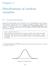
BIOL Gradation of a histogram (a) into the normal curve (b)
|
|
|
- Aileen Boyd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (التوزيع الطبيعي ( Distribution Normal (Gaussian) One of the most important distributions in statistics is a continuous distribution called the normal distribution or Gaussian distribution. Consider the following, if we measured cells or people or plants or biochemical reactions (as absorbance values in a spectrophotometer) etc. we would find a range of variation. If we were to put these measurements into appropriate categories or class intervals and then plot the numbers in each category as a histogram it would look like Figure (a): Fig. Gradation of a histogram (a) into the normal curve (b) As the of observations n used to construct the histogram approaches infinity, and the width of the class intervals goes to zero, and we construct a curve over the histogram, this curve will be a smooth continuous, bell-shaped curve, with no gaps between the histogram and curve (Fig. b). Data of this sort are said to be normally distributed. Most of our measurements (data points) would be close to the mean, and progressively fewer would depart widely from the mean. Normal Curve equation The normal distribution curve is an infinite number of possible curves, all described by the same algebraic expression namely probability density function: ( x µ ) /2 y = e 2π Where y is the height of the curve for a given value x, e is the base of the natural logarithms (approximately ), and π is the well-known constant (about ). The parameters µ and 2 are the mean and the variance, respectively, of the normal random variable. µ x It is obvious that, the mathematical equation for the probability distribution of the continuous normal variable depends upon the two parameters µ and. Once µ and are specified, the normal curve is completely determined. 51
2 Properties of the Normal Distribution 1. It has the appearance of bell-shaped curve extending infinitely in both directions. 2. Unimodal, symmetrical about the mean µ, and its mode occurs at x = µ. 3. The normal curve approaches the horizontal axis as we proceed in either direction away from the mean. 4. The total area under the curve and above the horizontal axis is equal to Whether the mean or standard deviation is large or small, the relative area between any two designated points is always the same. Let s look at three commonly used points along the abscissa. In Figure below (where µ = 100 and = 15), we see the following a % of the area (data) is contained within µ ± 1, b % of the area is contained within µ ± 2, c % of the area is contained within µ ± 3 These rules are commonly known as the Empirical Rule % 95.45% 68.26% Example on the Empirical Rule µ-3 µ-2 µ-1 µ µ+ 1 µ+ 2 µ+ 3 Women participating in a three-day experimental diet regime have been demonstrated to have normally distributed weight loss with mean 600 g and a standard deviation 200 g. a) What percentage of these women will have a weight loss between 400 and 800 g? Since 68.26% of the area (data) is contained within µ ± 1, Thus, the percentage of these women will have a weight loss between 400 and 800 g which equal to 600 ± 200 or µ ± 1 is approximately 68% 6. The normal distribution depends on the values of the parameters µ, the population mean and 2, the population variance. a. Two normal curves, which have the same standard deviation but different means. 52
3 µ 1 µ 2 x µ 1 < µ 2 The two curves are identical in form but are centered at different positions along the horizontal axis. b. Two normal curves with the same mean but different standard deviations. µ 1 = µ 2 x 1 < 2 The two curves are centered at exactly the same position on the horizontal axis, but the curve with the larger standard deviation is lower and spreads out farther. c. Two normal curves that have different means and different standard deviations. 1 2 µ 1 µ 2 x µ 1 < µ 2 1 < 2 The two curves are centered at different positions on the horizontal axis and their shapes reflect the two different values of. Areas under the Normal Curve The area under the curve bounded by the two ordinates x = x 1 and x = x 2 equals the probability that the random variable x falls between x = x 1 and x = x 2. Thus, for the normal curve in the Figure below, the P(x 1 < x < x 2 ) is represented by the area of the shaded region. 53
4 The area under the curve between any two ordinates depend upon the values of µ and and consequently, the probability associated with distributions differ in mean and standard deviation are different Suppose the Figure below, where we have shaded regions corresponding to P(x 1 < x < x 2 ) for two curves with different means and variances. a. the P(x 1 < x < x 2 ), where x is the random variable describing distribution I, and indicated by the cross-hatched area b. P(x l < x < x 2 ) where x is the random variable describing distribution II and given by the entire shaded region Obviously, the probability associated with distribution I and distribution II are different from each other. (التوزيع الطبيعي المعياري) Standard normal distribution Is a normal distribution with mean µ = zero and variance 2 =1 Converting normal distribution into a standard normal distribution (Standardizing the normal curve) Any normal distribution can be transformed into the standard normal distribution with mean zero and variance 1, by apply the following formula: = x µ z This standardization is called the z-transformation, and z is sometimes referred to as z score, z value, or normal deviate. 54
5 Importance of standard normal distribution In discussing normal distribution, we have seen that there are many normal distributions which depend on values of µ and 2. In order to determine areas under normal curve, to determine the probability that any normally distributed random variable falls in a given interval it is necessary to set up separate tables of normal curve areas for every conceivable value of µ and which would be a hopeless task. Standard normal distribution on the other hand has µ = 0 and 2 =1 which allow us to reduce the required number of tables of normal-curve areas to only one-that of the standard normal distribution. P(x 1 <x<x 2 ) =P (z 1 <z<z 2 ). When x is between the values x = x 1 and x = x 2, the random variable z will fall between the corresponding values x µ x µ z = 1 1 and z = 2 2 The original and transformed distributions are illustrated in the two Figures below. Fig. Normal distribution Fig. Standard normal distribution Since all the values of x falling between x 1 and x 2 have corresponding z values between z 1 and z 2, the area under x curve between the ordinates x = x 1 and x = x 2 in the above Figure equals the area under the z curve between the transformed ordinates z = z 1 and z = z 2. Hence we have P(x 1 <x<x 2 ) =P (z 1 <z<z 2 ). The use of the table named area under the normal curve The Appendix of all statistics textbook gives a table of the area under the standard normal curve lying to the left of any specified z value ranging from -3.8 to 3.8. Computing Normal Probabilities 1. State the problem. 2. What is the appropriate probability statement? 3. Sketch a curve and shade required area 4. Convert to a standard normal distribution 5. Find the probability in the standard normal table 55
