C OMPUTER G RAPHICS Thursday
|
|
|
- Leonard Warren
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 C OMPUTER G RAPHICS Thursday Professor s original PPT Courses Computer Graphics practice3.pdf TA s current PPT not uploaded yet
2 GRAPHICS PIPELINE What is Graphics Pipeline? the process to express a 3D image into 2D raster image also called rendering pipeline pixels arrayed in grid pattern VERTEX PROCESSING BLENDING RASTERIZING FRAGMENT PROCESSING 3D image 2D raster image PIPELINE
3 GRAPHICS PIPELINE VERTEX PROCESSING RASTERIZING FRAGMENT PROCESSING BLENDING Vertex Processing converts 3D image s 3D vertices into 2D vertices fit into screen needs multiple to get final 2D vertices from original 3D vertices
4 GRAPHICS PIPELINE VERTEX PROCESSING RASTERIZING FRAGMENT PROCESSING BLENDING Vertex Processing performed by multiplying vertex by matrices for efficient computation, 3D vertices start in homogeneous coordinate system
5 GRAPHICS PIPELINE VERTEX PROCESSING RASTERIZING FRAGMENT PROCESSING BLENDING Vertex Processing Q. Isn t it too much pressure to compute for 4~5 s per one vertex? A. Rendering time is barely affected by the number of transforming steps. Actually, it is much affected by the number of vertices.
6 MATRIX & OpenGL X Y = viewport perspective division projection modelview X 0 Y 0 Z 0 W 0 finally converted 2D vertex original 3D vertex (homogeneous)
7 MATRIX & OpenGL X Y = viewport perspective division projection modelview X 0 Y 0 Z 0 W 0 finally converted 2D vertex Matrix Handling OpenGL Functions void glmatrixmode (GLenum mode) choose which to operate GL_MODELVIEW: operate on modelview GL_PROJECTION: operate on projection GL_TEXTURE: operate on texture operates this part original 3D vertex (homogeneous)
8 MATRIX & OpenGL X Y = viewport perspective division projection modelview X 0 Y 0 Z 0 W 0 finally converted 2D vertex Matrix Handling OpenGL Functions void glmatrixmode (GLenum mode) choose which to operate GL_MODELVIEW: operate on modelview GL_PROJECTION: operate on projection GL_TEXTURE: operate on texture void glloadidentity () call identity as currently operating void glloadmatrixf (const GLfloat *M1) call M1 as currently operating void glmultmatirxf (const GLfloat *M2) multiply M2 to currently operating operates this part original 3D vertex (homogeneous)
9 MATRIX & OpenGL X Y = viewport perspective division projection modelview X 0 Y 0 Z 0 W 0 finally converted 2D vertex Matrix Handling OpenGL Functions void glmatrixmode (GLenum mode) choose which to operate GL_MODELVIEW: operate on modelview GL_PROJECTION: operate on projection GL_TEXTURE: operate on texture void glloadidentity () call identity as currently operating void glloadmatrixf (const GLfloat *M1) call M1 as currently operating void glmultmatirxf (const GLfloat *M2) multiply M2 to currently operating operates this part original 3D vertex (homogeneous) glloadidentity();
10 MATRIX & OpenGL X Y = viewport perspective division projection modelview X 0 Y 0 Z 0 W 0 finally converted 2D vertex Matrix Handling OpenGL Functions void glmatrixmode (GLenum mode) choose which to operate GL_MODELVIEW: operate on modelview GL_PROJECTION: operate on projection GL_TEXTURE: operate on texture void glloadidentity () call identity as currently operating void glloadmatrixf (const GLfloat *M1) call M1 as currently operating void glmultmatirxf (const GLfloat *M2) multiply M2 to currently operating operates this part original 3D vertex (homogeneous) float m[] = 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f ; glloadmatrixf(m); glmultimatrixf(m);
11 MATRIX & OpenGL X Y = viewport perspective division projection modelview X 0 Y 0 Z 0 W 0 finally converted 2D vertex Matrix Operating in OpenGL Programming operates this part original 3D vertex (homogeneous) glloadidentity(); glsomething1(); glsomething2();
12 MATRIX & OpenGL X Y = viewport perspective division projection modelview X 0 Y 0 Z 0 W 0 finally converted 2D vertex Matrix Operating in OpenGL Programming operates this part original 3D vertex (homogeneous) glloadidentity(); glsomething1(); glsomething2(); OpenGL command lines work between modelview and original 3D vertex in order. X Y = projection perspective viewport modelview identity something1 something2 X 0 Y 0 Z 0 W 0
13 OpenGL 1: TRANSFORMATION Main Transforming OpenGL Functions void gltranslatef (GLfloat dx, GLfloat dy, GLfloat dz) translate the crayon dx/dy/dz: translating dx/dy/dz by x/y/z axis void glscalef (GLfloat sx, GLfloat sy, GLfloat sz) scale the crayon sx/sy/sz: translating sx/sy/sz by x/y/z axis void glrotatef (GLfloat angle, GLfloat x, GLfloat y, GLfloat z) Rotating the crayon angle: rotating angle x/y/z: rotating axis (0.0 if not rotating, 1.0 if rotating) example: glrotatef (45, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); rotating 45 by z-axis
14 OpenGL 1: TRANSFORMATION Two Ways to Draw at Proper Position on Paper DESK PAPER OR draw like this move crayon move paper
15 OpenGL 1: TRANSFORMATION Two Ways to Draw at Proper Position on Paper DESK PAPER OR draw like this move crayon move paper 1 moving crayon = translate rotate scale usual MCS to WCS idea X Y = projection perspective viewport modelview translation rotation scale X 0 Y 0 Z 0 W 0 2 moving paper = scale rotate translate usual opengl programming idea X Y = projection perspective viewport modelview scale rotation translation X 0 Y 0 Z 0 W 0
16 OpenGL 1: TRANSFORMATION Two Ways to Draw at Proper Position on Paper glloadidentity(); gltranslatef(0.707, 0.0, 0.0); glrotatef(45.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); glutsolidcube(0.3); glloadidentity(); glrotatef(45.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); gltranslatef(0.5, -0.5, 0.0); glutsolidcube(0.3); 1 moving crayon = translate rotate scale usual MCS to WCS idea X Y = projection perspective viewport modelview translation rotation scale X 0 Y 0 Z 0 W 0 2 moving paper = scale rotate translate usual opengl programming idea X Y = projection perspective viewport modelview scale rotation translation X 0 Y 0 Z 0 W 0
17 OpenGL 1: TRANSFORMATION EXAMPLE: Three Rectangles (differ by transforming order) void MyDisplay() glclear(gl_color_buffer_bit); glviewport(0, 0, 300, 300); // red rectangle glcolor3f(1.0, 0.0, 0.0); glloadidentity(); glutsolidcube(0.3); // green rectangle glcolor3f(0.0, 1.0, 0.0); glloadidentity(); glrotatef(45.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); gltranslatef(0.6, 0.0, 0.0); glutsolidcube(0.3); // blue rectangle glcolor3f(0.0, 0.0, 1.0); glloadidentity(); gltranslatef(0.6, 0.0, 0.0); glrotatef(45.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); glutsolidcube(0.3); int main(int argc, char** argv) glutinitdisplaymode(glut_rgba); glutinitwindowsize(300, 300); glutcreatewindow("opengl Sample Drawing"); glclearcolor(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0); glmatrixmode(gl_projection); glloadidentity(); glortho(-1.0, 1.0, -1.0, 1.0, -1.0, 1.0); glutdisplayfunc(mydisplay); glutmainloop(); return 0; glflush();
