The Grade 3 Common Core State Standards for Geometry specify that students should
|
|
|
- Rafe Alexander
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Students in third grade describe, analyze, and compare properties of two-dimensional shapes. They compare and classify shapes by their sides and angles, and they use these classifications to define shapes. Students also relate their fraction work to geometry by expressing the area of part of a shape as a unit fraction of the whole. More specifically, students understand that shapes in different categories may share attributes. They explore properties of shapes to understand that shared attributes can define a larger category. For example, students realize that rhombuses, squares, and rectangles have four sides and that they are all quadrilaterals, and students can identify other examples of quadrilaterals that do not belong to this category. They conceptualize that a quadrilateral must be a closed figure with four straight sides and begin to notice characteristics of angles and relationships between opposite sides. Students also partition shapes into parts with equal areas. They express the area of the whole. This builds on students work with fractions and area. Students are responsible for partitioning shapes into halves, thirds, fourths, sixths, and eighths. For example, given a shape, students partition it into equal parts and recognize that the parts all have the same area. They identify the fraction name of each part and are able to partition a shape into parts with equal areas in several different ways. The Grade Common Core State Standards for specify that students should The following hands-on activities will help students understand the attributes of shapes. The activities will equip students with the experiences necessary to identify squares, rectangles, and rhombuses as quadrilaterals. They should be encouraged to provide details when describing the properties of quadrilaterals. Mathematically proficient third graders use clear and precise language in their discussions with others and in their own reasoning. 16
2 Contents Lesson 1 Categorizing Shapes Objective: Categorize shapes. Manipulative: Pattern Blocks Lesson Partitioning Shapes Objective: Partition shapes into equal areas. Manipulative: Pattern Blocks Lesson Partitioning More Shapes Objective: Partition shapes into equal areas. Manipulative: Geoboard 16
3 1 Categorizing Shapes Objective The reasoning skills that students have developed at this age allow them to explore and solve more complex geometric problems. They become more precise as they describe and classify shapes. As they compare shapes, they explain and justify their reasoning. In this lesson, students use Pattern Blocks to model and create new shapes with various attributes. Common Core State Standards.G.1 Talk About It Discuss the Try It! activity. Ask: Can Sasha have a triangle as her new shape? Why or why not? Guide discussion around quadrilaterals having 4 sides and triangles having sides. Ask: Can Sasha make a pentagon as her new shape? Why or why not? Again, guide discussion that pentagons have 5 sides, not 4 sides. Ask: Could Sasha create a shape that has 4 sides that are all unequal lengths? Why or why not? Guide students to conclude that a quadrilateral just needs 4 sides, no matter their lengths. Solve It Reread the problem with students. Have them draw their new shape to share with the class. Then, have them write a few sentences explaining why their shape is a quadrilateral and how it is different from the three quadrilaterals that Sasha already made. More Ideas For other ways to teach about categorizing shapes Have pairs use Pattern Blocks and a spinner numbered, 4, 5, 6, and 8. Have one student spin the spinner. Then have the students create several shapes with that number of sides. Have students describe and compare their shapes and categorize them if possible. Have pairs take a handful of Pattern Blocks. Ask students to sort the shapes they chose into groups that share the same characteristics. Have students explain their groupings, focusing on number of sides, number of corners, comparisons between angles, etc. Formative Assessment Have students try the following problem. Which shape is not a quadrilateral? A. square B. rectangle C. triangle D. rhombus 164
4 Try It! 0 minutes Pairs Here is a problem about categorizing shapes. Sasha has been making quadrilaterals and she wants to make a new one. So far, she has made a rectangle, square, and rhombus. Help Sasha find a quadrilateral she has not yet made. Compare the properties of the new quadrilateral with the properties of the ones she has already made. Introduce the problem. Then have students do the activity to solve the problem. Distribute Pattern Blocks to students. Materials Pattern Blocks (10 triangles and 7 each of the other shapes per pair) 1. Say: Find or make each of the shapes Sasha has already made. Have students find or make a rectangle, square, and rhombus using Pattern Blocks. Ask: What property do all these shapes have that make them a quadrilateral? Elicit that they all have 4 sides.. Ask: What other properties do the shapes have? Guide discussion to squares having square corners (right angles) and 4 sides the same length, rectangles having square corners and opposite sides the same length, and rhombuses having 4 equal sides, but not necessarily square corners. Say: Sasha wants to make a new quadrilateral. Find or make some shapes that could be Sasha s. Watch for students who are counting all the sides of the smaller blocks, and not the big picture sides once a new shape is created. Have students trace around their new shape to see the real sides of the new shape.. Say: Look at all your shapes. Compare their properties. Have students look for common attributes among their shapes (beyond having 4 sides) and group the shapes according to these attributes. Discuss the attributes with students. 165
5 Lesson 1 Name Answer Key Use Pattern Blocks to model the shapes. (Check students work.) 1. Circle quadrilaterals. square and rhombus circled. Circle hexagons. last two shapes circled Model the shape. Draw or trace a shape that has at least one same property. (Check students models.). 4. any shape that has 5 sides this can be any kind of triangle Use Pattern Blocks to model and trace the shapes described different quadrilaterals Possible answers: square, rectangle, rhombus, trapezoid, parallelogram ETA handmind 166 Hands-On Standards, Common Core Edition Download student pages at handmind.com/hosstudent.
6 Answer Name Key Challenge! Jessica says that all rhombuses are quadrilaterals. Mike says all quadrilaterals are rhombuses. Who is right? Explain your answer using words and drawings. Challenges: Jessica is right. All rhombuses are quadrilaterals with 4 sides and opposite sides parallel. There are more kinds of quadrilaterals than rhombuses, so all quadrilaterals cannot be rhombuses. Students may make drawings of squares or rectangles or trapezoids to show other quadrilaterals. ETA handmind Download student pages at handmind.com/hosstudent. Hands-On Standards, Common Core Edition 167
7 .G. Objective Common Core State Standards Partitioning Shapes In this lesson, students build upon their understanding of fractions and area. Using concrete models, students are able to visualize how smaller shapes fill the area of larger shapes. They count to figure out how many equal pieces there are in each whole and determine the fraction for one equal piece in relation to the whole. Students use Pattern Blocks to partition shapes into smaller shapes and discover the fractional pieces. Talk About It Discuss the Try It! activity. Say: We can say that one triangle represents 1 of the area of the trapezoid. Ask: What fraction of the area is represented by two triangle pieces? Ask: What fraction of the area is represented by three triangle pieces? Elicit that the fraction is. Elicit further that three thirds is all the thirds, so refers to the whole area. Tell students that means the same thing as 1. Solve It Reread the problem with students. Have them write the denominator of the fraction ( parts) and then the numerator, showing how many parts each triangle represents. More Ideas For other ways to teach about partitioning shapes into equal areas Have students use Pattern Blocks to explore questions such as how many triangles make up a hexagon, how many rhombuses make up a hexagon, and so on. Have them trace the partitioned shape, and write a fraction representing one piece of the partitioned shape. Have students use Color Tiles to create partitioned rectangles and squares. Have them create partitions of halves, thirds, fourths, sixths, and eighths. Have them write the total number of partitions and the fraction that each partition represents. Formative Assessment Have students try the following problem. What fraction of the hexagon is one green triangle? A. 1 B. 1 4 C. 1 5 D
8 Try It! 5 minutes Pairs Here is a problem about partitioning shapes into equal areas. Kyle is working with Pattern Blocks. He has divided a trapezoid block into equal triangles. How many triangles did he use? What fraction of the trapezoid does one triangle represent? Introduce the problem. Then have students do the activity to solve the problem. Distribute Pattern Blocks, paper, and pencils to students. Materials Pattern Blocks (10 triangles and 7 each of the other shapes per pair) paper (1 sheet per pair) pencils (1 per pair) 1. Say: Find the red trapezoid in your set of blocks. Find some green triangles. Let s see if we can put together some triangles to make a trapezoid.. Say: We are making the trapezoid with smaller equal pieces. So each equal piece will be a fraction of the whole shape. Ask: How many triangles are needed to make the trapezoid? Watch for students who try to make the whole with different-sized shapes. Explain that the smaller shapes comprising the whole must all be the same size.. Ask: What fraction of the trapezoid does one triangle represent? Say: The total number of smaller parts is the denominator of the fraction. Write on the board. Elicit that since you asked what fraction of the whole one triangle represents, the numerator is 1. Complete the fraction on the board, 1. Have students draw the model and label one of the thirds. 169
9 Lesson Name Answer Key Use Pattern Blocks of equal size to divide the shape. Determine the number of equal pieces. Write the fraction for one piece. (Check students work.) 1. yellow hexagon, divided using blue rhombuses. blue rhombus, divided using green triangles 1 1 Use Pattern Blocks of equal size to divide the shape. Draw the model. Write the fraction for one piece.. hexagon, divided using red trapezoids (Check students models.) 4. hexagon, divided using green triangles parallelogram, divided using blue rhombuses 6. parallelogram, divided using green triangles ETA handmind 170 Hands-On Standards, Common Core Edition Download student pages at handmind.com/hosstudent.
