APPLICATION OF MULTIPLE RANDOM CENTROID (MRC) BASED K-MEANS CLUSTERING ALGORITHM IN INSURANCE A REVIEW ARTICLE
|
|
|
- Joanna May Randall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 APPLICATION OF MULTIPLE RANDOM CENTROID (MRC) BASED K-MEANS CLUSTERING ALGORITHM IN INSURANCE A REVIEW ARTICLE Sundari NallamReddy, Samarandra Behera, Sanjeev Karadagi, Dr. Anantha Desik ABSTRACT: Tata Consultancy Services, Hyderabad, India In this paper we present a review of some applications of cluster analysis in the field of Insurance and allied sciences. Primarily there are two types of clustering techniques used in predictive analytics based on the business problems, Partition-based clustering technique and Hierarchical agglomerative clustering approach. Hierarchical agglomeration based clustering approach is time consuming and complexity increases with increase in number of dimensions. Partition based algorithms contrary to hierarchical tries to divide the search space before arriving at the final clusters. Both methods have its merits and demerits and hence proper knowledge of domain, number of variables and computation prowess is required before deciding on the algorithm. Insurance industry is rich in data and attributes that can be used for data analytics are varied in nature. Hence, Hierarchical methods are generally not suitable for Insurance. K-means algorithms depending on partition-based clustering techniques are popular and widely used and applied to a variety of domains specifically in Insurance. However, K-means algorithms are extremely sensitive to the choice of initial centroid. Several different initialization approaches were proposed for the K-means algorithm in the last decades due to such sensitivity. This paper proposes an iterative Multiple Random method for selection of initial cluster centroid in K- means clustering instead of the simple random seed methods. Performance assessment of the proposed initialization method over two different Insurance datasets with different dimensions of distance functions, numbers of observations, groups and clustering complexities are discussed in detail. The proposed algorithm is developed in-house using Java and results are compared with some of the standard available software. Results from two insurance datasets varying in business problems and attributes, clearly indicates that the proposed initialization method is more effective and converges to more accurate clustering results than those of the simple random initialization methods. 1. INTRODUCTION This is an era of knowledge and information. There is virtually an explosion of information these days and fiercely competitive Insurance industry is definitely among the top user of data driven insights. In the digital journey Insurers are trying to understand competitive landscapes using deep insights of the customers. These insights are helping Insurance organizations to serve customers better and offer the right products at the right time thereby increasing profits. It is well understood by Insurer that, every customers need is different. Customer financial and investment needs are different and varies significantly. So, segment of customers, which is group of customers with similar Insurance need, differs from some other segments for the same Insurer. Insurance organization started their digital journey by trying to understand these subtle differences by applying advance analytics techniques. 15
2 Cluster analysis is the mostly used technique to segments the customers in all the business areas. Insurance business predominantly used this technique in underwriting, customer analysis, claim and marketing analytics. The application of hybrid methods i.e. analyzing data by applying predictive techniques inside each segments are relatively new but very powerful methodologies in Insurance. In view of this there is a lot of importance of cluster analysis in the insurance industry. Clustering is an important unsupervised learning technique where a set of patterns, usually vectors in a multidimensional space, are used for identifying group of similar characteristics. Each group, called cluster, consists of vectors that are similar between themselves and dissimilar to vectors of other groups. However, cluster analysis is considered to be the most popular tool in statistical data analysis which is widely applied in a variety of scientific areas such as data mining, pattern recognition, geographic information systems, information retrieval, microbiology analysis and Insurance & Finance. There are several clustering techniques available and those are organized into the following categories as partitioning methods, hierarchical methods, density-based methods, grid-based methods, model-based methods, methods for high-dimensional data and constraint-based clustering [1]. Partition-based clustering [2] attempts to analyze data and assembles it in a set of groups separate from each other. This paper is limited to discussion about K-Means algorithm which comes under partitioning methods where number of clusters is known a priori. Also, data in Insurance varies a lot and hence parametric data analysis implementation requires a lot of data cleansing and normalization. Segmentation approaches provides clean data on which accurate predictive models can be built. K means algorithm also helps in restricting the search spaces to a user defined value i.e. K, which enables faster data analytics implementation contrary to Hierarchical methods [3] to [7]. This paper has been organized as following. We discuss the K-means clustering algorithm using the two distance function Euclidean & Manhattan, followed by discussion on the importance of Initial Centroid (I- Centroid) and different approaches for initial seed. This is succeeded by a discussion on proposed Multiple Random Centroid (MRC Method) and the algorithm based on it. Computational results based on developed Java program using the two initial seeds methods, comparison with standard software, performance were discussed subsequently followed by conclusion and future work. 2. K-means Clustering K-means is one of the most famous partition clustering algorithms and considered the top ten most influential data mining algorithms. It is at the same time very simple and quite scalable, as it has linear asymptotic running time with respect to any variable of the problem. K-means clustering is a method of cluster analysis which aims to partition n observations (x1, x2 xn), where each observation is a d-dimensional real vector into k clusters in which each observation belongs to the cluster with the nearest mean. In general K-means is one of the most important and best performances of the clustering algorithms. However, there are some drawbacks for K-means algorithm like sensitivity to the initial cluster centroids which is addressed in this paper. Moreover, when the number of data points is large, it takes enormous time to find the global optimal solution. K-means has several limitations which are listed below: Scalability: It scales poorly computationally. Initial means: The clustering result is extremely sensitive to the initial means. Noise: Noise or outliers deteriorates the quality of the clustering result. Number of clusters: The number of clusters must be determined before the means clustering begins. Local minima: It always converges to local minima. 16
3 K-Means Algorithm: K-Means is one of the fastest Algorithm which converges very fast, the algorithm begins with random initial centroid and keep reassigning the patterns to clusters based on similarity between the patterns and the cluster centroid until a convergence criterion will met after certain no. of iterations. The K-Means algorithm is popular because it is easy to implement and time complexity is O(n), where n is the number of patterns. The basic K- Means process as follows Step1 Assign the number of clusters (k parameters in k-means). Step2 K-means selects randomly k cluster centroids. Step3 Assign objects to clusters based on distance function. Step4 When all objects have been assigned, Re-compute new cluster centroids by averaging the observations assigned to a cluster. Step5 Repeat (3-4) until convergence criterion is satisfied. Pseudo code for K-means algorithm: Require: k 2 and t 1, where k = no. of clusters & t = no. of iterations 1: Select initial cluster Centroids, c1, c2,..cl 2: Repeat 3: For each point xj in a dataset do 4: For all do 5: Compute the dissimilarity d(xj,ci) 6: End for. 7: assign point xj to closest cluster Ci; 8: End for. 9: For all do 10: Update as the centroid of cluster Ci; 11: End for. The implementation of K-means algorithm requires several important factors to be considered like Initial seed, distance function, normalization of the data and convergence/stopping criteria. Importance of Initial seed: Starting points in K-means algorithm has significant impact on the results. Choosing different starting point values lead to different clusters with different error values which effects K-means initialization process. Selection of the first centroids, which are far apart and falls into different clusters, has several benefits. It decrease amount of computation and optimize algorithm performance by minimizing the objective function of K-means algorithm, which leads to better results. Generally the process of initializing the centroids with any random seed and computing the clusters without seeing the closeness of these initial centroids to the data may lead to more computations and also may not provide good results. To come out of this challenge researchers generally use different random & heuristic process to compute the initial centroids. After the process of selecting the start point randomly; some calculations are performed to guess whether the point is suitable to be considered as a first initial centroid or not. Such decision is based on the process of computing distances between the selected centroid and other points within the dataset. The proposed algorithm uses N no. of random points and calculates the SSE (Sum of Squared Error) of random centroids from different points of data like, first, first quartile, 17
