EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 09 - Parallelism
|
|
|
- Allen Gilbert
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 09 - Parallelism Feb 19, 2013 John Wawrzynek Spring 2013 EECS150 - Lec09-parallel Page 1 Parallelism Parallelism is the act of doing more than one thing at a time. Optimization in hardware design often involves using parallelism to trade between cost and performance. Example, Student final grade calculation: read mt1, mt2, mt3, project; grade = 0.2 mt mt mt project; write grade; High performance hardware implementation: As many operations as possible are done in parallel. Spring 2013 EECS150 - Lec09-parallel Page 2
2 Parallelism Is there a lower cost hardware implementation? Different tree organization? Can factor out multiply by 0.2: How about sharing operators (multipliers and adders)? Spring 2013 EECS150 - Lec09-parallel Page 3 Time multiplex single ALU for all adds and multiplies: Attempts to minimize cost at the expense of time. Need to add extra register, muxes, control. Time-Multiplexing If we adopt above approach, we can then consider the combinational hardware circuit diagram as an abstract computation-graph. Using other primitives, other coverings are possible. This time-multiplexing covers the computation graph by performing the action of each node one at a time. (Sort of emulates it.) Spring 2013 EECS150 - Lec09-parallel Page 4
3 HW versus SW This time-multiplexed ALU approach is very similar to what a conventional software version would accomplish: CPUs time-multiplex function units (ALUs, etc.) add r2,r1,r3 add r2,r2,r4 mult r2,r4,r5. This model matches our tendency to express computation sequentially - even though most computations naturally contain parallelism. Our programming languages also strengthen a sequential tendency. In hardware we have the ability to exploit problem parallelism - gives us a knob to tradeoff performance & cost. Maybe best to express computations as abstract computations graphs (rather than programs ) - should lead to wider range of implementations. Note: modern processors spend much of their cost budget attempting to restore execution parallelism: super-scalar execution. Spring 2013 EECS150 - Lec09-parallel Page 5 Example: Video Codec Exploiting Parallelism in HW Separate algorithm blocks implemented in separate HW blocks, or HW is time-multiplexed. Entire operation is pipelined (with possible pipelining within the blocks). Loop unrolling used within blocks or for entire computation. Spring 2013 EECS150 - Lec09-parallel Page 6
4 Optimizing Iterative Computations Hardware implementations of computations almost always involves looping. Why? Is this true with software? Are there programs without loops? Maybe in through away code. We probably would not bother building such a thing into hardware, would we? (FPGA may change this.) Fact is, our computations are closely tied to loops. Almost all our HW includes some looping mechanism. What do we use looping for? Spring 2013 EECS150 - Lec09-parallel Page 7 Optimizing Iterative Computations Types of loops: 1) Looping over input data (streaming): ex: MP3 player, video compressor, music synthesizer. 2) Looping over memory data ex: vector inner product, matrix multiply, list-processing 1) & 2) are really very similar. 1) is often turned into 2) by buffering up input data, and processing offline. Even for online processing, buffers are used to smooth out temporary rate mismatches. 3) CPUs are one big loop. Instruction fetch execute Instruction fetch execute but change their personality with each iteration. 4) Others? Loops offer opportunity for parallelism by executing more than one iteration at once, using parallel iteration execution &/or pipelining Spring 2013 EECS150 - Lec09-parallel Page 8
5 Pipelining Principle With looping usually we are less interested in the latency of one iteration and more in the loop execution rate, or throughput. These can be different due to parallel iteration execution &/or pipelining. Pipelining review from CS61C: Analog to washing clothes: step 1: wash step 2: dry step 3: fold (20 minutes) (20 minutes) (20 minutes) 60 minutes x 4 loads 4 hours wash dry fold 20 min overlapped 2 hours Spring 2013 EECS150 - Lec09-parallel Page 9 Pipelining wash dry fold In the limit, as we increase the number of loads, the average time per load approaches 20 minutes. The latency (time from start to end) for one load = 60 min. The throughput = 3 loads/hour The pipelined throughput # of pipe stages x un-pipelined throughput. Spring 2013 EECS150 - Lec09-parallel Page 10
6 Pipelining General principle: Assume T=8ns T FF (setup +clk q)=1ns F = 1/9ns = 111MHz Cut the CL block into pieces (stages) and separate with registers: T = 4ns + 1ns + 4ns +1ns = 10ns F = 1/(4ns +1ns) = 200MHz Assume T1 = T2 = 4ns CL block produces a new result every 5ns instead of every 9ns. Spring 2013 EECS150 - Lec09-parallel Page 11 Limits on Pipelining Without FF overhead, throughput improvement α # of stages. After many stages are added FF overhead begins to dominate: FF overhead is the setup and clk to Q times. Other limiters to effective pipelining: clock skew contributes to clock overhead unequal stages FFs dominate cost clock distribution power consumption feedback (dependencies between loop iterations) Spring 2013 EECS150 - Lec09-parallel Page 12
7 Pipelining Example F(x) = y i = a x i 2 + b x i + c Computation graph: x and y are assumed to be streams Divide into 3 (nearly) equal stages. Insert pipeline registers at dashed lines. Can we pipeline basic operators? Spring 2013 EECS150 - Lec09-parallel Page 13 Possible, but usually not done. (arithmetic units can often be made sufficiently fast without internal pipelining) Example: Pipelined Adder Spring 2013 EECS150 - Lec09-parallel Page 14
8 Pipelining Loops with Feedback Example 1: y i = y i-1 + x i + a unpipelined version: add 1 x i +y i-1 x i+1 +y i add 2 y i y i+1 Loop carry dependency Can we cut the feedback and overlap iterations? Try putting a register after add1: add 1 x i +y i-1 x i+1 +y i add 2 y i y i+1 Can t overlap the iterations because of the dependency. The extra register doesn t help the situation (actually hurts). In general, can t pipeline feedback loops. Spring 2013 EECS150 - Lec09-parallel Page 15 Pipelining Loops with Feedback However, we can overlap the nonfeedback part of the iterations: Loop carry dependency Add is associative and communitive. Therefore we can reorder the computation to shorten the delay of the feedback path: y i = (y i-1 + x i ) + a = (a + x i ) + y i-1 add 1 x i +a x i+1 +a x i+2 +a Shorten the feedback path. add 2 y i y i+1 y i+2 Pipelining is limited to 2 stages. Spring 2013 EECS150 - Lec09-parallel Page 16
9 Beyond Pipelining - SIMD Parallelism An obvious way to exploit more parallelism from loops is to make multiple instances of the loop execution data-path and run them in parallel, sharing the some controller. For P instances, throughput improves by a factor of P. example: y i = f(x i ) x i x i+1 x i+2 x i+3 Usually called SIMD parallelism. Single f f f f Instruction Multiple Data y i y i+1 y i+2 y i+3 Assumes the next 4 x values available at once. The validity of this assumption depends on the ratio of f repeat rate to input rate (or memory bandwidth). Cost α P. Usually, much higher than for pipelining. However, potentially provides a high speedup. Often applied after pipelining. Limited, once again, by loop carry dependencies. Feedback translates to dependencies between parallel data-paths. Vector processors use this technique. Spring 2013 EECS150 - Lec09-parallel Page 17 SIMD Parallelism with Feedback Example, from earlier: y i = a y i-1 + x i + b In this example end up with carry ripple situation. Could employ look-ahead / parallel-prefix optimization techniques to speed up propagation. As with pipelining, this technique is most effective in the absence of a loop carry dependence. Spring 2013 EECS150 - Lec09-parallel Page 18
