Solving Linear Recurrence Relations (8.2)
|
|
|
- Alexandra Anderson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EECS 203 Spring 2016 Lecture 18 Page 1 of 10 Review: Recurrence relations (Chapter 8) Last time we started in on recurrence relations. In computer science, one of the primary reasons we look at solving a recurrence relation is because many algorithms, whether really recursive or not (in the sense of calling themselves over and over again) often are implemented by breaking the problem down into smaller parts and solving those. In order to get a solid sense of their runtime, we need to be able to either solve the relation or at least get a sense of its complexity (think big-o). Recall the Towers of Hanoi problem (moving discs) and it s solution: Define T(n) = number of moves when there are n discs. T(1) = 1 T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1 In class last time we guessed at the solution and used an inductive proof to show that the guess (that T(n)=2 n -1) was correct. Today we are going to look at how to find closed form solutions to these problems generally. Last time we worked through solving linear, homogeneous, recurrence relations with constant coefficients of degree 2 Solving Linear Recurrence Relations (8.2) The recurrence is linear because the all the a n terms are just the terms (not raised to some power nor are they part of some function). So a n=2a n-1 is linear but a n=2(a n-1) 2 is not. It is homogeneous because all terms are multiples of some previous value of a n. So a n=2a n-1 is homogeneous, but a n=2a n-1+1 is not. It is of degree k because a n is expressed in terms of the last k terms of the sequence. And it has constant coefficients because all the c terms are constants (not a function of n). We claimed (without proof) that finding the characteristic equation would help. Now, if we divide both sides of this equation by r n-k and move the things around a bit, we get:
2 EECS 203 Spring 2016 Lecture 18 Page 2 of 10 Some new examples: Indicate if the following are linear, homogeneous and have constant coefficients. If they are, find the characteristic equation associated with the recursion. 1. a n=2a n-1+a n-2 2. a n=a n-1+a n a n=2a n-1-4a n-2 4. a n=a n-2+a n-3 5. a n=na n-1+a n-2 Working with LH RR with CC and degree 2 That feels like it jumps out of nowhere. Let s focus on what it says, time allowing we will try to show it makes sense (or at least a bit of sense). The proof is on pages 515 and 516 of the text. Consider the Fibonacci sequence defined by a n=a n-1+a n-2. This is saying we need to find the roots of the characteristic equation and then the solution for this relation is of the form, where r 1 and r 2 are those roots. Notice that α is just an arbitrary constant (that we d have to figure out ) Last time we worked out examples 3 and 4 from the text. Let s try this one: an=3an-1-2an-2; a0=3, a1=4
3 EECS 203 Spring 2016 Lecture 18 Page 3 of 10 Repeated roots Let s do a n=6a n-1-9a n-2 where a 0=1 and a 1=6 What is the characteristic equation? What are the roots of the characteristic equation? What is the solution to the recurrence? General form for arbitrary degree In this class, we will only be working with relations of this type of degree 2. But there is a more general result.
4 EECS 203 Spring 2016 Lecture 18 Page 4 of 10 Again, we aren t going to worry about this general case, but I want you aware it exists. Linear Nonhomogeneous Recurrence Relations with Constant Coefficients Consider (the fairly common) case of a nonhomogeneous relation. That is, we add something that isn t a term of a n but might be a function of n. So order to solve this, we are going to take three steps:. In Solve the associated homogeneous recurrent relation (that is the one that doesn t have that F(n) term!) Find a particular solution based on F(n). Add those two results. We know how to do the first thing. And finding the particular solution in general can be annoying, but for most polynomials we can make progress as follows: In the general case, we ll have the situation that s=1. But that means we need to watch out if the homogeneous solution has a root that is 1 (which seems to happen a lot more than you d expect). Worked Example (Towers of Hanoi) Let s compute a n=2a n-1 +1 with a 1=1 (recall this is what we had for Towers of Hanoi). The associated HRR is r-2=0, so r=2. So the homogeneous part is 2 n. Now we need the particular part. When dealing with the particular solution F(n)=1*1 n, so s doesn t share a root with the characteristic equation (1 2). So our solution is of the form p 0 (a constant). Thus we ve got a n=2 n +p 0. Solving for the
5 EECS 203 Spring 2016 Lecture 18 Page 5 of 10 initial case we get a 0=1=2 0 +p 0. So p 0=-1. And we ve now found, rather than guessed, the closed form for the recurrence relation for Towers of Hanoi. Divide and Conquer and the associated recurrence relations (8.3) Let s look at a few fun algorithms that are what we call divide and conquer -type algorithms. We introduced a binary search algorithm in Section 3.1. This binary search algorithm reduces the search for an element in a search sequence of size n to the binary search for this element in a search sequence of size n/2, when n is even. (Hence, the problem of size n has been reduced to one problem of size n/2.) Two comparisons are needed to implement this reduction (one to determine which half of the list to use and the other to determine whether any terms of the list remain). (page 528) If f(n) is the run time to find an element in a sorted list of n elements (assume n is a power of 2), how many comparisons do we need? Write this as a recurrence relation. Consider a merge sort where we split the list in half, sort each half, and then merge the two sorted lists. What is the recurrence relation that describes the runtime of this algorithm? Assume it takes n steps to merge two lists each of size (n/2) i i Why is n a reasonable number of steps to merge two sorted lists of size n/2 into a sorted list of n items?
6 EECS 203 Spring 2016 Lecture 18 Page 6 of 10 The Master Theorem As we often don t care about specific values, just the order of the complexity of the algorithm, we can generally get away without solving these recurrence relations we are instead happy if we know the order of the solution. And it turns out, there is a plug-and-chug way to do this: The Master Theorem. Examples 1. Using the above, what are the values of a, b, c and d for the binary search algorithm? What is that algorithm s complexity? 2. Using the above, what are the values of a, b, c and d for the merge sort algorithm? What is that algorithm s complexity? 3. Consider the relation F(N)=3F(N/3)+N (which is a merge sort split into 3 parts).
