Summed-Area Tables. And Their Application to Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections Thorsten Scheuermann 3D Application Research Group
|
|
|
- Elwin Williams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Summed-Area Tables And Their Application to Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections Thorsten Scheuermann 3D Application Research Group
2 Overview >Presenting work started by Justin Hensley, Ph.D. student at UNC and a 4 ATI Fellowship recipient > Summed-area tables > Use for blurring > Efficient creation >Rendering dynamic reflections with per-pixel glossiness using dual-paraboloid maps and summed-area tables GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections
3 Summed-Area Tables (SATs) >Each element s mn of a summed-area table S contains the sum of all elements above and to the left of the original table/texture T [Crow84] m n s mn = t ij i= j= Original Summed-area table GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections 3
4 Using a Summed-Area Table >Summed-area tables allow filtering the original texture with an arbitrary box filter in constant time - - UL UR h average = LR UR LL w* h UL LL w LR GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections 4
5 Filtering Example Code float4 texd_sat_blur(sampler tsat, float uv, float size) { float4 result = texd(tsat, uv.5 * size); // LR result -= texd(tsat, uv float(.5, -.5) * size); // UR result -= texd(tsat, uv float(-.5,.5) * size); // LL result = texd(tsat, uv -.5 * size); // UL result /= size.x * size.y; } return result; GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections 5
6 Efficient Summed-Area Table Creation >Summed-area table construction can be decomposed into horizontal and vertical phase >Each phase consists of log (texture size) passes >Each pass adds two elements from the previous pass >Ping-pong between two rendertargets for each pass >Horizontal Phase: passindex P( x, y) = P ( x, y) P ( x, y) i i i GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections 6
7 Horizontal Phase Example Sampling off the texture returns so that the sum doesn t get affected. Pass index GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections 7
8 Saving Render Passes >Adding two samples per pass requires *log (56) = 6 passes for a 56x56 texture >To reduce number of passes we can add more samples per pass >Pass count reduces to *log #samples (texture size) >Using 6 samples per pass we only need 4 passes for converting a 56x56 texture to a summed-area table > Converting 5x5 needs 6 passes but two passes only need to add two texture samples GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections 8
9 SAT Creation Vertex Shaders float fpassindex; float vpixelsize; float4x4 mvp; struct VsOutput { float4 pos : POSITION; float4 uv[8] : TEXCOORD; // 6 UVs stuffed in 8 float4 s }; VsOutput main(float4 inpos: POSITION, float inuv : TEXCOORD) { VsOutput o; [ ] // transform vertex (assuming app has set up screen-aligned // quad drawing) o.pos = mul (inpos, mvp); GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections 9
10 SAT Creation Vertex Shader [ ] float passoffset = pow(6., fpassindex) * vpixelsize.x; // output first two texcoords o.uv[].xy = inuv; o.uv[].wz = o.uv[].xy - float(passoffset, ); // compute remaining 4 texcoords for neighboring pixels for (int i=; i<8; i) { o.uv[i].xy = o.uv[].xy float((. * i) * passoffset, ); o.uv[i].wz = o.uv[].xy float((. * i.) * passoffset, ); } } return o; GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections
11 SAT Creation Pixel Shader float4 SATPass(sampler tsrc, float4 uv[8]) { float4 t[8]; // add 6 texture samples with pyramidal scheme // to maintain precision for (int i=; i<8; i) { t[i] = texd(tsrc, uv[i].xy) texd(tsrc, uv[i].wz); } t[] = t[]; t[] = t[3]; t[4] = t[5]; t[6] = t[7]; t[] = t[]; t[4] = t[6]; } return t[]t[4]; GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections
12 Precision Requirements >For proper reconstruction a summed-area table needs log (texture width)log (texture height)bit depth of source texture bits of precision >Use float3-rendertargets to compute and store summed-area tables >Precision errors are unbiased and average out as you use larger box filter kernels GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections
13 Summed-Area Table Example GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections 3
14 Boundary Conditions >To make sure sampling off the texture does not mess up the results we need to set up the correct texture clamping behavior >Two possibilities: > Clamp to border color with a color of (,,, ) > Render a black border around the texture to be converted into SAT and set Clamp to Edge mode GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections 4
15 SAT Precision Improvement Trick >Bias input texture by -.5 before generating summed-area table >When reconstructing samples from SAT, undo bias by adding.5 to final result > This helps because now we take advantage of the sign bit >Even better: Use average color of input as bias (instead of.5) >Improving precision of summed-area tables is particularly useful when using hardware with limited pixel pipeline precision No precision improvement With precision improvement GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections 5
16 Dynamic Glossy Reflections Game Plan >Render dynamic cubemap >Convert to dual-paraboloid map >Convert dual-paraboloid map faces to summed-area tables >Apply SAT DP-map to glossy object >Sounds like a lot of work, but is actually quite fast on modern hardware > Will show real-time demo in a minute GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections 6
17 The Return of the Dual- Paraboloid Map! >Dual-paraboloid map = two textures that store an environment as reflected in parabolic mirrors Color channels Alpha channel GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections 7
18 DP Sampling Shader float3 texdp (sampler tfront, sampler tback, float3 dir) { // convert 3D lookup vector into D texture coordinates float frontuv = float(.5, -.5) * dir.xy / (. - dir.z).5; float backuv = float(.5, -.5) * dir.xy / (. dir.z).5; // sample DP map faces and blend together float4 cfront = texd (tfront, frontuv); float4 cback = texd (tback, backuv); } return cfront.rgb cback.rgb; GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections 8
19 9 GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections Cubemap to DP Map Conversion Cubemap to DP Map Conversion >Convert uv position on DP map face to 3D vector using these equations: (from [Blythe99]) >Perform cubemap lookup and store result in DP face >Precompute lookup textures or do math on the fly = v u v u v u v v u u R = v v v u v u v v u u R Front face: Back face: Front lookup texture Back lookup texture
20 Why Bother With DP Mapping? >Summed-area table concept does not map to cubemaps which are in spherical domain > Summed-area tables only work on rectangular D images >Filtering with a box filter in dual-paraboloid space causes less distortion GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections
21 Putting it All Together GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections
22 SAT DP Sampling Shader >Very similar to DP sampling, but uses SAT texture lookup function: float3 texdp_sat (sampler tfront, sampler tback, float3 dir, float filtersize) { // convert 3D lookup vector into D texture coordinates float frontuv = float(.5, -.5) * dir.xy / (. - dir.z).5; float backuv = float(.5, -.5) * dir.xy / (. dir.z).5; // sample DP map faces and blend together float4 cfront = texd_sat_blur (tfront, frontuv, filtersize); float4 cback = texd_sat_blur (tback, backuv, filtersize); float4 crefl = cfront cback; } // normalize result return crefl.rgb / crefl.a; GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections
23 Demo GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections 3
24 Other Possibilities >Average several box-filtered environment map samples to approximate smoother blur filter kernels >Approximate Phong BRDF by combining very blurred sample in normal direction and less blurry sample in reflection vector direction for specular lobe GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections 4
25 Direct DP Face Rendering >Alternative to rendering cubemap, then converting to DP map: >Transform environment using parabolic projection function and render directly into DP faces >Unfortunately parabolic projection is non-linear and maps lines to curves > Linear rasterization of graphics hardware causes artifacts > Might be OK if your geometry is tesselated highly enough >See [Coombe4] for details GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections 5
26 Disadvantages >Precision requirements for summed-area tables >float3 textures used for summed-area tables do not currently support bilinear filtering > Not so much of an issue when you blur enough > Can perform bilinear filtering manually in the shader GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections 6
27 Conclusion >Using summed-area tables for blurring >Efficient summed-area table generation scheme >Converting cubemap into dual-paraboloid maps >Using summed-area tables and dual-paraboloid mapping together to achieve dynamic glossy environment reflections GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections 7
28 Acknowledgements >Justin Hensley >Thanks to Eli Turner for the demo artwork GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections 8
29 References >[Crow84] Crow, F. C., Summed-area tables for texture mapping. Proceedings of the th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques ACM Press: >[Coombe4] Coombe, G., Harris, M. and Lastra, A., Radiosity on Graphics Hardware. Graphics Interfaces, 4. >[Blythe99] Blythe, D., Advanced Graphics Programming Techniques Using OpenGL. SIGGRAPH 999 course notes. GDC 5: Dynamic Glossy Environment Reflections 9
Interactive Summed-Area Table Generation for Glossy Environmental Reflections
 Interactive Summed-Area Table Generation for Glossy Environmental Reflections Justin Hensley Thorsten Scheuermann Montek Singh Anselmo Lastra University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill ATI Research Overview
Interactive Summed-Area Table Generation for Glossy Environmental Reflections Justin Hensley Thorsten Scheuermann Montek Singh Anselmo Lastra University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill ATI Research Overview
Fast HDR Image-Based Lighting Using Summed-Area Tables
 Fast HDR Image-Based Lighting Using Summed-Area Tables Justin Hensley 1, Thorsten Scheuermann 2, Montek Singh 1 and Anselmo Lastra 1 1 University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC, USA {hensley, montek,
Fast HDR Image-Based Lighting Using Summed-Area Tables Justin Hensley 1, Thorsten Scheuermann 2, Montek Singh 1 and Anselmo Lastra 1 1 University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC, USA {hensley, montek,
Cubemap Filtering with CubeMapGen. Thorsten Scheuermann John Isidoro 3D Application Research Group
 Cubemap Filtering with CubeMapGen Thorsten Scheuermann John Isidoro 3D Application Research Group Outline >CubeMapGen tool >Angular extent filtering >Edge fixup methods >Pre-filtered per-pixel glossy reflections
Cubemap Filtering with CubeMapGen Thorsten Scheuermann John Isidoro 3D Application Research Group Outline >CubeMapGen tool >Angular extent filtering >Edge fixup methods >Pre-filtered per-pixel glossy reflections
Shaders (some slides taken from David M. course)
 Shaders (some slides taken from David M. course) Doron Nussbaum Doron Nussbaum COMP 3501 - Shaders 1 Traditional Rendering Pipeline Traditional pipeline (older graphics cards) restricts developer to texture
Shaders (some slides taken from David M. course) Doron Nussbaum Doron Nussbaum COMP 3501 - Shaders 1 Traditional Rendering Pipeline Traditional pipeline (older graphics cards) restricts developer to texture
Drawing a Crowd. David Gosselin Pedro V. Sander Jason L. Mitchell. 3D Application Research Group ATI Research
 Drawing a Crowd David Gosselin Pedro V. Sander Jason L. Mitchell 3D Application Research Group ATI Research Introduction In this chapter, we present a technique for efficiently rendering a large crowd
Drawing a Crowd David Gosselin Pedro V. Sander Jason L. Mitchell 3D Application Research Group ATI Research Introduction In this chapter, we present a technique for efficiently rendering a large crowd
Filtering Cubemaps Angular Extent Filtering and Edge Seam Fixup Methods
 Filtering Cubemaps Angular Extent Filtering and Edge Seam Fixup Methods John R. Isidoro 3D Application Research Group ATI Research Introduction Hardware cube mapping is ubiquitous. Straightforward hardware
Filtering Cubemaps Angular Extent Filtering and Edge Seam Fixup Methods John R. Isidoro 3D Application Research Group ATI Research Introduction Hardware cube mapping is ubiquitous. Straightforward hardware
CS 354R: Computer Game Technology
 CS 354R: Computer Game Technology Texture and Environment Maps Fall 2018 Texture Mapping Problem: colors, normals, etc. are only specified at vertices How do we add detail between vertices without incurring
CS 354R: Computer Game Technology Texture and Environment Maps Fall 2018 Texture Mapping Problem: colors, normals, etc. are only specified at vertices How do we add detail between vertices without incurring
CS 450: COMPUTER GRAPHICS TEXTURE MAPPING SPRING 2015 DR. MICHAEL J. REALE
 CS 450: COMPUTER GRAPHICS TEXTURE MAPPING SPRING 2015 DR. MICHAEL J. REALE INTRODUCTION Texturing = process that takes a surface and modifies its appearance at each location using some image, function,
CS 450: COMPUTER GRAPHICS TEXTURE MAPPING SPRING 2015 DR. MICHAEL J. REALE INTRODUCTION Texturing = process that takes a surface and modifies its appearance at each location using some image, function,
Real Time Skin Rendering
 Real Time Skin Rendering David Gosselin 3D Application Research Group ATI Research, Inc. Overview Background Texture space lighting Spatially varying blur Dilation Adding shadows Specular with shadows
Real Time Skin Rendering David Gosselin 3D Application Research Group ATI Research, Inc. Overview Background Texture space lighting Spatially varying blur Dilation Adding shadows Specular with shadows
