OUTLINE. Hierarchical Models Z-Fighting Primitives Besides Triangles Back Face Culling
|
|
|
- Karen Tyler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MATRIX STACKS
2 OUTLINE Hierarchical Models Z-Fighting Primitives Besides Triangles Back Face Culling
3 HIERARCHICAL MODELS Building scenes where objects move in relation to each other rather than independently Building complex objects from simpler shapes
4 MATRIX STACKS Stack of transformation matrices OpenGL built in matrix stack deprecated (of course) But graphicslib3d library contains MatrixStack with methods: pushmatrix() make a copy of top matrix and push on stack popmatrix() return and remove top matrix on stack multmatrix(m) multiply top matrix on stack by m peek() return top matrix, but don t remove rotate(d, x, y, z) apply to top matrix on stack translate(x, y, z) apply to top matrix on stack scale(x, y, z) apply to top matrix on stack Instead of wrangling multiple model and view matrices in code, can manage them all on a single stack
5 USING A STACK Let s say we want to view our scene from a particular position and watch the objects move Strategy: Set our camera location Push a matrix (identity) onto the stack and multiply it by the view matrix Create the first object and its model matrix Do a push (duplicates the previous matrix) and multiply it by the model matrix Create the next object and model matrix Do a push and multiply it by the model matrix You probably see the pattern here
6 USING A STACK Now, when we draw each object: Call gldrawarrays to draw the object Pop the appropriate matrices off the stack Call gldrawarrays to draw the next object Pop the appropriate matrices off the stack Another pattern
7 JAVA JOGL CODE IN DISPLAY() (1/4) // push view matrix onto the stack mvstack.pushmatrix(); mvstack.translate(-camerax, -cameray, -cameraz); double amt = (double)(system.currenttimemillis())/1000.0; // Assuming we have the location of proj_loc already gl.gluniformmatrix4fv(proj_loc, 1, false, pmat.getfloatvalues(), 0);
8 JAVA JOGL CODE IN DISPLAY() (2/4) // pyramid == sun mvstack.pushmatrix(); mvstack.translate(pyrlocx, pyrlocy, pyrlocz); mvstack.pushmatrix(); mvstack.rotate((system.currenttimemillis())/10.0,1.0,0.0,0.0); gl.gluniformmatrix4fv(mv_loc, 1, false, mvstack.peek().getfloatvalues(), 0); gl.glbindbuffer(gl_array_buffer, vbo[1]); gl.glvertexattribpointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, false, 0, 0); gl.glenablevertexattribarray(0); gl.glenable(gl_depth_test); gl.gldrawarrays(gl_triangles, 0, 18); mvstack.popmatrix(); // Note: we only pop the rotation matrix, not translation
9 JAVA JOGL CODE IN DISPLAY() (3/4) // cube == planet mvstack.pushmatrix(); mvstack.translate(math.sin(amt)*4.0f, 0.0f, Math.cos(amt)*4.0f); mvstack.pushmatrix(); mvstack.rotate((system.currenttimemillis())/10.0,0.0,1.0,0.0); gl.gluniformmatrix4fv(mv_loc, 1, false, mvstack.peek().getfloatvalues(), 0); gl.glbindbuffer(gl_array_buffer, vbo[0]); gl.glvertexattribpointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, false, 0, 0); gl.glenablevertexattribarray(0); gl.gldrawarrays(gl_triangles, 0, 36); mvstack.popmatrix(); // Again, only pop the rotation matrix
10 JAVA JOGL CODE IN DISPLAY() (4/4) // smaller cube == moon mvstack.pushmatrix(); mvstack.translate(0.0f, Math.sin(amt)*2.0f, Math.cos(amt)*2.0f); mvstack.rotate((system.currenttimemillis())/10.0,0.0,0.0,1.0); mvstack.scale(0.25, 0.25, 0.25); gl.gluniformmatrix4fv(mv_loc, 1, false, mvstack.peek().getfloatvalues(), 0); gl.glbindbuffer(gl_array_buffer, vbo[0]); gl.glvertexattribpointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, false, 0, 0); gl.glenablevertexattribarray(0); gl.gldrawarrays(gl_triangles, 0, 36); // Here s where we clean up the stack by popping all mvstack.popmatrix(); mvstack.popmatrix(); mvstack.popmatrix(); mvstack.popmatrix();
11 USING A STACK Since the stack code is all in display(), it gets called each time the frame changes So these matrices are different for each new change
12 SO.. WHY AREN T WE DOING THIS WITH SPHERES? Well we haven t looked at how do create sphere objects yet First, sphere vertices are more elegantly defined by a mathematical function than by listing vertices Second, we need to worry about curved surfaces Otherwise our sphere will look faceted, not smooth We will get to all of that soon
13 Z-FIGHTING When the depth (z axis) of two objects is similar, the display can get confused Often seen in terrain and shadows Caused by floating point rounding error and limited precision in the of z-buffer values
14 Z-FIGHTING Some solutions: Move objects apart slightly Don t make the near clipping plane too close to the camera
15 OPENGL PRIMITIVES AND THEIR INTERPRETATIONS GL_TRIANGLES GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP GL_TRIANGLE_FAN
16 OPENGL PRIMITIVES AND THEIR INTERPRETATIONS GL_LINES GL_LINE_STRIP
17 BACK FACE CULLING Affects rendering efficiency in a good way Every primitive we draw has a front face and a back face When we construct a cube out of triangles, only the front face of each triangle shows The cube is a closed object But OpenGL is still interpolating colors, etc. for the back face We can enable back face culling by: glenable(gl_cullface); We may also need to tell OpenGL how to tell what is a back face: gl_frontface(gl_ccw); Default is CCW counter clockwise that is, if the vertices progress in a counter clockwise order Called the winding order
18 BACK FACE CULLING If using back face culling, want to make your objects so that triangles defining the exterior are the same winding order Usually counter-clockwise May use culling in interesting ways With transparent objects, may want to see inside, not outside Probably don t want to use back face culling in objects that are not closed
19 SUMMARY Hierarchical Models Z-Fighting Primitives Besides Triangles Back Face Culling 19
Introduction to OpenGL
 OpenGL is an alternative to Direct3D for 3D graphics rendering Originally developed by Silicon Graphics Inc (SGI), turned over to multi-vendor group (OpenGL Architecture Review Board) in 1992 Unlike DirectX,
OpenGL is an alternative to Direct3D for 3D graphics rendering Originally developed by Silicon Graphics Inc (SGI), turned over to multi-vendor group (OpenGL Architecture Review Board) in 1992 Unlike DirectX,
SFU CMPT 361 Computer Graphics Fall 2017 Assignment 2. Assignment due Thursday, October 19, 11:59pm
 SFU CMPT 361 Computer Graphics Fall 2017 Assignment 2 Assignment due Thursday, October 19, 11:59pm For this assignment, you are to interpret a 3D graphics specification language, along with doing some
