Solutions. Suppose we insert all elements of U into the table, and let n(b) be the number of elements of U that hash to bucket b. Then.
|
|
|
- Gwen Reed
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Assignment 3 1. Exercise [ on p. 229] Modify hashing by chaining (i.e., bucketvector with BucketType = List) so that BucketType = OrderedList. How is the runtime of search, insert, and remove affected? 2. Exercise [ on p. 229] Assume hashing by chaining as above (and as in fsu:thashtable<>). Denote by U the universe of keys. (This can be the set of all objects of the data type stored in the table, or some subset of that constrained by the particular use of the table.) Show that if U km, where m is the number of buckets, then there is a subset of U of size k consisting of keys that all hash to the same bucket. (Note that k is just an integer, not the size of anything.) 3. For the following binary tree, complete the table showing each step in a traversal and the number of edges covered by each step (begin, next,..., next): iteration step current location no of edge moves Q / \ 1. initialize W E \ / \ R T Y (null) 4. Describe an order in which vertices of a BST can be saved to ensure that reconstructing a BST from the saved data will result in the same tree. Argue correctness of your assertion. 5. Use the result of Assignment 1 Problem 3(e) [problem 4-5(e) in the textbook] to prove: Height-balanced binary trees satisfy height(n) = Θ(log n), where n = number of vertices in the tree. 1
2 2 Solutions Problem 1: Modify hashing by chaining (i.e., bucketvector with BucketType = List) so that BucketType = OrderedList. How is the runtime of search, insert, and remove affected? Effect on Search and Remove: Sequential search in an ordered list is, on average, 1/2 the size of the list. The expected search time is unchanged asymptotically [Θ(1) when the number of buckets is Θ(n)], although the measured runtimes would be decreased somewhat. Effect on Insert: Insert consists of search followed by insertion into the ordered list. This increases the insert time by 1/2 the size of the bucket, on average. Again, the expected insert time is not changed asymptotically, but the measured times would be increased somewhat. Problem 2: Assume hashing by chaining as above (and as in fsu:thashtable<>). Denote by U the universe of keys. (This can be the set of all objects of the data type stored in the table, or some subset of that constrained by the particular use of the table.) Show that if U nm, where m is the number of buckets, then there is a subset of U of size n consisting of keys that all hash to the same bucket. Suppose we insert all elements of U into the table, and let n(b) be the number of elements of U that hash to bucket b. Then m 1 U = n(b) nm. 0 Since there are m items in the summation, at least one n(b) must be at least as large as n, for otherwise U = m 1 0 n(b) < m 1 0 n = nm. Problem 3: For the following binary tree, complete the table showing each step in a traversal and the number of edges covered by each step (begin, next,..., next): iteration step current location no of edge moves Q / \ 1. initialize W E \ / \... R T Y (null)
3 3 Here is the completed table: iteration step current location no of edge moves Q / \ 1. initialize W 2 W E R 1 \ / \ Q 2 R T Y T E Y (null) 3 Note the total of 12 edge moves, which is equal to 2n, n = 6. This is the number of edge moves during an entire traversal, since each edge is traversed twice (once descending, once ascending) and there are two extra moves, ( jumping on and jumping off ), for a todal of 2e + 2 = 2(e + 1) = 2n. Problem 4: Describe an order in which vertices of a BST can be saved to ensure that reconstructing a BST from the saved data will result in the same tree. Argue correctness of your assertion. Save the node data in level order (using a level order traversal, or a level order iterator) or pre-order (using a preorder traversal or preorder iterator). When reconstructing the BST, the data will be inserted in this order, because a former left child is encountered after its former parent and before its former right child. But this means the order will also have been preserved, so that the new insertion will end up as the left child of the previously inserted former parent. Similarly for the former right child. Problem 5: Use the result of Assignment 1 Problem 3(e) [problem 4-5(e) in the textbook] to prove: Height-balanced binary trees satisfy height(n) = Θ(log n), where n = number of vertices in the tree. An AVL tree is a binary tree in which the heights of the left and right subtrees of each node differ by at most 1. Note this definition is equivalent to the recursive version: an AVL tree is a binary tree in which the heights of the left and right subtrees of the root differ by at most 1 and in which the left and right subtrees are again AVL trees. The name AVL derives from the names of the two inventors of the technology, G.M. Adelson-Velskii and E.M. Landis [An algorithm for the organization of information, 1962.] We will adopt the more neutral terminology height-balanced tree (abbreviated HB tree or HBT) in discussing the abstract data type and its
4 implementations, but retain the attributive names when discussing the underlying algorithms. Because an HB tree (HBT) is a binary search tree (BST), there is a well defined binary search algorithm in an HBT that follows descending paths. An important feature of HBTs is that they have height Θ(log n), where n is the number of nodes in the HBT, so an HBT must be fairly bushy. (In stark contrast, a BST can be severely leggy, with height n 1. We can define bushy and leggy asymptotically as having height O(log n) and Ω(n), respectively.) In the following, let H and n denote the height and number of vertices of a tree, respectively. Theorem 1. For any height-balanced tree, H = Θ(log n). Proof. First note that H Ω(log n) for any binary tree, because the number of vertices cannot exceed the number of possible vertex locations: n H = 2 H+1 1. Taking the logarithm base 2 of each side, we get the result. We concentrate now on second part of the claim, that H O(log n) assuming the binary tree is height balanced. Let n(h) be the minimum number of vertices an HB tree of height H can have. Clearly n(0) = 1, since a tree of height 0 consists exactly of the root vertex. Also n(1) = 2, by looking at all cases. As an inductive step, note that an HB tree of height H with minimal vertex count must have one subtree of height H 1 and another subtree of height H 2 (otherwise a vertex could be removed and n(h) would not be minumal). Thus n(h) = n(h 1) + n(h 2) + 1. In summary, we have the following recurrance relation: n(0) = 1 n(1) = 2 n(h) = n(h 1) + n(h 2) Note the similarity with the Fibannaci recursion given by: f(0) = 0 f(1) = 1 f(h) = f(h 1) + f(h 2)
5 5 Assertion 1: n(h) > f(h + 2) 1 Proof: Base cases: n(0) = 1 and f(2) 1 = 1 1 = 0, so n(0) > f(2) 1. n(1) = 2 and f(3) 1 = 2 1 = 1, so n(1) > f(2) 1. Inductive step: Applying the definitions of the two recursions and the inductive hypothesis, we have: n(h + 1) = n(h) + n(h 1) + 1 > (f(h + 2) 1) + (f(h + 1) 1) + 1 = f(h + 2) + f(h + 1) 1 = f(h + 3) 1 This proves Assertion 1. Because both sides of the inequality are integers, we can rephrase the previous assertion as: Assertion 2: n(h) >= f(h + 2) Exercise 4-5 in your textbook concludes that f(h + 2) >= φ H / 5, where φ = (1 + 5)/2, the golden ratio. Whence we obtain: Assertion 3: n(h) >= φ H / 5 Taking the logarithm (base φ) of both sides, we see that H O(log n(h)). Because n(h) is the minimum number of vertices an HBT of height H can have, it follows that H O(log n) which completes the proof of Theorem 1. Theorem 2. BST search in an HBT has worst case run time O(log n). Proof. The BST search algorithm consists of a loop that examines nodes in a descending path, starting at the root. Such a path has length no greater than the height of the tree, which is Θ(log n) by Theorem 1.