How to Work on Next Gen Effects Now: Bridging DX10 and DX9. Guennadi Riguer ATI Technologies
 How to Work on Next Gen Effects Now: Bridging DX10 and DX9 Guennadi Riguer ATI Technologies Overview New pipeline and new cool things Simulating some DX10 features in DX9 Experimental techniques Why This
How to Work on Next Gen Effects Now: Bridging DX10 and DX9 Guennadi Riguer ATI Technologies Overview New pipeline and new cool things Simulating some DX10 features in DX9 Experimental techniques Why This
Image Processing Tricks in OpenGL. Simon Green NVIDIA Corporation
 Image Processing Tricks in OpenGL Simon Green NVIDIA Corporation Overview Image Processing in Games Histograms Recursive filters JPEG Discrete Cosine Transform Image Processing in Games Image processing
Image Processing Tricks in OpenGL Simon Green NVIDIA Corporation Overview Image Processing in Games Histograms Recursive filters JPEG Discrete Cosine Transform Image Processing in Games Image processing
Screen Space Ambient Occlusion TSBK03: Advanced Game Programming
 Screen Space Ambient Occlusion TSBK03: Advanced Game Programming August Nam-Ki Ek, Oscar Johnson and Ramin Assadi March 5, 2015 This project report discusses our approach of implementing Screen Space Ambient
Screen Space Ambient Occlusion TSBK03: Advanced Game Programming August Nam-Ki Ek, Oscar Johnson and Ramin Assadi March 5, 2015 This project report discusses our approach of implementing Screen Space Ambient
Dual-Paraboloid Shadow Mapping. A paper by Stefan Brabec, Thomas Annen, Hans-Peter Seidel Presented By Patrick Wouterse, Selmar Kok
 A paper by Stefan Brabec, Thomas Annen, Hans-Peter Seidel Presented By Patrick Wouterse, Selmar Kok Introduction and Background An improved perspective shadow mapping technique Less memory and render passes
A paper by Stefan Brabec, Thomas Annen, Hans-Peter Seidel Presented By Patrick Wouterse, Selmar Kok Introduction and Background An improved perspective shadow mapping technique Less memory and render passes
Real Time Skin Rendering
 Real Time Skin Rendering David Gosselin 3D Application Research Group ATI Research, Inc. Overview Background Texture space lighting Blur and dilation Adding shadows Specular with shadows Demo 2 Why Skin
Real Time Skin Rendering David Gosselin 3D Application Research Group ATI Research, Inc. Overview Background Texture space lighting Blur and dilation Adding shadows Specular with shadows Demo 2 Why Skin
The Application Stage. The Game Loop, Resource Management and Renderer Design
 1 The Application Stage The Game Loop, Resource Management and Renderer Design Application Stage Responsibilities 2 Set up the rendering pipeline Resource Management 3D meshes Textures etc. Prepare data
1 The Application Stage The Game Loop, Resource Management and Renderer Design Application Stage Responsibilities 2 Set up the rendering pipeline Resource Management 3D meshes Textures etc. Prepare data
Applications of Explicit Early-Z Z Culling. Jason Mitchell ATI Research
 Applications of Explicit Early-Z Z Culling Jason Mitchell ATI Research Outline Architecture Hardware depth culling Applications Volume Ray Casting Skin Shading Fluid Flow Deferred Shading Early-Z In past
Applications of Explicit Early-Z Z Culling Jason Mitchell ATI Research Outline Architecture Hardware depth culling Applications Volume Ray Casting Skin Shading Fluid Flow Deferred Shading Early-Z In past
Shadow Mapping for Hemispherical and Omnidirectional Light Sources
 Shadow Mapping for Hemispherical and Omnidirectional Light Sources Abstract Stefan Brabec Thomas Annen Hans-Peter Seidel Computer Graphics Group Max-Planck-Institut für Infomatik Stuhlsatzenhausweg 85,
Shadow Mapping for Hemispherical and Omnidirectional Light Sources Abstract Stefan Brabec Thomas Annen Hans-Peter Seidel Computer Graphics Group Max-Planck-Institut für Infomatik Stuhlsatzenhausweg 85,
Could you make the XNA functions yourself?
 1 Could you make the XNA functions yourself? For the second and especially the third assignment, you need to globally understand what s going on inside the graphics hardware. You will write shaders, which
1 Could you make the XNA functions yourself? For the second and especially the third assignment, you need to globally understand what s going on inside the graphics hardware. You will write shaders, which
Projective Shadows. D. Sim Dietrich Jr.
 Projective Shadows D. Sim Dietrich Jr. Topics Projective Shadow Types Implementation on DirectX 7 HW Implementation on DirectX8 HW Integrating Shadows into an engine Types of Projective Shadows Static
Projective Shadows D. Sim Dietrich Jr. Topics Projective Shadow Types Implementation on DirectX 7 HW Implementation on DirectX8 HW Integrating Shadows into an engine Types of Projective Shadows Static
Bringing Hollywood to Real Time. Abe Wiley 3D Artist 3-D Application Research Group
 Bringing Hollywood to Real Time Abe Wiley 3D Artist 3-D Application Research Group Overview > Film Pipeline Overview and compare with Games > The RhinoFX/ATI Relationship > Ruby 1 and 2 The Movies > Breakdown
Bringing Hollywood to Real Time Abe Wiley 3D Artist 3-D Application Research Group Overview > Film Pipeline Overview and compare with Games > The RhinoFX/ATI Relationship > Ruby 1 and 2 The Movies > Breakdown
Tutorial on GPU Programming #2. Joong-Youn Lee Supercomputing Center, KISTI
 Tutorial on GPU Programming #2 Joong-Youn Lee Supercomputing Center, KISTI Contents Graphics Pipeline Vertex Programming Fragment Programming Introduction to Cg Language Graphics Pipeline The process to
Tutorial on GPU Programming #2 Joong-Youn Lee Supercomputing Center, KISTI Contents Graphics Pipeline Vertex Programming Fragment Programming Introduction to Cg Language Graphics Pipeline The process to
Texture Mapping. Michael Kazhdan ( /467) HB Ch. 14.8,14.9 FvDFH Ch. 16.3, , 16.6
 Texture Mapping Michael Kazhdan (61.457/467) HB Ch. 14.8,14.9 FvDFH Ch. 16.3, 16.4.5, 16.6 Textures We know how to go from this to this J. Birn Textures But what about this to this? J. Birn Textures How
Texture Mapping Michael Kazhdan (61.457/467) HB Ch. 14.8,14.9 FvDFH Ch. 16.3, 16.4.5, 16.6 Textures We know how to go from this to this J. Birn Textures But what about this to this? J. Birn Textures How
Mattan Erez. The University of Texas at Austin
 EE382V: Principles in Computer Architecture Parallelism and Locality Fall 2008 Lecture 10 The Graphics Processing Unit Mattan Erez The University of Texas at Austin Outline What is a GPU? Why should we
EE382V: Principles in Computer Architecture Parallelism and Locality Fall 2008 Lecture 10 The Graphics Processing Unit Mattan Erez The University of Texas at Austin Outline What is a GPU? Why should we
Real-Time Rendering (Echtzeitgraphik) Michael Wimmer
 Real-Time Rendering (Echtzeitgraphik) Michael Wimmer wimmer@cg.tuwien.ac.at Walking down the graphics pipeline Application Geometry Rasterizer What for? Understanding the rendering pipeline is the key
Real-Time Rendering (Echtzeitgraphik) Michael Wimmer wimmer@cg.tuwien.ac.at Walking down the graphics pipeline Application Geometry Rasterizer What for? Understanding the rendering pipeline is the key
Rendering Subdivision Surfaces Efficiently on the GPU
