Using Shaders for Lighting
|
|
|
- Avis Patricia Kelley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Using Shaders for Lighting This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License Mike Bailey mjb@cs.oregonstate.edu lighting.pptx Lighting Definitions 2 L N R E ER Ambient = Light intensity that is everywhere Diffuse = Light intensity proportional to cos(θ) Specular = Light intensity proportional to cos S (Φ) A-D-S = Lighting model that includes Ambient, Diffuse, and Specular Flat Interpolation = Use a single polygon normal to compute one A-D-S for the entire polygon Per-vertex lighting= Compute A-D-S using each vertex normal and then interpolate the sum over the entire polygon Per-fragment lighting = Interpolate the vertex normals across the entire polygon and compute A-D-S at each fragment CubeMap Reflection = Using the Eye Reflection Vector (ER) to look-up the reflection of a wall texture 1
2 A-D-S Lighting 3 Ambient: K a Diffuse: K d *cosθ Specular: K s *cos n φ 4 Ambient-only Diffuse-only Specular-only ADS Shininess=50 ADS Shininess=1000 ADS Shininess= Flat 2
3 A-D-S Lighting with Flat Interpolation 5 Each facet has a single lighting value applied to every pixel within it. Vertex Shader diffuse = max( dot(l,n), 0. ) * Color.rgb; vec3 R = normalize( reflect( -L, N ) ); vec3 spec = LightColor * pow( max( dot( R, E), 0. ), Shininess ); Flat-rasterize ambient, diffuse, specular gl_fragcolor.rgb = Ka*ambient + Kd*diffuse + Ks*spec; What you see depends on the light color and the material color 6 L R L G L B White Light What the light can produce E R E G E B What the eye sees M R M G M B What the material can reflect Green Light E R E G E B = L R * M R = L G * M G = L B * M B 3
4 A-D-S Lighting with Smooth Interpolation 7 Note: The light intensity is computed at each vertex and interpolated throughout the facet. This creates artifacts such Mach Banding and the fact that the bright spot is not circular. You can do this in stock OpenGL or in a shader. Vertex Shader diffuse = max( dot(l,n), 0. ) * Color.rgb; vec3 R = normalize( reflect( -L, N ) ); vec3 spec = LightColor * pow( max( dot( R, E), 0. ), Shininess ); Smooth-rasterize ambient, diffuse, spec gl_fragcolor.rgb = Ka*ambient + Kd*diffuse + Ks*spec; A-D-S Lighting with Normal Interpolation 8 Note: The normal is interpolated throughout the facet. The light intensity is computed at each fragment. This avoids Mach Banding and makes the bright spot circular. You can only do this in a shader. Smooth-rasterize N, L, E diffuse = max( dot(l,n), 0. ) * Color.rgb; vec3 R = normalize( reflect( -L, N ) ); vec3 spec = LightColor * pow( max( dot( R, E ), 0. ), Shininess ); gl_fragcolor.rgb = Ka*ambient + Kd*diffuse + Ks*spec; 4
5 The Difference Between Per-Vertex Lighting and Per-Fragment Lighting 9 Per-vertex Per-fragment The Difference Between Per-Vertex Lighting and Per-Fragment Lighting 10 Per-vertex Per-fragment 5
6 Flat shading 11 Normal interpolation A-D-S Lighting with Normal Interpolation and a CubeMap Reflection 12 Note: A cube map reflection is blended in, given a stronger impression that the surface is shiny. Smooth-rasterize N, L, E diffuse = max( dot(l,n), 0. ) * Color.rgb; vec3 R = normalize( reflect( -L, N ) ); vec3 spec = LightColor * pow( max( dot( R, E ), 0. ), Shininess ); vec3 reflcolor = texturecube( ReflectUnit, R ).rgb; gl_fragcolor.rgb = Ka*ambient + Kd*diffuse + Ks*spec + Kr*reflcolor.rgb; 6
7 A-D-S Anisotropic Lighting with Normal Interpolation 13 Note: The bright spot is not circular because the material has different properties in different directions. Materials such as fur, hair, and brushed metal behave this way. James Kajiya and Timothy Kay, Rendering Fur with Three Dimensional Textures, Proceedings of SIGGRAPH 1989, Volume 23, Number 3, July 1989, pp float dl = dot( T, L ); vec3 diffuse = sqrt( 1. - dl*dl ) * Color.rgb; float de = dot( T, E ); vec3 spec = LightColor * pow( dl * de + sqrt( 1. - dl*dl ) * sqrt( 1. - de*de ), Shininess ); gl_fragcolor.rgb = Ka*ambient + Kd*diffuse + Ks*spec; Summary 14 Flat Normal Anisotropic Smooth Reflection 7
8 #version 330 compatibility 15 uniform float ulightx, ulighty, ulightz; flat out vec3 vnf; out vec3 vns; flat out vec3 vlf; out vec3 vls; flat out vec3 vef; out vec3 ves; vec3 eyelightposition = vec3( ulightx, ulighty, ulightz ); void main( ) vec4 ECposition = umodelviewmatrix * avertex; Nf = normalize( unormalmatrix * anormal ); Ns = Nf; Lf = eyelightposition - ECposition.xyz; Ls = Lf; Ef = vec3( 0., 0., 0. ) - ECposition.xyz; Es = Ef ; // surface normal vector // vector from the point // to the light position // vector from the point // to the eye position gl_position = umodelviewprojectionmatrix * avertex; Computer } Graphics #version 330 compatibility 16 uniform float uka, ukd, uks; uniform vec4 ucolor; uniform vec4 uspecularcolor; uniform float ushininess; uniform bool uflat, uhalf; flat in vec3 vnf; in vec3v Ns; flat in vec3 vlf; in vec3v Ls; flat in vec3 vef; in vec3 ves; out vec4 ffragcolor; void main( ) vec3 Normal; vec3 Light; vec3 Eye; if( uflat ) } else } Normal = normalize(vnf); Light = normalize(vlf); Eye = normalize(vef); Normal = normalize(vns); Light = normalize(vls); Eye = normalize(ves); 8
9 17 vec4 ambient = uka * ucolor; float d = max( dot(normal,light), 0. ); vec4 diffuse = ukd * d * ucolor; float s = 0.; if( dot(normal,light) > 0. ) // only do specular if the light can see the point vec3 ref = normalize( 2. * Normal * dot(normal,light) - Light ); s = pow( max( dot(eye,ref),0. ), ushininess ); } vec4 specular = uks * s * uspecularcolor; } ffragcolor = vec4( ambient.rgb + diffuse.rgb + specular.rgb, 1. ); 9
Using Shaders for Lighting
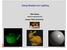 Using Shaders for Lighting Mike Bailey mjb@cs.oregonstate.edu Lighting Definitions L N R E N = Normal L = Light vector E = Eye vector R = Light reflection vector ER = Eye reflection vector Color = LightColor
Using Shaders for Lighting Mike Bailey mjb@cs.oregonstate.edu Lighting Definitions L N R E N = Normal L = Light vector E = Eye vector R = Light reflection vector ER = Eye reflection vector Color = LightColor
Introduction to the OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL)
 1 Introduction to the OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL) This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial- NoDerivatives 4.0 International License Mike Bailey mjb@cs.oregonstate.edu
1 Introduction to the OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL) This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial- NoDerivatives 4.0 International License Mike Bailey mjb@cs.oregonstate.edu
The Basic Computer Graphics Pipeline, OpenGL-style. Introduction to the OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL)
 Introduction to the OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL) 1 The Basic Pipeline, OpenGL-style Vertex, Normal, Color ModelViewMatrix, ProjectionMatrix, ModelViewProjectionMatrix 2 MC Model WC View Per-vertex Projection