EECS 151/251A Fall 2017 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits. Instructor: John Wawrzynek and Nicholas Weaver. Lecture 14 EE141
 EECS 151/251A Fall 2017 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits Instructor: John Wawrzynek and Nicholas Weaver Lecture 14 EE141 Outline Parallelism EE141 2 Parallelism Parallelism is the act of doing more
EECS 151/251A Fall 2017 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits Instructor: John Wawrzynek and Nicholas Weaver Lecture 14 EE141 Outline Parallelism EE141 2 Parallelism Parallelism is the act of doing more
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 24 - High-Level Design (Part 3) + ECC
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 24 - High-Level Design (Part 3) + ECC April 12, 2012 John Wawrzynek Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec24-hdl3 Page 1 Parallelism Parallelism is the act of doing more than one thing
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 24 - High-Level Design (Part 3) + ECC April 12, 2012 John Wawrzynek Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec24-hdl3 Page 1 Parallelism Parallelism is the act of doing more than one thing
Pipeline: Introduction
 Pipeline: Introduction These slides are derived from: CSCE430/830 Computer Architecture course by Prof. Hong Jiang and Dave Patterson UCB Some figures and tables have been derived from : Computer System
Pipeline: Introduction These slides are derived from: CSCE430/830 Computer Architecture course by Prof. Hong Jiang and Dave Patterson UCB Some figures and tables have been derived from : Computer System
Module 4c: Pipelining
 Module 4c: Pipelining R E F E R E N C E S : S T A L L I N G S, C O M P U T E R O R G A N I Z A T I O N A N D A R C H I T E C T U R E M O R R I S M A N O, C O M P U T E R O R G A N I Z A T I O N A N D A
Module 4c: Pipelining R E F E R E N C E S : S T A L L I N G S, C O M P U T E R O R G A N I Z A T I O N A N D A R C H I T E C T U R E M O R R I S M A N O, C O M P U T E R O R G A N I Z A T I O N A N D A
Pipelining. Maurizio Palesi
 * Pipelining * Adapted from David A. Patterson s CS252 lecture slides, http://www.cs.berkeley/~pattrsn/252s98/index.html Copyright 1998 UCB 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer
* Pipelining * Adapted from David A. Patterson s CS252 lecture slides, http://www.cs.berkeley/~pattrsn/252s98/index.html Copyright 1998 UCB 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer
Lecture 19 Introduction to Pipelining
 CSE 30321 Lecture 19 Pipelining (Part 1) 1 Lecture 19 Introduction to Pipelining CSE 30321 Lecture 19 Pipelining (Part 1) Basic pipelining basic := single, in-order issue single issue one instruction at
CSE 30321 Lecture 19 Pipelining (Part 1) 1 Lecture 19 Introduction to Pipelining CSE 30321 Lecture 19 Pipelining (Part 1) Basic pipelining basic := single, in-order issue single issue one instruction at
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - High-Level Design (Part 1)
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - High-Level Design (Part 1) April 21, 2009 John Wawrzynek Spring 2009 EECS150 - Lec24-hdl1 Page 1 Introduction High-level Design Specifies: How data is moved around
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - High-Level Design (Part 1) April 21, 2009 John Wawrzynek Spring 2009 EECS150 - Lec24-hdl1 Page 1 Introduction High-level Design Specifies: How data is moved around
Alexandria University
 Alexandria University Faculty of Engineering Computer and Communications Department CC322: CC423: Advanced Computer Architecture Sheet 3: Instruction- Level Parallelism and Its Exploitation 1. What would
Alexandria University Faculty of Engineering Computer and Communications Department CC322: CC423: Advanced Computer Architecture Sheet 3: Instruction- Level Parallelism and Its Exploitation 1. What would
Pipelining concepts The DLX architecture A simple DLX pipeline Pipeline Hazards and Solution to overcome
 Thoai Nam Pipelining concepts The DLX architecture A simple DLX pipeline Pipeline Hazards and Solution to overcome Reference: Computer Architecture: A Quantitative Approach, John L Hennessy & David a Patterson,
Thoai Nam Pipelining concepts The DLX architecture A simple DLX pipeline Pipeline Hazards and Solution to overcome Reference: Computer Architecture: A Quantitative Approach, John L Hennessy & David a Patterson,
Chapter 4. The Processor
 Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS implementations A simplified
Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS implementations A simplified
CPU Pipelining Issues
 CPU Pipelining Issues What have you been beating your head against? This pipe stuff makes my head hurt! L17 Pipeline Issues & Memory 1 Pipelining Improve performance by increasing instruction throughput
CPU Pipelining Issues What have you been beating your head against? This pipe stuff makes my head hurt! L17 Pipeline Issues & Memory 1 Pipelining Improve performance by increasing instruction throughput
Computer Systems Architecture Spring 2016
 Computer Systems Architecture Spring 2016 Lecture 01: Introduction Shuai Wang Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University [Adapted from Computer Architecture: A Quantitative Approach,
Computer Systems Architecture Spring 2016 Lecture 01: Introduction Shuai Wang Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University [Adapted from Computer Architecture: A Quantitative Approach,
Pipelining concepts The DLX architecture A simple DLX pipeline Pipeline Hazards and Solution to overcome
 Pipeline Thoai Nam Outline Pipelining concepts The DLX architecture A simple DLX pipeline Pipeline Hazards and Solution to overcome Reference: Computer Architecture: A Quantitative Approach, John L Hennessy
Pipeline Thoai Nam Outline Pipelining concepts The DLX architecture A simple DLX pipeline Pipeline Hazards and Solution to overcome Reference: Computer Architecture: A Quantitative Approach, John L Hennessy
ELCT 501: Digital System Design
 ELCT 501: Digital System Lecture 8: Pipelining Dr. Mohamed Abd El Ghany, Pipelining: Its Natural! Laundry Example Ann, brian, cathy, Dave each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes
ELCT 501: Digital System Lecture 8: Pipelining Dr. Mohamed Abd El Ghany, Pipelining: Its Natural! Laundry Example Ann, brian, cathy, Dave each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes
PIPELINE AND VECTOR PROCESSING
 PIPELINE AND VECTOR PROCESSING PIPELINING: Pipelining is a technique of decomposing a sequential process into sub operations, with each sub process being executed in a special dedicated segment that operates
PIPELINE AND VECTOR PROCESSING PIPELINING: Pipelining is a technique of decomposing a sequential process into sub operations, with each sub process being executed in a special dedicated segment that operates
Chapter 4. The Processor
 Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware 4.1 Introduction We will examine two MIPS implementations
Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware 4.1 Introduction We will examine two MIPS implementations
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 13 - Combinational Logic & Arithmetic Circuits Part 3
 EECS15 - Digital Design Lecture 13 - Combinational Logic & Arithmetic Circuits Part 3 October 8, 22 John Wawrzynek Fall 22 EECS15 - Lec13-cla3 Page 1 Multiplication a 3 a 2 a 1 a Multiplicand b 3 b 2 b
EECS15 - Digital Design Lecture 13 - Combinational Logic & Arithmetic Circuits Part 3 October 8, 22 John Wawrzynek Fall 22 EECS15 - Lec13-cla3 Page 1 Multiplication a 3 a 2 a 1 a Multiplicand b 3 b 2 b
Suggested Readings! Recap: Pipelining improves throughput! Processor comparison! Lecture 17" Short Pipelining Review! ! Readings!
