Pairwise Sequence Alignment: Dynamic Programming Algorithms. COMP Spring 2015 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University
|
|
|
- Duane Bates
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pairwise Sequence Alignment: Dynamic Programming Algorithms COMP Spring 2015 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University
2 DP Algorithms for Pairwise Alignment The number of all possible pairwise alignments (if gaps are allowed) is exponential in the length of the sequences Therefore, the approach of score every possible alignment and choose the best is infeasible in practice Efficient algorithms for pairwise alignment have been devised using dynamic programming (DP)
3 DP Algorithms for Pairwise Alignment The key property of DP is that the problem can be divided into many smaller parts and the solution can be obtained from the solutions to these smaller parts
4 The Needleman-Wunch Algorithm for Global Pairwise Alignment The problem is to align two sequences x (x1x2...xm) and y (y1y2...yn) finding the best scoring alignment in which all residues of both sequences are included The score is assumed to be a measure of similarity, so the highest score is desired Alternatively, the score could be an evolutionary distance, in which case the smallest score would be sought, and all uses of max in the algorithm would be replaced by min
5 The Needleman-Wunch Algorithm for Global Pairwise Alignment The key concept in all these algorithms is the matrix S of optimal scores of subsequence alignments The matrix has (m+1) rows labeled 0 m and (n+1) columns labeled 0 n The rows correspond to the residues of sequence x, and the columns correspond to the residues of sequence y
6 The Needleman-Wunch Algorithm for Global Pairwise Alignment We ll use as a working example the two sequences x=thisline and y=isaligned with BLOSUM-62 substitution matrix as the scoring matrix and linear gap penalty g=e The optimal alignment of these two sequences is T H I S - L I - N E I S A L I G N E D
7 The Matrix S E=-8 Si,j stores the score for the optimal alignment of all residues up to xi of sequence x will all residues up to yj of sequence y S i,0 = S 0,i = ig
8 The Matrix S To complete the matrix, we use the formula S i,j = max S i 1,j 1 + s(x i,y j ) S i 1,j + g S i,j 1 + g
9 The Matrix S E=-8 S i,j = max S i 1,j 1 + s(x i,y j ) S i 1,j + g S i,j 1 + g The global alignment can be obtained by traceback
10 The alignment we obtained is not the one we expected in that it contains no gaps (the gap at the end is added only because the two sequences are of different lengths) The problem is that the worst score in the BLOSUM-62 matrix is -4, which is significantly less than the gap penalty (-8), so gaps are unlikely to be present in the optimal alignment
11 If instead we use a linear gap penalty of -4, inserting a gap becomes less severe, and a gapped alignment is more likely to be obtained Therefore it is very important to match the gap penalty to the substitution matrix used
12 The Matrix S E=-4 S i,j = max S i 1,j 1 + s(x i,y j ) S i 1,j + g S i,j 1 + g The global alignment can be obtained by traceback
13 Multiple Optimal Alignments There may be more than one optimal alignment During traceback this is indicated by encountering an element that was derived from more than one of the three possible alternatives The algorithm does not distinguish between these possible alignments, although there may be reasons (such as knowledge of molecular structure of function) for preferring one to the others Most programs will arbitrarily report just one single alignment
14 Semiglobal Alignments In certain applications, we don t want to penalize gaps at the beginning or end of either of the two sequences in the alignment The resulting alignment is called semiglobal alignment To obtain it, we have two modifications to the Needleman- Wunch algorithm: (1) we initialize Si,0 and S0,j to 0 for all i and j, and (2) the traceback starts at the highest-scoring element in the bottom row or right-most column
15 Semiglobal Alignment
16 General Gap Penalty The algorithm we presented works with a linear gap penalty of the form g(ngap) = -ngape For a general gap penalty model g(ngap), one must consider the possibility of arriving at Si,j directly via insertion of a gap of length up to i in sequence x or j in sequence y
17 General Gap Penalty
18 General Gap Penalty The algorithm now has to be modified to S i,j = max S i 1,j 1 + s(x i,y j ) (S i ngap1,j + g(n gap1 )) 1 ngap1 i (S i,j ngap2 + g(n gap2 )) 1 ngap2 j This algorithm takes time that is proportional to mn 2, where m and n are the sequence lengths with n>m
19 Affine Gap Penalty For an affine gap penalty g(ngap)=-i-(ngap-1)e, we can refine this algorithm to obtain an O(mn) algorithm Define two matrices V i,j = max{s i ngap1,j + g(n gap1 )} 1 ngap1 i W i,j = max{s i,j ngap2 + g(n gap2 )} 1 ngap2 j
20 Affine Gap Penalty These matrices can be defined recursively as V i,j = max W i,j = max { Si 1,j I V i 1,j E { Si,j 1 I W i,j 1 E Now, the matrix S can be written as S i,j = max S i 1,j 1 + s(x i,y j ) V i,j W i,j
21 Local Pairwise Alignment As mentioned before, sometimes local alignment is more appropriate (e.g., aligning two proteins that have just one domain in common) The algorithmic differences between the algorithm for local alignment (Smith-Waterman algorithm) and the one for global alignment: Whenever the score of the optimal sub-alignment is less than zero, it is rejected (the matrix element is set to 0) Traceback starts from the highest-scoring matrix element
22 Local Pairwise Alignment S i,j = max S i 1,j 1 + s(x i,y j ) (S i ngap1,j + g(n gap1 )) 1 ngap1 i (S i,j ngap2 + g(n gap2 )) 1 ngap2 j 0
23 Local Pairwise Alignment E=-8
24 Local Pairwise Alignment E=-4
25 Linear Space Alignment Is there a linear-space algorithm for the problem? If only the maximal score is needed, the problem is simple But even if the alignment itself is needed, there is a linear-space algorithm (originally due to Hirschberg 1975, and introduced into computational biology by Myers and Miller 1988)
26 Linear Space Alignment Main observation S i,j = max 0 k n {S i 2,k + Sr i 2,n k} S r i,j score of the best alignment of last i residues of x with last j residues of y
27 Linear Space Alignment Compute and save row m/2 Compute and save row m/2 Find k* that satisfies Recurse S m,n S r m,n S m 2,k + S r m 2,n k = S m,n
Pairwise Sequence Alignment: Dynamic Programming Algorithms COMP 571 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University
 1 Pairwise Sequence Alignment: Dynamic Programming Algorithms COMP 571 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University DP Algorithms for Pairwise Alignment 2 The number of all possible pairwise alignments (if gaps are allowed)