6 Example Suppose that the hemoglobin levels for healthy adult males are approximately normally distributed with a mean of 16 and variance of Find the probability that a randomly chosen healthy adult male has a hemoglobin level less than 14. Solution We are to find P(x < 14) To find the P(x < 14), sketch a curve and evaluate the area under the normal curve to the left of x = 14. This can be done by transforming x = 14 to the corresponding z value and obtaining the area to the left of z from the table. =0.9 Since µ = 16 and = = We find Z = = P(x < 14) = P(Z < 2.22) = x Z Therefore, only about 1.3% of healthy adult males have hemoglobin levels less than 14. Example Suppose that the serum cholesterol levels of Palestinian women aged are approximately normally distributed with a mean of 4.7 mmol/l and a variance of Find the probability that a randomly chosen Palestinian woman aged has a serum cholesterol level more than 5.6 mmol. Solution In this example we are to find the P(x> 5.6) Again, sketch a curve, this time following the model of the figure below. To find the P(x> 5.6), we need to evaluate the area under the normal curve to the right of x = 5.6. This can be done by transforming x = 5.6 to the corresponding z value, obtaining the area to the left of z from the table, and then subtracting this area from 1. Since µ = 4.7 and = = 0.5 We find = = 0.5 z = x µ = 1.8 Hence P(x> 5.6) = P(z > 1.8) = 1 P(z < 1.8) = = =0.5 x Z So about 4% of Palestinian women aged have a serum cholesterol levels of more than 5.6 mmol/l. 56
7 Example IQ scores (IQ is Intelligence Quotient) on the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale are approximately normally distributed with mean µ = 100 and = 15. a. What is the proportion of persons having IQs between 80 and 120? Solution Let x 1 = 80 and x 2 = 120 This question means that we are to find the probability P(x 1 <IQ<x 2 ) = P(80< IQ <120) Sketch a normal curve like the one in the figure below. Shade in the area desired. Find the z values corresponding to x 1 = 80 and x 2 = 120 x µ z = = = = Z 2 = = = Since, P(x 1 <x<x 2 ) =P (z 1 <z<z 2 ) Therefore, P(80<IQ<120) = P( 1.33<z<1.33) The P( 1.33<z<1.33) is given by the area of the shaded region in the figure. This area may be found by subtracting the area to the left of the ordinate z = 1.33 from the entire area to the left of z = By using the table named area under the normal curve we have P(80<IQ<120) = P( 1.33<z<1.33) = P(z<1.33) P(z< 1.33) = = Therefore the proportion of persons having IQs between 80 and 120 is , about 82%. Inverse Normal Distribution OR, Finding z values when probabilities (areas) are given 1. State the problem 2. Draw a picture IQ Z
8 3. Use the table to find the probability closest to the one you need 4. Read off the z-value 5. Unstandardise i.e. x = µ + z Example Given a normal distribution with µ = 40 and = 6, find the value of x that has a. 45% of the area below it b. 14% of the area above it. Solution In this problem we reverse the process and begin with a known area or probability, find the z value, and then determine x by rearranging the formula µ z = x to give x = z + µ a. An area of 0.45 to the left of the desired x value is shaded in the figure below. We require a z value that leaves an area of 0.45 to the left. From the table we find P(z <?) = 0.45 so that the desired z value is x = = Hence, ( )( ) 40 = b. 14% of the area above it. 40 x In the figure below, we shade an area equal to 0.14 to the right of the desired x value. This time we require a z value that leaves 0.14 of the area to the right and hence an area of 0.86 to the left. Again from the table we find P(z <?) = 0.86 so that the desired z value is 1.08 and x = (6)(1.08) + 40 = = x 58
Section 10.4 Normal Distributions
 Section 10.4 Normal Distributions Random Variables Suppose a bank is interested in improving its services to customers. The manager decides to begin by finding the amount of time tellers spend on each
Section 10.4 Normal Distributions Random Variables Suppose a bank is interested in improving its services to customers. The manager decides to begin by finding the amount of time tellers spend on each
Math 14 Lecture Notes Ch. 6.1
 6.1 Normal Distribution What is normal? a 10-year old boy that is 4' tall? 5' tall? 6' tall? a 25-year old woman with a shoe size of 5? 7? 9? an adult alligator that weighs 200 pounds? 500 pounds? 800
6.1 Normal Distribution What is normal? a 10-year old boy that is 4' tall? 5' tall? 6' tall? a 25-year old woman with a shoe size of 5? 7? 9? an adult alligator that weighs 200 pounds? 500 pounds? 800
Normal Distribution. 6.4 Applications of Normal Distribution
 Normal Distribution 6.4 Applications of Normal Distribution 1 /20 Homework Read Sec 6-4. Discussion question p316 Do p316 probs 1-10, 16-22, 31, 32, 34-37, 39 2 /20 3 /20 Objective Find the probabilities
Normal Distribution 6.4 Applications of Normal Distribution 1 /20 Homework Read Sec 6-4. Discussion question p316 Do p316 probs 1-10, 16-22, 31, 32, 34-37, 39 2 /20 3 /20 Objective Find the probabilities
Learning Objectives. Continuous Random Variables & The Normal Probability Distribution. Continuous Random Variable
 Learning Objectives Continuous Random Variables & The Normal Probability Distribution 1. Understand characteristics about continuous random variables and probability distributions 2. Understand the uniform
Learning Objectives Continuous Random Variables & The Normal Probability Distribution 1. Understand characteristics about continuous random variables and probability distributions 2. Understand the uniform
Density Curve (p52) Density curve is a curve that - is always on or above the horizontal axis.
