Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties
|
|
|
- Alvin Melton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties Videos Proof Overview: Modules 9 and 10: Module 9 Review: Module 10 Review: M.5BF56BFCC5400FD4B6D A.vcr&sid=679 Constructions Acute Angle Acute Triangle Altitude Angle Bisector Centroid Circle through Three Points Circumcenter Circumscribed Circle Congruent Angles Congruent Line Segments Congruent Triangles Equiangular Triangle Equilateral Triangle Incenter Inscribed Circle Isosceles Triangle Median Obtuse Angle Obtuse Triangle Orthocenter Parallel Line Perpendicular Bisector Perpendicular Line Right Angle Right Triangle Scalene Triangle Segment Segment Bisector Tangents to Circles
2 Definitions (Note: The following are the most commonly used definitions in proofs. For a complete list of definitions for the course, refer to the glossary.) Acute Angle: An angle that measures less than 90. Altitude: A perpendicular segment from a vertex of a triangle to its opposite side. Angle: A figure consisting of two non-collinear rays or segments with a common endpoint. Bisector: A line or segment that divides another figure into two congruent parts. Circle: A set of all points in a plane that are a given distance from a point identified as the center. Complementary Angles: Two angles that add up to 90. Congruent Angles: Two angles with exactly the same degree measure. Congruent Segments: Two segments with exactly the same length. Congruent Triangles: Two triangles are congruent if and only if their corresponding parts are congruent: Corresponding Parts of Congruent Triangles are Congruent (CPCTC). Line: A one-dimensional figure that consists of an infinite number of points extending in opposite directions. Line Segment: A part of a line that has two endpoints. Median: A segment from a vertex of a triangle to the midpoint of the opposite side. Midpoint: A point that divides a segment into two equal parts. The ordered pair of this point can be found by the midpoint formula: Obtuse Angle: An angle that measures more than 90, but less than 180. Parallel Lines: Two lines that lie within the same plane and never intersect. Parallel lines have the same slope. Perpendicular Lines: Two lines that intersect at 90 angles. Perpendicular lines have slopes that are the negative reciprocals of one another. Perpendicular Bisector: A line that divides a segment into two halves and intersects the segment at a 90 angle. Plane: An infinite flat surface that has length and width but no depth. Point: A location that has no dimension. Ray: Part of a line that has one endpoint and continues in one direction infinitely. Right Angle: An angle that measures exactly 90. Similar Triangles: Two triangles are similar if corresponding angles are congruent and corresponding sides are proportional. Supplementary Angles: Two angles that add up to 180. Straight Angle: An angle that measures exactly 180. Vertex: The common endpoint of two segments or rays that form a corner of an angle. Theorems and Postulates Addition Property of Equality For real numbers a, b, and c, if a = b, then a + c = b + c.
3 Additive Identity The sum of any real number and zero is that same real number. In other words, for any real number a, a + 0 = a. Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then alternate exterior angles are congruent. Alternate Interior Angles Theorem If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then alternate interior angles are congruent. Angle Addition Postulate The measure of an angle created by two adjacent angles may be found by adding the measures of the two adjacent angles. Angle-Angle (AA) Similarity Postulate If two corresponding angles of two or more triangles are congruent, the triangles are similar. Angle-Angle-Side (AAS) Postulate If two angles and a non-included side are congruent to the corresponding two angles and side of a second triangle, the two triangles are congruent. Angle-Side-Angle (ASA) Postulate If two angles and the included side of one triangle are congruent to two angles and the included side of another triangle, the triangles are congruent. Arc Addition Postulate The measure of an arc created by two adjacent arcs may be found by adding the measures of the two adjacent arcs. Area of a Square The area of a square is a measurement representing the space within the interior of a square. It is found by the formula A = s 2 where A is the area and s is the length of a side. Area of a Triangle The area of a triangle is a measurement representing the space within the interior of a triangle. It is found by the formula A =1/2bh where A is the area, b is the length of the base, and h is the length of the height. Associative Property of Addition For real numbers a, b, and c, a + (b + c) = (a + b) + c. Associative Property of Multiplication For real numbers a, b, and c, a (b c) = (a b) c.
4 Bisecting Diagonal Theorem The diagonal of a kite connecting the vertex angles bisects the diagonal connecting the nonvertex angles. Bisecting Vertex Angles Theorem The diagonal of a kite connecting the vertex angles is an angle bisector of these vertex angles. Central Angle Theorem The measure of a central angle is equal to the measure of the arc it intercepts. Commutative Property of Addition For real numbers a and b, a + b = b + a. Commutative Property of Multiplication For real numbers a and b, a b = b a. Concurrency of Altitudes Theorem The lines containing the altitudes of a triangle are concurrent. Concurrency of Angle Bisectors Theorem The angle bisectors of a triangle are concurrent at a point equidistant from the sides of the triangle. Concurrency of Medians Theorem The medians of a triangle are concurrent at a point that is two-thirds the distance from each vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side. Concurrency of Perpendicular Bisectors Theorem The perpendicular bisectors of the sides of a triangle are concurrent at a point equidistant from the vertices. Congruent Arcs and Chords Theorem Two minor arcs within the same circle or between congruent circles are congruent if and only if their corresponding chords are congruent. Congruent Arcs Theorem Two arcs are congruent if the central angles that intercept them are also congruent. Congruent Inscribed Angles Theorem Two or more distinct inscribed angles that intercept the same arc, or congruent arcs, are congruent. Coplanar Points Postulate Through any three non-collinear points, there is exactly one plane.
5 Corresponding Angles Postulate If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then corresponding angles are congruent. Cross Product Property For real numbers a, b, c, and d, a/b=c/d is equivalent to a d = b c or ad = bc. Diagonals of an Isosceles Trapezoid Theorem The diagonals of an isosceles trapezoid are congruent. Distance between Two Points Postulate The distance between two points can be found by taking the absolute value of the difference between the coordinates of the two points. Distributive Property For real numbers a, b, and c, a(b + c) = ab + ac. Division Property of Equality For real numbers, a, b, and c, if a = b and c 0, then a/b=c/d. Exterior Angle to a Circle Theorem If two secants, two tangents, or a secant and a tangent intersect outside a circle, the measure of the created angle between them is one-half the absolute value of the difference of the measures of their intercepted arcs. Exterior Angle Sum Theorem The sum of the exterior angles of any polygon total 360. Corollary to the Exterior Angle Sum Theorem The angle measure of any single exterior angle to a regular polygon may be found by dividing 360 by the number of sides. The Hinge Theorem If two sides of one triangle are congruent to two sides of another triangle, and the included angle of the first is larger than the included angle of the second, then the third side of the first triangle is longer than the third side of the second triangle. The Converse of the Hinge Theorem If two sides of one triangle are congruent to two sides of another triangle, and the third sides are not congruent, then the larger included angle is opposite the longer third side. Hypotenuse-Leg (HL) Theorem If two right triangles have congruent hypotenuses and corresponding, congruent legs, the two right triangles are congruent. Inscribed Angle to a Semicircle Theorem An inscribed angle that intercepts a semicircle is a right angle.
