Moving obstacle avoidance of a mobile robot using a single camera
|
|
|
- Harvey Leonard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Available online at Procedia Engineering 41 (2012 ) International Symposium on Robotics and Intelligent Sensors 2012 (IRIS 2012) Moving obstacle avoidance of a mobile robot using a single camera Jeongdae Kim, Yongtae Do * Major of Electronic Control Engineering, Daegu University, , South Korea Abstract This paper presents some preliminary results of the detection of moving obstacles (particularly walking humans) by the use of a single camera attached to a mobile robot. When a camera moves, simple moving object detection techniques for a stationary camera, such as background subtraction or image differencing, cannot be employed. We thus detect objects that move near the robot by block-based motion estimation. In the method, an image is firstly divided into small blocks, and then the motion of each block is searched by comparing two consecutive images. If the motion between matching blocks is significantly large, the block in the current image is classified as belonging to moving objects. The method is verified by the indoor navigation experiments of a robot The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd. Selection and/or peer-review under responsibility of the Centre of Humanoid Robots and Bio-Sensor (HuRoBs), Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti Teknologi MARA. Open access under CC BY-NC-ND license. Keywords: Mobile robot; Obstacle avoidance, Block-based motion estimation; Robot vision. Nomenclature B image block S size of image block x, y coordinates 1. Introduction Since George Devol and Joseph Engelberger built the first practical robot more than half century ago, the vast majority of robots have been installed on factory floors to perform their tasks. The surroundings of the industrial robots, that we call manipulators, are well controlled so as to guarantee safe work. However, in recent years, many robots become mobile and navigate in uncontrolled dynamic environments, such as museum [1], city hall [2], airport [3], etc. Hence, the safety of a robot and surrounding objects including humans who reside in the same space with the robot becomes important. There is a rich literature on the autonomous navigation of a mobile robot with obstacle sensing capability. Various sensors that can be usefully employed for a mobile robot are well described in [4]. The arrangement of a circular array of ultrasonic sensors around the body of a mobile robot is now one of the most popular methods of obstacle avoidance [5]. An ultrasonic range finder can be built in a low cost but suffers from low angular resolution. It may fail to identify a narrow open space like a doorway if its distance from the sensor is not close. An infrared detector provides another simple and cheap way of obstacle sensing [6]. As it is optical sensing, the measurement resolution can be higher than that of ultrasonic rangers. However, infrared sensors are sensitive to external light condition, and their detection range is rather short (less than * Corresponding author. Tel.: ; fax: address: ytdo@daegu.ac.kr Published by Elsevier Ltd. doi: /j.proeng Open access under CC BY-NC-ND license.
2 912 Jeongdae Kim and Yongtae Do / Procedia Engineering 41 ( 2012 ) few meters and often some centimetres). Objects at long distances from a robot can be detected accurately by the use of a laser scanner [7], but the system is expensive and often bulky. Recently introduced time-of-flight (TOF) cameras have many advantages for the autonomous navigation of a mobile robot. In comparison to laser scanner, TOF camera provides 3D information with a real-time frame rate and is much faster [8]. However, camera calibration and data pre-processing are necessary to get stable measurement. In addition, TOF cameras are still expensive like laser scanners. Stereoscopic 3D sensing has been a long time topic for perceiving the space around a mobile robot [9]. It can be said a natural way of sensing because most animals and humans obtain information about their surroundings using two eyes. Stereoscopy, however, has a difficulty in providing reliable 3D information quickly due mainly to stereo matching problem. Vision sensing has certainly high potential for a robot to perceive its surroundings. Recently, thanks to the rapid advance in solid state electronics, cameras become smaller and cheaper, and many mobile robots now possess visual sensing capability. When a single camera is mounted on a mobile robot for the autonomous navigation, it is often used for localization by detecting landmarks rather than obstacle detection because detecting obstacles usually requires at least two cameras to obtain depth information. Nevertheless, there are some attempts to find obstacles using a single camera. Ulrich and Nourbakhsh [10], for example, tried to detect obstacles based on colour cues. Image pixels that have different colour values to those trained with an empty trapezoidal area in front of the mobile robot are considered to belong to obstacles. This method is simple and can produce a high-resolution binary detection image in real time. However, we found that the method is quite sensitive to the colours of obstacles. In this paper, we describe a method to detect moving objects using a single camera mounted on a mobile robot. If a site map is given, the robot needs to find only dynamic obstacles including humans who approach to the robot. The moving objects are found by matching the blocks in two consequent images. The camera image is divided into regular blocks, and each individual block is classified as belonging to either a moving obstacle or the stationary background based on its motion. 2. Block-based motion estimation The Block-Based Motion Estimation (BBME) method has been widely used particularly in video coding [11]. Video images have temporal redundancy, which is related to the spatial similarity that temporally correlated frames have. Thus, this information redundancy needs to be reduced for the efficient treatment of video images if the picture quality loss is acceptable. Similar advantages can be expected in stereo image matching as well. Since the block based matching has a regular algorithmic structure [12], it is possible to optimally implement the method for the real-time processing of the two slightly different images of stereo cameras. Fig. 1. Block-based motion estimation
3 Jeongdae Kim and Yongtae Do / Procedia Engineering 41 ( 2012 ) In BBME, an image frame is divided into non-overlapping blocks of pixels. Then, the motion vector of a given block is determined by conducting an algorithmic search which tries to minimize the value of a matching criterion. The most commonly used criterion is the Sum of Absolute Differences (SAD), which is calculated between the current image block and a block in the previous image frame as follows: S S (, ) (, ) x= 1 y= 1 t t 1 SAD = B x y B x y (1) The spatial distance between the best matched blocks represents a motion vector, and the vector can be regarded as a disparity if the motion is horizontal. The search for the best block is limited within a range, called search window, considering the possible range of the motion. Fig. 1 illustrates the BBME method. 3. Detection of approaching obstacles using BBME The work of this paper has a purpose to avoid collisions between a mobile robot and dynamic obstacles. In many cases, the precise 3D reconstruction of obstacles is not necessary. Instead, some rough information, such as the approximate position of obstacles, is enough for a robot to proceed into free space (if any exists). To narrow down the problem scope, we make the following assumptions: The map of the working space where a robot will navigate is given. It means that we know the properties of static obstacles, such as their positions and sizes. Then, only moving obstacles need to be detected. The robot is moving on a planar ground. This assumption is usually valid in indoor environments. Most dynamic obstacles are humans and their speed is slow or similar to that of a robot. Thus, it is possible to avoid approaching obstacles even if they are detected in a rather close distance. Fig. 2. Flow chart of the algorithm If a camera is fixed, there are several effective and simple techniques to find moving objects in the scene, such as background subtraction [13]. However, if a camera is mounted on a mobile robot, such techniques cannot be used because, in the scene images taken by a moving camera, no entities look static. Then, the problem becomes rather complicated because we should find real moving objects among all that look moving due to camera motion. Particularly, detecting objects that move in the opposite direction to the navigation of a robot is important because it can cause a danger to both the robot and the approaching objects. We applied the BBME method to moving object detection in the video images of a moving camera. Fig.2 summarizes the proposed algorithm. Firstly, the current image frame was divided into small blocks. Then, a block which best matches the divided searching block was detected in the previous image frame within the search window using a block-based stereo matching function in OpenCV, cvfindstereocorrespondencebm [14]. The function is for finding the best matching blocks in the images of two cameras located at different positions while the search in this paper is for the two images snapped at different moments by the same camera. However, the search in both cases is commonly for finding corresponding blocks in
4 914 Jeongdae Kim and Yongtae Do / Procedia Engineering 41 ( 2012 ) the two slightly different images. In addition, the different picture-taking moments mean different camera positions if a camera moves. Further discussion about camera motion can be referred to [15-17]. The horizontal component of the motion vector is significantly larger than the vertical motion vector when both obstacles and a robot move on the same planar ground. Thus, the block search was done only in horizontal direction so as to increase the speed and accuracy of block matching. Secondly, the detected disparity (i.e., the length of the horizontal motion vector) between the matching blocks was converted to the grey value as exampled in Fig. 3(b). The brighter part in the image indicates the bigger motion. Thus, if an object approaches to the robot, the relative speed between the object and the robot is high, and the object looks bright in a disparity map. Thirdly, grey value distribution of the disparity map was examined as the histogram presented in Fig. 3(c). The threshold value to classify the grey pixels into those belong to the approaching objects or others was determined simply at the global peak of the histogram. A binary image obtained by thresholding is presented in Fig. 3(d). Fourthly, the binary image was projected vertically as shown in Fig. 3(e), and the position of the approaching person was estimated as shown in Fig. 3(f). Fig. 3. Example of block-based moving object detection: (a) Scene image; (b) Disparity map; (c) Histogram; (d) Binary image of rapid moving blocks; (e) Vertical projection of (d); (f) Detected moving object. 4. Results We implemented our method on a mobile robot that navigated in a corridor. The robot has a web camera producing colour images in the size of pixels by 30 frames/sec rate. As highly accurate positioning of obstacles is not required, the image size was reduced by ½ before processing. Each image was then divided into blocks of pixels and the searching window was set horizontally to pixels. Fig. 4 shows some experimental results of our moving obstacle detection algorithm. The top images show the cases of successful obstacle detection, while the bottom images show failure cases. Note that people in Fig. 4(e) and (f) are the same ones in Fig. 4(b) and (c), respectively. But they are at different distances, and the results are different. When people are at a farther distance, their motion in sequential images appears slower, and they may not be found as moving objects. Thus, the algorithm can be applied more successfully to objects at closer distances to the camera (i.e., robot). Colour also affects the performance of the algorithm because one of the two people in the figures was detected while the other in a different colour was missed. In Fig. 4(d), our algorithm detected the empty wall wrongly as a moving object. The motion of the light reflected brightly on the white side wall due to the camera motion might be the cause.
