Guidance note Geometry geometrical reasoning
|
|
|
- Peter James
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 of 7 The National Strategies Secondary Guidance note Geometry geometrical reasoning This material has been written to support a mathematics teacher in a mainstream classroom. The context is a geometry unit which might address some or all of these objectives: know that if two 2-D shapes are congruent, corresponding sides and angles are equal (Y8) solve geometrical problems using side and angle properties of equilateral, isosceles and rightangled triangles and special quadrilaterals, explaining reasoning with diagrams and text; classify quadrilaterals by their geometrical properties (Y8) All pupils have an entitlement to explore these ideas. Pupils working at level 3 and below can access these relatively sophisticated concepts and make links between them if they are given the resources and activities to support their thinking and developing understanding. Possible barriers to progress can be tackled using approaches such as those described below. These materials offer a starting point and are not the only way to address the difficulties highlighted here. Teachers know their pupils and will bring to these suggestions their own ideas and creative approaches. The guidance is presented in a consistent format, describing the potential barrier to progress, and then offering ideas for teaching and questions which can support the suggested pupil activities and opportunities for mathematical talk. Finally, supporting resources are listed and a range of relevant assessment criteria is shown. It should be noted that where primary resources and support are referenced content will need to be adapted to ensure age-appropriateness.
2 2 of 7 The National Strategies Secondary Geometry and measures objective Possible barrier know that if two 2-D shapes are congruent, corresponding sides and angles are equal (Y8) Pupils do not understand that an angle is a dynamic measurement of turn and is not a shape. Teaching ideas and questions For a useful starter activity to encourage communication of both positional and directional movement ask pupils: If I move this object like this, how could I describe the movement to a friend on the telephone so they could copy the movement? Discuss the concept of turning through an angle, raised through questions such as: Where do you see things that turn? Choose one of these and tell me about the angles through which it turns. How could we measure the amount of turn? What units do we use for measuring turns? What equipment might we use? Pupil activities and opportunities for mathematical talk Ask pupils to copy a movement that includes at least one turn. Repeat with different types of movement to explore the vocabulary that pupils know. Provide instructions to pupils to move from point A to point B in the classroom, including turning through given angles to emphasise the dynamic nature of angles. For example: Go from your desk to the desk nearest the door by turning through 90 clockwise and Encourage pupils to use other angles to estimate turning through angles, such as 60, 45, 20, and then illustrate their estimation process with diagrams. A clock face provides a useful context for such turns. Ensure that pupils know how to use tracing paper effectively to make angle comparisons and estimates.
3 3 of 7 The National Strategies Secondary Supporting references/resources Use practical resources wherever possible. In particular, when working on angle topics, allow pupils to walk through the angles before trying to represent anything on paper. geoboards square and triangular dotty paper a right angle checker (made by pupils themselves) matching, sorting activities for shapes, such as bingo or lotto tracing paper programmable toys, computer simulations and games The Nrich site includes a free-to-use virtual geoboard. The Interactive Teaching Program (ITP) Calculating angles is available from the National Strategies website; search for the ITP by title. L1 measure and order objects using direct comparison L2 distinguish between straight and turning movements, recognise right angles in turns and understand angle as a measurement of turn
4 4 of 7 The National Strategies Secondary Geometry and measures objective solve geometrical problems using side and angle properties of equilateral, isosceles and right-angled triangles and special quadrilaterals, explaining reasoning with diagrams and text (Y8) Possible barrier Pupils do not recognise angles greater and less than 90. Teaching ideas and questions Ask pupils: Show me a right angle in the classroom or made with your body. Turn through an angle of 90. How do you know that the angle you have turned is 90? Turn through an angle greater than 90 and one less than 90. Which of your turns was larger? How do you know? Convince me that you need to turn through two right angles in order to face the opposite direction. Show a shape on a geoboard and ask: How can you change this shape so that it has a right angle? Make a shape of your own with two right angles. Show pupils a map and ask: Show me an example of the compass directions you could use to get from to. Give different instructions for the same movement. Pupil activities and opportunities for mathematical talk Ask pupils to turn through a right, acute or obtuse angle, and then to try to draw the movement they have made. Invite pupils to choose, from a collection of shapes, a shape with one right angle, two acute angles, etc. Demonstrate the comparison with right angles (that is, greater than or less than a right angle) for each angle they identify. Use the always/sometimes/never true strategy to explore statements such as: a triangle can have an obtuse angle. a triangle cannot have two obtuse angles.
5 5 of 7 The National Strategies Secondary Supporting references/resources geostrips geoboards square and triangular dotty paper corners of everyday objects a right angle checker (made by pupils themselves) matching, sorting activities for shapes, such as bingo or lotto. tracing paper The Nrich site includes a free-to-use virtual geoboard. The Interactive Teaching Program (ITP) Calculating angles is available from the National Strategies website; search for the ITP by title. L1 L1 L2 recognise and use a simple pattern or relationship use everyday language to describe properties of 2-D and 3-D shapes distinguish between straight and turning movements, recognise right angles in turns and understand angle as a measurement of turn
6 6 of 7 The National Strategies Secondary Geometry and measures objective Possible barrier solve geometrical problems using side and angle properties of equilateral, isosceles and right-angled triangles and special quadrilaterals, explaining reasoning with diagrams and text; classify quadrilaterals by their geometrical properties (Y8) Pupils find it hard to identify and talk about properties of shapes. Teaching ideas and questions With a selection of 2-D shapes available, ask the following questions: Show me a 2-D shape with three sides (or straight sides, a curved side, corners). Convince me that a shape with three sides has three corners. Show me a triangle/quadrilateral and another triangle/quadrilateral. Why is this a triangle/quadrilateral? What is the same/different about (diagrams of) these two triangles/quadrilaterals? Is this statement always, sometimes or never true? A shape with three sides has three corners. A shape with four straight sides is a square. A triangle has a right angle. A triangle has an obtuse angle. Ask pupils to consider what happens to the properties of shapes when the shapes are reflected: What looks the same and what looks different? Is this statement always, sometimes or never true? Rotated shapes are the same size and shape as the original shape. Reflected shapes are the same size and shape as the original shape. Pupil activities and opportunities for mathematical talk Make use of the vocabulary of shape properties, such as types of angle, sides, vertices, straight, parallel, when describing shapes. Encourage pupils to use appropriate mathematical vocabulary to support their communication of reasoning about shapes. Invite pupils to identify properties and support them in recording the properties of particular shapes. Give pupils a range of simple 2-D shapes and ask them to sort them into different piles. Allow them to classify the shapes according to their own classification. Ask them to explain why they have put shapes together in particular groups. Ask what properties they used to help them decide. Get pupils to make up sets of different sized squares, circles, similar triangles, etc. to compare in order to illustrate that angle properties of shapes stay the same when a shape is enlarged.
