AW Math 10 UNIT 7 RIGHT ANGLE TRIANGLES
|
|
|
- Gordon Washington
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AW Math 10 UNIT 7 RIGHT ANGLE TRIANGLES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagorean Theorem 3 More Pythagorean Theorem Eploring Pythagorean Theorem Using Pythagorean Theorem in Problem Solving 4 Pythagorean Triples Pythagorean Triples 5 Trigonometry Trigonometry Quiz 1 6 The Sine Ratio The Cosine Ratio The Tangent Ratio The Trigonometric Ratios 7 Using The Sine Ratio Using The Cosine Ratio Using The Tangent Ratio Finding Sides In Right Triangles 8 Angle of Elevation and Depression Using Angle of Elevation and Depression Quiz 2 9 Finding Angles in Right Triangles Finding Angles In Right Triangles Practice Test Practice Test How are you doing? Get this page from your teacher Self- Assessment Self-Assessment On the net page, complete the self-assessment assignment. Unit Test Unit Test Show me your stuff! Mental Math Mental Math Non-calculator practice 1
2 Self Assessment In the following chart, show how confident you feel about each statement by drawing one of the following:,, or. Then discuss this with your teacher BEFORE you write the test! Statement After completing this chapter; I can use the Pythagorean theorem to calculate the missing side of a right triangle I know when to choose sine (sin), cosine (cos) or tangent (tan) based on the information given I can use the three basic trigonometric functions (sin, cos, tan) to find a missing side or angle of a right triangle I can determine the angle of elevation and the angle of depression for words or a diagram, and use them with the trigonometric ratios I can determine places in the workplace where I could use trigonometry Vocabulary: Unit 7 angle of depression angle of elevation cosine hypotenuse leg Pythagorean Theorem Pythagorean Triple right triangle sine tangent 2
3 TRIANGLES In this unit, you will be looking at triangles, specifically right angle triangles, also called right triangles. You will learn about Pythagorean Theorem and the basic trigonometric ratios. But first it is necessary to start with some facts about triangles. Fact 1: Every triangle contains 3 sides and 3 angles or vertices (plural of verte). Fact 2: The measurements of these angles always total Remember this from the last unit?? Fact 3: To identify the side or verte in a triangle, it is important to label the triangle following a standard protocol. Each verte of a triangle is labeled with a capital case letter like A - and each side is labeled with the lower case letter that matches the opposite verte. An eample is below. A c b B a C Another way to label the sides is with the capital letters of the two vertices the side connects. An eample is below. A c b Side a can be called BC. Side b can be called AC. Side c can be called AB. B a C 3
4 ASSIGNMENT 1 LABELLING TRIANGLES 1) Label each side of the triangles below using a single lower case letter matching the opposite verte. a) X b) R Y Z S T c) d) D A E F B C 2) Label each verte of the triangles below using a single capital letter matching the opposite side. a) b) f a b d e c c) d) q p r w y 4
5 PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM Pythagorean Theorem states the relationship between the sides of a right triangle. So, more facts about triangles are necessary. Fact 4: A triangle that contains a 90 0 angle (a right angle) is called a right triangle (or right-angle triangle). Fact 5: The side of the triangle that is opposite the 90 0 angle is always called the hypotenuse. It is labelled in the triangle below. The other two sides of the triangle are called legs. hypotenuse Fact 6: The hypotenuse is always the longest side in the triangle. It is always opposite the largest angle which is the 90 0 or right angle. Fact 7: Pythagorean Theorem states that in any right triangle, the sum of the squares of the lengths of the legs is equal to the square of the length of the hypotenuse. So in ΔABC with the right angle at C, the following relationship is true: c 2 = a 2 + b 2 where a and b are the other 2 legs of the triangle. c b a 5
6 Often Pythagorean Theorem is illustrated as the square of the sides as follows: Notice that the length of side a is 3 boes, side b is 4 boes, and side c is 5 boes. So if we calculate the area of each square, the following is true: c c = c 2 = 5 5 = 25 b b = b 2 = 4 4 = 16 a a = a 2 = 3 3 = 9 And we know that c 2 = a 2 + b 2 So 25 = which is a true statement! We can also rearrange the equation to find the length one of the legs; c 2 = a 2 + b 2 a 2 = c 2 b 2 b 2 = c 2 a 2 When we use Pythagorean Theorem to find a length of the hypotenuse or a leg, you need to have a calculator that has the square root function on it. The computer symbol looks like this: or ASSIGNMENT 2 EXPLORING PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM 1) Using the following triangles, use lettering provided to state the Pythagorean relations that apply. a) b) E F X z y Y Z D 6
7 2) Find the missing value in each of the following to 2 decimal places. Remember to use the square root to solve for each final side length. An eample is done for you. Eample: b 2 = b 2 = b 2 = 169 b = 169 = 13 a) p 2 = b) m 2 = c) y 2 = d) z 2 = ) Calculate the missing side length () in each triangle to 1 decimal place (as needed). a) b) c) d)
8 MORE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM Pythagorean Theorem can be used to solve for an unknown side in a right triangle. It is important to recognize if you are trying to solve for the hypotenuse or one of the legs. If you are solving for the hypotenuse, you will add the squares of the other two sides, getting a larger side length (the hypotenuse is the longest side length). But if you are given the hypotenuse, subtract the square of the leg from the square of the hypotenuse in order to get a smaller side (than the hypotenuse). Eample 1: Use Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the missing side to one decimal place. P Solution: q 2 = p 2 + r cm q q 2 = q 2 = q 2 = Q 5.2 cm R q 2 = q 6.44 cm Side q is approimately 6.4 cm Eample 2: Use Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the missing side to one decimal place. A Solution: c 2 = a 2 + b 2 b 12.8 in So, b 2 = c 2 a 2 b 2 = b 2 = C 8.78 in B b 2 = b = b 9.31 cm Side b is approimately 9.31 cm 8
9 ASSIGNMENT 3 USING PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM IN PROBLEM SOLVING 1) Solve for the length of the bracket in the picture, to one decimal place. 2) What is the length of the guy wire in the picture below, to one decimal place? 3) A ramp into a house rises up ( ) 3.5 meters over a horizontal distance ( ) of 10.5 metres. How long is the ramp? Use the triangle below and show your work. 4) You need to find the width of a lake, PQ, as shown. The measurements of the other sides are given on the diagram. You are certain that P = What is the width of the lake? 9
10 5) A ladder is leaned against a house. The base of the ladder is d feet away from the house. Draw a diagram and then write the Pythagorean relationship that eists for these lengths. Use l for the ladder, h for the house, and d for the distance the ladder is from the house. You are not required to solve this question. 6) A 40 foot ladder reaches 38 feet up the side of a house. How far from the side of the house is the base of the ladder? Draw a diagram and show your work. 7) A flagpole is 12 metres tall. It makes a shadow on the ground that is 15 metres long. How long is a line that joins the top of the flagpole with the end of the shadow? Draw a diagram and show your work. 8) The size of a flat screen TV is given by the length of the diagonal of the screen (joining opposite corners). What is the length of a diagonal if the sides are 40.5 inches by inches? Draw a diagram and show your work. 10
11 PYTHAGOREAN TRIPLES A Pythagorean Triple is a set of three numbers that satisfy the Pythagorean Theorem and are all whole numbers (no decimals). If a set of numbers satisfies the Pythagorean relationship, then the triangle must be a right triangle. An eample is shown below. A 5 13 C 12 B Left Side = c 2 Right Side = a 2 + b 2 = 13 2 = = 169 = = 169 Therefore, Left Side = Right Side. This triangle is a right angle triangle, and the set of numbers, 5, 12, and 13 are a Pythagorean Triple. ASSIGNMENT 4 PYTHAGOREAN TRIPLES 1) Which of the following triangles are right triangles? Show your work as proof. a) b) c) d)
12 TRIGONOMETRY Trigonometry is one of the most important topics in mathematics. Trigonometry is used in many fields including engineering, architecture, surveying, aviation, navigation, carpentry, forestry, and computer graphics. Also, until satellites, the most accurate maps were constructed using trigonometry. The word trigonometry means triangle measurements. It is necessary to finish our triangle facts here. Fact 8: In trigonometry, the other two sides (or legs) of the triangle are referred to as the opposite and adjacent sides, depending on their relationship to the angle of interest in the triangle. In this eample, if we pick angle DEF the angle labelled with the Greek letter theta then we are able to distinguish the sides as illustrated in the diagram below. D opposite hypotenuse F adjacent E The side that is opposite the angle of interest, in this case, is called the opposite side. The side that is nearest to angle and makes up part of the angle is called the adjacent side. To help you, remember that adjacent means beside. Although the hypotenuse occupies one of the two adjacent positions, it is never called the adjacent side. It simply remains the hypotenuse. This is why it is identified first. It is recommended to label the side in the order hypotenuse, opposite, and finally adjacent. You may use initials for these side, h, o, and a, but always use lower case letters to avoid miing up the labelling with a verte. 12