4 median etc. The random point with maximum SSE is considered as the initial centroid to start the algorithm. 3. Proposed Seed Algorithm 1. Set seed 2. For i, 1 to n 3. Assign random seed to cj 4. SSE between the (cj, x) X is the seed from data 5. Consider Cj where SSE is higher. Distance Functions: Generally different distance functions used calculate the distances but the propose algorithm we have used Euclidean & Manhattan distances. Euclidean The Euclidean distance between two points in the plane with coordinates (x, y) and (a, b) is given by - Manhattan The Manhattan distance (sum of the magnitudes of differences in each dimension) is given as- The developed program supports both the functions depending on the data and we have compared the results for these distance functions. Normalization: The proposed K-means algorithm runs only for numerical data, all the categorical variables that needs to be converted into numerical or binary variables. In addition to it the numerical variable needs to be standardized so as to bring all the variables in proportion to one another. This data standardization is carried out using Z- statistics otherwise distance computation will be difficult as there will be large variation in variables. Where Value is individual value of the variable for each observation, Mean is the average of that variable and 18
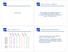
5 Stopping /Convergence: There are different methods used for convergence of the algorithm like the difference between corresponding difference between the centroids to be small and we have used the below process for convergence no (or minimum) re-assignments of data points to different clusters, no (or minimum) change of centroids, or minimum decrease in the sum of squared error (SSE), Ci is the jth cluster, mj is the centroid of cluster Cj (the mean vector of all the data points in Cj), and dist(x, mj) is the distance between data point x and centroid mj. We also used Sum square of group cluster (SBG), which is the sum of the squared distance of a cluster of a cluster centroid, Ci, to the overall means C of all the data points. The higher the total SBG of a clustering the more separated the clusters are from one another. The total SBG directly related to pairwise distance between the centroids. 4. Data Sets The performance evaluation of the proposed initialization method is applied on two real world insurance datasets. These datasets are deliberately chosen from two entirely different business problem i.e. identifying new customers for Insurance products and Claims in General Insurance (GI) to test the robustness of the proposed algorithm. Testing the proposed algorithm in this way also provided confidence on the generalization of this algorithm to some other business problems. Dataset1is of 21 variables of 4000 records and dataset2 new business insurance file is of 12 variables of records. Furthermore, the performance of K-means algorithm with the proposed initialization method is evaluated using popular evaluation method such as Sum of Square Errors (SSE). The results of such evaluation are compared with K-means algorithm with other methods, also it is compared against SAS and some free software. 5. Experimental Results The implementation of the proposed algorithm using multiple random initial centroids is compared with the using simple random initial centroids. Also this implementation is compared against the K-means results of the SAS Enterprise Miner (EM) and open source products. The experiment implementation is summarized in coding K-means algorithm and the process of selecting initial centroids of clusters using Java programming language and thus, the algorithm runs on any platform. Moreover, the algorithm allows the user to load many datasets and various file formats such as csv or sas data etc. Also various options like five initial centroid processes and two distance functions i.e. Euclidean and Manhattan are provided. Table 1 shows the comparison of K-means performance results using the proposed method, initial centroid, SAS and open source centroids. It is observed that the cluster results are almost similar lines for other methods and SSE of proposed method are better than initial centroid methods. The MRC method cluster results percentage almost matches with the SAS & open source outputs. The SBG values are also better than the initial centroid method. 19
6 Table-1: Dataset-1 Percentage of observation in each cluster and SSE, SBG Values Cluster No MRC-Method I-Centroid SAS Open Source Euclidean Manhattan Euclidean Manhattan Euclidean Euclidean Manhattan SSE NA SBG NA NA NA Table-2 is for validation of the MRC method taking three folds of different random data from the dataset-1 to test the algorithm performance. The results shows almost all the random samples the cluster percentages are similar and even SSE &SBG values are very small. The proposed method is hence found to be robust in terms of efficiency across various datasets. Table-2: Three fold validation of the proposed algorithm Cluster No. First Sample Second Sample Third Sample Euclidean Manhattan Euclidean Manhattan Euclidean Manhattan SSE SBG Table-3 depicts the implementation on a large dataset which provided better results considering the cluster % of initial method and also the results are similar to the output of SAS & open source software. The SSE values are far better than initial centroid methods. The proposed algorithm merged the cluster if the no. of data points is zero and in this case the algorithm considered only six clusters even though we run 7 cluster solution. Table-3: Dataset-2 Percentage of observation in each cluster and SSE, SBG Values Cluster No MRC-Method I-Centroid SAS Open Source Euclidean Manhattan Euclidean Manhattan Euclidean Euclidean Manhattan NA NA SSE NA Table - 4 provides the result from the validation of the MRC method on Dataset-2 taking three samples of data randomly from the dataset to test the algorithm performance. The results shows almost all the random samples the cluster percentages are similar and even SSE & SBG values are very small. The Euclidean distance cluster5 and SSE are better than Manhattan values. Again, the proposed method outperform in terms of efficiency and robustness across multiple samples. 20
7 Table-4: Dataset-2 Threefold validation of the proposed algorithm Cluster No First Set Second Set Third Set Euclidean Manhattan Euclidean Manhattan Euclidean Manhattan SSE SBG Conclusion Clustering is used in many fields such as data mining, knowledge discovery, statistics and machine learning. A good clustering algorithm produces high quality clusters to yield low inter cluster similarity and high intra cluster similarity. This paper presents a new way to select initial centroids using Multiple Random method in K- means algorithm. This initialization method is as fast and as simple as the K-means algorithms, which makes it attractive in practice. There are already so methods in practice for initial centroid selection. The main reason of this method is to make K-means less sensitive to the initialization process and to get consistent results every time algorithm runs. Experimental results demonstrate that the modification appears to give efficient performance when dealing with different insurance real-world datasets, and it is observed that the proposed method has substantially outperformed the standard K-means in terms of values & accuracy. References [1] T. Abraham and J. F. Roddick, "Survey of Spatio-Temporal Databases," GeoInformatica, vol. 3, March [2] R. Maitra, "Initializing partition-optimization algorithms," IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, vol. 6, pp , 2009 [3] Pena J., Lozano J. and Larranaga P., An Empirical comparison of four initialization methods for the K-means algorithm, Pattern Recognition Letters 20 (1999), [4] Ting Su and Jennifer Dy, "A Deterministic Method for Initializing K-means Clustering," Tools with Artificial Intelligence, ICTAI th IEEE International Conference, pp , Nov [5] S. Kalyani and K.S. Swarup, "Particle swarm optimization based K-means clustering approach for security assessment in power systems," Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 30, pp , [6] Mishra, S. K. and Raghavan, V. V., An empirical study of the performance of heuristic methods for clustering. In Pattern Recognition in Practice, E. S. Gelsema and L. N. Kanal, Eds ,
CLUSTERING. CSE 634 Data Mining Prof. Anita Wasilewska TEAM 16
 CLUSTERING CSE 634 Data Mining Prof. Anita Wasilewska TEAM 16 1. K-medoids: REFERENCES https://www.coursera.org/learn/cluster-analysis/lecture/nj0sb/3-4-the-k-medoids-clustering-method https://anuradhasrinivas.files.wordpress.com/2013/04/lesson8-clustering.pdf
CLUSTERING CSE 634 Data Mining Prof. Anita Wasilewska TEAM 16 1. K-medoids: REFERENCES https://www.coursera.org/learn/cluster-analysis/lecture/nj0sb/3-4-the-k-medoids-clustering-method https://anuradhasrinivas.files.wordpress.com/2013/04/lesson8-clustering.pdf
Unsupervised Learning
 Outline Unsupervised Learning Basic concepts K-means algorithm Representation of clusters Hierarchical clustering Distance functions Which clustering algorithm to use? NN Supervised learning vs. unsupervised
Outline Unsupervised Learning Basic concepts K-means algorithm Representation of clusters Hierarchical clustering Distance functions Which clustering algorithm to use? NN Supervised learning vs. unsupervised
CSE 5243 INTRO. TO DATA MINING
 CSE 5243 INTRO. TO DATA MINING Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Methods Huan Sun, CSE@The Ohio State University Slides adapted from UIUC CS412, Fall 2017, by Prof. Jiawei Han 2 Chapter 10. Cluster
CSE 5243 INTRO. TO DATA MINING Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Methods Huan Sun, CSE@The Ohio State University Slides adapted from UIUC CS412, Fall 2017, by Prof. Jiawei Han 2 Chapter 10. Cluster
Unsupervised Data Mining: Clustering. Izabela Moise, Evangelos Pournaras, Dirk Helbing
 Unsupervised Data Mining: Clustering Izabela Moise, Evangelos Pournaras, Dirk Helbing Izabela Moise, Evangelos Pournaras, Dirk Helbing 1 1. Supervised Data Mining Classification Regression Outlier detection
Unsupervised Data Mining: Clustering Izabela Moise, Evangelos Pournaras, Dirk Helbing Izabela Moise, Evangelos Pournaras, Dirk Helbing 1 1. Supervised Data Mining Classification Regression Outlier detection
CHAPTER 4 K-MEANS AND UCAM CLUSTERING ALGORITHM
 CHAPTER 4 K-MEANS AND UCAM CLUSTERING 4.1 Introduction ALGORITHM Clustering has been used in a number of applications such as engineering, biology, medicine and data mining. The most popular clustering
CHAPTER 4 K-MEANS AND UCAM CLUSTERING 4.1 Introduction ALGORITHM Clustering has been used in a number of applications such as engineering, biology, medicine and data mining. The most popular clustering
CSE 5243 INTRO. TO DATA MINING
 CSE 5243 INTRO. TO DATA MINING Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Methods Huan Sun, CSE@The Ohio State University 09/25/2017 Slides adapted from UIUC CS412, Fall 2017, by Prof. Jiawei Han 2 Chapter 10.