7 7 of 7 The National Strategies Secondary Supporting references/resources Paper folding is a useful strategy for generating a variety of 2-D shapes. geostrips matching, sorting activities for shapes such as bingo or lotto. geoboards The Nrich site includes a free-to-use virtual geoboard. P8 L1 L3 respond to mathematical vocabulary such as straight, circle, larger to describe the shape and size of solids and flat shapes use everyday language to describe properties of 2-D and 3-D shapes classify 3-D and 2-D shapes in various ways using mathematical properties such as reflective symmetry for 2-D shapes
POSITION, DIRECTION AND MOVEMENT Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Use mathematical
 POSITION, DIRECTION AND MOVEMENT Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Use mathematical Use mathematical Describe positions on a Identify, describe and vocabulary to describe vocabulary to describe
POSITION, DIRECTION AND MOVEMENT Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 Use mathematical Use mathematical Describe positions on a Identify, describe and vocabulary to describe vocabulary to describe
Year. Small Steps Guidance and Examples. Block 3: Properties of Shapes. Released March 2018
 Released March 2018 The sequence of small steps has been produced by White Rose Maths. White Rose Maths gives permission to schools and teachers to use the small steps in their own teaching in their own
Released March 2018 The sequence of small steps has been produced by White Rose Maths. White Rose Maths gives permission to schools and teachers to use the small steps in their own teaching in their own
UNIT PLAN. Big Idea/Theme: Polygons can be identified, classified, and described.
 UNIT PLAN Grade Level: 5 Unit #: 11 Unit Name Geometry Polygons Time: 15 lessons, 18 days Big Idea/Theme: Polygons can be identified, classified, and described. Culminating Assessment: (requirements of
UNIT PLAN Grade Level: 5 Unit #: 11 Unit Name Geometry Polygons Time: 15 lessons, 18 days Big Idea/Theme: Polygons can be identified, classified, and described. Culminating Assessment: (requirements of
An angle that has a measure less than a right angle.
 Unit 1 Study Strategies: Two-Dimensional Figures Lesson Vocab Word Definition Example Formed by two rays or line segments that have the same 1 Angle endpoint. The shared endpoint is called the vertex.
Unit 1 Study Strategies: Two-Dimensional Figures Lesson Vocab Word Definition Example Formed by two rays or line segments that have the same 1 Angle endpoint. The shared endpoint is called the vertex.
Unit 4 Reasoning about shape. Year 4. Five daily lessons. Autumn term. Unit Objectives. Link Objectives
 Unit 4 Reasoning about shape Five daily lessons Year 4 Autumn term (Key objectives in bold) Unit Objectives Year 4 Describe and visualise 3-D and 2-D shapes, Page 102 including the tetrahedron and heptagon.
Unit 4 Reasoning about shape Five daily lessons Year 4 Autumn term (Key objectives in bold) Unit Objectives Year 4 Describe and visualise 3-D and 2-D shapes, Page 102 including the tetrahedron and heptagon.
Key Milestone Indicator(s) Basic Advancing Deep. With help or structure, there is counting forwards to and across 100, beginning with 0 or 1.
 Milestone 1 Assessment criteria for mathematics Learning Objective To know and use numbers Counting Key Milestone Indicator(s) Basic Advancing Deep Count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning
Milestone 1 Assessment criteria for mathematics Learning Objective To know and use numbers Counting Key Milestone Indicator(s) Basic Advancing Deep Count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning
Properties of polygons Year level: 6 7
 Properties of polygons Year level: 6 7 Unit of work contributed by Anne Pillman, Marryatville Primary School, SA L6558 Exploring s. Copyright Alberta Education About the unit Unit description This unit
Properties of polygons Year level: 6 7 Unit of work contributed by Anne Pillman, Marryatville Primary School, SA L6558 Exploring s. Copyright Alberta Education About the unit Unit description This unit
SECTION SIX Teaching/ Learning Geometry. General Overview
 SECTION SIX Teaching/ Learning Geometry General Overview The learning outcomes for Geometry focus on the development of an understanding of the properties of three-dimensional and plane shapes and how
SECTION SIX Teaching/ Learning Geometry General Overview The learning outcomes for Geometry focus on the development of an understanding of the properties of three-dimensional and plane shapes and how
The National Strategies Secondary Mathematics exemplification: Y8, 9
 Mathematics exemplification: Y8, 9 183 As outcomes, Year 8 pupils should, for example: Understand a proof that the sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 and of a quadrilateral is 360, and that the exterior
Mathematics exemplification: Y8, 9 183 As outcomes, Year 8 pupils should, for example: Understand a proof that the sum of the angles of a triangle is 180 and of a quadrilateral is 360, and that the exterior
PYP 5C s Maths Daily Lesson Plan 2012/2013 Strand: Space and Shape (2-D and 3-D shapes)
 Day/ Date Monday/ October 8 th, 2012 To know the vocabulary used to describe 2D and 3D shapes Use the proper vocabulary for 2D shapes (corner, sides, parallel, lines of symmetry, angles acute, obtuse,
Day/ Date Monday/ October 8 th, 2012 To know the vocabulary used to describe 2D and 3D shapes Use the proper vocabulary for 2D shapes (corner, sides, parallel, lines of symmetry, angles acute, obtuse,
Year. Small Steps Guidance and Examples. Block 1 Properties of Shapes. Released March 2018
 Released March 2018 The sequence of small steps has been produced by White Rose Maths. White Rose Maths gives permission to schools and teachers to use the small steps in their own teaching in their own
Released March 2018 The sequence of small steps has been produced by White Rose Maths. White Rose Maths gives permission to schools and teachers to use the small steps in their own teaching in their own
Woodcote Primary School Climbing the Ladders of Learning: Maths Milestone 1.1
 Climbing the Ladders of Learning: Maths Milestone 1.1 Number s I can join in with counting beyond 10 I can take away one from a number of objects I can talk about, recognise & copy simple repeating patterns
Climbing the Ladders of Learning: Maths Milestone 1.1 Number s I can join in with counting beyond 10 I can take away one from a number of objects I can talk about, recognise & copy simple repeating patterns
Consolidation of Grade 6 EQAO Questions Geometry and Spatial Sense
 Consolidation of Grade 6 EQAO Questions Geometry and Spatial Sense SE2 Families of Schools Year GV1 GV2 GV3 Spring 2006 Spring 2007 Spring 2008 MC14 MC24 MC13 OR9 MC17 OR30 OR9 MC21 MC18 MC3 MC23 OR30
Consolidation of Grade 6 EQAO Questions Geometry and Spatial Sense SE2 Families of Schools Year GV1 GV2 GV3 Spring 2006 Spring 2007 Spring 2008 MC14 MC24 MC13 OR9 MC17 OR30 OR9 MC21 MC18 MC3 MC23 OR30
5th Grade Geometry
 Slide 1 / 112 Slide 2 / 112 5th Grade Geometry 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 112 Geometry Unit Topics Click on the topic to go to that section Polygons Classifying Triangles & Quadrilaterals Coordinate
Slide 1 / 112 Slide 2 / 112 5th Grade Geometry 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 112 Geometry Unit Topics Click on the topic to go to that section Polygons Classifying Triangles & Quadrilaterals Coordinate
Unit 14: Transformations (Geometry) Date Topic Page
 Unit 14: Transformations (Geometry) Date Topic Page image pre-image transformation translation image pre-image reflection clockwise counterclockwise origin rotate 180 degrees rotate 270 degrees rotate
Unit 14: Transformations (Geometry) Date Topic Page image pre-image transformation translation image pre-image reflection clockwise counterclockwise origin rotate 180 degrees rotate 270 degrees rotate
Standard 2.0 Knowledge of Geometry: Students will apply the properties of one-,
 VSC - Mathematics Print pages on legal paper, landscape mode. Grade PK Grade K Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 Geometry: Students will apply the properties of one-, two-,
VSC - Mathematics Print pages on legal paper, landscape mode. Grade PK Grade K Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 Geometry: Students will apply the properties of one-, two-,
Mathematics. Scheme of Work. Year 7. New Mathematics Framework
 Mathematics Scheme of Work Year 7 New Mathematics Framework 1 YEAR 7: Overview of year 7 scheme of work YEAR 7 Topics Assessment Tests Term 1 Algebra 1 Number 1 Geometry and Measures 1 Test 1 Sequences
Mathematics Scheme of Work Year 7 New Mathematics Framework 1 YEAR 7: Overview of year 7 scheme of work YEAR 7 Topics Assessment Tests Term 1 Algebra 1 Number 1 Geometry and Measures 1 Test 1 Sequences
Name Date Class. Original content Copyright by Holt McDougal. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor.
