Polarization. Components of Polarization: Malus Law. VS203B Lecture Notes Spring, Topic: Polarization
|
|
|
- Terence Carroll
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VS03B Lecture Notes Spring, Topic: Polarization Polarization Recall that I stated that we had to model light as a transverse wave so that we could use the model to explain polarization. The electric energy of a polarized beam acts in a specific direction that is perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the light. vertical horizontal diagonal Polarization arises whenever radiated energy, or light, comes from an excited molecule oscillating in one direction. In the natural environment these oscillations are oriented randomly and tend to shift over time so normal light is unpolarized (i.e. it is made up of components of every possible polarization.) But when light is created in a controlled environment, such as in a laser, all the oscillations are correlated and you can selectively amplify one orientation of the polarization. Alternately, you can select one component of the polarization by... passing unpolarized light through a specially designed filter. reflecting unpolarized light off an appropriately tilted surface. scattering unpolarized light in a specific direction from small particles. Components of Polarization: Malus Law Like any vector, the vector representing the polarization of light can always be split into a horizontal and vertical component. I = A Asin A Acos Since the intensity is the square of the amplitude, it follows that the intensity of the horizontal and vertical components are: I = A cos, I = A sin x y Malus Law where is the angle between the orientation of the light and the horizontal component. 50
2 VS03B Lecture Notes Spring, Topic: Polarization Polarizating Filter, Polaroid, Polarizers For polarized light, the electric vector oscillates in a specific direction. When light strikes a conducting material, the free electrons within the material absorb the oscillating energy and begin to oscillate themselves. The ease with which the electrons can oscillate in a specific direction dictates how much light of that polarization gets absorbed. In many metals, the molecules are amorphous, or randomly arranged, so light of all polarizations are equally absorbed. That is why metal is reflective, but not transmissive (opaque). To create a polarizer, you need to design a material that only allows oscillation of molecules in a single direction. One example is an array of thin vertical wires. If the wires are thin enough (on the order of wavelength) then electrons only oscillate in one direction and only that orientation of polarization is absorbed. The component of polarization in the orthogonal direction will transmit. This had been difficult to do for visible light until Edwin Land invented the polaroid, which is is created by stretching hydrocarbon molecules on a sheet into long strands, then impregnating them with conducting iodine. In effect this acts like a set of thin wires. Light polarized in the direction of the molecules is absorbed by free flowing electrons. Light of opposite orientation is not absorbed and so is transmitted. If a polarizer was perfect, then if one passed unpolarized light through the filter, only 50% of the light would be transmitted. For linearly polarized light, the intensity of light that is transmitted is the projection of the polarization vector onto the transmitting axis of the polarizer. This is where Malus law becomes very useful. First, we will establish the convention of units of light, or intensity. You can think of them as photons. Second we define a polarizer s transmission axis as the axis that is parallel to the polarization that is transmitted. Rules for unpolarized light: of light passing through a linear polarizer, leaves 50 units of light, which will be polarized along the transmission axis of the polarizer. 50 units (polarization axis is vertical or 90 ) Do a demonstration to show that three filters transmits more light than two filters 51
3 VS03B Lecture Notes Spring, Topic: Polarization Rules for polarized light: The number of units of intensity that gets through is proportional to the square of the cosine of the angle between the orientation of the incident polarization and the transmission axis of the polarizer. In other words, the transmitted intensity is the component of intensity of the original polarization that lies along the transmission axis of the polarizer. vertical polarization (polarization axis is vertical or 90 ) angle between polarized light and polaroid axis is 0 = cos = = I Io Io If you turn the polaroid 10 degrees (to 100 degrees), then the angle between the light polarization and the axis of the polaroid is 10, so: I = I cos 10 = 0.97 I = 97 units o If you turn the polaroid another 80 degrees (to 180 degrees), then the angle between the light polarization and the axis of the polaroid is 90. At 0 and 180 degrees the polarization is the same horizontally polarized. I = I o cos 90 = 0 units o The orientation of the emergent light is always the same as the transmission axis of the polarizing filter preceding it. So when polarizers are put in series, you can easily determine the polarization and the final emergent number of units provided that you go step by step through each polarizing filter. I = I o = cos 45 5 I = I o = cos axis vertical polarization 5
4 VS03B Lecture Notes Spring, Topic: Polarization Example: Unpolarized light is incident on a polarizing filter whose orientation is vertical (90 degrees) It is followed by a filter whose orientation is 180 degrees. If of light intensity are incident on the pair of filters, how many units emerge? If you add a third filter oriented at 45 degrees from horizontal, in between the two original filters, how much light emerges? 180 axis no light emerges 50 units 180 axis 45 axis I = 5cos 45 = 1.5 units 50 units I = 50 cos 45 = 5 units So adding another actually increases the amount of transmitted light! Does the same improvement occur when you reorder the filters: Likely not! 53
5 VS03B Lecture Notes Spring, Topic: Polarization Polarization by Reflection: When light reflects normally, or perpendicularly from a surface, the amount of reflectance is governed by the law: n n R = n + n As the angle of incidence changes, the amount of reflected light depends on the polarization. If one orientation of polarization reflects more than the other, then the reflected light would be partially polarized. The reflection for the two polarization components follows this graph: E p E s is the component of the polarization that is parallel to the reflecting surface. E p is the component of polarization that is perpendicular to E s. R s is the reflectance of the Es component. R p is the reflectance of the Ep component. At 90º, Rs and Rp are 100 % E s 0 n=1.5 R s R p B E s reflectance (%) % 56.3 E s E p In this figure, the angle of incidence is equal to Brewster s angle, B ; the angle for which only the s-component of the polarization is reflected. When the angle of incidence is not equal to Brewster s angle, there is still a tendency for one polarization to reflect more than the other (see graph on the right). The angle at which light of only one polarization reflects is called Brewster s Angle ( Β ). The actual angle depends on the index of refraction of the reflecting surface. The formula for Brewster s angle is: n B = arctan n An oblique reflection can create polarized light. Unpolarized light that is diffusely reflected is generally not polarized. It comes in and gets reflected at all angles. But unpolarized light that is specularly reflected does have some polarization. Specular reflections follow the regular incidence-reflection rule. Specular reflections are mirror reflections and also appear as highlights when reflected off objects. DEMO: A good demonstration is to look at a reflection from a table (a black book is also an excellent choice) Place a polarizer over your eye and rotate it and you ll see the reflections appear and disappear. So what about polarized sunglasses? They minimize specular reflections from horizontal objects degrees is not an uncommon angle to see these specular reflections. (driving, boating, skiing etc.) So, if the transmission axis is vertical, one minimizes the amount of horizontally polarized light that reaches the eye. Blocking the horizontally polarized light increases contrast by reducing glare. If you are selling glasses with polarizers to your patients, it is very simple to demonstrate their advantage by looking at the reflection off a table. With some LCD displays, the reflected light is linearly polarized. So, if you are looking at it through polarizing sunglasses, it will appear black. This also happens when you are looking at an LCD gas pump. Good LCD displays employ circular polarization to avoid this problem angle (deg) This shows a typical plot for the reflectance of the s- and p-components of the polarization as a function of angle for a reflecting medium with an index of refraction of 1.5. At Brewster s angle (56.3º in this case), only the s- component, or the polarization component that is parallel to the reflecting surface, is reflected. The formula used to calculate Brewster s angle for any surface is: n B = arctan n