 1! 2! Suggested Readings!! Readings!! H&P: Chapter 4.5-4.7!! (Over the next 3-4 lectures)! Lecture 17" Short Pipelining Review! 3! Processor components! Multicore processors and programming! Recap: Pipelining
1! 2! Suggested Readings!! Readings!! H&P: Chapter 4.5-4.7!! (Over the next 3-4 lectures)! Lecture 17" Short Pipelining Review! 3! Processor components! Multicore processors and programming! Recap: Pipelining
ECE260: Fundamentals of Computer Engineering
 Pipelining James Moscola Dept. of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania Based on Computer Organization and Design, 5th Edition by Patterson & Hennessy What is Pipelining? Pipelining
Pipelining James Moscola Dept. of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania Based on Computer Organization and Design, 5th Edition by Patterson & Hennessy What is Pipelining? Pipelining
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 7 - Computer Aided Design (CAD) - Part II (Logic Simulation) Finite State Machine Review
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 7 - Computer Aided Design (CAD) - Part II (Logic Simulation) Feb 9, 2010 John Wawrzynek Spring 2010 EECS150 - Lec7-CAD2 Page 1 Finite State Machine Review State Transition
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 7 - Computer Aided Design (CAD) - Part II (Logic Simulation) Feb 9, 2010 John Wawrzynek Spring 2010 EECS150 - Lec7-CAD2 Page 1 Finite State Machine Review State Transition
EITF20: Computer Architecture Part2.2.1: Pipeline-1
 EITF20: Computer Architecture Part2.2.1: Pipeline-1 Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Reiteration Pipelining Harzards Structural hazards Data hazards Control hazards Implementation issues Multi-cycle
EITF20: Computer Architecture Part2.2.1: Pipeline-1 Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Reiteration Pipelining Harzards Structural hazards Data hazards Control hazards Implementation issues Multi-cycle
Outline. Introduction to Structured VLSI Design. Signed and Unsigned Integers. 8 bit Signed/Unsigned Integers
 Outline Introduction to Structured VLSI Design Integer Arithmetic and Pipelining Multiplication in the digital domain HW mapping Pipelining optimization Joachim Rodrigues Signed and Unsigned Integers n-1
Outline Introduction to Structured VLSI Design Integer Arithmetic and Pipelining Multiplication in the digital domain HW mapping Pipelining optimization Joachim Rodrigues Signed and Unsigned Integers n-1
Typical DSP application
 DSP markets DSP markets Typical DSP application TI DSP History: Modem applications 1982 TMS32010, TI introduces its first programmable general-purpose DSP to market Operating at 5 MIPS. It was ideal for
DSP markets DSP markets Typical DSP application TI DSP History: Modem applications 1982 TMS32010, TI introduces its first programmable general-purpose DSP to market Operating at 5 MIPS. It was ideal for
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN. 5 th Edition. The Hardware/Software Interface. Chapter 4. The Processor
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 4 The Processor COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition The Processor - Introduction
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 4 The Processor COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition The Processor - Introduction
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN. 5 th Edition. The Hardware/Software Interface. Chapter 4. The Processor
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle
Chapter 4. Instruction Execution. Introduction. CPU Overview. Multiplexers. Chapter 4 The Processor 1. The Processor.
