Unit #22 - The Chain Rule, Higher Partial Derivatives & Optimization Section 14.7
|
|
|
- Rosemary Avice Ferguson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit #22 - The Chain Rule, Higher Partial Derivatives & Optimization Section 14.7 Some material from Calculus, Single and MultiVariable by Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, McCallum et. al. Copyright 2005 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. This material is used by permission of John Wiley & Sons, Inc. TEST PREPARATION PROBLEMS 1. f(x,y) = 3x 2 y +5xy 3 f x = 6xy +5y 3 f y = 3x 2 +15xy 2 f xx = 6y f xy = 6x+15y 2 f yx = 6x+15y 2 f yy = +30xy 3. f(x,y) = (x+y) 3 f x = 3(x+y) 2 f y = 3(x+y) 2 f xx = 6(x+y) f xy = 6(x+y) f yx = 6(x+y) f yy = 6(x+y) 5. f(x,y) = e 2xy f x = e 2xy 2y f y = e 2xy 2x f xx = e 2xy (2y)(2y) f xy = e 2xy (2y)(2x)+e 2xy (2) f yx = e 2xy (2x)(2y)+e 2xy (2) f yy = e 2xy (2x)(2x) 1
2 9. f(x,y) = sin(x 2 +y 2 ) f x = cos(x 2 +y 2 )2x f y = cos(x 2 +y 2 )2y f xx = sin(x 2 +y 2 )(2x)(2x) +cos(x 2 +y 2 )(2) f xy = sin(x 2 +y 2 )(2y)(2x) f yx = sin(x 2 +y 2 )(2y)(2x) f yy = sin(x 2 +y 2 )(2y)(2y) +cos(x 2 +y 2 )(2) 10. f(x,y) = 3sin(2x)cos(5y) f x = 6cos(2x)cos(5y) f y = 15sin(2x)sin(5y) f xx = 3sin(2x)(4)cos(5y) = 12sin(2x)cos(5y) f xy = 6cos(2x)( sin(5y))(5) = 30cos(2x)sin(5y) f yx = 15cos(2x)(2)sin(5y) = 30cos(2x)sin(5y) f yy = 15sin(2x)( cos(5y))(5) = 75sin(2x)cos(5y) 11. f(x,y) = (x y +1) 2 To compute the two-variable second-degree Taylor polynomial, we need all the first and second partial derivatives of f(x, y). f = (x y +1) 2 f(0,0) = 1 f x = 2(x y +1) f x (0,0) = 2 f y = 2(x y +1)( 1) f y (0,0) = 2 f xx = 2 f xx (0,0) = 2 f xy = 2 f xy (0,0) = 2 f yy = 2 f yy (0,0) = 2 Using the Taylor polynomial formula (which is an extension of our linearization/tangent plane formula), at the point (x,y) = (0,0), f(x,y) f(0,0)+f x (0,0)(x 0)+f y (0,0)(y 0) f xx(0,0)(x 0) 2 +f xy (0,0)(x 0)(y 0)+ 1 2 f yy(0,0)(y 0) 2 = 1+2x 2y x2 2xy = 1+2x 2y +x 2 2xy +y 2 2
3 Note that, because our original function was a quadratic in x and y, this Taylor approximation is exactly the same function we started with (try expanding (x y+1) 2 to see this). 15. f(x,y) = e x cos(y) f = e x cos(y) f(0,0) = 1 f x = e x cos(y) f x (0,0) = 1 f y = e x sin(y) f y (0,0) = 0 f xx = e x cos(y) f xx (0,0) = 1 f xy = e x sin(y) f xy (0,0) = 0 f yy = e x cos(y) f yy (0,0) = 1 Using the Taylor polynomial formula (which is an extension of our linearization/tangent plane formula), at the point (x,y) = (0,0), f(x,y) f(0,0)+f x (0,0)(x 0)+f y (0,0)(y 0) f xx(0,0)(x 0) 2 +f xy (0,0)(x 0)(y 0)+ 1 2 f yy(0,0)(y 0) 2 = 1+x+0y x2 0xy = 1+x+ 1 2 x2 1 2 y (a) f x (P) is positive. Moving to the right leads to higher contours. (b) f y (P) is zero. Moving upwards in y stays on the same contour. (c) f xx (P) is positive. x slope is positive (from (a)), and because the contours are getting closer, the positive slopes are getting steeper, so the slopes are increasing. (d) f yy (P) is zero. Slopes aren t changing at all in the y direction. Either the y slopes are always zero, so don t change when we increase x, or our x slopes are constant when we move in y. 3
4 (a) f x (P) is positive, since increasing x leads to higher contours. (b) f y (P) is zero (as with #19). (c) f xx (P) is negative, since the contours get further apart, so the positive slopes are getting less steep, or decreasing. (d) f yy (P) is zero (as with #19). (e) f xy (P) is zero (as with #19). 21. (a) f x (P) is negative, since increasing x leads to lower contours. (b) f y (P) is zero. (c) f xx (P) is negative. The contours are getting closer together, so negative slopes are getting more steep, so slopes are decreasing. (d) f yy (P) is zero. 22. (a) f x (P) is negative. (b) f y (P) is zero. (c) f xx (P) is positive. x slopes are negative, but getting less steep, so their numeric values are increasing. (d) f yy (P) is zero. 23. (a) f x (P) is zero. 4
5 (b) f y (P) is negative. Moving upwards in y leads to lower contours. (c) f xx (P) is zero. (d) f yy (P) is negative. Moving upwards in y gives steeper negative slopes. 24. (a) f x (P) is zero. (b) f y (P) is positive. (c) f xx (P) is zero. (d) f yy (P) is negative. Slopes are positive, but getting less steep as we move upwards in y. 25. (a) f x (P) is positive. Moving to the right leads to higher contours. (b) f y (P) is positive. Moving upwards in y leads to higher contours. (c) f xx (P) is zero. Contours are evenly spaced, so slopes aren t changing, so their rate of change is zero. (d) f yy (P) is zero. Contours are evenly spaced, so slopes aren t changing, so their rate of change is zero. Contours are evenly spaced, so slopes aren t changing, so their rate of change is zero. 26. (a) f x (P) is negative. 5
6 (b) f y (P) is negative. (c) f xx (P) is zero. Contours are evenly spaced, so slopes aren t changing. (d) f yy (P) is zero. 27. (a) f x (P) is positive. Moving right goes to higher contours. (b) f y (P) is negative. Moving upwards in y leads to lower contours. (c) f xx (P) is negative. x slopes are positive and getting flatter as we move right. (d) f yy (P) is negative. y slopes are negative and getting steeper as we move upwards. (e) f xy (P) is positive. Consider either the x slopes are positive and getting steeper as we move upwards (so the values of the slope are getting numerically larger), or the y slopes are negative and getting flatter as we move right (so going from large negative values closer to zero, or increasing). 28. (a) f x (P) is negative. (b) f y (P) is positive. (c) f xx (P) is positive. x slopes are negative and get flatter as we move to the right. (d) f yy (P) is positive. y slopes are positive and getting steeper. (e) f xy (P) is negative. Consider either x slopes, which are negative, get steeper as you move upwards, or the y slopes, which are positive, get flatter as you move to the right. 6
Limits and Continuity: section 12.2
 Limits and Continuity: section 1. Definition. Let f(x,y) be a function with domain D, and let (a,b) be a point in the plane. We write f (x,y) = L if for each ε > 0 there exists some δ > 0 such that if
Limits and Continuity: section 1. Definition. Let f(x,y) be a function with domain D, and let (a,b) be a point in the plane. We write f (x,y) = L if for each ε > 0 there exists some δ > 0 such that if
Unit #19 : Level Curves, Partial Derivatives
 Unit #19 : Level Curves, Partial Derivatives Goals: To learn how to use and interpret contour diagrams as a way of visualizing functions of two variables. To study linear functions of two variables. To
Unit #19 : Level Curves, Partial Derivatives Goals: To learn how to use and interpret contour diagrams as a way of visualizing functions of two variables. To study linear functions of two variables. To
y= sin( x) y= cos( x)
 . The graphs of sin(x) and cos(x). Now I am going to define the two basic trig functions: sin(x) and cos(x). Study the diagram at the right. The circle has radius. The arm OP starts at the positive horizontal
. The graphs of sin(x) and cos(x). Now I am going to define the two basic trig functions: sin(x) and cos(x). Study the diagram at the right. The circle has radius. The arm OP starts at the positive horizontal
Linear and quadratic Taylor polynomials for functions of several variables.