6 Inscribed Angle Theorem The measure of an inscribed angle is equal to half the measure of its intercepted arc. Inscribed Quadrilateral Theorem The opposite angles of an inscribed quadrilateral to a circle are supplementary. Interior Angle Sum Theorem If n represents the number of sides in any polygon, the expression to find the sum of the interior angles in a polygon is (n 2) 180. Corollary to the Interior Angle Sum Theorem A single interior angle measure of a regular polygon may be found by dividing by the number of sides. The expression for finding a single interior angle measure in a regular polygon is Intersecting Lines Postulate If two lines intersect, then they intersect in exactly one point. Intersecting Planes Postulate If two distinct planes intersect, then they intersect in exactly one line. Isosceles Trapezoid Theorem If the legs of a trapezoid are congruent, then the base angles are congruent. Isosceles Triangle Theorem If two sides of a triangle are congruent, then the angles opposite those sides are congruent. The Converse of the Isosceles Triangle Theorem If two angles of a triangle are congruent, then the sides opposite those angles are congruent making the triangle an isosceles triangle. Midsegment of a Triangle Theorem A segment connecting the midpoints of two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side and half its length. Midsegment of a Trapezoid Theorem The length of the midsegment of a trapezoid is half of the total of the lengths of the bases. Multiplication Property of Equality For real numbers a, b, and c, if a = b, then ac = bc. Nonvertex Angles Theorem The nonvertex angles of a kite are congruent. Opposite Angle Theorem If two angles of a triangle are not congruent, then the longer side lies opposite the larger angle.
7 Opposite Side Theorem If two sides of a triangle are not congruent, then the larger angle lies opposite the larger side. Parallel Postulate Given a line and a point not on that line, there exists only one line through the given point parallel to the given line. Perpendicular Diagonals Theorem The diagonals of a kite are perpendicular. Perpendicular Diameters and Chords Theorem If a diameter is perpendicular to a chord, then the diameter bisects the chord and the minor arc between the endpoints of the chord. Pieces of Right Triangles Similarity Theorem If an altitude is drawn from the right angle of a right triangle, the two smaller triangles created are similar to one another and to the larger triangle. First Corollary to the Pieces of Right Triangles Similarity Theorem The length of the altitude from the right angle of a right triangle is the geometric mean between the segments of the hypotenuse created by the intersection of the altitude and the hypotenuse. Second Corollary to the Pieces of Right Triangles Similarity Theorem Each leg of a right triangle is the geometric mean between the hypotenuse and the segment of the hypotenuse created by the altitude adjacent to the given leg. Points Postulate Through any two points there exists exactly one line. Properties of Kites Two pairs of adjacent, congruent sides. Nonvertex angles are congruent. Diagonals are perpendicular. The diagonal connecting the vertex angles bisects the diagonal connecting the nonvertex angles. The diagonal connecting the vertex angles bisects those angles. The angles created by the diagonal connecting the nonvertex angles are congruent above and below the diagonal. Properties of Parallelograms Opposite sides are congruent and parallel. The diagonals bisect each other. Opposite angles are congruent. Consecutive angles are supplementary.
8 Properties of Rectangles Opposite sides are congruent and parallel. The diagonals bisect each other. Opposite angles are congruent. Consecutive angles are supplementary. Each angle is a right angle. The diagonals are congruent. Properties of a Rhombus Opposite sides are congruent and parallel. The diagonals bisect each other. Opposite angles are congruent. Consecutive angles are supplementary. All four sides are congruent. The diagonals are perpendicular. The diagonals are angle bisectors. Properties of a Square Opposite sides are congruent and parallel. The diagonals bisect each other. Opposite angles are congruent. Consecutive angles are supplementary. Each angle is a right angle. The diagonals are congruent. All four sides are congruent. The diagonals are perpendicular. The diagonals are angle bisectors. Properties of a Trapezoid One pair of parallel sides. Consecutive angles between the bases are supplementary. Proportional Perimeter Theorem If two triangles are similar, the perimeters of each triangle are proportional to their corresponding sides. Pythagorean Theorem If a right triangle has sides a and b and hypotenuse c then a 2 + b 2 = c 2. Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem In a triangle with sides a, b, and c, if a 2 + b 2 = c 2, then the triangle is a right triangle.
9 Reflexive Property of Equality For real number a, a = a. Same-Side Interior Angles If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then same-side interior angles are supplementary. Secant Interior Angle Theorem The measure of a secant angle is equal to half the sum of the arcs it and its vertical angle intercept. Secant-Tangent Intersection Theorem When a secant and tangent intersect at the point of tangency, the angles created at the point of intersection are half the measurement of the arcs they intersect. Segment Addition Postulate If point C is between points A and B, then AC + CB = AB. Side-Angle-Side (SAS) Postulate If two sides and the included angle of one triangle are congruent to two sides and the included angle of another triangle, then the triangles are congruent. Side-Angle-Side Similarity Postulate If two or more triangles have corresponding, congruent angles and the sides that make up these angles are proportional, then the triangles are similar. Side-Side-Side (SSS) Postulate If the sides of one triangle are congruent to the sides of a second triangle, then the triangles are congruent. Side-Side-Side Similarity Theorem If two or more triangles have three corresponding, proportional sides, then the triangles are similar. Square Root Property of Equality For any real number a, square root of a squared = a. Substitution Property of Equality For real numbers a and b, if a = b, then a can replace b in any expression and vice versa. Subtraction Property of Equality For real numbers a, b, and c, if a = b, then a c = b c. Supplementary Angles of a Trapezoid Theorem Consecutive angles between the two bases of a trapezoid are supplementary.
