CHAPTER 1 : KINEMATICS
|
|
|
- Linda Hodge
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 KINEMATICS : It relates to the study of the relative motion between the parts of a machine. Let us consider a reciprocating engine, in this the piston is made to reciprocate in the cylinderdue to the applied steam pressure on the piston. The reciprocating motion of the piston is converted into the rotary motion of crankshaft with help of connecting rod & the crank. Fig. 1.1 KINEMATICS LINK/ELEMENT : Each part of a machine which has relative motion to some other part is known as kinematic link. E.g. In a steam engine, the piston & piston rod is one link; the second link is connecting rod; third link is crank; fourth link is cylinder which is fixed link. The various types of links are : a) Rigid Link : The link which don't undergo a any deformation while transmitting required motion & force is called rigid link. E.g. piston & piston rod. Fig. 1.2 b) Flexible Link : The links which are partly deformed while transmitting motion in such a way that they don't affect require transmission of motion are called flexible link. E.g. Chain drive, belt drive. Fig. 1.3 c) Fluid Link : The link which transmit the require motion through the fluid by pressure/compression are called fluid links. E.g. hydraulic press.
2 Fig. 1.4 Links are further classified depends upon its end on which it revolves/turns as binary link, ternary link & quaternary link. Fig. 1.5 DIFFERENCE BETWEEN STRUCTURE, MACHINE & MECHANISM : Structure Machine Mechanism Assembly of rigid links where there is no relative motion between one another. No energy is transformed in to useful work. Member of structure transmit forces only. Assembly of links where there is a relative motion between one another. Transfer availbale energy into useful work. The link of machine transform both power & motion. Assembly of links where by fixing one link, the motion of any other link produces definite motion of other links. No energy is transformed in to useful work. Mechanism transform only motion. E.g. Bridges, Machine frame E.g. Lathe, Milling machine E.g. Clock, Type writter CONSTRAINED MOTION : Various type of constrained motions are, a) Completely constrained motion : When the motion between a pair takes place in a definite direction w.r.t. direction of force applied then the motion is called completely constrained motion. E.g. as shown in fig. a motion of square bar in square hole, in fig. b motion of shaft with collar. (a) Fig. 1.6 (b)
3 b) Incompletely constrained motion : When the motion between a pair can take place in more than one direction is called incompletely constrained motion. E.g. Cicular shaft in circular hole as it may either rotate or slide in a hole. Fig. 1.7 c) Succefully constrained motion : When the relative motion between the links is not completely constrained by itself but by some other means is called the succefully constrained motion. E.g. Keyway is provided in a circular shaft moving in a circular hole which prevents its possible sliding motion & rotating motion. Fig. 1.8 KINEMATIC PAIR : Two links of a machine when in contact with each other are said to be a pair. Kinematic pair consist of two links which have relative motion between them. Classification of kinematic pair as below. a) According to nature of relative motion between links :- 1. Sliding Pair : It consists of two links connected in such a manner that one is constrained to have a sliding motion relative to other. E.g. piston & cylinder as shown in fig. 1.2, rectangular bar in rectangular hole as shown in fig. 1.6(a). 2. Turning Pair : It consists of two links connected in such a manner that one is constrained to turn about fixed axis of another link. E.g. Shaft with collar at both ends revolving in a circular hole as shown in fig. 1.6(b), bicycle wheel revolving about its axle. 3. Screw Pair : When the nature of contact between the pair of links is such that the one element can turn about the other by screw threads is called screw pair. E.g. motion of bolt in nut. Fig. 1.9
4 4. Rolling Pair : If the two links have their relative motion of rolling nature is called rolling pair. E.g. railway wheel rolling over a fixed rail, ball bearing & roller bearing. Fig Spherical Pair : When two elements are connected that one link having sphere turns about other fixed link is called spherical pair. E.g. ball & socket joint, ballpen stand. Fig b) According to nature of contact between the links :- 1. Lower Pair : When two elements have surface contact while in motion & relative motion is purly turning or sliding then such pair is called lower pair. E.g. All sliding, turning & screw pairs are lower pair. 2. Higher Pair : When two elements have line or point contact during relative motion between them is called higher pair. E.g. motion of gears, cams & followers, belts & rope drive. Fig c) According to mechanical arrangement :- 1. Closed Pair : When the links of pairs are held together mechanically, they form a
5 closed pair. All lower pairs are example of closed pair. 2. Unclosed/open Pair : When two links of a pair are not held together mechanically but held in contact by the action of external forces are called unclosed pair. E.g. cam & follower as shown in fig KINEMATIC CHAIN : It is a combination of kinematic pairs in which each link forms a part of two kinematic pairs & the relative motion between the link is completely/successfully constrained. A D (a) Fig (b) Fig. 1.13(a) shows the arrangement of three links forming three pairs but the relative motion between the links is not possible hence it is known as locked chain & form a structure. Fig. 1.13(b) shows the arrangement of four links AB, BC, CD & DA joined by pin joints form a kinematic chain where there are four kinematic pairs AB-BC, BC-CD, CD-DA & DA-AB. By moving link AB, other links also get the constrained movement. The following relationship holds for a kinematic chain. n = 2p 4 Where n = No. of links & p = No. of pairs Also n = 2/3(J + 2) Where J = No. of joints TYPES OF KINEMATIC CHAIN : The various types of kinematic chains are, a) Four bar chain/quadric kinematic chain :- It consist of four links, each of them forming turning pairs. The four links may be of different lengths. As shown in fig. 1.13(b), link AD is fixed. The link which rotates completely is known as crank as link AB & link which partial rotation is called lever as link BC. b) Single slider crank chain :- It consist of one sliding pair & three turning pairs. It is usually formed in receprocating steam engine mechanism & IC engine mechanism. As shown in fig this type of mechanism converts receprocating motion into rotary motion & vice versa. Fig c) Double slider crank chain :- As shown in fig 1.15 a kinematic chain consisting of two turning pair & two sliding pairs is called double slider crank chain. Here link 1 & 4 as one sliding pair and link 3 & 4 as second sliding pair. Link 1 & 2 as well as link 2 & 3 as turning
6 pair. Crank Link-2 Slider Block Link-3 Fixed Link-1 Fixed Link-1 Fig Slider Block Link-4 INVERSION : In kinematic chain when any one link is fixed it becomes mechanism. So it is possible to obtainas many mechanisms as the number of links by fixing different linkes in turn in kinematic chain. Method of obtaining different mechanisms by fixing different links in turn of the basic kinematic chain is known as inversion of mechanism. INVERSION OF FOUR BAR KINEMATIC CHAIN : a) Beam Engine : Beam engine is also known as crank & lever mechanism. In this mechanism rotary motion of crank is converted into receprocating motion of piston. As shown in fig. 1.15(a) link 1 is fixed, link 2 is crank which rotates, link 3 is a lever which oscilate about fixed point. One end of lever 3 is connected to piston rod & other end with link 2. Link 3 Link 2 Link 4 Fig. 1.15(a) Link 1 b) Locomotive coupling rod : It is also known as double crank mechanism. As shown in fig. 1.15(b) it consists of four links. Link 2 & 4 having equal length act as a crank & connected to the respective wheels. Link 3 act as a coupling rod & link 1 is fixed. This mechanism is used for transmitting rotary motion from one wheel to other wheel. Link 1 Link 1 Link 2 Link 4 Fig. 1.15(b) Link 3
7 c) Watt's strainght line mechanism : As shown in fig. 1.15(c), links AB & CD are parallel. They are connected with link BC. AB & CD are levers & fixed at pint A & D respectively. For small displacement of lever AB & AD, point P on link BC will trace an appx. straight line for small angular movement of link 2 & 4. Fig. 1.15(c) d) Ackermann stearing gear : As shown in fig. 1.15(d), two long links AB & CD are not equal in length. They remain parallel when vehicle travelling in straight line. Two short links BC & AD both are equal in length and make make angle 'a' vertical line. When vehicle is steared, the inner wheel 3 & 4 will turn through larger angle '0', while outer wheel 1 & 2 will turn through smaller angle 'a'. The axis of each wheel when extended they meet at one point 'I' known as instanteneous centre. Wheel 3 Wheel 1 Wheel 4 Wheel 2 Fig. 1.15(d) INVERSION OF SINGLE SLIDER CRANK CHAIN : a) Reciprocating engine mechanism : In this mechanism, the inversion is obtained by fixing the link 4 as shown in fig When link 2 (crank) rotates, the link 3(connecting rod) oscillates about pin pivoted to the fixed link 4 & cross head/piston reciprocates in the cylinder. Fig b) Oscillating cylinder engine : In this mechanism as shown in fing. 1.17, link 3 is fixed. When the link 2(crank) rotates, the link 1 (piston rod) receprocates & link 4(cylinder) oscillates.