 ams/econ 11b supplementary notes ucsc Linear quadratic Taylor polynomials for functions of several variables. c 016, Yonatan Katznelson Finding the extreme (minimum or maximum) values of a function, is
ams/econ 11b supplementary notes ucsc Linear quadratic Taylor polynomials for functions of several variables. c 016, Yonatan Katznelson Finding the extreme (minimum or maximum) values of a function, is
LECTURE 18 - OPTIMIZATION
 LECTURE 18 - OPTIMIZATION CHRIS JOHNSON Abstract. In this lecture we ll describe extend the optimization techniques you learned in your first semester calculus class to optimize functions of multiple variables.
LECTURE 18 - OPTIMIZATION CHRIS JOHNSON Abstract. In this lecture we ll describe extend the optimization techniques you learned in your first semester calculus class to optimize functions of multiple variables.
True/False. MATH 1C: SAMPLE EXAM 1 c Jeffrey A. Anderson ANSWER KEY
 MATH 1C: SAMPLE EXAM 1 c Jeffrey A. Anderson ANSWER KEY True/False 10 points: points each) For the problems below, circle T if the answer is true and circle F is the answer is false. After you ve chosen
MATH 1C: SAMPLE EXAM 1 c Jeffrey A. Anderson ANSWER KEY True/False 10 points: points each) For the problems below, circle T if the answer is true and circle F is the answer is false. After you ve chosen
Unit #5 - Implicit Differentiation, Related Rates Section 3.7
 Unit #5 - Implicit Differentiation, Relate Rates Section 3.7 Some material from Calculus, Single an MultiVariable b Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, McCallum et. al. Copright 005 b John Wile & Sons, Inc. This
Unit #5 - Implicit Differentiation, Relate Rates Section 3.7 Some material from Calculus, Single an MultiVariable b Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, McCallum et. al. Copright 005 b John Wile & Sons, Inc. This
Section 4.2 selected answers Math 131 Multivariate Calculus D Joyce, Spring 2014
 4. Determine the nature of the critical points of Section 4. selected answers Math 11 Multivariate Calculus D Joyce, Spring 014 Exercises from section 4.: 6, 1 16.. Determine the nature of the critical
4. Determine the nature of the critical points of Section 4. selected answers Math 11 Multivariate Calculus D Joyce, Spring 014 Exercises from section 4.: 6, 1 16.. Determine the nature of the critical
Worksheet 2.2: Partial Derivatives
 Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 2.2: Partial Derivatives From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Be familiar with the definition of a derivative as the slope of a tangent line (the
Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 2.2: Partial Derivatives From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Be familiar with the definition of a derivative as the slope of a tangent line (the
Functions of Several Variables
 . Functions of Two Variables Functions of Several Variables Rectangular Coordinate System in -Space The rectangular coordinate system in R is formed by mutually perpendicular axes. It is a right handed
. Functions of Two Variables Functions of Several Variables Rectangular Coordinate System in -Space The rectangular coordinate system in R is formed by mutually perpendicular axes. It is a right handed
Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through 11.
 Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through 11. Show all your work on the standard
Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through 11. Show all your work on the standard
13.2 LIMITS AND CONTINUITY
 3.2 Limits and Continuity Contemporary Calculus 3.2 LIMITS AND CONTINUITY Our development of the properties and the calculus of functions z = f(x,y) of two (and more) variables parallels the development
3.2 Limits and Continuity Contemporary Calculus 3.2 LIMITS AND CONTINUITY Our development of the properties and the calculus of functions z = f(x,y) of two (and more) variables parallels the development
The Tangent Line as The Best Linear Approximation
 The Tangent Line as The Best Linear Approximation Mark Howell Gonzaga High School Arlington, VA A tangent line to a curve, y f (x), at a point where x a has two important properties: it contains the point
The Tangent Line as The Best Linear Approximation Mark Howell Gonzaga High School Arlington, VA A tangent line to a curve, y f (x), at a point where x a has two important properties: it contains the point
t dt ds Then, in the last class, we showed that F(s) = <2s/3, 1 2s/3, s/3> is arclength parametrization. Therefore,
 13.4. Curvature Curvature Let F(t) be a vector values function. We say it is regular if F (t)=0 Let F(t) be a vector valued function which is arclength parametrized, which means F t 1 for all t. Then,
13.4. Curvature Curvature Let F(t) be a vector values function. We say it is regular if F (t)=0 Let F(t) be a vector valued function which is arclength parametrized, which means F t 1 for all t. Then,
Level Curves and Contour Maps (sec 14.1) & Partial Derivatives (sec 14.3) Today, We Will: Level Curves. Notes. Notes. Notes.