Introduction to the OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL) 1 The Basic Pipeline, OpenGL-style Vertex, Normal, Color ModelViewMatrix, ProjectionMatrix, ModelViewProjectionMatrix 2 MC Model WC View Per-vertex Projection
GLSL Introduction. Fu-Chung Huang. Thanks for materials from many other people
 GLSL Introduction Fu-Chung Huang Thanks for materials from many other people Programmable Shaders //per vertex inputs from main attribute aposition; attribute anormal; //outputs to frag. program varying
GLSL Introduction Fu-Chung Huang Thanks for materials from many other people Programmable Shaders //per vertex inputs from main attribute aposition; attribute anormal; //outputs to frag. program varying
The Transition from RenderMan to the OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL)
 1 The Transition from RenderMan to the OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL) Mike Bailey mjb@cs.oregonstate.edu This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial- NoDerivatives 4.0 International
1 The Transition from RenderMan to the OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL) Mike Bailey mjb@cs.oregonstate.edu This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial- NoDerivatives 4.0 International
Lecture 17: Shading in OpenGL. CITS3003 Graphics & Animation
 Lecture 17: Shading in OpenGL CITS3003 Graphics & Animation E. Angel and D. Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 6E Addison-Wesley 2012 Objectives Introduce the OpenGL shading methods - per vertex shading
Lecture 17: Shading in OpenGL CITS3003 Graphics & Animation E. Angel and D. Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 6E Addison-Wesley 2012 Objectives Introduce the OpenGL shading methods - per vertex shading
Computer Graphics Lighting
 Lighting 1 Mike Bailey mjb@cs.oregonstate.edu This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial- NoDerivatives 4.0 International License Lighting.pptx Why Do We Care About Lighting?
Lighting 1 Mike Bailey mjb@cs.oregonstate.edu This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial- NoDerivatives 4.0 International License Lighting.pptx Why Do We Care About Lighting?
Computer Graphics Lighting. Why Do We Care About Lighting?
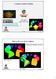 Lighting 1 Mike Bailey mjb@cs.oregonstate.edu This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial- NoDerivatives 4.0 International License Lighting.pptx Why Do We Care About Lighting?
Lighting 1 Mike Bailey mjb@cs.oregonstate.edu This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial- NoDerivatives 4.0 International License Lighting.pptx Why Do We Care About Lighting?
Illumination and Shading
 Illumination and Shading Illumination (Lighting)! Model the interaction of light with surface points to determine their final color and brightness! The illumination can be computed either at vertices or
Illumination and Shading Illumination (Lighting)! Model the interaction of light with surface points to determine their final color and brightness! The illumination can be computed either at vertices or
ECS 175 COMPUTER GRAPHICS. Ken Joy.! Winter 2014
 ECS 175 COMPUTER GRAPHICS Ken Joy Winter 2014 Shading To be able to model shading, we simplify Uniform Media no scattering of light Opaque Objects No Interreflection Point Light Sources RGB Color (eliminating
ECS 175 COMPUTER GRAPHICS Ken Joy Winter 2014 Shading To be able to model shading, we simplify Uniform Media no scattering of light Opaque Objects No Interreflection Point Light Sources RGB Color (eliminating
TSBK 07! Computer Graphics! Ingemar Ragnemalm, ISY
 1(84) Information Coding / Computer Graphics, ISY, LiTH TSBK 07 Computer Graphics Ingemar Ragnemalm, ISY 1(84) Lecture 5 3D graphics part 3 Illumination Illumination applied: Shading Surface detail: Mappings
1(84) Information Coding / Computer Graphics, ISY, LiTH TSBK 07 Computer Graphics Ingemar Ragnemalm, ISY 1(84) Lecture 5 3D graphics part 3 Illumination Illumination applied: Shading Surface detail: Mappings
Objectives Shading in OpenGL. Front and Back Faces. OpenGL shading. Introduce the OpenGL shading methods. Discuss polygonal shading
 Objectives Shading in OpenGL Introduce the OpenGL shading methods - per vertex shading vs per fragment shading - Where to carry out Discuss polygonal shading - Flat - Smooth - Gouraud CITS3003 Graphics
Objectives Shading in OpenGL Introduce the OpenGL shading methods - per vertex shading vs per fragment shading - Where to carry out Discuss polygonal shading - Flat - Smooth - Gouraud CITS3003 Graphics
GLSL Introduction. Fu-Chung Huang. Thanks for materials from many other people
 GLSL Introduction Fu-Chung Huang Thanks for materials from many other people Shader Languages Currently 3 major shader languages Cg (Nvidia) HLSL (Microsoft) Derived from Cg GLSL (OpenGL) Main influences
GLSL Introduction Fu-Chung Huang Thanks for materials from many other people Shader Languages Currently 3 major shader languages Cg (Nvidia) HLSL (Microsoft) Derived from Cg GLSL (OpenGL) Main influences
Introduction to Shaders for Visualization. The Basic Computer Graphics Pipeline
 Introduction to Shaders for Visualization Mike Bailey The Basic Computer Graphics Pipeline Model Transform View Transform Per-vertex Lighting Projection Transform Homogeneous Division Viewport Transform
Introduction to Shaders for Visualization Mike Bailey The Basic Computer Graphics Pipeline Model Transform View Transform Per-vertex Lighting Projection Transform Homogeneous Division Viewport Transform
Illumination Models & Shading
 Illumination Models & Shading Lighting vs. Shading Lighting Interaction between materials and light sources Physics Shading Determining the color of a pixel Computer Graphics ZBuffer(Scene) PutColor(x,y,Col(P));
Illumination Models & Shading Lighting vs. Shading Lighting Interaction between materials and light sources Physics Shading Determining the color of a pixel Computer Graphics ZBuffer(Scene) PutColor(x,y,Col(P));
Shader Programming 1. Examples. Vertex displacement mapping. Daniel Wesslén 1. Post-processing, animated procedural textures
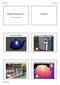 Shader Programming 1 Examples Daniel Wesslén, dwn@hig.se Per-pixel lighting Texture convolution filtering Post-processing, animated procedural textures Vertex displacement mapping Daniel Wesslén 1 Fragment
Shader Programming 1 Examples Daniel Wesslén, dwn@hig.se Per-pixel lighting Texture convolution filtering Post-processing, animated procedural textures Vertex displacement mapping Daniel Wesslén 1 Fragment
Computer Graphics. Illumination and Shading
 Rendering Pipeline modelling of geometry transformation into world coordinates placement of cameras and light sources transformation into camera coordinates backface culling projection clipping w.r.t.