13 Eample 1: Using the triangle below, answer the questions ) What is the hypotenuse? 2) What is the opposite side to? 3) What is the adjacent side to? Solution: 1) What is the hypotenuse? 15 2) What is the opposite side to? 9 3) What is the adjacent side to? 12 This eample uses the same triangle as in Eample 1; however, this time, the other acute angle is labelled as. This is done to show that the opposite and adjacent sides switch when the other angle is the angle of interest. The hypotenuse always stays the same. Eample 2: Using the triangle below, answer the questions Solution: 1) What is the hypotenuse? 2) What is the opposite side to? 3) What is the adjacent side to? 1) What is the hypotenuse? 15 2) What is the opposite side to? 12 3) What is the adjacent side to? 9 13
14 ASSIGNMENT 5 TRIGONOMETRY For each of the right triangles below, mark the hypotenuse, and the sides that are opposite and adjacent sides to as shown in the eample. Eample: h = hypotenuse h o o = opposite a = adjacent a 1) 2) 3) 4) ASK YOUR TEACHER FOR QUIZ 1 14
15 TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS In the previous unit about similar figures, you learned that the ratios of corresponding sides of similar triangles are equal. When the angles of different triangles are the same, the ratio of the sides within the triangle will always be the same. They depend only on the measure of the angle of interest, not the size of the triangle. These ratios are the trigonometric ratios. There are three trigonometric ratios we are concerned with: sine, cosine, and tangent. THE SINE RATIO The sine of angle means the ratio of the length of opposite side to the length of the hypotenuse. It is abbreviated as sin but read as sine. It is written like this: opposite sin = or sin = hypotenuse o h Eample 1: Find the sine of in this triangle. Round to 4 decimal places Solution: The opposite side is 5 and the hypotenuse is 13. So o h 5 13 sin = = = So sin = Note: Rounding to 4 decimal places is standard when calculating trigonometric ratios. Eample 2: Use your calculator to determine the following sine ratios. Round to 4 decimal places. a) sin 15 0 b) sin 67 0 c) sin 42 0 ***** REMEMBER TO SET YOUR CALCULATOR ON DEGREES (DEG) **** Solution: Type sin followed by the angle, and then = to solve a) sin 15 0 = b) sin 67 0 = c) sin 42 0 =
16 THE COSINE RATIO The cosine of angle means the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse. It is abbreviated as cos but read as cosine. It is written like this: adjacent cos = or cos = hypotenuse a h Eample 1: Find the cosine of in this triangle Solution: The adjacent side is 12 and the hypotenuse is 13. So a h cos = = = Note: Rounding to 4 decimal places is standard when calculating trigonometric ratios. Eample 2: Use your calculator to determine the following cosine ratios. Round to 4 decimal places. a) cos 15 0 b) cos 67 0 c) cos 42 0 ***** REMEMBER TO SET YOUR CALCULATOR ON DEGREES (DEG) **** Solution: Type cos followed by the angle, and then = to solve a) cos 15 0 = b) cos 67 0 = c) cos 42 0 =
17 THE TANGENT RATIO The tangent of angle means the ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side. It is abbreviated as tan but read as tangent. It is written like this: opposite tan = or tan = adjacent o a Eample 1: Find the tangent of in this triangle Solution: The opposite side is 5 and the adjacent side is 12. So o a 5 12 tan = = = Note: Rounding to 4 decimal places is standard when calculating trigonometric ratios. Eample 2: Use your calculator to determine the following tangent ratios. Round to 4 decimal places. a) tan 15 0 b) tan 67 0 c) tan 42 0 ***** REMEMBER TO SET YOUR CALCULATOR ON DEGREES (DEG) **** Solution: Type tan followed by the angle, and then = to solve a) tan 15 0 = b) tan 67 0 = c) tan 42 0 =
18 ASSIGNMENT 6 THE TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS 1) Calculate the value of sin to four decimal places. 5.2 in 8.1 in 6.9 m 9.6 in 4.3 m 2) Use your calculator to determine the value of each of the following sine ratios to four decimal places. a) sin 10 0 = b) sin 48 0 = c) sin 77 0 = d) sin 85 0 = 3) Calculate the value of cos to four decimal places. 5.2 in 8.1 in 12.4 cm 7.9 cm 9.6 in 4) Use your calculator to determine the value of each of the following cosine ratios to four decimal places. e) cos 10 0 = f) cos 48 0 = g) cos 77 0 = h) cos 85 0 = 18
19 5) Calculate the value of tan to four decimal places. 6.5 m 5.2 in 8.1 in 9.6 in 5.1 m 6) Use your calculator to determine the value of each of the following tangent ratios to four decimal places. i) tan 10 0 = j) tan 48 0 = k) tan 77 0 = l) tan 85 0 = 7) There are two special sine ratios. Calculate the following. a) sin 0 0 = b) sin 90 0 = 8) There are two special cosine ratios. Calculate the following. a) cos 0 0 = b) cos 90 0 = 9) There are some special tangent ratios. Calculate the following. a) tan 0 0 = b) tan 45 0 = c) tan 89 0 = d) tan 90 0 = Note what the answer key says that the tan 90 0 equals. Just because your calculator says one thing, doesn t mean the calculator knows what is going on! 19
20 USING THE SINE RATIO Whenever one side and one angle of a right triangle are already known, the remaining sides can be found using the trigonometric ratios. The sine ratio can be used to find missing parts of a right triangle. Eample 1: Use the sine ratio to solve for in the triangle below. 9 = 35 0 Solution: Step 1: Label the sides of the triangle with h, o and a h = 35 0 a 9 m o Step 2: Circle the number with the side it represents and the unknown () with the side it represents. Step 3: Identify the ratio required to solve for Since o and h are being used, the correct ratio is sin Step 4: Substitute the correct values into the correct ratio. sin = o h sin 35 0 = 9 Step 5: Solve using the process Cross Multiply and Divide. Since sin 35 0 sin 35 =, then sin 35 0 sin 35 = becomes = = 9 1 sin 35 0 = 15.7 m 20
21 Eample 2: A ladder 8.5 m long makes an angle of 72 0 with the ground. How far up the side of a building will the ladder reach? Solution: Sketch a diagram and place the information from the question on this diagram. Remember that there will always be a right triangle in your diagram. It is often helpful to draw that triangle and copy the key information from the sketch. h o 8.5 m 72 0 a Step 1: Label the sides of the triangle with h, o and a See above right. Step 2: Circle the number with the side it represents and the unknown () with the side it represents. Step 3: Identify the ratio required to solve for Since o and h are being used, the correct ratio is sin Step 4: Substitute the correct values into the correct ratio. sin = o h sin 72 0 = 8.5 Step 5: Solve using the process Cross Multiply and Divide. sin 72 sin 72 Since sin 72 0 =, then sin 72 0 = becomes = = sin = 8.1 m 21
22 USING THE COSINE RATIO Whenever one side and one angle of a right triangle are already known, the remaining sides can be found using the trigonometric ratios. The cosine ratio can be used to find missing parts of a right triangle. Eample 1: Use the correct trig ratio to solve for in the triangle below. 5 cm = 30 0 Solution: Step 1: Label the sides of the triangle with h, o and a h 5 cm o = 30 0 a Step 2: Circle the number with the side it represents and the unknown () with the side it represents. Step 3: Identify the ratio required to solve for Since a and h are being used, the correct ratio is cos Step 4: Write down the chosen ratio and substitute the correct values into the correct ratio. cos = a h cos 30 0 = 5 Step 5: Solve using the process Cross Multiply and Divide. Since cos 30 0 cos30 =, then cos 30 0 cos30 = becomes = = cos = 4.3 cm 22
23 USING THE TANGENT RATIO Whenever one side and one angle of a right triangle are already known, the remaining sides can be found using the trigonometric ratios. The tangent ratio can be used to find missing parts of a right triangle. Eample 1: Use the correct trig ratio to solve for in the triangle below. 2 mm = 15 0 Solution: Step 1: Label the sides of the triangle with h, o and a = 15 0 h a 2 mm o Step 2: Circle the number with the side it represents and the unknown () with the side it represents. Step 3: Identify the ratio required to solve for Since o and a are being used, the correct ratio is tan Step 4: Substitute the correct values into the correct ratio. tan = tan 15 = o a 2 Step 5: Solve using the process Cross Multiply and Divide. Since tan 15 0 tan15 =, then tan 15 0 tan15 = becomes = = 2 1 tan 15 0 = 7.5 mm 23
24 ASSIGNMENT 7 FINDING SIDES IN RIGHT TRIANGLES 1) Calculate the length of the side indicated in the following diagrams. Round to one decimal place. a) 5.2 m 23 0 b) cm c) cm 24
25 d) 12.3 m 11 0 e) 9.2 m 37 0 f) 6.5 cm
26 ANGLE OF ELEVATION AND DEPRESSION When you look up at an airplane flying overhead for eample, the angle between the horizontal and your line of sight is called the angle of elevation. When you look down from a cliff to a boat passing by, the angle between the horizontal and your line of sight is called the angle of depression. When you are given the angle of depression, it is important to carefully use this angle in your triangle. Eample 1: You are standing at the top of a cliff. You spot a boat 200 m away at an angle of depression of 55 0 to the horizon. How far is the boat from the coast? Draw a diagram to illustrate this situation. Solution: Draw a diagram, label it with the information, and then solve the triangle. horizon 55 0 Angle of depression 200 m The angle inside the triangle is the complement to the angle of depression. To find that angle, do the following: = =