18 OpenGL 2: VIEWPORT SKIP!!
19 OpenGL 3: INTERACTION Interacting With Users (Callback Functions) OpenGL provides Callback Functions to let users interact with program Keyboard Callback: reacts when user pushes some keys Special Key Callback: reacts when user pushes special keys (like F1, F2 keys) Mouse Callback: reacts when user start to push mouse button Motion Callback: reacts when user drags the mouse and take off the finger Menu Callback: shows menu above the window Timer Callback: reacts at every specific time intervals EXAMPLE: Change Rectangle Size by Mouse Dragging
20 OpenGL 3: INTERACTION #include <gl/glut.h> GLint TopLeftX, TopLeftY, BottomRightX, BottomRightY; void MyDisplay() glviewport(0, 0, 300, 300); glclear(gl_color_buffer_bit); glcolor3f(0.5, 0.5, 0.5); glbegin(gl_polygon); glvertex3f(topleftx / 300.0, (300 - TopLeftY) / 300.0, 0.0); glvertex3f(topleftx / 300.0, (300 - BottomRightY) / 300.0, 0.0); glvertex3f(bottomrightx / 300.0, (300 - BottomRightY) / 300.0, 0.0); glvertex3f(bottomrightx / 300.0, (300 - TopLeftY) / 300.0, 0.0); glend(); glflush(); EXAMPLE: Changing Rectangle Size by Mouse Dragging void MyMouseClick(GLint Button, GLint State, GLint X, GLint Y) if(button == GLUT_LEFT_BUTTON && State == GLUT_DOWN) TopLeftX = X; TopLeftY = Y; void MyMouseMove(GLint X, GLint Y) BottomRightX = X; BottomRightY = Y; glutpostredisplay(); // marks the current window as needing to be redisplayed. int main(int argc, char** argv) glutinitwindowsize(300, 300); glutcreatewindow("opengl Drawing Example"); glclearcolor(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0); glmatrixmode(gl_projection); glloadidentity(); glortho(0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0, -1.0, 1.0); glutdisplayfunc(mydisplay); glutmousefunc(mymouseclick); glutmotionfunc(mymousemove); glutmainloop(); return 0;
21 OpenGL 3: INTERACTION Difference Between OpenGL s drawing field and Window v1x = TopLeftX / 300; v1y = (300 - TopLeftY) / 300; v2x = TopLeftX / 300; v2y = (300 - BottomRightY) / 300; v3x = BottomRightX / 300; v3y = (300 - BottomRightY) / 300; v4x = BottomRightX / 300; v4y = (300 - TopLeftY) / 300;
22 OpenGL 4: MATRIX STACKS Save Transformed Coordinate with Stacks void glpushmatrix () save current position in the stack no matter how many times you transform and transform coordinates, you can come back to this saved coordinate position void glpopmatrix () load the most currently saved position once loaded position is removed from the stack
23 OpenGL 4: MATRIX STACKS EXAMPLE 1: Solar System
24 OpenGL 4: MATRIX STACKS #include <gl/freeglut.h> #include <gl/glu.h> #include <gl/gl.h> EXAMPLE 1: Solar System static int Day = 0, Time = 0; void MyDisplay() glclear(gl_color_buffer_bit GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); glenable(gl_depth_test); glloadidentity(); gltranslatef(0.0, 0.0, -2.0); /***The earth***/ glpushmatrix(); // 지구의공전 glrotatef((float)day, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0); gltranslatef(0.7, 0.0, 0.0); // 지구의자전 glrotatef((float)time, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0); glcolor3f(0.5, 0.6, 0.7); glutsolidsphere(0.1, 30, 8); /***The moon***/ glpushmatrix(); // 달의공전 glrotatef((float)time, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0); gltranslatef(0.2, 0.0, 0.0); glcolor3f(0.9, 0.8, 0.2); glutsolidsphere(0.04, 30, 8); glpopmatrix(); glpopmatrix(); /***The sun***/ glcolor3f(1.0, 0.3, 0.4); glutsolidsphere(0.2, 30, 16); glutswapbuffers(); void MyTimer(int value) Day = (Day + 10) % 360; Time = (Time + 5) % 360; gluttimerfunc(100, MyTimer, 1); glutpostredisplay(); int main(int argc, char** argv) glutinit(&argc, argv); glutinitdisplaymode(glut_double GLUT_RGB GLUT_DEPTH); glutinitwindowsize(500, 500); glutcreatewindow("solar system"); glclearcolor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0); glmatrixmode(gl_projection); glloadidentity(); glortho(-1.0, 1.0, -1.0, 1.0, -1.0, 3.0); glutdisplayfunc(mydisplay); gluttimerfunc(100, MyTimer, 1); glutmainloop(); return 0;
25 OpenGL 4: MATRIX STACKS EXAMPLE 2: Rotating Teapot with Mouse
26 OpenGL 4: MATRIX STACKS #include <gl/glut.h> bool bdrag = false; float g_fdistance = f; float g_fspinx = 0.0f; float g_fspiny = 0.0f; int ptlastmousepositx, ptlastmouseposity; int ptcurrentmousepositx, ptcurrentmouseposity; EXAMPLE 2: Rotating Teapot with Mouse (1/2) void ChangeSize(GLsizei width, GLsizei height) GLfloat faspect = (GLfloat)width/(GLfloat)height; GLfloat nrange = height/4.0; if(height == 0) height = 1; glviewport(0, 0, width, height); glmatrixmode(gl_projection); glloadidentity(); if (width <= height) glortho (-nrange, nrange, -nrange/faspect, nrange/faspect, -nrange*4.0f, nrange*4.0f); else glortho (-nrange*faspect, nrange*faspect, -nrange, nrange, -nrange*4.0f, nrange*4.0f); glloadidentity(); void MyMouseClick(GLint Button, GLint State, GLint X, GLint Y) if(button == GLUT_LEFT_BUTTON ) if (State == GLUT_DOWN) ptlastmousepositx = ptcurrentmousepositx = X; ptlastmouseposity = ptcurrentmouseposity = Y; bdrag = true; else if (State == GLUT_UP) bdrag = false;
27 OpenGL 4: MATRIX STACKS void MyMouseMove(GLint X, GLint Y) ptcurrentmousepositx = X; ptcurrentmouseposity = Y; EXAMPLE 2: Rotating Teapot with Mouse (2/2) if( bdrag ) g_fspinx -= (ptcurrentmousepositx - ptlastmousepositx); g_fspiny -= (ptcurrentmouseposity - ptlastmouseposity); ptlastmousepositx = ptcurrentmousepositx; ptlastmouseposity = ptcurrentmouseposity; glutpostredisplay(); void RenderScene(void) glclear(gl_color_buffer_bit GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); glpushmatrix(); gltranslatef(0.0f, 0.0f, g_fdistance); glrotatef( -g_fspiny, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f ); glrotatef( -g_fspinx, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f ); glcolor3f(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f); glutwireteapot(100.0); glpopmatrix(); glutswapbuffers(); int main(int argc, char *argv[]) glutinit(&argc, argv); glutinitdisplaymode(glut_double GLUT_RGB GLUT_DEPTH); glutinitwindowsize(600, 600); glutcreatewindow( Rotate an object using mouse"); glutreshapefunc(changesize); glutmousefunc(mymouseclick); glutmotionfunc(mymousemove); glutdisplayfunc(renderscene); glutmainloop(); return 0;
28 PRACTICE ASSIGNMENT: Advanced Solar System What to do Create solar system with SUN, EARTH, MOON, MARS! SUN is yellow, and it stays firm EARTH is blue, and it revolves around SUN while it also self-rotates MOON is green, and it revolves around EARTH without self-rotation SUN, EARTH, MOON are almost implemented in practice3_2.cpp What you have to do 1: modify SUN, EARTH, MOON s color in pratice3_2.cpp What you have to do 2: add MARS to practice3_2.cpp MARS is red and it revolves around SUN while it also self-rotates MARS is as twice far from SUN as the EARTH is far from the SUN MARS has two times longer orbital period than EARTH MARS self-rotates twice faster than EARTH MARS has the same size with EARTH Submission Send to teddysiah@gmail.com attaching practice3_2.cpp only Due: not decided yet
Transformation, Input and Interaction. Hanyang University
 Transformation, Input and Interaction Hanyang University Transformation, projection, viewing Pipeline of transformations Standard sequence of transforms Cornell CS4620 Fall 2008 Lecture 8 3 2008 Steve