Rendering Pipeline modelling of geometry transformation into world coordinates placement of cameras and light sources transformation into camera coordinates backface culling projection clipping w.r.t.
Stripes, Rings, and Dots!
 1 Stripes, Rings, and Dots! Mike Bailey mjb@cs.oregonstate.edu This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License stripesringsanddots.pptx
1 Stripes, Rings, and Dots! Mike Bailey mjb@cs.oregonstate.edu This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License stripesringsanddots.pptx
-=Bui Tuong Phong's Lighting=- University of Utah, but with shaders. Anton Gerdelan Trinity College Dublin
 -=Bui Tuong Phong's Lighting=- University of Utah, 1973 but with shaders Anton Gerdelan Trinity College Dublin Before we do anything - normals Q. What does a normal do? Q. How do we usually calculate them?
-=Bui Tuong Phong's Lighting=- University of Utah, 1973 but with shaders Anton Gerdelan Trinity College Dublin Before we do anything - normals Q. What does a normal do? Q. How do we usually calculate them?
CS5620 Intro to Computer Graphics
 So Far wireframe hidden surfaces Next step 1 2 Light! Need to understand: How lighting works Types of lights Types of surfaces How shading works Shading algorithms What s Missing? Lighting vs. Shading
So Far wireframe hidden surfaces Next step 1 2 Light! Need to understand: How lighting works Types of lights Types of surfaces How shading works Shading algorithms What s Missing? Lighting vs. Shading
Computer Graphics with OpenGL ES (J. Han) Chapter 6 Fragment shader
 Computer Graphics with OpenGL ES (J. Han) Chapter 6 Fragment shader Vertex and Fragment Shaders The inputs to the fragment shader Varyings: The per-vertex output variables produced by the vertex shader
Computer Graphics with OpenGL ES (J. Han) Chapter 6 Fragment shader Vertex and Fragment Shaders The inputs to the fragment shader Varyings: The per-vertex output variables produced by the vertex shader
Virtual Reality for Human Computer Interaction
 Virtual Reality for Human Computer Interaction Appearance: Lighting Representation of Light and Color Do we need to represent all I! to represent a color C(I)? No we can approximate using a three-color
Virtual Reality for Human Computer Interaction Appearance: Lighting Representation of Light and Color Do we need to represent all I! to represent a color C(I)? No we can approximate using a three-color
CPSC 314 LIGHTING AND SHADING
 CPSC 314 LIGHTING AND SHADING UGRAD.CS.UBC.CA/~CS314 slide credits: Mikhail Bessmeltsev et al 1 THE RENDERING PIPELINE Vertices and attributes Vertex Shader Modelview transform Per-vertex attributes Vertex
CPSC 314 LIGHTING AND SHADING UGRAD.CS.UBC.CA/~CS314 slide credits: Mikhail Bessmeltsev et al 1 THE RENDERING PIPELINE Vertices and attributes Vertex Shader Modelview transform Per-vertex attributes Vertex
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 8a: Per-Vertex lighting, Shading and Per-Fragment lighting
 Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 8a: Per-Vertex lighting, Shading and Per-Fragment lighting Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Computation of Vectors To calculate
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 8a: Per-Vertex lighting, Shading and Per-Fragment lighting Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Computation of Vectors To calculate
w Foley, Section16.1 Reading
 Shading w Foley, Section16.1 Reading Introduction So far, we ve talked exclusively about geometry. w What is the shape of an object? w How do I place it in a virtual 3D space? w How do I know which pixels
Shading w Foley, Section16.1 Reading Introduction So far, we ve talked exclusively about geometry. w What is the shape of an object? w How do I place it in a virtual 3D space? w How do I know which pixels
Lab 9 - Metal and Glass
 Lab 9 - Metal and Glass Let the form of an object be what it may, light, shade, and perspective will always make it beautiful. -John Constable Prologue Support code: /course/cs1230/src/labs/lab09 This
Lab 9 - Metal and Glass Let the form of an object be what it may, light, shade, and perspective will always make it beautiful. -John Constable Prologue Support code: /course/cs1230/src/labs/lab09 This
Models and Architectures
 Models and Architectures Objectives Learn the basic design of a graphics system Introduce graphics pipeline architecture Examine software components for an interactive graphics system 1 Image Formation
Models and Architectures Objectives Learn the basic design of a graphics system Introduce graphics pipeline architecture Examine software components for an interactive graphics system 1 Image Formation
CS Illumination and Shading. Slide 1
 CS 112 - Illumination and Shading Slide 1 Illumination/Lighting Interaction between light and surfaces Physics of optics and thermal radiation Very complex: Light bounces off several surface before reaching
CS 112 - Illumination and Shading Slide 1 Illumination/Lighting Interaction between light and surfaces Physics of optics and thermal radiation Very complex: Light bounces off several surface before reaching
The Rasterization Pipeline
 Lecture 5: The Rasterization Pipeline Computer Graphics and Imaging UC Berkeley CS184/284A, Spring 2016 What We ve Covered So Far z x y z x y (0, 0) (w, h) Position objects and the camera in the world
Lecture 5: The Rasterization Pipeline Computer Graphics and Imaging UC Berkeley CS184/284A, Spring 2016 What We ve Covered So Far z x y z x y (0, 0) (w, h) Position objects and the camera in the world
Computergrafik. Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2016
 Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2016 Today More shading Environment maps Reflection mapping Irradiance environment maps Ambient occlusion Reflection and refraction Toon shading
Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2016 Today More shading Environment maps Reflection mapping Irradiance environment maps Ambient occlusion Reflection and refraction Toon shading
CPSC / Illumination and Shading
 CPSC 599.64 / 601.64 Rendering Pipeline usually in one step modelling of geometry transformation into world coordinate system placement of cameras and light sources transformation into camera coordinate
CPSC 599.64 / 601.64 Rendering Pipeline usually in one step modelling of geometry transformation into world coordinate system placement of cameras and light sources transformation into camera coordinate
Reading. Shading. An abundance of photons. Introduction. Required: Angel , 6.5, Optional: Angel 6.4 OpenGL red book, chapter 5.