27 ASSIGNMENT 8 USING ANGLE OF ELEVATION AND DEPRESSION Check that your calculator is on degrees DEG. Using the angle of elevation and the angle of depression correctly in triangles is a challenging concept. If you are having difficulties with these net 2 pages, make sure you discuss it with your teacher. 1) In the triangle below, what is the measure of the angle of elevation? Measure 2) Write the degree measurement of the angle of elevation in each diagram. Then find the length of the unknown side, to one decimal place. Show all work. a) Angle of elevation = 43 0 w 18.5 ft b) Angle of elevation = m 27
28 3) In the diagram below, what is the measure of the angle of depression? How do we name the angle of depression in this diagram? (See page 3 if you need a review.) A 63 0 D Measure Name B C 4) Write a degree measurement in the triangle for each diagram. Then find the length of the unknown side, to one decimal place. Show all work. a) 61 0 y 6.4 cm b) in. z 28
29 5) The angle of elevation from the ground to the top of a flagpole is Draw a sketch to illustrate this situation. 6) From a building, the angle of depression to a fountain is The fountain is 75 metres away (along the ground) from the building. Draw a sketch to illustrate this situation. 7) From the top of a 45 metre tall pole, the angle of depression to the ground is Draw a sketch to illustrate this situation, and then find the distance from the top of the pole to the ground along the sight line. 8) A ramp makes an angle of 22 0 with the ground. If the end of the ramp is 1.5 m vertically ( ) above the ground, how long ( ) is the ramp? 29
30 9) A weather balloon, which is blowing in the wind, is tied to the ground with a 15 m string. How high is the balloon () if the angle between the string and the ground is 38 0? balloon 15 m string ) A child s slide makes a 20 0 angle to the ground as it rises to a platform. If the horizontal distance that the slide covers is 25 m long, how long is the slide? platform ) A flagpole is anchored to the ground by a guy wire that is 12 m long. The guy wire makes an angle of 63 0 with the ground. How far from the base of the flagpole must the guy wire be anchored into the ground? 12) A man stands 15 m from the base of a tree. He views the top of the tree at an angle of elevation of How tall is the tree? 13) How far from the side of a house is the base of a ladder if the angle of elevation is 70 0 and the ladder reaches 15 feet up the side of the house? ASK YOUR TEACHER FOR QUIZ 2 30
31 FINDING ANGLES IN RIGHT TRIANGLES So far in this unit, you have used the trigonometric ratios to find the length of a side. But if you know the trigonometric ratio, you can calculate the size of the angle. This requires an inverse operation. You can use your calculator to find the opposite of the usual ratio provided you can calculate the ratio. To do this you need 2 sides in the triangle. You can think of the inverse in terms of something simpler: addition is the opposite or inverse of subtraction. In the same way, trig functions have an inverse. To calculate the inverse, you usually use a 2nd function and the sin/cos/tan buttons on your calculator in sequence. If you look at your calculator just above the sin/cos/tan buttons, you should see the following: sin -1, cos -1, tan -1. These are the inverse functions. If you use these buttons, you will be able to turn a ratio into an angle. Eample 1: Calculate each angle to the nearest whole degree. a) sin X = b) cos Y = c) tan Z = Solution: Use the appropriate inverse function on your calculator. NOTE: Every calculator is different in how the buttons are keyed in order to achieve the desired outcome. Most calculators will need to key 2ndF sin or Shift sin in order to get sin -1 displayed. Then key in the value with or without brackets as necessary. a) sin X = X = sin -1 (0.2546) X = Angle X is b) cos Y = Y = cos -1 (0.1598) Y = Angle Y is c) tan Z = Z = tan -1 (3.2785) Z = Angle Z is
32 Eample 2: Determine the angle in the following triangle. 5 m 3 m Solution: 1) h, o, a the triangle 2) Circle the letters with their partner numbers 3) Choose the appropriate trig ratio. In this case, h 5 m it is tangent. o 4) Write down the ratio and fill it in. tan = tan = o a 5 3 5) Use the inverse function to solve for. 3 m a = tan -1 (5 3) = Angle is approimately
33 ASSIGNMENT 9 FINDING ANGLES IN RIGHT TRIANGLES 1) Calculate the following angles to the nearest whole degree. Show your work! a) sin D = b) cos F = c) tan G = d) sin P = e) cos Q = f) tan R = ) After an hour of flying, a jet has travelled 300 miles, but gone off course 48 miles west of its planned flight path. What angle,, is the jet off course? 48 mi 300 mi 3) At what angle,, to the ground is an 8 m long conveyor belt if it is fastened 5 m from the base of the loading ramp? 33
34 4) If a boat is 150 m from the base of a 90 m cliff, what is the angle of elevation from the boat to the top of the cliff? 5) In a right triangle, ΔXYZ, the ratio of the opposite side to X to the hypotenuse is 7:8 or 7 8. What is the approimate size of X? 6) What is the angle of depression,, from the top of a 65 m cliff to an object 48 m from its base? 34
AWM 11 UNIT 4 TRIGONOMETRY OF RIGHT TRIANGLES
 AWM 11 UNIT 4 TRIGONOMETRY OF RIGHT TRIANGLES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagorean Theorem Exploring Pythagorean Theorem 3 More Pythagorean Theorem Using
AWM 11 UNIT 4 TRIGONOMETRY OF RIGHT TRIANGLES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagorean Theorem Exploring Pythagorean Theorem 3 More Pythagorean Theorem Using
Finding Angles and Solving Right Triangles NEW SKILLS: WORKING WITH INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS. Calculate each angle to the nearest degree.
 324 MathWorks 10 Workbook 7.5 Finding Angles and Solving Right Triangles NEW SKILLS: WORKING WITH INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS The trigonometric ratios discussed in this chapter are unaffected by the size
324 MathWorks 10 Workbook 7.5 Finding Angles and Solving Right Triangles NEW SKILLS: WORKING WITH INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS The trigonometric ratios discussed in this chapter are unaffected by the size
2.0 Trigonometry Review Date: Pythagorean Theorem: where c is always the.
 2.0 Trigonometry Review Date: Key Ideas: The three angles in a triangle sum to. Pythagorean Theorem: where c is always the. In trigonometry problems, all vertices (corners or angles) of the triangle are
2.0 Trigonometry Review Date: Key Ideas: The three angles in a triangle sum to. Pythagorean Theorem: where c is always the. In trigonometry problems, all vertices (corners or angles) of the triangle are
UNIT 9 - RIGHT TRIANGLES AND TRIG FUNCTIONS
 UNIT 9 - RIGHT TRIANGLES AND TRIG FUNCTIONS Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem Objectives: SWBAT use the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem to solve problems. SWBAT use side lengths to classify triangles
UNIT 9 - RIGHT TRIANGLES AND TRIG FUNCTIONS Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem Objectives: SWBAT use the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem to solve problems. SWBAT use side lengths to classify triangles
Name: Block: What I can do for this unit:
 Unit 8: Trigonometry Student Tracking Sheet Math 10 Common Name: Block: What I can do for this unit: After Practice After Review How I Did 8-1 I can use and understand triangle similarity and the Pythagorean
Unit 8: Trigonometry Student Tracking Sheet Math 10 Common Name: Block: What I can do for this unit: After Practice After Review How I Did 8-1 I can use and understand triangle similarity and the Pythagorean
Solving Right Triangles. How do you solve right triangles?
 Solving Right Triangles How do you solve right triangles? The Trigonometric Functions we will be looking at SINE COSINE TANGENT The Trigonometric Functions SINE COSINE TANGENT SINE Pronounced sign TANGENT
Solving Right Triangles How do you solve right triangles? The Trigonometric Functions we will be looking at SINE COSINE TANGENT The Trigonometric Functions SINE COSINE TANGENT SINE Pronounced sign TANGENT
Introduction to Trigonometry
 NAME COMMON CORE GEOMETRY- Unit 6 Introduction to Trigonometry DATE PAGE TOPIC HOMEWORK 1/22 2-4 Lesson 1 : Incredibly Useful Ratios Homework Worksheet 1/23 5-6 LESSON 2: Using Trigonometry to find missing
NAME COMMON CORE GEOMETRY- Unit 6 Introduction to Trigonometry DATE PAGE TOPIC HOMEWORK 1/22 2-4 Lesson 1 : Incredibly Useful Ratios Homework Worksheet 1/23 5-6 LESSON 2: Using Trigonometry to find missing
Be sure to label all answers and leave answers in exact simplified form.
 Pythagorean Theorem word problems Solve each of the following. Please draw a picture and use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve. Be sure to label all answers and leave answers in exact simplified form. 1.
Pythagorean Theorem word problems Solve each of the following. Please draw a picture and use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve. Be sure to label all answers and leave answers in exact simplified form. 1.