10 Answer Name Key Challenge! Explain why the smaller pieces you used in the previous problems must be of equal size to describe fractions of larger shapes. Challenge: (Sample) Fractions are equal parts of a whole. To describe fractions of the larger shape, the smaller shapes must be equal. ETA handmind Download student pages at handmind.com/hosstudent. Hands-On Standards, Common Core Edition 171
11 Objective Partitioning More Shapes In the previous lesson, students partitioned shapes into parts with equal areas using Pattern Blocks. Now students will build on this understanding using the Geoboard. By using the Geoboard, students can create a different variety of shapes and partition those into equal areas and describe the area of each part as a unit fraction of the whole..g. Common Core State Standards Talk About It Discuss the Try It! activity. Ask: Why couldn t Elana s shape be a trapezoid? Guide discussion to cover the need for a shape with square corners (right angles.) Ask: Why couldn t Elana s shape be a square? Discuss that on a Geoboard a square can be made of 1, 4, 9, or 16 equal squares, not 8. Ask: What quadrilateral is made of 8 equal squares on a Geoboard? Discuss that Elana s shape is a rectangle, because a rectangle can be made with rows of 4, or 4 rows of. Solve It With students, reread the problem. Have them draw Elana s shape on Inch Grid Paper (BLM 8) and shade 1 of it. Have them write two sentences describing 8 their shape and telling why it matches Elana s description of her shape. More Ideas For other ways to teach about partitioning shapes into equal areas Have students make a large rectangle on the Geoboard. Have them partition the rectangle into smaller equal sections as many ways as they can and record each of the ways on grid paper. For each way, have students count the number of smaller equal sections and write the fraction for one piece. Have one student create a shape on the Geoboard and give it to a partner. Then have the partner partition the shape into smaller equal parts. Have students describe their shape, the number of equal parts in it, and how one fractional piece would be represented. Formative Assessment Have students try the following problem. If the following is 1, what is the whole? 6 A. B. C. D. 17
12 Try It! 5 minutes Pairs Here is a problem about partitioning shapes into equal areas. Elana created a shape on her Geoboard. She described it as a quadrilateral and said that 1 of it was a square. What shape did she make? 8 Introduce the problem. Then have students do the activity to solve the problem. Distribute Geoboards, Inch Grid Paper (BLM 8), and pencils to students. Materials Geoboard (1 per pair) Inch Grid Paper (BLM 8; 1 per student) pencils (1 per student) 1. Say: Elana says her shape is a quadrilateral. Ask: What does that tell us? What are some shapes that are quadrilaterals? List shapes on the board: square, rectangle, trapezoid, rhombus, etc. Say: Make a trapezoid on your Geoboard.. Say: Elana also said that 1 of the shape is 8 a square. Ask: How many squares is her shape divided into? Can you divide your trapezoid into 8 equal squares? Why not? Elicit that the shape must have square corners (right angles). Say: Make a square on your Geoboard. Watch for students who do not partition the larger shape into equal smaller parts. Remind students that the smaller parts need to be the same size and shape, because fractional parts mean equal parts.. Ask: How many smaller squares are in your square? Can you make a square with 8 equal square parts on your Geoboard? Say: Make a quadrilateral that you can divide into 8 equal square parts. 17
13 Lesson Name Answer Key Use a Geoboard to model a whole shape using the part given. Draw the whole shape on the grid. (Check students work.) 1. triangle = 1 square a 4 4 square made of equal triangles rectangle = 1 4 rectangle a 4 or 4 rectangle made of 4 equal rectangles square = 1 9 square 4 4. trapezoid = 1 hexagon ETA handmind 174 a square made of 9 equal squares a hexagon made of equal trapezoids Hands-On Standards, Common Core Edition Download student pages at handmind.com/hosstudent.
14 Answer Name Key Challenge! Cheryl says she can make a pentagon on her Geoboard using 6 right triangles. Use your Geoboard to try this, and draw the shapes to show if Cheryl is correct. Describe your work. Challenge: (Sample) A pentagon, or house, can be made using right triangles as the roof, and then 4 alternating right triangles to make the bottom of the house. ETA handmind Download student pages at handmind.com/hosstudent. Hands-On Standards, Common Core Edition 175
Identify and Classify Quadrilaterals
 5 Objective Identify and Classify Quadrilaterals In this lesson, students investigate the properties of quadrilaterals by making models. They learn that some quadrilaterals can be classified in more than
5 Objective Identify and Classify Quadrilaterals In this lesson, students investigate the properties of quadrilaterals by making models. They learn that some quadrilaterals can be classified in more than
Geometry. Plane Shapes. Talk About It. More Ideas. Formative Assessment. Have students try the following problem. Which shape has parallel lines?
 2 Objective Plane s The reasoning skills that students develop at this age allow them to explore more complex geometric problems and properties. They should develop more precise ways to describe and classify
2 Objective Plane s The reasoning skills that students develop at this age allow them to explore more complex geometric problems and properties. They should develop more precise ways to describe and classify
Exploring Quadrilaterals: Sides and Angles
 7 5.G.1 5.G.2 5.G.3 5.G.4 Objective Common Core State Standards Exploring Quadrilaterals: Sides and Angles Students can be expected to examine the features of a variety of shapes, such as quadrilaterals,
7 5.G.1 5.G.2 5.G.3 5.G.4 Objective Common Core State Standards Exploring Quadrilaterals: Sides and Angles Students can be expected to examine the features of a variety of shapes, such as quadrilaterals,
Three-Dimensional Shapes
 Lesson 11.1 Three-Dimensional Shapes Three-dimensional objects come in different shapes. sphere cone cylinder rectangular prism cube Circle the objects that match the shape name. 1. rectangular prism 2.
Lesson 11.1 Three-Dimensional Shapes Three-dimensional objects come in different shapes. sphere cone cylinder rectangular prism cube Circle the objects that match the shape name. 1. rectangular prism 2.