1 Pairwise Sequence Alignment: Dynamic Programming Algorithms COMP 571 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University DP Algorithms for Pairwise Alignment 2 The number of all possible pairwise alignments (if gaps are allowed)
Lecture 10. Sequence alignments
 Lecture 10 Sequence alignments Alignment algorithms: Overview Given a scoring system, we need to have an algorithm for finding an optimal alignment for a pair of sequences. We want to maximize the score
Lecture 10 Sequence alignments Alignment algorithms: Overview Given a scoring system, we need to have an algorithm for finding an optimal alignment for a pair of sequences. We want to maximize the score
An Analysis of Pairwise Sequence Alignment Algorithm Complexities: Needleman-Wunsch, Smith-Waterman, FASTA, BLAST and Gapped BLAST
 An Analysis of Pairwise Sequence Alignment Algorithm Complexities: Needleman-Wunsch, Smith-Waterman, FASTA, BLAST and Gapped BLAST Alexander Chan 5075504 Biochemistry 218 Final Project An Analysis of Pairwise
An Analysis of Pairwise Sequence Alignment Algorithm Complexities: Needleman-Wunsch, Smith-Waterman, FASTA, BLAST and Gapped BLAST Alexander Chan 5075504 Biochemistry 218 Final Project An Analysis of Pairwise
Sequence Alignment. part 2
 Sequence Alignment part 2 Dynamic programming with more realistic scoring scheme Using the same initial sequences, we ll look at a dynamic programming example with a scoring scheme that selects for matches
Sequence Alignment part 2 Dynamic programming with more realistic scoring scheme Using the same initial sequences, we ll look at a dynamic programming example with a scoring scheme that selects for matches
Biology 644: Bioinformatics
 Find the best alignment between 2 sequences with lengths n and m, respectively Best alignment is very dependent upon the substitution matrix and gap penalties The Global Alignment Problem tries to find
Find the best alignment between 2 sequences with lengths n and m, respectively Best alignment is very dependent upon the substitution matrix and gap penalties The Global Alignment Problem tries to find
Brief review from last class
 Sequence Alignment Brief review from last class DNA is has direction, we will use only one (5 -> 3 ) and generate the opposite strand as needed. DNA is a 3D object (see lecture 1) but we will model it
Sequence Alignment Brief review from last class DNA is has direction, we will use only one (5 -> 3 ) and generate the opposite strand as needed. DNA is a 3D object (see lecture 1) but we will model it
Mouse, Human, Chimpanzee
 More Alignments 1 Mouse, Human, Chimpanzee Mouse to Human Chimpanzee to Human 2 Mouse v.s. Human Chromosome X of Mouse to Human 3 Local Alignment Given: two sequences S and T Find: substrings of S and
More Alignments 1 Mouse, Human, Chimpanzee Mouse to Human Chimpanzee to Human 2 Mouse v.s. Human Chromosome X of Mouse to Human 3 Local Alignment Given: two sequences S and T Find: substrings of S and
Algorithmic Approaches for Biological Data, Lecture #20
 Algorithmic Approaches for Biological Data, Lecture #20 Katherine St. John City University of New York American Museum of Natural History 20 April 2016 Outline Aligning with Gaps and Substitution Matrices
Algorithmic Approaches for Biological Data, Lecture #20 Katherine St. John City University of New York American Museum of Natural History 20 April 2016 Outline Aligning with Gaps and Substitution Matrices
Sequence Comparison: Dynamic Programming. Genome 373 Genomic Informatics Elhanan Borenstein
 Sequence omparison: Dynamic Programming Genome 373 Genomic Informatics Elhanan Borenstein quick review: hallenges Find the best global alignment of two sequences Find the best global alignment of multiple
Sequence omparison: Dynamic Programming Genome 373 Genomic Informatics Elhanan Borenstein quick review: hallenges Find the best global alignment of two sequences Find the best global alignment of multiple
Computational Genomics and Molecular Biology, Fall
 Computational Genomics and Molecular Biology, Fall 2015 1 Sequence Alignment Dannie Durand Pairwise Sequence Alignment The goal of pairwise sequence alignment is to establish a correspondence between the
Computational Genomics and Molecular Biology, Fall 2015 1 Sequence Alignment Dannie Durand Pairwise Sequence Alignment The goal of pairwise sequence alignment is to establish a correspondence between the
Profiles and Multiple Alignments. COMP 571 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University
 Profiles and Multiple Alignments COMP 571 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University Outline Profiles and sequence logos Profile hidden Markov models Aligning profiles Multiple sequence alignment by gradual sequence
Profiles and Multiple Alignments COMP 571 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University Outline Profiles and sequence logos Profile hidden Markov models Aligning profiles Multiple sequence alignment by gradual sequence
Acceleration of Algorithm of Smith-Waterman Using Recursive Variable Expansion.
 www.ijarcet.org 54 Acceleration of Algorithm of Smith-Waterman Using Recursive Variable Expansion. Hassan Kehinde Bello and Kazeem Alagbe Gbolagade Abstract Biological sequence alignment is becoming popular
www.ijarcet.org 54 Acceleration of Algorithm of Smith-Waterman Using Recursive Variable Expansion. Hassan Kehinde Bello and Kazeem Alagbe Gbolagade Abstract Biological sequence alignment is becoming popular
CISC 889 Bioinformatics (Spring 2003) Multiple Sequence Alignment
 CISC 889 Bioinformatics (Spring 2003) Multiple Sequence Alignment Courtesy of jalview 1 Motivations Collective statistic Protein families Identification and representation of conserved sequence features
CISC 889 Bioinformatics (Spring 2003) Multiple Sequence Alignment Courtesy of jalview 1 Motivations Collective statistic Protein families Identification and representation of conserved sequence features
Lecture 2 Pairwise sequence alignment. Principles Computational Biology Teresa Przytycka, PhD
 Lecture 2 Pairwise sequence alignment. Principles Computational Biology Teresa Przytycka, PhD Assumptions: Biological sequences evolved by evolution. Micro scale changes: For short sequences (e.g. one
Lecture 2 Pairwise sequence alignment. Principles Computational Biology Teresa Przytycka, PhD Assumptions: Biological sequences evolved by evolution. Micro scale changes: For short sequences (e.g. one
Today s Lecture. Edit graph & alignment algorithms. Local vs global Computational complexity of pairwise alignment Multiple sequence alignment
 Today s Lecture Edit graph & alignment algorithms Smith-Waterman algorithm Needleman-Wunsch algorithm Local vs global Computational complexity of pairwise alignment Multiple sequence alignment 1 Sequence
Today s Lecture Edit graph & alignment algorithms Smith-Waterman algorithm Needleman-Wunsch algorithm Local vs global Computational complexity of pairwise alignment Multiple sequence alignment 1 Sequence
