Classification of Hand-Written Numeric Digits
|
|
|
- Ophelia Conley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Classification of Hand-Written Numeric Digits Nyssa Aragon, William Lane, Fan Zhang December 12, Objective The specific hand-written recognition application that this project is emphasizing is reading numeric digits written on a tablet or mobile device. We were interested in two goals. First of all, we wanted to build a model that can classify a hand-written digit on a tablet with high accuracy. Second of all, we were interested in how training on a specific set of users will improve the predictions of digits written by those users. 2 Data The primary dataset used is the Pen-Based Recognition of Handwritten Digits Data Set from the UCI Machine Learning Repository. [1] This dataset is produced by collecting roughly 250 digit samples each from 44 writers, written on a pressure sensitive tablet that sent the location of the pen at fixed time intervals of 100 milliseconds. [2] Each digit is written inside a 500 x 500 pixel box, and then was scaled to an integer value between 0 and 100 to create consistent scaling between each observation. Spatial resampling is used to obtain 8 regularly spaced points on an arc trajectory. The data can be visualized by plotting the 8 sampled points based on their (x, y) coordinates, along with lines from point to point. Because the tablet sensed the location of the pen throughout time, the order of the points gives the direction that the pen was moving. The data set contains the x and y coordinates of each of the 8 points, for a total of 16 integer variables ranging from 0 to 100. There are 7494 test data points and 3498 training data points. Table 1: Number of Digits Used Total Training Test The training set consists of samples written by 30 writers and the testing set consists of samples written by 14 writers. The models were evaluated based on the performance on the testing dataset after being trained on the training dataset. We also explore the difference between errors when the training and 1
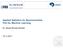
2 (a) Sample Points w/ Ordered Line Segments ( 3 ) (b) Sample Points w/ Ordered Line Segments ( 8 ) Figure 1 testing sets are sourced from separate writers and when the training and testing sets have some writers in common. 3 Model After using various supervised learning techniques, the optimized error for each approach is shown in the table. Table 2: Error Rates Over Diverse Classifiers SVM KNN Random Forest Softmax K-Means Test Error The Support Vector Machine and K-Nearest Neighbor models perform the best. The data, which consists of 8 (x, y) coordinates is perhaps not surprisingly most responsive to Euclidean-distance based classifiers. The SVM model is implemented using the e1071 package in R [3]. The one-against-one approach is used to extend binary classifying SVMs to multiclass predictors, meaning a series of SVMs for each pair group of the digits are created. The class probabilities for each test observation are computed using quadratic optimization. The digit with the highest probability is chosen as the prediction. Following the idea that a prediction made with low probability may be a weaker prediction, the data is separated into two groups: one group has a predicted digit with probability above the threshold of 0.525, another 2
3 with a predicted digit with a probability under the threshold. Table 3: Error Rates Grouped By Probability Threshold SVM Test Error KNN Test Error SVM Pr < SVM Pr Primary Model The main model capitalizes on this relationship. Predictions based on the SVM model is used where the probability of the prediction is above the threshold, while predictions based on the KNN model is used where the probability of the SVM prediction is below the threshold. The value of the threshold and the cost parameter for the SVM regularization is chosen based on which values give the lowest error, with the threshold at and the cost parameter at The model combining SVM and KNN models gives a final test error rate of Error rates in range of 1-2 % are considered competitive for this dataset [5]. 3.2 Sampling From the Whole Dataset The previous models were evaluated based on the error classifying the test set of 14 writers, after being trained on the training set of 30 independent writers. Because an individual may exhibit unique patterns when writing a digit, It is supposed that the correlation between two samples of a specific digit written by one individual is higher than the correlation between two samples of a specific digit written by two separate individuals. One of our motivations was to learn how much continuous learning on a tablet would improve the predictions. In order to gain insight into this problem, we remove samples from the test data and augment them into the training set, then find the error on classifying the remaining test data. In order to train on a representative sample of the test writer s digits, we randomly selected a portion of the test data to migrate to the training set, increasing this proportion by 5% each time until we are training on half of the test data and predicting on the other half. This simulates a situation where specific users gradually feed the learning system a number of their own inputs with the correct labels. The results show that as the model receives more and more input from the set of test users, the model performs better and better with a minimum error rate of just under 1%. On the whole, SVM still outperforms KNN. Additionally, we compared the error based on training and testing data come from separate sources to the error based on a 3-fold cross-validation. Using the primary model found in section 4, the error is found using a 3-fold cross-validation where the three sets are randomly sampled from the combined test and training datasets. A 3-fold cross-validation gives test and training sets of approximately the same size as the original sets. When the training and testing sets do not come from separate writing sources, the error reduces from 1.52% to 0.56%. 3
4 Figure 2: Error (Percent Misclassified) by Test Users Input 4
5 Using the same model that produced the optimal error of the isolated test dataset, the cross-validation error is When the training and testing sets do not come from separate writing sources, the error reduces from 1.52% to 0.56%. 4 Conclusion The supervised learning techniques that performed best with this data were Support Vector Machines and K-Nearest Neighbor. Our final model was one that used SVM predictions when the SVM was confident and KNN predictions when the SVM was less confident. The models performed better when it was trained on samples from the same writers who wrote the test samples, indicating that a model that continues to learn to a specific tablet-user will better predict that user s writing. References [1] Bache, K. & L i c h m a n, M. ( ). U C I Machine Learning Repository [ Irvine, CA: University of California, School of Information and Computer Science. [2] I. S. Dhillon, D. S. Modha, and W. S. Spangler, Class Visualization of High-Dimensional Data with Applications, August 1999, pg. 18. [3] David Meyer, Evgenia Dimitriadou, Kurt Hornik, Andreas Weingessel and Friedrich Leisch (2012). e1071: Misc Functions of the Department of Statistics (e1071), TU Wien. R package version [4] Venables, W. N. & Ripley, B. D. (2002) Modern Applied Statistics with S. Fourth Edition. Springer, New York. ISBN [5] Keysers et al. Deformation Models for Image Recognition, IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Vol. 29, No. 8. August 2007, pg