Transformation, Input and Interaction Hanyang University Transformation, projection, viewing Pipeline of transformations Standard sequence of transforms Cornell CS4620 Fall 2008 Lecture 8 3 2008 Steve
Modeling Transform. Chapter 4 Geometric Transformations. Overview. Instancing. Specify transformation for objects 李同益
 Modeling Transform Chapter 4 Geometric Transformations 李同益 Specify transformation for objects Allow definitions of objects in own coordinate systems Allow use of object definition multiple times in a scene
Modeling Transform Chapter 4 Geometric Transformations 李同益 Specify transformation for objects Allow definitions of objects in own coordinate systems Allow use of object definition multiple times in a scene
Order of Transformations
 Order of Transformations Because the same transformation is applied to many vertices, the cost of forming a matrix M=ABCD is not significant compared to the cost of computing Mp for many vertices p Note
Order of Transformations Because the same transformation is applied to many vertices, the cost of forming a matrix M=ABCD is not significant compared to the cost of computing Mp for many vertices p Note
Books, OpenGL, GLUT, GLUI, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, and G3D
 Books, OpenGL, GLUT, GLUI, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, and G3D CS334 Spring 2012 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Computer Graphics Pipeline Geometric Primitives
Books, OpenGL, GLUT, GLUI, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, and G3D CS334 Spring 2012 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Computer Graphics Pipeline Geometric Primitives
Precept 2 Aleksey Boyko February 18, 2011
 Precept 2 Aleksey Boyko February 18, 2011 Getting started Initialization Drawing Transformations Cameras Animation Input Keyboard Mouse Joystick? Textures Lights Programmable pipeline elements (shaders)
Precept 2 Aleksey Boyko February 18, 2011 Getting started Initialization Drawing Transformations Cameras Animation Input Keyboard Mouse Joystick? Textures Lights Programmable pipeline elements (shaders)
// double buffering and RGB glutinitdisplaymode(glut_double GLUT_RGBA); // your own initializations
 #include int main(int argc, char** argv) { glutinit(&argc, argv); Typical OpenGL/GLUT Main Program // GLUT, GLU, and OpenGL defs // program arguments // initialize glut and gl // double buffering
#include int main(int argc, char** argv) { glutinit(&argc, argv); Typical OpenGL/GLUT Main Program // GLUT, GLU, and OpenGL defs // program arguments // initialize glut and gl // double buffering
Books, OpenGL, GLUT, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, G3D, and Qt
 Books, OpenGL, GLUT, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, G3D, and Qt CS334 Fall 2015 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Books (and by now means complete ) Interactive Computer
Books, OpenGL, GLUT, CUDA, OpenCL, OpenCV, PointClouds, G3D, and Qt CS334 Fall 2015 Daniel G. Aliaga Department of Computer Science Purdue University Books (and by now means complete ) Interactive Computer
CSC 470 Computer Graphics
 CSC 470 Computer Graphics Transformations of Objects CSC 470 Computer Graphics, Dr.N. Georgieva, CSI/CUNY 1 Transformations of objects - 2D CSC 470 Computer Graphics, Dr.N. Georgieva, CSI/CUNY 2 Using
CSC 470 Computer Graphics Transformations of Objects CSC 470 Computer Graphics, Dr.N. Georgieva, CSI/CUNY 1 Transformations of objects - 2D CSC 470 Computer Graphics, Dr.N. Georgieva, CSI/CUNY 2 Using
Computer graphics MN1
 Computer graphics MN1 http://www.opengl.org Todays lecture What is OpenGL? How do I use it? Rendering pipeline Points, vertices, lines,, polygons Matrices and transformations Lighting and shading Code
Computer graphics MN1 http://www.opengl.org Todays lecture What is OpenGL? How do I use it? Rendering pipeline Points, vertices, lines,, polygons Matrices and transformations Lighting and shading Code
Computer Graphics CS 543 Lecture 5 (Part 2) Implementing Transformations
 Computer Graphics CS 543 Lecture 5 (Part 2) Implementing Transformations Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Objectives Learn how to implement transformations
Computer Graphics CS 543 Lecture 5 (Part 2) Implementing Transformations Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Objectives Learn how to implement transformations
CS559: Computer Graphics. Lecture 12: OpenGL Li Zhang Spring 2008
 CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 12: OpenGL Li Zhang Spring 2008 Reading Redbook Ch 1 & 2 So far: 3D Geometry Pipeline Model Space (Object Space) Rotation Translation Resizing World Space M Rotation Translation
CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 12: OpenGL Li Zhang Spring 2008 Reading Redbook Ch 1 & 2 So far: 3D Geometry Pipeline Model Space (Object Space) Rotation Translation Resizing World Space M Rotation Translation
 OpenGL for dummies hello.c #include int main(int argc, char** argv) { glutinit(&argc, argv); glutinitdisplaymode (GLUT_SINGLE GLUT_RGB); glutinitwindowsize (250, 250); glutinitwindowposition
OpenGL for dummies hello.c #include int main(int argc, char** argv) { glutinit(&argc, argv); glutinitdisplaymode (GLUT_SINGLE GLUT_RGB); glutinitwindowsize (250, 250); glutinitwindowposition
Computer Graphics. Chapter 7 2D Geometric Transformations
 Computer Graphics Chapter 7 2D Geometric Transformations Chapter 7 Two-Dimensional Geometric Transformations Part III. OpenGL Functions for Two-Dimensional Geometric Transformations OpenGL Geometric Transformation
Computer Graphics Chapter 7 2D Geometric Transformations Chapter 7 Two-Dimensional Geometric Transformations Part III. OpenGL Functions for Two-Dimensional Geometric Transformations OpenGL Geometric Transformation
Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 11: Implementing Transformations. Prof Emmanuel Agu. Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI)
 Computer Graphics (CS 47) Lecture : Implementing Transformations Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Objectives Learn how to implement transformations in OpenGL
Computer Graphics (CS 47) Lecture : Implementing Transformations Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Objectives Learn how to implement transformations in OpenGL
Lecture 2 CISC440/640 Spring Department of Computer and Information Science
 Lecture 2 CISC440/640 Spring 2015 Department of Computer and Information Science Today s Topic The secrets of Glut-tony 2 So let s do some graphics! For the next week or so this is your world: -1 1-1 1
Lecture 2 CISC440/640 Spring 2015 Department of Computer and Information Science Today s Topic The secrets of Glut-tony 2 So let s do some graphics! For the next week or so this is your world: -1 1-1 1
Introduction to OpenGL
 Introduction to OpenGL Tutorial 1: Create a window and draw a 2D square Introduction: The aim of the first tutorial is to introduce you to the magic world of graphics based on the OpenGL and GLUT APIs.
Introduction to OpenGL Tutorial 1: Create a window and draw a 2D square Introduction: The aim of the first tutorial is to introduce you to the magic world of graphics based on the OpenGL and GLUT APIs.
GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT, GL_PROJECTION, GL_MODELVIEW
 OpenGL Syntax Functions have prefix gl and initial capital letters for each word glclearcolor(), glenable(), glpushmatrix() glu for GLU functions glulookat(), gluperspective() constants begin with GL_,
OpenGL Syntax Functions have prefix gl and initial capital letters for each word glclearcolor(), glenable(), glpushmatrix() glu for GLU functions glulookat(), gluperspective() constants begin with GL_,
Lecture 4 of 41. Lab 1a: OpenGL Basics
 Lab 1a: OpenGL Basics William H. Hsu Department of Computing and Information Sciences, KSU KSOL course pages: http://snipurl.com/1y5gc Course web site: http://www.kddresearch.org/courses/cis636 Instructor
Lab 1a: OpenGL Basics William H. Hsu Department of Computing and Information Sciences, KSU KSOL course pages: http://snipurl.com/1y5gc Course web site: http://www.kddresearch.org/courses/cis636 Instructor
Modeling Objects by Polygonal Approximations. Linear and Affine Transformations (Maps)
 Modeling Objects by Polygonal Approximations Define volumetric objects in terms of surfaces patches that surround the volume Each surface patch is approximated set of polygons Each polygon is specified
Modeling Objects by Polygonal Approximations Define volumetric objects in terms of surfaces patches that surround the volume Each surface patch is approximated set of polygons Each polygon is specified
Computer graphics MN1
 Computer graphics MN1 Hierarchical modeling Transformations in OpenGL glmatrixmode(gl_modelview); glloadidentity(); // identity matrix gltranslatef(4.0, 5.0, 6.0); glrotatef(45.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0); gltranslatef(-4.0,
Computer graphics MN1 Hierarchical modeling Transformations in OpenGL glmatrixmode(gl_modelview); glloadidentity(); // identity matrix gltranslatef(4.0, 5.0, 6.0); glrotatef(45.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0); gltranslatef(-4.0,
C++ is Fun Part 13 at Turbine/Warner Bros.! Russell Hanson
 C++ is Fun Part 13 at Turbine/Warner Bros.! Russell Hanson Syllabus 1) First program and introduction to data types and control structures with applications for games learning how to use the programming
C++ is Fun Part 13 at Turbine/Warner Bros.! Russell Hanson Syllabus 1) First program and introduction to data types and control structures with applications for games learning how to use the programming
Lecture 5: Viewing. CSE Computer Graphics (Fall 2010)
 Lecture 5: Viewing CSE 40166 Computer Graphics (Fall 2010) Review: from 3D world to 2D pixels 1. Transformations are represented by matrix multiplication. o Modeling o Viewing o Projection 2. Clipping
Lecture 5: Viewing CSE 40166 Computer Graphics (Fall 2010) Review: from 3D world to 2D pixels 1. Transformations are represented by matrix multiplication. o Modeling o Viewing o Projection 2. Clipping
Lecture 3. Understanding of OPenGL programming
 Lecture 3 Understanding of OPenGL programming What is OpenGL GL: stands for Graphic Library Software interface for rendering purposes for 2D or 3D geometric data objects. Various Pieces gl: The basic libraries.
Lecture 3 Understanding of OPenGL programming What is OpenGL GL: stands for Graphic Library Software interface for rendering purposes for 2D or 3D geometric data objects. Various Pieces gl: The basic libraries.
CS D Transformation. Junqiao Zhao 赵君峤
 CS10101001 3D Transformation Junqiao Zhao 赵君峤 Department of Computer Science and Technology College of Electronics and Information Engineering Tongji University Review Translation Linear transformation
CS10101001 3D Transformation Junqiao Zhao 赵君峤 Department of Computer Science and Technology College of Electronics and Information Engineering Tongji University Review Translation Linear transformation
To Do. Computer Graphics (Fall 2008) Course Outline. Course Outline. Methodology for Lecture. Demo: Surreal (HW 3)
 Computer Graphics (Fall 2008) COMS 4160, Lecture 9: OpenGL 1 http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~cs4160 To Do Start thinking (now) about HW 3. Milestones are due soon. Course Course 3D Graphics Pipeline 3D Graphics
Computer Graphics (Fall 2008) COMS 4160, Lecture 9: OpenGL 1 http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~cs4160 To Do Start thinking (now) about HW 3. Milestones are due soon. Course Course 3D Graphics Pipeline 3D Graphics
Graphics Programming
 Graphics Programming 3 rd Week, 2011 OpenGL API (1) API (application programming interface) Interface between an application program and a graphics system Application Program OpenGL API Graphics Library
Graphics Programming 3 rd Week, 2011 OpenGL API (1) API (application programming interface) Interface between an application program and a graphics system Application Program OpenGL API Graphics Library
CS 4204 Computer Graphics
 CS 424 Computer Graphics 2D Transformations Yong Cao Virginia Tech References: Introduction to Computer Graphics course notes by Doug Bowman Interactive Computer Graphics, Fourth Edition, Ed Angle Transformations
CS 424 Computer Graphics 2D Transformations Yong Cao Virginia Tech References: Introduction to Computer Graphics course notes by Doug Bowman Interactive Computer Graphics, Fourth Edition, Ed Angle Transformations
Computer Graphics (CS 4731) Lecture 11: Implementing Transformations. Prof Emmanuel Agu. Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI)
 Computer Graphics (CS 47) Lecture : Implementing Transformations Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Objectives Learn how to implement transformations in OpenGL
Computer Graphics (CS 47) Lecture : Implementing Transformations Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Objectives Learn how to implement transformations in OpenGL
12. Selection. - The objects selected are specified by hit records in the selection buffer. E.R. Bachmann & P.L. McDowell MV 4202 Page 1 of 13
 12. Selection Picking is a method of capturing mouse clicks at some window position and determining what objects are beneath it. The basic idea is to enter the selection rendering mode with a small viewing
12. Selection Picking is a method of capturing mouse clicks at some window position and determining what objects are beneath it. The basic idea is to enter the selection rendering mode with a small viewing
Cameras (and eye) Ideal Pinhole. Real Pinhole. Real + lens. Depth of field
 Cameras (and eye) Ideal Pinhole Real Pinhole Real + lens Depth of field 1 Z-buffer How do we draw objects? Polygon Based Fast Raytracing Ray/Object intersections Slow Copyright Pixar 2 Raytracing for each
Cameras (and eye) Ideal Pinhole Real Pinhole Real + lens Depth of field 1 Z-buffer How do we draw objects? Polygon Based Fast Raytracing Ray/Object intersections Slow Copyright Pixar 2 Raytracing for each
Computer Graphics. OpenGL
 Computer Graphics OpenGL What is OpenGL? OpenGL (Open Graphics Library) is a library for computer graphics It consists of several procedures and functions that allow a programmer to specify the objects
Computer Graphics OpenGL What is OpenGL? OpenGL (Open Graphics Library) is a library for computer graphics It consists of several procedures and functions that allow a programmer to specify the objects
Lectures OpenGL Introduction
 Lectures OpenGL Introduction By Tom Duff Pixar Animation Studios Emeryville, California and George Ledin Jr Sonoma State University Rohnert Park, California 2004, Tom Duff and George Ledin Jr 1 What is
Lectures OpenGL Introduction By Tom Duff Pixar Animation Studios Emeryville, California and George Ledin Jr Sonoma State University Rohnert Park, California 2004, Tom Duff and George Ledin Jr 1 What is
Teacher Assistant : Tamir Grossinger Reception hours: by - Building 37 / office -102 Assignments: 4 programing using
 Teacher Assistant : Tamir Grossinger email: tamirgr@gmail.com Reception hours: by email - Building 37 / office -102 Assignments: 4 programing using C++ 1 theoretical You can find everything you need in