 Name _ Date Class 8-1 Building Blocks of Geometry Use the diagram to name each geometric figure. 1. two points 2. a plane 3. a line segment 4. a point shared by two lines 5. a line Use the diagram to give
Name _ Date Class 8-1 Building Blocks of Geometry Use the diagram to name each geometric figure. 1. two points 2. a plane 3. a line segment 4. a point shared by two lines 5. a line Use the diagram to give
7. 2 More Things Under. Construction. A Develop Understanding Task
 7 Construction A Develop Understanding Task Like a rhombus, an equilateral triangle has three congruent sides. Show and describe how you might locate the third vertex point on an equilateral triangle,
7 Construction A Develop Understanding Task Like a rhombus, an equilateral triangle has three congruent sides. Show and describe how you might locate the third vertex point on an equilateral triangle,
ELGIN ACADEMY Mathematics Department Evaluation Booklet (Core) Name Reg
 ELGIN ACADEMY Mathematics Department Evaluation Booklet (Core) Name Reg CfEL You should be able to use this evaluation booklet to help chart your progress in the Maths department throughout S1 and S2.
ELGIN ACADEMY Mathematics Department Evaluation Booklet (Core) Name Reg CfEL You should be able to use this evaluation booklet to help chart your progress in the Maths department throughout S1 and S2.
Mathematics Success Level E
 T877 [OBJECTIVE] The student will classify two-dimensional figures based on properties. [PREREQUISITE SKILLS] Lesson 29, knowledge of basic geometry terminology including: parallel sides, congruent sides,
T877 [OBJECTIVE] The student will classify two-dimensional figures based on properties. [PREREQUISITE SKILLS] Lesson 29, knowledge of basic geometry terminology including: parallel sides, congruent sides,
Year 2 Spring Term Week 5 to 7 - Geometry: Properties of Shape
 1 Year 2 Spring Term Week 5 to 7 - Geometry: Properties of Shape Recognise 2-D and 3-D shapes Count sides on 2-D shapes Count vertices on 2-D shapes Draw 2-D shapes Lines of symmetry Sort 2-D shapes Make
1 Year 2 Spring Term Week 5 to 7 - Geometry: Properties of Shape Recognise 2-D and 3-D shapes Count sides on 2-D shapes Count vertices on 2-D shapes Draw 2-D shapes Lines of symmetry Sort 2-D shapes Make
Objective: Reason about attributes to construct quadrilaterals on square or triangular grid paper.
 Lesson 16 Objective: Reason about attributes to construct quadrilaterals on square or Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (12
Lesson 16 Objective: Reason about attributes to construct quadrilaterals on square or Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (12
Year 6 Maths Scheme of Work
 Year 6 National Curriculum The 2014 2015 Year 6 cohort will be using the old national curriculum as this is what will be used for the KS2 SATs 2015. Below are the objectives students are required to meet
Year 6 National Curriculum The 2014 2015 Year 6 cohort will be using the old national curriculum as this is what will be used for the KS2 SATs 2015. Below are the objectives students are required to meet
This table connects the content provided by Education Perfect to the NSW Syllabus..
 Education Perfect Maths is a comprehensive online learning and assessment resource. Designed by teachers and written by our in-house team of maths experts, our content aligns to the NSW Syllabus and covers
Education Perfect Maths is a comprehensive online learning and assessment resource. Designed by teachers and written by our in-house team of maths experts, our content aligns to the NSW Syllabus and covers
INFORMATION FOR PARENTS AND CARERS TARGETS IN MATHEMATICS
 INITIAL TARGETS I can share 6 objects between 2 children. I can write and use numbers (less than 10) in role play. I can count up to 10 objects independently. I can read and write numbers to 10 independently.
INITIAL TARGETS I can share 6 objects between 2 children. I can write and use numbers (less than 10) in role play. I can count up to 10 objects independently. I can read and write numbers to 10 independently.
Geometry. Standardized Practice Have students try the following problem.
 1 Students need a basic understanding of angles to learn the properties of twodimensional shapes. In this lesson, students use models to represent, measure, and classify angles. Objective Recognize types
1 Students need a basic understanding of angles to learn the properties of twodimensional shapes. In this lesson, students use models to represent, measure, and classify angles. Objective Recognize types
In this task, students will investigate the attributes of quadrilaterals.
 PRACTICE TASK: Investigating Quadrilaterals In this task, students will investigate the attributes of quadrilaterals. STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICAL CONTENT MCC5.G.3 Understanding that attributes belonging
PRACTICE TASK: Investigating Quadrilaterals In this task, students will investigate the attributes of quadrilaterals. STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICAL CONTENT MCC5.G.3 Understanding that attributes belonging
Objective: Analyze and classify triangles based on side length, angle measure or both.