5 Jeongdae Kim and Yongtae Do / Procedia Engineering 41 ( 2012 ) Fig. 4. Experimental results: Successful cases are shown in (a), (b) and (c), while detection failures are presented in (d), (e) and (f). 5. Conclusions A vision-based moving obstacle detection method for the safe navigation of a mobile robot has been described. The method can quickly detect approaching obstacles like walking humans in an indoor space using a single camera which is mounted on the robot. In many cases of our experiment, the method detected moving objects well, but sometimes it failed by a number of factors, such as distance to objects, object s colour, and reflected light. Future work is thus improving the performance of the proposed algorithm against various practical environmental factors. Acknowledgements This research was supported by the MKE(The Ministry of Knowledge Economy), Korea, under the Core Technology Development for Breakthrough of Robot Vision Research support program supervised by the NIPA(National IT Industry Promotion Agency) (NIPA-2012-H ) References [1] Burgard W, et al. The interactivemuseum tour-guide robot. In: AAAI-98 Proceedings, Madison, Wisconsin; [2] Kang J-G, An S-Y, Oh S-Y. Navigation strategy for the service robot in the elevator environment. In: Proc. Int. Conf. on Control, Automation and Systems, Seoul, Korea; 2007, p [3] Capezio F, et al. The ANSER project: Airport nonstop surveillance expert robot. In: Proc. IROS, San Diego, CA; 2007, p [4] Everett HR. Sensors for mobile robots. CRC Press; [5] Kim S, Kim H. Optimally overlapped ultrasonic sensor ring design for minimal positional uncertainty in obstacle detection. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2010; 8(6): [6] Alwan M, et al. Characterization of infrared range-finder pbs-03jn for 2-d mapping. In: Proc. IEEE ICRA, Barcelona, Spain; 2005, p [7] Ye C, Borenstein J. Characterization of a 2-d laser scanner for mobile robot obstacle negotiation. In: Proc. IEEE ICRA, Washington, DC, December; 2002, p [8] Werner B, Surmann H, Pervolz K. 3D time-of-flight cameras for mobile robotics. In: Proc. IROS, Beijing, China; 2006, p [9] Chilian A, Hirschmuller H. Stereo camera based navigation of mobile robots on rough terrain. In: Proc. IROS, St. Louis, USA; 2009, p [10] Ulrich I, Nourbakhsh I. Appearance-based obstacle detection with monocular color vision. In: Proc. AAAI; [11] Nobie D, et al. Two novel algorithms for high quality motion estimation in high definition video sequences. In: Proc. SIBGRAPI, Maceio, Alagoas; 2011, p [12] Piccardi M. Background subtraction techniques: a review. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. on SMC, 4; 2005, p [13] Konolige K. Small vision systems: hardware and implementation. In: Proc. Int. Symp. Robotics Research, pages, Hayama, Japan; 1997, p [14] (Accesssed 25/05/2012).
6 916 Jeongdae Kim and Yongtae Do / Procedia Engineering 41 ( 2012 ) [15] Williams TD. Depth from camera motion in a real world scene. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1980; 2: [16] Matthies L, Kanade T, Szeliski R. Kalman Filter-based Algorithms for Estimating Depth from Image Sequences. Int. J. Comput. Vision. 1989; 3(2): [17] Civera J, Davison AJ, Montiel J. Inverse Depth Parametrization for Monocular SLAM. IEEE Trans. Rob. 2008; 24(5):
Indoor UAV Positioning Using Stereo Vision Sensor
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 41 (2012 ) 575 579 International Symposium on Robotics and Intelligent Sensors 2012 (IRIS 2012) Indoor UAV Positioning Using Stereo Vision
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 41 (2012 ) 575 579 International Symposium on Robotics and Intelligent Sensors 2012 (IRIS 2012) Indoor UAV Positioning Using Stereo Vision
Out-of-Plane Rotated Object Detection using Patch Feature based Classifier
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 41 (2012 ) 170 174 International Symposium on Robotics and Intelligent Sensors 2012 (IRIS 2012) Out-of-Plane Rotated Object Detection using
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 41 (2012 ) 170 174 International Symposium on Robotics and Intelligent Sensors 2012 (IRIS 2012) Out-of-Plane Rotated Object Detection using
Detecting motion by means of 2D and 3D information
 Detecting motion by means of 2D and 3D information Federico Tombari Stefano Mattoccia Luigi Di Stefano Fabio Tonelli Department of Electronics Computer Science and Systems (DEIS) Viale Risorgimento 2,
Detecting motion by means of 2D and 3D information Federico Tombari Stefano Mattoccia Luigi Di Stefano Fabio Tonelli Department of Electronics Computer Science and Systems (DEIS) Viale Risorgimento 2,
High-speed Three-dimensional Mapping by Direct Estimation of a Small Motion Using Range Images
 MECATRONICS - REM 2016 June 15-17, 2016 High-speed Three-dimensional Mapping by Direct Estimation of a Small Motion Using Range Images Shinta Nozaki and Masashi Kimura School of Science and Engineering
MECATRONICS - REM 2016 June 15-17, 2016 High-speed Three-dimensional Mapping by Direct Estimation of a Small Motion Using Range Images Shinta Nozaki and Masashi Kimura School of Science and Engineering
Localization algorithm using a virtual label for a mobile robot in indoor and outdoor environments
 Artif Life Robotics (2011) 16:361 365 ISAROB 2011 DOI 10.1007/s10015-011-0951-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Ki Ho Yu Min Cheol Lee Jung Hun Heo Youn Geun Moon Localization algorithm using a virtual label for a mobile
Artif Life Robotics (2011) 16:361 365 ISAROB 2011 DOI 10.1007/s10015-011-0951-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Ki Ho Yu Min Cheol Lee Jung Hun Heo Youn Geun Moon Localization algorithm using a virtual label for a mobile
Image processing techniques for driver assistance. Razvan Itu June 2014, Technical University Cluj-Napoca
 Image processing techniques for driver assistance Razvan Itu June 2014, Technical University Cluj-Napoca Introduction Computer vision & image processing from wiki: any form of signal processing for which
Image processing techniques for driver assistance Razvan Itu June 2014, Technical University Cluj-Napoca Introduction Computer vision & image processing from wiki: any form of signal processing for which
Dominant plane detection using optical flow and Independent Component Analysis
 Dominant plane detection using optical flow and Independent Component Analysis Naoya OHNISHI 1 and Atsushi IMIYA 2 1 School of Science and Technology, Chiba University, Japan Yayoicho 1-33, Inage-ku, 263-8522,
Dominant plane detection using optical flow and Independent Component Analysis Naoya OHNISHI 1 and Atsushi IMIYA 2 1 School of Science and Technology, Chiba University, Japan Yayoicho 1-33, Inage-ku, 263-8522,
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Computer Science 56 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 56 (2015 ) 150 155 The 12th International Conference on Mobile Systems and Pervasive Computing (MobiSPC 2015) A Shadow
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 56 (2015 ) 150 155 The 12th International Conference on Mobile Systems and Pervasive Computing (MobiSPC 2015) A Shadow
A Rapid Automatic Image Registration Method Based on Improved SIFT
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Environmental Sciences 11 (2011) 85 91 A Rapid Automatic Image Registration Method Based on Improved SIFT Zhu Hongbo, Xu Xuejun, Wang Jing, Chen Xuesong,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Environmental Sciences 11 (2011) 85 91 A Rapid Automatic Image Registration Method Based on Improved SIFT Zhu Hongbo, Xu Xuejun, Wang Jing, Chen Xuesong,
Real-time Door Detection based on AdaBoost learning algorithm
 Real-time Door Detection based on AdaBoost learning algorithm Jens Hensler, Michael Blaich, and Oliver Bittel University of Applied Sciences Konstanz, Germany Laboratory for Mobile Robots Brauneggerstr.
