Theoretically Perfect Sensor
|
|
|
- Easter Noreen Parrish
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sampling 1/60
2 Sampling The ray tracer samples the geometry, only gathering information from the parts of the world that interact with a finite number of rays In contrast, a scanline renderer can push all the triangles onto the image plane however, the simple approach of testing which pixel centers are inside which triangles is also a form of sampling one needs to calculate the overlap between projected triangles and finite size (square) pixels in order to avoid sampling 2/60
3 Theoretically Perfect Sensor The value seen by a theoretically perfect sensor corresponds to the fraction of the sensor covered by the object as well as the exposure time Impractical for rendering, especially for complex scenes Coverage: Signal: 3/60
4 Real World Sensors Even the eye and camera have to deal with the fact that they do not collect all of the information 4/60
5 Aliasing 5/60
6 Example: Jaggies Send a ray from the center of each pixel and shade the entire pixel based on the color returned by that ray Jaggies occur because lines of pixels do not line up with lines of objects (This occurs in scanline rendering as well ) 6/60
7 Aliasing Sampling causes aliasing artifacts An alias or imposter appears in the place of the actual feature For example, in the previous slide, a jagged line appears in the place of the straight line Anti-aliasing techniques are used to prevent and alleviate these aliasing artifacts caused by inadequate sampling 7/60
8 Example: Texturing Artifacts Texture coordinates nonuniformly mapped onto a surface cause the sampling rate to vary across the texture Incorrect Aliasing Correct 8/60
9 Example: Sparkling Highlights Aliasing in normal vectors can cause noise in specular highlights in the Blinn-Phong shading model Incorrect Aliasing Correct 9/60
10 Example: Wagon Wheel Effect A spinning wheel appears to spin backwards when its motion is insufficiently sampled in time This is temporal aliasing 10/60
11 Sampling Rate Sampling artifacts can be reduced by increasing the number of pixels in an image (and consequently the total number of samples) Increasing the resolution of an image is costly Requires additional time to render because the number of rays cast increases Displaying the high resolution image and/or using the image as a texture requires both additional storage and computation, problematic for many applications Optimizing the Sampling Rate Use the lowest possible sampling rate that does not result in noticeable aliasing artifacts What is this ideal sampling rate? 11/60
12 1D Example 12/60
13 Sampling Rate: 4 Samples per Period 13/60
14 Discrete Samples 14/60
15 Continuous Reconstruction 15/60
16 Sampling Rate: 2 Samples per Period 16/60
17 Discrete Samples 17/60
18 Continuous Reconstruction 18/60
19 Sampling Rate: 1 Sample per Period 19/60
20 Discrete Samples 20/60
21 Continuous Reconstruction Continuous reconstruction from discrete samples no longer matches the original function Appears to be a different function Aliased! 21/60
22 Sampling Rate: 2/3 Sample per Period 22/60
23 Discrete Samples 23/60
24 Continuous Reconstruction Continuous reconstruction from discrete samples no longer matches the original function Appears to be a different function Aliased! 24/60
25 Aliasing For this sampling rate, these two cosine waves of different frequencies and amplitudes become aliased Can t tell the difference between them 25/60
26 Nyquist Frequency 26/60
27 Aliasing Sampling at too low a rate results in aliasing Aliasing refers to an effect that causes two different signals to become indistinguishable an alias or imposter Nyquist-Shannon Sampling Theorem If a function f(t) contains no frequencies higher than W hertz, it can be completely determined by samples at a series of points spaced 1/(2W) seconds apart That is, 2 samples per period are required to prevent aliasing 27/60
28 Anti-Aliasing Given a fixed sampling frequency (e.g. #pixels in a feature), the Nyquist frequency is defined as half the sampling frequency Need 2 samples per period to prevent aliasing If the real world function being sampled has no frequencies above the Nyquist frequency, no aliasing occurs But any real world frequencies above the Nyquist frequency will appear as aliases to the sampler Before sampling, pre-filter out all frequencies in the real world signal higher than the Nyquist frequency in order to prevent aliasing We can do this by transforming the function into frequency space 28/60
29 Fourier Transform 29/60
30 Fourier Transform Used to transform from the spatial domain to the frequency domain, and vice versa: F(k) f(x) 2πjkx = f ( x) e dx = F( k) e dk 2πjkx f(x) F(k) 30/60
31 Constant Function 31/60
32 Low Frequency Cosine 32/60
33 High Frequency Cosine 33/60
34 Narrow Gaussian Narrow Wide 34/60
35 Wider Gaussian Wider Narrower 35/60
36 Anti-Aliasing 36/60
37 Sum of 2 Different Frequency and Amplitude Cosine Functions 37/60
38 Discrete Samples 38/60
39 Reconstructed Alias 39/60
40 Pre-filtering in Fourier Space 1. Compute the Fourier transform of the signal 40/60
41 Pre-filtering in Fourier Space 2. Apply a low-pass filter to the Fourier transform of the signal to remove all frequencies higher than the Nyquist frequency 41/60
42 Pre-filtering in Fourier Space 2. Apply a low-pass filter to the Fourier transform of the signal to remove all frequencies higher than the Nyquist frequency 42/60
43 Pre-filtering in Fourier Space 3. Compute the inverse Fourier transform of the low-pass filtered signal 43/60
44 Pre-filtering in Fourier Space 4. The lower frequency component of the original function can then be sampled and reconstructed without aliasing. 44/60
45 Pre-filtering in Fourier Space 4. The lower frequency component of the original function can then be sampled and reconstructed without aliasing. 45/60
46 Pre-filtering in Fourier Space 4. The lower frequency component of the original function can then be sampled and reconstructed without aliasing. 46/60
47 Pre-filter Before Sampling! If we sample before filtering, high frequency components will masquerade as low frequency components There is no way to discern the high frequencies masquerading as low frequencies from the actual low frequencies We must pre-filter before sampling in order to avoid aliasing 47/60
48 Blurring vs. Antialiasing Blurring Jaggies After Sampling Pre-filtering 48/60
49 Images 49/60
50 Images Images have discrete values and are not continuous functions Use a discrete Fourier transform for pre-filtering The Fast Fourier Transform is a divide and conquer algorithm that enables us to compute the discrete Fourier transform and its inverse in O(n log n) time where n is the number of samples Compute the 2D Fourier transform by applying 1D discrete Fourier transforms (i.e. FFTs) along each dimension 1. Compute the discrete Fourier transform (via FFT) Transform the discrete image values into another array of discrete values 2. Perform operations 3. Compute the inverse discrete Fourier transform (via FFT) 50/60
51 Constant Function Spatial Domain Frequency Domain 51/60
52 Spatial Domain Frequency Domain 52/60
53 Spatial Domain Frequency Domain 53/60
54 Spatial Domain Frequency Domain 54/60
55 Spatial Domain Frequency Domain 55/60
56 Real World Image Spatial Domain Frequency Domain 56/60
57 Lowest Frequencies Spatial Domain Frequency Domain 57/60
58 Intermediate Frequencies Spatial Domain Frequency Domain 58/60
59 Larger Intermediate Frequencies Spatial Domain Frequency Domain 59/60
60 Highest Frequencies (edges) Spatial Domain Frequency Domain 60/60
61 Convolution 61/60
