OPTICS MIRRORS AND LENSES
|
|
|
- Cleopatra Phillips
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Downloaded from OPTICS MIRRORS AND LENSES 1. An object AB is kept in front of a concave mirror as shown in the figure. (i)complete the ray diagram showing the image formation of the object. (ii) How will the position and intensity of the image be affected if the lower half of the mirror s reflecting surface is painted black? Ans. 2.How does focal length of a lens change when red light incident on it is replaced by violet light? Give reason for your answer. 3.Define power of a lens. Write its units. Deduce the relation 1/f = 1/f 1 +1/f 2 for two thin lenses kept in contact coaxially. Downloaded from
2 Downloaded from 4.A convex lens of focal length 25 cm is placed coaxially in contact with a concave lens of focal length 20 cm. Determine the power of the combination. Will the system be converging or diverging in nature? 6.A thin convex lens having two surfaces of radii of curvature R1 and R2 is made of a material of refractive index 2. It is kept in a medium of refractive index 1. Derive, with the help of a ray diagram, the lens maker formula when a point object placed on the principal axis in front of the radius of curvature R1 produces an image I on the other side of the lens. Downloaded from
3 Downloaded from 8.A biconvex lens made of a transparent material of refractive index 1.25 is immersed in water of refractive index Will the lens behave as a converging lens? Give reason. 10.A converging lens of refractive index 1 5 is kept in a liquid medium having same refractive index. What would be the focal length of the lens in this medium? Draw a plot showing the variation of power of a lens with the wavelength of the incident light. A diverging lens of refractive index 1 5 and of focal length 20 cm in air has the same radii of curvature for both sides. If it is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1 7, calculate the focal length of the lens in the liquid. Downloaded from
4 12. With Downloaded the help of a suitable ray diagram, from derive the mirror formula for a concave mirror. Downloaded from
5 Downloaded from 1.(i) A ray of monochromatic light is incident on one of the faces of an equilateral triangular prismof refracting angle A. Trace the path of ray passing through the prism. Hence, derive anexpression for the refractive index of the material of the prism in terms of the angle minimumdeviation and its refracting angle. (ii) Three light rays red (R), green (G) and blue (B) areincident on the right angled prism abc at face ab. The refractive indices of the material of the prism for red,green and blue wavelengths are respectively 1.39, 1.44 and Trace the paths of these rays reasoning outthe difference in their behaviour. ANS. Downloaded from
6 Downloaded from Q2 3.Define magnifying power of a telescope. Write its expression. 4.a)How is the working of a telescope different from that of a microscope? b)the focal lengths of the objective and eyepiece of a microscope are 1.25 cm and 5 cmrespectively. Find the position of the object relative to the objective in order to obtain an angularmagnification of 30 in normal adjustment. Downloaded from
7 Downloaded from 5.Draw a labelled ray diagram of a reflecting telescope. Mention its two advantages over therefracting telescope.ans. 7.Draw a ray diagram showing the image formation by a compound microscope. Hence obtainexpression for total magnification when the image is formed at infinity. SEE DIA Q.NO.12 8.Draw a labelled ray diagram of a refracting telescope. Define its magnifying power and write the expression for it. Write two important limitations of a refracting telescope over a reflecting type telescope. Downloaded from
8 Downloaded from 9.Three rays of light, red (R), green (G) and blue (B), are incident on the face AB of a right angledprism, as shown in the figure. The refractive indices of the material of the prism for red, green andblue are 1.39, 1.44 and 1.47 respectively. Which one of the three rays will emerge out of the prism?give reason to support your answer. ANS. 10.(i) Draw a schematic labelled ray diagram of a reflecting type telescope. (ii) Write two important advantages justifying why reflecting type telescopes are preferred over refracting telescopes. (iii) The objective of a telescope is of larger focal length and of larger aperture (compared to the eyepiece). Why? Give reasons.ans. Downloaded from
9 Downloaded from 11.(a) Draw a labelled ray diagram of a compound microscope. (b) Derive an expression for its magnifying power. (c) Why is objective of a microscope of short aperture and short focal length? Give reason. Downloaded from
10 Downloaded from 12.(a) Draw a labelled ray diagram showing the formation of a final image by a compound microscope at least distance of distinct vision. 13.Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the image formation by an astronomical telescope. Derive the expression for its magnifying power in normal adjustment. Downloaded from
11 Downloaded from WAVE OPTICS HUYGEN PRINCIPLE 1.How is a wavefront defined? Using Huygen s construction draw a figure showing the propagation of a plane wave refracting at a plane surface separating two media. Hence verify Snell s law of refraction. ANS: Downloaded from
12 Downloaded from 2.How is a wavefront defined? Using Huygen s construction draw a figure showing the Propagation of a plane wave reflecting at the interface of the two media. Show that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. ANS:- Downloaded from
13 Downloaded from INTERFERENCE 3.Describe Young s double slit experiment to produce interference pattern due to a monochromatic source of light. Deduce the expression for the fringe width. Downloaded from
14 Downloaded from Downloaded from
15 Downloaded from Downloaded from
16 Downloaded from 5.How does the fringe width of interference fringes change, when the whole apparatus of Young s experiment is kept in a liquid of refractive index 1.3? ANS:- 6.How will the angular separation and visibility of fringes in Young s double slit experiment changewhen (i) screen is moved away from the plane of the slits, and (ii) width of the source slit isincreased? ANS:- 7.How would the angular separation of interference fringes in Young s double slit experiment change when the distance between the slits and screen is doubled? 8.In Young s double slit experiment, monochromatic light of wavelength 630 nm illuminates the pair of slits and produces an interference pattern in which two consecutive bright fringes are separated by 8.1 mm. Another source of monochromatic light produces the interference pattern in which the two consecutive bright fringes are separated by 7.2 mm. Find the wavelength of light from the second source. What is the effect on the interference fringes if the monochromatic source is replaced by a source of white light? Downloaded from
17 Downloaded from 9.In Young s double slit experiment, the two slits 0 15 mm apart are illuminated by monochromatic light of wavelength 450 nm. The screen is 1.0 m away from the slits. (a) Find the distance of the second (i) bright fringe, (ii) dark fringe from the central maximum. (b) How will the fringe pattern change if the screen is moved away from the slits? ANS. Downloaded from
18 Downloaded from DIFFRACTION 10.(a) Describe briefly how a diffraction pattern is obtained on a screen due to a single narrow slit illuminated by a monochromatic source of light. Hence obtain the conditions for the angular width of secondary maxima and secondary minima. Downloaded from