Getting Ready to Teach Unit 6
 Getting Ready to Teach Unit 6 Learning Path in the Common Core Standards In this unit, students study the attributes of triangles, quadrilaterals, and other polygons. They find perimeter and area of various
Getting Ready to Teach Unit 6 Learning Path in the Common Core Standards In this unit, students study the attributes of triangles, quadrilaterals, and other polygons. They find perimeter and area of various
Mathematics Success Level E
 T877 [OBJECTIVE] The student will classify two-dimensional figures based on properties. [PREREQUISITE SKILLS] Lesson 29, knowledge of basic geometry terminology including: parallel sides, congruent sides,
T877 [OBJECTIVE] The student will classify two-dimensional figures based on properties. [PREREQUISITE SKILLS] Lesson 29, knowledge of basic geometry terminology including: parallel sides, congruent sides,
Geometry. Students at Dommerich Elementary helped design and construct a mosaic to show parts of their community and local plants and animals.
 Geometry Describing and analyzing two-dimensional shapes Students at Dommerich Elementary helped design and construct a mosaic to show parts of their community and local plants and animals. 479 Make a
Geometry Describing and analyzing two-dimensional shapes Students at Dommerich Elementary helped design and construct a mosaic to show parts of their community and local plants and animals. 479 Make a
Describe Plane Shapes
 Lesson 12.1 Describe Plane Shapes You can use math words to describe plane shapes. point an exact position or location line endpoints line segment ray a straight path that goes in two directions without
Lesson 12.1 Describe Plane Shapes You can use math words to describe plane shapes. point an exact position or location line endpoints line segment ray a straight path that goes in two directions without
Grade 3 Mathematics Item Specification C1 TK
 Claim 1: Concepts and Procedures Students can explain and apply mathematical concepts and carry out mathematical procedures with precision and fluency. Content Domain: Geometry Target K [a]: Reason with
Claim 1: Concepts and Procedures Students can explain and apply mathematical concepts and carry out mathematical procedures with precision and fluency. Content Domain: Geometry Target K [a]: Reason with
TOPIC 16 STUDY GUIDE LINES, ANGLES AND SHAPES
 Name: Teacher: TOPIC 16 STUDY GUIDE LINES, ANGLES AND SHAPES Study Guide Due: Test Date: Parents, 4th Graders are focusing on giving their best effort. One way to show that they are going above and beyond
Name: Teacher: TOPIC 16 STUDY GUIDE LINES, ANGLES AND SHAPES Study Guide Due: Test Date: Parents, 4th Graders are focusing on giving their best effort. One way to show that they are going above and beyond
Geometry !!!!! Tri-Folds 3.G.1 - # 1. 4 Mystery Shape 5 Compare & Contrast. 3rd Grade Math. Compare. Name: Date: Contrast
 4 Mystery Shape 5 Compare & Contrast 1. Draw and label a shape that has one more side than a triangle. Draw it. 2. Draw and label a shape that has three more sides than a triangle. 3. Draw and label a
4 Mystery Shape 5 Compare & Contrast 1. Draw and label a shape that has one more side than a triangle. Draw it. 2. Draw and label a shape that has three more sides than a triangle. 3. Draw and label a
Lesson 99. Three-Dimensional Shapes. sphere cone cylinder. Circle the objects that match the shape name.
 Three-Dimensional Shapes Lesson 99 COMMON CORE STANDARD CC.2.G.1 Lesson Objective: Identify threedimensional shapes. Three-dimensional objects come in different shapes. sphere cone cylinder rectangular
Three-Dimensional Shapes Lesson 99 COMMON CORE STANDARD CC.2.G.1 Lesson Objective: Identify threedimensional shapes. Three-dimensional objects come in different shapes. sphere cone cylinder rectangular
Number and Operations - Fractions
 NF.1.3c Number and Operations - Fractions NF.1.3 NF.1.2b NF.1.2a Understand Fractions February 3 - February 20 NF.1.2 NF.1.1 Math! Lessons Develop understanding of fractions as numbers. Understand a fraction
NF.1.3c Number and Operations - Fractions NF.1.3 NF.1.2b NF.1.2a Understand Fractions February 3 - February 20 NF.1.2 NF.1.1 Math! Lessons Develop understanding of fractions as numbers. Understand a fraction
HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT 2016/2017 INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT
 HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT 2016/2017 INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT Third Grade Quarter 4 Unit 10: Geometry and Measurement Word Problems Approximately 40 Days Begin around March 27 th This 40-day final unit
HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT 2016/2017 INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT Third Grade Quarter 4 Unit 10: Geometry and Measurement Word Problems Approximately 40 Days Begin around March 27 th This 40-day final unit
About Finish Line Mathematics 5
 Table of COntents About Finish Line Mathematics 5 Unit 1: Big Ideas from Grade 1 7 Lesson 1 1.NBT.2.a c Understanding Tens and Ones [connects to 2.NBT.1.a, b] 8 Lesson 2 1.OA.6 Strategies to Add and Subtract
Table of COntents About Finish Line Mathematics 5 Unit 1: Big Ideas from Grade 1 7 Lesson 1 1.NBT.2.a c Understanding Tens and Ones [connects to 2.NBT.1.a, b] 8 Lesson 2 1.OA.6 Strategies to Add and Subtract
Geometry. Standardized Practice Have students try the following problem.
 1 Students need a basic understanding of angles to learn the properties of twodimensional shapes. In this lesson, students use models to represent, measure, and classify angles. Objective Recognize types
1 Students need a basic understanding of angles to learn the properties of twodimensional shapes. In this lesson, students use models to represent, measure, and classify angles. Objective Recognize types
The School District of Palm Beach County 3 rd Grade Mathematics Scope st Trimester
 1 st Trimester Measurement and Data (MD) MD.2.3 MD.2.4 Represent and interpret data. Draw a scaled picture graph and a scaled bar graph to represent a data set with several categories. Solve one- and two-step
1 st Trimester Measurement and Data (MD) MD.2.3 MD.2.4 Represent and interpret data. Draw a scaled picture graph and a scaled bar graph to represent a data set with several categories. Solve one- and two-step
Does a group of parallel line segments need to be the same length?
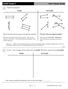 1 Parallel Line Segments Parallel t Parallel What is the same about the groups of parallel line segments? They are always the same distance apart. They do not intersect each other. If you extend the line
1 Parallel Line Segments Parallel t Parallel What is the same about the groups of parallel line segments? They are always the same distance apart. They do not intersect each other. If you extend the line
Construct Triangles. Geometry. Objective. Common Core State Standards. Talk About It. Solve It. More Ideas. Formative Assessment
 2 Construct Triangles 7.G.2 Objective Common Core State Standards Triangles are polygons with three sides, and they are classified by their sides and angles. The sum of the angles of any triangle is 180,
2 Construct Triangles 7.G.2 Objective Common Core State Standards Triangles are polygons with three sides, and they are classified by their sides and angles. The sum of the angles of any triangle is 180,
3teacherchicks.blogspot.com
 Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division. 3.OA.1.Interpret products of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 5 7 as the total number of objects in 5 groups of 7 objects each. For example,
Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division. 3.OA.1.Interpret products of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 5 7 as the total number of objects in 5 groups of 7 objects each. For example,
The School District of Palm Beach County 3 rd Grade Mathematics Scope st Trimester
 1 st Trimester Measurement and Data (MD) MD.2.3 MD.2.4 Represent and interpret data. Draw a scaled picture graph and a scaled bar graph to represent a data set with several categories. Solve one- and two-step
1 st Trimester Measurement and Data (MD) MD.2.3 MD.2.4 Represent and interpret data. Draw a scaled picture graph and a scaled bar graph to represent a data set with several categories. Solve one- and two-step
15.2 Draw Quadrilaterals
 ? Name 15.2 Draw Quadrilaterals Essential Question How can you draw quadrilaterals? Geometry and Measurement 3.6.B Also 3.6.A MATHEMATICAL PROCESSES 3.1.D, 3.1.G Unlock the Problem Connect You have learned
? Name 15.2 Draw Quadrilaterals Essential Question How can you draw quadrilaterals? Geometry and Measurement 3.6.B Also 3.6.A MATHEMATICAL PROCESSES 3.1.D, 3.1.G Unlock the Problem Connect You have learned
Sand Creek Zone Curriculum Map
 Quarter 1 Concept: Add and subtract 0. 3.NBT.2 Fluently add and subtract 0 using strategies and algorithms based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction.
