Implementation of a Bi-Variate Gaussian Random Number Generator on FPGA without Using Multipliers
|
|
|
- Pauline Simmons
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Implementation of a Bi-Variate Gaussian Random Number Generator on FPGA without Using Multipliers Eldho P Sunny 1, Haripriya. P 2 M.Tech Student [VLSI & Embedded Systems], Sree Narayana Gurukulam College of Engineering, Kadayiruppu, Kolenchery, Kerala, India 1 Asst.Professor, Department of Electronics and Communication, Sree Narayana Gurukulam College of Engineering, Kadayiruppu, Kolenchery, Kerala, India 2 Abstract: The multivariate Gaussian distribution is used to model random processes with distinct pair-wise correlations, such as stock prices that tend to rise and fall together. Multivariate Gaussian vectors with length n are usually produced by first generating a vector of n independent Gaussian samples, then multiplying with a correlation inducing matrix requiring Operations(n 2 ) multiplications. This paper presents a method of generating bivariate vectors directly from the uniform distribution and eliminating the need for any multipliers. The method relies only on small read only memories and adders, and so can be implemented using only logic resources (lookup-tables and registers), saving multipliers, and block-memory resources for the numerical simulation that the multivariate generator is driving. As an optimization, only positive values are considered for the implementation. FPGA-optimized Random Number Generators (RNGs) used for uniform distribution are more resource efficient than software-optimized RNGs, as they can take advantage of bit-wise operations and FPGA-specific features. This paper use a new type of FPGA RNG called a LUT-SR RNG, which takes advantage of bit-wise XOR operations and the ability to turn LUTs into shift-registers of varying lengths. This paper model a Gaussian random number generator where its inputs elements are correlation matrix of standard deviation from previous history. Keywords: Field-programmable gate array (FPGA), Monte Carlo simulation, bivariate samples, random number generation. I. INTRODUCTION THE multivariate Gaussian distribution is used to capture simple correlations between related stochastic processes, such as the stock prices of companies in similar business sectors, where the stock prices of companies in the sector tend to rise and fall together. To simulate the behavior of such processes, multivariate Gaussian random number generators (MVGRNGs) are used to generate random samples, which are then used to drive Monte Carlo simulations. Such simulations often require a huge number of independent runs in order to provide an accurate answer, such as the valueat-risk calculations performed by financial institutions, which are used to estimate how much money the institution might lose over the next day. Such long-running simulations are an ideal target for field programmable gate array (FPGA) acceleration, as they offer abundant parallelism, and are computationally bound [1] [3]; however, they are reliant on a fast, resource-efficient, and accurate source of random samples from the multivariate Gaussian distribution. This paper is an implementation of a bivariate random number generator was resource usage to standard bit-wise logic elements. This paper follows 1) An algorithm for generating samples from the multivariate Gaussian distribution using only uniform random bits, table- lookup, and addition; 2)A hardware architecture for implementing an MVGRNG using only lookup-tables (LUTs) and flip-flops (FFs), which allows a regular densely-packed placement strategy and achieves 500 MHz+ clock speeds. Copyright to IJAREEIE 561
2 II. MULTIVARIATE GAUSSIAN RANDOM NUMBERS Generation of the univariate Gaussian distribution with a specific mean, μ, and variance, σ 2, is achieved by first generating a standard Gaussian variate r with mean zero and variance one, then applying a linear transformation (1) Where r is N(0, 1). Note that the standard Gaussian variate is multiplied by the standard deviation (SD) σ, rather than the variance σ 2. Generation of a multivariate Gaussian distribution is very similar, except in this case, each output sample is, a length n vector x. The mean and variance also increase in dimension, so the mean is a length n vector m, and the variance becomes an n n covariance matrix Σ. The covariance matrix is a symmetric matrix, which captures the variance of each output component on the diagonal, and the correlations between each component on the off-diagonal elements. Generation is similar to the univariate linear transform, except the starting point is a vector r of n independent identically distributed (IID) standard Gaussian random numbers An alternative method is to use the singular value decomposition (SVD) algorithm. This decomposes the matrix into an orthogonal matrix U and a diagonal matrix S, such that Σ = USUT. This decomposition allows the construction of the solution A = U S. The disadvantage of the SVD-based construction is that in general all the elements of the matrix are nonzero, resulting in an n 2 cost in both the number of stored elements, and in the number of multiply-accumulates per transformed vector. However, the SVD algorithm is able to handle a wider range of covariance matrices, such as illconditioned matrices that are very close to singular and reduced rank matrices, where the output vector depends on fewer than n random factors. Such difficult covariance matrices frequently occur in practice [7], so this paper focuses on the use of a dense SVD-style decomposition. III. GENERATION USING LUTS AND ADDERS The standard generation method uses direct matrix multiplication, forming each output element from a linear combination of r (the vector of n IID Gaussian samples) i 1,..., n. (3) If there is no advance knowledge about the covariance matrix and the SVD decomposition is used, this requires n2 multiply accumulations. In addition, this method also requires the generation of the n elements of r, which are IID standard Gaussian samples. Both the generation of r and the multiplication with A require significant resources (i.e., DSPs and block-rams in an FPGA), so simplifying the process and reducing the resource cost are highly desirable. The method proposed in this paper is that, instead of generating expensive independent Gaussian samples and then inducing the desired covariance structure with n2 multiplications, cheap uniform samples will be converted to correlated Gaussian samples using n 2 table-lookups. Each table contains a pre-calculated discretized Gaussian distribution with the correct SD, so the only operations required are table-lookups and additions. The following text frequently refers to tables, which in this context means an array of read-only elements (a ROM) which will be implemented in the FPGA using LUTs. Unless otherwise specified, each table contains k elements, and is indexed using the syntax L[i ] to access table elements L[1],..., L[k]. Where arrays of tables are used, sub-scripts identify a table within the array, which can then be indexed as for a standalone table, e.g., L2,3 [4]. Tables can also be interchangeably treated as discrete random number generators, where the discrete PDF of each table is given by assigning each element of the table an equal probability of 1/k. For example, if u is an IID uniform sample between 0 and 1, a random sample x from table L is generated as Where u U (0, 1). The central idea of this method is to construct an n n array of tables G, such that the discrete distribution of each table Gi, j approximates a Gaussian distribution with SD Ai, j G i, j N(0,A i, j ). (5) Now instead of starting from a Gaussian vector r, the input is an IID uniform vector u. Generation of each output element uses each element of u as a random index into the table, then sums the elements selected from each table i 1,..., n. (6) Copyright to IJAREEIE (2) (4)