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 4 The Processor The Processor - Introduction
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 4 The Processor The Processor - Introduction
EITF20: Computer Architecture Part2.2.1: Pipeline-1
 EITF20: Computer Architecture Part2.2.1: Pipeline-1 Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Reiteration Pipelining Harzards Structural hazards Data hazards Control hazards Implementation issues Multi-cycle
EITF20: Computer Architecture Part2.2.1: Pipeline-1 Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Reiteration Pipelining Harzards Structural hazards Data hazards Control hazards Implementation issues Multi-cycle
Lecture: Pipeline Wrap-Up and Static ILP
 Lecture: Pipeline Wrap-Up and Static ILP Topics: multi-cycle instructions, precise exceptions, deep pipelines, compiler scheduling, loop unrolling, software pipelining (Sections C.5, 3.2) 1 Multicycle
Lecture: Pipeline Wrap-Up and Static ILP Topics: multi-cycle instructions, precise exceptions, deep pipelines, compiler scheduling, loop unrolling, software pipelining (Sections C.5, 3.2) 1 Multicycle
Lecture 9: Case Study MIPS R4000 and Introduction to Advanced Pipelining Professor Randy H. Katz Computer Science 252 Spring 1996
 Lecture 9: Case Study MIPS R4000 and Introduction to Advanced Pipelining Professor Randy H. Katz Computer Science 252 Spring 1996 RHK.SP96 1 Review: Evaluating Branch Alternatives Two part solution: Determine
Lecture 9: Case Study MIPS R4000 and Introduction to Advanced Pipelining Professor Randy H. Katz Computer Science 252 Spring 1996 RHK.SP96 1 Review: Evaluating Branch Alternatives Two part solution: Determine
EITF20: Computer Architecture Part2.2.1: Pipeline-1
 EITF20: Computer Architecture Part2.2.1: Pipeline-1 Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Reiteration Pipelining Harzards Structural hazards Data hazards Control hazards Implementation issues Multi-cycle
EITF20: Computer Architecture Part2.2.1: Pipeline-1 Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Reiteration Pipelining Harzards Structural hazards Data hazards Control hazards Implementation issues Multi-cycle
Pipelining, Instruction Level Parallelism and Memory in Processors. Advanced Topics ICOM 4215 Computer Architecture and Organization Fall 2010
 Pipelining, Instruction Level Parallelism and Memory in Processors Advanced Topics ICOM 4215 Computer Architecture and Organization Fall 2010 NOTE: The material for this lecture was taken from several
Pipelining, Instruction Level Parallelism and Memory in Processors Advanced Topics ICOM 4215 Computer Architecture and Organization Fall 2010 NOTE: The material for this lecture was taken from several
What is Pipelining? RISC remainder (our assumptions)
 What is Pipelining? Is a key implementation techniques used to make fast CPUs Is an implementation techniques whereby multiple instructions are overlapped in execution It takes advantage of parallelism
What is Pipelining? Is a key implementation techniques used to make fast CPUs Is an implementation techniques whereby multiple instructions are overlapped in execution It takes advantage of parallelism
Floating Point/Multicycle Pipelining in DLX
 Floating Point/Multicycle Pipelining in DLX Completion of DLX EX stage floating point arithmetic operations in one or two cycles is impractical since it requires: A much longer CPU clock cycle, and/or
Floating Point/Multicycle Pipelining in DLX Completion of DLX EX stage floating point arithmetic operations in one or two cycles is impractical since it requires: A much longer CPU clock cycle, and/or
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Logic Simulation. Encoder Example
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Logic Simulation Feb 7, 2013 John Wawrzynek Spring 2013 EECS150 - Lec06-sim Page 1 Encoder Example What is y if x == 4 b1111? always @(x) : encode if (x == 4'b0001)
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Logic Simulation Feb 7, 2013 John Wawrzynek Spring 2013 EECS150 - Lec06-sim Page 1 Encoder Example What is y if x == 4 b1111? always @(x) : encode if (x == 4'b0001)
What is Pipelining? Time per instruction on unpipelined machine Number of pipe stages
 What is Pipelining? Is a key implementation techniques used to make fast CPUs Is an implementation techniques whereby multiple instructions are overlapped in execution It takes advantage of parallelism
What is Pipelining? Is a key implementation techniques used to make fast CPUs Is an implementation techniques whereby multiple instructions are overlapped in execution It takes advantage of parallelism
3/12/2014. Single Cycle (Review) CSE 2021: Computer Organization. Single Cycle with Jump. Multi-Cycle Implementation. Why Multi-Cycle?
 CSE 2021: Computer Organization Single Cycle (Review) Lecture-10b CPU Design : Pipelining-1 Overview, Datapath and control Shakil M. Khan 2 Single Cycle with Jump Multi-Cycle Implementation Instruction:
CSE 2021: Computer Organization Single Cycle (Review) Lecture-10b CPU Design : Pipelining-1 Overview, Datapath and control Shakil M. Khan 2 Single Cycle with Jump Multi-Cycle Implementation Instruction:
CO Computer Architecture and Programming Languages CAPL. Lecture 18 & 19
 CO2-3224 Computer Architecture and Programming Languages CAPL Lecture 8 & 9 Dr. Kinga Lipskoch Fall 27 Single Cycle Disadvantages & Advantages Uses the clock cycle inefficiently the clock cycle must be
CO2-3224 Computer Architecture and Programming Languages CAPL Lecture 8 & 9 Dr. Kinga Lipskoch Fall 27 Single Cycle Disadvantages & Advantages Uses the clock cycle inefficiently the clock cycle must be
L19 Pipelined CPU I 1. Where are the registers? Study Chapter 6 of Text. Pipelined CPUs. Comp 411 Fall /07/07
 Pipelined CPUs Where are the registers? Study Chapter 6 of Text L19 Pipelined CPU I 1 Review of CPU Performance MIPS = Millions of Instructions/Second MIPS = Freq CPI Freq = Clock Frequency, MHz CPI =
Pipelined CPUs Where are the registers? Study Chapter 6 of Text L19 Pipelined CPU I 1 Review of CPU Performance MIPS = Millions of Instructions/Second MIPS = Freq CPI Freq = Clock Frequency, MHz CPI =
Module 5 Introduction to Parallel Processing Systems
 Module 5 Introduction to Parallel Processing Systems 1. What is the difference between pipelining and parallelism? In general, parallelism is simply multiple operations being done at the same time.this
Module 5 Introduction to Parallel Processing Systems 1. What is the difference between pipelining and parallelism? In general, parallelism is simply multiple operations being done at the same time.this
EE178 Spring 2018 Lecture Module 4. Eric Crabill
 EE178 Spring 2018 Lecture Module 4 Eric Crabill Goals Implementation tradeoffs Design variables: throughput, latency, area Pipelining for throughput Retiming for throughput and latency Interleaving for
EE178 Spring 2018 Lecture Module 4 Eric Crabill Goals Implementation tradeoffs Design variables: throughput, latency, area Pipelining for throughput Retiming for throughput and latency Interleaving for
EE 8217 *Reconfigurable Computing Systems Engineering* Sample of Final Examination
 1 Student name: Date: June 26, 2008 General requirements for the exam: 1. This is CLOSED BOOK examination; 2. No questions allowed within the examination period; 3. If something is not clear in question
1 Student name: Date: June 26, 2008 General requirements for the exam: 1. This is CLOSED BOOK examination; 2. No questions allowed within the examination period; 3. If something is not clear in question
EEL 4783: HDL in Digital System Design
 EEL 4783: HDL in Digital System Design Lecture 3: Architeching Speed Prof. Mingjie Lin 1 Flowchart of CAD 2 Digital Circuits: Definition of Speed Throughput Latency The amount of data that is processed
EEL 4783: HDL in Digital System Design Lecture 3: Architeching Speed Prof. Mingjie Lin 1 Flowchart of CAD 2 Digital Circuits: Definition of Speed Throughput Latency The amount of data that is processed
Chapter 4. The Processor
 Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS implementations A simplified
Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS implementations A simplified
Chapter 8. Pipelining
 Chapter 8. Pipelining Overview Pipelining is widely used in modern processors. Pipelining improves system performance in terms of throughput. Pipelined organization requires sophisticated compilation techniques.