Exploring high-dimensional classification boundaries
 Exploring high-dimensional classification boundaries Hadley Wickham, Doina Caragea, Di Cook January 20, 2006 1 Introduction Given p-dimensional training data containing d groups (the design space), a classification
Exploring high-dimensional classification boundaries Hadley Wickham, Doina Caragea, Di Cook January 20, 2006 1 Introduction Given p-dimensional training data containing d groups (the design space), a classification
A Method for Comparing Multiple Regression Models
 CSIS Discussion Paper No. 141 A Method for Comparing Multiple Regression Models Yuki Hiruta Yasushi Asami Department of Urban Engineering, the University of Tokyo e-mail: hiruta@ua.t.u-tokyo.ac.jp asami@csis.u-tokyo.ac.jp
CSIS Discussion Paper No. 141 A Method for Comparing Multiple Regression Models Yuki Hiruta Yasushi Asami Department of Urban Engineering, the University of Tokyo e-mail: hiruta@ua.t.u-tokyo.ac.jp asami@csis.u-tokyo.ac.jp
Bagging for One-Class Learning
 Bagging for One-Class Learning David Kamm December 13, 2008 1 Introduction Consider the following outlier detection problem: suppose you are given an unlabeled data set and make the assumptions that one
Bagging for One-Class Learning David Kamm December 13, 2008 1 Introduction Consider the following outlier detection problem: suppose you are given an unlabeled data set and make the assumptions that one
Technical Whitepaper. Machine Learning in kdb+: k-nearest Neighbor classification and pattern recognition with q. Author:
 Technical Whitepaper Machine Learning in kdb+: k-nearest Neighbor classification and pattern recognition with q Author: Emanuele Melis works for Kx as kdb+ consultant. Currently based in the UK, he has
Technical Whitepaper Machine Learning in kdb+: k-nearest Neighbor classification and pattern recognition with q Author: Emanuele Melis works for Kx as kdb+ consultant. Currently based in the UK, he has
Wild Mushrooms Classification Edible or Poisonous
 Wild Mushrooms Classification Edible or Poisonous Yulin Shen ECE 539 Project Report Professor: Hu Yu Hen 2013 Fall ( I allow code to be released in the public domain) pg. 1 Contents Introduction. 3 Practicality
Wild Mushrooms Classification Edible or Poisonous Yulin Shen ECE 539 Project Report Professor: Hu Yu Hen 2013 Fall ( I allow code to be released in the public domain) pg. 1 Contents Introduction. 3 Practicality
10/5/2017 MIST.6060 Business Intelligence and Data Mining 1. Nearest Neighbors. In a p-dimensional space, the Euclidean distance between two records,
 10/5/2017 MIST.6060 Business Intelligence and Data Mining 1 Distance Measures Nearest Neighbors In a p-dimensional space, the Euclidean distance between two records, a = a, a,..., a ) and b = b, b,...,
10/5/2017 MIST.6060 Business Intelligence and Data Mining 1 Distance Measures Nearest Neighbors In a p-dimensional space, the Euclidean distance between two records, a = a, a,..., a ) and b = b, b,...,
Rank Measures for Ordering
 Rank Measures for Ordering Jin Huang and Charles X. Ling Department of Computer Science The University of Western Ontario London, Ontario, Canada N6A 5B7 email: fjhuang33, clingg@csd.uwo.ca Abstract. Many
Rank Measures for Ordering Jin Huang and Charles X. Ling Department of Computer Science The University of Western Ontario London, Ontario, Canada N6A 5B7 email: fjhuang33, clingg@csd.uwo.ca Abstract. Many
Support Vector Selection and Adaptation and Its Application in Remote Sensing
 Support Vector Selection and Adaptation and Its Application in Remote Sensing Gülşen Taşkın Kaya Computational Science and Engineering Istanbul Technical University Istanbul, Turkey gtaskink@purdue.edu
Support Vector Selection and Adaptation and Its Application in Remote Sensing Gülşen Taşkın Kaya Computational Science and Engineering Istanbul Technical University Istanbul, Turkey gtaskink@purdue.edu
Applying Supervised Learning
 Applying Supervised Learning When to Consider Supervised Learning A supervised learning algorithm takes a known set of input data (the training set) and known responses to the data (output), and trains
Applying Supervised Learning When to Consider Supervised Learning A supervised learning algorithm takes a known set of input data (the training set) and known responses to the data (output), and trains
Improving the Random Forest Algorithm by Randomly Varying the Size of the Bootstrap Samples for Low Dimensional Data Sets
 Improving the Random Forest Algorithm by Randomly Varying the Size of the Bootstrap Samples for Low Dimensional Data Sets Md Nasim Adnan and Md Zahidul Islam Centre for Research in Complex Systems (CRiCS)
Improving the Random Forest Algorithm by Randomly Varying the Size of the Bootstrap Samples for Low Dimensional Data Sets Md Nasim Adnan and Md Zahidul Islam Centre for Research in Complex Systems (CRiCS)
Data Cleaning and Prototyping Using K-Means to Enhance Classification Accuracy
 Data Cleaning and Prototyping Using K-Means to Enhance Classification Accuracy Lutfi Fanani 1 and Nurizal Dwi Priandani 2 1 Department of Computer Science, Brawijaya University, Malang, Indonesia. 2 Department
Data Cleaning and Prototyping Using K-Means to Enhance Classification Accuracy Lutfi Fanani 1 and Nurizal Dwi Priandani 2 1 Department of Computer Science, Brawijaya University, Malang, Indonesia. 2 Department
Evaluation Measures. Sebastian Pölsterl. April 28, Computer Aided Medical Procedures Technische Universität München
 Evaluation Measures Sebastian Pölsterl Computer Aided Medical Procedures Technische Universität München April 28, 2015 Outline 1 Classification 1. Confusion Matrix 2. Receiver operating characteristics
Evaluation Measures Sebastian Pölsterl Computer Aided Medical Procedures Technische Universität München April 28, 2015 Outline 1 Classification 1. Confusion Matrix 2. Receiver operating characteristics
Lorentzian Distance Classifier for Multiple Features
 Yerzhan Kerimbekov 1 and Hasan Şakir Bilge 2 1 Department of Computer Engineering, Ahmet Yesevi University, Ankara, Turkey 2 Department of Electrical-Electronics Engineering, Gazi University, Ankara, Turkey
Yerzhan Kerimbekov 1 and Hasan Şakir Bilge 2 1 Department of Computer Engineering, Ahmet Yesevi University, Ankara, Turkey 2 Department of Electrical-Electronics Engineering, Gazi University, Ankara, Turkey
CS 340 Lec. 4: K-Nearest Neighbors
 CS 340 Lec. 4: K-Nearest Neighbors AD January 2011 AD () CS 340 Lec. 4: K-Nearest Neighbors January 2011 1 / 23 K-Nearest Neighbors Introduction Choice of Metric Overfitting and Underfitting Selection
CS 340 Lec. 4: K-Nearest Neighbors AD January 2011 AD () CS 340 Lec. 4: K-Nearest Neighbors January 2011 1 / 23 K-Nearest Neighbors Introduction Choice of Metric Overfitting and Underfitting Selection
The Comparative Study of Machine Learning Algorithms in Text Data Classification*
 The Comparative Study of Machine Learning Algorithms in Text Data Classification* Wang Xin School of Science, Beijing Information Science and Technology University Beijing, China Abstract Classification
The Comparative Study of Machine Learning Algorithms in Text Data Classification* Wang Xin School of Science, Beijing Information Science and Technology University Beijing, China Abstract Classification
April 3, 2012 T.C. Havens
 April 3, 2012 T.C. Havens Different training parameters MLP with different weights, number of layers/nodes, etc. Controls instability of classifiers (local minima) Similar strategies can be used to generate