7.1/7.2 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem and its Converse
 7.1/7.2 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem and its Converse Remember what we know about a right triangle: In a right triangle, the square of the length of the is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths
7.1/7.2 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem and its Converse Remember what we know about a right triangle: In a right triangle, the square of the length of the is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths
Assignment Guide: Chapter 8 Geometry (L3)
 Assignment Guide: Chapter 8 Geometry (L3) (91) 8.1 The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse Page 495-497 #7-31 odd, 37-47 odd (92) 8.2 Special Right Triangles Page 503-504 #7-12, 15-20, 23-28 (93) 8.2
Assignment Guide: Chapter 8 Geometry (L3) (91) 8.1 The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse Page 495-497 #7-31 odd, 37-47 odd (92) 8.2 Special Right Triangles Page 503-504 #7-12, 15-20, 23-28 (93) 8.2
Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4, Lesson 3. Primary Trigonometric Ratios
 Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4, Lesson 3 Suggested Time: 75 minutes Primary Trigonometric Ratios What s important in this lesson: In this lesson, you will use trigonometry (sin, cos, tan) to measure
Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4, Lesson 3 Suggested Time: 75 minutes Primary Trigonometric Ratios What s important in this lesson: In this lesson, you will use trigonometry (sin, cos, tan) to measure
Chapter 7 - Trigonometry
 Chapter 7 Notes Lessons 7.1 7.5 Geometry 1 Chapter 7 - Trigonometry Table of Contents (you can click on the links to go directly to the lesson you want). Lesson Pages 7.1 and 7.2 - Trigonometry asics Pages
Chapter 7 Notes Lessons 7.1 7.5 Geometry 1 Chapter 7 - Trigonometry Table of Contents (you can click on the links to go directly to the lesson you want). Lesson Pages 7.1 and 7.2 - Trigonometry asics Pages
Unit 1 Trigonometry. Topics and Assignments. General Outcome: Develop spatial sense and proportional reasoning. Specific Outcomes:
 1 Unit 1 Trigonometry General Outcome: Develop spatial sense and proportional reasoning. Specific Outcomes: 1.1 Develop and apply the primary trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, tangent) to solve problems
1 Unit 1 Trigonometry General Outcome: Develop spatial sense and proportional reasoning. Specific Outcomes: 1.1 Develop and apply the primary trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, tangent) to solve problems
Review of Sine, Cosine, and Tangent for Right Triangle
 Review of Sine, Cosine, and Tangent for Right Triangle In trigonometry problems, all vertices (corners or angles) of the triangle are labeled with capital letters. The right angle is usually labeled C.
Review of Sine, Cosine, and Tangent for Right Triangle In trigonometry problems, all vertices (corners or angles) of the triangle are labeled with capital letters. The right angle is usually labeled C.
Geometry- Unit 6 Notes. Simplifying Radicals
 Geometry- Unit 6 Notes Name: Review: Evaluate the following WITHOUT a calculator. a) 2 2 b) 3 2 c) 4 2 d) 5 2 e) 6 2 f) 7 2 g) 8 2 h) 9 2 i) 10 2 j) 2 2 k) ( 2) 2 l) 2 0 Simplifying Radicals n r Example
Geometry- Unit 6 Notes Name: Review: Evaluate the following WITHOUT a calculator. a) 2 2 b) 3 2 c) 4 2 d) 5 2 e) 6 2 f) 7 2 g) 8 2 h) 9 2 i) 10 2 j) 2 2 k) ( 2) 2 l) 2 0 Simplifying Radicals n r Example
Trigonometry Ratios. For each of the right triangles below, the labelled angle is equal to 40. Why then are these triangles similar to each other?
 Name: Trigonometry Ratios A) An Activity with Similar Triangles Date: For each of the right triangles below, the labelled angle is equal to 40. Why then are these triangles similar to each other? Page
Name: Trigonometry Ratios A) An Activity with Similar Triangles Date: For each of the right triangles below, the labelled angle is equal to 40. Why then are these triangles similar to each other? Page
G.8 Right Triangles STUDY GUIDE
 G.8 Right Triangles STUDY GUIDE Name Date Block Chapter 7 Right Triangles Review and Study Guide Things to Know (use your notes, homework, quizzes, textbook as well as flashcards at quizlet.com (http://quizlet.com/4216735/geometry-chapter-7-right-triangles-flashcardsflash-cards/)).
G.8 Right Triangles STUDY GUIDE Name Date Block Chapter 7 Right Triangles Review and Study Guide Things to Know (use your notes, homework, quizzes, textbook as well as flashcards at quizlet.com (http://quizlet.com/4216735/geometry-chapter-7-right-triangles-flashcardsflash-cards/)).
Unit 6: Triangle Geometry
 Unit 6: Triangle Geometry Student Tracking Sheet Math 9 Principles Name: lock: What I can do for this unit: fter Practice fter Review How I id 6-1 I can recognize similar triangles using the ngle Test,
Unit 6: Triangle Geometry Student Tracking Sheet Math 9 Principles Name: lock: What I can do for this unit: fter Practice fter Review How I id 6-1 I can recognize similar triangles using the ngle Test,
Chapter 3: Right Triangle Trigonometry
 10C Name: Chapter 3: Right Triangle Trigonometry 3.1 The Tangent Ratio Outcome : Develop and apply the tangent ratio to solve problems that involve right triangles. Definitions: Adjacent side: the side
10C Name: Chapter 3: Right Triangle Trigonometry 3.1 The Tangent Ratio Outcome : Develop and apply the tangent ratio to solve problems that involve right triangles. Definitions: Adjacent side: the side
Lesson Title 2: Problem TK Solving with Trigonometric Ratios
 Part UNIT RIGHT solving TRIANGLE equations TRIGONOMETRY and inequalities Lesson Title : Problem TK Solving with Trigonometric Ratios Georgia Performance Standards MMG: Students will define and apply sine,
Part UNIT RIGHT solving TRIANGLE equations TRIGONOMETRY and inequalities Lesson Title : Problem TK Solving with Trigonometric Ratios Georgia Performance Standards MMG: Students will define and apply sine,
Trigonometric Ratios and Functions
 Algebra 2/Trig Unit 8 Notes Packet Name: Date: Period: # Trigonometric Ratios and Functions (1) Worksheet (Pythagorean Theorem and Special Right Triangles) (2) Worksheet (Special Right Triangles) (3) Page
Algebra 2/Trig Unit 8 Notes Packet Name: Date: Period: # Trigonometric Ratios and Functions (1) Worksheet (Pythagorean Theorem and Special Right Triangles) (2) Worksheet (Special Right Triangles) (3) Page
10-1. Three Trigonometric Functions. Vocabulary. Lesson
 Chapter 10 Lesson 10-1 Three Trigonometric Functions BIG IDEA The sine, cosine, and tangent of an acute angle are each a ratio of particular sides of a right triangle with that acute angle. Vocabulary
Chapter 10 Lesson 10-1 Three Trigonometric Functions BIG IDEA The sine, cosine, and tangent of an acute angle are each a ratio of particular sides of a right triangle with that acute angle. Vocabulary
Objectives: After completing this section, you should be able to do the following: Calculate the lengths of sides and angles of a right triangle using
 Ch 13 - RIGHT TRIANGLE TRIGONOMETRY Objectives: After completing this section, you should be able to do the following: Calculate the lengths of sides and angles of a right triangle using trigonometric
Ch 13 - RIGHT TRIANGLE TRIGONOMETRY Objectives: After completing this section, you should be able to do the following: Calculate the lengths of sides and angles of a right triangle using trigonometric
Unit 6 Introduction to Trigonometry
 Lesson 1: Incredibly Useful Ratios Opening Exercise Unit 6 Introduction to Trigonometry Use right triangle ΔABC to answer 1 3. 1. Name the side of the triangle opposite A in two different ways. 2. Name
Lesson 1: Incredibly Useful Ratios Opening Exercise Unit 6 Introduction to Trigonometry Use right triangle ΔABC to answer 1 3. 1. Name the side of the triangle opposite A in two different ways. 2. Name
CK-12 Geometry: Inverse Trigonometric Ratios
 CK-12 Geometry: Inverse Trigonometric Ratios Learning Objectives Use the inverse trigonometric ratios to find an angle in a right triangle. Solve a right triangle. Apply inverse trigonometric ratios to
CK-12 Geometry: Inverse Trigonometric Ratios Learning Objectives Use the inverse trigonometric ratios to find an angle in a right triangle. Solve a right triangle. Apply inverse trigonometric ratios to
Algebra II. Slide 1 / 92. Slide 2 / 92. Slide 3 / 92. Trigonometry of the Triangle. Trig Functions
 Slide 1 / 92 Algebra II Slide 2 / 92 Trigonometry of the Triangle 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 92 Trigonometry of the Right Triangle Inverse
Slide 1 / 92 Algebra II Slide 2 / 92 Trigonometry of the Triangle 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 92 Trigonometry of the Right Triangle Inverse
Chapter 7. Right Triangles and Trigonometry
 hapter 7 Right Triangles and Trigonometry 7.1 pply the Pythagorean Theorem 7.2 Use the onverse of the Pythagorean Theorem 7.3 Use Similar Right Triangles 7.4 Special Right Triangles 7.5 pply the Tangent
hapter 7 Right Triangles and Trigonometry 7.1 pply the Pythagorean Theorem 7.2 Use the onverse of the Pythagorean Theorem 7.3 Use Similar Right Triangles 7.4 Special Right Triangles 7.5 pply the Tangent
Angles of a Triangle. Activity: Show proof that the sum of the angles of a triangle add up to Finding the third angle of a triangle
 Angles of a Triangle Activity: Show proof that the sum of the angles of a triangle add up to 180 0 Finding the third angle of a triangle Pythagorean Theorem Is defined as the square of the length of the
Angles of a Triangle Activity: Show proof that the sum of the angles of a triangle add up to 180 0 Finding the third angle of a triangle Pythagorean Theorem Is defined as the square of the length of the
Ch 8: Right Triangles and Trigonometry 8-1 The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse 8-2 Special Right Triangles 8-3 The Tangent Ratio
 Ch 8: Right Triangles and Trigonometry 8-1 The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse 8- Special Right Triangles 8-3 The Tangent Ratio 8-1: The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse Focused Learning Target:
Ch 8: Right Triangles and Trigonometry 8-1 The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse 8- Special Right Triangles 8-3 The Tangent Ratio 8-1: The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse Focused Learning Target:
A lg e b ra II. Trig o n o m e try o f th e Tria n g le
 1 A lg e b ra II Trig o n o m e try o f th e Tria n g le 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org 2 Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Trigonometry of the Right Triangle Inverse Trig Functions Problem
1 A lg e b ra II Trig o n o m e try o f th e Tria n g le 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org 2 Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Trigonometry of the Right Triangle Inverse Trig Functions Problem
Warm-Up Up Exercises. Use this diagram for Exercises If PR = 12 and m R = 19, find p. ANSWER If m P = 58 and r = 5, find p.