 Level Curves and Contour Maps (sec 14.1) & Partial Derivatives (sec 14.3) 11 February 2015 Today, We Will: Wrap-up our discussion of level curves and contour maps. Define partial derivatives of a function
Level Curves and Contour Maps (sec 14.1) & Partial Derivatives (sec 14.3) 11 February 2015 Today, We Will: Wrap-up our discussion of level curves and contour maps. Define partial derivatives of a function
Partial Derivatives (Online)
 7in x 10in Felder c04_online.tex V3 - January 21, 2015 9:44 A.M. Page 1 CHAPTER 4 Partial Derivatives (Online) 4.7 Tangent Plane Approximations and Power Series It is often helpful to use a linear approximation
7in x 10in Felder c04_online.tex V3 - January 21, 2015 9:44 A.M. Page 1 CHAPTER 4 Partial Derivatives (Online) 4.7 Tangent Plane Approximations and Power Series It is often helpful to use a linear approximation
Solution 2. ((3)(1) (2)(1), (4 3), (4)(2) (3)(3)) = (1, 1, 1) D u (f) = (6x + 2yz, 2y + 2xz, 2xy) (0,1,1) = = 4 14
 Vector and Multivariable Calculus L Marizza A Bailey Practice Trimester Final Exam Name: Problem 1. To prepare for true/false and multiple choice: Compute the following (a) (4, 3) ( 3, 2) Solution 1. (4)(
Vector and Multivariable Calculus L Marizza A Bailey Practice Trimester Final Exam Name: Problem 1. To prepare for true/false and multiple choice: Compute the following (a) (4, 3) ( 3, 2) Solution 1. (4)(
Answer sheet: Second Midterm for Math 2339
 Answer sheet: Second Midterm for Math 2339 March 31, 2009 Problem 1. Let (a) f(x,y,z) = ln(z x 2 y 2 ). Evaluate f(1, 1, 2 + e). f(1, 1, 2 + e) = ln(2 + e 1 1) = lne = 1 (b) Find the domain of f. dom(f)
Answer sheet: Second Midterm for Math 2339 March 31, 2009 Problem 1. Let (a) f(x,y,z) = ln(z x 2 y 2 ). Evaluate f(1, 1, 2 + e). f(1, 1, 2 + e) = ln(2 + e 1 1) = lne = 1 (b) Find the domain of f. dom(f)
REVIEW I MATH 254 Calculus IV. Exam I (Friday, April 29) will cover sections
 REVIEW I MATH 254 Calculus IV Exam I (Friday, April 29 will cover sections 14.1-8. 1. Functions of multivariables The definition of multivariable functions is similar to that of functions of one variable.
REVIEW I MATH 254 Calculus IV Exam I (Friday, April 29 will cover sections 14.1-8. 1. Functions of multivariables The definition of multivariable functions is similar to that of functions of one variable.
Direction Fields; Euler s Method
 Direction Fields; Euler s Method It frequently happens that we cannot solve first order systems dy (, ) dx = f xy or corresponding initial value problems in terms of formulas. Remarkably, however, this
Direction Fields; Euler s Method It frequently happens that we cannot solve first order systems dy (, ) dx = f xy or corresponding initial value problems in terms of formulas. Remarkably, however, this
Multivariate Calculus: Review Problems for Examination Two
 Multivariate Calculus: Review Problems for Examination Two Note: Exam Two is on Tuesday, August 16. The coverage is multivariate differential calculus and double integration. You should review the double
Multivariate Calculus: Review Problems for Examination Two Note: Exam Two is on Tuesday, August 16. The coverage is multivariate differential calculus and double integration. You should review the double
Answer sheet: Second Midterm for Math 2339
 Answer sheet: Second Midterm for Math 2339 October 26, 2010 Problem 1. True or false: (check one of the box, and briefly explain why) (1) If a twice differentiable f(x,y) satisfies f x (a,b) = f y (a,b)
Answer sheet: Second Midterm for Math 2339 October 26, 2010 Problem 1. True or false: (check one of the box, and briefly explain why) (1) If a twice differentiable f(x,y) satisfies f x (a,b) = f y (a,b)
Functions Modeling Change A Preparation for Calculus Third Edition
 Powerpoint slides copied from or based upon: Functions Modeling Change A Preparation for Calculus Third Edition Connally, Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, Et Al. Copyright 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 CHAPTER
Powerpoint slides copied from or based upon: Functions Modeling Change A Preparation for Calculus Third Edition Connally, Hughes-Hallett, Gleason, Et Al. Copyright 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 CHAPTER
we wish to minimize this function; to make life easier, we may minimize
 Optimization and Lagrange Multipliers We studied single variable optimization problems in Calculus 1; given a function f(x), we found the extremes of f relative to some constraint. Our ability to find
Optimization and Lagrange Multipliers We studied single variable optimization problems in Calculus 1; given a function f(x), we found the extremes of f relative to some constraint. Our ability to find
Not for reproduction
 x=a GRAPHING CALCULATORS AND COMPUTERS (a, d ) y=d (b, d ) (a, c ) y=c (b, c) (a) _, by _, 4 x=b FIGURE 1 The viewing rectangle a, b by c, d _4 4 In this section we assume that you have access to a graphing
x=a GRAPHING CALCULATORS AND COMPUTERS (a, d ) y=d (b, d ) (a, c ) y=c (b, c) (a) _, by _, 4 x=b FIGURE 1 The viewing rectangle a, b by c, d _4 4 In this section we assume that you have access to a graphing
, etc. Let s work with the last one. We can graph a few points determined by this equation.
 1. Lines By a line, we simply mean a straight curve. We will always think of lines relative to the cartesian plane. Consider the equation 2x 3y 4 = 0. We can rewrite it in many different ways : 2x 3y =
1. Lines By a line, we simply mean a straight curve. We will always think of lines relative to the cartesian plane. Consider the equation 2x 3y 4 = 0. We can rewrite it in many different ways : 2x 3y =
4.2.1 directional derivatives and the gradient in R 2
 4.2. PARTIAL DIFFERENTIATION IN R 2 161 4.2.1 directional derivatives and the gradient in R 2 Now that we have a little experience in partial differentiation let s return to the problem of the directional
4.2. PARTIAL DIFFERENTIATION IN R 2 161 4.2.1 directional derivatives and the gradient in R 2 Now that we have a little experience in partial differentiation let s return to the problem of the directional
(1) Tangent Lines on Surfaces, (2) Partial Derivatives, (3) Notation and Higher Order Derivatives.