3 In practice k will be selected to be a power of 2, so each element of u is actually a uniform integer constructed from the concatenation of log 2(k) random bits. The simplest method of generating a table-based approximation to the Gaussian distribution is direct cumulative distribution function (CDF) inversion. To generate a table L with SD σ, table elements are chosen according to i 1, k (7) Where Φ 1 is Gaussian inverse CDF. The table G corresponding to a given target matrix A can then be specified as i, j 1,... n, z 1,... k. (8) Construction of G allows the direct transformation of uniform samples (random bits) into multivariate Gaussian samples using [6], requiring only table-lookups and addition. Replacing continuous samples with discrete tables means that the output distribution range is no longer continuous; instead, each sample is drawn from within a discrete multidimensional lattice. IV. HARDWARE ARCHITECTURE The central idea in this paper, of replacing Gaussian samples and multipliers with uniform samples and tables, allows for many types of possible implementations. For example, the tables can be implemented using LUTs or block-rams, and the generator can vary in throughput from 1 to n cycles per generated vector. This paper focuses on the highest performance mode of the generator, to provide the maximum contrast with previous implementations, while still providing good efficiency and quality. The specific choices made are as follows. 1) Logic Resources Only: tables are implemented using LUTs, so the only resources used are LUTs and FFs (no DSPs or block-rams). 2) Parallel Generation: the generator operates in a fully parallel mode, providing one new n-element vector per cycle, unlike previous approaches which generated one vector for every n cycle. 3) Maximum Clock Rate: the generator operates at the maximum realistic clock-rate for the target FPGA. For the Virtex-5 this is effectively 550 MHz, as this is the maximum clock rate of the DSP and RAM blocks that will be used in the simulation that the generator is driving. 4) Regular Architecture: simulations typically consume almost all resources in the FPGA (due to replication of simulation cores), and a regular, explicitly placed highly routable, and generator allows fast place-and route while still achieving high overall clock-rate. 5) No Matrix Specialization: the generator is not optimized for a specific correlation matrix, and should support the loading of any correlation structure without structural modification. Fig. 1 Gaussian random no generator top module. V. SIMULATIONS AND EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS For the simulation purpose the σ values of the covariance matrices, clock and a reset signal are given as inputs. The σ values can be obtained from the expert advice or from the previous experience. The clock can attain the maximum value Copyright to IJAREEIE 563
4 of the used platform. The reset is made logic high for one clock for loading the sigma values i.e. the covariance matrices values and then the random number generated for corresponding σ values is available in every clock cycle after reset is made logic low. Output is random numbers for the corresponding experiment for which it can be used for fast simulations like Monte Carlo simulation. For memory optimization and bit representation and evaluation in Xilinx, we in this experiment use σ values represented as bits. The bits can vary from to , 105 values can be represented by this method by using 217 bits. This reduces the memory utilization to a great extent.so the real value of σ values is converted into its corresponding bits representation which can be obtained by multiplying the value with 104 converting it into binary and appending zeros to the MSB. So by this method real value 1 is equivalent to binary of 1000 and real value of 2 is equivalent to binary of So the 1, 2 and 3 can be represented respectively as , , and The output random number generated is also in the binary format of 32 bits because of the addition involved in obtaining output and it can be converted into its real values by multiplying with 10-8 and convert to decimal. The obtained σ values are used for updating the LUT values by multiplying each RAM values with the corresponding covariance matrics values (σ values). Then this updated RAM-LUT is used for random number generation. Fig. 2 Architecture of the bivariate Gaussian random number generator. A bivariate random number generator is implemented in the vertex 5 platform and many optimizations are done for the fast processing and less memory usage. An optimization is on avoiding the negative values understanding that the Gaussian profile maps its mirror image in both positive and negative side. So the adder used here works in the first quadrant. The LUTs used here also avoids negative values and reduce memory in terms of an extra bit needed to indicate it. This also gives more accurate outputs as the number of samples taken exactly doubles. The values stored in the LUT S have equal probability [5]. Copyright to IJAREEIE 564
5 Fig. 3 Architecture of the IID uniform vector generator u1and u2. This type of FPGA-optimized uniform random number generator, called a LUT-SR RNG. These RNGs takes advantage of the ability to configure LUTs as independent shift-registers, allowing high-quality long period generators to be implemented using only a small amount of logic. In addition the period and quality scale with the number of output bits, unlike generators adapted from software. A key advantage of the LUT-SR generators over previous FPGAoptimized uniform random number generators is that they can be reconstructed using a simple algorithms. In concert with the tables of maximum period generators, this allows FPGA engineers to use the new RNGs without needing to find generator instances themselves [6]. Fig. 4 Architecture of Adder module (Carry select adder) Carry select adder is used for the fast addition. The basic idea is to add 2 bits using 3 1-bit full adders and a 2-bit multiplexer. One adder adds the least significant bit in the normal fashion. The other two add the most significant bit, one of them assuming that the carry in will be 0 and the other assuming that the carry in will be 1. Then the multiplexer chooses the output from one of these adders based on the carry produced by the adder for the least significant bit [8]. TABLE I Copyright to IJAREEIE 565
6 THE DEVICE UTILISATION SUMMARY GENERATED USING XILINX ISE TABLE II THE TIMING ANALYSIS REPORT. Fig. 5 Output window generated using isim simulator Xilinx 14.1 Copyright to IJAREEIE 566
7 VI. CONCLUSION This paper presented a method for bi-variate Gaussian random number generator in FPGAs, which decomposes the generation into a series of table-lookups and additions. This method can be extended to use in numerical Monte Carlo simulations; risk analysis etc as it only uses LUTs and FFs, and so all DSP and block-ram resources can be used in the simulation core that the generator is driving. This can be extended to multivariate generators as a future work. Adder/subtracter module can be included for getting more accurate and extended values. ACKNOWLEDGMENT The authors would like to thank the Department of Electronics and communication, SNGCE Kadayirippu for their support. We would also like to thank friends and resource persons who give technical support, valuable advice and encouragement throughout the project. REFERENCES [1] D. B. Thomas and W. Luk, Credit risk modelling using hardware accelerated monte-carlo simulation, in Proc. ACM Symp. FPGAs Custom Comput. ach., 2008, pp [2] N. Woods and T. VanCourt, FPGA acceleration of Quasi-Monte Carlo in finance, in Proc. Int. Conf. Field Programm. Logic Appl., 2008, pp [3] A. Kaganov, P. Chow, and A. Lakhany, FPGA acceleration of Monte- Carlo based credit derivative pricing, in Proc. Int. Conf. Field Programm. Logic Appl., 2008, pp [4] D. B. Thomas and W. Luk, Multivariate Gaussian random number generation targeting reconfigurable hardware, ACM Trans. Recon. Technol. Syst., vol. no. 12, pp , [5] Multiplierless Algorithm for Multivariate Gaussian Random Number Generation in FPGAs David B. Thomas, Member, IEEE, and Wayne Luk, Fellow, IEEE [6] FPGA-Optimised Uniform Random Number Generators using LUTs and Shift Registers David B. Thomas and Wayne Luk Imperial College London [7] N. J. Higham, Computing the nearest correlation matrix a problem from finance, IMA J. Num. Anal., vol. 22, pp , Oct [8] Bedrij, O. J., (1962), Carry-select adder, IRE Trans. Electron. Comput. Pp Copyright to IJAREEIE 567
THE multivariate Gaussian distribution is used to capture
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEMS, VOL. 21, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2013 2193 Multiplierless Algorithm for Multivariate Gaussian Random Number Generation in FPGAs David B. Thomas,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEMS, VOL. 21, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2013 2193 Multiplierless Algorithm for Multivariate Gaussian Random Number Generation in FPGAs David B. Thomas,
A Hardware Architecture for Direct Generation of Multi-Variate Gaussian Random Numbers
 A Hardware Architecture for Direct Generation of Multi-Variate Gaussian Random Numbers David B. Thomas and Wayne Luk {dt10,wl}@doc.ic.ac.uk Imperial College London Abstract The multi-variate Gaussian distribution