7 EECS 203 Spring 2016 Lecture 18 Page 7 of 10 A graph G=(V,E) consists of: a non-empty set V of vertices (or nodes) a set E of edges Each edge is associated with two vertices (possibly equal). In a directed graph: all edges are directed. Undirected graph: all edges are undirected. Mixed graph: some of each. Some graphs:
8 EECS 203 Spring 2016 Lecture 18 Page 8 of 10 Basic Terminology Vertices u and v are adjacent if they are connected by an edge e o In an undirected graph: e = {u,v} o In a directed graph: e = (u,v) The degree of a vertex deg(v) is the number of edge-ends incident to it. o A self-loop edge is counted twice. o In a directed graph, distinguish: in-degree deg (v): number of incoming edges out-degree deg+(v): number of outgoing edges A subgraph of a graph G = (V,E) is a graph H = (W,F) where W V and F E. o A subgraph H is a proper subgraph if H G. The union of two simple graphs G1 = (V1, E1) and G2 = (V2, E2) is the simple graph with vertex set V1 V2 and edge set E1 E2. o The union of G1 and G2 is denoted by G1 G2. Two vertices u and v in an undirected graph G are called adjacent (or neighbors) in G if u and v are endpoints of an edge e of G. Such an edge e is called incident with the vertices u and v and e is said to connect u and v. The set of all neighbors of a vertex v of G = (V,E), denoted by N(v), is called the neighborhood of V. If A is a subset of V, we denote by N(A) the set of all vertices in G that are adjacent to at least one vertex in A. Examples and Questions: 1. What is the degree of each node? 2. Draw the graph A=(V,E) where V={a, b, c, d}, E={{a,b}, {b,d}} 3. Draw the graph B=(V,E) where V={a, b, c, d}, E={{a,b}, {d,b}, {c,a}} 4. We now have 4 graphs total (A, B, G, H). Are any of them subgraphs of the other? 5. Draw the graph X=(V,E) where V={a, b, c, d}, E={(a,b), (b,d)}
9 EECS 203 Spring 2016 Lecture 18 Page 9 of 10
10 EECS 203 Spring 2016 Lecture 18 Page 10 of 10
DEFINITION OF GRAPH GRAPH THEORY GRAPHS ACCORDING TO THEIR VERTICES AND EDGES EXAMPLE GRAPHS ACCORDING TO THEIR VERTICES AND EDGES
 DEFINITION OF GRAPH GRAPH THEORY Prepared by Engr. JP Timola Reference: Discrete Math by Kenneth H. Rosen A graph G = (V,E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices (or nodes) and E, a set of edges. Each
DEFINITION OF GRAPH GRAPH THEORY Prepared by Engr. JP Timola Reference: Discrete Math by Kenneth H. Rosen A graph G = (V,E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices (or nodes) and E, a set of edges. Each
(Refer Slide Time: 01.26)
 Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture # 22 Why Sorting? Today we are going to be looking at sorting.
Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture # 22 Why Sorting? Today we are going to be looking at sorting.
Last week: Breadth-First Search
 1 Last week: Breadth-First Search Set L i = [] for i=1,,n L 0 = {w}, where w is the start node For i = 0,, n-1: For u in L i : For each v which is a neighbor of u: If v isn t yet visited: - mark v as visited,
1 Last week: Breadth-First Search Set L i = [] for i=1,,n L 0 = {w}, where w is the start node For i = 0,, n-1: For u in L i : For each v which is a neighbor of u: If v isn t yet visited: - mark v as visited,
Today. Types of graphs. Complete Graphs. Trees. Hypercubes.
 Today. Types of graphs. Complete Graphs. Trees. Hypercubes. Complete Graph. K n complete graph on n vertices. All edges are present. Everyone is my neighbor. Each vertex is adjacent to every other vertex.
Today. Types of graphs. Complete Graphs. Trees. Hypercubes. Complete Graph. K n complete graph on n vertices. All edges are present. Everyone is my neighbor. Each vertex is adjacent to every other vertex.
Introduction to Graph Theory
 Introduction to Graph Theory Tandy Warnow January 20, 2017 Graphs Tandy Warnow Graphs A graph G = (V, E) is an object that contains a vertex set V and an edge set E. We also write V (G) to denote the vertex
Introduction to Graph Theory Tandy Warnow January 20, 2017 Graphs Tandy Warnow Graphs A graph G = (V, E) is an object that contains a vertex set V and an edge set E. We also write V (G) to denote the vertex
UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis
![UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis](/thumbs/80/81039886.jpg) UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis Lecture 16 Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-s14/ Lecture 16 Notes Goals for this week Graph basics Types
UCSD CSE 21, Spring 2014 [Section B00] Mathematics for Algorithm and System Analysis Lecture 16 Class URL: http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-s14/ Lecture 16 Notes Goals for this week Graph basics Types
γ(ɛ) (a, b) (a, d) (d, a) (a, b) (c, d) (d, d) (e, e) (e, a) (e, e) (a) Draw a picture of G.
 MAD 3105 Spring 2006 Solutions for Review for Test 2 1. Define a graph G with V (G) = {a, b, c, d, e}, E(G) = {r, s, t, u, v, w, x, y, z} and γ, the function defining the edges, is given by the table ɛ
MAD 3105 Spring 2006 Solutions for Review for Test 2 1. Define a graph G with V (G) = {a, b, c, d, e}, E(G) = {r, s, t, u, v, w, x, y, z} and γ, the function defining the edges, is given by the table ɛ
(5.2) 151 Math Exercises. Graph Terminology and Special Types of Graphs. Malek Zein AL-Abidin
 King Saud University College of Science Department of Mathematics 151 Math Exercises (5.2) Graph Terminology and Special Types of Graphs Malek Zein AL-Abidin ه Basic Terminology First, we give some terminology
King Saud University College of Science Department of Mathematics 151 Math Exercises (5.2) Graph Terminology and Special Types of Graphs Malek Zein AL-Abidin ه Basic Terminology First, we give some terminology
CPSC 536N: Randomized Algorithms Term 2. Lecture 10
 CPSC 536N: Randomized Algorithms 011-1 Term Prof. Nick Harvey Lecture 10 University of British Columbia In the first lecture we discussed the Max Cut problem, which is NP-complete, and we presented a very
CPSC 536N: Randomized Algorithms 011-1 Term Prof. Nick Harvey Lecture 10 University of British Columbia In the first lecture we discussed the Max Cut problem, which is NP-complete, and we presented a very
Clustering Using Graph Connectivity
 Clustering Using Graph Connectivity Patrick Williams June 3, 010 1 Introduction It is often desirable to group elements of a set into disjoint subsets, based on the similarity between the elements in the
Clustering Using Graph Connectivity Patrick Williams June 3, 010 1 Introduction It is often desirable to group elements of a set into disjoint subsets, based on the similarity between the elements in the
CPCS Discrete Structures 1
 Let us switch to a new topic: Graphs CPCS 222 - Discrete Structures 1 Introduction to Graphs Definition: A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices, and E, a set of unordered pairs
Let us switch to a new topic: Graphs CPCS 222 - Discrete Structures 1 Introduction to Graphs Definition: A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices, and E, a set of unordered pairs
1 Leaffix Scan, Rootfix Scan, Tree Size, and Depth
 Lecture 17 Graph Contraction I: Tree Contraction Parallel and Sequential Data Structures and Algorithms, 15-210 (Spring 2012) Lectured by Kanat Tangwongsan March 20, 2012 In this lecture, we will explore
Lecture 17 Graph Contraction I: Tree Contraction Parallel and Sequential Data Structures and Algorithms, 15-210 (Spring 2012) Lectured by Kanat Tangwongsan March 20, 2012 In this lecture, we will explore
