Combination Labelings Of Graphs
|
|
|
- Donald Patrick
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Applied Mathematics E-Notes, (0), - c ISSN 0-0 Available free at mirror sites of Combiatio Labeligs Of Graphs Pak Chig Li y Received February 0 Abstract Suppose G = (V; E) is a simple, coected, udirected graph with vertices ad m edges Let f be a bijectio from V oto f; ; :::; g which labels the vertices of G The vertex-labelig f iduces a edge-labelig f C of G as follows: a edge uv E with f(u) > f(v) is assiged the label f C (uv) = f(v) f(u) If the edge labels of G are pairwise distict, the we say G is a combiatio graph I this paper, we will show that complete k-ary trees, wheel graphs, Peterse graphs GP (; ); GP (; ), grid graphs ad certai caterpillar graphs are combiatio graphs We will also show that, except for several special cases, complete bipartite graphs are ot combiatio graphs Itroductio Suppose G = (V; E) is a simple, coected, udirected graph with vertices ad m edges Let f be a bijectio from V oto f; ; :::; g which labels the vertices of G The vertex-labelig f iduces a edge-labelig f C of G as follows: a edge uv E with f(u) > f(v) is assiged the label f C (uv) = f(u) f(v) The labelig f C is called the combiatio labelig of G iduced by the labelig f Whe the combiatio labelig f C is ijective, we say that it is a valid combiatio labelig If the graph G has a valid combiatio labelig, the we say G is a combiatio graph The study of graph labeligs has bee ad cotiues to be a popular topic of graph theory The dyamic survey by Gillia [] shows the diversity of graph labeligs Graceful labeligs are similar to combiatio labeligs A graceful labelig of a simple graph G = (V; E) is a labelig of its vertices with distict itegers from the set f0; ; :::; jejg, such that each edge is uiquely ideti ed by the absolute di erece betwee its edpoits Graceful labeligs have bee extesively studied A well-kow cojecture of graceful labeligs, kow as the graceful tree cojecture, states that all trees have graceful labeligs For a recet survey, see [] By comparig the rage of allowable (iduced) labels o the edges of a graceful labelig versus that of a combiatio labelig, if a graph has both a valid combiatio labelig ad a graceful labelig, it would see that it would be more di cult to d a graceful labelig Fially, it is kow that K ; has a graceful labelig but o valid combiatio labelig, while the -cycle has a valid combiatio labelig but o graceful labelig N Mathematics Subject Classi catios: 0C y Departmet of Computer Sciece, Uiversity of Maitoba, Wiipeg, Maitoba, Caada RT
2 P C Li I this paper, we cocetrate o the labelig of vertices of a graph which iduces a combiatio labelig o the edges of the graph This problem was itroduced by Hedge ad Shetty [] i 00 I this paper, we will study combiatio labeligs for several classes of graphs ad aswer some questios that were posed by i [] More speci cally, we will show that complete k-ary trees, wheel graphs, geeralized Peterse graphs GP (; ); GP (; ), ad grid graphs are combiatio graphs I additio, we will show that, except for some special cases, complete bi-partite graphs are ot combiatio graphs I Sectio we will show that full k-ary trees, wheel graphs, geeralized Peterse graphs GP (; ); GP (; ), ad grid graphs are combiatio graphs I Sectio, we show that complete bi-partite graphs are ot combiatio graphs, except for a few special cases Classes of Combiatio Graphs I this sectio, we will study several classes of graphs ad show that they are combiatio graphs We begi with rooted trees Trees A rooted tree is a tree where oe of the vertices (or odes) is distiguished from the other This distiguished vertex is kow as the root of the tree The odes of a tree ca be categorized as either o-leaf odes or leaf odes A ode is a leaf ode if it has degree Otherwise, it is a o-leaf ode The depth of a vertex i a rooted tree is the umber of edges o the path from the root to the vertex The height of a tree is the largest depth of ay leaf ode A k-ary tree is a rooted tree where each ode has at most k childre A complete k-ary tree is a k-ary tree where each o-leaf ode has exactly k childre ad the leaf odes have the same depth Our approach will be to show that a rooted tree with the property that all leaf odes have the same depth is a combiatio graph This immediately implies that a complete k-ary tree is a combiatio graph We begi with a simple, useful fact that ca easily be proved by algebraic maipulatios > LEMMA If > k > 0, the k+ k LEMMA Let T be a rooted tree with the property that the depth of ay two leaf odes are the same The T is a combiatio graph PROOF Let T be a rooted tree satisfyig the assumptios stated i the lemma We may assume that T has at least three vertices sice a tree cosistig oe or two odes is a combiatio graph We will d a assigmet f of labels for the odes of T so that the iduced edge labels of T are pairwise distict To label the odes, we will visit ad label (usig the positive itegers) the odes usig a breadth- rst traversal startig at the root such that: the smallest available value is used to label the curret ode beig visited, ad
3 0 Combiatio Labeligs of Graphs if the depth of two o-leaf odes u ad v are the same ad f(u) < f(v), the the labels assiged to the childre of u are less tha the labels assiged to the childre of v Note that this labelig process does ot ecessarily eed to a uique labelig sice sibligs ca be labeled i ay order As the labels are assiged i a breadth- rst maer, the label of a ode at depth k is smaller tha the label of a ode at depth k + Figure illustrates oe labelig costructed by the labelig process o a give tree Cosider a edge e = uv i the tree T, where f(u) < f(v) are the labels assiged f(v) to the two edpoits of e The label iduced o this edge is f(u) Note that u is the paret of v Suppose the o-leaf ode u has childre v ; v ; :::; v k 0 with f(v ) < f(v ) < < f(v k 0 ) ad k 0 Note that by labelig process, it must be that f(v ) + = f(v ); f(v ) = f(v ) + ; :::; f(v k 0 ) + = f(v k 0 ) By Lemma, f(v 0 k ) f(u) > f(v 0 ) k f(u) > > f(v ) f(u) Therefore, edges betwee a paret ad its sibligs have distict labeligs Now cosider two odes u; w havig the same depth ad f(w) = f(u) + Suppose ode u is a o-leaf ode As all leaf odes have the same depth, the ode w must also be a o-leaf ode By the labelig process, the childre of u must be labeled a; a + ; :::; a + l ad the childre of w must be labeled a + l + ; a + l + ; :::; a + l + m a+l for some a ad l; m By Lemma, f(u) < a+l+ f(u)+ = a+l+ f(w) Therefore all the edges of the same level of the tree are pairwise distict Fially, cosider two o-leaf odes u; w where the depth of u is d, the depth of w is d +, for some d, such that f(u) is the largest label assiged to odes of depth d ad f(w) is the smallest label assiged to odes of depth d + The we see that f(w) = f(u) + Suppose the childre of u are labeled a; a + ; :::; a + l for some a ad l The the childre of w are a + l + ; :::; a + l + m for some m By Lemma a+l, f(u) < a+l+ f(w) This shows that the edges at level d have labels less tha those at level d + Combiig these three results, we see that the tree T is a combiatio graph Lemma immediately implies that complete k-ary trees are combiatio graphs We state this i the followig Corollary THEOREM The complete k-ary tree is a combiatio graph Caterpillars We ow cosider aother class of trees called caterpillars A tree is a caterpillar if, upo removig all leaves ad their icidet edges, a path is left This path is called the cetral path of the caterpillar graph Note that i the caterpillar, the cetral path ca be exteded to a loger path sice each edpoit of the path must be adjacet to a vertex i the caterpillar Let us call this path the exteded cetral path of the caterpillar We will call a edge that is ot o the exteded cetral path of a caterpillar a leg We begi by showig that if a caterpillar has eough legs, the it is a combiatio graph To do this we start with a simple lemma that ca be veri ed through algebraic
4 P C Li 0 Figure : A labelig of a ode rooted tree maipulatio LEMMA If l; m 0 ad + (l + m), the l < l+m THEOREM Let G = (V; E) be a caterpillar with exteded cetral path P cosistig of p vertices If G has at least p vertices, the T is a combiatio graph PROOF We partitio the vertex set of V ito two smaller sets A ad B by rst dividig the path P ito two (disjoit) sub-paths Q ad R of equal or almost equal legth The we place a vertex v ito A if v Q or v is adjacet to a vertex o Q Otherwise, we place v ito B At least oe of G[A] or G[B] cotai at least (p )= = p edges that are ot edges of P, where G[A](G[B]) deote the subgraph of G iduced by the vertex set A(B) Without loss of geerality, assume G[A] has this property We ow costruct a labelig f of the vertices of V Label the path P startig from oe ed to the other ed with labels ; ; :::; p so that the vertex that is labeled with the value is the ed-vertex of P which belogs to A Now label the remaiig vertices of G that are ot o the path P so that if u; v are ot o P, up ; vp E, p ; p P ad f(p ) < f(p ), the f(u) < f(v) This ca be accomplished by startig at the ed of P label with value, ad movig alog the path P As a leg is ecoutered, we label the vertex of the leg that is ot o the path with the ext available value We claim that this labelig is a combiatio labelig of G We see that the edges o the path P have labels ; ; :::; p ad the smallest edge p+ label of a edge ot o the path is at least > p It is clear that the edge labels of ay two edges i G[A] but ot o P satis es Lemma ad therefore are pairwise distict Fially, the smallest label assiged to a leaf ode i B but ot o P is at least p + (p ) + = p = (p ) I G[B], the label p is the largest label assiged to a vertex o P that ca be adjacet to vertices ot o P Therefore, Lemma ca