6 VS03B Lecture Notes Spring, Topic: Polarization Polarization by Scattering: Linearly polarized light is emitted at angle of 90º from the scattering particle. DEMO: Use polarized laser pointer and pass it through a scattering liquid (milk powder in water) rotate it until the light scattered to the side disappears. Then use a linear polarizer to show that when the scattered light is at a maximum, it is also polarized. Birefringence: In a crystal, the structure is often anisotropic as opposed to glass or plastic, which is isotropic. That means that the atomic lattice that makes up the molecules looks different when viewed from different orientations. The electrons within the lattice will also vibrate differently depending on the direction and so light of one polarization will encounter a transparent material with a different refractive index than the other component of polarization. This dependency of index on the direction of polarization is called Birefringence. Birefringence gives rise to double refraction Calcite crystal is a classic example. Birefringence is often found in crystals but it is also found in ordered arrangements of molecules. In the latter case, it is called form birefringence. The cornea is an example of a tissue that has form birefringence. Within the stroma, the lamellae are comprised of long colinear strands of collagen which are laid down in sheets. The strands are anisotropic so the component of light along the strands sees a slight different refractive index than the perpendicular component. If the layers of sheets were oriented randomly, then the form birefringence of one sheet would cancel the other. But the lamellae have a preferred orientation there is an overall birefringence. The actual index of refraction difference between the two polarization components is so it is small. By comparison, calcite has a difference of about 0. so the double refraction is very strong. Dichroism If a crystal absorbs one of the polarization directions more than another, it is called dichroic. The polarizing filters in your glasses and the ones that you used for the demo are dichroic. The eye has dichroic crystals near the fovea (macular pigment granules) which gives rise to a selective absorption of some orientations of polarizations. It is subtle, and is likely just a byproduct of another system (i.e. there is no mechanistic reason for it) but when you rotate a polarizer in front of the eye you see a corresponding rotating pattern, called Haidinger s Brushes. They will sometimes appear colored because the preferential absorption also depends on the color of the light. 55
Polarization. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Polarization Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Polaroid sunglasses are familiar to most of us. They have a special ability to cut the glare of light reflected from water or glass (see [link]). Polaroids have this ability
Polarization Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Polaroid sunglasses are familiar to most of us. They have a special ability to cut the glare of light reflected from water or glass (see [link]). Polaroids have this ability
Basic Optics : Microlithography Optics Part 4: Polarization
 Electromagnetic Radiation Polarization: Linear, Circular, Elliptical Ordinary and extraordinary rays Polarization by reflection: Brewster angle Polarization by Dichroism Double refraction (Birefringence)
Electromagnetic Radiation Polarization: Linear, Circular, Elliptical Ordinary and extraordinary rays Polarization by reflection: Brewster angle Polarization by Dichroism Double refraction (Birefringence)
OpenStax-CNX module: m Polarization * Bobby Bailey. Based on Polarization by OpenStax
 OpenStax-CNX module: m52456 1 27.9 Polarization * Bobby Bailey Based on Polarization by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 Abstract
OpenStax-CNX module: m52456 1 27.9 Polarization * Bobby Bailey Based on Polarization by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 Abstract
Diffraction. Single-slit diffraction. Diffraction by a circular aperture. Chapter 38. In the forward direction, the intensity is maximal.
 Diffraction Chapter 38 Huygens construction may be used to find the wave observed on the downstream side of an aperture of any shape. Diffraction The interference pattern encodes the shape as a Fourier
Diffraction Chapter 38 Huygens construction may be used to find the wave observed on the downstream side of an aperture of any shape. Diffraction The interference pattern encodes the shape as a Fourier
Chapter 33 cont. The Nature of Light and Propagation of Light (lecture 2) Dr. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 33 cont The Nature of Light and Propagation of Light (lecture 2) Dr. Armen Kocharian Polarization of Light Waves The direction of polarization of each individual wave is defined to be the direction
Chapter 33 cont The Nature of Light and Propagation of Light (lecture 2) Dr. Armen Kocharian Polarization of Light Waves The direction of polarization of each individual wave is defined to be the direction
10.5 Polarization of Light
 10.5 Polarization of Light Electromagnetic waves have electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of propagation. These fields can take many different directions
10.5 Polarization of Light Electromagnetic waves have electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of propagation. These fields can take many different directions
1.! Questions about reflected intensity. [Use the formulas on p. 8 of Light.] , no matter
![1.! Questions about reflected intensity. [Use the formulas on p. 8 of Light.] , no matter 1.! Questions about reflected intensity. [Use the formulas on p. 8 of Light.] , no matter](/thumbs/81/83191942.jpg) Reading: Light Key concepts: Huygens s principle; reflection; refraction; reflectivity; total reflection; Brewster angle; polarization by absorption, reflection and Rayleigh scattering. 1.! Questions about
Reading: Light Key concepts: Huygens s principle; reflection; refraction; reflectivity; total reflection; Brewster angle; polarization by absorption, reflection and Rayleigh scattering. 1.! Questions about
Chapter 24. Wave Optics
 Chapter 24 Wave Optics Diffraction Huygen s principle requires that the waves spread out after they pass through slits This spreading out of light from its initial line of travel is called diffraction
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Diffraction Huygen s principle requires that the waves spread out after they pass through slits This spreading out of light from its initial line of travel is called diffraction
Polarization of Light
 Department of Physics University of Engineering & Management Kolkata Polarization of Light Transverse Wave Direction of oscillation Direction of propagation of energy A transverse wave is a moving wave
Department of Physics University of Engineering & Management Kolkata Polarization of Light Transverse Wave Direction of oscillation Direction of propagation of energy A transverse wave is a moving wave
SPH4U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS
 SPH4U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS THE WAVE NATURE OF LIGHT L Polarization of Light (P.532-537) What is Polarized Light? Polarized sunglasses eliminate the glare of reflected light off the surface of a stream while
SPH4U UNIVERSITY PHYSICS THE WAVE NATURE OF LIGHT L Polarization of Light (P.532-537) What is Polarized Light? Polarized sunglasses eliminate the glare of reflected light off the surface of a stream while
Lecture 17 (Polarization and Scattering) Physics Spring 2018 Douglas Fields
 Lecture 17 (Polarization and Scattering) Physics 262-01 Spring 2018 Douglas Fields Reading Quiz When unpolarized light passes through an ideal polarizer, the intensity of the transmitted light is: A) Unchanged
Lecture 17 (Polarization and Scattering) Physics 262-01 Spring 2018 Douglas Fields Reading Quiz When unpolarized light passes through an ideal polarizer, the intensity of the transmitted light is: A) Unchanged
Chapter 24. Wave Optics. Wave Optics. The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena
 Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
specular diffuse reflection.