Lecture 4: examples of topological spaces, coarser and finer topologies, bases and closed sets
 Lecture 4: examples of topological spaces, coarser and finer topologies, bases and closed sets Saul Glasman 14 September 2016 Let s give the definition of an open subset of R. Definition 1. Let U R. We
Lecture 4: examples of topological spaces, coarser and finer topologies, bases and closed sets Saul Glasman 14 September 2016 Let s give the definition of an open subset of R. Definition 1. Let U R. We
MITOCW watch?v=tkwnms5irbu
 MITOCW watch?v=tkwnms5irbu The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
MITOCW watch?v=tkwnms5irbu The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
Graphs. Introduction To Graphs: Exercises. Definitions:
 Graphs Eng.Jehad Aldahdooh Introduction To Graphs: Definitions: A graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices (or nodes) and E, a set of edges. Each edge has either one or two vertices associated
Graphs Eng.Jehad Aldahdooh Introduction To Graphs: Definitions: A graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices (or nodes) and E, a set of edges. Each edge has either one or two vertices associated
Discrete Mathematics for CS Spring 2008 David Wagner Note 13. An Introduction to Graphs
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Spring 2008 David Wagner Note 13 An Introduction to Graphs Formulating a simple, precise specification of a computational problem is often a prerequisite to writing a
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Spring 2008 David Wagner Note 13 An Introduction to Graphs Formulating a simple, precise specification of a computational problem is often a prerequisite to writing a
Student name: Student ID: MATH 61 (Butler) Midterm II, 12 November 2008
 Student name: Student ID: MATH 61 (Butler) Midterm II, 1 November 008 This test is closed book and closed notes, with the exception that you are allowed one 8 1 11 page of handwritten notes. No calculator
Student name: Student ID: MATH 61 (Butler) Midterm II, 1 November 008 This test is closed book and closed notes, with the exception that you are allowed one 8 1 11 page of handwritten notes. No calculator
CS 171: Introduction to Computer Science II. Quicksort
 CS 171: Introduction to Computer Science II Quicksort Roadmap MergeSort Recursive Algorithm (top-down) Practical Improvements Non-recursive algorithm (bottom-up) Analysis QuickSort Algorithm Analysis Practical
CS 171: Introduction to Computer Science II Quicksort Roadmap MergeSort Recursive Algorithm (top-down) Practical Improvements Non-recursive algorithm (bottom-up) Analysis QuickSort Algorithm Analysis Practical
CS 4349 Lecture October 18th, 2017
 CS 4349 Lecture October 18th, 2017 Main topics for #lecture include #minimum_spanning_trees. Prelude Homework 6 due today. Homework 7 due Wednesday, October 25th. Homework 7 has one normal homework problem.
CS 4349 Lecture October 18th, 2017 Main topics for #lecture include #minimum_spanning_trees. Prelude Homework 6 due today. Homework 7 due Wednesday, October 25th. Homework 7 has one normal homework problem.
1. Suppose you are given a magic black box that somehow answers the following decision problem in polynomial time:
 1. Suppose you are given a magic black box that somehow answers the following decision problem in polynomial time: Input: A CNF formula ϕ with n variables x 1, x 2,..., x n. Output: True if there is an
1. Suppose you are given a magic black box that somehow answers the following decision problem in polynomial time: Input: A CNF formula ϕ with n variables x 1, x 2,..., x n. Output: True if there is an
17/05/2018. Outline. Outline. Divide and Conquer. Control Abstraction for Divide &Conquer. Outline. Module 2: Divide and Conquer
 Module 2: Divide and Conquer Divide and Conquer Control Abstraction for Divide &Conquer 1 Recurrence equation for Divide and Conquer: If the size of problem p is n and the sizes of the k sub problems are
Module 2: Divide and Conquer Divide and Conquer Control Abstraction for Divide &Conquer 1 Recurrence equation for Divide and Conquer: If the size of problem p is n and the sizes of the k sub problems are
Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2013 Vazirani Note 7
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2013 Vazirani Note 7 An Introduction to Graphs A few centuries ago, residents of the city of Königsberg, Prussia were interested in a certain problem.
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2013 Vazirani Note 7 An Introduction to Graphs A few centuries ago, residents of the city of Königsberg, Prussia were interested in a certain problem.
CHAPTER 2. Graphs. 1. Introduction to Graphs and Graph Isomorphism
 CHAPTER 2 Graphs 1. Introduction to Graphs and Graph Isomorphism 1.1. The Graph Menagerie. Definition 1.1.1. A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of a set V of vertices and a set E of edges, represented
CHAPTER 2 Graphs 1. Introduction to Graphs and Graph Isomorphism 1.1. The Graph Menagerie. Definition 1.1.1. A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of a set V of vertices and a set E of edges, represented
CSE 101, Winter Discussion Section Week 1. January 8 - January 15
 CSE 101, Winter 2018 Discussion Section Week 1 January 8 - January 15 Important Annotations were added (post-lecture) to the tablet slides, to fill in a few gaps (Lecture 1) Look through Additional Resources
CSE 101, Winter 2018 Discussion Section Week 1 January 8 - January 15 Important Annotations were added (post-lecture) to the tablet slides, to fill in a few gaps (Lecture 1) Look through Additional Resources
Math 575 Exam 3. (t). What is the chromatic number of G?
 Math 575 Exam 3 Name 1 (a) Draw the Grötsch graph See your notes (b) Suppose that G is a graph having 6 vertices and 9 edges and that the chromatic polynomial of G is given below Fill in the missing coefficients
Math 575 Exam 3 Name 1 (a) Draw the Grötsch graph See your notes (b) Suppose that G is a graph having 6 vertices and 9 edges and that the chromatic polynomial of G is given below Fill in the missing coefficients
Table of Laplace Transforms
 Table of Laplace Transforms 1 1 2 3 4, p > -1 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 Heaviside Function 27 28. Dirac Delta Function 29 30. 31 32. 1 33 34. 35 36. 37 Laplace Transforms
Table of Laplace Transforms 1 1 2 3 4, p > -1 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 Heaviside Function 27 28. Dirac Delta Function 29 30. 31 32. 1 33 34. 35 36. 37 Laplace Transforms
EECS 203 Spring 2016 Lecture 8 Page 1 of 6
 EECS 203 Spring 2016 Lecture 8 Page 1 of 6 Algorithms (3.1-3.3) Algorithms are a huge topic. In CSE we have 2 theory classes purely dedicated to algorithms (EECS 477 and EECS 586) and a number of classes
EECS 203 Spring 2016 Lecture 8 Page 1 of 6 Algorithms (3.1-3.3) Algorithms are a huge topic. In CSE we have 2 theory classes purely dedicated to algorithms (EECS 477 and EECS 586) and a number of classes
Ma/CS 6b Class 5: Graph Connectivity
 Ma/CS 6b Class 5: Graph Connectivity By Adam Sheffer Communications Network We are given a set of routers and wish to connect pairs of them to obtain a connected communications network. The network should
Ma/CS 6b Class 5: Graph Connectivity By Adam Sheffer Communications Network We are given a set of routers and wish to connect pairs of them to obtain a connected communications network. The network should
Trees. 3. (Minimally Connected) G is connected and deleting any of its edges gives rise to a disconnected graph.