Chapter 8. Pipelining Overview Pipelining is widely used in modern processors. Pipelining improves system performance in terms of throughput. Pipelined organization requires sophisticated compilation techniques.
Page 1. Pipelining: Its Natural! Chapter 3. Pipelining. Pipelined Laundry Start work ASAP. Sequential Laundry A B C D. 6 PM Midnight
 Pipelining: Its Natural! Chapter 3 Pipelining Laundry Example Ann, Brian, Cathy, Dave each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes A B C D Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder
Pipelining: Its Natural! Chapter 3 Pipelining Laundry Example Ann, Brian, Cathy, Dave each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes A B C D Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder
Early Performance-Cost Estimation of Application-Specific Data Path Pipelining
 Early Performance-Cost Estimation of Application-Specific Data Path Pipelining Jelena Trajkovic Computer Science Department École Polytechnique de Montréal, Canada Email: jelena.trajkovic@polymtl.ca Daniel
Early Performance-Cost Estimation of Application-Specific Data Path Pipelining Jelena Trajkovic Computer Science Department École Polytechnique de Montréal, Canada Email: jelena.trajkovic@polymtl.ca Daniel
Pipelining and Exploiting Instruction-Level Parallelism (ILP)
 Pipelining and Exploiting Instruction-Level Parallelism (ILP) Pipelining and Instruction-Level Parallelism (ILP). Definition of basic instruction block Increasing Instruction-Level Parallelism (ILP) &
Pipelining and Exploiting Instruction-Level Parallelism (ILP) Pipelining and Instruction-Level Parallelism (ILP). Definition of basic instruction block Increasing Instruction-Level Parallelism (ILP) &
Computer Architecture
 Lecture 3: Pipelining Iakovos Mavroidis Computer Science Department University of Crete 1 Previous Lecture Measurements and metrics : Performance, Cost, Dependability, Power Guidelines and principles in
Lecture 3: Pipelining Iakovos Mavroidis Computer Science Department University of Crete 1 Previous Lecture Measurements and metrics : Performance, Cost, Dependability, Power Guidelines and principles in
Pipelined CPUs. Study Chapter 4 of Text. Where are the registers?
 Pipelined CPUs Where are the registers? Study Chapter 4 of Text Second Quiz on Friday. Covers lectures 8-14. Open book, open note, no computers or calculators. L17 Pipelined CPU I 1 Review of CPU Performance
Pipelined CPUs Where are the registers? Study Chapter 4 of Text Second Quiz on Friday. Covers lectures 8-14. Open book, open note, no computers or calculators. L17 Pipelined CPU I 1 Review of CPU Performance
Background: Pipelining Basics. Instruction Scheduling. Pipelining Details. Idealized Instruction Data-Path. Last week Register allocation
 Instruction Scheduling Last week Register allocation Background: Pipelining Basics Idea Begin executing an instruction before completing the previous one Today Instruction scheduling The problem: Pipelined
Instruction Scheduling Last week Register allocation Background: Pipelining Basics Idea Begin executing an instruction before completing the previous one Today Instruction scheduling The problem: Pipelined
Working on the Pipeline
 Computer Science 6C Spring 27 Working on the Pipeline Datapath Control Signals Computer Science 6C Spring 27 MemWr: write memory MemtoReg: ALU; Mem RegDst: rt ; rd RegWr: write register 4 PC Ext Imm6 Adder
Computer Science 6C Spring 27 Working on the Pipeline Datapath Control Signals Computer Science 6C Spring 27 MemWr: write memory MemtoReg: ALU; Mem RegDst: rt ; rd RegWr: write register 4 PC Ext Imm6 Adder
Lecture 6 MIPS R4000 and Instruction Level Parallelism. Computer Architectures S
 Lecture 6 MIPS R4000 and Instruction Level Parallelism Computer Architectures 521480S Case Study: MIPS R4000 (200 MHz, 64-bit instructions, MIPS-3 instruction set) 8 Stage Pipeline: first half of fetching
Lecture 6 MIPS R4000 and Instruction Level Parallelism Computer Architectures 521480S Case Study: MIPS R4000 (200 MHz, 64-bit instructions, MIPS-3 instruction set) 8 Stage Pipeline: first half of fetching
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 5 - Verilog Logic Synthesis
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 5 - Verilog Logic Synthesis Jan 31, 2012 John Wawrzynek Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec05-verilog_synth Page 1 Outline Quick review of essentials of state elements Finite State
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 5 - Verilog Logic Synthesis Jan 31, 2012 John Wawrzynek Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec05-verilog_synth Page 1 Outline Quick review of essentials of state elements Finite State
Advanced Parallel Architecture Lessons 5 and 6. Annalisa Massini /2017
 Advanced Parallel Architecture Lessons 5 and 6 Annalisa Massini - Pipelining Hennessy, Patterson Computer architecture A quantitive approach Appendix C Sections C.1, C.2 Pipelining Pipelining is an implementation
Advanced Parallel Architecture Lessons 5 and 6 Annalisa Massini - Pipelining Hennessy, Patterson Computer architecture A quantitive approach Appendix C Sections C.1, C.2 Pipelining Pipelining is an implementation
What is Pipelining. work is done at each stage. The work is not finished until it has passed through all stages.