5 Combiatio Labeligs of Graphs be applied to the labels of the legs of the etire graph G to show that the legs of G have pairwise distict labels THEOREM Let G = (V; E) be a caterpillar with exteded cetral path P cosistig of p vertices If each vertex of P, except for its two edpoits, is adjacet to at least oe vertex that is ot o P, the G is a combiatio graph PROOF Start at oe ed of the path P ad label the edpoit Follow the path ad label each vertex visited with the ext available label To label the vertices that are ot o P, use the labelig scheme as i Theorem If f(u) is the label of a vertex u ot o P that is adjacet to a vertex v o P with label f(v), the f(u) f(v) To see this, ote that the smallest value that f(u) ca be is p + f(v) Sice p v, we have f(u) p + f(v) f(v) Applyig Lemma, we see that G is a combiatio graph Geeralized Peterse Graph GP (; k) Suppose k; are positive itegers such that > k The geeralized Peterse graph, deote by GP (; k), is the simple graph with vertices u ; u ; ::; u ; v ; v ; :::; v ad edges u i u i+ ; v i v i+k ; u i v i ; i, where the idexes are take modulo We will show that GP (; ) ad GP (; ) are combiatio graphs LEMMA If the + THEOREM If, the GP (; ) is a combiatio graph PROOF Figure gives a valid combiatio labelig for GP (; ) Therefore, assume that Label the vertices of GP (; ) as follows: f(u ) = ; f(u ) = ; :::; f(u ) = ; f(u ) = ; f(u ) = ; f(v ) = + ; f(v ) = + ; :::; f(v ) = ; f(v ) = ; f(v ) = We claim that this is a valid combiatio labelig of GP (; ) The edges u i u i+ ; i have labels ; ; :::; ; The edges vi v i+ ; i have labels +; :::; ; ; ; = The edges ui v i+ ; i have labels ; + ; :::; By Lemma, + By Lemma, +i i < +i+ i+ I additio, it is easy to see that if, the + Therefore, the edge labels ; ; :::; ; + ; ; + ; + ; :::; ; ; ; are all distict ad are listed i icreasig order LEMMA If, the If =, the = LEMMA If, the + < < + If, the < + THEOREM For, the GP (; ) is a combiatio graph PROOF Figure gives valid combiatio labeligs for GP (; ), where Therefore, assume that Label the vertices of GP (; ) as follows: f(u ) = ; f(u ) = ; :::; f(u ) = ; f(u ) = ; f(u ) = ; f(v ) = ; f(v ) = + ; :::; f(v ) = ; f(v ) = ; f(v ) = We claim that this is a valid combiatio labelig of GP (; ) The edges u i u i+ ; i have labels ; ; :::; ; + The edges v i v i+ ; i have labels ; + ; :::; ; + ; ; ad The edges ui v i+ ; i have labels ; + ; :::; Note that
6 P C Li Figure : A valid combiatio labelig of GP (; ): + = ; = ; = ad = We claim that we ca order the edge labels i mootoe icreasig order We ca order this smallest edge labels as < < < + < < where the last iequality holds as > Cotiuig, we have + + By Lemma, + we have either < + < < where the last iequality follows from Lemma, or + + < + < < Fially, we have < < This gives a sequece of strict iequalities ivolvig each edge label Therefore, GP (; ) is a combiatio graph Wheel Graphs Let be a positive iteger greater tha A wheel graph o + vertices is a graph cosistig of a cycle of legth ad a vertex ot o the cycle that is adjacet to every vertex o the cycle We deote this graph by W I [], it was cojectured that for all, W is a combiatio graph We will show that this cojecture is true We begi with some simple, useful results that ca be veri ed by algebraic maipulatios LEMMA If is a eve umber, the = = LEMMA If 0 is a eve umber, the =+ =+ I additio, if 0 is a eve umber, the =+ < =+ LEMMA If is a odd umber, the b=c < b=c We ow proceed to label the wheel graph W We will give a labelig that almost works ad the modify it slightly to so that it gives a valid combiatio labelig of W THEOREM If, the W is a combiatio graph PROOF Valid combiatio labeligs for = ; were give i [] Let us assume that Deote the cycle of legth of W by C Let x be the vertex that is ot
7 Combiatio Labeligs of Graphs Figure : Valid combiatio labeligs for GP (; ) for : i C ad is adjacet to each vertex of C Deote the vertices of C by v 0 ; v ; :::; v where v i is adjacet to v i+ modulo We ow give a labelig of the vertices of W Label vertex x with value O the cycle C, label v 0 with, v with, v with, etc I geeral, after labelig vertex v i with value k, we skip over vertex v i+, ad label v i+ with value k + if it has ot already bee labeled If v i+ has already bee labeled, the we label v i+ with value k + The idexes are take modulo Let us deote this labelig by f f(v Uder this labelig there exists (at least oe) i such that i) f(v i+) = f(v i) f(v i ) Whe f(v ) is odd, we have f(v ) = Therefore f(v ) = d=e = b=c = f(v ) f(v ) However, this is the oly occurrece because for ay vertex whose label l is greater tha b=c +, its eighbors o C have labels l b=c ad l d=e The oly l value of l which satis es l b=c = l l d=e is l = Usig a similar argumet for f(v whe is eve, we see that i) f(v i+) = f(v i) f(v i ) happes oly whe i = ad f(v ) = We make a slight modi catio to the labelig f by performig the followig swaps: If is odd, we swap the labels ad i the labelig f If is eve, we swap the labels ad i the labelig f Let us deote this ew labelig by g We claim that g is a combiatio labelig l of W It is clear that two adjacet edges o C do ot have labels l k ad l k for l > k because of the modi catios made above Figure gives examples for = 0; I the case where is odd, the edge labels of W, iduced by g are ; ; :::; ad b=c+ ; b=c+ ; :::; b=c ; b=c ; b=c ; b=c+ ; b=c ; b=c ; b=c+ ;
8 P C Li 0 0 Figure : Combiatio labeligs for W ad W 0 : b=c+ ad b=c+ Note that b=c+ = b=c If remove b=c ; b=c from the sequece above, the remaiig values are all distict ad i fact, < < + < b=c+ b=c+ b=c+ < < b=c b=c < b=c+ < b=c < b=c+ (= b=c ) < b=c+ By Lemma, b=c+ < < < Sice < < b=c b=c b=c b=c b=c b=c+, all the edge labels are distict, whe is odd We ow cosider the case whe is eve The edge labels of W,iduced by g are =+ ; ; :::; ; ; =+ ; =+ ; =+ ; :::; = ; = ; = ; = ; =+ ; =+ ad If we remove = ; = ad from this list, the remaiig values are clearly distict ad < + < =+ =+ < =+ < < = = = = < = = =+ < = <= = = =+ Note that as = = < = ad by Lemma, = < =, all edge labels except for possibility are distict By Lemma =+, =+ for all eve 0 For = 0; ; ; ;, we have < < =+ Therefore all the edge labels are distict i W =+ Grid Graphs = ; Let k; be positive itegers with k Let G = (V; E) be the k grid graph More precisely, V = f(i; j) : 0 i k ; 0 j g ad E = ff(i; j ); (i; j )g : 0 j ; j = j + g [ ff(i ; j); (i ; j)g : 0 i k ; i = i + g Aother way of costructig the k grid graph is to take the Cartesia product of the paths P k ad P We claim that for large eough values of k ad, the k grid graph is a combiatio graph To prove this, we begi with a useful fact LEMMA 0 Let k If d k +p k k+ e, the k < + THEOREM Let k If d k +p k k+ e, the the k grid graph is
9 Combiatio Labeligs of Graphs a combiatio graph PROOF Label the vertex (i; j) with the value i + j + Thethe edges have + iduced labels i the set f; ; :::; k ; k; ; + ; :::; k ; k gf; + + ; :::; (k ) + g Clearly, the labels ; + ; :::; k for a icreasig sequece ad therefore are pairwise distict Sice d k +p k k+ e, Lemma 0 implies = + > k Therefore, the edge labels are pairwise distict + Other Results We state several related results LEMMA Let G be a graph with vertices If G is a combiatio graph, the at most oe vertex of G has degree PROOF Suppose there are at least two vertices that have degree i G ad G is a combiatio graph Cosider a valid combiatio labelig Let x < y be vertex labels of two vertices of degree Suppose y The y is adjacet vertices labeled y ad y But y = y, which cotradicts assumptio that G is a combiatio graph Therefore y implyig x = ; y = The both x; y are adjacet to the vertex labeled As =, this cotradicts assumptio that G is a combiatio graph Therefore, at most oe vertex of G ca have degree This immediately implies that K is ot a combiatio graph wheever The proof of Lemma also shows that if a combiatio graph has a vertex of degree, the label of that vertex must be or We ow show that some combiatio graph o vertices with the maximum umber of edges possible must cotai a vertex of degree whose label is LEMMA Let m be the maximum umber of edges i ay combiatio graph with vertices The there is a combiatio graph G with vertices ad m edges such the vertex labeled with value is adjacet to all the other vertices PROOF Suppose that G is a combiatio graph with vertices, m edges ad the vertex v labeled with value does ot have degree The, let the vertices that are ot adjacet to v have labels a ; a ; :::; a k, where k Remove from G all edges whose iduced edge labelig belogs i fa ; a ; :::; a k g There are at most k such edges, as G is a combiatio graph Fially, add edges to G so that v has degree The resultig graph is still a combiatio graph Sice the origial graph was a combiatio graph ad has maximum umber of edges possible, the umber of edges removed must be k We ca use Lemma to show that ay combiatio graph with vertices ca have at most edges I the cotrary, suppose G is a combiatio graph with vertices ad edges By Lemma there must exists a graph H with vertices ad edges such that the vertex labeled with value is adjacet the other vertices The oly remaiig edges that are permissible the edges ; ; ; ; But sice = ad =, at most of these edges ca be i the graph H give a total of edges, which is a cotradictio A similar argumet ca be applied to obtai the followig boud from []