6 6 Theorem 3. HBT insert and remove have worst case run time O(log n). Proof. The challenge is to make sure that the HBT properties are maintained as we insert and remove elements. It turns out that the HBT properties do not necessarily hold after an ordinary BST insert or remove operation, but that there are repair algorithms that bring the resulting BST back into compliance with the HBT definition. These algorithms restructure the BST by pruning and re-hanging subtrees and are called rotations. Rotations are constant time algorithms, and they are combined into repair algorithms that iterate along a descending path in the HBT. These repair algorithms thus have runtime bounded by O(log n). It follows that BST insert or remove, followed by HBT repair, has run time O(log n + log n) = O(log n). Note that the constants associated with insert and remove will be significantly larger than those for search, so much so that it is sometimes more efficient to build ordinary BST structures, if the insertions are sufficiently random to ensure a bushy tree, and thus not pay the cost of maintaining the HBT property.
Algorithms. AVL Tree
 Algorithms AVL Tree Balanced binary tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time needed to perform insertion and deletion and many other
Algorithms AVL Tree Balanced binary tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time needed to perform insertion and deletion and many other
Analysis of Algorithms
 Analysis of Algorithms Concept Exam Code: 16 All questions are weighted equally. Assume worst case behavior and sufficiently large input sizes unless otherwise specified. Strong induction Consider this
Analysis of Algorithms Concept Exam Code: 16 All questions are weighted equally. Assume worst case behavior and sufficiently large input sizes unless otherwise specified. Strong induction Consider this
Fundamental Algorithms
 WS 2007/2008 Fundamental Algorithms Dmytro Chibisov, Jens Ernst Fakultät für Informatik TU München http://www14.in.tum.de/lehre/2007ws/fa-cse/ Fall Semester 2007 1. AVL Trees As we saw in the previous
WS 2007/2008 Fundamental Algorithms Dmytro Chibisov, Jens Ernst Fakultät für Informatik TU München http://www14.in.tum.de/lehre/2007ws/fa-cse/ Fall Semester 2007 1. AVL Trees As we saw in the previous
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS. Hierarchical data structures: AVL tree, Bayer tree, Heap
 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS Hierarchical data structures: AVL tree, Bayer tree, Heap Summary of the previous lecture TREE is hierarchical (non linear) data structure Binary trees Definitions Full tree,
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS Hierarchical data structures: AVL tree, Bayer tree, Heap Summary of the previous lecture TREE is hierarchical (non linear) data structure Binary trees Definitions Full tree,
AVL Tree Definition. An example of an AVL tree where the heights are shown next to the nodes. Adelson-Velsky and Landis
 Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 0 AVL Trees v 6 3 8 z 0 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser
Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 0 AVL Trees v 6 3 8 z 0 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser
COMP Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures
 COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures Shahin Kamali Lecture 9 - Jan. 22, 2018 CLRS 12.2, 12.3, 13.2, read problem 13-3 University of Manitoba COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures
COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures Shahin Kamali Lecture 9 - Jan. 22, 2018 CLRS 12.2, 12.3, 13.2, read problem 13-3 University of Manitoba COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures
Midterm solutions. n f 3 (n) = 3
 Introduction to Computer Science 1, SE361 DGIST April 20, 2016 Professors Min-Soo Kim and Taesup Moon Midterm solutions Midterm solutions The midterm is a 1.5 hour exam (4:30pm 6:00pm). This is a closed
Introduction to Computer Science 1, SE361 DGIST April 20, 2016 Professors Min-Soo Kim and Taesup Moon Midterm solutions Midterm solutions The midterm is a 1.5 hour exam (4:30pm 6:00pm). This is a closed
COMP Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures
 COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures Shahin Kamali Lecture 9 - Jan. 22, 2018 CLRS 12.2, 12.3, 13.2, read problem 13-3 University of Manitoba 1 / 12 Binary Search Trees (review) Structure
COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures Shahin Kamali Lecture 9 - Jan. 22, 2018 CLRS 12.2, 12.3, 13.2, read problem 13-3 University of Manitoba 1 / 12 Binary Search Trees (review) Structure
CSE 332, Spring 2010, Midterm Examination 30 April 2010
 CSE 332, Spring 2010, Midterm Examination 30 April 2010 Please do not turn the page until the bell rings. Rules: The exam is closed-book, closed-note. You may use a calculator for basic arithmetic only.
CSE 332, Spring 2010, Midterm Examination 30 April 2010 Please do not turn the page until the bell rings. Rules: The exam is closed-book, closed-note. You may use a calculator for basic arithmetic only.