Real-time Door Detection based on AdaBoost learning algorithm Jens Hensler, Michael Blaich, and Oliver Bittel University of Applied Sciences Konstanz, Germany Laboratory for Mobile Robots Brauneggerstr.
AMR 2011/2012: Final Projects
 AMR 2011/2012: Final Projects 0. General Information A final project includes: studying some literature (typically, 1-2 papers) on a specific subject performing some simulations or numerical tests on an
AMR 2011/2012: Final Projects 0. General Information A final project includes: studying some literature (typically, 1-2 papers) on a specific subject performing some simulations or numerical tests on an
Optimizing Monocular Cues for Depth Estimation from Indoor Images
 Optimizing Monocular Cues for Depth Estimation from Indoor Images Aditya Venkatraman 1, Sheetal Mahadik 2 1, 2 Department of Electronics and Telecommunication, ST Francis Institute of Technology, Mumbai,
Optimizing Monocular Cues for Depth Estimation from Indoor Images Aditya Venkatraman 1, Sheetal Mahadik 2 1, 2 Department of Electronics and Telecommunication, ST Francis Institute of Technology, Mumbai,
Vehicle Detection Method using Haar-like Feature on Real Time System
 Vehicle Detection Method using Haar-like Feature on Real Time System Sungji Han, Youngjoon Han and Hernsoo Hahn Abstract This paper presents a robust vehicle detection approach using Haar-like feature.
Vehicle Detection Method using Haar-like Feature on Real Time System Sungji Han, Youngjoon Han and Hernsoo Hahn Abstract This paper presents a robust vehicle detection approach using Haar-like feature.
Realtime Omnidirectional Stereo for Obstacle Detection and Tracking in Dynamic Environments
 Proc. 2001 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems pp. 31-36, Maui, Hawaii, Oct./Nov. 2001. Realtime Omnidirectional Stereo for Obstacle Detection and Tracking in Dynamic Environments Hiroshi
Proc. 2001 IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems pp. 31-36, Maui, Hawaii, Oct./Nov. 2001. Realtime Omnidirectional Stereo for Obstacle Detection and Tracking in Dynamic Environments Hiroshi
Fast Natural Feature Tracking for Mobile Augmented Reality Applications
 Fast Natural Feature Tracking for Mobile Augmented Reality Applications Jong-Seung Park 1, Byeong-Jo Bae 2, and Ramesh Jain 3 1 Dept. of Computer Science & Eng., University of Incheon, Korea 2 Hyundai
Fast Natural Feature Tracking for Mobile Augmented Reality Applications Jong-Seung Park 1, Byeong-Jo Bae 2, and Ramesh Jain 3 1 Dept. of Computer Science & Eng., University of Incheon, Korea 2 Hyundai
Indoor Positioning System Based on Distributed Camera Sensor Networks for Mobile Robot
 Indoor Positioning System Based on Distributed Camera Sensor Networks for Mobile Robot Yonghoon Ji 1, Atsushi Yamashita 1, and Hajime Asama 1 School of Engineering, The University of Tokyo, Japan, t{ji,
Indoor Positioning System Based on Distributed Camera Sensor Networks for Mobile Robot Yonghoon Ji 1, Atsushi Yamashita 1, and Hajime Asama 1 School of Engineering, The University of Tokyo, Japan, t{ji,
Accurate 3D Face and Body Modeling from a Single Fixed Kinect
 Accurate 3D Face and Body Modeling from a Single Fixed Kinect Ruizhe Wang*, Matthias Hernandez*, Jongmoo Choi, Gérard Medioni Computer Vision Lab, IRIS University of Southern California Abstract In this
Accurate 3D Face and Body Modeling from a Single Fixed Kinect Ruizhe Wang*, Matthias Hernandez*, Jongmoo Choi, Gérard Medioni Computer Vision Lab, IRIS University of Southern California Abstract In this
DISTANCE MEASUREMENT USING STEREO VISION
 DISTANCE MEASUREMENT USING STEREO VISION Sheetal Nagar 1, Jitendra Verma 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, IIMT, Greater Noida (India) 2 Department of computer science Engineering,
DISTANCE MEASUREMENT USING STEREO VISION Sheetal Nagar 1, Jitendra Verma 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, IIMT, Greater Noida (India) 2 Department of computer science Engineering,
Virtual Range Scan for Avoiding 3D Obstacles Using 2D Tools
 Virtual Range Scan for Avoiding 3D Obstacles Using 2D Tools Stefan Stiene* and Joachim Hertzberg Institute of Computer Science, Knowledge-Based Systems Research Group University of Osnabrück Albrechtstraße
Virtual Range Scan for Avoiding 3D Obstacles Using 2D Tools Stefan Stiene* and Joachim Hertzberg Institute of Computer Science, Knowledge-Based Systems Research Group University of Osnabrück Albrechtstraße
Fast Face Detection Assisted with Skin Color Detection
 IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-issn: 2278-0661,p-ISSN: 2278-8727, Volume 18, Issue 4, Ver. II (Jul.-Aug. 2016), PP 70-76 www.iosrjournals.org Fast Face Detection Assisted with Skin Color
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-issn: 2278-0661,p-ISSN: 2278-8727, Volume 18, Issue 4, Ver. II (Jul.-Aug. 2016), PP 70-76 www.iosrjournals.org Fast Face Detection Assisted with Skin Color
Indoor Mobile Robot Navigation and Obstacle Avoidance Using a 3D Camera and Laser Scanner
 AARMS Vol. 15, No. 1 (2016) 51 59. Indoor Mobile Robot Navigation and Obstacle Avoidance Using a 3D Camera and Laser Scanner Peter KUCSERA 1 Thanks to the developing sensor technology in mobile robot navigation
AARMS Vol. 15, No. 1 (2016) 51 59. Indoor Mobile Robot Navigation and Obstacle Avoidance Using a 3D Camera and Laser Scanner Peter KUCSERA 1 Thanks to the developing sensor technology in mobile robot navigation
Efficient SLAM Scheme Based ICP Matching Algorithm Using Image and Laser Scan Information
 Proceedings of the World Congress on Electrical Engineering and Computer Systems and Science (EECSS 2015) Barcelona, Spain July 13-14, 2015 Paper No. 335 Efficient SLAM Scheme Based ICP Matching Algorithm
Proceedings of the World Congress on Electrical Engineering and Computer Systems and Science (EECSS 2015) Barcelona, Spain July 13-14, 2015 Paper No. 335 Efficient SLAM Scheme Based ICP Matching Algorithm
Development of Vision System on Humanoid Robot HRP-2
 Development of Vision System on Humanoid Robot HRP-2 Yutaro Fukase Institute of Technology, Shimizu Corporation, Japan fukase@shimz.co.jp Junichiro Maeda Institute of Technology, Shimizu Corporation, Japan
Development of Vision System on Humanoid Robot HRP-2 Yutaro Fukase Institute of Technology, Shimizu Corporation, Japan fukase@shimz.co.jp Junichiro Maeda Institute of Technology, Shimizu Corporation, Japan
Development of 3D Positioning Scheme by Integration of Multiple Wiimote IR Cameras
 Proceedings of the 5th IIAE International Conference on Industrial Application Engineering 2017 Development of 3D Positioning Scheme by Integration of Multiple Wiimote IR Cameras Hui-Yuan Chan *, Ting-Hao
Proceedings of the 5th IIAE International Conference on Industrial Application Engineering 2017 Development of 3D Positioning Scheme by Integration of Multiple Wiimote IR Cameras Hui-Yuan Chan *, Ting-Hao
Ensemble of Bayesian Filters for Loop Closure Detection