 Section 11.3 Partial Derivatives (1) Tangent Lines on Surfaces, (2) Partial Derivatives, (3) Notation and Higher Order Derivatives. MATH 127 (Section 11.3) Partial Derivatives The University of Kansas
Section 11.3 Partial Derivatives (1) Tangent Lines on Surfaces, (2) Partial Derivatives, (3) Notation and Higher Order Derivatives. MATH 127 (Section 11.3) Partial Derivatives The University of Kansas
3d plots. John Perry. Fall 2013
 MAT 305: 3d plots University of Southern Mississippi Fall 2013 Outline 1 2 3 Outline 1 2 3 The point3d() command point3d((x, y, z), options) where (x,y,z) is a 3-tuple (the location in 3 of this point)
MAT 305: 3d plots University of Southern Mississippi Fall 2013 Outline 1 2 3 Outline 1 2 3 The point3d() command point3d((x, y, z), options) where (x,y,z) is a 3-tuple (the location in 3 of this point)
(c) 0 (d) (a) 27 (b) (e) x 2 3x2
 1. Sarah the architect is designing a modern building. The base of the building is the region in the xy-plane bounded by x =, y =, and y = 3 x. The building itself has a height bounded between z = and
1. Sarah the architect is designing a modern building. The base of the building is the region in the xy-plane bounded by x =, y =, and y = 3 x. The building itself has a height bounded between z = and
Green Globs And Graphing Equations
 Green Globs And Graphing Equations Green Globs and Graphing Equations has four parts to it which serve as a tool, a review or testing device, and two games. The menu choices are: Equation Plotter which
Green Globs And Graphing Equations Green Globs and Graphing Equations has four parts to it which serve as a tool, a review or testing device, and two games. The menu choices are: Equation Plotter which
Minima, Maxima, Saddle points
 Minima, Maxima, Saddle points Levent Kandiller Industrial Engineering Department Çankaya University, Turkey Minima, Maxima, Saddle points p./9 Scalar Functions Let us remember the properties for maxima,
Minima, Maxima, Saddle points Levent Kandiller Industrial Engineering Department Çankaya University, Turkey Minima, Maxima, Saddle points p./9 Scalar Functions Let us remember the properties for maxima,
Changing Variables in Multiple Integrals
 Changing Variables in Multiple Integrals 3. Examples and comments; putting in limits. If we write the change of variable formula as (x, y) (8) f(x, y)dx dy = g(u, v) dudv, (u, v) where (x, y) x u x v (9)
Changing Variables in Multiple Integrals 3. Examples and comments; putting in limits. If we write the change of variable formula as (x, y) (8) f(x, y)dx dy = g(u, v) dudv, (u, v) where (x, y) x u x v (9)
Math 213 Calculus III Practice Exam 2 Solutions Fall 2002
 Math 13 Calculus III Practice Exam Solutions Fall 00 1. Let g(x, y, z) = e (x+y) + z (x + y). (a) What is the instantaneous rate of change of g at the point (,, 1) in the direction of the origin? We want
Math 13 Calculus III Practice Exam Solutions Fall 00 1. Let g(x, y, z) = e (x+y) + z (x + y). (a) What is the instantaneous rate of change of g at the point (,, 1) in the direction of the origin? We want
Functions of Several Variables, Limits and Derivatives
 Functions of Several Variables, Limits and Derivatives Introduction and Goals: The main goal of this lab is to help you visualize surfaces in three dimensions. We investigate how one can use Maple to evaluate
Functions of Several Variables, Limits and Derivatives Introduction and Goals: The main goal of this lab is to help you visualize surfaces in three dimensions. We investigate how one can use Maple to evaluate
2.1 Derivatives and Rates of Change
 2.1 Derivatives and Rates of Change In this chapter we study a special type of limit, called a derivative, that occurs when we want to find a slope of a tangent line, or a velocity, or any instantaneous
2.1 Derivatives and Rates of Change In this chapter we study a special type of limit, called a derivative, that occurs when we want to find a slope of a tangent line, or a velocity, or any instantaneous
Contents. MATH 32B-2 (18W) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables. 1 Homework 1 - Solutions 3. 2 Homework 2 - Solutions 13
 MATH 32B-2 (8) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables Contents Homework - Solutions 3 2 Homework 2 - Solutions 3 3 Homework 3 - Solutions 9 MATH 32B-2 (8) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus
MATH 32B-2 (8) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables Contents Homework - Solutions 3 2 Homework 2 - Solutions 3 3 Homework 3 - Solutions 9 MATH 32B-2 (8) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus
3.3 Optimizing Functions of Several Variables 3.4 Lagrange Multipliers
 3.3 Optimizing Functions of Several Variables 3.4 Lagrange Multipliers Prof. Tesler Math 20C Fall 2018 Prof. Tesler 3.3 3.4 Optimization Math 20C / Fall 2018 1 / 56 Optimizing y = f (x) In Math 20A, we
3.3 Optimizing Functions of Several Variables 3.4 Lagrange Multipliers Prof. Tesler Math 20C Fall 2018 Prof. Tesler 3.3 3.4 Optimization Math 20C / Fall 2018 1 / 56 Optimizing y = f (x) In Math 20A, we
Chapter 1: Interval computation
 Chapter 1: Interval computation July 8, 2017 Problem. Given f : R n R and a box [x] R n, prove that x [x],f (x) 0. Interval arithmetic can solve efficiently this problem. Example. Is the function f (x)
Chapter 1: Interval computation July 8, 2017 Problem. Given f : R n R and a box [x] R n, prove that x [x],f (x) 0. Interval arithmetic can solve efficiently this problem. Example. Is the function f (x)
Adding and subtracting rational expressions is quite similar to adding and subtracting rational numbers (fractions).