AVL Trees Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser AVL Trees 1
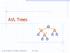 AVL Trees v 6 3 8 z 20 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser AVL Trees AVL Tree Definition Adelson-Velsky and Landis binary search tree balanced each internal node v the heights of the children of v can 2 3 7
AVL Trees v 6 3 8 z 20 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser AVL Trees AVL Tree Definition Adelson-Velsky and Landis binary search tree balanced each internal node v the heights of the children of v can 2 3 7
Balanced Binary Search Trees
 Balanced Binary Search Trees In the previous section we looked at building a binary search tree. As we learned, the performance of the binary search tree can degrade to O(n) for operations like getand
Balanced Binary Search Trees In the previous section we looked at building a binary search tree. As we learned, the performance of the binary search tree can degrade to O(n) for operations like getand
Properties of red-black trees
 Red-Black Trees Introduction We have seen that a binary search tree is a useful tool. I.e., if its height is h, then we can implement any basic operation on it in O(h) units of time. The problem: given
Red-Black Trees Introduction We have seen that a binary search tree is a useful tool. I.e., if its height is h, then we can implement any basic operation on it in O(h) units of time. The problem: given
COMP171. AVL-Trees (Part 1)
 COMP11 AVL-Trees (Part 1) AVL Trees / Slide 2 Data, a set of elements Data structure, a structured set of elements, linear, tree, graph, Linear: a sequence of elements, array, linked lists Tree: nested
COMP11 AVL-Trees (Part 1) AVL Trees / Slide 2 Data, a set of elements Data structure, a structured set of elements, linear, tree, graph, Linear: a sequence of elements, array, linked lists Tree: nested
We will show that the height of a RB tree on n vertices is approximately 2*log n. In class I presented a simple structural proof of this claim:
 We have seen that the insert operation on a RB takes an amount of time proportional to the number of the levels of the tree (since the additional operations required to do any rebalancing require constant
We have seen that the insert operation on a RB takes an amount of time proportional to the number of the levels of the tree (since the additional operations required to do any rebalancing require constant
ECE250: Algorithms and Data Structures AVL Trees (Part A)
 ECE250: Algorithms and Data Structures AVL Trees (Part A) Ladan Tahvildari, PEng, SMIEEE Associate Professor Software Technologies Applied Research (STAR) Group Dept. of Elect. & Comp. Eng. University
ECE250: Algorithms and Data Structures AVL Trees (Part A) Ladan Tahvildari, PEng, SMIEEE Associate Professor Software Technologies Applied Research (STAR) Group Dept. of Elect. & Comp. Eng. University
COSC160: Data Structures Balanced Trees. Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor
 COSC160: Data Structures Balanced Trees Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor Outline I. Balanced Trees I. AVL Trees I. Balance Constraint II. Examples III. Searching IV. Insertions V. Removals
COSC160: Data Structures Balanced Trees Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor Outline I. Balanced Trees I. AVL Trees I. Balance Constraint II. Examples III. Searching IV. Insertions V. Removals
CSI33 Data Structures
 Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College November 21, 2018 Outline Outline 1 C++ Supplement 1.3: Balanced Binary Search Trees Balanced Binary Search Trees Outline
Outline Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Bronx Community College November 21, 2018 Outline Outline 1 C++ Supplement 1.3: Balanced Binary Search Trees Balanced Binary Search Trees Outline
Figure 4.1: The evolution of a rooted tree.
 106 CHAPTER 4. INDUCTION, RECURSION AND RECURRENCES 4.6 Rooted Trees 4.6.1 The idea of a rooted tree We talked about how a tree diagram helps us visualize merge sort or other divide and conquer algorithms.
106 CHAPTER 4. INDUCTION, RECURSION AND RECURRENCES 4.6 Rooted Trees 4.6.1 The idea of a rooted tree We talked about how a tree diagram helps us visualize merge sort or other divide and conquer algorithms.
Solutions. (a) Claim: A d-ary tree of height h has at most 1 + d +...
 Design and Analysis of Algorithms nd August, 016 Problem Sheet 1 Solutions Sushant Agarwal Solutions 1. A d-ary tree is a rooted tree in which each node has at most d children. Show that any d-ary tree
Design and Analysis of Algorithms nd August, 016 Problem Sheet 1 Solutions Sushant Agarwal Solutions 1. A d-ary tree is a rooted tree in which each node has at most d children. Show that any d-ary tree
Inf 2B: AVL Trees. Lecture 5 of ADS thread. Kyriakos Kalorkoti. School of Informatics University of Edinburgh
 Inf 2B: AVL Trees Lecture 5 of ADS thread Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Dictionaries A Dictionary stores key element pairs, called items. Several elements might have
Inf 2B: AVL Trees Lecture 5 of ADS thread Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Dictionaries A Dictionary stores key element pairs, called items. Several elements might have
Lecture 6: Analysis of Algorithms (CS )
 Lecture 6: Analysis of Algorithms (CS583-002) Amarda Shehu October 08, 2014 1 Outline of Today s Class 2 Traversals Querying Insertion and Deletion Sorting with BSTs 3 Red-black Trees Height of a Red-black
Lecture 6: Analysis of Algorithms (CS583-002) Amarda Shehu October 08, 2014 1 Outline of Today s Class 2 Traversals Querying Insertion and Deletion Sorting with BSTs 3 Red-black Trees Height of a Red-black
Search Trees - 1 Venkatanatha Sarma Y
 Search Trees - 1 Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11 Objectives To introduce, discuss and analyse the different ways to realise balanced Binary Search Trees
Search Trees - 1 Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11 Objectives To introduce, discuss and analyse the different ways to realise balanced Binary Search Trees
CSCI2100B Data Structures Trees
 CSCI2100B Data Structures Trees Irwin King king@cse.cuhk.edu.hk http://www.cse.cuhk.edu.hk/~king Department of Computer Science & Engineering The Chinese University of Hong Kong Introduction General Tree
CSCI2100B Data Structures Trees Irwin King king@cse.cuhk.edu.hk http://www.cse.cuhk.edu.hk/~king Department of Computer Science & Engineering The Chinese University of Hong Kong Introduction General Tree
Search Trees. Undirected graph Directed graph Tree Binary search tree
 Search Trees Undirected graph Directed graph Tree Binary search tree 1 Binary Search Tree Binary search key property: Let x be a node in a binary search tree. If y is a node in the left subtree of x, then
Search Trees Undirected graph Directed graph Tree Binary search tree 1 Binary Search Tree Binary search key property: Let x be a node in a binary search tree. If y is a node in the left subtree of x, then
Red-Black Trees. Based on materials by Dennis Frey, Yun Peng, Jian Chen, and Daniel Hood
 Red-Black Trees Based on materials by Dennis Frey, Yun Peng, Jian Chen, and Daniel Hood Quick Review of Binary Search Trees n Given a node n... q All elements of n s left subtree are less than n.data q