April 3, 2012 T.C. Havens Different training parameters MLP with different weights, number of layers/nodes, etc. Controls instability of classifiers (local minima) Similar strategies can be used to generate
Classification Algorithms in Data Mining
 August 9th, 2016 Suhas Mallesh Yash Thakkar Ashok Choudhary CIS660 Data Mining and Big Data Processing -Dr. Sunnie S. Chung Classification Algorithms in Data Mining Deciding on the classification algorithms
August 9th, 2016 Suhas Mallesh Yash Thakkar Ashok Choudhary CIS660 Data Mining and Big Data Processing -Dr. Sunnie S. Chung Classification Algorithms in Data Mining Deciding on the classification algorithms
Project Presentation. Pattern Recognition. Under the guidance of Prof. Sumeet Agar wal
 Project Presentation in Pattern Recognition Under the guidance of Prof. Sumeet Agar wal By- ABHISHEK KUMAR (2009CS10175) GAURAV AGARWAL (2009EE10390) Aim Classification of customers based on their attributes
Project Presentation in Pattern Recognition Under the guidance of Prof. Sumeet Agar wal By- ABHISHEK KUMAR (2009CS10175) GAURAV AGARWAL (2009EE10390) Aim Classification of customers based on their attributes
Robustness of Selective Desensitization Perceptron Against Irrelevant and Partially Relevant Features in Pattern Classification
 Robustness of Selective Desensitization Perceptron Against Irrelevant and Partially Relevant Features in Pattern Classification Tomohiro Tanno, Kazumasa Horie, Jun Izawa, and Masahiko Morita University
Robustness of Selective Desensitization Perceptron Against Irrelevant and Partially Relevant Features in Pattern Classification Tomohiro Tanno, Kazumasa Horie, Jun Izawa, and Masahiko Morita University
Combined Weak Classifiers
 Combined Weak Classifiers Chuanyi Ji and Sheng Ma Department of Electrical, Computer and System Engineering Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, NY 12180 chuanyi@ecse.rpi.edu, shengm@ecse.rpi.edu Abstract
Combined Weak Classifiers Chuanyi Ji and Sheng Ma Department of Electrical, Computer and System Engineering Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, NY 12180 chuanyi@ecse.rpi.edu, shengm@ecse.rpi.edu Abstract
Sensor-based Semantic-level Human Activity Recognition using Temporal Classification
 Sensor-based Semantic-level Human Activity Recognition using Temporal Classification Weixuan Gao gaow@stanford.edu Chuanwei Ruan chuanwei@stanford.edu Rui Xu ray1993@stanford.edu I. INTRODUCTION Human
Sensor-based Semantic-level Human Activity Recognition using Temporal Classification Weixuan Gao gaow@stanford.edu Chuanwei Ruan chuanwei@stanford.edu Rui Xu ray1993@stanford.edu I. INTRODUCTION Human
CS4445 Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery in Databases. A Term 2008 Exam 2 October 14, 2008
 CS4445 Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery in Databases. A Term 2008 Exam 2 October 14, 2008 Prof. Carolina Ruiz Department of Computer Science Worcester Polytechnic Institute NAME: Prof. Ruiz Problem
CS4445 Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery in Databases. A Term 2008 Exam 2 October 14, 2008 Prof. Carolina Ruiz Department of Computer Science Worcester Polytechnic Institute NAME: Prof. Ruiz Problem
Midterm Examination CS540-2: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
 Midterm Examination CS540-2: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence March 15, 2018 LAST NAME: FIRST NAME: Problem Score Max Score 1 12 2 13 3 9 4 11 5 8 6 13 7 9 8 16 9 9 Total 100 Question 1. [12] Search
Midterm Examination CS540-2: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence March 15, 2018 LAST NAME: FIRST NAME: Problem Score Max Score 1 12 2 13 3 9 4 11 5 8 6 13 7 9 8 16 9 9 Total 100 Question 1. [12] Search
Feature-weighted k-nearest Neighbor Classifier
 Proceedings of the 27 IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computational Intelligence (FOCI 27) Feature-weighted k-nearest Neighbor Classifier Diego P. Vivencio vivencio@comp.uf scar.br Estevam R. Hruschka
Proceedings of the 27 IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computational Intelligence (FOCI 27) Feature-weighted k-nearest Neighbor Classifier Diego P. Vivencio vivencio@comp.uf scar.br Estevam R. Hruschka
Neural Network Weight Selection Using Genetic Algorithms
 Neural Network Weight Selection Using Genetic Algorithms David Montana presented by: Carl Fink, Hongyi Chen, Jack Cheng, Xinglong Li, Bruce Lin, Chongjie Zhang April 12, 2005 1 Neural Networks Neural networks
Neural Network Weight Selection Using Genetic Algorithms David Montana presented by: Carl Fink, Hongyi Chen, Jack Cheng, Xinglong Li, Bruce Lin, Chongjie Zhang April 12, 2005 1 Neural Networks Neural networks
3D Object Recognition using Multiclass SVM-KNN
 3D Object Recognition using Multiclass SVM-KNN R. Muralidharan, C. Chandradekar April 29, 2014 Presented by: Tasadduk Chowdhury Problem We address the problem of recognizing 3D objects based on various
3D Object Recognition using Multiclass SVM-KNN R. Muralidharan, C. Chandradekar April 29, 2014 Presented by: Tasadduk Chowdhury Problem We address the problem of recognizing 3D objects based on various
A Feature based on Encoding the Relative Position of a Point in the Character for Online Handwritten Character Recognition
 A Feature based on Encoding the Relative Position of a Point in the Character for Online Handwritten Character Recognition Dinesh Mandalapu, Sridhar Murali Krishna HP Laboratories India HPL-2007-109 July
A Feature based on Encoding the Relative Position of a Point in the Character for Online Handwritten Character Recognition Dinesh Mandalapu, Sridhar Murali Krishna HP Laboratories India HPL-2007-109 July
MS1b Statistical Data Mining Part 3: Supervised Learning Nonparametric Methods
 MS1b Statistical Data Mining Part 3: Supervised Learning Nonparametric Methods Yee Whye Teh Department of Statistics Oxford http://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/~teh/datamining.html Outline Supervised Learning: Nonparametric
MS1b Statistical Data Mining Part 3: Supervised Learning Nonparametric Methods Yee Whye Teh Department of Statistics Oxford http://www.stats.ox.ac.uk/~teh/datamining.html Outline Supervised Learning: Nonparametric
Character Recognition from Google Street View Images
 Character Recognition from Google Street View Images Indian Institute of Technology Course Project Report CS365A By Ritesh Kumar (11602) and Srikant Singh (12729) Under the guidance of Professor Amitabha
Character Recognition from Google Street View Images Indian Institute of Technology Course Project Report CS365A By Ritesh Kumar (11602) and Srikant Singh (12729) Under the guidance of Professor Amitabha
Lecture 25: Review I
 Lecture 25: Review I Reading: Up to chapter 5 in ISLR. STATS 202: Data mining and analysis Jonathan Taylor 1 / 18 Unsupervised learning In unsupervised learning, all the variables are on equal standing,
Lecture 25: Review I Reading: Up to chapter 5 in ISLR. STATS 202: Data mining and analysis Jonathan Taylor 1 / 18 Unsupervised learning In unsupervised learning, all the variables are on equal standing,
Intro to Artificial Intelligence
 Intro to Artificial Intelligence Ahmed Sallam { Lecture 5: Machine Learning ://. } ://.. 2 Review Probabilistic inference Enumeration Approximate inference 3 Today What is machine learning? Supervised
Intro to Artificial Intelligence Ahmed Sallam { Lecture 5: Machine Learning ://. } ://.. 2 Review Probabilistic inference Enumeration Approximate inference 3 Today What is machine learning? Supervised
From dynamic classifier selection to dynamic ensemble selection Albert H.R. Ko, Robert Sabourin, Alceu Souza Britto, Jr.