62 Anti-Aliasing Let f and g be functions in the spatial domain, and F(f) and F(g) be the transformations of these functions in the frequency domain Here f is our image, F(f) is the frequency space representation of our image, and F(g) is the low pass filter we wish to apply in the frequency domain via multiplication component by component, i.e. F(f) F(g) this multiplication zeroes out high frequency components of F(f) Finally we apply the inverse transform to the final result to obtain: 62/60
63 RECALL: Pre-filtering in Fourier Space 2. Apply a low-pass filter to the Fourier transform of the signal to remove all frequencies higher than the Nyquist frequency 63/60
64 Convolution Applying this low pass filter F(g) to the transform of the function f in the frequency domain is equivalent to a spatial convolution of the function f with the inverse transform of the filter (i.e. g ): The spatial convolution is defined by 64/60
65 Convolution We can skip the FFT entirely, and instead apply convolution in the spatial domain Unfortunately, (recall) narrow low pass filters in the frequency domain result in wide convolution kernels in the spatial domain (and vice versa) So it takes a lot of work to apply a narrow low pass frequency domain filter in the spatial domain via convolution (one has to consider a large number of non-local pixels) We d prefer a small local convolution kernel in the spatial domain This gives a wide frequency domain filter, and so won t perfectly filter out all high frequencies But, meh, it s ok-ish 65/60
66 RECALL: Narrow Gaussian Narrow Wide 66/60
67 RECALL: Wider Gaussian Wider Narrower 67/60
68 Box Filter 68/60
69 Box Filter A box filter contains uniform weights throughout a certain range [x0,x1] x [y0, y1] and zeroes everywhere else Applying a box filter via discrete convolution: Overlay the filter on the 2D array of image values Multiply each pair of overlayed values Sum (integrate) the results to obtain a new value usually defined at the center of the filter 1 / 16 1 / 16 1 / 16 1 / 16 1 / 16 1 / 16 1 / 16 1 / 16 1 / 16 1 / 16 1 / 16 1 / 16 1 / 16 1 / 16 1 / 16 1 / 16 69/60
70 Box Filter Approximates a Low-Pass Filter Spatial Domain Frequency Domain 70/60
71 Wider Box Filter Removes More Frequencies Spatial Domain Frequency Domain 71/60
72 Supersampling 72/60
73 Supersampling Average multiple point samples distributed throughout a single pixel to obtain the value for that pixel Rendering a 100 by 100 image using uniform 4 by 4 supersampling is equivalent to rendering a 400 by 400 image and applying a 4 by 4 box filter on every 16 th point (deleting the other 15 out of 16 points) Sample at a higher resolution, but still store the same (lower) resolution image NB: As the number of points per pixel approaches infinity, it approximates the area coverage integral (a smart random distribution is often used ) 73/60
74 Point Sampling 4 by 4 Supersampling Exact Area Coverage 74/60
75 This Matters! 75/60
76 This Matters! Jaggies Anti-aliased 76/60
77 Sketch Your Scene 77/60
78 Question 1 Sketch the most important parts first Model the most important parts in CG first too, in case you run out of time Is it hard to draw? Will it be hard to model Does it make sense or need explanation? Will your CG scene make sense? Etc. 78/60
Theoretically Perfect Sensor
 Sampling 1/67 Sampling The ray tracer samples the geometry, only gathering information from the parts of the world that interact with a finite number of rays In contrast, a scanline renderer can push all
Sampling 1/67 Sampling The ray tracer samples the geometry, only gathering information from the parts of the world that interact with a finite number of rays In contrast, a scanline renderer can push all
CS354 Computer Graphics Sampling and Aliasing
 Slide Credit: http://www.siggraph.org/education/materials/hypergraph/aliasing/alias0.htm CS354 Computer Graphics Sampling and Aliasing Qixing Huang February 12th 2018 Sampling and Aliasing Display is discrete
Slide Credit: http://www.siggraph.org/education/materials/hypergraph/aliasing/alias0.htm CS354 Computer Graphics Sampling and Aliasing Qixing Huang February 12th 2018 Sampling and Aliasing Display is discrete
Aliasing. Can t draw smooth lines on discrete raster device get staircased lines ( jaggies ):
 (Anti)Aliasing and Image Manipulation for (y = 0; y < Size; y++) { for (x = 0; x < Size; x++) { Image[x][y] = 7 + 8 * sin((sqr(x Size) + SQR(y Size)) / 3.0); } } // Size = Size / ; Aliasing Can t draw
(Anti)Aliasing and Image Manipulation for (y = 0; y < Size; y++) { for (x = 0; x < Size; x++) { Image[x][y] = 7 + 8 * sin((sqr(x Size) + SQR(y Size)) / 3.0); } } // Size = Size / ; Aliasing Can t draw
Drawing a Triangle (and an introduction to sampling)
 Lecture 4: Drawing a Triangle (and an introduction to sampling) Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Spring 2017 Assignment 1 is out! https://15462-s17.github.io/asst1_drawsvg/ Let s draw some triangles
Lecture 4: Drawing a Triangle (and an introduction to sampling) Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Spring 2017 Assignment 1 is out! https://15462-s17.github.io/asst1_drawsvg/ Let s draw some triangles
Advanced Computer Graphics. Aliasing. Matthias Teschner. Computer Science Department University of Freiburg
 Advanced Computer Graphics Aliasing Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline motivation Fourier analysis filtering sampling reconstruction / aliasing antialiasing University
Advanced Computer Graphics Aliasing Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Outline motivation Fourier analysis filtering sampling reconstruction / aliasing antialiasing University
Sampling and Reconstruction
 Page 1 Sampling and Reconstruction The sampling and reconstruction process Real world: continuous Digital world: discrete Basic signal processing Fourier transforms The convolution theorem The sampling
Page 1 Sampling and Reconstruction The sampling and reconstruction process Real world: continuous Digital world: discrete Basic signal processing Fourier transforms The convolution theorem The sampling
Computer Graphics. Texture Filtering & Sampling Theory. Hendrik Lensch. Computer Graphics WS07/08 Texturing
 Computer Graphics Texture Filtering & Sampling Theory Hendrik Lensch Overview Last time Texture Parameterization Procedural Shading Today Texturing Filtering 2D Texture Mapping Forward mapping Object surface
Computer Graphics Texture Filtering & Sampling Theory Hendrik Lensch Overview Last time Texture Parameterization Procedural Shading Today Texturing Filtering 2D Texture Mapping Forward mapping Object surface
Announcements. Written Assignment 2 out (due March 8) Computer Graphics
 Announcements Written Assignment 2 out (due March 8) 1 Advanced Ray Tracing (Recursive) Ray Tracing Antialiasing Motion Blur Distribution Ray Tracing Ray Tracing and Radiosity Assumptions Simple shading
Announcements Written Assignment 2 out (due March 8) 1 Advanced Ray Tracing (Recursive) Ray Tracing Antialiasing Motion Blur Distribution Ray Tracing Ray Tracing and Radiosity Assumptions Simple shading
Aliasing and Antialiasing. ITCS 4120/ Aliasing and Antialiasing
 Aliasing and Antialiasing ITCS 4120/5120 1 Aliasing and Antialiasing What is Aliasing? Errors and Artifacts arising during rendering, due to the conversion from a continuously defined illumination field
Aliasing and Antialiasing ITCS 4120/5120 1 Aliasing and Antialiasing What is Aliasing? Errors and Artifacts arising during rendering, due to the conversion from a continuously defined illumination field
The main goal of Computer Graphics is to generate 2D images 2D images are continuous 2D functions (or signals)
 Motivation The main goal of Computer Graphics is to generate 2D images 2D images are continuous 2D functions (or signals) monochrome f(x,y) or color r(x,y), g(x,y), b(x,y) These functions are represented