SFU CMPT 361 Computer Graphics Fall 2017 Assignment 2 Assignment due Thursday, October 19, 11:59pm For this assignment, you are to interpret a 3D graphics specification language, along with doing some
Geometry Primitives. Computer Science Department University of Malta. Sandro Spina Computer Graphics and Simulation Group. CGSG Geometry Primitives
 Geometry Primitives Sandro Spina Computer Graphics and Simulation Group Computer Science Department University of Malta 1 The Building Blocks of Geometry The objects in our virtual worlds are composed
Geometry Primitives Sandro Spina Computer Graphics and Simulation Group Computer Science Department University of Malta 1 The Building Blocks of Geometry The objects in our virtual worlds are composed
Hierarchical Models. Roadmap. Importance of shadows. Importance of shadows. Importance of shadows. Importance of shadows
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 8 Hierarchical Models Projections and Shadows Hierarchical Models [Angel Ch. 8] Roadmap Last lecture: Viewing and projection Today: Shadows via projections Hierarchical
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 8 Hierarchical Models Projections and Shadows Hierarchical Models [Angel Ch. 8] Roadmap Last lecture: Viewing and projection Today: Shadows via projections Hierarchical
WebGL A quick introduction. J. Madeira V. 0.2 September 2017
 WebGL A quick introduction J. Madeira V. 0.2 September 2017 1 Interactive Computer Graphics Graphics library / package is intermediary between application and display hardware Application program maps
WebGL A quick introduction J. Madeira V. 0.2 September 2017 1 Interactive Computer Graphics Graphics library / package is intermediary between application and display hardware Application program maps
Geometry Shaders. And how to use them
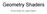 Geometry Shaders And how to use them OpenGL Pipeline (part of it) Vertex data Vertex shader Vertices Primitives Geometry shader Primitives Fragments Fragment shader Color Depth Stencil Vertex Data Attributes
Geometry Shaders And how to use them OpenGL Pipeline (part of it) Vertex data Vertex shader Vertices Primitives Geometry shader Primitives Fragments Fragment shader Color Depth Stencil Vertex Data Attributes
HIERARCHICAL TRANSFORMATIONS A Practical Introduction
 HIERARCHICAL TRANSFORMATIONS A Practical Introduction Christopher Peters HPCViz, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden chpeters@kth.se https://www.kth.se/profile/chpeters/ Transformations Many objects
HIERARCHICAL TRANSFORMATIONS A Practical Introduction Christopher Peters HPCViz, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden chpeters@kth.se https://www.kth.se/profile/chpeters/ Transformations Many objects
Modeling Objects. Modeling. Symbol-Instance Table. Instance Transformation. Each appearance of the object in the model is an instance
 Modeling Objects Modeling Hierarchical Transformations Hierarchical Models Scene Graphs A prototype has a default size, position, and orientation You need to perform modeling transformations to position
Modeling Objects Modeling Hierarchical Transformations Hierarchical Models Scene Graphs A prototype has a default size, position, and orientation You need to perform modeling transformations to position
2D Drawing Primitives
 THE SIERPINSKI GASKET We use as a sample problem the drawing of the Sierpinski gasket an interesting shape that has a long history and is of interest in areas such as fractal geometry. The Sierpinski gasket
THE SIERPINSKI GASKET We use as a sample problem the drawing of the Sierpinski gasket an interesting shape that has a long history and is of interest in areas such as fractal geometry. The Sierpinski gasket
API for creating a display window and using keyboard/mouse interations. See RayWindow.cpp to see how these are used for Assignment3
 OpenGL Introduction Introduction OpenGL OpenGL is an API for computer graphics. Hardware-independent Windowing or getting input is not included in the API Low-level Only knows about triangles (kind of,
OpenGL Introduction Introduction OpenGL OpenGL is an API for computer graphics. Hardware-independent Windowing or getting input is not included in the API Low-level Only knows about triangles (kind of,
Today s Agenda. Basic design of a graphics system. Introduction to OpenGL
 Today s Agenda Basic design of a graphics system Introduction to OpenGL Image Compositing Compositing one image over another is most common choice can think of each image drawn on a transparent plastic
Today s Agenda Basic design of a graphics system Introduction to OpenGL Image Compositing Compositing one image over another is most common choice can think of each image drawn on a transparent plastic
3D Programming. 3D Programming Concepts. Outline. 3D Concepts. 3D Concepts -- Coordinate Systems. 3D Concepts Displaying 3D Models
 3D Programming Concepts Outline 3D Concepts Displaying 3D Models 3D Programming CS 4390 3D Computer 1 2 3D Concepts 3D Model is a 3D simulation of an object. Coordinate Systems 3D Models 3D Shapes 3D Concepts
3D Programming Concepts Outline 3D Concepts Displaying 3D Models 3D Programming CS 4390 3D Computer 1 2 3D Concepts 3D Model is a 3D simulation of an object. Coordinate Systems 3D Models 3D Shapes 3D Concepts
HIERARCHICAL TRANSFORMATIONS A Practical Introduction
 HIERARCHICAL TRANSFORMATIONS A Practical Introduction HPCViz, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden https://www.kth.se/profile/chpeters/ Transformations Many objects are composed of hierarchies Transformations
HIERARCHICAL TRANSFORMATIONS A Practical Introduction HPCViz, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden https://www.kth.se/profile/chpeters/ Transformations Many objects are composed of hierarchies Transformations
PROFESSIONAL. WebGL Programming DEVELOPING 3D GRAPHICS FOR THE WEB. Andreas Anyuru WILEY. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
 PROFESSIONAL WebGL Programming DEVELOPING 3D GRAPHICS FOR THE WEB Andreas Anyuru WILEY John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. INTRODUCTION xxl CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCING WEBGL 1 The Basics of WebGL 1 So Why Is WebGL So Great?
PROFESSIONAL WebGL Programming DEVELOPING 3D GRAPHICS FOR THE WEB Andreas Anyuru WILEY John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. INTRODUCTION xxl CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCING WEBGL 1 The Basics of WebGL 1 So Why Is WebGL So Great?