 7.2: Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions, Simplifying Complex Fractions Adding and subtracting rational expressions is quite similar to adding and subtracting rational numbers (fractions). Adding
7.2: Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions, Simplifying Complex Fractions Adding and subtracting rational expressions is quite similar to adding and subtracting rational numbers (fractions). Adding
Worksheet 2.1: Introduction to Multivariate Functions (Functions of Two or More Independent Variables)
 Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 2.1: Introduction to Multivariate Functions (Functions of Two or More Independent Variables) From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Know the meaning
Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 2.1: Introduction to Multivariate Functions (Functions of Two or More Independent Variables) From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Know the meaning
Math 131. Implicit Differentiation Larson Section 2.5
 Math 131. Implicit Differentiation Larson Section.5 So far we have ealt with ifferentiating explicitly efine functions, that is, we are given the expression efining the function, such as f(x) = 5 x. However,
Math 131. Implicit Differentiation Larson Section.5 So far we have ealt with ifferentiating explicitly efine functions, that is, we are given the expression efining the function, such as f(x) = 5 x. However,
PreCalculus Summer Assignment
 PreCalculus Summer Assignment Welcome to PreCalculus! We are excited for a fabulous year. Your summer assignment is available digitally on the Lyman website. You are expected to print your own copy. Expectations:
PreCalculus Summer Assignment Welcome to PreCalculus! We are excited for a fabulous year. Your summer assignment is available digitally on the Lyman website. You are expected to print your own copy. Expectations:
Math 20A lecture 10 The Gradient Vector
 Math 20A lecture 10 p. 1/12 Math 20A lecture 10 The Gradient Vector T.J. Barnet-Lamb tbl@brandeis.edu Brandeis University Math 20A lecture 10 p. 2/12 Announcements Homework five posted, due this Friday
Math 20A lecture 10 p. 1/12 Math 20A lecture 10 The Gradient Vector T.J. Barnet-Lamb tbl@brandeis.edu Brandeis University Math 20A lecture 10 p. 2/12 Announcements Homework five posted, due this Friday
Math 32A Graphs and Contour Worksheet
 Math 32 Graphs and ontour Worksheet Sections 5., 5.4 November 8, 208 This worksheet helps you practice matching graphs with its equations. Here are some general techniques and tricks that may help: (i)
Math 32 Graphs and ontour Worksheet Sections 5., 5.4 November 8, 208 This worksheet helps you practice matching graphs with its equations. Here are some general techniques and tricks that may help: (i)
1.1 Functions. Cartesian Coordinate System
 1.1 Functions This section deals with the topic of functions, one of the most important topics in all of mathematics. Let s discuss the idea of the Cartesian coordinate system first. Cartesian Coordinate
1.1 Functions This section deals with the topic of functions, one of the most important topics in all of mathematics. Let s discuss the idea of the Cartesian coordinate system first. Cartesian Coordinate
Algebra I Notes Slope Unit 04a
 OBJECTIVE: F.IF.B.6 Interpret functions that arise in applications in terms of the context. Calculate and interpret the average rate of change of a function (presented symbolically or as a table) over
OBJECTIVE: F.IF.B.6 Interpret functions that arise in applications in terms of the context. Calculate and interpret the average rate of change of a function (presented symbolically or as a table) over
Math 3 Coordinate Geometry Part 2 Graphing Solutions
 Math 3 Coordinate Geometry Part 2 Graphing Solutions 1 SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS GRAPHICALLY The solution of two linear equations is the point where the two lines intersect. For example, in the graph
Math 3 Coordinate Geometry Part 2 Graphing Solutions 1 SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS GRAPHICALLY The solution of two linear equations is the point where the two lines intersect. For example, in the graph
SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS through 2.1.4
 SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS 2.1.2 through 2.1.4 Students used the equation = m + b to graph lines and describe patterns in previous courses. Lesson 2.1.1 is a review. When the equation of a line is written
SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS 2.1.2 through 2.1.4 Students used the equation = m + b to graph lines and describe patterns in previous courses. Lesson 2.1.1 is a review. When the equation of a line is written
Date: 16 July 2016, Saturday Time: 14:00-16:00 STUDENT NO:... Math 102 Calculus II Midterm Exam II Solutions TOTAL. Please Read Carefully:
 Date: 16 July 2016, Saturday Time: 14:00-16:00 NAME:... STUDENT NO:... YOUR DEPARTMENT:... Math 102 Calculus II Midterm Exam II Solutions 1 2 3 4 TOTAL 25 25 25 25 100 Please do not write anything inside
Date: 16 July 2016, Saturday Time: 14:00-16:00 NAME:... STUDENT NO:... YOUR DEPARTMENT:... Math 102 Calculus II Midterm Exam II Solutions 1 2 3 4 TOTAL 25 25 25 25 100 Please do not write anything inside
Section 1: Section 2: Section 3: Section 4:
 Announcements Topics: In the Functions of Several Variables module: - Section 1: Introduction to Functions of Several Variables (Basic Definitions and Notation) - Section 2: Graphs, Level Curves + Contour
Announcements Topics: In the Functions of Several Variables module: - Section 1: Introduction to Functions of Several Variables (Basic Definitions and Notation) - Section 2: Graphs, Level Curves + Contour
PURE MATHEMATICS 212 Multivariable Calculus CONTENTS. Page. 1. Assignment Summary... i 2. Summary Assignments...2
 PURE MATHEMATICS 212 Multivariable Calculus CONTENTS Page 1. Assignment Summary... i 2. Summary...1 3. Assignments...2 i PMTH212, Multivariable Calculus Assignment Summary 2010 Assignment Date to be Posted
PURE MATHEMATICS 212 Multivariable Calculus CONTENTS Page 1. Assignment Summary... i 2. Summary...1 3. Assignments...2 i PMTH212, Multivariable Calculus Assignment Summary 2010 Assignment Date to be Posted
SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS through 7.1.5
 SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS 7.1. through 7.1.5 Students have used the equation = m + b throughout this course to graph lines and describe patterns. When the equation is written in -form, the m is the
SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS 7.1. through 7.1.5 Students have used the equation = m + b throughout this course to graph lines and describe patterns. When the equation is written in -form, the m is the
NAME: Section # SSN: X X X X
 Math 155 FINAL EXAM A May 5, 2003 NAME: Section # SSN: X X X X Question Grade 1 5 (out of 25) 6 10 (out of 25) 11 (out of 20) 12 (out of 20) 13 (out of 10) 14 (out of 10) 15 (out of 16) 16 (out of 24)
Math 155 FINAL EXAM A May 5, 2003 NAME: Section # SSN: X X X X Question Grade 1 5 (out of 25) 6 10 (out of 25) 11 (out of 20) 12 (out of 20) 13 (out of 10) 14 (out of 10) 15 (out of 16) 16 (out of 24)
1. Answer: x or x. Explanation Set up the two equations, then solve each equation. x. Check
 Thinkwell s Placement Test 5 Answer Key If you answered 7 or more Test 5 questions correctly, we recommend Thinkwell's Algebra. If you answered fewer than 7 Test 5 questions correctly, we recommend Thinkwell's
Thinkwell s Placement Test 5 Answer Key If you answered 7 or more Test 5 questions correctly, we recommend Thinkwell's Algebra. If you answered fewer than 7 Test 5 questions correctly, we recommend Thinkwell's
Quadratic Functions. *These are all examples of polynomial functions.
 Look at: f(x) = 4x-7 f(x) = 3 f(x) = x 2 + 4 Quadratic Functions *These are all examples of polynomial functions. Definition: Let n be a nonnegative integer and let a n, a n 1,..., a 2, a 1, a 0 be real
Look at: f(x) = 4x-7 f(x) = 3 f(x) = x 2 + 4 Quadratic Functions *These are all examples of polynomial functions. Definition: Let n be a nonnegative integer and let a n, a n 1,..., a 2, a 1, a 0 be real
2 Unit Bridging Course Day 10
 1 / 31 Unit Bridging Course Day 10 Circular Functions III The cosine function, identities and derivatives Clinton Boys / 31 The cosine function The cosine function, abbreviated to cos, is very similar
1 / 31 Unit Bridging Course Day 10 Circular Functions III The cosine function, identities and derivatives Clinton Boys / 31 The cosine function The cosine function, abbreviated to cos, is very similar
f for Directional Derivatives and Gradient The gradient vector is calculated using partial derivatives of the function f(x,y).