 Reading Required: Angel 6.1-6.3, 6.5, 6.7-6.8 Optional: Shading Angel 6.4 OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 1 2 Introduction An abundance of photons So far, we ve talked exclusively about geometry. Properly
Reading Required: Angel 6.1-6.3, 6.5, 6.7-6.8 Optional: Shading Angel 6.4 OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 1 2 Introduction An abundance of photons So far, we ve talked exclusively about geometry. Properly
Lighting and Shading II. Angel and Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 7E Addison-Wesley 2015
 Lighting and Shading II 1 Objectives Continue discussion of shading Introduce modified Phong model Consider computation of required vectors 2 Ambient Light Ambient light is the result of multiple interactions
Lighting and Shading II 1 Objectives Continue discussion of shading Introduce modified Phong model Consider computation of required vectors 2 Ambient Light Ambient light is the result of multiple interactions
INFOGR Computer Graphics
 INFOGR Computer Graphics Jacco Bikker & Debabrata Panja - April-July 2017 Lecture 10: Shaders Welcome! INFOGR2016/17 Today s Agenda: Recap: Diffuse Materials The Phong Shading Model Environment
INFOGR Computer Graphics Jacco Bikker & Debabrata Panja - April-July 2017 Lecture 10: Shaders Welcome! INFOGR2016/17 Today s Agenda: Recap: Diffuse Materials The Phong Shading Model Environment
COMP environment mapping Mar. 12, r = 2n(n v) v
 Rendering mirror surfaces The next texture mapping method assumes we have a mirror surface, or at least a reflectance function that contains a mirror component. Examples might be a car window or hood,
Rendering mirror surfaces The next texture mapping method assumes we have a mirror surface, or at least a reflectance function that contains a mirror component. Examples might be a car window or hood,
CS 381 Computer Graphics, Fall 2008 Midterm Exam Solutions. The Midterm Exam was given in class on Thursday, October 23, 2008.
 CS 381 Computer Graphics, Fall 2008 Midterm Exam Solutions The Midterm Exam was given in class on Thursday, October 23, 2008. 1. [4 pts] Drawing Where? Your instructor says that objects should always be
CS 381 Computer Graphics, Fall 2008 Midterm Exam Solutions The Midterm Exam was given in class on Thursday, October 23, 2008. 1. [4 pts] Drawing Where? Your instructor says that objects should always be
Methodology for Lecture. Importance of Lighting. Outline. Shading Models. Brief primer on Color. Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2010)
 Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2010) CS 184, Lecture 11: OpenGL 3 http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs184 Methodology for Lecture Lecture deals with lighting (teapot shaded as in HW1) Some Nate
Foundations of Computer Graphics (Spring 2010) CS 184, Lecture 11: OpenGL 3 http://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs184 Methodology for Lecture Lecture deals with lighting (teapot shaded as in HW1) Some Nate
Computer Graphics Coursework 1
 Computer Graphics Coursework 1 Deadline Deadline: 4pm, 24/10/2016 4pm 23/10/2015 Outline The aim of the coursework is to modify the vertex and fragment shaders in the provided OpenGL framework to implement
Computer Graphics Coursework 1 Deadline Deadline: 4pm, 24/10/2016 4pm 23/10/2015 Outline The aim of the coursework is to modify the vertex and fragment shaders in the provided OpenGL framework to implement
CS452/552; EE465/505. Intro to Lighting
 CS452/552; EE465/505 Intro to Lighting 2-10 15 Outline! Projection Normalization! Introduction to Lighting (and Shading) Read: Angel Chapter 5., sections 5.4-5.7 Parallel Projections Chapter 6, sections
CS452/552; EE465/505 Intro to Lighting 2-10 15 Outline! Projection Normalization! Introduction to Lighting (and Shading) Read: Angel Chapter 5., sections 5.4-5.7 Parallel Projections Chapter 6, sections
Bump Mapping. Mike Bailey. What is Bump-Mapping?
 1 Bump Mapping This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License Mike Bailey mjb@cs.oregonstate.edu bumpmapping.pptx What is Bump-Mapping?
1 Bump Mapping This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License Mike Bailey mjb@cs.oregonstate.edu bumpmapping.pptx What is Bump-Mapping?
