UNIT 9 - RIGHT TRIANGLES AND TRIG FUNCTIONS
|
|
|
- Shavonne Cox
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UNIT 9 - RIGHT TRIANGLES AND TRIG FUNCTIONS Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem Objectives: SWBAT use the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem to solve problems. SWBAT use side lengths to classify triangles by their angle measures. Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem If a b c works, then the triangle is a right triangle. Examples: Determine whether the triangle is a right triangle No Along the same lines No Yes Acute Theorem~ Obtuse Theorem~ If c < b + a, then it is an acute triangle If c > b + a, then it is an obtuse triangle Adding b + a is larger than c Adding b + a is smaller than c
2 Examples: Classify the triangle as acute, obtuse, or right (if possible). 4) 5, 1, 1 5) 7,14, Right Triangle c is larger Obtuse Triangle 6) 6, 1, 0 7) 10, 11, c is larger a +b is larger Obtuse Triangle Acute Triangle 8) 1, 1, 170 9) 5, 4 5, 4 Figure out which is the largest side Figure out which is the largest side is the c Right Triangle is the c a +b is larger Acute Triangle
3 Inequalities in One Triangles Objectives: SWBAT use triangle measurements to decide which side is longest or which angle is largest. SWBAT use the triangle inequality. SWBAT Recognize side inequalities of a Triangle Comparing Triangles vs. Angle Theorem 1. The smallest angle is opposite the smallest side. The smallest angle is opposite the smallest side Examples Name the shortest and longest sides of the triangle mm 180 Smallest Angle 6 mm Medium Angle 48 mm 96 Larg e Angle 96 Smallest KM Medium LM Larg est KL 6 68 mo 180 Smallest Angle 49 mm Medium Angle 6 mm 49 Larg e Angle 68 Smallest MN Medium ON Larg est MO
4 Name the smallest and largest angles of the triangle.. 4. E 9 F H G Smallest Angle G Medium Angle E Larg e Angle F 6 I J Smallest Angle H Medium Angle I Larg e Angle J List all the angles and sides in ascending order mp 180 mp mp45 Smallest Angle M TIED Smallest Angle P Larg e Angle N Smallest MN TIED Smallest NP Larg est MP ma mb mc 180 x x 6 5x x x 150 ma x 15 mb mc Smallest Angle A Medium Angle B Smallest BC Larg e Angle C Medium AC Larg est AB
5 Triangle Inequality Theorem 1. The smallest side must be larger than the difference of the other two sides. The largest side must be the smaller than the sum of the other two sides. Smallest Larg est Subtract s Add s. If the triangles does not fulfill both stipulations it can t be a triangle. Is it possible to have the following dimensions for triangle ABC? Add two sides together, must be larger than the rd side (do this times) 7. AB = 8, BC = 15, and AC = AB = 6, BC = 8, and AC = 14 AB BC AC AB AC BC AC BC AB Since all checks work then it is a triangle. AB BC AC Can' t Equal Since this doesn t work, it can t be a triangle. 9. AB = 1, BC = 1, and AC = 10. AB = 5, BC = 5, and AC = 5 AB BC AC 11 Can' t Equal AB BC AC Since this doesn t work, it can t be a triangle. AB AC BC AC BC AB Since all checks work then it is a triangle.
6 Find the possible measures for XY in XYZ. 11. XZ = and YZ = 1. XZ = 8 and YZ = XZ = 7 and YZ = 11 Smallest Subtract 1 s Smallest Subtract 10 8 s Smallest Subtract s Larg est Add 5 s Larg est Add s Larg est Add s Smallest L arg est 1 5 Answer : 1 x XZ = 1 and YZ = 15 Smallest L arg est Smallest L arg est 10 Answer : 4 18 x 10 Answer : 4 x 18 Smallest Subtract 15 1 s Larg est Add s Smallest L arg est 7 Answer : x 7
7 Special Right Triangles Day Right Triangles Objectives: SWBAT find the side lengths of special right triangles. Review: Rationalizing the Denominator Can t have a root in the denominator so fix this you need to rationalize Multiply the numerator and denominator by the root and simplify Re duce
8 Write the sides and angles from shortest to longest mp 150 mp mp0 s Angles s Angles Smallest MN Smallest Angle P Smallest DB Smallest Angle C Medium NP Medium Angle M Medium CD Medium Angle B Larg est PM Larg e Angle N Larg est CB Larg e Angle D So in a right triangle, the largest angle or right angle will always be opposite the Largest or Hypotenuse. The smallest angle will always be opposite from the smallest side. So in a Special Right Triangle, Label the sides (short, medium / middle, and hypotenuse) by their length given the following angle measurements.
9 Rules for the Special Right Triangle If you are getting Larger than you _Multiply. x 60 x If you are getting Smaller than you Divide. 0 x What I Have. What I want. What I do. SHORT LEG MIDDLE / LONG LEG HYPOTENUSE Middle / Long Leg Multiply by Hypotenuse Multiply by Short Leg Divide by Hypotenuse Find Short Leg First then find the Hypotenuse Short Leg Divide by Middle / Long Leg Find Short Leg First then find the Middle Leg Examples: Find the short leg given the hypo. 1.. Hypotenuse What I Have: Small Leg What I Need: Getting: Smaller / Bigger (Circle) Hypo Small 16 8 Hypotenuse What I Have: Small Leg What I Need: Getting: Smaller / Bigger (Circle) Hypo Small 1 6
10 Find the hypo given the short leg.. 4. Hypotenuse What I Have: Small Leg What I Need: Getting: Smaller / Bigger (Circle) Small Hypo 17 4 Find the middle leg given the short leg. Hypotenuse What I Have: Small Leg What I Need: Getting: Smaller / Bigger (Circle) Small Hypo Small Leg What I Have: Middle / Long Leg What I Need: Getting: Smaller / Bigger (Circle) Small Middle / Long Small Leg What I Have: Middle / Long Leg What I Need: Getting: Smaller / Bigger (Circle) Small Middle / Long
11 Find the short leg given the middle leg Middle / Long Leg What I Have: Small Leg What I Need: Getting: Smaller / Bigger (Circle) Middle / Long Small Middle / Long Leg What I Have: Small Leg What I Need: Getting: Smaller / Bigger (Circle) Hypo Small Re duce Outsides
12 Identify the name of the leg, then solve for the variable in the following Right Triangles Small Leg What I Have: Middle / Long Leg What I Need: Getting: Smaller / Bigger (Circle) Small Middle / Long What I Have: Middle / Long Leg Small Leg What I Need: Getting: Smaller / Bigger (Circle) Middle / Long Small Middle to Hypo Find the Short Leg First Hypo to Middle Find the Short Leg First Middle / Long Short Small Leg 10 Short Hypo 10 0 Hypo Short 1 6 Short Leg 6 Short Middle / Long 6 6
13 1. Middle / Long Short Small Leg Short Hypo The size of a television is determined by the diagonal measure of its rectangular screen. The figure below represents a television screen. What is the size of the TV? Round to the nearest inch. Looking for the Hypo Given the Middle Leg Find the Small Leg First Middle / Long Short Small Leg 15 Short Hypo in
14 Rationalizing the Denominator Special Right Triangles Day Objectives: SWBAT find the side lengths of special right triangles. Can t have a root in the denominator so fix this you need to rationalize Multiply the numerator and denominator by the root and simplify Examples: Root 4 Can be Broken Down Re duce Re duce 1
15 Rules for the Special Right Triangle If you are getting Larger than you _Multiply. x 45 x If you are getting Smaller than you Divide. x 45 What I Have. What I want. What I do. LEG HYPO Multiply by Hypotenuse LEG Divide by Find the hypo given the leg. 1.. Getting: Smaller / Bigger (Circle) Getting: Smaller / Bigger (Circle) LEG HYPO LEG HYPO 11 11
16 Find the leg given the hypo Getting: Smaller / Bigger (Circle) Getting: Smaller / Bigger (Circle) Hypo Leg Examples: Solve for the variable in the following Right Triangles Hypo Leg Re duce 8 Getting: Smaller / Bigger (Circle) LEG HYPO 1 1 Getting: Smaller / Bigger (Circle) LEG HYPO 6 6
17 7. 8. Hypo Leg Hypo Leg Re duce 9. Given the following quadrilateral is a rectangle. y 45 z 4 Leg Hypo 4 w 4
18 10. Jason is adding a climbing wall to tis little brother s swing set. If he starts building 5 feet out from the existing structure, and wants to have a 45 degree, how long should the wall be (round to the nearest tenth)? LEG HYPO ft