CSE 5243 INTRO. TO DATA MINING Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Methods Huan Sun, CSE@The Ohio State University 09/25/2017 Slides adapted from UIUC CS412, Fall 2017, by Prof. Jiawei Han 2 Chapter 10.
New Approach for K-mean and K-medoids Algorithm
 New Approach for K-mean and K-medoids Algorithm Abhishek Patel Department of Information & Technology, Parul Institute of Engineering & Technology, Vadodara, Gujarat, India Purnima Singh Department of
New Approach for K-mean and K-medoids Algorithm Abhishek Patel Department of Information & Technology, Parul Institute of Engineering & Technology, Vadodara, Gujarat, India Purnima Singh Department of
BBS654 Data Mining. Pinar Duygulu. Slides are adapted from Nazli Ikizler
 BBS654 Data Mining Pinar Duygulu Slides are adapted from Nazli Ikizler 1 Classification Classification systems: Supervised learning Make a rational prediction given evidence There are several methods for
BBS654 Data Mining Pinar Duygulu Slides are adapted from Nazli Ikizler 1 Classification Classification systems: Supervised learning Make a rational prediction given evidence There are several methods for
INF4820. Clustering. Erik Velldal. Nov. 17, University of Oslo. Erik Velldal INF / 22
 INF4820 Clustering Erik Velldal University of Oslo Nov. 17, 2009 Erik Velldal INF4820 1 / 22 Topics for Today More on unsupervised machine learning for data-driven categorization: clustering. The task
INF4820 Clustering Erik Velldal University of Oslo Nov. 17, 2009 Erik Velldal INF4820 1 / 22 Topics for Today More on unsupervised machine learning for data-driven categorization: clustering. The task
A Review of K-mean Algorithm
 A Review of K-mean Algorithm Jyoti Yadav #1, Monika Sharma *2 1 PG Student, CSE Department, M.D.U Rohtak, Haryana, India 2 Assistant Professor, IT Department, M.D.U Rohtak, Haryana, India Abstract Cluster
A Review of K-mean Algorithm Jyoti Yadav #1, Monika Sharma *2 1 PG Student, CSE Department, M.D.U Rohtak, Haryana, India 2 Assistant Professor, IT Department, M.D.U Rohtak, Haryana, India Abstract Cluster
Analyzing Outlier Detection Techniques with Hybrid Method
 Analyzing Outlier Detection Techniques with Hybrid Method Shruti Aggarwal Assistant Professor Department of Computer Science and Engineering Sri Guru Granth Sahib World University. (SGGSWU) Fatehgarh Sahib,
Analyzing Outlier Detection Techniques with Hybrid Method Shruti Aggarwal Assistant Professor Department of Computer Science and Engineering Sri Guru Granth Sahib World University. (SGGSWU) Fatehgarh Sahib,
Olmo S. Zavala Romero. Clustering Hierarchical Distance Group Dist. K-means. Center of Atmospheric Sciences, UNAM.
 Center of Atmospheric Sciences, UNAM November 16, 2016 Cluster Analisis Cluster analysis or clustering is the task of grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (called a cluster)
Center of Atmospheric Sciences, UNAM November 16, 2016 Cluster Analisis Cluster analysis or clustering is the task of grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (called a cluster)
CHAPTER 4: CLUSTER ANALYSIS
 CHAPTER 4: CLUSTER ANALYSIS WHAT IS CLUSTER ANALYSIS? A cluster is a collection of data-objects similar to one another within the same group & dissimilar to the objects in other groups. Cluster analysis
CHAPTER 4: CLUSTER ANALYSIS WHAT IS CLUSTER ANALYSIS? A cluster is a collection of data-objects similar to one another within the same group & dissimilar to the objects in other groups. Cluster analysis
University of Florida CISE department Gator Engineering. Clustering Part 2
 Clustering Part 2 Dr. Sanjay Ranka Professor Computer and Information Science and Engineering University of Florida, Gainesville Partitional Clustering Original Points A Partitional Clustering Hierarchical
Clustering Part 2 Dr. Sanjay Ranka Professor Computer and Information Science and Engineering University of Florida, Gainesville Partitional Clustering Original Points A Partitional Clustering Hierarchical
Clustering. CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Spring Soleymani
 Clustering CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Spring 2016 Soleymani Outline Clustering Definition Clustering main approaches Partitional (flat) Hierarchical Clustering validation
Clustering CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Spring 2016 Soleymani Outline Clustering Definition Clustering main approaches Partitional (flat) Hierarchical Clustering validation
Unsupervised Learning : Clustering
 Unsupervised Learning : Clustering Things to be Addressed Traditional Learning Models. Cluster Analysis K-means Clustering Algorithm Drawbacks of traditional clustering algorithms. Clustering as a complex
Unsupervised Learning : Clustering Things to be Addressed Traditional Learning Models. Cluster Analysis K-means Clustering Algorithm Drawbacks of traditional clustering algorithms. Clustering as a complex
Hard clustering. Each object is assigned to one and only one cluster. Hierarchical clustering is usually hard. Soft (fuzzy) clustering
 An unsupervised machine learning problem Grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (a cluster) are more similar (in some sense or another) to each other than to those in other
An unsupervised machine learning problem Grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (a cluster) are more similar (in some sense or another) to each other than to those in other
Exploratory Analysis: Clustering
 Exploratory Analysis: Clustering (some material taken or adapted from slides by Hinrich Schutze) Heejun Kim June 26, 2018 Clustering objective Grouping documents or instances into subsets or clusters Documents
Exploratory Analysis: Clustering (some material taken or adapted from slides by Hinrich Schutze) Heejun Kim June 26, 2018 Clustering objective Grouping documents or instances into subsets or clusters Documents
Accelerating Unique Strategy for Centroid Priming in K-Means Clustering
 IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 3 Issue 07 December 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Accelerating Unique Strategy for Centroid Priming in K-Means Clustering
IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 3 Issue 07 December 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 Accelerating Unique Strategy for Centroid Priming in K-Means Clustering
Gene Clustering & Classification
 BINF, Introduction to Computational Biology Gene Clustering & Classification Young-Rae Cho Associate Professor Department of Computer Science Baylor University Overview Introduction to Gene Clustering
BINF, Introduction to Computational Biology Gene Clustering & Classification Young-Rae Cho Associate Professor Department of Computer Science Baylor University Overview Introduction to Gene Clustering
Data Mining Chapter 9: Descriptive Modeling Fall 2011 Ming Li Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University
 Data Mining Chapter 9: Descriptive Modeling Fall 2011 Ming Li Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University Descriptive model A descriptive model presents the main features of the data
Data Mining Chapter 9: Descriptive Modeling Fall 2011 Ming Li Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University Descriptive model A descriptive model presents the main features of the data
Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques. Chapter March 8, 2007 Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques 1
 Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques Chapter 7.1-4 March 8, 2007 Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques 1 1. What is Cluster Analysis? 2. Types of Data in Cluster Analysis Chapter 7 Cluster Analysis 3. A
Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques Chapter 7.1-4 March 8, 2007 Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques 1 1. What is Cluster Analysis? 2. Types of Data in Cluster Analysis Chapter 7 Cluster Analysis 3. A
CS 2750 Machine Learning. Lecture 19. Clustering. CS 2750 Machine Learning. Clustering. Groups together similar instances in the data sample
 Lecture 9 Clustering Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 539 Sennott Square Clustering Groups together similar instances in the data sample Basic clustering problem: distribute data into k different groups
Lecture 9 Clustering Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 539 Sennott Square Clustering Groups together similar instances in the data sample Basic clustering problem: distribute data into k different groups
Clustering Part 1. CSC 4510/9010: Applied Machine Learning. Dr. Paula Matuszek
 CSC 4510/9010: Applied Machine Learning 1 Clustering Part 1 Dr. Paula Matuszek Paula.Matuszek@villanova.edu Paula.Matuszek@gmail.com (610) 647-9789 What is Clustering? 2 Given some instances with data:
CSC 4510/9010: Applied Machine Learning 1 Clustering Part 1 Dr. Paula Matuszek Paula.Matuszek@villanova.edu Paula.Matuszek@gmail.com (610) 647-9789 What is Clustering? 2 Given some instances with data:
Unsupervised Learning Partitioning Methods
 Unsupervised Learning Partitioning Methods Road Map 1. Basic Concepts 2. K-Means 3. K-Medoids 4. CLARA & CLARANS Cluster Analysis Unsupervised learning (i.e., Class label is unknown) Group data to form
Unsupervised Learning Partitioning Methods Road Map 1. Basic Concepts 2. K-Means 3. K-Medoids 4. CLARA & CLARANS Cluster Analysis Unsupervised learning (i.e., Class label is unknown) Group data to form
ECLT 5810 Clustering
 ECLT 5810 Clustering What is Cluster Analysis? Cluster: a collection of data objects Similar to one another within the same cluster Dissimilar to the objects in other clusters Cluster analysis Grouping
ECLT 5810 Clustering What is Cluster Analysis? Cluster: a collection of data objects Similar to one another within the same cluster Dissimilar to the objects in other clusters Cluster analysis Grouping
INF4820, Algorithms for AI and NLP: Evaluating Classifiers Clustering
 INF4820, Algorithms for AI and NLP: Evaluating Classifiers Clustering Erik Velldal University of Oslo Sept. 18, 2012 Topics for today 2 Classification Recap Evaluating classifiers Accuracy, precision,
INF4820, Algorithms for AI and NLP: Evaluating Classifiers Clustering Erik Velldal University of Oslo Sept. 18, 2012 Topics for today 2 Classification Recap Evaluating classifiers Accuracy, precision,
Data Mining. Dr. Raed Ibraheem Hamed. University of Human Development, College of Science and Technology Department of Computer Science
 Data Mining Dr. Raed Ibraheem Hamed University of Human Development, College of Science and Technology Department of Computer Science 2016 201 Road map What is Cluster Analysis? Characteristics of Clustering
Data Mining Dr. Raed Ibraheem Hamed University of Human Development, College of Science and Technology Department of Computer Science 2016 201 Road map What is Cluster Analysis? Characteristics of Clustering
An Unsupervised Technique for Statistical Data Analysis Using Data Mining
 International Journal of Information Sciences and Application. ISSN 0974-2255 Volume 5, Number 1 (2013), pp. 11-20 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com An Unsupervised Technique
International Journal of Information Sciences and Application. ISSN 0974-2255 Volume 5, Number 1 (2013), pp. 11-20 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com An Unsupervised Technique
What to come. There will be a few more topics we will cover on supervised learning
 Summary so far Supervised learning learn to predict Continuous target regression; Categorical target classification Linear Regression Classification Discriminative models Perceptron (linear) Logistic regression
Summary so far Supervised learning learn to predict Continuous target regression; Categorical target classification Linear Regression Classification Discriminative models Perceptron (linear) Logistic regression
Cluster Analysis. Prof. Thomas B. Fomby Department of Economics Southern Methodist University Dallas, TX April 2008 April 2010
 Cluster Analysis Prof. Thomas B. Fomby Department of Economics Southern Methodist University Dallas, TX 7575 April 008 April 010 Cluster Analysis, sometimes called data segmentation or customer segmentation,
Cluster Analysis Prof. Thomas B. Fomby Department of Economics Southern Methodist University Dallas, TX 7575 April 008 April 010 Cluster Analysis, sometimes called data segmentation or customer segmentation,
TOWARDS NEW ESTIMATING INCREMENTAL DIMENSIONAL ALGORITHM (EIDA)
 TOWARDS NEW ESTIMATING INCREMENTAL DIMENSIONAL ALGORITHM (EIDA) 1 S. ADAEKALAVAN, 2 DR. C. CHANDRASEKAR 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Information Technology, J.J. College of Arts and Science, Pudukkottai,
TOWARDS NEW ESTIMATING INCREMENTAL DIMENSIONAL ALGORITHM (EIDA) 1 S. ADAEKALAVAN, 2 DR. C. CHANDRASEKAR 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Information Technology, J.J. College of Arts and Science, Pudukkottai,
Improved Performance of Unsupervised Method by Renovated K-Means
 Improved Performance of Unsupervised Method by Renovated P.Ashok Research Scholar, Bharathiar University, Coimbatore Tamilnadu, India. ashokcutee@gmail.com Dr.G.M Kadhar Nawaz Department of Computer Application
Improved Performance of Unsupervised Method by Renovated P.Ashok Research Scholar, Bharathiar University, Coimbatore Tamilnadu, India. ashokcutee@gmail.com Dr.G.M Kadhar Nawaz Department of Computer Application
K-Means Clustering With Initial Centroids Based On Difference Operator
 K-Means Clustering With Initial Centroids Based On Difference Operator Satish Chaurasiya 1, Dr.Ratish Agrawal 2 M.Tech Student, School of Information and Technology, R.G.P.V, Bhopal, India Assistant Professor,
K-Means Clustering With Initial Centroids Based On Difference Operator Satish Chaurasiya 1, Dr.Ratish Agrawal 2 M.Tech Student, School of Information and Technology, R.G.P.V, Bhopal, India Assistant Professor,
Data Mining Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Algorithms. Slides From Lecture Notes for Chapter 8. Introduction to Data Mining
 Data Mining Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Algorithms Slides From Lecture Notes for Chapter 8 Introduction to Data Mining by Tan, Steinbach, Kumar Tan,Steinbach, Kumar Introduction to Data Mining
Data Mining Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Algorithms Slides From Lecture Notes for Chapter 8 Introduction to Data Mining by Tan, Steinbach, Kumar Tan,Steinbach, Kumar Introduction to Data Mining
INF4820 Algorithms for AI and NLP. Evaluating Classifiers Clustering
 INF4820 Algorithms for AI and NLP Evaluating Classifiers Clustering Erik Velldal & Stephan Oepen Language Technology Group (LTG) September 23, 2015 Agenda Last week Supervised vs unsupervised learning.