Motivation The main goal of Computer Graphics is to generate 2D images 2D images are continuous 2D functions (or signals) monochrome f(x,y) or color r(x,y), g(x,y), b(x,y) These functions are represented
Computer Graphics. Sampling Theory & Anti-Aliasing. Philipp Slusallek
 Computer Graphics Sampling Theory & Anti-Aliasing Philipp Slusallek Dirac Comb (1) Constant & δ-function flash Comb/Shah function 2 Dirac Comb (2) Constant & δ-function Duality f(x) = K F(ω) = K (ω) And
Computer Graphics Sampling Theory & Anti-Aliasing Philipp Slusallek Dirac Comb (1) Constant & δ-function flash Comb/Shah function 2 Dirac Comb (2) Constant & δ-function Duality f(x) = K F(ω) = K (ω) And
Drawing a Triangle (and an Intro to Sampling)
 Lecture 4: Drawing a Triangle (and an Intro to Sampling) Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Spring 2018 HW 0.5 Due, HW 1 Out Today! GOAL: Implement a basic rasterizer - (Topic of today s lecture) - We
Lecture 4: Drawing a Triangle (and an Intro to Sampling) Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Spring 2018 HW 0.5 Due, HW 1 Out Today! GOAL: Implement a basic rasterizer - (Topic of today s lecture) - We
Motivation. The main goal of Computer Graphics is to generate 2D images. 2D images are continuous 2D functions (or signals)
 Motivation The main goal of Computer Graphics is to generate 2D images 2D images are continuous 2D functions (or signals) monochrome f(x,y) or color r(x,y), g(x,y), b(x,y) These functions are represented
Motivation The main goal of Computer Graphics is to generate 2D images 2D images are continuous 2D functions (or signals) monochrome f(x,y) or color r(x,y), g(x,y), b(x,y) These functions are represented
To Do. Advanced Computer Graphics. Sampling and Reconstruction. Outline. Sign up for Piazza
 Advanced Computer Graphics CSE 63 [Spring 207], Lecture 3 Ravi Ramamoorthi http://www.cs.ucsd.edu/~ravir Sign up for Piazza To Do Assignment, Due Apr 28. Anyone need help finding partners? Any issues with
Advanced Computer Graphics CSE 63 [Spring 207], Lecture 3 Ravi Ramamoorthi http://www.cs.ucsd.edu/~ravir Sign up for Piazza To Do Assignment, Due Apr 28. Anyone need help finding partners? Any issues with
Lecture 6 Basic Signal Processing
 Lecture 6 Basic Signal Processing Copyright c1996, 1997 by Pat Hanrahan Motivation Many aspects of computer graphics and computer imagery differ from aspects of conventional graphics and imagery because
Lecture 6 Basic Signal Processing Copyright c1996, 1997 by Pat Hanrahan Motivation Many aspects of computer graphics and computer imagery differ from aspects of conventional graphics and imagery because
28 SAMPLING. ALIASING AND ANTI-ALIASING
 28 SAMPLING. ALIASING AND ANTI-ALIASING Textbook: 16 UGRAD.CS.UBC.CA/~CS314 Alla Sheffer, 2016 ALIASING & ANTI-ALIASING Adobe, inc., https://helpx.adobe.com/photoshop/key concepts/aliasing anti aliasing.html
28 SAMPLING. ALIASING AND ANTI-ALIASING Textbook: 16 UGRAD.CS.UBC.CA/~CS314 Alla Sheffer, 2016 ALIASING & ANTI-ALIASING Adobe, inc., https://helpx.adobe.com/photoshop/key concepts/aliasing anti aliasing.html
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps
 Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps Last Time? Monte-Carlo Integration Importance Sampling Ray Tracing vs. Path Tracing source hemisphere What is a Pixel? Sampling & Reconstruction Filters in Computer Graphics
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps Last Time? Monte-Carlo Integration Importance Sampling Ray Tracing vs. Path Tracing source hemisphere What is a Pixel? Sampling & Reconstruction Filters in Computer Graphics
Basics. Sampling and Reconstruction. Sampling and Reconstruction. Outline. (Spatial) Aliasing. Advanced Computer Graphics (Fall 2010)
 Advanced Computer Graphics (Fall 2010) CS 283, Lecture 3: Sampling and Reconstruction Ravi Ramamoorthi http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs283/fa10 Some slides courtesy Thomas Funkhouser and Pat Hanrahan
Advanced Computer Graphics (Fall 2010) CS 283, Lecture 3: Sampling and Reconstruction Ravi Ramamoorthi http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs283/fa10 Some slides courtesy Thomas Funkhouser and Pat Hanrahan
Aliasing And Anti-Aliasing Sampling and Reconstruction
 Aliasing And Anti-Aliasing Sampling and Reconstruction An Introduction Computer Overview Intro - Aliasing Problem definition, Examples Ad-hoc Solutions Sampling theory Fourier transform Convolution Reconstruction
Aliasing And Anti-Aliasing Sampling and Reconstruction An Introduction Computer Overview Intro - Aliasing Problem definition, Examples Ad-hoc Solutions Sampling theory Fourier transform Convolution Reconstruction
Image Filtering, Warping and Sampling
 Image Filtering, Warping and Sampling Connelly Barnes CS 4810 University of Virginia Acknowledgement: slides by Jason Lawrence, Misha Kazhdan, Allison Klein, Tom Funkhouser, Adam Finkelstein and David
Image Filtering, Warping and Sampling Connelly Barnes CS 4810 University of Virginia Acknowledgement: slides by Jason Lawrence, Misha Kazhdan, Allison Klein, Tom Funkhouser, Adam Finkelstein and David
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps
 Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps Last Time? Monte-Carlo Integration Importance Sampling Ray Tracing vs. Path Tracing source hemisphere Sampling sensitive to choice of samples less sensitive to choice of samples
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps Last Time? Monte-Carlo Integration Importance Sampling Ray Tracing vs. Path Tracing source hemisphere Sampling sensitive to choice of samples less sensitive to choice of samples
Outline. Sampling and Reconstruction. Sampling and Reconstruction. Foundations of Computer Graphics (Fall 2012)
 Foundations of Computer Graphics (Fall 2012) CS 184, Lectures 19: Sampling and Reconstruction http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs184 Outline Basic ideas of sampling, reconstruction, aliasing Signal processing
Foundations of Computer Graphics (Fall 2012) CS 184, Lectures 19: Sampling and Reconstruction http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs184 Outline Basic ideas of sampling, reconstruction, aliasing Signal processing
Outline. Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2012)
 Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2012) CS 184, Lectures 19: Sampling and Reconstruction http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs184 Basic ideas of sampling, reconstruction, aliasing Signal processing
Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2012) CS 184, Lectures 19: Sampling and Reconstruction http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs184 Basic ideas of sampling, reconstruction, aliasing Signal processing
Ray Tracing. Johns Hopkins Department of Computer Science Course : Rendering Techniques, Professor: Jonathan Cohen
 Ray Tracing Recursive Ray Tracing Gather light from various directions by tracing rays Each pixel shows light at a surface trace ray from eye to surface Each surface illuminated by lights and other surfaces
Ray Tracing Recursive Ray Tracing Gather light from various directions by tracing rays Each pixel shows light at a surface trace ray from eye to surface Each surface illuminated by lights and other surfaces
EECS 487: Interactive Computer Graphics
 Ray Tracing EECS 487: Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 29: Distributed Ray Tracing Introduction and context ray casting Recursive ray tracing shadows reflection refraction Ray tracing implementation
Ray Tracing EECS 487: Interactive Computer Graphics Lecture 29: Distributed Ray Tracing Introduction and context ray casting Recursive ray tracing shadows reflection refraction Ray tracing implementation
Lets assume each object has a defined colour. Hence our illumination model is looks unrealistic.