Lecture 3: February Local Alignment: The Smith-Waterman Algorithm
 CSCI1820: Sequence Alignment Spring 2017 Lecture 3: February 7 Lecturer: Sorin Istrail Scribe: Pranavan Chanthrakumar Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept. Notes are also adapted from
CSCI1820: Sequence Alignment Spring 2017 Lecture 3: February 7 Lecturer: Sorin Istrail Scribe: Pranavan Chanthrakumar Note: LaTeX template courtesy of UC Berkeley EECS dept. Notes are also adapted from
Programming assignment for the course Sequence Analysis (2006)
 Programming assignment for the course Sequence Analysis (2006) Original text by John W. Romein, adapted by Bart van Houte (bart@cs.vu.nl) Introduction Please note: This assignment is only obligatory for
Programming assignment for the course Sequence Analysis (2006) Original text by John W. Romein, adapted by Bart van Houte (bart@cs.vu.nl) Introduction Please note: This assignment is only obligatory for
Notes on Dynamic-Programming Sequence Alignment
 Notes on Dynamic-Programming Sequence Alignment Introduction. Following its introduction by Needleman and Wunsch (1970), dynamic programming has become the method of choice for rigorous alignment of DNA
Notes on Dynamic-Programming Sequence Alignment Introduction. Following its introduction by Needleman and Wunsch (1970), dynamic programming has become the method of choice for rigorous alignment of DNA
Bioinformatics 1: lecture 4. Followup of lecture 3? Molecular evolution Global, semi-global and local Affine gap penalty
 Bioinformatics 1: lecture 4 Followup of lecture 3? Molecular evolution Global, semi-global and local Affine gap penalty How sequences evolve point mutations (single base changes) deletion (loss of residues
Bioinformatics 1: lecture 4 Followup of lecture 3? Molecular evolution Global, semi-global and local Affine gap penalty How sequences evolve point mutations (single base changes) deletion (loss of residues
Today s Lecture. Multiple sequence alignment. Improved scoring of pairwise alignments. Affine gap penalties Profiles
 Today s Lecture Multiple sequence alignment Improved scoring of pairwise alignments Affine gap penalties Profiles 1 The Edit Graph for a Pair of Sequences G A C G T T G A A T G A C C C A C A T G A C G
Today s Lecture Multiple sequence alignment Improved scoring of pairwise alignments Affine gap penalties Profiles 1 The Edit Graph for a Pair of Sequences G A C G T T G A A T G A C C C A C A T G A C G
Local Alignment & Gap Penalties CMSC 423
 Local Alignment & ap Penalties CMSC 423 lobal, Semi-global, Local Alignments Last time, we saw a dynamic programming algorithm for global alignment: both strings s and t must be completely matched: s t
Local Alignment & ap Penalties CMSC 423 lobal, Semi-global, Local Alignments Last time, we saw a dynamic programming algorithm for global alignment: both strings s and t must be completely matched: s t
Sequence analysis Pairwise sequence alignment
 UMF11 Introduction to bioinformatics, 25 Sequence analysis Pairwise sequence alignment 1. Sequence alignment Lecturer: Marina lexandersson 12 September, 25 here are two types of sequence alignments, global
UMF11 Introduction to bioinformatics, 25 Sequence analysis Pairwise sequence alignment 1. Sequence alignment Lecturer: Marina lexandersson 12 September, 25 here are two types of sequence alignments, global
Sequence alignment is an essential concept for bioinformatics, as most of our data analysis and interpretation techniques make use of it.
 Sequence Alignments Overview Sequence alignment is an essential concept for bioinformatics, as most of our data analysis and interpretation techniques make use of it. Sequence alignment means arranging
Sequence Alignments Overview Sequence alignment is an essential concept for bioinformatics, as most of our data analysis and interpretation techniques make use of it. Sequence alignment means arranging
Sequence comparison: Local alignment
 Sequence comparison: Local alignment Genome 559: Introuction to Statistical an Computational Genomics Prof. James H. Thomas http://faculty.washington.eu/jht/gs559_217/ Review global alignment en traceback
Sequence comparison: Local alignment Genome 559: Introuction to Statistical an Computational Genomics Prof. James H. Thomas http://faculty.washington.eu/jht/gs559_217/ Review global alignment en traceback
EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics
 EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics Lecture 04: Variations of sequence alignments http://www.pitt.edu/~mcs2/teaching/biocomp/tutorials/global.html Slides adapted from Dr. Shaojie Zhang (University
EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics Lecture 04: Variations of sequence alignments http://www.pitt.edu/~mcs2/teaching/biocomp/tutorials/global.html Slides adapted from Dr. Shaojie Zhang (University
Sequence Alignment. COMPSCI 260 Spring 2016
 Sequence Alignment COMPSCI 260 Spring 2016 Why do we want to compare DNA or protein sequences? Find genes similar to known genes IdenGfy important (funcgonal) sequences by finding conserved regions As
Sequence Alignment COMPSCI 260 Spring 2016 Why do we want to compare DNA or protein sequences? Find genes similar to known genes IdenGfy important (funcgonal) sequences by finding conserved regions As
Computational Molecular Biology
 Computational Molecular Biology Erwin M. Bakker Lecture 2 Materials used from R. Shamir [2] and H.J. Hoogeboom [4]. 1 Molecular Biology Sequences DNA A, T, C, G RNA A, U, C, G Protein A, R, D, N, C E,
Computational Molecular Biology Erwin M. Bakker Lecture 2 Materials used from R. Shamir [2] and H.J. Hoogeboom [4]. 1 Molecular Biology Sequences DNA A, T, C, G RNA A, U, C, G Protein A, R, D, N, C E,
Sequence Analysis '17: lecture 4. Molecular evolution Global, semi-global and local Affine gap penalty
 Sequence Analysis '17: lecture 4 Molecular evolution Global, semi-global and local Affine gap penalty How sequences evolve point mutations (single base changes) deletion (loss of residues within the sequence)
Sequence Analysis '17: lecture 4 Molecular evolution Global, semi-global and local Affine gap penalty How sequences evolve point mutations (single base changes) deletion (loss of residues within the sequence)
Lecture Overview. Sequence search & alignment. Searching sequence databases. Sequence Alignment & Search. Goals: Motivations:
 Lecture Overview Sequence Alignment & Search Karin Verspoor, Ph.D. Faculty, Computational Bioscience Program University of Colorado School of Medicine With credit and thanks to Larry Hunter for creating
Lecture Overview Sequence Alignment & Search Karin Verspoor, Ph.D. Faculty, Computational Bioscience Program University of Colorado School of Medicine With credit and thanks to Larry Hunter for creating
Sequence Alignment & Search