10 P C Li m ( = if is eve ( )= if is odd: () I [], it was show that K r;r is ot a combiatio graph for r We ow geeralize this for complete bipartite graphs K l;k Note that if a graph G = (V; E 0 ) is ot a combiatio graph, the it is clear that if we add additioal edges to E 0 it will ot be a combiatio graph We record this i the followig lemma LEMMA Suppose G = (V; E) ad E 0 E If (V; E 0 ) is ot a combiatio graph, the G is ot a combiatio graph THEOREM Let K l;k = (A; B) be the complete bipartite graph with k elemets i the partite set A, ad l elemets i the other partite set B The K l;k is a combiatio graph if ad oly if k = or l = or k = l = PROOF The case where k = l = the cycle of legth which is clearly a combiatio graph Suppose k = (or if l = ) ad let A deote the partite set with oe vertex Label the loe vertex of the partite set A with value ad label the vertices i the other partite set with values ; ; :::; l + Clearly this is a valid labelig Suppose l ad k > l We will show that K l;k is ot a combiatio graph To do this, suppose to the cotrary that K l;k is a combiatio graph where the vertices of the graph is labeled usig a valid combiatio labelig The the vertices with label ad l + k must be i the same partite set For if ot, the without loss of geerality suppose A, l + k B This forces vertex with label l + k to be i B, which i tur forces vertex with label l + k to be i B, ad so o Therefore, the partite set A cotais oly oe vertex, the vertex with label This cotradicts our assumptio that jaj We ow have two scearios: ; l + k A or ; l + k B Case : Suppose ; l + k A If the vertex with label l + k B, the usig a argumet similar to the oe above, we have ; ; :::; l + k B This implies that k+ l = As k >, = k+ k ad ; k B, we have two edges with the same label, which is a cotradictio Therefore, it must be that l + k A By repeatedly applyig this argumet ad the assumptio that jbj = k, we see that the labels i A are f; k + ; k + ; :::; l + kg ad the labels i B are f; ; :::; k + g As k > ad k+ = k+, there are two edge labels with the same value, which is a cotradictio k Therefore, case leads to a cotradictio Case : Suppose ; l + k B The, usig a argumet similar to that of case, we have that A cotais vertices with labels ; ; :::; l + ad B cotais vertices with labels ; l + ; :::; l + k The labels l; l + A Sice k > l, l + l + k implyig l+ that l + B This alog with the fact that l = l+ l+ implies that two edges have the same labelig, which is a cotradictio Therefore, case also leads to a cotradictio COROLLARY Suppose G is a complete k-partite with partite sets A ; A ; ::; A k where k ad ja i j for i = to k The G is ot a combiatio graph
11 Combiatio Labeligs of Graphs PROOF Costruct a graph H from G by removig all edges betwee A i ; A j where < i = j k Partitio the vertices of H ito two sets A ad [ k i= A i The graph H is a complete bipartite graph By Theorem, it is ot a combiatio graph By Lemma, G is ot a combiatio graph We would like to ed by statig the followig ope problem: Are all trees combiatio graphs? Based o istaces that we have cosidered, which all tured out to be combiatio graphs, we believe ad cojecture that all trees are combiatio graphs Ackowledgmet Research supported by NSERC Discovery Grat 0-0 Refereces [] M Edwards ad L Howard, A survey of graceful trees, Atlatic Electroic Joural of Mathematics, (00), 0 [] J A Gallia, Graph labelig, Electroic Joural of Combiatorics, DS, pages [] S M Hedge ad S Shetty, Combiatorial labeligs of graphs, AMEN, (00),
On (K t e)-saturated Graphs
 Noame mauscript No. (will be iserted by the editor O (K t e-saturated Graphs Jessica Fuller Roald J. Gould the date of receipt ad acceptace should be iserted later Abstract Give a graph H, we say a graph
Noame mauscript No. (will be iserted by the editor O (K t e-saturated Graphs Jessica Fuller Roald J. Gould the date of receipt ad acceptace should be iserted later Abstract Give a graph H, we say a graph
INTERSECTION CORDIAL LABELING OF GRAPHS
 INTERSECTION CORDIAL LABELING OF GRAPHS G Meea, K Nagaraja Departmet of Mathematics, PSR Egieerig College, Sivakasi- 66 4, Virudhuagar(Dist) Tamil Nadu, INDIA meeag9@yahoocoi Departmet of Mathematics,
INTERSECTION CORDIAL LABELING OF GRAPHS G Meea, K Nagaraja Departmet of Mathematics, PSR Egieerig College, Sivakasi- 66 4, Virudhuagar(Dist) Tamil Nadu, INDIA meeag9@yahoocoi Departmet of Mathematics,
Some cycle and path related strongly -graphs
 Some cycle ad path related strogly -graphs I. I. Jadav, G. V. Ghodasara Research Scholar, R. K. Uiversity, Rajkot, Idia. H. & H. B. Kotak Istitute of Sciece,Rajkot, Idia. jadaviram@gmail.com gaurag ejoy@yahoo.co.i
Some cycle ad path related strogly -graphs I. I. Jadav, G. V. Ghodasara Research Scholar, R. K. Uiversity, Rajkot, Idia. H. & H. B. Kotak Istitute of Sciece,Rajkot, Idia. jadaviram@gmail.com gaurag ejoy@yahoo.co.i
Super Vertex Magic and E-Super Vertex Magic. Total Labelling
 Proceedigs of the Iteratioal Coferece o Applied Mathematics ad Theoretical Computer Sciece - 03 6 Super Vertex Magic ad E-Super Vertex Magic Total Labellig C.J. Deei ad D. Atoy Xavier Abstract--- For a
Proceedigs of the Iteratioal Coferece o Applied Mathematics ad Theoretical Computer Sciece - 03 6 Super Vertex Magic ad E-Super Vertex Magic Total Labellig C.J. Deei ad D. Atoy Xavier Abstract--- For a
A Note on Chromatic Transversal Weak Domination in Graphs
 Iteratioal Joural of Mathematics Treds ad Techology Volume 17 Number 2 Ja 2015 A Note o Chromatic Trasversal Weak Domiatio i Graphs S Balamuruga 1, P Selvalakshmi 2 ad A Arivalaga 1 Assistat Professor,
Iteratioal Joural of Mathematics Treds ad Techology Volume 17 Number 2 Ja 2015 A Note o Chromatic Trasversal Weak Domiatio i Graphs S Balamuruga 1, P Selvalakshmi 2 ad A Arivalaga 1 Assistat Professor,
Some non-existence results on Leech trees
 Some o-existece results o Leech trees László A.Székely Hua Wag Yog Zhag Uiversity of South Carolia This paper is dedicated to the memory of Domiique de Cae, who itroduced LAS to Leech trees.. Abstract
Some o-existece results o Leech trees László A.Székely Hua Wag Yog Zhag Uiversity of South Carolia This paper is dedicated to the memory of Domiique de Cae, who itroduced LAS to Leech trees.. Abstract
Mean cordiality of some snake graphs
 Palestie Joural of Mathematics Vol. 4() (015), 49 445 Palestie Polytechic Uiversity-PPU 015 Mea cordiality of some sake graphs R. Poraj ad S. Sathish Narayaa Commuicated by Ayma Badawi MSC 010 Classificatios:
Palestie Joural of Mathematics Vol. 4() (015), 49 445 Palestie Polytechic Uiversity-PPU 015 Mea cordiality of some sake graphs R. Poraj ad S. Sathish Narayaa Commuicated by Ayma Badawi MSC 010 Classificatios:
n n B. How many subsets of C are there of cardinality n. We are selecting elements for such a
 4. [10] Usig a combiatorial argumet, prove that for 1: = 0 = Let A ad B be disjoit sets of cardiality each ad C = A B. How may subsets of C are there of cardiality. We are selectig elemets for such a subset
4. [10] Usig a combiatorial argumet, prove that for 1: = 0 = Let A ad B be disjoit sets of cardiality each ad C = A B. How may subsets of C are there of cardiality. We are selectig elemets for such a subset
1 Graph Sparsfication
 CME 305: Discrete Mathematics ad Algorithms 1 Graph Sparsficatio I this sectio we discuss the approximatio of a graph G(V, E) by a sparse graph H(V, F ) o the same vertex set. I particular, we cosider
CME 305: Discrete Mathematics ad Algorithms 1 Graph Sparsficatio I this sectio we discuss the approximatio of a graph G(V, E) by a sparse graph H(V, F ) o the same vertex set. I particular, we cosider
Average Connectivity and Average Edge-connectivity in Graphs
 Average Coectivity ad Average Edge-coectivity i Graphs Jaehoo Kim, Suil O July 1, 01 Abstract Coectivity ad edge-coectivity of a graph measure the difficulty of breakig the graph apart, but they are very
Average Coectivity ad Average Edge-coectivity i Graphs Jaehoo Kim, Suil O July 1, 01 Abstract Coectivity ad edge-coectivity of a graph measure the difficulty of breakig the graph apart, but they are very
Perhaps the method will give that for every e > U f() > p - 3/+e There is o o-trivial upper boud for f() ad ot eve f() < Z - e. seems to be kow, where
 ON MAXIMUM CHORDAL SUBGRAPH * Paul Erdos Mathematical Istitute of the Hugaria Academy of Scieces ad Reu Laskar Clemso Uiversity 1. Let G() deote a udirected graph, with vertices ad V(G) deote the vertex
ON MAXIMUM CHORDAL SUBGRAPH * Paul Erdos Mathematical Istitute of the Hugaria Academy of Scieces ad Reu Laskar Clemso Uiversity 1. Let G() deote a udirected graph, with vertices ad V(G) deote the vertex
Lecture 6. Lecturer: Ronitt Rubinfeld Scribes: Chen Ziv, Eliav Buchnik, Ophir Arie, Jonathan Gradstein
 068.670 Subliear Time Algorithms November, 0 Lecture 6 Lecturer: Roitt Rubifeld Scribes: Che Ziv, Eliav Buchik, Ophir Arie, Joatha Gradstei Lesso overview. Usig the oracle reductio framework for approximatig
068.670 Subliear Time Algorithms November, 0 Lecture 6 Lecturer: Roitt Rubifeld Scribes: Che Ziv, Eliav Buchik, Ophir Arie, Joatha Gradstei Lesso overview. Usig the oracle reductio framework for approximatig
The Adjacency Matrix and The nth Eigenvalue
 Spectral Graph Theory Lecture 3 The Adjacecy Matrix ad The th Eigevalue Daiel A. Spielma September 5, 2012 3.1 About these otes These otes are ot ecessarily a accurate represetatio of what happeed i class.