 Shading Models There are two main types of rendering that we cover, polygon rendering ray tracing Polygon rendering is used to apply illumination models to polygons, whereas ray tracing applies to arbitrary
Shading Models There are two main types of rendering that we cover, polygon rendering ray tracing Polygon rendering is used to apply illumination models to polygons, whereas ray tracing applies to arbitrary
Anti-aliasing and Monte Carlo Path Tracing. Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2017
 Anti-aliasing and Monte Carlo Path Tracing Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2017 1 Reading Required: Marschner and Shirley, Section 13.4 (online handout) Pharr, Jakob, and Humphreys, Physically Based Ray Tracing:
Anti-aliasing and Monte Carlo Path Tracing Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2017 1 Reading Required: Marschner and Shirley, Section 13.4 (online handout) Pharr, Jakob, and Humphreys, Physically Based Ray Tracing:
Anti-aliasing and sampling
 Anti-aliasing and sampling 1996-2017 Josef Pelikán CGG MFF UK Praha pepca@cgg.mff.cuni.cz http://cgg.mff.cuni.cz/~pepca/ Sampling 2017 Josef Pelikán, http://cgg.mff.cuni.cz/~pepca 1 / 34 Spatial and temporal
Anti-aliasing and sampling 1996-2017 Josef Pelikán CGG MFF UK Praha pepca@cgg.mff.cuni.cz http://cgg.mff.cuni.cz/~pepca/ Sampling 2017 Josef Pelikán, http://cgg.mff.cuni.cz/~pepca 1 / 34 Spatial and temporal
Anti-aliasing and Monte Carlo Path Tracing
 Reading Required: Anti-aliasing and Monte Carlo Path Tracing Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2017 Marschner and Shirley, Section 13.4 (online handout) Pharr, Jakob, and Humphreys, Physically Based Ray Tracing:
Reading Required: Anti-aliasing and Monte Carlo Path Tracing Brian Curless CSE 557 Autumn 2017 Marschner and Shirley, Section 13.4 (online handout) Pharr, Jakob, and Humphreys, Physically Based Ray Tracing:
Sampling and Monte-Carlo Integration
 Sampling and Monte-Carlo Integration Sampling and Monte-Carlo Integration Last Time Pixels are samples Sampling theorem Convolution & multiplication Aliasing: spectrum replication Ideal filter And its
Sampling and Monte-Carlo Integration Sampling and Monte-Carlo Integration Last Time Pixels are samples Sampling theorem Convolution & multiplication Aliasing: spectrum replication Ideal filter And its
Advanced Ray Tracing
 Advanced Ray Tracing Thanks to Fredo Durand and Barb Cutler The Ray Tree Ni surface normal Ri reflected ray Li shadow ray Ti transmitted (refracted) ray 51 MIT EECS 6.837, Cutler and Durand 1 Ray Tree
Advanced Ray Tracing Thanks to Fredo Durand and Barb Cutler The Ray Tree Ni surface normal Ri reflected ray Li shadow ray Ti transmitted (refracted) ray 51 MIT EECS 6.837, Cutler and Durand 1 Ray Tree
Lecture 2: 2D Fourier transforms and applications
 Lecture 2: 2D Fourier transforms and applications B14 Image Analysis Michaelmas 2017 Dr. M. Fallon Fourier transforms and spatial frequencies in 2D Definition and meaning The Convolution Theorem Applications
Lecture 2: 2D Fourier transforms and applications B14 Image Analysis Michaelmas 2017 Dr. M. Fallon Fourier transforms and spatial frequencies in 2D Definition and meaning The Convolution Theorem Applications
Today. Anti-aliasing Surface Parametrization Soft Shadows Global Illumination. Exercise 2. Path Tracing Radiosity
 Today Anti-aliasing Surface Parametrization Soft Shadows Global Illumination Path Tracing Radiosity Exercise 2 Sampling Ray Casting is a form of discrete sampling. Rendered Image: Sampling of the ground
Today Anti-aliasing Surface Parametrization Soft Shadows Global Illumination Path Tracing Radiosity Exercise 2 Sampling Ray Casting is a form of discrete sampling. Rendered Image: Sampling of the ground
Topic 12: Texture Mapping. Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates Bump mapping, mip-mapping & env mapping
 Topic 12: Texture Mapping Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates Bump mapping, mip-mapping & env mapping Texture sources: Photographs Texture sources: Procedural Texture sources: Solid textures
Topic 12: Texture Mapping Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates Bump mapping, mip-mapping & env mapping Texture sources: Photographs Texture sources: Procedural Texture sources: Solid textures
Topic 11: Texture Mapping 11/13/2017. Texture sources: Solid textures. Texture sources: Synthesized
 Topic 11: Texture Mapping Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates Bump mapping, mip mapping & env mapping Texture sources: Photographs Texture sources: Procedural Texture sources: Solid textures
Topic 11: Texture Mapping Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates Bump mapping, mip mapping & env mapping Texture sources: Photographs Texture sources: Procedural Texture sources: Solid textures
Visual Pathways to the Brain
 Visual Pathways to the Brain 1 Left half of visual field which is imaged on the right half of each retina is transmitted to right half of brain. Vice versa for right half of visual field. From each eye
Visual Pathways to the Brain 1 Left half of visual field which is imaged on the right half of each retina is transmitted to right half of brain. Vice versa for right half of visual field. From each eye
I have a meeting with Peter Lee and Bob Cosgrove on Wednesday to discuss the future of the cluster. Computer Graphics
 Announcements Assignment 4 will be out later today Problem Set 3 is due today or tomorrow by 9am in my mail box (4 th floor NSH) How are the machines working out? I have a meeting with Peter Lee and Bob
Announcements Assignment 4 will be out later today Problem Set 3 is due today or tomorrow by 9am in my mail box (4 th floor NSH) How are the machines working out? I have a meeting with Peter Lee and Bob
Topic 11: Texture Mapping 10/21/2015. Photographs. Solid textures. Procedural
 Topic 11: Texture Mapping Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates Bump mapping, mip mapping & env mapping Topic 11: Photographs Texture Mapping Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates
Topic 11: Texture Mapping Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates Bump mapping, mip mapping & env mapping Topic 11: Photographs Texture Mapping Motivation Sources of texture Texture coordinates
Anti-aliasing and Monte Carlo Path Tracing. Brian Curless CSE 457 Autumn 2017
 Anti-aliasing and Monte Carlo Path Tracing Brian Curless CSE 457 Autumn 2017 1 Reading Required: Marschner and Shirley, Section 13.4 (online handout) Further reading: Pharr, Jakob, and Humphreys, Physically
Anti-aliasing and Monte Carlo Path Tracing Brian Curless CSE 457 Autumn 2017 1 Reading Required: Marschner and Shirley, Section 13.4 (online handout) Further reading: Pharr, Jakob, and Humphreys, Physically
CS5620 Intro to Computer Graphics
 So Far wireframe hidden surfaces Next step 1 2 Light! Need to understand: How lighting works Types of lights Types of surfaces How shading works Shading algorithms What s Missing? Lighting vs. Shading
So Far wireframe hidden surfaces Next step 1 2 Light! Need to understand: How lighting works Types of lights Types of surfaces How shading works Shading algorithms What s Missing? Lighting vs. Shading
The simplest and most obvious method to go from a continuous to a discrete image is by point sampling,
 Sampling our scenes are described with triangles giving a continuous 2d color field our images are digital/discrete made up of a grid of dots need to make a bridge between these two worlds else we will
Sampling our scenes are described with triangles giving a continuous 2d color field our images are digital/discrete made up of a grid of dots need to make a bridge between these two worlds else we will
Distributed Ray Tracing
 CT5510: Computer Graphics Distributed Ray Tracing BOCHANG MOON Distributed Ray Tracing Motivation The classical ray tracing produces very clean images (look fake) Perfect focus Perfect reflections Sharp
CT5510: Computer Graphics Distributed Ray Tracing BOCHANG MOON Distributed Ray Tracing Motivation The classical ray tracing produces very clean images (look fake) Perfect focus Perfect reflections Sharp
Computer Graphics. Lecture 8 Antialiasing, Texture Mapping
 Computer Graphics Lecture 8 Antialiasing, Texture Mapping Today Texture mapping Antialiasing Antialiasing-textures Texture Mapping : Why needed? Adding details using high resolution polygon meshes is costly
Computer Graphics Lecture 8 Antialiasing, Texture Mapping Today Texture mapping Antialiasing Antialiasing-textures Texture Mapping : Why needed? Adding details using high resolution polygon meshes is costly
Fall CSCI 420: Computer Graphics. 7.1 Rasterization. Hao Li.