CMSC427 Final Practice v2 Fall 2017
 CMSC427 Final Practice v2 Fall 2017 This is to represent the flow of the final and give you an idea of relative weighting. No promises that knowing this will predict how you ll do on the final. Some questions
CMSC427 Final Practice v2 Fall 2017 This is to represent the flow of the final and give you an idea of relative weighting. No promises that knowing this will predict how you ll do on the final. Some questions
Computer graphic -- Programming with OpenGL I
 Computer graphic -- Programming with OpenGL I A simple example using OpenGL Download the example code "basic shapes", and compile and run it Take a look at it, and hit ESC when you're done. It shows the
Computer graphic -- Programming with OpenGL I A simple example using OpenGL Download the example code "basic shapes", and compile and run it Take a look at it, and hit ESC when you're done. It shows the
Describe the Orthographic and Perspective projections. How do we combine together transform matrices?
 Aims and objectives By the end of the lecture you will be able to Work with multiple transform matrices Describe the viewing process in OpenGL Design and build a camera control APIs Describe the Orthographic
Aims and objectives By the end of the lecture you will be able to Work with multiple transform matrices Describe the viewing process in OpenGL Design and build a camera control APIs Describe the Orthographic
Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring Programming with OpenGL Part 2: First Program
 Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2017 Programming with OpenGL Part 2: First Program Objectives Refine the first program Introduce a standard program structure - Initialization Program Structure Most
Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2017 Programming with OpenGL Part 2: First Program Objectives Refine the first program Introduce a standard program structure - Initialization Program Structure Most
OpenGL: Open Graphics Library. Introduction to OpenGL Part II. How do I render a geometric primitive? What is OpenGL
 OpenGL: Open Graphics Library Introduction to OpenGL Part II CS 351-50 Graphics API ( Application Programming Interface) Software library Layer between programmer and graphics hardware (and other software
OpenGL: Open Graphics Library Introduction to OpenGL Part II CS 351-50 Graphics API ( Application Programming Interface) Software library Layer between programmer and graphics hardware (and other software
Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 )
 CS380: Computer Graphics Clipping and Culling Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL: http://sglab.kaist.ac.kr/~sungeui/cg/ Class Objectives Understand clipping and culling Understand view-frustum, back-face
CS380: Computer Graphics Clipping and Culling Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL: http://sglab.kaist.ac.kr/~sungeui/cg/ Class Objectives Understand clipping and culling Understand view-frustum, back-face
Topics and things to know about them:
 Practice Final CMSC 427 Distributed Tuesday, December 11, 2007 Review Session, Monday, December 17, 5:00pm, 4424 AV Williams Final: 10:30 AM Wednesday, December 19, 2007 General Guidelines: The final will
Practice Final CMSC 427 Distributed Tuesday, December 11, 2007 Review Session, Monday, December 17, 5:00pm, 4424 AV Williams Final: 10:30 AM Wednesday, December 19, 2007 General Guidelines: The final will
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #5: Visibility, OpenGL
 CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #5: Visibility, OpenGL Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2016 Announcements Tomorrow: assignment 1 due Grading
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #5: Visibility, OpenGL Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2016 Announcements Tomorrow: assignment 1 due Grading
Ciril Bohak. - INTRODUCTION TO WEBGL
 2016 Ciril Bohak ciril.bohak@fri.uni-lj.si - INTRODUCTION TO WEBGL What is WebGL? WebGL (Web Graphics Library) is an implementation of OpenGL interface for cmmunication with graphical hardware, intended
2016 Ciril Bohak ciril.bohak@fri.uni-lj.si - INTRODUCTION TO WEBGL What is WebGL? WebGL (Web Graphics Library) is an implementation of OpenGL interface for cmmunication with graphical hardware, intended
CHAPTER 1 Graphics Systems and Models 3
 ?????? 1 CHAPTER 1 Graphics Systems and Models 3 1.1 Applications of Computer Graphics 4 1.1.1 Display of Information............. 4 1.1.2 Design.................... 5 1.1.3 Simulation and Animation...........
?????? 1 CHAPTER 1 Graphics Systems and Models 3 1.1 Applications of Computer Graphics 4 1.1.1 Display of Information............. 4 1.1.2 Design.................... 5 1.1.3 Simulation and Animation...........
OPENGL AND GLSL. Computer Graphics
 OPENGL AND GLSL Computer Graphics 1 OUTLINE I. Detecting GLSL Errors II. Drawing a (gasp) Triangle! III. (Simple) Animation 2 Interactive Computer Graphics, http://www.mechapen.com/projects.html WHAT IS
OPENGL AND GLSL Computer Graphics 1 OUTLINE I. Detecting GLSL Errors II. Drawing a (gasp) Triangle! III. (Simple) Animation 2 Interactive Computer Graphics, http://www.mechapen.com/projects.html WHAT IS
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #10: View Frustum Culling
 CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #10: View Frustum Culling Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2015 Announcements Project 4 due tomorrow Project
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #10: View Frustum Culling Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2015 Announcements Project 4 due tomorrow Project
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #9: Visibility. Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2018
 CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #9: Visibility Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2018 Announcements Midterm Scores are on TritonEd Exams to be
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #9: Visibility Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2018 Announcements Midterm Scores are on TritonEd Exams to be
Graphics Programming. Computer Graphics, VT 2016 Lecture 2, Chapter 2. Fredrik Nysjö Centre for Image analysis Uppsala University
 Graphics Programming Computer Graphics, VT 2016 Lecture 2, Chapter 2 Fredrik Nysjö Centre for Image analysis Uppsala University Graphics programming Typically deals with How to define a 3D scene with a
Graphics Programming Computer Graphics, VT 2016 Lecture 2, Chapter 2 Fredrik Nysjö Centre for Image analysis Uppsala University Graphics programming Typically deals with How to define a 3D scene with a
CS 4620 Program 3: Pipeline
 CS 4620 Program 3: Pipeline out: Wednesday 14 October 2009 due: Friday 30 October 2009 1 Introduction In this assignment, you will implement several types of shading in a simple software graphics pipeline.
CS 4620 Program 3: Pipeline out: Wednesday 14 October 2009 due: Friday 30 October 2009 1 Introduction In this assignment, you will implement several types of shading in a simple software graphics pipeline.