Teacher Assistant : Tamir Grossinger email: tamirgr@gmail.com Reception hours: by email - Building 37 / office -102 Assignments: 4 programing using C++ 1 theoretical You can find everything you need in
20 GLuint objects; 36 Scale += 0.1; 37 break; 38 case GLUT_KEY_DOWN:
 1 1. 1 #include 2 #include 3 Program 1 (OpenGL Sample016) 4 // 5 static int MouseX = 0; // X 6 static int MouseY = 0; // Y 7 static float SpinX = 0; // X 8 static float SpinY = 0;
1 1. 1 #include 2 #include 3 Program 1 (OpenGL Sample016) 4 // 5 static int MouseX = 0; // X 6 static int MouseY = 0; // Y 7 static float SpinX = 0; // X 8 static float SpinY = 0;
COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB # 3
 COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB # 3 Chapter 2: COMPUTER GRAPHICS by F.S HILLs. Initial steps in drawing figures (polygon, rectangle etc) Objective: Basic understanding of simple code in OpenGL and initial steps
COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB # 3 Chapter 2: COMPUTER GRAPHICS by F.S HILLs. Initial steps in drawing figures (polygon, rectangle etc) Objective: Basic understanding of simple code in OpenGL and initial steps
UNIT 7 LIGHTING AND SHADING. 1. Explain phong lighting model. Indicate the advantages and disadvantages. (Jun2012) 10M
 UNIT 7 LIGHTING AND SHADING 1. Explain phong lighting model. Indicate the advantages and disadvantages. (Jun2012) 10M Ans: Phong developed a simple model that can be computed rapidly It considers three
UNIT 7 LIGHTING AND SHADING 1. Explain phong lighting model. Indicate the advantages and disadvantages. (Jun2012) 10M Ans: Phong developed a simple model that can be computed rapidly It considers three
Computer Graphics Course 2005
 Computer Graphics Course 2005 Introduction to GLUT, GLU and OpenGL Administrative Stuff Teaching Assistant: Rony Goldenthal Reception Hour: Wed. 18:00 19:00 Room 31 (Ross 1) Questions: E-mail: cg@cs Newsgroups:
Computer Graphics Course 2005 Introduction to GLUT, GLU and OpenGL Administrative Stuff Teaching Assistant: Rony Goldenthal Reception Hour: Wed. 18:00 19:00 Room 31 (Ross 1) Questions: E-mail: cg@cs Newsgroups:
Programming with OpenGL Part 3: Three Dimensions
 Programming with OpenGL Part 3: Three Dimensions Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico Objectives Develop a more sophisticated
Programming with OpenGL Part 3: Three Dimensions Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico Objectives Develop a more sophisticated
Introduction to Computer Graphics with OpenGL/GLUT
 Introduction to Computer Graphics with OpenGL/GLUT What is OpenGL? A software interface to graphics hardware Graphics rendering API (Low Level) High-quality color images composed of geometric and image
Introduction to Computer Graphics with OpenGL/GLUT What is OpenGL? A software interface to graphics hardware Graphics rendering API (Low Level) High-quality color images composed of geometric and image
CS 4204 Computer Graphics
 CS 4204 Computer Graphics OpenGL Basics Yong Cao Virginia Tech References: 2001 Siggraph, An Interactive Introduction to OpenGL Programming, Dave Shreiner,Ed Angel, Vicki Shreiner Official Presentation
CS 4204 Computer Graphics OpenGL Basics Yong Cao Virginia Tech References: 2001 Siggraph, An Interactive Introduction to OpenGL Programming, Dave Shreiner,Ed Angel, Vicki Shreiner Official Presentation
OpenGL/GLUT Intro. Week 1, Fri Jan 12
 University of British Columbia CPSC 314 Computer Graphics Jan-Apr 2007 Tamara Munzner OpenGL/GLUT Intro Week 1, Fri Jan 12 http://www.ugrad.cs.ubc.ca/~cs314/vjan2007 News Labs start next week Reminder:
University of British Columbia CPSC 314 Computer Graphics Jan-Apr 2007 Tamara Munzner OpenGL/GLUT Intro Week 1, Fri Jan 12 http://www.ugrad.cs.ubc.ca/~cs314/vjan2007 News Labs start next week Reminder:
Programming with OpenGL Part 2: Complete Programs Computer Graphics I, Fall
 Programming with OpenGL Part 2: Complete Programs 91.427 Computer Graphics I, Fall 2008 1 1 Objectives Refine first program Alter default values Introduce standard program structure Simple viewing 2-D
Programming with OpenGL Part 2: Complete Programs 91.427 Computer Graphics I, Fall 2008 1 1 Objectives Refine first program Alter default values Introduce standard program structure Simple viewing 2-D
Transformations. CS 537 Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science
 Transformations CS 537 Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science 1 Objectives Introduce standard transformations - Rotation - Translation - Scaling - Shear Derive
Transformations CS 537 Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science 1 Objectives Introduce standard transformations - Rotation - Translation - Scaling - Shear Derive
Duc Nguyen CSE 420 Computer Graphics 10/10/2018 Homework 1
 Duc Nguyen CSE 420 Computer Graphics 10/10/2018 Homework 1 1. The endpoints of a given line are (0, 0) and (18, 6). Compute the first 4 values of y manually using Bresenham's Line Algorithm as x steps
Duc Nguyen CSE 420 Computer Graphics 10/10/2018 Homework 1 1. The endpoints of a given line are (0, 0) and (18, 6). Compute the first 4 values of y manually using Bresenham's Line Algorithm as x steps
OpenGL refresher. Advanced Computer Graphics 2012
 Advanced Computer Graphics 2012 What you will see today Outline General OpenGL introduction Setting up: GLUT and GLEW Elementary rendering Transformations in OpenGL Texture mapping Programmable shading
Advanced Computer Graphics 2012 What you will see today Outline General OpenGL introduction Setting up: GLUT and GLEW Elementary rendering Transformations in OpenGL Texture mapping Programmable shading
Computer Graphics Introduction to OpenGL
 Computer Graphics 2015 3. Introduction to OpenGL Hongxin Zhang State Key Lab of CAD&CG, Zhejiang University 2015-09-28 2. 2D Graphics Algorithms (cont.) Rasterization Computer Graphics @ ZJU Hongxin Zhang,
Computer Graphics 2015 3. Introduction to OpenGL Hongxin Zhang State Key Lab of CAD&CG, Zhejiang University 2015-09-28 2. 2D Graphics Algorithms (cont.) Rasterization Computer Graphics @ ZJU Hongxin Zhang,
CMSC 425: Lecture 4 More about OpenGL and GLUT Tuesday, Feb 5, 2013
 CMSC 425: Lecture 4 More about OpenGL and GLUT Tuesday, Feb 5, 2013 Reading: See any standard reference on OpenGL or GLUT. Basic Drawing: In the previous lecture, we showed how to create a window in GLUT,
CMSC 425: Lecture 4 More about OpenGL and GLUT Tuesday, Feb 5, 2013 Reading: See any standard reference on OpenGL or GLUT. Basic Drawing: In the previous lecture, we showed how to create a window in GLUT,
Drawing Primitives. OpenGL basics
 CSC 706 Computer Graphics / Dr. N. Gueorguieva 1 OpenGL Libraries Drawing Primitives OpenGL basics OpenGL core library OpenGL32 on Windows GL on most unix/linux systems (libgl.a) OpenGL Utility Library
CSC 706 Computer Graphics / Dr. N. Gueorguieva 1 OpenGL Libraries Drawing Primitives OpenGL basics OpenGL core library OpenGL32 on Windows GL on most unix/linux systems (libgl.a) OpenGL Utility Library
Chapter 13 Selection and Feedback
 OpenGL Programming Guide (Addison-Wesley Publishing Company) Chapter 13 Selection and Feedback Chapter Objectives After reading this chapter, you ll be able to do the following: Create applications that
OpenGL Programming Guide (Addison-Wesley Publishing Company) Chapter 13 Selection and Feedback Chapter Objectives After reading this chapter, you ll be able to do the following: Create applications that
Hierarchical Modeling: Tree of Transformations, Display Lists and Functions, Matrix and Attribute Stacks,
 Hierarchical Modeling: Tree of Transformations, Display Lists and Functions, Matrix and Attribute Stacks, Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 1 Modeling complex objects/motion Decompose object hierarchically
Hierarchical Modeling: Tree of Transformations, Display Lists and Functions, Matrix and Attribute Stacks, Hierarchical Modeling Hofstra University 1 Modeling complex objects/motion Decompose object hierarchically
