE REFRACTION OF LIGHT 1. 1995 Q18 P1 Light travels through glass of refractive index 1.5 with a speed v. Calculate the value of v (speed of light in air = 3.0 x 10 8 m/s) (3
REFLECTION & REFRACTION
 REFLECTION & REFRACTION OBJECTIVE: To study and verify the laws of reflection and refraction using a plane mirror and a glass block. To see the virtual images that can be formed by the reflection and refraction
REFLECTION & REFRACTION OBJECTIVE: To study and verify the laws of reflection and refraction using a plane mirror and a glass block. To see the virtual images that can be formed by the reflection and refraction
Refracon. Refracon The spoon in the glass photo can be translated into a ray diagram.
 The of Light Learning Goals: to understand why light refracts when travelling through different media to calculate the index of refraction to use the index of refraction to calculate the speed of light
The of Light Learning Goals: to understand why light refracts when travelling through different media to calculate the index of refraction to use the index of refraction to calculate the speed of light
Phys102 Lecture 21/22 Light: Reflection and Refraction
 Phys102 Lecture 21/22 Light: Reflection and Refraction Key Points The Ray Model of Light Reflection and Mirrors Refraction, Snell s Law Total internal Reflection References 23-1,2,3,4,5,6. The Ray Model
Phys102 Lecture 21/22 Light: Reflection and Refraction Key Points The Ray Model of Light Reflection and Mirrors Refraction, Snell s Law Total internal Reflection References 23-1,2,3,4,5,6. The Ray Model
Unit 9 Light & Optics
 Unit 9 Light & Optics 1 A quick review of the properties of light. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation Light travels as transverse waves having wavelength and frequency. fλ=c The velocity of EMR
Unit 9 Light & Optics 1 A quick review of the properties of light. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation Light travels as transverse waves having wavelength and frequency. fλ=c The velocity of EMR
Chapter 5 Mirrors and Lenses
 Chapter 5 Notes: Mirrors and Lenses Name: Block: The Ray Model of Light The ray model of light represents light as a line, or ray, indicating the path of a beam of light. Light travels in straight lines
Chapter 5 Notes: Mirrors and Lenses Name: Block: The Ray Model of Light The ray model of light represents light as a line, or ray, indicating the path of a beam of light. Light travels in straight lines
TEAMS National Competition High School Version Photometry 25 Questions
 TEAMS National Competition High School Version Photometry 25 Questions Page 1 of 14 Telescopes and their Lenses Although telescopes provide us with the extraordinary power to see objects miles away, the
TEAMS National Competition High School Version Photometry 25 Questions Page 1 of 14 Telescopes and their Lenses Although telescopes provide us with the extraordinary power to see objects miles away, the
Lecture 16: Geometrical Optics. Reflection Refraction Critical angle Total internal reflection. Polarisation of light waves
 Lecture 6: Geometrical Optics Reflection Refraction Critical angle Total internal reflection Polarisation of light waves Geometrical Optics Optics Branch of Physics, concerning the interaction of light
Lecture 6: Geometrical Optics Reflection Refraction Critical angle Total internal reflection Polarisation of light waves Geometrical Optics Optics Branch of Physics, concerning the interaction of light
Light Refraction. 7. For the three situations below, draw a normal line and measure and record the angles of incidence and the angles of refraction.