CS451Real-time Rendering Pipeline
 1 CS451Real-time Rendering Pipeline JYH-MING LIEN DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE GEORGE MASON UNIVERSITY Based on Tomas Akenine-Möller s lecture note You say that you render a 3D 2 scene, but what does
1 CS451Real-time Rendering Pipeline JYH-MING LIEN DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE GEORGE MASON UNIVERSITY Based on Tomas Akenine-Möller s lecture note You say that you render a 3D 2 scene, but what does
Programming with OpenGL Part 2: Complete Programs Computer Graphics I, Fall
 Programming with OpenGL Part 2: Complete Programs 91.427 Computer Graphics I, Fall 2008 1 1 Objectives Refine first program Alter default values Introduce standard program structure Simple viewing 2-D
Programming with OpenGL Part 2: Complete Programs 91.427 Computer Graphics I, Fall 2008 1 1 Objectives Refine first program Alter default values Introduce standard program structure Simple viewing 2-D
Rasterization Overview
 Rendering Overview The process of generating an image given a virtual camera objects light sources Various techniques rasterization (topic of this course) raytracing (topic of the course Advanced Computer
Rendering Overview The process of generating an image given a virtual camera objects light sources Various techniques rasterization (topic of this course) raytracing (topic of the course Advanced Computer
CMSC427 Fall 2017 OpenGL Notes A: Starting with JOGL and OpenGL Objectives of notes Readings Computer Graphics Programming in OpenGL with Java
 CMSC427 Fall 2017 OpenGL Notes A: Starting with JOGL and OpenGL Objectives of notes Show how to program full OpenGL in JOGL Start on shader programing Readings Computer Graphics Programming in OpenGL with
CMSC427 Fall 2017 OpenGL Notes A: Starting with JOGL and OpenGL Objectives of notes Show how to program full OpenGL in JOGL Start on shader programing Readings Computer Graphics Programming in OpenGL with
EECE 478. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives. Rasterization & Scenes. Rasterization. Compositing
 EECE 478 Rasterization & Scenes Rasterization Learning Objectives Be able to describe the complete graphics pipeline. Describe the process of rasterization for triangles and lines. Compositing Manipulate
EECE 478 Rasterization & Scenes Rasterization Learning Objectives Be able to describe the complete graphics pipeline. Describe the process of rasterization for triangles and lines. Compositing Manipulate
Transforms 1 Christian Miller CS Fall 2011
 Transforms 1 Christian Miller CS 354 - Fall 2011 Transformations What happens if you multiply a square matrix and a vector together? You get a different vector with the same number of coordinates These
Transforms 1 Christian Miller CS 354 - Fall 2011 Transformations What happens if you multiply a square matrix and a vector together? You get a different vector with the same number of coordinates These
RASTERISED RENDERING
 DH2323 DGI16 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER GRAPHICS AND INTERACTION RASTERISED RENDERING Christopher Peters HPCViz, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden chpeters@kth.se http://kth.academia.edu/christopheredwardpeters
DH2323 DGI16 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER GRAPHICS AND INTERACTION RASTERISED RENDERING Christopher Peters HPCViz, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden chpeters@kth.se http://kth.academia.edu/christopheredwardpeters
The Rendering Pipeline (1)
 The Rendering Pipeline (1) Alessandro Martinelli alessandro.martinelli@unipv.it 30 settembre 2014 The Rendering Pipeline (1) Rendering Architecture First Rendering Pipeline Second Pipeline: Illumination
The Rendering Pipeline (1) Alessandro Martinelli alessandro.martinelli@unipv.it 30 settembre 2014 The Rendering Pipeline (1) Rendering Architecture First Rendering Pipeline Second Pipeline: Illumination
Hierarchical Modeling
 Hierarchical Modeling Geometric Primitives Remember that most graphics APIs have only a few geometric primitives Spheres, cubes, triangles, etc These primitives are instanced in order to apply transforms
Hierarchical Modeling Geometric Primitives Remember that most graphics APIs have only a few geometric primitives Spheres, cubes, triangles, etc These primitives are instanced in order to apply transforms
CSC Graphics Programming. Budditha Hettige Department of Statistics and Computer Science
 CSC 307 1.0 Graphics Programming Department of Statistics and Computer Science Graphics Programming 2 Common Uses for Computer Graphics Applications for real-time 3D graphics range from interactive games
CSC 307 1.0 Graphics Programming Department of Statistics and Computer Science Graphics Programming 2 Common Uses for Computer Graphics Applications for real-time 3D graphics range from interactive games
Advanced Lighting Techniques Due: Monday November 2 at 10pm
 CMSC 23700 Autumn 2015 Introduction to Computer Graphics Project 3 October 20, 2015 Advanced Lighting Techniques Due: Monday November 2 at 10pm 1 Introduction This assignment is the third and final part
CMSC 23700 Autumn 2015 Introduction to Computer Graphics Project 3 October 20, 2015 Advanced Lighting Techniques Due: Monday November 2 at 10pm 1 Introduction This assignment is the third and final part
Outline. Introduction Surface of Revolution Hierarchical Modeling Blinn-Phong Shader Custom Shader(s)
 Modeler Help Outline Introduction Surface of Revolution Hierarchical Modeling Blinn-Phong Shader Custom Shader(s) Objects in the Scene Controls of the object selected in the Scene. Currently the Scene
Modeler Help Outline Introduction Surface of Revolution Hierarchical Modeling Blinn-Phong Shader Custom Shader(s) Objects in the Scene Controls of the object selected in the Scene. Currently the Scene
Game Architecture. 2/19/16: Rasterization
 Game Architecture 2/19/16: Rasterization Viewing To render a scene, need to know Where am I and What am I looking at The view transform is the matrix that does this Maps a standard view space into world
Game Architecture 2/19/16: Rasterization Viewing To render a scene, need to know Where am I and What am I looking at The view transform is the matrix that does this Maps a standard view space into world
HIERARCHICAL TRANSFORMATIONS A Practical Introduction
 HIERARCHICAL TRANSFORMATIONS A Practical Introduction Christopher Peters CST, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden chpeters@kth.se https://www.kth.se/profile/chpeters/ Before we begin... Lab work
HIERARCHICAL TRANSFORMATIONS A Practical Introduction Christopher Peters CST, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden chpeters@kth.se https://www.kth.se/profile/chpeters/ Before we begin... Lab work
Clipping & Culling. Lecture 11 Spring Trivial Rejection Outcode Clipping Plane-at-a-time Clipping Backface Culling
 Clipping & Culling Trivial Rejection Outcode Clipping Plane-at-a-time Clipping Backface Culling Lecture 11 Spring 2015 What is Clipping? Clipping is a procedure for spatially partitioning geometric primitives,