19 Trigonometric Ratios Day 1 Objectives: SWBAT set up the fractions for sine, the cosine and the tangent Trigonometric Ratios: Sine The Ratio in a Triangle Opposite Hypotenuse Cosine The Ratio in a Triangle Adjacent Hypotenuse Tangent The Ratio in a Triangle Opposite Adjacent Θ Greek Letter Theta / Angle you will be using 1.. A) List the angles from smallest to largest. A) List the angles from smallest to largest. Smallest Angle A Can' t Tell Without Numbers Medium Angle C Larg e Angle B DO NOT ASSUME B) What is the cosine of angle A? B) What is the tangent of angle M? cos A Adjacent Hypo tan A Opposite m Adjacent n
20 Find the sine, the cosine, and the tangent. 4. R. S Sine: sin S Opposite Hypo 5 1 Sine: sin R Opposite Hypo 1 1 Cosine: cos S Adjacent Hypo 1 1 Cosine: cos R Adjacent Hypo 5 1 Tangent: tan S Opposite Adjacent 5 1 Tangent: tan R Opposite Adjacent 1 5 Where are the fractions exactly the same? Sine and Cosine of the other acute angles will match 5. Set up the following fractions for each trig relationship. You must use Pythagorean Theorem to find the missing rd side of the right triangle. a b c A. sin(θ) = sin S Opposite Hypo 5 b 5 9 b 5 b 16 b 4 B. cos(θ) = cos S Adjacent Hypo 4 5 C. tan(θ) = tan S Opposite Adjacent 4 4
21 Trigonometric Ratios Day II Objectives: SWBAT find the sine, the cosine and the tangent of an acute angle. Trigonometric Ratios: Sine The Ratio in a Triangle Opposite Hypotenuse Cosine The Ratio in a Triangle Adjacent Hypotenuse Tangent The Ratio in a Triangle Opposite Adjacent Degree Mode of a Calculator Most calculator have multiple modes for handling sine, cosine, and tangent (based on the type of math and information). Make sure you calculator is in DEG mode Use a calculator to approximate the measure value. (round to nearest thousandth) 1. sin 0 =. tan 5 4 =. cos 77 = 4. sin 5 14 =
22 For each example, answer the following. Round to the nearest thousandth A) Will BC be larger or smaller than AB? Why? A) Which will be larger NP or PM? Why? Larger because A is larger PM because N is larger than M B) Find x(round to the nearest thousandth). B) Find y (Round decimal places). sin A Opposite Hypo x sin51 15 sin51 x 1 15 Cross Multiply x 15sin x x cos M Adjacent Hypo y cos8 14 cos8 y 1 14 Cross Multiply y 14 cos y y 11. 0
23 7. 8. A) Will AC be larger or smaller than AB? Why? A) What side will be the longest side? Why? Smaller because C is larger TR because it is opposite the Right Angle B) Find z (Round to the nearest thousandth). B) Find y (Round decimal places). tan C Opposite Adjacent z tan55 8 tan55 z 1 8 Cross Multiply z 8 tan z z cos T cos Adjacent Hypo 51 8 y cos y Cross Multiply y cos Trig Functions are Just Decimals y y y y 1. 71
24 9. A) What will the largest side be in ABC? Why? The largest side will be AC because it is opposite the Right Angle B) What will the shortest side be in ABC? Why? BC will be the smallest because A is opposite the smallest angle C) Find the value of x (Round to the nearest thousandth). sin Solve for x in the diagram below. Round to the nearest Thousandth. Can t Find x without Another side to that triangle Opposite Hypo x sin9 15 sin9 x 1 15 Cross Multiply x 15 sin x x a b c 11 y 1 11 y 441 y 0 y cos A Adjacent Hypo cos4 x cos x Cross Multiply x cos. Trig Functions are Just Decimals y y y y
25 11. A 4 foot ladder is leaned at a 70 degree angle against a building. How far is the base of the ladder from the building? cos A Adjacent Hypo x cos70 4 cos70 y 1 4 Cross Multiply y 4 cos y y ft
26 Solving Right Triangles Inverses of Sine, Cosine, and Tangent Objectives: SWBAT solve a right triangle (Write just like sine, cosine, tangent if you are looking for an angle, switch the fraction and the angle and put in the inverse sign) Sin(A) = x or a fraction 1 sin ( x) ma Cos (A) = x or a fraction Tan (A) = x or a fraction 1 cos ( x) ma 1 tan ( x) ma Number of Degrees in a Triangle 180 Degrees in a Triangle Examples: Write the correct ratio for each trig function sin A =. cos A = 5 1. tan A = 4. sin B = cos B = 6. tan B = cos C = Can t Do 8. sin C = Can t Do 9. tan C = Can t Do You can t do any trig functions from C or 90 degree angles.
27 Use a calculator to approximate the measure of angle A. (round to nearest thousandth) 1. sin A = 0.4. tan A = 5 sin ma tan.5 1 ma.85 ma 68.0 ma. cos A = cos A = 17 cos ma cos ma ma ma Use the diagram to find the indicated measurement. 5. CR 6. m T Pythagorean Theorem for last side Trig ratios to find one of the Angles a b c a a a 80 a 4 5 or cos cos m B 1 m B mb 1 C 7. m C T 8 R Use 180 Degrees in a Triangle to find the last angle 180 mt mc mr 180 mt mt mt
28 Solve the right triangle (find all angles and sides) 8. Pythagorean Theorem for last side Trig ratios to find one of the Angles a b c a a a 65 a 65 or 8.06 sin m A ma Use 180 Degrees in a Triangle to find the last angle 180 mc ma mb 180 mc mc mc
29 Solve the right triangle (find all angles and sides) R M 8 L S 11 T 14 8 N Pythagorean Theorem for last side Use 180 degree theorem 1 st on # a b c 180 mm mn ml 8 11 c ml c 180 ml118 c c ml Trig ratios to find one of the Angles tan m T mt 1 8 Use 180 Degree theorem to finish the Angles 180 mr ms mt 180 mr mr mr Use Trig Function to find a side ML sin sin 8 ML 6.57 ML Use Pythagorean to find last side a b c a a a a 1.6
30 Solving Right Triangles If you need to find a side use If you need to find an angle use Pythagorean Theorem 180 Degrees in a Triangle Trig Functions Inverse Trig Functions Special Right Triangles
31 Trigonometric Ratios Application Objectives: SWBAT apply Trig Functions to Real Life Scenarios Angle of Elevation Looking up from the horizon Angle of Depression Looking Down from the horizon 1. A six foot person (measuring from his eye level to the ground) is looking up at a tree. How tall is the tree? y tan48 10 tan48 y 1 10 Cross Multiply y 10 tan 48 1 y ft Height of the Tree y 6 ft Person ft
32 . Maria is at the top of a cliff and sees a seal in the water. If the cliff is 40 feet above the water and the angle of depression is 5 degrees, what is the horizontal distance from the seal to the cliff? tan 5 40 y tan y Cross Multiply y tan y ft. At the circus, a person in the audience at ground level watches the high-wire routine. A 6 foot tall acrobat is standing on a platform that is 5 feet above the ground. How far is the audience member from the base of the platform, if the angle of elevation from the audience member s line of sight to the top of the acrobat s head is 7 degrees? 1 sin7 x sin7 1 1 x Cross Multiply x sin 7 11 y ft
33 4. Two buildings, of different sizes, are on opposite sides of a street. The street is 60 feet long. The taller building is 100 ft. tall, and the angle of depression from the top of the taller building to the top of the shorter building is Find the height of the shorter building. y tan tan y 1 60 Cross Multiply 60 tan y y ft Smaller Building Tall Small ft 5. Dante is standing at ground level x feet from the base of the Empire State Building in New York City. The angle of elevation formed from the ground to the top of the building is The height of the Empire State Building is 147 feet. What his distance from the Empire State Building to the nearest foot? 147 tan x tan x Cross Multiply x tan y ft
34 6. A person is 6.5 feet tall and has a shadow for feet. What is the angle of elevation to the sun at the time? 6.5 tan x tan x 65.5 x
AW Math 10 UNIT 7 RIGHT ANGLE TRIANGLES
 AW Math 10 UNIT 7 RIGHT ANGLE TRIANGLES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagorean Theorem 3 More Pythagorean Theorem Eploring Pythagorean Theorem Using Pythagorean
AW Math 10 UNIT 7 RIGHT ANGLE TRIANGLES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagorean Theorem 3 More Pythagorean Theorem Eploring Pythagorean Theorem Using Pythagorean
G.8 Right Triangles STUDY GUIDE
 G.8 Right Triangles STUDY GUIDE Name Date Block Chapter 7 Right Triangles Review and Study Guide Things to Know (use your notes, homework, quizzes, textbook as well as flashcards at quizlet.com (http://quizlet.com/4216735/geometry-chapter-7-right-triangles-flashcardsflash-cards/)).