Lecture 2 2D transformations Introduction to OpenGL
 Lecture 2 2D transformations Introduction to OpenGL OpenGL where it fits what it contains how you work with it OpenGL parts: GL = Graphics Library (core lib) GLU = GL Utilities (always present) GLX, AGL,
Lecture 2 2D transformations Introduction to OpenGL OpenGL where it fits what it contains how you work with it OpenGL parts: GL = Graphics Library (core lib) GLU = GL Utilities (always present) GLX, AGL,
3D computer graphics: geometric modeling of objects in the computer and rendering them
 SE313: Computer Graphics and Visual Programming Computer Graphics Notes Gazihan Alankus, Spring 2012 Computer Graphics 3D computer graphics: geometric modeling of objects in the computer and rendering
SE313: Computer Graphics and Visual Programming Computer Graphics Notes Gazihan Alankus, Spring 2012 Computer Graphics 3D computer graphics: geometric modeling of objects in the computer and rendering
Computer Graphics. Chapter 10 Three-Dimensional Viewing
 Computer Graphics Chapter 10 Three-Dimensional Viewing Chapter 10 Three-Dimensional Viewing Part I. Overview of 3D Viewing Concept 3D Viewing Pipeline vs. OpenGL Pipeline 3D Viewing-Coordinate Parameters
Computer Graphics Chapter 10 Three-Dimensional Viewing Chapter 10 Three-Dimensional Viewing Part I. Overview of 3D Viewing Concept 3D Viewing Pipeline vs. OpenGL Pipeline 3D Viewing-Coordinate Parameters
CS559: Computer Graphics. Lecture 12: OpenGL Transformation Li Zhang Spring 2008
 CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 2: OpenGL Transformation Li Zhang Spring 28 Today Transformation in OpenGL Reading Chapter 3 Last time Primitive Details glpolygonmode(glenum face, GLenum mode); face:
CS559: Computer Graphics Lecture 2: OpenGL Transformation Li Zhang Spring 28 Today Transformation in OpenGL Reading Chapter 3 Last time Primitive Details glpolygonmode(glenum face, GLenum mode); face:
Objectives. transformation. General Transformations. Affine Transformations. Notation. Pipeline Implementation. Introduce standard transformations
 Objectives Transformations CS Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science Introduce standard transformations - Rotation - Translation - Scaling - Shear Derive homogeneous
Objectives Transformations CS Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science Introduce standard transformations - Rotation - Translation - Scaling - Shear Derive homogeneous
2. OpenGL -I. 2.1 What is OpenGL? Things OpenGL can do: -23-
 2.1 What is OpenGL? -23-2. OpenGL -I - Device-independent, application program interface (API) to graphics hardware - 3D-oriented - Event-driven Things OpenGL can do: - wireframe models - depth-cuing effect
2.1 What is OpenGL? -23-2. OpenGL -I - Device-independent, application program interface (API) to graphics hardware - 3D-oriented - Event-driven Things OpenGL can do: - wireframe models - depth-cuing effect
Erik Anchondo cse 520 lab 4
 Erik Anchondo 2-6-19 cse 520 lab 4 1. Wrote a glsl program that displays a colored tetrahedron. The tetrahedron starts to rotate on the x axis when the mouse button is clicked once. If the mouse button
Erik Anchondo 2-6-19 cse 520 lab 4 1. Wrote a glsl program that displays a colored tetrahedron. The tetrahedron starts to rotate on the x axis when the mouse button is clicked once. If the mouse button
2/3/16. Interaction. Triangles (Clarification) Choice of Programming Language. Buffer Objects. The CPU-GPU bus. CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 3
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 3 Interaction Jernej Barbic University of Southern California [Angel Ch. 2] Triangles (Clarification) Can be any shape or size Well-shaped triangles have advantages for
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 3 Interaction Jernej Barbic University of Southern California [Angel Ch. 2] Triangles (Clarification) Can be any shape or size Well-shaped triangles have advantages for
Interaction Computer Graphics I Lecture 3
 15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 3 Interaction Client/Server Model Callbacks Double Buffering Hidden Surface Removal Simple Transformations January 21, 2003 [Angel Ch. 3] Frank Pfenning Carnegie Mellon
15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 3 Interaction Client/Server Model Callbacks Double Buffering Hidden Surface Removal Simple Transformations January 21, 2003 [Angel Ch. 3] Frank Pfenning Carnegie Mellon
Lecture 5b. Transformation
 Lecture 5b Transformation Refresher Transformation matrices [4 x 4]: the fourth coordinate is homogenous coordinate. Rotation Transformation: Axis of rotation must through origin (0,0,0). If not, translation
Lecture 5b Transformation Refresher Transformation matrices [4 x 4]: the fourth coordinate is homogenous coordinate. Rotation Transformation: Axis of rotation must through origin (0,0,0). If not, translation
Interaction. CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 3
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 3 Interaction Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Client/Server Model Callbacks Double Buffering Hidden Surface Removal Simple Transformations [Angel Ch.
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 3 Interaction Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Client/Server Model Callbacks Double Buffering Hidden Surface Removal Simple Transformations [Angel Ch.
Interaction. CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 3
 CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 3 Interaction January 18, 2012 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Client/Server Model Callbacks Double Buffering Hidden Surface Removal Simple Transformations
CSCI 480 Computer Graphics Lecture 3 Interaction January 18, 2012 Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Client/Server Model Callbacks Double Buffering Hidden Surface Removal Simple Transformations
yahoo.com
 What is the workshop about? We use software such as AutoCAD, 3D Studio, Maya and many others for a host of applications ranging from Technical Drawings to Machine Design to Game Making to Special Effects
What is the workshop about? We use software such as AutoCAD, 3D Studio, Maya and many others for a host of applications ranging from Technical Drawings to Machine Design to Game Making to Special Effects
Computer Graphics. Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University
 Computer Graphics Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Introduction to OpenGL General OpenGL Introduction An Example OpenGL Program Drawing with OpenGL Transformations Animation and Depth Buffering
Computer Graphics Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Introduction to OpenGL General OpenGL Introduction An Example OpenGL Program Drawing with OpenGL Transformations Animation and Depth Buffering
by modifying the glutinitwindowsize() function you can change the screen size to whatever you please.
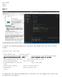 Zoe Veale Lab 2 Draw2 part 1: I edited the glutinitwindowsize() function tom change the size of my screen window. int main(int argc, char** argv) glutinit(&argc, argv); //initialize toolkit glutinitdisplaymode
Zoe Veale Lab 2 Draw2 part 1: I edited the glutinitwindowsize() function tom change the size of my screen window. int main(int argc, char** argv) glutinit(&argc, argv); //initialize toolkit glutinitdisplaymode
Computer Graphics. Transformations. CSC 470 Computer Graphics 1
 Computer Graphics Transformations CSC 47 Computer Graphics 1 Today s Lecture Transformations How to: Rotate Scale and Translate 2 Introduction An important concept in computer graphics is Affine Transformations.
Computer Graphics Transformations CSC 47 Computer Graphics 1 Today s Lecture Transformations How to: Rotate Scale and Translate 2 Introduction An important concept in computer graphics is Affine Transformations.