Clipping & Culling Trivial Rejection Outcode Clipping Plane-at-a-time Clipping Backface Culling Lecture 11 Spring 2015 What is Clipping? Clipping is a procedure for spatially partitioning geometric primitives,
1 Preview. Dr. Scott Gordon Computer Science Dept. CSUS. Virtual Cameras, Viewing Transformations: CSc-155 Advanced Computer Graphics
 CSc-155 Advanced Computer Graphics 1 Preview Dr. Scott Gordon Computer Science Dept. CSUS Course Description Modeling, viewing, and rendering techniques in 3D computer graphics systems. Topics include:
CSc-155 Advanced Computer Graphics 1 Preview Dr. Scott Gordon Computer Science Dept. CSUS Course Description Modeling, viewing, and rendering techniques in 3D computer graphics systems. Topics include:
Projection Matrix Tricks. Eric Lengyel
 Projection Matrix Tricks Eric Lengyel Outline Projection Matrix Internals Infinite Projection Matrix Depth Modification Oblique Near Clipping Plane Slides available at http://www.terathon.com www.terathon.com/
Projection Matrix Tricks Eric Lengyel Outline Projection Matrix Internals Infinite Projection Matrix Depth Modification Oblique Near Clipping Plane Slides available at http://www.terathon.com www.terathon.com/
CS488. Visible-Surface Determination. Luc RENAMBOT
 CS488 Visible-Surface Determination Luc RENAMBOT 1 Visible-Surface Determination So far in the class we have dealt mostly with simple wireframe drawings of the models The main reason for this is so that
CS488 Visible-Surface Determination Luc RENAMBOT 1 Visible-Surface Determination So far in the class we have dealt mostly with simple wireframe drawings of the models The main reason for this is so that
Shadows in the graphics pipeline
 Shadows in the graphics pipeline Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 19 February There are a number of visual cues that help let the viewer know about the 3D relationships between objects
Shadows in the graphics pipeline Steve Marschner Cornell University CS 569 Spring 2008, 19 February There are a number of visual cues that help let the viewer know about the 3D relationships between objects
Lecture 5: Transforms II. Computer Graphics and Imaging UC Berkeley CS184/284A
 Lecture 5: Transforms II Computer Graphics and Imaging UC Berkeley 3D Transforms 3D Transformations Use homogeneous coordinates again: 3D point = (x, y, z, 1) T 3D vector = (x, y, z, 0) T Use 4 4 matrices
Lecture 5: Transforms II Computer Graphics and Imaging UC Berkeley 3D Transforms 3D Transformations Use homogeneous coordinates again: 3D point = (x, y, z, 1) T 3D vector = (x, y, z, 0) T Use 4 4 matrices
How shapes are represented in 3D Graphics. Aims and objectives By the end of the lecture you will be able to describe
 Today s lecture Today we will learn about The mathematics of 3D space vectors How shapes are represented in 3D Graphics Modelling shapes as polygons Aims and objectives By the end of the lecture you will
Today s lecture Today we will learn about The mathematics of 3D space vectors How shapes are represented in 3D Graphics Modelling shapes as polygons Aims and objectives By the end of the lecture you will
TDA362/DIT223 Computer Graphics EXAM (Same exam for both CTH- and GU students)
 TDA362/DIT223 Computer Graphics EXAM (Same exam for both CTH- and GU students) Saturday, January 13 th, 2018, 08:30-12:30 Examiner Ulf Assarsson, tel. 031-772 1775 Permitted Technical Aids None, except
TDA362/DIT223 Computer Graphics EXAM (Same exam for both CTH- and GU students) Saturday, January 13 th, 2018, 08:30-12:30 Examiner Ulf Assarsson, tel. 031-772 1775 Permitted Technical Aids None, except
Advanced Graphics. OpenGL and Shaders I. Alex Benton, University of Cambridge Supported in part by Google UK, Ltd
 Advanced Graphics OpenGL and Shaders I 1 Alex Benton, University of Cambridge A.Benton@damtp.cam.ac.uk Supported in part by Google UK, Ltd 3D technologies today Java OpenGL Common, re-usable language;
Advanced Graphics OpenGL and Shaders I 1 Alex Benton, University of Cambridge A.Benton@damtp.cam.ac.uk Supported in part by Google UK, Ltd 3D technologies today Java OpenGL Common, re-usable language;
Due: Thursday, February 6 th, 11:59 pm TA: Mason Remy
 Due: Thursday, February 6 th, 11:59 pm TA: Mason Remy Checking out, building, and using the sample solution Part 1: Surface of Revolution Part 2: Hierarchical Modeling Part 3: Blinn-Phong Shader Part 4:
Due: Thursday, February 6 th, 11:59 pm TA: Mason Remy Checking out, building, and using the sample solution Part 1: Surface of Revolution Part 2: Hierarchical Modeling Part 3: Blinn-Phong Shader Part 4:
For each question, indicate whether the statement is true or false by circling T or F, respectively.
 True/False For each question, indicate whether the statement is true or false by circling T or F, respectively. 1. (T/F) Rasterization occurs before vertex transformation in the graphics pipeline. 2. (T/F)
True/False For each question, indicate whether the statement is true or false by circling T or F, respectively. 1. (T/F) Rasterization occurs before vertex transformation in the graphics pipeline. 2. (T/F)
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 6a: Hierarchical 3D Models. Prof Emmanuel Agu. Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI)
 Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 6a: Hierarchical 3D Models Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Instance Transformation Start with unique object (a symbol)
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 6a: Hierarchical 3D Models Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Instance Transformation Start with unique object (a symbol)
Viewing with Computers (OpenGL)
 We can now return to three-dimension?', graphics from a computer perspective. Because viewing in computer graphics is based on the synthetic-camera model, we should be able to construct any of the classical
We can now return to three-dimension?', graphics from a computer perspective. Because viewing in computer graphics is based on the synthetic-camera model, we should be able to construct any of the classical
VISIBILITY & CULLING. Don t draw what you can t see. Thomas Larsson, Afshin Ameri DVA338, Spring 2018, MDH
 VISIBILITY & CULLING Don t draw what you can t see. Thomas Larsson, Afshin Ameri DVA338, Spring 2018, MDH Visibility Visibility Given a set of 3D objects, which surfaces are visible from a specific point
VISIBILITY & CULLING Don t draw what you can t see. Thomas Larsson, Afshin Ameri DVA338, Spring 2018, MDH Visibility Visibility Given a set of 3D objects, which surfaces are visible from a specific point
2D/3D Geometric Transformations and Scene Graphs
 2D/3D Geometric Transformations and Scene Graphs Week 4 Acknowledgement: The course slides are adapted from the slides prepared by Steve Marschner of Cornell University 1 A little quick math background
2D/3D Geometric Transformations and Scene Graphs Week 4 Acknowledgement: The course slides are adapted from the slides prepared by Steve Marschner of Cornell University 1 A little quick math background
CS 381 Computer Graphics, Fall 2012 Midterm Exam Solutions. The Midterm Exam was given in class on Tuesday, October 16, 2012.