G.8 Right Triangles STUDY GUIDE Name Date Block Chapter 7 Right Triangles Review and Study Guide Things to Know (use your notes, homework, quizzes, textbook as well as flashcards at quizlet.com (http://quizlet.com/4216735/geometry-chapter-7-right-triangles-flashcardsflash-cards/)).
Solving Right Triangles. How do you solve right triangles?
 Solving Right Triangles How do you solve right triangles? The Trigonometric Functions we will be looking at SINE COSINE TANGENT The Trigonometric Functions SINE COSINE TANGENT SINE Pronounced sign TANGENT
Solving Right Triangles How do you solve right triangles? The Trigonometric Functions we will be looking at SINE COSINE TANGENT The Trigonometric Functions SINE COSINE TANGENT SINE Pronounced sign TANGENT
AWM 11 UNIT 4 TRIGONOMETRY OF RIGHT TRIANGLES
 AWM 11 UNIT 4 TRIGONOMETRY OF RIGHT TRIANGLES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagorean Theorem Exploring Pythagorean Theorem 3 More Pythagorean Theorem Using
AWM 11 UNIT 4 TRIGONOMETRY OF RIGHT TRIANGLES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagorean Theorem Exploring Pythagorean Theorem 3 More Pythagorean Theorem Using
UNIT 5 TRIGONOMETRY Lesson 5.4: Calculating Sine, Cosine, and Tangent. Instruction. Guided Practice 5.4. Example 1
 Lesson : Calculating Sine, Cosine, and Tangent Guided Practice Example 1 Leo is building a concrete pathway 150 feet long across a rectangular courtyard, as shown in the following figure. What is the length
Lesson : Calculating Sine, Cosine, and Tangent Guided Practice Example 1 Leo is building a concrete pathway 150 feet long across a rectangular courtyard, as shown in the following figure. What is the length
You ll use the six trigonometric functions of an angle to do this. In some cases, you will be able to use properties of the = 46
 Math 1330 Section 6.2 Section 7.1: Right-Triangle Applications In this section, we ll solve right triangles. In some problems you will be asked to find one or two specific pieces of information, but often
Math 1330 Section 6.2 Section 7.1: Right-Triangle Applications In this section, we ll solve right triangles. In some problems you will be asked to find one or two specific pieces of information, but often
Unit 1 Trigonometry. Topics and Assignments. General Outcome: Develop spatial sense and proportional reasoning. Specific Outcomes:
 1 Unit 1 Trigonometry General Outcome: Develop spatial sense and proportional reasoning. Specific Outcomes: 1.1 Develop and apply the primary trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, tangent) to solve problems
1 Unit 1 Trigonometry General Outcome: Develop spatial sense and proportional reasoning. Specific Outcomes: 1.1 Develop and apply the primary trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, tangent) to solve problems
Geometry- Unit 6 Notes. Simplifying Radicals
 Geometry- Unit 6 Notes Name: Review: Evaluate the following WITHOUT a calculator. a) 2 2 b) 3 2 c) 4 2 d) 5 2 e) 6 2 f) 7 2 g) 8 2 h) 9 2 i) 10 2 j) 2 2 k) ( 2) 2 l) 2 0 Simplifying Radicals n r Example
Geometry- Unit 6 Notes Name: Review: Evaluate the following WITHOUT a calculator. a) 2 2 b) 3 2 c) 4 2 d) 5 2 e) 6 2 f) 7 2 g) 8 2 h) 9 2 i) 10 2 j) 2 2 k) ( 2) 2 l) 2 0 Simplifying Radicals n r Example
Assignment Guide: Chapter 8 Geometry (L3)
 Assignment Guide: Chapter 8 Geometry (L3) (91) 8.1 The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse Page 495-497 #7-31 odd, 37-47 odd (92) 8.2 Special Right Triangles Page 503-504 #7-12, 15-20, 23-28 (93) 8.2
Assignment Guide: Chapter 8 Geometry (L3) (91) 8.1 The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse Page 495-497 #7-31 odd, 37-47 odd (92) 8.2 Special Right Triangles Page 503-504 #7-12, 15-20, 23-28 (93) 8.2
7.1/7.2 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem and its Converse
 7.1/7.2 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem and its Converse Remember what we know about a right triangle: In a right triangle, the square of the length of the is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths
7.1/7.2 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem and its Converse Remember what we know about a right triangle: In a right triangle, the square of the length of the is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths
You ll use the six trigonometric functions of an angle to do this. In some cases, you will be able to use properties of the = 46
 Math 1330 Section 6.2 Section 7.1: Right-Triangle Applications In this section, we ll solve right triangles. In some problems you will be asked to find one or two specific pieces of information, but often
Math 1330 Section 6.2 Section 7.1: Right-Triangle Applications In this section, we ll solve right triangles. In some problems you will be asked to find one or two specific pieces of information, but often
Trigonometry Ratios. For each of the right triangles below, the labelled angle is equal to 40. Why then are these triangles similar to each other?
 Name: Trigonometry Ratios A) An Activity with Similar Triangles Date: For each of the right triangles below, the labelled angle is equal to 40. Why then are these triangles similar to each other? Page
Name: Trigonometry Ratios A) An Activity with Similar Triangles Date: For each of the right triangles below, the labelled angle is equal to 40. Why then are these triangles similar to each other? Page
2.0 Trigonometry Review Date: Pythagorean Theorem: where c is always the.
 2.0 Trigonometry Review Date: Key Ideas: The three angles in a triangle sum to. Pythagorean Theorem: where c is always the. In trigonometry problems, all vertices (corners or angles) of the triangle are
2.0 Trigonometry Review Date: Key Ideas: The three angles in a triangle sum to. Pythagorean Theorem: where c is always the. In trigonometry problems, all vertices (corners or angles) of the triangle are
SM 2. Date: Section: Objective: The Pythagorean Theorem: In a triangle, or
 SM 2 Date: Section: Objective: The Pythagorean Theorem: In a triangle, or. It doesn t matter which leg is a and which leg is b. The hypotenuse is the side across from the right angle. To find the length
SM 2 Date: Section: Objective: The Pythagorean Theorem: In a triangle, or. It doesn t matter which leg is a and which leg is b. The hypotenuse is the side across from the right angle. To find the length
Be sure to label all answers and leave answers in exact simplified form.
 Pythagorean Theorem word problems Solve each of the following. Please draw a picture and use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve. Be sure to label all answers and leave answers in exact simplified form. 1.
Pythagorean Theorem word problems Solve each of the following. Please draw a picture and use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve. Be sure to label all answers and leave answers in exact simplified form. 1.
Algebra II. Slide 1 / 92. Slide 2 / 92. Slide 3 / 92. Trigonometry of the Triangle. Trig Functions
 Slide 1 / 92 Algebra II Slide 2 / 92 Trigonometry of the Triangle 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 92 Trigonometry of the Right Triangle Inverse
Slide 1 / 92 Algebra II Slide 2 / 92 Trigonometry of the Triangle 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 92 Trigonometry of the Right Triangle Inverse
Practice A. Solving Right Triangles. sin. cos A 5. tan 2
 Name Date Class Solving Right Triangles In Exercises 1 3, fill in the blanks to complete the description of the inverse trigonometric ratios. 1. If sin A = x, then sin 1 x =. 2. If cos A =, then cos 1
Name Date Class Solving Right Triangles In Exercises 1 3, fill in the blanks to complete the description of the inverse trigonometric ratios. 1. If sin A = x, then sin 1 x =. 2. If cos A =, then cos 1
A lg e b ra II. Trig o n o m e try o f th e Tria n g le
 1 A lg e b ra II Trig o n o m e try o f th e Tria n g le 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org 2 Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Trigonometry of the Right Triangle Inverse Trig Functions Problem
1 A lg e b ra II Trig o n o m e try o f th e Tria n g le 2015-04-21 www.njctl.org 2 Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Trigonometry of the Right Triangle Inverse Trig Functions Problem
Warm-Up Up Exercises. Use this diagram for Exercises If PR = 12 and m R = 19, find p. ANSWER If m P = 58 and r = 5, find p.