 Ensemble of Bayesian Filters for Loop Closure Detection Mohammad Omar Salameh, Azizi Abdullah, Shahnorbanun Sahran Pattern Recognition Research Group Center for Artificial Intelligence Faculty of Information
Ensemble of Bayesian Filters for Loop Closure Detection Mohammad Omar Salameh, Azizi Abdullah, Shahnorbanun Sahran Pattern Recognition Research Group Center for Artificial Intelligence Faculty of Information
Modifications of VFH navigation methods for mobile robots
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 48 (01 ) 10 14 MMaMS 01 Modifications of VFH navigation methods for mobile robots Andre Babinec a * Martin Dean a Františe Ducho a Anton Vito
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 48 (01 ) 10 14 MMaMS 01 Modifications of VFH navigation methods for mobile robots Andre Babinec a * Martin Dean a Františe Ducho a Anton Vito
Laser Eye a new 3D sensor for active vision
 Laser Eye a new 3D sensor for active vision Piotr Jasiobedzki1, Michael Jenkin2, Evangelos Milios2' Brian Down1, John Tsotsos1, Todd Campbell3 1 Dept. of Computer Science, University of Toronto Toronto,
Laser Eye a new 3D sensor for active vision Piotr Jasiobedzki1, Michael Jenkin2, Evangelos Milios2' Brian Down1, John Tsotsos1, Todd Campbell3 1 Dept. of Computer Science, University of Toronto Toronto,
Transactions on Information and Communications Technologies vol 16, 1996 WIT Press, ISSN
 ransactions on Information and Communications echnologies vol 6, 996 WI Press, www.witpress.com, ISSN 743-357 Obstacle detection using stereo without correspondence L. X. Zhou & W. K. Gu Institute of Information
ransactions on Information and Communications echnologies vol 6, 996 WI Press, www.witpress.com, ISSN 743-357 Obstacle detection using stereo without correspondence L. X. Zhou & W. K. Gu Institute of Information
OBSTACLE DETECTION USING STRUCTURED BACKGROUND
 OBSTACLE DETECTION USING STRUCTURED BACKGROUND Ghaida Al Zeer, Adnan Abou Nabout and Bernd Tibken Chair of Automatic Control, Faculty of Electrical, Information and Media Engineering University of Wuppertal,
OBSTACLE DETECTION USING STRUCTURED BACKGROUND Ghaida Al Zeer, Adnan Abou Nabout and Bernd Tibken Chair of Automatic Control, Faculty of Electrical, Information and Media Engineering University of Wuppertal,
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Computer Science 59 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 59 (2015 ) 550 558 International Conference on Computer Science and Computational Intelligence (ICCSCI 2015) The Implementation
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 59 (2015 ) 550 558 International Conference on Computer Science and Computational Intelligence (ICCSCI 2015) The Implementation
VISION-BASED PERCEPTION AND SENSOR DATA INTEGRATION FOR A PLANETARY EXPLORATION ROVER
 VISION-BASED PERCEPTION AND SENSOR DATA INTEGRATION FOR A PLANETARY EXPLORATION ROVER Zereik E. 1, Biggio A. 2, Merlo A. 2, and Casalino G. 1 1 DIST, University of Genoa, Via Opera Pia 13, 16145 Genoa,
VISION-BASED PERCEPTION AND SENSOR DATA INTEGRATION FOR A PLANETARY EXPLORATION ROVER Zereik E. 1, Biggio A. 2, Merlo A. 2, and Casalino G. 1 1 DIST, University of Genoa, Via Opera Pia 13, 16145 Genoa,
Iwan Ulrich and Illah Nourbakhsh
 From: AAAI-00 Proceedings. Copyright 2000, AAAI (www.aaai.org). All rights reserved. Appearance-Based Obstacle Detection with Monocular Color Vision Iwan Ulrich and Illah Nourbakhsh The Robotics Institute,
From: AAAI-00 Proceedings. Copyright 2000, AAAI (www.aaai.org). All rights reserved. Appearance-Based Obstacle Detection with Monocular Color Vision Iwan Ulrich and Illah Nourbakhsh The Robotics Institute,
Pick and Place ABB Working with a Liner Follower Robot
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 41 (2012 ) 1336 1342 International Symposium on Robotics and Intelligent Sensors 2012 (IRIS 2012) Pick and Place ABB Working with a Liner
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 41 (2012 ) 1336 1342 International Symposium on Robotics and Intelligent Sensors 2012 (IRIS 2012) Pick and Place ABB Working with a Liner
Obstacle Detection and Avoidance using Stereo Vision System with Region of Interest (ROI) on FPGA
 Obstacle Detection and Avoidance using Stereo Vision System with Region of Interest (ROI) on FPGA Mr. Rohit P. Sadolikar 1, Prof. P. C. Bhaskar 2 1,2 Department of Technology, Shivaji University, Kolhapur-416004,
Obstacle Detection and Avoidance using Stereo Vision System with Region of Interest (ROI) on FPGA Mr. Rohit P. Sadolikar 1, Prof. P. C. Bhaskar 2 1,2 Department of Technology, Shivaji University, Kolhapur-416004,
Pattern Feature Detection for Camera Calibration Using Circular Sample
 Pattern Feature Detection for Camera Calibration Using Circular Sample Dong-Won Shin and Yo-Sung Ho (&) Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST), 13 Cheomdan-gwagiro, Buk-gu, Gwangju 500-71,
Pattern Feature Detection for Camera Calibration Using Circular Sample Dong-Won Shin and Yo-Sung Ho (&) Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST), 13 Cheomdan-gwagiro, Buk-gu, Gwangju 500-71,
Real Time Motion Detection Using Background Subtraction Method and Frame Difference
 Real Time Motion Detection Using Background Subtraction Method and Frame Difference Lavanya M P PG Scholar, Department of ECE, Channabasaveshwara Institute of Technology, Gubbi, Tumkur Abstract: In today
Real Time Motion Detection Using Background Subtraction Method and Frame Difference Lavanya M P PG Scholar, Department of ECE, Channabasaveshwara Institute of Technology, Gubbi, Tumkur Abstract: In today
Motion Estimation for Video Coding Standards
 Motion Estimation for Video Coding Standards Prof. Ja-Ling Wu Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taiwan University Introduction of Motion Estimation The goal of video compression
Motion Estimation for Video Coding Standards Prof. Ja-Ling Wu Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering National Taiwan University Introduction of Motion Estimation The goal of video compression
On-road obstacle detection system for driver assistance
 Asia Pacific Journal of Engineering Science and Technology 3 (1) (2017) 16-21 Asia Pacific Journal of Engineering Science and Technology journal homepage: www.apjest.com Full length article On-road obstacle
Asia Pacific Journal of Engineering Science and Technology 3 (1) (2017) 16-21 Asia Pacific Journal of Engineering Science and Technology journal homepage: www.apjest.com Full length article On-road obstacle
URBAN STRUCTURE ESTIMATION USING PARALLEL AND ORTHOGONAL LINES
 URBAN STRUCTURE ESTIMATION USING PARALLEL AND ORTHOGONAL LINES An Undergraduate Research Scholars Thesis by RUI LIU Submitted to Honors and Undergraduate Research Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
URBAN STRUCTURE ESTIMATION USING PARALLEL AND ORTHOGONAL LINES An Undergraduate Research Scholars Thesis by RUI LIU Submitted to Honors and Undergraduate Research Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment
An Image Based Approach to Compute Object Distance