 Sequence Alignment & Search Karin Verspoor, Ph.D. Faculty, Computational Bioscience Program University of Colorado School of Medicine With credit and thanks to Larry Hunter for creating the first version
Sequence Alignment & Search Karin Verspoor, Ph.D. Faculty, Computational Bioscience Program University of Colorado School of Medicine With credit and thanks to Larry Hunter for creating the first version
Special course in Computer Science: Advanced Text Algorithms
 Special course in Computer Science: Advanced Text Algorithms Lecture 6: Alignments Elena Czeizler and Ion Petre Department of IT, Abo Akademi Computational Biomodelling Laboratory http://www.users.abo.fi/ipetre/textalg
Special course in Computer Science: Advanced Text Algorithms Lecture 6: Alignments Elena Czeizler and Ion Petre Department of IT, Abo Akademi Computational Biomodelling Laboratory http://www.users.abo.fi/ipetre/textalg
Dynamic Programming User Manual v1.0 Anton E. Weisstein, Truman State University Aug. 19, 2014
 Dynamic Programming User Manual v1.0 Anton E. Weisstein, Truman State University Aug. 19, 2014 Dynamic programming is a group of mathematical methods used to sequentially split a complicated problem into
Dynamic Programming User Manual v1.0 Anton E. Weisstein, Truman State University Aug. 19, 2014 Dynamic programming is a group of mathematical methods used to sequentially split a complicated problem into
Computational Biology Lecture 6: Affine gap penalty function, multiple sequence alignment Saad Mneimneh
 Computational Biology Lecture 6: Affine gap penalty function, multiple sequence alignment Saad Mneimneh We saw earlier how we can use a concave gap penalty function γ, i.e. one that satisfies γ(x+1) γ(x)
Computational Biology Lecture 6: Affine gap penalty function, multiple sequence alignment Saad Mneimneh We saw earlier how we can use a concave gap penalty function γ, i.e. one that satisfies γ(x+1) γ(x)
Heuristic methods for pairwise alignment:
 Bi03c_1 Unit 03c: Heuristic methods for pairwise alignment: k-tuple-methods k-tuple-methods for alignment of pairs of sequences Bi03c_2 dynamic programming is too slow for large databases Use heuristic
Bi03c_1 Unit 03c: Heuristic methods for pairwise alignment: k-tuple-methods k-tuple-methods for alignment of pairs of sequences Bi03c_2 dynamic programming is too slow for large databases Use heuristic
Principles of Bioinformatics. BIO540/STA569/CSI660 Fall 2010
 Principles of Bioinformatics BIO540/STA569/CSI660 Fall 2010 Lecture 11 Multiple Sequence Alignment I Administrivia Administrivia The midterm examination will be Monday, October 18 th, in class. Closed
Principles of Bioinformatics BIO540/STA569/CSI660 Fall 2010 Lecture 11 Multiple Sequence Alignment I Administrivia Administrivia The midterm examination will be Monday, October 18 th, in class. Closed
Sequence alignment algorithms
 Sequence alignment algorithms Bas E. Dutilh Systems Biology: Bioinformatic Data Analysis Utrecht University, February 23 rd 27 After this lecture, you can decide when to use local and global sequence alignments
Sequence alignment algorithms Bas E. Dutilh Systems Biology: Bioinformatic Data Analysis Utrecht University, February 23 rd 27 After this lecture, you can decide when to use local and global sequence alignments
BLAST MCDB 187. Friday, February 8, 13
 BLAST MCDB 187 BLAST Basic Local Alignment Sequence Tool Uses shortcut to compute alignments of a sequence against a database very quickly Typically takes about a minute to align a sequence against a database
BLAST MCDB 187 BLAST Basic Local Alignment Sequence Tool Uses shortcut to compute alignments of a sequence against a database very quickly Typically takes about a minute to align a sequence against a database
Bioinformatics for Biologists
 Bioinformatics for Biologists Sequence Analysis: Part I. Pairwise alignment and database searching Fran Lewitter, Ph.D. Director Bioinformatics & Research Computing Whitehead Institute Topics to Cover
Bioinformatics for Biologists Sequence Analysis: Part I. Pairwise alignment and database searching Fran Lewitter, Ph.D. Director Bioinformatics & Research Computing Whitehead Institute Topics to Cover
Bioinformatics explained: Smith-Waterman
 Bioinformatics Explained Bioinformatics explained: Smith-Waterman May 1, 2007 CLC bio Gustav Wieds Vej 10 8000 Aarhus C Denmark Telephone: +45 70 22 55 09 Fax: +45 70 22 55 19 www.clcbio.com info@clcbio.com
Bioinformatics Explained Bioinformatics explained: Smith-Waterman May 1, 2007 CLC bio Gustav Wieds Vej 10 8000 Aarhus C Denmark Telephone: +45 70 22 55 09 Fax: +45 70 22 55 19 www.clcbio.com info@clcbio.com
Computational Biology Lecture 4: Overlap detection, Local Alignment, Space Efficient Needleman-Wunsch Saad Mneimneh
 Computational Biology Lecture 4: Overlap detection, Local Alignment, Space Efficient Needleman-Wunsch Saad Mneimneh Overlap detection: Semi-Global Alignment An overlap of two sequences is considered an
Computational Biology Lecture 4: Overlap detection, Local Alignment, Space Efficient Needleman-Wunsch Saad Mneimneh Overlap detection: Semi-Global Alignment An overlap of two sequences is considered an
Chapter 6. Multiple sequence alignment (week 10)
 Course organization Introduction ( Week 1,2) Part I: Algorithms for Sequence Analysis (Week 1-11) Chapter 1-3, Models and theories» Probability theory and Statistics (Week 3)» Algorithm complexity analysis
Course organization Introduction ( Week 1,2) Part I: Algorithms for Sequence Analysis (Week 1-11) Chapter 1-3, Models and theories» Probability theory and Statistics (Week 3)» Algorithm complexity analysis
Reconstructing long sequences from overlapping sequence fragment. Searching databases for related sequences and subsequences
 SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT ALGORITHMS 1 Why compare sequences? Reconstructing long sequences from overlapping sequence fragment Searching databases for related sequences and subsequences Storing, retrieving and
SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT ALGORITHMS 1 Why compare sequences? Reconstructing long sequences from overlapping sequence fragment Searching databases for related sequences and subsequences Storing, retrieving and
Acceleration of the Smith-Waterman algorithm for DNA sequence alignment using an FPGA platform
 Acceleration of the Smith-Waterman algorithm for DNA sequence alignment using an FPGA platform Barry Strengholt Matthijs Brobbel Delft University of Technology Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Mathematics
Acceleration of the Smith-Waterman algorithm for DNA sequence alignment using an FPGA platform Barry Strengholt Matthijs Brobbel Delft University of Technology Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Mathematics
24 Grundlagen der Bioinformatik, SS 10, D. Huson, April 26, This lecture is based on the following papers, which are all recommended reading:
 24 Grundlagen der Bioinformatik, SS 10, D. Huson, April 26, 2010 3 BLAST and FASTA This lecture is based on the following papers, which are all recommended reading: D.J. Lipman and W.R. Pearson, Rapid
24 Grundlagen der Bioinformatik, SS 10, D. Huson, April 26, 2010 3 BLAST and FASTA This lecture is based on the following papers, which are all recommended reading: D.J. Lipman and W.R. Pearson, Rapid
Sequence Alignment AGGCTATCACCTGACCTCCAGGCCGATGCCC TAGCTATCACGACCGCGGTCGATTTGCCCGAC -AGGCTATCACCTGACCTCCAGGCCGA--TGCCC--
 Sequence Alignment Sequence Alignment AGGCTATCACCTGACCTCCAGGCCGATGCCC TAGCTATCACGACCGCGGTCGATTTGCCCGAC -AGGCTATCACCTGACCTCCAGGCCGA--TGCCC-- TAG-CTATCAC--GACCGC--GGTCGATTTGCCCGAC Distance from sequences
Sequence Alignment Sequence Alignment AGGCTATCACCTGACCTCCAGGCCGATGCCC TAGCTATCACGACCGCGGTCGATTTGCCCGAC -AGGCTATCACCTGACCTCCAGGCCGA--TGCCC-- TAG-CTATCAC--GACCGC--GGTCGATTTGCCCGAC Distance from sequences
Lecture 9: Core String Edits and Alignments
 Biosequence Algorithms, Spring 2005 Lecture 9: Core String Edits and Alignments Pekka Kilpeläinen University of Kuopio Department of Computer Science BSA Lecture 9: String Edits and Alignments p.1/30 III:
Biosequence Algorithms, Spring 2005 Lecture 9: Core String Edits and Alignments Pekka Kilpeläinen University of Kuopio Department of Computer Science BSA Lecture 9: String Edits and Alignments p.1/30 III:
1 Computing alignments in only linear space
 1 Computing alignments in only linear space One of the defects of dynamic programming for all the problems we have discussed is that the dynamic programming tables use Θ(nm) space when the input strings
1 Computing alignments in only linear space One of the defects of dynamic programming for all the problems we have discussed is that the dynamic programming tables use Θ(nm) space when the input strings
EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics
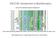 EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics Lecture 06: Multiple Sequence Alignment https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/79/rplp0_90_clustalw_aln.gif/575px-rplp0_90_clustalw_aln.gif Slides
EECS730: Introduction to Bioinformatics Lecture 06: Multiple Sequence Alignment https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/79/rplp0_90_clustalw_aln.gif/575px-rplp0_90_clustalw_aln.gif Slides
12 Dynamic Programming (2) Matrix-chain Multiplication Segmented Least Squares
 12 Dynamic Programming (2) Matrix-chain Multiplication Segmented Least Squares Optimal substructure Dynamic programming is typically applied to optimization problems. An optimal solution to the original
12 Dynamic Programming (2) Matrix-chain Multiplication Segmented Least Squares Optimal substructure Dynamic programming is typically applied to optimization problems. An optimal solution to the original
A CAM(Content Addressable Memory)-based architecture for molecular sequence matching
 A CAM(Content Addressable Memory)-based architecture for molecular sequence matching P.K. Lala 1 and J.P. Parkerson 2 1 Department Electrical Engineering, Texas A&M University, Texarkana, Texas, USA 2
A CAM(Content Addressable Memory)-based architecture for molecular sequence matching P.K. Lala 1 and J.P. Parkerson 2 1 Department Electrical Engineering, Texas A&M University, Texarkana, Texas, USA 2
Chapter 8 Multiple sequence alignment. Chaochun Wei Spring 2018
 1896 1920 1987 2006 Chapter 8 Multiple sequence alignment Chaochun Wei Spring 2018 Contents 1. Reading materials 2. Multiple sequence alignment basic algorithms and tools how to improve multiple alignment
1896 1920 1987 2006 Chapter 8 Multiple sequence alignment Chaochun Wei Spring 2018 Contents 1. Reading materials 2. Multiple sequence alignment basic algorithms and tools how to improve multiple alignment
Computational Molecular Biology
 Computational Molecular Biology Erwin M. Bakker Lecture 3, mainly from material by R. Shamir [2] and H.J. Hoogeboom [4]. 1 Pairwise Sequence Alignment Biological Motivation Algorithmic Aspect Recursive
Computational Molecular Biology Erwin M. Bakker Lecture 3, mainly from material by R. Shamir [2] and H.J. Hoogeboom [4]. 1 Pairwise Sequence Alignment Biological Motivation Algorithmic Aspect Recursive
TCCAGGTG-GAT TGCAAGTGCG-T. Local Sequence Alignment & Heuristic Local Aligners. Review: Probabilistic Interpretation. Chance or true homology?
 Local Sequence Alignment & Heuristic Local Aligners Lectures 18 Nov 28, 2011 CSE 527 Computational Biology, Fall 2011 Instructor: Su-In Lee TA: Christopher Miles Monday & Wednesday 12:00-1:20 Johnson Hall
Local Sequence Alignment & Heuristic Local Aligners Lectures 18 Nov 28, 2011 CSE 527 Computational Biology, Fall 2011 Instructor: Su-In Lee TA: Christopher Miles Monday & Wednesday 12:00-1:20 Johnson Hall
Cache and Energy Efficient Alignment of Very Long Sequences
 Cache and Energy Efficient Alignment of Very Long Sequences Chunchun Zhao Department of Computer and Information Science and Engineering University of Florida Email: czhao@cise.ufl.edu Sartaj Sahni Department
Cache and Energy Efficient Alignment of Very Long Sequences Chunchun Zhao Department of Computer and Information Science and Engineering University of Florida Email: czhao@cise.ufl.edu Sartaj Sahni Department
Alignment of Long Sequences
 Alignment of Long Sequences BMI/CS 776 www.biostat.wisc.edu/bmi776/ Spring 2009 Mark Craven craven@biostat.wisc.edu Pairwise Whole Genome Alignment: Task Definition Given a pair of genomes (or other large-scale
Alignment of Long Sequences BMI/CS 776 www.biostat.wisc.edu/bmi776/ Spring 2009 Mark Craven craven@biostat.wisc.edu Pairwise Whole Genome Alignment: Task Definition Given a pair of genomes (or other large-scale
Compares a sequence of protein to another sequence or database of a protein, or a sequence of DNA to another sequence or library of DNA.
 Compares a sequence of protein to another sequence or database of a protein, or a sequence of DNA to another sequence or library of DNA. Fasta is used to compare a protein or DNA sequence to all of the
Compares a sequence of protein to another sequence or database of a protein, or a sequence of DNA to another sequence or library of DNA. Fasta is used to compare a protein or DNA sequence to all of the
Outline. Sequence Alignment. Types of Sequence Alignment. Genomics & Computational Biology. Section 2. How Computers Store Information
 enomics & omputational Biology Section Lan Zhang Sep. th, Outline How omputers Store Information Sequence lignment Dot Matrix nalysis Dynamic programming lobal: NeedlemanWunsch lgorithm Local: SmithWaterman
enomics & omputational Biology Section Lan Zhang Sep. th, Outline How omputers Store Information Sequence lignment Dot Matrix nalysis Dynamic programming lobal: NeedlemanWunsch lgorithm Local: SmithWaterman
In this section we describe how to extend the match refinement to the multiple case and then use T-Coffee to heuristically compute a multiple trace.