 Warm-Up Up Exercises Use this diagram for Exercises 1 4. 1. If PR = 12 and m R = 19, find p. ANSWER 11.3 2. If m P = 58 and r = 5, find p. ANSWER 8.0 Warm-Up Up Exercises Use this diagram for Exercises
Warm-Up Up Exercises Use this diagram for Exercises 1 4. 1. If PR = 12 and m R = 19, find p. ANSWER 11.3 2. If m P = 58 and r = 5, find p. ANSWER 8.0 Warm-Up Up Exercises Use this diagram for Exercises
Unit 6 Introduction to Trigonometry
 Lesson 1: Incredibly Useful Ratios Opening Exercise Unit 6 Introduction to Trigonometry Use right triangle ΔABC to answer 1 3. 1. Name the side of the triangle opposite A in two different ways. 2. Name
Lesson 1: Incredibly Useful Ratios Opening Exercise Unit 6 Introduction to Trigonometry Use right triangle ΔABC to answer 1 3. 1. Name the side of the triangle opposite A in two different ways. 2. Name
Summer Review for Students Entering Pre-Calculus with Trigonometry. TI-84 Plus Graphing Calculator is required for this course.
 1. Using Function Notation and Identifying Domain and Range 2. Multiplying Polynomials and Solving Quadratics 3. Solving with Trig Ratios and Pythagorean Theorem 4. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions
1. Using Function Notation and Identifying Domain and Range 2. Multiplying Polynomials and Solving Quadratics 3. Solving with Trig Ratios and Pythagorean Theorem 4. Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions
CK-12 Geometry: Inverse Trigonometric Ratios
 CK-12 Geometry: Inverse Trigonometric Ratios Learning Objectives Use the inverse trigonometric ratios to find an angle in a right triangle. Solve a right triangle. Apply inverse trigonometric ratios to
CK-12 Geometry: Inverse Trigonometric Ratios Learning Objectives Use the inverse trigonometric ratios to find an angle in a right triangle. Solve a right triangle. Apply inverse trigonometric ratios to
Review Journal 7 Page 57
 Student Checklist Unit 1 - Trigonometry 1 1A Prerequisites: I can use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve a missing side of a right triangle. Note p. 2 1B Prerequisites: I can convert within the imperial
Student Checklist Unit 1 - Trigonometry 1 1A Prerequisites: I can use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve a missing side of a right triangle. Note p. 2 1B Prerequisites: I can convert within the imperial
Find sin R and sin S. Then find cos R and cos S. Write each answer as a fraction and as a decimal. Round to four decimal places, if necessary.
 Name Homework Packet 7.6 7.7 LESSON 7.6 For use with pages 473-480 AND LESSON 7.7 For use with pages 483 489 Find sin R and sin S. Then find cos R and cos S. Write each answer as a fraction and as a decimal.
Name Homework Packet 7.6 7.7 LESSON 7.6 For use with pages 473-480 AND LESSON 7.7 For use with pages 483 489 Find sin R and sin S. Then find cos R and cos S. Write each answer as a fraction and as a decimal.
Inequalities in Triangles Geometry 5-5
 Inequalities in Triangles Geometry 5-5 Name: ate: Period: Theorem 5-10 Theorem 5-11 If two sides of a triangle are not If two angles of a triangle are not congruent, then the larger angle congruent, then
Inequalities in Triangles Geometry 5-5 Name: ate: Period: Theorem 5-10 Theorem 5-11 If two sides of a triangle are not If two angles of a triangle are not congruent, then the larger angle congruent, then
Chapter 7. Right Triangles and Trigonometry
 hapter 7 Right Triangles and Trigonometry 7.1 pply the Pythagorean Theorem 7.2 Use the onverse of the Pythagorean Theorem 7.3 Use Similar Right Triangles 7.4 Special Right Triangles 7.5 pply the Tangent
hapter 7 Right Triangles and Trigonometry 7.1 pply the Pythagorean Theorem 7.2 Use the onverse of the Pythagorean Theorem 7.3 Use Similar Right Triangles 7.4 Special Right Triangles 7.5 pply the Tangent
Introduction to Trigonometry
 NAME COMMON CORE GEOMETRY- Unit 6 Introduction to Trigonometry DATE PAGE TOPIC HOMEWORK 1/22 2-4 Lesson 1 : Incredibly Useful Ratios Homework Worksheet 1/23 5-6 LESSON 2: Using Trigonometry to find missing
NAME COMMON CORE GEOMETRY- Unit 6 Introduction to Trigonometry DATE PAGE TOPIC HOMEWORK 1/22 2-4 Lesson 1 : Incredibly Useful Ratios Homework Worksheet 1/23 5-6 LESSON 2: Using Trigonometry to find missing
Name: Block: What I can do for this unit:
 Unit 8: Trigonometry Student Tracking Sheet Math 10 Common Name: Block: What I can do for this unit: After Practice After Review How I Did 8-1 I can use and understand triangle similarity and the Pythagorean
Unit 8: Trigonometry Student Tracking Sheet Math 10 Common Name: Block: What I can do for this unit: After Practice After Review How I Did 8-1 I can use and understand triangle similarity and the Pythagorean
5.5 Right Triangles. 1. For an acute angle A in right triangle ABC, the trigonometric functions are as follow:
 5.5 Right Triangles 1. For an acute angle A in right triangle ABC, the trigonometric functions are as follow: sin A = side opposite hypotenuse cos A = side adjacent hypotenuse B tan A = side opposite side
5.5 Right Triangles 1. For an acute angle A in right triangle ABC, the trigonometric functions are as follow: sin A = side opposite hypotenuse cos A = side adjacent hypotenuse B tan A = side opposite side
5B.4 ~ Calculating Sine, Cosine, Tangent, Cosecant, Secant and Cotangent WB: Pgs :1-10 Pgs : 1-7
 SECONDARY 2 HONORS ~ UNIT 5B (Similarity, Right Triangle Trigonometry, and Proof) Assignments from your Student Workbook are labeled WB Those from your hardbound Student Resource Book are labeled RB. Do
SECONDARY 2 HONORS ~ UNIT 5B (Similarity, Right Triangle Trigonometry, and Proof) Assignments from your Student Workbook are labeled WB Those from your hardbound Student Resource Book are labeled RB. Do
Geometry. Chapter 7 Right Triangles and Trigonometry. Name Period
 Geometry Chapter 7 Right Triangles and Trigonometry Name Period 1 Chapter 7 Right Triangles and Trigonometry ***In order to get full credit for your assignments they must me done on time and you must SHOW
Geometry Chapter 7 Right Triangles and Trigonometry Name Period 1 Chapter 7 Right Triangles and Trigonometry ***In order to get full credit for your assignments they must me done on time and you must SHOW
DAY 1 - GEOMETRY FLASHBACK
 DAY 1 - GEOMETRY FLASHBACK Sine Opposite Hypotenuse Cosine Adjacent Hypotenuse sin θ = opp. hyp. cos θ = adj. hyp. tan θ = opp. adj. Tangent Opposite Adjacent a 2 + b 2 = c 2 csc θ = hyp. opp. sec θ =
DAY 1 - GEOMETRY FLASHBACK Sine Opposite Hypotenuse Cosine Adjacent Hypotenuse sin θ = opp. hyp. cos θ = adj. hyp. tan θ = opp. adj. Tangent Opposite Adjacent a 2 + b 2 = c 2 csc θ = hyp. opp. sec θ =
Trigonometric Ratios and Functions
 Algebra 2/Trig Unit 8 Notes Packet Name: Date: Period: # Trigonometric Ratios and Functions (1) Worksheet (Pythagorean Theorem and Special Right Triangles) (2) Worksheet (Special Right Triangles) (3) Page
Algebra 2/Trig Unit 8 Notes Packet Name: Date: Period: # Trigonometric Ratios and Functions (1) Worksheet (Pythagorean Theorem and Special Right Triangles) (2) Worksheet (Special Right Triangles) (3) Page
Summer Review for Students Entering Pre-Calculus with Trigonometry. TI-84 Plus Graphing Calculator is required for this course.