10 Symmetric Property of Equality For real numbers a and b, if a = b, then b = a. Transitive Property of Equality For real numbers a, b, and c, if a = b and b = c, then a = c. Triangle Altitude Similarity Theorem If two triangles are similar, the corresponding altitudes are proportional to each set of corresponding sides. Triangle Exterior Angle Theorem The measure of each exterior angle of a triangle equals the sum of the measures of its two remote interior angles. Triangle Inequality Theorem The sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the third side. Corollary to the Triangle Inequality Theorem The length of the third side of a triangle is less than the total and greater than the absolute value of the difference of the other two sides. Triangle Proportionality Theorem If a line is parallel to one side of a triangle and also intersects the other two sides, the line divides the sides proportionally. Triangle Sum Theorem The sum of the measures of the angles in a triangle is 180. Vertical Angles Theorem Vertical angles are congruent. Algebraic Properties Question 1: For any real numbers a, b, and c, if a = b, then a + c = b + c. Example: If x = 2, then x + 3 = Answer : Addition Property of Equality Question 2: a (b c) = (a b) c Example: 2 (3 4) = (2 3) = = 24
11 Answer : Associative Property of Multiplication Question 3: a + b = b + a Example: = = 8 Answer : Commutative Property of Addition Question 4: a(b + c) = ab + ac or a(b - c) = ab - ac Example: 2(4 + 5) = 2(4) + 2(5) 2(9) = = 18 or 2(4-5) = 2(4) - 2(5) 2(-1) = = -2 Answer : Distributive Property Question 5: For any real numbers a, b, and c, if a = b, then a/c = b/c as long as c is not zero. *The denominator cannot equal zero because division by zero is undefined. Example: if x = 4, x/3 = 4/3 Answer : Division Property of Equality Question 6: a + (b + c) = (a + b) + c Example: 2 + (3 + 4) = (2 + 3) = = 9 Answer : Associative Property of Addition Question 7: For any real numbers a, b, and c, if a = b, then ac = bc Example: If x = 4, then x(3) = 4(3). Answer : Multiplication Property of Equality Question 8: For any real numbers a, b, and c, if a = b, then a - c = b - c. Example: If x = 2, then x - 3 = 2-3. Answer : Subtraction Property of Equality Question 9:
12 a b = b a Example: 3 2 = = 6 Answer : Commutative Property of Multiplication Question 10: For any real number a, a = a. Example: 3 = 3 Answer : Reflexive Property of Equality Question 11: For all real numbers a, b, and c, if a = b and b = c, then a = c. Example: If x = 5 and 5 = (2 + 3), then x = (2 + 3). Answer : Transitive Property of Equality Question 12: For all real numbers a, b, if a = b, then b = a. Example: x = 2 means the same as 2 = x. Answer : Symmetric Property of Equality Question 13: For all real numbers a, b, and c, if a = b, then b can be replaced with a everywhere it occurs within an expression. Example: If x = 5, then x + 2 becomes Answer : Substitution Property of Equality
Postulates, Theorems, and Corollaries. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Post. 1-1-1 Through any two points there is exactly one line. Post. 1-1-2 Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. Post. 1-1-3 If two points lie in a
Chapter 1 Post. 1-1-1 Through any two points there is exactly one line. Post. 1-1-2 Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. Post. 1-1-3 If two points lie in a
theorems & postulates & stuff (mr. ko)
 theorems & postulates & stuff (mr. ko) postulates 1 ruler postulate The points on a line can be matched one to one with the real numbers. The real number that corresponds to a point is the coordinate of
theorems & postulates & stuff (mr. ko) postulates 1 ruler postulate The points on a line can be matched one to one with the real numbers. The real number that corresponds to a point is the coordinate of
Theorems & Postulates Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1
 Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 30-60 -90 Triangle In a 30-60 -90 triangle, the length of the hypotenuse is two times the length of the shorter leg, and the length of the longer leg is the length
Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 30-60 -90 Triangle In a 30-60 -90 triangle, the length of the hypotenuse is two times the length of the shorter leg, and the length of the longer leg is the length
MANHATTAN HUNTER SCIENCE HIGH SCHOOL GEOMETRY CURRICULUM
 COORDINATE Geometry Plotting points on the coordinate plane. Using the Distance Formula: Investigate, and apply the Pythagorean Theorem as it relates to the distance formula. (G.GPE.7, 8.G.B.7, 8.G.B.8)
COORDINATE Geometry Plotting points on the coordinate plane. Using the Distance Formula: Investigate, and apply the Pythagorean Theorem as it relates to the distance formula. (G.GPE.7, 8.G.B.7, 8.G.B.8)
WAYNESBORO AREA SCHOOL DISTRICT CURRICULUM ACCELERATED GEOMETRY (June 2014)
 UNIT: Chapter 1 Essentials of Geometry UNIT : How do we describe and measure geometric figures? Identify Points, Lines, and Planes (1.1) How do you name geometric figures? Undefined Terms Point Line Plane
UNIT: Chapter 1 Essentials of Geometry UNIT : How do we describe and measure geometric figures? Identify Points, Lines, and Planes (1.1) How do you name geometric figures? Undefined Terms Point Line Plane
Segment Addition Postulate: If B is BETWEEN A and C, then AB + BC = AC. If AB + BC = AC, then B is BETWEEN A and C.
 Ruler Postulate: The points on a line can be matched one to one with the REAL numbers. The REAL number that corresponds to a point is the COORDINATE of the point. The DISTANCE between points A and B, written
Ruler Postulate: The points on a line can be matched one to one with the REAL numbers. The REAL number that corresponds to a point is the COORDINATE of the point. The DISTANCE between points A and B, written
Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never
 1stSemesterReviewTrueFalse.nb 1 Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never Classify each statement as TRUE or FALSE. 1. Three given points are always coplanar. 2. A
1stSemesterReviewTrueFalse.nb 1 Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never Classify each statement as TRUE or FALSE. 1. Three given points are always coplanar. 2. A
Index COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Symbols & Numerics
 Symbols & Numerics. (dot) character, point representation, 37 symbol, perpendicular lines, 54 // (double forward slash) symbol, parallel lines, 54, 60 : (colon) character, ratio of quantity representation
Symbols & Numerics. (dot) character, point representation, 37 symbol, perpendicular lines, 54 // (double forward slash) symbol, parallel lines, 54, 60 : (colon) character, ratio of quantity representation
If B is the If two angles are
 If If B is between A and C, then 1 2 If P is in the interior of RST, then If B is the If two angles are midpoint of AC, vertical, then then 3 4 If angles are adjacent, then If angles are a linear pair,
If If B is between A and C, then 1 2 If P is in the interior of RST, then If B is the If two angles are midpoint of AC, vertical, then then 3 4 If angles are adjacent, then If angles are a linear pair,
Geometry Rules. Triangles:
 Triangles: Geometry Rules 1. Types of Triangles: By Sides: Scalene - no congruent sides Isosceles - 2 congruent sides Equilateral - 3 congruent sides By Angles: Acute - all acute angles Right - one right
Triangles: Geometry Rules 1. Types of Triangles: By Sides: Scalene - no congruent sides Isosceles - 2 congruent sides Equilateral - 3 congruent sides By Angles: Acute - all acute angles Right - one right
SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal)
 1 SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal) 1. Basic Terms and Definitions: a) Line-segment: A part of a line with two end points is called a line-segment. b) Ray: A part
1 SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal) 1. Basic Terms and Definitions: a) Line-segment: A part of a line with two end points is called a line-segment. b) Ray: A part
added to equal quantities, their sum is equal. Same holds for congruence.