 An Image Based Approach to Compute Object Distance Ashfaqur Rahman * Department of Computer Science, American International University Bangladesh Dhaka 1213, Bangladesh Abdus Salam, Mahfuzul Islam, and
An Image Based Approach to Compute Object Distance Ashfaqur Rahman * Department of Computer Science, American International University Bangladesh Dhaka 1213, Bangladesh Abdus Salam, Mahfuzul Islam, and
Improving Door Detection for Mobile Robots by fusing Camera and Laser-Based Sensor Data
 Improving Door Detection for Mobile Robots by fusing Camera and Laser-Based Sensor Data Jens Hensler, Michael Blaich, and Oliver Bittel University of Applied Sciences Brauneggerstr. 55, 78462 Konstanz,
Improving Door Detection for Mobile Robots by fusing Camera and Laser-Based Sensor Data Jens Hensler, Michael Blaich, and Oliver Bittel University of Applied Sciences Brauneggerstr. 55, 78462 Konstanz,
Video Inter-frame Forgery Identification Based on Optical Flow Consistency
 Sensors & Transducers 24 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Video Inter-frame Forgery Identification Based on Optical Flow Consistency Qi Wang, Zhaohong Li, Zhenzhen Zhang, Qinglong
Sensors & Transducers 24 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Video Inter-frame Forgery Identification Based on Optical Flow Consistency Qi Wang, Zhaohong Li, Zhenzhen Zhang, Qinglong
Perceptual Quality Improvement of Stereoscopic Images
 Perceptual Quality Improvement of Stereoscopic Images Jong In Gil and Manbae Kim Dept. of Computer and Communications Engineering Kangwon National University Chunchon, Republic of Korea, 200-701 E-mail:
Perceptual Quality Improvement of Stereoscopic Images Jong In Gil and Manbae Kim Dept. of Computer and Communications Engineering Kangwon National University Chunchon, Republic of Korea, 200-701 E-mail:
Robot localization method based on visual features and their geometric relationship
 , pp.46-50 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2015.85.11 Robot localization method based on visual features and their geometric relationship Sangyun Lee 1, Changkyung Eem 2, and Hyunki Hong 3 1 Department
, pp.46-50 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2015.85.11 Robot localization method based on visual features and their geometric relationship Sangyun Lee 1, Changkyung Eem 2, and Hyunki Hong 3 1 Department
Matching Evaluation of 2D Laser Scan Points using Observed Probability in Unstable Measurement Environment
 Matching Evaluation of D Laser Scan Points using Observed Probability in Unstable Measurement Environment Taichi Yamada, and Akihisa Ohya Abstract In the real environment such as urban areas sidewalk,
Matching Evaluation of D Laser Scan Points using Observed Probability in Unstable Measurement Environment Taichi Yamada, and Akihisa Ohya Abstract In the real environment such as urban areas sidewalk,
Real-time Stereo Vision for Urban Traffic Scene Understanding
 Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium 2000 Dearborn (MI), USA October 3-5, 2000 Real-time Stereo Vision for Urban Traffic Scene Understanding U. Franke, A. Joos DaimlerChrylser AG D-70546
Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium 2000 Dearborn (MI), USA October 3-5, 2000 Real-time Stereo Vision for Urban Traffic Scene Understanding U. Franke, A. Joos DaimlerChrylser AG D-70546
Chapter 9 Object Tracking an Overview
 Chapter 9 Object Tracking an Overview The output of the background subtraction algorithm, described in the previous chapter, is a classification (segmentation) of pixels into foreground pixels (those belonging
Chapter 9 Object Tracking an Overview The output of the background subtraction algorithm, described in the previous chapter, is a classification (segmentation) of pixels into foreground pixels (those belonging
DEALING WITH SENSOR ERRORS IN SCAN MATCHING FOR SIMULTANEOUS LOCALIZATION AND MAPPING
 Inženýrská MECHANIKA, roč. 15, 2008, č. 5, s. 337 344 337 DEALING WITH SENSOR ERRORS IN SCAN MATCHING FOR SIMULTANEOUS LOCALIZATION AND MAPPING Jiří Krejsa, Stanislav Věchet* The paper presents Potential-Based
Inženýrská MECHANIKA, roč. 15, 2008, č. 5, s. 337 344 337 DEALING WITH SENSOR ERRORS IN SCAN MATCHING FOR SIMULTANEOUS LOCALIZATION AND MAPPING Jiří Krejsa, Stanislav Věchet* The paper presents Potential-Based
A development of PSD sensor system for navigation and map building in the indoor environment
 A development of PSD sensor system for navigation and map building in the indoor environment Tae Cheol Jeong*, Chang Hwan Lee **, Jea yong Park ***, Woong keun Hyun **** Department of Electronics Engineering,
A development of PSD sensor system for navigation and map building in the indoor environment Tae Cheol Jeong*, Chang Hwan Lee **, Jea yong Park ***, Woong keun Hyun **** Department of Electronics Engineering,
Integrated Laser-Camera Sensor for the Detection and Localization of Landmarks for Robotic Applications
 28 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation Pasadena, CA, USA, May 19-23, 28 Integrated Laser-Camera Sensor for the Detection and Localization of Landmarks for Robotic Applications Dilan
28 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation Pasadena, CA, USA, May 19-23, 28 Integrated Laser-Camera Sensor for the Detection and Localization of Landmarks for Robotic Applications Dilan
MOVING OBJECT DETECTION USING BACKGROUND SUBTRACTION ALGORITHM USING SIMULINK
 MOVING OBJECT DETECTION USING BACKGROUND SUBTRACTION ALGORITHM USING SIMULINK Mahamuni P. D 1, R. P. Patil 2, H.S. Thakar 3 1 PG Student, E & TC Department, SKNCOE, Vadgaon Bk, Pune, India 2 Asst. Professor,
MOVING OBJECT DETECTION USING BACKGROUND SUBTRACTION ALGORITHM USING SIMULINK Mahamuni P. D 1, R. P. Patil 2, H.S. Thakar 3 1 PG Student, E & TC Department, SKNCOE, Vadgaon Bk, Pune, India 2 Asst. Professor,
Outdoor Scene Reconstruction from Multiple Image Sequences Captured by a Hand-held Video Camera
 Outdoor Scene Reconstruction from Multiple Image Sequences Captured by a Hand-held Video Camera Tomokazu Sato, Masayuki Kanbara and Naokazu Yokoya Graduate School of Information Science, Nara Institute
Outdoor Scene Reconstruction from Multiple Image Sequences Captured by a Hand-held Video Camera Tomokazu Sato, Masayuki Kanbara and Naokazu Yokoya Graduate School of Information Science, Nara Institute
A GENETIC ALGORITHM FOR MOTION DETECTION
 A GENETIC ALGORITHM FOR MOTION DETECTION Jarosław Mamica, Tomasz Walkowiak Institute of Engineering Cybernetics, Wrocław University of Technology ul. Janiszewskiego 11/17, 50-37 Wrocław, POLAND, Phone:
A GENETIC ALGORITHM FOR MOTION DETECTION Jarosław Mamica, Tomasz Walkowiak Institute of Engineering Cybernetics, Wrocław University of Technology ul. Janiszewskiego 11/17, 50-37 Wrocław, POLAND, Phone:
An Innovative Image Processing Method Using Sum of Absolute Difference Algorithm For Real-time Military Applications
 An Innovative Image Processing Method Using Sum of Absolute Difference Algorithm For Real-time Military Applications K.Kishore M.Tech Student, Dept of (ECE), Nova College of Engineering and Technology.