 CS 381 Computer Graphics, Fall 2012 Midterm Exam Solutions The Midterm Exam was given in class on Tuesday, October 16, 2012. 1. [7 pts] Synthetic-Camera Model. Describe the Synthetic-Camera Model : how
CS 381 Computer Graphics, Fall 2012 Midterm Exam Solutions The Midterm Exam was given in class on Tuesday, October 16, 2012. 1. [7 pts] Synthetic-Camera Model. Describe the Synthetic-Camera Model : how
CS 4620 Midterm 1. Tuesday 22 October minutes
 CS 4620 Midterm 1 Tuesday 22 October 2013 90 minutes Problem 1: Transformations (20 pts) Consider the affine transformation on R 3 defined in homogeneous coordinates by the matrix: 1 M = 1 0 0 2 0 1 0
CS 4620 Midterm 1 Tuesday 22 October 2013 90 minutes Problem 1: Transformations (20 pts) Consider the affine transformation on R 3 defined in homogeneous coordinates by the matrix: 1 M = 1 0 0 2 0 1 0
Filled Area Primitives. CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics METU, 2007
 Filled Area Primitives CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics METU, 2007 Filled Area Primitives Two basic approaches to area filling on raster systems: Determine the overlap intervals for scan lines
Filled Area Primitives CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics METU, 2007 Filled Area Primitives Two basic approaches to area filling on raster systems: Determine the overlap intervals for scan lines
Perspective matrix, OpenGL style
 Perspective matrix, OpenGL style Stefan Gustavson May 7, 016 Gortler s book presents perspective transformation using a slightly different matrix than what is common in OpenGL applications. This document
Perspective matrix, OpenGL style Stefan Gustavson May 7, 016 Gortler s book presents perspective transformation using a slightly different matrix than what is common in OpenGL applications. This document
Notes on Assignment. Notes on Assignment. Notes on Assignment. Notes on Assignment
 Notes on Assignment Notes on Assignment Objects on screen - made of primitives Primitives are points, lines, polygons - watch vertex ordering The main object you need is a box When the MODELVIEW matrix
Notes on Assignment Notes on Assignment Objects on screen - made of primitives Primitives are points, lines, polygons - watch vertex ordering The main object you need is a box When the MODELVIEW matrix
Pipeline Operations. CS 4620 Lecture Steve Marschner. Cornell CS4620 Spring 2018 Lecture 11
 Pipeline Operations CS 4620 Lecture 11 1 Pipeline you are here APPLICATION COMMAND STREAM 3D transformations; shading VERTEX PROCESSING TRANSFORMED GEOMETRY conversion of primitives to pixels RASTERIZATION
Pipeline Operations CS 4620 Lecture 11 1 Pipeline you are here APPLICATION COMMAND STREAM 3D transformations; shading VERTEX PROCESSING TRANSFORMED GEOMETRY conversion of primitives to pixels RASTERIZATION
Today. Parity. General Polygons? Non-Zero Winding Rule. Winding Numbers. CS559 Lecture 11 Polygons, Transformations
 CS559 Lecture Polygons, Transformations These are course notes (not used as slides) Written by Mike Gleicher, Oct. 005 With some slides adapted from the notes of Stephen Chenney Final version (after class)
CS559 Lecture Polygons, Transformations These are course notes (not used as slides) Written by Mike Gleicher, Oct. 005 With some slides adapted from the notes of Stephen Chenney Final version (after class)
Computer Graphics Shadow Algorithms
 Computer Graphics Shadow Algorithms Computer Graphics Computer Science Department University of Freiburg WS 11 Outline introduction projection shadows shadow maps shadow volumes conclusion Motivation shadows
Computer Graphics Shadow Algorithms Computer Graphics Computer Science Department University of Freiburg WS 11 Outline introduction projection shadows shadow maps shadow volumes conclusion Motivation shadows
Building Models. Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York
 Building Models Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives Introduce simple data structures for building polygonal models - Vertex lists - Edge lists Deprecated
Building Models Prof. George Wolberg Dept. of Computer Science City College of New York Objectives Introduce simple data structures for building polygonal models - Vertex lists - Edge lists Deprecated
Precept 2 Aleksey Boyko February 18, 2011
 Precept 2 Aleksey Boyko February 18, 2011 Getting started Initialization Drawing Transformations Cameras Animation Input Keyboard Mouse Joystick? Textures Lights Programmable pipeline elements (shaders)
Precept 2 Aleksey Boyko February 18, 2011 Getting started Initialization Drawing Transformations Cameras Animation Input Keyboard Mouse Joystick? Textures Lights Programmable pipeline elements (shaders)
Culling. Computer Graphics CSE 167 Lecture 12
 Culling Computer Graphics CSE 167 Lecture 12 CSE 167: Computer graphics Culling Definition: selecting from a large quantity In computer graphics: selecting primitives (or batches of primitives) that are
Culling Computer Graphics CSE 167 Lecture 12 CSE 167: Computer graphics Culling Definition: selecting from a large quantity In computer graphics: selecting primitives (or batches of primitives) that are
Hierarchical Modeling. University of Texas at Austin CS384G - Computer Graphics Fall 2010 Don Fussell
 Hierarchical Modeling University of Texas at Austin CS384G - Computer Graphics Fall 2010 Don Fussell Reading Angel, sections 9.1-9.6 [reader pp. 169-185] OpenGL Programming Guide, chapter 3 Focus especially
Hierarchical Modeling University of Texas at Austin CS384G - Computer Graphics Fall 2010 Don Fussell Reading Angel, sections 9.1-9.6 [reader pp. 169-185] OpenGL Programming Guide, chapter 3 Focus especially
Institutionen för systemteknik