 Fall 2015 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 7.1 Rasterization Hao Li http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 Rendering Pipeline 2 Outline Scan Conversion for Lines Scan Conversion for Polygons Antialiasing 3 Rasterization
Fall 2015 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 7.1 Rasterization Hao Li http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 Rendering Pipeline 2 Outline Scan Conversion for Lines Scan Conversion for Polygons Antialiasing 3 Rasterization
Image processing in frequency Domain
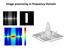 Image processing in frequency Domain Introduction to Frequency Domain Deal with images in: -Spatial domain -Frequency domain Frequency Domain In the frequency or Fourier domain, the value and location
Image processing in frequency Domain Introduction to Frequency Domain Deal with images in: -Spatial domain -Frequency domain Frequency Domain In the frequency or Fourier domain, the value and location
Image Sampling and Quantisation
 Image Sampling and Quantisation Introduction to Signal and Image Processing Prof. Dr. Philippe Cattin MIAC, University of Basel 1 of 46 22.02.2016 09:17 Contents Contents 1 Motivation 2 Sampling Introduction
Image Sampling and Quantisation Introduction to Signal and Image Processing Prof. Dr. Philippe Cattin MIAC, University of Basel 1 of 46 22.02.2016 09:17 Contents Contents 1 Motivation 2 Sampling Introduction
Image Processing, Warping, and Sampling
 Image Processing, Warping, and Sampling Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) HB Ch. 4.8 FvDFH Ch. 14.10 Outline Image Processing Image Warping Image Sampling Image Processing What about the case when the modification
Image Processing, Warping, and Sampling Michael Kazhdan (601.457/657) HB Ch. 4.8 FvDFH Ch. 14.10 Outline Image Processing Image Warping Image Sampling Image Processing What about the case when the modification
Image Sampling & Quantisation
 Image Sampling & Quantisation Biomedical Image Analysis Prof. Dr. Philippe Cattin MIAC, University of Basel Contents 1 Motivation 2 Sampling Introduction and Motivation Sampling Example Quantisation Example
Image Sampling & Quantisation Biomedical Image Analysis Prof. Dr. Philippe Cattin MIAC, University of Basel Contents 1 Motivation 2 Sampling Introduction and Motivation Sampling Example Quantisation Example
Dr Pavan Chakraborty IIIT-Allahabad
 GVC-43 Lecture - 5 Ref: Donald Hearn & M. Pauline Baker, Comuter Grahics Foley, van Dam, Feiner & Hughes, Comuter Grahics Princiles & Practice Dr Pavan Chakraborty IIIT-Allahabad Summary of line drawing
GVC-43 Lecture - 5 Ref: Donald Hearn & M. Pauline Baker, Comuter Grahics Foley, van Dam, Feiner & Hughes, Comuter Grahics Princiles & Practice Dr Pavan Chakraborty IIIT-Allahabad Summary of line drawing
Lighting and Shading
 Lighting and Shading Today: Local Illumination Solving the rendering equation is too expensive First do local illumination Then hack in reflections and shadows Local Shading: Notation light intensity in,
Lighting and Shading Today: Local Illumination Solving the rendering equation is too expensive First do local illumination Then hack in reflections and shadows Local Shading: Notation light intensity in,
Filtering theory: Battling Aliasing with Antialiasing. Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology
 Filtering theory: Battling Aliasing with Antialiasing Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology 1 What is aliasing? 2 Why care at all? l Quality!! l Example: Final fantasy The
Filtering theory: Battling Aliasing with Antialiasing Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology 1 What is aliasing? 2 Why care at all? l Quality!! l Example: Final fantasy The
Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps
 Last Time? Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps 2D Texture Mapping Perspective Correct Interpolation Common Texture Coordinate Projections Bump Mapping Displacement Mapping Environment Mapping Texture Maps for
Last Time? Sampling, Aliasing, & Mipmaps 2D Texture Mapping Perspective Correct Interpolation Common Texture Coordinate Projections Bump Mapping Displacement Mapping Environment Mapping Texture Maps for
Reading. 18. Projections and Z-buffers. Required: Watt, Section , 6.3, 6.6 (esp. intro and subsections 1, 4, and 8 10), Further reading:
 Reading Required: Watt, Section 5.2.2 5.2.4, 6.3, 6.6 (esp. intro and subsections 1, 4, and 8 10), Further reading: 18. Projections and Z-buffers Foley, et al, Chapter 5.6 and Chapter 6 David F. Rogers
Reading Required: Watt, Section 5.2.2 5.2.4, 6.3, 6.6 (esp. intro and subsections 1, 4, and 8 10), Further reading: 18. Projections and Z-buffers Foley, et al, Chapter 5.6 and Chapter 6 David F. Rogers
Fourier analysis and sampling theory
 Reading Required: Shirley, Ch. 9 Recommended: Fourier analysis and sampling theory Ron Bracewell, The Fourier Transform and Its Applications, McGraw-Hill. Don P. Mitchell and Arun N. Netravali, Reconstruction
Reading Required: Shirley, Ch. 9 Recommended: Fourier analysis and sampling theory Ron Bracewell, The Fourier Transform and Its Applications, McGraw-Hill. Don P. Mitchell and Arun N. Netravali, Reconstruction
Problem Set 4 Part 1 CMSC 427 Distributed: Thursday, November 1, 2007 Due: Tuesday, November 20, 2007
 Problem Set 4 Part 1 CMSC 427 Distributed: Thursday, November 1, 2007 Due: Tuesday, November 20, 2007 Programming For this assignment you will write a simple ray tracer. It will be written in C++ without
Problem Set 4 Part 1 CMSC 427 Distributed: Thursday, November 1, 2007 Due: Tuesday, November 20, 2007 Programming For this assignment you will write a simple ray tracer. It will be written in C++ without
Computer Vision. Fourier Transform. 20 January Copyright by NHL Hogeschool and Van de Loosdrecht Machine Vision BV All rights reserved
 Van de Loosdrecht Machine Vision Computer Vision Fourier Transform 20 January 2017 Copyright 2001 2017 by NHL Hogeschool and Van de Loosdrecht Machine Vision BV All rights reserved j.van.de.loosdrecht@nhl.nl,
Van de Loosdrecht Machine Vision Computer Vision Fourier Transform 20 January 2017 Copyright 2001 2017 by NHL Hogeschool and Van de Loosdrecht Machine Vision BV All rights reserved j.van.de.loosdrecht@nhl.nl,
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 14. Rasterization. Scan Conversion Antialiasing [Angel Ch. 6] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California
![CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 14. Rasterization. Scan Conversion Antialiasing [Angel Ch. 6] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 14. Rasterization. Scan Conversion Antialiasing [Angel Ch. 6] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California](/thumbs/86/93458757.jpg) CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 14 Rasterization Scan Conversion Antialiasing [Angel Ch. 6] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California 1 Rasterization (scan conversion) Final step in pipeline:
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 14 Rasterization Scan Conversion Antialiasing [Angel Ch. 6] Jernej Barbic University of Southern California 1 Rasterization (scan conversion) Final step in pipeline:
COMP371 COMPUTER GRAPHICS
 COMP371 COMPUTER GRAPHICS LECTURE 14 RASTERIZATION 1 Lecture Overview Review of last class Line Scan conversion Polygon Scan conversion Antialiasing 2 Rasterization The raster display is a matrix of picture
COMP371 COMPUTER GRAPHICS LECTURE 14 RASTERIZATION 1 Lecture Overview Review of last class Line Scan conversion Polygon Scan conversion Antialiasing 2 Rasterization The raster display is a matrix of picture
Homework 3: Shading, Raytracing, and Image Processing
 Computer Graphics CSE 457, Spring 1999 Craig Kaplan Douglas Zongker Homework 3: Shading, Raytracing, and Image Processing Received: Friday May 7, 1999 Due: Friday May 21, 1999 DIRECTIONS Please provide
Computer Graphics CSE 457, Spring 1999 Craig Kaplan Douglas Zongker Homework 3: Shading, Raytracing, and Image Processing Received: Friday May 7, 1999 Due: Friday May 21, 1999 DIRECTIONS Please provide
Last Time: Acceleration Data Structures for Ray Tracing. Schedule. Today. Shadows & Light Sources. Shadows
 Last Time: Acceleration Data Structures for Ray Tracing Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Scan Conversion
Last Time: Acceleration Data Structures for Ray Tracing Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Scan Conversion
Rasterization. Rasterization (scan conversion) Digital Differential Analyzer (DDA) Rasterizing a line. Digital Differential Analyzer (DDA)
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 14 Rasterization Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Scan Conversion Antialiasing [Angel Ch. 6] Rasterization (scan conversion) Final step in pipeline: rasterization
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 14 Rasterization Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Scan Conversion Antialiasing [Angel Ch. 6] Rasterization (scan conversion) Final step in pipeline: rasterization
lecture 18 - ray tracing - environment mapping - refraction
 lecture 18 - ray tracing - environment mapping - refraction Recall Ray Casting (lectures 7, 8) for each pixel (x,y) { cast a ray through that pixel into the scene, and find the closest surface along the
lecture 18 - ray tracing - environment mapping - refraction Recall Ray Casting (lectures 7, 8) for each pixel (x,y) { cast a ray through that pixel into the scene, and find the closest surface along the
Computer Vision and Graphics (ee2031) Digital Image Processing I
 Computer Vision and Graphics (ee203) Digital Image Processing I Dr John Collomosse J.Collomosse@surrey.ac.uk Centre for Vision, Speech and Signal Processing University of Surrey Learning Outcomes After
Computer Vision and Graphics (ee203) Digital Image Processing I Dr John Collomosse J.Collomosse@surrey.ac.uk Centre for Vision, Speech and Signal Processing University of Surrey Learning Outcomes After
An Intuitive Explanation of Fourier Theory
 An Intuitive Explanation of Fourier Theory Steven Lehar slehar@cns.bu.edu Fourier theory is pretty complicated mathematically. But there are some beautifully simple holistic concepts behind Fourier theory
An Intuitive Explanation of Fourier Theory Steven Lehar slehar@cns.bu.edu Fourier theory is pretty complicated mathematically. But there are some beautifully simple holistic concepts behind Fourier theory
Attributes of Graphics Primitives
 ttributes for Graphics Output Primitives ttributes of Graphics Primitives in 2 points, lines polygons, circles, ellipses & other curves (also filled) characters in 3 triangles & other polygons anti-aliasing
ttributes for Graphics Output Primitives ttributes of Graphics Primitives in 2 points, lines polygons, circles, ellipses & other curves (also filled) characters in 3 triangles & other polygons anti-aliasing
Sampling: Antialiasing - Intro
 Sampling: Antialiasing - Intro Aliasing effects occur due to fact that the basic tracer 1. Casts a single ray per pixel 2. Casts the rays in a regular pattern Only a single color is possible for a given
Sampling: Antialiasing - Intro Aliasing effects occur due to fact that the basic tracer 1. Casts a single ray per pixel 2. Casts the rays in a regular pattern Only a single color is possible for a given
Fourier Transform in Image Processing. CS/BIOEN 6640 U of Utah Guido Gerig (slides modified from Marcel Prastawa 2012)
 Fourier Transform in Image Processing CS/BIOEN 6640 U of Utah Guido Gerig (slides modified from Marcel Prastawa 2012) 1D: Common Transform Pairs Summary source FT Properties: Convolution See book DIP 4.2.5:
Fourier Transform in Image Processing CS/BIOEN 6640 U of Utah Guido Gerig (slides modified from Marcel Prastawa 2012) 1D: Common Transform Pairs Summary source FT Properties: Convolution See book DIP 4.2.5:
ECS 175 COMPUTER GRAPHICS. Ken Joy.! Winter 2014
 ECS 175 COMPUTER GRAPHICS Ken Joy Winter 2014 Shading To be able to model shading, we simplify Uniform Media no scattering of light Opaque Objects No Interreflection Point Light Sources RGB Color (eliminating
ECS 175 COMPUTER GRAPHICS Ken Joy Winter 2014 Shading To be able to model shading, we simplify Uniform Media no scattering of light Opaque Objects No Interreflection Point Light Sources RGB Color (eliminating
CS 4620 Midterm, March 21, 2017
 CS 460 Midterm, March 1, 017 This 90-minute exam has 4 questions worth a total of 100 points. Use the back of the pages if you need more space. Academic Integrity is expected of all students of Cornell
CS 460 Midterm, March 1, 017 This 90-minute exam has 4 questions worth a total of 100 points. Use the back of the pages if you need more space. Academic Integrity is expected of all students of Cornell
Sampling, Resampling, and Warping. COS 426, Spring 2014 Tom Funkhouser
 Sampling, Resampling, and Warping COS 426, Spring 2014 Tom Funkhouser Image Processing Goal: read an image, process it, write the result input.jpg output.jpg imgpro input.jpg output.jpg histogram_equalization
Sampling, Resampling, and Warping COS 426, Spring 2014 Tom Funkhouser Image Processing Goal: read an image, process it, write the result input.jpg output.jpg imgpro input.jpg output.jpg histogram_equalization
Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 )
 CS380: Computer Graphics Ray Tracing Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL: http://sglab.kaist.ac.kr/~sungeui/cg/ Class Objectives Understand overall algorithm of recursive ray tracing Ray generations Intersection
CS380: Computer Graphics Ray Tracing Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL: http://sglab.kaist.ac.kr/~sungeui/cg/ Class Objectives Understand overall algorithm of recursive ray tracing Ray generations Intersection
Filtering theory: Battling Aliasing with Antialiasing. Tomas Akenine-Möller Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology
 Filtering theory: Battling Aliasing with Antialiasing Tomas Akenine-Möller Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology 1 What is aliasing? 2 Why care at all? l Quality!! l Example:
Filtering theory: Battling Aliasing with Antialiasing Tomas Akenine-Möller Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology 1 What is aliasing? 2 Why care at all? l Quality!! l Example:
Reading. 2. Fourier analysis and sampling theory. Required: Watt, Section 14.1 Recommended:
 Reading Required: Watt, Section 14.1 Recommended: 2. Fourier analysis and sampling theory Ron Bracewell, The Fourier Transform and Its Applications, McGraw-Hill. Don P. Mitchell and Arun N. Netravali,
Reading Required: Watt, Section 14.1 Recommended: 2. Fourier analysis and sampling theory Ron Bracewell, The Fourier Transform and Its Applications, McGraw-Hill. Don P. Mitchell and Arun N. Netravali,
EF432. Introduction to spagetti and meatballs
 EF432 Introduction to spagetti and meatballs CSC 418/2504: Computer Graphics Course web site (includes course information sheet): http://www.dgp.toronto.edu/~karan/courses/418/ Instructors: L2501, T 6-8pm
EF432 Introduction to spagetti and meatballs CSC 418/2504: Computer Graphics Course web site (includes course information sheet): http://www.dgp.toronto.edu/~karan/courses/418/ Instructors: L2501, T 6-8pm
Anti-aliasing. Images and Aliasing
 CS 130 Anti-aliasing Images and Aliasing Aliasing errors caused by rasterizing How to correct them, in general 2 1 Aliased Lines Stair stepping and jaggies 3 Remove the jaggies Anti-aliased Lines 4 2 Aliasing
CS 130 Anti-aliasing Images and Aliasing Aliasing errors caused by rasterizing How to correct them, in general 2 1 Aliased Lines Stair stepping and jaggies 3 Remove the jaggies Anti-aliased Lines 4 2 Aliasing
Scaled representations
 Scaled representations Big bars (resp. spots, hands, etc.) and little bars are both interesting Stripes and hairs, say Inefficient to detect big bars with big filters And there is superfluous detail in
Scaled representations Big bars (resp. spots, hands, etc.) and little bars are both interesting Stripes and hairs, say Inefficient to detect big bars with big filters And there is superfluous detail in
Today. Acceleration Data Structures for Ray Tracing. Cool results from Assignment 2. Last Week: Questions? Schedule
 Today Acceleration Data Structures for Ray Tracing Cool results from Assignment 2 Last Week: koi seantek Ray Tracing Shadows Reflection Refraction Local Illumination Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution
Today Acceleration Data Structures for Ray Tracing Cool results from Assignment 2 Last Week: koi seantek Ray Tracing Shadows Reflection Refraction Local Illumination Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution
Computer Graphics. Rendering. by Brian Wyvill University of Calgary. cpsc/enel P 1
 Computer Graphics Rendering by Brian Wyvill University of Calgary cpsc/enel P Rendering Techniques Wire Frame Z Buffer Ray Tracing A Buffer cpsc/enel P 2 Rendering Visible Surface Determination Many Algorithms,
Computer Graphics Rendering by Brian Wyvill University of Calgary cpsc/enel P Rendering Techniques Wire Frame Z Buffer Ray Tracing A Buffer cpsc/enel P 2 Rendering Visible Surface Determination Many Algorithms,
Building a Fast Ray Tracer
 Abstract Ray tracing is often used in renderers, as it can create very high quality images at the expense of run time. It is useful because of its ability to solve many different problems in image rendering.
Abstract Ray tracing is often used in renderers, as it can create very high quality images at the expense of run time. It is useful because of its ability to solve many different problems in image rendering.
Today. Global illumination. Shading. Interactive applications. Rendering pipeline. Computergrafik. Shading Introduction Local shading models
 Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2009 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation of physics Global
Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2009 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation of physics Global
2D rendering takes a photo of the 2D scene with a virtual camera that selects an axis aligned rectangle from the scene. The photograph is placed into
 2D rendering takes a photo of the 2D scene with a virtual camera that selects an axis aligned rectangle from the scene. The photograph is placed into the viewport of the current application window. A pixel
2D rendering takes a photo of the 2D scene with a virtual camera that selects an axis aligned rectangle from the scene. The photograph is placed into the viewport of the current application window. A pixel
Spatial Enhancement Definition
 Spatial Enhancement Nickolas Faust The Electro- Optics, Environment, and Materials Laboratory Georgia Tech Research Institute Georgia Institute of Technology Definition Spectral enhancement relies on changing
Spatial Enhancement Nickolas Faust The Electro- Optics, Environment, and Materials Laboratory Georgia Tech Research Institute Georgia Institute of Technology Definition Spectral enhancement relies on changing
IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS
 2017 Imaging Science Ph.D. Qualifying Examination June 9, 2017 9:00AM to 12:00PM IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS You must complete two (2) of the three (3) questions given for each of the core graduate classes.
2017 Imaging Science Ph.D. Qualifying Examination June 9, 2017 9:00AM to 12:00PM IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS You must complete two (2) of the three (3) questions given for each of the core graduate classes.
Local vs. Global Illumination & Radiosity
 Last Time? Local vs. Global Illumination & Radiosity Ray Casting & Ray-Object Intersection Recursive Ray Tracing Distributed Ray Tracing An early application of radiative heat transfer in stables. Reading
Last Time? Local vs. Global Illumination & Radiosity Ray Casting & Ray-Object Intersection Recursive Ray Tracing Distributed Ray Tracing An early application of radiative heat transfer in stables. Reading
Applications of Image Filters
 02/04/0 Applications of Image Filters Computer Vision CS 543 / ECE 549 University of Illinois Derek Hoiem Review: Image filtering g[, ] f [.,.] h[.,.] 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 90
02/04/0 Applications of Image Filters Computer Vision CS 543 / ECE 549 University of Illinois Derek Hoiem Review: Image filtering g[, ] f [.,.] h[.,.] 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 90
Anti-aliased and accelerated ray tracing. University of Texas at Austin CS384G - Computer Graphics Fall 2010 Don Fussell
 Anti-aliased and accelerated ray tracing University of Texas at Austin CS384G - Computer Graphics Fall 2010 Don Fussell Reading Required: Watt, sections 12.5.3 12.5.4, 14.7 Further reading: A. Glassner.