A Hardware Architecture for Direct Generation of Multi-Variate Gaussian Random Numbers David B. Thomas and Wayne Luk {dt10,wl}@doc.ic.ac.uk Imperial College London Abstract The multi-variate Gaussian distribution
Power and Area Efficient Implementation for Parallel FIR Filters Using FFAs and DA
 Power and Area Efficient Implementation for Parallel FIR Filters Using FFAs and DA Krishnapriya P.N 1, Arathy Iyer 2 M.Tech Student [VLSI & Embedded Systems], Sree Narayana Gurukulam College of Engineering,
Power and Area Efficient Implementation for Parallel FIR Filters Using FFAs and DA Krishnapriya P.N 1, Arathy Iyer 2 M.Tech Student [VLSI & Embedded Systems], Sree Narayana Gurukulam College of Engineering,
International Journal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
 An Efficient Implementation of Double Precision Floating Point Multiplier Using Booth Algorithm Pallavi Ramteke 1, Dr. N. N. Mhala 2, Prof. P. R. Lakhe M.Tech [IV Sem], Dept. of Comm. Engg., S.D.C.E, [Selukate],
An Efficient Implementation of Double Precision Floating Point Multiplier Using Booth Algorithm Pallavi Ramteke 1, Dr. N. N. Mhala 2, Prof. P. R. Lakhe M.Tech [IV Sem], Dept. of Comm. Engg., S.D.C.E, [Selukate],
Implementation of Double Precision Floating Point Multiplier on FPGA
 Implementation of Double Precision Floating Point Multiplier on FPGA A.Keerthi 1, K.V.Koteswararao 2 PG Student [VLSI], Dept. of ECE, Sree Vidyanikethan Engineering College, Tirupati, India 1 Assistant
Implementation of Double Precision Floating Point Multiplier on FPGA A.Keerthi 1, K.V.Koteswararao 2 PG Student [VLSI], Dept. of ECE, Sree Vidyanikethan Engineering College, Tirupati, India 1 Assistant
Multivariate Gaussian Random Number Generation Targeting Reconfigurable Hardware
 Multivariate Gaussian Random Number Generation Targeting Reconfigurable Hardware DAVID B. THOMAS and WAYNE LUK Imperial College London The multivariate Gaussian distribution is often used to model correlations
Multivariate Gaussian Random Number Generation Targeting Reconfigurable Hardware DAVID B. THOMAS and WAYNE LUK Imperial College London The multivariate Gaussian distribution is often used to model correlations
An Efficient Carry Select Adder with Less Delay and Reduced Area Application
 An Efficient Carry Select Adder with Less Delay and Reduced Area Application Pandu Ranga Rao #1 Priyanka Halle #2 # Associate Professor Department of ECE Sreyas Institute of Engineering and Technology,
An Efficient Carry Select Adder with Less Delay and Reduced Area Application Pandu Ranga Rao #1 Priyanka Halle #2 # Associate Professor Department of ECE Sreyas Institute of Engineering and Technology,
GENERATION OF PSEUDO-RANDOM NUMBER BY USING WELL AND RESEEDING METHOD. V.Divya Bharathi 1, Arivasanth.M 2
 GENERATION OF PSEUDO-RANDOM NUMBER BY USING WELL AND RESEEDING METHOD V.Divya Bharathi 1, Arivasanth.M 2 1 PG Scholar, M.E-VLSI Design,Srinivasan Engineering College, Perambalur, TamilNadu, India. 2 Assistant
GENERATION OF PSEUDO-RANDOM NUMBER BY USING WELL AND RESEEDING METHOD V.Divya Bharathi 1, Arivasanth.M 2 1 PG Scholar, M.E-VLSI Design,Srinivasan Engineering College, Perambalur, TamilNadu, India. 2 Assistant
A Multiplierless Algorithm for Multi-Variate Gaussian Random Number Generation in FPGAs
 TRANSACTIONS ON VLSI A Multiplierless Algorithm for MultiVariate Gaussian Random Number Generation in FPGAs David B. Thomas, Member, IEEE, and Wayne Luk, Fellow, IEEE Abstract The multivariate Gaussian
TRANSACTIONS ON VLSI A Multiplierless Algorithm for MultiVariate Gaussian Random Number Generation in FPGAs David B. Thomas, Member, IEEE, and Wayne Luk, Fellow, IEEE Abstract The multivariate Gaussian
FPGA Implementation of Low Complexity Video Encoder using Optimized 3D-DCT
 FPGA Implementation of Low Complexity Video Encoder using Optimized 3D-DCT Rajalekshmi R Embedded Systems Sree Buddha College of Engineering, Pattoor India Arya Lekshmi M Electronics and Communication
FPGA Implementation of Low Complexity Video Encoder using Optimized 3D-DCT Rajalekshmi R Embedded Systems Sree Buddha College of Engineering, Pattoor India Arya Lekshmi M Electronics and Communication
Design and Implementation of VLSI 8 Bit Systolic Array Multiplier
 Design and Implementation of VLSI 8 Bit Systolic Array Multiplier Khumanthem Devjit Singh, K. Jyothi MTech student (VLSI & ES), GIET, Rajahmundry, AP, India Associate Professor, Dept. of ECE, GIET, Rajahmundry,
Design and Implementation of VLSI 8 Bit Systolic Array Multiplier Khumanthem Devjit Singh, K. Jyothi MTech student (VLSI & ES), GIET, Rajahmundry, AP, India Associate Professor, Dept. of ECE, GIET, Rajahmundry,
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY FPGA
 IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY FPGA Implementations of Tiny Mersenne Twister Guoping Wang Department of Engineering, Indiana University Purdue University Fort
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY FPGA Implementations of Tiny Mersenne Twister Guoping Wang Department of Engineering, Indiana University Purdue University Fort
FPGA architecture and design technology
 CE 435 Embedded Systems Spring 2017 FPGA architecture and design technology Nikos Bellas Computer and Communications Engineering Department University of Thessaly 1 FPGA fabric A generic island-style FPGA
CE 435 Embedded Systems Spring 2017 FPGA architecture and design technology Nikos Bellas Computer and Communications Engineering Department University of Thessaly 1 FPGA fabric A generic island-style FPGA
ISSN Vol.05,Issue.09, September-2017, Pages:
 WWW.IJITECH.ORG ISSN 2321-8665 Vol.05,Issue.09, September-2017, Pages:1693-1697 AJJAM PUSHPA 1, C. H. RAMA MOHAN 2 1 PG Scholar, Dept of ECE(DECS), Shirdi Sai Institute of Science and Technology, Anantapuramu,
WWW.IJITECH.ORG ISSN 2321-8665 Vol.05,Issue.09, September-2017, Pages:1693-1697 AJJAM PUSHPA 1, C. H. RAMA MOHAN 2 1 PG Scholar, Dept of ECE(DECS), Shirdi Sai Institute of Science and Technology, Anantapuramu,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEMS /$ IEEE
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEMS 1 Exploration of Heterogeneous FPGAs for Mapping Linear Projection Designs Christos-S. Bouganis, Member, IEEE, Iosifina Pournara, and Peter
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEMS 1 Exploration of Heterogeneous FPGAs for Mapping Linear Projection Designs Christos-S. Bouganis, Member, IEEE, Iosifina Pournara, and Peter
A High Speed Binary Floating Point Multiplier Using Dadda Algorithm
 455 A High Speed Binary Floating Point Multiplier Using Dadda Algorithm B. Jeevan, Asst. Professor, Dept. of E&IE, KITS, Warangal. jeevanbs776@gmail.com S. Narender, M.Tech (VLSI&ES), KITS, Warangal. narender.s446@gmail.com
455 A High Speed Binary Floating Point Multiplier Using Dadda Algorithm B. Jeevan, Asst. Professor, Dept. of E&IE, KITS, Warangal. jeevanbs776@gmail.com S. Narender, M.Tech (VLSI&ES), KITS, Warangal. narender.s446@gmail.com
FPGA Matrix Multiplier
 FPGA Matrix Multiplier In Hwan Baek Henri Samueli School of Engineering and Applied Science University of California Los Angeles Los Angeles, California Email: chris.inhwan.baek@gmail.com David Boeck Henri
FPGA Matrix Multiplier In Hwan Baek Henri Samueli School of Engineering and Applied Science University of California Los Angeles Los Angeles, California Email: chris.inhwan.baek@gmail.com David Boeck Henri
A High Speed Design of 32 Bit Multiplier Using Modified CSLA
 Journal From the SelectedWorks of Journal October, 2014 A High Speed Design of 32 Bit Multiplier Using Modified CSLA Vijaya kumar vadladi David Solomon Raju. Y This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Journal From the SelectedWorks of Journal October, 2014 A High Speed Design of 32 Bit Multiplier Using Modified CSLA Vijaya kumar vadladi David Solomon Raju. Y This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
IMPLEMENTATION OF AN ADAPTIVE FIR FILTER USING HIGH SPEED DISTRIBUTED ARITHMETIC
 IMPLEMENTATION OF AN ADAPTIVE FIR FILTER USING HIGH SPEED DISTRIBUTED ARITHMETIC Thangamonikha.A 1, Dr.V.R.Balaji 2 1 PG Scholar, Department OF ECE, 2 Assitant Professor, Department of ECE 1, 2 Sri Krishna
IMPLEMENTATION OF AN ADAPTIVE FIR FILTER USING HIGH SPEED DISTRIBUTED ARITHMETIC Thangamonikha.A 1, Dr.V.R.Balaji 2 1 PG Scholar, Department OF ECE, 2 Assitant Professor, Department of ECE 1, 2 Sri Krishna
DESIGN AND PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF CARRY SELECT ADDER
 DESIGN AND PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF CARRY SELECT ADDER Bhuvaneswaran.M 1, Elamathi.K 2 Assistant Professor, Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram, Tamil Nadu, India 1 Assistant Professor, Muthayammal