 5 Multiple Match Refinement and T-Coffee In this section we describe how to extend the match refinement to the multiple case and then use T-Coffee to heuristically compute a multiple trace. This exposition
5 Multiple Match Refinement and T-Coffee In this section we describe how to extend the match refinement to the multiple case and then use T-Coffee to heuristically compute a multiple trace. This exposition
Multiple Sequence Alignment. Mark Whitsitt - NCSA
 Multiple Sequence Alignment Mark Whitsitt - NCSA What is a Multiple Sequence Alignment (MA)? GMHGTVYANYAVDSSDLLLAFGVRFDDRVTGKLEAFASRAKIVHIDIDSAEIGKNKQPHV GMHGTVYANYAVEHSDLLLAFGVRFDDRVTGKLEAFASRAKIVHIDIDSAEIGKNKTPHV
Multiple Sequence Alignment Mark Whitsitt - NCSA What is a Multiple Sequence Alignment (MA)? GMHGTVYANYAVDSSDLLLAFGVRFDDRVTGKLEAFASRAKIVHIDIDSAEIGKNKQPHV GMHGTVYANYAVEHSDLLLAFGVRFDDRVTGKLEAFASRAKIVHIDIDSAEIGKNKTPHV
CS 284A: Algorithms for Computational Biology Notes on Lecture: BLAST. The statistics of alignment scores.
 CS 284A: Algorithms for Computational Biology Notes on Lecture: BLAST. The statistics of alignment scores. prepared by Oleksii Kuchaiev, based on presentation by Xiaohui Xie on February 20th. 1 Introduction
CS 284A: Algorithms for Computational Biology Notes on Lecture: BLAST. The statistics of alignment scores. prepared by Oleksii Kuchaiev, based on presentation by Xiaohui Xie on February 20th. 1 Introduction
CS273: Algorithms for Structure Handout # 4 and Motion in Biology Stanford University Thursday, 8 April 2004
 CS273: Algorithms for Structure Handout # 4 and Motion in Biology Stanford University Thursday, 8 April 2004 Lecture #4: 8 April 2004 Topics: Sequence Similarity Scribe: Sonil Mukherjee 1 Introduction
CS273: Algorithms for Structure Handout # 4 and Motion in Biology Stanford University Thursday, 8 April 2004 Lecture #4: 8 April 2004 Topics: Sequence Similarity Scribe: Sonil Mukherjee 1 Introduction
COS 551: Introduction to Computational Molecular Biology Lecture: Oct 17, 2000 Lecturer: Mona Singh Scribe: Jacob Brenner 1. Database Searching
 COS 551: Introduction to Computational Molecular Biology Lecture: Oct 17, 2000 Lecturer: Mona Singh Scribe: Jacob Brenner 1 Database Searching In database search, we typically have a large sequence database
COS 551: Introduction to Computational Molecular Biology Lecture: Oct 17, 2000 Lecturer: Mona Singh Scribe: Jacob Brenner 1 Database Searching In database search, we typically have a large sequence database
Comparative Analysis of Protein Alignment Algorithms in Parallel environment using CUDA
 Comparative Analysis of Protein Alignment Algorithms in Parallel environment using BLAST versus Smith-Waterman Shadman Fahim shadmanbracu09@gmail.com Shehabul Hossain rudrozzal@gmail.com Gulshan Jubaed
Comparative Analysis of Protein Alignment Algorithms in Parallel environment using BLAST versus Smith-Waterman Shadman Fahim shadmanbracu09@gmail.com Shehabul Hossain rudrozzal@gmail.com Gulshan Jubaed
Pairwise alignment II
 Pairwise alignment II Agenda - Previous Lesson: Minhala + Introduction - Review Dynamic Programming - Pariwise Alignment Biological Motivation Today: - Quick Review: Sequence Alignment (Global, Local,
Pairwise alignment II Agenda - Previous Lesson: Minhala + Introduction - Review Dynamic Programming - Pariwise Alignment Biological Motivation Today: - Quick Review: Sequence Alignment (Global, Local,
Stephen Scott.
 1 / 33 sscott@cse.unl.edu 2 / 33 Start with a set of sequences In each column, residues are homolgous Residues occupy similar positions in 3D structure Residues diverge from a common ancestral residue
1 / 33 sscott@cse.unl.edu 2 / 33 Start with a set of sequences In each column, residues are homolgous Residues occupy similar positions in 3D structure Residues diverge from a common ancestral residue
Distributed Protein Sequence Alignment
 Distributed Protein Sequence Alignment ABSTRACT J. Michael Meehan meehan@wwu.edu James Hearne hearne@wwu.edu Given the explosive growth of biological sequence databases and the computational complexity
Distributed Protein Sequence Alignment ABSTRACT J. Michael Meehan meehan@wwu.edu James Hearne hearne@wwu.edu Given the explosive growth of biological sequence databases and the computational complexity
Biochemistry 324 Bioinformatics. Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA)
 Biochemistry 324 Bioinformatics Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA) Big- Οh notation Greek omicron symbol Ο The Big-Oh notation indicates the complexity of an algorithm in terms of execution speed and storage
Biochemistry 324 Bioinformatics Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA) Big- Οh notation Greek omicron symbol Ο The Big-Oh notation indicates the complexity of an algorithm in terms of execution speed and storage
OPEN MP-BASED PARALLEL AND SCALABLE GENETIC SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT
 OPEN MP-BASED PARALLEL AND SCALABLE GENETIC SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT Asif Ali Khan*, Laiq Hassan*, Salim Ullah* ABSTRACT: In bioinformatics, sequence alignment is a common and insistent task. Biologists align
OPEN MP-BASED PARALLEL AND SCALABLE GENETIC SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT Asif Ali Khan*, Laiq Hassan*, Salim Ullah* ABSTRACT: In bioinformatics, sequence alignment is a common and insistent task. Biologists align
GLOBEX Bioinformatics (Summer 2015) Multiple Sequence Alignment
 GLOBEX Bioinformatics (Summer 2015) Multiple Sequence Alignment Scoring Dynamic Programming algorithms Heuristic algorithms CLUSTAL W Courtesy of jalview Motivations Collective (or aggregate) statistic
GLOBEX Bioinformatics (Summer 2015) Multiple Sequence Alignment Scoring Dynamic Programming algorithms Heuristic algorithms CLUSTAL W Courtesy of jalview Motivations Collective (or aggregate) statistic
Keywords -Bioinformatics, sequence alignment, Smith- waterman (SW) algorithm, GPU, CUDA
 Volume 5, Issue 5, May 2015 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Accelerating Smith-Waterman
Volume 5, Issue 5, May 2015 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Accelerating Smith-Waterman
Gaps ATTACGTACTCCATG ATTACGT CATG. In an edit script we need 4 edit operations for the gap of length 4.