8 Fig c) Crank & slotted lever type quick return motion mechanism : As shown in fig. 1.18, in this mechanism the link 3 is fixed, the link 2 revolves about centre C. A slider link 1 attached to the crank pin at B slides along the sotted link 4 & make the slotted lever oscillated about pivoted point A. Link PR transmits motion from slotted link to ram which receprocates with the tool along the line of stroke which is prependicular to fixed link 3. This mechanism is mostly used in shaping machine & slotting machine. Here B>a, hence during cuttnig stroke ram speed is less than that during forward stroke. As ram moves quicker than it moves in forward direction this mechanism is known as quick return mechanism. Fig d) Hand Pump : As shown in fig. 1.19, by keeping the link 3 fixed, this type of inversion is obtained. This mechanism is mostly used for operating hand pump. Link 2 Link 1 Link 3 Link 4 Fig. 1.19
9 INVERSION OF DOUBLE SLIDER CRANK CHAIN : a) Scotch yoke mechanism : As shown in fign 1.20, this is an inversion of double slider crank chain which can be used for transforming rotary motion into receprocating motion. Here fixing link 1, rotary link 2(crank), link 4 will receprocate in link 1 & link 3 will receprocate in link 4. Fig b) Elliptical trammel mechanism : As shown in fig in this mechanism, two perpendicular slots are cut in a single plate as link 4. Two sliding blocks, one in each slot (link 1 & 3) are placed forming sliding pair with link 4. The blocks are connected by pin jonints through link 2. When link 1 & 3 slide along the respective slots, the point P on the link 2 will trace an ellipse on the surface of link 4. Fig c) Oldham's Coupling : As shown in fig oldham's coupling is used to connect to parallel shafts where axes are at a small distance apart. The shafts have flanges at the ends, in which slots are cut. These form link 1 & link 3. The intermediate piece form the link 4 which slides or receprotes in link 4 & link 3. The link 2 is fixed. When the driving shaft rotates, the driving flange link 1 rotates along with the shaft which causes the rotation of intermediate link 4 which also slider along the slots in link 1 & link 3 as a result of which the driven flnage link 3 also start rotating. The driven shaft also rotates as it is connected to given flange link 3. Let us, peripherical velocity or sliding velocity of the disc. = Angular velocity of the shaft (w) X Distance between shaft (r)
10 Fig ~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~*~
September 20, Chapter 5. Simple Mechanisms. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, Ph.D., PE
 Chapter 5 Simple Mechanisms 1 Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, Ph.D., PE 2 Assignment #1 All questions at the end of chapter 1 st Exam: Saturday 29/9/2018 3 Kinematic Link or Element kinematic link (link) or
Chapter 5 Simple Mechanisms 1 Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, Ph.D., PE 2 Assignment #1 All questions at the end of chapter 1 st Exam: Saturday 29/9/2018 3 Kinematic Link or Element kinematic link (link) or
Kinematics of Machines. Brown Hills College of Engineering & Technology
 Introduction: mechanism and machines, kinematic links, kinematic pairs, kinematic chains, plane and space mechanism, kinematic inversion, equivalent linkages, four link planar mechanisms, mobility and
Introduction: mechanism and machines, kinematic links, kinematic pairs, kinematic chains, plane and space mechanism, kinematic inversion, equivalent linkages, four link planar mechanisms, mobility and
SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL. Mechanical Engineering. Postal Correspondence Course. Theory of Machines. GATE, IES & PSUs
 TOM - ME GATE, IES, PSU 1 SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL Mechanical Engineering ME Postal Correspondence Course Theory of Machines GATE, IES & PSUs TOM - ME GATE, IES, PSU 2 C O N T E N T TOPIC 1. MACHANISMS AND
TOM - ME GATE, IES, PSU 1 SAMPLE STUDY MATERIAL Mechanical Engineering ME Postal Correspondence Course Theory of Machines GATE, IES & PSUs TOM - ME GATE, IES, PSU 2 C O N T E N T TOPIC 1. MACHANISMS AND
WEEKS 1-2 MECHANISMS
 References WEEKS 1-2 MECHANISMS (METU, Department of Mechanical Engineering) Text Book: Mechanisms Web Page: http://www.me.metu.edu.tr/people/eres/me301/in dex.ht Analitik Çözümlü Örneklerle Mekanizma
References WEEKS 1-2 MECHANISMS (METU, Department of Mechanical Engineering) Text Book: Mechanisms Web Page: http://www.me.metu.edu.tr/people/eres/me301/in dex.ht Analitik Çözümlü Örneklerle Mekanizma
Theory of Machines Course # 1
 Theory of Machines Course # 1 Ayman Nada Assistant Professor Jazan University, KSA. arobust@tedata.net.eg March 29, 2010 ii Sucess is not coming in a day 1 2 Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Introduction Mechanisms
Theory of Machines Course # 1 Ayman Nada Assistant Professor Jazan University, KSA. arobust@tedata.net.eg March 29, 2010 ii Sucess is not coming in a day 1 2 Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Introduction Mechanisms
Modelling of mechanical system CREATING OF KINEMATIC CHAINS
 Modelling of mechanical system CREATING OF KINEMATIC CHAINS Mechanism Definitions 1. a system or structure of moving parts that performs some function 2. is each system reciprocally joined moveable bodies
Modelling of mechanical system CREATING OF KINEMATIC CHAINS Mechanism Definitions 1. a system or structure of moving parts that performs some function 2. is each system reciprocally joined moveable bodies
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction Generally all considerations in the force analysis of mechanisms, whether static or dynamic, the links are assumed to be rigid. The complexity of the mathematical analysis of mechanisms
Chapter 1 Introduction Generally all considerations in the force analysis of mechanisms, whether static or dynamic, the links are assumed to be rigid. The complexity of the mathematical analysis of mechanisms
Kinematics Fundamentals CREATING OF KINEMATIC CHAINS
 Kinematics Fundamentals CREATING OF KINEMATIC CHAINS Mechanism Definitions 1. a system or structure of moving parts that performs some function 2. is each system reciprocally joined moveable bodies the
Kinematics Fundamentals CREATING OF KINEMATIC CHAINS Mechanism Definitions 1. a system or structure of moving parts that performs some function 2. is each system reciprocally joined moveable bodies the
MECHANICS OF MACHINERY
 MECHNICS OF MCHINERY (For B.E. Mechanical Engineering Students) s per New Revised Syllabus of PJ bdul Kalam Technological University Dr. S. Ramachandran, M.E., Ph.D., Dr..G. Mathew, PhD (NIT-Durgapur)
MECHNICS OF MCHINERY (For B.E. Mechanical Engineering Students) s per New Revised Syllabus of PJ bdul Kalam Technological University Dr. S. Ramachandran, M.E., Ph.D., Dr..G. Mathew, PhD (NIT-Durgapur)
Kinematics: Intro. Kinematics is study of motion
 Kinematics is study of motion Kinematics: Intro Concerned with mechanisms and how they transfer and transform motion Mechanisms can be machines, skeletons, etc. Important for CG since need to animate complex