Visualisatie BMT. Rendering. Arjan Kok
 Visualisatie BMT Rendering Arjan Kok a.j.f.kok@tue.nl 1 Lecture overview Color Rendering Illumination 2 Visualization pipeline Raw Data Data Enrichment/Enhancement Derived Data Visualization Mapping Abstract
Visualisatie BMT Rendering Arjan Kok a.j.f.kok@tue.nl 1 Lecture overview Color Rendering Illumination 2 Visualization pipeline Raw Data Data Enrichment/Enhancement Derived Data Visualization Mapping Abstract
Illumination & Shading: Part 1
 Illumination & Shading: Part 1 Light Sources Empirical Illumination Shading Local vs Global Illumination Lecture 10 Comp 236 Spring 2005 Computer Graphics Jargon: Illumination Models Illumination - the
Illumination & Shading: Part 1 Light Sources Empirical Illumination Shading Local vs Global Illumination Lecture 10 Comp 236 Spring 2005 Computer Graphics Jargon: Illumination Models Illumination - the
Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 16: Lighting, Shading and Materials (Part 1)
 Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 16: Lighting, Shading and Materials (Part 1) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Why do we need Lighting & shading? Sphere
Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 16: Lighting, Shading and Materials (Part 1) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Why do we need Lighting & shading? Sphere
 Mike Bailey mjb@cs.oregonstate.edu 1 http://cs.oregonstate.edu/~mjb/fundsem This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Oregon Attribution-NonCommercial- State University NoDerivatives 4.0 International
Mike Bailey mjb@cs.oregonstate.edu 1 http://cs.oregonstate.edu/~mjb/fundsem This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Oregon Attribution-NonCommercial- State University NoDerivatives 4.0 International
Rendering. Illumination Model. Wireframe rendering simple, ambiguous Color filling flat without any 3D information
 llumination Model Wireframe rendering simple, ambiguous Color filling flat without any 3D information Requires modeling interaction of light with the object/surface to have a different color (shade in
llumination Model Wireframe rendering simple, ambiguous Color filling flat without any 3D information Requires modeling interaction of light with the object/surface to have a different color (shade in
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 7b: Intro to lighting, Shading and Materials + Phong Lighting Model
 Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 7b: Intro to lighting, Shading and Materials + Phong Lighting Model Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Why do we need Lighting
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 7b: Intro to lighting, Shading and Materials + Phong Lighting Model Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Why do we need Lighting
Shading. Brian Curless CSE 457 Spring 2017
 Shading Brian Curless CSE 457 Spring 2017 1 Reading Optional: Angel and Shreiner: chapter 5. Marschner and Shirley: chapter 10, chapter 17. Further reading: OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 2 Basic 3D graphics
Shading Brian Curless CSE 457 Spring 2017 1 Reading Optional: Angel and Shreiner: chapter 5. Marschner and Shirley: chapter 10, chapter 17. Further reading: OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 2 Basic 3D graphics
Shading. Slides by Ulf Assarsson and Tomas Akenine-Möller Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology
 Shading Slides by Ulf Assarsson and Tomas Akenine-Möller Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology Overview of today s lecture l A simple most basic real-time lighting model
Shading Slides by Ulf Assarsson and Tomas Akenine-Möller Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology Overview of today s lecture l A simple most basic real-time lighting model
C O M P U T E R G R A P H I C S. Computer Graphics. Three-Dimensional Graphics V. Guoying Zhao 1 / 65
 Computer Graphics Three-Dimensional Graphics V Guoying Zhao 1 / 65 Shading Guoying Zhao 2 / 65 Objectives Learn to shade objects so their images appear three-dimensional Introduce the types of light-material
Computer Graphics Three-Dimensional Graphics V Guoying Zhao 1 / 65 Shading Guoying Zhao 2 / 65 Objectives Learn to shade objects so their images appear three-dimensional Introduce the types of light-material
Light Sources. Spotlight model
 lecture 12 Light Sources sunlight (parallel) Sunny day model : "point source at infinity" - lighting - materials: diffuse, specular, ambient spotlight - shading: Flat vs. Gouraud vs Phong light bulb ambient
lecture 12 Light Sources sunlight (parallel) Sunny day model : "point source at infinity" - lighting - materials: diffuse, specular, ambient spotlight - shading: Flat vs. Gouraud vs Phong light bulb ambient
The Graphics Pipeline and OpenGL III: OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL 1.10)!
 ! The Graphics Pipeline and OpenGL III: OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL 1.10)! Gordon Wetzstein! Stanford University! EE 267 Virtual Reality! Lecture 4! stanford.edu/class/ee267/! Lecture Overview! Review
! The Graphics Pipeline and OpenGL III: OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL 1.10)! Gordon Wetzstein! Stanford University! EE 267 Virtual Reality! Lecture 4! stanford.edu/class/ee267/! Lecture Overview! Review
CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Fall
 Illumination Models and Surface-Rendering Methods CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Fall 2007 2008 Illumination Models and Surface Rendering Methods In order to achieve realism in computer generated
Illumination Models and Surface-Rendering Methods CEng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Fall 2007 2008 Illumination Models and Surface Rendering Methods In order to achieve realism in computer generated
Illumination & Shading I
 CS 543: Computer Graphics Illumination & Shading I Robert W. Lindeman Associate Professor Interactive Media & Game Development Department of Computer Science Worcester Polytechnic Institute gogo@wpi.edu
CS 543: Computer Graphics Illumination & Shading I Robert W. Lindeman Associate Professor Interactive Media & Game Development Department of Computer Science Worcester Polytechnic Institute gogo@wpi.edu
Today. Global illumination. Shading. Interactive applications. Rendering pipeline. Computergrafik. Shading Introduction Local shading models
 Computergrafik Thomas Buchberger, Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2008 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation
Computergrafik Thomas Buchberger, Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2008 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation
OpenGL Lighting Computer Graphics Spring Frank Palermo
 OpenGL Lighting 15-462 Computer Graphics Spring 2009 Frank Palermo OpenGL is just a bunch of hacks. -Adrien Treuille What Adrien Means... What Adrien means is that OpenGL was designed to produce reasonable-looking
OpenGL Lighting 15-462 Computer Graphics Spring 2009 Frank Palermo OpenGL is just a bunch of hacks. -Adrien Treuille What Adrien Means... What Adrien means is that OpenGL was designed to produce reasonable-looking
Shading and Illumination
 Shading and Illumination OpenGL Shading Without Shading With Shading Physics Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function (BRDF) f r (ω i,ω ) = dl(ω ) L(ω i )cosθ i dω i = dl(ω ) L(ω i )( ω i n)dω
Shading and Illumination OpenGL Shading Without Shading With Shading Physics Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function (BRDF) f r (ω i,ω ) = dl(ω ) L(ω i )cosθ i dω i = dl(ω ) L(ω i )( ω i n)dω