 Code: Day: Lokal: M7002E 19 March E1026 Institutionen för systemteknik Examination in: M7002E, Computer Graphics and Virtual Environments Number of sections: 7 Max. score: 100 (normally 60 is required
Code: Day: Lokal: M7002E 19 March E1026 Institutionen för systemteknik Examination in: M7002E, Computer Graphics and Virtual Environments Number of sections: 7 Max. score: 100 (normally 60 is required
Lecture 3 Sections 2.2, 4.4. Mon, Aug 31, 2009
 Model s Lecture 3 Sections 2.2, 4.4 World s Eye s Clip s s s Window s Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Aug 31, 2009 Outline Model s World s Eye s Clip s s s Window s 1 2 3 Model s World s Eye s Clip s s s Window
Model s Lecture 3 Sections 2.2, 4.4 World s Eye s Clip s s s Window s Hampden-Sydney College Mon, Aug 31, 2009 Outline Model s World s Eye s Clip s s s Window s 1 2 3 Model s World s Eye s Clip s s s Window
Shadow Algorithms. CSE 781 Winter Han-Wei Shen
 Shadow Algorithms CSE 781 Winter 2010 Han-Wei Shen Why Shadows? Makes 3D Graphics more believable Provides additional cues for the shapes and relative positions of objects in 3D What is shadow? Shadow:
Shadow Algorithms CSE 781 Winter 2010 Han-Wei Shen Why Shadows? Makes 3D Graphics more believable Provides additional cues for the shapes and relative positions of objects in 3D What is shadow? Shadow:
Transformations. Rotation and Scaling
 Transformations In OpenGL, transformation are performed in the opposite order they are called 4 3 2 1 translate(1., 1.,.); rotatez(45.); scale(2., 2.,.); DrawSquare(.,., 1.); 4 3 2 1 scale(2., 2.,.); rotatez(45.);
Transformations In OpenGL, transformation are performed in the opposite order they are called 4 3 2 1 translate(1., 1.,.); rotatez(45.); scale(2., 2.,.); DrawSquare(.,., 1.); 4 3 2 1 scale(2., 2.,.); rotatez(45.);
CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics
 CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 2 Part 1 Primitives and Buffers Matt Burlick - Drexel University - CS 432 1 Rendering in OpenGL Ok, so now we want to actually draw stuff! OpenGL (like most
CS 432 Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 2 Part 1 Primitives and Buffers Matt Burlick - Drexel University - CS 432 1 Rendering in OpenGL Ok, so now we want to actually draw stuff! OpenGL (like most
CS Simple Raytracer for students new to Rendering
 CS 294-13 Simple Raytracer for students new to Rendering Ravi Ramamoorthi This assignment should be done only by those small number of students who have not yet written a raytracer. For those students
CS 294-13 Simple Raytracer for students new to Rendering Ravi Ramamoorthi This assignment should be done only by those small number of students who have not yet written a raytracer. For those students
Motivation. Culling Don t draw what you can t see! What can t we see? Low-level Culling
 Motivation Culling Don t draw what you can t see! Thomas Larsson Mälardalen University April 7, 2016 Image correctness Rendering speed One day we will have enough processing power!? Goals of real-time
Motivation Culling Don t draw what you can t see! Thomas Larsson Mälardalen University April 7, 2016 Image correctness Rendering speed One day we will have enough processing power!? Goals of real-time
Pipeline Operations. CS 4620 Lecture 14
 Pipeline Operations CS 4620 Lecture 14 2014 Steve Marschner 1 Pipeline you are here APPLICATION COMMAND STREAM 3D transformations; shading VERTEX PROCESSING TRANSFORMED GEOMETRY conversion of primitives
Pipeline Operations CS 4620 Lecture 14 2014 Steve Marschner 1 Pipeline you are here APPLICATION COMMAND STREAM 3D transformations; shading VERTEX PROCESSING TRANSFORMED GEOMETRY conversion of primitives
The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must turn your exam in when time is announced or risk not having it accepted.
 CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 10 Student Name: Class Account Username: Instructions: Read them carefully! The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must turn your exam in when
CS 184: Foundations of Computer Graphics page 1 of 10 Student Name: Class Account Username: Instructions: Read them carefully! The exam begins at 2:40pm and ends at 4:00pm. You must turn your exam in when
3D Graphics and OpenGl. First Steps
 3D Graphics and OpenGl First Steps Rendering of 3D Graphics Objects defined in (virtual/mathematical) 3D space. Rendering of 3D Graphics Objects defined in (virtual/mathematical) 3D space. We see surfaces
3D Graphics and OpenGl First Steps Rendering of 3D Graphics Objects defined in (virtual/mathematical) 3D space. Rendering of 3D Graphics Objects defined in (virtual/mathematical) 3D space. We see surfaces
The Importance of Matrices in the DirectX API. by adding support in the programming language for frequently used calculations.
 Hermann Chong Dr. King Linear Algebra Applications 28 November 2001 The Importance of Matrices in the DirectX API In the world of 3D gaming, there are two APIs (Application Program Interface) that reign
Hermann Chong Dr. King Linear Algebra Applications 28 November 2001 The Importance of Matrices in the DirectX API In the world of 3D gaming, there are two APIs (Application Program Interface) that reign
Programming using OpenGL: A first Introduction
 Programming using OpenGL: A first Introduction CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Machiraju/Zhang/Möller 1 Today Overview GL, GLU, GLUT, and GLUI First example OpenGL functions and
Programming using OpenGL: A first Introduction CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Machiraju/Zhang/Möller 1 Today Overview GL, GLU, GLUT, and GLUI First example OpenGL functions and
The original image. Let s get started! The final result.