 Trees 1 Introduction Trees are very special kind of (undirected) graphs. Formally speaking, a tree is a connected graph that is acyclic. 1 This definition has some drawbacks: given a graph it is not trivial
Trees 1 Introduction Trees are very special kind of (undirected) graphs. Formally speaking, a tree is a connected graph that is acyclic. 1 This definition has some drawbacks: given a graph it is not trivial
This chapter covers recursive definition, including finding closed forms.
 Chapter 12 Recursive Definition This chapter covers recursive definition, including finding closed forms. 12.1 Recursive definitions Thus far, we have defined objects of variable length using semi-formal
Chapter 12 Recursive Definition This chapter covers recursive definition, including finding closed forms. 12.1 Recursive definitions Thus far, we have defined objects of variable length using semi-formal
Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2009 Satish Rao,David Tse Note 8
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2009 Satish Rao,David Tse Note 8 An Introduction to Graphs Formulating a simple, precise specification of a computational problem is often a prerequisite
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2009 Satish Rao,David Tse Note 8 An Introduction to Graphs Formulating a simple, precise specification of a computational problem is often a prerequisite
Lecture 7. s.t. e = (u,v) E x u + x v 1 (2) v V x v 0 (3)
 COMPSCI 632: Approximation Algorithms September 18, 2017 Lecturer: Debmalya Panigrahi Lecture 7 Scribe: Xiang Wang 1 Overview In this lecture, we will use Primal-Dual method to design approximation algorithms
COMPSCI 632: Approximation Algorithms September 18, 2017 Lecturer: Debmalya Panigrahi Lecture 7 Scribe: Xiang Wang 1 Overview In this lecture, we will use Primal-Dual method to design approximation algorithms
Introduction to Graphs
 Graphs Introduction to Graphs Graph Terminology Directed Graphs Special Graphs Graph Coloring Representing Graphs Connected Graphs Connected Component Reading (Epp s textbook) 10.1-10.3 1 Introduction
Graphs Introduction to Graphs Graph Terminology Directed Graphs Special Graphs Graph Coloring Representing Graphs Connected Graphs Connected Component Reading (Epp s textbook) 10.1-10.3 1 Introduction
1 Variations of the Traveling Salesman Problem
 Stanford University CS26: Optimization Handout 3 Luca Trevisan January, 20 Lecture 3 In which we prove the equivalence of three versions of the Traveling Salesman Problem, we provide a 2-approximate algorithm,
Stanford University CS26: Optimization Handout 3 Luca Trevisan January, 20 Lecture 3 In which we prove the equivalence of three versions of the Traveling Salesman Problem, we provide a 2-approximate algorithm,
Distributed Algorithms 6.046J, Spring, Nancy Lynch
 Distributed Algorithms 6.046J, Spring, 205 Nancy Lynch What are Distributed Algorithms? Algorithms that run on networked processors, or on multiprocessors that share memory. They solve many kinds of problems:
Distributed Algorithms 6.046J, Spring, 205 Nancy Lynch What are Distributed Algorithms? Algorithms that run on networked processors, or on multiprocessors that share memory. They solve many kinds of problems:
CSE 331: Introduction to Algorithm Analysis and Design Graphs
 CSE 331: Introduction to Algorithm Analysis and Design Graphs 1 Graph Definitions Graph: A graph consists of a set of verticies V and a set of edges E such that: G = (V, E) V = {v 0, v 1,..., v n 1 } E
CSE 331: Introduction to Algorithm Analysis and Design Graphs 1 Graph Definitions Graph: A graph consists of a set of verticies V and a set of edges E such that: G = (V, E) V = {v 0, v 1,..., v n 1 } E
Binary Decision Diagrams
 Logic and roof Hilary 2016 James Worrell Binary Decision Diagrams A propositional formula is determined up to logical equivalence by its truth table. If the formula has n variables then its truth table
Logic and roof Hilary 2016 James Worrell Binary Decision Diagrams A propositional formula is determined up to logical equivalence by its truth table. If the formula has n variables then its truth table
Chapter 23. Minimum Spanning Trees
 Chapter 23. Minimum Spanning Trees We are given a connected, weighted, undirected graph G = (V,E;w), where each edge (u,v) E has a non-negative weight (often called length) w(u,v). The Minimum Spanning
Chapter 23. Minimum Spanning Trees We are given a connected, weighted, undirected graph G = (V,E;w), where each edge (u,v) E has a non-negative weight (often called length) w(u,v). The Minimum Spanning
CS 561, Lecture 9. Jared Saia University of New Mexico
 CS 561, Lecture 9 Jared Saia University of New Mexico Today s Outline Minimum Spanning Trees Safe Edge Theorem Kruskal and Prim s algorithms Graph Representation 1 Graph Definition A graph is a pair of
CS 561, Lecture 9 Jared Saia University of New Mexico Today s Outline Minimum Spanning Trees Safe Edge Theorem Kruskal and Prim s algorithms Graph Representation 1 Graph Definition A graph is a pair of
Induction Review. Graphs. EECS 310: Discrete Math Lecture 5 Graph Theory, Matching. Common Graphs. a set of edges or collection of two-elt subsets
 EECS 310: Discrete Math Lecture 5 Graph Theory, Matching Reading: MIT OpenCourseWare 6.042 Chapter 5.1-5.2 Induction Review Basic Induction: Want to prove P (n). Prove base case P (1). Prove P (n) P (n+1)
EECS 310: Discrete Math Lecture 5 Graph Theory, Matching Reading: MIT OpenCourseWare 6.042 Chapter 5.1-5.2 Induction Review Basic Induction: Want to prove P (n). Prove base case P (1). Prove P (n) P (n+1)
On Covering a Graph Optimally with Induced Subgraphs
 On Covering a Graph Optimally with Induced Subgraphs Shripad Thite April 1, 006 Abstract We consider the problem of covering a graph with a given number of induced subgraphs so that the maximum number
On Covering a Graph Optimally with Induced Subgraphs Shripad Thite April 1, 006 Abstract We consider the problem of covering a graph with a given number of induced subgraphs so that the maximum number
CMPSCI 311: Introduction to Algorithms Practice Final Exam
 CMPSCI 311: Introduction to Algorithms Practice Final Exam Name: ID: Instructions: Answer the questions directly on the exam pages. Show all your work for each question. Providing more detail including
CMPSCI 311: Introduction to Algorithms Practice Final Exam Name: ID: Instructions: Answer the questions directly on the exam pages. Show all your work for each question. Providing more detail including
Kruskal s MST Algorithm
 Kruskal s MST Algorithm CLRS Chapter 23, DPV Chapter 5 Version of November 5, 2014 Main Topics of This Lecture Kruskal s algorithm Another, but different, greedy MST algorithm Introduction to UNION-FIND
Kruskal s MST Algorithm CLRS Chapter 23, DPV Chapter 5 Version of November 5, 2014 Main Topics of This Lecture Kruskal s algorithm Another, but different, greedy MST algorithm Introduction to UNION-FIND
Programming and Data Structure
 Programming and Data Structure Dr. P.P.Chakraborty Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture # 09 Problem Decomposition by Recursion - II We will
Programming and Data Structure Dr. P.P.Chakraborty Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture # 09 Problem Decomposition by Recursion - II We will
Minimum Spanning Trees
 Minimum Spanning Trees Overview Problem A town has a set of houses and a set of roads. A road connects and only houses. A road connecting houses u and v has a repair cost w(u, v). Goal: Repair enough (and
Minimum Spanning Trees Overview Problem A town has a set of houses and a set of roads. A road connects and only houses. A road connecting houses u and v has a repair cost w(u, v). Goal: Repair enough (and
1 Minimum Cut Problem
 CS 6 Lecture 6 Min Cut and Karger s Algorithm Scribes: Peng Hui How, Virginia Williams (05) Date: November 7, 07 Anthony Kim (06), Mary Wootters (07) Adapted from Virginia Williams lecture notes Minimum
CS 6 Lecture 6 Min Cut and Karger s Algorithm Scribes: Peng Hui How, Virginia Williams (05) Date: November 7, 07 Anthony Kim (06), Mary Wootters (07) Adapted from Virginia Williams lecture notes Minimum
Lecture 19 Thursday, March 29. Examples of isomorphic, and non-isomorphic graphs will be given in class.