 Summer Review for Students Entering Pre-Calculus with Trigonometry 1. Using Function Notation and Identifying Domain and Range 2. Multiplying Polynomials and Solving Quadratics 3. Solving with Trig Ratios
Summer Review for Students Entering Pre-Calculus with Trigonometry 1. Using Function Notation and Identifying Domain and Range 2. Multiplying Polynomials and Solving Quadratics 3. Solving with Trig Ratios
UNIT 2 RIGHT TRIANGLE TRIGONOMETRY Lesson 2: Applying Trigonometric Ratios Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: manipulating the Pythagorean Theorem given any two sides of a right triangle defining the three basic trigonometric ratios (sine,
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: manipulating the Pythagorean Theorem given any two sides of a right triangle defining the three basic trigonometric ratios (sine,
Name: Unit 8 Right Triangles and Trigonometry Unit 8 Similarity and Trigonometry. Date Target Assignment Done!
 Unit 8 Similarity and Trigonometry Date Target Assignment Done! M 1-22 8.1a 8.1a Worksheet T 1-23 8.1b 8.1b Worksheet W 1-24 8.2a 8.2a Worksheet R 1-25 8.2b 8.2b Worksheet F 1-26 Quiz Quiz 8.1-8.2 M 1-29
Unit 8 Similarity and Trigonometry Date Target Assignment Done! M 1-22 8.1a 8.1a Worksheet T 1-23 8.1b 8.1b Worksheet W 1-24 8.2a 8.2a Worksheet R 1-25 8.2b 8.2b Worksheet F 1-26 Quiz Quiz 8.1-8.2 M 1-29
Chapter 6 Review. Find MG and NG. In Exercises 1 4, find the indicated measure. State how you know. 1. AD 2. GJ. 3. PQ 4. m
 Name Date Chapter 6 Review In Exercises 1 4, find the indicated measure. State how you know. 1. AD 2. GJ 3. PQ 4. m DGF 5.In the figure at the right, what value of x makes G the incenter of JKL? 6. LG
Name Date Chapter 6 Review In Exercises 1 4, find the indicated measure. State how you know. 1. AD 2. GJ 3. PQ 4. m DGF 5.In the figure at the right, what value of x makes G the incenter of JKL? 6. LG
Packet Unit 5 Trigonometry Honors Math 2 17
 Packet Unit 5 Trigonometry Honors Math 2 17 Homework Day 12 Part 1 Cumulative Review of this unit Show ALL work for the following problems! Use separate paper, if needed. 1) If AC = 34, AB = 16, find sin
Packet Unit 5 Trigonometry Honors Math 2 17 Homework Day 12 Part 1 Cumulative Review of this unit Show ALL work for the following problems! Use separate paper, if needed. 1) If AC = 34, AB = 16, find sin
The Pythagorean Theorem: For a right triangle, the sum of the two leg lengths squared is equal to the length of the hypotenuse squared.
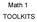 Math 1 TOOLKITS TOOLKIT: Pythagorean Theorem & Its Converse The Pythagorean Theorem: For a right triangle, the sum of the two leg lengths squared is equal to the length of the hypotenuse squared. a 2 +
Math 1 TOOLKITS TOOLKIT: Pythagorean Theorem & Its Converse The Pythagorean Theorem: For a right triangle, the sum of the two leg lengths squared is equal to the length of the hypotenuse squared. a 2 +
Chapter 3: Right Triangle Trigonometry
 10C Name: Chapter 3: Right Triangle Trigonometry 3.1 The Tangent Ratio Outcome : Develop and apply the tangent ratio to solve problems that involve right triangles. Definitions: Adjacent side: the side
10C Name: Chapter 3: Right Triangle Trigonometry 3.1 The Tangent Ratio Outcome : Develop and apply the tangent ratio to solve problems that involve right triangles. Definitions: Adjacent side: the side
Geometry: Chapter 7. Name: Class: Date: 1. Find the length of the leg of this right triangle. Give an approximation to 3 decimal places.
 Name: Class: Date: Geometry: Chapter 7 1. Find the length of the leg of this right triangle. Give an approximation to 3 decimal places. a. 12.329 c. 12.650 b. 11.916 d. 27.019 2. ABC is a right triangle.
Name: Class: Date: Geometry: Chapter 7 1. Find the length of the leg of this right triangle. Give an approximation to 3 decimal places. a. 12.329 c. 12.650 b. 11.916 d. 27.019 2. ABC is a right triangle.
hypotenuse adjacent leg Preliminary Information: SOH CAH TOA is an acronym to represent the following three 28 m 28 m opposite leg 13 m
 On Twitter: twitter.com/engagingmath On FaceBook: www.mathworksheetsgo.com/facebook I. odel Problems II. Practice Problems III. Challenge Problems IV. Answer ey Web Resources Using the inverse sine, cosine,
On Twitter: twitter.com/engagingmath On FaceBook: www.mathworksheetsgo.com/facebook I. odel Problems II. Practice Problems III. Challenge Problems IV. Answer ey Web Resources Using the inverse sine, cosine,
Objectives: After completing this section, you should be able to do the following: Calculate the lengths of sides and angles of a right triangle using
 Ch 13 - RIGHT TRIANGLE TRIGONOMETRY Objectives: After completing this section, you should be able to do the following: Calculate the lengths of sides and angles of a right triangle using trigonometric
Ch 13 - RIGHT TRIANGLE TRIGONOMETRY Objectives: After completing this section, you should be able to do the following: Calculate the lengths of sides and angles of a right triangle using trigonometric
Warm Up: please factor completely
 Warm Up: please factor completely 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. vocabulary KEY STANDARDS ADDRESSED: MA3A2. Students will use the circle to define the trigonometric functions. a. Define and understand angles measured
Warm Up: please factor completely 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. vocabulary KEY STANDARDS ADDRESSED: MA3A2. Students will use the circle to define the trigonometric functions. a. Define and understand angles measured
10-1. Three Trigonometric Functions. Vocabulary. Lesson
 Chapter 10 Lesson 10-1 Three Trigonometric Functions BIG IDEA The sine, cosine, and tangent of an acute angle are each a ratio of particular sides of a right triangle with that acute angle. Vocabulary
Chapter 10 Lesson 10-1 Three Trigonometric Functions BIG IDEA The sine, cosine, and tangent of an acute angle are each a ratio of particular sides of a right triangle with that acute angle. Vocabulary
Lesson Title 2: Problem TK Solving with Trigonometric Ratios
 Part UNIT RIGHT solving TRIANGLE equations TRIGONOMETRY and inequalities Lesson Title : Problem TK Solving with Trigonometric Ratios Georgia Performance Standards MMG: Students will define and apply sine,
Part UNIT RIGHT solving TRIANGLE equations TRIGONOMETRY and inequalities Lesson Title : Problem TK Solving with Trigonometric Ratios Georgia Performance Standards MMG: Students will define and apply sine,
Assignment. Pg. 567 #16-33, even pg 577 # 1-17 odd, 32-37
 Assignment Intro to Ch. 8 8.1 8. Da 1 8. Da 8. Da 1 8. Da Review Quiz 8. Da 1 8. Da 8. Etra Practice 8.5 8.5 In-class project 8.6 Da 1 8.6 Da Ch. 8 review Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet
Assignment Intro to Ch. 8 8.1 8. Da 1 8. Da 8. Da 1 8. Da Review Quiz 8. Da 1 8. Da 8. Etra Practice 8.5 8.5 In-class project 8.6 Da 1 8.6 Da Ch. 8 review Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet
Cumulative Review: SOHCAHTOA and Angles of Elevation and Depression
 Cumulative Review: SOHCAHTOA and Angles of Elevation and Depression Part 1: Model Problems The purpose of this worksheet is to provide students the opportunity to review the following topics in right triangle
Cumulative Review: SOHCAHTOA and Angles of Elevation and Depression Part 1: Model Problems The purpose of this worksheet is to provide students the opportunity to review the following topics in right triangle
Math-2 Lesson 8-7: Unit 5 Review (Part -2)
 Math- Lesson 8-7: Unit 5 Review (Part -) Trigonometric Functions sin cos A A SOH-CAH-TOA Some old horse caught another horse taking oats away. opposite ( length ) o sin A hypotenuse ( length ) h SOH adjacent
Math- Lesson 8-7: Unit 5 Review (Part -) Trigonometric Functions sin cos A A SOH-CAH-TOA Some old horse caught another horse taking oats away. opposite ( length ) o sin A hypotenuse ( length ) h SOH adjacent
3.0 Trigonometry Review
 3.0 Trigonometry Review In trigonometry problems, all vertices (corners or angles) of the triangle are labeled with capital letters. The right angle is usually labeled C. Sides are usually labeled with
3.0 Trigonometry Review In trigonometry problems, all vertices (corners or angles) of the triangle are labeled with capital letters. The right angle is usually labeled C. Sides are usually labeled with
Math-3 Lesson 6-1. Trigonometric Ratios for Right Triangles and Extending to Obtuse angles.