Spectral Graph Theory Lecture 3 The Adjacecy Matrix ad The th Eigevalue Daiel A. Spielma September 5, 2012 3.1 About these otes These otes are ot ecessarily a accurate represetatio of what happeed i class.
New Results on Energy of Graphs of Small Order
 Global Joural of Pure ad Applied Mathematics. ISSN 0973-1768 Volume 13, Number 7 (2017), pp. 2837-2848 Research Idia Publicatios http://www.ripublicatio.com New Results o Eergy of Graphs of Small Order
Global Joural of Pure ad Applied Mathematics. ISSN 0973-1768 Volume 13, Number 7 (2017), pp. 2837-2848 Research Idia Publicatios http://www.ripublicatio.com New Results o Eergy of Graphs of Small Order
CHAPTER IV: GRAPH THEORY. Section 1: Introduction to Graphs
 CHAPTER IV: GRAPH THEORY Sectio : Itroductio to Graphs Sice this class is called Number-Theoretic ad Discrete Structures, it would be a crime to oly focus o umber theory regardless how woderful those topics
CHAPTER IV: GRAPH THEORY Sectio : Itroductio to Graphs Sice this class is called Number-Theoretic ad Discrete Structures, it would be a crime to oly focus o umber theory regardless how woderful those topics
CIS 121 Data Structures and Algorithms with Java Spring Stacks and Queues Monday, February 12 / Tuesday, February 13
 CIS Data Structures ad Algorithms with Java Sprig 08 Stacks ad Queues Moday, February / Tuesday, February Learig Goals Durig this lab, you will: Review stacks ad queues. Lear amortized ruig time aalysis
CIS Data Structures ad Algorithms with Java Sprig 08 Stacks ad Queues Moday, February / Tuesday, February Learig Goals Durig this lab, you will: Review stacks ad queues. Lear amortized ruig time aalysis
Lecture 2: Spectra of Graphs
 Spectral Graph Theory ad Applicatios WS 20/202 Lecture 2: Spectra of Graphs Lecturer: Thomas Sauerwald & He Su Our goal is to use the properties of the adjacecy/laplacia matrix of graphs to first uderstad
Spectral Graph Theory ad Applicatios WS 20/202 Lecture 2: Spectra of Graphs Lecturer: Thomas Sauerwald & He Su Our goal is to use the properties of the adjacecy/laplacia matrix of graphs to first uderstad
CIS 121. Introduction to Trees
 CIS 121 Itroductio to Trees 1 Tree ADT Tree defiitio q A tree is a set of odes which may be empty q If ot empty, the there is a distiguished ode r, called root ad zero or more o-empty subtrees T 1, T 2,
CIS 121 Itroductio to Trees 1 Tree ADT Tree defiitio q A tree is a set of odes which may be empty q If ot empty, the there is a distiguished ode r, called root ad zero or more o-empty subtrees T 1, T 2,
Graphs. Minimum Spanning Trees. Slides by Rose Hoberman (CMU)
 Graphs Miimum Spaig Trees Slides by Rose Hoberma (CMU) Problem: Layig Telephoe Wire Cetral office 2 Wirig: Naïve Approach Cetral office Expesive! 3 Wirig: Better Approach Cetral office Miimize the total
Graphs Miimum Spaig Trees Slides by Rose Hoberma (CMU) Problem: Layig Telephoe Wire Cetral office 2 Wirig: Naïve Approach Cetral office Expesive! 3 Wirig: Better Approach Cetral office Miimize the total
On Infinite Groups that are Isomorphic to its Proper Infinite Subgroup. Jaymar Talledo Balihon. Abstract
 O Ifiite Groups that are Isomorphic to its Proper Ifiite Subgroup Jaymar Talledo Baliho Abstract Two groups are isomorphic if there exists a isomorphism betwee them Lagrage Theorem states that the order
O Ifiite Groups that are Isomorphic to its Proper Ifiite Subgroup Jaymar Talledo Baliho Abstract Two groups are isomorphic if there exists a isomorphism betwee them Lagrage Theorem states that the order
Xiaozhou (Steve) Li, Atri Rudra, Ram Swaminathan. HP Laboratories HPL Keyword(s): graph coloring; hardness of approximation
 Flexible Colorig Xiaozhou (Steve) Li, Atri Rudra, Ram Swamiatha HP Laboratories HPL-2010-177 Keyword(s): graph colorig; hardess of approximatio Abstract: Motivated b y reliability cosideratios i data deduplicatio
Flexible Colorig Xiaozhou (Steve) Li, Atri Rudra, Ram Swamiatha HP Laboratories HPL-2010-177 Keyword(s): graph colorig; hardess of approximatio Abstract: Motivated b y reliability cosideratios i data deduplicatio
Matrix Partitions of Split Graphs
 Matrix Partitios of Split Graphs Tomás Feder, Pavol Hell, Ore Shklarsky Abstract arxiv:1306.1967v2 [cs.dm] 20 Ju 2013 Matrix partitio problems geeralize a umber of atural graph partitio problems, ad have
Matrix Partitios of Split Graphs Tomás Feder, Pavol Hell, Ore Shklarsky Abstract arxiv:1306.1967v2 [cs.dm] 20 Ju 2013 Matrix partitio problems geeralize a umber of atural graph partitio problems, ad have
Random Graphs and Complex Networks T
 Radom Graphs ad Complex Networks T-79.7003 Charalampos E. Tsourakakis Aalto Uiversity Lecture 3 7 September 013 Aoucemet Homework 1 is out, due i two weeks from ow. Exercises: Probabilistic iequalities
Radom Graphs ad Complex Networks T-79.7003 Charalampos E. Tsourakakis Aalto Uiversity Lecture 3 7 September 013 Aoucemet Homework 1 is out, due i two weeks from ow. Exercises: Probabilistic iequalities
MAXIMUM MATCHINGS IN COMPLETE MULTIPARTITE GRAPHS
 Fura Uiversity Electroic Joural of Udergraduate Matheatics Volue 00, 1996 6-16 MAXIMUM MATCHINGS IN COMPLETE MULTIPARTITE GRAPHS DAVID SITTON Abstract. How ay edges ca there be i a axiu atchig i a coplete
Fura Uiversity Electroic Joural of Udergraduate Matheatics Volue 00, 1996 6-16 MAXIMUM MATCHINGS IN COMPLETE MULTIPARTITE GRAPHS DAVID SITTON Abstract. How ay edges ca there be i a axiu atchig i a coplete
3. b. Present a combinatorial argument that for all positive integers n : : 2 n
 . b. Preset a combiatorial argumet that for all positive itegers : : Cosider two distict sets A ad B each of size. Sice they are distict, the cardiality of A B is. The umber of ways of choosig a pair of
. b. Preset a combiatorial argumet that for all positive itegers : : Cosider two distict sets A ad B each of size. Sice they are distict, the cardiality of A B is. The umber of ways of choosig a pair of
A RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN BOUNDS ON THE SUM OF SQUARES OF DEGREES OF A GRAPH
 J. Appl. Math. & Computig Vol. 21(2006), No. 1-2, pp. 233-238 Website: http://jamc.et A RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN BOUNDS ON THE SUM OF SQUARES OF DEGREES OF A GRAPH YEON SOO YOON AND JU KYUNG KIM Abstract.
J. Appl. Math. & Computig Vol. 21(2006), No. 1-2, pp. 233-238 Website: http://jamc.et A RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN BOUNDS ON THE SUM OF SQUARES OF DEGREES OF A GRAPH YEON SOO YOON AND JU KYUNG KIM Abstract.