 1.3 Density curves p50 Some times the overall pattern of a large number of observations is so regular that we can describe it by a smooth curve. It is easier to work with a smooth curve, because the histogram
1.3 Density curves p50 Some times the overall pattern of a large number of observations is so regular that we can describe it by a smooth curve. It is easier to work with a smooth curve, because the histogram
Chapter 6. THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
 Chapter 6. THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION Introducing Normally Distributed Variables The distributions of some variables like thickness of the eggshell, serum cholesterol concentration in blood, white blood cells
Chapter 6. THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION Introducing Normally Distributed Variables The distributions of some variables like thickness of the eggshell, serum cholesterol concentration in blood, white blood cells
Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions
 Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Review and Preview 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution 6-3 Applications of Normal Distributions 6-4 Sampling Distributions and Estimators 6-5 The Central
Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Review and Preview 6-2 The Standard Normal Distribution 6-3 Applications of Normal Distributions 6-4 Sampling Distributions and Estimators 6-5 The Central
Chapter 6. The Normal Distribution. McGraw-Hill, Bluman, 7 th ed., Chapter 6 1
 Chapter 6 The Normal Distribution McGraw-Hill, Bluman, 7 th ed., Chapter 6 1 Bluman, Chapter 6 2 Chapter 6 Overview Introduction 6-1 Normal Distributions 6-2 Applications of the Normal Distribution 6-3
Chapter 6 The Normal Distribution McGraw-Hill, Bluman, 7 th ed., Chapter 6 1 Bluman, Chapter 6 2 Chapter 6 Overview Introduction 6-1 Normal Distributions 6-2 Applications of the Normal Distribution 6-3
Prepare a stem-and-leaf graph for the following data. In your final display, you should arrange the leaves for each stem in increasing order.
 Chapter 2 2.1 Descriptive Statistics A stem-and-leaf graph, also called a stemplot, allows for a nice overview of quantitative data without losing information on individual observations. It can be a good
Chapter 2 2.1 Descriptive Statistics A stem-and-leaf graph, also called a stemplot, allows for a nice overview of quantitative data without losing information on individual observations. It can be a good
Chapter 6. THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
 Chapter 6. THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION Introducing Normally Distributed Variables The distributions of some variables like thickness of the eggshell, serum cholesterol concentration in blood, white blood cells
Chapter 6. THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION Introducing Normally Distributed Variables The distributions of some variables like thickness of the eggshell, serum cholesterol concentration in blood, white blood cells
Ch6: The Normal Distribution
 Ch6: The Normal Distribution Introduction Review: A continuous random variable can assume any value between two endpoints. Many continuous random variables have an approximately normal distribution, which
Ch6: The Normal Distribution Introduction Review: A continuous random variable can assume any value between two endpoints. Many continuous random variables have an approximately normal distribution, which
23.2 Normal Distributions
 1_ Locker LESSON 23.2 Normal Distributions Common Core Math Standards The student is expected to: S-ID.4 Use the mean and standard deviation of a data set to fit it to a normal distribution and to estimate
1_ Locker LESSON 23.2 Normal Distributions Common Core Math Standards The student is expected to: S-ID.4 Use the mean and standard deviation of a data set to fit it to a normal distribution and to estimate
The standard deviation 1 n
 The standard deviation 1 SD = (xj x) n 2 The SD gives a measure of how the data are clustered around the mean. If the SD is larger, then the data are more spread out we are more likely to find data that
The standard deviation 1 SD = (xj x) n 2 The SD gives a measure of how the data are clustered around the mean. If the SD is larger, then the data are more spread out we are more likely to find data that
Measures of Dispersion
 Lesson 7.6 Objectives Find the variance of a set of data. Calculate standard deviation for a set of data. Read data from a normal curve. Estimate the area under a curve. Variance Measures of Dispersion
Lesson 7.6 Objectives Find the variance of a set of data. Calculate standard deviation for a set of data. Read data from a normal curve. Estimate the area under a curve. Variance Measures of Dispersion
Distributions of random variables
 Chapter 3 Distributions of random variables 31 Normal distribution Among all the distributions we see in practice, one is overwhelmingly the most common The symmetric, unimodal, bell curve is ubiquitous
Chapter 3 Distributions of random variables 31 Normal distribution Among all the distributions we see in practice, one is overwhelmingly the most common The symmetric, unimodal, bell curve is ubiquitous
6-1 THE STANDARD NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
 6-1 THE STANDARD NORMAL DISTRIBUTION The major focus of this chapter is the concept of a normal probability distribution, but we begin with a uniform distribution so that we can see the following two very
6-1 THE STANDARD NORMAL DISTRIBUTION The major focus of this chapter is the concept of a normal probability distribution, but we begin with a uniform distribution so that we can see the following two very
Chapter 5: The standard deviation as a ruler and the normal model p131
 Chapter 5: The standard deviation as a ruler and the normal model p131 Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12? Is it fair to say: 67 is
Chapter 5: The standard deviation as a ruler and the normal model p131 Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12? Is it fair to say: 67 is
CHAPTER 6. The Normal Probability Distribution
 The Normal Probability Distribution CHAPTER 6 The normal probability distribution is the most widely used distribution in statistics as many statistical procedures are built around it. The central limit
The Normal Probability Distribution CHAPTER 6 The normal probability distribution is the most widely used distribution in statistics as many statistical procedures are built around it. The central limit
Part I, Chapters 4 & 5. Data Tables and Data Analysis Statistics and Figures
 Part I, Chapters 4 & 5 Data Tables and Data Analysis Statistics and Figures Descriptive Statistics 1 Are data points clumped? (order variable / exp. variable) Concentrated around one value? Concentrated
Part I, Chapters 4 & 5 Data Tables and Data Analysis Statistics and Figures Descriptive Statistics 1 Are data points clumped? (order variable / exp. variable) Concentrated around one value? Concentrated
Introduction to the Practice of Statistics Fifth Edition Moore, McCabe
 Introduction to the Practice of Statistics Fifth Edition Moore, McCabe Section 1.3 Homework Answers Assignment 5 1.80 If you ask a computer to generate "random numbers between 0 and 1, you uniform will
Introduction to the Practice of Statistics Fifth Edition Moore, McCabe Section 1.3 Homework Answers Assignment 5 1.80 If you ask a computer to generate "random numbers between 0 and 1, you uniform will
Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data Section 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution Describing Location in a Distribution Learning Objectives After this section, you should be able to: FIND and
Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data Section 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution Describing Location in a Distribution Learning Objectives After this section, you should be able to: FIND and
The Normal Distribution
 The Normal Distribution Lecture 20 Section 6.3.1 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Sep 28, 2011 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, 2011 1 / 41 Outline
The Normal Distribution Lecture 20 Section 6.3.1 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Sep 28, 2011 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) The Normal Distribution Wed, Sep 28, 2011 1 / 41 Outline
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers HW 34. Sketch
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers HW 34. Sketch
Lecture Slides. Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition. by Mario F. Triola. and the Triola Statistics Series. Section 6.2-1
 Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition and the Triola Statistics Series by Mario F. Triola Section 6.2-1 Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Review and Preview 6-2 The Standard
Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Twelfth Edition and the Triola Statistics Series by Mario F. Triola Section 6.2-1 Chapter 6 Normal Probability Distributions 6-1 Review and Preview 6-2 The Standard
Distributions of Continuous Data
 C H A P T ER Distributions of Continuous Data New cars and trucks sold in the United States average about 28 highway miles per gallon (mpg) in 2010, up from about 24 mpg in 2004. Some of the improvement
C H A P T ER Distributions of Continuous Data New cars and trucks sold in the United States average about 28 highway miles per gallon (mpg) in 2010, up from about 24 mpg in 2004. Some of the improvement
Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture:
 Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture: Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 or 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12 Is it fair
Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture: Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 or 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12 Is it fair
Probability and Statistics. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Probability and Statistics Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 14.6 Descriptive Statistics (Graphical) Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Data in Categories Histograms
Probability and Statistics Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 14.6 Descriptive Statistics (Graphical) Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Data in Categories Histograms
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Density Curves
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Density Curves
Chapter 1. Looking at Data-Distribution
 Chapter 1. Looking at Data-Distribution Statistics is the scientific discipline that provides methods to draw right conclusions: 1)Collecting the data 2)Describing the data 3)Drawing the conclusions Raw
Chapter 1. Looking at Data-Distribution Statistics is the scientific discipline that provides methods to draw right conclusions: 1)Collecting the data 2)Describing the data 3)Drawing the conclusions Raw
IT 403 Practice Problems (1-2) Answers
 IT 403 Practice Problems (1-2) Answers #1. Using Tukey's Hinges method ('Inclusionary'), what is Q3 for this dataset? 2 3 5 7 11 13 17 a. 7 b. 11 c. 12 d. 15 c (12) #2. How do quartiles and percentiles
IT 403 Practice Problems (1-2) Answers #1. Using Tukey's Hinges method ('Inclusionary'), what is Q3 for this dataset? 2 3 5 7 11 13 17 a. 7 b. 11 c. 12 d. 15 c (12) #2. How do quartiles and percentiles
Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture:
 Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture: Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 or 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12 Is it fair
Lecture 3 Questions that we should be able to answer by the end of this lecture: Which is the better exam score? 67 on an exam with mean 50 and SD 10 or 62 on an exam with mean 40 and SD 12 Is it fair
Chapter 2: Modeling Distributions of Data
 Chapter 2: Modeling Distributions of Data Section 2.2 The Practice of Statistics, 4 th edition - For AP* STARNES, YATES, MOORE Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution
Chapter 2: Modeling Distributions of Data Section 2.2 The Practice of Statistics, 4 th edition - For AP* STARNES, YATES, MOORE Chapter 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.1 Describing Location in a Distribution
MAT 102 Introduction to Statistics Chapter 6. Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions and the Normal Distribution
 MAT 102 Introduction to Statistics Chapter 6 Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions and the Normal Distribution 6.2 Continuous Probability Distributions Characteristics of a Continuous Probability
MAT 102 Introduction to Statistics Chapter 6 Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distributions and the Normal Distribution 6.2 Continuous Probability Distributions Characteristics of a Continuous Probability
Lecture 6: Chapter 6 Summary
 1 Lecture 6: Chapter 6 Summary Z-score: Is the distance of each data value from the mean in standard deviation Standardizes data values Standardization changes the mean and the standard deviation: o Z
1 Lecture 6: Chapter 6 Summary Z-score: Is the distance of each data value from the mean in standard deviation Standardizes data values Standardization changes the mean and the standard deviation: o Z
appstats6.notebook September 27, 2016
 Chapter 6 The Standard Deviation as a Ruler and the Normal Model Objectives: 1.Students will calculate and interpret z scores. 2.Students will compare/contrast values from different distributions using
Chapter 6 The Standard Deviation as a Ruler and the Normal Model Objectives: 1.Students will calculate and interpret z scores. 2.Students will compare/contrast values from different distributions using
courtesy 1
 1 The Normal Distribution 2 Topic Overview Introduction Normal Distributions Applications of the Normal Distribution The Central Limit Theorem 3 Objectives 1. Identify the properties of a normal distribution.
1 The Normal Distribution 2 Topic Overview Introduction Normal Distributions Applications of the Normal Distribution The Central Limit Theorem 3 Objectives 1. Identify the properties of a normal distribution.
Section 2.2 Normal Distributions. Normal Distributions
 Section 2.2 Normal Distributions Normal Distributions One particularly important class of density curves are the Normal curves, which describe Normal distributions. All Normal curves are symmetric, single-peaked,
Section 2.2 Normal Distributions Normal Distributions One particularly important class of density curves are the Normal curves, which describe Normal distributions. All Normal curves are symmetric, single-peaked,
Chapter 6: Continuous Random Variables & the Normal Distribution. 6.1 Continuous Probability Distribution
 Chapter 6: Continuous Random Variables & the Normal Distribution 6.1 Continuous Probability Distribution and the Normal Probability Distribution 6.2 Standardizing a Normal Distribution 6.3 Applications
Chapter 6: Continuous Random Variables & the Normal Distribution 6.1 Continuous Probability Distribution and the Normal Probability Distribution 6.2 Standardizing a Normal Distribution 6.3 Applications
Continuous Improvement Toolkit. Normal Distribution. Continuous Improvement Toolkit.