 Lesson 8 Light and Optics The Nature of Light Properties of Light: Reflection Refraction Interference Diffraction Polarization Dispersion and Prisms Total Internal Reflection Huygens s Principle The Nature
Lesson 8 Light and Optics The Nature of Light Properties of Light: Reflection Refraction Interference Diffraction Polarization Dispersion and Prisms Total Internal Reflection Huygens s Principle The Nature
Polarization of waves on ropes
 Polarization of waves on ropes Youtube clip one: the gentleman excites first a wave of vertical polarization, and next of horizontal polarization. Youtube clip two: vertical, horizontal, and even circular
Polarization of waves on ropes Youtube clip one: the gentleman excites first a wave of vertical polarization, and next of horizontal polarization. Youtube clip two: vertical, horizontal, and even circular
Basic Polarization Techniques and Devices 1998, 2003 Meadowlark Optics, Inc
 Basic Polarization Techniques and Devices 1998, 2003 Meadowlark Optics, Inc This application note briefly describes polarized light, retardation and a few of the tools used to manipulate the polarization
Basic Polarization Techniques and Devices 1998, 2003 Meadowlark Optics, Inc This application note briefly describes polarized light, retardation and a few of the tools used to manipulate the polarization
Chapter 24. Wave Optics. Wave Optics. The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena
 Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Be careful not to leave your fingerprints on the optical surfaces of lenses or Polaroid sheets.
 POLARIZATION OF LIGHT REFERENCES Halliday, D. and Resnick, A., Physics, 4 th edition, New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 1992, Volume II, Chapter 48-1, 48-2, 48-3. (2weights) (1weight-exercises 1 and 3
POLARIZATION OF LIGHT REFERENCES Halliday, D. and Resnick, A., Physics, 4 th edition, New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 1992, Volume II, Chapter 48-1, 48-2, 48-3. (2weights) (1weight-exercises 1 and 3
B.Sc.( Srmester-3) Subject: Physics Course: US03CPHY01 Title: Optics
 B.Sc.( Srmester-3) Subject: Physics Course: US03CPHY01 Title: Optics UNIT III Polarization Introduction:- Interference and diffraction phenomena proved that light is a wave motion. These phenomena are
B.Sc.( Srmester-3) Subject: Physics Course: US03CPHY01 Title: Optics UNIT III Polarization Introduction:- Interference and diffraction phenomena proved that light is a wave motion. These phenomena are
Reflection, Refraction and Polarization of Light
 Reflection, Refraction and Polarization of Light Physics 246/Spring2012 In today's laboratory several properties of light, including the laws of reflection, refraction, total internal reflection and polarization,
Reflection, Refraction and Polarization of Light Physics 246/Spring2012 In today's laboratory several properties of light, including the laws of reflection, refraction, total internal reflection and polarization,
Chapter 38. Diffraction Patterns and Polarization
 Chapter 38 Diffraction Patterns and Polarization Diffraction Light of wavelength comparable to or larger than the width of a slit spreads out in all forward directions upon passing through the slit This
Chapter 38 Diffraction Patterns and Polarization Diffraction Light of wavelength comparable to or larger than the width of a slit spreads out in all forward directions upon passing through the slit This
Internal Reflection. Total Internal Reflection. Internal Reflection in Prisms. Fiber Optics. Pool Checkpoint 3/20/2013. Physics 1161: Lecture 18
 Physics 1161: Lecture 18 Internal Reflection Rainbows, Fiber Optics, Sun Dogs, Sun Glasses sections 26-8 & 25-5 Internal Reflection in Prisms Total Internal Reflection Recall Snell s Law: n 1 sin( 1 )=
Physics 1161: Lecture 18 Internal Reflection Rainbows, Fiber Optics, Sun Dogs, Sun Glasses sections 26-8 & 25-5 Internal Reflection in Prisms Total Internal Reflection Recall Snell s Law: n 1 sin( 1 )=
Polarization of light
 Polarization of light TWO WEIGHTS RECOMENDED READINGS 1) G. King: Vibrations and Waves, Ch.5, pp. 109-11. Wiley, 009. ) E. Hecht: Optics, Ch.4 and Ch.8. Addison Wesley, 00. 3) PASCO Instruction Manual
Polarization of light TWO WEIGHTS RECOMENDED READINGS 1) G. King: Vibrations and Waves, Ch.5, pp. 109-11. Wiley, 009. ) E. Hecht: Optics, Ch.4 and Ch.8. Addison Wesley, 00. 3) PASCO Instruction Manual
5: Electromagnetic Waves (Chapters 33 & 34) Snapshot of a light wave. Wave vs Particle. A Brief History of Light
 A Brief History of Light 5: Electromagnetic Waves (Chapters 33 & 34) Phys130, A01 Dr. Robert MacDonald Isaac Newton, 1600 s: Light is like little bullets. Scientists: Okay, right, that makes sense! Thomas
A Brief History of Light 5: Electromagnetic Waves (Chapters 33 & 34) Phys130, A01 Dr. Robert MacDonald Isaac Newton, 1600 s: Light is like little bullets. Scientists: Okay, right, that makes sense! Thomas
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 4-3 WAVE CHARACTERISTICS Reading Activity Questions? Essential Idea: All waves can be described by the same sets of mathematical ideas.
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON 4-3 WAVE CHARACTERISTICS Reading Activity Questions? Essential Idea: All waves can be described by the same sets of mathematical ideas.