 CIS 160 - Spring 2018 (instructor Val Tannen) Lecture 19 Thursday, March 29 GRAPH THEORY Graph isomorphism Definition 19.1 Two graphs G 1 = (V 1, E 1 ) and G 2 = (V 2, E 2 ) are isomorphic, write G 1 G
CIS 160 - Spring 2018 (instructor Val Tannen) Lecture 19 Thursday, March 29 GRAPH THEORY Graph isomorphism Definition 19.1 Two graphs G 1 = (V 1, E 1 ) and G 2 = (V 2, E 2 ) are isomorphic, write G 1 G
Introduction III. Graphs. Motivations I. Introduction IV
 Introduction I Graphs Computer Science & Engineering 235: Discrete Mathematics Christopher M. Bourke cbourke@cse.unl.edu Graph theory was introduced in the 18th century by Leonhard Euler via the Königsberg
Introduction I Graphs Computer Science & Engineering 235: Discrete Mathematics Christopher M. Bourke cbourke@cse.unl.edu Graph theory was introduced in the 18th century by Leonhard Euler via the Königsberg
Design and Analysis of Algorithms Prof. Madhavan Mukund Chennai Mathematical Institute
 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Prof. Madhavan Mukund Chennai Mathematical Institute Module 07 Lecture - 38 Divide and Conquer: Closest Pair of Points We now look at another divide and conquer algorithm,
Design and Analysis of Algorithms Prof. Madhavan Mukund Chennai Mathematical Institute Module 07 Lecture - 38 Divide and Conquer: Closest Pair of Points We now look at another divide and conquer algorithm,
Figure 4.1: The evolution of a rooted tree.
 106 CHAPTER 4. INDUCTION, RECURSION AND RECURRENCES 4.6 Rooted Trees 4.6.1 The idea of a rooted tree We talked about how a tree diagram helps us visualize merge sort or other divide and conquer algorithms.
106 CHAPTER 4. INDUCTION, RECURSION AND RECURRENCES 4.6 Rooted Trees 4.6.1 The idea of a rooted tree We talked about how a tree diagram helps us visualize merge sort or other divide and conquer algorithms.
Advanced algorithms. topological ordering, minimum spanning tree, Union-Find problem. Jiří Vyskočil, Radek Mařík 2012
 topological ordering, minimum spanning tree, Union-Find problem Jiří Vyskočil, Radek Mařík 2012 Subgraph subgraph A graph H is a subgraph of a graph G, if the following two inclusions are satisfied: 2
topological ordering, minimum spanning tree, Union-Find problem Jiří Vyskočil, Radek Mařík 2012 Subgraph subgraph A graph H is a subgraph of a graph G, if the following two inclusions are satisfied: 2
Section 8.2 Graph Terminology. Undirected Graphs. Definition: Two vertices u, v in V are adjacent or neighbors if there is an edge e between u and v.
 Section 8.2 Graph Terminology Undirected Graphs Definition: Two vertices u, v in V are adjacent or neighbors if there is an edge e between u and v. The edge e connects u and v. The vertices u and v are
Section 8.2 Graph Terminology Undirected Graphs Definition: Two vertices u, v in V are adjacent or neighbors if there is an edge e between u and v. The edge e connects u and v. The vertices u and v are
(Re)Introduction to Graphs and Some Algorithms
 (Re)Introduction to Graphs and Some Algorithms Graph Terminology (I) A graph is defined by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. The edge set must work over the defined vertices in the vertex set.
(Re)Introduction to Graphs and Some Algorithms Graph Terminology (I) A graph is defined by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. The edge set must work over the defined vertices in the vertex set.
Discrete Structures CISC 2315 FALL Graphs & Trees
 Discrete Structures CISC 2315 FALL 2010 Graphs & Trees Graphs A graph is a discrete structure, with discrete components Components of a Graph edge vertex (node) Vertices A graph G = (V, E), where V is
Discrete Structures CISC 2315 FALL 2010 Graphs & Trees Graphs A graph is a discrete structure, with discrete components Components of a Graph edge vertex (node) Vertices A graph G = (V, E), where V is
Approximation slides 1. An optimal polynomial algorithm for the Vertex Cover and matching in Bipartite graphs
 Approximation slides 1 An optimal polynomial algorithm for the Vertex Cover and matching in Bipartite graphs Approximation slides 2 Linear independence A collection of row vectors {v T i } are independent
Approximation slides 1 An optimal polynomial algorithm for the Vertex Cover and matching in Bipartite graphs Approximation slides 2 Linear independence A collection of row vectors {v T i } are independent
U.C. Berkeley CS170 : Algorithms, Fall 2013 Midterm 1 Professor: Satish Rao October 10, Midterm 1 Solutions
 U.C. Berkeley CS170 : Algorithms, Fall 2013 Midterm 1 Professor: Satish Rao October 10, 2013 Midterm 1 Solutions 1 True/False 1. The Mayan base 20 system produces representations of size that is asymptotically
U.C. Berkeley CS170 : Algorithms, Fall 2013 Midterm 1 Professor: Satish Rao October 10, 2013 Midterm 1 Solutions 1 True/False 1. The Mayan base 20 system produces representations of size that is asymptotically
We can use a max-heap to sort data.