 Continuous Improvement Toolkit Normal Distribution The Continuous Improvement Map Managing Risk FMEA Understanding Performance** Check Sheets Data Collection PDPC RAID Log* Risk Analysis* Benchmarking***
Continuous Improvement Toolkit Normal Distribution The Continuous Improvement Map Managing Risk FMEA Understanding Performance** Check Sheets Data Collection PDPC RAID Log* Risk Analysis* Benchmarking***
Table of Contents (As covered from textbook)
 Table of Contents (As covered from textbook) Ch 1 Data and Decisions Ch 2 Displaying and Describing Categorical Data Ch 3 Displaying and Describing Quantitative Data Ch 4 Correlation and Linear Regression
Table of Contents (As covered from textbook) Ch 1 Data and Decisions Ch 2 Displaying and Describing Categorical Data Ch 3 Displaying and Describing Quantitative Data Ch 4 Correlation and Linear Regression
UNIT 15 GRAPHICAL PRESENTATION OF DATA-I
 UNIT 15 GRAPHICAL PRESENTATION OF DATA-I Graphical Presentation of Data-I Structure 15.1 Introduction Objectives 15.2 Graphical Presentation 15.3 Types of Graphs Histogram Frequency Polygon Frequency Curve
UNIT 15 GRAPHICAL PRESENTATION OF DATA-I Graphical Presentation of Data-I Structure 15.1 Introduction Objectives 15.2 Graphical Presentation 15.3 Types of Graphs Histogram Frequency Polygon Frequency Curve
STA Module 4 The Normal Distribution
 STA 2023 Module 4 The Normal Distribution Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. Explain what it means for a variable to be normally distributed or approximately normally
STA 2023 Module 4 The Normal Distribution Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. Explain what it means for a variable to be normally distributed or approximately normally
STA /25/12. Module 4 The Normal Distribution. Learning Objectives. Let s Look at Some Examples of Normal Curves
 STA 2023 Module 4 The Normal Distribution Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. Explain what it means for a variable to be normally distributed or approximately normally
STA 2023 Module 4 The Normal Distribution Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to 1. Explain what it means for a variable to be normally distributed or approximately normally
Normal Data ID1050 Quantitative & Qualitative Reasoning
 Normal Data ID1050 Quantitative & Qualitative Reasoning Histogram for Different Sample Sizes For a small sample, the choice of class (group) size dramatically affects how the histogram appears. Say we
Normal Data ID1050 Quantitative & Qualitative Reasoning Histogram for Different Sample Sizes For a small sample, the choice of class (group) size dramatically affects how the histogram appears. Say we
Chapter 2: The Normal Distributions
 Chapter 2: The Normal Distributions Measures of Relative Standing & Density Curves Z-scores (Measures of Relative Standing) Suppose there is one spot left in the University of Michigan class of 2014 and
Chapter 2: The Normal Distributions Measures of Relative Standing & Density Curves Z-scores (Measures of Relative Standing) Suppose there is one spot left in the University of Michigan class of 2014 and
Stat 528 (Autumn 2008) Density Curves and the Normal Distribution. Measures of center and spread. Features of the normal distribution
 Stat 528 (Autumn 2008) Density Curves and the Normal Distribution Reading: Section 1.3 Density curves An example: GRE scores Measures of center and spread The normal distribution Features of the normal
Stat 528 (Autumn 2008) Density Curves and the Normal Distribution Reading: Section 1.3 Density curves An example: GRE scores Measures of center and spread The normal distribution Features of the normal
MAT 142 College Mathematics. Module ST. Statistics. Terri Miller revised July 14, 2015
 MAT 142 College Mathematics Statistics Module ST Terri Miller revised July 14, 2015 2 Statistics Data Organization and Visualization Basic Terms. A population is the set of all objects under study, a sample
MAT 142 College Mathematics Statistics Module ST Terri Miller revised July 14, 2015 2 Statistics Data Organization and Visualization Basic Terms. A population is the set of all objects under study, a sample
Section 7.2: Applications of the Normal Distribution
 Section 7.2: Applications of the Normal Distribution Objectives By the end of this lesson, you will be able to... 1. find and interpret the area under a normal curve 2. find the value of a normal random
Section 7.2: Applications of the Normal Distribution Objectives By the end of this lesson, you will be able to... 1. find and interpret the area under a normal curve 2. find the value of a normal random
The Normal Distribution
 Chapter 6 The Normal Distribution Continuous random variables are used to approximate probabilities where there are many possibilities or an infinite number of possibilities on a given trial. One of the
Chapter 6 The Normal Distribution Continuous random variables are used to approximate probabilities where there are many possibilities or an infinite number of possibilities on a given trial. One of the
height VUD x = x 1 + x x N N 2 + (x 2 x) 2 + (x N x) 2. N
 Math 3: CSM Tutorial: Probability, Statistics, and Navels Fall 2 In this worksheet, we look at navel ratios, means, standard deviations, relative frequency density histograms, and probability density functions.
Math 3: CSM Tutorial: Probability, Statistics, and Navels Fall 2 In this worksheet, we look at navel ratios, means, standard deviations, relative frequency density histograms, and probability density functions.
CHAPTER 1. Introduction. Statistics: Statistics is the science of collecting, organizing, analyzing, presenting and interpreting data.