Chapter 24. Wave Optics
 Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
normal angle of incidence increases special angle no light is reflected
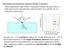 Reflection from transparent materials (Chapt. 33 last part) When unpolarized light strikes a transparent surface like glass there is both transmission and reflection, obeying Snell s law and the law of
Reflection from transparent materials (Chapt. 33 last part) When unpolarized light strikes a transparent surface like glass there is both transmission and reflection, obeying Snell s law and the law of
9. Polarization. 1) General observations [Room 310]
![9. Polarization. 1) General observations [Room 310] 9. Polarization. 1) General observations [Room 310]](/thumbs/74/70594885.jpg) 9. Polarization In this lab we are going to study the various phenomena related to the polarization of light. We will also learn how to analyze, control and transfer the polarization state of light. This
9. Polarization In this lab we are going to study the various phenomena related to the polarization of light. We will also learn how to analyze, control and transfer the polarization state of light. This
Dispersion Polarization
 Dispersion Polarization Phys Phys 2435: 22: Chap. 33, 31, Pg 1 Dispersion New Topic Phys 2435: Chap. 33, Pg 2 The Visible Spectrum Remember that white light contains all the colors of the s p e c t r u
Dispersion Polarization Phys Phys 2435: 22: Chap. 33, 31, Pg 1 Dispersion New Topic Phys 2435: Chap. 33, Pg 2 The Visible Spectrum Remember that white light contains all the colors of the s p e c t r u
Polarization. Lecture outline
 Polarization Lecture outline Why is polarization important? Classification of polarization Four ways to polarize EM waves Polarization in active remote sensing systems 1 Definitions Polarization is the
Polarization Lecture outline Why is polarization important? Classification of polarization Four ways to polarize EM waves Polarization in active remote sensing systems 1 Definitions Polarization is the
Assignment 8 Due November 29, Problems
 Assignment 8 Due November 29, 2011 Text readings Fresnel equations, chapter 4.6 Polarization, chapter 8, sections 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, and 8. Problems Problem 1 Polarization by Reflection: Given a polarizer
Assignment 8 Due November 29, 2011 Text readings Fresnel equations, chapter 4.6 Polarization, chapter 8, sections 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, and 8. Problems Problem 1 Polarization by Reflection: Given a polarizer
Experiment 8 Wave Optics
 Physics 263 Experiment 8 Wave Optics In this laboratory, we will perform two experiments on wave optics. 1 Double Slit Interference In two-slit interference, light falls on an opaque screen with two closely
Physics 263 Experiment 8 Wave Optics In this laboratory, we will perform two experiments on wave optics. 1 Double Slit Interference In two-slit interference, light falls on an opaque screen with two closely
Polarization of Light
 Polarization of Light Introduction Light, viewed classically, is a transverse electromagnetic wave. Namely, the underlying oscillation (in this case oscillating electric and magnetic fields) is along directions
Polarization of Light Introduction Light, viewed classically, is a transverse electromagnetic wave. Namely, the underlying oscillation (in this case oscillating electric and magnetic fields) is along directions
Chapter 33 The Nature and Propagation of Light by C.-R. Hu
 Chapter 33 The Nature and Propagation of Light by C.-R. Hu Light is a transverse wave of the electromagnetic field. In 1873, James C. Maxwell predicted it from the Maxwell equations. The speed of all electromagnetic
Chapter 33 The Nature and Propagation of Light by C.-R. Hu Light is a transverse wave of the electromagnetic field. In 1873, James C. Maxwell predicted it from the Maxwell equations. The speed of all electromagnetic
Polarization of Light
 From http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/optics/lightandcolor/polarization.html by Mortimer Abramowitz, Shannon Neaves and Michael Davidson and http://technology.niagarac.on.ca/courses/tech238g/lasers.html by
From http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/optics/lightandcolor/polarization.html by Mortimer Abramowitz, Shannon Neaves and Michael Davidson and http://technology.niagarac.on.ca/courses/tech238g/lasers.html by
Polarization. OpenStax
 OpenStax-CNX module: m58525 1 Polarization OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this section, you will be able to:
OpenStax-CNX module: m58525 1 Polarization OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Lecture 24: TUE 20 APR 2010 Ch : E&M Waves
 Physics 2102 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 24: TUE 20 APR 2010 Ch.33.6 10: E&M Waves Radiation Pressure Waves not only carry energy but also momentum. The effect is very small (we don t ordinarily feel pressure
Physics 2102 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 24: TUE 20 APR 2010 Ch.33.6 10: E&M Waves Radiation Pressure Waves not only carry energy but also momentum. The effect is very small (we don t ordinarily feel pressure
PHYSICS 116 POLARIZATION AND LIGHT MEASUREMENTS
 Name Date Lab Time Lab TA PHYSICS 116 POLARIZATION AND LIGHT MEASUREMENTS I. POLARIZATION Natural unpolarized light is made up of waves vibrating in all directions. When a beam of unpolarized light is
Name Date Lab Time Lab TA PHYSICS 116 POLARIZATION AND LIGHT MEASUREMENTS I. POLARIZATION Natural unpolarized light is made up of waves vibrating in all directions. When a beam of unpolarized light is
All forms of EM waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum = 3.00 x 10 8 m/s This speed is constant in air as well
 Pre AP Physics Light & Optics Chapters 14-16 Light is an electromagnetic wave Electromagnetic waves: Oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to the direction the wave moves Difference
Pre AP Physics Light & Optics Chapters 14-16 Light is an electromagnetic wave Electromagnetic waves: Oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to the direction the wave moves Difference
Engineering Physics 1 Dr. M. K. Srivastava Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology- Roorkee. Module-01 Lecture 03 Double Refraction
 Engineering Physics 1 Dr. M. K. Srivastava Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology- Roorkee Module-01 Lecture 03 Double Refraction Okay, this is the third lecture of the five lecture series
Engineering Physics 1 Dr. M. K. Srivastava Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology- Roorkee Module-01 Lecture 03 Double Refraction Okay, this is the third lecture of the five lecture series
1. Particle Scattering. Cogito ergo sum, i.e. Je pense, donc je suis. - René Descartes
 1. Particle Scattering Cogito ergo sum, i.e. Je pense, donc je suis. - René Descartes Generally gas and particles do not scatter isotropically. The phase function, scattering efficiency, and single scattering
1. Particle Scattering Cogito ergo sum, i.e. Je pense, donc je suis. - René Descartes Generally gas and particles do not scatter isotropically. The phase function, scattering efficiency, and single scattering
Lecture 24 EM waves Geometrical optics
 Physics 2102 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 24 EM waves Geometrical optics EM spherical waves The intensity of a wave is power per unit area. If one has a source that emits isotropically (equally in all directions)
Physics 2102 Jonathan Dowling Lecture 24 EM waves Geometrical optics EM spherical waves The intensity of a wave is power per unit area. If one has a source that emits isotropically (equally in all directions)
13. Brewster angle measurement
 13. Brewster angle measurement Brewster angle measurement Objective: 1. Verification of Malus law 2. Measurement of reflection coefficient of a glass plate for p- and s- polarizations 3. Determination
13. Brewster angle measurement Brewster angle measurement Objective: 1. Verification of Malus law 2. Measurement of reflection coefficient of a glass plate for p- and s- polarizations 3. Determination
At the interface between two materials, where light can be reflected or refracted. Within a material, where the light can be scattered or absorbed.