DESIGN AND PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF CARRY SELECT ADDER Bhuvaneswaran.M 1, Elamathi.K 2 Assistant Professor, Muthayammal Engineering college, Rasipuram, Tamil Nadu, India 1 Assistant Professor, Muthayammal
Implementation of Lifting-Based Two Dimensional Discrete Wavelet Transform on FPGA Using Pipeline Architecture
 International Journal of Computer Trends and Technology (IJCTT) volume 5 number 5 Nov 2013 Implementation of Lifting-Based Two Dimensional Discrete Wavelet Transform on FPGA Using Pipeline Architecture
International Journal of Computer Trends and Technology (IJCTT) volume 5 number 5 Nov 2013 Implementation of Lifting-Based Two Dimensional Discrete Wavelet Transform on FPGA Using Pipeline Architecture
RESEARCH ARTICLE Software/Hardware Parallel Long Period Random Number Generation Framework Based on the Well Method
 International Journal of Advances in Engineering, 2015, 1(3), 84-89 ISSN: 2394-9260 (printed version); ISSN: 2394-9279 (online version); url:http://www.ijae.in RESEARCH ARTICLE Software/Hardware Parallel
International Journal of Advances in Engineering, 2015, 1(3), 84-89 ISSN: 2394-9260 (printed version); ISSN: 2394-9279 (online version); url:http://www.ijae.in RESEARCH ARTICLE Software/Hardware Parallel
VLSI Implementation of Low Power Area Efficient FIR Digital Filter Structures Shaila Khan 1 Uma Sharma 2
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 05, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 VLSI Implementation of Low Power Area Efficient FIR Digital Filter Structures Shaila
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 05, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 VLSI Implementation of Low Power Area Efficient FIR Digital Filter Structures Shaila
International Journal for Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology (IJRASET) IIR filter design using CSA for DSP applications
 IIR filter design using CSA for DSP applications Sagara.K.S 1, Ravi L.S 2 1 PG Student, Dept. of ECE, RIT, Hassan, 2 Assistant Professor Dept of ECE, RIT, Hassan Abstract- In this paper, a design methodology
IIR filter design using CSA for DSP applications Sagara.K.S 1, Ravi L.S 2 1 PG Student, Dept. of ECE, RIT, Hassan, 2 Assistant Professor Dept of ECE, RIT, Hassan Abstract- In this paper, a design methodology
FPGA Implementation of Multiplierless 2D DWT Architecture for Image Compression
 FPGA Implementation of Multiplierless 2D DWT Architecture for Image Compression Divakara.S.S, Research Scholar, J.S.S. Research Foundation, Mysore Cyril Prasanna Raj P Dean(R&D), MSEC, Bangalore Thejas
FPGA Implementation of Multiplierless 2D DWT Architecture for Image Compression Divakara.S.S, Research Scholar, J.S.S. Research Foundation, Mysore Cyril Prasanna Raj P Dean(R&D), MSEC, Bangalore Thejas
Design and Characterization of High Speed Carry Select Adder
 Design and Characterization of High Speed Carry Select Adder Santosh Elangadi MTech Student, Dept of ECE, BVBCET, Hubli, Karnataka, India Suhas Shirol Professor, Dept of ECE, BVBCET, Hubli, Karnataka,
Design and Characterization of High Speed Carry Select Adder Santosh Elangadi MTech Student, Dept of ECE, BVBCET, Hubli, Karnataka, India Suhas Shirol Professor, Dept of ECE, BVBCET, Hubli, Karnataka,
A SIMULINK-TO-FPGA MULTI-RATE HIERARCHICAL FIR FILTER DESIGN
 A SIMULINK-TO-FPGA MULTI-RATE HIERARCHICAL FIR FILTER DESIGN Xiaoying Li 1 Fuming Sun 2 Enhua Wu 1, 3 1 University of Macau, Macao, China 2 University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing, China
A SIMULINK-TO-FPGA MULTI-RATE HIERARCHICAL FIR FILTER DESIGN Xiaoying Li 1 Fuming Sun 2 Enhua Wu 1, 3 1 University of Macau, Macao, China 2 University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing, China
How Much Logic Should Go in an FPGA Logic Block?
 How Much Logic Should Go in an FPGA Logic Block? Vaughn Betz and Jonathan Rose Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Toronto Toronto, Ontario, Canada M5S 3G4 {vaughn, jayar}@eecgutorontoca
How Much Logic Should Go in an FPGA Logic Block? Vaughn Betz and Jonathan Rose Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Toronto Toronto, Ontario, Canada M5S 3G4 {vaughn, jayar}@eecgutorontoca
ERROR MODELLING OF DUAL FIXED-POINT ARITHMETIC AND ITS APPLICATION IN FIELD PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC
 ERROR MODELLING OF DUAL FIXED-POINT ARITHMETIC AND ITS APPLICATION IN FIELD PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC Chun Te Ewe, Peter Y. K. Cheung and George A. Constantinides Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering,
ERROR MODELLING OF DUAL FIXED-POINT ARITHMETIC AND ITS APPLICATION IN FIELD PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC Chun Te Ewe, Peter Y. K. Cheung and George A. Constantinides Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering,
A Low Power Asynchronous FPGA with Autonomous Fine Grain Power Gating and LEDR Encoding
 A Low Power Asynchronous FPGA with Autonomous Fine Grain Power Gating and LEDR Encoding N.Rajagopala krishnan, k.sivasuparamanyan, G.Ramadoss Abstract Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) are widely
A Low Power Asynchronous FPGA with Autonomous Fine Grain Power Gating and LEDR Encoding N.Rajagopala krishnan, k.sivasuparamanyan, G.Ramadoss Abstract Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) are widely
THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLEDGE
 THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLEDGE Design and Implementation of Optimized Floating Point Matrix Multiplier Based on FPGA Maruti L. Doddamani IV Semester, M.Tech (Digital Electronics), Department
THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLEDGE Design and Implementation of Optimized Floating Point Matrix Multiplier Based on FPGA Maruti L. Doddamani IV Semester, M.Tech (Digital Electronics), Department
Implementation of Floating Point Multiplier Using Dadda Algorithm
 Implementation of Floating Point Multiplier Using Dadda Algorithm Abstract: Floating point multiplication is the most usefull in all the computation application like in Arithematic operation, DSP application.
Implementation of Floating Point Multiplier Using Dadda Algorithm Abstract: Floating point multiplication is the most usefull in all the computation application like in Arithematic operation, DSP application.
Implementation of Ripple Carry and Carry Skip Adders with Speed and Area Efficient
 ISSN (Online) : 2278-1021 Implementation of Ripple Carry and Carry Skip Adders with Speed and Area Efficient PUSHPALATHA CHOPPA 1, B.N. SRINIVASA RAO 2 PG Scholar (VLSI Design), Department of ECE, Avanthi
ISSN (Online) : 2278-1021 Implementation of Ripple Carry and Carry Skip Adders with Speed and Area Efficient PUSHPALATHA CHOPPA 1, B.N. SRINIVASA RAO 2 PG Scholar (VLSI Design), Department of ECE, Avanthi
2015 Paper E2.1: Digital Electronics II
 s 2015 Paper E2.1: Digital Electronics II Answer ALL questions. There are THREE questions on the paper. Question ONE counts for 40% of the marks, other questions 30% Time allowed: 2 hours (Not to be removed
s 2015 Paper E2.1: Digital Electronics II Answer ALL questions. There are THREE questions on the paper. Question ONE counts for 40% of the marks, other questions 30% Time allowed: 2 hours (Not to be removed
An Efficient Implementation of Floating Point Multiplier
 An Efficient Implementation of Floating Point Multiplier Mohamed Al-Ashrafy Mentor Graphics Mohamed_Samy@Mentor.com Ashraf Salem Mentor Graphics Ashraf_Salem@Mentor.com Wagdy Anis Communications and Electronics
An Efficient Implementation of Floating Point Multiplier Mohamed Al-Ashrafy Mentor Graphics Mohamed_Samy@Mentor.com Ashraf Salem Mentor Graphics Ashraf_Salem@Mentor.com Wagdy Anis Communications and Electronics
Implementation of Double Precision Floating Point Multiplier Using Wallace Tree Multiplier
 Implementation of Double Precision Floating Point Multiplier Using Wallace Tree Multiplier Y. Ramya sri 1, V B K L Aruna 2 P.G. Student, Department of Electronics Engineering, V.R Siddhartha Engineering
Implementation of Double Precision Floating Point Multiplier Using Wallace Tree Multiplier Y. Ramya sri 1, V B K L Aruna 2 P.G. Student, Department of Electronics Engineering, V.R Siddhartha Engineering
FPGA Implementation of a High Speed Multistage Pipelined Adder Based CORDIC Structure for Large Operand Word Lengths
 International Journal of Computer Science and Telecommunications [Volume 3, Issue 5, May 2012] 105 ISSN 2047-3338 FPGA Implementation of a High Speed Multistage Pipelined Adder Based CORDIC Structure for