Some New Results on Prime Graphs
 Ope Joural of Discrete Mathematics, 202, 2, 99-04 http://dxdoiorg/0426/ojdm202209 Published Olie July 202 (http://wwwscirporg/joural/ojdm) Some New Results o Prime Graphs Samir Vaidya, Udaya M Prajapati
Ope Joural of Discrete Mathematics, 202, 2, 99-04 http://dxdoiorg/0426/ojdm202209 Published Olie July 202 (http://wwwscirporg/joural/ojdm) Some New Results o Prime Graphs Samir Vaidya, Udaya M Prajapati
4-PRIME CORDIAL LABELING OF SOME DEGREE SPLITTING GRAPHS
 Iteratioal Joural of Maagemet, IT & Egieerig Vol. 8 Issue 7, July 018, ISSN: 49-0558 Impact Factor: 7.119 Joural Homepage: Double-Blid Peer Reviewed Refereed Ope Access Iteratioal Joural - Icluded i the
Iteratioal Joural of Maagemet, IT & Egieerig Vol. 8 Issue 7, July 018, ISSN: 49-0558 Impact Factor: 7.119 Joural Homepage: Double-Blid Peer Reviewed Refereed Ope Access Iteratioal Joural - Icluded i the
Symmetric Class 0 subgraphs of complete graphs
 DIMACS Techical Report 0-0 November 0 Symmetric Class 0 subgraphs of complete graphs Vi de Silva Departmet of Mathematics Pomoa College Claremot, CA, USA Chaig Verbec, Jr. Becer Friedma Istitute Booth
DIMACS Techical Report 0-0 November 0 Symmetric Class 0 subgraphs of complete graphs Vi de Silva Departmet of Mathematics Pomoa College Claremot, CA, USA Chaig Verbec, Jr. Becer Friedma Istitute Booth
USING TOPOLOGICAL METHODS TO FORCE MAXIMAL COMPLETE BIPARTITE SUBGRAPHS OF KNESER GRAPHS
 USING TOPOLOGICAL METHODS TO FORCE MAXIMAL COMPLETE BIPARTITE SUBGRAPHS OF KNESER GRAPHS GWEN SPENCER AND FRANCIS EDWARD SU 1. Itroductio Sata likes to ru a lea ad efficiet toy-makig operatio. He also
USING TOPOLOGICAL METHODS TO FORCE MAXIMAL COMPLETE BIPARTITE SUBGRAPHS OF KNESER GRAPHS GWEN SPENCER AND FRANCIS EDWARD SU 1. Itroductio Sata likes to ru a lea ad efficiet toy-makig operatio. He also
Strong Complementary Acyclic Domination of a Graph
 Aals of Pure ad Applied Mathematics Vol 8, No, 04, 83-89 ISSN: 79-087X (P), 79-0888(olie) Published o 7 December 04 wwwresearchmathsciorg Aals of Strog Complemetary Acyclic Domiatio of a Graph NSaradha
Aals of Pure ad Applied Mathematics Vol 8, No, 04, 83-89 ISSN: 79-087X (P), 79-0888(olie) Published o 7 December 04 wwwresearchmathsciorg Aals of Strog Complemetary Acyclic Domiatio of a Graph NSaradha
Improved Random Graph Isomorphism
 Improved Radom Graph Isomorphism Tomek Czajka Gopal Paduraga Abstract Caoical labelig of a graph cosists of assigig a uique label to each vertex such that the labels are ivariat uder isomorphism. Such
Improved Radom Graph Isomorphism Tomek Czajka Gopal Paduraga Abstract Caoical labelig of a graph cosists of assigig a uique label to each vertex such that the labels are ivariat uder isomorphism. Such
c-dominating Sets for Families of Graphs
 c-domiatig Sets for Families of Graphs Kelsie Syder Mathematics Uiversity of Mary Washigto April 6, 011 1 Abstract The topic of domiatio i graphs has a rich history, begiig with chess ethusiasts i the
c-domiatig Sets for Families of Graphs Kelsie Syder Mathematics Uiversity of Mary Washigto April 6, 011 1 Abstract The topic of domiatio i graphs has a rich history, begiig with chess ethusiasts i the
Characterizing graphs of maximum principal ratio
 Characterizig graphs of maximum pricipal ratio Michael Tait ad Josh Tobi November 9, 05 Abstract The pricipal ratio of a coected graph, deoted γg, is the ratio of the maximum ad miimum etries of its first
Characterizig graphs of maximum pricipal ratio Michael Tait ad Josh Tobi November 9, 05 Abstract The pricipal ratio of a coected graph, deoted γg, is the ratio of the maximum ad miimum etries of its first
A study on Interior Domination in Graphs
 IOSR Joural of Mathematics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 2278-5728, p-issn: 219-765X. Volume 12, Issue 2 Ver. VI (Mar. - Apr. 2016), PP 55-59 www.iosrjourals.org A study o Iterior Domiatio i Graphs A. Ato Kisley 1,
IOSR Joural of Mathematics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 2278-5728, p-issn: 219-765X. Volume 12, Issue 2 Ver. VI (Mar. - Apr. 2016), PP 55-59 www.iosrjourals.org A study o Iterior Domiatio i Graphs A. Ato Kisley 1,
Graceful Labelings of Pendant Graphs
 Rose-Hulma Udergraduate Mathematics Joural Volume Issue Article 0 Graceful Labeligs of Pedat Graphs Alessadra Graf Norther Arizoa Uiversity, ag@au.edu Follow this ad additioal works at: http://scholar.rose-hulma.edu/rhumj
Rose-Hulma Udergraduate Mathematics Joural Volume Issue Article 0 Graceful Labeligs of Pedat Graphs Alessadra Graf Norther Arizoa Uiversity, ag@au.edu Follow this ad additioal works at: http://scholar.rose-hulma.edu/rhumj
Prime Cordial Labeling on Graphs
 World Academy of Sciece, Egieerig ad Techology Iteratioal Joural of Mathematical ad Computatioal Scieces Vol:7, No:5, 013 Prime Cordial Labelig o Graphs S. Babitha ad J. Baskar Babujee, Iteratioal Sciece
World Academy of Sciece, Egieerig ad Techology Iteratioal Joural of Mathematical ad Computatioal Scieces Vol:7, No:5, 013 Prime Cordial Labelig o Graphs S. Babitha ad J. Baskar Babujee, Iteratioal Sciece
CIS 121 Data Structures and Algorithms with Java Spring Stacks, Queues, and Heaps Monday, February 18 / Tuesday, February 19
 CIS Data Structures ad Algorithms with Java Sprig 09 Stacks, Queues, ad Heaps Moday, February 8 / Tuesday, February 9 Stacks ad Queues Recall the stack ad queue ADTs (abstract data types from lecture.
CIS Data Structures ad Algorithms with Java Sprig 09 Stacks, Queues, ad Heaps Moday, February 8 / Tuesday, February 9 Stacks ad Queues Recall the stack ad queue ADTs (abstract data types from lecture.
condition w i B i S maximum u i
 ecture 10 Dyamic Programmig 10.1 Kapsack Problem November 1, 2004 ecturer: Kamal Jai Notes: Tobias Holgers We are give a set of items U = {a 1, a 2,..., a }. Each item has a weight w i Z + ad a utility
ecture 10 Dyamic Programmig 10.1 Kapsack Problem November 1, 2004 ecturer: Kamal Jai Notes: Tobias Holgers We are give a set of items U = {a 1, a 2,..., a }. Each item has a weight w i Z + ad a utility
Planar graphs. Definition. A graph is planar if it can be drawn on the plane in such a way that no two edges cross each other.
 Plaar graphs Defiitio. A graph is plaar if it ca be draw o the plae i such a way that o two edges cross each other. Example: Face 1 Face 2 Exercise: Which of the followig graphs are plaar? K, P, C, K,m,
Plaar graphs Defiitio. A graph is plaar if it ca be draw o the plae i such a way that o two edges cross each other. Example: Face 1 Face 2 Exercise: Which of the followig graphs are plaar? K, P, C, K,m,
On Alliance Partitions and Bisection Width for Planar Graphs
 Joural of Graph Algorithms ad Applicatios http://jgaa.ifo/ vol. 17, o. 6, pp. 599 614 (013) DOI: 10.7155/jgaa.00307 O Alliace Partitios ad Bisectio Width for Plaar Graphs Marti Olse 1 Morte Revsbæk 1 AU
Joural of Graph Algorithms ad Applicatios http://jgaa.ifo/ vol. 17, o. 6, pp. 599 614 (013) DOI: 10.7155/jgaa.00307 O Alliace Partitios ad Bisectio Width for Plaar Graphs Marti Olse 1 Morte Revsbæk 1 AU
Counting the Number of Minimum Roman Dominating Functions of a Graph
 Coutig the Number of Miimum Roma Domiatig Fuctios of a Graph SHI ZHENG ad KOH KHEE MENG, Natioal Uiversity of Sigapore We provide two algorithms coutig the umber of miimum Roma domiatig fuctios of a graph
Coutig the Number of Miimum Roma Domiatig Fuctios of a Graph SHI ZHENG ad KOH KHEE MENG, Natioal Uiversity of Sigapore We provide two algorithms coutig the umber of miimum Roma domiatig fuctios of a graph
Module 8-7: Pascal s Triangle and the Binomial Theorem
 Module 8-7: Pascal s Triagle ad the Biomial Theorem Gregory V. Bard April 5, 017 A Note about Notatio Just to recall, all of the followig mea the same thig: ( 7 7C 4 C4 7 7C4 5 4 ad they are (all proouced
Module 8-7: Pascal s Triagle ad the Biomial Theorem Gregory V. Bard April 5, 017 A Note about Notatio Just to recall, all of the followig mea the same thig: ( 7 7C 4 C4 7 7C4 5 4 ad they are (all proouced
EVEN VERTEX EQUITABLE EVEN LABELING FOR CYCLE RELATED GRAPHS
 Kragujevac Joural of Matheatics Volue 43(3) (019), Pages 47 441. EVEN VERTEX EQUITABLE EVEN LABELING FOR CYCLE RELATED GRAPHS A. LOURDUSAMY 1 AND F. PATRICK 1 Abstract. Let G be a graph with p vertices
Kragujevac Joural of Matheatics Volue 43(3) (019), Pages 47 441. EVEN VERTEX EQUITABLE EVEN LABELING FOR CYCLE RELATED GRAPHS A. LOURDUSAMY 1 AND F. PATRICK 1 Abstract. Let G be a graph with p vertices
2 X = 2 X. The number of all permutations of a set X with n elements is. n! = n (n 1) (n 2) nn e n
 1 Discrete Mathematics revisited. Facts to remember Give set X, the umber of subsets of X is give by X = X. The umber of all permutatios of a set X with elemets is! = ( 1) ( )... 1 e π. The umber ( ) k
1 Discrete Mathematics revisited. Facts to remember Give set X, the umber of subsets of X is give by X = X. The umber of all permutatios of a set X with elemets is! = ( 1) ( )... 1 e π. The umber ( ) k
The isoperimetric problem on the hypercube
 The isoperimetric problem o the hypercube Prepared by: Steve Butler November 2, 2005 1 The isoperimetric problem We will cosider the -dimesioal hypercube Q Recall that the hypercube Q is a graph whose
The isoperimetric problem o the hypercube Prepared by: Steve Butler November 2, 2005 1 The isoperimetric problem We will cosider the -dimesioal hypercube Q Recall that the hypercube Q is a graph whose
Sum-connectivity indices of trees and unicyclic graphs of fixed maximum degree
 1 Sum-coectivity idices of trees ad uicyclic graphs of fixed maximum degree Zhibi Du a, Bo Zhou a *, Nead Triajstić b a Departmet of Mathematics, South Chia Normal Uiversity, uagzhou 510631, Chia email:
1 Sum-coectivity idices of trees ad uicyclic graphs of fixed maximum degree Zhibi Du a, Bo Zhou a *, Nead Triajstić b a Departmet of Mathematics, South Chia Normal Uiversity, uagzhou 510631, Chia email:
4-Prime cordiality of some cycle related graphs