Kinematics is study of motion Kinematics: Intro Concerned with mechanisms and how they transfer and transform motion Mechanisms can be machines, skeletons, etc. Important for CG since need to animate complex
ME 321 Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines
 .0 INTRODUCTION ME Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines All Text References in these notes are for: Mechanism Design: Analysis and Synthesis, Volume, Fourth Edition, Erdman, Sandor and Kota, Prentice-Hall,
.0 INTRODUCTION ME Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines All Text References in these notes are for: Mechanism Design: Analysis and Synthesis, Volume, Fourth Edition, Erdman, Sandor and Kota, Prentice-Hall,
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ESE TOPICWISE OBJECTIVE SOLVED PAPER-II FROM (1995-2018) UPSC Engineering Services Examination State Engineering Service Examination & Public Sector Examination. IES MASTER PUBLICATION
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ESE TOPICWISE OBJECTIVE SOLVED PAPER-II FROM (1995-2018) UPSC Engineering Services Examination State Engineering Service Examination & Public Sector Examination. IES MASTER PUBLICATION
1.9 Snap Action Mechanisms 19
 Theory of Mechanism and Machines Chapter- Introduction Prepared y rij hooshan sst. Professor. S.. College of Engg. nd Technology Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, (India) Supported y: Purvi hooshan In This Chapter
Theory of Mechanism and Machines Chapter- Introduction Prepared y rij hooshan sst. Professor. S.. College of Engg. nd Technology Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, (India) Supported y: Purvi hooshan In This Chapter
MACHINE THEORY Bachelor in Mechanical Engineering INTRODUCTION TO MACHINE DESIGN
 MACHINE THEORY Bachelor in Mechanical Engineering INTRODUCTION TO MACHINE DESIGN Ignacio Valiente Blanco José Luis Pérez Díaz David Mauricio Alba Lucero Efrén Díez Jiménez Timm Lauri Berit Sanders Machine
MACHINE THEORY Bachelor in Mechanical Engineering INTRODUCTION TO MACHINE DESIGN Ignacio Valiente Blanco José Luis Pérez Díaz David Mauricio Alba Lucero Efrén Díez Jiménez Timm Lauri Berit Sanders Machine
PROBLEMS AND EXERCISES PROBLEMS
 64 Fundamentals of Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines and Mechanisms PROBLEMS AND EXERCISES PROBLEMS 1. In Figure 1.14c an inverted slider-crank mechanism is shown. b. If the input is the displacement
64 Fundamentals of Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines and Mechanisms PROBLEMS AND EXERCISES PROBLEMS 1. In Figure 1.14c an inverted slider-crank mechanism is shown. b. If the input is the displacement
Analytical and Applied Kinematics
 Analytical and Applied Kinematics Vito Moreno moreno@engr.uconn.edu 860-614-2365 (cell) http://www.engr.uconn.edu/~moreno Office EB1, hours Thursdays 10:00 to 5:00 1 This course introduces a unified and
Analytical and Applied Kinematics Vito Moreno moreno@engr.uconn.edu 860-614-2365 (cell) http://www.engr.uconn.edu/~moreno Office EB1, hours Thursdays 10:00 to 5:00 1 This course introduces a unified and
Chapter 4. Mechanism Design and Analysis
 Chapter 4. Mechanism Design and Analysis All mechanical devices containing moving parts are composed of some type of mechanism. A mechanism is a group of links interacting with each other through joints
Chapter 4. Mechanism Design and Analysis All mechanical devices containing moving parts are composed of some type of mechanism. A mechanism is a group of links interacting with each other through joints
1 AM-167/202/242/282/322 Parts Manual. Table Of Contents
 AM-167/202/242/282/322 Parts Manual Table Of Contents Mower Beam with Bearings...2 Mower Beam with Bearings...4 Cutting Discs...6 Main Gearbox...8 V-Belt Pulley...10 Headstock...12 Carrier Beam...14 V-Belt
AM-167/202/242/282/322 Parts Manual Table Of Contents Mower Beam with Bearings...2 Mower Beam with Bearings...4 Cutting Discs...6 Main Gearbox...8 V-Belt Pulley...10 Headstock...12 Carrier Beam...14 V-Belt
Position and Displacement Analysis
 Position and Displacement Analysis Introduction: In this chapter we introduce the tools to identifying the position of the different points and links in a given mechanism. Recall that for linkages with
Position and Displacement Analysis Introduction: In this chapter we introduce the tools to identifying the position of the different points and links in a given mechanism. Recall that for linkages with
Kinematics of Machines Prof. A. K. Mallik Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur. Module 10 Lecture 1
 Kinematics of Machines Prof. A. K. Mallik Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module 10 Lecture 1 So far, in this course we have discussed planar linkages, which
Kinematics of Machines Prof. A. K. Mallik Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module 10 Lecture 1 So far, in this course we have discussed planar linkages, which
What s inside your experiment kit: Checklist: Find Inspect Check off KIT CONTENTS. GOOD TO KNOW! If you are missing any. No. Description Qty. Item No.
 EXPERIMENT MANUAL Franckh-Kosmos Verlags-GmbH & Co. KG, Pfizerstr. 5-7, 7084 Stuttgart, Germany +49 (0) 7 29-0 www.kosmos.de Thames & Kosmos, 30 Friendship St., Providence, RI, 02903, USA -800-587-2872
EXPERIMENT MANUAL Franckh-Kosmos Verlags-GmbH & Co. KG, Pfizerstr. 5-7, 7084 Stuttgart, Germany +49 (0) 7 29-0 www.kosmos.de Thames & Kosmos, 30 Friendship St., Providence, RI, 02903, USA -800-587-2872
KINEMATICS OF MACHINES. Dr.V.SUNDARESWARAN PROFESSOR OF MECHANICAL ENGG. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, GUINDY ANNA UNIVERSITY CHENNAI
 KINEMATICS OF MACHINES Dr.V.SUNDARESWARAN PROFESSOR OF MECHANICAL ENGG. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, GUINDY ANNA UNIVERSITY CHENNAI 600 025 MECHANICS Science dealing with motion DIVISIONS OF MECHANICS Statics
KINEMATICS OF MACHINES Dr.V.SUNDARESWARAN PROFESSOR OF MECHANICAL ENGG. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, GUINDY ANNA UNIVERSITY CHENNAI 600 025 MECHANICS Science dealing with motion DIVISIONS OF MECHANICS Statics
Redexim-Charterhouse Verti-Drain 7316 pag 01 code 0401
 Redexim-Charterhouse Verti-Drain 7316 pag 01 code 0401 1 4191100 Winged nut 10 2 4100800 Self lock nut M6 10 3 2282183 Bottom PTO protection cover 1 4 4001030 Bolt M6 x 16 10 5 2281782 Top PTO protection
Redexim-Charterhouse Verti-Drain 7316 pag 01 code 0401 1 4191100 Winged nut 10 2 4100800 Self lock nut M6 10 3 2282183 Bottom PTO protection cover 1 4 4001030 Bolt M6 x 16 10 5 2281782 Top PTO protection
Kinematics of Machines Prof. A. K. Mallik Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur. Module - 3 Lecture - 1
 Kinematics of Machines Prof. A. K. Mallik Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module - 3 Lecture - 1 In an earlier lecture, we have already mentioned that there
Kinematics of Machines Prof. A. K. Mallik Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module - 3 Lecture - 1 In an earlier lecture, we have already mentioned that there
Lesson 1: Introduction to Pro/MECHANICA Motion
 Lesson 1: Introduction to Pro/MECHANICA Motion 1.1 Overview of the Lesson The purpose of this lesson is to provide you with a brief overview of Pro/MECHANICA Motion, also called Motion in this book. Motion