International Journal of Computer Science and Telecommunications [Volume 3, Issue 5, May 2012] 105 ISSN 2047-3338 FPGA Implementation of a High Speed Multistage Pipelined Adder Based CORDIC Structure for
Binary Adders. Ripple-Carry Adder
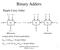 Ripple-Carry Adder Binary Adders x n y n x y x y c n FA c n - c 2 FA c FA c s n MSB position Longest delay (Critical-path delay): d c(n) = n d carry = 2n gate delays d s(n-) = (n-) d carry +d sum = 2n
Ripple-Carry Adder Binary Adders x n y n x y x y c n FA c n - c 2 FA c FA c s n MSB position Longest delay (Critical-path delay): d c(n) = n d carry = 2n gate delays d s(n-) = (n-) d carry +d sum = 2n
Implementing Multipliers in Xilinx Virtex II FPGAs
 HUNT ENGINEERING Chestnut Court, Burton Row, Brent Knoll, Somerset, TA9 4BP, UK Tel: (+44) (0)1278 760188, Fax: (+44) (0)1278 760199, Email: sales@hunteng.co.uk http://www.hunteng.co.uk http://www.hunt-dsp.com
HUNT ENGINEERING Chestnut Court, Burton Row, Brent Knoll, Somerset, TA9 4BP, UK Tel: (+44) (0)1278 760188, Fax: (+44) (0)1278 760199, Email: sales@hunteng.co.uk http://www.hunteng.co.uk http://www.hunt-dsp.com
Comparison of Adders for optimized Exponent Addition circuit in IEEE754 Floating point multiplier using VHDL
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 11, Issue 07 (July 2015), PP.60-65 Comparison of Adders for optimized Exponent Addition
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 11, Issue 07 (July 2015), PP.60-65 Comparison of Adders for optimized Exponent Addition
FIR Filter Architecture for Fixed and Reconfigurable Applications
 FIR Filter Architecture for Fixed and Reconfigurable Applications Nagajyothi 1,P.Sayannna 2 1 M.Tech student, Dept. of ECE, Sudheer reddy college of Engineering & technology (w), Telangana, India 2 Assosciate
FIR Filter Architecture for Fixed and Reconfigurable Applications Nagajyothi 1,P.Sayannna 2 1 M.Tech student, Dept. of ECE, Sudheer reddy college of Engineering & technology (w), Telangana, India 2 Assosciate
IMPLEMENTATION OF DOUBLE PRECISION FLOATING POINT RADIX-2 FFT USING VHDL
 IMPLEMENTATION OF DOUBLE PRECISION FLOATING POINT RADIX-2 FFT USING VHDL Tharanidevi.B 1, Jayaprakash.R 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Bharathiyar Institute of Engineering for Woman, Salem, TamilNadu,
IMPLEMENTATION OF DOUBLE PRECISION FLOATING POINT RADIX-2 FFT USING VHDL Tharanidevi.B 1, Jayaprakash.R 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Bharathiyar Institute of Engineering for Woman, Salem, TamilNadu,
University, Patiala, Punjab, India 1 2
 1102 Design and Implementation of Efficient Adder based Floating Point Multiplier LOKESH BHARDWAJ 1, SAKSHI BAJAJ 2 1 Student, M.tech, VLSI, 2 Assistant Professor,Electronics and Communication Engineering
1102 Design and Implementation of Efficient Adder based Floating Point Multiplier LOKESH BHARDWAJ 1, SAKSHI BAJAJ 2 1 Student, M.tech, VLSI, 2 Assistant Professor,Electronics and Communication Engineering
Implementation of Efficient Modified Booth Recoder for Fused Sum-Product Operator
 Implementation of Efficient Modified Booth Recoder for Fused Sum-Product Operator A.Sindhu 1, K.PriyaMeenakshi 2 PG Student [VLSI], Dept. of ECE, Muthayammal Engineering College, Rasipuram, Tamil Nadu,
Implementation of Efficient Modified Booth Recoder for Fused Sum-Product Operator A.Sindhu 1, K.PriyaMeenakshi 2 PG Student [VLSI], Dept. of ECE, Muthayammal Engineering College, Rasipuram, Tamil Nadu,
Efficient design and FPGA implementation of JPEG encoder
 IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP) Volume 6, Issue 5, Ver. II (Sep. - Oct. 2016), PP 47-53 e-issn: 2319 4200, p-issn No. : 2319 4197 www.iosrjournals.org Efficient design and FPGA implementation
IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP) Volume 6, Issue 5, Ver. II (Sep. - Oct. 2016), PP 47-53 e-issn: 2319 4200, p-issn No. : 2319 4197 www.iosrjournals.org Efficient design and FPGA implementation
A Comparison of Two Algorithms Involving Montgomery Modular Multiplication
 ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization Volume 6, Special Issue 5,
ISSN (Online) : 2319-8753 ISSN (Print) : 2347-6710 International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology An ISO 3297: 2007 Certified Organization Volume 6, Special Issue 5,
Advanced WG and MOWG Stream Cipher with Secured Initial vector
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 5, Issue 12, December 2015 471 Advanced WG and MOWG Stream Cipher with Secured Initial vector Dijomol Alias Pursuing M.Tech in VLSI
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 5, Issue 12, December 2015 471 Advanced WG and MOWG Stream Cipher with Secured Initial vector Dijomol Alias Pursuing M.Tech in VLSI
PROJECT REPORT IMPLEMENTATION OF LOGARITHM COMPUTATION DEVICE AS PART OF VLSI TOOLS COURSE
 PROJECT REPORT ON IMPLEMENTATION OF LOGARITHM COMPUTATION DEVICE AS PART OF VLSI TOOLS COURSE Project Guide Prof Ravindra Jayanti By Mukund UG3 (ECE) 200630022 Introduction The project was implemented
PROJECT REPORT ON IMPLEMENTATION OF LOGARITHM COMPUTATION DEVICE AS PART OF VLSI TOOLS COURSE Project Guide Prof Ravindra Jayanti By Mukund UG3 (ECE) 200630022 Introduction The project was implemented
Satellite Image Processing Using Singular Value Decomposition and Discrete Wavelet Transform
 Satellite Image Processing Using Singular Value Decomposition and Discrete Wavelet Transform Kodhinayaki E 1, vinothkumar S 2, Karthikeyan T 3 Department of ECE 1, 2, 3, p.g scholar 1, project coordinator
Satellite Image Processing Using Singular Value Decomposition and Discrete Wavelet Transform Kodhinayaki E 1, vinothkumar S 2, Karthikeyan T 3 Department of ECE 1, 2, 3, p.g scholar 1, project coordinator
Parallelized Radix-4 Scalable Montgomery Multipliers
 Parallelized Radix-4 Scalable Montgomery Multipliers Nathaniel Pinckney and David Money Harris 1 1 Harvey Mudd College, 301 Platt. Blvd., Claremont, CA, USA e-mail: npinckney@hmc.edu ABSTRACT This paper
Parallelized Radix-4 Scalable Montgomery Multipliers Nathaniel Pinckney and David Money Harris 1 1 Harvey Mudd College, 301 Platt. Blvd., Claremont, CA, USA e-mail: npinckney@hmc.edu ABSTRACT This paper
Parallel FIR Filters. Chapter 5
 Chapter 5 Parallel FIR Filters This chapter describes the implementation of high-performance, parallel, full-precision FIR filters using the DSP48 slice in a Virtex-4 device. ecause the Virtex-4 architecture
Chapter 5 Parallel FIR Filters This chapter describes the implementation of high-performance, parallel, full-precision FIR filters using the DSP48 slice in a Virtex-4 device. ecause the Virtex-4 architecture
An HEVC Fractional Interpolation Hardware Using Memory Based Constant Multiplication
 2018 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE) An HEVC Fractional Interpolation Hardware Using Memory Based Constant Multiplication Ahmet Can Mert, Ercan Kalali, Ilker Hamzaoglu Faculty
2018 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE) An HEVC Fractional Interpolation Hardware Using Memory Based Constant Multiplication Ahmet Can Mert, Ercan Kalali, Ilker Hamzaoglu Faculty
FPGA Implementation of 16-Point Radix-4 Complex FFT Core Using NEDA
 FPGA Implementation of 16-Point FFT Core Using NEDA Abhishek Mankar, Ansuman Diptisankar Das and N Prasad Abstract--NEDA is one of the techniques to implement many digital signal processing systems that
FPGA Implementation of 16-Point FFT Core Using NEDA Abhishek Mankar, Ansuman Diptisankar Das and N Prasad Abstract--NEDA is one of the techniques to implement many digital signal processing systems that
HIGH-PERFORMANCE RECONFIGURABLE FIR FILTER USING PIPELINE TECHNIQUE
 HIGH-PERFORMANCE RECONFIGURABLE FIR FILTER USING PIPELINE TECHNIQUE Anni Benitta.M #1 and Felcy Jeba Malar.M *2 1# Centre for excellence in VLSI Design, ECE, KCG College of Technology, Chennai, Tamilnadu
HIGH-PERFORMANCE RECONFIGURABLE FIR FILTER USING PIPELINE TECHNIQUE Anni Benitta.M #1 and Felcy Jeba Malar.M *2 1# Centre for excellence in VLSI Design, ECE, KCG College of Technology, Chennai, Tamilnadu
Pipelined Quadratic Equation based Novel Multiplication Method for Cryptographic Applications
 , Vol 7(4S), 34 39, April 204 ISSN (Print): 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Pipelined Quadratic Equation based Novel Multiplication Method for Cryptographic Applications B. Vignesh *, K. P. Sridhar
, Vol 7(4S), 34 39, April 204 ISSN (Print): 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Pipelined Quadratic Equation based Novel Multiplication Method for Cryptographic Applications B. Vignesh *, K. P. Sridhar
INTEGER SEQUENCE WINDOW BASED RECONFIGURABLE FIR FILTERS.