 1 CHAPTER 1 Introduction Statistics: Statistics is the science of collecting, organizing, analyzing, presenting and interpreting data. Variable: Any characteristic of a person or thing that can be expressed
1 CHAPTER 1 Introduction Statistics: Statistics is the science of collecting, organizing, analyzing, presenting and interpreting data. Variable: Any characteristic of a person or thing that can be expressed
4.3 The Normal Distribution
 4.3 The Normal Distribution Objectives. Definition of normal distribution. Standard normal distribution. Specialties of the graph of the standard normal distribution. Percentiles of the standard normal
4.3 The Normal Distribution Objectives. Definition of normal distribution. Standard normal distribution. Specialties of the graph of the standard normal distribution. Percentiles of the standard normal
Chapter 5. Normal. Normal Curve. the Normal. Curve Examples. Standard Units Standard Units Examples. for Data
 curve Approximation Part II Descriptive Statistics The Approximation Approximation The famous normal curve can often be used as an 'ideal' histogram, to which histograms for data can be compared. Its equation
curve Approximation Part II Descriptive Statistics The Approximation Approximation The famous normal curve can often be used as an 'ideal' histogram, to which histograms for data can be compared. Its equation
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data
 CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Density Curves
CHAPTER 2 Modeling Distributions of Data 2.2 Density Curves and Normal Distributions The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Density Curves
Math 120 Introduction to Statistics Mr. Toner s Lecture Notes 3.1 Measures of Central Tendency
 Math 1 Introduction to Statistics Mr. Toner s Lecture Notes 3.1 Measures of Central Tendency lowest value + highest value midrange The word average: is very ambiguous and can actually refer to the mean,
Math 1 Introduction to Statistics Mr. Toner s Lecture Notes 3.1 Measures of Central Tendency lowest value + highest value midrange The word average: is very ambiguous and can actually refer to the mean,
Chapter 2: The Normal Distribution
 Chapter 2: The Normal Distribution 2.1 Density Curves and the Normal Distributions 2.2 Standard Normal Calculations 1 2 Histogram for Strength of Yarn Bobbins 15.60 16.10 16.60 17.10 17.60 18.10 18.60
Chapter 2: The Normal Distribution 2.1 Density Curves and the Normal Distributions 2.2 Standard Normal Calculations 1 2 Histogram for Strength of Yarn Bobbins 15.60 16.10 16.60 17.10 17.60 18.10 18.60
8 2 Properties of a normal distribution.notebook Properties of the Normal Distribution Pages
 8 2 Properties of the Normal Distribution Pages 422 431 normal distribution a common continuous probability distribution in which the data are distributed symmetrically and unimodally about the mean. Can
8 2 Properties of the Normal Distribution Pages 422 431 normal distribution a common continuous probability distribution in which the data are distributed symmetrically and unimodally about the mean. Can
Student Learning Objectives
 Student Learning Objectives A. Understand that the overall shape of a distribution of a large number of observations can be summarized by a smooth curve called a density curve. B. Know that an area under
Student Learning Objectives A. Understand that the overall shape of a distribution of a large number of observations can be summarized by a smooth curve called a density curve. B. Know that an area under
Statistical Methods. Instructor: Lingsong Zhang. Any questions, ask me during the office hour, or me, I will answer promptly.
 Statistical Methods Instructor: Lingsong Zhang 1 Issues before Class Statistical Methods Lingsong Zhang Office: Math 544 Email: lingsong@purdue.edu Phone: 765-494-7913 Office Hour: Monday 1:00 pm - 2:00
Statistical Methods Instructor: Lingsong Zhang 1 Issues before Class Statistical Methods Lingsong Zhang Office: Math 544 Email: lingsong@purdue.edu Phone: 765-494-7913 Office Hour: Monday 1:00 pm - 2:00
MAT 110 WORKSHOP. Updated Fall 2018
 MAT 110 WORKSHOP Updated Fall 2018 UNIT 3: STATISTICS Introduction Choosing a Sample Simple Random Sample: a set of individuals from the population chosen in a way that every individual has an equal chance
MAT 110 WORKSHOP Updated Fall 2018 UNIT 3: STATISTICS Introduction Choosing a Sample Simple Random Sample: a set of individuals from the population chosen in a way that every individual has an equal chance
Normal Curves and Sampling Distributions
 Normal Curves and Sampling Distributions 6 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Section 6.2 Standard Units and Areas Under the Standard Normal Distribution Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights
Normal Curves and Sampling Distributions 6 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Section 6.2 Standard Units and Areas Under the Standard Normal Distribution Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights
So..to be able to make comparisons possible, we need to compare them with their respective distributions.
 Unit 3 ~ Modeling Distributions of Data 1 ***Section 2.1*** Measures of Relative Standing and Density Curves (ex) Suppose that a professional soccer team has the money to sign one additional player and
Unit 3 ~ Modeling Distributions of Data 1 ***Section 2.1*** Measures of Relative Standing and Density Curves (ex) Suppose that a professional soccer team has the money to sign one additional player and
Name: Date: Period: Chapter 2. Section 1: Describing Location in a Distribution
 Name: Date: Period: Chapter 2 Section 1: Describing Location in a Distribution Suppose you earned an 86 on a statistics quiz. The question is: should you be satisfied with this score? What if it is the
Name: Date: Period: Chapter 2 Section 1: Describing Location in a Distribution Suppose you earned an 86 on a statistics quiz. The question is: should you be satisfied with this score? What if it is the
Key: 5 9 represents a team with 59 wins. (c) The Kansas City Royals and Cleveland Indians, who both won 65 games.
 AP statistics Chapter 2 Notes Name Modeling Distributions of Data Per Date 2.1A Distribution of a variable is the a variable takes and it takes that value. When working with quantitative data we can calculate
AP statistics Chapter 2 Notes Name Modeling Distributions of Data Per Date 2.1A Distribution of a variable is the a variable takes and it takes that value. When working with quantitative data we can calculate
IQR = number. summary: largest. = 2. Upper half: Q3 =
 Step by step box plot Height in centimeters of players on the 003 Women s Worldd Cup soccer team. 157 1611 163 163 164 165 165 165 168 168 168 170 170 170 171 173 173 175 180 180 Determine the 5 number
Step by step box plot Height in centimeters of players on the 003 Women s Worldd Cup soccer team. 157 1611 163 163 164 165 165 165 168 168 168 170 170 170 171 173 173 175 180 180 Determine the 5 number
Section 2.2 Normal Distributions
 Section 2.2 Mrs. Daniel AP Statistics We abbreviate the Normal distribution with mean µ and standard deviation σ as N(µ,σ). Any particular Normal distribution is completely specified by two numbers: its
Section 2.2 Mrs. Daniel AP Statistics We abbreviate the Normal distribution with mean µ and standard deviation σ as N(µ,σ). Any particular Normal distribution is completely specified by two numbers: its
Sec 6.3. Bluman, Chapter 6 1
 Sec 6.3 Bluman, Chapter 6 1 Bluman, Chapter 6 2 Review: Find the z values; the graph is symmetrical. z = ±1. 96 z 0 z the total area of the shaded regions=5% Bluman, Chapter 6 3 Review: Find the z values;
Sec 6.3 Bluman, Chapter 6 1 Bluman, Chapter 6 2 Review: Find the z values; the graph is symmetrical. z = ±1. 96 z 0 z the total area of the shaded regions=5% Bluman, Chapter 6 3 Review: Find the z values;
10.4 Measures of Central Tendency and Variation
 10.4 Measures of Central Tendency and Variation Mode-->The number that occurs most frequently; there can be more than one mode ; if each number appears equally often, then there is no mode at all. (mode
10.4 Measures of Central Tendency and Variation Mode-->The number that occurs most frequently; there can be more than one mode ; if each number appears equally often, then there is no mode at all. (mode
10.4 Measures of Central Tendency and Variation
 10.4 Measures of Central Tendency and Variation Mode-->The number that occurs most frequently; there can be more than one mode ; if each number appears equally often, then there is no mode at all. (mode
10.4 Measures of Central Tendency and Variation Mode-->The number that occurs most frequently; there can be more than one mode ; if each number appears equally often, then there is no mode at all. (mode
Measures of Position
 Measures of Position In this section, we will learn to use fractiles. Fractiles are numbers that partition, or divide, an ordered data set into equal parts (each part has the same number of data entries).