 Warm-Up Up Exercises Use this diagram for Exercises 1 4. 1. If PR = 12 and m R = 19, find p. ANSWER 11.3 2. If m P = 58 and r = 5, find p. ANSWER 8.0 Warm-Up Up Exercises Use this diagram for Exercises
Warm-Up Up Exercises Use this diagram for Exercises 1 4. 1. If PR = 12 and m R = 19, find p. ANSWER 11.3 2. If m P = 58 and r = 5, find p. ANSWER 8.0 Warm-Up Up Exercises Use this diagram for Exercises
You ll use the six trigonometric functions of an angle to do this. In some cases, you will be able to use properties of the = 46
 Math 1330 Section 6.2 Section 7.1: Right-Triangle Applications In this section, we ll solve right triangles. In some problems you will be asked to find one or two specific pieces of information, but often
Math 1330 Section 6.2 Section 7.1: Right-Triangle Applications In this section, we ll solve right triangles. In some problems you will be asked to find one or two specific pieces of information, but often
Intro Right Triangle Trig
 Ch. Y Intro Right Triangle Trig In our work with similar polygons, we learned that, by definition, the angles of similar polygons were congruent and their sides were in proportion - which means their ratios
Ch. Y Intro Right Triangle Trig In our work with similar polygons, we learned that, by definition, the angles of similar polygons were congruent and their sides were in proportion - which means their ratios
2.10 Theorem of Pythagoras
 2.10 Theorem of Pythagoras Dr. Robert J. Rapalje, Retired Central Florida, USA Before introducing the Theorem of Pythagoras, we begin with some perfect square equations. Perfect square equations (see the
2.10 Theorem of Pythagoras Dr. Robert J. Rapalje, Retired Central Florida, USA Before introducing the Theorem of Pythagoras, we begin with some perfect square equations. Perfect square equations (see the
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 7.1
 Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name Date Tangent Ratio Tangent Ratio, Cotangent Ratio, and Inverse Tangent Vocabulary Match each description to its corresponding term for triangle EFG. F
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name Date Tangent Ratio Tangent Ratio, Cotangent Ratio, and Inverse Tangent Vocabulary Match each description to its corresponding term for triangle EFG. F
hypotenuse adjacent leg Preliminary Information: SOH CAH TOA is an acronym to represent the following three 28 m 28 m opposite leg 13 m
 On Twitter: twitter.com/engagingmath On FaceBook: www.mathworksheetsgo.com/facebook I. odel Problems II. Practice Problems III. Challenge Problems IV. Answer ey Web Resources Using the inverse sine, cosine,
On Twitter: twitter.com/engagingmath On FaceBook: www.mathworksheetsgo.com/facebook I. odel Problems II. Practice Problems III. Challenge Problems IV. Answer ey Web Resources Using the inverse sine, cosine,
Historical Note Trigonometry Ratios via Similarity
 Section 12-6 Trigonometry Ratios via Similarity 1 12-6 Trigonometry Ratios via Similarity h 40 190 ft of elevation Figure 12-83 Measurements of buildings, structures, and some other objects are frequently
Section 12-6 Trigonometry Ratios via Similarity 1 12-6 Trigonometry Ratios via Similarity h 40 190 ft of elevation Figure 12-83 Measurements of buildings, structures, and some other objects are frequently
UNIT 5 TRIGONOMETRY Lesson 5.4: Calculating Sine, Cosine, and Tangent. Instruction. Guided Practice 5.4. Example 1
 Lesson : Calculating Sine, Cosine, and Tangent Guided Practice Example 1 Leo is building a concrete pathway 150 feet long across a rectangular courtyard, as shown in the following figure. What is the length
Lesson : Calculating Sine, Cosine, and Tangent Guided Practice Example 1 Leo is building a concrete pathway 150 feet long across a rectangular courtyard, as shown in the following figure. What is the length
14.1 Similar Triangles and the Tangent Ratio Per Date Trigonometric Ratios Investigate the relationship of the tangent ratio.
 14.1 Similar Triangles and the Tangent Ratio Per Date Trigonometric Ratios Investigate the relationship of the tangent ratio. Using the space below, draw at least right triangles, each of which has one
14.1 Similar Triangles and the Tangent Ratio Per Date Trigonometric Ratios Investigate the relationship of the tangent ratio. Using the space below, draw at least right triangles, each of which has one
3.0 Trigonometry Review
 3.0 Trigonometry Review In trigonometry problems, all vertices (corners or angles) of the triangle are labeled with capital letters. The right angle is usually labeled C. Sides are usually labeled with
3.0 Trigonometry Review In trigonometry problems, all vertices (corners or angles) of the triangle are labeled with capital letters. The right angle is usually labeled C. Sides are usually labeled with
2.1 The Tangent Ratio
 2.1 The Tangent Ratio C 2.1 Concept: 14, 15 PreAP FPCM 10 (Ms. Carignan) Outcome FP10.4 Trigonometry Chapter 2 Page 1 PreAP FPCM 10 (Ms. Carignan) Outcome FP10.4 Trigonometry Chapter 2 Page 2 Online Video
2.1 The Tangent Ratio C 2.1 Concept: 14, 15 PreAP FPCM 10 (Ms. Carignan) Outcome FP10.4 Trigonometry Chapter 2 Page 1 PreAP FPCM 10 (Ms. Carignan) Outcome FP10.4 Trigonometry Chapter 2 Page 2 Online Video
architecture, physics... you name it, they probably use it.
 The Cosine Ratio Cosine Ratio, Secant Ratio, and Inverse Cosine.4 Learning Goals In this lesson, you will: Use the cosine ratio in a right triangle to solve for unknown side lengths. Use the secant ratio
The Cosine Ratio Cosine Ratio, Secant Ratio, and Inverse Cosine.4 Learning Goals In this lesson, you will: Use the cosine ratio in a right triangle to solve for unknown side lengths. Use the secant ratio
Name: Unit 8 Right Triangles and Trigonometry Unit 8 Similarity and Trigonometry. Date Target Assignment Done!
 Unit 8 Similarity and Trigonometry Date Target Assignment Done! M 1-22 8.1a 8.1a Worksheet T 1-23 8.1b 8.1b Worksheet W 1-24 8.2a 8.2a Worksheet R 1-25 8.2b 8.2b Worksheet F 1-26 Quiz Quiz 8.1-8.2 M 1-29
Unit 8 Similarity and Trigonometry Date Target Assignment Done! M 1-22 8.1a 8.1a Worksheet T 1-23 8.1b 8.1b Worksheet W 1-24 8.2a 8.2a Worksheet R 1-25 8.2b 8.2b Worksheet F 1-26 Quiz Quiz 8.1-8.2 M 1-29
UNIT 10 Trigonometry UNIT OBJECTIVES 287
 UNIT 10 Trigonometry Literally translated, the word trigonometry means triangle measurement. Right triangle trigonometry is the study of the relationships etween the side lengths and angle measures of
UNIT 10 Trigonometry Literally translated, the word trigonometry means triangle measurement. Right triangle trigonometry is the study of the relationships etween the side lengths and angle measures of
5.5 Right Triangles. 1. For an acute angle A in right triangle ABC, the trigonometric functions are as follow:
 5.5 Right Triangles 1. For an acute angle A in right triangle ABC, the trigonometric functions are as follow: sin A = side opposite hypotenuse cos A = side adjacent hypotenuse B tan A = side opposite side
5.5 Right Triangles 1. For an acute angle A in right triangle ABC, the trigonometric functions are as follow: sin A = side opposite hypotenuse cos A = side adjacent hypotenuse B tan A = side opposite side
9-1 Notes. Learning Goal: What are trigonometric ratios and how can we use them to solve for a side? Flashback!