 INTEGER SEQUENCE WINDOW BASED RECONFIGURABLE FIR FILTERS Arulalan Rajan 1, H S Jamadagni 1, Ashok Rao 2 1 Centre for Electronics Design and Technology, Indian Institute of Science, India (mrarul,hsjam)@cedt.iisc.ernet.in
INTEGER SEQUENCE WINDOW BASED RECONFIGURABLE FIR FILTERS Arulalan Rajan 1, H S Jamadagni 1, Ashok Rao 2 1 Centre for Electronics Design and Technology, Indian Institute of Science, India (mrarul,hsjam)@cedt.iisc.ernet.in
Fast FPGA Routing Approach Using Stochestic Architecture
 . Fast FPGA Routing Approach Using Stochestic Architecture MITESH GURJAR 1, NAYAN PATEL 2 1 M.E. Student, VLSI and Embedded System Design, GTU PG School, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India. 2 Professor, Sabar Institute
. Fast FPGA Routing Approach Using Stochestic Architecture MITESH GURJAR 1, NAYAN PATEL 2 1 M.E. Student, VLSI and Embedded System Design, GTU PG School, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India. 2 Professor, Sabar Institute
A New Architecture of High Performance WG Stream Cipher
 A New Architecture of High Performance WG Stream Cipher Grace Mary S. 1, Abhila R. Krishna 2 1 P G Scholar, VLSI and Embedded Systems, Department of ECE T K M Institute of Technology, Kollam, India 2 Assistant
A New Architecture of High Performance WG Stream Cipher Grace Mary S. 1, Abhila R. Krishna 2 1 P G Scholar, VLSI and Embedded Systems, Department of ECE T K M Institute of Technology, Kollam, India 2 Assistant
Power Optimized Programmable Truncated Multiplier and Accumulator Using Reversible Adder
 Power Optimized Programmable Truncated Multiplier and Accumulator Using Reversible Adder Syeda Mohtashima Siddiqui M.Tech (VLSI & Embedded Systems) Department of ECE G Pulla Reddy Engineering College (Autonomous)
Power Optimized Programmable Truncated Multiplier and Accumulator Using Reversible Adder Syeda Mohtashima Siddiqui M.Tech (VLSI & Embedded Systems) Department of ECE G Pulla Reddy Engineering College (Autonomous)
Novel design of multiplier-less FFT processors
 Signal Processing 8 (00) 140 140 www.elsevier.com/locate/sigpro Novel design of multiplier-less FFT processors Yuan Zhou, J.M. Noras, S.J. Shepherd School of EDT, University of Bradford, Bradford, West
Signal Processing 8 (00) 140 140 www.elsevier.com/locate/sigpro Novel design of multiplier-less FFT processors Yuan Zhou, J.M. Noras, S.J. Shepherd School of EDT, University of Bradford, Bradford, West
MONTE CARLO applications are ideally suited to fieldprogrammable
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEMS, VOL. 21, NO. 4, APRIL 2013 761 The LUT-SR Family of Uniform Random Number Generators for FPGA Architectures David B. Thomas, Member, IEEE,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VERY LARGE SCALE INTEGRATION (VLSI) SYSTEMS, VOL. 21, NO. 4, APRIL 2013 761 The LUT-SR Family of Uniform Random Number Generators for FPGA Architectures David B. Thomas, Member, IEEE,
DESIGN OF HYBRID PARALLEL PREFIX ADDERS
 DESIGN OF HYBRID PARALLEL PREFIX ADDERS S. Sadiq Basha Dept. of ECE Vemu Institute of Technology Chittor,A.P Sadiqbasha4u@gmail.com H. Chandra Sekhar Associate Professor, ECE Vemu Institute of Technology
DESIGN OF HYBRID PARALLEL PREFIX ADDERS S. Sadiq Basha Dept. of ECE Vemu Institute of Technology Chittor,A.P Sadiqbasha4u@gmail.com H. Chandra Sekhar Associate Professor, ECE Vemu Institute of Technology
System Verification of Hardware Optimization Based on Edge Detection
 Circuits and Systems, 2013, 4, 293-298 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/cs.2013.43040 Published Online July 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/cs) System Verification of Hardware Optimization Based on Edge Detection
Circuits and Systems, 2013, 4, 293-298 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/cs.2013.43040 Published Online July 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/cs) System Verification of Hardware Optimization Based on Edge Detection
CHAPTER 9 MULTIPLEXERS, DECODERS, AND PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES
 CHAPTER 9 MULTIPLEXERS, DECODERS, AND PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES This chapter in the book includes: Objectives Study Guide 9.1 Introduction 9.2 Multiplexers 9.3 Three-State Buffers 9.4 Decoders and Encoders
CHAPTER 9 MULTIPLEXERS, DECODERS, AND PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICES This chapter in the book includes: Objectives Study Guide 9.1 Introduction 9.2 Multiplexers 9.3 Three-State Buffers 9.4 Decoders and Encoders
Modified Welch Power Spectral Density Computation with Fast Fourier Transform
 Modified Welch Power Spectral Density Computation with Fast Fourier Transform Sreelekha S 1, Sabi S 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication, Sree Budha College of Engineering, Kerala, India 2 Professor,
Modified Welch Power Spectral Density Computation with Fast Fourier Transform Sreelekha S 1, Sabi S 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication, Sree Budha College of Engineering, Kerala, India 2 Professor,
Design and Implementation of 3-D DWT for Video Processing Applications
 Design and Implementation of 3-D DWT for Video Processing Applications P. Mohaniah 1, P. Sathyanarayana 2, A. S. Ram Kumar Reddy 3 & A. Vijayalakshmi 4 1 E.C.E, N.B.K.R.IST, Vidyanagar, 2 E.C.E, S.V University
Design and Implementation of 3-D DWT for Video Processing Applications P. Mohaniah 1, P. Sathyanarayana 2, A. S. Ram Kumar Reddy 3 & A. Vijayalakshmi 4 1 E.C.E, N.B.K.R.IST, Vidyanagar, 2 E.C.E, S.V University
DIGITAL IMPLEMENTATION OF THE SIGMOID FUNCTION FOR FPGA CIRCUITS
 DIGITAL IMPLEMENTATION OF THE SIGMOID FUNCTION FOR FPGA CIRCUITS Alin TISAN, Stefan ONIGA, Daniel MIC, Attila BUCHMAN Electronic and Computer Department, North University of Baia Mare, Baia Mare, Romania
DIGITAL IMPLEMENTATION OF THE SIGMOID FUNCTION FOR FPGA CIRCUITS Alin TISAN, Stefan ONIGA, Daniel MIC, Attila BUCHMAN Electronic and Computer Department, North University of Baia Mare, Baia Mare, Romania
FPGA Implementation of Low-Area Floating Point Multiplier Using Vedic Mathematics
 FPGA Implementation of Low-Area Floating Point Multiplier Using Vedic Mathematics R. Sai Siva Teja 1, A. Madhusudhan 2 1 M.Tech Student, 2 Assistant Professor, Dept of ECE, Anurag Group of Institutions
FPGA Implementation of Low-Area Floating Point Multiplier Using Vedic Mathematics R. Sai Siva Teja 1, A. Madhusudhan 2 1 M.Tech Student, 2 Assistant Professor, Dept of ECE, Anurag Group of Institutions
Gauss for Econometrics: Simulation
 Gauss for Econometrics: Simulation R.G. Pierse 1. Introduction Simulation is a very useful tool in econometric modelling. It allows the economist to examine the properties of models and estimators when
Gauss for Econometrics: Simulation R.G. Pierse 1. Introduction Simulation is a very useful tool in econometric modelling. It allows the economist to examine the properties of models and estimators when
Area And Power Optimized One-Dimensional Median Filter
 Area And Power Optimized One-Dimensional Median Filter P. Premalatha, Ms. P. Karthika Rani, M.E., PG Scholar, Assistant Professor, PA College of Engineering and Technology, PA College of Engineering and
Area And Power Optimized One-Dimensional Median Filter P. Premalatha, Ms. P. Karthika Rani, M.E., PG Scholar, Assistant Professor, PA College of Engineering and Technology, PA College of Engineering and
FPGA Based Design and Simulation of 32- Point FFT Through Radix-2 DIT Algorith
 FPGA Based Design and Simulation of 32- Point FFT Through Radix-2 DIT Algorith Sudhanshu Mohan Khare M.Tech (perusing), Dept. of ECE Laxmi Naraian College of Technology, Bhopal, India M. Zahid Alam Associate