Quarter 1 Concept: Add and subtract 0. 3.NBT.2 Fluently add and subtract 0 using strategies and algorithms based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction.
Geometry Sixth Grade
 Standard 6-4: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of shape, location, and movement within a coordinate system; similarity, complementary, and supplementary
Standard 6-4: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of shape, location, and movement within a coordinate system; similarity, complementary, and supplementary
CPSD: Grade 3 Mathematics. Module 4. area. Apx. 30 days Apx. 25 days Apx. 25 days Apx. 20 days Apx. 25 days Apx. 10 days 25 days
 CPSD: Grade 3 Mathematics Module 1 Module 2 Module 3 Module 4 Module 5 Module 6 Module 7 Properties of multiplication and division and solving problems with units of 2-5 and 10 Place value and problem
CPSD: Grade 3 Mathematics Module 1 Module 2 Module 3 Module 4 Module 5 Module 6 Module 7 Properties of multiplication and division and solving problems with units of 2-5 and 10 Place value and problem
Quadrilaterals Mini- Lesson
 Quadrilaterals Mini- Lesson Students investigate and compare the characteristics of quadrilaterals. This activity helps students to: Identify the characteristics (equal side length, equal angle, lines
Quadrilaterals Mini- Lesson Students investigate and compare the characteristics of quadrilaterals. This activity helps students to: Identify the characteristics (equal side length, equal angle, lines
Describe Triangles. About the Math Professional Development 12.7 LESSON AT A GLANCE
 12.7 LESSON Describe Triangles FOUS OHERENE RIGOR LESSON AT A GLANE F R Focus: ommon ore State Standards 3.G.A.1 Understand that shapes in different categories (e.g., rhombuses, rectangles, and others)
12.7 LESSON Describe Triangles FOUS OHERENE RIGOR LESSON AT A GLANE F R Focus: ommon ore State Standards 3.G.A.1 Understand that shapes in different categories (e.g., rhombuses, rectangles, and others)
Geometry. Talk About It. More Ideas. Formative Assessment. Have children try the following problem.
 K.G.2 K.G.3 K.G.4 176 10 Objective Common Core State Standards Cubes and Spheres In mathematics, three-dimensional figures are also called solids. If something is three-dimensional, it is considered to
K.G.2 K.G.3 K.G.4 176 10 Objective Common Core State Standards Cubes and Spheres In mathematics, three-dimensional figures are also called solids. If something is three-dimensional, it is considered to
Geometry and Spatial Reasoning. Two-Dimensional Figures Important Book
 Geometry and Spatial Reasoning Activity: TEKS: Two-Dimensional Figures Important Book (4.8) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student identifies and describes attributes of geometric figures using formal
Geometry and Spatial Reasoning Activity: TEKS: Two-Dimensional Figures Important Book (4.8) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student identifies and describes attributes of geometric figures using formal
Answer Key Lesson 6: Classifying Shapes
 Student Guide The Flatopia Polygon Zoo Professor Peabody had a dream that he lived in a two-dimensional town called Flatopia. There were two-dimensional creatures in town, all shaped like polygons. Help
Student Guide The Flatopia Polygon Zoo Professor Peabody had a dream that he lived in a two-dimensional town called Flatopia. There were two-dimensional creatures in town, all shaped like polygons. Help
15. First make a parallelogram by rotating the original triangle. Then tile with the Parallelogram.
 Shapes and Designs: Homework Examples from ACE Investigation 1: Question 15 Investigation 2: Questions 4, 20, 24 Investigation 3: Questions 2, 12 Investigation 4: Questions 9 12, 22. ACE Question ACE Investigation
Shapes and Designs: Homework Examples from ACE Investigation 1: Question 15 Investigation 2: Questions 4, 20, 24 Investigation 3: Questions 2, 12 Investigation 4: Questions 9 12, 22. ACE Question ACE Investigation
Objective: Reason about attributes to construct quadrilaterals on square or triangular grid paper.
 Lesson 16 Objective: Reason about attributes to construct quadrilaterals on square or Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (12
Lesson 16 Objective: Reason about attributes to construct quadrilaterals on square or Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (12
CUMBERLAND COUNTY SCHOOL DISTRICT BENCHMARK ASSESSMENT CURRICULUM PACING GUIDE
 School: Cumberland County Elementary School CUMBERLAND COUNTY SCHOOL DISTRICT BENCHMARK ASSESSMENT CURRICULUM PACING GUIDE Subject: Math Grade: Third Benchmark Assessment 1 Instructional Timeline: Weeks
School: Cumberland County Elementary School CUMBERLAND COUNTY SCHOOL DISTRICT BENCHMARK ASSESSMENT CURRICULUM PACING GUIDE Subject: Math Grade: Third Benchmark Assessment 1 Instructional Timeline: Weeks
Reason with shapes and their attributes.
 Grade 3 Geometry and Perimeter SDadfa;sdklfjas;Unit Overview Reason with shapes and their attributes. 1. Understand that shapes in different categories (e.g., rhombuses, rectangles, and others) may share
Grade 3 Geometry and Perimeter SDadfa;sdklfjas;Unit Overview Reason with shapes and their attributes. 1. Understand that shapes in different categories (e.g., rhombuses, rectangles, and others) may share
3rd Grade. Shapes and Perimeter.
 1 3rd Grade Shapes and Perimeter 2015 11 10 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Area Perimeter Lines, Rays and Line Segments Angles Click on a topic to go to that section Parallel and Intersecting Lines
1 3rd Grade Shapes and Perimeter 2015 11 10 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Area Perimeter Lines, Rays and Line Segments Angles Click on a topic to go to that section Parallel and Intersecting Lines
5th Grade Geometry
 Slide 1 / 112 Slide 2 / 112 5th Grade Geometry 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 112 Geometry Unit Topics Click on the topic to go to that section Polygons Classifying Triangles & Quadrilaterals Coordinate
Slide 1 / 112 Slide 2 / 112 5th Grade Geometry 2015-11-23 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 112 Geometry Unit Topics Click on the topic to go to that section Polygons Classifying Triangles & Quadrilaterals Coordinate
Dividing Rectangles into Rows and Columns Part 1. 2nd Grade. Slide 1 / 201 Slide 2 / 201. Slide 3 / 201. Slide 4 / 201. Slide 6 / 201.
 Slide / 0 Slide / 0 nd Grade Geometry Presentation Part 05--0 www.njctl.org Slide / 0 Table of Contents Presentation D Shapes - Sides and Angles - Part D Shapes - Part Lab: D Shapes Lab D Shapes - Part
Slide / 0 Slide / 0 nd Grade Geometry Presentation Part 05--0 www.njctl.org Slide / 0 Table of Contents Presentation D Shapes - Sides and Angles - Part D Shapes - Part Lab: D Shapes Lab D Shapes - Part
In this task, students will investigate the attributes of quadrilaterals.