Lesson 1: Introduction to Pro/MECHANICA Motion 1.1 Overview of the Lesson The purpose of this lesson is to provide you with a brief overview of Pro/MECHANICA Motion, also called Motion in this book. Motion
Engineering Mechanics. Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies
 Engineering Mechanics Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies System is in equilibrium if and only if the sum of all the forces and moment (about any point) equals zero. Equilibrium Supports and Equilibrium Any structure
Engineering Mechanics Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies System is in equilibrium if and only if the sum of all the forces and moment (about any point) equals zero. Equilibrium Supports and Equilibrium Any structure
Chapter 4: Kinematics of Rigid Bodies
 Chapter 4: Kinematics of Rigid Bodies Advanced Dynamics Lecturer: Hossein Nejat Fall 2016 A rigid body is defined to be a collection of particles whose distance of separation is invariant. In this circumstance,
Chapter 4: Kinematics of Rigid Bodies Advanced Dynamics Lecturer: Hossein Nejat Fall 2016 A rigid body is defined to be a collection of particles whose distance of separation is invariant. In this circumstance,
Kinematics of Machines Prof. A. K. Mallik Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur. Module - 2 Lecture - 1
 Kinematics of Machines Prof. A. K. Mallik Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module - 2 Lecture - 1 The topic of today s lecture is mobility analysis. By mobility
Kinematics of Machines Prof. A. K. Mallik Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Module - 2 Lecture - 1 The topic of today s lecture is mobility analysis. By mobility
Page 3. Page Page 4. Page 5. Page 6. Page 2. Page 7
 Parts manual Verti-Drain 416 Page 01 Code 1640 TM Page 3 Page -10 Page 4 Page Page 6 Page 2 Page Page 8 Page : PTO Page : Tines, adapters and turf hold down kits Page 13: Optional core collector Page
Parts manual Verti-Drain 416 Page 01 Code 1640 TM Page 3 Page -10 Page 4 Page Page 6 Page 2 Page Page 8 Page : PTO Page : Tines, adapters and turf hold down kits Page 13: Optional core collector Page
Universal Tristop Cylinder for Cam Brakes
 Tristop for Cam Brakes 3rd Edition This publication is not subject to any update service. New versions are available in INFORM at www.wabco-auto.com Copyright WABCO 2006 Vehicle Control Systems An American
Tristop for Cam Brakes 3rd Edition This publication is not subject to any update service. New versions are available in INFORM at www.wabco-auto.com Copyright WABCO 2006 Vehicle Control Systems An American
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF WEIGHT SHIFT STEERING MECHANISM BASED ON FOUR BAR MECHANISM
 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 8, Issue 12, December 2017, pp. 417 424, Article ID: IJMET_08_12_041 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=8&itype=12
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 8, Issue 12, December 2017, pp. 417 424, Article ID: IJMET_08_12_041 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=8&itype=12
This is trial version
 s, s, Ejector coupling devices, Unscrewing components, Two-stage ejectors, Latch locking units, Mould slides-modular system 2.01 2.02 Ordering example : Z 40 / 1,6 x 40 Shaft Overall length Z02/... 2.1
s, s, Ejector coupling devices, Unscrewing components, Two-stage ejectors, Latch locking units, Mould slides-modular system 2.01 2.02 Ordering example : Z 40 / 1,6 x 40 Shaft Overall length Z02/... 2.1
MACHINES AND MECHANISMS
 MACHINES AND MECHANISMS APPLIED KINEMATIC ANALYSIS Fourth Edition David H. Myszka University of Dayton PEARSON ж rentice Hall Pearson Education International Boston Columbus Indianapolis New York San Francisco
MACHINES AND MECHANISMS APPLIED KINEMATIC ANALYSIS Fourth Edition David H. Myszka University of Dayton PEARSON ж rentice Hall Pearson Education International Boston Columbus Indianapolis New York San Francisco
Mechanics Place in Science Mechanisms and Structures Number Synthesis Paradoxes and Isomers Transformations and Inversions Grashof s Law
 INTODUCTION TO MECHANISM SYNTHESIS Mechanics Place in Science Mechanisms and Structures Number Synthesis Paradoxes and Isomers Transformations and Inversions Grashof s Law ME312: Dynamics of Mechanisms
INTODUCTION TO MECHANISM SYNTHESIS Mechanics Place in Science Mechanisms and Structures Number Synthesis Paradoxes and Isomers Transformations and Inversions Grashof s Law ME312: Dynamics of Mechanisms
SUPPORTING LINEAR MOTION: A COMPLETE GUIDE TO IMPLEMENTING DYNAMIC LOAD SUPPORT FOR LINEAR MOTION SYSTEMS
 SUPPORTING LINEAR MOTION: A COMPLETE GUIDE TO IMPLEMENTING DYNAMIC LOAD SUPPORT FOR LINEAR MOTION SYSTEMS Released by: Keith Knight Catalyst Motion Group Engineering Team Members info@catalystmotiongroup.com
SUPPORTING LINEAR MOTION: A COMPLETE GUIDE TO IMPLEMENTING DYNAMIC LOAD SUPPORT FOR LINEAR MOTION SYSTEMS Released by: Keith Knight Catalyst Motion Group Engineering Team Members info@catalystmotiongroup.com
Redexim-Charterhouse Verti-Core 1300/ 1700/ 2100 pag 01 code 0202
 Redexim-Charterhouse Verti-Core 1300/ 1700/ 2100 pag 01 code 0202 Part# 1300 Part# 1700 Part# 2100 DESCRIPTION REMARKS QUA 1 844.060.060 Same Same Winged nut - M6 10 2 830.060.060 Same Same Self lock nut
Redexim-Charterhouse Verti-Core 1300/ 1700/ 2100 pag 01 code 0202 Part# 1300 Part# 1700 Part# 2100 DESCRIPTION REMARKS QUA 1 844.060.060 Same Same Winged nut - M6 10 2 830.060.060 Same Same Self lock nut
A rigid body free to move in a reference frame will, in the general case, have complex motion, which is simultaneously a combination of rotation and
 050389 - Analtical Elements of Mechanisms Introduction. Degrees of Freedom he number of degrees of freedom (DOF) of a sstem is equal to the number of independent parameters (measurements) that are needed
050389 - Analtical Elements of Mechanisms Introduction. Degrees of Freedom he number of degrees of freedom (DOF) of a sstem is equal to the number of independent parameters (measurements) that are needed
Cam makes a higher kinematic pair with follower. Cam mechanisms are widely used because with them, different types of motion can be possible.
 CAM MECHANISMS Cam makes a higher kinematic pair with follower. Cam mechanisms are widely used because with them, different types of motion can be possible. Cams can provide unusual and irregular motions
CAM MECHANISMS Cam makes a higher kinematic pair with follower. Cam mechanisms are widely used because with them, different types of motion can be possible. Cams can provide unusual and irregular motions
Manipulation and Fluid Power. October 07, 2008
 2008 TE Sessions Supported by Manipulation and Fluid Power October 07, 2008 www.robojackets.org Manipulation Keys to Understanding Manipulators What is a manipulator? What kinds of manipulators are there?
2008 TE Sessions Supported by Manipulation and Fluid Power October 07, 2008 www.robojackets.org Manipulation Keys to Understanding Manipulators What is a manipulator? What kinds of manipulators are there?