 Mr. Cheung s Geometry Cheat Sheet Theorem List Version 6.0 Updated 3/14/14 (The following is to be used as a guideline. The rest you need to look up on your own, but hopefully this will help. The original
Mr. Cheung s Geometry Cheat Sheet Theorem List Version 6.0 Updated 3/14/14 (The following is to be used as a guideline. The rest you need to look up on your own, but hopefully this will help. The original
GEOMETRY is the study of points in space
 CHAPTER 5 Logic and Geometry SECTION 5-1 Elements of Geometry GEOMETRY is the study of points in space POINT indicates a specific location and is represented by a dot and a letter R S T LINE is a set of
CHAPTER 5 Logic and Geometry SECTION 5-1 Elements of Geometry GEOMETRY is the study of points in space POINT indicates a specific location and is represented by a dot and a letter R S T LINE is a set of
ALLEGHANY COUNTY SCHOOLS CURRICULUM GUIDE
 GRADE/COURSE: Geometry GRADING PERIOD: 1 Year Course Time SEMESTER 1: 1 ST SIX WEEKS Pre-Test, Class Meetings, Homeroom Chapter 1 12 days Lines and Angles Point Line AB Ray AB Segment AB Plane ABC Opposite
GRADE/COURSE: Geometry GRADING PERIOD: 1 Year Course Time SEMESTER 1: 1 ST SIX WEEKS Pre-Test, Class Meetings, Homeroom Chapter 1 12 days Lines and Angles Point Line AB Ray AB Segment AB Plane ABC Opposite
Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist
 3 undefined terms: point, line, plane Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist Section Definition Postulate Theorem 1.2 Space Collinear Non-collinear Coplanar Non-coplanar Intersection 1.3 Segment
3 undefined terms: point, line, plane Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist Section Definition Postulate Theorem 1.2 Space Collinear Non-collinear Coplanar Non-coplanar Intersection 1.3 Segment
Geometry Cheat Sheet
 Geometry Cheat Sheet Chapter 1 Postulate 1-6 Segment Addition Postulate - If three points A, B, and C are collinear and B is between A and C, then AB + BC = AC. Postulate 1-7 Angle Addition Postulate -
Geometry Cheat Sheet Chapter 1 Postulate 1-6 Segment Addition Postulate - If three points A, B, and C are collinear and B is between A and C, then AB + BC = AC. Postulate 1-7 Angle Addition Postulate -
Suggested List of Mathematical Language. Geometry
 Suggested List of Mathematical Language Geometry Problem Solving A additive property of equality algorithm apply constraints construct discover explore generalization inductive reasoning parameters reason
Suggested List of Mathematical Language Geometry Problem Solving A additive property of equality algorithm apply constraints construct discover explore generalization inductive reasoning parameters reason
Math 3315: Geometry Vocabulary Review Human Dictionary: WORD BANK
 Math 3315: Geometry Vocabulary Review Human Dictionary: WORD BANK [acute angle] [acute triangle] [adjacent interior angle] [alternate exterior angles] [alternate interior angles] [altitude] [angle] [angle_addition_postulate]
Math 3315: Geometry Vocabulary Review Human Dictionary: WORD BANK [acute angle] [acute triangle] [adjacent interior angle] [alternate exterior angles] [alternate interior angles] [altitude] [angle] [angle_addition_postulate]
Killingly Public Schools. Grades Draft Sept. 2002
 Killingly Public Schools Grades 10-12 Draft Sept. 2002 ESSENTIALS OF GEOMETRY Grades 10-12 Language of Plane Geometry CONTENT STANDARD 10-12 EG 1: The student will use the properties of points, lines,
Killingly Public Schools Grades 10-12 Draft Sept. 2002 ESSENTIALS OF GEOMETRY Grades 10-12 Language of Plane Geometry CONTENT STANDARD 10-12 EG 1: The student will use the properties of points, lines,
Unit Number of Days Dates. 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/ Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9
 8 th Grade Geometry Curriculum Map Overview 2016-2017 Unit Number of Days Dates 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/19 2 - Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9 3 - Congruence Transformations
8 th Grade Geometry Curriculum Map Overview 2016-2017 Unit Number of Days Dates 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/19 2 - Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9 3 - Congruence Transformations
If two sides and the included angle of one triangle are congruent to two sides and the included angle of 4 Congruence
 Postulates Through any two points there is exactly one line. Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. If two points lie in a plane, then the line containing those
Postulates Through any two points there is exactly one line. Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. If two points lie in a plane, then the line containing those
Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist
 3 undefined terms: point, line, plane Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist Section Definition Postulate Theorem 1.2 Space Collinear Non-collinear Coplanar Non-coplanar Intersection 1.3 Segment
3 undefined terms: point, line, plane Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist Section Definition Postulate Theorem 1.2 Space Collinear Non-collinear Coplanar Non-coplanar Intersection 1.3 Segment
Geometry Curriculum Map
 Geometry Curriculum Map Unit 1 st Quarter Content/Vocabulary Assessment AZ Standards Addressed Essentials of Geometry 1. What are points, lines, and planes? 1. Identify Points, Lines, and Planes 1. Observation
Geometry Curriculum Map Unit 1 st Quarter Content/Vocabulary Assessment AZ Standards Addressed Essentials of Geometry 1. What are points, lines, and planes? 1. Identify Points, Lines, and Planes 1. Observation
Perimeter. Area. Surface Area. Volume. Circle (circumference) C = 2πr. Square. Rectangle. Triangle. Rectangle/Parallelogram A = bh
 Perimeter Circle (circumference) C = 2πr Square P = 4s Rectangle P = 2b + 2h Area Circle A = πr Triangle A = bh Rectangle/Parallelogram A = bh Rhombus/Kite A = d d Trapezoid A = b + b h A area a apothem
Perimeter Circle (circumference) C = 2πr Square P = 4s Rectangle P = 2b + 2h Area Circle A = πr Triangle A = bh Rectangle/Parallelogram A = bh Rhombus/Kite A = d d Trapezoid A = b + b h A area a apothem
Thomas Jefferson High School for Science and Technology Program of Studies TJ Math 1
 Course Description: This course is designed for students who have successfully completed the standards for Honors Algebra I. Students will study geometric topics in depth, with a focus on building critical
Course Description: This course is designed for students who have successfully completed the standards for Honors Algebra I. Students will study geometric topics in depth, with a focus on building critical
Geometry Fall Final Review 2016
 Geometry Fall Final Review 2016 Name: Per: The Fall Final Exam will count as 25% of your semester average that is as much as an entire 6 weeks avg! *Review Problems: In order to be fully prepared for AND
Geometry Fall Final Review 2016 Name: Per: The Fall Final Exam will count as 25% of your semester average that is as much as an entire 6 weeks avg! *Review Problems: In order to be fully prepared for AND
Geometry - Concepts 9-12 Congruent Triangles and Special Segments
 Geometry - Concepts 9-12 Congruent Triangles and Special Segments Concept 9 Parallel Lines and Triangles (Section 3.5) ANGLE Classifications Acute: Obtuse: Right: SIDE Classifications Scalene: Isosceles:
Geometry - Concepts 9-12 Congruent Triangles and Special Segments Concept 9 Parallel Lines and Triangles (Section 3.5) ANGLE Classifications Acute: Obtuse: Right: SIDE Classifications Scalene: Isosceles:
CURRICULUM GUIDE. Honors Geometry
 CURRICULUM GUIDE Honors Geometry This level of Geometry is approached at an accelerated pace. Topics of postulates, theorems and proofs are discussed both traditionally and with a discovery approach. The
CURRICULUM GUIDE Honors Geometry This level of Geometry is approached at an accelerated pace. Topics of postulates, theorems and proofs are discussed both traditionally and with a discovery approach. The
Course: Geometry Level: Regular Date: 11/2016. Unit 1: Foundations for Geometry 13 Days 7 Days. Unit 2: Geometric Reasoning 15 Days 8 Days
 Geometry Curriculum Chambersburg Area School District Course Map Timeline 2016 Units *Note: unit numbers are for reference only and do not indicate the order in which concepts need to be taught Suggested
Geometry Curriculum Chambersburg Area School District Course Map Timeline 2016 Units *Note: unit numbers are for reference only and do not indicate the order in which concepts need to be taught Suggested
Geometry Vocabulary Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1
 Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 Acute Angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute Triangle A that has all acute Adjacent Alternate Interior Angle Two coplanar with a common vertex and
Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 Acute Angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute Triangle A that has all acute Adjacent Alternate Interior Angle Two coplanar with a common vertex and
DEFINITIONS. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle.