 Directional Derivatives and Gradient The gradient vector is calculated using partial derivatives of the function f(x,y). For a function f(x,y), the gradient vector, denoted as f (pronounced grad f ) is
Directional Derivatives and Gradient The gradient vector is calculated using partial derivatives of the function f(x,y). For a function f(x,y), the gradient vector, denoted as f (pronounced grad f ) is
= f (a, b) + (hf x + kf y ) (a,b) +
 Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections 2 Double Integrals over more general regions, Definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals, Properties of Double Integrals
Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections 2 Double Integrals over more general regions, Definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals, Properties of Double Integrals
7/14/2011 FIRST HOURLY PRACTICE IV Maths 21a, O.Knill, Summer 2011
 7/14/2011 FIRST HOURLY PRACTICE IV Maths 21a, O.Knill, Summer 2011 Name: Start by printing your name in the above box. Try to answer each question on the same page as the question is asked. If needed,
7/14/2011 FIRST HOURLY PRACTICE IV Maths 21a, O.Knill, Summer 2011 Name: Start by printing your name in the above box. Try to answer each question on the same page as the question is asked. If needed,
Section 18-1: Graphical Representation of Linear Equations and Functions
 Section 18-1: Graphical Representation of Linear Equations and Functions Prepare a table of solutions and locate the solutions on a coordinate system: f(x) = 2x 5 Learning Outcome 2 Write x + 3 = 5 as
Section 18-1: Graphical Representation of Linear Equations and Functions Prepare a table of solutions and locate the solutions on a coordinate system: f(x) = 2x 5 Learning Outcome 2 Write x + 3 = 5 as
Summer 2017 MATH Suggested Solution to Exercise Find the tangent hyperplane passing the given point P on each of the graphs: (a)
 Smmer 2017 MATH2010 1 Sggested Soltion to Exercise 6 1 Find the tangent hyperplane passing the given point P on each of the graphs: (a) z = x 2 y 2 ; y = z log x z P (2, 3, 5), P (1, 1, 1), (c) w = sin(x
Smmer 2017 MATH2010 1 Sggested Soltion to Exercise 6 1 Find the tangent hyperplane passing the given point P on each of the graphs: (a) z = x 2 y 2 ; y = z log x z P (2, 3, 5), P (1, 1, 1), (c) w = sin(x
Announcements. Topics: To Do:
 Announcements Topics: In the Functions of Several Variables module: - Section 3: Limits and Continuity - Section 4: Partial Derivatives - Section 5: Tangent Plane, Linearization, and Differentiability
Announcements Topics: In the Functions of Several Variables module: - Section 3: Limits and Continuity - Section 4: Partial Derivatives - Section 5: Tangent Plane, Linearization, and Differentiability
Natasha S. Sharma, PhD
 Revisiting the function evaluation problem Most functions cannot be evaluated exactly: 2 x, e x, ln x, trigonometric functions since by using a computer we are limited to the use of elementary arithmetic
Revisiting the function evaluation problem Most functions cannot be evaluated exactly: 2 x, e x, ln x, trigonometric functions since by using a computer we are limited to the use of elementary arithmetic
PURE MATHEMATICS 212 Multivariable Calculus CONTENTS. Page. 1. Assignment Summary... i 2. Introduction Timetable Assignments...
 PURE MATHEMATICS 212 Multivariable Calculus CONTENTS Page 1. Assignment Summary... i 2. Introduction...1 3. Timetable... 3 4. Assignments...5 i PMTH212, Multivariable Calculus Assignment Summary 2009
PURE MATHEMATICS 212 Multivariable Calculus CONTENTS Page 1. Assignment Summary... i 2. Introduction...1 3. Timetable... 3 4. Assignments...5 i PMTH212, Multivariable Calculus Assignment Summary 2009
2.9 Linear Approximations and Differentials
 2.9 Linear Approximations and Differentials 2.9.1 Linear Approximation Consider the following graph, Recall that this is the tangent line at x = a. We had the following definition, f (a) = lim x a f(x)
2.9 Linear Approximations and Differentials 2.9.1 Linear Approximation Consider the following graph, Recall that this is the tangent line at x = a. We had the following definition, f (a) = lim x a f(x)
Math 206 First Midterm October 5, 2012
 Math 206 First Midterm October 5, 2012 Name: EXAM SOLUTIONS Instructor: Section: 1. Do not open this exam until you are told to do so. 2. This exam has 8 pages including this cover AND IS DOUBLE SIDED.
Math 206 First Midterm October 5, 2012 Name: EXAM SOLUTIONS Instructor: Section: 1. Do not open this exam until you are told to do so. 2. This exam has 8 pages including this cover AND IS DOUBLE SIDED.