 PRACTICE TASK: Investigating Quadrilaterals In this task, students will investigate the attributes of quadrilaterals. STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICAL CONTENT MCC5.G.3 Understanding that attributes belonging
PRACTICE TASK: Investigating Quadrilaterals In this task, students will investigate the attributes of quadrilaterals. STANDARDS FOR MATHEMATICAL CONTENT MCC5.G.3 Understanding that attributes belonging
UNIT PLAN. Big Idea/Theme: Polygons can be identified, classified, and described.
 UNIT PLAN Grade Level: 5 Unit #: 11 Unit Name Geometry Polygons Time: 15 lessons, 18 days Big Idea/Theme: Polygons can be identified, classified, and described. Culminating Assessment: (requirements of
UNIT PLAN Grade Level: 5 Unit #: 11 Unit Name Geometry Polygons Time: 15 lessons, 18 days Big Idea/Theme: Polygons can be identified, classified, and described. Culminating Assessment: (requirements of
Chapter 6 Rational Numbers and Proportional Reasoning
 Chapter 6 Rational Numbers and Proportional Reasoning Students should build their understanding of fractions as parts of a whole and as division. They will need to see and explore a variety of models of
Chapter 6 Rational Numbers and Proportional Reasoning Students should build their understanding of fractions as parts of a whole and as division. They will need to see and explore a variety of models of
Answer Key. Name. Here is a birthday cake cut into pieces. How many pieces do you see? ANSWER: 24 pieces
 Here is a birthday cake cut into pieces. How many pieces do you see? ANSWER: pieces COMMENTS & EXTENSIONS: Trace your hand on graph paper. How many of the graph paper squares does your hand cover? Which
Here is a birthday cake cut into pieces. How many pieces do you see? ANSWER: pieces COMMENTS & EXTENSIONS: Trace your hand on graph paper. How many of the graph paper squares does your hand cover? Which
Geometry. Set 1. Daily Practice And Answer Keys
 Geometry Set 1 Daily Practice And Answer Keys Website: http://alex.state.al.us/ccrs/node/314 Name Date Daily Practice Geometry DAY 1 1. The figure above is shaded on the top side and white on the under
Geometry Set 1 Daily Practice And Answer Keys Website: http://alex.state.al.us/ccrs/node/314 Name Date Daily Practice Geometry DAY 1 1. The figure above is shaded on the top side and white on the under
Answer Key Lesson 11: Workshop: Shapes and Properties
 Answer Key esson 11: Use the nine Power Polygons below for Questions 1 and 2. 1. A. Sort the shapes with four sides into ox A. Sort the Shapes with one or more right angles into ox. Some shapes will go
Answer Key esson 11: Use the nine Power Polygons below for Questions 1 and 2. 1. A. Sort the shapes with four sides into ox A. Sort the Shapes with one or more right angles into ox. Some shapes will go
Reflections (Flips) Geometry. Objective. Common Core State Standards Talk About It. Solve It. More Ideas. Formative Assessment
 2 Reflections (Flips) Objective Students can expand their understanding of congruence by studying flips (reflections), turns (rotations), and slides (translations). A reflection flips a figure over a line
2 Reflections (Flips) Objective Students can expand their understanding of congruence by studying flips (reflections), turns (rotations), and slides (translations). A reflection flips a figure over a line
THE COMPETITIVE EDGE
 SAMPLE PAGES FOR THE READY EOG ASSESSMENT THE COMPETITIVE EDGE THIRD GRADE MATHEMATICS with COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS 2012 EDITION J ANE H EREFORD CPC CONTEMPORARY PUBLISHING COMPANY OF RALEIGH, INC.
SAMPLE PAGES FOR THE READY EOG ASSESSMENT THE COMPETITIVE EDGE THIRD GRADE MATHEMATICS with COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS 2012 EDITION J ANE H EREFORD CPC CONTEMPORARY PUBLISHING COMPANY OF RALEIGH, INC.
MCC5.G.3 Understand that attributes belonging to a category of two-dimensional figures also belong to all subcategories of that categories.
 Fifth Grade Mathematics Unit 6 CONSTRUCTING TASK: Property Lists of Quadrilaterals Adapted from Van De Walle, Teaching Student-Centered Math pg. 207 The purpose of this task is for students to become familiar
Fifth Grade Mathematics Unit 6 CONSTRUCTING TASK: Property Lists of Quadrilaterals Adapted from Van De Walle, Teaching Student-Centered Math pg. 207 The purpose of this task is for students to become familiar
Lesson 4. Objective: Compare and classify quadrilaterals. Lesson Suggested Lesson Structure. Multiply by 4 (8 minutes)
 Lesson 4 3 7 Lesson 4 Objective: Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (12 minutes) (7 minutes) (31 minutes) (10 minutes) (60 minutes)
Lesson 4 3 7 Lesson 4 Objective: Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief Total Time (12 minutes) (7 minutes) (31 minutes) (10 minutes) (60 minutes)
Title: Identifying, Classifying, and Creating Quadrilaterals - Qualifying Quadrilaterals
 Title: Identifying, Classifying, and Creating Quadrilaterals - Qualifying Quadrilaterals Brief Overview: Through problem solving, oral and written communication, higher-order thinking and a variety of
Title: Identifying, Classifying, and Creating Quadrilaterals - Qualifying Quadrilaterals Brief Overview: Through problem solving, oral and written communication, higher-order thinking and a variety of
Instructional Alignment Chart
 CLUSTER HEADING: STANDARD: N/A CLUSTER HEADING: Identify and describe shapes (squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, and spheres). STANDARD: K.G.3 Identify shapes as
CLUSTER HEADING: STANDARD: N/A CLUSTER HEADING: Identify and describe shapes (squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, and spheres). STANDARD: K.G.3 Identify shapes as
Vocabulary. Term Page Definition Clarifying Example. apothem. center of a circle. center of a regular polygon. central angle of a regular polygon
 CHAPTER 9 Vocabulary The table contains important vocabulary terms from Chapter 9. As you work through the chapter, fill in the page number, definition, and a clarifying example. apothem Term Page Definition
CHAPTER 9 Vocabulary The table contains important vocabulary terms from Chapter 9. As you work through the chapter, fill in the page number, definition, and a clarifying example. apothem Term Page Definition
The Grade 5 Common Core State Standards for Measurement and Data specify that students should
 Measurement and Data Students have learned that measurement is the process of comparing a quantity to a standard unit. In fifth grade, students convert units within a given measurement system and use these
Measurement and Data Students have learned that measurement is the process of comparing a quantity to a standard unit. In fifth grade, students convert units within a given measurement system and use these
Skill: Polygons. Vocabulary: Polygon a closed two-dimensional figure with straight edges
 Skill: Polygons Standard: 5.13.a ~ The student, using plane figures (square, rectangle, triangle, parallelogram, rhombus, and trapezoid), will develop definitions of these plane figures; 5.13.b ~ The student,
Skill: Polygons Standard: 5.13.a ~ The student, using plane figures (square, rectangle, triangle, parallelogram, rhombus, and trapezoid), will develop definitions of these plane figures; 5.13.b ~ The student,
Constructing Symmetrical Shapes
 1 Constructing Symmetrical Shapes 1 Construct 2-D shapes with one line of symmetry A line of symmetry may be horizontal or vertical 2 a) Use symmetry to complete the picture b) Describe the method you
1 Constructing Symmetrical Shapes 1 Construct 2-D shapes with one line of symmetry A line of symmetry may be horizontal or vertical 2 a) Use symmetry to complete the picture b) Describe the method you
Reteach. Chapter 14. Grade 4
 Reteach Chapter 14 Grade 4 Lesson 1 Reteach Draw Points, Lines, and Rays A point is an exact location that is represented by a dot. Example: point R R A line goes on forever in both directions. Example:
Reteach Chapter 14 Grade 4 Lesson 1 Reteach Draw Points, Lines, and Rays A point is an exact location that is represented by a dot. Example: point R R A line goes on forever in both directions. Example:
Choose the correct answer. For 1 3, use the diagram. Which triangle is right and isosceles? Which angle is an acute angle? J L K
 Choose the correct answer. For, use the diagram. Page Which triangle is right and isosceles? Which angle is an acute angle? J L K N Which is a right angle? J L K M Which is an obtuse angle? J L Which triangle
Choose the correct answer. For, use the diagram. Page Which triangle is right and isosceles? Which angle is an acute angle? J L K N Which is a right angle? J L K M Which is an obtuse angle? J L Which triangle
Lesson 2 Pre-Visit A Diamond Filled with Shapes
 Lesson 2 Pre-Visit A Diamond Filled with Shapes Objective: Students will be able to: Define the term polygon. Recognize different polygons evident in baseball. Draw and identify different polygons. Time
Lesson 2 Pre-Visit A Diamond Filled with Shapes Objective: Students will be able to: Define the term polygon. Recognize different polygons evident in baseball. Draw and identify different polygons. Time
Addition and Multiplication with Volume and Area
 Grade 5 Module 5 Addition and Multiplication with Volume and Area OVERVIEW In this 25-day module, students work with two- and three-dimensional figures. Volume is introduced to students through concrete
Grade 5 Module 5 Addition and Multiplication with Volume and Area OVERVIEW In this 25-day module, students work with two- and three-dimensional figures. Volume is introduced to students through concrete
4 Mathematics Curriculum. Module Overview... i Topic A: Lines and Angles... 4.A.1. Topic B: Angle Measurement... 4.B.1
 New York State Common Core 4 Mathematics Curriculum G R A D E Table of Contents GRADE 4 MODULE 4 Angle Measure and Plane Figures GRADE 4 MODULE 4 Module Overview... i Topic A: Lines and Angles... 4.A.1
New York State Common Core 4 Mathematics Curriculum G R A D E Table of Contents GRADE 4 MODULE 4 Angle Measure and Plane Figures GRADE 4 MODULE 4 Module Overview... i Topic A: Lines and Angles... 4.A.1
PERSPECTIVES ON GEOMETRY PRE-ASSESSMENT ANSWER SHEET (GEO )
 PERSPECTIVES ON GEOMETRY PRE-ASSESSMENT ANSWER SHEET (GEO.11.02.2) Name Date Site TURN IN BOTH TEST AND ANSWER SHEET TO YOUR INSTRUCTOR WHEN DONE. 1. 18. I. 2. 19. 3. 20. 4. 21. 5. 22. 6. 23. 7. 24. 8.
PERSPECTIVES ON GEOMETRY PRE-ASSESSMENT ANSWER SHEET (GEO.11.02.2) Name Date Site TURN IN BOTH TEST AND ANSWER SHEET TO YOUR INSTRUCTOR WHEN DONE. 1. 18. I. 2. 19. 3. 20. 4. 21. 5. 22. 6. 23. 7. 24. 8.
 Student Mathematician: Date: Some, All or None Tell whether each statement below is true or false by circling the correct answer. If the statement is false, give a counterexample using words and/or pictures.
Student Mathematician: Date: Some, All or None Tell whether each statement below is true or false by circling the correct answer. If the statement is false, give a counterexample using words and/or pictures.
CCSS Standard. CMSD Dynamic Pacing Guide 3 rd Grade Math I Can Statements + Introduced and Assessed Introduced First Nine Weeks
 3.NBT.1 Use place value understanding to round whole numbers to the nearest 10 or 100. 3.OA.8 Solve two-step word problems using the four operations. Represent these problems using equations with a letter
3.NBT.1 Use place value understanding to round whole numbers to the nearest 10 or 100. 3.OA.8 Solve two-step word problems using the four operations. Represent these problems using equations with a letter
Answer Key Lesson 6: Classifying Shapes
 Student Guide The Flatopia Polygon Zoo Professor Peabody had a dream that he lived in a two-dimensional town called Flatopia. There were two-dimensional creatures in town, all shaped like polygons. Help
Student Guide The Flatopia Polygon Zoo Professor Peabody had a dream that he lived in a two-dimensional town called Flatopia. There were two-dimensional creatures in town, all shaped like polygons. Help
Multiply. 7.A.9. Lesson 1: Solve word problems in varied contexts using a letter to represent the unknown. Date: 1/29/14
 COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 1 Pattern Sheet 3 7 Multiply. Lesson 1: Solve word problems in varied contexts using a letter to represent the unknown. Date: 1/29/14 7.A.9 COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS
COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 1 Pattern Sheet 3 7 Multiply. Lesson 1: Solve word problems in varied contexts using a letter to represent the unknown. Date: 1/29/14 7.A.9 COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS
Grade 3. EDM Version 4. Everyday Math: Unit. Measurement and Geometry. Study Guide
 EDM Version 4 Grade 3 Everyday Math: Unit Measurement and Geometry. Study Guide Thank you! Catherine Wiist @ Abc123is4me http://www.teacherspayteachers.com/store/abc123is4me (All new products are discounted
EDM Version 4 Grade 3 Everyday Math: Unit Measurement and Geometry. Study Guide Thank you! Catherine Wiist @ Abc123is4me http://www.teacherspayteachers.com/store/abc123is4me (All new products are discounted
Fraction and Mixed-Number Addition and Subtraction
 Fraction and Mixed-Number Addition and Subtraction Objective To guide students in the use of pattern blocks to add and subtract fractions and mixed numbers. www.everydaymathonline.com epresentations etoolkit
Fraction and Mixed-Number Addition and Subtraction Objective To guide students in the use of pattern blocks to add and subtract fractions and mixed numbers. www.everydaymathonline.com epresentations etoolkit
The Mysterious Polygonians
 The Mysterious Polygonians MA.C.1.2.1.3.1,.2, and.3 LESSON FOCUS Creating and describing two-dimensional figures. COMPANION ANCHORS LESSONS Lines, Line Segments, Rays, and Angles; Recognizing Polygons;
The Mysterious Polygonians MA.C.1.2.1.3.1,.2, and.3 LESSON FOCUS Creating and describing two-dimensional figures. COMPANION ANCHORS LESSONS Lines, Line Segments, Rays, and Angles; Recognizing Polygons;
Unit Lesson Plan: Measuring Length and Area: Area of shapes
 Unit Lesson Plan: Measuring Length and Area: Area of shapes Day 1: Area of Square, Rectangles, and Parallelograms Day 2: Area of Triangles Trapezoids, Rhombuses, and Kites Day 3: Quiz over Area of those
Unit Lesson Plan: Measuring Length and Area: Area of shapes Day 1: Area of Square, Rectangles, and Parallelograms Day 2: Area of Triangles Trapezoids, Rhombuses, and Kites Day 3: Quiz over Area of those
1. Tell whether each figure is a polygon. Explain how you know. a. b. c. d. e. f. Common Polygons
 A C E Applications Connections Extensions Applications 1. Tell whether each figure is a polygon. Explain how you know. a. b. c. d. e. f. 2. Copy and complete the table. Sort the Shapes Set into groups
A C E Applications Connections Extensions Applications 1. Tell whether each figure is a polygon. Explain how you know. a. b. c. d. e. f. 2. Copy and complete the table. Sort the Shapes Set into groups
Third Grade Mathematics
 Third Grade Mathematics By the end of grade three, students develop understandings of multiplication and division of whole numbers. They use properties to develop increasingly more sophisticated strategies
Third Grade Mathematics By the end of grade three, students develop understandings of multiplication and division of whole numbers. They use properties to develop increasingly more sophisticated strategies
Weeks 1 through 6 Aug. 6- Sept. 13 Weeks indicate introduction of standards
 1 Weeks 1 through 6 Aug. 6- Sept. 13 Weeks indicate introduction of standards Review Addition and Subtraction with Regrouping I can add numbers with regrouping. I can subtract numbers with regrouping.