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 13 4 4 Lesson 13 Objective: Analyze and classify triangles based on side length, angle measure or Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 13 4 4 Lesson 13 Objective: Analyze and classify triangles based on side length, angle measure or Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem
ANNUAL NATIONAL ASSESSMENT 2014 ASSESSMENT GUIDELINES MATHEMATICS GRADE 7
 ANNUAL NATIONAL ASSESSMENT 2014 ASSESSMENT GUIDELINES MATHEMATICS GRADE 7 INTRODUCTION The 2014 cycle of Annual National Assessment (ANA 2014) will be administered in all public and designated 1 independent
ANNUAL NATIONAL ASSESSMENT 2014 ASSESSMENT GUIDELINES MATHEMATICS GRADE 7 INTRODUCTION The 2014 cycle of Annual National Assessment (ANA 2014) will be administered in all public and designated 1 independent
MCC5.G.3 Understand that attributes belonging to a category of two-dimensional figures also belong to all subcategories of that categories.
 Fifth Grade Mathematics Unit 6 CONSTRUCTING TASK: Property Lists of Quadrilaterals Adapted from Van De Walle, Teaching Student-Centered Math pg. 207 The purpose of this task is for students to become familiar
Fifth Grade Mathematics Unit 6 CONSTRUCTING TASK: Property Lists of Quadrilaterals Adapted from Van De Walle, Teaching Student-Centered Math pg. 207 The purpose of this task is for students to become familiar
Geometry Sixth Grade
 Standard 6-4: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of shape, location, and movement within a coordinate system; similarity, complementary, and supplementary
Standard 6-4: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of shape, location, and movement within a coordinate system; similarity, complementary, and supplementary
Students will draw and use straws to make the three types of angles, within triangles.
 PRACTICETASK: Tangling with Triangles Adapted from Ohio Department of Education Students will draw and use straws to make the three types of angles, within triangles. STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICAL CONTENT
PRACTICETASK: Tangling with Triangles Adapted from Ohio Department of Education Students will draw and use straws to make the three types of angles, within triangles. STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICAL CONTENT
Chapter Review. In the figure shown, m n and r is a transversal. If m 4 = 112, find the measure of each angle. Explain your reasoning.
 In the figure shown, m n and r is a transversal. If m 4 = 112, find the measure of each angle. Explain your reasoning. 1. 6 Since 4 and 6 are alternate interior angles, they are congruent. So, m 6 = 112.
In the figure shown, m n and r is a transversal. If m 4 = 112, find the measure of each angle. Explain your reasoning. 1. 6 Since 4 and 6 are alternate interior angles, they are congruent. So, m 6 = 112.
Getting Ready to Teach Unit 6
 Getting Ready to Teach Unit 6 Learning Path in the Common Core Standards In this unit, students study the attributes of triangles, quadrilaterals, and other polygons. They find perimeter and area of various
Getting Ready to Teach Unit 6 Learning Path in the Common Core Standards In this unit, students study the attributes of triangles, quadrilaterals, and other polygons. They find perimeter and area of various
acute angle An angle with a measure less than that of a right angle. Houghton Mifflin Co. 2 Grade 5 Unit 6
 acute angle An angle with a measure less than that of a right angle. Houghton Mifflin Co. 2 Grade 5 Unit 6 angle An angle is formed by two rays with a common end point. Houghton Mifflin Co. 3 Grade 5 Unit
acute angle An angle with a measure less than that of a right angle. Houghton Mifflin Co. 2 Grade 5 Unit 6 angle An angle is formed by two rays with a common end point. Houghton Mifflin Co. 3 Grade 5 Unit
Chapter 8. Properties of Triangles and Quadrilaterals. 02/2017 LSowatsky
 Chapter 8 Properties of Triangles and Quadrilaterals 02/2017 LSowatsky 1 8-1A: Points, Lines, and Planes I can Identify and label basic geometric figures. LSowatsky 2 Vocabulary: Point: a point has no
Chapter 8 Properties of Triangles and Quadrilaterals 02/2017 LSowatsky 1 8-1A: Points, Lines, and Planes I can Identify and label basic geometric figures. LSowatsky 2 Vocabulary: Point: a point has no
6th Grade ~ Conceptual Foundations for Unit of Study 8 Geometry DRAFT 6/30/11 Geometry (Spatial Sense & Reasoning) 1. Shapes, Solids and Properties
 Geometry is the only CCSSM Domain that consistently appears in every grade level K-12. At all grade levels, geometry content goals can be summarized into four main geometric ideas: 1. Shapes, Solids and
Geometry is the only CCSSM Domain that consistently appears in every grade level K-12. At all grade levels, geometry content goals can be summarized into four main geometric ideas: 1. Shapes, Solids and
Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane
 Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane Let s describe ways figures can move in the plane. 1.1: Which One Doesn t Belong: Diagrams Which one doesn t belong? 1.2: Triangle Square Dance m.openup.org/1/8-1-1-2
Unit 1, Lesson 1: Moving in the Plane Let s describe ways figures can move in the plane. 1.1: Which One Doesn t Belong: Diagrams Which one doesn t belong? 1.2: Triangle Square Dance m.openup.org/1/8-1-1-2
Foundation. Scheme of Work. Year 9. September 2016 to July 2017
 Foundation Scheme of Work Year 9 September 06 to July 07 Assessments Students will be assessed by completing two tests (topic) each Half Term. These are to be recorded on Go Schools. There will not be
Foundation Scheme of Work Year 9 September 06 to July 07 Assessments Students will be assessed by completing two tests (topic) each Half Term. These are to be recorded on Go Schools. There will not be
Geometry Vocabulary. acute angle-an angle measuring less than 90 degrees
 Geometry Vocabulary acute angle-an angle measuring less than 90 degrees angle-the turn or bend between two intersecting lines, line segments, rays, or planes angle bisector-an angle bisector is a ray that
Geometry Vocabulary acute angle-an angle measuring less than 90 degrees angle-the turn or bend between two intersecting lines, line segments, rays, or planes angle bisector-an angle bisector is a ray that
Closed shapes with straight sides
 41 Unit 6 and 7 Properties of 2D shapes Activity 1 Closed shapes with straight sides (polygons). Let s revise the 2D shapes you learnt about in Grade 5 Closed shapes with straight sides triangle quadrilateral
41 Unit 6 and 7 Properties of 2D shapes Activity 1 Closed shapes with straight sides (polygons). Let s revise the 2D shapes you learnt about in Grade 5 Closed shapes with straight sides triangle quadrilateral
Mathematics Curriculum Medium Term Planning Year Five
 Curriculum Medium Term Planning Year Five Year Five Programme of Study Number Number and Place Value Statutory Requirements Pupils should be taught to: read, write, order and compare numbers to at least