 At the interface between two materials, where light can be reflected or refracted. Within a material, where the light can be scattered or absorbed. The eye sees by focusing a diverging bundle of rays from
At the interface between two materials, where light can be reflected or refracted. Within a material, where the light can be scattered or absorbed. The eye sees by focusing a diverging bundle of rays from
4.4 Polarisation [26 marks]
![4.4 Polarisation [26 marks] 4.4 Polarisation [26 marks]](/thumbs/89/98671418.jpg) 4.4 Polarisation [26 marks] 1. Unpolarized light of intensity I 0 is incident on the first of two polarizing sheets. Initially the planes of polarization of the sheets are perpendicular. Which sheet must
4.4 Polarisation [26 marks] 1. Unpolarized light of intensity I 0 is incident on the first of two polarizing sheets. Initially the planes of polarization of the sheets are perpendicular. Which sheet must
Reprint (R36) Polarization: the invisible property of light. Presented by Dr. Richard Young at the 2008 Aerospace Lighting Institute Advanced Seminar
 Reprint (R36) Presented by Dr. Richard Young at the 2008 Aerospace Lighting Institute Advanced Seminar February 2008 Gooch & Housego 4632 36 th Street, Orlando, FL 32811 Tel: 1 407 422 3171 Fax: 1 407
Reprint (R36) Presented by Dr. Richard Young at the 2008 Aerospace Lighting Institute Advanced Seminar February 2008 Gooch & Housego 4632 36 th Street, Orlando, FL 32811 Tel: 1 407 422 3171 Fax: 1 407
Polarization of Light: from Basics to Instruments (in less than 100 slides) Originally by N. Manset, CFHT, Modified and expanded by K.
 Polarization of Light: from Basics to Instruments (in less than slides) Originally by N. Manset, CFHT, Modified and expanded by K. Hodapp Part I: Different polarization states of light Light as an electromagnetic
Polarization of Light: from Basics to Instruments (in less than slides) Originally by N. Manset, CFHT, Modified and expanded by K. Hodapp Part I: Different polarization states of light Light as an electromagnetic
PHYS:1200 LECTURE 32 LIGHT AND OPTICS (4)
 1 PHYS:1200 LECTURE 32 LIGHT AND OPTICS (4) The first three lectures in this unit dealt with what is for called geometric optics. Geometric optics, treats light as a collection of rays that travel in straight
1 PHYS:1200 LECTURE 32 LIGHT AND OPTICS (4) The first three lectures in this unit dealt with what is for called geometric optics. Geometric optics, treats light as a collection of rays that travel in straight
Lecture 26, March 16, Chapter 35, Polarization
 Physics 5B Lecture 26, March 16, 2012 Chapter 35, Polarization Simple Spectrometer d sin m Resolving power, to separate two lines closely spaced in wavelength by : R mn Resolving Power Two lines not resolved.
Physics 5B Lecture 26, March 16, 2012 Chapter 35, Polarization Simple Spectrometer d sin m Resolving power, to separate two lines closely spaced in wavelength by : R mn Resolving Power Two lines not resolved.
Refraction and Polarization of Light
 Chapter 9 Refraction and Polarization of Light Name: Lab Partner: Section: 9.1 Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to demonstrate several consequences of the fact that materials have di erent indexes
Chapter 9 Refraction and Polarization of Light Name: Lab Partner: Section: 9.1 Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to demonstrate several consequences of the fact that materials have di erent indexes
OPTICS MIRRORS AND LENSES
 Downloaded from OPTICS MIRRORS AND LENSES 1. An object AB is kept in front of a concave mirror as shown in the figure. (i)complete the ray diagram showing the image formation of the object. (ii) How will
Downloaded from OPTICS MIRRORS AND LENSES 1. An object AB is kept in front of a concave mirror as shown in the figure. (i)complete the ray diagram showing the image formation of the object. (ii) How will
IB-2 Polarization Practice
 Name: 1. Plane-polarized light is incident normally on a polarizer which is able to rotate in the plane perpendicular to the light as shown below. In diagram 1, the intensity of the incident light is 8
Name: 1. Plane-polarized light is incident normally on a polarizer which is able to rotate in the plane perpendicular to the light as shown below. In diagram 1, the intensity of the incident light is 8
Electromagnetic waves
 Electromagnetic waves Now we re back to thinking of light as specifically being an electromagnetic wave u u u oscillating electric and magnetic fields perpendicular to each other propagating through space
Electromagnetic waves Now we re back to thinking of light as specifically being an electromagnetic wave u u u oscillating electric and magnetic fields perpendicular to each other propagating through space
Refraction and Polarization of Light
 Chapter 9 Refraction and Polarization of Light Name: Lab Partner: Section: 9.1 Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to demonstrate several consequences of the fact that materials have di erent indexes
Chapter 9 Refraction and Polarization of Light Name: Lab Partner: Section: 9.1 Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to demonstrate several consequences of the fact that materials have di erent indexes
LECTURE 37: Ray model of light and Snell's law
 Lectures Page 1 Select LEARNING OBJECTIVES: LECTURE 37: Ray model of light and Snell's law Understand when the ray model of light is applicable. Be able to apply Snell's Law of Refraction to any system.
Lectures Page 1 Select LEARNING OBJECTIVES: LECTURE 37: Ray model of light and Snell's law Understand when the ray model of light is applicable. Be able to apply Snell's Law of Refraction to any system.