EDAF80 Introduction to Computer Graphics. Seminar 3. Shaders. Michael Doggett. Slides by Carl Johan Gribel,
 EDAF80 Introduction to Computer Graphics Seminar 3 Shaders Michael Doggett 2017 Slides by Carl Johan Gribel, 2010-13 Today OpenGL Shader Language (GLSL) Shading theory Assignment 3: (you guessed it) writing
EDAF80 Introduction to Computer Graphics Seminar 3 Shaders Michael Doggett 2017 Slides by Carl Johan Gribel, 2010-13 Today OpenGL Shader Language (GLSL) Shading theory Assignment 3: (you guessed it) writing
Programmable Graphics Hardware
 CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 14 Programmable Graphics Hardware [Ch. 9] March 2, 2011 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California OpenGL Extensions Shading Languages Vertex Program Fragment Program
CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 14 Programmable Graphics Hardware [Ch. 9] March 2, 2011 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California OpenGL Extensions Shading Languages Vertex Program Fragment Program
INFOGR Computer Graphics
 INFOGR Computer Graphics Jacco Bikker & Debabrata Panja - April-July 2018 Lecture 10: Shaders Welcome! Ƹ Ƹ Ƹ x M final = T totorso R T down R = x y z 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 Operations: 1. Translate
INFOGR Computer Graphics Jacco Bikker & Debabrata Panja - April-July 2018 Lecture 10: Shaders Welcome! Ƹ Ƹ Ƹ x M final = T totorso R T down R = x y z 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 Operations: 1. Translate
9. Illumination and Shading
 9. Illumination and Shading Approaches for visual realism: - Remove hidden surfaces - Shade visible surfaces and reproduce shadows - Reproduce surface properties Texture Degree of transparency Roughness,
9. Illumination and Shading Approaches for visual realism: - Remove hidden surfaces - Shade visible surfaces and reproduce shadows - Reproduce surface properties Texture Degree of transparency Roughness,
CSE 167: Lecture #8: GLSL. Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2012
 CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #8: GLSL Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2012 Announcements Homework project #4 due Friday, November 2 nd Introduction:
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #8: GLSL Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2012 Announcements Homework project #4 due Friday, November 2 nd Introduction:
Lessons Learned from HW4. Shading. Objectives. Why we need shading. Shading. Scattering
 Lessons Learned from HW Shading CS Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science Only have an idle() function if something is animated Set idle function to NULL, when
Lessons Learned from HW Shading CS Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science Only have an idle() function if something is animated Set idle function to NULL, when
Shader Programming. Daniel Wesslén, Stefan Seipel, Examples
 Shader Programming Daniel Wesslén, dwn@hig.se Stefan Seipel, ssl@hig.se Examples 1 Per-pixel lighting Texture convolution filtering 2 Post-processing, animated procedural textures Vertex displacement mapping
Shader Programming Daniel Wesslén, dwn@hig.se Stefan Seipel, ssl@hig.se Examples 1 Per-pixel lighting Texture convolution filtering 2 Post-processing, animated procedural textures Vertex displacement mapping
To Do. Demo for mytest3. Methodology for Lecture. Importance of Lighting. Brief primer on Color. Computer Graphics
 Computer Graphics CSE 167 [Win 17], Lecture 7: OpenGL Shading Ravi Ramamoorthi http://viscomp.ucsd.edu/classes/cse167/wi17 To Do This week s lectures have all info for HW 2 Start EARLY Methodology for
Computer Graphics CSE 167 [Win 17], Lecture 7: OpenGL Shading Ravi Ramamoorthi http://viscomp.ucsd.edu/classes/cse167/wi17 To Do This week s lectures have all info for HW 2 Start EARLY Methodology for
Computer Graphics. Illumination and Shading
 () Illumination and Shading Dr. Ayman Eldeib Lighting So given a 3-D triangle and a 3-D viewpoint, we can set the right pixels But what color should those pixels be? If we re attempting to create a realistic
() Illumination and Shading Dr. Ayman Eldeib Lighting So given a 3-D triangle and a 3-D viewpoint, we can set the right pixels But what color should those pixels be? If we re attempting to create a realistic
Ligh%ng in OpenGL. The Phong Illumina%on Model. Vector Background
 Ligh%ng in OpenGL The Phong Illumina%on Model Vector Background 1 Vector Dot Product The dot product of two vectors is a number:! x $ # 1 v 1 = # y 1 # " z 1 %! x $ # 2 v 2 = # y 2 # " z 2 % In GLSL you
Ligh%ng in OpenGL The Phong Illumina%on Model Vector Background 1 Vector Dot Product The dot product of two vectors is a number:! x $ # 1 v 1 = # y 1 # " z 1 %! x $ # 2 v 2 = # y 2 # " z 2 % In GLSL you
GLSL Geometry Shaders
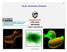 GLSL Geometry Shaders 1 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License Mike Bailey mjb@cs.oregonstate.edu geometry_shaders.pptx Here s
GLSL Geometry Shaders 1 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License Mike Bailey mjb@cs.oregonstate.edu geometry_shaders.pptx Here s
CS 4620 Program 3: Pipeline
 CS 4620 Program 3: Pipeline out: Wednesday 14 October 2009 due: Friday 30 October 2009 1 Introduction In this assignment, you will implement several types of shading in a simple software graphics pipeline.
CS 4620 Program 3: Pipeline out: Wednesday 14 October 2009 due: Friday 30 October 2009 1 Introduction In this assignment, you will implement several types of shading in a simple software graphics pipeline.
Shading. Shading = find color values at pixels of screen (when rendering a virtual 3D scene).
 Light Shading Shading Shading = find color values at pixels of screen (when rendering a virtual 3D scene). Shading Shading = find color values at pixels of screen (when rendering a virtual 3D scene). Same
Light Shading Shading Shading = find color values at pixels of screen (when rendering a virtual 3D scene). Shading Shading = find color values at pixels of screen (when rendering a virtual 3D scene). Same
Lighting/Shading III. Week 7, Wed Mar 3
 University of British Columbia CPSC 314 Computer Graphics Jan-Apr 2010 Tamara Munzner Lighting/Shading III Week 7, Wed Mar 3 http://www.ugrad.cs.ubc.ca/~cs314/vjan2010 reminders News don't need to tell
University of British Columbia CPSC 314 Computer Graphics Jan-Apr 2010 Tamara Munzner Lighting/Shading III Week 7, Wed Mar 3 http://www.ugrad.cs.ubc.ca/~cs314/vjan2010 reminders News don't need to tell
Shading I Computer Graphics I, Fall 2008
 Shading I 1 Objectives Learn to shade objects ==> images appear threedimensional Introduce types of light-material interactions Build simple reflection model Phong model Can be used with real time graphics
Shading I 1 Objectives Learn to shade objects ==> images appear threedimensional Introduce types of light-material interactions Build simple reflection model Phong model Can be used with real time graphics
Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 18: Lighting, Shading and Materials (Part 3)
 Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 18: Lighting, Shading and Materials (Part 3) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Recall: Flat Shading compute lighting once
Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 18: Lighting, Shading and Materials (Part 3) Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Recall: Flat Shading compute lighting once