 Rendering Subdivision Surfaces Efficiently on the GPU Gy. Antal, L. Szirmay-Kalos and L. A. Jeni Department of Algorithms and their Applications, Faculty of Informatics, Eötvös Loránd Science University,
Rendering Subdivision Surfaces Efficiently on the GPU Gy. Antal, L. Szirmay-Kalos and L. A. Jeni Department of Algorithms and their Applications, Faculty of Informatics, Eötvös Loránd Science University,
AGDC Per-Pixel Shading. Sim Dietrich
 AGDC Per-Pixel Shading Sim Dietrich Goal Of This Talk The new features of Dx8 and the next generation of HW make huge strides in the area of Per-Pixel Shading Most developers have yet to adopt Per-Pixel
AGDC Per-Pixel Shading Sim Dietrich Goal Of This Talk The new features of Dx8 and the next generation of HW make huge strides in the area of Per-Pixel Shading Most developers have yet to adopt Per-Pixel
Wednesday, July 24, 13
 The Chase Pushing the Limits of Modern Mobile GPU Renaldas Zioma, Unity Technologies Ole Ciliox, Unity Technologies The Chase High-End Mobile Demo Built with off-the-shelf Unity 4.2 The Chase Goals Impressive
The Chase Pushing the Limits of Modern Mobile GPU Renaldas Zioma, Unity Technologies Ole Ciliox, Unity Technologies The Chase High-End Mobile Demo Built with off-the-shelf Unity 4.2 The Chase Goals Impressive
CS GPU and GPGPU Programming Lecture 3: GPU Architecture 2. Markus Hadwiger, KAUST
 CS 380 - GPU and GPGPU Programming Lecture 3: GPU Architecture 2 Markus Hadwiger, KAUST Reading Assignment #2 (until Feb. 9) Read (required): GLSL book, chapter 4 (The OpenGL Programmable Pipeline) GPU
CS 380 - GPU and GPGPU Programming Lecture 3: GPU Architecture 2 Markus Hadwiger, KAUST Reading Assignment #2 (until Feb. 9) Read (required): GLSL book, chapter 4 (The OpenGL Programmable Pipeline) GPU
Real - Time Rendering. Pipeline optimization. Michal Červeňanský Juraj Starinský
 Real - Time Rendering Pipeline optimization Michal Červeňanský Juraj Starinský Motivation Resolution 1600x1200, at 60 fps Hw power not enough Acceleration is still necessary 3.3.2010 2 Overview Application
Real - Time Rendering Pipeline optimization Michal Červeňanský Juraj Starinský Motivation Resolution 1600x1200, at 60 fps Hw power not enough Acceleration is still necessary 3.3.2010 2 Overview Application
Programmable GPUs. Real Time Graphics 11/13/2013. Nalu 2004 (NVIDIA Corporation) GeForce 6. Virtua Fighter 1995 (SEGA Corporation) NV1
 Programmable GPUs Real Time Graphics Virtua Fighter 1995 (SEGA Corporation) NV1 Dead or Alive 3 2001 (Tecmo Corporation) Xbox (NV2A) Nalu 2004 (NVIDIA Corporation) GeForce 6 Human Head 2006 (NVIDIA Corporation)
Programmable GPUs Real Time Graphics Virtua Fighter 1995 (SEGA Corporation) NV1 Dead or Alive 3 2001 (Tecmo Corporation) Xbox (NV2A) Nalu 2004 (NVIDIA Corporation) GeForce 6 Human Head 2006 (NVIDIA Corporation)
Sign up for crits! Announcments
 Sign up for crits! Announcments Reading for Next Week FvD 16.1-16.3 local lighting models GL 5 lighting GL 9 (skim) texture mapping Modern Game Techniques CS248 Lecture Nov 13 Andrew Adams Overview The
Sign up for crits! Announcments Reading for Next Week FvD 16.1-16.3 local lighting models GL 5 lighting GL 9 (skim) texture mapping Modern Game Techniques CS248 Lecture Nov 13 Andrew Adams Overview The
Programming Graphics Hardware
 Tutorial 5 Programming Graphics Hardware Randy Fernando, Mark Harris, Matthias Wloka, Cyril Zeller Overview of the Tutorial: Morning 8:30 9:30 10:15 10:45 Introduction to the Hardware Graphics Pipeline
Tutorial 5 Programming Graphics Hardware Randy Fernando, Mark Harris, Matthias Wloka, Cyril Zeller Overview of the Tutorial: Morning 8:30 9:30 10:15 10:45 Introduction to the Hardware Graphics Pipeline
Basics of GPU-Based Programming
 Module 1: Introduction to GPU-Based Methods Basics of GPU-Based Programming Overview Rendering pipeline on current GPUs Low-level languages Vertex programming Fragment programming High-level shading languages
Module 1: Introduction to GPU-Based Methods Basics of GPU-Based Programming Overview Rendering pipeline on current GPUs Low-level languages Vertex programming Fragment programming High-level shading languages
The GPGPU Programming Model
 The Programming Model Institute for Data Analysis and Visualization University of California, Davis Overview Data-parallel programming basics The GPU as a data-parallel computer Hello World Example Programming
The Programming Model Institute for Data Analysis and Visualization University of California, Davis Overview Data-parallel programming basics The GPU as a data-parallel computer Hello World Example Programming
Graphics Hardware. Instructor Stephen J. Guy
 Instructor Stephen J. Guy Overview What is a GPU Evolution of GPU GPU Design Modern Features Programmability! Programming Examples Overview What is a GPU Evolution of GPU GPU Design Modern Features Programmability!
Instructor Stephen J. Guy Overview What is a GPU Evolution of GPU GPU Design Modern Features Programmability! Programming Examples Overview What is a GPU Evolution of GPU GPU Design Modern Features Programmability!
Outline of Lecture. Real-Time High Quality Rendering. Geometry or Vertex Pipeline. Basic Hardware Pipeline. Pixel or Fragment Pipeline
 Real-Time High Quality Rendering CSE 274 [Fall 2015], Lecture 2 Graphics Hardware Pipeline, Reflection and Rendering Equations, Taonomy of Methods http://www.cs.ucsd.edu/~ravir Outline of Lecture Taonomy
Real-Time High Quality Rendering CSE 274 [Fall 2015], Lecture 2 Graphics Hardware Pipeline, Reflection and Rendering Equations, Taonomy of Methods http://www.cs.ucsd.edu/~ravir Outline of Lecture Taonomy
#Short presentation of the guys
 1 #Short presentation of the guys Let me introduce myself, I am Sébastien Lagarde and, together with my co-worker Antoine Zanuttini, we are part of a team currently working on a PC/XBOX360/PS3 game. For
1 #Short presentation of the guys Let me introduce myself, I am Sébastien Lagarde and, together with my co-worker Antoine Zanuttini, we are part of a team currently working on a PC/XBOX360/PS3 game. For
Module Contact: Dr Stephen Laycock, CMP Copyright of the University of East Anglia Version 1
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series PG Examination 2013-14 COMPUTER GAMES DEVELOPMENT CMPSME27 Time allowed: 2 hours Answer any THREE questions. (40 marks each) Notes are
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Computing Sciences Main Series PG Examination 2013-14 COMPUTER GAMES DEVELOPMENT CMPSME27 Time allowed: 2 hours Answer any THREE questions. (40 marks each) Notes are
INF3320 Computer Graphics and Discrete Geometry
 INF3320 Computer Graphics and Discrete Geometry Texturing Christopher Dyken Martin Reimers 06.10.2010 Page 1 Texturing Linear interpolation Real Time Rendering: Chapter 5: Visual Appearance Chapter 6:
INF3320 Computer Graphics and Discrete Geometry Texturing Christopher Dyken Martin Reimers 06.10.2010 Page 1 Texturing Linear interpolation Real Time Rendering: Chapter 5: Visual Appearance Chapter 6:
Last Time. Why are Shadows Important? Today. Graphics Pipeline. Clipping. Rasterization. Why are Shadows Important?