 Sorting 7B N log N Sorts 1 Heap Sort We can use a max-heap to sort data. Convert an array to a max-heap. Remove the root from the heap and store it in its proper position in the same array. Repeat until
Sorting 7B N log N Sorts 1 Heap Sort We can use a max-heap to sort data. Convert an array to a max-heap. Remove the root from the heap and store it in its proper position in the same array. Repeat until
MATH20902: Discrete Maths, Solutions to Problem Set 1. These solutions, as well as the corresponding problems, are available at
 MATH20902: Discrete Maths, Solutions to Problem Set 1 These solutions, as well as the corresponding problems, are available at https://bit.ly/mancmathsdiscrete.. (1). The upper panel in the figure below
MATH20902: Discrete Maths, Solutions to Problem Set 1 These solutions, as well as the corresponding problems, are available at https://bit.ly/mancmathsdiscrete.. (1). The upper panel in the figure below
Algorithms: Lecture 7. Chalmers University of Technology
 Algorithms: Lecture 7 Chalmers University of Technology Today s Lecture Divide & Conquer Counting Inversions Closest Pair of Points Multiplication of large integers Intro to the forthcoming problems Graphs:
Algorithms: Lecture 7 Chalmers University of Technology Today s Lecture Divide & Conquer Counting Inversions Closest Pair of Points Multiplication of large integers Intro to the forthcoming problems Graphs:
Lecture 4: September 11, 2003
 Algorithmic Modeling and Complexity Fall 2003 Lecturer: J. van Leeuwen Lecture 4: September 11, 2003 Scribe: B. de Boer 4.1 Overview This lecture introduced Fixed Parameter Tractable (FPT) problems. An
Algorithmic Modeling and Complexity Fall 2003 Lecturer: J. van Leeuwen Lecture 4: September 11, 2003 Scribe: B. de Boer 4.1 Overview This lecture introduced Fixed Parameter Tractable (FPT) problems. An
(Refer Slide Time: 05:25)
 Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering IIT Delhi Lecture 30 Applications of DFS in Directed Graphs Today we are going to look at more applications
Data Structures and Algorithms Dr. Naveen Garg Department of Computer Science and Engineering IIT Delhi Lecture 30 Applications of DFS in Directed Graphs Today we are going to look at more applications
Basic Combinatorics. Math 40210, Section 01 Fall Homework 4 Solutions
 Basic Combinatorics Math 40210, Section 01 Fall 2012 Homework 4 Solutions 1.4.2 2: One possible implementation: Start with abcgfjiea From edge cd build, using previously unmarked edges: cdhlponminjkghc
Basic Combinatorics Math 40210, Section 01 Fall 2012 Homework 4 Solutions 1.4.2 2: One possible implementation: Start with abcgfjiea From edge cd build, using previously unmarked edges: cdhlponminjkghc
15 Graph Theory Counting the Number of Relations. 2. onto (surjective).
 2. onto (surjective). You should convince yourself that if these two properties hold, then it is always going to be the case that f 1 is a function. In order to do this, you should remember the definition
2. onto (surjective). You should convince yourself that if these two properties hold, then it is always going to be the case that f 1 is a function. In order to do this, you should remember the definition
CSE 421 Greedy Alg: Union Find/Dijkstra s Alg
 CSE 1 Greedy Alg: Union Find/Dijkstra s Alg Shayan Oveis Gharan 1 Dijkstra s Algorithm Dijkstra(G, c, s) { d s 0 foreach (v V) d[v] //This is the key of node v foreach (v V) insert v onto a priority queue
CSE 1 Greedy Alg: Union Find/Dijkstra s Alg Shayan Oveis Gharan 1 Dijkstra s Algorithm Dijkstra(G, c, s) { d s 0 foreach (v V) d[v] //This is the key of node v foreach (v V) insert v onto a priority queue
Complete Cototal Domination
 Chapter 5 Complete Cototal Domination Number of a Graph Published in Journal of Scientific Research Vol. () (2011), 547-555 (Bangladesh). 64 ABSTRACT Let G = (V,E) be a graph. A dominating set D V is said
Chapter 5 Complete Cototal Domination Number of a Graph Published in Journal of Scientific Research Vol. () (2011), 547-555 (Bangladesh). 64 ABSTRACT Let G = (V,E) be a graph. A dominating set D V is said
Lecture 3 February 9, 2010
 6.851: Advanced Data Structures Spring 2010 Dr. André Schulz Lecture 3 February 9, 2010 Scribe: Jacob Steinhardt and Greg Brockman 1 Overview In the last lecture we continued to study binary search trees
6.851: Advanced Data Structures Spring 2010 Dr. André Schulz Lecture 3 February 9, 2010 Scribe: Jacob Steinhardt and Greg Brockman 1 Overview In the last lecture we continued to study binary search trees
Adjacent: Two distinct vertices u, v are adjacent if there is an edge with ends u, v. In this case we let uv denote such an edge.
 1 Graph Basics What is a graph? Graph: a graph G consists of a set of vertices, denoted V (G), a set of edges, denoted E(G), and a relation called incidence so that each edge is incident with either one
1 Graph Basics What is a graph? Graph: a graph G consists of a set of vertices, denoted V (G), a set of edges, denoted E(G), and a relation called incidence so that each edge is incident with either one
CSE 2123 Recursion. Jeremy Morris
 CSE 2123 Recursion Jeremy Morris 1 Past Few Weeks For the past few weeks we have been focusing on data structures Classes & Object-oriented programming Collections Lists, Sets, Maps, etc. Now we turn our
CSE 2123 Recursion Jeremy Morris 1 Past Few Weeks For the past few weeks we have been focusing on data structures Classes & Object-oriented programming Collections Lists, Sets, Maps, etc. Now we turn our
2. CONNECTIVITY Connectivity
 2. CONNECTIVITY 70 2. Connectivity 2.1. Connectivity. Definition 2.1.1. (1) A path in a graph G = (V, E) is a sequence of vertices v 0, v 1, v 2,..., v n such that {v i 1, v i } is an edge of G for i =
2. CONNECTIVITY 70 2. Connectivity 2.1. Connectivity. Definition 2.1.1. (1) A path in a graph G = (V, E) is a sequence of vertices v 0, v 1, v 2,..., v n such that {v i 1, v i } is an edge of G for i =
Recursion defining an object (or function, algorithm, etc.) in terms of itself. Recursion can be used to define sequences
 Section 5.3 1 Recursion 2 Recursion Recursion defining an object (or function, algorithm, etc.) in terms of itself. Recursion can be used to define sequences Previously sequences were defined using a specific
Section 5.3 1 Recursion 2 Recursion Recursion defining an object (or function, algorithm, etc.) in terms of itself. Recursion can be used to define sequences Previously sequences were defined using a specific
Lecture 6: Sequential Sorting
 15-150 Lecture 6: Sequential Sorting Lecture by Dan Licata February 2, 2012 Today s lecture is about sorting. Along the way, we ll learn about divide and conquer algorithms, the tree method, and complete
15-150 Lecture 6: Sequential Sorting Lecture by Dan Licata February 2, 2012 Today s lecture is about sorting. Along the way, we ll learn about divide and conquer algorithms, the tree method, and complete
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Algorithms For Inference Fall 2014
 Suggested Reading: Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.438 Algorithms For Inference Fall 2014 Probabilistic Modelling and Reasoning: The Junction
Suggested Reading: Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.438 Algorithms For Inference Fall 2014 Probabilistic Modelling and Reasoning: The Junction
Introduction to Algorithms / Algorithms I Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Shortest Paths Date: 10/13/15
 600.363 Introduction to Algorithms / 600.463 Algorithms I Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Shortest Paths Date: 10/13/15 14.1 Introduction Today we re going to talk about algorithms for computing shortest
600.363 Introduction to Algorithms / 600.463 Algorithms I Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Shortest Paths Date: 10/13/15 14.1 Introduction Today we re going to talk about algorithms for computing shortest
Master Theorem, Introduction to Graphs
 Master Theorem, Introduction to Graphs CSE21 Winter 2017, Day 10 (B00), Day 6-7 (A00) February 1, 2017 http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-w17 Divide & Conquer: General Strategy Divide the problem of
Master Theorem, Introduction to Graphs CSE21 Winter 2017, Day 10 (B00), Day 6-7 (A00) February 1, 2017 http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-w17 Divide & Conquer: General Strategy Divide the problem of
GRAPHS, GRAPH MODELS, GRAPH TERMINOLOGY, AND SPECIAL TYPES OF GRAPHS
 GRAPHS, GRAPH MODELS, GRAPH TERMINOLOGY, AND SPECIAL TYPES OF GRAPHS DR. ANDREW SCHWARTZ, PH.D. 10.1 Graphs and Graph Models (1) A graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices (or nodes)
GRAPHS, GRAPH MODELS, GRAPH TERMINOLOGY, AND SPECIAL TYPES OF GRAPHS DR. ANDREW SCHWARTZ, PH.D. 10.1 Graphs and Graph Models (1) A graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices (or nodes)
Matching Algorithms. Proof. If a bipartite graph has a perfect matching, then it is easy to see that the right hand side is a necessary condition.