FPGA Based Design and Simulation of 32- Point FFT Through Radix-2 DIT Algorith Sudhanshu Mohan Khare M.Tech (perusing), Dept. of ECE Laxmi Naraian College of Technology, Bhopal, India M. Zahid Alam Associate
Robust Lossless Image Watermarking in Integer Wavelet Domain using SVD
 Robust Lossless Image Watermarking in Integer Domain using SVD 1 A. Kala 1 PG scholar, Department of CSE, Sri Venkateswara College of Engineering, Chennai 1 akala@svce.ac.in 2 K. haiyalnayaki 2 Associate
Robust Lossless Image Watermarking in Integer Domain using SVD 1 A. Kala 1 PG scholar, Department of CSE, Sri Venkateswara College of Engineering, Chennai 1 akala@svce.ac.in 2 K. haiyalnayaki 2 Associate
INTRODUCTION TO FPGA ARCHITECTURE
 3/3/25 INTRODUCTION TO FPGA ARCHITECTURE DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN (BASIC TECHNIQUES) a b a y 2input Black Box y b Functional Schematic a b y a b y a b y 2 Truth Table (AND) Truth Table (OR) Truth Table (XOR)
3/3/25 INTRODUCTION TO FPGA ARCHITECTURE DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN (BASIC TECHNIQUES) a b a y 2input Black Box y b Functional Schematic a b y a b y a b y 2 Truth Table (AND) Truth Table (OR) Truth Table (XOR)
FPGA Implementation of High Speed AES Algorithm for Improving The System Computing Speed
 FPGA Implementation of High Speed AES Algorithm for Improving The System Computing Speed Vijaya Kumar. B.1 #1, T. Thammi Reddy.2 #2 #1. Dept of Electronics and Communication, G.P.R.Engineering College,
FPGA Implementation of High Speed AES Algorithm for Improving The System Computing Speed Vijaya Kumar. B.1 #1, T. Thammi Reddy.2 #2 #1. Dept of Electronics and Communication, G.P.R.Engineering College,
Prachi Sharma 1, Rama Laxmi 2, Arun Kumar Mishra 3 1 Student, 2,3 Assistant Professor, EC Department, Bhabha College of Engineering
 A Review: Design of 16 bit Arithmetic and Logical unit using Vivado 14.7 and Implementation on Basys 3 FPGA Board Prachi Sharma 1, Rama Laxmi 2, Arun Kumar Mishra 3 1 Student, 2,3 Assistant Professor,
A Review: Design of 16 bit Arithmetic and Logical unit using Vivado 14.7 and Implementation on Basys 3 FPGA Board Prachi Sharma 1, Rama Laxmi 2, Arun Kumar Mishra 3 1 Student, 2,3 Assistant Professor,
An FPGA Based Floating Point Arithmetic Unit Using Verilog
 An FPGA Based Floating Point Arithmetic Unit Using Verilog T. Ramesh 1 G. Koteshwar Rao 2 1PG Scholar, Vaagdevi College of Engineering, Telangana. 2Assistant Professor, Vaagdevi College of Engineering,
An FPGA Based Floating Point Arithmetic Unit Using Verilog T. Ramesh 1 G. Koteshwar Rao 2 1PG Scholar, Vaagdevi College of Engineering, Telangana. 2Assistant Professor, Vaagdevi College of Engineering,
TSEA44 - Design for FPGAs
 2015-11-24 Now for something else... Adapting designs to FPGAs Why? Clock frequency Area Power Target FPGA architecture: Xilinx FPGAs with 4 input LUTs (such as Virtex-II) Determining the maximum frequency
2015-11-24 Now for something else... Adapting designs to FPGAs Why? Clock frequency Area Power Target FPGA architecture: Xilinx FPGAs with 4 input LUTs (such as Virtex-II) Determining the maximum frequency
Implementation of a High Speed Binary Floating point Multiplier Using Dadda Algorithm in FPGA
 Implementation of a High Speed Binary Floating point Multiplier Using Dadda Algorithm in FPGA Ms.Komal N.Batra 1, Prof. Ashish B. Kharate 2 1 PG Student, ENTC Department, HVPM S College of Engineering
Implementation of a High Speed Binary Floating point Multiplier Using Dadda Algorithm in FPGA Ms.Komal N.Batra 1, Prof. Ashish B. Kharate 2 1 PG Student, ENTC Department, HVPM S College of Engineering
OPTIMIZATION OF AREA COMPLEXITY AND DELAY USING PRE-ENCODED NR4SD MULTIPLIER.
 OPTIMIZATION OF AREA COMPLEXITY AND DELAY USING PRE-ENCODED NR4SD MULTIPLIER. A.Anusha 1 R.Basavaraju 2 anusha201093@gmail.com 1 basava430@gmail.com 2 1 PG Scholar, VLSI, Bharath Institute of Engineering
OPTIMIZATION OF AREA COMPLEXITY AND DELAY USING PRE-ENCODED NR4SD MULTIPLIER. A.Anusha 1 R.Basavaraju 2 anusha201093@gmail.com 1 basava430@gmail.com 2 1 PG Scholar, VLSI, Bharath Institute of Engineering
AES Core Specification. Author: Homer Hsing
 AES Core Specification Author: Homer Hsing homer.hsing@gmail.com Rev. 0.1.1 October 30, 2012 This page has been intentionally left blank. www.opencores.org Rev 0.1.1 ii Revision History Rev. Date Author
AES Core Specification Author: Homer Hsing homer.hsing@gmail.com Rev. 0.1.1 October 30, 2012 This page has been intentionally left blank. www.opencores.org Rev 0.1.1 ii Revision History Rev. Date Author
A Modified SVD-DCT Method for Enhancement of Low Contrast Satellite Images
 A Modified SVD-DCT Method for Enhancement of Low Contrast Satellite Images G.Praveena 1, M.Venkatasrinu 2, 1 M.tech student, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Madanapalle Institute
A Modified SVD-DCT Method for Enhancement of Low Contrast Satellite Images G.Praveena 1, M.Venkatasrinu 2, 1 M.tech student, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Madanapalle Institute
Implementation of a Fast Sign Detection Algoritm for the RNS Moduli Set {2 N+1-1, 2 N -1, 2 N }, N = 16, 64
 GLOBAL IMPACT FACTOR 0.238 I2OR PIF 2.125 Implementation of a Fast Sign Detection Algoritm for the RNS Moduli Set {2 N+1-1, 2 N -1, 2 N }, N = 16, 64 1 GARNEPUDI SONY PRIYANKA, 2 K.V.K.V.L. PAVAN KUMAR
GLOBAL IMPACT FACTOR 0.238 I2OR PIF 2.125 Implementation of a Fast Sign Detection Algoritm for the RNS Moduli Set {2 N+1-1, 2 N -1, 2 N }, N = 16, 64 1 GARNEPUDI SONY PRIYANKA, 2 K.V.K.V.L. PAVAN KUMAR
Xilinx Based Simulation of Line detection Using Hough Transform
 Xilinx Based Simulation of Line detection Using Hough Transform Vijaykumar Kawde 1 Assistant Professor, Department of EXTC Engineering, LTCOE, Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra, India 1 ABSTRACT: In auto focusing
Xilinx Based Simulation of Line detection Using Hough Transform Vijaykumar Kawde 1 Assistant Professor, Department of EXTC Engineering, LTCOE, Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra, India 1 ABSTRACT: In auto focusing
Performance Analysis of CORDIC Architectures Targeted by FPGA Devices
 International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Performance Analysis of CORDIC Architectures Targeted by FPGA Devices Guddeti Nagarjuna Reddy 1, R.Jayalakshmi 2, Dr.K.Umapathy
International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Performance Analysis of CORDIC Architectures Targeted by FPGA Devices Guddeti Nagarjuna Reddy 1, R.Jayalakshmi 2, Dr.K.Umapathy
Evaluation of High Speed Hardware Multipliers - Fixed Point and Floating point
 International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering (IJECE) Vol. 3, No. 6, December 2013, pp. 805~814 ISSN: 2088-8708 805 Evaluation of High Speed Hardware Multipliers - Fixed Point and Floating
International Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering (IJECE) Vol. 3, No. 6, December 2013, pp. 805~814 ISSN: 2088-8708 805 Evaluation of High Speed Hardware Multipliers - Fixed Point and Floating
Improving Reconfiguration Speed for Dynamic Circuit Specialization using Placement Constraints
 Improving Reconfiguration Speed for Dynamic Circuit Specialization using Placement Constraints Amit Kulkarni, Tom Davidson, Karel Heyse, and Dirk Stroobandt ELIS department, Computer Systems Lab, Ghent
Improving Reconfiguration Speed for Dynamic Circuit Specialization using Placement Constraints Amit Kulkarni, Tom Davidson, Karel Heyse, and Dirk Stroobandt ELIS department, Computer Systems Lab, Ghent
Figurel. TEEE-754 double precision floating point format. Keywords- Double precision, Floating point, Multiplier,FPGA,IEEE-754.