 From dynamic classifier selection to dynamic ensemble selection Albert H.R. Ko, Robert Sabourin, Alceu Souza Britto, Jr Eider Sánchez Contenidos 1. Introduction 2. Proposed dynamic ensemble selection KNORA
From dynamic classifier selection to dynamic ensemble selection Albert H.R. Ko, Robert Sabourin, Alceu Souza Britto, Jr Eider Sánchez Contenidos 1. Introduction 2. Proposed dynamic ensemble selection KNORA
SUPERVISED LEARNING METHODS. Stanley Liang, PhD Candidate, Lassonde School of Engineering, York University Helix Science Engagement Programs 2018
 SUPERVISED LEARNING METHODS Stanley Liang, PhD Candidate, Lassonde School of Engineering, York University Helix Science Engagement Programs 2018 2 CHOICE OF ML You cannot know which algorithm will work
SUPERVISED LEARNING METHODS Stanley Liang, PhD Candidate, Lassonde School of Engineering, York University Helix Science Engagement Programs 2018 2 CHOICE OF ML You cannot know which algorithm will work
Using Machine Learning to Identify Security Issues in Open-Source Libraries. Asankhaya Sharma Yaqin Zhou SourceClear
 Using Machine Learning to Identify Security Issues in Open-Source Libraries Asankhaya Sharma Yaqin Zhou SourceClear Outline - Overview of problem space Unidentified security issues How Machine Learning
Using Machine Learning to Identify Security Issues in Open-Source Libraries Asankhaya Sharma Yaqin Zhou SourceClear Outline - Overview of problem space Unidentified security issues How Machine Learning
Trimmed bagging a DEPARTMENT OF DECISION SCIENCES AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT (KBI) Christophe Croux, Kristel Joossens and Aurélie Lemmens
 Faculty of Economics and Applied Economics Trimmed bagging a Christophe Croux, Kristel Joossens and Aurélie Lemmens DEPARTMENT OF DECISION SCIENCES AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT (KBI) KBI 0721 Trimmed Bagging
Faculty of Economics and Applied Economics Trimmed bagging a Christophe Croux, Kristel Joossens and Aurélie Lemmens DEPARTMENT OF DECISION SCIENCES AND INFORMATION MANAGEMENT (KBI) KBI 0721 Trimmed Bagging
Nearest Neighbor Classification
 Nearest Neighbor Classification Charles Elkan elkan@cs.ucsd.edu October 9, 2007 The nearest-neighbor method is perhaps the simplest of all algorithms for predicting the class of a test example. The training
Nearest Neighbor Classification Charles Elkan elkan@cs.ucsd.edu October 9, 2007 The nearest-neighbor method is perhaps the simplest of all algorithms for predicting the class of a test example. The training
An Empirical Study on Lazy Multilabel Classification Algorithms
 An Empirical Study on Lazy Multilabel Classification Algorithms Eleftherios Spyromitros, Grigorios Tsoumakas and Ioannis Vlahavas Machine Learning & Knowledge Discovery Group Department of Informatics
An Empirical Study on Lazy Multilabel Classification Algorithms Eleftherios Spyromitros, Grigorios Tsoumakas and Ioannis Vlahavas Machine Learning & Knowledge Discovery Group Department of Informatics
An Effective Performance of Feature Selection with Classification of Data Mining Using SVM Algorithm
 Proceedings of the National Conference on Recent Trends in Mathematical Computing NCRTMC 13 427 An Effective Performance of Feature Selection with Classification of Data Mining Using SVM Algorithm A.Veeraswamy
Proceedings of the National Conference on Recent Trends in Mathematical Computing NCRTMC 13 427 An Effective Performance of Feature Selection with Classification of Data Mining Using SVM Algorithm A.Veeraswamy
Beyond Bags of Features
 : for Recognizing Natural Scene Categories Matching and Modeling Seminar Instructed by Prof. Haim J. Wolfson School of Computer Science Tel Aviv University December 9 th, 2015
: for Recognizing Natural Scene Categories Matching and Modeling Seminar Instructed by Prof. Haim J. Wolfson School of Computer Science Tel Aviv University December 9 th, 2015
 Wrapper Feature Selection using Discrete Cuckoo Optimization Algorithm Abstract S.J. Mousavirad and H. Ebrahimpour-Komleh* 1 Department of Computer and Electrical Engineering, University of Kashan, Kashan,
Wrapper Feature Selection using Discrete Cuckoo Optimization Algorithm Abstract S.J. Mousavirad and H. Ebrahimpour-Komleh* 1 Department of Computer and Electrical Engineering, University of Kashan, Kashan,
THE ENSEMBLE CONCEPTUAL CLUSTERING OF SYMBOLIC DATA FOR CUSTOMER LOYALTY ANALYSIS
 THE ENSEMBLE CONCEPTUAL CLUSTERING OF SYMBOLIC DATA FOR CUSTOMER LOYALTY ANALYSIS Marcin Pełka 1 1 Wroclaw University of Economics, Faculty of Economics, Management and Tourism, Department of Econometrics
THE ENSEMBLE CONCEPTUAL CLUSTERING OF SYMBOLIC DATA FOR CUSTOMER LOYALTY ANALYSIS Marcin Pełka 1 1 Wroclaw University of Economics, Faculty of Economics, Management and Tourism, Department of Econometrics
Machine Learning in Biology
 Università degli studi di Padova Machine Learning in Biology Luca Silvestrin (Dottorando, XXIII ciclo) Supervised learning Contents Class-conditional probability density Linear and quadratic discriminant
Università degli studi di Padova Machine Learning in Biology Luca Silvestrin (Dottorando, XXIII ciclo) Supervised learning Contents Class-conditional probability density Linear and quadratic discriminant
Distribution-free Predictive Approaches
 Distribution-free Predictive Approaches The methods discussed in the previous sections are essentially model-based. Model-free approaches such as tree-based classification also exist and are popular for
Distribution-free Predictive Approaches The methods discussed in the previous sections are essentially model-based. Model-free approaches such as tree-based classification also exist and are popular for
Predict the box office of US movies