8 Piecewise Polynomial Interpolation
 Applied Math Notes by R. J. LeVeque 8 Piecewise Polynomial Interpolation 8. Pitfalls of high order interpolation Suppose we know the value of a function at several points on an interval and we wish to
Applied Math Notes by R. J. LeVeque 8 Piecewise Polynomial Interpolation 8. Pitfalls of high order interpolation Suppose we know the value of a function at several points on an interval and we wish to
so f can now be rewritten as a product of g(x) = x 2 and the previous piecewisedefined
 Version PREVIEW HW 01 hoffman 575) 1 This print-out should have 9 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering. FuncPcwise01a 001 10.0
Version PREVIEW HW 01 hoffman 575) 1 This print-out should have 9 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering. FuncPcwise01a 001 10.0
Multivariate Calculus Review Problems for Examination Two
 Multivariate Calculus Review Problems for Examination Two Note: Exam Two is on Thursday, February 28, class time. The coverage is multivariate differential calculus and double integration: sections 13.3,
Multivariate Calculus Review Problems for Examination Two Note: Exam Two is on Thursday, February 28, class time. The coverage is multivariate differential calculus and double integration: sections 13.3,
Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 2003
 Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 23 1. Let g(x, y, z) = 2x 2 + y 2 + 4z 2. (a) Describe the shapes of the level surfaces of g. (b) In three different graphs, sketch the three cross
Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 23 1. Let g(x, y, z) = 2x 2 + y 2 + 4z 2. (a) Describe the shapes of the level surfaces of g. (b) In three different graphs, sketch the three cross
Topic 3.1: Introduction to Multivariate Functions (Functions of Two or More Variables)
 BSU Math 275 Notes Topic 3.1: Introduction to Multivariate Functions (Functions of Two or More Variables) Textbook Section: 14.1 From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes): Know the meaning
BSU Math 275 Notes Topic 3.1: Introduction to Multivariate Functions (Functions of Two or More Variables) Textbook Section: 14.1 From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes): Know the meaning
(1) Given the following system of linear equations, which depends on a parameter a R, 3x y + 5z = 2 4x + y + (a 2 14)z = a + 2
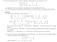 (1 Given the following system of linear equations, which depends on a parameter a R, x + 2y 3z = 4 3x y + 5z = 2 4x + y + (a 2 14z = a + 2 (a Classify the system of equations depending on the values of
(1 Given the following system of linear equations, which depends on a parameter a R, x + 2y 3z = 4 3x y + 5z = 2 4x + y + (a 2 14z = a + 2 (a Classify the system of equations depending on the values of
Kevin James. MTHSC 206 Section 14.5 The Chain Rule
 MTHSC 206 Section 14.5 The Chain Rule Theorem (Chain Rule - Case 1) Suppose that z = f (x, y) is a differentiable function and that x(t) and y(t) are both differentiable functions as well. Then, dz dt
MTHSC 206 Section 14.5 The Chain Rule Theorem (Chain Rule - Case 1) Suppose that z = f (x, y) is a differentiable function and that x(t) and y(t) are both differentiable functions as well. Then, dz dt
0.4 Family of Functions/Equations
 0.4 Family of Functions/Equations By a family of functions, we are referring to a function definition such as f(x) = mx + 2 for m = 2, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 2. 2 2 This says, work with all the functions obtained
0.4 Family of Functions/Equations By a family of functions, we are referring to a function definition such as f(x) = mx + 2 for m = 2, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 2. 2 2 This says, work with all the functions obtained
Packages in Julia. Downloading Packages A Word of Caution Sawtooth, Revisited
 Packages in Julia Downloading Packages A Word of Caution Sawtooth, Revisited Downloading Packages Because Julia is an open-source language, there are a ton of packages available online that enable such
Packages in Julia Downloading Packages A Word of Caution Sawtooth, Revisited Downloading Packages Because Julia is an open-source language, there are a ton of packages available online that enable such
Introduction to Matlab
 Technische Universität München WT 21/11 Institut für Informatik Prof Dr H-J Bungartz Dipl-Tech Math S Schraufstetter Benjamin Peherstorfer, MSc October 22nd, 21 Introduction to Matlab Engineering Informatics
Technische Universität München WT 21/11 Institut für Informatik Prof Dr H-J Bungartz Dipl-Tech Math S Schraufstetter Benjamin Peherstorfer, MSc October 22nd, 21 Introduction to Matlab Engineering Informatics
Math 133A, September 10: Numerical Methods (Euler & Runge-Kutta) Section 1: Numerical Methods
 Math 133A, September 10: Numerical Methods (Euler & Runge-Kutta) Section 1: Numerical Methods We have seen examples of first-order differential equations which can, by one method of another, be solved
Math 133A, September 10: Numerical Methods (Euler & Runge-Kutta) Section 1: Numerical Methods We have seen examples of first-order differential equations which can, by one method of another, be solved
Math 11 Fall Multivariable Calculus. Final Exam
 Math 11 Fall 2004 Multivariable Calculus for Two-Term Advanced Placement First-Year Students Final Exam Tuesday, December 7, 11:30-2:30 Murdough, Cook Auditorium Your name (please print): Instructions:
Math 11 Fall 2004 Multivariable Calculus for Two-Term Advanced Placement First-Year Students Final Exam Tuesday, December 7, 11:30-2:30 Murdough, Cook Auditorium Your name (please print): Instructions:
NOTES Linear Equations
 NOTES Linear Equations Linear Parent Function Linear Parent Function the equation that all other linear equations are based upon (y = x) Horizontal and Vertical Lines (HOYY VUXX) V vertical line H horizontal
NOTES Linear Equations Linear Parent Function Linear Parent Function the equation that all other linear equations are based upon (y = x) Horizontal and Vertical Lines (HOYY VUXX) V vertical line H horizontal
SYSTEMS OF NONLINEAR EQUATIONS
 SYSTEMS OF NONLINEAR EQUATIONS Widely used in the mathematical modeling of real world phenomena. We introduce some numerical methods for their solution. For better intuition, we examine systems of two
SYSTEMS OF NONLINEAR EQUATIONS Widely used in the mathematical modeling of real world phenomena. We introduce some numerical methods for their solution. For better intuition, we examine systems of two
Module 3: Stand Up Conics
 MATH55 Module 3: Stand Up Conics Main Math concepts: Conic Sections (i.e. Parabolas, Ellipses, Hyperbolas), nd degree equations Auxilliary ideas: Analytic vs. Co-ordinate-free Geometry, Parameters, Calculus.
MATH55 Module 3: Stand Up Conics Main Math concepts: Conic Sections (i.e. Parabolas, Ellipses, Hyperbolas), nd degree equations Auxilliary ideas: Analytic vs. Co-ordinate-free Geometry, Parameters, Calculus.
Trigonometric Equations for the Four-Point. Rectangular Data Array
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 6, 2012, no. 62, 3067-3071 Trigonometric Equations for the Four-Point Rectangular Data Array G. L. Silver 868 Kristi Lane Los Alamos, NM 87455, USA GaryLeeSil@aol.com
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 6, 2012, no. 62, 3067-3071 Trigonometric Equations for the Four-Point Rectangular Data Array G. L. Silver 868 Kristi Lane Los Alamos, NM 87455, USA GaryLeeSil@aol.com
Interpolation. TANA09 Lecture 7. Error analysis for linear interpolation. Linear Interpolation. Suppose we have a table x x 1 x 2...
 TANA9 Lecture 7 Interpolation Suppose we have a table x x x... x n+ Interpolation Introduction. Polynomials. Error estimates. Runge s phenomena. Application - Equation solving. Spline functions and interpolation.
TANA9 Lecture 7 Interpolation Suppose we have a table x x x... x n+ Interpolation Introduction. Polynomials. Error estimates. Runge s phenomena. Application - Equation solving. Spline functions and interpolation.
Linear Transformations
 Linear Transformations The two basic vector operations are addition and scaling From this perspective, the nicest functions are those which preserve these operations: Def: A linear transformation is a
Linear Transformations The two basic vector operations are addition and scaling From this perspective, the nicest functions are those which preserve these operations: Def: A linear transformation is a
Reminder: y =f(x) mean that a function f uses a variable (an ingredient) x to make the result y.