 9-1 Notes Learning Goal: What are trigonometric ratios and how can we use them to solve for a side? Example 1) Solve for the missing side in the right triangle shown below. What s your thinking? Flashback!
9-1 Notes Learning Goal: What are trigonometric ratios and how can we use them to solve for a side? Example 1) Solve for the missing side in the right triangle shown below. What s your thinking? Flashback!
MBF 3C. Foundations for College Mathematics Grade 11 College Mitchell District High School. Unit 1 Trigonometry 9 Video Lessons
 MBF 3C Foundations for College Mathematics Grade 11 College Mitchell District High School Unit 1 Trigonometry 9 Video Lessons Allow no more than 15 class days for this unit This includes time for review
MBF 3C Foundations for College Mathematics Grade 11 College Mitchell District High School Unit 1 Trigonometry 9 Video Lessons Allow no more than 15 class days for this unit This includes time for review
DAY 1 - GEOMETRY FLASHBACK
 DAY 1 - GEOMETRY FLASHBACK Sine Opposite Hypotenuse Cosine Adjacent Hypotenuse sin θ = opp. hyp. cos θ = adj. hyp. tan θ = opp. adj. Tangent Opposite Adjacent a 2 + b 2 = c 2 csc θ = hyp. opp. sec θ =
DAY 1 - GEOMETRY FLASHBACK Sine Opposite Hypotenuse Cosine Adjacent Hypotenuse sin θ = opp. hyp. cos θ = adj. hyp. tan θ = opp. adj. Tangent Opposite Adjacent a 2 + b 2 = c 2 csc θ = hyp. opp. sec θ =
You ll use the six trigonometric functions of an angle to do this. In some cases, you will be able to use properties of the = 46
 Math 1330 Section 6.2 Section 7.1: Right-Triangle Applications In this section, we ll solve right triangles. In some problems you will be asked to find one or two specific pieces of information, but often
Math 1330 Section 6.2 Section 7.1: Right-Triangle Applications In this section, we ll solve right triangles. In some problems you will be asked to find one or two specific pieces of information, but often
Congruence and Similarity in Triangles Pg. 378 # 1, 4 8, 12. Solving Similar Triangle Problems Pg. 386 # 2-12
 UNIT 7 SIMILAR TRIANGLES AND TRIGONOMETRY Date Lesson TOPIC Homework May 4 7.1 7.1 May 8 7.2 7.2 Congruence and Similarity in Triangles Pg. 378 # 1, 4 8, 12 Solving Similar Triangle Problems Pg. 386 #
UNIT 7 SIMILAR TRIANGLES AND TRIGONOMETRY Date Lesson TOPIC Homework May 4 7.1 7.1 May 8 7.2 7.2 Congruence and Similarity in Triangles Pg. 378 # 1, 4 8, 12 Solving Similar Triangle Problems Pg. 386 #
Section 10.6 Right Triangle Trigonometry
 153 Section 10.6 Right Triangle Trigonometry Objective #1: Understanding djacent, Hypotenuse, and Opposite sides of an acute angle in a right triangle. In a right triangle, the otenuse is always the longest
153 Section 10.6 Right Triangle Trigonometry Objective #1: Understanding djacent, Hypotenuse, and Opposite sides of an acute angle in a right triangle. In a right triangle, the otenuse is always the longest
Find sin R and sin S. Then find cos R and cos S. Write each answer as a fraction and as a decimal. Round to four decimal places, if necessary.
 Name Homework Packet 7.6 7.7 LESSON 7.6 For use with pages 473-480 AND LESSON 7.7 For use with pages 483 489 Find sin R and sin S. Then find cos R and cos S. Write each answer as a fraction and as a decimal.
Name Homework Packet 7.6 7.7 LESSON 7.6 For use with pages 473-480 AND LESSON 7.7 For use with pages 483 489 Find sin R and sin S. Then find cos R and cos S. Write each answer as a fraction and as a decimal.
Assignment. Pg. 567 #16-33, even pg 577 # 1-17 odd, 32-37
 Assignment Intro to Ch. 8 8.1 8. Da 1 8. Da 8. Da 1 8. Da Review Quiz 8. Da 1 8. Da 8. Etra Practice 8.5 8.5 In-class project 8.6 Da 1 8.6 Da Ch. 8 review Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet
Assignment Intro to Ch. 8 8.1 8. Da 1 8. Da 8. Da 1 8. Da Review Quiz 8. Da 1 8. Da 8. Etra Practice 8.5 8.5 In-class project 8.6 Da 1 8.6 Da Ch. 8 review Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet
Geometry. Chapter 7 Right Triangles and Trigonometry. Name Period
 Geometry Chapter 7 Right Triangles and Trigonometry Name Period 1 Chapter 7 Right Triangles and Trigonometry ***In order to get full credit for your assignments they must me done on time and you must SHOW
Geometry Chapter 7 Right Triangles and Trigonometry Name Period 1 Chapter 7 Right Triangles and Trigonometry ***In order to get full credit for your assignments they must me done on time and you must SHOW
Chapter 15 Right Triangle Trigonometry
 Chapter 15 Right Triangle Trigonometry Sec. 1 Right Triangle Trigonometry The most difficult part of Trigonometry is spelling it. Once we get by that, the rest is a piece of cake. efore we start naming
Chapter 15 Right Triangle Trigonometry Sec. 1 Right Triangle Trigonometry The most difficult part of Trigonometry is spelling it. Once we get by that, the rest is a piece of cake. efore we start naming
Unit O Student Success Sheet (SSS) Right Triangle Trigonometry (sections 4.3, 4.8)
 Unit O Student Success Sheet (SSS) Right Triangle Trigonometry (sections 4.3, 4.8) Standards: Geom 19.0, Geom 20.0, Trig 7.0, Trig 8.0, Trig 12.0 Segerstrom High School -- Math Analysis Honors Name: Period:
Unit O Student Success Sheet (SSS) Right Triangle Trigonometry (sections 4.3, 4.8) Standards: Geom 19.0, Geom 20.0, Trig 7.0, Trig 8.0, Trig 12.0 Segerstrom High School -- Math Analysis Honors Name: Period:
Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4, Lesson 2. Ratios of Sides of Right-Angle Triangles
 Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4, Lesson 2 Ratios of Sides of Right-Angle s Suggested Time: 75 minutes What s important in this lesson: In this lesson, you will learn through investigation, the relationship
Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4, Lesson 2 Ratios of Sides of Right-Angle s Suggested Time: 75 minutes What s important in this lesson: In this lesson, you will learn through investigation, the relationship
The Pythagorean Theorem: For a right triangle, the sum of the two leg lengths squared is equal to the length of the hypotenuse squared.
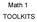 Math 1 TOOLKITS TOOLKIT: Pythagorean Theorem & Its Converse The Pythagorean Theorem: For a right triangle, the sum of the two leg lengths squared is equal to the length of the hypotenuse squared. a 2 +
Math 1 TOOLKITS TOOLKIT: Pythagorean Theorem & Its Converse The Pythagorean Theorem: For a right triangle, the sum of the two leg lengths squared is equal to the length of the hypotenuse squared. a 2 +
SOH CAH TOA Worksheet Name. Find the following ratios using the given right triangles
 Name: Algebra II Period: 9.1 Introduction to Trig 12.1 Worksheet Name GETTIN' TRIGGY WIT IT SOH CAH TOA Find the following ratios using the given right triangles. 1. 2. Sin A = Sin B = Sin A = Sin B =
Name: Algebra II Period: 9.1 Introduction to Trig 12.1 Worksheet Name GETTIN' TRIGGY WIT IT SOH CAH TOA Find the following ratios using the given right triangles. 1. 2. Sin A = Sin B = Sin A = Sin B =
Triangle Trigonometry
 Honors Finite/Brief: Trigonometry review notes packet Triangle Trigonometry Right Triangles All triangles (including non-right triangles) Law of Sines: a b c sin A sin B sin C Law of Cosines: a b c bccos
Honors Finite/Brief: Trigonometry review notes packet Triangle Trigonometry Right Triangles All triangles (including non-right triangles) Law of Sines: a b c sin A sin B sin C Law of Cosines: a b c bccos
Intro Right Triangle Trig
 Ch. Y Intro Right Triangle Trig In our work with similar polygons, we learned that, by definition, the angles of similar polygons were congruent and their sides were in proportion - which means their ratios
Ch. Y Intro Right Triangle Trig In our work with similar polygons, we learned that, by definition, the angles of similar polygons were congruent and their sides were in proportion - which means their ratios
Be sure to label all answers and leave answers in exact simplified form.