 18.433 Combinatorial Optimization Matching Algorithms September 9,14,16 Lecturer: Santosh Vempala Given a graph G = (V, E), a matching M is a set of edges with the property that no two of the edges have
18.433 Combinatorial Optimization Matching Algorithms September 9,14,16 Lecturer: Santosh Vempala Given a graph G = (V, E), a matching M is a set of edges with the property that no two of the edges have
Lecture 8: The Traveling Salesman Problem
 Lecture 8: The Traveling Salesman Problem Let G = (V, E) be an undirected graph. A Hamiltonian cycle of G is a cycle that visits every vertex v V exactly once. Instead of Hamiltonian cycle, we sometimes
Lecture 8: The Traveling Salesman Problem Let G = (V, E) be an undirected graph. A Hamiltonian cycle of G is a cycle that visits every vertex v V exactly once. Instead of Hamiltonian cycle, we sometimes
Crossing bridges. Crossing bridges Great Ideas in Theoretical Computer Science. Lecture 12: Graphs I: The Basics. Königsberg (Prussia)
 15-251 Great Ideas in Theoretical Computer Science Lecture 12: Graphs I: The Basics February 22nd, 2018 Crossing bridges Königsberg (Prussia) Now Kaliningrad (Russia) Is there a way to walk through the
15-251 Great Ideas in Theoretical Computer Science Lecture 12: Graphs I: The Basics February 22nd, 2018 Crossing bridges Königsberg (Prussia) Now Kaliningrad (Russia) Is there a way to walk through the
Lecture 2 : Counting X-trees
 Lecture 2 : Counting X-trees MATH285K - Spring 2010 Lecturer: Sebastien Roch References: [SS03, Chapter 1,2] 1 Trees We begin by recalling basic definitions and properties regarding finite trees. DEF 2.1
Lecture 2 : Counting X-trees MATH285K - Spring 2010 Lecturer: Sebastien Roch References: [SS03, Chapter 1,2] 1 Trees We begin by recalling basic definitions and properties regarding finite trees. DEF 2.1
Recursive definition of sets and structural induction
 CS2209A 2017 Applied Logic for Computer Science Lecture 21, 22 Recursive definition of sets and structural induction Instructor: Marc Moreno Maza 1 Tower of Hanoi game Rules of the game: Start with all
CS2209A 2017 Applied Logic for Computer Science Lecture 21, 22 Recursive definition of sets and structural induction Instructor: Marc Moreno Maza 1 Tower of Hanoi game Rules of the game: Start with all
Graphs V={A,B,C,D,E} E={ (A,D),(A,E),(B,D), (B,E),(C,D),(C,E)}
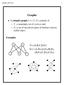 Graphs and Trees 1 Graphs (simple) graph G = (V, ) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices and, a set of unordered pairs of distinct vertices called edges. xamples V={,,,,} ={ (,),(,),(,), (,),(,),(,)}
Graphs and Trees 1 Graphs (simple) graph G = (V, ) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices and, a set of unordered pairs of distinct vertices called edges. xamples V={,,,,} ={ (,),(,),(,), (,),(,),(,)}
Trees. Arash Rafiey. 20 October, 2015
 20 October, 2015 Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called a tree if G is connected and contains no cycle. Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called
20 October, 2015 Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called a tree if G is connected and contains no cycle. Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called
Eulerian Tours and Fleury s Algorithm
 Eulerian Tours and Fleury s Algorithm CSE21 Winter 2017, Day 12 (B00), Day 8 (A00) February 8, 2017 http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-w17 Vocabulary Path (or walk): describes a route from one vertex
Eulerian Tours and Fleury s Algorithm CSE21 Winter 2017, Day 12 (B00), Day 8 (A00) February 8, 2017 http://vlsicad.ucsd.edu/courses/cse21-w17 Vocabulary Path (or walk): describes a route from one vertex
Approximation Algorithms
 15-251: Great Ideas in Theoretical Computer Science Spring 2019, Lecture 14 March 5, 2019 Approximation Algorithms 1 2 SAT 3SAT Clique Hamiltonian- Cycle given a Boolean formula F, is it satisfiable? same,
15-251: Great Ideas in Theoretical Computer Science Spring 2019, Lecture 14 March 5, 2019 Approximation Algorithms 1 2 SAT 3SAT Clique Hamiltonian- Cycle given a Boolean formula F, is it satisfiable? same,
Encoding/Decoding, Counting graphs
 Encoding/Decoding, Counting graphs Russell Impagliazzo and Miles Jones Thanks to Janine Tiefenbruck http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse21-bd/ May 13, 2016 11-avoiding binary strings Let s consider
Encoding/Decoding, Counting graphs Russell Impagliazzo and Miles Jones Thanks to Janine Tiefenbruck http://cseweb.ucsd.edu/classes/sp16/cse21-bd/ May 13, 2016 11-avoiding binary strings Let s consider
1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1
![1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1 1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1](/thumbs/80/82301067.jpg) Asymptotics, Recurrence and Basic Algorithms 1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1 1. O(logn) 2. O(n) 3. O(nlogn) 4. O(n 2 ) 5. O(2 n ) 2. [1 pt] What is the solution
Asymptotics, Recurrence and Basic Algorithms 1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1 1. O(logn) 2. O(n) 3. O(nlogn) 4. O(n 2 ) 5. O(2 n ) 2. [1 pt] What is the solution
Divide & Conquer. 2. Conquer the sub-problems by solving them recursively. 1. Divide the problem into number of sub-problems
 Divide & Conquer Divide & Conquer The Divide & Conquer approach breaks down the problem into multiple smaller sub-problems, solves the sub-problems recursively, then combines the solutions of the sub-problems
Divide & Conquer Divide & Conquer The Divide & Conquer approach breaks down the problem into multiple smaller sub-problems, solves the sub-problems recursively, then combines the solutions of the sub-problems
CS 373: Combinatorial Algorithms, Spring 1999
 CS 373: Combinatorial Algorithms, Spring 1999 Final Exam (May 7, 1999) Name: Net ID: Alias: This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam! If you brought anything with you besides writing instruments and your