1 Weeks 1 through 6 Aug. 6- Sept. 13 Weeks indicate introduction of standards Review Addition and Subtraction with Regrouping I can add numbers with regrouping. I can subtract numbers with regrouping.
Year. Small Steps Guidance and Examples. Block 1 Properties of Shapes. Released March 2018
 Released March 2018 The sequence of small steps has been produced by White Rose Maths. White Rose Maths gives permission to schools and teachers to use the small steps in their own teaching in their own
Released March 2018 The sequence of small steps has been produced by White Rose Maths. White Rose Maths gives permission to schools and teachers to use the small steps in their own teaching in their own
Name 8-6A. 1. What type of quadrilateral is shown below? A Rectangle B Trapezoid C Rhombus D Square. 2. What is true about every rhombus?
 Quick Check 1. What type of quadrilateral is shown below? A Rectangle B Trapezoid C Rhombus D Square 2. What is true about every rhombus? A All angles are equal. B All sides are equal. C Exactly one pair
Quick Check 1. What type of quadrilateral is shown below? A Rectangle B Trapezoid C Rhombus D Square 2. What is true about every rhombus? A All angles are equal. B All sides are equal. C Exactly one pair
Eureka Math. Grade 2, Module 8. Teacher Edition
 A Story of Units Eureka Math Grade 2, Module 8 Teacher Edition NOTE: Student sheets should be printed at 100% scale to preserve the intended size of figures for accurate measurements. Adjust copier or
A Story of Units Eureka Math Grade 2, Module 8 Teacher Edition NOTE: Student sheets should be printed at 100% scale to preserve the intended size of figures for accurate measurements. Adjust copier or
Ballston Spa Central School District The Common Core State Standards in Our Schools. Third Grade Math
 1 Ballston Spa Central School District The Common Core State s in Our Schools Third Grade Math Operations and Algebraic Thinking Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division 3.OA.1.Interpret
1 Ballston Spa Central School District The Common Core State s in Our Schools Third Grade Math Operations and Algebraic Thinking Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division 3.OA.1.Interpret
3rd Grade Texas Math Crosswalk Document:
 New TX Math 3.1(A) apply mathematics to problems arising in everyday life, society, and the workplace; 3.1(B) use a problem-solving model that incorporates analyzing given information, formulating a plan
New TX Math 3.1(A) apply mathematics to problems arising in everyday life, society, and the workplace; 3.1(B) use a problem-solving model that incorporates analyzing given information, formulating a plan
Geometry. Talk About It. Solve It. More Ideas. Formative Assessment
 2 7.G.2 Objective Common Core State Standards Construct Triangles Triangles are polygons with three sides, and they are classified by their sides and angles. The sum of the angles of any triangle is 180,
2 7.G.2 Objective Common Core State Standards Construct Triangles Triangles are polygons with three sides, and they are classified by their sides and angles. The sum of the angles of any triangle is 180,
Minnesota 4 th Grade 2007 Math Strands & Standards
 Minnesota 4 th Grade 2007 Math Strands & Standards Number & Operation Algebra Geometry & Measurement Demonstrate mastery of multiplication and division basic facts; multiply multi-digit numbers; solve
Minnesota 4 th Grade 2007 Math Strands & Standards Number & Operation Algebra Geometry & Measurement Demonstrate mastery of multiplication and division basic facts; multiply multi-digit numbers; solve
5th Grade Mathematics Essential Standards
 Standard 1 Number Sense (10-20% of ISTEP/Acuity) Students compute with whole numbers*, decimals, and fractions and understand the relationship among decimals, fractions, and percents. They understand the
Standard 1 Number Sense (10-20% of ISTEP/Acuity) Students compute with whole numbers*, decimals, and fractions and understand the relationship among decimals, fractions, and percents. They understand the
An angle that has a measure less than a right angle.
 Unit 1 Study Strategies: Two-Dimensional Figures Lesson Vocab Word Definition Example Formed by two rays or line segments that have the same 1 Angle endpoint. The shared endpoint is called the vertex.
Unit 1 Study Strategies: Two-Dimensional Figures Lesson Vocab Word Definition Example Formed by two rays or line segments that have the same 1 Angle endpoint. The shared endpoint is called the vertex.
Mathematics Curriculum
 6 G R A D E Mathematics Curriculum GRADE 6 5 Table of Contents 1... 1 Topic A: Area of Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons (6.G.A.1)... 11 Lesson 1: The Area of Parallelograms Through Rectangle Facts...
6 G R A D E Mathematics Curriculum GRADE 6 5 Table of Contents 1... 1 Topic A: Area of Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons (6.G.A.1)... 11 Lesson 1: The Area of Parallelograms Through Rectangle Facts...
Common Core State Standards - Standards for Mathematical Practice
 Common Core State Standards - Standards for Mathematical Practice The Standards for Mathematical Practice describe varieties of expertise that mathematics educators at all levels should seek to develop
Common Core State Standards - Standards for Mathematical Practice The Standards for Mathematical Practice describe varieties of expertise that mathematics educators at all levels should seek to develop
c. If each square foot of sod costs 65 cents, how much will she have to pay to cover her yard?