Anti-aliased and accelerated ray tracing University of Texas at Austin CS384G - Computer Graphics Fall 2010 Don Fussell Reading Required: Watt, sections 12.5.3 12.5.4, 14.7 Further reading: A. Glassner.
Distribution Ray-Tracing. Programação 3D Simulação e Jogos
 Distribution Ray-Tracing Programação 3D Simulação e Jogos Bibliography K. Suffern; Ray Tracing from the Ground Up, http://www.raytracegroundup.com Chapter 4, 5 for Anti-Aliasing Chapter 6 for Disc Sampling
Distribution Ray-Tracing Programação 3D Simulação e Jogos Bibliography K. Suffern; Ray Tracing from the Ground Up, http://www.raytracegroundup.com Chapter 4, 5 for Anti-Aliasing Chapter 6 for Disc Sampling
Anti-aliased and accelerated ray tracing. University of Texas at Austin CS384G - Computer Graphics
 Anti-aliased and accelerated ray tracing University of Texas at Austin CS384G - Computer Graphics Fall 2010 Don Fussell eading! equired:! Watt, sections 12.5.3 12.5.4, 14.7! Further reading:! A. Glassner.
Anti-aliased and accelerated ray tracing University of Texas at Austin CS384G - Computer Graphics Fall 2010 Don Fussell eading! equired:! Watt, sections 12.5.3 12.5.4, 14.7! Further reading:! A. Glassner.
Logistics. CS 586/480 Computer Graphics II. Questions from Last Week? Slide Credits
 CS 586/480 Computer Graphics II Dr. David Breen Matheson 408 Thursday 6PM Æ 8:50PM Presentation 4 10/28/04 Logistics Read research paper and prepare summary and question P. Hanrahan, "Ray Tracing Algebraic
CS 586/480 Computer Graphics II Dr. David Breen Matheson 408 Thursday 6PM Æ 8:50PM Presentation 4 10/28/04 Logistics Read research paper and prepare summary and question P. Hanrahan, "Ray Tracing Algebraic
Topics and things to know about them:
 Practice Final CMSC 427 Distributed Tuesday, December 11, 2007 Review Session, Monday, December 17, 5:00pm, 4424 AV Williams Final: 10:30 AM Wednesday, December 19, 2007 General Guidelines: The final will
Practice Final CMSC 427 Distributed Tuesday, December 11, 2007 Review Session, Monday, December 17, 5:00pm, 4424 AV Williams Final: 10:30 AM Wednesday, December 19, 2007 General Guidelines: The final will
CS 543: Computer Graphics. Rasterization
 CS 543: Computer Graphics Rasterization Robert W. Lindeman Associate Professor Interactive Media & Game Development Department of Computer Science Worcester Polytechnic Institute gogo@wpi.edu (with lots
CS 543: Computer Graphics Rasterization Robert W. Lindeman Associate Professor Interactive Media & Game Development Department of Computer Science Worcester Polytechnic Institute gogo@wpi.edu (with lots
Ray-tracing Acceleration. Acceleration Data Structures for Ray Tracing. Shadows. Shadows & Light Sources. Antialiasing Supersampling.
 Ray-tracing Acceleration Acceleration Data Structures for Ray Tracing Thanks to Fredo Durand and Barb Cutler Soft shadows Antialiasing (getting rid of jaggies) Glossy reflection Motion blur Depth of field
Ray-tracing Acceleration Acceleration Data Structures for Ray Tracing Thanks to Fredo Durand and Barb Cutler Soft shadows Antialiasing (getting rid of jaggies) Glossy reflection Motion blur Depth of field
Image Processing. Overview. Trade spatial resolution for intensity resolution Reduce visual artifacts due to quantization. Sampling and Reconstruction
 Image Processing Overview Image Representation What is an image? Halftoning and Dithering Trade spatial resolution for intensity resolution Reduce visual artifacts due to quantization Sampling and Reconstruction
Image Processing Overview Image Representation What is an image? Halftoning and Dithering Trade spatial resolution for intensity resolution Reduce visual artifacts due to quantization Sampling and Reconstruction
EF432. Introduction to spagetti and meatballs
 EF432 Introduction to spagetti and meatballs CSC 418/2504: Computer Graphics Course web site (includes course information sheet): http://www.dgp.toronto.edu/~karan/courses/418/fall2015 Instructor: Karan
EF432 Introduction to spagetti and meatballs CSC 418/2504: Computer Graphics Course web site (includes course information sheet): http://www.dgp.toronto.edu/~karan/courses/418/fall2015 Instructor: Karan
Edges, interpolation, templates. Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD (with thanks to David Forsyth)
 Edges, interpolation, templates Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD (with thanks to David Forsyth) Edge detection edge detection has many applications in image processing an edge detector implements
Edges, interpolation, templates Nuno Vasconcelos ECE Department, UCSD (with thanks to David Forsyth) Edge detection edge detection has many applications in image processing an edge detector implements
graphics pipeline computer graphics graphics pipeline 2009 fabio pellacini 1
 graphics pipeline computer graphics graphics pipeline 2009 fabio pellacini 1 graphics pipeline sequence of operations to generate an image using object-order processing primitives processed one-at-a-time
graphics pipeline computer graphics graphics pipeline 2009 fabio pellacini 1 graphics pipeline sequence of operations to generate an image using object-order processing primitives processed one-at-a-time
Sampling and Reconstruction
 Sampling and Reconstruction Sampling and Reconstruction Sampling and Spatial Resolution Spatial Aliasing Problem: Spatial aliasing is insufficient sampling of data along the space axis, which occurs because
Sampling and Reconstruction Sampling and Reconstruction Sampling and Spatial Resolution Spatial Aliasing Problem: Spatial aliasing is insufficient sampling of data along the space axis, which occurs because
graphics pipeline computer graphics graphics pipeline 2009 fabio pellacini 1
 graphics pipeline computer graphics graphics pipeline 2009 fabio pellacini 1 graphics pipeline sequence of operations to generate an image using object-order processing primitives processed one-at-a-time
graphics pipeline computer graphics graphics pipeline 2009 fabio pellacini 1 graphics pipeline sequence of operations to generate an image using object-order processing primitives processed one-at-a-time
COMP 4801 Final Year Project. Ray Tracing for Computer Graphics. Final Project Report FYP Runjing Liu. Advised by. Dr. L.Y.
 COMP 4801 Final Year Project Ray Tracing for Computer Graphics Final Project Report FYP 15014 by Runjing Liu Advised by Dr. L.Y. Wei 1 Abstract The goal of this project was to use ray tracing in a rendering
COMP 4801 Final Year Project Ray Tracing for Computer Graphics Final Project Report FYP 15014 by Runjing Liu Advised by Dr. L.Y. Wei 1 Abstract The goal of this project was to use ray tracing in a rendering
Michael Moody School of Pharmacy University of London 29/39 Brunswick Square London WC1N 1AX, U.K.
 This material is provided for educational use only. The information in these slides including all data, images and related materials are the property of : Michael Moody School of Pharmacy University of
This material is provided for educational use only. The information in these slides including all data, images and related materials are the property of : Michael Moody School of Pharmacy University of