Curriculum Medium Term Planning Year Five Year Five Programme of Study Number Number and Place Value Statutory Requirements Pupils should be taught to: read, write, order and compare numbers to at least
Name Date Teacher Practice A
 Practice A Triangles Identify each triangle by its angles and sides. 1. 2. 3. Find each angle measure. 4. Find x in the acute 5. Find y in the right 6. Find r in the obtuse 7. Find x in the acute 8. Find
Practice A Triangles Identify each triangle by its angles and sides. 1. 2. 3. Find each angle measure. 4. Find x in the acute 5. Find y in the right 6. Find r in the obtuse 7. Find x in the acute 8. Find
Mathematics Expectations Page 1 Grade 06
 Mathematics Expectations Page 1 Grade 06 Problem Solving Mathematical Process Expectations 6m1 develop, select, and apply problem-solving strategies as they pose and solve problems and conduct investigations,
Mathematics Expectations Page 1 Grade 06 Problem Solving Mathematical Process Expectations 6m1 develop, select, and apply problem-solving strategies as they pose and solve problems and conduct investigations,
Arithmetic. Edexcel Primary curriculum. Mathematics Grade 6. S.no Topics Levels
 Edexcel Primary curriculum Mathematics Grade 6 Arithmetic S.no Topics Levels 1 Read and write whole numbers in words and figures. Low(P1) 2 Add and subtract mentally pairs of 2-digit numbers. Low(P1) 3
Edexcel Primary curriculum Mathematics Grade 6 Arithmetic S.no Topics Levels 1 Read and write whole numbers in words and figures. Low(P1) 2 Add and subtract mentally pairs of 2-digit numbers. Low(P1) 3
Classify Triangles. by the Angle Measure &The Side Lengths. Properties a SCALENE Triangle angles 1.Sum of the interior
 Classify s by the Angle Measure &The Side Lengths Foldable Resource & Reference Properties a SCALENE angles 1.Sum of the interior equals. 180 2. The measure of each is side length is. different Note: If
Classify s by the Angle Measure &The Side Lengths Foldable Resource & Reference Properties a SCALENE angles 1.Sum of the interior equals. 180 2. The measure of each is side length is. different Note: If
Ready to Go On? Skills Intervention Building Blocks of Geometry
 8-1 Ready to Go On? Skills Intervention Building Blocks of Geometry A point is an exact location. A line is a straight path that extends without end in opposite directions. A plane is a flat surface that
8-1 Ready to Go On? Skills Intervention Building Blocks of Geometry A point is an exact location. A line is a straight path that extends without end in opposite directions. A plane is a flat surface that
Skill. 69 Graph Ordered Pairs. (First Quadrant) Using Skill 69 COMMON ERRORS. 285 Holt Mathematics. OBJECTIVE Graph ordered pairs (first quadrant)
 Skill Graph Ordered Pairs (First Quadrant) Using Skill OBJECTIVE Graph ordered pairs (first quadrant) Minutes Direct students attention to the definition at the top of the page. Work through the example
Skill Graph Ordered Pairs (First Quadrant) Using Skill OBJECTIVE Graph ordered pairs (first quadrant) Minutes Direct students attention to the definition at the top of the page. Work through the example
Right Angle Triangle. Square. Opposite sides are parallel
 Triangles 3 sides ngles add up to 18⁰ Right ngle Triangle Equilateral Triangle ll sides are the same length ll angles are 6⁰ Scalene Triangle ll sides are different lengths ll angles are different Isosceles
Triangles 3 sides ngles add up to 18⁰ Right ngle Triangle Equilateral Triangle ll sides are the same length ll angles are 6⁰ Scalene Triangle ll sides are different lengths ll angles are different Isosceles
Geometry Honors Unit 2: Transformations, Triangles & Congruence (Gr. 9-10)
 Geometry Honors Unit 2: Transformations, Triangles & Congruence (Gr. 9-10) Content Area: Course(s): Time Period: Length: Status: Mathematics Generic Course, Geometry 1st Marking Period 8 Weeks Published
Geometry Honors Unit 2: Transformations, Triangles & Congruence (Gr. 9-10) Content Area: Course(s): Time Period: Length: Status: Mathematics Generic Course, Geometry 1st Marking Period 8 Weeks Published
Brunswick School Department: Grade 5
 Understandings Questions Mathematics Lines are the fundamental building blocks of polygons. Different tools are used to measure different things. Standard units provide common language for communicating
Understandings Questions Mathematics Lines are the fundamental building blocks of polygons. Different tools are used to measure different things. Standard units provide common language for communicating
My Target Level 1c. My areas for development:
 My Target Level 1c I can read numbers up to 10 (R) I can count up to 10 objects (R) I can say the number names in order up to 20 (R) I can write at least 4 numbers up to 10. When someone gives me a small
My Target Level 1c I can read numbers up to 10 (R) I can count up to 10 objects (R) I can say the number names in order up to 20 (R) I can write at least 4 numbers up to 10. When someone gives me a small
Geometric Ideas. Name
 Geometric Ideas R 6-1 Lines, line segments, and rays are basic geometric ideas. They are sometimes described by the relationship they have to other lines, line segments, and rays. Draw Write Say Description
Geometric Ideas R 6-1 Lines, line segments, and rays are basic geometric ideas. They are sometimes described by the relationship they have to other lines, line segments, and rays. Draw Write Say Description
Developmental Math An Open Program Unit 7 Geometry First Edition
 Developmental Math An Open Program Unit 7 Geometry First Edition Lesson 1 Basic Geometric Concepts and Figures TOPICS 7.1.1 Figures in 1 and 2 Dimensions 1 Identify and define points, lines, line segments,
Developmental Math An Open Program Unit 7 Geometry First Edition Lesson 1 Basic Geometric Concepts and Figures TOPICS 7.1.1 Figures in 1 and 2 Dimensions 1 Identify and define points, lines, line segments,
4 Mathematics Curriculum. Module Overview... i Topic A: Lines and Angles... 4.A.1. Topic B: Angle Measurement... 4.B.1
 New York State Common Core 4 Mathematics Curriculum G R A D E Table of Contents GRADE 4 MODULE 4 Angle Measure and Plane Figures GRADE 4 MODULE 4 Module Overview... i Topic A: Lines and Angles... 4.A.1
New York State Common Core 4 Mathematics Curriculum G R A D E Table of Contents GRADE 4 MODULE 4 Angle Measure and Plane Figures GRADE 4 MODULE 4 Module Overview... i Topic A: Lines and Angles... 4.A.1
Quadrilaterals & Transformations Study Guide
 s & Transformations Study Guide What do I need to know for the upcoming Summative Assessment? s Classifications and Properties of: o o Trapezoid o Kite o Parallelogram o Rhombus o Rectangle o Square The
s & Transformations Study Guide What do I need to know for the upcoming Summative Assessment? s Classifications and Properties of: o o Trapezoid o Kite o Parallelogram o Rhombus o Rectangle o Square The
(6.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student uses geometric vocabulary to describe angles, polygons, and circles.