AGDC Per-Pixel Shading. Sim Dietrich
 AGDC Per-Pixel Shading Sim Dietrich Goal Of This Talk The new features of Dx8 and the next generation of HW make huge strides in the area of Per-Pixel Shading Most developers have yet to adopt Per-Pixel
AGDC Per-Pixel Shading Sim Dietrich Goal Of This Talk The new features of Dx8 and the next generation of HW make huge strides in the area of Per-Pixel Shading Most developers have yet to adopt Per-Pixel
Today s class. Simple shadows Shading Lighting in OpenGL. Informationsteknologi. Wednesday, November 21, 2007 Computer Graphics - Class 10 1
 Today s class Simple shadows Shading Lighting in OpenGL Wednesday, November 21, 27 Computer Graphics - Class 1 1 Simple shadows Simple shadows can be gotten by using projection matrices Consider a light
Today s class Simple shadows Shading Lighting in OpenGL Wednesday, November 21, 27 Computer Graphics - Class 1 1 Simple shadows Simple shadows can be gotten by using projection matrices Consider a light
Today. Global illumination. Shading. Interactive applications. Rendering pipeline. Computergrafik. Shading Introduction Local shading models
 Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2009 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation of physics Global
Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2009 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation of physics Global
Pipeline Operations. CS 4620 Lecture Steve Marschner. Cornell CS4620 Spring 2018 Lecture 11
 Pipeline Operations CS 4620 Lecture 11 1 Pipeline you are here APPLICATION COMMAND STREAM 3D transformations; shading VERTEX PROCESSING TRANSFORMED GEOMETRY conversion of primitives to pixels RASTERIZATION
Pipeline Operations CS 4620 Lecture 11 1 Pipeline you are here APPLICATION COMMAND STREAM 3D transformations; shading VERTEX PROCESSING TRANSFORMED GEOMETRY conversion of primitives to pixels RASTERIZATION
Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics. Spring Shading
 Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2017 Shading Why we need shading Suppose we build a model of a sphere using many polygons and then color it using a fixed color. We get something like But we rather
Comp 410/510 Computer Graphics Spring 2017 Shading Why we need shading Suppose we build a model of a sphere using many polygons and then color it using a fixed color. We get something like But we rather
SUMMARY. CS380: Introduction to Computer Graphics Texture Mapping Chapter 15. Min H. Kim KAIST School of Computing 18/05/03.
 CS380: Introduction to Computer Graphics Texture Mapping Chapter 15 Min H. Kim KAIST School of Computing Materials SUMMARY 2 1 Light blob from PVC plastic Recall: Given any vector w (not necessarily of
CS380: Introduction to Computer Graphics Texture Mapping Chapter 15 Min H. Kim KAIST School of Computing Materials SUMMARY 2 1 Light blob from PVC plastic Recall: Given any vector w (not necessarily of
PROFESSIONAL. WebGL Programming DEVELOPING 3D GRAPHICS FOR THE WEB. Andreas Anyuru WILEY. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
 PROFESSIONAL WebGL Programming DEVELOPING 3D GRAPHICS FOR THE WEB Andreas Anyuru WILEY John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. INTRODUCTION xxl CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCING WEBGL 1 The Basics of WebGL 1 So Why Is WebGL So Great?
PROFESSIONAL WebGL Programming DEVELOPING 3D GRAPHICS FOR THE WEB Andreas Anyuru WILEY John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. INTRODUCTION xxl CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCING WEBGL 1 The Basics of WebGL 1 So Why Is WebGL So Great?
Illumination Model. The governing principles for computing the. Apply the lighting model at a set of points across the entire surface.
 Illumination and Shading Illumination (Lighting) Model the interaction of light with surface points to determine their final color and brightness OpenGL computes illumination at vertices illumination Shading
Illumination and Shading Illumination (Lighting) Model the interaction of light with surface points to determine their final color and brightness OpenGL computes illumination at vertices illumination Shading
How do we draw a picture?
 1 How do we draw a picture? Define geometry. Now what? We can draw the edges of the faces. Wireframe. We can only draw the edges of faces that are visible. We can fill in the faces. Giving each object
1 How do we draw a picture? Define geometry. Now what? We can draw the edges of the faces. Wireframe. We can only draw the edges of faces that are visible. We can fill in the faces. Giving each object
Illumination and Shading
 Illumination and Shading Illumination and Shading z Illumination Models y Ambient y Diffuse y Attenuation y Specular Reflection z Interpolated Shading Models y Flat, Gouraud, Phong y Problems CS4451: Fall
Illumination and Shading Illumination and Shading z Illumination Models y Ambient y Diffuse y Attenuation y Specular Reflection z Interpolated Shading Models y Flat, Gouraud, Phong y Problems CS4451: Fall
CGT520 Lighting. Lighting. T-vertices. Normal vector. Color of an object can be specified 1) Explicitly as a color buffer
 CGT520 Lighting Lighting Color of an object can be specified 1) Explicitly as a color buffer Bedrich Benes, Ph.D. Purdue University Department of Computer Graphics 2) Implicitly from the illumination model.
CGT520 Lighting Lighting Color of an object can be specified 1) Explicitly as a color buffer Bedrich Benes, Ph.D. Purdue University Department of Computer Graphics 2) Implicitly from the illumination model.
CS452/552; EE465/505. Lighting & Shading
 CS452/552; EE465/505 Lighting & Shading 2-17 15 Outline! More on Lighting and Shading Read: Angel Chapter 6 Lab2: due tonight use ASDW to move a 2D shape around; 1 to center Local Illumination! Approximate
CS452/552; EE465/505 Lighting & Shading 2-17 15 Outline! More on Lighting and Shading Read: Angel Chapter 6 Lab2: due tonight use ASDW to move a 2D shape around; 1 to center Local Illumination! Approximate
Computer Graphics. Shading. Based on slides by Dianna Xu, Bryn Mawr College
 Computer Graphics Shading Based on slides by Dianna Xu, Bryn Mawr College Image Synthesis and Shading Perception of 3D Objects Displays almost always 2 dimensional. Depth cues needed to restore the third
Computer Graphics Shading Based on slides by Dianna Xu, Bryn Mawr College Image Synthesis and Shading Perception of 3D Objects Displays almost always 2 dimensional. Depth cues needed to restore the third
Shading. Brian Curless CSE 457 Spring 2015
 Shading Brian Curless CSE 457 Spring 2015 1 Reading Required: Angel chapter 5. Optional: OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 2 Basic 3D graphics With affine matrices, we can now transform virtual 3D objects in
Shading Brian Curless CSE 457 Spring 2015 1 Reading Required: Angel chapter 5. Optional: OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 2 Basic 3D graphics With affine matrices, we can now transform virtual 3D objects in
CS559 Computer Graphics Fall 2015
 CS559 Computer Graphics Fall 2015 Practice Midterm Exam Time: 2 hrs 1. [XX Y Y % = ZZ%] MULTIPLE CHOICE SECTION. Circle or underline the correct answer (or answers). You do not need to provide a justification
CS559 Computer Graphics Fall 2015 Practice Midterm Exam Time: 2 hrs 1. [XX Y Y % = ZZ%] MULTIPLE CHOICE SECTION. Circle or underline the correct answer (or answers). You do not need to provide a justification
Reading. Shading. Introduction. An abundance of photons. Required: Angel , Optional: OpenGL red book, chapter 5.