 AN FPGA BASED HIGH SPEED DOUBLE PRECISION FLOATING POINT MULTIPLIER USING VERILOG N.GIRIPRASAD (1), K.MADHAVA RAO (2) VLSI System Design,Tudi Ramireddy Institute of Technology & Sciences (1) Asst.Prof.,
AN FPGA BASED HIGH SPEED DOUBLE PRECISION FLOATING POINT MULTIPLIER USING VERILOG N.GIRIPRASAD (1), K.MADHAVA RAO (2) VLSI System Design,Tudi Ramireddy Institute of Technology & Sciences (1) Asst.Prof.,
discrete logic do not
 Welcome to my second year course on Digital Electronics. You will find that the slides are supported by notes embedded with the Powerpoint presentations. All my teaching materials are also available on
Welcome to my second year course on Digital Electronics. You will find that the slides are supported by notes embedded with the Powerpoint presentations. All my teaching materials are also available on
Built-In Self-Test for Programmable I/O Buffers in FPGAs and SoCs
 Built-In Self-Test for Programmable I/O Buffers in FPGAs and SoCs Sudheer Vemula, Student Member, IEEE, and Charles Stroud, Fellow, IEEE Abstract The first Built-In Self-Test (BIST) approach for the programmable
Built-In Self-Test for Programmable I/O Buffers in FPGAs and SoCs Sudheer Vemula, Student Member, IEEE, and Charles Stroud, Fellow, IEEE Abstract The first Built-In Self-Test (BIST) approach for the programmable
Design and Implementation of CVNS Based Low Power 64-Bit Adder
 Design and Implementation of CVNS Based Low Power 64-Bit Adder Ch.Vijay Kumar Department of ECE Embedded Systems & VLSI Design Vishakhapatnam, India Sri.Sagara Pandu Department of ECE Embedded Systems
Design and Implementation of CVNS Based Low Power 64-Bit Adder Ch.Vijay Kumar Department of ECE Embedded Systems & VLSI Design Vishakhapatnam, India Sri.Sagara Pandu Department of ECE Embedded Systems
International Journal of Research in Computer and Communication Technology, Vol 4, Issue 11, November- 2015
 Design of Dadda Algorithm based Floating Point Multiplier A. Bhanu Swetha. PG.Scholar: M.Tech(VLSISD), Department of ECE, BVCITS, Batlapalem. E.mail:swetha.appari@gmail.com V.Ramoji, Asst.Professor, Department
Design of Dadda Algorithm based Floating Point Multiplier A. Bhanu Swetha. PG.Scholar: M.Tech(VLSISD), Department of ECE, BVCITS, Batlapalem. E.mail:swetha.appari@gmail.com V.Ramoji, Asst.Professor, Department
Implementation of Full -Parallelism AES Encryption and Decryption
 Implementation of Full -Parallelism AES Encryption and Decryption M.Anto Merline M.E-Commuication Systems, ECE Department K.Ramakrishnan College of Engineering-Samayapuram, Trichy. Abstract-Advanced Encryption
Implementation of Full -Parallelism AES Encryption and Decryption M.Anto Merline M.E-Commuication Systems, ECE Department K.Ramakrishnan College of Engineering-Samayapuram, Trichy. Abstract-Advanced Encryption
Improved Design of High Performance Radix-10 Multiplication Using BCD Codes
 International OPEN ACCESS Journal ISSN: 2249-6645 Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Improved Design of High Performance Radix-10 Multiplication Using BCD Codes 1 A. Anusha, 2 C.Ashok Kumar 1 M.Tech
International OPEN ACCESS Journal ISSN: 2249-6645 Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Improved Design of High Performance Radix-10 Multiplication Using BCD Codes 1 A. Anusha, 2 C.Ashok Kumar 1 M.Tech
Image Contrast Enhancement in Wavelet Domain
 Advances in Computational Sciences and Technology ISSN 0973-6107 Volume 10, Number 6 (2017) pp. 1915-1922 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Image Contrast Enhancement in Wavelet
Advances in Computational Sciences and Technology ISSN 0973-6107 Volume 10, Number 6 (2017) pp. 1915-1922 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Image Contrast Enhancement in Wavelet
Design of 2-D DWT VLSI Architecture for Image Processing
 Design of 2-D DWT VLSI Architecture for Image Processing Betsy Jose 1 1 ME VLSI Design student Sri Ramakrishna Engineering College, Coimbatore B. Sathish Kumar 2 2 Assistant Professor, ECE Sri Ramakrishna
Design of 2-D DWT VLSI Architecture for Image Processing Betsy Jose 1 1 ME VLSI Design student Sri Ramakrishna Engineering College, Coimbatore B. Sathish Kumar 2 2 Assistant Professor, ECE Sri Ramakrishna
Analysis of Radix- SDF Pipeline FFT Architecture in VLSI Using Chip Scope
 Analysis of Radix- SDF Pipeline FFT Architecture in VLSI Using Chip Scope G. Mohana Durga 1, D.V.R. Mohan 2 1 M.Tech Student, 2 Professor, Department of ECE, SRKR Engineering College, Bhimavaram, Andhra
Analysis of Radix- SDF Pipeline FFT Architecture in VLSI Using Chip Scope G. Mohana Durga 1, D.V.R. Mohan 2 1 M.Tech Student, 2 Professor, Department of ECE, SRKR Engineering College, Bhimavaram, Andhra
High Performance Architecture for Reciprocal Function Evaluation on Virtex II FPGA
 EurAsia-ICT 00, Shiraz-Iran, 9-31 Oct. High Performance Architecture for Reciprocal Function Evaluation on Virtex II FPGA M. Anane, H. Bessalah and N. Anane Centre de Développement des Technologies Avancées
EurAsia-ICT 00, Shiraz-Iran, 9-31 Oct. High Performance Architecture for Reciprocal Function Evaluation on Virtex II FPGA M. Anane, H. Bessalah and N. Anane Centre de Développement des Technologies Avancées
IMPLEMENTATION OF CONFIGURABLE FLOATING POINT MULTIPLIER
 IMPLEMENTATION OF CONFIGURABLE FLOATING POINT MULTIPLIER 1 GOKILA D, 2 Dr. MANGALAM H 1 Department of ECE, United Institute of Technology, Coimbatore, Tamil nadu, India 2 Department of ECE, Sri Krishna
IMPLEMENTATION OF CONFIGURABLE FLOATING POINT MULTIPLIER 1 GOKILA D, 2 Dr. MANGALAM H 1 Department of ECE, United Institute of Technology, Coimbatore, Tamil nadu, India 2 Department of ECE, Sri Krishna
Probability Models.S4 Simulating Random Variables
 Operations Research Models and Methods Paul A. Jensen and Jonathan F. Bard Probability Models.S4 Simulating Random Variables In the fashion of the last several sections, we will often create probability
Operations Research Models and Methods Paul A. Jensen and Jonathan F. Bard Probability Models.S4 Simulating Random Variables In the fashion of the last several sections, we will often create probability
ARITHMETIC operations based on residue number systems
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 53, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2006 133 Improved Memoryless RNS Forward Converter Based on the Periodicity of Residues A. B. Premkumar, Senior Member,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 53, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2006 133 Improved Memoryless RNS Forward Converter Based on the Periodicity of Residues A. B. Premkumar, Senior Member,