Red-Black Trees Based on materials by Dennis Frey, Yun Peng, Jian Chen, and Daniel Hood Quick Review of Binary Search Trees n Given a node n... q All elements of n s left subtree are less than n.data q
Introduction. for large input, even access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit times closer to O(log N) binary search tree
 Chapter 4 Trees 2 Introduction for large input, even access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 3 Terminology recursive definition
Chapter 4 Trees 2 Introduction for large input, even access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 3 Terminology recursive definition
COMP Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures
 COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures Shahin Kamali Binary Search Trees CLRS 12.2, 12.3, 13.2, read problem 13-3 University of Manitoba COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures
COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures Shahin Kamali Binary Search Trees CLRS 12.2, 12.3, 13.2, read problem 13-3 University of Manitoba COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures
Analysis of Algorithms
 Analysis of Algorithms Trees-I Prof. Muhammad Saeed Tree Representation.. Analysis Of Algorithms 2 .. Tree Representation Analysis Of Algorithms 3 Nomenclature Nodes (13) Size (13) Degree of a node Depth
Analysis of Algorithms Trees-I Prof. Muhammad Saeed Tree Representation.. Analysis Of Algorithms 2 .. Tree Representation Analysis Of Algorithms 3 Nomenclature Nodes (13) Size (13) Degree of a node Depth
Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees
 Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees 1 * are self-adjusting binary search trees in which the shape of the tree is changed based upon the accesses performed upon the elements. When an element of a splay tree
Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees 1 * are self-adjusting binary search trees in which the shape of the tree is changed based upon the accesses performed upon the elements. When an element of a splay tree
Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees
 Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees 1 * are self-adjusting binary search trees in which the shape of the tree is changed based upon the accesses performed upon the elements. When an element of a splay tree
Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees 1 * are self-adjusting binary search trees in which the shape of the tree is changed based upon the accesses performed upon the elements. When an element of a splay tree
9/29/2016. Chapter 4 Trees. Introduction. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology
 Introduction Chapter 4 Trees for large input, even linear access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit average running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 2 Terminology recursive
Introduction Chapter 4 Trees for large input, even linear access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit average running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 2 Terminology recursive
Efficient Access to Non-Sequential Elements of a Search Tree
 Efficient Access to Non-Sequential Elements of a Search Tree Lubomir Stanchev Computer Science Department Indiana University - Purdue University Fort Wayne Fort Wayne, IN, USA stanchel@ipfw.edu Abstract
Efficient Access to Non-Sequential Elements of a Search Tree Lubomir Stanchev Computer Science Department Indiana University - Purdue University Fort Wayne Fort Wayne, IN, USA stanchel@ipfw.edu Abstract
AVL Trees. (AVL Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 17
 AVL Trees (AVL Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 17 Balanced Binary Tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time
AVL Trees (AVL Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 17 Balanced Binary Tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time
Part 2: Balanced Trees
 Part 2: Balanced Trees 1 AVL Trees We could dene a perfectly balanced binary search tree with N nodes to be a complete binary search tree, one in which every level except the last is completely full. A
Part 2: Balanced Trees 1 AVL Trees We could dene a perfectly balanced binary search tree with N nodes to be a complete binary search tree, one in which every level except the last is completely full. A
Friday Four Square! 4:15PM, Outside Gates
 Binary Search Trees Friday Four Square! 4:15PM, Outside Gates Implementing Set On Monday and Wednesday, we saw how to implement the Map and Lexicon, respectively. Let's now turn our attention to the Set.
Binary Search Trees Friday Four Square! 4:15PM, Outside Gates Implementing Set On Monday and Wednesday, we saw how to implement the Map and Lexicon, respectively. Let's now turn our attention to the Set.
Chapter 4: Trees. 4.2 For node B :
 Chapter : Trees. (a) A. (b) G, H, I, L, M, and K.. For node B : (a) A. (b) D and E. (c) C. (d). (e).... There are N nodes. Each node has two pointers, so there are N pointers. Each node but the root has
Chapter : Trees. (a) A. (b) G, H, I, L, M, and K.. For node B : (a) A. (b) D and E. (c) C. (d). (e).... There are N nodes. Each node has two pointers, so there are N pointers. Each node but the root has
We assume uniform hashing (UH):
 We assume uniform hashing (UH): the probe sequence of each key is equally likely to be any of the! permutations of 0,1,, 1 UH generalizes the notion of SUH that produces not just a single number, but a
We assume uniform hashing (UH): the probe sequence of each key is equally likely to be any of the! permutations of 0,1,, 1 UH generalizes the notion of SUH that produces not just a single number, but a
CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming. Lecture 25 Fall 2018 Instructor: B 2
 CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming Lecture 25 Fall 2018 Instructor: B 2 Last Time Binary search trees (Ch 14) The locate method Further Implementation 2 Today s Outline Binary search trees
CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming Lecture 25 Fall 2018 Instructor: B 2 Last Time Binary search trees (Ch 14) The locate method Further Implementation 2 Today s Outline Binary search trees
Lecture 16 Notes AVL Trees
 Lecture 16 Notes AVL Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Spring 2016) Frank Pfenning 1 Introduction Binary search trees are an excellent data structure to implement associative arrays,
Lecture 16 Notes AVL Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Spring 2016) Frank Pfenning 1 Introduction Binary search trees are an excellent data structure to implement associative arrays,
Treaps. 1 Binary Search Trees (BSTs) CSE341T/CSE549T 11/05/2014. Lecture 19
 CSE34T/CSE549T /05/04 Lecture 9 Treaps Binary Search Trees (BSTs) Search trees are tree-based data structures that can be used to store and search for items that satisfy a total order. There are many types
CSE34T/CSE549T /05/04 Lecture 9 Treaps Binary Search Trees (BSTs) Search trees are tree-based data structures that can be used to store and search for items that satisfy a total order. There are many types