UNDERSTANDING MOTION SIMULATION
 W H I T E P A P E R UNDERSTANDING MOTION SIMULATION Overview What is motion simulation? What problems can it solve? How can it benefit the product design process? This paper addresses some of these issues
W H I T E P A P E R UNDERSTANDING MOTION SIMULATION Overview What is motion simulation? What problems can it solve? How can it benefit the product design process? This paper addresses some of these issues
Understanding Motion Simulation
 white paper Understanding Motion Simulation inspiration SUMMARY What is motion simulation? What problems can it solve? How can it benefit the product design process? This paper addresses some of these
white paper Understanding Motion Simulation inspiration SUMMARY What is motion simulation? What problems can it solve? How can it benefit the product design process? This paper addresses some of these
Mechanisms. Updated: 18Apr16 v7
 Mechanisms Updated: 8Apr6 v7 Mechanism Converts input motion or force into a desired output with four combinations of input and output motion Rotational to Oscillating Rotational to Rotational Rotational
Mechanisms Updated: 8Apr6 v7 Mechanism Converts input motion or force into a desired output with four combinations of input and output motion Rotational to Oscillating Rotational to Rotational Rotational
Model 2704 Parts List * = Standard Equipment 〇 = Circuit Diagram
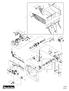 2704 11-05 99 98 97 82 88 89 83 84 85 86 87 101 103 100 106 81 71 105 104 73 74 75 76 77 78 80 79 57 62 58 56 63 65 66 67 68 64 69 70 59 60 61 31 30 29 32 34 35 41 40 42 36 37 38 39 43 4445 46 21 22 20
2704 11-05 99 98 97 82 88 89 83 84 85 86 87 101 103 100 106 81 71 105 104 73 74 75 76 77 78 80 79 57 62 58 56 63 65 66 67 68 64 69 70 59 60 61 31 30 29 32 34 35 41 40 42 36 37 38 39 43 4445 46 21 22 20
Structural Configurations of Manipulators
 Structural Configurations of Manipulators 1 In this homework, I have given information about the basic structural configurations of the manipulators with the concerned illustrations. 1) The Manipulator
Structural Configurations of Manipulators 1 In this homework, I have given information about the basic structural configurations of the manipulators with the concerned illustrations. 1) The Manipulator
Mechanism. Mechanism consists of linkages and joints.
 Mechanism Machines are mechanical devices used to accomplish work. A mechanism is a heart of a machine. It is the mechanical portion of the machine that has the function of transferring motion and forces
Mechanism Machines are mechanical devices used to accomplish work. A mechanism is a heart of a machine. It is the mechanical portion of the machine that has the function of transferring motion and forces
SolidWorks Assembly Files. Assemblies Mobility. The Mating Game Mating features. Mechanical Mates Relative rotation about axes
 Assemblies Mobility SolidWorks Assembly Files An assembly file is a collection of parts The first part brought into an assembly file is fixed Other parts are constrained relative to that part (or other
Assemblies Mobility SolidWorks Assembly Files An assembly file is a collection of parts The first part brought into an assembly file is fixed Other parts are constrained relative to that part (or other
2.1 Introduction. 2.2 Degree of Freedom DOF of a rigid body
 Chapter 2 Kinematics 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Degree of Freedom 2.2.1 DOF of a rigid body In order to control and guide the mechanisms to move as we desired, we need to set proper constraints. In order to
Chapter 2 Kinematics 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Degree of Freedom 2.2.1 DOF of a rigid body In order to control and guide the mechanisms to move as we desired, we need to set proper constraints. In order to
2 Connections of component parts
 2 Connections of component parts In the last Section you saw how the plane motion of individual rigid bodies could be represented in terms of linear and angular displacements. I now want to consider the
2 Connections of component parts In the last Section you saw how the plane motion of individual rigid bodies could be represented in terms of linear and angular displacements. I now want to consider the
3D Model Based Mechanisms Learning Software User Manual (Version 4) Freely Available for Academic Use!!! September 2015
 MechAnalyzer 3D Model Based Mechanisms Learning Software User Manual (Version 4) Features: Forward Kinematics More than 10 Mechanisms Inversions Velocity and Acceleration Module (VAD) Freely Available
MechAnalyzer 3D Model Based Mechanisms Learning Software User Manual (Version 4) Features: Forward Kinematics More than 10 Mechanisms Inversions Velocity and Acceleration Module (VAD) Freely Available
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 1
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Modern mechanical and aerospace systems are often very complex and consist of many components interconnected by joints and force elements such as springs, dampers, and actuators.
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Modern mechanical and aerospace systems are often very complex and consist of many components interconnected by joints and force elements such as springs, dampers, and actuators.
PARTS LISTING WR
 13 ST624E 1.1998 PARTS LISTING 601 00 23-71 WR 01-07-98 ST624 Engine Assembly 9 12 13 41 43 44 51 53 31 33 34 53 58 58 59 60 57 63 60 67 68. AUGER FRAME. PULLEY 69. PULLEY 10 - ENGINE, 6HP (See Engine
13 ST624E 1.1998 PARTS LISTING 601 00 23-71 WR 01-07-98 ST624 Engine Assembly 9 12 13 41 43 44 51 53 31 33 34 53 58 58 59 60 57 63 60 67 68. AUGER FRAME. PULLEY 69. PULLEY 10 - ENGINE, 6HP (See Engine
INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 1
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Modern mechanical and aerospace systems are often very complex and consist of many components interconnected by joints and force elements such as springs, dampers, and actuators.
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Modern mechanical and aerospace systems are often very complex and consist of many components interconnected by joints and force elements such as springs, dampers, and actuators.
Mechanism Kinematics and Dynamics
 Mechanism Kinematics and Dynamics Final Project 1. The window shield wiper For the window wiper, (1). Select the length of all links such that the wiper tip X p (t) can cover a 120 cm window width. (2).
Mechanism Kinematics and Dynamics Final Project 1. The window shield wiper For the window wiper, (1). Select the length of all links such that the wiper tip X p (t) can cover a 120 cm window width. (2).
31AE660G022 Snow Thrower 1028 (2002) Page 1 of 13 Belt Drive & Engine Accessories
 31AE660G022 Snow Thrower 1028 (2002) Page 1 of 13 Belt Drive & Engine Accessories 31AE660G022 Snow Thrower 1028 (2002) Page 2 of 13 Belt Drive & Engine Accessories 1 710-1652 1 /P Hex Washer Screw 1/4-20
31AE660G022 Snow Thrower 1028 (2002) Page 1 of 13 Belt Drive & Engine Accessories 31AE660G022 Snow Thrower 1028 (2002) Page 2 of 13 Belt Drive & Engine Accessories 1 710-1652 1 /P Hex Washer Screw 1/4-20
[3] Rigid Body Analysis
![[3] Rigid Body Analysis [3] Rigid Body Analysis](/thumbs/92/109073357.jpg) [3] Rigid Body Analysis Page 1 of 53 [3] Rigid Body Analysis [3.1] Equilibrium of a Rigid Body [3.2] Equations of Equilibrium [3.3] Equilibrium in 3-D [3.4] Simple Trusses [3.5] The Method of Joints [3.6]
[3] Rigid Body Analysis Page 1 of 53 [3] Rigid Body Analysis [3.1] Equilibrium of a Rigid Body [3.2] Equations of Equilibrium [3.3] Equilibrium in 3-D [3.4] Simple Trusses [3.5] The Method of Joints [3.6]
Mini slides SLT/SLS/SLF
 Mini slides SLT/SLS/SLF Precision, rigid guide Highly flexible Adjustable end position cushioning 03/10 Subject to change Products 04/05 1 / 1 Mini slides SLT/SLS/SLF Features SLS SLF SLT SLT/SLS/SLF SLT
Mini slides SLT/SLS/SLF Precision, rigid guide Highly flexible Adjustable end position cushioning 03/10 Subject to change Products 04/05 1 / 1 Mini slides SLT/SLS/SLF Features SLS SLF SLT SLT/SLS/SLF SLT
Solutions to Chapter 6 Exercise Problems A 1 O 4 B 2