 Name: Light Refraction Read from Lesson 1 of the Refraction and Lenses chapter at The Physics Classroom: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/refrn/u14l1a.html http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/refrn/u14l1b.html
Name: Light Refraction Read from Lesson 1 of the Refraction and Lenses chapter at The Physics Classroom: http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/refrn/u14l1a.html http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/refrn/u14l1b.html
Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition
 Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition Chapter 28: REFLECTION & REFRACTION This lecture will help you understand: Reflection Principle of Least Time Law of Reflection Refraction Cause of Refraction Dispersion
Conceptual Physics 11 th Edition Chapter 28: REFLECTION & REFRACTION This lecture will help you understand: Reflection Principle of Least Time Law of Reflection Refraction Cause of Refraction Dispersion
: Imaging Systems Laboratory II. Laboratory 2: Snell s Law, Dispersion and the Prism March 19 & 21, n 1 n 2
 05-3: Imaging Systems Laboratory II Laboratory : Snell s Law, Dispersion and the Prism March 9 &, 00 Abstract. This laboratory exercise will demonstrate two basic properties of the way light interacts
05-3: Imaging Systems Laboratory II Laboratory : Snell s Law, Dispersion and the Prism March 9 &, 00 Abstract. This laboratory exercise will demonstrate two basic properties of the way light interacts
Unit 11 Light and Optics Holt Chapter 14 Student Outline Light and Refraction
 Holt Chapter 14 Student Outline Light and Refraction Variables introduced or used in chapter: Quantity Symbol Units Speed of light frequency wavelength angle Object Distance Image Distance Radius of Curvature
Holt Chapter 14 Student Outline Light and Refraction Variables introduced or used in chapter: Quantity Symbol Units Speed of light frequency wavelength angle Object Distance Image Distance Radius of Curvature
Chapter 22. Reflection and Refraction of Light
 Chapter 22 Reflection and Refraction of Light Nature of Light Light has a dual nature. Particle Wave Wave characteristics will be discussed in this chapter. Reflection Refraction These characteristics
Chapter 22 Reflection and Refraction of Light Nature of Light Light has a dual nature. Particle Wave Wave characteristics will be discussed in this chapter. Reflection Refraction These characteristics
Polarisation and Diffraction
 2015 EdExcel A Level Physics 2015 EdExcel A Level Physics Topic Topic 5 5 Polarisation and Diffraction Polarization Polarization is a characteristic of all transverse waves. Oscillation which take places
2015 EdExcel A Level Physics 2015 EdExcel A Level Physics Topic Topic 5 5 Polarisation and Diffraction Polarization Polarization is a characteristic of all transverse waves. Oscillation which take places
All forms of EM waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum = 3.00 x 10 8 m/s This speed is constant in air as well
 Pre AP Physics Light & Optics Chapters 14-16 Light is an electromagnetic wave Electromagnetic waves: Oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to the direction the wave moves Difference
Pre AP Physics Light & Optics Chapters 14-16 Light is an electromagnetic wave Electromagnetic waves: Oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to the direction the wave moves Difference
Prac%ce Quiz 6. These are Q s from old quizzes. I do not guarantee that the Q s on this year s quiz will be the same, or even similar.
 Prac%ce Quiz 6 These are Q s from old quizzes. I do not guarantee that the Q s on this year s quiz will be the same, or even similar. You see an airplane straight overhead at an altitude of 5.2km. Sound
Prac%ce Quiz 6 These are Q s from old quizzes. I do not guarantee that the Q s on this year s quiz will be the same, or even similar. You see an airplane straight overhead at an altitude of 5.2km. Sound
PY106 Class31. Index of refraction. Refraction. Index of refraction. Sample values of n. Rays and wavefronts. index of refraction: n v.
 Refraction Index of refraction When an EM wave travels in a vacuum, its speed is: c = 3.00 x 10 8 m/s. In any other medium, light generally travels at a slower speed. The speed of light v in a material
Refraction Index of refraction When an EM wave travels in a vacuum, its speed is: c = 3.00 x 10 8 m/s. In any other medium, light generally travels at a slower speed. The speed of light v in a material
HALF YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2015/2016. Answer ALL questions showing your working Where necessary give your answers correct to 2 decimal places.
 Track 3 GIRLS SECONDARY, MRIEHEL HALF YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2015/2016 FORM: 4 PHYSICS Time: 1½ hrs Name: Class: Answer ALL questions showing your working Where necessary give your answers correct to 2 decimal
Track 3 GIRLS SECONDARY, MRIEHEL HALF YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2015/2016 FORM: 4 PHYSICS Time: 1½ hrs Name: Class: Answer ALL questions showing your working Where necessary give your answers correct to 2 decimal
Grade 7/8 Math Circles Fall October 9/10/11 Angles and Light
 Facult of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Grade 7/8 Math Circles Fall 2018 - October 9/10/11 Angles and Light Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Toda we will be learning about angles.
Facult of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Grade 7/8 Math Circles Fall 2018 - October 9/10/11 Angles and Light Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Toda we will be learning about angles.
Computer Graphics. Ray Tracing. Based on slides by Dianna Xu, Bryn Mawr College
 Computer Graphics Ray Tracing Based on slides by Dianna Xu, Bryn Mawr College Ray Tracing Example Created by Anto Matkovic Ray Tracing Example Ray Tracing Example Ray Tracing Most light rays do not reach
Computer Graphics Ray Tracing Based on slides by Dianna Xu, Bryn Mawr College Ray Tracing Example Created by Anto Matkovic Ray Tracing Example Ray Tracing Example Ray Tracing Most light rays do not reach