 PIPELINING What is Pipelining A technique used in advanced microprocessors where the microprocessor begins executing a second instruction before the first has been completed. - A Pipeline is a series of
PIPELINING What is Pipelining A technique used in advanced microprocessors where the microprocessor begins executing a second instruction before the first has been completed. - A Pipeline is a series of
Computer Architecture. Lecture 6.1: Fundamentals of
 CS3350B Computer Architecture Winter 2015 Lecture 6.1: Fundamentals of Instructional Level Parallelism Marc Moreno Maza www.csd.uwo.ca/courses/cs3350b [Adapted from lectures on Computer Organization and
CS3350B Computer Architecture Winter 2015 Lecture 6.1: Fundamentals of Instructional Level Parallelism Marc Moreno Maza www.csd.uwo.ca/courses/cs3350b [Adapted from lectures on Computer Organization and
Instruction Pipelining Review
 Instruction Pipelining Review Instruction pipelining is CPU implementation technique where multiple operations on a number of instructions are overlapped. An instruction execution pipeline involves a number
Instruction Pipelining Review Instruction pipelining is CPU implementation technique where multiple operations on a number of instructions are overlapped. An instruction execution pipeline involves a number
Pipelining: Overview. CPSC 252 Computer Organization Ellen Walker, Hiram College
 Pipelining: Overview CPSC 252 Computer Organization Ellen Walker, Hiram College Pipelining the Wash Divide into 4 steps: Wash, Dry, Fold, Put Away Perform the steps in parallel Wash 1 Wash 2, Dry 1 Wash
Pipelining: Overview CPSC 252 Computer Organization Ellen Walker, Hiram College Pipelining the Wash Divide into 4 steps: Wash, Dry, Fold, Put Away Perform the steps in parallel Wash 1 Wash 2, Dry 1 Wash
Advanced Synthesis Techniques
 Advanced Synthesis Techniques Reminder From Last Year Use UltraFast Design Methodology for Vivado www.xilinx.com/ultrafast Recommendations for Rapid Closure HDL: use HDL Language Templates & DRC Constraints:
Advanced Synthesis Techniques Reminder From Last Year Use UltraFast Design Methodology for Vivado www.xilinx.com/ultrafast Recommendations for Rapid Closure HDL: use HDL Language Templates & DRC Constraints:
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 20 - Finite State Machines Revisited
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 20 - Finite State Machines Revisited April 2, 2009 John Wawrzynek Spring 2009 EECS150 - Lec20-fsm Page 1 Finite State Machines (FSMs) FSM circuits are a type of sequential
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 20 - Finite State Machines Revisited April 2, 2009 John Wawrzynek Spring 2009 EECS150 - Lec20-fsm Page 1 Finite State Machines (FSMs) FSM circuits are a type of sequential
CPE Computer Architecture. Appendix A: Pipelining: Basic and Intermediate Concepts
 CPE 110408443 Computer Architecture Appendix A: Pipelining: Basic and Intermediate Concepts Sa ed R. Abed [Computer Engineering Department, Hashemite University] Outline Basic concept of Pipelining The
CPE 110408443 Computer Architecture Appendix A: Pipelining: Basic and Intermediate Concepts Sa ed R. Abed [Computer Engineering Department, Hashemite University] Outline Basic concept of Pipelining The
INSTITUTO SUPERIOR TÉCNICO. Architectures for Embedded Computing
 UNIVERSIDADE TÉCNICA DE LISBOA INSTITUTO SUPERIOR TÉCNICO Departamento de Engenharia Informática Architectures for Embedded Computing MEIC-A, MEIC-T, MERC Lecture Slides Version 3.0 - English Lecture 05
UNIVERSIDADE TÉCNICA DE LISBOA INSTITUTO SUPERIOR TÉCNICO Departamento de Engenharia Informática Architectures for Embedded Computing MEIC-A, MEIC-T, MERC Lecture Slides Version 3.0 - English Lecture 05
Lecture 6: Pipelining
 Lecture 6: Pipelining i CSCE 26 Computer Organization Instructor: Saraju P. ohanty, Ph. D. NOTE: The figures, text etc included in slides are borrowed from various books, websites, authors pages, and other
Lecture 6: Pipelining i CSCE 26 Computer Organization Instructor: Saraju P. ohanty, Ph. D. NOTE: The figures, text etc included in slides are borrowed from various books, websites, authors pages, and other
Modern Computer Architecture
 Modern Computer Architecture Lecture2 Pipelining: Basic and Intermediate Concepts Hongbin Sun 国家集成电路人才培养基地 Xi an Jiaotong University Pipelining: Its Natural! Laundry Example Ann, Brian, Cathy, Dave each
Modern Computer Architecture Lecture2 Pipelining: Basic and Intermediate Concepts Hongbin Sun 国家集成电路人才培养基地 Xi an Jiaotong University Pipelining: Its Natural! Laundry Example Ann, Brian, Cathy, Dave each
CS 110 Computer Architecture. Pipelining. Guest Lecture: Shu Yin. School of Information Science and Technology SIST
 CS 110 Computer Architecture Pipelining Guest Lecture: Shu Yin http://shtech.org/courses/ca/ School of Information Science and Technology SIST ShanghaiTech University Slides based on UC Berkley's CS61C
CS 110 Computer Architecture Pipelining Guest Lecture: Shu Yin http://shtech.org/courses/ca/ School of Information Science and Technology SIST ShanghaiTech University Slides based on UC Berkley's CS61C
Advanced Computer Architecture
 Advanced Computer Architecture Chapter 1 Introduction into the Sequential and Pipeline Instruction Execution Martin Milata What is a Processors Architecture Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) Describes
Advanced Computer Architecture Chapter 1 Introduction into the Sequential and Pipeline Instruction Execution Martin Milata What is a Processors Architecture Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) Describes
Data Hazards Compiler Scheduling Pipeline scheduling or instruction scheduling: Compiler generates code to eliminate hazard
 Data Hazards Compiler Scheduling Pipeline scheduling or instruction scheduling: Compiler generates code to eliminate hazard Consider: a = b + c; d = e - f; Assume loads have a latency of one clock cycle:
Data Hazards Compiler Scheduling Pipeline scheduling or instruction scheduling: Compiler generates code to eliminate hazard Consider: a = b + c; d = e - f; Assume loads have a latency of one clock cycle:
Memory Hierarchy. Memory Flavors Principle of Locality Program Traces Memory Hierarchies Associativity. (Study Chapter 5)