INF4820 Algorithms for AI and NLP Evaluating Classifiers Clustering Erik Velldal & Stephan Oepen Language Technology Group (LTG) September 23, 2015 Agenda Last week Supervised vs unsupervised learning.
NORMALIZATION INDEXING BASED ENHANCED GROUPING K-MEAN ALGORITHM
 NORMALIZATION INDEXING BASED ENHANCED GROUPING K-MEAN ALGORITHM Saroj 1, Ms. Kavita2 1 Student of Masters of Technology, 2 Assistant Professor Department of Computer Science and Engineering JCDM college
NORMALIZATION INDEXING BASED ENHANCED GROUPING K-MEAN ALGORITHM Saroj 1, Ms. Kavita2 1 Student of Masters of Technology, 2 Assistant Professor Department of Computer Science and Engineering JCDM college
ECLT 5810 Clustering
 ECLT 5810 Clustering What is Cluster Analysis? Cluster: a collection of data objects Similar to one another within the same cluster Dissimilar to the objects in other clusters Cluster analysis Grouping
ECLT 5810 Clustering What is Cluster Analysis? Cluster: a collection of data objects Similar to one another within the same cluster Dissimilar to the objects in other clusters Cluster analysis Grouping
CS 1675 Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 18. Clustering. Clustering. Groups together similar instances in the data sample
 CS 1675 Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 18 Clustering Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 539 Sennott Square Clustering Groups together similar instances in the data sample Basic clustering problem:
CS 1675 Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 18 Clustering Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 539 Sennott Square Clustering Groups together similar instances in the data sample Basic clustering problem:
Lesson 3. Prof. Enza Messina
 Lesson 3 Prof. Enza Messina Clustering techniques are generally classified into these classes: PARTITIONING ALGORITHMS Directly divides data points into some prespecified number of clusters without a hierarchical
Lesson 3 Prof. Enza Messina Clustering techniques are generally classified into these classes: PARTITIONING ALGORITHMS Directly divides data points into some prespecified number of clusters without a hierarchical
Unsupervised Learning and Clustering
 Unsupervised Learning and Clustering Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr CS 551, Spring 2009 CS 551, Spring 2009 c 2009, Selim Aksoy (Bilkent University)
Unsupervised Learning and Clustering Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr CS 551, Spring 2009 CS 551, Spring 2009 c 2009, Selim Aksoy (Bilkent University)
Clustering. K-means clustering
 Clustering K-means clustering Clustering Motivation: Identify clusters of data points in a multidimensional space, i.e. partition the data set {x 1,...,x N } into K clusters. Intuition: A cluster is a
Clustering K-means clustering Clustering Motivation: Identify clusters of data points in a multidimensional space, i.e. partition the data set {x 1,...,x N } into K clusters. Intuition: A cluster is a
Iteration Reduction K Means Clustering Algorithm
 Iteration Reduction K Means Clustering Algorithm Kedar Sawant 1 and Snehal Bhogan 2 1 Department of Computer Engineering, Agnel Institute of Technology and Design, Assagao, Goa 403507, India 2 Department
Iteration Reduction K Means Clustering Algorithm Kedar Sawant 1 and Snehal Bhogan 2 1 Department of Computer Engineering, Agnel Institute of Technology and Design, Assagao, Goa 403507, India 2 Department
Keywords Clustering, Goals of clustering, clustering techniques, clustering algorithms.
 Volume 3, Issue 5, May 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com A Survey of Clustering
Volume 3, Issue 5, May 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com A Survey of Clustering
AN IMPROVED HYBRIDIZED K- MEANS CLUSTERING ALGORITHM (IHKMCA) FOR HIGHDIMENSIONAL DATASET & IT S PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS
 AN IMPROVED HYBRIDIZED K- MEANS CLUSTERING ALGORITHM (IHKMCA) FOR HIGHDIMENSIONAL DATASET & IT S PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS H.S Behera Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Veer Surendra Sai University
AN IMPROVED HYBRIDIZED K- MEANS CLUSTERING ALGORITHM (IHKMCA) FOR HIGHDIMENSIONAL DATASET & IT S PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS H.S Behera Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Veer Surendra Sai University
K-Means. Oct Youn-Hee Han
 K-Means Oct. 2015 Youn-Hee Han http://link.koreatech.ac.kr ²K-Means algorithm An unsupervised clustering algorithm K stands for number of clusters. It is typically a user input to the algorithm Some criteria
K-Means Oct. 2015 Youn-Hee Han http://link.koreatech.ac.kr ²K-Means algorithm An unsupervised clustering algorithm K stands for number of clusters. It is typically a user input to the algorithm Some criteria
Cluster Analysis. CSE634 Data Mining
 Cluster Analysis CSE634 Data Mining Agenda Introduction Clustering Requirements Data Representation Partitioning Methods K-Means Clustering K-Medoids Clustering Constrained K-Means clustering Introduction
Cluster Analysis CSE634 Data Mining Agenda Introduction Clustering Requirements Data Representation Partitioning Methods K-Means Clustering K-Medoids Clustering Constrained K-Means clustering Introduction
Cluster Analysis. Mu-Chun Su. Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Central University 2003/3/11 1
 Cluster Analysis Mu-Chun Su Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Central University 2003/3/11 1 Introduction Cluster analysis is the formal study of algorithms and methods
Cluster Analysis Mu-Chun Su Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Central University 2003/3/11 1 Introduction Cluster analysis is the formal study of algorithms and methods
Unsupervised Learning and Clustering
 Unsupervised Learning and Clustering Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr CS 551, Spring 2008 CS 551, Spring 2008 c 2008, Selim Aksoy (Bilkent University)
Unsupervised Learning and Clustering Selim Aksoy Department of Computer Engineering Bilkent University saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr CS 551, Spring 2008 CS 551, Spring 2008 c 2008, Selim Aksoy (Bilkent University)
Text Documents clustering using K Means Algorithm
 Text Documents clustering using K Means Algorithm Mrs Sanjivani Tushar Deokar Assistant professor sanjivanideokar@gmail.com Abstract: With the advancement of technology and reduced storage costs, individuals
Text Documents clustering using K Means Algorithm Mrs Sanjivani Tushar Deokar Assistant professor sanjivanideokar@gmail.com Abstract: With the advancement of technology and reduced storage costs, individuals
Document Clustering: Comparison of Similarity Measures
 Document Clustering: Comparison of Similarity Measures Shouvik Sachdeva Bhupendra Kastore Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur CS365 Project, 2014 Outline 1 Introduction The Problem and the Motivation
Document Clustering: Comparison of Similarity Measures Shouvik Sachdeva Bhupendra Kastore Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur CS365 Project, 2014 Outline 1 Introduction The Problem and the Motivation
Cluster Analysis. Ying Shen, SSE, Tongji University
 Cluster Analysis Ying Shen, SSE, Tongji University Cluster analysis Cluster analysis groups data objects based only on the attributes in the data. The main objective is that The objects within a group
Cluster Analysis Ying Shen, SSE, Tongji University Cluster analysis Cluster analysis groups data objects based only on the attributes in the data. The main objective is that The objects within a group
Understanding Clustering Supervising the unsupervised
 Understanding Clustering Supervising the unsupervised Janu Verma IBM T.J. Watson Research Center, New York http://jverma.github.io/ jverma@us.ibm.com @januverma Clustering Grouping together similar data
Understanding Clustering Supervising the unsupervised Janu Verma IBM T.J. Watson Research Center, New York http://jverma.github.io/ jverma@us.ibm.com @januverma Clustering Grouping together similar data
Kapitel 4: Clustering
 Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Institut für Informatik Lehr- und Forschungseinheit für Datenbanksysteme Knowledge Discovery in Databases WiSe 2017/18 Kapitel 4: Clustering Vorlesung: Prof. Dr.
Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Institut für Informatik Lehr- und Forschungseinheit für Datenbanksysteme Knowledge Discovery in Databases WiSe 2017/18 Kapitel 4: Clustering Vorlesung: Prof. Dr.
Road map. Basic concepts
 Clustering Basic concepts Road map K-means algorithm Representation of clusters Hierarchical clustering Distance functions Data standardization Handling mixed attributes Which clustering algorithm to use?
Clustering Basic concepts Road map K-means algorithm Representation of clusters Hierarchical clustering Distance functions Data standardization Handling mixed attributes Which clustering algorithm to use?
Exploratory Data Analysis using Self-Organizing Maps. Madhumanti Ray
 Exploratory Data Analysis using Self-Organizing Maps Madhumanti Ray Content Introduction Data Analysis methods Self-Organizing Maps Conclusion Visualization of high-dimensional data items Exploratory data
Exploratory Data Analysis using Self-Organizing Maps Madhumanti Ray Content Introduction Data Analysis methods Self-Organizing Maps Conclusion Visualization of high-dimensional data items Exploratory data
An Initial Seed Selection Algorithm for K-means Clustering of Georeferenced Data to Improve
 An Initial Seed Selection Algorithm for K-means Clustering of Georeferenced Data to Improve Replicability of Cluster Assignments for Mapping Application Fouad Khan Central European University-Environmental
An Initial Seed Selection Algorithm for K-means Clustering of Georeferenced Data to Improve Replicability of Cluster Assignments for Mapping Application Fouad Khan Central European University-Environmental
Data Informatics. Seon Ho Kim, Ph.D.
 Data Informatics Seon Ho Kim, Ph.D. seonkim@usc.edu Clustering Overview Supervised vs. Unsupervised Learning Supervised learning (classification) Supervision: The training data (observations, measurements,
Data Informatics Seon Ho Kim, Ph.D. seonkim@usc.edu Clustering Overview Supervised vs. Unsupervised Learning Supervised learning (classification) Supervision: The training data (observations, measurements,
Unsupervised Learning. Presenter: Anil Sharma, PhD Scholar, IIIT-Delhi
 Unsupervised Learning Presenter: Anil Sharma, PhD Scholar, IIIT-Delhi Content Motivation Introduction Applications Types of clustering Clustering criterion functions Distance functions Normalization Which
Unsupervised Learning Presenter: Anil Sharma, PhD Scholar, IIIT-Delhi Content Motivation Introduction Applications Types of clustering Clustering criterion functions Distance functions Normalization Which
Enhancing K-means Clustering Algorithm with Improved Initial Center
 Enhancing K-means Clustering Algorithm with Improved Initial Center Madhu Yedla #1, Srinivasa Rao Pathakota #2, T M Srinivasa #3 # Department of Computer Science and Engineering, National Institute of
Enhancing K-means Clustering Algorithm with Improved Initial Center Madhu Yedla #1, Srinivasa Rao Pathakota #2, T M Srinivasa #3 # Department of Computer Science and Engineering, National Institute of
Clustering Part 3. Hierarchical Clustering
 Clustering Part Dr Sanjay Ranka Professor Computer and Information Science and Engineering University of Florida, Gainesville Hierarchical Clustering Two main types: Agglomerative Start with the points
Clustering Part Dr Sanjay Ranka Professor Computer and Information Science and Engineering University of Florida, Gainesville Hierarchical Clustering Two main types: Agglomerative Start with the points
Clustering. Chapter 10 in Introduction to statistical learning
 Clustering Chapter 10 in Introduction to statistical learning 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 1 Clustering ² Clustering is the art of finding groups in data (Kaufman and Rousseeuw, 1990). ² What
Clustering Chapter 10 in Introduction to statistical learning 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 1 Clustering ² Clustering is the art of finding groups in data (Kaufman and Rousseeuw, 1990). ² What
Introduction to Data Mining
 Introduction to Data Mining Lecture #14: Clustering Seoul National University 1 In This Lecture Learn the motivation, applications, and goal of clustering Understand the basic methods of clustering (bottom-up
Introduction to Data Mining Lecture #14: Clustering Seoul National University 1 In This Lecture Learn the motivation, applications, and goal of clustering Understand the basic methods of clustering (bottom-up
Clustering. RNA-seq: What is it good for? Finding Similarly Expressed Genes. Data... And Lots of It!
 RNA-seq: What is it good for? Clustering High-throughput RNA sequencing experiments (RNA-seq) offer the ability to measure simultaneously the expression level of thousands of genes in a single experiment!
RNA-seq: What is it good for? Clustering High-throughput RNA sequencing experiments (RNA-seq) offer the ability to measure simultaneously the expression level of thousands of genes in a single experiment!