1 /* 4 C:\opencv\build\include. 6 C:\opencv\build\x86\vc10\lib
 1 1. Program 1 OpenCV (OpenCV Sample001) 1 /* 2 - > - > - >VC++ 3 ( ) 4 C:\opencv\build\include 5 ( ) 6 C:\opencv\build\x86\vc10\lib 7 - > - > - > - > 8 (240 O p e n C V ) 9 opencv_core240d.lib 10 opencv_imgproc240d.lib
1 1. Program 1 OpenCV (OpenCV Sample001) 1 /* 2 - > - > - >VC++ 3 ( ) 4 C:\opencv\build\include 5 ( ) 6 C:\opencv\build\x86\vc10\lib 7 - > - > - > - > 8 (240 O p e n C V ) 9 opencv_core240d.lib 10 opencv_imgproc240d.lib
Introduction to OpenGL Transformations, Viewing and Lighting. Ali Bigdelou
 Introduction to OpenGL Transformations, Viewing and Lighting Ali Bigdelou Modeling From Points to Polygonal Objects Vertices (points) are positioned in the virtual 3D scene Connect points to form polygons
Introduction to OpenGL Transformations, Viewing and Lighting Ali Bigdelou Modeling From Points to Polygonal Objects Vertices (points) are positioned in the virtual 3D scene Connect points to form polygons
RECITATION - 1. Ceng477 Fall
 RECITATION - 1 Ceng477 Fall 2007-2008 2/ 53 Agenda General rules for the course General info on the libraries GLUT OpenGL GLUI Details about GLUT Functions Probably we will not cover this part 3/ 53 General
RECITATION - 1 Ceng477 Fall 2007-2008 2/ 53 Agenda General rules for the course General info on the libraries GLUT OpenGL GLUI Details about GLUT Functions Probably we will not cover this part 3/ 53 General
Computer graphics MN1
 Computer graphics MN1 http://www.opengl.org Todays lecture What is OpenGL? HowdoI useit? Rendering pipeline Points, vertices, lines, polygons Matrices and transformations Lighting and shading Code examples
Computer graphics MN1 http://www.opengl.org Todays lecture What is OpenGL? HowdoI useit? Rendering pipeline Points, vertices, lines, polygons Matrices and transformations Lighting and shading Code examples
Introduction to OpenGL
 Introduction to OpenGL Banafsheh Azari http://www.uni-weimar.de/cms/medien/cg.html What You ll See Today What is OpenGL? Related Libraries OpenGL Command Syntax B. Azari http://www.uni-weimar.de/cms/medien/cg.html
Introduction to OpenGL Banafsheh Azari http://www.uni-weimar.de/cms/medien/cg.html What You ll See Today What is OpenGL? Related Libraries OpenGL Command Syntax B. Azari http://www.uni-weimar.de/cms/medien/cg.html
Using OpenGL with CUDA
 Using OpenGL with CUDA Installing OpenGL and GLUT; compiling with nvcc Basics of OpenGL and GLUT in C Interoperability between OpenGL and CUDA OpenGL = Open Graphic Library creation of 3D graphic primitives
Using OpenGL with CUDA Installing OpenGL and GLUT; compiling with nvcc Basics of OpenGL and GLUT in C Interoperability between OpenGL and CUDA OpenGL = Open Graphic Library creation of 3D graphic primitives
Basic Graphics Programming
 15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 2 Basic Graphics Programming Graphics Pipeline OpenGL API Primitives: Lines, Polygons Attributes: Color Example January 17, 2002 [Angel Ch. 2] Frank Pfenning Carnegie
15-462 Computer Graphics I Lecture 2 Basic Graphics Programming Graphics Pipeline OpenGL API Primitives: Lines, Polygons Attributes: Color Example January 17, 2002 [Angel Ch. 2] Frank Pfenning Carnegie
QUESTION 1 [10] 2 COS340-A October/November 2009
![QUESTION 1 [10] 2 COS340-A October/November 2009 QUESTION 1 [10] 2 COS340-A October/November 2009](/thumbs/91/107455423.jpg) 2 COS340-A QUESTION 1 [10] a) OpenGL uses z-buffering for hidden surface removal. Explain how the z-buffer algorithm works and give one advantage of using this method. (5) Answer: OpenGL uses a hidden-surface
2 COS340-A QUESTION 1 [10] a) OpenGL uses z-buffering for hidden surface removal. Explain how the z-buffer algorithm works and give one advantage of using this method. (5) Answer: OpenGL uses a hidden-surface
OpenGL Transformations
 OpenGL Transformations R. J. Renka Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of North Texas 02/18/2014 Introduction The most essential aspect of OpenGL is the vertex pipeline described in
OpenGL Transformations R. J. Renka Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of North Texas 02/18/2014 Introduction The most essential aspect of OpenGL is the vertex pipeline described in
CS 4731 Lecture 3: Introduction to OpenGL and GLUT: Part II. Emmanuel Agu
 CS 4731 Lecture 3: Introduction to OpenGL and GLUT: Part II Emmanuel Agu Recall: OpenGL Skeleton void main(int argc, char** argv){ // First initialize toolkit, set display mode and create window glutinit(&argc,
CS 4731 Lecture 3: Introduction to OpenGL and GLUT: Part II Emmanuel Agu Recall: OpenGL Skeleton void main(int argc, char** argv){ // First initialize toolkit, set display mode and create window glutinit(&argc,
BOUNCING BALL IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR
 COMPUTER GRAPHICS LECTURE 07 BOUNCING BALL IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR WWW.IMRANIHSAN.COM /* * GL07BouncingBall.cpp: A ball bouncing inside the window */ #include // for MS Windows #include
COMPUTER GRAPHICS LECTURE 07 BOUNCING BALL IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR WWW.IMRANIHSAN.COM /* * GL07BouncingBall.cpp: A ball bouncing inside the window */ #include // for MS Windows #include
Project Sketchpad. Ivan Sutherland (MIT 1963) established the basic interactive paradigm that characterizes interactive computer graphics:
 Project Sketchpad Ivan Sutherland (MIT 1963) established the basic interactive paradigm that characterizes interactive computer graphics: User sees an object on the display User points to (picks) the object
Project Sketchpad Ivan Sutherland (MIT 1963) established the basic interactive paradigm that characterizes interactive computer graphics: User sees an object on the display User points to (picks) the object
Fall CSCI 420: Computer Graphics. 2.2 Transformations. Hao Li.
 Fall 2017 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 2.2 Transformations Hao Li http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 OpenGL Transformations Matrices Model-view matrix (4x4 matrix) Projection matrix (4x4 matrix) vertices in 3D Model-view
Fall 2017 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 2.2 Transformations Hao Li http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 OpenGL Transformations Matrices Model-view matrix (4x4 matrix) Projection matrix (4x4 matrix) vertices in 3D Model-view
CSCI E-74. Simulation and Gaming
 CSCI E-74 Virtual and Augmented Reality for Simulation and Gaming Fall term 2017 Gianluca De Novi, PhD Lesson 3 General Introduction to OpenGL APIs and TRS Perspective Simulation Perspective simulation
CSCI E-74 Virtual and Augmented Reality for Simulation and Gaming Fall term 2017 Gianluca De Novi, PhD Lesson 3 General Introduction to OpenGL APIs and TRS Perspective Simulation Perspective simulation
Spring 2013, CS 112 Programming Assignment 2 Submission Due: April 26, 2013
 Spring 2013, CS 112 Programming Assignment 2 Submission Due: April 26, 2013 PROJECT GOAL: Write a restricted OpenGL library. The goal of the project is to compute all the transformation matrices with your
Spring 2013, CS 112 Programming Assignment 2 Submission Due: April 26, 2013 PROJECT GOAL: Write a restricted OpenGL library. The goal of the project is to compute all the transformation matrices with your
OpenGL Tutorial. Ceng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics
 OpenGL Tutorial Ceng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Adapted from: http://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/spr06/cos426/assn3/opengl_tutorial.ppt OpenGL IS an API OpenGL IS nothing more than
OpenGL Tutorial Ceng 477 Introduction to Computer Graphics Adapted from: http://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/spr06/cos426/assn3/opengl_tutorial.ppt OpenGL IS an API OpenGL IS nothing more than
Assignment 1. Simple Graphics program using OpenGL
 Assignment 1 Simple Graphics program using OpenGL In this assignment we will use basic OpenGL functions to draw some basic graphical figures. Example: Consider following program to draw a point on screen.
Assignment 1 Simple Graphics program using OpenGL In this assignment we will use basic OpenGL functions to draw some basic graphical figures. Example: Consider following program to draw a point on screen.