CS 261 Data Structures. AVL Trees
 CS 261 Data Structures AVL Trees 1 Binary Search Tree Complexity of BST operations: proportional to the length of the path from a node to the root Unbalanced tree: operations may be O(n) E.g.: adding elements
CS 261 Data Structures AVL Trees 1 Binary Search Tree Complexity of BST operations: proportional to the length of the path from a node to the root Unbalanced tree: operations may be O(n) E.g.: adding elements
CMSC351 - Fall 2014, Homework #2
 CMSC351 - Fall 2014, Homework #2 Due: October 8th at the start of class Name: Section: Grades depend on neatness and clarity. Write your answers with enough detail about your approach and concepts used,
CMSC351 - Fall 2014, Homework #2 Due: October 8th at the start of class Name: Section: Grades depend on neatness and clarity. Write your answers with enough detail about your approach and concepts used,
Lecture 13: AVL Trees and Binary Heaps
 Data Structures Brett Bernstein Lecture 13: AVL Trees and Binary Heaps Review Exercises 1. ( ) Interview question: Given an array show how to shue it randomly so that any possible reordering is equally
Data Structures Brett Bernstein Lecture 13: AVL Trees and Binary Heaps Review Exercises 1. ( ) Interview question: Given an array show how to shue it randomly so that any possible reordering is equally
Binary search trees (chapters )
 Binary search trees (chapters 18.1 18.3) Binary search trees In a binary search tree (BST), every node is greater than all its left descendants, and less than all its right descendants (recall that this
Binary search trees (chapters 18.1 18.3) Binary search trees In a binary search tree (BST), every node is greater than all its left descendants, and less than all its right descendants (recall that this
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Department of Computer Science. Second Examination
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Department of Computer Science Second Examination CS 225 Data Structures and Software Principles Spring 2012 7p-9p, Tuesday, April 3 Name: NetID: Lab Section
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Department of Computer Science Second Examination CS 225 Data Structures and Software Principles Spring 2012 7p-9p, Tuesday, April 3 Name: NetID: Lab Section
Search Trees. Chapter 11
 Search Trees Chapter 6 4 8 9 Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Binar Search Trees A binar search tree is a proper binar tree storing ke-value
Search Trees Chapter 6 4 8 9 Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Binar Search Trees A binar search tree is a proper binar tree storing ke-value
Algorithms. Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees
 Algorithms Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees Recall the rules for BST deletion 1. If vertex to be deleted is a leaf, just delete it. 2. If vertex to be deleted has just one child, replace it with that
Algorithms Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees Recall the rules for BST deletion 1. If vertex to be deleted is a leaf, just delete it. 2. If vertex to be deleted has just one child, replace it with that
Lecture 16 AVL Trees
 Lecture 16 AVL Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Fall 2018) Frank Pfenning Binary search trees are an excellent data structure to implement associative arrays, maps, sets, and similar
Lecture 16 AVL Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Fall 2018) Frank Pfenning Binary search trees are an excellent data structure to implement associative arrays, maps, sets, and similar
Binary search trees (chapters )
 Binary search trees (chapters 18.1 18.3) Binary search trees In a binary search tree (BST), every node is greater than all its left descendants, and less than all its right descendants (recall that this
Binary search trees (chapters 18.1 18.3) Binary search trees In a binary search tree (BST), every node is greater than all its left descendants, and less than all its right descendants (recall that this
10/23/2013. AVL Trees. Height of an AVL Tree. Height of an AVL Tree. AVL Trees
 // AVL Trees AVL Trees An AVL tree is a binary search tree with a balance condition. AVL is named for its inventors: Adel son-vel skii and Landis AVL tree approximates the ideal tree (completely balanced
// AVL Trees AVL Trees An AVL tree is a binary search tree with a balance condition. AVL is named for its inventors: Adel son-vel skii and Landis AVL tree approximates the ideal tree (completely balanced
Lecture: Analysis of Algorithms (CS )
 Lecture: Analysis of Algorithms (CS583-002) Amarda Shehu Fall 2017 1 Binary Search Trees Traversals, Querying, Insertion, and Deletion Sorting with BSTs 2 Example: Red-black Trees Height of a Red-black
Lecture: Analysis of Algorithms (CS583-002) Amarda Shehu Fall 2017 1 Binary Search Trees Traversals, Querying, Insertion, and Deletion Sorting with BSTs 2 Example: Red-black Trees Height of a Red-black
CSci 231 Final Review
 CSci 231 Final Review Here is a list of topics for the final. Generally you are responsible for anything discussed in class (except topics that appear italicized), and anything appearing on the homeworks.
CSci 231 Final Review Here is a list of topics for the final. Generally you are responsible for anything discussed in class (except topics that appear italicized), and anything appearing on the homeworks.
Solutions for Algorithm Design Exercises and Tests
 Chapter 4 Solutions for Algorithm Design Exercises and Tests 4.1 Divide and Conquer 4.1.1 Solutions for Selected Exercises Solution for Exercise #1 in Section 1.9 Solution for Part (a): This problem requires
Chapter 4 Solutions for Algorithm Design Exercises and Tests 4.1 Divide and Conquer 4.1.1 Solutions for Selected Exercises Solution for Exercise #1 in Section 1.9 Solution for Part (a): This problem requires
Binary search trees. Binary search trees are data structures based on binary trees that support operations on dynamic sets.
 COMP3600/6466 Algorithms 2018 Lecture 12 1 Binary search trees Reading: Cormen et al, Sections 12.1 to 12.3 Binary search trees are data structures based on binary trees that support operations on dynamic
COMP3600/6466 Algorithms 2018 Lecture 12 1 Binary search trees Reading: Cormen et al, Sections 12.1 to 12.3 Binary search trees are data structures based on binary trees that support operations on dynamic
CHAPTER 10 AVL TREES. 3 8 z 4
 CHAPTER 10 AVL TREES v 6 3 8 z 4 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY
CHAPTER 10 AVL TREES v 6 3 8 z 4 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY
Chapter 13. Michelle Bodnar, Andrew Lohr. April 12, 2016
 Chapter 13 Michelle Bodnar, Andrew Lohr April 1, 016 Exercise 13.1-1 8 4 1 6 10 14 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 We shorten IL to so that it can be more easily displayed in the document. The following has black height.
Chapter 13 Michelle Bodnar, Andrew Lohr April 1, 016 Exercise 13.1-1 8 4 1 6 10 14 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 We shorten IL to so that it can be more easily displayed in the document. The following has black height.
MAT 7003 : Mathematical Foundations. (for Software Engineering) J Paul Gibson, A207.