 Name Date 1. Use your ruler to draw a rectangle that measures 4 1 by 2 3 inches, and find its area. 2 4 2. Heather has a rectangular yard. She measures it and finds out it is 24 1 feet long by 12 4 feet
Name Date 1. Use your ruler to draw a rectangle that measures 4 1 by 2 3 inches, and find its area. 2 4 2. Heather has a rectangular yard. She measures it and finds out it is 24 1 feet long by 12 4 feet
Washington County School District Pacing Guide 3 rd Grade Math
 Dates August September October Enduring Skills/Understandings understanding of multiplication and division strategies for multiplication and division within 100. Subskill: Students use place value understanding
Dates August September October Enduring Skills/Understandings understanding of multiplication and division strategies for multiplication and division within 100. Subskill: Students use place value understanding
Third Grade Math: I Can Statements
 Third Grade Math: I Can Statements Processes, Content Statements & Expectations (Disciplinary Knowledge) Operations and Algebraic Thinking 3.OA Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and
Third Grade Math: I Can Statements Processes, Content Statements & Expectations (Disciplinary Knowledge) Operations and Algebraic Thinking 3.OA Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and
Skill. 69 Graph Ordered Pairs. (First Quadrant) Using Skill 69 COMMON ERRORS. 285 Holt Mathematics. OBJECTIVE Graph ordered pairs (first quadrant)
 Skill Graph Ordered Pairs (First Quadrant) Using Skill OBJECTIVE Graph ordered pairs (first quadrant) Minutes Direct students attention to the definition at the top of the page. Work through the example
Skill Graph Ordered Pairs (First Quadrant) Using Skill OBJECTIVE Graph ordered pairs (first quadrant) Minutes Direct students attention to the definition at the top of the page. Work through the example
6th Grade ~ Conceptual Foundations for Unit of Study 8 Geometry DRAFT 6/30/11 Geometry (Spatial Sense & Reasoning) 1. Shapes, Solids and Properties
 Geometry is the only CCSSM Domain that consistently appears in every grade level K-12. At all grade levels, geometry content goals can be summarized into four main geometric ideas: 1. Shapes, Solids and
Geometry is the only CCSSM Domain that consistently appears in every grade level K-12. At all grade levels, geometry content goals can be summarized into four main geometric ideas: 1. Shapes, Solids and
Geometry. Dilations. Talk About It. More Ideas. Formative Assessment
 5 Objective Common Core State Standards Dilations A dilation is a transformation that produces an image that is the same shape as the original but of a different size. Dilations with a greater than 1 produce
5 Objective Common Core State Standards Dilations A dilation is a transformation that produces an image that is the same shape as the original but of a different size. Dilations with a greater than 1 produce
Monrovia School District Grade Three Common Core Math Pacing
 Trimester 3 Pretest (optional) March 29 Monrovia School District Grade Three Common Core Math Pacing 2017-2018 Trimester 3 Pretest Exam Use the information as an additional pacing tool to guide instruction.
Trimester 3 Pretest (optional) March 29 Monrovia School District Grade Three Common Core Math Pacing 2017-2018 Trimester 3 Pretest Exam Use the information as an additional pacing tool to guide instruction.
Geometry ~ Unit 4
 Title Quadrilaterals and Coordinate Proof CISD Safety Net Standards: G.5A Big Ideas/Enduring Understandings Module 9 Properties of quadrilaterals can be used to solve real-world problems. Suggested Time
Title Quadrilaterals and Coordinate Proof CISD Safety Net Standards: G.5A Big Ideas/Enduring Understandings Module 9 Properties of quadrilaterals can be used to solve real-world problems. Suggested Time
4 th Grade MCA3 Standards, Benchmarks, Test Specifications & Sampler Questions
 4 th Grade MCA3 Standards, Benchmarks, Test Specifications & Sampler Questions Standard No. Benchmark (4 th Grade) Sampler Item Demonstrate fluency with multiplication and division facts. 4.1.1.1 Factors
4 th Grade MCA3 Standards, Benchmarks, Test Specifications & Sampler Questions Standard No. Benchmark (4 th Grade) Sampler Item Demonstrate fluency with multiplication and division facts. 4.1.1.1 Factors
Go to Grade 5 Everyday Mathematics Sample Lesson
 McGraw-Hill makes no representations or warranties as to the accuracy of any information contained in this McGraw-Hill Material, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular
McGraw-Hill makes no representations or warranties as to the accuracy of any information contained in this McGraw-Hill Material, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular
2nd Grade. 2D Shapes - Part 1 Angles and Sides. Slide 1 / 117 Slide 2 / 117. Slide 3 / 117. Slide 4 / 117. Slide 6 / 117.
 Slide 1 / 117 Slide 2 / 117 2nd Grade Geometry Presentation 1 2015-11-30 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 117 Table of ontents Presentation 1 2 Shapes - Sides and ngles - Part 1 2 Shapes - Part 2 Lab: 2 Shapes
Slide 1 / 117 Slide 2 / 117 2nd Grade Geometry Presentation 1 2015-11-30 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 117 Table of ontents Presentation 1 2 Shapes - Sides and ngles - Part 1 2 Shapes - Part 2 Lab: 2 Shapes
MISSOURI MATHEMATICS CORE ACADEMIC STANDARDS CROSSWALK TO MISSOURI GLES/CLES CONTENT ALIGNMENTS AND SHIFTS Grade 3 DRAFT
 Grade 3 Critical Areas In Grade 3, instructional time should focus on four critical areas: 1. developing understanding of multiplication and division and strategies for multiplication and division within
Grade 3 Critical Areas In Grade 3, instructional time should focus on four critical areas: 1. developing understanding of multiplication and division and strategies for multiplication and division within
Thinking. Addition and Multiplication Patterns. Solving Word Problems. Identifying, Drawing, Examining, Classifying Quadrilaterals
 Gwinnett County Public Schools Mathematics 2012-2013 Third Grade Curriculum Map 1 st Quarter 2 nd Quarter 3 rd Quarter 4 th Quarter Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Unit 8 Operations and
Gwinnett County Public Schools Mathematics 2012-2013 Third Grade Curriculum Map 1 st Quarter 2 nd Quarter 3 rd Quarter 4 th Quarter Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Unit 8 Operations and
Next Generation Math Standards----Grade 3 Cognitive Complexity/Depth of Knowledge Rating: Low, Moderate, High
 Next Generation Math Standards----Grade 3 Cognitive Complexity/Depth of Knowledge Rating: Low,, BIG IDEAS (3) BIG IDEA 1: Develop understandings of multiplication and division and strategies for basic
Next Generation Math Standards----Grade 3 Cognitive Complexity/Depth of Knowledge Rating: Low,, BIG IDEAS (3) BIG IDEA 1: Develop understandings of multiplication and division and strategies for basic
Unit Maps: Grade 1 Math
 Numbers and Place Value 1.3 Place value. The student represents and compares whole numbers, the relative position and magnitude of whole numbers, and relationships within the numeration system related
Numbers and Place Value 1.3 Place value. The student represents and compares whole numbers, the relative position and magnitude of whole numbers, and relationships within the numeration system related
CCSS Mathematics Implementation Guide Grade 3 (Draft) First Nine Weeks
 0 03 First Nine Weeks Big Ideas We are able to use place value understanding to round whole numbers to the nearest 0 or 00. What are the steps in rounding whole numbers? When would rounding be useful?.
0 03 First Nine Weeks Big Ideas We are able to use place value understanding to round whole numbers to the nearest 0 or 00. What are the steps in rounding whole numbers? When would rounding be useful?.
Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Academic Standards Mathematics
 5 th GRADE Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Standard 1 - Number Sense Students compute with whole numbers*, decimals, and fractions and understand the relationship among decimals, fractions,
5 th GRADE Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Standard 1 - Number Sense Students compute with whole numbers*, decimals, and fractions and understand the relationship among decimals, fractions,
Principles and Standards for School Mathematics. Content Standards. Process Standards. Emphasis across the Grades. Principles
 1 Navigating through Geometry Grades 3-5 Principles and Standards for School Mathematics Presented by Dr. Karol L. Yeatts Navigations Writer Navigating through Algebra Grades 3-5 Navigating through Number
1 Navigating through Geometry Grades 3-5 Principles and Standards for School Mathematics Presented by Dr. Karol L. Yeatts Navigations Writer Navigating through Algebra Grades 3-5 Navigating through Number
Visual Representations: Geometry in Art. Common Core State Standards. Students will decompose polygons into triangles, rectangles, and trapezoids.
 Lesson in Action Visual Representations: Geometry in Art AT A GLANCE Launch Warm up with a review Have students demonstrate and explain different solutions to the Compare and contrast the two visual representations.
Lesson in Action Visual Representations: Geometry in Art AT A GLANCE Launch Warm up with a review Have students demonstrate and explain different solutions to the Compare and contrast the two visual representations.