 Gaps ATTACGTACTCCATG ATTACGT CATG In an edit script we need 4 edit operations for the gap of length 4. In maximal score alignments we treat the dash " " like any other character, hence we charge the s(x,
Gaps ATTACGTACTCCATG ATTACGT CATG In an edit script we need 4 edit operations for the gap of length 4. In maximal score alignments we treat the dash " " like any other character, hence we charge the s(x,
DNA Alignment With Affine Gap Penalties
 DNA Alignment With Affine Gap Penalties Laurel Schuster Why Use Affine Gap Penalties? When aligning two DNA sequences, one goal may be to infer the mutations that made them different. Though it s impossible
DNA Alignment With Affine Gap Penalties Laurel Schuster Why Use Affine Gap Penalties? When aligning two DNA sequences, one goal may be to infer the mutations that made them different. Though it s impossible
Biological Sequence Matching Using Fuzzy Logic
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 2, Issue 7, July-2011 1 Biological Sequence Matching Using Fuzzy Logic Nivit Gill, Shailendra Singh Abstract: Sequence alignment is the
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 2, Issue 7, July-2011 1 Biological Sequence Matching Using Fuzzy Logic Nivit Gill, Shailendra Singh Abstract: Sequence alignment is the
Bioinformatics explained: BLAST. March 8, 2007
 Bioinformatics Explained Bioinformatics explained: BLAST March 8, 2007 CLC bio Gustav Wieds Vej 10 8000 Aarhus C Denmark Telephone: +45 70 22 55 09 Fax: +45 70 22 55 19 www.clcbio.com info@clcbio.com Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics Explained Bioinformatics explained: BLAST March 8, 2007 CLC bio Gustav Wieds Vej 10 8000 Aarhus C Denmark Telephone: +45 70 22 55 09 Fax: +45 70 22 55 19 www.clcbio.com info@clcbio.com Bioinformatics
Alignment Based Similarity distance Measure for Better Web Sessions Clustering
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Computer Science 5 (2011) 450 457 The 2 nd International Conference on Ambient Systems, Networks and Technologies (ANT) Alignment Based Similarity distance
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Computer Science 5 (2011) 450 457 The 2 nd International Conference on Ambient Systems, Networks and Technologies (ANT) Alignment Based Similarity distance
Scoring and heuristic methods for sequence alignment CG 17
 Scoring and heuristic methods for sequence alignment CG 17 Amino Acid Substitution Matrices Used to score alignments. Reflect evolution of sequences. Unitary Matrix: M ij = 1 i=j { 0 o/w Genetic Code Matrix:
Scoring and heuristic methods for sequence alignment CG 17 Amino Acid Substitution Matrices Used to score alignments. Reflect evolution of sequences. Unitary Matrix: M ij = 1 i=j { 0 o/w Genetic Code Matrix:
Similarity searches in biological sequence databases
 Similarity searches in biological sequence databases Volker Flegel september 2004 Page 1 Outline Keyword search in databases General concept Examples SRS Entrez Expasy Similarity searches in databases
Similarity searches in biological sequence databases Volker Flegel september 2004 Page 1 Outline Keyword search in databases General concept Examples SRS Entrez Expasy Similarity searches in databases
A Study On Pair-Wise Local Alignment Of Protein Sequence For Identifying The Structural Similarity
 A Study On Pair-Wise Local Alignment Of Protein Sequence For Identifying The Structural Similarity G. Pratyusha, Department of Computer Science & Engineering, V.R.Siddhartha Engineering College(Autonomous)
A Study On Pair-Wise Local Alignment Of Protein Sequence For Identifying The Structural Similarity G. Pratyusha, Department of Computer Science & Engineering, V.R.Siddhartha Engineering College(Autonomous)
EECS 4425: Introductory Computational Bioinformatics Fall Suprakash Datta
 EECS 4425: Introductory Computational Bioinformatics Fall 2018 Suprakash Datta datta [at] cse.yorku.ca Office: CSEB 3043 Phone: 416-736-2100 ext 77875 Course page: http://www.cse.yorku.ca/course/4425 Many
EECS 4425: Introductory Computational Bioinformatics Fall 2018 Suprakash Datta datta [at] cse.yorku.ca Office: CSEB 3043 Phone: 416-736-2100 ext 77875 Course page: http://www.cse.yorku.ca/course/4425 Many
Biologically significant sequence alignments using Boltzmann probabilities
 Biologically significant sequence alignments using Boltzmann probabilities P Clote Department of Biology, Boston College Gasson Hall 16, Chestnut Hill MA 0267 clote@bcedu Abstract In this paper, we give
Biologically significant sequence alignments using Boltzmann probabilities P Clote Department of Biology, Boston College Gasson Hall 16, Chestnut Hill MA 0267 clote@bcedu Abstract In this paper, we give
PROTEIN MULTIPLE ALIGNMENT MOTIVATION: BACKGROUND: Marina Sirota
 Marina Sirota MOTIVATION: PROTEIN MULTIPLE ALIGNMENT To study evolution on the genetic level across a wide range of organisms, biologists need accurate tools for multiple sequence alignment of protein
Marina Sirota MOTIVATION: PROTEIN MULTIPLE ALIGNMENT To study evolution on the genetic level across a wide range of organisms, biologists need accurate tools for multiple sequence alignment of protein
Software Implementation of Smith-Waterman Algorithm in FPGA
 Software Implementation of Smith-Waterman lgorithm in FP NUR FRH IN SLIMN, NUR DLILH HMD SBRI, SYED BDUL MULIB L JUNID, ZULKIFLI BD MJID, BDUL KRIMI HLIM Faculty of Electrical Engineering Universiti eknologi
Software Implementation of Smith-Waterman lgorithm in FP NUR FRH IN SLIMN, NUR DLILH HMD SBRI, SYED BDUL MULIB L JUNID, ZULKIFLI BD MJID, BDUL KRIMI HLIM Faculty of Electrical Engineering Universiti eknologi
The implementation of bit-parallelism for DNA sequence alignment
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PPER OPE CCESS The implementation of bit-parallelism for D sequence alignment To cite this article: Setyorini et al 27 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 835 24 View the article
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PPER OPE CCESS The implementation of bit-parallelism for D sequence alignment To cite this article: Setyorini et al 27 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 835 24 View the article
Using Blocks in Pairwise Sequence Alignment
 Using Blocks in Pairwise Sequence Alignment Joe Meehan December 6, 2002 Biochemistry 218 Computational Molecular Biology Introduction Since the introduction of dynamic programming techniques in the early
Using Blocks in Pairwise Sequence Alignment Joe Meehan December 6, 2002 Biochemistry 218 Computational Molecular Biology Introduction Since the introduction of dynamic programming techniques in the early
FASTA. Besides that, FASTA package provides SSEARCH, an implementation of the optimal Smith- Waterman algorithm.