 Pythagorean Theorem word problems Solve each of the following. Please draw a picture and use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve. Be sure to label all answers and leave answers in exact simplified form. 1.
Pythagorean Theorem word problems Solve each of the following. Please draw a picture and use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve. Be sure to label all answers and leave answers in exact simplified form. 1.
T.4 Applications of Right Angle Trigonometry
 22 T.4 Applications of Right Angle Trigonometry Solving Right Triangles Geometry of right triangles has many applications in the real world. It is often used by carpenters, surveyors, engineers, navigators,
22 T.4 Applications of Right Angle Trigonometry Solving Right Triangles Geometry of right triangles has many applications in the real world. It is often used by carpenters, surveyors, engineers, navigators,
Math 21 Home. Book 9: Triangles. Name:
 Math 21 Home Book 9: Triangles Name: Start Date: Completion Date: Year Overview: Earning and Spending Money Home Travel and Transportation Recreation and Wellness 1. Budget 2. Personal Banking 3. Interest
Math 21 Home Book 9: Triangles Name: Start Date: Completion Date: Year Overview: Earning and Spending Money Home Travel and Transportation Recreation and Wellness 1. Budget 2. Personal Banking 3. Interest
DAY 1 - Pythagorean Theorem
 1 U n i t 6 10P Date: Name: DAY 1 - Pythagorean Theorem 1. 2. 3. 1 2 U n i t 6 10P Date: Name: 4. 5. 6. 7. 2 3 U n i t 6 10P Date: Name: IF there s time Investigation: Complete the table below using the
1 U n i t 6 10P Date: Name: DAY 1 - Pythagorean Theorem 1. 2. 3. 1 2 U n i t 6 10P Date: Name: 4. 5. 6. 7. 2 3 U n i t 6 10P Date: Name: IF there s time Investigation: Complete the table below using the
Cumulative Review: SOHCAHTOA and Angles of Elevation and Depression
 Cumulative Review: SOHCAHTOA and Angles of Elevation and Depression Part 1: Model Problems The purpose of this worksheet is to provide students the opportunity to review the following topics in right triangle
Cumulative Review: SOHCAHTOA and Angles of Elevation and Depression Part 1: Model Problems The purpose of this worksheet is to provide students the opportunity to review the following topics in right triangle
a + b2 = c2 thirdside a b sin A sin B sin C one opposite angle other opposite a2 = b2 + 2bccos QHI. F-i. fr+c a - 2bc angle cosa= I ol o =
 Angle of elevation is always measured UP from the HORIZONTAL. Angle of depression always measured DOWN from the HORIZONTAL. - given asked asked MAP 4C1 Triconometry Reference Sheet Formula Picture When
Angle of elevation is always measured UP from the HORIZONTAL. Angle of depression always measured DOWN from the HORIZONTAL. - given asked asked MAP 4C1 Triconometry Reference Sheet Formula Picture When
Name Class Date. Investigating a Ratio in a Right Triangle
 Name lass Date Trigonometric Ratios Going Deeper Essential question: How do you find the tangent, sine, and cosine ratios for acute angles in a right triangle? In this chapter, you will be working etensively
Name lass Date Trigonometric Ratios Going Deeper Essential question: How do you find the tangent, sine, and cosine ratios for acute angles in a right triangle? In this chapter, you will be working etensively
Packet Unit 5 Right Triangles Honors Common Core Math 2 1
 Packet Unit 5 Right Triangles Honors Common Core Math 2 1 Day 1 HW Find the value of each trigonometric ratio. Write the ratios for sinp, cosp, and tanp. Remember to simplify! 9. 10. 11. Packet Unit 5
Packet Unit 5 Right Triangles Honors Common Core Math 2 1 Day 1 HW Find the value of each trigonometric ratio. Write the ratios for sinp, cosp, and tanp. Remember to simplify! 9. 10. 11. Packet Unit 5
UNIT 2 RIGHT TRIANGLE TRIGONOMETRY Lesson 1: Exploring Trigonometric Ratios Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: measuring angles with a protractor understanding how to label angles and sides in triangles converting fractions into decimals
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: measuring angles with a protractor understanding how to label angles and sides in triangles converting fractions into decimals
Pythagorean Theorem Distance and Midpoints
 Slide 1 / 78 Pythagorean Theorem Distance and Midpoints Slide 2 / 78 Table of Contents Pythagorean Theorem Distance Formula Midpoints Click on a topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 78 Slide 4 / 78 Pythagorean
Slide 1 / 78 Pythagorean Theorem Distance and Midpoints Slide 2 / 78 Table of Contents Pythagorean Theorem Distance Formula Midpoints Click on a topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 78 Slide 4 / 78 Pythagorean
Name: Class: Date: Chapter 3 - Foundations 7. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: Chapter 3 - Foundations 7 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Determine the value of tan 59, to four decimal places. a.
Name: Class: Date: Chapter 3 - Foundations 7 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Determine the value of tan 59, to four decimal places. a.
Summer Review for Students Entering Pre-Calculus with Trigonometry. TI-84 Plus Graphing Calculator is required for this course.
 Summer Review for Students Entering Pre-Calculus with Trigonometry 1. Using Function Notation and Identifying Domain and Range 2. Multiplying Polynomials and Solving Quadratics 3. Solving with Trig Ratios
Summer Review for Students Entering Pre-Calculus with Trigonometry 1. Using Function Notation and Identifying Domain and Range 2. Multiplying Polynomials and Solving Quadratics 3. Solving with Trig Ratios
Packet Unit 5 Trigonometry Honors Math 2 17
 Packet Unit 5 Trigonometry Honors Math 2 17 Homework Day 12 Part 1 Cumulative Review of this unit Show ALL work for the following problems! Use separate paper, if needed. 1) If AC = 34, AB = 16, find sin
Packet Unit 5 Trigonometry Honors Math 2 17 Homework Day 12 Part 1 Cumulative Review of this unit Show ALL work for the following problems! Use separate paper, if needed. 1) If AC = 34, AB = 16, find sin
Summer Review for Students Entering Pre-Calculus with Trigonometry. TI-84 Plus Graphing Calculator is required for this course.
 1. Using Function Notation and Identifying Domain and Range 2. Multiplying Polynomials and Solving Quadratics 3. Solving with Trig Ratios and Pythagorean Theorem 4. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions
1. Using Function Notation and Identifying Domain and Range 2. Multiplying Polynomials and Solving Quadratics 3. Solving with Trig Ratios and Pythagorean Theorem 4. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions
a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h.
 Sec. Right Triangle Trigonometry Right Triangle Trigonometry Sides Find the requested unknown side of the following triangles. Name: a. b. c. d.? 44 8 5? 7? 44 9 58 0? e. f. g. h.?? 4 7 5? 38 44 6 49º?
Sec. Right Triangle Trigonometry Right Triangle Trigonometry Sides Find the requested unknown side of the following triangles. Name: a. b. c. d.? 44 8 5? 7? 44 9 58 0? e. f. g. h.?? 4 7 5? 38 44 6 49º?
Chapter 2. Right Triangles and Static Trigonometry
 Chapter 2 Right Triangles and Static Trigonometry 1 Chapter 2.1 A Right Triangle View of Trigonometry 2 Overview Values of six trig functions from their ratio definitions Bridge definitions of trig functions
Chapter 2 Right Triangles and Static Trigonometry 1 Chapter 2.1 A Right Triangle View of Trigonometry 2 Overview Values of six trig functions from their ratio definitions Bridge definitions of trig functions
Practice For use with pages
 9.1 For use with pages 453 457 Find the square roots of the number. 1. 36. 361 3. 79 4. 1089 5. 4900 6. 10,000 Approimate the square root to the nearest integer. 7. 39 8. 85 9. 105 10. 136 11. 17.4 1.
9.1 For use with pages 453 457 Find the square roots of the number. 1. 36. 361 3. 79 4. 1089 5. 4900 6. 10,000 Approimate the square root to the nearest integer. 7. 39 8. 85 9. 105 10. 136 11. 17.4 1.
Trigonometry is concerned with the connection between the sides and angles in any right angled triangle.
 Trigonometry Obj: I can to use trigonometry to find unknown sides and unknown angles in a triangle. Trigonometry is concerned with the connection between the sides and angles in any right angled triangle.
Trigonometry Obj: I can to use trigonometry to find unknown sides and unknown angles in a triangle. Trigonometry is concerned with the connection between the sides and angles in any right angled triangle.