19 Downloaded from 11.(a) In a single slit diffraction experiment, a slit of which d is illuminated by red light of wavelength 650 nm. For what value of d will: (i) the first minimum fall at an angle of diffraction of 30, and (ii) the first maximum fall at an angle of diffraction of 30? (b) Why does the intensity of the secondary maximum become less as compared to the central maximum? Downloaded from
20 Downloaded from 12.(a) Why do we not encounter diffraction effects of light in everyday observations? (b) In the observed diffraction pattern due to a single slit, how will the width of central maximum be affected if(i) the width of the slit is doubled;(ii) the wavelength of the light used is increased?justify your answer in each case. POLARISTION 14.(a) How does an unpolarised light incident on a polaroid get polarised? Describe briefly, with the help of a necessary diagram, the polarisation of light by reflection from a transparent medium. (b) Two polaroids A and B are kept in crossed position. How should a third polaroid C be placed between them so that the intensity of polarised light transmitted by polaroid B reduces to 1/8th of the intensity of unpolarised light incident on A? ANS:- A polaroid consists of long chain molecules aligned in a particular direction. The electric vectors along the direction of the aligned molecules get absorbed. So, when an unpolarised light falls on a polaroid, it lets only those of its electric vectors that are oscillating along a direction perpendicular to its aligned molecules to pass through it. The incident light thus gets linearly polarised. Whenever unpolarised light is incident on the boundary between two transparent media, the reflected light gets partially or completely polarised. When reflected light is perpendicular to the refracted light, the reflected light is a completely polarised light. Downloaded from
21 Downloaded from 15 (a) Describe briefly, with the help of suitable diagram, how the transverse nature of light can be demonstrated by the phenomenon of polarization. (b) When unpolarized light passes from air to a transparent medium, under what condition does the reflected light get polarized? ANS:- (a) Light from a source S is allowed to fall normally on the flat surface of a thin plate of a tourmaline crystal, cut parallel to its axis. Only a part of this light is transmitted through A. If now the plate A is rotated, the character of transmitted light remains unchanged. Now another similar plate B is placed at some distance from A such that the axis of B is parallel to that of A. If the light transmitted through A is passed through B, the light is almost completely transmitted through B and no change is observed in the light coming out of B. If now the crystal A is kept fixed and B is gradually rotated in its own plane, the intensity of light emerging out of B decreases and becomes zero when the axis of B is perpendicular to that of A. If B is further rotated, the intensity begins to increase and becomes maximum when the axes of A and B are again parallel. Thus, we see that the intensity of light transmitted through B is maximum when axes of A and B are parallel and minimum when they are at right angles. From this experiment, it is obvious that light waves are transverse and not longitudinal; because, if they were longitudinal, the rotation of crystal B would not produce any change in the intensity of light. (b) The reflected ray is totally plane polarised, when reflected and refracted rays are perpendicular to each other. 15.What is plane polarised light? Two polaroids are placed at 90 to each other and the transmitted intensity is zero. What happens when one more polaroid is placed between these two, bisecting the angle between them? How will the intensity of transmitted light vary on further rotating the third polaroid? (b) If a light beam shows no intensity variation when transmitted through a polaroid which is rotated, does it mean that the light is unpolarised? Explain briefly. ANS Downloaded from
22 Downloaded from 16.Define the term linearly polarised light. When does the intensity of transmitted light become maximum, when a polaroid sheet is rotated between two crossed polaroids? 17.(a) What is linearly polarized light? Describe briefly using a diagram how sunlight is polarised. Downloaded from
23 Downloaded from ANS:- (a) Molecules in air behave like a dipole radiator. When the sunlight falls on a molecule, dipole molecule does not scatter energy along the dipole axis, however the electric field vector of light wave vibrates just in one direction perpendicular to the direction of the propagation. The light wave having direction of electric field vector in a plane is said to be linearly polarised. In figure, a dipole molecule is lying along x-axis. Molecules behave like dipole radiators and scatter no energy along the dipole axis. The unpolarised light travelling along x-axis strikes on the dipole molecule get scattered along y and z directions. Light traversing along y and z directions is plane polarised light. 18. When unpolarised light is incident on the boundary separating the two transparent media, explain, with the help of a suitable diagram, the conditions under which the reflected light gets polarised. Hence define Brewster s angle and write its relationship in terms of the relative refractive index of the two media. 19. Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. Unpolarised light of intensity Io is indident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 30 with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3. Downloaded from
24 Downloaded from Downloaded from
UNIT VI OPTICS ALL THE POSSIBLE FORMULAE
 58 UNIT VI OPTICS ALL THE POSSIBLE FORMULAE Relation between focal length and radius of curvature of a mirror/lens, f = R/2 Mirror formula: Magnification produced by a mirror: m = - = - Snell s law: 1
58 UNIT VI OPTICS ALL THE POSSIBLE FORMULAE Relation between focal length and radius of curvature of a mirror/lens, f = R/2 Mirror formula: Magnification produced by a mirror: m = - = - Snell s law: 1
Downloaded from
 6. OPTICS RAY OPTICS GIST 1. REFLECTION BY CONVEX AND CONCAVE MIRRORS. a. Mirror formula v where u is the object distance, v is the image distance and f is the focal length. b. Magnification v v m is -ve
6. OPTICS RAY OPTICS GIST 1. REFLECTION BY CONVEX AND CONCAVE MIRRORS. a. Mirror formula v where u is the object distance, v is the image distance and f is the focal length. b. Magnification v v m is -ve
specular diffuse reflection.
 Lesson 8 Light and Optics The Nature of Light Properties of Light: Reflection Refraction Interference Diffraction Polarization Dispersion and Prisms Total Internal Reflection Huygens s Principle The Nature
Lesson 8 Light and Optics The Nature of Light Properties of Light: Reflection Refraction Interference Diffraction Polarization Dispersion and Prisms Total Internal Reflection Huygens s Principle The Nature
Review Session 1. Dr. Flera Rizatdinova
 Review Session 1 Dr. Flera Rizatdinova Summary of Chapter 23 Index of refraction: Angle of reflection equals angle of incidence Plane mirror: image is virtual, upright, and the same size as the object
Review Session 1 Dr. Flera Rizatdinova Summary of Chapter 23 Index of refraction: Angle of reflection equals angle of incidence Plane mirror: image is virtual, upright, and the same size as the object
Downloaded from UNIT 06 Optics
 1 Mark UNIT 06 Optics Q1: A partially plane polarised beam of light is passed through a polaroid. Show graphically the variation of the transmitted light intensity with angle of rotation of the Polaroid.
1 Mark UNIT 06 Optics Q1: A partially plane polarised beam of light is passed through a polaroid. Show graphically the variation of the transmitted light intensity with angle of rotation of the Polaroid.