An Innovative Image Processing Method Using Sum of Absolute Difference Algorithm For Real-time Military Applications K.Kishore M.Tech Student, Dept of (ECE), Nova College of Engineering and Technology.
An Approach for Real Time Moving Object Extraction based on Edge Region Determination
 An Approach for Real Time Moving Object Extraction based on Edge Region Determination Sabrina Hoque Tuli Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Chittagong University of Engineering and Technology,
An Approach for Real Time Moving Object Extraction based on Edge Region Determination Sabrina Hoque Tuli Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Chittagong University of Engineering and Technology,
Stereo Vision Image Processing Strategy for Moving Object Detecting
 Stereo Vision Image Processing Strategy for Moving Object Detecting SHIUH-JER HUANG, FU-REN YING Department of Mechanical Engineering National Taiwan University of Science and Technology No. 43, Keelung
Stereo Vision Image Processing Strategy for Moving Object Detecting SHIUH-JER HUANG, FU-REN YING Department of Mechanical Engineering National Taiwan University of Science and Technology No. 43, Keelung
Estimating Camera Position And Posture by Using Feature Landmark Database
 Estimating Camera Position And Posture by Using Feature Landmark Database Motoko Oe 1, Tomokazu Sato 2 and Naokazu Yokoya 2 1 IBM Japan 2 Nara Institute of Science and Technology, Japan Abstract. Estimating
Estimating Camera Position And Posture by Using Feature Landmark Database Motoko Oe 1, Tomokazu Sato 2 and Naokazu Yokoya 2 1 IBM Japan 2 Nara Institute of Science and Technology, Japan Abstract. Estimating
Epipolar geometry-based ego-localization using an in-vehicle monocular camera
 Epipolar geometry-based ego-localization using an in-vehicle monocular camera Haruya Kyutoku 1, Yasutomo Kawanishi 1, Daisuke Deguchi 1, Ichiro Ide 1, Hiroshi Murase 1 1 : Nagoya University, Japan E-mail:
Epipolar geometry-based ego-localization using an in-vehicle monocular camera Haruya Kyutoku 1, Yasutomo Kawanishi 1, Daisuke Deguchi 1, Ichiro Ide 1, Hiroshi Murase 1 1 : Nagoya University, Japan E-mail:
Jo-Car2 Autonomous Mode. Path Planning (Cost Matrix Algorithm)
 Chapter 8.2 Jo-Car2 Autonomous Mode Path Planning (Cost Matrix Algorithm) Introduction: In order to achieve its mission and reach the GPS goal safely; without crashing into obstacles or leaving the lane,
Chapter 8.2 Jo-Car2 Autonomous Mode Path Planning (Cost Matrix Algorithm) Introduction: In order to achieve its mission and reach the GPS goal safely; without crashing into obstacles or leaving the lane,
Using temporal seeding to constrain the disparity search range in stereo matching
 Using temporal seeding to constrain the disparity search range in stereo matching Thulani Ndhlovu Mobile Intelligent Autonomous Systems CSIR South Africa Email: tndhlovu@csir.co.za Fred Nicolls Department
Using temporal seeding to constrain the disparity search range in stereo matching Thulani Ndhlovu Mobile Intelligent Autonomous Systems CSIR South Africa Email: tndhlovu@csir.co.za Fred Nicolls Department
Application of Dijkstra s Algorithm in the Smart Exit Sign
 The 31st International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction and Mining (ISARC 2014) Application of Dijkstra s Algorithm in the Smart Exit Sign Jehyun Cho a, Ghang Lee a, Jongsung Won a
The 31st International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction and Mining (ISARC 2014) Application of Dijkstra s Algorithm in the Smart Exit Sign Jehyun Cho a, Ghang Lee a, Jongsung Won a
Real-Time Obstacle Avoidance by an Autonomous Mobile Robot using an Active Vision Sensor and a Vertically Emitted Laser Slit
 Real-Time Avoidance by an Autonomous Mobile Robot using an Active Vision Sensor and a Vertically Emitted Laser Slit Seydou SOUMARE, Akihisa OHYA and Shin ichi YUTA Intelligent Robot Laboratory, University
Real-Time Avoidance by an Autonomous Mobile Robot using an Active Vision Sensor and a Vertically Emitted Laser Slit Seydou SOUMARE, Akihisa OHYA and Shin ichi YUTA Intelligent Robot Laboratory, University
Localization, Where am I?
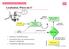 5.1 Localization, Where am I?? position Position Update (Estimation?) Encoder Prediction of Position (e.g. odometry) YES matched observations Map data base predicted position Matching Odometry, Dead Reckoning
5.1 Localization, Where am I?? position Position Update (Estimation?) Encoder Prediction of Position (e.g. odometry) YES matched observations Map data base predicted position Matching Odometry, Dead Reckoning
A Fast Laser Motion Detection and Approaching Behavior Monitoring Method for Moving Object Alarm System (MOAS)
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 41 (2012 ) 749 756 International Symposium on Robotics and Intelligent Sensors 2012 (IRIS 2012) A Fast Laser Motion Detection and Approaching
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 41 (2012 ) 749 756 International Symposium on Robotics and Intelligent Sensors 2012 (IRIS 2012) A Fast Laser Motion Detection and Approaching
Complex Sensors: Cameras, Visual Sensing. The Robotics Primer (Ch. 9) ECE 497: Introduction to Mobile Robotics -Visual Sensors
 Complex Sensors: Cameras, Visual Sensing The Robotics Primer (Ch. 9) Bring your laptop and robot everyday DO NOT unplug the network cables from the desktop computers or the walls Tuesday s Quiz is on Visual
Complex Sensors: Cameras, Visual Sensing The Robotics Primer (Ch. 9) Bring your laptop and robot everyday DO NOT unplug the network cables from the desktop computers or the walls Tuesday s Quiz is on Visual
Robust Control of Bipedal Humanoid (TPinokio)
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 41 (2012 ) 643 649 International Symposium on Robotics and Intelligent Sensors 2012 (IRIS 2012) Robust Control of Bipedal Humanoid (TPinokio)
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 41 (2012 ) 643 649 International Symposium on Robotics and Intelligent Sensors 2012 (IRIS 2012) Robust Control of Bipedal Humanoid (TPinokio)
Semantic Mapping and Reasoning Approach for Mobile Robotics
 Semantic Mapping and Reasoning Approach for Mobile Robotics Caner GUNEY, Serdar Bora SAYIN, Murat KENDİR, Turkey Key words: Semantic mapping, 3D mapping, probabilistic, robotic surveying, mine surveying
Semantic Mapping and Reasoning Approach for Mobile Robotics Caner GUNEY, Serdar Bora SAYIN, Murat KENDİR, Turkey Key words: Semantic mapping, 3D mapping, probabilistic, robotic surveying, mine surveying
CS4758: Rovio Augmented Vision Mapping Project
 CS4758: Rovio Augmented Vision Mapping Project Sam Fladung, James Mwaura Abstract The goal of this project is to use the Rovio to create a 2D map of its environment using a camera and a fixed laser pointer
CS4758: Rovio Augmented Vision Mapping Project Sam Fladung, James Mwaura Abstract The goal of this project is to use the Rovio to create a 2D map of its environment using a camera and a fixed laser pointer
Using 3D Laser Range Data for SLAM in Outdoor Environments
 Using 3D Laser Range Data for SLAM in Outdoor Environments Christian Brenneke, Oliver Wulf, Bernardo Wagner Institute for Systems Engineering, University of Hannover, Germany [brenneke, wulf, wagner]@rts.uni-hannover.de
Using 3D Laser Range Data for SLAM in Outdoor Environments Christian Brenneke, Oliver Wulf, Bernardo Wagner Institute for Systems Engineering, University of Hannover, Germany [brenneke, wulf, wagner]@rts.uni-hannover.de