A trigonometric ratio is a,
 ALGEBRA II Chapter 13 Notes The word trigonometry is derived from the ancient Greek language and means measurement of triangles. Section 13.1 Right-Triangle Trigonometry Objectives: 1. Find the trigonometric
ALGEBRA II Chapter 13 Notes The word trigonometry is derived from the ancient Greek language and means measurement of triangles. Section 13.1 Right-Triangle Trigonometry Objectives: 1. Find the trigonometric
Math-2 Lesson 8-7: Unit 5 Review (Part -2)
 Math- Lesson 8-7: Unit 5 Review (Part -) Trigonometric Functions sin cos A A SOH-CAH-TOA Some old horse caught another horse taking oats away. opposite ( length ) o sin A hypotenuse ( length ) h SOH adjacent
Math- Lesson 8-7: Unit 5 Review (Part -) Trigonometric Functions sin cos A A SOH-CAH-TOA Some old horse caught another horse taking oats away. opposite ( length ) o sin A hypotenuse ( length ) h SOH adjacent
Name: Pythagorean Theorem February 3, 2014
 1. John leaves school to go home. He walks 6 blocks North and then 8 blocks west. How far is John from the school? 5. A 26 foot long ladder is leaning up against a house with its base 10 feet away from
1. John leaves school to go home. He walks 6 blocks North and then 8 blocks west. How far is John from the school? 5. A 26 foot long ladder is leaning up against a house with its base 10 feet away from
Math 144 Activity #2 Right Triangle Trig and the Unit Circle
 1 p 1 Right Triangle Trigonometry Math 1 Activity #2 Right Triangle Trig and the Unit Circle We use right triangles to study trigonometry. In right triangles, we have found many relationships between the
1 p 1 Right Triangle Trigonometry Math 1 Activity #2 Right Triangle Trig and the Unit Circle We use right triangles to study trigonometry. In right triangles, we have found many relationships between the
Intro Right Triangle Trig
 Ch. Y Intro Right Triangle Trig In our work with similar polygons, we learned that, by definition, the angles of similar polygons were congruent and their sides were in proportion - which means their ratios
Ch. Y Intro Right Triangle Trig In our work with similar polygons, we learned that, by definition, the angles of similar polygons were congruent and their sides were in proportion - which means their ratios
Assignment. Framing a Picture Similar and Congruent Polygons
 Assignment Assignment for Lesson.1 Name Date Framing a Picture Similar and Congruent Polygons Determine whether each pair of polygons is similar. If necessary, write the similarity statement. Determine
Assignment Assignment for Lesson.1 Name Date Framing a Picture Similar and Congruent Polygons Determine whether each pair of polygons is similar. If necessary, write the similarity statement. Determine
UNIT 4 MODULE 2: Geometry and Trigonometry
 Year 12 Further Mathematics UNIT 4 MODULE 2: Geometry and Trigonometry CHAPTER 8 - TRIGONOMETRY This module covers the application of geometric and trigonometric knowledge and techniques to various two-
Year 12 Further Mathematics UNIT 4 MODULE 2: Geometry and Trigonometry CHAPTER 8 - TRIGONOMETRY This module covers the application of geometric and trigonometric knowledge and techniques to various two-
RIGHT TRIANGLES. Dates, assignments, and quizzes subject to change without advance notice. Monday Tuesday Block Day Friday
 Name: Period RIGHT TRIANGLES I can define, identify and illustrate the following terms: Square root radicals Rationalize Pythagorean Theorem Special Right Triangles Sine Cosine Tangent θ (Theta) Angle
Name: Period RIGHT TRIANGLES I can define, identify and illustrate the following terms: Square root radicals Rationalize Pythagorean Theorem Special Right Triangles Sine Cosine Tangent θ (Theta) Angle
MAP4CI Date Lesson Text Assigned Work Done Ref. Pythagorean Theorem, Pg 72 # 4-7, 9,10 ab P9 93 # 3, 6, 10, 11, 12
 MAP4CI 2015-2016 Name: Trigonometry Unit 2 Outline Reminder: Write a missed Quiz or Test in room 540 at lunch or on your spare on the first day of return to school. If you have any concerns, please see
MAP4CI 2015-2016 Name: Trigonometry Unit 2 Outline Reminder: Write a missed Quiz or Test in room 540 at lunch or on your spare on the first day of return to school. If you have any concerns, please see
SM 2. Date: Section: Objective: The Pythagorean Theorem: In a triangle, or
 SM 2 Date: Section: Objective: The Pythagorean Theorem: In a triangle, or. It doesn t matter which leg is a and which leg is b. The hypotenuse is the side across from the right angle. To find the length
SM 2 Date: Section: Objective: The Pythagorean Theorem: In a triangle, or. It doesn t matter which leg is a and which leg is b. The hypotenuse is the side across from the right angle. To find the length
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 8-1 Similarity in Right Triangles
 8 Find this vocabular word in Lesson 8-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Finding Geometric Means The geometric mean of two positive numbers is the positive square root of their. Find the geometric mean of
8 Find this vocabular word in Lesson 8-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Finding Geometric Means The geometric mean of two positive numbers is the positive square root of their. Find the geometric mean of
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 13-1 Right-Angle Trigonometry
 Find these vocabulary words in Lesson 13-1 and the Multilingual Glossary. Vocabulary Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 13-1 Right-Angle Trigonometry trigonometric function sine cosine tangent cosecant
Find these vocabulary words in Lesson 13-1 and the Multilingual Glossary. Vocabulary Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 13-1 Right-Angle Trigonometry trigonometric function sine cosine tangent cosecant
Inequalities in Triangles Geometry 5-5
 Inequalities in Triangles Geometry 5-5 Name: ate: Period: Theorem 5-10 Theorem 5-11 If two sides of a triangle are not If two angles of a triangle are not congruent, then the larger angle congruent, then
Inequalities in Triangles Geometry 5-5 Name: ate: Period: Theorem 5-10 Theorem 5-11 If two sides of a triangle are not If two angles of a triangle are not congruent, then the larger angle congruent, then
Solving Right Triangles. LEARN ABOUT the Math
 7.5 Solving Right Triangles GOL Use primary trigonometric ratios to calculate side lengths and angle measures in right triangles. LERN OUT the Math farmers co-operative wants to buy and install a grain
7.5 Solving Right Triangles GOL Use primary trigonometric ratios to calculate side lengths and angle measures in right triangles. LERN OUT the Math farmers co-operative wants to buy and install a grain
10-2. More Right-Triangle Trigonometry. Vocabulary. Finding an Angle from a Trigonometric Ratio. Lesson
 hapter 10 Lesson 10-2 More Right-Triangle Trigonometry IG IDE If you know two sides of a right triangle, you can use inverse trigonometric functions to fi nd the measures of the acute angles. Vocabulary
hapter 10 Lesson 10-2 More Right-Triangle Trigonometry IG IDE If you know two sides of a right triangle, you can use inverse trigonometric functions to fi nd the measures of the acute angles. Vocabulary
Inverses of Trigonometric. Who uses this? Hikers can use inverse trigonometric functions to navigate in the wilderness. (See Example 3.
 1-4 Inverses of Trigonometric Functions Objectives Evaluate inverse trigonometric functions. Use trigonometric equations and inverse trigonometric functions to solve problems. Vocabulary inverse sine function
1-4 Inverses of Trigonometric Functions Objectives Evaluate inverse trigonometric functions. Use trigonometric equations and inverse trigonometric functions to solve problems. Vocabulary inverse sine function
This simple one is based on looking at various sized right angled triangles with angles 37 (36á9 ), 53 (53á1 ) and 90.
 TRIGONOMETRY IN A RIGHT ANGLED TRIANGLE There are various ways of introducing Trigonometry, including the use of computers, videos and graphics calculators. This simple one is based on looking at various
TRIGONOMETRY IN A RIGHT ANGLED TRIANGLE There are various ways of introducing Trigonometry, including the use of computers, videos and graphics calculators. This simple one is based on looking at various
Study Guide and Review - Chapter 10
 State whether each sentence is true or false. If false, replace the underlined word, phrase, expression, or number to make a true sentence. 1. A triangle with sides having measures of 3, 4, and 6 is a
State whether each sentence is true or false. If false, replace the underlined word, phrase, expression, or number to make a true sentence. 1. A triangle with sides having measures of 3, 4, and 6 is a
Study Guide and Review - Chapter 10
 State whether each sentence is true or false. If false, replace the underlined word, phrase, expression, or number to make a true sentence. 1. A triangle with sides having measures of 3, 4, and 6 is a
State whether each sentence is true or false. If false, replace the underlined word, phrase, expression, or number to make a true sentence. 1. A triangle with sides having measures of 3, 4, and 6 is a
Review Journal 7 Page 57
 Student Checklist Unit 1 - Trigonometry 1 1A Prerequisites: I can use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve a missing side of a right triangle. Note p. 2 1B Prerequisites: I can convert within the imperial
Student Checklist Unit 1 - Trigonometry 1 1A Prerequisites: I can use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve a missing side of a right triangle. Note p. 2 1B Prerequisites: I can convert within the imperial
Semester 2 Review Problems will be sectioned by chapters. The chapters will be in the order by which we covered them.
 Semester 2 Review Problems will be sectioned by chapters. The chapters will be in the order by which we covered them. Chapter 9 and 10: Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios 1. The hypotenuse of a right
Semester 2 Review Problems will be sectioned by chapters. The chapters will be in the order by which we covered them. Chapter 9 and 10: Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios 1. The hypotenuse of a right