Chapter 24. Wave Optics
 Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Chapter 24. Wave Optics
 Chapter 24 Wave Optics Diffraction Huygen s principle requires that the waves spread out after they pass through slits This spreading out of light from its initial line of travel is called diffraction
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Diffraction Huygen s principle requires that the waves spread out after they pass through slits This spreading out of light from its initial line of travel is called diffraction
Diffraction. Single-slit diffraction. Diffraction by a circular aperture. Chapter 38. In the forward direction, the intensity is maximal.
 Diffraction Chapter 38 Huygens construction may be used to find the wave observed on the downstream side of an aperture of any shape. Diffraction The interference pattern encodes the shape as a Fourier
Diffraction Chapter 38 Huygens construction may be used to find the wave observed on the downstream side of an aperture of any shape. Diffraction The interference pattern encodes the shape as a Fourier
Chapter 38. Diffraction Patterns and Polarization
 Chapter 38 Diffraction Patterns and Polarization Diffraction Light of wavelength comparable to or larger than the width of a slit spreads out in all forward directions upon passing through the slit This
Chapter 38 Diffraction Patterns and Polarization Diffraction Light of wavelength comparable to or larger than the width of a slit spreads out in all forward directions upon passing through the slit This
Physics 214 Midterm Fall 2003 Form A
 1. A ray of light is incident at the center of the flat circular surface of a hemispherical glass object as shown in the figure. The refracted ray A. emerges from the glass bent at an angle θ 2 with respect
1. A ray of light is incident at the center of the flat circular surface of a hemispherical glass object as shown in the figure. The refracted ray A. emerges from the glass bent at an angle θ 2 with respect
Downloaded from
 6. OPTICS RAY OPTICS GIST Laws of reflection: 1. The incident ray, normal and reflected ray all lie in the same plane.. The angle of incidence is always equal to angle of reflection. New Cartesian sign
6. OPTICS RAY OPTICS GIST Laws of reflection: 1. The incident ray, normal and reflected ray all lie in the same plane.. The angle of incidence is always equal to angle of reflection. New Cartesian sign
Chapter 24 - The Wave Nature of Light
 Chapter 24 - The Wave Nature of Light Summary Four Consequences of the Wave nature of Light: Diffraction Dispersion Interference Polarization Huygens principle: every point on a wavefront is a source of
Chapter 24 - The Wave Nature of Light Summary Four Consequences of the Wave nature of Light: Diffraction Dispersion Interference Polarization Huygens principle: every point on a wavefront is a source of
AP* Optics Free Response Questions
 AP* Optics Free Response Questions 1978 Q5 MIRRORS An object 6 centimeters high is placed 30 centimeters from a concave mirror of focal length 10 centimeters as shown above. (a) On the diagram above, locate
AP* Optics Free Response Questions 1978 Q5 MIRRORS An object 6 centimeters high is placed 30 centimeters from a concave mirror of focal length 10 centimeters as shown above. (a) On the diagram above, locate
All forms of EM waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum = 3.00 x 10 8 m/s This speed is constant in air as well
 Pre AP Physics Light & Optics Chapters 14-16 Light is an electromagnetic wave Electromagnetic waves: Oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to the direction the wave moves Difference
Pre AP Physics Light & Optics Chapters 14-16 Light is an electromagnetic wave Electromagnetic waves: Oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to the direction the wave moves Difference
3. LENSES & PRISM
 3. LENSES & PRISM. A transparent substance bounded by two surfaces of definite geometrical shape is called lens.. A lens may be considered to be made up of a number of small prisms put together. 3. Principal
3. LENSES & PRISM. A transparent substance bounded by two surfaces of definite geometrical shape is called lens.. A lens may be considered to be made up of a number of small prisms put together. 3. Principal
What is it? How does it work? How do we use it?
 What is it? How does it work? How do we use it? Dual Nature http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dfpeprq7ogc o Electromagnetic Waves display wave behavior o Created by oscillating electric and magnetic fields
What is it? How does it work? How do we use it? Dual Nature http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dfpeprq7ogc o Electromagnetic Waves display wave behavior o Created by oscillating electric and magnetic fields
INTRODUCTION REFLECTION AND REFRACTION AT BOUNDARIES. Introduction. Reflection and refraction at boundaries. Reflection at a single surface
 Chapter 8 GEOMETRICAL OPTICS Introduction Reflection and refraction at boundaries. Reflection at a single surface Refraction at a single boundary Dispersion Summary INTRODUCTION It has been shown that
Chapter 8 GEOMETRICAL OPTICS Introduction Reflection and refraction at boundaries. Reflection at a single surface Refraction at a single boundary Dispersion Summary INTRODUCTION It has been shown that
Chapter 82 Example and Supplementary Problems
 Chapter 82 Example and Supplementary Problems Nature of Polarized Light: 1) A partially polarized beam is composed of 2.5W/m 2 of polarized and 4.0W/m 2 of unpolarized light. Determine the degree of polarization
Chapter 82 Example and Supplementary Problems Nature of Polarized Light: 1) A partially polarized beam is composed of 2.5W/m 2 of polarized and 4.0W/m 2 of unpolarized light. Determine the degree of polarization
index of refraction-light speed
 AP Physics Study Guide Chapters 22, 23, 24 Reflection, Refraction and Interference Name Write each of the equations specified below, include units for all quantities. Law of Reflection Lens-Mirror Equation
AP Physics Study Guide Chapters 22, 23, 24 Reflection, Refraction and Interference Name Write each of the equations specified below, include units for all quantities. Law of Reflection Lens-Mirror Equation
ONE MARK QUESTIONS GEOMETRICAL OPTICS QUESTION BANK
 ONE MARK QUESTIONS 1. What is lateral shift? 2. What should be the angle of incidence to have maximum lateral shift? 3. For what angle, lateral shift is minimum? 4. What is Normal shift? 5. What is total
ONE MARK QUESTIONS 1. What is lateral shift? 2. What should be the angle of incidence to have maximum lateral shift? 3. For what angle, lateral shift is minimum? 4. What is Normal shift? 5. What is total
The image is virtual and erect. When a mirror is rotated through a certain angle, the reflected ray is rotated through twice this angle.
 1 Class XII: Physics Chapter 9: Ray optics and Optical Instruments Top Concepts 1. Laws of Reflection. The reflection at a plane surface always takes place in accordance with the following two laws: (i)
1 Class XII: Physics Chapter 9: Ray optics and Optical Instruments Top Concepts 1. Laws of Reflection. The reflection at a plane surface always takes place in accordance with the following two laws: (i)
Light: Geometric Optics
 Light: Geometric Optics The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but
Light: Geometric Optics The Ray Model of Light Light very often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but
Thin Lenses 4/16/2018 1
 Thin Lenses f 4/16/2018 1 Thin Lenses: Converging Lens C 2 F 1 F 2 C 1 r 2 f r 1 Parallel rays refract twice Converge at F 2 a distance f from center of lens F 2 is a real focal pt because rays pass through
Thin Lenses f 4/16/2018 1 Thin Lenses: Converging Lens C 2 F 1 F 2 C 1 r 2 f r 1 Parallel rays refract twice Converge at F 2 a distance f from center of lens F 2 is a real focal pt because rays pass through
Light:- it is an agent which produces in us the sensation of sight. It is a form of energy.