 Last Time Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Real-Time Shadows Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Graphics Pipeline Clipping Rasterization
Last Time Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Real-Time Shadows Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Graphics Pipeline Clipping Rasterization
High-quality Shadows with Improved Paraboloid Mapping
 High-quality Shadows with Improved Paraboloid Mapping Juraj Vanek, Jan Navrátil, Adam Herout, and Pavel Zemčík Brno University of Technology, Faculty of Information Technology, Czech Republic http://www.fit.vutbr.cz
High-quality Shadows with Improved Paraboloid Mapping Juraj Vanek, Jan Navrátil, Adam Herout, and Pavel Zemčík Brno University of Technology, Faculty of Information Technology, Czech Republic http://www.fit.vutbr.cz
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 10: Soft Shadows (Maps and Volumes), Normal and Bump Mapping
 Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 10: Soft Shadows (Maps and Volumes), Normal and Bump Mapping Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Shadow Buffer Theory Observation:
Computer Graphics (CS 543) Lecture 10: Soft Shadows (Maps and Volumes), Normal and Bump Mapping Prof Emmanuel Agu Computer Science Dept. Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) Shadow Buffer Theory Observation:
Optimizing for DirectX Graphics. Richard Huddy European Developer Relations Manager
 Optimizing for DirectX Graphics Richard Huddy European Developer Relations Manager Also on today from ATI... Start & End Time: 12:00pm 1:00pm Title: Precomputed Radiance Transfer and Spherical Harmonic
Optimizing for DirectX Graphics Richard Huddy European Developer Relations Manager Also on today from ATI... Start & End Time: 12:00pm 1:00pm Title: Precomputed Radiance Transfer and Spherical Harmonic
Today. Global illumination. Shading. Interactive applications. Rendering pipeline. Computergrafik. Shading Introduction Local shading models
 Computergrafik Thomas Buchberger, Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2008 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation
Computergrafik Thomas Buchberger, Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2008 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation
Shadow Techniques. Sim Dietrich NVIDIA Corporation
 Shadow Techniques Sim Dietrich NVIDIA Corporation sim.dietrich@nvidia.com Lighting & Shadows The shadowing solution you choose can greatly influence the engine decisions you make This talk will outline
Shadow Techniques Sim Dietrich NVIDIA Corporation sim.dietrich@nvidia.com Lighting & Shadows The shadowing solution you choose can greatly influence the engine decisions you make This talk will outline
Shadow Rendering EDA101 Advanced Shading and Rendering
 Shadow Rendering EDA101 Advanced Shading and Rendering 2006 Tomas Akenine-Möller 1 Why, oh why? (1) Shadows provide cues about spatial relationships among objects 2006 Tomas Akenine-Möller 2 Why, oh why?
Shadow Rendering EDA101 Advanced Shading and Rendering 2006 Tomas Akenine-Möller 1 Why, oh why? (1) Shadows provide cues about spatial relationships among objects 2006 Tomas Akenine-Möller 2 Why, oh why?
For Intuition about Scene Lighting. Today. Limitations of Planar Shadows. Cast Shadows on Planar Surfaces. Shadow/View Duality.
 Last Time Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Real-Time Shadows Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Graphics Pipeline Clipping Rasterization
Last Time Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Real-Time Shadows Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Graphics Pipeline Clipping Rasterization
#Short presentation of the guys
 1 #Short presentation of the guys Let me introduce myself, I am Sébastien Lagarde and, together with my co-worker Antoine Zanuttini, we are part of a team currently working on Remember me, the new Capcom
1 #Short presentation of the guys Let me introduce myself, I am Sébastien Lagarde and, together with my co-worker Antoine Zanuttini, we are part of a team currently working on Remember me, the new Capcom
Canonical Shaders for Optimal Performance. Sébastien Dominé Manager of Developer Technology Tools
 Canonical Shaders for Optimal Performance Sébastien Dominé Manager of Developer Technology Tools Agenda Introduction FX Composer 1.0 High Performance Shaders Basics Vertex versus Pixel Talk to your compiler
Canonical Shaders for Optimal Performance Sébastien Dominé Manager of Developer Technology Tools Agenda Introduction FX Composer 1.0 High Performance Shaders Basics Vertex versus Pixel Talk to your compiler
Rendering Algorithms: Real-time indirect illumination. Spring 2010 Matthias Zwicker
 Rendering Algorithms: Real-time indirect illumination Spring 2010 Matthias Zwicker Today Real-time indirect illumination Ray tracing vs. Rasterization Screen space techniques Visibility & shadows Instant
Rendering Algorithms: Real-time indirect illumination Spring 2010 Matthias Zwicker Today Real-time indirect illumination Ray tracing vs. Rasterization Screen space techniques Visibility & shadows Instant
CS GPU and GPGPU Programming Lecture 11: GPU Texturing 1. Markus Hadwiger, KAUST
 CS 380 - GPU and GPGPU Programming Lecture 11: GPU Texturing 1 Markus Hadwiger, KAUST Reading Assignment #6 (until Mar. 9) Read (required): Programming Massively Parallel Processors book, Chapter 4 (CUDA
CS 380 - GPU and GPGPU Programming Lecture 11: GPU Texturing 1 Markus Hadwiger, KAUST Reading Assignment #6 (until Mar. 9) Read (required): Programming Massively Parallel Processors book, Chapter 4 (CUDA
28 SAMPLING. ALIASING AND ANTI-ALIASING
 28 SAMPLING. ALIASING AND ANTI-ALIASING Textbook: 16 UGRAD.CS.UBC.CA/~CS314 Alla Sheffer, 2016 ALIASING & ANTI-ALIASING Adobe, inc., https://helpx.adobe.com/photoshop/key concepts/aliasing anti aliasing.html
28 SAMPLING. ALIASING AND ANTI-ALIASING Textbook: 16 UGRAD.CS.UBC.CA/~CS314 Alla Sheffer, 2016 ALIASING & ANTI-ALIASING Adobe, inc., https://helpx.adobe.com/photoshop/key concepts/aliasing anti aliasing.html
DirectX Programming #4. Kang, Seongtae Computer Graphics, 2009 Spring
 DirectX Programming #4 Kang, Seongtae Computer Graphics, 2009 Spring Programmable Shader For recent hardwares, vertex and pixel processing stage of the graphics pipeline is programmable Programmable Vertex
DirectX Programming #4 Kang, Seongtae Computer Graphics, 2009 Spring Programmable Shader For recent hardwares, vertex and pixel processing stage of the graphics pipeline is programmable Programmable Vertex
Point-Based rendering on GPU hardware. Advanced Computer Graphics 2008
 Point-Based rendering on GPU hardware Advanced Computer Graphics 2008 Outline Why use the GPU? Splat rasterization Image-aligned squares Perspective correct rasterization Splat shading Flat shading Gouroud
Point-Based rendering on GPU hardware Advanced Computer Graphics 2008 Outline Why use the GPU? Splat rasterization Image-aligned squares Perspective correct rasterization Splat shading Flat shading Gouroud
Lecture 9: Deferred Shading. Visual Computing Systems CMU , Fall 2013
 Lecture 9: Deferred Shading Visual Computing Systems The course so far The real-time graphics pipeline abstraction Principle graphics abstractions Algorithms and modern high performance implementations
Lecture 9: Deferred Shading Visual Computing Systems The course so far The real-time graphics pipeline abstraction Principle graphics abstractions Algorithms and modern high performance implementations
Graphics Hardware. Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) is a Subsidiary hardware. With massively multi-threaded many-core. Dedicated to 2D and 3D graphics
 Why GPU? Chapter 1 Graphics Hardware Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) is a Subsidiary hardware With massively multi-threaded many-core Dedicated to 2D and 3D graphics Special purpose low functionality, high
Why GPU? Chapter 1 Graphics Hardware Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) is a Subsidiary hardware With massively multi-threaded many-core Dedicated to 2D and 3D graphics Special purpose low functionality, high
GPU Memory Model. Adapted from:
 GPU Memory Model Adapted from: Aaron Lefohn University of California, Davis With updates from slides by Suresh Venkatasubramanian, University of Pennsylvania Updates performed by Gary J. Katz, University
GPU Memory Model Adapted from: Aaron Lefohn University of California, Davis With updates from slides by Suresh Venkatasubramanian, University of Pennsylvania Updates performed by Gary J. Katz, University
A Trip Down The (2011) Rasterization Pipeline
 A Trip Down The (2011) Rasterization Pipeline Aaron Lefohn - Intel / University of Washington Mike Houston AMD / Stanford 1 This talk Overview of the real-time rendering pipeline available in ~2011 corresponding
A Trip Down The (2011) Rasterization Pipeline Aaron Lefohn - Intel / University of Washington Mike Houston AMD / Stanford 1 This talk Overview of the real-time rendering pipeline available in ~2011 corresponding
https://ilearn.marist.edu/xsl-portal/tool/d4e4fd3a-a3...