Measures of Position In this section, we will learn to use fractiles. Fractiles are numbers that partition, or divide, an ordered data set into equal parts (each part has the same number of data entries).
Ms Nurazrin Jupri. Frequency Distributions
 Frequency Distributions Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and simplify the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results.
Frequency Distributions Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and simplify the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results.
Frequency Distributions
 Displaying Data Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and summarize the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results. Remember,
Displaying Data Frequency Distributions After collecting data, the first task for a researcher is to organize and summarize the data so that it is possible to get a general overview of the results. Remember,
Vocabulary. 5-number summary Rule. Area principle. Bar chart. Boxplot. Categorical data condition. Categorical variable.
 5-number summary 68-95-99.7 Rule Area principle Bar chart Bimodal Boxplot Case Categorical data Categorical variable Center Changing center and spread Conditional distribution Context Contingency table
5-number summary 68-95-99.7 Rule Area principle Bar chart Bimodal Boxplot Case Categorical data Categorical variable Center Changing center and spread Conditional distribution Context Contingency table
CHAPTER 2: Describing Location in a Distribution
 CHAPTER 2: Describing Location in a Distribution 2.1 Goals: 1. Compute and use z-scores given the mean and sd 2. Compute and use the p th percentile of an observation 3. Intro to density curves 4. More
CHAPTER 2: Describing Location in a Distribution 2.1 Goals: 1. Compute and use z-scores given the mean and sd 2. Compute and use the p th percentile of an observation 3. Intro to density curves 4. More
MATH& 146 Lesson 10. Section 1.6 Graphing Numerical Data
 MATH& 146 Lesson 10 Section 1.6 Graphing Numerical Data 1 Graphs of Numerical Data One major reason for constructing a graph of numerical data is to display its distribution, or the pattern of variability
MATH& 146 Lesson 10 Section 1.6 Graphing Numerical Data 1 Graphs of Numerical Data One major reason for constructing a graph of numerical data is to display its distribution, or the pattern of variability
Downloaded from
 UNIT 2 WHAT IS STATISTICS? Researchers deal with a large amount of data and have to draw dependable conclusions on the basis of data collected for the purpose. Statistics help the researchers in making
UNIT 2 WHAT IS STATISTICS? Researchers deal with a large amount of data and have to draw dependable conclusions on the basis of data collected for the purpose. Statistics help the researchers in making
Chapter 3 - Displaying and Summarizing Quantitative Data
 Chapter 3 - Displaying and Summarizing Quantitative Data 3.1 Graphs for Quantitative Data (LABEL GRAPHS) August 25, 2014 Histogram (p. 44) - Graph that uses bars to represent different frequencies or relative
Chapter 3 - Displaying and Summarizing Quantitative Data 3.1 Graphs for Quantitative Data (LABEL GRAPHS) August 25, 2014 Histogram (p. 44) - Graph that uses bars to represent different frequencies or relative
Chapter 6 The Standard Deviation as Ruler and the Normal Model
 ST 305 Chapter 6 Reiland The Standard Deviation as Ruler and the Normal Model Chapter Objectives: At the end of this chapter you should be able to: 1) describe how adding or subtracting the same value
ST 305 Chapter 6 Reiland The Standard Deviation as Ruler and the Normal Model Chapter Objectives: At the end of this chapter you should be able to: 1) describe how adding or subtracting the same value
8: Statistics. Populations and Samples. Histograms and Frequency Polygons. Page 1 of 10
 8: Statistics Statistics: Method of collecting, organizing, analyzing, and interpreting data, as well as drawing conclusions based on the data. Methodology is divided into two main areas. Descriptive Statistics:
8: Statistics Statistics: Method of collecting, organizing, analyzing, and interpreting data, as well as drawing conclusions based on the data. Methodology is divided into two main areas. Descriptive Statistics:
Chapter 3 Analyzing Normal Quantitative Data
 Chapter 3 Analyzing Normal Quantitative Data Introduction: In chapters 1 and 2, we focused on analyzing categorical data and exploring relationships between categorical data sets. We will now be doing
Chapter 3 Analyzing Normal Quantitative Data Introduction: In chapters 1 and 2, we focused on analyzing categorical data and exploring relationships between categorical data sets. We will now be doing
AP Statistics. Study Guide
 Measuring Relative Standing Standardized Values and z-scores AP Statistics Percentiles Rank the data lowest to highest. Counting up from the lowest value to the select data point we discover the percentile
Measuring Relative Standing Standardized Values and z-scores AP Statistics Percentiles Rank the data lowest to highest. Counting up from the lowest value to the select data point we discover the percentile
The Normal Curve. June 20, Bryan T. Karazsia, M.A.
 The Normal Curve June 20, 2006 Bryan T. Karazsia, M.A. Overview Hand-in Homework Why are distributions so important (particularly the normal distribution)? What is the normal distribution? Z-scores Using
The Normal Curve June 20, 2006 Bryan T. Karazsia, M.A. Overview Hand-in Homework Why are distributions so important (particularly the normal distribution)? What is the normal distribution? Z-scores Using
The Normal Distribution. John McGready, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 The Normal Distribution John McGready, PhD Johns Hopkins University General Properties of The Normal Distribution The material in this video is subject to the copyright of the owners of the material and
The Normal Distribution John McGready, PhD Johns Hopkins University General Properties of The Normal Distribution The material in this video is subject to the copyright of the owners of the material and
The first few questions on this worksheet will deal with measures of central tendency. These data types tell us where the center of the data set lies.
 Instructions: You are given the following data below these instructions. Your client (Courtney) wants you to statistically analyze the data to help her reach conclusions about how well she is teaching.