 MAT 7003 : Mathematical Foundations (for Software Engineering) J Paul Gibson, A207 paul.gibson@it-sudparis.eu http://www-public.it-sudparis.eu/~gibson/teaching/mat7003/ Graphs and Trees http://www-public.it-sudparis.eu/~gibson/teaching/mat7003/l2-graphsandtrees.pdf
MAT 7003 : Mathematical Foundations (for Software Engineering) J Paul Gibson, A207 paul.gibson@it-sudparis.eu http://www-public.it-sudparis.eu/~gibson/teaching/mat7003/ Graphs and Trees http://www-public.it-sudparis.eu/~gibson/teaching/mat7003/l2-graphsandtrees.pdf
EXAM ELEMENTARY MATH FOR GMT: ALGORITHM ANALYSIS NOVEMBER 7, 2013, 13:15-16:15, RUPPERT D
 SOLUTIONS EXAM ELEMENTARY MATH FOR GMT: ALGORITHM ANALYSIS NOVEMBER 7, 2013, 13:15-16:15, RUPPERT D This exam consists of 6 questions, worth 10 points in total, and a bonus question for 1 more point. Using
SOLUTIONS EXAM ELEMENTARY MATH FOR GMT: ALGORITHM ANALYSIS NOVEMBER 7, 2013, 13:15-16:15, RUPPERT D This exam consists of 6 questions, worth 10 points in total, and a bonus question for 1 more point. Using
AVL Trees / Slide 2. AVL Trees / Slide 4. Let N h be the minimum number of nodes in an AVL tree of height h. AVL Trees / Slide 6
 COMP11 Spring 008 AVL Trees / Slide Balanced Binary Search Tree AVL-Trees Worst case height of binary search tree: N-1 Insertion, deletion can be O(N) in the worst case We want a binary search tree with
COMP11 Spring 008 AVL Trees / Slide Balanced Binary Search Tree AVL-Trees Worst case height of binary search tree: N-1 Insertion, deletion can be O(N) in the worst case We want a binary search tree with
Course Review. Cpt S 223 Fall 2009
 Course Review Cpt S 223 Fall 2009 1 Final Exam When: Tuesday (12/15) 8-10am Where: in class Closed book, closed notes Comprehensive Material for preparation: Lecture slides & class notes Homeworks & program
Course Review Cpt S 223 Fall 2009 1 Final Exam When: Tuesday (12/15) 8-10am Where: in class Closed book, closed notes Comprehensive Material for preparation: Lecture slides & class notes Homeworks & program
Advanced Set Representation Methods
 Advanced Set Representation Methods AVL trees. 2-3(-4) Trees. Union-Find Set ADT DSA - lecture 4 - T.U.Cluj-Napoca - M. Joldos 1 Advanced Set Representation. AVL Trees Problem with BSTs: worst case operation
Advanced Set Representation Methods AVL trees. 2-3(-4) Trees. Union-Find Set ADT DSA - lecture 4 - T.U.Cluj-Napoca - M. Joldos 1 Advanced Set Representation. AVL Trees Problem with BSTs: worst case operation
21# 33# 90# 91# 34# # 39# # # 31# 98# 0# 1# 2# 3# 4# 5# 6# 7# 8# 9# 10# #
 1. Prove that n log n n is Ω(n). York University EECS 11Z Winter 1 Problem Set 3 Instructor: James Elder Solutions log n n. Thus n log n n n n n log n n Ω(n).. Show that n is Ω (n log n). We seek a c >,
1. Prove that n log n n is Ω(n). York University EECS 11Z Winter 1 Problem Set 3 Instructor: James Elder Solutions log n n. Thus n log n n n n n log n n Ω(n).. Show that n is Ω (n log n). We seek a c >,
lecture17: AVL Trees
 lecture17: Largely based on slides by Cinda Heeren CS 225 UIUC 9th July, 2013 Announcements mt2 tonight! mp5.1 extra credit due Friday (7/12) An interesting tree Can you make a BST that looks like a zig
lecture17: Largely based on slides by Cinda Heeren CS 225 UIUC 9th July, 2013 Announcements mt2 tonight! mp5.1 extra credit due Friday (7/12) An interesting tree Can you make a BST that looks like a zig
Binary search trees. We can define a node in a search tree using a Python class definition as follows: class SearchTree:
 Binary search trees An important use of binary trees is to store values that we may want to look up later. For instance, a binary search tree could be used to store a dictionary of words. A binary search
Binary search trees An important use of binary trees is to store values that we may want to look up later. For instance, a binary search tree could be used to store a dictionary of words. A binary search
Topics. Trees Vojislav Kecman. Which graphs are trees? Terminology. Terminology Trees as Models Some Tree Theorems Applications of Trees CMSC 302
 Topics VCU, Department of Computer Science CMSC 302 Trees Vojislav Kecman Terminology Trees as Models Some Tree Theorems Applications of Trees Binary Search Tree Decision Tree Tree Traversal Spanning Trees
Topics VCU, Department of Computer Science CMSC 302 Trees Vojislav Kecman Terminology Trees as Models Some Tree Theorems Applications of Trees Binary Search Tree Decision Tree Tree Traversal Spanning Trees
CS60020: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning. Sourangshu Bhattacharya
 CS62: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Binary Search Tree - Best Time All BST operations are O(d), where d is tree depth minimum d is d = ëlog for a binary tree
CS62: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Binary Search Tree - Best Time All BST operations are O(d), where d is tree depth minimum d is d = ëlog for a binary tree
TREES. Trees - Introduction
 TREES Chapter 6 Trees - Introduction All previous data organizations we've studied are linear each element can have only one predecessor and successor Accessing all elements in a linear sequence is O(n)
TREES Chapter 6 Trees - Introduction All previous data organizations we've studied are linear each element can have only one predecessor and successor Accessing all elements in a linear sequence is O(n)
CS60020: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning. Sourangshu Bhattacharya
 CS62: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Balanced search trees Balanced search tree: A search-tree data structure for which a height of O(lg n) is guaranteed when
CS62: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Balanced search trees Balanced search tree: A search-tree data structure for which a height of O(lg n) is guaranteed when
Binary Search Trees Treesort
 Treesort CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Friday, November 13, 2009 Glenn G. Chappell Department of Computer Science University of Alaska Fairbanks CHAPPELLG@member.ams.org 2005 2009
Treesort CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Friday, November 13, 2009 Glenn G. Chappell Department of Computer Science University of Alaska Fairbanks CHAPPELLG@member.ams.org 2005 2009
LECTURE 18 AVL TREES
 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LECTURE 18 AVL TREES IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD PROTOTYPICAL EXAMPLES These two examples demonstrate how we can correct for imbalances: starting
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LECTURE 18 AVL TREES IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD PROTOTYPICAL EXAMPLES These two examples demonstrate how we can correct for imbalances: starting
Section 05: Solutions