 Predict the box office of US movies Group members: Hanqing Ma, Jin Sun, Zeyu Zhang 1. Introduction Our task is to predict the box office of the upcoming movies using the properties of the movies, such
Predict the box office of US movies Group members: Hanqing Ma, Jin Sun, Zeyu Zhang 1. Introduction Our task is to predict the box office of the upcoming movies using the properties of the movies, such
ECE 5470 Classification, Machine Learning, and Neural Network Review
 ECE 5470 Classification, Machine Learning, and Neural Network Review Due December 1. Solution set Instructions: These questions are to be answered on this document which should be submitted to blackboard
ECE 5470 Classification, Machine Learning, and Neural Network Review Due December 1. Solution set Instructions: These questions are to be answered on this document which should be submitted to blackboard
Trade-offs in Explanatory
 1 Trade-offs in Explanatory 21 st of February 2012 Model Learning Data Analysis Project Madalina Fiterau DAP Committee Artur Dubrawski Jeff Schneider Geoff Gordon 2 Outline Motivation: need for interpretable
1 Trade-offs in Explanatory 21 st of February 2012 Model Learning Data Analysis Project Madalina Fiterau DAP Committee Artur Dubrawski Jeff Schneider Geoff Gordon 2 Outline Motivation: need for interpretable
A study of classification algorithms using Rapidminer
 Volume 119 No. 12 2018, 15977-15988 ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu A study of classification algorithms using Rapidminer Dr.J.Arunadevi 1, S.Ramya 2, M.Ramesh Raja
Volume 119 No. 12 2018, 15977-15988 ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu A study of classification algorithms using Rapidminer Dr.J.Arunadevi 1, S.Ramya 2, M.Ramesh Raja
An Empirical Study of Lazy Multilabel Classification Algorithms
 An Empirical Study of Lazy Multilabel Classification Algorithms E. Spyromitros and G. Tsoumakas and I. Vlahavas Department of Informatics, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, 54124 Thessaloniki, Greece
An Empirical Study of Lazy Multilabel Classification Algorithms E. Spyromitros and G. Tsoumakas and I. Vlahavas Department of Informatics, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, 54124 Thessaloniki, Greece
Facial Expression Classification with Random Filters Feature Extraction
 Facial Expression Classification with Random Filters Feature Extraction Mengye Ren Facial Monkey mren@cs.toronto.edu Zhi Hao Luo It s Me lzh@cs.toronto.edu I. ABSTRACT In our work, we attempted to tackle
Facial Expression Classification with Random Filters Feature Extraction Mengye Ren Facial Monkey mren@cs.toronto.edu Zhi Hao Luo It s Me lzh@cs.toronto.edu I. ABSTRACT In our work, we attempted to tackle
An Empirical Comparison of Ensemble Methods Based on Classification Trees. Mounir Hamza and Denis Larocque. Department of Quantitative Methods
 An Empirical Comparison of Ensemble Methods Based on Classification Trees Mounir Hamza and Denis Larocque Department of Quantitative Methods HEC Montreal Canada Mounir Hamza and Denis Larocque 1 June 2005
An Empirical Comparison of Ensemble Methods Based on Classification Trees Mounir Hamza and Denis Larocque Department of Quantitative Methods HEC Montreal Canada Mounir Hamza and Denis Larocque 1 June 2005
An Empirical Study of Hoeffding Racing for Model Selection in k-nearest Neighbor Classification
 An Empirical Study of Hoeffding Racing for Model Selection in k-nearest Neighbor Classification Flora Yu-Hui Yeh and Marcus Gallagher School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering University
An Empirical Study of Hoeffding Racing for Model Selection in k-nearest Neighbor Classification Flora Yu-Hui Yeh and Marcus Gallagher School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering University
On Classification: An Empirical Study of Existing Algorithms Based on Two Kaggle Competitions
 On Classification: An Empirical Study of Existing Algorithms Based on Two Kaggle Competitions CAMCOS Report Day December 9th, 2015 San Jose State University Project Theme: Classification The Kaggle Competition
On Classification: An Empirical Study of Existing Algorithms Based on Two Kaggle Competitions CAMCOS Report Day December 9th, 2015 San Jose State University Project Theme: Classification The Kaggle Competition
CANCER PREDICTION USING PATTERN CLASSIFICATION OF MICROARRAY DATA. By: Sudhir Madhav Rao &Vinod Jayakumar Instructor: Dr.
 CANCER PREDICTION USING PATTERN CLASSIFICATION OF MICROARRAY DATA By: Sudhir Madhav Rao &Vinod Jayakumar Instructor: Dr. Michael Nechyba 1. Abstract The objective of this project is to apply well known
CANCER PREDICTION USING PATTERN CLASSIFICATION OF MICROARRAY DATA By: Sudhir Madhav Rao &Vinod Jayakumar Instructor: Dr. Michael Nechyba 1. Abstract The objective of this project is to apply well known
BRACE: A Paradigm For the Discretization of Continuously Valued Data
 Proceedings of the Seventh Florida Artificial Intelligence Research Symposium, pp. 7-2, 994 BRACE: A Paradigm For the Discretization of Continuously Valued Data Dan Ventura Tony R. Martinez Computer Science
Proceedings of the Seventh Florida Artificial Intelligence Research Symposium, pp. 7-2, 994 BRACE: A Paradigm For the Discretization of Continuously Valued Data Dan Ventura Tony R. Martinez Computer Science
COSC160: Detection and Classification. Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor
 COSC160: Detection and Classification Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor Outline I. Problem I. Strategies II. Features for training III. Using spatial information? IV. Reducing dimensionality
COSC160: Detection and Classification Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor Outline I. Problem I. Strategies II. Features for training III. Using spatial information? IV. Reducing dimensionality