CS 373: Combinatorial Algorithms, Spring 1999 Final Exam (May 7, 1999) Name: Net ID: Alias: This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam! If you brought anything with you besides writing instruments and your
Some Hardness Proofs
 Some Hardness Proofs Magnus Lie Hetland January 2011 This is a very brief overview of some well-known hard (NP Hard and NP complete) problems, and the main ideas behind their hardness proofs. The document
Some Hardness Proofs Magnus Lie Hetland January 2011 This is a very brief overview of some well-known hard (NP Hard and NP complete) problems, and the main ideas behind their hardness proofs. The document
Problem Set 2 Solutions
 Problem Set 2 Solutions Graph Theory 2016 EPFL Frank de Zeeuw & Claudiu Valculescu 1. Prove that the following statements about a graph G are equivalent. - G is a tree; - G is minimally connected (it is
Problem Set 2 Solutions Graph Theory 2016 EPFL Frank de Zeeuw & Claudiu Valculescu 1. Prove that the following statements about a graph G are equivalent. - G is a tree; - G is minimally connected (it is
MergeSort, Recurrences, Asymptotic Analysis Scribe: Michael P. Kim Date: April 1, 2015
 CS161, Lecture 2 MergeSort, Recurrences, Asymptotic Analysis Scribe: Michael P. Kim Date: April 1, 2015 1 Introduction Today, we will introduce a fundamental algorithm design paradigm, Divide-And-Conquer,
CS161, Lecture 2 MergeSort, Recurrences, Asymptotic Analysis Scribe: Michael P. Kim Date: April 1, 2015 1 Introduction Today, we will introduce a fundamental algorithm design paradigm, Divide-And-Conquer,
Recursively Defined Functions
 Section 5.3 Recursively Defined Functions Definition: A recursive or inductive definition of a function consists of two steps. BASIS STEP: Specify the value of the function at zero. RECURSIVE STEP: Give
Section 5.3 Recursively Defined Functions Definition: A recursive or inductive definition of a function consists of two steps. BASIS STEP: Specify the value of the function at zero. RECURSIVE STEP: Give
Lecture 22 Tuesday, April 10
 CIS 160 - Spring 2018 (instructor Val Tannen) Lecture 22 Tuesday, April 10 GRAPH THEORY Directed Graphs Directed graphs (a.k.a. digraphs) are an important mathematical modeling tool in Computer Science,
CIS 160 - Spring 2018 (instructor Val Tannen) Lecture 22 Tuesday, April 10 GRAPH THEORY Directed Graphs Directed graphs (a.k.a. digraphs) are an important mathematical modeling tool in Computer Science,
1 Definition of Reduction
 1 Definition of Reduction Problem A is reducible, or more technically Turing reducible, to problem B, denoted A B if there a main program M to solve problem A that lacks only a procedure to solve problem
1 Definition of Reduction Problem A is reducible, or more technically Turing reducible, to problem B, denoted A B if there a main program M to solve problem A that lacks only a procedure to solve problem
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS
 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS QUESTION BANK Module 1 OBJECTIVE: Algorithms play the central role in both the science and the practice of computing. There are compelling reasons to study algorithms.
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS QUESTION BANK Module 1 OBJECTIVE: Algorithms play the central role in both the science and the practice of computing. There are compelling reasons to study algorithms.
Graphs. CS16: Introduction to Data Structures & Algorithms Spring 2018
 Graphs CS16: Introduction to Data Structures & Algorithms Spring 2018 Outline What is a Graph Terminology Properties Graph Types Representations Performance BFS/DFS Applications 2 What is a Graph A graph
Graphs CS16: Introduction to Data Structures & Algorithms Spring 2018 Outline What is a Graph Terminology Properties Graph Types Representations Performance BFS/DFS Applications 2 What is a Graph A graph
Definition: A graph G = (V, E) is called a tree if G is connected and acyclic. The following theorem captures many important facts about trees.
 Tree 1. Trees and their Properties. Spanning trees 3. Minimum Spanning Trees 4. Applications of Minimum Spanning Trees 5. Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithms 1.1 Properties of Trees: Definition: A graph G
Tree 1. Trees and their Properties. Spanning trees 3. Minimum Spanning Trees 4. Applications of Minimum Spanning Trees 5. Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithms 1.1 Properties of Trees: Definition: A graph G
Algorithms Exam TIN093/DIT600
 Algorithms Exam TIN093/DIT600 Course: Algorithms Course code: TIN 093 (CTH), DIT 600 (GU) Date, time: 22nd October 2016, 14:00 18:00 Building: M Responsible teacher: Peter Damaschke, Tel. 5405 Examiner:
Algorithms Exam TIN093/DIT600 Course: Algorithms Course code: TIN 093 (CTH), DIT 600 (GU) Date, time: 22nd October 2016, 14:00 18:00 Building: M Responsible teacher: Peter Damaschke, Tel. 5405 Examiner:
DIVIDE & CONQUER. Problem of size n. Solution to sub problem 1
 DIVIDE & CONQUER Definition: Divide & conquer is a general algorithm design strategy with a general plan as follows: 1. DIVIDE: A problem s instance is divided into several smaller instances of the same
DIVIDE & CONQUER Definition: Divide & conquer is a general algorithm design strategy with a general plan as follows: 1. DIVIDE: A problem s instance is divided into several smaller instances of the same
Fast algorithms for max independent set
 Fast algorithms for max independent set N. Bourgeois 1 B. Escoffier 1 V. Th. Paschos 1 J.M.M. van Rooij 2 1 LAMSADE, CNRS and Université Paris-Dauphine, France {bourgeois,escoffier,paschos}@lamsade.dauphine.fr
Fast algorithms for max independent set N. Bourgeois 1 B. Escoffier 1 V. Th. Paschos 1 J.M.M. van Rooij 2 1 LAMSADE, CNRS and Université Paris-Dauphine, France {bourgeois,escoffier,paschos}@lamsade.dauphine.fr