 Math-3 Lesson 6-1 Trigonometric Ratios for Right Triangles and Extending to Obtuse angles. Right Triangle: has one angle whose measure is. 90 The short sides of the triangle are called legs. The side osite
Math-3 Lesson 6-1 Trigonometric Ratios for Right Triangles and Extending to Obtuse angles. Right Triangle: has one angle whose measure is. 90 The short sides of the triangle are called legs. The side osite
1.6 Applying Trig Functions to Angles of Rotation
 wwwck1org Chapter 1 Right Triangles and an Introduction to Trigonometry 16 Applying Trig Functions to Angles of Rotation Learning Objectives Find the values of the six trigonometric functions for angles
wwwck1org Chapter 1 Right Triangles and an Introduction to Trigonometry 16 Applying Trig Functions to Angles of Rotation Learning Objectives Find the values of the six trigonometric functions for angles
Finding Angles and Solving Right Triangles NEW SKILLS: WORKING WITH INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS. Calculate each angle to the nearest degree.
 324 MathWorks 10 Workbook 7.5 Finding Angles and Solving Right Triangles NEW SKILLS: WORKING WITH INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS The trigonometric ratios discussed in this chapter are unaffected by the size
324 MathWorks 10 Workbook 7.5 Finding Angles and Solving Right Triangles NEW SKILLS: WORKING WITH INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS The trigonometric ratios discussed in this chapter are unaffected by the size
Packet Unit 5 Right Triangles Honors Common Core Math 2 1
 Packet Unit 5 Right Triangles Honors Common Core Math 2 1 Day 1 HW Find the value of each trigonometric ratio. Write the ratios for sinp, cosp, and tanp. Remember to simplify! 9. 10. 11. Packet Unit 5
Packet Unit 5 Right Triangles Honors Common Core Math 2 1 Day 1 HW Find the value of each trigonometric ratio. Write the ratios for sinp, cosp, and tanp. Remember to simplify! 9. 10. 11. Packet Unit 5
Unit 2: Trigonometry. This lesson is not covered in your workbook. It is a review of trigonometry topics from previous courses.
 Unit 2: Trigonometry This lesson is not covered in your workbook. It is a review of trigonometry topics from previous courses. Pythagorean Theorem Recall that, for any right angled triangle, the square
Unit 2: Trigonometry This lesson is not covered in your workbook. It is a review of trigonometry topics from previous courses. Pythagorean Theorem Recall that, for any right angled triangle, the square
Pythagorean Theorem Distance and Midpoints
 Slide 1 / 78 Pythagorean Theorem Distance and Midpoints Slide 2 / 78 Table of Contents Pythagorean Theorem Distance Formula Midpoints Click on a topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 78 Slide 4 / 78 Pythagorean
Slide 1 / 78 Pythagorean Theorem Distance and Midpoints Slide 2 / 78 Table of Contents Pythagorean Theorem Distance Formula Midpoints Click on a topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 78 Slide 4 / 78 Pythagorean
Name: Class: Date: Chapter 3 - Foundations 7. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: Chapter 3 - Foundations 7 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Determine the value of tan 59, to four decimal places. a.
Name: Class: Date: Chapter 3 - Foundations 7 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Determine the value of tan 59, to four decimal places. a.
Solv S ing olv ing ight ight riang les iangles 8-3 Solving Right Triangles Warm Up Use ABC for Exercises If a = 8 and b = 5, find c
 Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Warm Up Use ABC for Exercises 1 3. 1. If a = 8 and b = 5, find c. 2. If a = 60 and c = 61, find b. 11 3. If b = 6 and c = 10, find sin B. 0.6 Find AB. 4. A(8, 10),
Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Warm Up Use ABC for Exercises 1 3. 1. If a = 8 and b = 5, find c. 2. If a = 60 and c = 61, find b. 11 3. If b = 6 and c = 10, find sin B. 0.6 Find AB. 4. A(8, 10),
If AB = 36 and AC = 12, what is the length of AD?
 Name: ate: 1. ship at sea heads directly toward a cliff on the shoreline. The accompanying diagram shows the top of the cliff,, sighted from two locations, and B, separated by distance S. If m = 30, m
Name: ate: 1. ship at sea heads directly toward a cliff on the shoreline. The accompanying diagram shows the top of the cliff,, sighted from two locations, and B, separated by distance S. If m = 30, m
Chapter 7 Diagnostic Test
 Chapter 7 Diagnostic Test STUDENT BOOK PAGES 370 419 1. Epress each ratio in simplest form. 4. 5 12 : 42 18 45 c) 20 : 8 d) 63 2. Solve each proportion. 12 4 2 = 15 45 = 3 c) 7.5 22.5 = d) 12 4.8 = 9.6
Chapter 7 Diagnostic Test STUDENT BOOK PAGES 370 419 1. Epress each ratio in simplest form. 4. 5 12 : 42 18 45 c) 20 : 8 d) 63 2. Solve each proportion. 12 4 2 = 15 45 = 3 c) 7.5 22.5 = d) 12 4.8 = 9.6
Unit O Student Success Sheet (SSS) Right Triangle Trigonometry (sections 4.3, 4.8)
 Unit O Student Success Sheet (SSS) Right Triangle Trigonometry (sections 4.3, 4.8) Standards: Geom 19.0, Geom 20.0, Trig 7.0, Trig 8.0, Trig 12.0 Segerstrom High School -- Math Analysis Honors Name: Period:
Unit O Student Success Sheet (SSS) Right Triangle Trigonometry (sections 4.3, 4.8) Standards: Geom 19.0, Geom 20.0, Trig 7.0, Trig 8.0, Trig 12.0 Segerstrom High School -- Math Analysis Honors Name: Period:
MR. JIMENEZ FINAL EXAM REVIEW GEOMETRY 2011
 PAGE 1 1. The area of a circle is 25.5 in. 2. Find the circumference of the circle. Round your answers to the nearest tenth. 2. The circumference of a circle is 13.1 in. Find the area of the circle. Round
PAGE 1 1. The area of a circle is 25.5 in. 2. Find the circumference of the circle. Round your answers to the nearest tenth. 2. The circumference of a circle is 13.1 in. Find the area of the circle. Round
Angles of a Triangle. Activity: Show proof that the sum of the angles of a triangle add up to Finding the third angle of a triangle
 Angles of a Triangle Activity: Show proof that the sum of the angles of a triangle add up to 180 0 Finding the third angle of a triangle Pythagorean Theorem Is defined as the square of the length of the
Angles of a Triangle Activity: Show proof that the sum of the angles of a triangle add up to 180 0 Finding the third angle of a triangle Pythagorean Theorem Is defined as the square of the length of the
Review of Sine, Cosine, and Tangent for Right Triangle
 Review of Sine, Cosine, and Tangent for Right Triangle In trigonometry problems, all vertices (corners or angles) of the triangle are labeled with capital letters. The right angle is usually labeled C.
Review of Sine, Cosine, and Tangent for Right Triangle In trigonometry problems, all vertices (corners or angles) of the triangle are labeled with capital letters. The right angle is usually labeled C.