Clustering in Ratemaking: Applications in Territories Clustering
 Clustering in Ratemaking: Applications in Territories Clustering Ji Yao, PhD FIA ASTIN 13th-16th July 2008 INTRODUCTION Structure of talk Quickly introduce clustering and its application in insurance ratemaking
Clustering in Ratemaking: Applications in Territories Clustering Ji Yao, PhD FIA ASTIN 13th-16th July 2008 INTRODUCTION Structure of talk Quickly introduce clustering and its application in insurance ratemaking
A SURVEY ON CLUSTERING ALGORITHMS Ms. Kirti M. Patil 1 and Dr. Jagdish W. Bakal 2
 Ms. Kirti M. Patil 1 and Dr. Jagdish W. Bakal 2 1 P.G. Scholar, Department of Computer Engineering, ARMIET, Mumbai University, India 2 Principal of, S.S.J.C.O.E, Mumbai University, India ABSTRACT Now a
Ms. Kirti M. Patil 1 and Dr. Jagdish W. Bakal 2 1 P.G. Scholar, Department of Computer Engineering, ARMIET, Mumbai University, India 2 Principal of, S.S.J.C.O.E, Mumbai University, India ABSTRACT Now a
Semi-Supervised Clustering with Partial Background Information
 Semi-Supervised Clustering with Partial Background Information Jing Gao Pang-Ning Tan Haibin Cheng Abstract Incorporating background knowledge into unsupervised clustering algorithms has been the subject
Semi-Supervised Clustering with Partial Background Information Jing Gao Pang-Ning Tan Haibin Cheng Abstract Incorporating background knowledge into unsupervised clustering algorithms has been the subject
International Journal of Computer Engineering and Applications, Volume VIII, Issue III, Part I, December 14
 International Journal of Computer Engineering and Applications, Volume VIII, Issue III, Part I, December 14 DESIGN OF AN EFFICIENT DATA ANALYSIS CLUSTERING ALGORITHM Dr. Dilbag Singh 1, Ms. Priyanka 2
International Journal of Computer Engineering and Applications, Volume VIII, Issue III, Part I, December 14 DESIGN OF AN EFFICIENT DATA ANALYSIS CLUSTERING ALGORITHM Dr. Dilbag Singh 1, Ms. Priyanka 2
CLUSTERING BIG DATA USING NORMALIZATION BASED k-means ALGORITHM
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology ISSN 2320 088X IMPACT FACTOR: 5.258 IJCSMC,
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology ISSN 2320 088X IMPACT FACTOR: 5.258 IJCSMC,
INF4820 Algorithms for AI and NLP. Evaluating Classifiers Clustering
 INF4820 Algorithms for AI and NLP Evaluating Classifiers Clustering Murhaf Fares & Stephan Oepen Language Technology Group (LTG) September 27, 2017 Today 2 Recap Evaluation of classifiers Unsupervised
INF4820 Algorithms for AI and NLP Evaluating Classifiers Clustering Murhaf Fares & Stephan Oepen Language Technology Group (LTG) September 27, 2017 Today 2 Recap Evaluation of classifiers Unsupervised
Clustering. Robert M. Haralick. Computer Science, Graduate Center City University of New York
 Clustering Robert M. Haralick Computer Science, Graduate Center City University of New York Outline K-means 1 K-means 2 3 4 5 Clustering K-means The purpose of clustering is to determine the similarity
Clustering Robert M. Haralick Computer Science, Graduate Center City University of New York Outline K-means 1 K-means 2 3 4 5 Clustering K-means The purpose of clustering is to determine the similarity
Lecture-17: Clustering with K-Means (Contd: DT + Random Forest)
 Lecture-17: Clustering with K-Means (Contd: DT + Random Forest) Medha Vidyotma April 24, 2018 1 Contd. Random Forest For Example, if there are 50 scholars who take the measurement of the length of the
Lecture-17: Clustering with K-Means (Contd: DT + Random Forest) Medha Vidyotma April 24, 2018 1 Contd. Random Forest For Example, if there are 50 scholars who take the measurement of the length of the
Data Warehousing and Machine Learning
 Data Warehousing and Machine Learning Preprocessing Thomas D. Nielsen Aalborg University Department of Computer Science Spring 2008 DWML Spring 2008 1 / 35 Preprocessing Before you can start on the actual
Data Warehousing and Machine Learning Preprocessing Thomas D. Nielsen Aalborg University Department of Computer Science Spring 2008 DWML Spring 2008 1 / 35 Preprocessing Before you can start on the actual
Mine Blood Donors Information through Improved K- Means Clustering Bondu Venkateswarlu 1 and Prof G.S.V.Prasad Raju 2
 Mine Blood Donors Information through Improved K- Means Clustering Bondu Venkateswarlu 1 and Prof G.S.V.Prasad Raju 2 1 Department of Computer Science and Systems Engineering, Andhra University, Visakhapatnam-
Mine Blood Donors Information through Improved K- Means Clustering Bondu Venkateswarlu 1 and Prof G.S.V.Prasad Raju 2 1 Department of Computer Science and Systems Engineering, Andhra University, Visakhapatnam-
Dynamic Clustering Of High Speed Data Streams
 www.ijcsi.org 224 Dynamic Clustering Of High Speed Data Streams J. Chandrika 1, Dr. K.R. Ananda Kumar 2 1 Department of CS & E, M C E,Hassan 573 201 Karnataka, India 2 Department of CS & E, SJBIT, Bangalore
www.ijcsi.org 224 Dynamic Clustering Of High Speed Data Streams J. Chandrika 1, Dr. K.R. Ananda Kumar 2 1 Department of CS & E, M C E,Hassan 573 201 Karnataka, India 2 Department of CS & E, SJBIT, Bangalore
Clustering and Visualisation of Data
 Clustering and Visualisation of Data Hiroshi Shimodaira January-March 28 Cluster analysis aims to partition a data set into meaningful or useful groups, based on distances between data points. In some
Clustering and Visualisation of Data Hiroshi Shimodaira January-March 28 Cluster analysis aims to partition a data set into meaningful or useful groups, based on distances between data points. In some
Mining di Dati Web. Lezione 3 - Clustering and Classification
 Mining di Dati Web Lezione 3 - Clustering and Classification Introduction Clustering and classification are both learning techniques They learn functions describing data Clustering is also known as Unsupervised
Mining di Dati Web Lezione 3 - Clustering and Classification Introduction Clustering and classification are both learning techniques They learn functions describing data Clustering is also known as Unsupervised
A Naïve Soft Computing based Approach for Gene Expression Data Analysis
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 38 (2012 ) 2124 2128 International Conference on Modeling Optimization and Computing (ICMOC-2012) A Naïve Soft Computing based Approach for
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 38 (2012 ) 2124 2128 International Conference on Modeling Optimization and Computing (ICMOC-2012) A Naïve Soft Computing based Approach for
Working with Unlabeled Data Clustering Analysis. Hsiao-Lung Chan Dept Electrical Engineering Chang Gung University, Taiwan
 Working with Unlabeled Data Clustering Analysis Hsiao-Lung Chan Dept Electrical Engineering Chang Gung University, Taiwan chanhl@mail.cgu.edu.tw Unsupervised learning Finding centers of similarity using
Working with Unlabeled Data Clustering Analysis Hsiao-Lung Chan Dept Electrical Engineering Chang Gung University, Taiwan chanhl@mail.cgu.edu.tw Unsupervised learning Finding centers of similarity using
Data Mining: Models and Methods
 Data Mining: Models and Methods Author, Kirill Goltsman A White Paper July 2017 --------------------------------------------------- www.datascience.foundation Copyright 2016-2017 What is Data Mining? Data
Data Mining: Models and Methods Author, Kirill Goltsman A White Paper July 2017 --------------------------------------------------- www.datascience.foundation Copyright 2016-2017 What is Data Mining? Data
An improved MapReduce Design of Kmeans for clustering very large datasets
 An improved MapReduce Design of Kmeans for clustering very large datasets Amira Boukhdhir Laboratoire SOlE Higher Institute of management Tunis Tunis, Tunisia Boukhdhir _ amira@yahoo.fr Oussama Lachiheb
An improved MapReduce Design of Kmeans for clustering very large datasets Amira Boukhdhir Laboratoire SOlE Higher Institute of management Tunis Tunis, Tunisia Boukhdhir _ amira@yahoo.fr Oussama Lachiheb
Applied Clustering Techniques. Jing Dong
 Applied Clustering Techniques Jing Dong Nov 31, 2016 What is cluster analysis? What is Cluster Analysis? Cluster: o Similar to one another within the same cluster o Dissimilar to the objects in other clusters
Applied Clustering Techniques Jing Dong Nov 31, 2016 What is cluster analysis? What is Cluster Analysis? Cluster: o Similar to one another within the same cluster o Dissimilar to the objects in other clusters
ECG782: Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing
 ECG782: Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing Object Recognition http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg782/ 2 Outline Knowledge Representation Statistical Pattern Recognition Neural Networks Boosting
ECG782: Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing Object Recognition http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg782/ 2 Outline Knowledge Representation Statistical Pattern Recognition Neural Networks Boosting
Data mining techniques for actuaries: an overview
 Data mining techniques for actuaries: an overview Emiliano A. Valdez joint work with Banghee So and Guojun Gan University of Connecticut Advances in Predictive Analytics (APA) Conference University of
Data mining techniques for actuaries: an overview Emiliano A. Valdez joint work with Banghee So and Guojun Gan University of Connecticut Advances in Predictive Analytics (APA) Conference University of
Big Data Analytics! Special Topics for Computer Science CSE CSE Feb 9
 Big Data Analytics! Special Topics for Computer Science CSE 4095-001 CSE 5095-005! Feb 9 Fei Wang Associate Professor Department of Computer Science and Engineering fei_wang@uconn.edu Clustering I What
Big Data Analytics! Special Topics for Computer Science CSE 4095-001 CSE 5095-005! Feb 9 Fei Wang Associate Professor Department of Computer Science and Engineering fei_wang@uconn.edu Clustering I What
Finding Clusters 1 / 60
 Finding Clusters Types of Clustering Approaches: Linkage Based, e.g. Hierarchical Clustering Clustering by Partitioning, e.g. k-means Density Based Clustering, e.g. DBScan Grid Based Clustering 1 / 60
Finding Clusters Types of Clustering Approaches: Linkage Based, e.g. Hierarchical Clustering Clustering by Partitioning, e.g. k-means Density Based Clustering, e.g. DBScan Grid Based Clustering 1 / 60
Classifying Documents by Distributed P2P Clustering
 Classifying Documents by Distributed P2P Clustering Martin Eisenhardt Wolfgang Müller Andreas Henrich Chair of Applied Computer Science I University of Bayreuth, Germany {eisenhardt mueller2 henrich}@uni-bayreuth.de
Classifying Documents by Distributed P2P Clustering Martin Eisenhardt Wolfgang Müller Andreas Henrich Chair of Applied Computer Science I University of Bayreuth, Germany {eisenhardt mueller2 henrich}@uni-bayreuth.de