Adaptive Gesture Recognition System Integrating Multiple Inputs
 Adaptive Gesture Recognition System Integrating Multiple Inputs Master Thesis - Colloquium Tobias Staron University of Hamburg Faculty of Mathematics, Informatics and Natural Sciences Technical Aspects
Adaptive Gesture Recognition System Integrating Multiple Inputs Master Thesis - Colloquium Tobias Staron University of Hamburg Faculty of Mathematics, Informatics and Natural Sciences Technical Aspects
SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector. Author: Wei Liu et al. Presenter: Siyu Jiang
 SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector Author: Wei Liu et al. Presenter: Siyu Jiang Outline 1. Motivations 2. Contributions 3. Methodology 4. Experiments 5. Conclusions 6. Extensions Motivation Motivation
SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector Author: Wei Liu et al. Presenter: Siyu Jiang Outline 1. Motivations 2. Contributions 3. Methodology 4. Experiments 5. Conclusions 6. Extensions Motivation Motivation
Lecture 9: Support Vector Machines
 Lecture 9: Support Vector Machines William Webber (william@williamwebber.com) COMP90042, 2014, Semester 1, Lecture 8 What we ll learn in this lecture Support Vector Machines (SVMs) a highly robust and
Lecture 9: Support Vector Machines William Webber (william@williamwebber.com) COMP90042, 2014, Semester 1, Lecture 8 What we ll learn in this lecture Support Vector Machines (SVMs) a highly robust and
Sentiment Analysis for Amazon Reviews
 Sentiment Analysis for Amazon Reviews Wanliang Tan wanliang@stanford.edu Xinyu Wang xwang7@stanford.edu Xinyu Xu xinyu17@stanford.edu Abstract Sentiment analysis of product reviews, an application problem,
Sentiment Analysis for Amazon Reviews Wanliang Tan wanliang@stanford.edu Xinyu Wang xwang7@stanford.edu Xinyu Xu xinyu17@stanford.edu Abstract Sentiment analysis of product reviews, an application problem,
Classifying Depositional Environments in Satellite Images
 Classifying Depositional Environments in Satellite Images Alex Miltenberger and Rayan Kanfar Department of Geophysics School of Earth, Energy, and Environmental Sciences Stanford University 1 Introduction
Classifying Depositional Environments in Satellite Images Alex Miltenberger and Rayan Kanfar Department of Geophysics School of Earth, Energy, and Environmental Sciences Stanford University 1 Introduction
CS294-1 Final Project. Algorithms Comparison
 CS294-1 Final Project Algorithms Comparison Deep Learning Neural Network AdaBoost Random Forest Prepared By: Shuang Bi (24094630) Wenchang Zhang (24094623) 2013-05-15 1 INTRODUCTION In this project, we
CS294-1 Final Project Algorithms Comparison Deep Learning Neural Network AdaBoost Random Forest Prepared By: Shuang Bi (24094630) Wenchang Zhang (24094623) 2013-05-15 1 INTRODUCTION In this project, we
Applied Statistics for Neuroscientists Part IIa: Machine Learning
 Applied Statistics for Neuroscientists Part IIa: Machine Learning Dr. Seyed-Ahmad Ahmadi 04.04.2017 16.11.2017 Outline Machine Learning Difference between statistics and machine learning Modeling the problem
Applied Statistics for Neuroscientists Part IIa: Machine Learning Dr. Seyed-Ahmad Ahmadi 04.04.2017 16.11.2017 Outline Machine Learning Difference between statistics and machine learning Modeling the problem
Evaluation of different biological data and computational classification methods for use in protein interaction prediction.
 Evaluation of different biological data and computational classification methods for use in protein interaction prediction. Yanjun Qi, Ziv Bar-Joseph, Judith Klein-Seetharaman Protein 2006 Motivation Correctly
Evaluation of different biological data and computational classification methods for use in protein interaction prediction. Yanjun Qi, Ziv Bar-Joseph, Judith Klein-Seetharaman Protein 2006 Motivation Correctly
Kernels + K-Means Introduction to Machine Learning. Matt Gormley Lecture 29 April 25, 2018
 10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Kernels + K-Means Matt Gormley Lecture 29 April 25, 2018 1 Reminders Homework 8:
10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Kernels + K-Means Matt Gormley Lecture 29 April 25, 2018 1 Reminders Homework 8:
Equation to LaTeX. Abhinav Rastogi, Sevy Harris. I. Introduction. Segmentation.
 Equation to LaTeX Abhinav Rastogi, Sevy Harris {arastogi,sharris5}@stanford.edu I. Introduction Copying equations from a pdf file to a LaTeX document can be time consuming because there is no easy way
Equation to LaTeX Abhinav Rastogi, Sevy Harris {arastogi,sharris5}@stanford.edu I. Introduction Copying equations from a pdf file to a LaTeX document can be time consuming because there is no easy way
THE MNIST DATABASE of handwritten digits Yann LeCun, Courant Institute, NYU Corinna Cortes, Google Labs, New York
 THE MNIST DATABASE of handwritten digits Yann LeCun, Courant Institute, NYU Corinna Cortes, Google Labs, New York The MNIST database of handwritten digits, available from this page, has a training set
THE MNIST DATABASE of handwritten digits Yann LeCun, Courant Institute, NYU Corinna Cortes, Google Labs, New York The MNIST database of handwritten digits, available from this page, has a training set
Otto Group Product Classification Challenge
 Otto Group Product Classification Challenge Hoang Duong May 19, 2015 1 Introduction The Otto Group Product Classification Challenge is the biggest Kaggle competition to date with 3590 participating teams.
Otto Group Product Classification Challenge Hoang Duong May 19, 2015 1 Introduction The Otto Group Product Classification Challenge is the biggest Kaggle competition to date with 3590 participating teams.