 Reflection:- Light:- it is an agent which produces in us the sensation of sight. It is a form of energy. Transparent medium:- It is a medium through which light can be propagated easily.(e.g., sun, candle,
Reflection:- Light:- it is an agent which produces in us the sensation of sight. It is a form of energy. Transparent medium:- It is a medium through which light can be propagated easily.(e.g., sun, candle,
Basic optics. Geometrical optics and images Interference Diffraction Diffraction integral. we use simple models that say a lot! more rigorous approach
 Basic optics Geometrical optics and images Interference Diffraction Diffraction integral we use simple models that say a lot! more rigorous approach Basic optics Geometrical optics and images Interference
Basic optics Geometrical optics and images Interference Diffraction Diffraction integral we use simple models that say a lot! more rigorous approach Basic optics Geometrical optics and images Interference
Chapter 33 cont. The Nature of Light and Propagation of Light (lecture 2) Dr. Armen Kocharian
 Chapter 33 cont The Nature of Light and Propagation of Light (lecture 2) Dr. Armen Kocharian Polarization of Light Waves The direction of polarization of each individual wave is defined to be the direction
Chapter 33 cont The Nature of Light and Propagation of Light (lecture 2) Dr. Armen Kocharian Polarization of Light Waves The direction of polarization of each individual wave is defined to be the direction
EM Waves Practice Problems
 PSI AP Physics 2 Name 1. Sir Isaac Newton was one of the first physicists to study light. What properties of light did he explain by using the particle model? 2. Who was the first person who was credited
PSI AP Physics 2 Name 1. Sir Isaac Newton was one of the first physicists to study light. What properties of light did he explain by using the particle model? 2. Who was the first person who was credited
A 4. An electromagnetic wave travelling through a transparent medium is given by y. in S units. Then what is the refractive index of the medium?
 SECTION (A) : PRINCIPLE OF SUPERPOSITION, PATH DIFFERENCE, WAVEFRONTS, AND COHERENCE A 1. Two sources of intensity I & 4I are used in an interference experiment. Find the intensity at points where the
SECTION (A) : PRINCIPLE OF SUPERPOSITION, PATH DIFFERENCE, WAVEFRONTS, AND COHERENCE A 1. Two sources of intensity I & 4I are used in an interference experiment. Find the intensity at points where the
Chapter 24. Wave Optics. Wave Optics. The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena
 Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
LIGHT. Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses
 LIGHT Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses Light = Electromagnetic Wave Requires No Medium to Travel Oscillating Electric and Magnetic Field Travel at the speed of light
LIGHT Speed of light Law of Reflection Refraction Snell s Law Mirrors Lenses Light = Electromagnetic Wave Requires No Medium to Travel Oscillating Electric and Magnetic Field Travel at the speed of light
Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics 7. Reflection at a Spherical Surface L.O 7.. State laws of reflection Laws of reflection state: L.O The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal all lie in the same
Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics 7. Reflection at a Spherical Surface L.O 7.. State laws of reflection Laws of reflection state: L.O The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal all lie in the same
Optics and Images. Lenses and Mirrors. Matthew W. Milligan
 Optics and Images Lenses and Mirrors Light: Interference and Optics I. Light as a Wave - wave basics review - electromagnetic radiation II. Diffraction and Interference - diffraction, Huygen s principle
Optics and Images Lenses and Mirrors Light: Interference and Optics I. Light as a Wave - wave basics review - electromagnetic radiation II. Diffraction and Interference - diffraction, Huygen s principle
Chapter 24 The Wave Nature of Light
 Chapter 24 The Wave Nature of Light 24.1 Waves Versus Particles; Huygens Principle and Diffraction Huygens principle: Every point on a wave front acts as a point source; the wavefront as it develops is
Chapter 24 The Wave Nature of Light 24.1 Waves Versus Particles; Huygens Principle and Diffraction Huygens principle: Every point on a wave front acts as a point source; the wavefront as it develops is
L 32 Light and Optics [3]
![L 32 Light and Optics [3] L 32 Light and Optics [3]](/thumbs/78/77867745.jpg) L 32 Light and Optics [3] Measurements of the speed of light The bending of light refraction Total internal reflection Dispersion Dispersion Rainbows Atmospheric scattering Blue sky red sunsets Light and
L 32 Light and Optics [3] Measurements of the speed of light The bending of light refraction Total internal reflection Dispersion Dispersion Rainbows Atmospheric scattering Blue sky red sunsets Light and
Geometrical Optics INTRODUCTION. Wave Fronts and Rays
 Geometrical Optics INTRODUCTION In this experiment, the optical characteristics of mirrors, lenses, and prisms will be studied based on using the following physics definitions and relationships plus simple
Geometrical Optics INTRODUCTION In this experiment, the optical characteristics of mirrors, lenses, and prisms will be studied based on using the following physics definitions and relationships plus simple
CONTENTS Huygens Theory of Double Refraction Principal Working Nicol Prism as a Polariser and an Analyser Quarter Wave Plate Half Wave Plate
 CONTENTS Huygens Theory of Double Refraction Principal Construction Working Nicol Prism as a Polariser and an Analyser Quarter Wave Plate Half Wave Plate POLARISATION Huygens Theory of Double Refraction
CONTENTS Huygens Theory of Double Refraction Principal Construction Working Nicol Prism as a Polariser and an Analyser Quarter Wave Plate Half Wave Plate POLARISATION Huygens Theory of Double Refraction
Midterm II Physics 9B Summer 2002 Session I
 Midterm II Physics 9B Summer 00 Session I Name: Last 4 digits of ID: Total Score: ) Two converging lenses, L and L, are placed on an optical bench, 6 cm apart. L has a 0 cm focal length and is placed to
Midterm II Physics 9B Summer 00 Session I Name: Last 4 digits of ID: Total Score: ) Two converging lenses, L and L, are placed on an optical bench, 6 cm apart. L has a 0 cm focal length and is placed to
PHYSICS 213 PRACTICE EXAM 3*
 PHYSICS 213 PRACTICE EXAM 3* *The actual exam will contain EIGHT multiple choice quiz-type questions covering concepts from lecture (16 points), ONE essay-type question covering an important fundamental
PHYSICS 213 PRACTICE EXAM 3* *The actual exam will contain EIGHT multiple choice quiz-type questions covering concepts from lecture (16 points), ONE essay-type question covering an important fundamental
Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics. The branch of physics which studies the properties of light using the ray model of light.
 Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics The branch of physics which studies the properties of light using the ray model of light. Overview Geometrical Optics Spherical Mirror Refraction Thin Lens f u v r and f 2
Chapter 7: Geometrical Optics The branch of physics which studies the properties of light using the ray model of light. Overview Geometrical Optics Spherical Mirror Refraction Thin Lens f u v r and f 2
PHYS:1200 LECTURE 32 LIGHT AND OPTICS (4)
 1 PHYS:1200 LECTURE 32 LIGHT AND OPTICS (4) The first three lectures in this unit dealt with what is for called geometric optics. Geometric optics, treats light as a collection of rays that travel in straight
1 PHYS:1200 LECTURE 32 LIGHT AND OPTICS (4) The first three lectures in this unit dealt with what is for called geometric optics. Geometric optics, treats light as a collection of rays that travel in straight
Light & Optical Systems Reflection & Refraction. Notes
 Light & Optical Systems Reflection & Refraction Notes What is light? Light is electromagnetic radiation Ultra-violet + visible + infra-red Behavior of Light Light behaves in 2 ways particles (photons)
Light & Optical Systems Reflection & Refraction Notes What is light? Light is electromagnetic radiation Ultra-violet + visible + infra-red Behavior of Light Light behaves in 2 ways particles (photons)
9. RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
 9. RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS 1. Define the terms (a) ray of light & (b) beam of light A ray is defined as the straight line path joining the two points by which light is travelling. A beam is
9. RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS 1. Define the terms (a) ray of light & (b) beam of light A ray is defined as the straight line path joining the two points by which light is travelling. A beam is
Unit 5.C Physical Optics Essential Fundamentals of Physical Optics
 Unit 5.C Physical Optics Essential Fundamentals of Physical Optics Early Booklet E.C.: + 1 Unit 5.C Hwk. Pts.: / 25 Unit 5.C Lab Pts.: / 20 Late, Incomplete, No Work, No Units Fees? Y / N 1. Light reflects
Unit 5.C Physical Optics Essential Fundamentals of Physical Optics Early Booklet E.C.: + 1 Unit 5.C Hwk. Pts.: / 25 Unit 5.C Lab Pts.: / 20 Late, Incomplete, No Work, No Units Fees? Y / N 1. Light reflects
4. A bulb has a luminous flux of 2400 lm. What is the luminous intensity of the bulb?
 1. Match the physical quantities (first column) with the units (second column). 4. A bulb has a luminous flux of 2400 lm. What is the luminous intensity of the bulb? (π=3.) Luminous flux A. candela Radiant
1. Match the physical quantities (first column) with the units (second column). 4. A bulb has a luminous flux of 2400 lm. What is the luminous intensity of the bulb? (π=3.) Luminous flux A. candela Radiant
Optics. a- Before the beginning of the nineteenth century, light was considered to be a stream of particles.
 Optics 1- Light Nature: a- Before the beginning of the nineteenth century, light was considered to be a stream of particles. The particles were either emitted by the object being viewed or emanated from
Optics 1- Light Nature: a- Before the beginning of the nineteenth century, light was considered to be a stream of particles. The particles were either emitted by the object being viewed or emanated from
For more info
 Huygens Principle:- Wave-front of a wave, at any instant, is defined as the locus of all the particles in the medium which are being disturbed at the same instant of time and are in the same phase of vibration.
Huygens Principle:- Wave-front of a wave, at any instant, is defined as the locus of all the particles in the medium which are being disturbed at the same instant of time and are in the same phase of vibration.
LIGHT CLASS X STUDY MATERIAL & QUESTION BANK:
 LIGHT CLASS X STUDY MATERIAL & QUESTION BANK: 1. REFLECTION OF LIGHT: The phenomenon of light coming back into the same medium after it strikes a smooth surface is called reflection. 2. LAWS OF REFLECTION:
LIGHT CLASS X STUDY MATERIAL & QUESTION BANK: 1. REFLECTION OF LIGHT: The phenomenon of light coming back into the same medium after it strikes a smooth surface is called reflection. 2. LAWS OF REFLECTION:
Physics 1C, Summer 2011 (Session 1) Practice Midterm 2 (50+4 points) Solutions
 Physics 1C, Summer 2011 (Session 1) Practice Midterm 2 (50+4 points) s Problem 1 (5x2 = 10 points) Label the following statements as True or False, with a one- or two-sentence explanation for why you chose
Physics 1C, Summer 2011 (Session 1) Practice Midterm 2 (50+4 points) s Problem 1 (5x2 = 10 points) Label the following statements as True or False, with a one- or two-sentence explanation for why you chose
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 26.1 The Reflection of Light 26.2 Forming Images With a Plane Mirror 26.3 Spherical Mirrors 26.4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 26.5 The Refraction of Light 26.6 Ray
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 26.1 The Reflection of Light 26.2 Forming Images With a Plane Mirror 26.3 Spherical Mirrors 26.4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 26.5 The Refraction of Light 26.6 Ray
On Fig. 7.1, draw a ray diagram to show the formation of this image.
 1- A small object is placed 30 cm from the centre of a convex lens of focal length 60 cm An enlarged image is observed from the other side of the lens (a) On Fig 71, draw a ray diagram to show the formation
1- A small object is placed 30 cm from the centre of a convex lens of focal length 60 cm An enlarged image is observed from the other side of the lens (a) On Fig 71, draw a ray diagram to show the formation
2011 Optical Science & Engineering PhD Qualifying Examination Optical Sciences Track: Advanced Optics Time allowed: 90 minutes
 2011 Optical Science & Engineering PhD Qualifying Examination Optical Sciences Track: Advanced Optics Time allowed: 90 minutes Answer all four questions. All questions count equally. 3(a) A linearly polarized
2011 Optical Science & Engineering PhD Qualifying Examination Optical Sciences Track: Advanced Optics Time allowed: 90 minutes Answer all four questions. All questions count equally. 3(a) A linearly polarized
Chapter 8: Physical Optics
 Chapter 8: Physical Optics Whether light is a particle or a wave had puzzled physicists for centuries. In this chapter, we only analyze light as a wave using basic optical concepts such as interference
Chapter 8: Physical Optics Whether light is a particle or a wave had puzzled physicists for centuries. In this chapter, we only analyze light as a wave using basic optical concepts such as interference
Outline The Refraction of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror 26-3 Spherical Mirror 26-4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation
 Chapter 6 Geometrical Optics Outline 6-1 The Reflection of Light 6- Forming Images with a Plane Mirror 6-3 Spherical Mirror 6-4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 6-5 The Refraction of Light 6-6 Ray Tracing
Chapter 6 Geometrical Optics Outline 6-1 The Reflection of Light 6- Forming Images with a Plane Mirror 6-3 Spherical Mirror 6-4 Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation 6-5 The Refraction of Light 6-6 Ray Tracing
Chapter 24. Wave Optics. Wave Optics. The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena
 Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Wave Optics The wave nature of light is needed to explain various phenomena Interference Diffraction Polarization The particle nature of light was the basis for ray (geometric) optics
normal angle of incidence increases special angle no light is reflected
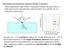 Reflection from transparent materials (Chapt. 33 last part) When unpolarized light strikes a transparent surface like glass there is both transmission and reflection, obeying Snell s law and the law of
Reflection from transparent materials (Chapt. 33 last part) When unpolarized light strikes a transparent surface like glass there is both transmission and reflection, obeying Snell s law and the law of
Where n = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4
 Syllabus: Interference and diffraction introduction interference in thin film by reflection Newton s rings Fraunhofer diffraction due to single slit, double slit and diffraction grating Interference 1.