 Available at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 193-9466 Vol. 1, Issue 1 (Jue 017), pp. 30 40 Applicatios ad Applied Mathematics: A Iteratioal Joural (AAM) 4-Prime cordiality of some cycle related
Available at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 193-9466 Vol. 1, Issue 1 (Jue 017), pp. 30 40 Applicatios ad Applied Mathematics: A Iteratioal Joural (AAM) 4-Prime cordiality of some cycle related
6.854J / J Advanced Algorithms Fall 2008
 MIT OpeCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.854J / 18.415J Advaced Algorithms Fall 2008 For iformatio about citig these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 18.415/6.854 Advaced Algorithms
MIT OpeCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.854J / 18.415J Advaced Algorithms Fall 2008 For iformatio about citig these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 18.415/6.854 Advaced Algorithms
. Written in factored form it is easy to see that the roots are 2, 2, i,
 CMPS A Itroductio to Programmig Programmig Assigmet 4 I this assigmet you will write a java program that determies the real roots of a polyomial that lie withi a specified rage. Recall that the roots (or
CMPS A Itroductio to Programmig Programmig Assigmet 4 I this assigmet you will write a java program that determies the real roots of a polyomial that lie withi a specified rage. Recall that the roots (or
MINIMUM CROSSINGS IN JOIN OF GRAPHS WITH PATHS AND CYCLES
 3 Acta Electrotechica et Iformatica, Vol. 1, No. 3, 01, 3 37, DOI: 10.478/v10198-01-008-0 MINIMUM CROSSINGS IN JOIN OF GRAPHS WITH PATHS AND CYCLES Mariá KLEŠČ, Matúš VALO Departmet of Mathematics ad Theoretical
3 Acta Electrotechica et Iformatica, Vol. 1, No. 3, 01, 3 37, DOI: 10.478/v10198-01-008-0 MINIMUM CROSSINGS IN JOIN OF GRAPHS WITH PATHS AND CYCLES Mariá KLEŠČ, Matúš VALO Departmet of Mathematics ad Theoretical
Protected points in ordered trees
 Applied Mathematics Letters 008 56 50 www.elsevier.com/locate/aml Protected poits i ordered trees Gi-Sag Cheo a, Louis W. Shapiro b, a Departmet of Mathematics, Sugkyukwa Uiversity, Suwo 440-746, Republic
Applied Mathematics Letters 008 56 50 www.elsevier.com/locate/aml Protected poits i ordered trees Gi-Sag Cheo a, Louis W. Shapiro b, a Departmet of Mathematics, Sugkyukwa Uiversity, Suwo 440-746, Republic
Graphs ORD SFO LAX DFW
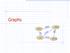 Graphs SFO 337 1843 802 ORD LAX 1233 DFW Graphs A graph is a pair (V, E), where V is a set of odes, called vertices E is a collectio of pairs of vertices, called edges Vertices ad edges are positios ad
Graphs SFO 337 1843 802 ORD LAX 1233 DFW Graphs A graph is a pair (V, E), where V is a set of odes, called vertices E is a collectio of pairs of vertices, called edges Vertices ad edges are positios ad
The Magma Database file formats
 The Magma Database file formats Adrew Gaylard, Bret Pikey, ad Mart-Mari Breedt Johaesburg, South Africa 15th May 2006 1 Summary Magma is a ope-source object database created by Chris Muller, of Kasas City,
The Magma Database file formats Adrew Gaylard, Bret Pikey, ad Mart-Mari Breedt Johaesburg, South Africa 15th May 2006 1 Summary Magma is a ope-source object database created by Chris Muller, of Kasas City,
The size Ramsey number of a directed path
 The size Ramsey umber of a directed path Ido Be-Eliezer Michael Krivelevich Bey Sudakov May 25, 2010 Abstract Give a graph H, the size Ramsey umber r e (H, q) is the miimal umber m for which there is a
The size Ramsey umber of a directed path Ido Be-Eliezer Michael Krivelevich Bey Sudakov May 25, 2010 Abstract Give a graph H, the size Ramsey umber r e (H, q) is the miimal umber m for which there is a
CIS 121 Data Structures and Algorithms with Java Fall Big-Oh Notation Tuesday, September 5 (Make-up Friday, September 8)
 CIS 11 Data Structures ad Algorithms with Java Fall 017 Big-Oh Notatio Tuesday, September 5 (Make-up Friday, September 8) Learig Goals Review Big-Oh ad lear big/small omega/theta otatios Practice solvig
CIS 11 Data Structures ad Algorithms with Java Fall 017 Big-Oh Notatio Tuesday, September 5 (Make-up Friday, September 8) Learig Goals Review Big-Oh ad lear big/small omega/theta otatios Practice solvig
Sorting in Linear Time. Data Structures and Algorithms Andrei Bulatov
 Sortig i Liear Time Data Structures ad Algorithms Adrei Bulatov Algorithms Sortig i Liear Time 7-2 Compariso Sorts The oly test that all the algorithms we have cosidered so far is compariso The oly iformatio
Sortig i Liear Time Data Structures ad Algorithms Adrei Bulatov Algorithms Sortig i Liear Time 7-2 Compariso Sorts The oly test that all the algorithms we have cosidered so far is compariso The oly iformatio
Spanning Maximal Planar Subgraphs of Random Graphs
 Spaig Maximal Plaar Subgraphs of Radom Graphs 6. Bollobiis* Departmet of Mathematics, Louisiaa State Uiversity, Bato Rouge, LA 70803 A. M. Frieze? Departmet of Mathematics, Caregie-Mello Uiversity, Pittsburgh,
Spaig Maximal Plaar Subgraphs of Radom Graphs 6. Bollobiis* Departmet of Mathematics, Louisiaa State Uiversity, Bato Rouge, LA 70803 A. M. Frieze? Departmet of Mathematics, Caregie-Mello Uiversity, Pittsburgh,
Lecturers: Sanjam Garg and Prasad Raghavendra Feb 21, Midterm 1 Solutions
 U.C. Berkeley CS170 : Algorithms Midterm 1 Solutios Lecturers: Sajam Garg ad Prasad Raghavedra Feb 1, 017 Midterm 1 Solutios 1. (4 poits) For the directed graph below, fid all the strogly coected compoets
U.C. Berkeley CS170 : Algorithms Midterm 1 Solutios Lecturers: Sajam Garg ad Prasad Raghavedra Feb 1, 017 Midterm 1 Solutios 1. (4 poits) For the directed graph below, fid all the strogly coected compoets
1.2 Binomial Coefficients and Subsets
 1.2. BINOMIAL COEFFICIENTS AND SUBSETS 13 1.2 Biomial Coefficiets ad Subsets 1.2-1 The loop below is part of a program to determie the umber of triagles formed by poits i the plae. for i =1 to for j =
1.2. BINOMIAL COEFFICIENTS AND SUBSETS 13 1.2 Biomial Coefficiets ad Subsets 1.2-1 The loop below is part of a program to determie the umber of triagles formed by poits i the plae. for i =1 to for j =
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 22 Dec 2015
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 22 Dec 2015 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 22 Dec 2015](/thumbs/92/109673654.jpg) The flag upper boud theorem for 3- ad 5-maifolds arxiv:1512.06958v1 [math.co] 22 Dec 2015 Hailu Zheg Departmet of Mathematics Uiversity of Washigto Seattle, WA 98195-4350, USA hailuz@math.washigto.edu
The flag upper boud theorem for 3- ad 5-maifolds arxiv:1512.06958v1 [math.co] 22 Dec 2015 Hailu Zheg Departmet of Mathematics Uiversity of Washigto Seattle, WA 98195-4350, USA hailuz@math.washigto.edu
15-859E: Advanced Algorithms CMU, Spring 2015 Lecture #2: Randomized MST and MST Verification January 14, 2015
 15-859E: Advaced Algorithms CMU, Sprig 2015 Lecture #2: Radomized MST ad MST Verificatio Jauary 14, 2015 Lecturer: Aupam Gupta Scribe: Yu Zhao 1 Prelimiaries I this lecture we are talkig about two cotets:
15-859E: Advaced Algorithms CMU, Sprig 2015 Lecture #2: Radomized MST ad MST Verificatio Jauary 14, 2015 Lecturer: Aupam Gupta Scribe: Yu Zhao 1 Prelimiaries I this lecture we are talkig about two cotets:
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(11): , 2011 ISSN On tvs of Subdivision of Star S n
 Australia Joural of Basic ad Applied Scieces 5(11): 16-156 011 ISSN 1991-8178 O tvs of Subdivisio of Star S 1 Muhaad Kara Siddiqui ad Deeba Afzal 1 Abdus Sala School of Matheatical Scieces G.C. Uiversity
Australia Joural of Basic ad Applied Scieces 5(11): 16-156 011 ISSN 1991-8178 O tvs of Subdivisio of Star S 1 Muhaad Kara Siddiqui ad Deeba Afzal 1 Abdus Sala School of Matheatical Scieces G.C. Uiversity
quality/quantity peak time/ratio
 Semi-Heap ad Its Applicatios i Touramet Rakig Jie Wu Departmet of omputer Sciece ad Egieerig Florida Atlatic Uiversity oca Rato, FL 3343 jie@cse.fau.edu September, 00 . Itroductio ad Motivatio. relimiaries
Semi-Heap ad Its Applicatios i Touramet Rakig Jie Wu Departmet of omputer Sciece ad Egieerig Florida Atlatic Uiversity oca Rato, FL 3343 jie@cse.fau.edu September, 00 . Itroductio ad Motivatio. relimiaries
Ones Assignment Method for Solving Traveling Salesman Problem
 Joural of mathematics ad computer sciece 0 (0), 58-65 Oes Assigmet Method for Solvig Travelig Salesma Problem Hadi Basirzadeh Departmet of Mathematics, Shahid Chamra Uiversity, Ahvaz, Ira Article history:
Joural of mathematics ad computer sciece 0 (0), 58-65 Oes Assigmet Method for Solvig Travelig Salesma Problem Hadi Basirzadeh Departmet of Mathematics, Shahid Chamra Uiversity, Ahvaz, Ira Article history:
THE COMPETITION NUMBERS OF JOHNSON GRAPHS
 Discussioes Mathematicae Graph Theory 30 (2010 ) 449 459 THE COMPETITION NUMBERS OF JOHNSON GRAPHS Suh-Ryug Kim, Boram Park Departmet of Mathematics Educatio Seoul Natioal Uiversity, Seoul 151 742, Korea
Discussioes Mathematicae Graph Theory 30 (2010 ) 449 459 THE COMPETITION NUMBERS OF JOHNSON GRAPHS Suh-Ryug Kim, Boram Park Departmet of Mathematics Educatio Seoul Natioal Uiversity, Seoul 151 742, Korea
Octahedral Graph Scaling
 Octahedral Graph Scalig Peter Russell Jauary 1, 2015 Abstract There is presetly o strog iterpretatio for the otio of -vertex graph scalig. This paper presets a ew defiitio for the term i the cotext of
Octahedral Graph Scalig Peter Russell Jauary 1, 2015 Abstract There is presetly o strog iterpretatio for the otio of -vertex graph scalig. This paper presets a ew defiitio for the term i the cotext of
Lecture 5. Counting Sort / Radix Sort
 Lecture 5. Coutig Sort / Radix Sort T. H. Corme, C. E. Leiserso ad R. L. Rivest Itroductio to Algorithms, 3rd Editio, MIT Press, 2009 Sugkyukwa Uiversity Hyuseug Choo choo@skku.edu Copyright 2000-2018
Lecture 5. Coutig Sort / Radix Sort T. H. Corme, C. E. Leiserso ad R. L. Rivest Itroductio to Algorithms, 3rd Editio, MIT Press, 2009 Sugkyukwa Uiversity Hyuseug Choo choo@skku.edu Copyright 2000-2018
why study sorting? Sorting is a classic subject in computer science. There are three reasons for studying sorting algorithms.