 Solutions to Chapter 6 Exercise Problems Problem 6.1: Design a double rocker, four-bar linkage so that the base link is 2-in and the output rocker is 1-in long. The input link turns counterclockwise 60
Solutions to Chapter 6 Exercise Problems Problem 6.1: Design a double rocker, four-bar linkage so that the base link is 2-in and the output rocker is 1-in long. The input link turns counterclockwise 60
KINEMATIC AND DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF CRANK SHAFT USED IN POWER PRESS Ravi Mangukiya 1, Mihir Mendapara 2, M. B. Vaghela 3 1, 2
 KINEMATIC AND DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF CRANK SHAFT USED IN POWER PRESS Ravi Mangukiya 1, Mihir Mendapara 2, M. B. Vaghela 3 1, 2 UG Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, B.H. Gardi College of Engineering
KINEMATIC AND DYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF CRANK SHAFT USED IN POWER PRESS Ravi Mangukiya 1, Mihir Mendapara 2, M. B. Vaghela 3 1, 2 UG Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, B.H. Gardi College of Engineering
ST927E Spare Parts
 ST927E 1996-01 Spare Parts ELECTRIC START REPAIR PARTS 9 8 7 6 6 601 00 15-88 MOTOR, STARTER TEC. 120V 7 601 00 15-89 SCREW 1/4-20X.50 HWASEMSTOR 8 601 00 15-90 SCREW #6-32 X 2.50 9 601 00 15-91 CORD,
ST927E 1996-01 Spare Parts ELECTRIC START REPAIR PARTS 9 8 7 6 6 601 00 15-88 MOTOR, STARTER TEC. 120V 7 601 00 15-89 SCREW 1/4-20X.50 HWASEMSTOR 8 601 00 15-90 SCREW #6-32 X 2.50 9 601 00 15-91 CORD,
SCRAMBLER 50 Model #A02EA05CA Rev. 01. E 2001 Polaris Sales Inc. PARTS MANUAL PN and MICROFICHE PN /02
 SCRAMBLER 0 Model #A0EA0CA Rev. 0 E 00 Polaris Sales Inc. PARTS MANUAL PN 0 and MICROFICHE PN /0 Thispageleft intentionallyblank. TABLE OF CONTENTS Scrambler 0 A0EA0CA Parts Manual A AIR CLEANER... AXLE,
SCRAMBLER 0 Model #A0EA0CA Rev. 0 E 00 Polaris Sales Inc. PARTS MANUAL PN 0 and MICROFICHE PN /0 Thispageleft intentionallyblank. TABLE OF CONTENTS Scrambler 0 A0EA0CA Parts Manual A AIR CLEANER... AXLE,
CALCULATION AND DESIGN OF CHAIN TRANSMISSIONS
 CALCULATION AND DESIGN OF CHAIN TRANSMISSIONS Project and calculation of the chain transmission follows standards CSN 0 809 and DIN 89. Chain selection and the first chain project are coming from Diagram
CALCULATION AND DESIGN OF CHAIN TRANSMISSIONS Project and calculation of the chain transmission follows standards CSN 0 809 and DIN 89. Chain selection and the first chain project are coming from Diagram
CATALOG OF REPLACEMENT PARTS MODEL FP400 FOOD PROCESSOR. A product of HOBART CORPORATION 701 S. RIDGE AVENUE TROY, OHIO
 CATALOG OF REPLACEMENT PARTS MODEL FP400 FOOD PROCESSOR FP400 ML-104751 A product of HOBART CORPORATION 701 S. RIDGE AVENUE TROY, OHIO 45374-0001 FORM 43012 (June 2001) 1 2 3 56 55 54 53 52 50 51 48 49
CATALOG OF REPLACEMENT PARTS MODEL FP400 FOOD PROCESSOR FP400 ML-104751 A product of HOBART CORPORATION 701 S. RIDGE AVENUE TROY, OHIO 45374-0001 FORM 43012 (June 2001) 1 2 3 56 55 54 53 52 50 51 48 49
The Datum Flow Chain
 The Datum Flow Chain Goals of this class Pull together features, constraint, key characteristics, and tolerances Present a diagramming technique for designing assemblies top-down Do an example What Happens
The Datum Flow Chain Goals of this class Pull together features, constraint, key characteristics, and tolerances Present a diagramming technique for designing assemblies top-down Do an example What Happens
M-2300-ZX Focus SVT Brake Conversion Kit INSTRUCTION SHEET
 Please contact the Tech Hot Line for the most current instruction information (586) 468-1356!!! PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY PRIOR TO INSTALLATION!!! OVERVIEW: This kit is designed
Please contact the Tech Hot Line for the most current instruction information (586) 468-1356!!! PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY PRIOR TO INSTALLATION!!! OVERVIEW: This kit is designed
Redexim-Charterhouse Verti-Drain 7521 page 01 code 0104
 Redexim-Charterhouse Verti-Drain 7521 page 01 code 0104 1 2382640 Solid tine 24x400 (1 x16 ) For USA part# 9990030 16 2 2382639 Solid tine 18x400 (3/4 x16 ) For USA part# 9990029 use adapter 21 16 3 2382638
Redexim-Charterhouse Verti-Drain 7521 page 01 code 0104 1 2382640 Solid tine 24x400 (1 x16 ) For USA part# 9990030 16 2 2382639 Solid tine 18x400 (3/4 x16 ) For USA part# 9990029 use adapter 21 16 3 2382638
EZ-9000 Tape Dispenser, EZ-9000-RP Tape Dispenser Part Number / MAY 2012 REV 1.0
 PLEASE NOTE Some of the part numbers are now different depending on when the unit was manufactured. The drawing will note where the appearance is different and the parts list will give you the correct
PLEASE NOTE Some of the part numbers are now different depending on when the unit was manufactured. The drawing will note where the appearance is different and the parts list will give you the correct
Manipulator Path Control : Path Planning, Dynamic Trajectory and Control Analysis
 Manipulator Path Control : Path Planning, Dynamic Trajectory and Control Analysis Motion planning for industrial manipulators is a challenging task when obstacles are present in the workspace so that collision-free
Manipulator Path Control : Path Planning, Dynamic Trajectory and Control Analysis Motion planning for industrial manipulators is a challenging task when obstacles are present in the workspace so that collision-free
Balancing of Primary Forces of Multi-cylinder Inline
 Balancing of Primary Forces of Multi-cylinder Inline Engines The multi-cylinder engines with the cylinder centre lines in the same plane and on the same side of the centre line of the crankshaft, are known
Balancing of Primary Forces of Multi-cylinder Inline Engines The multi-cylinder engines with the cylinder centre lines in the same plane and on the same side of the centre line of the crankshaft, are known
RD 100. Spare parts list. RD 100 s/n BES Construction Tools PC AB No
 RD 100 Spare parts list RD 100 s/n BES100496 2018 Construction Tools PC AB No. 9800153901 2018-10 General information This spare parts list applies to the following: Part number 8311030410 RD 100 Description
RD 100 Spare parts list RD 100 s/n BES100496 2018 Construction Tools PC AB No. 9800153901 2018-10 General information This spare parts list applies to the following: Part number 8311030410 RD 100 Description
1/2
 http://partsradar.arinet.com/scripts/empartisapi.dll?mf&app=ariens&session=27f5776d-d5a8-4417-865b-d472735c5bb5&cat=2&assem=4658&imgma 1/2 Ref # Par t # Descr iption Context Note Foot Note Min Qty UOM
http://partsradar.arinet.com/scripts/empartisapi.dll?mf&app=ariens&session=27f5776d-d5a8-4417-865b-d472735c5bb5&cat=2&assem=4658&imgma 1/2 Ref # Par t # Descr iption Context Note Foot Note Min Qty UOM
STRAND E: Measurement. UNIT 13 Areas Student Text Contents. Section Squares, Rectangles and Triangles Area and Circumference of Circles
 UNIT 13 Areas Student Text Contents STRAND E: Measurement Unit 13 Areas Student Text Contents Section 13.1 Squares, Rectangles and Triangles 13. Area and Circumference of Circles 13.3 Sector Areas and
UNIT 13 Areas Student Text Contents STRAND E: Measurement Unit 13 Areas Student Text Contents Section 13.1 Squares, Rectangles and Triangles 13. Area and Circumference of Circles 13.3 Sector Areas and
Ball Spline Types LT and LF
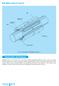 Ball Spline Types and LF Ball Spline nut Snap ring Seal Retainer Spline shaft Fig. Construction of Ball Spline Type Construction and Features Ball Spline types and LF have four or six trains of loadbearing
Ball Spline Types and LF Ball Spline nut Snap ring Seal Retainer Spline shaft Fig. Construction of Ball Spline Type Construction and Features Ball Spline types and LF have four or six trains of loadbearing
Stress Analysis of Cross Groove Type Constant Velocity Joint
 TECHNICAL REPORT Stress Analysis of Cross Groove Type Constant Velocity Joint H. SAITO T. MAEDA The driveshaft is the part that transmits the vehicle's engine torque and rotation to the tires, and predicting
TECHNICAL REPORT Stress Analysis of Cross Groove Type Constant Velocity Joint H. SAITO T. MAEDA The driveshaft is the part that transmits the vehicle's engine torque and rotation to the tires, and predicting
The OHMIC RESISTORS Pty. Ltd.