 Reading Required: Angel 6.1-6.5, 6.7-6.8 Optional: Shading OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 1 2 Introduction So far, we ve talked exclusively about geometry. What is the shape of an obect? How do I place it
Reading Required: Angel 6.1-6.5, 6.7-6.8 Optional: Shading OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 1 2 Introduction So far, we ve talked exclusively about geometry. What is the shape of an obect? How do I place it
The Graphics Pipeline and OpenGL III: OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL 1.10)!
 ! The Graphics Pipeline and OpenGL III: OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL 1.10)! Gordon Wetzstein! Stanford University! EE 267 Virtual Reality! Lecture 4! stanford.edu/class/ee267/! Updates! for 24h lab access:
! The Graphics Pipeline and OpenGL III: OpenGL Shading Language (GLSL 1.10)! Gordon Wetzstein! Stanford University! EE 267 Virtual Reality! Lecture 4! stanford.edu/class/ee267/! Updates! for 24h lab access:
Introduction to the OpenGL Shading Language
 Introduction to the OpenGL Shading Language Randi Rost Director of Developer Relations, 3Dlabs 08-Dec-2005 1 Why use graphics programmability? Graphics hardware has changed radically Fixed functionality
Introduction to the OpenGL Shading Language Randi Rost Director of Developer Relations, 3Dlabs 08-Dec-2005 1 Why use graphics programmability? Graphics hardware has changed radically Fixed functionality
INF3320 Computer Graphics and Discrete Geometry
 INF3320 Computer Graphics and Discrete Geometry Texturing Christopher Dyken Martin Reimers 06.10.2010 Page 1 Texturing Linear interpolation Real Time Rendering: Chapter 5: Visual Appearance Chapter 6:
INF3320 Computer Graphics and Discrete Geometry Texturing Christopher Dyken Martin Reimers 06.10.2010 Page 1 Texturing Linear interpolation Real Time Rendering: Chapter 5: Visual Appearance Chapter 6:
Shading. CSE 457 Winter 2015
 Shading CSE 457 Winter 2015 Reading Required: Angel chapter 5. Optional: OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 2 Basic 3D graphics With affine matrices, we can now transform virtual 3D objects in their local coordinate
Shading CSE 457 Winter 2015 Reading Required: Angel chapter 5. Optional: OpenGL red book, chapter 5. 2 Basic 3D graphics With affine matrices, we can now transform virtual 3D objects in their local coordinate
CS 418: Interactive Computer Graphics. Basic Shading in WebGL. Eric Shaffer
 CS 48: Interactive Computer Graphics Basic Shading in WebGL Eric Shaffer Some slides adapted from Angel and Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 7E Addison-Wesley 205 Phong Reflectance Model Blinn-Phong
CS 48: Interactive Computer Graphics Basic Shading in WebGL Eric Shaffer Some slides adapted from Angel and Shreiner: Interactive Computer Graphics 7E Addison-Wesley 205 Phong Reflectance Model Blinn-Phong
Lets assume each object has a defined colour. Hence our illumination model is looks unrealistic.
 Shading Models There are two main types of rendering that we cover, polygon rendering ray tracing Polygon rendering is used to apply illumination models to polygons, whereas ray tracing applies to arbitrary
Shading Models There are two main types of rendering that we cover, polygon rendering ray tracing Polygon rendering is used to apply illumination models to polygons, whereas ray tracing applies to arbitrary
Pipeline Operations. CS 4620 Lecture 14
 Pipeline Operations CS 4620 Lecture 14 2014 Steve Marschner 1 Pipeline you are here APPLICATION COMMAND STREAM 3D transformations; shading VERTEX PROCESSING TRANSFORMED GEOMETRY conversion of primitives
Pipeline Operations CS 4620 Lecture 14 2014 Steve Marschner 1 Pipeline you are here APPLICATION COMMAND STREAM 3D transformations; shading VERTEX PROCESSING TRANSFORMED GEOMETRY conversion of primitives
Shading. Slides by Ulf Assarsson and Tomas Akenine-Möller Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology
 Shading Slides by Ulf Assarsson and Tomas Akenine-Möller Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology Overview of today s lecture l A simple most basic real-time lighting model
Shading Slides by Ulf Assarsson and Tomas Akenine-Möller Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology Overview of today s lecture l A simple most basic real-time lighting model
Illumination and Shading
 Illumination and Shading Illumination (Lighting) Model the interaction of light with surface points to determine their final color and brightness OpenGL computes illumination at vertices illumination Shading
Illumination and Shading Illumination (Lighting) Model the interaction of light with surface points to determine their final color and brightness OpenGL computes illumination at vertices illumination Shading
CSE 167: Lecture #8: Lighting. Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2011
 CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #8: Lighting Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2011 Announcements Homework project #4 due Friday, October 28 Introduction:
CSE 167: Introduction to Computer Graphics Lecture #8: Lighting Jürgen P. Schulze, Ph.D. University of California, San Diego Fall Quarter 2011 Announcements Homework project #4 due Friday, October 28 Introduction:
Homework 3: Programmable Shaders
 Homework 3: Programmable Shaders Introduction to Computer Graphics and Imaging (Summer 2012), Stanford University Due Monday, July 23, 11:59pm Warning: The coding portion of this homework involves features
Homework 3: Programmable Shaders Introduction to Computer Graphics and Imaging (Summer 2012), Stanford University Due Monday, July 23, 11:59pm Warning: The coding portion of this homework involves features
CS 4731: Computer Graphics Lecture 16: Phong Illumination and Shading. Emmanuel Agu
 CS 4731: Computer Graphics Lecture 16: Phong Illumination and Shading Emmanuel Agu Recall: Setting Light Property Define colors and position a light GLfloat light_ambient[] = {0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0}; GLfloat
CS 4731: Computer Graphics Lecture 16: Phong Illumination and Shading Emmanuel Agu Recall: Setting Light Property Define colors and position a light GLfloat light_ambient[] = {0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0}; GLfloat