 Memory Hierarchy Why are you dressed like that? Halloween was weeks ago! It makes me look faster, don t you think? Memory Flavors Principle of Locality Program Traces Memory Hierarchies Associativity (Study
Memory Hierarchy Why are you dressed like that? Halloween was weeks ago! It makes me look faster, don t you think? Memory Flavors Principle of Locality Program Traces Memory Hierarchies Associativity (Study
Lecture 2: Pipelining Basics. Today: chapter 1 wrap-up, basic pipelining implementation (Sections A.1 - A.4)
 Lecture 2: Pipelining Basics Today: chapter 1 wrap-up, basic pipelining implementation (Sections A.1 - A.4) 1 Defining Fault, Error, and Failure A fault produces a latent error; it becomes effective when
Lecture 2: Pipelining Basics Today: chapter 1 wrap-up, basic pipelining implementation (Sections A.1 - A.4) 1 Defining Fault, Error, and Failure A fault produces a latent error; it becomes effective when
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - High-level Design and Optimization 3, Parallelism and Pipelining
 EECS150 - Digitl Design Lecture 23 - High-level Design nd Optimiztion 3, Prllelism nd Pipelining Nov 12, 2002 John Wwrzynek Fll 2002 EECS150 - Lec23-HL3 Pge 1 Prllelism Prllelism is the ct of doing more
EECS150 - Digitl Design Lecture 23 - High-level Design nd Optimiztion 3, Prllelism nd Pipelining Nov 12, 2002 John Wwrzynek Fll 2002 EECS150 - Lec23-HL3 Pge 1 Prllelism Prllelism is the ct of doing more
Multi-cycle Instructions in the Pipeline (Floating Point)
 Lecture 6 Multi-cycle Instructions in the Pipeline (Floating Point) Introduction to instruction level parallelism Recap: Support of multi-cycle instructions in a pipeline (App A.5) Recap: Superpipelining
Lecture 6 Multi-cycle Instructions in the Pipeline (Floating Point) Introduction to instruction level parallelism Recap: Support of multi-cycle instructions in a pipeline (App A.5) Recap: Superpipelining
CS250 VLSI Systems Design Lecture 8: Introduction to Hardware Design Patterns
 CS250 VLSI Systems Design Lecture 8: Introduction to Hardware Design Patterns John Wawrzynek, Jonathan Bachrach, with Krste Asanovic, John Lazzaro and Rimas Avizienis (TA) UC Berkeley Fall 2012 Lecture
CS250 VLSI Systems Design Lecture 8: Introduction to Hardware Design Patterns John Wawrzynek, Jonathan Bachrach, with Krste Asanovic, John Lazzaro and Rimas Avizienis (TA) UC Berkeley Fall 2012 Lecture
Binary Adders. Ripple-Carry Adder
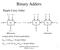 Ripple-Carry Adder Binary Adders x n y n x y x y c n FA c n - c 2 FA c FA c s n MSB position Longest delay (Critical-path delay): d c(n) = n d carry = 2n gate delays d s(n-) = (n-) d carry +d sum = 2n
Ripple-Carry Adder Binary Adders x n y n x y x y c n FA c n - c 2 FA c FA c s n MSB position Longest delay (Critical-path delay): d c(n) = n d carry = 2n gate delays d s(n-) = (n-) d carry +d sum = 2n
Vertex Shader Design I
 The following content is extracted from the paper shown in next page. If any wrong citation or reference missing, please contact ldvan@cs.nctu.edu.tw. I will correct the error asap. This course used only
The following content is extracted from the paper shown in next page. If any wrong citation or reference missing, please contact ldvan@cs.nctu.edu.tw. I will correct the error asap. This course used only
CS 1013 Advance Computer Architecture UNIT I
 CS 1013 Advance Computer Architecture UNIT I 1. What are embedded computers? List their characteristics. Embedded computers are computers that are lodged into other devices where the presence of the computer
CS 1013 Advance Computer Architecture UNIT I 1. What are embedded computers? List their characteristics. Embedded computers are computers that are lodged into other devices where the presence of the computer
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN 5 Edition th The Hardware/Software Interface Chapter 4 The Processor 4.1 Introduction Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count CPI and Cycle time Determined
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN 5 Edition th The Hardware/Software Interface Chapter 4 The Processor 4.1 Introduction Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count CPI and Cycle time Determined
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN
 ARM COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN Edition The Hardware/Software Interface Chapter 4 The Processor Modified and extended by R.J. Leduc - 2016 To understand this chapter, you will need to understand some
ARM COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN Edition The Hardware/Software Interface Chapter 4 The Processor Modified and extended by R.J. Leduc - 2016 To understand this chapter, you will need to understand some
Assuming ideal conditions (perfect pipelining and no hazards), how much time would it take to execute the same program in: b) A 5-stage pipeline?
 1. Imagine we have a non-pipelined processor running at 1MHz and want to run a program with 1000 instructions. a) How much time would it take to execute the program? 1 instruction per cycle. 1MHz clock
1. Imagine we have a non-pipelined processor running at 1MHz and want to run a program with 1000 instructions. a) How much time would it take to execute the program? 1 instruction per cycle. 1MHz clock
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 08 - Project Introduction Part 1
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 08 - Project Introduction Part 1 Feb 9, 2012 John Wawrzynek Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec08-proj1 Page 1 Project Overview A. Pipelined CPU review B.MIPS150 pipeline structure
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 08 - Project Introduction Part 1 Feb 9, 2012 John Wawrzynek Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec08-proj1 Page 1 Project Overview A. Pipelined CPU review B.MIPS150 pipeline structure
Pipelining and Vector Processing
 Chapter 8 Pipelining and Vector Processing 8 1 If the pipeline stages are heterogeneous, the slowest stage determines the flow rate of the entire pipeline. This leads to other stages idling. 8 2 Pipeline
Chapter 8 Pipelining and Vector Processing 8 1 If the pipeline stages are heterogeneous, the slowest stage determines the flow rate of the entire pipeline. This leads to other stages idling. 8 2 Pipeline
The Processor Pipeline. Chapter 4, Patterson and Hennessy, 4ed. Section 5.3, 5.4: J P Hayes.