 The OHMIC RESISTORS Pty. Ltd. The operating mechanism is arranged between and above two steel end plates held apart by three mild steel spacing rods. The handle mechanism is mounted above the top plate.
The OHMIC RESISTORS Pty. Ltd. The operating mechanism is arranged between and above two steel end plates held apart by three mild steel spacing rods. The handle mechanism is mounted above the top plate.
John Deere. MODEL: 510 Round Baler JD-P-PC1599
 John Deere MODEL: 510 Round Baler THIS IS A MANUAL PRODUCED BY JENSALES INC. WITHOUT THE AUTHORIZATION OF JOHN DEERE OR IT'S SUCCESSORS. JOHN DEERE AND IT'S SUCCESSORS ARE NOT RESPONSIBLE FOR THE QUALITY
John Deere MODEL: 510 Round Baler THIS IS A MANUAL PRODUCED BY JENSALES INC. WITHOUT THE AUTHORIZATION OF JOHN DEERE OR IT'S SUCCESSORS. JOHN DEERE AND IT'S SUCCESSORS ARE NOT RESPONSIBLE FOR THE QUALITY
Rev.1. Spare parts price list for representatives for Cosmic 48R & 48RX
 Spare parts price list for representatives for Cosmic 48R & 48RX 1 Spare parts price list for representatives for Cosmic 48R & 48RX Drw. no. Ref. no. Part no. Description Unit Date: Apr. 23, 2015 Used
Spare parts price list for representatives for Cosmic 48R & 48RX 1 Spare parts price list for representatives for Cosmic 48R & 48RX Drw. no. Ref. no. Part no. Description Unit Date: Apr. 23, 2015 Used
COSMOS. Understanding Motion Simulation ---- SolidWorks Corporation. Introduction 1. Motion simulation for mechanism analysis and synthesis 1-6
 ---- WHITE PAPER Understanding Motion Simulation CONTENTS Introduction 1 Motion simulation for mechanism analysis and synthesis 1-6 Using motion simulation along with FEA 6-9 Motion simulation and test
---- WHITE PAPER Understanding Motion Simulation CONTENTS Introduction 1 Motion simulation for mechanism analysis and synthesis 1-6 Using motion simulation along with FEA 6-9 Motion simulation and test
Animations in Creo 3.0
 Animations in Creo 3.0 ME170 Part I. Introduction & Outline Animations provide useful demonstrations and analyses of a mechanism's motion. This document will present two ways to create a motion animation
Animations in Creo 3.0 ME170 Part I. Introduction & Outline Animations provide useful demonstrations and analyses of a mechanism's motion. This document will present two ways to create a motion animation
PARTS LISTING WR
 13 ST 824E 1.1998 PARTS LISTING 601 00 23-16 WR 02-02-98 ST824 Electric Starter Assembly 8 9 10 6. ENGINE 6 601 00 15 88 MOTOR, STARTER 7 601 00 15 89 SCREW, 1/4-20X.50 8 60 100 15 90 SCREW, #6-32X2.50
13 ST 824E 1.1998 PARTS LISTING 601 00 23-16 WR 02-02-98 ST824 Electric Starter Assembly 8 9 10 6. ENGINE 6 601 00 15 88 MOTOR, STARTER 7 601 00 15 89 SCREW, 1/4-20X.50 8 60 100 15 90 SCREW, #6-32X2.50
2.007 Design and Manufacturing I Spring 2009
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.007 Design and Manufacturing I Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 2.007 Design and Manufacturing
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.007 Design and Manufacturing I Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 2.007 Design and Manufacturing
Virtual Testing Methodology for TPL Lifting Capacity of Agricultural Tractor TPL
 Virtual Testing Methodology for TPL Lifting Capacity of Agricultural Tractor TPL Dheeraj Pandey AM CAE International Tractors Limited Jalandhar Road, Hoshiarpur 146001 - India dheerajpandey@sonalika.com
Virtual Testing Methodology for TPL Lifting Capacity of Agricultural Tractor TPL Dheeraj Pandey AM CAE International Tractors Limited Jalandhar Road, Hoshiarpur 146001 - India dheerajpandey@sonalika.com
Powered Arm Orthosis III
 Worcester Polytechnic Institute Digital WPI Assistive Technology Resource Center Projects Assistive Technology Resource Center 1-1999 Powered Arm Orthosis III Christopher Felice Worcester Polytechnic Institute
Worcester Polytechnic Institute Digital WPI Assistive Technology Resource Center Projects Assistive Technology Resource Center 1-1999 Powered Arm Orthosis III Christopher Felice Worcester Polytechnic Institute
PW80 (4BCF) EUROPE,SOUTH AFRICA,JAPAN
 PW80 (4BCF) OPE,SOUTH AFRICA,JAPAN 1D4BC-300E1 ( 2D4BC-300E1 ) A2 PW80 PARTS CATALOGUE 2004 by Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd. 1st edition, May 2004 All rights reserved. Any reprinting or unauthorized use without
PW80 (4BCF) OPE,SOUTH AFRICA,JAPAN 1D4BC-300E1 ( 2D4BC-300E1 ) A2 PW80 PARTS CATALOGUE 2004 by Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd. 1st edition, May 2004 All rights reserved. Any reprinting or unauthorized use without
Lecture 3. Planar Kinematics
 Matthew T. Mason Mechanics of Manipulation Outline Where are we? s 1. Foundations and general concepts. 2.. 3. Spherical and spatial kinematics. Readings etc. The text: By now you should have read Chapter
Matthew T. Mason Mechanics of Manipulation Outline Where are we? s 1. Foundations and general concepts. 2.. 3. Spherical and spatial kinematics. Readings etc. The text: By now you should have read Chapter
Human Motion. Session Speaker Dr. M. D. Deshpande. AML2506 Biomechanics and Flow Simulation PEMP-AML2506
 AML2506 Biomechanics and Flow Simulation Day 02A Kinematic Concepts for Analyzing Human Motion Session Speaker Dr. M. D. Deshpande 1 Session Objectives At the end of this session the delegate would have
AML2506 Biomechanics and Flow Simulation Day 02A Kinematic Concepts for Analyzing Human Motion Session Speaker Dr. M. D. Deshpande 1 Session Objectives At the end of this session the delegate would have
1. Introduction 1 2. Mathematical Representation of Robots
 1. Introduction 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Brief History 1 1.3 Types of Robots 7 1.4 Technology of Robots 9 1.5 Basic Principles in Robotics 12 1.6 Notation 15 1.7 Symbolic Computation and Numerical Analysis
1. Introduction 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Brief History 1 1.3 Types of Robots 7 1.4 Technology of Robots 9 1.5 Basic Principles in Robotics 12 1.6 Notation 15 1.7 Symbolic Computation and Numerical Analysis
Model Library Mechanics
 Model Library Mechanics Using the libraries Mechanics 1D (Linear), Mechanics 1D (Rotary), Modal System incl. ANSYS interface, and MBS Mechanics (3D) incl. CAD import via STL and the additional options
Model Library Mechanics Using the libraries Mechanics 1D (Linear), Mechanics 1D (Rotary), Modal System incl. ANSYS interface, and MBS Mechanics (3D) incl. CAD import via STL and the additional options