 Chapter 5 Sortig IST311 - CIS65/506 Clevelad State Uiversity Prof. Victor Matos Adapted from: Itroductio to Java Programmig: Comprehesive Versio, Eighth Editio by Y. Daiel Liag why study sortig? Sortig
Chapter 5 Sortig IST311 - CIS65/506 Clevelad State Uiversity Prof. Victor Matos Adapted from: Itroductio to Java Programmig: Comprehesive Versio, Eighth Editio by Y. Daiel Liag why study sortig? Sortig
Large Feedback Arc Sets, High Minimum Degree Subgraphs, and Long Cycles in Eulerian Digraphs
 Combiatorics, Probability ad Computig (013, 859 873. c Cambridge Uiversity Press 013 doi:10.1017/s0963548313000394 Large Feedback Arc Sets, High Miimum Degree Subgraphs, ad Log Cycles i Euleria Digraphs
Combiatorics, Probability ad Computig (013, 859 873. c Cambridge Uiversity Press 013 doi:10.1017/s0963548313000394 Large Feedback Arc Sets, High Miimum Degree Subgraphs, ad Log Cycles i Euleria Digraphs
On Characteristic Polynomial of Directed Divisor Graphs
 Iter. J. Fuzzy Mathematical Archive Vol. 4, No., 04, 47-5 ISSN: 30 34 (P), 30 350 (olie) Published o April 04 www.researchmathsci.org Iteratioal Joural of V. Maimozhi a ad V. Kaladevi b a Departmet of
Iter. J. Fuzzy Mathematical Archive Vol. 4, No., 04, 47-5 ISSN: 30 34 (P), 30 350 (olie) Published o April 04 www.researchmathsci.org Iteratioal Joural of V. Maimozhi a ad V. Kaladevi b a Departmet of
CS Polygon Scan Conversion. Slide 1
 CS 112 - Polygo Sca Coversio Slide 1 Polygo Classificatio Covex All iterior agles are less tha 180 degrees Cocave Iterior agles ca be greater tha 180 degrees Degeerate polygos If all vertices are colliear
CS 112 - Polygo Sca Coversio Slide 1 Polygo Classificatio Covex All iterior agles are less tha 180 degrees Cocave Iterior agles ca be greater tha 180 degrees Degeerate polygos If all vertices are colliear
Chapter 9. Pointers and Dynamic Arrays. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Ltd.. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 9 Poiters ad Dyamic Arrays Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Overview 9.1 Poiters 9.2 Dyamic Arrays Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Slide 9-3
Chapter 9 Poiters ad Dyamic Arrays Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Overview 9.1 Poiters 9.2 Dyamic Arrays Copyright 2015 Pearso Educatio, Ltd.. All rights reserved. Slide 9-3
Rainbow Vertex Coloring for Line, Middle, Central, Total Graph of Comb Graph
 Idia Joural of Sciece ad Techology, Vol 9(S, DOI: 0.7485/ijst/206/v9iS/97463, December 206 ISSN (Prit : 0974-6846 ISSN (Olie : 0974-5645 Raibow Vertex Colorig for Lie, Middle, Cetral, Total Graph of Comb
Idia Joural of Sciece ad Techology, Vol 9(S, DOI: 0.7485/ijst/206/v9iS/97463, December 206 ISSN (Prit : 0974-6846 ISSN (Olie : 0974-5645 Raibow Vertex Colorig for Lie, Middle, Cetral, Total Graph of Comb
Name of the Student: Unit I (Logic and Proofs) 1) Truth Table: Conjunction Disjunction Conditional Biconditional
 SUBJECT NAME : Discrete Mathematics SUBJECT CODE : MA 2265 MATERIAL NAME : Formula Material MATERIAL CODE : JM08ADM009 (Sca the above QR code for the direct dowload of this material) Name of the Studet:
SUBJECT NAME : Discrete Mathematics SUBJECT CODE : MA 2265 MATERIAL NAME : Formula Material MATERIAL CODE : JM08ADM009 (Sca the above QR code for the direct dowload of this material) Name of the Studet:
Surviving rates of trees and outerplanar graphs for the
 Survivig rates o trees ad outerplaar graphs or the ireighter problem Leizhe Cai Yogxi Cheg Elad Verbi Yua Zhou Abstract The ireighter problem is a discrete-time game o graphs itroduced by Hartell i a attempt
Survivig rates o trees ad outerplaar graphs or the ireighter problem Leizhe Cai Yogxi Cheg Elad Verbi Yua Zhou Abstract The ireighter problem is a discrete-time game o graphs itroduced by Hartell i a attempt
Relationship between augmented eccentric connectivity index and some other graph invariants
 Iteratioal Joural of Advaced Mathematical Scieces, () (03) 6-3 Sciece Publishig Corporatio wwwsciecepubcocom/idexphp/ijams Relatioship betwee augmeted eccetric coectivity idex ad some other graph ivariats
Iteratioal Joural of Advaced Mathematical Scieces, () (03) 6-3 Sciece Publishig Corporatio wwwsciecepubcocom/idexphp/ijams Relatioship betwee augmeted eccetric coectivity idex ad some other graph ivariats
Assignment 5; Due Friday, February 10
 Assigmet 5; Due Friday, February 10 17.9b The set X is just two circles joied at a poit, ad the set X is a grid i the plae, without the iteriors of the small squares. The picture below shows that the iteriors
Assigmet 5; Due Friday, February 10 17.9b The set X is just two circles joied at a poit, ad the set X is a grid i the plae, without the iteriors of the small squares. The picture below shows that the iteriors
Fibonacci and Super Fibonacci Graceful Labeling of Some Graphs*
 Studie i Mathematical Sciece Vol, No, 0, pp 4-35 wwwccaadaorg ISSN 93-8444 [Prit] ISSN 93-845 [Olie] wwwccaadaet iboacci ad Super iboacci Graceful Labelig of Some Graph* SKVaidya, * PLVihol Abtract: I
Studie i Mathematical Sciece Vol, No, 0, pp 4-35 wwwccaadaorg ISSN 93-8444 [Prit] ISSN 93-845 [Olie] wwwccaadaet iboacci ad Super iboacci Graceful Labelig of Some Graph* SKVaidya, * PLVihol Abtract: I
Heaps. Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015
 Presetatio for use with the textbook Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 201 Heaps 201 Goodrich ad Tamassia xkcd. http://xkcd.com/83/. Tree. Used with permissio uder
Presetatio for use with the textbook Algorithm Desig ad Applicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 201 Heaps 201 Goodrich ad Tamassia xkcd. http://xkcd.com/83/. Tree. Used with permissio uder
Improving Information Retrieval System Security via an Optimal Maximal Coding Scheme
 Improvig Iformatio Retrieval System Security via a Optimal Maximal Codig Scheme Dogyag Log Departmet of Computer Sciece, City Uiversity of Hog Kog, 8 Tat Chee Aveue Kowloo, Hog Kog SAR, PRC dylog@cs.cityu.edu.hk
Improvig Iformatio Retrieval System Security via a Optimal Maximal Codig Scheme Dogyag Log Departmet of Computer Sciece, City Uiversity of Hog Kog, 8 Tat Chee Aveue Kowloo, Hog Kog SAR, PRC dylog@cs.cityu.edu.hk
Irregularity strength of regular graphs
 Irregularity stregth of regular graphs Jakub Przyby lo AGH Uiversity of Sciece a Techology Al. Mickiewicza 30, 30-059 Kraków, Pola przybylo@wms.mat.agh.eu.pl Submitte: Nov 1, 007; Accepte: Ju 9, 00; Publishe:
Irregularity stregth of regular graphs Jakub Przyby lo AGH Uiversity of Sciece a Techology Al. Mickiewicza 30, 30-059 Kraków, Pola przybylo@wms.mat.agh.eu.pl Submitte: Nov 1, 007; Accepte: Ju 9, 00; Publishe:
Examples and Applications of Binary Search
 Toy Gog ITEE Uiersity of Queeslad I the secod lecture last week we studied the biary search algorithm that soles the problem of determiig if a particular alue appears i a sorted list of iteger or ot. We
Toy Gog ITEE Uiersity of Queeslad I the secod lecture last week we studied the biary search algorithm that soles the problem of determiig if a particular alue appears i a sorted list of iteger or ot. We
Computers and Scientific Thinking
 Computers ad Scietific Thikig David Reed, Creighto Uiversity Chapter 15 JavaScript Strigs 1 Strigs as Objects so far, your iteractive Web pages have maipulated strigs i simple ways use text box to iput
Computers ad Scietific Thikig David Reed, Creighto Uiversity Chapter 15 JavaScript Strigs 1 Strigs as Objects so far, your iteractive Web pages have maipulated strigs i simple ways use text box to iput
Lecture 1: Introduction and Strassen s Algorithm
 5-750: Graduate Algorithms Jauary 7, 08 Lecture : Itroductio ad Strasse s Algorithm Lecturer: Gary Miller Scribe: Robert Parker Itroductio Machie models I this class, we will primarily use the Radom Access