VR-programming tools (procedural) More VRML later in this course! (declarative)
 Realtime 3D Computer Graphics & Virtual Reality OpenGL Introduction VR-programming Input and display devices are the main hardware interface to users Immersion embeds users through the generation of live-like
Realtime 3D Computer Graphics & Virtual Reality OpenGL Introduction VR-programming Input and display devices are the main hardware interface to users Immersion embeds users through the generation of live-like
FAKULTI TEKNOLOGI MAKLUMAT DAN KOMUNIKASI BITM INTERACTIVE COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB SESSION 4. C++ - OpenGL
 FAKULTI TEKNOLOGI MAKLUMAT DAN KOMUNIKASI BITM 3213 - INTERACTIVE COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB SESSION 4 C++ - OpenGL Part 1- C++ - Texture Mapping 1. Download texture file and put it into your current folder
FAKULTI TEKNOLOGI MAKLUMAT DAN KOMUNIKASI BITM 3213 - INTERACTIVE COMPUTER GRAPHICS LAB SESSION 4 C++ - OpenGL Part 1- C++ - Texture Mapping 1. Download texture file and put it into your current folder
Graphics Programming. August 31, Programming of the Sierpinski gasket. Programming with OpenGL and C/C++
 Computer Graphics Graphics Programming August 31, 2005 Contents Our Goal in This Chapter Programming of the Sierpinski gasket How To? Programming with OpenGL and C/C++ OpenGL API (Application Programmer
Computer Graphics Graphics Programming August 31, 2005 Contents Our Goal in This Chapter Programming of the Sierpinski gasket How To? Programming with OpenGL and C/C++ OpenGL API (Application Programmer
Questions HW1 Transform Q/A. Transform. Shaoting Zhang. May 11, 2008
 May 11, 2008 My office Hour: Mon. 1:00-3:00pm, Hill-418 All of the slides and codes can be found by clicking my name in the course s website 1 2 3 4 Question 1 What s the result? glcolor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0);
May 11, 2008 My office Hour: Mon. 1:00-3:00pm, Hill-418 All of the slides and codes can be found by clicking my name in the course s website 1 2 3 4 Question 1 What s the result? glcolor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0);
CSC Graphics Programming. Budditha Hettige Department of Statistics and Computer Science
 CSC 307 1.0 Graphics Programming Department of Statistics and Computer Science Graphics Programming GLUT 2 Events in OpenGL Event Example Keypress KeyDown KeyUp Mouse leftbuttondown leftbuttonup With mouse
CSC 307 1.0 Graphics Programming Department of Statistics and Computer Science Graphics Programming GLUT 2 Events in OpenGL Event Example Keypress KeyDown KeyUp Mouse leftbuttondown leftbuttonup With mouse
Computer Graphics Primitive Attributes
 Computer Graphics 2015 4. Primitive Attributes Hongxin Zhang State Key Lab of CAD&CG, Zhejiang University 2015-10-12 Previous lessons - Rasterization - line - circle /ellipse? => homework - OpenGL and
Computer Graphics 2015 4. Primitive Attributes Hongxin Zhang State Key Lab of CAD&CG, Zhejiang University 2015-10-12 Previous lessons - Rasterization - line - circle /ellipse? => homework - OpenGL and
CS418 OpenGL & GLUT Programming Tutorial (I) Presented by : Wei-Wen Feng 1/30/2008
 CS418 OpenGL & GLUT Programming Tutorial (I) Presented by : Wei-Wen Feng 1/30/2008 2008/2/3 Slide 2 I Am Your TA Name : Wei-Wen Wen Feng 4th Year Graduate Student in Graphics I will be Holding discussion/tutorial
CS418 OpenGL & GLUT Programming Tutorial (I) Presented by : Wei-Wen Feng 1/30/2008 2008/2/3 Slide 2 I Am Your TA Name : Wei-Wen Wen Feng 4th Year Graduate Student in Graphics I will be Holding discussion/tutorial
Transformations. CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 4
 CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 4 Transformations Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Vector Spaces Euclidean Spaces Frames Homogeneous Coordinates Transformation Matrices [Angel, Ch. 4]
CSCI 420 Computer Graphics Lecture 4 Transformations Jernej Barbic University of Southern California Vector Spaces Euclidean Spaces Frames Homogeneous Coordinates Transformation Matrices [Angel, Ch. 4]
3D Graphics Pipeline II Clipping. Instructor Stephen J. Guy
 3D Graphics Pipeline II Clipping Instructor Stephen J. Guy 3D Rendering Pipeline (for direct illumination) 3D Geometric Primitives 3D Model Primitives Modeling Transformation 3D World Coordinates Lighting
3D Graphics Pipeline II Clipping Instructor Stephen J. Guy 3D Rendering Pipeline (for direct illumination) 3D Geometric Primitives 3D Model Primitives Modeling Transformation 3D World Coordinates Lighting
Programming using OpenGL: A first Introduction
 Programming using OpenGL: A first Introduction CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Machiraju/Zhang/Möller 1 Today Overview GL, GLU, GLUT, and GLUI First example OpenGL functions and
Programming using OpenGL: A first Introduction CMPT 361 Introduction to Computer Graphics Torsten Möller Machiraju/Zhang/Möller 1 Today Overview GL, GLU, GLUT, and GLUI First example OpenGL functions and
CS 591B Lecture 9: The OpenGL Rendering Pipeline
 CS 591B Lecture 9: The OpenGL Rendering Pipeline 3D Polygon Rendering Many applications use rendering of 3D polygons with direct illumination Spring 2007 Rui Wang 3D Polygon Rendering Many applications
CS 591B Lecture 9: The OpenGL Rendering Pipeline 3D Polygon Rendering Many applications use rendering of 3D polygons with direct illumination Spring 2007 Rui Wang 3D Polygon Rendering Many applications
Ulf Assarsson Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology
 Ulf Assarsson Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology 1. I am located in room 4115 in EDIT-huset 2. Email: 3. Phone: 031-772 1775 (office) 4. Course assistant: Tomas Akenine-Mőller
Ulf Assarsson Department of Computer Engineering Chalmers University of Technology 1. I am located in room 4115 in EDIT-huset 2. Email: 3. Phone: 031-772 1775 (office) 4. Course assistant: Tomas Akenine-Mőller
CS380: Computer Graphics Basic OpenGL Structure. Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL:
 CS380: Computer Graphics Basic OpenGL Structure Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL: http://sglab.kaist.ac.kr/~sungeui/cg Class Objectives Understand the basic OpenGL program structure and how OpenGL supports
CS380: Computer Graphics Basic OpenGL Structure Sung-Eui Yoon ( 윤성의 ) Course URL: http://sglab.kaist.ac.kr/~sungeui/cg Class Objectives Understand the basic OpenGL program structure and how OpenGL supports
Matrix-Rechnung I ' z =... Universität Frankfurt
 Matrix-Rechnung I x =Ax = = 1.................................... ' ' ' ' ' 44 41 14 11 z y x a a a a w z y x Matrix-Rechnung II Matrixmultiplikation ist assoziativ, abernicht kommutativ. OpenGL multipliziert
Matrix-Rechnung I x =Ax = = 1.................................... ' ' ' ' ' 44 41 14 11 z y x a a a a w z y x Matrix-Rechnung II Matrixmultiplikation ist assoziativ, abernicht kommutativ. OpenGL multipliziert
Transformation Pipeline
 Transformation Pipeline Local (Object) Space Modeling World Space Clip Space Projection Eye Space Viewing Perspective divide NDC space Normalized l d Device Coordinatesd Viewport mapping Screen space Coordinate
Transformation Pipeline Local (Object) Space Modeling World Space Clip Space Projection Eye Space Viewing Perspective divide NDC space Normalized l d Device Coordinatesd Viewport mapping Screen space Coordinate
Lecture 3 Advanced Computer Graphics (CS & SE )
 Lecture 3 Advanced Computer Graphics (CS & SE 233.420) Programming with OpenGL Program Structure Primitives Attributes and States Programming in three dimensions Inputs and Interaction Working with Callbacks
Lecture 3 Advanced Computer Graphics (CS & SE 233.420) Programming with OpenGL Program Structure Primitives Attributes and States Programming in three dimensions Inputs and Interaction Working with Callbacks
Programming with OpenGL Part 1: Background
 Programming with OpenGL Part 1: Background Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico 1 Objectives Development of the OpenGL API
Programming with OpenGL Part 1: Background Ed Angel Professor of Computer Science, Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Media Arts University of New Mexico 1 Objectives Development of the OpenGL API