 Section 05: Solutions 1. Memory and B-Tree (a) Based on your understanding of how computers access and store memory, why might it be faster to access all the elements of an array-based queue than to access
Section 05: Solutions 1. Memory and B-Tree (a) Based on your understanding of how computers access and store memory, why might it be faster to access all the elements of an array-based queue than to access
AVL Trees (10.2) AVL Trees
 AVL Trees (0.) CSE 0 Winter 0 8 February 0 AVL Trees AVL trees are balanced. An AVL Tree is a binary search tree such that for every internal node v of T, the heights of the children of v can differ by
AVL Trees (0.) CSE 0 Winter 0 8 February 0 AVL Trees AVL trees are balanced. An AVL Tree is a binary search tree such that for every internal node v of T, the heights of the children of v can differ by
Multi-Way Search Trees
 Multi-Way Search Trees Manolis Koubarakis 1 Multi-Way Search Trees Multi-way trees are trees such that each internal node can have many children. Let us assume that the entries we store in a search tree
Multi-Way Search Trees Manolis Koubarakis 1 Multi-Way Search Trees Multi-way trees are trees such that each internal node can have many children. Let us assume that the entries we store in a search tree
CSE 373: AVL trees. Michael Lee Friday, Jan 19, 2018
 CSE 373: AVL trees Michael Lee Friday, Jan 19, 2018 1 Warmup Warmup: What is an invariant? What are the AVL tree invariants, exactly? Discuss with your neighbor. 2 AVL Trees: Invariants Core idea: add
CSE 373: AVL trees Michael Lee Friday, Jan 19, 2018 1 Warmup Warmup: What is an invariant? What are the AVL tree invariants, exactly? Discuss with your neighbor. 2 AVL Trees: Invariants Core idea: add
Search Trees (Ch. 9) > = Binary Search Trees 1
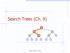 Search Trees (Ch. 9) < 6 > = 1 4 8 9 Binary Search Trees 1 Ordered Dictionaries Keys are assumed to come from a total order. New operations: closestbefore(k) closestafter(k) Binary Search Trees Binary
Search Trees (Ch. 9) < 6 > = 1 4 8 9 Binary Search Trees 1 Ordered Dictionaries Keys are assumed to come from a total order. New operations: closestbefore(k) closestafter(k) Binary Search Trees Binary
Trees. Reading: Weiss, Chapter 4. Cpt S 223, Fall 2007 Copyright: Washington State University
 Trees Reading: Weiss, Chapter 4 1 Generic Rooted Trees 2 Terms Node, Edge Internal node Root Leaf Child Sibling Descendant Ancestor 3 Tree Representations n-ary trees Each internal node can have at most
Trees Reading: Weiss, Chapter 4 1 Generic Rooted Trees 2 Terms Node, Edge Internal node Root Leaf Child Sibling Descendant Ancestor 3 Tree Representations n-ary trees Each internal node can have at most
Binary Search Trees, etc.
 Chapter 12 Binary Search Trees, etc. Binary Search trees are data structures that support a variety of dynamic set operations, e.g., Search, Minimum, Maximum, Predecessors, Successors, Insert, and Delete.
Chapter 12 Binary Search Trees, etc. Binary Search trees are data structures that support a variety of dynamic set operations, e.g., Search, Minimum, Maximum, Predecessors, Successors, Insert, and Delete.
Questions. 6. Suppose we were to define a hash code on strings s by:
 Questions 1. Suppose you are given a list of n elements. A brute force method to find duplicates could use two (nested) loops. The outer loop iterates over position i the list, and the inner loop iterates
Questions 1. Suppose you are given a list of n elements. A brute force method to find duplicates could use two (nested) loops. The outer loop iterates over position i the list, and the inner loop iterates
Outline. Definition. 2 Height-Balance. 3 Searches. 4 Rotations. 5 Insertion. 6 Deletions. 7 Reference. 1 Every node is either red or black.
 Outline 1 Definition Computer Science 331 Red-Black rees Mike Jacobson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Lectures #20-22 2 Height-Balance 3 Searches 4 Rotations 5 s: Main Case 6 Partial
Outline 1 Definition Computer Science 331 Red-Black rees Mike Jacobson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Lectures #20-22 2 Height-Balance 3 Searches 4 Rotations 5 s: Main Case 6 Partial
March 20/2003 Jayakanth Srinivasan,
 Definition : A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices, and E, a set of unordered pairs of distinct elements of V called edges. Definition : In a multigraph G = (V, E) two or
Definition : A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices, and E, a set of unordered pairs of distinct elements of V called edges. Definition : In a multigraph G = (V, E) two or
Course Review for Finals. Cpt S 223 Fall 2008
 Course Review for Finals Cpt S 223 Fall 2008 1 Course Overview Introduction to advanced data structures Algorithmic asymptotic analysis Programming data structures Program design based on performance i.e.,
Course Review for Finals Cpt S 223 Fall 2008 1 Course Overview Introduction to advanced data structures Algorithmic asymptotic analysis Programming data structures Program design based on performance i.e.,
Balanced search trees
 Balanced search trees Ordinary binary search trees have expected height Θ(log n) if items are inserted and deleted in random order, but for other orders the height can be Θ(n). This is undesirable, since
Balanced search trees Ordinary binary search trees have expected height Θ(log n) if items are inserted and deleted in random order, but for other orders the height can be Θ(n). This is undesirable, since
Section 05: Solutions
 Section 05: Solutions 1. Asymptotic Analysis (a) Applying definitions For each of the following, choose a c and n 0 which show f(n) O(g(n)). Explain why your values of c and n 0 work. (i) f(n) = 5000n
Section 05: Solutions 1. Asymptotic Analysis (a) Applying definitions For each of the following, choose a c and n 0 which show f(n) O(g(n)). Explain why your values of c and n 0 work. (i) f(n) = 5000n
/633 Introduction to Algorithms Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Sorting lower bound and Linear-time sorting Date: 9/19/17
 601.433/633 Introduction to Algorithms Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Sorting lower bound and Linear-time sorting Date: 9/19/17 5.1 Introduction You should all know a few ways of sorting in O(n log n)
601.433/633 Introduction to Algorithms Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Sorting lower bound and Linear-time sorting Date: 9/19/17 5.1 Introduction You should all know a few ways of sorting in O(n log n)
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures and Algorithms Spring 2009-2010 Outline BST Trees (contd.) 1 BST Trees (contd.) Outline BST Trees (contd.) 1 BST Trees (contd.) The bad news about BSTs... Problem with BSTs is that there