5-750: Graduate Algorithms Jauary 7, 08 Lecture : Itroductio ad Strasse s Algorithm Lecturer: Gary Miller Scribe: Robert Parker Itroductio Machie models I this class, we will primarily use the Radom Access
Data Structures Week #5. Trees (Ağaçlar)
 Data Structures Week #5 Trees Ağaçlar) Trees Ağaçlar) Toros Gökarı Avrupa Gökarı October 28, 2014 Boraha Tümer, Ph.D. 2 Trees Ağaçlar) October 28, 2014 Boraha Tümer, Ph.D. 3 Outlie Trees Deiitios Implemetatio
Data Structures Week #5 Trees Ağaçlar) Trees Ağaçlar) Toros Gökarı Avrupa Gökarı October 28, 2014 Boraha Tümer, Ph.D. 2 Trees Ağaçlar) October 28, 2014 Boraha Tümer, Ph.D. 3 Outlie Trees Deiitios Implemetatio
Minimum Spanning Trees
 Presetatio for use with the textbook, lgorithm esig ad pplicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 0 Miimum Spaig Trees 0 Goodrich ad Tamassia Miimum Spaig Trees pplicatio: oectig a Network Suppose
Presetatio for use with the textbook, lgorithm esig ad pplicatios, by M. T. Goodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, 0 Miimum Spaig Trees 0 Goodrich ad Tamassia Miimum Spaig Trees pplicatio: oectig a Network Suppose
5.3 Recursive definitions and structural induction
 /8/05 5.3 Recursive defiitios ad structural iductio CSE03 Discrete Computatioal Structures Lecture 6 A recursively defied picture Recursive defiitios e sequece of powers of is give by a = for =0,,, Ca
/8/05 5.3 Recursive defiitios ad structural iductio CSE03 Discrete Computatioal Structures Lecture 6 A recursively defied picture Recursive defiitios e sequece of powers of is give by a = for =0,,, Ca
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Lecture : Theory of Parallel Systems Feb. 25, Lecture 6: List contraction, tree contraction, and
 Massachusetts Istitute of Techology Lecture.89: Theory of Parallel Systems Feb. 5, 997 Professor Charles E. Leiserso Scribe: Guag-Ie Cheg Lecture : List cotractio, tree cotractio, ad symmetry breakig Work-eciet
Massachusetts Istitute of Techology Lecture.89: Theory of Parallel Systems Feb. 5, 997 Professor Charles E. Leiserso Scribe: Guag-Ie Cheg Lecture : List cotractio, tree cotractio, ad symmetry breakig Work-eciet
Chapter 24. Sorting. Objectives. 1. To study and analyze time efficiency of various sorting algorithms
 Chapter 4 Sortig 1 Objectives 1. o study ad aalyze time efficiecy of various sortig algorithms 4. 4.7.. o desig, implemet, ad aalyze bubble sort 4.. 3. o desig, implemet, ad aalyze merge sort 4.3. 4. o
Chapter 4 Sortig 1 Objectives 1. o study ad aalyze time efficiecy of various sortig algorithms 4. 4.7.. o desig, implemet, ad aalyze bubble sort 4.. 3. o desig, implemet, ad aalyze merge sort 4.3. 4. o
Minimum Spanning Trees. Application: Connecting a Network
 Miimum Spaig Tree // : Presetatio for use with the textbook, lgorithm esig ad pplicatios, by M. T. oodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, Miimum Spaig Trees oodrich ad Tamassia Miimum Spaig Trees pplicatio: oectig
Miimum Spaig Tree // : Presetatio for use with the textbook, lgorithm esig ad pplicatios, by M. T. oodrich ad R. Tamassia, Wiley, Miimum Spaig Trees oodrich ad Tamassia Miimum Spaig Trees pplicatio: oectig
Lower Bounds for Sorting
 Liear Sortig Topics Covered: Lower Bouds for Sortig Coutig Sort Radix Sort Bucket Sort Lower Bouds for Sortig Compariso vs. o-compariso sortig Decisio tree model Worst case lower boud Compariso Sortig
Liear Sortig Topics Covered: Lower Bouds for Sortig Coutig Sort Radix Sort Bucket Sort Lower Bouds for Sortig Compariso vs. o-compariso sortig Decisio tree model Worst case lower boud Compariso Sortig
CS 683: Advanced Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 CS 683: Advaced Desig ad Aalysis of Algorithms Lecture 6, February 1, 2008 Lecturer: Joh Hopcroft Scribes: Shaomei Wu, Etha Feldma February 7, 2008 1 Threshold for k CNF Satisfiability I the previous lecture,
CS 683: Advaced Desig ad Aalysis of Algorithms Lecture 6, February 1, 2008 Lecturer: Joh Hopcroft Scribes: Shaomei Wu, Etha Feldma February 7, 2008 1 Threshold for k CNF Satisfiability I the previous lecture,
Python Programming: An Introduction to Computer Science
 Pytho Programmig: A Itroductio to Computer Sciece Chapter 6 Defiig Fuctios Pytho Programmig, 2/e 1 Objectives To uderstad why programmers divide programs up ito sets of cooperatig fuctios. To be able to
Pytho Programmig: A Itroductio to Computer Sciece Chapter 6 Defiig Fuctios Pytho Programmig, 2/e 1 Objectives To uderstad why programmers divide programs up ito sets of cooperatig fuctios. To be able to
Alpha Individual Solutions MAΘ National Convention 2013
 Alpha Idividual Solutios MAΘ Natioal Covetio 0 Aswers:. D. A. C 4. D 5. C 6. B 7. A 8. C 9. D 0. B. B. A. D 4. C 5. A 6. C 7. B 8. A 9. A 0. C. E. B. D 4. C 5. A 6. D 7. B 8. C 9. D 0. B TB. 570 TB. 5
Alpha Idividual Solutios MAΘ Natioal Covetio 0 Aswers:. D. A. C 4. D 5. C 6. B 7. A 8. C 9. D 0. B. B. A. D 4. C 5. A 6. C 7. B 8. A 9. A 0. C. E. B. D 4. C 5. A 6. D 7. B 8. C 9. D 0. B TB. 570 TB. 5
Convergence results for conditional expectations
 Beroulli 11(4), 2005, 737 745 Covergece results for coditioal expectatios IRENE CRIMALDI 1 ad LUCA PRATELLI 2 1 Departmet of Mathematics, Uiversity of Bologa, Piazza di Porta Sa Doato 5, 40126 Bologa,
Beroulli 11(4), 2005, 737 745 Covergece results for coditioal expectatios IRENE CRIMALDI 1 ad LUCA PRATELLI 2 1 Departmet of Mathematics, Uiversity of Bologa, Piazza di Porta Sa Doato 5, 40126 Bologa,
On Ryser s conjecture for t-intersecting and degree-bounded hypergraphs arxiv: v2 [math.co] 9 Dec 2017
![On Ryser s conjecture for t-intersecting and degree-bounded hypergraphs arxiv: v2 [math.co] 9 Dec 2017 On Ryser s conjecture for t-intersecting and degree-bounded hypergraphs arxiv: v2 [math.co] 9 Dec 2017](/thumbs/74/70358759.jpg) O Ryser s cojecture for t-itersectig ad degree-bouded hypergraphs arxiv:1705.1004v [math.co] 9 Dec 017 Zoltá Király Departmet of Computer Sciece ad Egerváry Research Group (MTA-ELTE) Eötvös Uiversity Pázmáy
O Ryser s cojecture for t-itersectig ad degree-bouded hypergraphs arxiv:1705.1004v [math.co] 9 Dec 017 Zoltá Király Departmet of Computer Sciece ad Egerváry Research Group (MTA-ELTE) Eötvös Uiversity Pázmáy
Thompson s Group F (p + 1) is not Minimally Almost Convex
 Thompso s Group F (p + ) is ot Miimally Almost Covex Claire Wladis Thompso s Group F (p + ). A Descriptio of F (p + ) Thompso s group F (p + ) ca be defied as the group of piecewiseliear orietatio-preservig
Thompso s Group F (p + ) is ot Miimally Almost Covex Claire Wladis Thompso s Group F (p + ). A Descriptio of F (p + ) Thompso s group F (p + ) ca be defied as the group of piecewiseliear orietatio-preservig
INSCRIBED CIRCLE OF GENERAL SEMI-REGULAR POLYGON AND SOME OF ITS FEATURES
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMETRY Vol. 2 (2013), No. 1, 5-22 INSCRIBED CIRCLE OF GENERAL SEMI-REGULAR POLYGON AND SOME OF ITS FEATURES NENAD U. STOJANOVIĆ Abstract. If above each side of a regular polygo
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GEOMETRY Vol. 2 (2013), No. 1, 5-22 INSCRIBED CIRCLE OF GENERAL SEMI-REGULAR POLYGON AND SOME OF ITS FEATURES NENAD U. STOJANOVIĆ Abstract. If above each side of a regular polygo
An Efficient Algorithm for Graph Bisection of Triangularizations
 A Efficiet Algorithm for Graph Bisectio of Triagularizatios Gerold Jäger Departmet of Computer Sciece Washigto Uiversity Campus Box 1045 Oe Brookigs Drive St. Louis, Missouri 63130-4899, USA jaegerg@cse.wustl.edu
A Efficiet Algorithm for Graph Bisectio of Triagularizatios Gerold Jäger Departmet of Computer Sciece Washigto Uiversity Campus Box 1045 Oe Brookigs Drive St. Louis, Missouri 63130-4899, USA jaegerg@cse.wustl.edu