Supervised vs unsupervised clustering
 Classification Supervised vs unsupervised clustering Cluster analysis: Classes are not known a- priori. Classification: Classes are defined a-priori Sometimes called supervised clustering Extract useful
Classification Supervised vs unsupervised clustering Cluster analysis: Classes are not known a- priori. Classification: Classes are defined a-priori Sometimes called supervised clustering Extract useful
Slides for Data Mining by I. H. Witten and E. Frank
 Slides for Data Mining by I. H. Witten and E. Frank 7 Engineering the input and output Attribute selection Scheme-independent, scheme-specific Attribute discretization Unsupervised, supervised, error-
Slides for Data Mining by I. H. Witten and E. Frank 7 Engineering the input and output Attribute selection Scheme-independent, scheme-specific Attribute discretization Unsupervised, supervised, error-
Dynamic Thresholding for Image Analysis
 Dynamic Thresholding for Image Analysis Statistical Consulting Report for Edward Chan Clean Energy Research Center University of British Columbia by Libo Lu Department of Statistics University of British
Dynamic Thresholding for Image Analysis Statistical Consulting Report for Edward Chan Clean Energy Research Center University of British Columbia by Libo Lu Department of Statistics University of British
Package kernelfactory
 Package kernelfactory September 29, 2015 Type Package Title Kernel Factory: An Ensemble of Kernel Machines Version 0.3.0 Date 2015-09-29 Imports randomforest, AUC, genalg, kernlab, stats Author Michel
Package kernelfactory September 29, 2015 Type Package Title Kernel Factory: An Ensemble of Kernel Machines Version 0.3.0 Date 2015-09-29 Imports randomforest, AUC, genalg, kernlab, stats Author Michel
Machine Learning Techniques for Data Mining
 Machine Learning Techniques for Data Mining Eibe Frank University of Waikato New Zealand 10/25/2000 1 PART VII Moving on: Engineering the input and output 10/25/2000 2 Applying a learner is not all Already
Machine Learning Techniques for Data Mining Eibe Frank University of Waikato New Zealand 10/25/2000 1 PART VII Moving on: Engineering the input and output 10/25/2000 2 Applying a learner is not all Already
I211: Information infrastructure II
 Data Mining: Classifier Evaluation I211: Information infrastructure II 3-nearest neighbor labeled data find class labels for the 4 data points 1 0 0 6 0 0 0 5 17 1.7 1 1 4 1 7.1 1 1 1 0.4 1 2 1 3.0 0 0.1
Data Mining: Classifier Evaluation I211: Information infrastructure II 3-nearest neighbor labeled data find class labels for the 4 data points 1 0 0 6 0 0 0 5 17 1.7 1 1 4 1 7.1 1 1 1 0.4 1 2 1 3.0 0 0.1
Convolution Neural Networks for Chinese Handwriting Recognition
 Convolution Neural Networks for Chinese Handwriting Recognition Xu Chen Stanford University 450 Serra Mall, Stanford, CA 94305 xchen91@stanford.edu Abstract Convolutional neural networks have been proven
Convolution Neural Networks for Chinese Handwriting Recognition Xu Chen Stanford University 450 Serra Mall, Stanford, CA 94305 xchen91@stanford.edu Abstract Convolutional neural networks have been proven
Machine Learning Classifiers and Boosting
 Machine Learning Classifiers and Boosting Reading Ch 18.6-18.12, 20.1-20.3.2 Outline Different types of learning problems Different types of learning algorithms Supervised learning Decision trees Naïve
Machine Learning Classifiers and Boosting Reading Ch 18.6-18.12, 20.1-20.3.2 Outline Different types of learning problems Different types of learning algorithms Supervised learning Decision trees Naïve
CS 229 Midterm Review
 CS 229 Midterm Review Course Staff Fall 2018 11/2/2018 Outline Today: SVMs Kernels Tree Ensembles EM Algorithm / Mixture Models [ Focus on building intuition, less so on solving specific problems. Ask
CS 229 Midterm Review Course Staff Fall 2018 11/2/2018 Outline Today: SVMs Kernels Tree Ensembles EM Algorithm / Mixture Models [ Focus on building intuition, less so on solving specific problems. Ask
HALF&HALF BAGGING AND HARD BOUNDARY POINTS. Leo Breiman Statistics Department University of California Berkeley, CA
 1 HALF&HALF BAGGING AND HARD BOUNDARY POINTS Leo Breiman Statistics Department University of California Berkeley, CA 94720 leo@stat.berkeley.edu Technical Report 534 Statistics Department September 1998
1 HALF&HALF BAGGING AND HARD BOUNDARY POINTS Leo Breiman Statistics Department University of California Berkeley, CA 94720 leo@stat.berkeley.edu Technical Report 534 Statistics Department September 1998
Comparison of various classification models for making financial decisions
 Comparison of various classification models for making financial decisions Vaibhav Mohan Computer Science Department Johns Hopkins University Baltimore, MD 21218, USA vmohan3@jhu.edu Abstract Banks are
Comparison of various classification models for making financial decisions Vaibhav Mohan Computer Science Department Johns Hopkins University Baltimore, MD 21218, USA vmohan3@jhu.edu Abstract Banks are
Machine Learning. Classification
 10-701 Machine Learning Classification Inputs Inputs Inputs Where we are Density Estimator Probability Classifier Predict category Today Regressor Predict real no. Later Classification Assume we want to
10-701 Machine Learning Classification Inputs Inputs Inputs Where we are Density Estimator Probability Classifier Predict category Today Regressor Predict real no. Later Classification Assume we want to
Combination of PCA with SMOTE Resampling to Boost the Prediction Rate in Lung Cancer Dataset
 International Journal of Computer Applications (0975 8887) Combination of PCA with SMOTE Resampling to Boost the Prediction Rate in Lung Cancer Dataset Mehdi Naseriparsa Islamic Azad University Tehran
International Journal of Computer Applications (0975 8887) Combination of PCA with SMOTE Resampling to Boost the Prediction Rate in Lung Cancer Dataset Mehdi Naseriparsa Islamic Azad University Tehran
An Ensemble Method for Clustering
 DSC 2003 Working Papers Draft Versions) http://www.ci.tuwien.ac.at/conferences/dsc-2003/ An Ensemble Method for Clustering Andreas Weingessel, Evgenia Dimitriadou and Kurt Hornik Institut für Statistik
DSC 2003 Working Papers Draft Versions) http://www.ci.tuwien.ac.at/conferences/dsc-2003/ An Ensemble Method for Clustering Andreas Weingessel, Evgenia Dimitriadou and Kurt Hornik Institut für Statistik
Ensemble Learning: An Introduction. Adapted from Slides by Tan, Steinbach, Kumar
 Ensemble Learning: An Introduction Adapted from Slides by Tan, Steinbach, Kumar 1 General Idea D Original Training data Step 1: Create Multiple Data Sets... D 1 D 2 D t-1 D t Step 2: Build Multiple Classifiers
Ensemble Learning: An Introduction Adapted from Slides by Tan, Steinbach, Kumar 1 General Idea D Original Training data Step 1: Create Multiple Data Sets... D 1 D 2 D t-1 D t Step 2: Build Multiple Classifiers
Comparative analysis of classifier algorithm in data mining Aikjot Kaur Narula#, Dr.Raman Maini*
 Comparative analysis of classifier algorithm in data mining Aikjot Kaur Narula#, Dr.Raman Maini* #Student, Department of Computer Engineering, Punjabi university Patiala, India, aikjotnarula@gmail.com
Comparative analysis of classifier algorithm in data mining Aikjot Kaur Narula#, Dr.Raman Maini* #Student, Department of Computer Engineering, Punjabi university Patiala, India, aikjotnarula@gmail.com
Estimating Map Accuracy without a Spatially Representative Training Sample
 Estimating Map Accuracy without a Spatially Representative Training Sample David A. Patterson, Mathematical Sciences, The University of Montana-Missoula Brian M. Steele, Mathematical Sciences, The University
Estimating Map Accuracy without a Spatially Representative Training Sample David A. Patterson, Mathematical Sciences, The University of Montana-Missoula Brian M. Steele, Mathematical Sciences, The University