Reflection, Refraction and Polarization of Light Physics 246
 Reflection, Refraction and Polarization of Light Physics 46 In today's laboratory several properties of light, including the laws of reflection, refraction, total internal reflection and polarization,
Reflection, Refraction and Polarization of Light Physics 46 In today's laboratory several properties of light, including the laws of reflection, refraction, total internal reflection and polarization,
Understanding the Propagation of Light
 [ Assignment View ] [ Eðlisfræði 2, vor 2007 33. The Nature and Propagation of Light Assignment is due at 2:00am on Wednesday, January 17, 2007 Credit for problems submitted late will decrease to 0% after
[ Assignment View ] [ Eðlisfræði 2, vor 2007 33. The Nature and Propagation of Light Assignment is due at 2:00am on Wednesday, January 17, 2007 Credit for problems submitted late will decrease to 0% after
Light and the Properties of Reflection & Refraction
 Light and the Properties of Reflection & Refraction OBJECTIVE To study the imaging properties of a plane mirror. To prove the law of reflection from the previous imaging study. To study the refraction
Light and the Properties of Reflection & Refraction OBJECTIVE To study the imaging properties of a plane mirror. To prove the law of reflection from the previous imaging study. To study the refraction
Properties of Light I
 Properties of Light I Light definition Light Spectrum Wavelength in nm (1nm = 10-7 cm) Visible/White Light Cosmic Gamma X-Rays Ultra Violet Infra Red Micro Waves Radio Waves 1 Theory of Light Two complimentary
Properties of Light I Light definition Light Spectrum Wavelength in nm (1nm = 10-7 cm) Visible/White Light Cosmic Gamma X-Rays Ultra Violet Infra Red Micro Waves Radio Waves 1 Theory of Light Two complimentary
Chapter 24 - The Wave Nature of Light
 Chapter 24 - The Wave Nature of Light Summary Four Consequences of the Wave nature of Light: Diffraction Dispersion Interference Polarization Huygens principle: every point on a wavefront is a source of
Chapter 24 - The Wave Nature of Light Summary Four Consequences of the Wave nature of Light: Diffraction Dispersion Interference Polarization Huygens principle: every point on a wavefront is a source of
12/7/2012. Biomolecular structure. Diffraction, X-ray crystallography, light- and electron microscopy. CD spectroscopy, mass spectrometry
 phase difference at a given distance constructive/destructive interference Biomolecular structure. Diffraction, X-ray crystallography, light- and electron microscopy. CD spectroscopy, mass spectrometry
phase difference at a given distance constructive/destructive interference Biomolecular structure. Diffraction, X-ray crystallography, light- and electron microscopy. CD spectroscopy, mass spectrometry
Office Hours. Scattering and Polarization
 Office Hours Office hours are posted on the website. Molly: Tuesdays 2-4pm Dr. Keister: Wednesdays 10am-12 Prof. Goldman: Wednesdays 2-3:30pm All office hours are in the help room downstairs If none of
Office Hours Office hours are posted on the website. Molly: Tuesdays 2-4pm Dr. Keister: Wednesdays 10am-12 Prof. Goldman: Wednesdays 2-3:30pm All office hours are in the help room downstairs If none of
Human Retina. Sharp Spot: Fovea Blind Spot: Optic Nerve
 I am Watching YOU!! Human Retina Sharp Spot: Fovea Blind Spot: Optic Nerve Human Vision An optical Tuning Fork Optical Antennae: Rods & Cones Rods: Intensity Cones: Color Where does light actually come
I am Watching YOU!! Human Retina Sharp Spot: Fovea Blind Spot: Optic Nerve Human Vision An optical Tuning Fork Optical Antennae: Rods & Cones Rods: Intensity Cones: Color Where does light actually come
The sources must be coherent. This means they emit waves with a constant phase with respect to each other.
 CH. 24 Wave Optics The sources must be coherent. This means they emit waves with a constant phase with respect to each other. The waves need to have identical wavelengths. Can t be coherent without this.
CH. 24 Wave Optics The sources must be coherent. This means they emit waves with a constant phase with respect to each other. The waves need to have identical wavelengths. Can t be coherent without this.
Phys 102 Lecture 17 Introduction to ray optics
 Phys 102 Lecture 17 Introduction to ray optics 1 Physics 102 lectures on light Light as a wave Lecture 15 EM waves Lecture 16 Polarization Lecture 22 & 23 Interference & diffraction Light as a ray Lecture
Phys 102 Lecture 17 Introduction to ray optics 1 Physics 102 lectures on light Light as a wave Lecture 15 EM waves Lecture 16 Polarization Lecture 22 & 23 Interference & diffraction Light as a ray Lecture
Discussion Question 13A P212, Week 13 Electromagnetic Waves
 Discussion Question 13A P1, Week 13 Electromagnetic Waves This problem is a continuation of discussion question 1B from last week. Please refer to your work from last week as necessary. A laser beam travels
Discussion Question 13A P1, Week 13 Electromagnetic Waves This problem is a continuation of discussion question 1B from last week. Please refer to your work from last week as necessary. A laser beam travels
Polarization Exploration #10600
 1550 Finntown Road Waldoboro ME 04572 www.envisionlabs.com Polarization Exploration #10600 the light wave is always present, but it s omission from the diagrams and figures is solely for clarity of understanding
1550 Finntown Road Waldoboro ME 04572 www.envisionlabs.com Polarization Exploration #10600 the light wave is always present, but it s omission from the diagrams and figures is solely for clarity of understanding
Physics 4C Chapter 33: Electromagnetic Waves
 Physics 4C Chapter 33: Electromagnetic Waves Our greatest glory is not in never failing, but in rising up every time we fail. Ralph Waldo Emerson If you continue to do what you've always done, you'll continue
Physics 4C Chapter 33: Electromagnetic Waves Our greatest glory is not in never failing, but in rising up every time we fail. Ralph Waldo Emerson If you continue to do what you've always done, you'll continue
Course Updates. Reminders: 1) Assignment #12 due today. 2) Polarization, dispersion. 3) Last HW (#13 posted) due Monday, May 3rd
 Course Updates http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~varner/phys272-spr10/physics272.html Reminders: 1) Assignment #12 due today 2) Polarization, dispersion 3) Last HW (#13 posted) due Monday, May 3rd n 1 n 2 Total
Course Updates http://www.phys.hawaii.edu/~varner/phys272-spr10/physics272.html Reminders: 1) Assignment #12 due today 2) Polarization, dispersion 3) Last HW (#13 posted) due Monday, May 3rd n 1 n 2 Total
ECEG105/ECEU646 Optics for Engineers Course Notes Part 5: Polarization