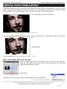 Vertical Photo Panels Effect In this Photoshop tutorial, we ll learn how to create the illusion that a single photo is being displayed as a series of vertical panels. It may look complicated, but as we
Vertical Photo Panels Effect In this Photoshop tutorial, we ll learn how to create the illusion that a single photo is being displayed as a series of vertical panels. It may look complicated, but as we
THE VIEWING TRANSFORMATION
 ECS 178 Course Notes THE VIEWING TRANSFORMATION Kenneth I. Joy Institute for Data Analysis and Visualization Department of Computer Science University of California, Davis Overview One of the most important
ECS 178 Course Notes THE VIEWING TRANSFORMATION Kenneth I. Joy Institute for Data Analysis and Visualization Department of Computer Science University of California, Davis Overview One of the most important
Computer Graphics Hands-on
 Computer Graphics Hands-on Two-Dimensional Transformations Objectives Visualize the fundamental 2D geometric operations translation, rotation about the origin, and scale about the origin Learn how to compose
Computer Graphics Hands-on Two-Dimensional Transformations Objectives Visualize the fundamental 2D geometric operations translation, rotation about the origin, and scale about the origin Learn how to compose
Lab 2-3D Transformations and Vertex Shaders
 Lab 2-3D Transformations and Vertex Shaders Support code: /course/cs1230/src/labs/lab02 Demo: /course/cs1230/bin/cs1230_lab02_demo Intro Last week you learned how to draw 2D shapes in OpenGL using VBOs
Lab 2-3D Transformations and Vertex Shaders Support code: /course/cs1230/src/labs/lab02 Demo: /course/cs1230/bin/cs1230_lab02_demo Intro Last week you learned how to draw 2D shapes in OpenGL using VBOs
CS 4620 Midterm, March 21, 2017
 CS 460 Midterm, March 1, 017 This 90-minute exam has 4 questions worth a total of 100 points. Use the back of the pages if you need more space. Academic Integrity is expected of all students of Cornell
CS 460 Midterm, March 1, 017 This 90-minute exam has 4 questions worth a total of 100 points. Use the back of the pages if you need more space. Academic Integrity is expected of all students of Cornell
C O M P U T E R G R A P H I C S. Computer Graphics. Three-Dimensional Graphics I. Guoying Zhao 1 / 52
 Computer Graphics Three-Dimensional Graphics I Guoying Zhao 1 / 52 Geometry Guoying Zhao 2 / 52 Objectives Introduce the elements of geometry Scalars Vectors Points Develop mathematical operations among
Computer Graphics Three-Dimensional Graphics I Guoying Zhao 1 / 52 Geometry Guoying Zhao 2 / 52 Objectives Introduce the elements of geometry Scalars Vectors Points Develop mathematical operations among
TSBK03 Screen-Space Ambient Occlusion
 TSBK03 Screen-Space Ambient Occlusion Joakim Gebart, Jimmy Liikala December 15, 2013 Contents 1 Abstract 1 2 History 2 2.1 Crysis method..................................... 2 3 Chosen method 2 3.1 Algorithm
TSBK03 Screen-Space Ambient Occlusion Joakim Gebart, Jimmy Liikala December 15, 2013 Contents 1 Abstract 1 2 History 2 2.1 Crysis method..................................... 2 3 Chosen method 2 3.1 Algorithm
Luiz Fernando Martha André Pereira
 Computer Graphics for Engineering Numerical simulation in technical sciences Color / OpenGL Luiz Fernando Martha André Pereira Graz, Austria June 2014 To Remember Computer Graphics Data Processing Data
Computer Graphics for Engineering Numerical simulation in technical sciences Color / OpenGL Luiz Fernando Martha André Pereira Graz, Austria June 2014 To Remember Computer Graphics Data Processing Data
Today. Rendering pipeline. Rendering pipeline. Object vs. Image order. Rendering engine Rendering engine (jtrt) Computergrafik. Rendering pipeline
 Computergrafik Today Rendering pipeline s View volumes, clipping Viewport Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2008 Rendering pipeline Rendering pipeline Hardware & software that draws 3D scenes on
Computergrafik Today Rendering pipeline s View volumes, clipping Viewport Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2008 Rendering pipeline Rendering pipeline Hardware & software that draws 3D scenes on
4: Polygons and pixels
 COMP711 Computer Graphics and Image Processing 4: Polygons and pixels Toby.Howard@manchester.ac.uk 1 Introduction We ll look at Properties of polygons: convexity, winding, faces, normals Scan conversion
COMP711 Computer Graphics and Image Processing 4: Polygons and pixels Toby.Howard@manchester.ac.uk 1 Introduction We ll look at Properties of polygons: convexity, winding, faces, normals Scan conversion
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture 11: Scene Graph 2. Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2013
 CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture 11: Scene Graph 2 Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2013 Announcements Homework project #5 due Nov. 8 th at 1:30pm
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture 11: Scene Graph 2 Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2013 Announcements Homework project #5 due Nov. 8 th at 1:30pm
Wed, October 12, 2011
 Practical Occlusion Culling in Killzone 3 Michal Valient Lead Tech, Guerrilla B.V. Talk takeaway Occlusion culling system used in Killzone 3 The reasons why to use software rasterization (Some) technical
Practical Occlusion Culling in Killzone 3 Michal Valient Lead Tech, Guerrilla B.V. Talk takeaway Occlusion culling system used in Killzone 3 The reasons why to use software rasterization (Some) technical
Queen s University CISC 454 Final Exam. April 19, :00pm Duration: 3 hours. One two sided aid sheet allowed. Initial of Family Name:
 Page 1 of 11 Queen s University CISC 454 Final Exam April 19, 2005 2:00pm Duration: 3 hours One two sided aid sheet allowed. Initial of Family Name: Student Number: (Write this at the top of every page.)
Page 1 of 11 Queen s University CISC 454 Final Exam April 19, 2005 2:00pm Duration: 3 hours One two sided aid sheet allowed. Initial of Family Name: Student Number: (Write this at the top of every page.)
Transformations. Write three rules based on what you figured out above: To reflect across the y-axis. (x,y) To reflect across y=x.
 Transformations Geometry 14.1 A transformation is a change in coordinates plotted on the plane. We will learn about four types of transformations on the plane: Translations, Reflections, Rotations, and
Transformations Geometry 14.1 A transformation is a change in coordinates plotted on the plane. We will learn about four types of transformations on the plane: Translations, Reflections, Rotations, and
2D ANIMATION & INTERACTION COURSE WEEK 5 QUICK REFERENCE
 The Imaginary Institute www.imaginary- institute.com 2Dcourse@imaginary- institute.com 2D ANIMATION & INTERACTION COURSE WEEK 5 QUICK REFERENCE RANDOM NUMBERS By using random numbers, you can generate
The Imaginary Institute www.imaginary- institute.com 2Dcourse@imaginary- institute.com 2D ANIMATION & INTERACTION COURSE WEEK 5 QUICK REFERENCE RANDOM NUMBERS By using random numbers, you can generate
Graphics Pipeline & APIs
 Graphics Pipeline & APIs CPU Vertex Processing Rasterization Fragment Processing glclear (GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); glpushmatrix (); gltranslatef (-0.15, -0.15, solidz); glmaterialfv(gl_front,
Graphics Pipeline & APIs CPU Vertex Processing Rasterization Fragment Processing glclear (GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); glpushmatrix (); gltranslatef (-0.15, -0.15, solidz); glmaterialfv(gl_front,
Models and Architectures
 Models and Architectures Objectives Learn the basic design of a graphics system Introduce graphics pipeline architecture Examine software components for an interactive graphics system 1 Image Formation
Models and Architectures Objectives Learn the basic design of a graphics system Introduce graphics pipeline architecture Examine software components for an interactive graphics system 1 Image Formation
Maya Lesson 3 Temple Base & Columns
 Maya Lesson 3 Temple Base & Columns Make a new Folder inside your Computer Animation Folder and name it: Temple Save using Save As, and select Incremental Save, with 5 Saves. Name: Lesson3Temple YourName.ma
Maya Lesson 3 Temple Base & Columns Make a new Folder inside your Computer Animation Folder and name it: Temple Save using Save As, and select Incremental Save, with 5 Saves. Name: Lesson3Temple YourName.ma