 (6.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student uses geometric vocabulary to describe angles, polygons, and circles. (6.6.a) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student uses geometric vocabulary to describe
(6.6) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student uses geometric vocabulary to describe angles, polygons, and circles. (6.6.a) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student uses geometric vocabulary to describe
202 The National Strategies Secondary Mathematics exemplification: Y7
 202 The National Strategies Secondary Mathematics exemplification: Y7 GEOMETRY ND MESURES Pupils should learn to: Understand and use the language and notation associated with reflections, translations
202 The National Strategies Secondary Mathematics exemplification: Y7 GEOMETRY ND MESURES Pupils should learn to: Understand and use the language and notation associated with reflections, translations
2. A straightedge can create straight line, but can't measure. A ruler can create straight lines and measure distances.
 5.1 Copies of Line Segments and Angles Answers 1. A drawing is a rough sketch and a construction is a process to create an exact and accurate geometric figure. 2. A straightedge can create straight line,
5.1 Copies of Line Segments and Angles Answers 1. A drawing is a rough sketch and a construction is a process to create an exact and accurate geometric figure. 2. A straightedge can create straight line,
Table of Contents. Introduction to the Math Practice Series...1
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction to the Math Practice Series...1 Common Mathematics/Geometry Symbols and Terms...2 Chapter 1: Introduction To Geometry...13 Shapes, Congruence, Similarity,
Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction to the Math Practice Series...1 Common Mathematics/Geometry Symbols and Terms...2 Chapter 1: Introduction To Geometry...13 Shapes, Congruence, Similarity,
Mathematics at Woodcroft Primary School
 Mathematics at Woodcroft Primary School Maths in the Early Years Foundation Stage: In Nursery and Reception they follow the Development Matters and Early Years Learning Goals. Maths is taught in a variety
Mathematics at Woodcroft Primary School Maths in the Early Years Foundation Stage: In Nursery and Reception they follow the Development Matters and Early Years Learning Goals. Maths is taught in a variety
Constructing Symmetrical Shapes
 1 Constructing Symmetrical Shapes 1 Construct 2-D shapes with one line of symmetry A line of symmetry may be horizontal or vertical 2 a) Use symmetry to complete the picture b) Describe the method you
1 Constructing Symmetrical Shapes 1 Construct 2-D shapes with one line of symmetry A line of symmetry may be horizontal or vertical 2 a) Use symmetry to complete the picture b) Describe the method you
Year 6 Summer Term Week 1 to 2 Geometry: Properties of Shapes
 Measure with a protractor Introduce angles Calculate angles Vertically opposite angles Angles in a triangle Angles in a triangle special cases Angles in a triangle missing angles Angles in special quadrilaterals
Measure with a protractor Introduce angles Calculate angles Vertically opposite angles Angles in a triangle Angles in a triangle special cases Angles in a triangle missing angles Angles in special quadrilaterals
Mathematical Reasoning. Lesson 41: Triangles and Quadrilaterals. LESSON 41: Triangles and Quadrilaterals
 LESSON 41: Triangles and Quadrilaterals Weekly Focus: geometry intro Weekly Skill: vocabulary, and measure perimeter, area Lesson Summary: For the warm up, students will solve a problem about the U.S.
LESSON 41: Triangles and Quadrilaterals Weekly Focus: geometry intro Weekly Skill: vocabulary, and measure perimeter, area Lesson Summary: For the warm up, students will solve a problem about the U.S.
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 10: Geometric Figures & Their Properties; Volume
 Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Geometric Figures & Their Properties; Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (4.6) The student will validate conclusions about geometric figures and
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Geometric Figures & Their Properties; Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (4.6) The student will validate conclusions about geometric figures and
Number. Measure. Geometry. Key:
 Year R Maths - Key Performance Indicator Can count reliably with numbers from one to 0. Can find one more or one less than a given number. Using quantities or objects, can add or subtract two single digit
Year R Maths - Key Performance Indicator Can count reliably with numbers from one to 0. Can find one more or one less than a given number. Using quantities or objects, can add or subtract two single digit
The Grade 3 Common Core State Standards for Geometry specify that students should
 Students in third grade describe, analyze, and compare properties of two-dimensional shapes. They compare and classify shapes by their sides and angles, and they use these classifications to define shapes.
Students in third grade describe, analyze, and compare properties of two-dimensional shapes. They compare and classify shapes by their sides and angles, and they use these classifications to define shapes.
Math 6, Unit 8 Notes: Geometric Relationships
 Math 6, Unit 8 Notes: Geometric Relationships Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays As we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful.
Math 6, Unit 8 Notes: Geometric Relationships Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays As we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful.
Title: Identifying, Classifying, and Creating Quadrilaterals - Qualifying Quadrilaterals
 Title: Identifying, Classifying, and Creating Quadrilaterals - Qualifying Quadrilaterals Brief Overview: Through problem solving, oral and written communication, higher-order thinking and a variety of
Title: Identifying, Classifying, and Creating Quadrilaterals - Qualifying Quadrilaterals Brief Overview: Through problem solving, oral and written communication, higher-order thinking and a variety of
Draft Schemes of Work Edexcel Primary Curriculum. May Dear Centre,
 EDEXCEL INTERNATIONAL One90 High Holborn London WC1V 7BH www.edexcel.com/international Draft Schemes of Work Edexcel Primary Curriculum May 2011 Dear Centre, The Schemes of Work in this booklet have been
EDEXCEL INTERNATIONAL One90 High Holborn London WC1V 7BH www.edexcel.com/international Draft Schemes of Work Edexcel Primary Curriculum May 2011 Dear Centre, The Schemes of Work in this booklet have been
ANNUAL NATIONAL ASSESSMENT 2014 ASSESSMENT GUIDELINES MATHEMATICS GRADE 8
 ANNUAL NATIONAL ASSESSMENT 2014 ASSESSMENT GUIDELINES MATHEMATICS GRADE 8 INTRODUCTION The 2014 cycle of Annual National Assessment (ANA 2014) will be administered in all public and designated 1 independent
ANNUAL NATIONAL ASSESSMENT 2014 ASSESSMENT GUIDELINES MATHEMATICS GRADE 8 INTRODUCTION The 2014 cycle of Annual National Assessment (ANA 2014) will be administered in all public and designated 1 independent
Go to Grade 5 Everyday Mathematics Sample Lesson
 McGraw-Hill makes no representations or warranties as to the accuracy of any information contained in this McGraw-Hill Material, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular
McGraw-Hill makes no representations or warranties as to the accuracy of any information contained in this McGraw-Hill Material, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular
GRADE 3 SUPPLEMENT. Set C2 Geometry: Triangles & More. Includes. Skills & Concepts
 GRADE 3 SUPPLEMENT Set C2 Geometry: Triangles & More Includes Activity 1: Start with a Point C2.1 Activity 2: Classifying Triangles C2.9 Activity 3: Measuring Circles C2.15 Independent Worksheet 1: Points,
GRADE 3 SUPPLEMENT Set C2 Geometry: Triangles & More Includes Activity 1: Start with a Point C2.1 Activity 2: Classifying Triangles C2.9 Activity 3: Measuring Circles C2.15 Independent Worksheet 1: Points,
Polygons A-F An Introduction to Symmetry
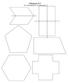 Polygons A-F An Introduction to Symmetry Classifying Angles Review STRAIGHT ANGLE RIGHT ANGLES OBTUSE ANGLES ACUTE ANGLES In a previous lesson, unit angles known as wedges were used to measure angles.