Solving Trigonometric Equations
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49398 1 Solving Trigonometric Equations OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 In this section, you
OpenStax-CNX module: m49398 1 Solving Trigonometric Equations OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 In this section, you
2.1 The Tangent Ratio
 2.1 The Tangent Ratio C 2.1 Concept: 14, 15 PreAP FPCM 10 (Ms. Carignan) Outcome FP10.4 Trigonometry Chapter 2 Page 1 PreAP FPCM 10 (Ms. Carignan) Outcome FP10.4 Trigonometry Chapter 2 Page 2 Online Video
2.1 The Tangent Ratio C 2.1 Concept: 14, 15 PreAP FPCM 10 (Ms. Carignan) Outcome FP10.4 Trigonometry Chapter 2 Page 1 PreAP FPCM 10 (Ms. Carignan) Outcome FP10.4 Trigonometry Chapter 2 Page 2 Online Video
UNIT 2 RIGHT TRIANGLE TRIGONOMETRY Lesson 1: Exploring Trigonometric Ratios Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: measuring angles with a protractor understanding how to label angles and sides in triangles converting fractions into decimals
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: measuring angles with a protractor understanding how to label angles and sides in triangles converting fractions into decimals
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 7.1
 Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name Date Tangent Ratio Tangent Ratio, Cotangent Ratio, and Inverse Tangent Vocabulary Match each description to its corresponding term for triangle EFG. F
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name Date Tangent Ratio Tangent Ratio, Cotangent Ratio, and Inverse Tangent Vocabulary Match each description to its corresponding term for triangle EFG. F
Second Semester Exam Review Packet
 Geometry Name Second Semester Exam Review Packet CHAPTER 7 THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM. This theorem is used to find the lengths of the sides of a right triangle. Label the parts of the right triangle. What
Geometry Name Second Semester Exam Review Packet CHAPTER 7 THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM. This theorem is used to find the lengths of the sides of a right triangle. Label the parts of the right triangle. What
Right Triangle Trigonometry
 Right Triangle Trigonometry 1 The six trigonometric functions of a right triangle, with an acute angle, are defined by ratios of two sides of the triangle. hyp opp The sides of the right triangle are:
Right Triangle Trigonometry 1 The six trigonometric functions of a right triangle, with an acute angle, are defined by ratios of two sides of the triangle. hyp opp The sides of the right triangle are:
Chapter 4: Triangle and Trigonometry
 Chapter 4: Triangle and Trigonometry Paper 1 & 2B 3.1.3 Triangles 3.1.3 Triangles 2A Understand a proof of Pythagoras Theorem. Understand the converse of Pythagoras Theorem. Use Pythagoras Trigonometry
Chapter 4: Triangle and Trigonometry Paper 1 & 2B 3.1.3 Triangles 3.1.3 Triangles 2A Understand a proof of Pythagoras Theorem. Understand the converse of Pythagoras Theorem. Use Pythagoras Trigonometry
14.1 Similar Triangles and the Tangent Ratio Per Date Trigonometric Ratios Investigate the relationship of the tangent ratio.
 14.1 Similar Triangles and the Tangent Ratio Per Date Trigonometric Ratios Investigate the relationship of the tangent ratio. Using the space below, draw at least right triangles, each of which has one
14.1 Similar Triangles and the Tangent Ratio Per Date Trigonometric Ratios Investigate the relationship of the tangent ratio. Using the space below, draw at least right triangles, each of which has one
I. Model Problems II. Practice III. Challenge Problems IV. Answer Key. Sine, Cosine Tangent
 On Twitter: twitter.com/engagingmath On FaceBook: www.mathworksheetsgo.com/facebook I. Model Problems II. Practice III. Challenge Problems IV. Answer Key Web Resources Sine, Cosine Tangent www.mathwarehouse.com/trigonometry/sine-cosine-tangent.html
On Twitter: twitter.com/engagingmath On FaceBook: www.mathworksheetsgo.com/facebook I. Model Problems II. Practice III. Challenge Problems IV. Answer Key Web Resources Sine, Cosine Tangent www.mathwarehouse.com/trigonometry/sine-cosine-tangent.html
Semester 2 Review Problems will be sectioned by chapters. The chapters will be in the order by which we covered them.
 Semester 2 Review Problems will be sectioned by chapters. The chapters will be in the order by which we covered them. Chapter 9 and 10: Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios 1. The hypotenuse of a right
Semester 2 Review Problems will be sectioned by chapters. The chapters will be in the order by which we covered them. Chapter 9 and 10: Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios 1. The hypotenuse of a right
Accel. Geometry - Concepts Similar Figures, Right Triangles, Trigonometry
 Accel. Geometry - Concepts 16-19 Similar Figures, Right Triangles, Trigonometry Concept 16 Ratios and Proportions (Section 7.1) Ratio: Proportion: Cross-Products Property If a b = c, then. d Properties
Accel. Geometry - Concepts 16-19 Similar Figures, Right Triangles, Trigonometry Concept 16 Ratios and Proportions (Section 7.1) Ratio: Proportion: Cross-Products Property If a b = c, then. d Properties
B. Dilate the following figure using a scale
 1 Dilations affect the size of the pre-image. he pre-image will enlarge or reduce by the ratio given by the scale factor. A dilation with a scale factor of k > 1 enlarges it. A dilation of 0 < k < 1 reduces
1 Dilations affect the size of the pre-image. he pre-image will enlarge or reduce by the ratio given by the scale factor. A dilation with a scale factor of k > 1 enlarges it. A dilation of 0 < k < 1 reduces
a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h.
 Sec. Right Triangle Trigonometry Right Triangle Trigonometry Sides Find the requested unknown side of the following triangles. Name: a. b. c. d.? 44 8 5? 7? 44 9 58 0? e. f. g. h.?? 4 7 5? 38 44 6 49º?
Sec. Right Triangle Trigonometry Right Triangle Trigonometry Sides Find the requested unknown side of the following triangles. Name: a. b. c. d.? 44 8 5? 7? 44 9 58 0? e. f. g. h.?? 4 7 5? 38 44 6 49º?
Congruence and Similarity in Triangles Pg. 378 # 1, 4 8, 12. Solving Similar Triangle Problems Pg. 386 # 2-12
 UNIT 7 SIMILAR TRIANGLES AND TRIGONOMETRY Date Lesson TOPIC Homework May 4 7.1 7.1 May 8 7.2 7.2 Congruence and Similarity in Triangles Pg. 378 # 1, 4 8, 12 Solving Similar Triangle Problems Pg. 386 #
UNIT 7 SIMILAR TRIANGLES AND TRIGONOMETRY Date Lesson TOPIC Homework May 4 7.1 7.1 May 8 7.2 7.2 Congruence and Similarity in Triangles Pg. 378 # 1, 4 8, 12 Solving Similar Triangle Problems Pg. 386 #
(13) Page #1 8, 12, 13, 15, 16, Even, 29 32, 39 44
 Geometry/Trigonometry Unit 7: Right Triangle Notes Name: Date: Period: # (1) Page 430 #1 15 (2) Page 430 431 #16 23, 25 27, 29 and 31 (3) Page 437 438 #1 8, 9 19 odd (4) Page 437 439 #10 20 Even, 23, and
Geometry/Trigonometry Unit 7: Right Triangle Notes Name: Date: Period: # (1) Page 430 #1 15 (2) Page 430 431 #16 23, 25 27, 29 and 31 (3) Page 437 438 #1 8, 9 19 odd (4) Page 437 439 #10 20 Even, 23, and
Math 4 Snow Day. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Class: Date: Math 4 Snow Day Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. Simplify the rational expression x x x x x x 0. x x. Which function has an amplitude
Class: Date: Math 4 Snow Day Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. Simplify the rational expression x x x x x x 0. x x. Which function has an amplitude
Geometry First Semester Practice Final (cont)
 49. Determine the width of the river, AE, if A. 6.6 yards. 10 yards C. 12.8 yards D. 15 yards Geometry First Semester Practice Final (cont) 50. In the similar triangles shown below, what is the value of
49. Determine the width of the river, AE, if A. 6.6 yards. 10 yards C. 12.8 yards D. 15 yards Geometry First Semester Practice Final (cont) 50. In the similar triangles shown below, what is the value of
Indirect proof. Write indirect proof for the following
 Indirect proof Write indirect proof for the following 1.. Practice C A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with two sets of congruent parallel sides. The opposite angles in a parallelogram are congruent.
Indirect proof Write indirect proof for the following 1.. Practice C A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with two sets of congruent parallel sides. The opposite angles in a parallelogram are congruent.