 DEFINITIONS Degree A degree is the 1 th part of a straight angle. 180 Right Angle A 90 angle is called a right angle. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle. Congruent
DEFINITIONS Degree A degree is the 1 th part of a straight angle. 180 Right Angle A 90 angle is called a right angle. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle. Congruent
Chapter 10 Similarity
 Chapter 10 Similarity Def: The ratio of the number a to the number b is the number. A proportion is an equality between ratios. a, b, c, and d are called the first, second, third, and fourth terms. The
Chapter 10 Similarity Def: The ratio of the number a to the number b is the number. A proportion is an equality between ratios. a, b, c, and d are called the first, second, third, and fourth terms. The
Proving Theorems about Lines and Angles
 Proving Theorems about Lines and Angles Angle Vocabulary Complementary- two angles whose sum is 90 degrees. Supplementary- two angles whose sum is 180 degrees. Congruent angles- two or more angles with
Proving Theorems about Lines and Angles Angle Vocabulary Complementary- two angles whose sum is 90 degrees. Supplementary- two angles whose sum is 180 degrees. Congruent angles- two or more angles with
algebraic representation algorithm alternate interior angles altitude analytical geometry x x x analytical proof x x angle
 Words PS R Comm CR Geo R Proof Trans Coor Catogoriers Key AA triangle similarity Constructed Response AAA triangle similarity Problem Solving AAS triangle congruence Resoning abscissa Communication absolute
Words PS R Comm CR Geo R Proof Trans Coor Catogoriers Key AA triangle similarity Constructed Response AAA triangle similarity Problem Solving AAS triangle congruence Resoning abscissa Communication absolute
U4 Polygon Notes January 11, 2017 Unit 4: Polygons
 Unit 4: Polygons 180 Complimentary Opposite exterior Practice Makes Perfect! Example: Example: Practice Makes Perfect! Def: Midsegment of a triangle - a segment that connects the midpoints of two sides
Unit 4: Polygons 180 Complimentary Opposite exterior Practice Makes Perfect! Example: Example: Practice Makes Perfect! Def: Midsegment of a triangle - a segment that connects the midpoints of two sides
Aldine ISD Benchmark Targets /Geometry SUMMER 2004
 ASSURANCES: By the end of Geometry, the student will be able to: 1. Use properties of triangles and quadrilaterals to solve problems. 2. Identify, classify, and draw two and three-dimensional objects (prisms,
ASSURANCES: By the end of Geometry, the student will be able to: 1. Use properties of triangles and quadrilaterals to solve problems. 2. Identify, classify, and draw two and three-dimensional objects (prisms,
Pacing Guide. Geometry. Quarter 1
 1 Start-Up/ Review ***************** ***** Note: Reteaching from Ready to Go On Quizzes indicate time built in for Intervention lessons/ student mastery of previously taught material. Wk 2 1.1: Understanding
1 Start-Up/ Review ***************** ***** Note: Reteaching from Ready to Go On Quizzes indicate time built in for Intervention lessons/ student mastery of previously taught material. Wk 2 1.1: Understanding
Geometry Midterm Review
 Geometry Midterm Review **Look at Study Guide and old tests The Midterm covers: Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Parts of Chapter 6 Chapter 1 1.1 point: - has no dimension - represented
Geometry Midterm Review **Look at Study Guide and old tests The Midterm covers: Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Parts of Chapter 6 Chapter 1 1.1 point: - has no dimension - represented
Geometry Mathematics. Grade(s) 10th - 12th, Duration 1 Year, 1 Credit Required Course
 Scope And Sequence Timeframe Unit Instructional Topics 9 Week(s) 9 Week(s) 9 Week(s) Geometric Structure Measurement Similarity Course Overview GENERAL DESCRIPTION: In this course the student will become
Scope And Sequence Timeframe Unit Instructional Topics 9 Week(s) 9 Week(s) 9 Week(s) Geometric Structure Measurement Similarity Course Overview GENERAL DESCRIPTION: In this course the student will become
West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District Basic Geometry Grades 9-12
 West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District Basic Geometry Grades 9-12 Unit 1: Basics of Geometry Content Area: Mathematics Course & Grade Level: Basic Geometry, 9 12 Summary and Rationale This unit
West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District Basic Geometry Grades 9-12 Unit 1: Basics of Geometry Content Area: Mathematics Course & Grade Level: Basic Geometry, 9 12 Summary and Rationale This unit
Geometry Review for Test 3 January 13, 2016
 Homework #7 Due Thursday, 14 January Ch 7 Review, pp. 292 295 #1 53 Test #3 Thurs, 14 Jan Emphasis on Ch 7 except Midsegment Theorem, plus review Betweenness of Rays Theorem Whole is Greater than Part
Homework #7 Due Thursday, 14 January Ch 7 Review, pp. 292 295 #1 53 Test #3 Thurs, 14 Jan Emphasis on Ch 7 except Midsegment Theorem, plus review Betweenness of Rays Theorem Whole is Greater than Part
VOCABULARY. Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, and 8. WORD IMAGE DEFINITION An angle with measure between 0 and A triangle with three acute angles.
 Acute VOCABULARY Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, and 8 WORD IMAGE DEFINITION Acute angle An angle with measure between 0 and 90 56 60 70 50 A with three acute. Adjacent Alternate interior Altitude of a Angle
Acute VOCABULARY Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, and 8 WORD IMAGE DEFINITION Acute angle An angle with measure between 0 and 90 56 60 70 50 A with three acute. Adjacent Alternate interior Altitude of a Angle
An Approach to Geometry (stolen in part from Moise and Downs: Geometry)
 An Approach to Geometry (stolen in part from Moise and Downs: Geometry) Undefined terms: point, line, plane The rules, axioms, theorems, etc. of elementary algebra are assumed as prior knowledge, and apply
An Approach to Geometry (stolen in part from Moise and Downs: Geometry) Undefined terms: point, line, plane The rules, axioms, theorems, etc. of elementary algebra are assumed as prior knowledge, and apply
Geometry CP Pen Argyl Area High School 2018
 Geometry emphasizes the development of logical thinking as it relates to geometric problems. Topics include using the correct language and notations of geometry, developing inductive and deductive reasoning,
Geometry emphasizes the development of logical thinking as it relates to geometric problems. Topics include using the correct language and notations of geometry, developing inductive and deductive reasoning,
, y 2. ), then PQ = - y 1 ) 2. x 1 + x 2
 Tools of Geometry Chapter 1 Undefined Terms (p. 5) A point is a location. It has neither shape nor size. A line is made up of points and has no thickness or width. A plane is a flat surface made up of
Tools of Geometry Chapter 1 Undefined Terms (p. 5) A point is a location. It has neither shape nor size. A line is made up of points and has no thickness or width. A plane is a flat surface made up of
Course: Geometry PAP Prosper ISD Course Map Grade Level: Estimated Time Frame 6-7 Block Days. Unit Title
 Unit Title Unit 1: Geometric Structure Estimated Time Frame 6-7 Block 1 st 9 weeks Description of What Students will Focus on on the terms and statements that are the basis for geometry. able to use terms
Unit Title Unit 1: Geometric Structure Estimated Time Frame 6-7 Block 1 st 9 weeks Description of What Students will Focus on on the terms and statements that are the basis for geometry. able to use terms
Honors Geometry Pacing Guide Honors Geometry Pacing First Nine Weeks
 Unit Topic To recognize points, lines and planes. To be able to recognize and measure segments and angles. To classify angles and name the parts of a degree To recognize collinearity and betweenness of
Unit Topic To recognize points, lines and planes. To be able to recognize and measure segments and angles. To classify angles and name the parts of a degree To recognize collinearity and betweenness of
Angles. Classification Acute Right Obtuse. Complementary s 2 s whose sum is 90 Supplementary s 2 s whose sum is 180. Angle Addition Postulate