 Assessment Preview - This is an example student view of this assessment done Exam 2 Part 1 of 5 - Modern Graphics Pipeline Question 1 of 27 Match each stage in the graphics pipeline with a description
Assessment Preview - This is an example student view of this assessment done Exam 2 Part 1 of 5 - Modern Graphics Pipeline Question 1 of 27 Match each stage in the graphics pipeline with a description
Today. Global illumination. Shading. Interactive applications. Rendering pipeline. Computergrafik. Shading Introduction Local shading models
 Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2009 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation of physics Global
Computergrafik Matthias Zwicker Universität Bern Herbst 2009 Today Introduction Local shading models Light sources strategies Compute interaction of light with surfaces Requires simulation of physics Global
Last Time. Reading for Today: Graphics Pipeline. Clipping. Rasterization
 Last Time Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Real-Time Shadows Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Scan Conversion (Rasterization) Visibility
Last Time Modeling Transformations Illumination (Shading) Real-Time Shadows Viewing Transformation (Perspective / Orthographic) Clipping Projection (to Screen Space) Scan Conversion (Rasterization) Visibility
rendering rasterization based rendering pipelined architecture, parallel mostly triangles (lines and points possible too)
 Rendering Scena 3D rendering Immagine screen buffer ( array 2D di pixel ) Rendering in games Real-time (20 or) 30 or 60 FPS Algorithm: rasterization based rendering Hardware based pipelined architecture,
Rendering Scena 3D rendering Immagine screen buffer ( array 2D di pixel ) Rendering in games Real-time (20 or) 30 or 60 FPS Algorithm: rasterization based rendering Hardware based pipelined architecture,
The Rasterization Pipeline
 Lecture 5: The Rasterization Pipeline (and its implementation on GPUs) Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Fall 2015 What you know how to do (at this point in the course) y y z x (w, h) z x Position objects
Lecture 5: The Rasterization Pipeline (and its implementation on GPUs) Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Fall 2015 What you know how to do (at this point in the course) y y z x (w, h) z x Position objects
Graphics Processing Unit Architecture (GPU Arch)
 Graphics Processing Unit Architecture (GPU Arch) With a focus on NVIDIA GeForce 6800 GPU 1 What is a GPU From Wikipedia : A specialized processor efficient at manipulating and displaying computer graphics
Graphics Processing Unit Architecture (GPU Arch) With a focus on NVIDIA GeForce 6800 GPU 1 What is a GPU From Wikipedia : A specialized processor efficient at manipulating and displaying computer graphics
CS GPU and GPGPU Programming Lecture 12: GPU Texturing 1. Markus Hadwiger, KAUST
 CS 380 - GPU and GPGPU Programming Lecture 12: GPU Texturing 1 Markus Hadwiger, KAUST Reading Assignment #6 (until Mar. 17) Read (required): Programming Massively Parallel Processors book, Chapter 4 (CUDA
CS 380 - GPU and GPGPU Programming Lecture 12: GPU Texturing 1 Markus Hadwiger, KAUST Reading Assignment #6 (until Mar. 17) Read (required): Programming Massively Parallel Processors book, Chapter 4 (CUDA
Interactive Cloth Simulation. Matthias Wloka NVIDIA Corporation
 Interactive Cloth Simulation Matthias Wloka NVIDIA Corporation MWloka@nvidia.com Overview Higher-order surfaces Vertex-shader deformations Lighting modes Per-vertex diffuse Per-pixel diffuse with bump-map
Interactive Cloth Simulation Matthias Wloka NVIDIA Corporation MWloka@nvidia.com Overview Higher-order surfaces Vertex-shader deformations Lighting modes Per-vertex diffuse Per-pixel diffuse with bump-map
Optimal Shaders Using High-Level Languages
 Optimal Shaders Using High-Level Languages The Good, The Bad, The Ugly All high level languages provide significant power and flexibility that: Make writing shaders easy Make writing slow shaders easy
Optimal Shaders Using High-Level Languages The Good, The Bad, The Ugly All high level languages provide significant power and flexibility that: Make writing shaders easy Make writing slow shaders easy
Rasterization and Graphics Hardware. Not just about fancy 3D! Rendering/Rasterization. The simplest case: Points. When do we care?
 Where does a picture come from? Rasterization and Graphics Hardware CS559 Course Notes Not for Projection November 2007, Mike Gleicher Result: image (raster) Input 2D/3D model of the world Rendering term
Where does a picture come from? Rasterization and Graphics Hardware CS559 Course Notes Not for Projection November 2007, Mike Gleicher Result: image (raster) Input 2D/3D model of the world Rendering term
Ruby: Dangerous Curves Effects Breakdown: How d they do that? Dan Ginsburg 3D Application Research Group
 Ruby: Dangerous Curves Effects Breakdown: How d they do that? Dan Ginsburg 3D Application Research Group Overview > RhinoFX/ATI relationship > Ruby shot-by-shot breakdown > Glows > Motion Blur > Reflections
Ruby: Dangerous Curves Effects Breakdown: How d they do that? Dan Ginsburg 3D Application Research Group Overview > RhinoFX/ATI relationship > Ruby shot-by-shot breakdown > Glows > Motion Blur > Reflections
Texture Mapping and Sampling
 Texture Mapping and Sampling CPSC 314 Wolfgang Heidrich The Rendering Pipeline Geometry Processing Geometry Database Model/View Transform. Lighting Perspective Transform. Clipping Scan Conversion Depth
Texture Mapping and Sampling CPSC 314 Wolfgang Heidrich The Rendering Pipeline Geometry Processing Geometry Database Model/View Transform. Lighting Perspective Transform. Clipping Scan Conversion Depth
Texturing Theory. Overview. All it takes is for the rendered image to look right. -Jim Blinn 11/10/2018
 References: Real-Time Rendering 3 rd Edition Chapter 6 Texturing Theory All it takes is for the rendered image to look right. -Jim Blinn Overview Introduction The Texturing Pipeline Example The Projector
References: Real-Time Rendering 3 rd Edition Chapter 6 Texturing Theory All it takes is for the rendered image to look right. -Jim Blinn Overview Introduction The Texturing Pipeline Example The Projector
Shaders in Eve Online Páll Ragnar Pálsson