A Comparison between Active and Passive 3D Vision Sensors: BumblebeeXB3 and Microsoft Kinect
 A Comparison between Active and Passive 3D Vision Sensors: BumblebeeXB3 and Microsoft Kinect Diana Beltran and Luis Basañez Technical University of Catalonia, Barcelona, Spain {diana.beltran,luis.basanez}@upc.edu
A Comparison between Active and Passive 3D Vision Sensors: BumblebeeXB3 and Microsoft Kinect Diana Beltran and Luis Basañez Technical University of Catalonia, Barcelona, Spain {diana.beltran,luis.basanez}@upc.edu
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development
 Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.14 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 3, Issue 3, March -2016 e-issn (O): 2348-4470 p-issn (P): 2348-6406 Research
Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.14 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 3, Issue 3, March -2016 e-issn (O): 2348-4470 p-issn (P): 2348-6406 Research
ScienceDirect. The use of Optical Methods for Leak Testing Dampers
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 69 ( 2014 ) 788 794 24th DAAAM International Symposium on Intelligent Manufacturing and Automation, 2013 The use of Optical
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 69 ( 2014 ) 788 794 24th DAAAM International Symposium on Intelligent Manufacturing and Automation, 2013 The use of Optical
FAST HUMAN DETECTION USING TEMPLATE MATCHING FOR GRADIENT IMAGES AND ASC DESCRIPTORS BASED ON SUBTRACTION STEREO
 FAST HUMAN DETECTION USING TEMPLATE MATCHING FOR GRADIENT IMAGES AND ASC DESCRIPTORS BASED ON SUBTRACTION STEREO Makoto Arie, Masatoshi Shibata, Kenji Terabayashi, Alessandro Moro and Kazunori Umeda Course
FAST HUMAN DETECTION USING TEMPLATE MATCHING FOR GRADIENT IMAGES AND ASC DESCRIPTORS BASED ON SUBTRACTION STEREO Makoto Arie, Masatoshi Shibata, Kenji Terabayashi, Alessandro Moro and Kazunori Umeda Course
A threshold decision of the object image by using the smart tag
 A threshold decision of the object image by using the smart tag Chang-Jun Im, Jin-Young Kim, Kwan Young Joung, Ho-Gil Lee Sensing & Perception Research Group Korea Institute of Industrial Technology (
A threshold decision of the object image by using the smart tag Chang-Jun Im, Jin-Young Kim, Kwan Young Joung, Ho-Gil Lee Sensing & Perception Research Group Korea Institute of Industrial Technology (
DEPTH AND GEOMETRY FROM A SINGLE 2D IMAGE USING TRIANGULATION
 2012 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo Workshops DEPTH AND GEOMETRY FROM A SINGLE 2D IMAGE USING TRIANGULATION Yasir Salih and Aamir S. Malik, Senior Member IEEE Centre for Intelligent
2012 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo Workshops DEPTH AND GEOMETRY FROM A SINGLE 2D IMAGE USING TRIANGULATION Yasir Salih and Aamir S. Malik, Senior Member IEEE Centre for Intelligent
EXPERIMENTAL ASSESSMENT OF THE QUANERGY M8 LIDAR SENSOR
 EXPERIMENTAL ASSESSMENT OF THE QUANERGY M8 LIDAR SENSOR M.-A. Mittet a, H. Nouira a, X. Roynard a, F. Goulette a, J.-E. Deschaud a a MINES ParisTech, PSL Research University, Centre for robotics, 60 Bd
EXPERIMENTAL ASSESSMENT OF THE QUANERGY M8 LIDAR SENSOR M.-A. Mittet a, H. Nouira a, X. Roynard a, F. Goulette a, J.-E. Deschaud a a MINES ParisTech, PSL Research University, Centre for robotics, 60 Bd
CS4758: Moving Person Avoider
 CS4758: Moving Person Avoider Yi Heng Lee, Sze Kiat Sim Abstract We attempt to have a quadrotor autonomously avoid people while moving through an indoor environment. Our algorithm for detecting people
CS4758: Moving Person Avoider Yi Heng Lee, Sze Kiat Sim Abstract We attempt to have a quadrotor autonomously avoid people while moving through an indoor environment. Our algorithm for detecting people
Human Motion Detection and Tracking for Video Surveillance
 Human Motion Detection and Tracking for Video Surveillance Prithviraj Banerjee and Somnath Sengupta Department of Electronics and Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur,
Human Motion Detection and Tracking for Video Surveillance Prithviraj Banerjee and Somnath Sengupta Department of Electronics and Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur,
DEPTH ESTIMATION USING STEREO FISH-EYE LENSES
 DEPTH ESTMATON USNG STEREO FSH-EYE LENSES Shishir Shah and J. K. Aggamal Computer and Vision Research Center Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, ENS 520 The University of Texas At Austin
DEPTH ESTMATON USNG STEREO FSH-EYE LENSES Shishir Shah and J. K. Aggamal Computer and Vision Research Center Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, ENS 520 The University of Texas At Austin
An Edge-Based Approach to Motion Detection*
 An Edge-Based Approach to Motion Detection* Angel D. Sappa and Fadi Dornaika Computer Vison Center Edifici O Campus UAB 08193 Barcelona, Spain {sappa, dornaika}@cvc.uab.es Abstract. This paper presents
An Edge-Based Approach to Motion Detection* Angel D. Sappa and Fadi Dornaika Computer Vison Center Edifici O Campus UAB 08193 Barcelona, Spain {sappa, dornaika}@cvc.uab.es Abstract. This paper presents
TERRAIN ANALYSIS FOR BLIND WHEELCHAIR USERS: COMPUTER VISION ALGORITHMS FOR FINDING CURBS AND OTHER NEGATIVE OBSTACLES
 Conference & Workshop on Assistive Technologies for People with Vision & Hearing Impairments Assistive Technology for All Ages CVHI 2007, M.A. Hersh (ed.) TERRAIN ANALYSIS FOR BLIND WHEELCHAIR USERS: COMPUTER
Conference & Workshop on Assistive Technologies for People with Vision & Hearing Impairments Assistive Technology for All Ages CVHI 2007, M.A. Hersh (ed.) TERRAIN ANALYSIS FOR BLIND WHEELCHAIR USERS: COMPUTER
EE631 Cooperating Autonomous Mobile Robots
 EE631 Cooperating Autonomous Mobile Robots Lecture: Multi-Robot Motion Planning Prof. Yi Guo ECE Department Plan Introduction Premises and Problem Statement A Multi-Robot Motion Planning Algorithm Implementation
EE631 Cooperating Autonomous Mobile Robots Lecture: Multi-Robot Motion Planning Prof. Yi Guo ECE Department Plan Introduction Premises and Problem Statement A Multi-Robot Motion Planning Algorithm Implementation
CS 4758: Automated Semantic Mapping of Environment
 CS 4758: Automated Semantic Mapping of Environment Dongsu Lee, ECE, M.Eng., dl624@cornell.edu Aperahama Parangi, CS, 2013, alp75@cornell.edu Abstract The purpose of this project is to program an Erratic
CS 4758: Automated Semantic Mapping of Environment Dongsu Lee, ECE, M.Eng., dl624@cornell.edu Aperahama Parangi, CS, 2013, alp75@cornell.edu Abstract The purpose of this project is to program an Erratic
Real-time target tracking using a Pan and Tilt platform
 Real-time target tracking using a Pan and Tilt platform Moulay A. Akhloufi Abstract In recent years, we see an increase of interest for efficient tracking systems in surveillance applications. Many of
Real-time target tracking using a Pan and Tilt platform Moulay A. Akhloufi Abstract In recent years, we see an increase of interest for efficient tracking systems in surveillance applications. Many of
Intelligent Outdoor Navigation of a Mobile Robot Platform Using a Low Cost High Precision RTK-GPS and Obstacle Avoidance System
 Intelligent Outdoor Navigation of a Mobile Robot Platform Using a Low Cost High Precision RTK-GPS and Obstacle Avoidance System Under supervision of: Prof. Dr. -Ing. Klaus-Dieter Kuhnert Dipl.-Inform.