 ECEG105/ECEU646 Optics for Engineers Course Notes Part 5: Polarization Prof. Charles A. DiMarzio Northeastern University Fall 2008 Sept 2008 11270-05-1 Wave Nature of Light Failure of Raytracing Zero-λ
ECEG105/ECEU646 Optics for Engineers Course Notes Part 5: Polarization Prof. Charles A. DiMarzio Northeastern University Fall 2008 Sept 2008 11270-05-1 Wave Nature of Light Failure of Raytracing Zero-λ
Total Internal Reflection
 Total nternal Reflection Consider light moving from glass (n.5) to air (n.) i r n sin n sin n n incident ra r refracted ra reflected ra GLASS AR sin n sin n >.e., light is bent awa from the normal. as
Total nternal Reflection Consider light moving from glass (n.5) to air (n.) i r n sin n sin n n incident ra r refracted ra reflected ra GLASS AR sin n sin n >.e., light is bent awa from the normal. as
Wavefronts and Rays. When light or other electromagnetic waves interact with systems much larger than the wavelength, it s a good approximation to
 Chapter 33: Optics Wavefronts and Rays When light or other electromagnetic waves interact with systems much larger than the wavelength, it s a good approximation to Neglect the wave nature of light. Consider
Chapter 33: Optics Wavefronts and Rays When light or other electromagnetic waves interact with systems much larger than the wavelength, it s a good approximation to Neglect the wave nature of light. Consider
(Refer Slide Time: 00:10)
 Fundamentals of optical and scanning electron microscopy Dr. S. Sankaran Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module 02 Unit-4 Phase contrast, Polarized
Fundamentals of optical and scanning electron microscopy Dr. S. Sankaran Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module 02 Unit-4 Phase contrast, Polarized
Properties of Light. 1. The Speed of Light 2. The Propagation of Light 3. Reflection and Refraction 4. Polarization
 Chapter 33 - Light Properties of Light 1. The Speed of Light 2. The Propagation of Light 3. Reflection and Refraction 4. Polarization MFMcGraw-PHY 2426 Chap33-Light - Revised: 6-24-2012 2 Electromagnetic
Chapter 33 - Light Properties of Light 1. The Speed of Light 2. The Propagation of Light 3. Reflection and Refraction 4. Polarization MFMcGraw-PHY 2426 Chap33-Light - Revised: 6-24-2012 2 Electromagnetic
Hot Sync. Materials Needed Today
 Chapter 11 Lesson 2 Materials Needed Today Please take these materials out of your backpack. Pencil Blank sheet of paper for a lab! Hot Sync Thursday 3/27/14 After learning how light acts. Write a new
Chapter 11 Lesson 2 Materials Needed Today Please take these materials out of your backpack. Pencil Blank sheet of paper for a lab! Hot Sync Thursday 3/27/14 After learning how light acts. Write a new
Lecture 16: Geometrical Optics. Reflection Refraction Critical angle Total internal reflection. Polarisation of light waves
 Lecture 6: Geometrical Optics Reflection Refraction Critical angle Total internal reflection Polarisation of light waves Geometrical Optics Optics Branch of Physics, concerning the interaction of light
Lecture 6: Geometrical Optics Reflection Refraction Critical angle Total internal reflection Polarisation of light waves Geometrical Optics Optics Branch of Physics, concerning the interaction of light
How can light reflections on the surface of water be blocked to see what is on the bottom of the sea?
 How can light reflections on the surface of water be blocked to see what is on the bottom of the sea? www.digital-photography-tips.net/stay_focussed-newsletter-march-2013.html Discover the answer to this
How can light reflections on the surface of water be blocked to see what is on the bottom of the sea? www.digital-photography-tips.net/stay_focussed-newsletter-march-2013.html Discover the answer to this
Protocol for Lab. Fundamentals
 Protocol for Lab Fundamentals Content 1. Beam propagation, law of reflection, and Snellius law... 3 1.1. Air-metal and air-plexiglass transition... 3 1.2. Air-water... 3 1.3. Plexiglass-water... 3 1.4.
Protocol for Lab Fundamentals Content 1. Beam propagation, law of reflection, and Snellius law... 3 1.1. Air-metal and air-plexiglass transition... 3 1.2. Air-water... 3 1.3. Plexiglass-water... 3 1.4.
Small particles scatter light
 Lec. 25, Tuesday, April 13 Chapter 13: Scattering and Polarization Homework is due in room G2B90 in boxes We are here Scattering: Smoke, haze, fog, clouds, air, water, Depends on wavelength, size of particle
Lec. 25, Tuesday, April 13 Chapter 13: Scattering and Polarization Homework is due in room G2B90 in boxes We are here Scattering: Smoke, haze, fog, clouds, air, water, Depends on wavelength, size of particle
Optics Polarization Birefringence
 Optics Polarization Birefringence Lana Sheridan De Anza College June 21, 2018 Last time the interferometer and gravitational waves polarization Brewster angle Overview polarization birefringence Rayleigh
Optics Polarization Birefringence Lana Sheridan De Anza College June 21, 2018 Last time the interferometer and gravitational waves polarization Brewster angle Overview polarization birefringence Rayleigh
Light and Electromagnetic Waves. Honors Physics
 Light and Electromagnetic Waves Honors Physics Electromagnetic Waves EM waves are a result of accelerated charges and disturbances in electric and magnetic fields (Radio wave example here) As electrons
Light and Electromagnetic Waves Honors Physics Electromagnetic Waves EM waves are a result of accelerated charges and disturbances in electric and magnetic fields (Radio wave example here) As electrons
Final Exam. Today s Review of Optics Polarization Reflection and transmission Linear and circular polarization Stokes parameters/jones calculus
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 40 Review Spring 206 Semester Matthew Jones Final Exam Date:Tuesday, May 3 th Time:7:00 to 9:00 pm Room: Phys 2 You can bring one double-sided pages of notes/formulas.
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 40 Review Spring 206 Semester Matthew Jones Final Exam Date:Tuesday, May 3 th Time:7:00 to 9:00 pm Room: Phys 2 You can bring one double-sided pages of notes/formulas.
Light: Geometric Optics
 Light: Geometric Optics The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but
Light: Geometric Optics The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but
Waves & Oscillations
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 40 Review Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Final Exam Date:Tuesday, May 3 th Time:7:00 to 9:00 pm Room: Phys 112 You can bring one double-sided pages of notes/formulas.
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 40 Review Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Final Exam Date:Tuesday, May 3 th Time:7:00 to 9:00 pm Room: Phys 112 You can bring one double-sided pages of notes/formulas.