 Shaders in Eve Online Páll Ragnar Pálsson EVE Online Eve Online Trinity First released 2003 Proprietary graphics engine DirectX 9 (DX11 on its way) Shader Model 3 (4 & 5 in development) HLSL Turning this
Shaders in Eve Online Páll Ragnar Pálsson EVE Online Eve Online Trinity First released 2003 Proprietary graphics engine DirectX 9 (DX11 on its way) Shader Model 3 (4 & 5 in development) HLSL Turning this
CS GPU and GPGPU Programming Lecture 3: GPU Architecture 2. Markus Hadwiger, KAUST
 CS 380 - GPU and GPGPU Programming Lecture 3: GPU Architecture 2 Markus Hadwiger, KAUST Reading Assignment #2 (until Feb. 17) Read (required): GLSL book, chapter 4 (The OpenGL Programmable Pipeline) GPU
CS 380 - GPU and GPGPU Programming Lecture 3: GPU Architecture 2 Markus Hadwiger, KAUST Reading Assignment #2 (until Feb. 17) Read (required): GLSL book, chapter 4 (The OpenGL Programmable Pipeline) GPU
Reading. 18. Projections and Z-buffers. Required: Watt, Section , 6.3, 6.6 (esp. intro and subsections 1, 4, and 8 10), Further reading:
 Reading Required: Watt, Section 5.2.2 5.2.4, 6.3, 6.6 (esp. intro and subsections 1, 4, and 8 10), Further reading: 18. Projections and Z-buffers Foley, et al, Chapter 5.6 and Chapter 6 David F. Rogers
Reading Required: Watt, Section 5.2.2 5.2.4, 6.3, 6.6 (esp. intro and subsections 1, 4, and 8 10), Further reading: 18. Projections and Z-buffers Foley, et al, Chapter 5.6 and Chapter 6 David F. Rogers
Introduction Rasterization Z-buffering Shading. Graphics 2012/2013, 4th quarter. Lecture 09: graphics pipeline (rasterization and shading)
 Lecture 9 Graphics pipeline (rasterization and shading) Graphics pipeline - part 1 (recap) Perspective projection by matrix multiplication: x pixel y pixel z canonical 1 x = M vpm per M cam y z 1 This
Lecture 9 Graphics pipeline (rasterization and shading) Graphics pipeline - part 1 (recap) Perspective projection by matrix multiplication: x pixel y pixel z canonical 1 x = M vpm per M cam y z 1 This
Fast Third-Order Texture Filtering
 Chapter 20 Fast Third-Order Texture Filtering Christian Sigg ETH Zurich Markus Hadwiger VRVis Research Center Current programmable graphics hardware makes it possible to implement general convolution filters
Chapter 20 Fast Third-Order Texture Filtering Christian Sigg ETH Zurich Markus Hadwiger VRVis Research Center Current programmable graphics hardware makes it possible to implement general convolution filters
CMSC427 Advanced shading getting global illumination by local methods. Credit: slides Prof. Zwicker
 CMSC427 Advanced shading getting global illumination by local methods Credit: slides Prof. Zwicker Topics Shadows Environment maps Reflection mapping Irradiance environment maps Ambient occlusion Reflection
CMSC427 Advanced shading getting global illumination by local methods Credit: slides Prof. Zwicker Topics Shadows Environment maps Reflection mapping Irradiance environment maps Ambient occlusion Reflection
Advanced Shading and Texturing
 Real-Time Graphics Architecture Kurt Akeley Pat Hanrahan http://www.graphics.stanford.edu/courses/cs448a-01-fall Advanced Shading and Texturing 1 Topics Features Bump mapping Environment mapping Shadow
Real-Time Graphics Architecture Kurt Akeley Pat Hanrahan http://www.graphics.stanford.edu/courses/cs448a-01-fall Advanced Shading and Texturing 1 Topics Features Bump mapping Environment mapping Shadow
2D rendering takes a photo of the 2D scene with a virtual camera that selects an axis aligned rectangle from the scene. The photograph is placed into
 2D rendering takes a photo of the 2D scene with a virtual camera that selects an axis aligned rectangle from the scene. The photograph is placed into the viewport of the current application window. A pixel
2D rendering takes a photo of the 2D scene with a virtual camera that selects an axis aligned rectangle from the scene. The photograph is placed into the viewport of the current application window. A pixel
A GPU Accelerated Spring Mass System for Surgical Simulation
 A GPU Accelerated Spring Mass System for Surgical Simulation Jesper MOSEGAARD #, Peder HERBORG, and Thomas Sangild SØRENSEN # Department of Computer Science, Centre for Advanced Visualization and Interaction,
A GPU Accelerated Spring Mass System for Surgical Simulation Jesper MOSEGAARD #, Peder HERBORG, and Thomas Sangild SØRENSEN # Department of Computer Science, Centre for Advanced Visualization and Interaction,
Interactive Rendering of Globally Illuminated Glossy Scenes
 Interactive Rendering of Globally Illuminated Glossy Scenes Wolfgang Stürzlinger, Rui Bastos Dept. of Computer Science, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill {stuerzl bastos}@cs.unc.edu Abstract.
Interactive Rendering of Globally Illuminated Glossy Scenes Wolfgang Stürzlinger, Rui Bastos Dept. of Computer Science, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill {stuerzl bastos}@cs.unc.edu Abstract.
Computer Graphics. Shadows
 Computer Graphics Lecture 10 Shadows Taku Komura Today Shadows Overview Projective shadows Shadow texture Shadow volume Shadow map Soft shadows Why Shadows? Shadows tell us about the relative locations
Computer Graphics Lecture 10 Shadows Taku Komura Today Shadows Overview Projective shadows Shadow texture Shadow volume Shadow map Soft shadows Why Shadows? Shadows tell us about the relative locations
CS GPU and GPGPU Programming Lecture 16+17: GPU Texturing 1+2. Markus Hadwiger, KAUST
 CS 380 - GPU and GPGPU Programming Lecture 16+17: GPU Texturing 1+2 Markus Hadwiger, KAUST Reading Assignment #10 (until April 23) Read (required): Brook for GPUs: Stream Computing on Graphics Hardware
CS 380 - GPU and GPGPU Programming Lecture 16+17: GPU Texturing 1+2 Markus Hadwiger, KAUST Reading Assignment #10 (until April 23) Read (required): Brook for GPUs: Stream Computing on Graphics Hardware
Reading. 12. Texture Mapping. Texture mapping. Non-parametric texture mapping. Required. w Watt, intro to Chapter 8 and intros to 8.1, 8.4, 8.6, 8.8.
 Reading Required Watt, intro to Chapter 8 and intros to 8.1, 8.4, 8.6, 8.8. Optional 12. Texture Mapping Watt, the rest of Chapter 8 Woo, Neider, & Davis, Chapter 9 James F. Blinn and Martin E. Neell.
Reading Required Watt, intro to Chapter 8 and intros to 8.1, 8.4, 8.6, 8.8. Optional 12. Texture Mapping Watt, the rest of Chapter 8 Woo, Neider, & Davis, Chapter 9 James F. Blinn and Martin E. Neell.