Polygons A-F An Introduction to Symmetry Classifying Angles Review STRAIGHT ANGLE RIGHT ANGLES OBTUSE ANGLES ACUTE ANGLES In a previous lesson, unit angles known as wedges were used to measure angles.
Pre-Algebra, Unit 10: Measurement, Area, and Volume Notes
 Pre-Algebra, Unit 0: Measurement, Area, and Volume Notes Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Objective: (4.6) The student will classify polygons. Take this opportunity to review vocabulary and previous
Pre-Algebra, Unit 0: Measurement, Area, and Volume Notes Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Objective: (4.6) The student will classify polygons. Take this opportunity to review vocabulary and previous
PERSPECTIVES ON GEOMETRY PRE-ASSESSMENT ANSWER SHEET (GEO )
 PERSPECTIVES ON GEOMETRY PRE-ASSESSMENT ANSWER SHEET (GEO.11.02.2) Name Date Site TURN IN BOTH TEST AND ANSWER SHEET TO YOUR INSTRUCTOR WHEN DONE. 1. 18. I. 2. 19. 3. 20. 4. 21. 5. 22. 6. 23. 7. 24. 8.
PERSPECTIVES ON GEOMETRY PRE-ASSESSMENT ANSWER SHEET (GEO.11.02.2) Name Date Site TURN IN BOTH TEST AND ANSWER SHEET TO YOUR INSTRUCTOR WHEN DONE. 1. 18. I. 2. 19. 3. 20. 4. 21. 5. 22. 6. 23. 7. 24. 8.
Band Topic Mastery Statements - I can Essential Knowledge - I know Whole order decimals and negative numbers.
 Year 7 Maths Assessment Criteria Assessment 1 Band Topic Mastery Statements - I can Essential Knowledge - I know Whole order decimals and negative numbers. know and understand place value in Numbers and
Year 7 Maths Assessment Criteria Assessment 1 Band Topic Mastery Statements - I can Essential Knowledge - I know Whole order decimals and negative numbers. know and understand place value in Numbers and
Maths Levels Criteria
 Maths Levels Criteria Level 1-5 pencilplayground.co.uk 2012 NUMBER I can count up to ten objects I can read and write numbers up to ten I can work out one more and one less then a number I can count backwards
Maths Levels Criteria Level 1-5 pencilplayground.co.uk 2012 NUMBER I can count up to ten objects I can read and write numbers up to ten I can work out one more and one less then a number I can count backwards
Geometry. Plane Shapes. Talk About It. More Ideas. Formative Assessment. Have students try the following problem. Which shape has parallel lines?
 2 Objective Plane s The reasoning skills that students develop at this age allow them to explore more complex geometric problems and properties. They should develop more precise ways to describe and classify
2 Objective Plane s The reasoning skills that students develop at this age allow them to explore more complex geometric problems and properties. They should develop more precise ways to describe and classify
Key Stage 3 Asssessment Descriptors - Mathematics
 Level 2 Number 1. Count sets of objects reliably: group objects in tens, twos or fives to count them 2. Begin to understand the place value of each digit, use this to order numbers up to 100: know relative
Level 2 Number 1. Count sets of objects reliably: group objects in tens, twos or fives to count them 2. Begin to understand the place value of each digit, use this to order numbers up to 100: know relative
Level 1 - Maths Targets TARGETS. With support, I can show my work using objects or pictures 12. I can order numbers to 10 3
 Ma Data Hling: Interpreting Processing representing Ma Shape, space measures: position shape Written Mental method s Operations relationship s between them Fractio ns Number s the Ma1 Using Str Levels
Ma Data Hling: Interpreting Processing representing Ma Shape, space measures: position shape Written Mental method s Operations relationship s between them Fractio ns Number s the Ma1 Using Str Levels
Maths Key Objectives Check list Year 1
 Maths Key Objectives Check list Year 1 Count to and across 100 from any number. Count, read and write numbers to 100 in numerals. Read and write mathematical symbols +, - and =. Identify one more and one
Maths Key Objectives Check list Year 1 Count to and across 100 from any number. Count, read and write numbers to 100 in numerals. Read and write mathematical symbols +, - and =. Identify one more and one
1. Revision Description Reflect and Review Teasers Recall basics of geometrical shapes.
 1. Revision Description Reflect and Review Teasers Recall basics of geometrical shapes. A book, a birthday cap and a dice are some examples of 3-D shapes. 1) Write two examples of 2-D shapes and 3-D shapes
1. Revision Description Reflect and Review Teasers Recall basics of geometrical shapes. A book, a birthday cap and a dice are some examples of 3-D shapes. 1) Write two examples of 2-D shapes and 3-D shapes
Identifying and Classifying Angles and Shapes
 Grade 5 Mathematics, Quarter 2, Unit 2.1 Identifying and Classifying Angles and Shapes Overview Number of instructional days: 10 (1 day = 45 minutes) Content to be learned Describe, compare, and classify
Grade 5 Mathematics, Quarter 2, Unit 2.1 Identifying and Classifying Angles and Shapes Overview Number of instructional days: 10 (1 day = 45 minutes) Content to be learned Describe, compare, and classify
Reteach. Chapter 14. Grade 4
 Reteach Chapter 14 Grade 4 Lesson 1 Reteach Draw Points, Lines, and Rays A point is an exact location that is represented by a dot. Example: point R R A line goes on forever in both directions. Example:
Reteach Chapter 14 Grade 4 Lesson 1 Reteach Draw Points, Lines, and Rays A point is an exact location that is represented by a dot. Example: point R R A line goes on forever in both directions. Example:
For Exercises 1 4, follow these directions. Use the given side lengths.
 A C E Applications Connections Extensions Applications For Exercises 1 4, follow these directions. Use the given side lengths. If possible, build a triangle with the side lengths. Sketch your triangle.