Intelligent Outdoor Navigation of a Mobile Robot Platform Using a Low Cost High Precision RTK-GPS and Obstacle Avoidance System Under supervision of: Prof. Dr. -Ing. Klaus-Dieter Kuhnert Dipl.-Inform.
IMPROVEMENT OF BACKGROUND SUBTRACTION METHOD FOR REAL TIME MOVING OBJECT DETECTION INTRODUCTION
 IMPROVEMENT OF BACKGROUND SUBTRACTION METHOD FOR REAL TIME MOVING OBJECT DETECTION Sina Adham Khiabani and Yun Zhang University of New Brunswick, Department of Geodesy and Geomatics Fredericton, Canada
IMPROVEMENT OF BACKGROUND SUBTRACTION METHOD FOR REAL TIME MOVING OBJECT DETECTION Sina Adham Khiabani and Yun Zhang University of New Brunswick, Department of Geodesy and Geomatics Fredericton, Canada
Automatic Generation of Indoor VR-Models by a Mobile Robot with a Laser Range Finder and a Color Camera
 Automatic Generation of Indoor VR-Models by a Mobile Robot with a Laser Range Finder and a Color Camera Christian Weiss and Andreas Zell Universität Tübingen, Wilhelm-Schickard-Institut für Informatik,
Automatic Generation of Indoor VR-Models by a Mobile Robot with a Laser Range Finder and a Color Camera Christian Weiss and Andreas Zell Universität Tübingen, Wilhelm-Schickard-Institut für Informatik,
Stereo-Based Obstacle Avoidance in Indoor Environments with Active Sensor Re-Calibration
 Stereo-Based Obstacle Avoidance in Indoor Environments with Active Sensor Re-Calibration Darius Burschka, Stephen Lee and Gregory Hager Computational Interaction and Robotics Laboratory Johns Hopkins University
Stereo-Based Obstacle Avoidance in Indoor Environments with Active Sensor Re-Calibration Darius Burschka, Stephen Lee and Gregory Hager Computational Interaction and Robotics Laboratory Johns Hopkins University
Spatio-Temporal Stereo Disparity Integration
 Spatio-Temporal Stereo Disparity Integration Sandino Morales and Reinhard Klette The.enpeda.. Project, The University of Auckland Tamaki Innovation Campus, Auckland, New Zealand pmor085@aucklanduni.ac.nz
Spatio-Temporal Stereo Disparity Integration Sandino Morales and Reinhard Klette The.enpeda.. Project, The University of Auckland Tamaki Innovation Campus, Auckland, New Zealand pmor085@aucklanduni.ac.nz
Field-of-view dependent registration of point clouds and incremental segmentation of table-tops using time-offlight
 Field-of-view dependent registration of point clouds and incremental segmentation of table-tops using time-offlight cameras Dipl.-Ing. Georg Arbeiter Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Engineering
Field-of-view dependent registration of point clouds and incremental segmentation of table-tops using time-offlight cameras Dipl.-Ing. Georg Arbeiter Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Engineering
Detecting Obstacles and Drop-offs using Stereo and Motion Cues for Safe Local Motion
 Detecting Obstacles and Drop-offs using Stereo and Motion Cues for Safe Local Motion Aniket Murarka Department of Computer Science The University of Texas at Austin aniket@cs.utexas.edu Mohan Sridharan
Detecting Obstacles and Drop-offs using Stereo and Motion Cues for Safe Local Motion Aniket Murarka Department of Computer Science The University of Texas at Austin aniket@cs.utexas.edu Mohan Sridharan
Range Sensors (time of flight) (1)
 Range Sensors (time of flight) (1) Large range distance measurement -> called range sensors Range information: key element for localization and environment modeling Ultrasonic sensors, infra-red sensors
Range Sensors (time of flight) (1) Large range distance measurement -> called range sensors Range information: key element for localization and environment modeling Ultrasonic sensors, infra-red sensors
A Fast Video Illumination Enhancement Method Based on Simplified VEC Model
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 29 (2012) 3668 3673 2012 International Workshop on Information and Electronics Engineering (IWIEE) A Fast Video Illumination Enhancement Method
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 29 (2012) 3668 3673 2012 International Workshop on Information and Electronics Engineering (IWIEE) A Fast Video Illumination Enhancement Method
Integration of Multiple-baseline Color Stereo Vision with Focus and Defocus Analysis for 3D Shape Measurement
 Integration of Multiple-baseline Color Stereo Vision with Focus and Defocus Analysis for 3D Shape Measurement Ta Yuan and Murali Subbarao tyuan@sbee.sunysb.edu and murali@sbee.sunysb.edu Department of
Integration of Multiple-baseline Color Stereo Vision with Focus and Defocus Analysis for 3D Shape Measurement Ta Yuan and Murali Subbarao tyuan@sbee.sunysb.edu and murali@sbee.sunysb.edu Department of
Face Tracking in Video
 Face Tracking in Video Hamidreza Khazaei and Pegah Tootoonchi Afshar Stanford University 350 Serra Mall Stanford, CA 94305, USA I. INTRODUCTION Object tracking is a hot area of research, and has many practical
Face Tracking in Video Hamidreza Khazaei and Pegah Tootoonchi Afshar Stanford University 350 Serra Mall Stanford, CA 94305, USA I. INTRODUCTION Object tracking is a hot area of research, and has many practical
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Computer Science 22 (2013 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 22 (2013 ) 945 953 17 th International Conference in Knowledge Based and Intelligent Information and Engineering Systems
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 22 (2013 ) 945 953 17 th International Conference in Knowledge Based and Intelligent Information and Engineering Systems
Tele-operation Construction Robot Control System with Virtual Reality Technology
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 15 (2011) 1071 1076 Advanced in Control Engineering and Information Science Tele-operation Construction Robot Control System with Virtual
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 15 (2011) 1071 1076 Advanced in Control Engineering and Information Science Tele-operation Construction Robot Control System with Virtual
Auto-focusing Technique in a Projector-Camera System
 2008 10th Intl. Conf. on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision Hanoi, Vietnam, 17 20 December 2008 Auto-focusing Technique in a Projector-Camera System Lam Bui Quang, Daesik Kim and Sukhan Lee School
2008 10th Intl. Conf. on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision Hanoi, Vietnam, 17 20 December 2008 Auto-focusing Technique in a Projector-Camera System Lam Bui Quang, Daesik Kim and Sukhan Lee School
HOG-Based Person Following and Autonomous Returning Using Generated Map by Mobile Robot Equipped with Camera and Laser Range Finder
 HOG-Based Person Following and Autonomous Returning Using Generated Map by Mobile Robot Equipped with Camera and Laser Range Finder Masashi Awai, Takahito Shimizu and Toru Kaneko Department of Mechanical
HOG-Based Person Following and Autonomous Returning Using Generated Map by Mobile Robot Equipped with Camera and Laser Range Finder Masashi Awai, Takahito Shimizu and Toru Kaneko Department of Mechanical
Gaze Computer Interaction on Stereo Display
 Gaze Computer Interaction on Stereo Display Yong-Moo KWON KIST 39-1 Hawalgogdong Sungbukku Seoul, 136-791, KOREA +82-2-958-5767 ymk@kist.re.kr Kyeong Won Jeon KIST 39-1 Hawalgogdong Sungbukku Seoul, 136-791,
Gaze Computer Interaction on Stereo Display Yong-Moo KWON KIST 39-1 Hawalgogdong Sungbukku Seoul, 136-791, KOREA +82-2-958-5767 ymk@kist.re.kr Kyeong Won Jeon KIST 39-1 Hawalgogdong Sungbukku Seoul, 136-791,