Texture Mapping. CS 537 Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science
 Texture Mapping CS 537 Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science 1 Objectives Introduce Mapping Methods - Texture Mapping - Environment Mapping - Bump Mapping Consider
Texture Mapping CS 537 Interactive Computer Graphics Prof. David E. Breen Department of Computer Science 1 Objectives Introduce Mapping Methods - Texture Mapping - Environment Mapping - Bump Mapping Consider
AMCS / CS 247 Scientific Visualization Lecture 10: (GPU) Texture Mapping. Markus Hadwiger, KAUST
 AMCS / CS 247 Scientific Visualization Lecture 10: (GPU) Texture Mapping Markus Hadwiger, KAUST Reading Assignment #5 (until Oct. 8) Read (required): Real-Time Volume Graphics, Chapter 2 (GPU Programming)
AMCS / CS 247 Scientific Visualization Lecture 10: (GPU) Texture Mapping Markus Hadwiger, KAUST Reading Assignment #5 (until Oct. 8) Read (required): Real-Time Volume Graphics, Chapter 2 (GPU Programming)
- Rasterization. Geometry. Scan Conversion. Rasterization
 Computer Graphics - The graphics pipeline - Geometry Modelview Geometry Processing Lighting Perspective Clipping Scan Conversion Texturing Fragment Tests Blending Framebuffer Fragment Processing - So far,
Computer Graphics - The graphics pipeline - Geometry Modelview Geometry Processing Lighting Perspective Clipping Scan Conversion Texturing Fragment Tests Blending Framebuffer Fragment Processing - So far,
There have been many debates in the past about whether eight bits of resolution
 08 SHADERS CH08 4/19/04 11:05 AM Page 133 chapter 8 Making Your Day Brighter There have been many debates in the past about whether eight bits of resolution per color component are enough to represent
08 SHADERS CH08 4/19/04 11:05 AM Page 133 chapter 8 Making Your Day Brighter There have been many debates in the past about whether eight bits of resolution per color component are enough to represent
Introduction to Visualization and Computer Graphics
 Introduction to Visualization and Computer Graphics DH2320, Fall 2015 Prof. Dr. Tino Weinkauf Introduction to Visualization and Computer Graphics Visibility Shading 3D Rendering Geometric Model Color Perspective
Introduction to Visualization and Computer Graphics DH2320, Fall 2015 Prof. Dr. Tino Weinkauf Introduction to Visualization and Computer Graphics Visibility Shading 3D Rendering Geometric Model Color Perspective
OpenGl Pipeline. triangles, lines, points, images. Per-vertex ops. Primitive assembly. Texturing. Rasterization. Per-fragment ops.
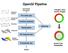 OpenGl Pipeline Individual Vertices Transformed Vertices Commands Processor Per-vertex ops Primitive assembly triangles, lines, points, images Primitives Fragments Rasterization Texturing Per-fragment
OpenGl Pipeline Individual Vertices Transformed Vertices Commands Processor Per-vertex ops Primitive assembly triangles, lines, points, images Primitives Fragments Rasterization Texturing Per-fragment
12.2 Programmable Graphics Hardware
 Fall 2018 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 12.2 Programmable Graphics Hardware Kyle Morgenroth http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 Introduction Recent major advance in real time graphics is the programmable pipeline:
Fall 2018 CSCI 420: Computer Graphics 12.2 Programmable Graphics Hardware Kyle Morgenroth http://cs420.hao-li.com 1 Introduction Recent major advance in real time graphics is the programmable pipeline:
Persistent Background Effects for Realtime Applications Greg Lane, April 2009
 Persistent Background Effects for Realtime Applications Greg Lane, April 2009 0. Abstract This paper outlines the general use of the GPU interface defined in shader languages, for the design of large-scale
Persistent Background Effects for Realtime Applications Greg Lane, April 2009 0. Abstract This paper outlines the general use of the GPU interface defined in shader languages, for the design of large-scale
Interactive Methods in Scientific Visualization
 Interactive Methods in Scientific Visualization GPU Volume Raycasting Christof Rezk-Salama University of Siegen, Germany Volume Rendering in a Nutshell Image Plane Eye Data Set Back-to-front iteration
Interactive Methods in Scientific Visualization GPU Volume Raycasting Christof Rezk-Salama University of Siegen, Germany Volume Rendering in a Nutshell Image Plane Eye Data Set Back-to-front iteration
Order Independent Transparency with Dual Depth Peeling. Louis Bavoil, Kevin Myers
 Order Independent Transparency with Dual Depth Peeling Louis Bavoil, Kevin Myers Document Change History Version Date Responsible Reason for Change 1.0 February 9 2008 Louis Bavoil Initial release Abstract
Order Independent Transparency with Dual Depth Peeling Louis Bavoil, Kevin Myers Document Change History Version Date Responsible Reason for Change 1.0 February 9 2008 Louis Bavoil Initial release Abstract
Whitepaper. Integrating Realistic Soft Shadows into Your Game Engine. Kevin Myers Randima (Randy) Fernando Louis Bavoil
 Whitepaper Integrating Realistic Soft Shadows into Your Game Engine Kevin Myers Randima (Randy) Fernando Louis Bavoil Version 1.0 - February 2008 Integrating Realistic Soft Shadows Into Your Game Engine
Whitepaper Integrating Realistic Soft Shadows into Your Game Engine Kevin Myers Randima (Randy) Fernando Louis Bavoil Version 1.0 - February 2008 Integrating Realistic Soft Shadows Into Your Game Engine
Evolution of GPUs Chris Seitz
 Evolution of GPUs Chris Seitz Overview Concepts: Real-time rendering Hardware graphics pipeline Evolution of the PC hardware graphics pipeline: 1995-1998: Texture mapping and z-buffer 1998: Multitexturing
Evolution of GPUs Chris Seitz Overview Concepts: Real-time rendering Hardware graphics pipeline Evolution of the PC hardware graphics pipeline: 1995-1998: Texture mapping and z-buffer 1998: Multitexturing
Real - Time Rendering. Graphics pipeline. Michal Červeňanský Juraj Starinský
 Real - Time Rendering Graphics pipeline Michal Červeňanský Juraj Starinský Overview History of Graphics HW Rendering pipeline Shaders Debugging 2 History of Graphics HW First generation Second generation
Real - Time Rendering Graphics pipeline Michal Červeňanský Juraj Starinský Overview History of Graphics HW Rendering pipeline Shaders Debugging 2 History of Graphics HW First generation Second generation
Per-Face Texture Mapping for Realtime Rendering. Realtime Ptex
 Per-Face Texture Mapping for Realtime Rendering Realtime Ptex Quick Note For CUDA/Compute folks: Ptex!= PTX Goals Render native Ptex datasets in real-time on commodity hardware Remove texture seams from
Per-Face Texture Mapping for Realtime Rendering Realtime Ptex Quick Note For CUDA/Compute folks: Ptex!= PTX Goals Render native Ptex datasets in real-time on commodity hardware Remove texture seams from
Levy: Constraint Texture Mapping, SIGGRAPH, CS 148, Summer 2012 Introduction to Computer Graphics and Imaging Justin Solomon
 Levy: Constraint Texture Mapping, SIGGRAPH, 2001 CS 148, Summer 2012 Introduction to Computer Graphics and Imaging Justin Solomon Instructor: Justin Solomon Email: justin.solomon@stanford.edu Office: Clark
Levy: Constraint Texture Mapping, SIGGRAPH, 2001 CS 148, Summer 2012 Introduction to Computer Graphics and Imaging Justin Solomon Instructor: Justin Solomon Email: justin.solomon@stanford.edu Office: Clark
Lab 3 Shadow Mapping. Giuseppe Maggiore
 Lab 3 Shadow Giuseppe Maggiore Adding Shadows to the Scene First we need to declare a very useful helper object that will allow us to draw textures to the screen without creating a quad vertex buffer //
Lab 3 Shadow Giuseppe Maggiore Adding Shadows to the Scene First we need to declare a very useful helper object that will allow us to draw textures to the screen without creating a quad vertex buffer //