 ngles Classification cute Right Obtuse Complementary s 2 s whose sum is 90 Supplementary s 2 s whose sum is 180 ngle ddition Postulate If the exterior sides of two adj s lie in a line, they are supplementary
ngles Classification cute Right Obtuse Complementary s 2 s whose sum is 90 Supplementary s 2 s whose sum is 180 ngle ddition Postulate If the exterior sides of two adj s lie in a line, they are supplementary
0613ge. Geometry Regents Exam 0613
 wwwjmaporg 0613ge 1 In trapezoid RSTV with bases and, diagonals and intersect at Q If trapezoid RSTV is not isosceles, which triangle is equal in area to? 2 In the diagram below, 3 In a park, two straight
wwwjmaporg 0613ge 1 In trapezoid RSTV with bases and, diagonals and intersect at Q If trapezoid RSTV is not isosceles, which triangle is equal in area to? 2 In the diagram below, 3 In a park, two straight
MCPS Geometry Pacing Guide Jennifer Mcghee
 Units to be covered 1 st Semester: Units to be covered 2 nd Semester: Tools of Geometry; Logic; Constructions; Parallel and Perpendicular Lines; Relationships within Triangles; Similarity of Triangles
Units to be covered 1 st Semester: Units to be covered 2 nd Semester: Tools of Geometry; Logic; Constructions; Parallel and Perpendicular Lines; Relationships within Triangles; Similarity of Triangles
Dover- Sherborn High School Mathematics Curriculum Geometry Honors
 Mathematics Curriculum A. DESCRIPTION This course represents an accelerated, rigorous approach to the topics of the traditional geometry course. Enrichment is gained through student projects and presentations,
Mathematics Curriculum A. DESCRIPTION This course represents an accelerated, rigorous approach to the topics of the traditional geometry course. Enrichment is gained through student projects and presentations,
High School Mathematics Geometry Vocabulary Word Wall Cards
 High School Mathematics Geometry Vocabulary Word Wall Cards Table of Contents Reasoning, Lines, and Transformations Basics of Geometry 1 Basics of Geometry 2 Geometry Notation Logic Notation Set Notation
High School Mathematics Geometry Vocabulary Word Wall Cards Table of Contents Reasoning, Lines, and Transformations Basics of Geometry 1 Basics of Geometry 2 Geometry Notation Logic Notation Set Notation
Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide
 Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide 1. Solve for x. True or False? (questions 2-5) 2. All rectangles are rhombuses. 3. If a quadrilateral is a kite, then it is a parallelogram. 4. If two parallel lines are
Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide 1. Solve for x. True or False? (questions 2-5) 2. All rectangles are rhombuses. 3. If a quadrilateral is a kite, then it is a parallelogram. 4. If two parallel lines are
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Department: Course: Chapter 1
 Department: Course: 2016-2017 Term, Phrase, or Expression Simple Definition Chapter 1 Comprehension Support Point Line plane collinear coplanar A location in space. It does not have a size or shape The
Department: Course: 2016-2017 Term, Phrase, or Expression Simple Definition Chapter 1 Comprehension Support Point Line plane collinear coplanar A location in space. It does not have a size or shape The
FONTANA UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT Glencoe Geometry Quarter 1 Standards and Objectives Pacing Map
 Glencoe Geometry Quarter 1 1 August 9-13 2 August 16-20 *1.0 Students demonstrate understanding by identifying and giving examples of undefined terms, axioms, theorems, and inductive and deductive reasoning.
Glencoe Geometry Quarter 1 1 August 9-13 2 August 16-20 *1.0 Students demonstrate understanding by identifying and giving examples of undefined terms, axioms, theorems, and inductive and deductive reasoning.
a triangle with all acute angles acute triangle angles that share a common side and vertex adjacent angles alternate exterior angles
 acute triangle a triangle with all acute angles adjacent angles angles that share a common side and vertex alternate exterior angles two non-adjacent exterior angles on opposite sides of the transversal;
acute triangle a triangle with all acute angles adjacent angles angles that share a common side and vertex alternate exterior angles two non-adjacent exterior angles on opposite sides of the transversal;
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES GEOMETRY. 3 rd Nine Weeks,
 STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES GEOMETRY 3 rd Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 1 OVERVIEW Geometry Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource for
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES GEOMETRY 3 rd Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 1 OVERVIEW Geometry Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource for
Geometry. AIR Study Guide
 Geometry AIR Study Guide Table of Contents Topic Slide Formulas 3 5 Angles 6 Lines and Slope 7 Transformations 8 Constructions 9 10 Triangles 11 Congruency and Similarity 12 Right Triangles Only 13 Other
Geometry AIR Study Guide Table of Contents Topic Slide Formulas 3 5 Angles 6 Lines and Slope 7 Transformations 8 Constructions 9 10 Triangles 11 Congruency and Similarity 12 Right Triangles Only 13 Other
Lines Plane A flat surface that has no thickness and extends forever.
 Lines Plane A flat surface that has no thickness and extends forever. Point an exact location Line a straight path that has no thickness and extends forever in opposite directions Ray Part of a line that
Lines Plane A flat surface that has no thickness and extends forever. Point an exact location Line a straight path that has no thickness and extends forever in opposite directions Ray Part of a line that
Geometry Third Quarter Study Guide
 Geometry Third Quarter Study Guide 1. Write the if-then form, the converse, the inverse and the contrapositive for the given statement: All right angles are congruent. 2. Find the measures of angles A,
Geometry Third Quarter Study Guide 1. Write the if-then form, the converse, the inverse and the contrapositive for the given statement: All right angles are congruent. 2. Find the measures of angles A,
Unit 10 Circles 10-1 Properties of Circles Circle - the set of all points equidistant from the center of a circle. Chord - A line segment with
 Unit 10 Circles 10-1 Properties of Circles Circle - the set of all points equidistant from the center of a circle. Chord - A line segment with endpoints on the circle. Diameter - A chord which passes through
Unit 10 Circles 10-1 Properties of Circles Circle - the set of all points equidistant from the center of a circle. Chord - A line segment with endpoints on the circle. Diameter - A chord which passes through
Carnegie Learning High School Math Series: Geometry Indiana Standards Worktext Correlations
 Carnegie Learning High School Math Series: Logic and Proofs G.LP.1 Understand and describe the structure of and relationships within an axiomatic system (undefined terms, definitions, axioms and postulates,
Carnegie Learning High School Math Series: Logic and Proofs G.LP.1 Understand and describe the structure of and relationships within an axiomatic system (undefined terms, definitions, axioms and postulates,
162. See also ASA triangle
 INDEX A AA triangle similarity (AA ), 490. See also Angle-angle triangle similarity AAS triangle, 352. See also Angle-angle-side triangle Abscissa, 210 Absolute value, 7 8 Acute angle, 17 Acute triangle,
INDEX A AA triangle similarity (AA ), 490. See also Angle-angle triangle similarity AAS triangle, 352. See also Angle-angle-side triangle Abscissa, 210 Absolute value, 7 8 Acute angle, 17 Acute triangle,
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Term Definition Figure
 Notes LT 1.1 - Distinguish and apply basic terms of geometry (coplanar, collinear, bisectors, congruency, parallel, perpendicular, etc.) Term Definition Figure collinear on the same line (note: you do
Notes LT 1.1 - Distinguish and apply basic terms of geometry (coplanar, collinear, bisectors, congruency, parallel, perpendicular, etc.) Term Definition Figure collinear on the same line (note: you do