Syllabus: Interference and diffraction introduction interference in thin film by reflection Newton s rings Fraunhofer diffraction due to single slit, double slit and diffraction grating Interference 1.
Textbook Reference: Physics (Wilson, Buffa, Lou): Chapter 24
 AP Physics-B Physical Optics Introduction: We have seen that the reflection and refraction of light can be understood in terms of both rays and wave fronts of light. Light rays are quite compatible with
AP Physics-B Physical Optics Introduction: We have seen that the reflection and refraction of light can be understood in terms of both rays and wave fronts of light. Light rays are quite compatible with
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics The Reflection of Light: Mirrors: Mirrors produce images because the light that strikes them is reflected, rather than absorbed. Reflected light does much more than produce
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics The Reflection of Light: Mirrors: Mirrors produce images because the light that strikes them is reflected, rather than absorbed. Reflected light does much more than produce
Light, Lenses, Mirrors
 Light, Lenses, Mirrors Optics Light is Dual in nature- has both particle and wave properties. Light = range of frequencies of electromagnetic waves that stimulates the eye s retina Facts About Light It
Light, Lenses, Mirrors Optics Light is Dual in nature- has both particle and wave properties. Light = range of frequencies of electromagnetic waves that stimulates the eye s retina Facts About Light It
Conceptual Physics Fundamentals
 Conceptual Physics Fundamentals Chapter 14: PROPERTIES OF LIGHT This lecture will help you understand: Reflection Refraction Dispersion Total Internal Reflection Lenses Polarization Properties of Light
Conceptual Physics Fundamentals Chapter 14: PROPERTIES OF LIGHT This lecture will help you understand: Reflection Refraction Dispersion Total Internal Reflection Lenses Polarization Properties of Light
34.2: Two Types of Image
 Chapter 34 Images 34.2: Two Types of Image For you to see an object, your eye intercepts some of the light rays spreading from the object and then redirect them onto the retina at the rear of the eye.
Chapter 34 Images 34.2: Two Types of Image For you to see an object, your eye intercepts some of the light rays spreading from the object and then redirect them onto the retina at the rear of the eye.
History of Light. 5 th Century B.C.
 History of Light 5 th Century B.C. Philosophers thought light was made up of streamers emitted by the eye making contact with an object Others thought that light was made of particles that traveled from
History of Light 5 th Century B.C. Philosophers thought light was made up of streamers emitted by the eye making contact with an object Others thought that light was made of particles that traveled from
Optics Vac Work MT 2008
 Optics Vac Work MT 2008 1. Explain what is meant by the Fraunhofer condition for diffraction. [4] An aperture lies in the plane z = 0 and has amplitude transmission function T(y) independent of x. It is
Optics Vac Work MT 2008 1. Explain what is meant by the Fraunhofer condition for diffraction. [4] An aperture lies in the plane z = 0 and has amplitude transmission function T(y) independent of x. It is
Chapter 36. Image Formation
 Chapter 36 Image Formation Apr 22, 2012 Light from distant things We learn about a distant thing from the light it generates or redirects. The lenses in our eyes create images of objects our brains can
Chapter 36 Image Formation Apr 22, 2012 Light from distant things We learn about a distant thing from the light it generates or redirects. The lenses in our eyes create images of objects our brains can
Winmeen Tnpsc Group 1 & 2 Self Preparation Course Physics UNIT 9. Ray Optics. surface at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
 Laws of reflection Physics UNIT 9 Ray Optics The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal drawn to the reflecting surface at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane. The angle of incidence
Laws of reflection Physics UNIT 9 Ray Optics The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal drawn to the reflecting surface at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane. The angle of incidence
Section 2 Flat Mirrors. Distinguish between specular and diffuse reflection of light. Apply the law of reflection for flat mirrors.
 Section 2 Flat Mirrors Objectives Distinguish between specular and diffuse reflection of light. Apply the law of reflection for flat mirrors. Describe the nature of images formed by flat mirrors. Section
Section 2 Flat Mirrors Objectives Distinguish between specular and diffuse reflection of light. Apply the law of reflection for flat mirrors. Describe the nature of images formed by flat mirrors. Section
Stevens High School AP Physics II Work for Not-school
 1. Gravitational waves are ripples in the fabric of space-time (more on this in the next unit) that travel at the speed of light (c = 3.00 x 10 8 m/s). In 2016, the LIGO (Laser Interferometry Gravitational
1. Gravitational waves are ripples in the fabric of space-time (more on this in the next unit) that travel at the speed of light (c = 3.00 x 10 8 m/s). In 2016, the LIGO (Laser Interferometry Gravitational
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 24 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 24 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 24 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
PHYS2002 Spring 2012 Practice Exam 3 (Chs. 25, 26, 27) Constants
 PHYS00 Spring 01 Practice Exam 3 (Chs. 5, 6, 7) Constants m m q q p e ε = 8.85 o o p e = 1.67 = 9.11 7 9 7 31 = + 1.60 = 1.60 μ = 4π k = 8.99 g = 9.8 m/s 1 kg 19 19 C kg T m/a N m C / N m C / C 1. A convex
PHYS00 Spring 01 Practice Exam 3 (Chs. 5, 6, 7) Constants m m q q p e ε = 8.85 o o p e = 1.67 = 9.11 7 9 7 31 = + 1.60 = 1.60 μ = 4π k = 8.99 g = 9.8 m/s 1 kg 19 19 C kg T m/a N m C / N m C / C 1. A convex
Physics 123 Optics Review
 Physics 123 Optics Review I. Definitions & Facts concave converging convex diverging real image virtual image real object virtual object upright inverted dispersion nearsighted, farsighted near point,
Physics 123 Optics Review I. Definitions & Facts concave converging convex diverging real image virtual image real object virtual object upright inverted dispersion nearsighted, farsighted near point,
Second Year Optics 2017 Problem Set 1
 Second Year Optics 2017 Problem Set 1 Q1 (Revision of first year material): Two long slits of negligible width, separated by a distance d are illuminated by monochromatic light of wavelength λ from a point
Second Year Optics 2017 Problem Set 1 Q1 (Revision of first year material): Two long slits of negligible width, separated by a distance d are illuminated by monochromatic light of wavelength λ from a point
Phy 133 Section 1: f. Geometric Optics: Assume the rays follow straight lines. (No diffraction). v 1 λ 1. = v 2. λ 2. = c λ 2. c λ 1.