Unit 8 Similarity and Trigonometry
 Unit 8 Similarity and Trigonometry Target 8.1: Prove and apply properties of similarity in triangles using AA~, SSS~, SAS~ 8.1a Prove Triangles Similar by AA ~, SSS~, SAS~ 8.1b Use Proportionality Theorems
Unit 8 Similarity and Trigonometry Target 8.1: Prove and apply properties of similarity in triangles using AA~, SSS~, SAS~ 8.1a Prove Triangles Similar by AA ~, SSS~, SAS~ 8.1b Use Proportionality Theorems
A trigonometric ratio is a,
 ALGEBRA II Chapter 13 Notes The word trigonometry is derived from the ancient Greek language and means measurement of triangles. Section 13.1 Right-Triangle Trigonometry Objectives: 1. Find the trigonometric
ALGEBRA II Chapter 13 Notes The word trigonometry is derived from the ancient Greek language and means measurement of triangles. Section 13.1 Right-Triangle Trigonometry Objectives: 1. Find the trigonometric
Theorem 8-1-1: The three altitudes in a right triangle will create three similar triangles
 G.T. 7: state and apply the relationships that exist when the altitude is drawn to the hypotenuse of a right triangle. Understand and use the geometric mean to solve for missing parts of triangles. 8-1
G.T. 7: state and apply the relationships that exist when the altitude is drawn to the hypotenuse of a right triangle. Understand and use the geometric mean to solve for missing parts of triangles. 8-1
SOH CAH TOA Worksheet Name. Find the following ratios using the given right triangles
 Name: Algebra II Period: 9.1 Introduction to Trig 12.1 Worksheet Name GETTIN' TRIGGY WIT IT SOH CAH TOA Find the following ratios using the given right triangles. 1. 2. Sin A = Sin B = Sin A = Sin B =
Name: Algebra II Period: 9.1 Introduction to Trig 12.1 Worksheet Name GETTIN' TRIGGY WIT IT SOH CAH TOA Find the following ratios using the given right triangles. 1. 2. Sin A = Sin B = Sin A = Sin B =
Unit No: F3HW 11. Unit Title: Maths Craft 2. 4 Trigonometry Sine and Cosine Rules. Engineering and Construction
 Unit No: F3HW 11 Unit Title: Maths Craft 4 Trigonometry Sine and Cosine Rules SINE AND COSINE RULES TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS Remember: The word SOH CAH TOA is a helpful reminder. In any right-angled triangle,
Unit No: F3HW 11 Unit Title: Maths Craft 4 Trigonometry Sine and Cosine Rules SINE AND COSINE RULES TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS Remember: The word SOH CAH TOA is a helpful reminder. In any right-angled triangle,
c 12 B. _ r.; = - 2 = T. .;Xplanation: 2) A 45 B. -xplanation: 5. s-,:; Student Name:
 3111201 USTestprep, Inc..USJ\~fflp naltic Geometr EOC Qui nswer Ke Geometr- (MCC9-12.G.SRT.6) Side Ratios In Right Triangles, (MCC9-12.G.SRT.7) Sine nd Cosine Of Complementar ngles 1) Student Name: Teacher
3111201 USTestprep, Inc..USJ\~fflp naltic Geometr EOC Qui nswer Ke Geometr- (MCC9-12.G.SRT.6) Side Ratios In Right Triangles, (MCC9-12.G.SRT.7) Sine nd Cosine Of Complementar ngles 1) Student Name: Teacher
Mathematical Techniques Chapter 10
 PART FOUR Formulas FM 5-33 Mathematical Techniques Chapter 10 GEOMETRIC FUNCTIONS The result of any operation performed by terrain analysts will only be as accurate as the measurements used. An interpretation
PART FOUR Formulas FM 5-33 Mathematical Techniques Chapter 10 GEOMETRIC FUNCTIONS The result of any operation performed by terrain analysts will only be as accurate as the measurements used. An interpretation
Name: Pythagorean Theorem February 3, 2014
 1. John leaves school to go home. He walks 6 blocks North and then 8 blocks west. How far is John from the school? 5. A 26 foot long ladder is leaning up against a house with its base 10 feet away from
1. John leaves school to go home. He walks 6 blocks North and then 8 blocks west. How far is John from the school? 5. A 26 foot long ladder is leaning up against a house with its base 10 feet away from
4. Given Quadrilateral HIJG ~ Quadrilateral MNOL, find x and y. x =
 Name: DUE: HOUR: 2016 2017 Geometry Final Exam Review 1. Find x. Round to the nearest hundredth. x = 2. Find x. x = 3. Given STU ~ PQR, find x. x = 4. Given Quadrilateral HIJG ~ Quadrilateral MNOL, find
Name: DUE: HOUR: 2016 2017 Geometry Final Exam Review 1. Find x. Round to the nearest hundredth. x = 2. Find x. x = 3. Given STU ~ PQR, find x. x = 4. Given Quadrilateral HIJG ~ Quadrilateral MNOL, find
Lesson 10.1 TRIG RATIOS AND COMPLEMENTARY ANGLES PAGE 231
 1 Lesson 10.1 TRIG RATIOS AND COMPLEMENTARY ANGLES PAGE 231 What is Trigonometry? 2 It is defined as the study of triangles and the relationships between their sides and the angles between these sides.
1 Lesson 10.1 TRIG RATIOS AND COMPLEMENTARY ANGLES PAGE 231 What is Trigonometry? 2 It is defined as the study of triangles and the relationships between their sides and the angles between these sides.
MAC Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives (Cont.) Module 2 Acute Angles and Right Triangles
 MAC 1114 Module 2 Acute Angles and Right Triangles Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Express the trigonometric ratios in terms of the sides of the triangle given
MAC 1114 Module 2 Acute Angles and Right Triangles Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Express the trigonometric ratios in terms of the sides of the triangle given
Section 10.6 Right Triangle Trigonometry
 153 Section 10.6 Right Triangle Trigonometry Objective #1: Understanding djacent, Hypotenuse, and Opposite sides of an acute angle in a right triangle. In a right triangle, the otenuse is always the longest
153 Section 10.6 Right Triangle Trigonometry Objective #1: Understanding djacent, Hypotenuse, and Opposite sides of an acute angle in a right triangle. In a right triangle, the otenuse is always the longest
Ch. 2 Trigonometry Notes
 First Name: Last Name: Block: Ch. Trigonometry Notes.0 PRE-REQUISITES: SOLVING RIGHT TRIANGLES.1 ANGLES IN STANDARD POSITION 6 Ch..1 HW: p. 83 #1,, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, 8. - TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS OF AN ANGLE
First Name: Last Name: Block: Ch. Trigonometry Notes.0 PRE-REQUISITES: SOLVING RIGHT TRIANGLES.1 ANGLES IN STANDARD POSITION 6 Ch..1 HW: p. 83 #1,, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, 8. - TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS OF AN ANGLE
Trigonometry A Right Triangle Approach
 We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with trigonometry a right
We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with trigonometry a right
Unit 6: Triangle Geometry
 Unit 6: Triangle Geometry Student Tracking Sheet Math 9 Principles Name: lock: What I can do for this unit: fter Practice fter Review How I id 6-1 I can recognize similar triangles using the ngle Test,
Unit 6: Triangle Geometry Student Tracking Sheet Math 9 Principles Name: lock: What I can do for this unit: fter Practice fter Review How I id 6-1 I can recognize similar triangles using the ngle Test,
Lesson 26 - Review of Right Triangle Trigonometry
 Lesson 26 - Review of Right Triangle Trigonometry PreCalculus Santowski PreCalculus - Santowski 1 (A) Review of Right Triangle Trig Trigonometry is the study and solution of Triangles. Solving a triangle
Lesson 26 - Review of Right Triangle Trigonometry PreCalculus Santowski PreCalculus - Santowski 1 (A) Review of Right Triangle Trig Trigonometry is the study and solution of Triangles. Solving a triangle
Mathematics Placement Assessment
 Mathematics Placement Assessment Courage, Humility, and Largeness of Heart Oldfields School Thank you for taking the time to complete this form accurately prior to returning this mathematics placement
Mathematics Placement Assessment Courage, Humility, and Largeness of Heart Oldfields School Thank you for taking the time to complete this form accurately prior to returning this mathematics placement
Geometry PreAP Spring Final Exam Review 2017
 Name Period Date Geometry PreAP Spring Final Exam Review 2017 Topic 1: Similar Figures 1) What does it mean for two polygons to be similar? 2) Use the definition from #1 to determine whether or not the
Name Period Date Geometry PreAP Spring Final Exam Review 2017 Topic 1: Similar Figures 1) What does it mean for two polygons to be similar? 2) Use the definition from #1 to determine whether or not the