 The Processor Pipeline Chapter 4, Patterson and Hennessy, 4ed. Section 5.3, 5.4: J P Hayes. Pipeline A Basic MIPS Implementation Memory-reference instructions Load Word (lw) and Store Word (sw) ALU instructions
The Processor Pipeline Chapter 4, Patterson and Hennessy, 4ed. Section 5.3, 5.4: J P Hayes. Pipeline A Basic MIPS Implementation Memory-reference instructions Load Word (lw) and Store Word (sw) ALU instructions
Chapter 4. The Processor
 Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS implementations A simplified
Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle time Determined by CPU hardware We will examine two MIPS implementations A simplified
CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture Lecture 6 - Hazards
 CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture Lecture 6 - Hazards Michela Taufer http://www.cis.udel.edu/~taufer/teaching/cis662f07 Powerpoint Lecture Notes from John Hennessy and David Patterson s: Computer
CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture Lecture 6 - Hazards Michela Taufer http://www.cis.udel.edu/~taufer/teaching/cis662f07 Powerpoint Lecture Notes from John Hennessy and David Patterson s: Computer
ECE 571 Advanced Microprocessor-Based Design Lecture 4
 ECE 571 Advanced Microprocessor-Based Design Lecture 4 Vince Weaver http://www.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 28 January 2016 Homework #1 was due Announcements Homework #2 will be posted
ECE 571 Advanced Microprocessor-Based Design Lecture 4 Vince Weaver http://www.eece.maine.edu/~vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 28 January 2016 Homework #1 was due Announcements Homework #2 will be posted
Unit 9 : Fundamentals of Parallel Processing
 Unit 9 : Fundamentals of Parallel Processing Lesson 1 : Types of Parallel Processing 1.1. Learning Objectives On completion of this lesson you will be able to : classify different types of parallel processing
Unit 9 : Fundamentals of Parallel Processing Lesson 1 : Types of Parallel Processing 1.1. Learning Objectives On completion of this lesson you will be able to : classify different types of parallel processing
A Key Theme of CIS 371: Parallelism. CIS 371 Computer Organization and Design. Readings. This Unit: (In-Order) Superscalar Pipelines
 A Key Theme of CIS 371: arallelism CIS 371 Computer Organization and Design Unit 10: Superscalar ipelines reviously: pipeline-level parallelism Work on execute of one instruction in parallel with decode
A Key Theme of CIS 371: arallelism CIS 371 Computer Organization and Design Unit 10: Superscalar ipelines reviously: pipeline-level parallelism Work on execute of one instruction in parallel with decode
Lecture 15: Pipelining. Spring 2018 Jason Tang
 Lecture 15: Pipelining Spring 2018 Jason Tang 1 Topics Overview of pipelining Pipeline performance Pipeline hazards 2 Sequential Laundry 6 PM 7 8 9 10 11 Midnight Time T a s k O r d e r A B C D 30 40 20
Lecture 15: Pipelining Spring 2018 Jason Tang 1 Topics Overview of pipelining Pipeline performance Pipeline hazards 2 Sequential Laundry 6 PM 7 8 9 10 11 Midnight Time T a s k O r d e r A B C D 30 40 20
Lecture 41: Introduction to Reconfigurable Computing
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 41: Introduction to Reconfigurable Computing Michael Le, Sp07 Head TA April 30, 2007 Slides Courtesy of Hayden So, Sp06 CS61c Head TA Following
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture 41: Introduction to Reconfigurable Computing Michael Le, Sp07 Head TA April 30, 2007 Slides Courtesy of Hayden So, Sp06 CS61c Head TA Following
CPS104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 19: Pipelining. Robert Wagner
 CPS104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 19: Pipelining Robert Wagner cps 104 Pipelining..1 RW Fall 2000 Lecture Overview A Pipelined Processor : Introduction to the concept of pipelined processor.
CPS104 Computer Organization and Programming Lecture 19: Pipelining Robert Wagner cps 104 Pipelining..1 RW Fall 2000 Lecture Overview A Pipelined Processor : Introduction to the concept of pipelined processor.
Logic Synthesis. EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Synthesis
 Logic Synthesis Verilog and VHDL started out as simulation languages, but quickly people wrote programs to automatically convert Verilog code into low-level circuit descriptions (netlists). EECS150 - Digital
Logic Synthesis Verilog and VHDL started out as simulation languages, but quickly people wrote programs to automatically convert Verilog code into low-level circuit descriptions (netlists). EECS150 - Digital
CENG 3531 Computer Architecture Spring a. T / F A processor can have different CPIs for different programs.
 Exam 2 April 12, 2012 You have 80 minutes to complete the exam. Please write your answers clearly and legibly on this exam paper. GRADE: Name. Class ID. 1. (22 pts) Circle the selected answer for T/F and
Exam 2 April 12, 2012 You have 80 minutes to complete the exam. Please write your answers clearly and legibly on this exam paper. GRADE: Name. Class ID. 1. (22 pts) Circle the selected answer for T/F and
EI338: Computer Systems and Engineering (Computer Architecture & Operating Systems)
 EI338: Computer Systems and Engineering (Computer Architecture & Operating Systems) Chentao Wu 吴晨涛 Associate Professor Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University SEIEE Building
EI338: Computer Systems and Engineering (Computer Architecture & Operating Systems) Chentao Wu 吴晨涛 Associate Professor Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University SEIEE Building
ECEC 355: Pipelining
 ECEC 355: Pipelining November 8, 2007 What is Pipelining Pipelining is an implementation technique whereby multiple instructions are overlapped in execution. A pipeline is similar in concept to an assembly
ECEC 355: Pipelining November 8, 2007 What is Pipelining Pipelining is an implementation technique whereby multiple instructions are overlapped in execution. A pipeline is similar in concept to an assembly
Pipelining: Hazards Ver. Jan 14, 2014
 POLITECNICO DI MILANO Parallelism in wonderland: are you ready to see how deep the rabbit hole goes? Pipelining: Hazards Ver. Jan 14, 2014 Marco D. Santambrogio: marco.santambrogio@polimi.it Simone Campanoni:
POLITECNICO DI MILANO Parallelism in wonderland: are you ready to see how deep the rabbit hole goes? Pipelining: Hazards Ver. Jan 14, 2014 Marco D. Santambrogio: marco.santambrogio@polimi.it Simone Campanoni:
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs)
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) September 12, 2002 John Wawrzynek Fall 2002 EECS150 - Lec06-FPGA Page 1 Outline What are FPGAs? Why use FPGAs (a short history
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) September 12, 2002 John Wawrzynek Fall 2002 EECS150 - Lec06-FPGA Page 1 Outline What are FPGAs? Why use FPGAs (a short history
ENGN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 06: Advanced Processor Design
 ENGN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 06: Advanced Processor Design Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University
ENGN1640: Design of Computing Systems Topic 06: Advanced Processor Design Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface. 5 th. Edition. Chapter 4. The Processor
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN The Hardware/Software Interface 5 th Edition Chapter 4 The Processor Introduction CPU performance factors Instruction count Determined by ISA and compiler CPI and Cycle
EE/CSCI 451: Parallel and Distributed Computation
 EE/CSCI 451: Parallel and Distributed Computation Lecture #11 2/21/2017 Xuehai Qian Xuehai.qian@usc.edu http://alchem.usc.edu/portal/xuehaiq.html University of Southern California 1 Outline Midterm 1:
EE/CSCI 451: Parallel and Distributed Computation Lecture #11 2/21/2017 Xuehai Qian Xuehai.qian@usc.edu http://alchem.usc.edu/portal/xuehaiq.html University of Southern California 1 Outline Midterm 1:
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Logic Simulation
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Logic Simulation Sep. 17, 013 Prof. Ronald Fearing Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley (slides courtesy of Prof. John Wawrzynek)
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Logic Simulation Sep. 17, 013 Prof. Ronald Fearing Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley (slides courtesy of Prof. John Wawrzynek)
Outline. EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) FPGA Overview. Why FPGAs?
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) September 12, 2002 John Wawrzynek Outline What are FPGAs? Why use FPGAs (a short history lesson). FPGA variations Internal logic
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 6 - Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) September 12, 2002 John Wawrzynek Outline What are FPGAs? Why use FPGAs (a short history lesson). FPGA variations Internal logic