22. A parallelogram is a quadrilateral in which both pairs of opposite sides are parallel.
 Chapter 4 Quadrilaterals 4.1 Properties of a Parallelogram Definitions 22. A parallelogram is a quadrilateral in which both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. 23. An altitude of a parallelogram is the
Chapter 4 Quadrilaterals 4.1 Properties of a Parallelogram Definitions 22. A parallelogram is a quadrilateral in which both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. 23. An altitude of a parallelogram is the
Triangles. Leg = s. Hypotenuse = s 2
 Honors Geometry Second Semester Final Review This review is designed to give the student a BASIC outline of what needs to be reviewed for the second semester final exam in Honors Geometry. It is up to
Honors Geometry Second Semester Final Review This review is designed to give the student a BASIC outline of what needs to be reviewed for the second semester final exam in Honors Geometry. It is up to
Pearson Mathematics Geometry
 A Correlation of Pearson Mathematics Geometry Indiana 2017 To the INDIANA ACADEMIC STANDARDS Mathematics (2014) Geometry The following shows where all of the standards that are part of the Indiana Mathematics
A Correlation of Pearson Mathematics Geometry Indiana 2017 To the INDIANA ACADEMIC STANDARDS Mathematics (2014) Geometry The following shows where all of the standards that are part of the Indiana Mathematics
Geometry Mathematics. Grade(s) 9th - 12th, Duration 1 Year, 1 Credit Required Course
 Course Description will provide a careful development of both inductive and deductive reasoning. While emphasizing the formal geometric topics of points, lines, planes, congruency, similarity, and characteristics
Course Description will provide a careful development of both inductive and deductive reasoning. While emphasizing the formal geometric topics of points, lines, planes, congruency, similarity, and characteristics
Ganado Unified School District Geometry
 Ganado Unified School District Geometry PACING Guide SY 2016-2017 Timeline & Resources 1st Quarter Unit 1 AZ & ELA Standards Essential Question Learning Goal Vocabulary CC.9-12.G.CO. Transformations and
Ganado Unified School District Geometry PACING Guide SY 2016-2017 Timeline & Resources 1st Quarter Unit 1 AZ & ELA Standards Essential Question Learning Goal Vocabulary CC.9-12.G.CO. Transformations and
2 Formula (given): Volume of a Pyramid V = 1/3 BH What does B represent? Formula: Area of a Trapezoid. 3 Centroid. 4 Midsegment of a triangle
 1 Formula: Area of a Trapezoid 2 Formula (given): Volume of a Pyramid V = 1/3 BH What does B represent? 3 Centroid 4 Midsegment of a triangle 5 Slope formula 6 Point Slope Form of Linear Equation *can
1 Formula: Area of a Trapezoid 2 Formula (given): Volume of a Pyramid V = 1/3 BH What does B represent? 3 Centroid 4 Midsegment of a triangle 5 Slope formula 6 Point Slope Form of Linear Equation *can
POTENTIAL REASONS: Definition of Congruence:
 Sec 1.6 CC Geometry Triangle Proofs Name: POTENTIAL REASONS: Definition of Congruence: Having the exact same size and shape and there by having the exact same measures. Definition of Midpoint: The point
Sec 1.6 CC Geometry Triangle Proofs Name: POTENTIAL REASONS: Definition of Congruence: Having the exact same size and shape and there by having the exact same measures. Definition of Midpoint: The point
Texas High School Geometry
 Texas High School Geometry This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet
Texas High School Geometry This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet
Geometry. Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section.
 Geometry Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section. Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles are always equal. If any
Geometry Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section. Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles are always equal. If any
Geometry Curriculum Map Modified: May 10, 2012 Activities: Timeline: Unit 1: Essentials of Geometry
 Timeline: Unit 1: Essentials of Geometry Activities: Resources: 2.5 weeks/12 days 2 weeks/11 days Vocabulary: Undefined terms, Collinear, Perimeter, Coplanar, Line Segment, Between, End Points, Ray, Opposite
Timeline: Unit 1: Essentials of Geometry Activities: Resources: 2.5 weeks/12 days 2 weeks/11 days Vocabulary: Undefined terms, Collinear, Perimeter, Coplanar, Line Segment, Between, End Points, Ray, Opposite
Geometry Foundations Pen Argyl Area High School 2018
 Geometry emphasizes the development of logical thinking as it relates to geometric problems. Topics include using the correct language and notations of geometry, developing inductive and deductive reasoning,
Geometry emphasizes the development of logical thinking as it relates to geometric problems. Topics include using the correct language and notations of geometry, developing inductive and deductive reasoning,
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES HONORS GEOMETRY. 3 rd Nine Weeks,
 STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES HONORS GEOMETRY 3 rd Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 1 OVERVIEW Geometry Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES HONORS GEOMETRY 3 rd Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 1 OVERVIEW Geometry Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource
Geometry Reasons for Proofs Chapter 1
 Geometry Reasons for Proofs Chapter 1 Lesson 1.1 Defined Terms: Undefined Terms: Point: Line: Plane: Space: Postulate 1: Postulate : terms that are explained using undefined and/or other defined terms
Geometry Reasons for Proofs Chapter 1 Lesson 1.1 Defined Terms: Undefined Terms: Point: Line: Plane: Space: Postulate 1: Postulate : terms that are explained using undefined and/or other defined terms
Geometry Definitions and Theorems. Chapter 9. Definitions and Important Terms & Facts
 Geometry Definitions and Theorems Chapter 9 Definitions and Important Terms & Facts A circle is the set of points in a plane at a given distance from a given point in that plane. The given point is the
Geometry Definitions and Theorems Chapter 9 Definitions and Important Terms & Facts A circle is the set of points in a plane at a given distance from a given point in that plane. The given point is the
6.1 Circles and Related Segments and Angles
 Chapter 6 Circles 6.1 Circles and Related Segments and Angles Definitions 32. A circle is the set of all points in a plane that are a fixed distance from a given point known as the center of the circle.
Chapter 6 Circles 6.1 Circles and Related Segments and Angles Definitions 32. A circle is the set of all points in a plane that are a fixed distance from a given point known as the center of the circle.
Acknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILAR TRIANGLES. 1. Definition: A ratio represents the comparison of two quantities.