Instructions: You are given the following data below these instructions. Your client (Courtney) wants you to statistically analyze the data to help her reach conclusions about how well she is teaching.
The Normal Distribution & z-scores
 & z-scores Distributions: Who needs them? Why are we interested in distributions? Important link between distributions and probabilities of events If we know the distribution of a set of events, then we
& z-scores Distributions: Who needs them? Why are we interested in distributions? Important link between distributions and probabilities of events If we know the distribution of a set of events, then we
Basic Statistical Terms and Definitions
 I. Basics Basic Statistical Terms and Definitions Statistics is a collection of methods for planning experiments, and obtaining data. The data is then organized and summarized so that professionals can
I. Basics Basic Statistical Terms and Definitions Statistics is a collection of methods for planning experiments, and obtaining data. The data is then organized and summarized so that professionals can
CHAPTER 2 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS
 CHAPTER 2 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS 1. Stem-and-Leaf Graphs, Line Graphs, and Bar Graphs The distribution of data is how the data is spread or distributed over the range of the data values. This is one of
CHAPTER 2 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS 1. Stem-and-Leaf Graphs, Line Graphs, and Bar Graphs The distribution of data is how the data is spread or distributed over the range of the data values. This is one of
2.1: Frequency Distributions and Their Graphs
 2.1: Frequency Distributions and Their Graphs Frequency Distribution - way to display data that has many entries - table that shows classes or intervals of data entries and the number of entries in each
2.1: Frequency Distributions and Their Graphs Frequency Distribution - way to display data that has many entries - table that shows classes or intervals of data entries and the number of entries in each
Female Brown Bear Weights
 CC-20 Normal Distributions Common Core State Standards MACC.92.S-ID..4 Use the mean and standard of a data set to fit it to a normal distribution and to estimate population percentages. Recognize that
CC-20 Normal Distributions Common Core State Standards MACC.92.S-ID..4 Use the mean and standard of a data set to fit it to a normal distribution and to estimate population percentages. Recognize that
Getting to Know Your Data
 Chapter 2 Getting to Know Your Data 2.1 Exercises 1. Give three additional commonly used statistical measures (i.e., not illustrated in this chapter) for the characterization of data dispersion, and discuss
Chapter 2 Getting to Know Your Data 2.1 Exercises 1. Give three additional commonly used statistical measures (i.e., not illustrated in this chapter) for the characterization of data dispersion, and discuss
a. divided by the. 1) Always round!! a) Even if class width comes out to a, go up one.
 Probability and Statistics Chapter 2 Notes I Section 2-1 A Steps to Constructing Frequency Distributions 1 Determine number of (may be given to you) a Should be between and classes 2 Find the Range a The
Probability and Statistics Chapter 2 Notes I Section 2-1 A Steps to Constructing Frequency Distributions 1 Determine number of (may be given to you) a Should be between and classes 2 Find the Range a The
STA Rev. F Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives (Cont.) Module 3 Descriptive Measures
 STA 2023 Module 3 Descriptive Measures Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Explain the purpose of a measure of center. 2. Obtain and interpret the mean, median, and
STA 2023 Module 3 Descriptive Measures Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Explain the purpose of a measure of center. 2. Obtain and interpret the mean, median, and
Lab 4: Distributions of random variables
 Lab 4: Distributions of random variables In this lab we ll investigate the probability distribution that is most central to statistics: the normal distribution If we are confident that our data are nearly
Lab 4: Distributions of random variables In this lab we ll investigate the probability distribution that is most central to statistics: the normal distribution If we are confident that our data are nearly
Probability & Statistics Chapter 6. Normal Distribution
 I. Graphs of Normal Probability Distributions Normal Distribution Studied by French mathematician Abraham de Moivre and German mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss. Gauss work was so important that the normal
I. Graphs of Normal Probability Distributions Normal Distribution Studied by French mathematician Abraham de Moivre and German mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss. Gauss work was so important that the normal
Chapter 2. Frequency distribution. Summarizing and Graphing Data
 Frequency distribution Chapter 2 Summarizing and Graphing Data Shows how data are partitioned among several categories (or classes) by listing the categories along with the number (frequency) of data values
Frequency distribution Chapter 2 Summarizing and Graphing Data Shows how data are partitioned among several categories (or classes) by listing the categories along with the number (frequency) of data values
1. The Normal Distribution, continued
 Math 1125-Introductory Statistics Lecture 16 10/9/06 1. The Normal Distribution, continued Recall that the standard normal distribution is symmetric about z = 0, so the area to the right of zero is 0.5000.
Math 1125-Introductory Statistics Lecture 16 10/9/06 1. The Normal Distribution, continued Recall that the standard normal distribution is symmetric about z = 0, so the area to the right of zero is 0.5000.
How individual data points are positioned within a data set.
 Section 3.4 Measures of Position Percentiles How individual data points are positioned within a data set. P k is the value such that k% of a data set is less than or equal to P k. For example if we said
Section 3.4 Measures of Position Percentiles How individual data points are positioned within a data set. P k is the value such that k% of a data set is less than or equal to P k. For example if we said
The Normal Distribution & z-scores
 & z-scores Distributions: Who needs them? Why are we interested in distributions? Important link between distributions and probabilities of events If we know the distribution of a set of events, then we
& z-scores Distributions: Who needs them? Why are we interested in distributions? Important link between distributions and probabilities of events If we know the distribution of a set of events, then we
Chapter2 Description of samples and populations. 2.1 Introduction.
 Chapter2 Description of samples and populations. 2.1 Introduction. Statistics=science of analyzing data. Information collected (data) is gathered in terms of variables (characteristics of a subject that
Chapter2 Description of samples and populations. 2.1 Introduction. Statistics=science of analyzing data. Information collected (data) is gathered in terms of variables (characteristics of a subject that
CCNY Math Review Chapter 2: Functions
 CCN Math Review Chapter : Functions Section.1: Functions.1.1: How functions are used.1.: Methods for defining functions.1.3: The graph of a function.1.: Domain and range.1.5: Relations, functions, and
CCN Math Review Chapter : Functions Section.1: Functions.1.1: How functions are used.1.: Methods for defining functions.1.3: The graph of a function.1.: Domain and range.1.5: Relations, functions, and