 Functions (.3) Reminder: y =f(x) mean that a function f uses a variable (an ingredient) x to make the result y.. Transformation of functions 3 We know many elementary functions like f ( x) = x + x + 3x+,
Functions (.3) Reminder: y =f(x) mean that a function f uses a variable (an ingredient) x to make the result y.. Transformation of functions 3 We know many elementary functions like f ( x) = x + x + 3x+,
SNAP Centre Workshop. Graphing Lines
 SNAP Centre Workshop Graphing Lines 45 Graphing a Line Using Test Values A simple way to linear equation involves finding test values, plotting the points on a coordinate plane, and connecting the points.
SNAP Centre Workshop Graphing Lines 45 Graphing a Line Using Test Values A simple way to linear equation involves finding test values, plotting the points on a coordinate plane, and connecting the points.
Lesson 4: Gradient Vectors, Level Curves, Maximums/Minimums/Saddle Points
 Lesson 4: Gradient Vectors, Level Curves, Maximums/Minimums/Saddle Points Example 1: The Gradient Vector 2 df Let f(x) x. Then 2x. This can be thought of as a vector that dx tells you the direction of
Lesson 4: Gradient Vectors, Level Curves, Maximums/Minimums/Saddle Points Example 1: The Gradient Vector 2 df Let f(x) x. Then 2x. This can be thought of as a vector that dx tells you the direction of
1 Shapes of Power Functions
 MA 1165 - Lecture 06 1 Wednesday, 1/28/09 1 Shapes of Power Functions I would like you to be familiar with the shape of the power functions, that is, the functions of the form f(x) = x n, (1) for n = 1,
MA 1165 - Lecture 06 1 Wednesday, 1/28/09 1 Shapes of Power Functions I would like you to be familiar with the shape of the power functions, that is, the functions of the form f(x) = x n, (1) for n = 1,
John Perry. Spring 2016
 MAT 305: Repeating a task on a set (or list, or tuple, or...) University of Southern Mississippi Spring 2016 Outline 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Outline 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Differential Equations What is y in terms of x?
MAT 305: Repeating a task on a set (or list, or tuple, or...) University of Southern Mississippi Spring 2016 Outline 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Outline 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Differential Equations What is y in terms of x?
Euler and improved Euler using SAGE
 Euler and improved Euler using SAGE The goal is to find an approximate solution to the problem y = f(x, y), y(a) = c, (1) where f(x, y) is some given function We shall try to approximate the value of the
Euler and improved Euler using SAGE The goal is to find an approximate solution to the problem y = f(x, y), y(a) = c, (1) where f(x, y) is some given function We shall try to approximate the value of the
A Mathematica Tutorial
 A Mathematica Tutorial -3-8 This is a brief introduction to Mathematica, the symbolic mathematics program. This tutorial is generic, in the sense that you can use it no matter what kind of computer you
A Mathematica Tutorial -3-8 This is a brief introduction to Mathematica, the symbolic mathematics program. This tutorial is generic, in the sense that you can use it no matter what kind of computer you
2.1 Quadraticsnts.notebook. September 10, 2018
 1 A quadratic function is a polynomial function of second degree. The graph of a quadratic function is called a parabola. 2 Standard Form: Intercept Form: Vertex Form: f(x) = a(x h) 2 + k vertex: (h, k)
1 A quadratic function is a polynomial function of second degree. The graph of a quadratic function is called a parabola. 2 Standard Form: Intercept Form: Vertex Form: f(x) = a(x h) 2 + k vertex: (h, k)
FAIRFIELD COUNTY MATH LEAGUE (FCML) )Find the arithmetic mean of the median and the mode of the numbers {13, 23, 24, 24, 15, 18, 24, 22}.
 FAIRFIELD COUNTY MATH LEAGUE (FCML)2015-2016 Match 4 Round 1 Arithmetic: Basic Statistics 1.) 2.25 2.) 6.) 18 1.)Find the arithmetic mean of the median and the mode of the numbers {1, 2, 24, 24, 15, 18,
FAIRFIELD COUNTY MATH LEAGUE (FCML)2015-2016 Match 4 Round 1 Arithmetic: Basic Statistics 1.) 2.25 2.) 6.) 18 1.)Find the arithmetic mean of the median and the mode of the numbers {1, 2, 24, 24, 15, 18,
4 Visualization and. Approximation
 4 Visualization and Approximation b A slope field for the differential equation y tan(x + y) tan(x) tan(y). It is not always possible to write down an explicit formula for the solution to a differential
4 Visualization and Approximation b A slope field for the differential equation y tan(x + y) tan(x) tan(y). It is not always possible to write down an explicit formula for the solution to a differential
5.1 Introduction to the Graphs of Polynomials
 Math 3201 5.1 Introduction to the Graphs of Polynomials In Math 1201/2201, we examined three types of polynomial functions: Constant Function - horizontal line such as y = 2 Linear Function - sloped line,
Math 3201 5.1 Introduction to the Graphs of Polynomials In Math 1201/2201, we examined three types of polynomial functions: Constant Function - horizontal line such as y = 2 Linear Function - sloped line,
Objectives. Materials
 Activity 13 Objectives Understand what a slope field represents in terms of Create a slope field for a given differential equation Materials TI-84 Plus / TI-83 Plus Graph paper Introduction One of the
Activity 13 Objectives Understand what a slope field represents in terms of Create a slope field for a given differential equation Materials TI-84 Plus / TI-83 Plus Graph paper Introduction One of the
Sec 4.1 Coordinates and Scatter Plots. Coordinate Plane: Formed by two real number lines that intersect at a right angle.
 Algebra I Chapter 4 Notes Name Sec 4.1 Coordinates and Scatter Plots Coordinate Plane: Formed by two real number lines that intersect at a right angle. X-axis: The horizontal axis Y-axis: The vertical
Algebra I Chapter 4 Notes Name Sec 4.1 Coordinates and Scatter Plots Coordinate Plane: Formed by two real number lines that intersect at a right angle. X-axis: The horizontal axis Y-axis: The vertical
MATH 142 Business Mathematics II
 MATH 142 Business Mathematics II Summer, 2016, WEEK 5 JoungDong Kim Week 5: 8.1, 8.2, 8.3 Chapter 8 Functions of Several Variables Section 8.1 Functions of several Variables Definition. An equation of
MATH 142 Business Mathematics II Summer, 2016, WEEK 5 JoungDong Kim Week 5: 8.1, 8.2, 8.3 Chapter 8 Functions of Several Variables Section 8.1 Functions of several Variables Definition. An equation of
Maple Commands for Surfaces and Partial Derivatives
 Math 235 Lab 2 Intro Maple Commands for Surfaces and Partial Derivatives We ve seen that a curve can be written as y = f(x), or more generally in parametric form using one parameter (usually t), and the
Math 235 Lab 2 Intro Maple Commands for Surfaces and Partial Derivatives We ve seen that a curve can be written as y = f(x), or more generally in parametric form using one parameter (usually t), and the