 FASTA INTRODUCTION Definition (by David J. Lipman and William R. Pearson in 1985) - Compares a sequence of protein to another sequence or database of a protein, or a sequence of DNA to another sequence
FASTA INTRODUCTION Definition (by David J. Lipman and William R. Pearson in 1985) - Compares a sequence of protein to another sequence or database of a protein, or a sequence of DNA to another sequence
A New Approach For Tree Alignment Based on Local Re-Optimization
 A New Approach For Tree Alignment Based on Local Re-Optimization Feng Yue and Jijun Tang Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of South Carolina Columbia, SC 29063, USA yuef, jtang
A New Approach For Tree Alignment Based on Local Re-Optimization Feng Yue and Jijun Tang Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of South Carolina Columbia, SC 29063, USA yuef, jtang
Global Alignment Scoring Matrices Local Alignment Alignment with Affine Gap Penalties
 Global Alignment Scoring Matrices Local Alignment Alignment with Affine Gap Penalties From LCS to Alignment: Change the Scoring The Longest Common Subsequence (LCS) problem the simplest form of sequence
Global Alignment Scoring Matrices Local Alignment Alignment with Affine Gap Penalties From LCS to Alignment: Change the Scoring The Longest Common Subsequence (LCS) problem the simplest form of sequence
GPU Accelerated Smith-Waterman
 GPU Accelerated Smith-Waterman Yang Liu 1,WayneHuang 1,2, John Johnson 1, and Sheila Vaidya 1 1 Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory 2 DOE Joint Genome Institute, UCRL-CONF-218814 {liu24, whuang, jjohnson,
GPU Accelerated Smith-Waterman Yang Liu 1,WayneHuang 1,2, John Johnson 1, and Sheila Vaidya 1 1 Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory 2 DOE Joint Genome Institute, UCRL-CONF-218814 {liu24, whuang, jjohnson,
Central Issues in Biological Sequence Comparison
 Central Issues in Biological Sequence Comparison Definitions: What is one trying to find or optimize? Algorithms: Can one find the proposed object optimally or in reasonable time optimize? Statistics:
Central Issues in Biological Sequence Comparison Definitions: What is one trying to find or optimize? Algorithms: Can one find the proposed object optimally or in reasonable time optimize? Statistics:
Algorithms IV. Dynamic Programming. Guoqiang Li. School of Software, Shanghai Jiao Tong University
 Algorithms IV Dynamic Programming Guoqiang Li School of Software, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Dynamic Programming Shortest Paths in Dags, Revisited Shortest Paths in Dags, Revisited The special distinguishing
Algorithms IV Dynamic Programming Guoqiang Li School of Software, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Dynamic Programming Shortest Paths in Dags, Revisited Shortest Paths in Dags, Revisited The special distinguishing
Dynamic Programming Part I: Examples. Bioinfo I (Institut Pasteur de Montevideo) Dynamic Programming -class4- July 25th, / 77
 Dynamic Programming Part I: Examples Bioinfo I (Institut Pasteur de Montevideo) Dynamic Programming -class4- July 25th, 2011 1 / 77 Dynamic Programming Recall: the Change Problem Other problems: Manhattan
Dynamic Programming Part I: Examples Bioinfo I (Institut Pasteur de Montevideo) Dynamic Programming -class4- July 25th, 2011 1 / 77 Dynamic Programming Recall: the Change Problem Other problems: Manhattan
BLAST, Profile, and PSI-BLAST
 BLAST, Profile, and PSI-BLAST Jianlin Cheng, PhD School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Central Florida 26 Free for academic use Copyright @ Jianlin Cheng & original sources
BLAST, Profile, and PSI-BLAST Jianlin Cheng, PhD School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Central Florida 26 Free for academic use Copyright @ Jianlin Cheng & original sources
BLAST & Genome assembly
 BLAST & Genome assembly Solon P. Pissis Tomáš Flouri Heidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies May 15, 2014 1 BLAST What is BLAST? The algorithm 2 Genome assembly De novo assembly Mapping assembly 3
BLAST & Genome assembly Solon P. Pissis Tomáš Flouri Heidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies May 15, 2014 1 BLAST What is BLAST? The algorithm 2 Genome assembly De novo assembly Mapping assembly 3
Dynamic Programming part 2
 Dynamic Programming part 2 Week 7 Objectives More dynamic programming examples - Matrix Multiplication Parenthesis - Longest Common Subsequence Subproblem Optimal structure Defining the dynamic recurrence
Dynamic Programming part 2 Week 7 Objectives More dynamic programming examples - Matrix Multiplication Parenthesis - Longest Common Subsequence Subproblem Optimal structure Defining the dynamic recurrence
Alignment ABC. Most slides are modified from Serafim s lectures
 Alignment ABC Most slides are modified from Serafim s lectures Complete genomes Evolution Evolution at the DNA level C ACGGTGCAGTCACCA ACGTTGCAGTCCACCA SEQUENCE EDITS REARRANGEMENTS Sequence conservation
Alignment ABC Most slides are modified from Serafim s lectures Complete genomes Evolution Evolution at the DNA level C ACGGTGCAGTCACCA ACGTTGCAGTCCACCA SEQUENCE EDITS REARRANGEMENTS Sequence conservation
CMSC423: Bioinformatic Algorithms, Databases and Tools Lecture 8. Note
 MS: Bioinformatic lgorithms, Databases and ools Lecture 8 Sequence alignment: inexact alignment dynamic programming, gapped alignment Note Lecture 7 suffix trees and suffix arrays will be rescheduled Exact
MS: Bioinformatic lgorithms, Databases and ools Lecture 8 Sequence alignment: inexact alignment dynamic programming, gapped alignment Note Lecture 7 suffix trees and suffix arrays will be rescheduled Exact
.. Fall 2011 CSC 570: Bioinformatics Alexander Dekhtyar..
 .. Fall 2011 CSC 570: Bioinformatics Alexander Dekhtyar.. PAM and BLOSUM Matrices Prepared by: Jason Banich and Chris Hoover Background As DNA sequences change and evolve, certain amino acids are more
.. Fall 2011 CSC 570: Bioinformatics Alexander Dekhtyar.. PAM and BLOSUM Matrices Prepared by: Jason Banich and Chris Hoover Background As DNA sequences change and evolve, certain amino acids are more
Multiple sequence alignment. November 20, 2018
 Multiple sequence alignment November 20, 2018 Why do multiple alignment? Gain insight into evolutionary history Can assess time of divergence by looking at the number of mutations needed to change one
Multiple sequence alignment November 20, 2018 Why do multiple alignment? Gain insight into evolutionary history Can assess time of divergence by looking at the number of mutations needed to change one
1. R. Durbin, S. Eddy, A. Krogh und G. Mitchison: Biological sequence analysis, Cambridge, 1998
 7 Multiple Sequence Alignment The exposition was prepared by Clemens GrÃP pl, based on earlier versions by Daniel Huson, Knut Reinert, and Gunnar Klau. It is based on the following sources, which are all
7 Multiple Sequence Alignment The exposition was prepared by Clemens GrÃP pl, based on earlier versions by Daniel Huson, Knut Reinert, and Gunnar Klau. It is based on the following sources, which are all
Fast Sequence Alignment Method Using CUDA-enabled GPU
 Fast Sequence Alignment Method Using CUDA-enabled GPU Yeim-Kuan Chang Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Cheng Kung University Tainan, Taiwan ykchang@mail.ncku.edu.tw De-Yu
Fast Sequence Alignment Method Using CUDA-enabled GPU Yeim-Kuan Chang Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Cheng Kung University Tainan, Taiwan ykchang@mail.ncku.edu.tw De-Yu