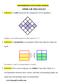 1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
Northern York County School District Curriculum
 Course Name Keystone Geometry (1.03 / 1.06 / 1.10) Grade Level Grade 10 Northern York County School District Curriculum Module Instructional Procedures Module 1: Geometric Properties and Reasoning Course
Course Name Keystone Geometry (1.03 / 1.06 / 1.10) Grade Level Grade 10 Northern York County School District Curriculum Module Instructional Procedures Module 1: Geometric Properties and Reasoning Course
CCSD Proficiency Scale - Language of Geometry
 CCSD Scale - Language of Geometry Content Area: HS Math Grade : Geometry Standard Code: G-CO.1 application G-CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular lines, parallel lines, and line
CCSD Scale - Language of Geometry Content Area: HS Math Grade : Geometry Standard Code: G-CO.1 application G-CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular lines, parallel lines, and line
Unit 1 Unit 1 A M. M.Sigley, Baker MS. Unit 1 Unit 1. 3 M.Sigley, Baker MS
 A M S 1 2 G O E A B 3 4 LINE POINT Undefined No thickness Extends infinitely in two directions Designated with two points Named with two capital letters or Undefined No size Named with a capital letter
A M S 1 2 G O E A B 3 4 LINE POINT Undefined No thickness Extends infinitely in two directions Designated with two points Named with two capital letters or Undefined No size Named with a capital letter
GEOMETRY. Background Knowledge/Prior Skills. Knows ab = a b. b =
 GEOMETRY Numbers and Operations Standard: 1 Understands and applies concepts of numbers and operations Power 1: Understands numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers, and number
GEOMETRY Numbers and Operations Standard: 1 Understands and applies concepts of numbers and operations Power 1: Understands numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers, and number
Centerville Jr. High School Curriculum Mapping Geometry 1 st Nine Weeks Matthew A. Lung Key Questions Resources/Activities Vocabulary Assessments
 Chapter/ Lesson 1/1 Indiana Standard(s) Centerville Jr. High School Curriculum Mapping Geometry 1 st Nine Weeks Matthew A. Lung Key Questions Resources/Activities Vocabulary Assessments What is inductive
Chapter/ Lesson 1/1 Indiana Standard(s) Centerville Jr. High School Curriculum Mapping Geometry 1 st Nine Weeks Matthew A. Lung Key Questions Resources/Activities Vocabulary Assessments What is inductive
Geometry Vocabulary Word Wall Cards
 Geometry Vocabulary Word Wall Cards Mathematics vocabulary word wall cards provide a display of mathematics content words and associated visual cues to assist in vocabulary development. The cards should
Geometry Vocabulary Word Wall Cards Mathematics vocabulary word wall cards provide a display of mathematics content words and associated visual cues to assist in vocabulary development. The cards should
HADDONFIELD PUBLIC SCHOOLS Curriculum Map for College Prep Geometry
 Curriculum Map for College Prep Geometry Chapter 1: September (2-3 weeks) Targeted NJ Core Curriculum Content Standards: CC.9-12.G.CO.1; CC.9-12.G.GPE.7; CC.9-12.G.MG.1 Enduring Understandings: Geometry
Curriculum Map for College Prep Geometry Chapter 1: September (2-3 weeks) Targeted NJ Core Curriculum Content Standards: CC.9-12.G.CO.1; CC.9-12.G.GPE.7; CC.9-12.G.MG.1 Enduring Understandings: Geometry
Assignment List. Chapter 1 Essentials of Geometry. Chapter 2 Reasoning and Proof. Chapter 3 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
 Geometry Assignment List Chapter 1 Essentials of Geometry 1.1 Identify Points, Lines, and Planes 5 #1, 4-38 even, 44-58 even 27 1.2 Use Segments and Congruence 12 #4-36 even, 37-45 all 26 1.3 Use Midpoint
Geometry Assignment List Chapter 1 Essentials of Geometry 1.1 Identify Points, Lines, and Planes 5 #1, 4-38 even, 44-58 even 27 1.2 Use Segments and Congruence 12 #4-36 even, 37-45 all 26 1.3 Use Midpoint
MADISON ACADEMY GEOMETRY PACING GUIDE
 MADISON ACADEMY GEOMETRY PACING GUIDE 2018-2019 Standards (ACT included) ALCOS#1 Know the precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment based on the undefined
MADISON ACADEMY GEOMETRY PACING GUIDE 2018-2019 Standards (ACT included) ALCOS#1 Know the precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment based on the undefined
Instructional Unit CPM Geometry Unit Content Objective Performance Indicator Performance Task State Standards Code:
 306 Instructional Unit Area 1. Areas of Squares and The students will be -Find the amount of carpet 2.4.11 E Rectangles able to determine the needed to cover various plane 2. Areas of Parallelograms and
306 Instructional Unit Area 1. Areas of Squares and The students will be -Find the amount of carpet 2.4.11 E Rectangles able to determine the needed to cover various plane 2. Areas of Parallelograms and
The Research- Driven Solution to Raise the Quality of High School Core Courses. Geometry. Course Outline
 The Research- Driven Solution to Raise the Quality of High School Core Courses Course Outline Course Outline Page 2 of 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 ACT Course Standards A. Prerequisites 1. Skills Acquired by Students
The Research- Driven Solution to Raise the Quality of High School Core Courses Course Outline Course Outline Page 2 of 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 ACT Course Standards A. Prerequisites 1. Skills Acquired by Students
Index triangle, 70, theorem, triangle, triangle, triangle, 70
 Index 30-60-90 triangle, 70, 122 360 theorem, 31 45-45-45 triangle, 122 45-45-90 triangle, 70 60-60-60 triangle, 70 AA similarity theorem, 110 AAA congruence theorem, 154 AAASA, 80 AAS theorem, 46 AASAS,
Index 30-60-90 triangle, 70, 122 360 theorem, 31 45-45-45 triangle, 122 45-45-90 triangle, 70 60-60-60 triangle, 70 AA similarity theorem, 110 AAA congruence theorem, 154 AAASA, 80 AAS theorem, 46 AASAS,
Manhattan Center for Science and Math High School Mathematics Department Curriculum
 Content/Discipline Geometry, Term 1 http://mcsmportal.net Marking Period 1 Topic and Essential Question Manhattan Center for Science and Math High School Mathematics Department Curriculum Unit 1 - (1)
Content/Discipline Geometry, Term 1 http://mcsmportal.net Marking Period 1 Topic and Essential Question Manhattan Center for Science and Math High School Mathematics Department Curriculum Unit 1 - (1)
Geometry/Trigonometry Unit 5: Polygon Notes Period:
 Geometry/Trigonometry Unit 5: Polygon Notes Name: Date: Period: # (1) Page 270 271 #8 14 Even, #15 20, #27-32 (2) Page 276 1 10, #11 25 Odd (3) Page 276 277 #12 30 Even (4) Page 283 #1-14 All (5) Page
Geometry/Trigonometry Unit 5: Polygon Notes Name: Date: Period: # (1) Page 270 271 #8 14 Even, #15 20, #27-32 (2) Page 276 1 10, #11 25 Odd (3) Page 276 277 #12 30 Even (4) Page 283 #1-14 All (5) Page
Geometry Practice Questions Semester 1
 Geometry Practice Questions Semester 1 MAFS.912.G-CO.1.1 - Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line,
Geometry Practice Questions Semester 1 MAFS.912.G-CO.1.1 - Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line,
0811ge. Geometry Regents Exam
 0811ge 1 The statement "x is a multiple of 3, and x is an even integer" is true when x is equal to 9 8 3 6 2 In the diagram below,. 4 Pentagon PQRST has parallel to. After a translation of, which line
0811ge 1 The statement "x is a multiple of 3, and x is an even integer" is true when x is equal to 9 8 3 6 2 In the diagram below,. 4 Pentagon PQRST has parallel to. After a translation of, which line
NFC ACADEMY COURSE OVERVIEW
 NFC ACADEMY COURSE OVERVIEW Geometry Honors is a full year, high school math course for the student who has successfully completed the prerequisite course, Algebra I. The course focuses on the skills and
NFC ACADEMY COURSE OVERVIEW Geometry Honors is a full year, high school math course for the student who has successfully completed the prerequisite course, Algebra I. The course focuses on the skills and
, Geometry, Quarter 1
 2017.18, Geometry, Quarter 1 The following Practice Standards and Literacy Skills will be used throughout the course: Standards for Mathematical Practice Literacy Skills for Mathematical Proficiency 1.
2017.18, Geometry, Quarter 1 The following Practice Standards and Literacy Skills will be used throughout the course: Standards for Mathematical Practice Literacy Skills for Mathematical Proficiency 1.