Random Forest A. Fornaser
 Random Forest A. Fornaser alberto.fornaser@unitn.it Sources Lecture 15: decision trees, information theory and random forests, Dr. Richard E. Turner Trees and Random Forests, Adele Cutler, Utah State University
Random Forest A. Fornaser alberto.fornaser@unitn.it Sources Lecture 15: decision trees, information theory and random forests, Dr. Richard E. Turner Trees and Random Forests, Adele Cutler, Utah State University
Random Search Report An objective look at random search performance for 4 problem sets
 Random Search Report An objective look at random search performance for 4 problem sets Dudon Wai Georgia Institute of Technology CS 7641: Machine Learning Atlanta, GA dwai3@gatech.edu Abstract: This report
Random Search Report An objective look at random search performance for 4 problem sets Dudon Wai Georgia Institute of Technology CS 7641: Machine Learning Atlanta, GA dwai3@gatech.edu Abstract: This report
SVM: Multiclass and Structured Prediction. Bin Zhao
 SVM: Multiclass and Structured Prediction Bin Zhao Part I: Multi-Class SVM 2-Class SVM Primal form Dual form http://www.glue.umd.edu/~zhelin/recog.html Real world classification problems Digit recognition
SVM: Multiclass and Structured Prediction Bin Zhao Part I: Multi-Class SVM 2-Class SVM Primal form Dual form http://www.glue.umd.edu/~zhelin/recog.html Real world classification problems Digit recognition
Deep Tracking: Biologically Inspired Tracking with Deep Convolutional Networks
 Deep Tracking: Biologically Inspired Tracking with Deep Convolutional Networks Si Chen The George Washington University sichen@gwmail.gwu.edu Meera Hahn Emory University mhahn7@emory.edu Mentor: Afshin
Deep Tracking: Biologically Inspired Tracking with Deep Convolutional Networks Si Chen The George Washington University sichen@gwmail.gwu.edu Meera Hahn Emory University mhahn7@emory.edu Mentor: Afshin
Structural Health Monitoring Using Guided Ultrasonic Waves to Detect Damage in Composite Panels
 Structural Health Monitoring Using Guided Ultrasonic Waves to Detect Damage in Composite Panels Colleen Rosania December, Introduction In the aircraft industry safety, maintenance costs, and optimum weight
Structural Health Monitoring Using Guided Ultrasonic Waves to Detect Damage in Composite Panels Colleen Rosania December, Introduction In the aircraft industry safety, maintenance costs, and optimum weight
Use of KNN for the Netflix Prize Ted Hong, Dimitris Tsamis Stanford University
 Use of KNN for the Netflix Prize Ted Hong, Dimitris Tsamis Stanford University {tedhong, dtsamis}@stanford.edu Abstract This paper analyzes the performance of various KNNs techniques as applied to the
Use of KNN for the Netflix Prize Ted Hong, Dimitris Tsamis Stanford University {tedhong, dtsamis}@stanford.edu Abstract This paper analyzes the performance of various KNNs techniques as applied to the
University of California, Berkeley
 University of California, Berkeley U.C. Berkeley Division of Biostatistics Working Paper Series Year 2014 Paper 321 A Scalable Supervised Subsemble Prediction Algorithm Stephanie Sapp Mark J. van der Laan
University of California, Berkeley U.C. Berkeley Division of Biostatistics Working Paper Series Year 2014 Paper 321 A Scalable Supervised Subsemble Prediction Algorithm Stephanie Sapp Mark J. van der Laan
Learning independent, diverse binary hash functions: pruning and locality
 Learning independent, diverse binary hash functions: pruning and locality Ramin Raziperchikolaei and Miguel Á. Carreira-Perpiñán Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of California, Merced
Learning independent, diverse binary hash functions: pruning and locality Ramin Raziperchikolaei and Miguel Á. Carreira-Perpiñán Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of California, Merced
NDoT: Nearest Neighbor Distance Based Outlier Detection Technique
 NDoT: Nearest Neighbor Distance Based Outlier Detection Technique Neminath Hubballi 1, Bidyut Kr. Patra 2, and Sukumar Nandi 1 1 Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology
NDoT: Nearest Neighbor Distance Based Outlier Detection Technique Neminath Hubballi 1, Bidyut Kr. Patra 2, and Sukumar Nandi 1 1 Department of Computer Science & Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology
Lecture 27: Review. Reading: All chapters in ISLR. STATS 202: Data mining and analysis. December 6, 2017
 Lecture 27: Review Reading: All chapters in ISLR. STATS 202: Data mining and analysis December 6, 2017 1 / 16 Final exam: Announcements Tuesday, December 12, 8:30-11:30 am, in the following rooms: Last
Lecture 27: Review Reading: All chapters in ISLR. STATS 202: Data mining and analysis December 6, 2017 1 / 16 Final exam: Announcements Tuesday, December 12, 8:30-11:30 am, in the following rooms: Last
Comparison of different preprocessing techniques and feature selection algorithms in cancer datasets
 Comparison of different preprocessing techniques and feature selection algorithms in cancer datasets Konstantinos Sechidis School of Computer Science University of Manchester sechidik@cs.man.ac.uk Abstract
Comparison of different preprocessing techniques and feature selection algorithms in cancer datasets Konstantinos Sechidis School of Computer Science University of Manchester sechidik@cs.man.ac.uk Abstract
Subject. Dataset. Copy paste feature of the diagram. Importing the dataset. Copy paste feature into the diagram.
 Subject Copy paste feature into the diagram. When we define the data analysis process into Tanagra, it is possible to copy components (or entire branches of components) towards another location into the
Subject Copy paste feature into the diagram. When we define the data analysis process into Tanagra, it is possible to copy components (or entire branches of components) towards another location into the
Online Mathematical Symbol Recognition using SVMs with Features from Functional Approximation
 Online Mathematical Symbol Recognition using SVMs with Features from Functional Approximation Birendra Keshari and Stephen M. Watt Ontario Research Centre for Computer Algebra Department of Computer Science
Online Mathematical Symbol Recognition using SVMs with Features from Functional Approximation Birendra Keshari and Stephen M. Watt Ontario Research Centre for Computer Algebra Department of Computer Science
SVM-KNN : Discriminative Nearest Neighbor Classification for Visual Category Recognition
 SVM-KNN : Discriminative Nearest Neighbor Classification for Visual Category Recognition Hao Zhang, Alexander Berg, Michael Maire Jitendra Malik EECS, UC Berkeley Presented by Adam Bickett Objective Visual
SVM-KNN : Discriminative Nearest Neighbor Classification for Visual Category Recognition Hao Zhang, Alexander Berg, Michael Maire Jitendra Malik EECS, UC Berkeley Presented by Adam Bickett Objective Visual
Sketchable Histograms of Oriented Gradients for Object Detection
 Sketchable Histograms of Oriented Gradients for Object Detection No Author Given No Institute Given Abstract. In this paper we investigate a new representation approach for visual object recognition. The
Sketchable Histograms of Oriented Gradients for Object Detection No Author Given No Institute Given Abstract. In this paper we investigate a new representation approach for visual object recognition. The
Link Prediction for Social Network
 Link Prediction for Social Network Ning Lin Computer Science and Engineering University of California, San Diego Email: nil016@eng.ucsd.edu Abstract Friendship recommendation has become an important issue
Link Prediction for Social Network Ning Lin Computer Science and Engineering University of California, San Diego Email: nil016@eng.ucsd.edu Abstract Friendship recommendation has become an important issue