Data Structures and Algorithms Spring 2009-2010 Outline BST Trees (contd.) 1 BST Trees (contd.) Outline BST Trees (contd.) 1 BST Trees (contd.) The bad news about BSTs... Problem with BSTs is that there
Lecture 8: The Traveling Salesman Problem
 Lecture 8: The Traveling Salesman Problem Let G = (V, E) be an undirected graph. A Hamiltonian cycle of G is a cycle that visits every vertex v V exactly once. Instead of Hamiltonian cycle, we sometimes
Lecture 8: The Traveling Salesman Problem Let G = (V, E) be an undirected graph. A Hamiltonian cycle of G is a cycle that visits every vertex v V exactly once. Instead of Hamiltonian cycle, we sometimes
Announcements. Midterm exam 2, Thursday, May 18. Today s topic: Binary trees (Ch. 8) Next topic: Priority queues and heaps. Break around 11:45am
 Announcements Midterm exam 2, Thursday, May 18 Closed book/notes but one sheet of paper allowed Covers up to stacks and queues Today s topic: Binary trees (Ch. 8) Next topic: Priority queues and heaps
Announcements Midterm exam 2, Thursday, May 18 Closed book/notes but one sheet of paper allowed Covers up to stacks and queues Today s topic: Binary trees (Ch. 8) Next topic: Priority queues and heaps
Ch04 Balanced Search Trees
 Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 05 Ch0 Balanced Search Trees v 3 8 z Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries,
Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 05 Ch0 Balanced Search Trees v 3 8 z Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries,
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees
 Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
CS 315 Data Structures mid-term 2
 CS 315 Data Structures mid-term 2 1) Shown below is an AVL tree T. Nov 14, 2012 Solutions to OPEN BOOK section. (a) Suggest a key whose insertion does not require any rotation. 18 (b) Suggest a key, if
CS 315 Data Structures mid-term 2 1) Shown below is an AVL tree T. Nov 14, 2012 Solutions to OPEN BOOK section. (a) Suggest a key whose insertion does not require any rotation. 18 (b) Suggest a key, if
Binary search trees 3. Binary search trees. Binary search trees 2. Reading: Cormen et al, Sections 12.1 to 12.3
 Binary search trees Reading: Cormen et al, Sections 12.1 to 12.3 Binary search trees 3 Binary search trees are data structures based on binary trees that support operations on dynamic sets. Each element
Binary search trees Reading: Cormen et al, Sections 12.1 to 12.3 Binary search trees 3 Binary search trees are data structures based on binary trees that support operations on dynamic sets. Each element
RANK-PAIRING HEAPS BERNHARD HAEUPLER 1, SIDDHARTHA SEN 2,4, AND ROBERT E. TARJAN 3,4
 RANK-PAIRING HEAPS BERNHARD HAEUPLER 1, SIDDHARTHA SEN 2,4, AND ROBERT E. TARJAN 3,4 Abstract. We introduce the rank-pairing heap, an implementation of heaps that combines the asymptotic efficiency of
RANK-PAIRING HEAPS BERNHARD HAEUPLER 1, SIDDHARTHA SEN 2,4, AND ROBERT E. TARJAN 3,4 Abstract. We introduce the rank-pairing heap, an implementation of heaps that combines the asymptotic efficiency of
Balanced Trees Part Two
 Balanced Trees Part Two Outline for Today Recap from Last Time Review of B-trees, 2-3-4 trees, and red/black trees. Order Statistic Trees BSTs with indexing. Augmented Binary Search Trees Building new
Balanced Trees Part Two Outline for Today Recap from Last Time Review of B-trees, 2-3-4 trees, and red/black trees. Order Statistic Trees BSTs with indexing. Augmented Binary Search Trees Building new
Computer Science 302 Spring 2007 Practice Final Examination: Part I
 Computer Science 302 Spring 2007 Practice Final Examination: Part I Name: This practice examination is much longer than the real final examination will be. If you can work all the problems here, you will
Computer Science 302 Spring 2007 Practice Final Examination: Part I Name: This practice examination is much longer than the real final examination will be. If you can work all the problems here, you will
Lesson 21: AVL Trees. Rotation
 The time required to perform operations on a binary search tree is proportional to the length of the path from root to leaf. This isn t bad in a well-balanced tree. But nothing prevents a tree from becoming
The time required to perform operations on a binary search tree is proportional to the length of the path from root to leaf. This isn t bad in a well-balanced tree. But nothing prevents a tree from becoming
Efficient Non-Sequential Access and More Ordering Choices in a Search Tree
 Efficient Non-Sequential Access and More Ordering Choices in a Search Tree Lubomir Stanchev Computer Science Department Indiana University - Purdue University Fort Wayne Fort Wayne, IN, USA stanchel@ipfw.edu
Efficient Non-Sequential Access and More Ordering Choices in a Search Tree Lubomir Stanchev Computer Science Department Indiana University - Purdue University Fort Wayne Fort Wayne, IN, USA stanchel@ipfw.edu
Recursively Defined Functions
 Section 5.3 Recursively Defined Functions Definition: A recursive or inductive definition of a function consists of two steps. BASIS STEP: Specify the value of the function at zero. RECURSIVE STEP: Give
Section 5.3 Recursively Defined Functions Definition: A recursive or inductive definition of a function consists of two steps. BASIS STEP: Specify the value of the function at zero. RECURSIVE STEP: Give
Quiz 1 Solutions. (a) f(n) = n g(n) = log n Circle all that apply: f = O(g) f = Θ(g) f = Ω(g)
 Introduction to Algorithms March 11, 2009 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.006 Spring 2009 Professors Sivan Toledo and Alan Edelman Quiz 1 Solutions Problem 1. Quiz 1 Solutions Asymptotic orders
Introduction to Algorithms March 11, 2009 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.006 Spring 2009 Professors Sivan Toledo and Alan Edelman Quiz 1 Solutions Problem 1. Quiz 1 Solutions Asymptotic orders
Final Exam. EECS 2011 Prof. J. Elder - 1 -
 Final Exam Ø Wed Apr 11 2pm 5pm Aviva Tennis Centre Ø Closed Book Ø Format similar to midterm Ø Will cover whole course, with emphasis on material after midterm (maps and hash tables, binary search, loop
Final Exam Ø Wed Apr 11 2pm 5pm Aviva Tennis Centre Ø Closed Book Ø Format similar to midterm Ø Will cover whole course, with emphasis on material after midterm (maps and hash tables, binary search, loop
Balanced Search Trees. CS 3110 Fall 2010
 Balanced Search Trees CS 3110 Fall 2010 Some Search Structures Sorted Arrays Advantages Search in O(log n) time (binary search) Disadvantages Need to know size in advance Insertion, deletion O(n) need
Balanced Search Trees CS 3110 Fall 2010 Some Search Structures Sorted Arrays Advantages Search in O(log n) time (binary search) Disadvantages Need to know size in advance Insertion, deletion O(n) need