 Phy 133 Section 1: f Geometric Optics: Assume the rays follow straight lines. (No diffraction). Law of Reflection: θ 1 = θ 1 ' (angle of incidence = angle of reflection) Refraction = bending of a wave
Phy 133 Section 1: f Geometric Optics: Assume the rays follow straight lines. (No diffraction). Law of Reflection: θ 1 = θ 1 ' (angle of incidence = angle of reflection) Refraction = bending of a wave
AP Physics Problems -- Waves and Light
 AP Physics Problems -- Waves and Light 1. 1975-4 (Physical Optics) a. Light of a single wavelength is incident on a single slit of width w. (w is a few wavelengths.) Sketch a graph of the intensity as
AP Physics Problems -- Waves and Light 1. 1975-4 (Physical Optics) a. Light of a single wavelength is incident on a single slit of width w. (w is a few wavelengths.) Sketch a graph of the intensity as
1. (25pts) Answer the following questions. Justify your answers. (Use the space provided below and the next page)
 . (25pts) Answer the following questions. Justify your answers. (Use the space provided below and the next page) a). An object (an arrow) is placed as shown in front of each of the following optical instruments.
. (25pts) Answer the following questions. Justify your answers. (Use the space provided below and the next page) a). An object (an arrow) is placed as shown in front of each of the following optical instruments.
College Physics B - PHY2054C
 Young College - PHY2054C Wave Optics: 10/29/2014 My Office Hours: Tuesday 10:00 AM - Noon 206 Keen Building Outline Young 1 2 3 Young 4 5 Assume a thin soap film rests on a flat glass surface. Young Young
Young College - PHY2054C Wave Optics: 10/29/2014 My Office Hours: Tuesday 10:00 AM - Noon 206 Keen Building Outline Young 1 2 3 Young 4 5 Assume a thin soap film rests on a flat glass surface. Young Young
GEOMETRIC OPTICS. LENSES refract light, so we need to know how light bends when entering and exiting a lens and how that interaction forms an image.
 I. What is GEOMTERIC OPTICS GEOMETRIC OPTICS In geometric optics, LIGHT is treated as imaginary rays. How these rays interact with at the interface of different media, including lenses and mirrors, is
I. What is GEOMTERIC OPTICS GEOMETRIC OPTICS In geometric optics, LIGHT is treated as imaginary rays. How these rays interact with at the interface of different media, including lenses and mirrors, is
Polarisation and Diffraction
 2015 EdExcel A Level Physics 2015 EdExcel A Level Physics Topic Topic 5 5 Polarisation and Diffraction Polarization Polarization is a characteristic of all transverse waves. Oscillation which take places
2015 EdExcel A Level Physics 2015 EdExcel A Level Physics Topic Topic 5 5 Polarisation and Diffraction Polarization Polarization is a characteristic of all transverse waves. Oscillation which take places
Final Exam. Today s Review of Optics Polarization Reflection and transmission Linear and circular polarization Stokes parameters/jones calculus
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 40 Review Spring 206 Semester Matthew Jones Final Exam Date:Tuesday, May 3 th Time:7:00 to 9:00 pm Room: Phys 2 You can bring one double-sided pages of notes/formulas.
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 40 Review Spring 206 Semester Matthew Jones Final Exam Date:Tuesday, May 3 th Time:7:00 to 9:00 pm Room: Phys 2 You can bring one double-sided pages of notes/formulas.
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics
 Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 1 Overview of Chapter 26 The Reflection of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror Spherical Mirrors Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation The Refraction of Light Ray Tracing
Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics 1 Overview of Chapter 26 The Reflection of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror Spherical Mirrors Ray Tracing and the Mirror Equation The Refraction of Light Ray Tracing
CHAPTER 26 INTERFERENCE AND DIFFRACTION
 CHAPTER 26 INTERFERENCE AND DIFFRACTION INTERFERENCE CONSTRUCTIVE DESTRUCTIVE YOUNG S EXPERIMENT THIN FILMS NEWTON S RINGS DIFFRACTION SINGLE SLIT MULTIPLE SLITS RESOLVING POWER 1 IN PHASE 180 0 OUT OF
CHAPTER 26 INTERFERENCE AND DIFFRACTION INTERFERENCE CONSTRUCTIVE DESTRUCTIVE YOUNG S EXPERIMENT THIN FILMS NEWTON S RINGS DIFFRACTION SINGLE SLIT MULTIPLE SLITS RESOLVING POWER 1 IN PHASE 180 0 OUT OF
Diffraction. Factors that affect Diffraction
 Diffraction What is one common property the four images share? Diffraction: Factors that affect Diffraction TELJR Publications 2017 1 Young s Experiment AIM: Does light have properties of a particle? Or
Diffraction What is one common property the four images share? Diffraction: Factors that affect Diffraction TELJR Publications 2017 1 Young s Experiment AIM: Does light have properties of a particle? Or
light Chapter Type equation here. Important long questions
 Type equation here. Light Chapter 9 Important long questions Q.9.1 Describe Young s double slit experiment for the demonstration of interference of. Derive an expression for fringe spacing? Ans. Young
Type equation here. Light Chapter 9 Important long questions Q.9.1 Describe Young s double slit experiment for the demonstration of interference of. Derive an expression for fringe spacing? Ans. Young
Experiment 8 Wave Optics
 Physics 263 Experiment 8 Wave Optics In this laboratory, we will perform two experiments on wave optics. 1 Double Slit Interference In two-slit interference, light falls on an opaque screen with two closely
Physics 263 Experiment 8 Wave Optics In this laboratory, we will perform two experiments on wave optics. 1 Double Slit Interference In two-slit interference, light falls on an opaque screen with two closely
Physics Midterm Exam (3:00-4:00 pm 10/20/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 60 MINUTES Name: Signature:
 Physics 431 - Midterm Exam (3:00-4:00 pm 10/20/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 60 MINUTES Name: SID: Signature: CLOSED BOOK. ONE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEET OF NOTES (double sided is allowed), AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR
Physics 431 - Midterm Exam (3:00-4:00 pm 10/20/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 60 MINUTES Name: SID: Signature: CLOSED BOOK. ONE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEET OF NOTES (double sided is allowed), AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR
General Physics II. Mirrors & Lenses
 General Physics II Mirrors & Lenses Nothing New! For the next several lectures we will be studying geometrical optics. You already know the fundamentals of what is going on!!! Reflection: θ 1 = θ r incident
General Physics II Mirrors & Lenses Nothing New! For the next several lectures we will be studying geometrical optics. You already know the fundamentals of what is going on!!! Reflection: θ 1 = θ r incident
Waves & Oscillations
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 40 Review Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Final Exam Date:Tuesday, May 3 th Time:7:00 to 9:00 pm Room: Phys 112 You can bring one double-sided pages of notes/formulas.