Illumination for the microscope
 Illumination for the microscope Köhler illumination: is a Method of specimen illumination used for transmitted and reflected light. Purpose of Koehler Illumination 1. To obtain even specimen illumination
Illumination for the microscope Köhler illumination: is a Method of specimen illumination used for transmitted and reflected light. Purpose of Koehler Illumination 1. To obtain even specimen illumination
6-1 LECTURE #6: OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS. Basic question: How do solids interact with light? The answers are linked to:
 LECTURE #6: OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Basic question: How do solids interact with light? The answers are linked to: Properties of light inside a solid Mechanisms behind light reflection, absorption
LECTURE #6: OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Basic question: How do solids interact with light? The answers are linked to: Properties of light inside a solid Mechanisms behind light reflection, absorption
LIGHT SCATTERING THEORY
 LIGHT SCATTERING THEORY Laser Diffraction (Static Light Scattering) When a Light beam Strikes a Particle Some of the light is: Diffracted Reflected Refracted Absorbed and Reradiated Reflected Refracted
LIGHT SCATTERING THEORY Laser Diffraction (Static Light Scattering) When a Light beam Strikes a Particle Some of the light is: Diffracted Reflected Refracted Absorbed and Reradiated Reflected Refracted
Image Formation by Refraction
 Image Formation by Refraction If you see a fish that appears to be swimming close to the front window of the aquarium, but then look through the side of the aquarium, you ll find that the fish is actually
Image Formation by Refraction If you see a fish that appears to be swimming close to the front window of the aquarium, but then look through the side of the aquarium, you ll find that the fish is actually
Introduction to Light and Polarized Light
 Aspects of Light Introduction to Light and Polarized Light Amplitude (height of wave) corresponds to the intensity (brightness) of light Wavelength corresponds to the energy of light In the visible spectrum
Aspects of Light Introduction to Light and Polarized Light Amplitude (height of wave) corresponds to the intensity (brightness) of light Wavelength corresponds to the energy of light In the visible spectrum
θ =θ i r n sinθ = n sinθ
 θ i = θ r n = 1 sinθ1 n sin θ Total Internal Reflection Consider light moving from glass (n 1 =1.5) to air (n =1.0) n 1 incident ray θ 1 θ r reflected ray GLASS sinθ sinθ 1 > 1 = n n 1 θ > θ 1 n θ refracted
θ i = θ r n = 1 sinθ1 n sin θ Total Internal Reflection Consider light moving from glass (n 1 =1.5) to air (n =1.0) n 1 incident ray θ 1 θ r reflected ray GLASS sinθ sinθ 1 > 1 = n n 1 θ > θ 1 n θ refracted
LECTURE 13 REFRACTION. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 13 REFRACTION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 13 2 Reading chapter 26.5 Index of refraction Snell s law Total internal reflection Total polarization Index of refraction 3 The speed of light in
LECTURE 13 REFRACTION Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 13 2 Reading chapter 26.5 Index of refraction Snell s law Total internal reflection Total polarization Index of refraction 3 The speed of light in
Light. Form of Electromagnetic Energy Only part of Electromagnetic Spectrum that we can really see
 Light Form of Electromagnetic Energy Only part of Electromagnetic Spectrum that we can really see Facts About Light The speed of light, c, is constant in a vacuum. Light can be: REFLECTED ABSORBED REFRACTED
Light Form of Electromagnetic Energy Only part of Electromagnetic Spectrum that we can really see Facts About Light The speed of light, c, is constant in a vacuum. Light can be: REFLECTED ABSORBED REFRACTED
Light and Sound. Wave Behavior and Interactions
 Light and Sound Wave Behavior and Interactions How do light/sound waves interact with matter? WORD Definition Example Picture REFLECTED REFRACTED is the change in direction of a wave when it changes speed
Light and Sound Wave Behavior and Interactions How do light/sound waves interact with matter? WORD Definition Example Picture REFLECTED REFRACTED is the change in direction of a wave when it changes speed
! "To accept Huygens's principle requires abandoning the idea that a ray has much intrinsic physical significance..." (pg. 5.)
 02. Malus and Polarization. 1. The Optical Ray. Pre-17th Century: The ray as the physical foundation of light.! Euclid: "visual rays" proceed from the eye to object of sight. 1690. Huygens's Traite de
02. Malus and Polarization. 1. The Optical Ray. Pre-17th Century: The ray as the physical foundation of light.! Euclid: "visual rays" proceed from the eye to object of sight. 1690. Huygens's Traite de
Light. Electromagnetic wave with wave-like nature Refraction Interference Diffraction
 Light Electromagnetic wave with wave-like nature Refraction Interference Diffraction Light Electromagnetic wave with wave-like nature Refraction Interference Diffraction Photons with particle-like nature
Light Electromagnetic wave with wave-like nature Refraction Interference Diffraction Light Electromagnetic wave with wave-like nature Refraction Interference Diffraction Photons with particle-like nature
9. Polarizers. Index of. Coefficient of Material Wavelength ( ) Brewster angle refraction (n)
 9. Polarizers All polarized light is to some degree elliptical in nature. Basic states of polarization like linear and circular are actually special cases of elliptically polarized light which is defined
9. Polarizers All polarized light is to some degree elliptical in nature. Basic states of polarization like linear and circular are actually special cases of elliptically polarized light which is defined
37 (15 pts) Apply Snell s law twice (external, then internal) to find it emerges at the same angle.
 37 (15 pts) Apply Snell s law twice (external, then internal) to find it emerges at the same angle. 38. (4 pts) Review the section on phase changes on reflection in Pedrotti section 3-3 Solution (a) For
37 (15 pts) Apply Snell s law twice (external, then internal) to find it emerges at the same angle. 38. (4 pts) Review the section on phase changes on reflection in Pedrotti section 3-3 Solution (a) For
The diffraction pattern from a hexagonally-shaped hole. Note the six-fold symmetry of the pattern. Observation of such complex patterns can reveal
 The diffraction pattern from a hexagonally-shaped hole. Note the six-fold symmetry of the pattern. Observation of such complex patterns can reveal the underlying symmetry structure of the object that diffracts
The diffraction pattern from a hexagonally-shaped hole. Note the six-fold symmetry of the pattern. Observation of such complex patterns can reveal the underlying symmetry structure of the object that diffracts
Chapter 82 Example and Supplementary Problems
 Chapter 82 Example and Supplementary Problems Nature of Polarized Light: 1) A partially polarized beam is composed of 2.5W/m 2 of polarized and 4.0W/m 2 of unpolarized light. Determine the degree of polarization
Chapter 82 Example and Supplementary Problems Nature of Polarized Light: 1) A partially polarized beam is composed of 2.5W/m 2 of polarized and 4.0W/m 2 of unpolarized light. Determine the degree of polarization
Lesson 1 Scattering, Diffraction, and Radiation
 Lesson 1 Scattering, Diffraction, and Radiation Chen-Bin Huang Department of Electrical Engineering Institute of Photonics Technologies National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan Various slides under courtesy
Lesson 1 Scattering, Diffraction, and Radiation Chen-Bin Huang Department of Electrical Engineering Institute of Photonics Technologies National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan Various slides under courtesy
DETERMINATION OF BREWSTER S ANGLE FOR GLASS AND PLASTIC USING A POLARIZED MONOCHROMATIC LIGHT SOURCE. Utsav Hanspal. Physics Honors Research Paper
 DETERMINATION OF BREWSTER S ANGLE FOR GLASS AND PLASTIC USING A POLARIZED MONOCHROMATIC LIGHT SOURCE Utsav Hanspal Physics Honors Research Paper Dr. Watson Hanspal 2 INTRODUCTION When light moves between
DETERMINATION OF BREWSTER S ANGLE FOR GLASS AND PLASTIC USING A POLARIZED MONOCHROMATIC LIGHT SOURCE Utsav Hanspal Physics Honors Research Paper Dr. Watson Hanspal 2 INTRODUCTION When light moves between