A C E Applications Connections Extensions Applications For Exercises 1 4, follow these directions. Use the given side lengths. If possible, build a triangle with the side lengths. Sketch your triangle.
Age Related Maths Expectations
 Step 1 Times Tables Addition Subtraction Multiplication Division Fractions Decimals Percentage & I can count in 2 s, 5 s and 10 s from 0 to 100 I can add in 1 s using practical resources I can add in 1
Step 1 Times Tables Addition Subtraction Multiplication Division Fractions Decimals Percentage & I can count in 2 s, 5 s and 10 s from 0 to 100 I can add in 1 s using practical resources I can add in 1
ACT Math and Science - Problem Drill 11: Plane Geometry
 ACT Math and Science - Problem Drill 11: Plane Geometry No. 1 of 10 1. Which geometric object has no dimensions, no length, width or thickness? (A) Angle (B) Line (C) Plane (D) Point (E) Polygon An angle
ACT Math and Science - Problem Drill 11: Plane Geometry No. 1 of 10 1. Which geometric object has no dimensions, no length, width or thickness? (A) Angle (B) Line (C) Plane (D) Point (E) Polygon An angle
LEARNING GUIDE BASIC EDUCATION ASSISTANCE FOR MINDANAO
 BASIC EDUCATION ASSISTANCE FOR MINDANAO THIRD YEAR - MATHEMATICS III GEOMETRY OF SHAPE AND SIZE Module 2 - Types of Polygons COPYRIGHT NOTICE Section 9 of the Presidential Decree No. 49 provides: No copyright
BASIC EDUCATION ASSISTANCE FOR MINDANAO THIRD YEAR - MATHEMATICS III GEOMETRY OF SHAPE AND SIZE Module 2 - Types of Polygons COPYRIGHT NOTICE Section 9 of the Presidential Decree No. 49 provides: No copyright
HPISD Curriculum: Grade 4 TAG Math
 Unit Overview HPISD Curriculum: Grade 4 TAG Math Title Estimated Duration 9 Weeks Geometry and Measurement 8 weeks 1 2 3 4 Properties/attributes of polygons, triangles, quadrilaterals Area and perimeter
Unit Overview HPISD Curriculum: Grade 4 TAG Math Title Estimated Duration 9 Weeks Geometry and Measurement 8 weeks 1 2 3 4 Properties/attributes of polygons, triangles, quadrilaterals Area and perimeter
1. Identify the different parts of a triangle 2. Classify triangles by their angle measures 3. Classify triangles by their side lengths
 Lesson 8 Lesson 8, page 1 of 6 Glencoe Geometry Chapter 4.1, 4.2 Classifying Triangles & Angle Measure By the end of this lesson, you should be able to 1. Identify the different parts of a triangle 2.
Lesson 8 Lesson 8, page 1 of 6 Glencoe Geometry Chapter 4.1, 4.2 Classifying Triangles & Angle Measure By the end of this lesson, you should be able to 1. Identify the different parts of a triangle 2.
(based on Assessment Criteria)
 NO. OF GRADE 10 ASSESSMENT SESSIONS (MATHEMATICS) INTERDISCIPLINARY 25 TOPIC- GEOMETRY AOI- Human Ingenuity SIGNIFICANT CONCEPTS- Geometry allows us to work out the relationships Between shapes, forms
NO. OF GRADE 10 ASSESSMENT SESSIONS (MATHEMATICS) INTERDISCIPLINARY 25 TOPIC- GEOMETRY AOI- Human Ingenuity SIGNIFICANT CONCEPTS- Geometry allows us to work out the relationships Between shapes, forms
Mathematics with ICT in Key Stage 3. Geometry lessons
 Mathematics with ICT in Key Stage 3 Geometry lessons Introduction The introduction to the document Integrating ICT into mathematics in Key Stage 3 states: Computers offer powerful opportunities for pupils
Mathematics with ICT in Key Stage 3 Geometry lessons Introduction The introduction to the document Integrating ICT into mathematics in Key Stage 3 states: Computers offer powerful opportunities for pupils
Maths medium term plan: autumn term Year 4
 Maths medium term plan: autumn term Year 4 Mental Maths objectives to be covered: Number objectives should be covered at least 4 times a term. Measurement/ geometry objectives should be covered at least
Maths medium term plan: autumn term Year 4 Mental Maths objectives to be covered: Number objectives should be covered at least 4 times a term. Measurement/ geometry objectives should be covered at least
CAMI Education linked to CAPS: Mathematics
 - 1 - TOPIC 1.1 Whole numbers _CAPS Curriculum TERM 1 CONTENT Mental calculations Revise the following done in Grade 6: Multiplication of whole numbers to at least 12 x 12. Multiplication facts for: units
- 1 - TOPIC 1.1 Whole numbers _CAPS Curriculum TERM 1 CONTENT Mental calculations Revise the following done in Grade 6: Multiplication of whole numbers to at least 12 x 12. Multiplication facts for: units
CAMI Education linked to CAPS: Mathematics
 - 1 - TOPIC 1.1 Whole numbers Grade 7_CAPS Curriculum TERM 1 CONTENT Mental calculations Revise the following done in Grade 6: Multiplication of whole numbers to at least 12 x 12. Multiplication facts
- 1 - TOPIC 1.1 Whole numbers Grade 7_CAPS Curriculum TERM 1 CONTENT Mental calculations Revise the following done in Grade 6: Multiplication of whole numbers to at least 12 x 12. Multiplication facts
Maths Scheme of Work P14
 Maths topic: calculation (approx 3 weeks) Key: = Main Objective o = On the Boil Objective o Blue Text = Repeated Objective Blue Text = NS Key Objectives and Non-Statutory Guidance Autumn Term Maths Scheme
Maths topic: calculation (approx 3 weeks) Key: = Main Objective o = On the Boil Objective o Blue Text = Repeated Objective Blue Text = NS Key Objectives and Non-Statutory Guidance Autumn Term Maths Scheme
Answer Key Lesson 6: Classifying Shapes
 Student Guide The Flatopia Polygon Zoo Professor Peabody had a dream that he lived in a two-dimensional town called Flatopia. There were two-dimensional creatures in town, all shaped like polygons. Help
Student Guide The Flatopia Polygon Zoo Professor Peabody had a dream that he lived in a two-dimensional town called Flatopia. There were two-dimensional creatures in town, all shaped like polygons. Help
Discovery Activity & Practice
 Discovery Activity & Practice For the inquiry activity, there are two options. Choose the 2- page version (pages 12-13) for students who need more workspace and extra guidance. For Warm-Up B, choose
Discovery Activity & Practice For the inquiry activity, there are two options. Choose the 2- page version (pages 12-13) for students who need more workspace and extra guidance. For Warm-Up B, choose