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 40 Review Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Final Exam Date:Tuesday, May 3 th Time:7:00 to 9:00 pm Room: Phys 112 You can bring one double-sided pages of notes/formulas.
Physics 11 - Waves Extra Practice Questions
 Physics - Waves xtra Practice Questions. Wave motion in a medium transfers ) energy, only ) mass, only. both mass and energy. neither mass nor energy. single vibratory disturbance that moves from point
Physics - Waves xtra Practice Questions. Wave motion in a medium transfers ) energy, only ) mass, only. both mass and energy. neither mass nor energy. single vibratory disturbance that moves from point
Textbook Reference: Glencoe Physics: Chapters 16-18
 Honors Physics-121B Geometric Optics Introduction: A great deal of evidence suggests that light travels in straight lines. A source of light like the sun casts distinct shadows. We can hear sound from
Honors Physics-121B Geometric Optics Introduction: A great deal of evidence suggests that light travels in straight lines. A source of light like the sun casts distinct shadows. We can hear sound from
Lecture Outline Chapter 26. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 26 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics Units of Chapter 26 The Reflection of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror Spherical Mirrors Ray Tracing
Lecture Outline Chapter 26 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics Units of Chapter 26 The Reflection of Light Forming Images with a Plane Mirror Spherical Mirrors Ray Tracing
Lab 10 - GEOMETRICAL OPTICS
 L10-1 Name Date Partners OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW Lab 10 - GEOMETRICAL OPTICS To examine Snell s Law. To observe total internal reflection. To understand and use the lens equations. To find the focal length
L10-1 Name Date Partners OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW Lab 10 - GEOMETRICAL OPTICS To examine Snell s Law. To observe total internal reflection. To understand and use the lens equations. To find the focal length
Person s Optics Test SSSS
 Person s Optics Test SSSS 2017-18 Competitors Names: School Name: All questions are worth one point unless otherwise stated. Show ALL WORK or you may not receive credit. Include correct units whenever
Person s Optics Test SSSS 2017-18 Competitors Names: School Name: All questions are worth one point unless otherwise stated. Show ALL WORK or you may not receive credit. Include correct units whenever
The sources must be coherent. This means they emit waves with a constant phase with respect to each other.
 CH. 24 Wave Optics The sources must be coherent. This means they emit waves with a constant phase with respect to each other. The waves need to have identical wavelengths. Can t be coherent without this.
CH. 24 Wave Optics The sources must be coherent. This means they emit waves with a constant phase with respect to each other. The waves need to have identical wavelengths. Can t be coherent without this.
SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT. Key Concepts. X-planation. Physical Sciences Grade In this session we:
 SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT Key Concepts In this session we: Explain what light is, where light comes from and why it is important Identify what happens when light strikes the surface of different objects
SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT Key Concepts In this session we: Explain what light is, where light comes from and why it is important Identify what happens when light strikes the surface of different objects
AP Physics: Curved Mirrors and Lenses
 The Ray Model of Light Light often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but is very useful for geometric
The Ray Model of Light Light often travels in straight lines. We represent light using rays, which are straight lines emanating from an object. This is an idealization, but is very useful for geometric
Homework Set 3 Due Thursday, 07/14
 Homework Set 3 Due Thursday, 07/14 Problem 1 A room contains two parallel wall mirrors, on opposite walls 5 meters apart. The mirrors are 8 meters long. Suppose that one person stands in a doorway, in
Homework Set 3 Due Thursday, 07/14 Problem 1 A room contains two parallel wall mirrors, on opposite walls 5 meters apart. The mirrors are 8 meters long. Suppose that one person stands in a doorway, in
DIFFRACTION 4.1 DIFFRACTION Difference between Interference and Diffraction Classification Of Diffraction Phenomena
 4.1 DIFFRACTION Suppose a light wave incident on a slit AB of sufficient width b, as shown in Figure 1. According to concept of rectilinear propagation of light the region A B on the screen should be uniformly
4.1 DIFFRACTION Suppose a light wave incident on a slit AB of sufficient width b, as shown in Figure 1. According to concept of rectilinear propagation of light the region A B on the screen should be uniformly
Recap: Refraction. Amount of bending depends on: - angle of incidence - refractive index of medium. (n 2 > n 1 ) n 2
 Amount of bending depends on: - angle of incidence - refractive index of medium Recap: Refraction λ 1 (n 2 > n 1 ) Snell s Law: When light passes from one transparent medium to another, the rays will be
Amount of bending depends on: - angle of incidence - refractive index of medium Recap: Refraction λ 1 (n 2 > n 1 ) Snell s Law: When light passes from one transparent medium to another, the rays will be
Algebra Based Physics
 Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 Algebra Based Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Table of ontents Slide 3 / 66 lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Spherical Mirror Refraction and
Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 Algebra Based Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Table of ontents Slide 3 / 66 lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Spherical Mirror Refraction and
HW Chapter 20 Q 2,3,4,5,6,10,13 P 1,2,3. Chapter 20. Classic and Modern Optics. Dr. Armen Kocharian
 HW Chapter 20 Q 2,3,4,5,6,10,13 P 1,2,3 Chapter 20 Classic and Modern Optics Dr. Armen Kocharian Electromagnetic waves and matter: A Brief History of Light 1000 AD It was proposed that light consisted
HW Chapter 20 Q 2,3,4,5,6,10,13 P 1,2,3 Chapter 20 Classic and Modern Optics Dr. Armen Kocharian Electromagnetic waves and matter: A Brief History of Light 1000 AD It was proposed that light consisted
Nicholas J. Giordano. Chapter 24. Geometrical Optics. Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 24 Geometrical Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Optics The study of light is called optics Some highlights in the history
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 24 Geometrical Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Optics The study of light is called optics Some highlights in the history