BG 240. Spare parts list. Trowel. Valid from serial number Atlas Copco Construction Tools AB No c
 BG 0 Spare parts list Trowel BG0 HSQP BG0 HSQP BG0 HSTP BG0 HSTP Valid from serial number BGB00000 BGB00000 BGF000000 BGF000000 0 Atlas Copco Construction Tools AB No. 900 0 0c 00 BG 0 Contents Contents
BG 0 Spare parts list Trowel BG0 HSQP BG0 HSQP BG0 HSTP BG0 HSTP Valid from serial number BGB00000 BGB00000 BGF000000 BGF000000 0 Atlas Copco Construction Tools AB No. 900 0 0c 00 BG 0 Contents Contents
What is a Manipulator? 2007 RoboJackets TE Sessions 10/16/2007. Keys to Understanding Manipulators TE Sessions Manipulators 10/16/07
 2007 TE Sessions Manipulators 10/16/07 www.robojackets.org Keys to Understanding Manipulators What is a manipulator? What kinds of manipulators are there? What are the different types of joints and linkages
2007 TE Sessions Manipulators 10/16/07 www.robojackets.org Keys to Understanding Manipulators What is a manipulator? What kinds of manipulators are there? What are the different types of joints and linkages
21C-64M1066 Bronco CRT Roto-Tiller (2008) Page 1 of 13 Drive System
 21C-64M1066 Bronco CRT Roto-Tiller (2008) Page 1 of 13 Drive System 21C-64M1066 Bronco CRT Roto-Tiller (2008) Page 2 of 13 Drive System 1 656-04023A 1 Engine Pulley Bronco 1 656-04005A 1 /P Engine Pulley
21C-64M1066 Bronco CRT Roto-Tiller (2008) Page 1 of 13 Drive System 21C-64M1066 Bronco CRT Roto-Tiller (2008) Page 2 of 13 Drive System 1 656-04023A 1 Engine Pulley Bronco 1 656-04005A 1 /P Engine Pulley
Kinematics And Dynamics Lab Manual EXPERIMENT NO:01 STATIC & DYNAMIC BALANCE EXPERIMENT
 EXPERIMENT NO:01 STATIC & DYNAMIC BALANCE EXPERIMENT Aim To balance the given masses statically by drawing force polygon and couple polygon and dynamically by trial and error method on a shaft. Theory
EXPERIMENT NO:01 STATIC & DYNAMIC BALANCE EXPERIMENT Aim To balance the given masses statically by drawing force polygon and couple polygon and dynamically by trial and error method on a shaft. Theory
TRU-POWER, INC. Product Line GENERAL PURPOSE ENGINE Model Name G65 Type RD Mfg Section ENGINE Illustration G65/GS65 CYLINDER HEAD
 TRU-POWER, INC. Product Line GENERAL PURPOSE ENGINE Model Name G65 Type RD Mfg Section ENGINE Illustration G65/GS65 CYLINDER HEAD 00 220-823-000 CYLINDER HEAD 00 002 225-823-000 GASKET, CYLINDER HEAD (NOT
TRU-POWER, INC. Product Line GENERAL PURPOSE ENGINE Model Name G65 Type RD Mfg Section ENGINE Illustration G65/GS65 CYLINDER HEAD 00 220-823-000 CYLINDER HEAD 00 002 225-823-000 GASKET, CYLINDER HEAD (NOT
Motion Control (wheeled robots)
 Motion Control (wheeled robots) Requirements for Motion Control Kinematic / dynamic model of the robot Model of the interaction between the wheel and the ground Definition of required motion -> speed control,
Motion Control (wheeled robots) Requirements for Motion Control Kinematic / dynamic model of the robot Model of the interaction between the wheel and the ground Definition of required motion -> speed control,
SYSTEMS ELECTRONICS GROUP
 SYSTEMS ELECTRONICS GROUP SYSTEMS M4500 MACHINE COMPONENTS RSV34-MS1 RESOLVER with MS CONNECTOR Brushless, Single-turn Resolver Rated to 3,000 RPM Rotary Position Transducer for M4500, M4020, M4040, M4041,
SYSTEMS ELECTRONICS GROUP SYSTEMS M4500 MACHINE COMPONENTS RSV34-MS1 RESOLVER with MS CONNECTOR Brushless, Single-turn Resolver Rated to 3,000 RPM Rotary Position Transducer for M4500, M4020, M4040, M4041,
Industrial Robots : Manipulators, Kinematics, Dynamics
 Industrial Robots : Manipulators, Kinematics, Dynamics z z y x z y x z y y x x In Industrial terms Robot Manipulators The study of robot manipulators involves dealing with the positions and orientations
Industrial Robots : Manipulators, Kinematics, Dynamics z z y x z y x z y y x x In Industrial terms Robot Manipulators The study of robot manipulators involves dealing with the positions and orientations
Workholding. Workholding CHUCKS CENTRES 3-JAW SELF CENTERING MONO-BLOCK JAW CHUCKS STEEL CENTRES 60º PLAINBACK FITTING CARBIDE CENTRES 60º
 CENTRES CHUCKS STEEL CENTRES 60º 3-JAW SELF CENTERING MONO-BLOCK JAW CHUCKS CARBIDE CENTRES 60º Taper Stock Code MT1 014-101 0.25kg MT2 014-102 0.25kg MT3 014-103 0.5kg MT4 014-104 1kg MT5 014-105 2.5kg
CENTRES CHUCKS STEEL CENTRES 60º 3-JAW SELF CENTERING MONO-BLOCK JAW CHUCKS CARBIDE CENTRES 60º Taper Stock Code MT1 014-101 0.25kg MT2 014-102 0.25kg MT3 014-103 0.5kg MT4 014-104 1kg MT5 014-105 2.5kg
PARTS MANUAL PN and MICROFICHE PN /03. PREDATOR 90 Model #A04KA09CA Model #A04KA09CB. E 2003 Polaris Sales Inc.
 PARTS MANUAL PN and MICROFICHE PN /0 PREDATOR 0 Model #A0KA0CA Model #A0KA0CB E 00 Polaris Sales Inc. This page left blank intentionally. TABLE OF CONTENTS PREDATOR 0 A0KA0CA and PREDATOR 0 A0KA0CB Parts
PARTS MANUAL PN and MICROFICHE PN /0 PREDATOR 0 Model #A0KA0CA Model #A0KA0CB E 00 Polaris Sales Inc. This page left blank intentionally. TABLE OF CONTENTS PREDATOR 0 A0KA0CA and PREDATOR 0 A0KA0CB Parts
RYOBI 10 in. (254 mm) TABLE SAW - MODEL NO. BTS20
 A0 OUTFEED SUPPORT RYOBI in. ( mm) TABLE SAW - MODEL NO. BTS0 FIGURE B: OUTFEED SUPPORT 0 OUTFEED SUPPORT... 0 SCREW (/-0 x / in.)... 00 OUTFEED SUPPORT ROD... 00 STOP SCREW (M X mm)... FIGURE C: BLADE
A0 OUTFEED SUPPORT RYOBI in. ( mm) TABLE SAW - MODEL NO. BTS0 FIGURE B: OUTFEED SUPPORT 0 OUTFEED SUPPORT... 0 SCREW (/-0 x / in.)... 00 OUTFEED SUPPORT ROD... 00 STOP SCREW (M X mm)... FIGURE C: BLADE
Removal and Installation8
 8 Screw Types 8-4 Top Cover Assembly 8-5 Left Hand Cover 8-6 Right Hand Cover 8-10 Front Panel Assembly 8-14 Left Rear Cover 8-15 Right Rear Cover 8-16 Extension Cover (60" Model only) 8-17 Media Lever
8 Screw Types 8-4 Top Cover Assembly 8-5 Left Hand Cover 8-6 Right Hand Cover 8-10 Front Panel Assembly 8-14 Left Rear Cover 8-15 Right Rear Cover 8-16 Extension Cover (60" Model only) 8-17 Media Lever
Week 12 - Lecture Mechanical Event Simulation. ME Introduction to CAD/CAE Tools
 Week 12 - Lecture Mechanical Event Simulation Lecture Topics Mechanical Event Simulation Overview Additional Element Types Joint Component Description General Constraint Refresh Mesh Control Force Estimation
Week 12 - Lecture Mechanical Event Simulation Lecture Topics Mechanical Event Simulation Overview Additional Element Types Joint Component Description General Constraint Refresh Mesh Control Force Estimation