I. INTRODUCTION II. RELATED WORK.
 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: A New Hybridized K-Means Clustering Based Outlier Detection Technique
ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: A New Hybridized K-Means Clustering Based Outlier Detection Technique
SYDE Winter 2011 Introduction to Pattern Recognition. Clustering
 SYDE 372 - Winter 2011 Introduction to Pattern Recognition Clustering Alexander Wong Department of Systems Design Engineering University of Waterloo Outline 1 2 3 4 5 All the approaches we have learned
SYDE 372 - Winter 2011 Introduction to Pattern Recognition Clustering Alexander Wong Department of Systems Design Engineering University of Waterloo Outline 1 2 3 4 5 All the approaches we have learned
An Efficient Approach towards K-Means Clustering Algorithm
 An Efficient Approach towards K-Means Clustering Algorithm Pallavi Purohit Department of Information Technology, Medi-caps Institute of Technology, Indore purohit.pallavi@gmail.co m Ritesh Joshi Department
An Efficient Approach towards K-Means Clustering Algorithm Pallavi Purohit Department of Information Technology, Medi-caps Institute of Technology, Indore purohit.pallavi@gmail.co m Ritesh Joshi Department
What is Clustering? Clustering. Characterizing Cluster Methods. Clusters. Cluster Validity. Basic Clustering Methodology
 Clustering Unsupervised learning Generating classes Distance/similarity measures Agglomerative methods Divisive methods Data Clustering 1 What is Clustering? Form o unsupervised learning - no inormation
Clustering Unsupervised learning Generating classes Distance/similarity measures Agglomerative methods Divisive methods Data Clustering 1 What is Clustering? Form o unsupervised learning - no inormation
International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN: Volume 5 Issue 11 Nov. 2016, Page No.
 www.ijecs.in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN: 2319-7242 Volume 5 Issue 11 Nov. 2016, Page No. 19054-19062 Review on K-Mode Clustering Antara Prakash, Simran Kalera, Archisha
www.ijecs.in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN: 2319-7242 Volume 5 Issue 11 Nov. 2016, Page No. 19054-19062 Review on K-Mode Clustering Antara Prakash, Simran Kalera, Archisha
Review on Various Clustering Methods for the Image Data
 Review on Various Clustering Methods for the Image Data Madhuri A. Tayal 1,M.M.Raghuwanshi 2 1 SRKNEC Nagpur, 2 NYSS Nagpur, 1, 2 Nagpur University Nagpur [Maharashtra], INDIA. 1 madhuri_kalpe@rediffmail.com,
Review on Various Clustering Methods for the Image Data Madhuri A. Tayal 1,M.M.Raghuwanshi 2 1 SRKNEC Nagpur, 2 NYSS Nagpur, 1, 2 Nagpur University Nagpur [Maharashtra], INDIA. 1 madhuri_kalpe@rediffmail.com,
Information Retrieval and Web Search Engines
 Information Retrieval and Web Search Engines Lecture 7: Document Clustering December 4th, 2014 Wolf-Tilo Balke and José Pinto Institut für Informationssysteme Technische Universität Braunschweig The Cluster
Information Retrieval and Web Search Engines Lecture 7: Document Clustering December 4th, 2014 Wolf-Tilo Balke and José Pinto Institut für Informationssysteme Technische Universität Braunschweig The Cluster
Fast Efficient Clustering Algorithm for Balanced Data
 Vol. 5, No. 6, 214 Fast Efficient Clustering Algorithm for Balanced Data Adel A. Sewisy Faculty of Computer and Information, Assiut University M. H. Marghny Faculty of Computer and Information, Assiut
Vol. 5, No. 6, 214 Fast Efficient Clustering Algorithm for Balanced Data Adel A. Sewisy Faculty of Computer and Information, Assiut University M. H. Marghny Faculty of Computer and Information, Assiut
Clustering CS 550: Machine Learning
 Clustering CS 550: Machine Learning This slide set mainly uses the slides given in the following links: http://www-users.cs.umn.edu/~kumar/dmbook/ch8.pdf http://www-users.cs.umn.edu/~kumar/dmbook/dmslides/chap8_basic_cluster_analysis.pdf
Clustering CS 550: Machine Learning This slide set mainly uses the slides given in the following links: http://www-users.cs.umn.edu/~kumar/dmbook/ch8.pdf http://www-users.cs.umn.edu/~kumar/dmbook/dmslides/chap8_basic_cluster_analysis.pdf
An Efficient Analysis for High Dimensional Dataset Using K-Means Hybridization with Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm
 An Efficient Analysis for High Dimensional Dataset Using K-Means Hybridization with Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm Prabha S. 1, Arun Prabha K. 2 1 Research Scholar, Department of Computer Science, Vellalar
An Efficient Analysis for High Dimensional Dataset Using K-Means Hybridization with Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm Prabha S. 1, Arun Prabha K. 2 1 Research Scholar, Department of Computer Science, Vellalar
CHAPTER 6 MODIFIED FUZZY TECHNIQUES BASED IMAGE SEGMENTATION
 CHAPTER 6 MODIFIED FUZZY TECHNIQUES BASED IMAGE SEGMENTATION 6.1 INTRODUCTION Fuzzy logic based computational techniques are becoming increasingly important in the medical image analysis arena. The significant
CHAPTER 6 MODIFIED FUZZY TECHNIQUES BASED IMAGE SEGMENTATION 6.1 INTRODUCTION Fuzzy logic based computational techniques are becoming increasingly important in the medical image analysis arena. The significant
Hierarchical Document Clustering
 Hierarchical Document Clustering Benjamin C. M. Fung, Ke Wang, and Martin Ester, Simon Fraser University, Canada INTRODUCTION Document clustering is an automatic grouping of text documents into clusters
Hierarchical Document Clustering Benjamin C. M. Fung, Ke Wang, and Martin Ester, Simon Fraser University, Canada INTRODUCTION Document clustering is an automatic grouping of text documents into clusters
Community Detection. Jian Pei: CMPT 741/459 Clustering (1) 2
 Clustering Community Detection http://image.slidesharecdn.com/communitydetectionitilecturejune0-0609559-phpapp0/95/community-detection-in-social-media--78.jpg?cb=3087368 Jian Pei: CMPT 74/459 Clustering
Clustering Community Detection http://image.slidesharecdn.com/communitydetectionitilecturejune0-0609559-phpapp0/95/community-detection-in-social-media--78.jpg?cb=3087368 Jian Pei: CMPT 74/459 Clustering
